Seeking a consistent view of energy and water flows through the climate system
|
|
|
- Kory Manning
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Seeking a consistent view of energy and water flows through the climate system Robert Pincus University of Colorado and NOAA/Earth System Research Lab
2
3 Atmospheric Energy Balance [Wm -2 ] 340.1± ~22 (atmospheric window) (absorbed solar)
4 Incoming solar Atmospheric absorption 7 Reflected solar Shortwave t Sensible heating All-sk y atmospheric window TO A imbalance 0 Latent heating Clear-sk y emission Longwave t Outgoing longwave radiation All-s ky longwave absorption Clear-sky refection Surface shortwave absorption Surface reflection Surface emission 9 Clear-sky emission to surface All-s ky emission to surface Surface imbalance 0
5 Syntheses satisfy large-scale constraints TOA energy balance to within ocean heat storage Surface energy balance ditto Surface water balance Satisfying these constraints requires creativity because individual best estimates don t satisfy balance constraints
6 Global Surface Energy Budget R n (SW) + R d (LW) R u (LW) S LE = N Wm -2 R n (SW) R u (LW) R d (LW) R n S LE S + LE KT TFK ISCCP FD SRB CERES EBAF-SFC Stephens et al (2012) ERA-I MERRA Radiation datasets suggests net surface radiation (R n ) is Wm -2 larger than TFK09, which determines R n as residual of S + LE + N, where S is determined from reanalysis, LE is inferred from global precipitation (LP=LE), and N is energy imbalance (~0.9 Wm -2 in KTF09). Can we explain the difference? Is S+LE too low? R n too high? What are the uncertainties? Do the difference impact our ability to track year-to-year and longerterm changes in surface energy budget?
7 An unconstrained view of the energy budget isn t balanced Work in progress by Tristan L Ecuyer (U. Wisconsin)
8 Syntheses satisfy large-scale constraints TOA energy balance to within ocean heat storage Surface energy balance ditto Surface water balance Satisfying these constraints requires creativity because individual best estimates don t satisfy balance constraints In practice, large-scale fluxes are determined by using satellite observations to infer flux validating against sparse point measurements
9 CERES is our most direct estimate of TOA flux, but still requires models for spectral corrections directional corrections temporal corrections Original CERES estimates were out of balance by W/m 2
10 How CERES achieves top-of-atmosphere energy balance Identify error sources and uncertainty! Assume Gaussian, unbiased errors P (F F obs,r obs )=e (F F obs) T S 1 obs (F F obs) e R R obs 2 R Adjust each error source as little as possible relative to its uncertainty to achieve balance within its uncertainty, i.e. minimize J =(F F obs ) T S 1 obs (F F obs)+ R R obs 2 R
11 1FEBRUARY 2009 L O E B E T A L. 755 TABLE 3. Net flux sensitivity (a i ), standard deviation of error (s i ), maximum likelihood error (x i ), and error effect on net TOA flux. Parameter Net TOA flux sensitivity, a i (W m 22 % 21 ) 2s uncertainty, d i (%) Maximum likelihood solution, x i (%) TOA flux adjustment (W m 22 ) SW gain LW gain Unfiltered SW Unfiltered LW (N) Unfiltered LW (D) SW radiance to flux LW radiance to flux Time-averaging SW Time-averaging LW Reference level, SW Reference level, LW Incoming solar Total SW 1.7 Total LW 2.5 Total net 24.2 a. Constrainment algorithm The global average net TOA flux is expressed as follows: Let a i 5 R N p i denote the partial derivatives of global mean net flux with respect to each parameter p i, and represent x i and a i as vectors x and a, so that Eq. (4) may be written as R N 5 E o ðf SW 1 F LW Þ; ð1þ a t x 5 e RN : ð5þ where E o is the annual mean solar insolation at the TOA averaged over the globe and F SW and F LW are the global average SW and LW TOA fluxes. If the earth were in radiative balance for the annual mean, R N would be zero. However, given a warming trend, there is a net imbalance because of heat storage within the We have one equation with N unknowns, where N is the number of parameters to adjust. The criterion for selecting these parameters is to choose the most likely set of parameters x i that satisfy Eq. (5) using a maximum likelihood estimate for the x i. The following assumptions are made: (i) x i has mean 0 for all i; (ii) all x i s
12 Surface radiation from CERES (and others) Surface radiation budget relies on radiative transfer models applied to profiles of clouds, aerosols, atmospheric state Properties are retrieved independently of CERES top-ofatmosphere fluxes; modeled fluxes using these properties may not reproduce top-of-atmosphere fluxes Adjust atmospheric properties as little as possible relative to uncertainty to match observed fluxes to within uncertainty
13 013 K A T O E T A L TABLE 4. Global annual mean irradiances in W m 22 computed using data from March 2000 through February Irradiance component Ed 2 SYN1deg- Month Surface EBAF Ed2.6r EBAF Ed2.6r TOA Incoming solar LW (all-sky) SW (all-sky) Net (all-sly) LW (clear-sky) SW (clear-sky) Net (clear-sly) Surface LW down (all-sky) LW up (all-sky) SW down (all-sky) SW up (all-sky) Net (all-sky) LW down (clear-sky) LW up (clear-sky) SW down (clear-sky) SW up (clear-sky) Net (clear-sky) Histogram of monthly mean downward (top) longwave tom) shortwave irradiance difference; 24 buoy observam 2001 through 2007 are used. The red line is for EBAFnd black line is for SRB surface irradiance (Stackhouse 1). Numbers shown in the figure are in W m 22 except for is the number of monthly observations. Note that biases Clear-sky irradiances are derived by weighted clear-sky fraction. irradiances; Approximately 5%, 12%, and 2% of grid surface downward shortwave, upward shortwave, and upward longwave adjustments, respectively, exceed
14 An unconstrained view of the energy budget isn t balanced Work in progress by Tristan L Ecuyer (U. Wisconsin)
15 Would consistency help? (i - a priori) The GEWEX integrated product does indeed start out by assuming that we can all use the same ancillary data. This includes issues like the same land/ocean mask, the same sea ice and the same vegetation class. Trickier is the same aerosols, and then the same temperature and humidity profiles. Temperature and humidity matter quite a bit for all the radiation as well as the turbulent fluxes. What we ran into is that while we agreed to use the new HIRS product for temperature and humidity, the near surface quantities seemed to introduce artifacts into SeaFLux and LandFlux The decision was let each product continue to diverge from the integrated assumption if they felt that the integrated assumptions were making the product worse. from Chris Kummerow (GEWEX data panel), Mar 2014
16 Would consistency help (ii - a posteriori) (More from work in progress by Tristan L Ecuyer) Assess mean and uncertainty in components of surface energy and water budgets on continental/basin scale Assume Gaussian, unbiased errors in flux components Adjust each component as little as possible relative to its uncertainty to achieve balance within its uncertainty
17 Work in progress by Tristan L Ecuyer (U. Wisconsin)
18 So I think this grand challenge will be with us for quite a while. The silver lining is that the precip and radiation datasets appear to be fairly stable (bias is fairly constant with time), which means they might provide some useful information for monitoring changes in the various components of the energy budget. All bets are off if there are huge swings in the heavy precipitation range from Norman Loeb, Mar 2014
19 Errors are strongly conditioned, not random This restricts our ability to stratify (even assuming understand our observations well) How can we best build a self-consistent view of energy and water flows through the climate system? Can reanalyses be revisited? How can we diagnose the limits of such a view?
Interannual variability of top-ofatmosphere. CERES instruments
 Interannual variability of top-ofatmosphere albedo observed by CERES instruments Seiji Kato NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA SORCE Science team meeting, Sedona, Arizona, Sep. 13-16, 2011 TOA irradiance
Interannual variability of top-ofatmosphere albedo observed by CERES instruments Seiji Kato NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA SORCE Science team meeting, Sedona, Arizona, Sep. 13-16, 2011 TOA irradiance
History of Earth Radiation Budget Measurements With results from a recent assessment
 History of Earth Radiation Budget Measurements With results from a recent assessment Ehrhard Raschke and Stefan Kinne Institute of Meteorology, University Hamburg MPI Meteorology, Hamburg, Germany Centenary
History of Earth Radiation Budget Measurements With results from a recent assessment Ehrhard Raschke and Stefan Kinne Institute of Meteorology, University Hamburg MPI Meteorology, Hamburg, Germany Centenary
Changes in Earth s Albedo Measured by satellite
 Changes in Earth s Albedo Measured by satellite Bruce A. Wielicki, Takmeng Wong, Norman Loeb, Patrick Minnis, Kory Priestley, Robert Kandel Presented by Yunsoo Choi Earth s albedo Earth s albedo The climate
Changes in Earth s Albedo Measured by satellite Bruce A. Wielicki, Takmeng Wong, Norman Loeb, Patrick Minnis, Kory Priestley, Robert Kandel Presented by Yunsoo Choi Earth s albedo Earth s albedo The climate
Deducing Earth s Global Energy Flows from a Simple Greenhouse Model
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 Article Deducing Earth s Global Energy Flows from a Simple Greenhouse Model
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 Article Deducing Earth s Global Energy Flows from a Simple Greenhouse Model
and Atmospheric Science, University of Miami, 4600 Rickenbacker Causeway, Miami, FL 33149, USA.
 Observed changes in top-of-the-atmosphere radiation and upper-ocean heating consistent within uncertainty. Steady accumulation of heat by Earth since 2000 according to satellite and ocean data Norman G.
Observed changes in top-of-the-atmosphere radiation and upper-ocean heating consistent within uncertainty. Steady accumulation of heat by Earth since 2000 according to satellite and ocean data Norman G.
Variability in Global Top-of-Atmosphere Shortwave Radiation Between 2000 And 2005
 Variability in Global Top-of-Atmosphere Shortwave Radiation Between 2000 And 2005 Norman G. Loeb NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA Collaborators: B.A. Wielicki, F.G. Rose, D.R. Doelling February
Variability in Global Top-of-Atmosphere Shortwave Radiation Between 2000 And 2005 Norman G. Loeb NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA Collaborators: B.A. Wielicki, F.G. Rose, D.R. Doelling February
The flow of Energy through the Earth s Climate System: Land and Ocean Exchanges
 The flow of Energy through the Earth s Climate System: Land and Ocean Exchanges Kevin E Trenberth and John T. Fasullo NCAR, Boulder, CO, USA Correspondence: Contact trenbert@ucar.edu INTRODUCTION Weather
The flow of Energy through the Earth s Climate System: Land and Ocean Exchanges Kevin E Trenberth and John T. Fasullo NCAR, Boulder, CO, USA Correspondence: Contact trenbert@ucar.edu INTRODUCTION Weather
How Accurate is the GFDL GCM Radiation Code? David Paynter,
 Radiation Processes in the GFDL GCM: How Accurate is the GFDL GCM Radiation Code? David Paynter, Alexandra Jones Dan Schwarzkopf, Stuart Freidenreich and V.Ramaswamy GFDL, Princeton, New Jersey 13th June
Radiation Processes in the GFDL GCM: How Accurate is the GFDL GCM Radiation Code? David Paynter, Alexandra Jones Dan Schwarzkopf, Stuart Freidenreich and V.Ramaswamy GFDL, Princeton, New Jersey 13th June
Lecture 3. Background materials. Planetary radiative equilibrium TOA outgoing radiation = TOA incoming radiation Figure 3.1
 Lecture 3. Changes in planetary albedo. Is there a clear signal caused by aerosols and clouds? Outline: 1. Background materials. 2. Papers for class discussion: Palle et al., Changes in Earth s reflectance
Lecture 3. Changes in planetary albedo. Is there a clear signal caused by aerosols and clouds? Outline: 1. Background materials. 2. Papers for class discussion: Palle et al., Changes in Earth s reflectance
9.4. The newly released 5-year Terra-based monthly CERES radiative flux and cloud product. David R. Doelling, D. F. Keyes AS&M, Inc.
 9.4 The newly released 5-year Terra-based monthly CERES radiative flux and cloud product David R. Doelling, D. F. Keyes AS&M, Inc., Hampton, VA D. F. Young, B. A. Wielicki, T. Wong NASA Langley Research
9.4 The newly released 5-year Terra-based monthly CERES radiative flux and cloud product David R. Doelling, D. F. Keyes AS&M, Inc., Hampton, VA D. F. Young, B. A. Wielicki, T. Wong NASA Langley Research
Patterns in the CERES Global Mean Data, Part 3. Cloud Area Fraction, Atmospheric Energy Budgets, DLR Update. Miklos Zagoni
 Patterns in the CERES Global Mean Data, Part 3. Cloud Area Fraction, Atmospheric Energy Budgets, DLR Update β eff eff = β obs ε obs ε IR IR Miklos Zagoni miklos.zagoni@t-online.hu 2018 Earth Radiation
Patterns in the CERES Global Mean Data, Part 3. Cloud Area Fraction, Atmospheric Energy Budgets, DLR Update β eff eff = β obs ε obs ε IR IR Miklos Zagoni miklos.zagoni@t-online.hu 2018 Earth Radiation
Surface Radiation Budget from ARM Satellite Retrievals
 Surface Radiation Budget from ARM Satellite Retrievals P. Minnis, D. P. Kratz, and T. P. charlock Atmospheric Sciences National Aeronautics and Space Administration Langley Research Center Hampton, Virginia
Surface Radiation Budget from ARM Satellite Retrievals P. Minnis, D. P. Kratz, and T. P. charlock Atmospheric Sciences National Aeronautics and Space Administration Langley Research Center Hampton, Virginia
The Arctic Energy Budget
 The Arctic Energy Budget The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth, NCAR]. Differential solar heating between low and high latitudes gives rise to a circulation of the atmosphere and ocean that
The Arctic Energy Budget The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth, NCAR]. Differential solar heating between low and high latitudes gives rise to a circulation of the atmosphere and ocean that
Solar Insolation and Earth Radiation Budget Measurements
 Week 13: November 19-23 Solar Insolation and Earth Radiation Budget Measurements Topics: 1. Daily solar insolation calculations 2. Orbital variations effect on insolation 3. Total solar irradiance measurements
Week 13: November 19-23 Solar Insolation and Earth Radiation Budget Measurements Topics: 1. Daily solar insolation calculations 2. Orbital variations effect on insolation 3. Total solar irradiance measurements
Can we measure from satellites the cloud effects on the atmospheric radiation budget?
 1 Can we measure from satellites the cloud effects on the atmospheric radiation budget? Ehrhard Raschke University of Hamburg Institute of Meteorology Abstract Clouds modify all radiation budget components
1 Can we measure from satellites the cloud effects on the atmospheric radiation budget? Ehrhard Raschke University of Hamburg Institute of Meteorology Abstract Clouds modify all radiation budget components
Understanding the Greenhouse Effect
 EESC V2100 The Climate System spring 200 Understanding the Greenhouse Effect Yochanan Kushnir Lamont Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University Palisades, NY 1096, USA kushnir@ldeo.columbia.edu Equilibrium
EESC V2100 The Climate System spring 200 Understanding the Greenhouse Effect Yochanan Kushnir Lamont Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University Palisades, NY 1096, USA kushnir@ldeo.columbia.edu Equilibrium
Air sea satellite flux datasets and what they do (and don't) tell us about the air sea interface in the Southern Ocean
 Air sea satellite flux datasets and what they do (and don't) tell us about the air sea interface in the Southern Ocean Carol Anne Clayson Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Southern Ocean Workshop Seattle,
Air sea satellite flux datasets and what they do (and don't) tell us about the air sea interface in the Southern Ocean Carol Anne Clayson Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Southern Ocean Workshop Seattle,
An update on Earth s energy balance in light of the latest global observations
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1580 An update on Earth s energy balance in light of the latest global observations Graeme L. Stephens, Juilin Li, Martin Wild, Carol Anne Clayson, Norman Loeb,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1580 An update on Earth s energy balance in light of the latest global observations Graeme L. Stephens, Juilin Li, Martin Wild, Carol Anne Clayson, Norman Loeb,
Radiation, Sensible Heat Flux and Evapotranspiration
 Radiation, Sensible Heat Flux and Evapotranspiration Climatological and hydrological field work Figure 1: Estimate of the Earth s annual and global mean energy balance. Over the long term, the incoming
Radiation, Sensible Heat Flux and Evapotranspiration Climatological and hydrological field work Figure 1: Estimate of the Earth s annual and global mean energy balance. Over the long term, the incoming
CERES_EBAF-Surface_Ed2.7 Data Quality Summary (June 7, 2013)
 CERES_EBAF-Surface_Ed2.7 (June 7, 2013) Investigation: CERES Data Product: EBAF-Surface Data Set: Terra (Instruments: CERES-FM1 or CERES-FM2) Aqua (Instruments: CERES-FM3 or CERES-FM4) Data Set Version:
CERES_EBAF-Surface_Ed2.7 (June 7, 2013) Investigation: CERES Data Product: EBAF-Surface Data Set: Terra (Instruments: CERES-FM1 or CERES-FM2) Aqua (Instruments: CERES-FM3 or CERES-FM4) Data Set Version:
Radiation in climate models.
 Lecture. Radiation in climate models. Objectives:. A hierarchy of the climate models.. Radiative and radiative-convective equilibrium.. Examples of simple energy balance models.. Radiation in the atmospheric
Lecture. Radiation in climate models. Objectives:. A hierarchy of the climate models.. Radiative and radiative-convective equilibrium.. Examples of simple energy balance models.. Radiation in the atmospheric
The Spectral Radiative Effects of Inhomogeneous Clouds and Aerosols
 The Spectral Radiative Effects of Inhomogeneous Clouds and Aerosols S. Schmidt, B. Kindel, & P. Pilewskie Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics University of Colorado SORCE Science Meeting, 13-16
The Spectral Radiative Effects of Inhomogeneous Clouds and Aerosols S. Schmidt, B. Kindel, & P. Pilewskie Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics University of Colorado SORCE Science Meeting, 13-16
5. General Circulation Models
 5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
Characterization of the Present-Day Arctic Atmosphere in CCSM4
 Characterization of the Present-Day Arctic Atmosphere in CCSM4 Gijs de Boer 1, Bill Chapman 2, Jennifer Kay 3, Brian Medeiros 3, Matthew Shupe 4, Steve Vavrus, and John Walsh 6 (1) (2) (3) (4) ESRL ()
Characterization of the Present-Day Arctic Atmosphere in CCSM4 Gijs de Boer 1, Bill Chapman 2, Jennifer Kay 3, Brian Medeiros 3, Matthew Shupe 4, Steve Vavrus, and John Walsh 6 (1) (2) (3) (4) ESRL ()
May 3, :41 AOGS - AS 9in x 6in b951-v16-ch13 LAND SURFACE ENERGY BUDGET OVER THE TIBETAN PLATEAU BASED ON SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING DATA
 Advances in Geosciences Vol. 16: Atmospheric Science (2008) Eds. Jai Ho Oh et al. c World Scientific Publishing Company LAND SURFACE ENERGY BUDGET OVER THE TIBETAN PLATEAU BASED ON SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING
Advances in Geosciences Vol. 16: Atmospheric Science (2008) Eds. Jai Ho Oh et al. c World Scientific Publishing Company LAND SURFACE ENERGY BUDGET OVER THE TIBETAN PLATEAU BASED ON SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING
Earth s Energy Budget: How Is the Temperature of Earth Controlled?
 1 NAME Investigation 2 Earth s Energy Budget: How Is the Temperature of Earth Controlled? Introduction As you learned from the reading, the balance between incoming energy from the sun and outgoing energy
1 NAME Investigation 2 Earth s Energy Budget: How Is the Temperature of Earth Controlled? Introduction As you learned from the reading, the balance between incoming energy from the sun and outgoing energy
Name(s) Period Date. Earth s Energy Budget: How Is the Temperature of Earth Controlled?
 Name(s) Period Date 1 Introduction Earth s Energy Budget: How Is the Temperature of Earth Controlled? As you learned from the reading, the balance between incoming energy from the sun and outgoing energy
Name(s) Period Date 1 Introduction Earth s Energy Budget: How Is the Temperature of Earth Controlled? As you learned from the reading, the balance between incoming energy from the sun and outgoing energy
Patterns in the CERES Global Mean Data
 Patterns in the CERES Global Mean Data Miklos Zagoni Fall 2017 CERES Science Team Meeting, September 27, NASA GSFC, Greenbelt, MD. "To search for something though it be mushrooms or some pattern is impossible,
Patterns in the CERES Global Mean Data Miklos Zagoni Fall 2017 CERES Science Team Meeting, September 27, NASA GSFC, Greenbelt, MD. "To search for something though it be mushrooms or some pattern is impossible,
Global Climate Change
 Global Climate Change Definition of Climate According to Webster dictionary Climate: the average condition of the weather at a place over a period of years exhibited by temperature, wind velocity, and
Global Climate Change Definition of Climate According to Webster dictionary Climate: the average condition of the weather at a place over a period of years exhibited by temperature, wind velocity, and
Patterns in the CERES Global Mean Data, Part 3
 Patterns in the CERES Global Mean Data, Part 3 1361 51 Wild et al. 2015 Total Solar Irradiance, Albedo, and Cloud Radiative Effects Miklos Zagoni 31 st CERES Science Team Meeting, May 7 9, 2019, Hampton,
Patterns in the CERES Global Mean Data, Part 3 1361 51 Wild et al. 2015 Total Solar Irradiance, Albedo, and Cloud Radiative Effects Miklos Zagoni 31 st CERES Science Team Meeting, May 7 9, 2019, Hampton,
How good are our models?
 direct Estimates of regional and global forcing: ^ How good are our models? Bill Collins with Andrew Conley, David Fillmore, and Phil Rasch National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado Models
direct Estimates of regional and global forcing: ^ How good are our models? Bill Collins with Andrew Conley, David Fillmore, and Phil Rasch National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado Models
Local Balance and Variability of Atmospheric Heat Budget over Oceans: Observation and Reanalysis-Based Estimates
 15 JANUARY 2014 W O N G E T A L. 893 Local Balance and Variability of Atmospheric Heat Budget over Oceans: Observation and Reanalysis-Based Estimates SUN WONG Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute
15 JANUARY 2014 W O N G E T A L. 893 Local Balance and Variability of Atmospheric Heat Budget over Oceans: Observation and Reanalysis-Based Estimates SUN WONG Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute
A perturbed physics ensemble climate modeling. requirements of energy and water cycle. Yong Hu and Bruce Wielicki
 A perturbed physics ensemble climate modeling study for defining satellite measurement requirements of energy and water cycle Yong Hu and Bruce Wielicki Motivation 1. Uncertainty of climate sensitivity
A perturbed physics ensemble climate modeling study for defining satellite measurement requirements of energy and water cycle Yong Hu and Bruce Wielicki Motivation 1. Uncertainty of climate sensitivity
J. Xing et al. Correspondence to: J. Xing
 Supplement of Atmos. Chem. Phys., 5, 7, 5 http://www.atmos-chem-phys.net/5/7/5/ doi:.5/acp575-supplement Author(s) 5. CC Attribution. License. Supplement of Can a coupled meteorology chemistry model reproduce
Supplement of Atmos. Chem. Phys., 5, 7, 5 http://www.atmos-chem-phys.net/5/7/5/ doi:.5/acp575-supplement Author(s) 5. CC Attribution. License. Supplement of Can a coupled meteorology chemistry model reproduce
On assessing temporal variability and trends of coupled arctic energy budgets. Michael Mayer Leo Haimberger
 On assessing temporal variability and trends of coupled arctic energy budgets Michael Mayer Leo Haimberger Motivation and outline Arctic climate system is subject to rapid changes and large interannual
On assessing temporal variability and trends of coupled arctic energy budgets Michael Mayer Leo Haimberger Motivation and outline Arctic climate system is subject to rapid changes and large interannual
Radiation balance of the Earth. 6. Earth radiation balance under present day conditions. Top of Atmosphere (TOA) Radiation balance
 Radiation balance of the Earth Top of Atmosphere (TOA) radiation balance 6. Earth radiation balance under present day conditions Atmospheric radiation balance: Difference between TOA and surface radiation
Radiation balance of the Earth Top of Atmosphere (TOA) radiation balance 6. Earth radiation balance under present day conditions Atmospheric radiation balance: Difference between TOA and surface radiation
Observational constraints on Arctic Ocean clouds and radiative fluxes during the early 21st century
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: ATMOSPHERES, VOL. 118, 7219 7236, doi:10.1002/jgrd.50489, 2013 Observational constraints on Arctic Ocean clouds and radiative fluxes during the early 21st century Jennifer
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: ATMOSPHERES, VOL. 118, 7219 7236, doi:10.1002/jgrd.50489, 2013 Observational constraints on Arctic Ocean clouds and radiative fluxes during the early 21st century Jennifer
Climate Feedbacks from ERBE Data
 Climate Feedbacks from ERBE Data Why Is Lindzen and Choi (2009) Criticized? Zhiyu Wang Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Utah March 9, 2010 / Earth Climate System Outline 1 Introduction
Climate Feedbacks from ERBE Data Why Is Lindzen and Choi (2009) Criticized? Zhiyu Wang Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Utah March 9, 2010 / Earth Climate System Outline 1 Introduction
APPLICATIONS WITH METEOROLOGICAL SATELLITES. W. Paul Menzel. Office of Research and Applications NOAA/NESDIS University of Wisconsin Madison, WI
 APPLICATIONS WITH METEOROLOGICAL SATELLITES by W. Paul Menzel Office of Research and Applications NOAA/NESDIS University of Wisconsin Madison, WI July 2004 Unpublished Work Copyright Pending TABLE OF CONTENTS
APPLICATIONS WITH METEOROLOGICAL SATELLITES by W. Paul Menzel Office of Research and Applications NOAA/NESDIS University of Wisconsin Madison, WI July 2004 Unpublished Work Copyright Pending TABLE OF CONTENTS
Is the Earth s climate system constrained?*+
 Is the Earth s climate system constrained?*+ Graeme Stephens, Denis O Brien, Peter Webster,Peter Pilewskie,Seiji Kato,Juilin Li *Stephens et al., 2014;The albedo of Earth, Rev Geophys, + Stephens and L
Is the Earth s climate system constrained?*+ Graeme Stephens, Denis O Brien, Peter Webster,Peter Pilewskie,Seiji Kato,Juilin Li *Stephens et al., 2014;The albedo of Earth, Rev Geophys, + Stephens and L
Sensitivity of climate forcing and response to dust optical properties in an idealized model
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jd007198, 2007 Sensitivity of climate forcing and response to dust optical properties in an idealized model Karen
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jd007198, 2007 Sensitivity of climate forcing and response to dust optical properties in an idealized model Karen
Earth s Energy Balance and the Atmosphere
 Earth s Energy Balance and the Atmosphere Topics we ll cover: Atmospheric composition greenhouse gases Vertical structure and radiative balance pressure, temperature Global circulation and horizontal energy
Earth s Energy Balance and the Atmosphere Topics we ll cover: Atmospheric composition greenhouse gases Vertical structure and radiative balance pressure, temperature Global circulation and horizontal energy
Constraints on Climate Sensitivity from Radiation Patterns in Climate Models
 1034 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 24 Constraints on Climate Sensitivity from Radiation Patterns in Climate Models MARKUS HUBER, IRINA MAHLSTEIN, AND MARTIN WILD Institute for Atmospheric and
1034 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 24 Constraints on Climate Sensitivity from Radiation Patterns in Climate Models MARKUS HUBER, IRINA MAHLSTEIN, AND MARTIN WILD Institute for Atmospheric and
Comparison of Long-term Downward Radiation Observations at Tateno with JRA-25 and ERA-40 Data
 Comparison of Long-term Downward Radiation Observations at Tateno with JRA-25 and ERA-40 Data Nozomu Ohkawara, Yasuo Hirose Ozone and Radiation Division, Aerological Observatory, Japan Meteorological Agency
Comparison of Long-term Downward Radiation Observations at Tateno with JRA-25 and ERA-40 Data Nozomu Ohkawara, Yasuo Hirose Ozone and Radiation Division, Aerological Observatory, Japan Meteorological Agency
ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY. Lecture 19. Learning objectives: develop a physical understanding of ocean thermodynamic processes
 ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY Lecture 19 Learning objectives: develop a physical understanding of ocean thermodynamic processes 1. Ocean surface heat fluxes; 2. Mixed layer temperature
ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY Lecture 19 Learning objectives: develop a physical understanding of ocean thermodynamic processes 1. Ocean surface heat fluxes; 2. Mixed layer temperature
- matter-energy interactions. - global radiation balance. Further Reading: Chapter 04 of the text book. Outline. - shortwave radiation balance
 (1 of 12) Further Reading: Chapter 04 of the text book Outline - matter-energy interactions - shortwave radiation balance - longwave radiation balance - global radiation balance (2 of 12) Previously, we
(1 of 12) Further Reading: Chapter 04 of the text book Outline - matter-energy interactions - shortwave radiation balance - longwave radiation balance - global radiation balance (2 of 12) Previously, we
Extratropical and Polar Cloud Systems
 Extratropical and Polar Cloud Systems Gunilla Svensson Department of Meteorology & Bolin Centre for Climate Research George Tselioudis Extratropical and Polar Cloud Systems Lecture 1 Extratropical cyclones
Extratropical and Polar Cloud Systems Gunilla Svensson Department of Meteorology & Bolin Centre for Climate Research George Tselioudis Extratropical and Polar Cloud Systems Lecture 1 Extratropical cyclones
Clouds in the Climate System: Why is this such a difficult problem, and where do we go from here?
 Clouds in the Climate System: Why is this such a difficult problem, and where do we go from here? Joel Norris Scripps Institution of Oceanography CERES Science Team Meeting April 29, 2009 Collaborators
Clouds in the Climate System: Why is this such a difficult problem, and where do we go from here? Joel Norris Scripps Institution of Oceanography CERES Science Team Meeting April 29, 2009 Collaborators
Satellite-based estimate of global aerosol-cloud radiative forcing by marine warm clouds
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2214 Satellite-based estimate of global aerosol-cloud radiative forcing by marine warm clouds Y.-C. Chen, M. W. Christensen, G. L. Stephens, and J. H. Seinfeld
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2214 Satellite-based estimate of global aerosol-cloud radiative forcing by marine warm clouds Y.-C. Chen, M. W. Christensen, G. L. Stephens, and J. H. Seinfeld
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model
 The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
Satellite Observations and Climate Modeling: What They Can and Cannot Reveal About Future Climate
 Satellite Observations and Climate Modeling: What They Can and Cannot Reveal About Future Climate INCOSE Chesapeake Chapter JHU/APL March 21, 2012 Albert Arking Dept of Earth and Planetary Sciences Johns
Satellite Observations and Climate Modeling: What They Can and Cannot Reveal About Future Climate INCOSE Chesapeake Chapter JHU/APL March 21, 2012 Albert Arking Dept of Earth and Planetary Sciences Johns
ATMOS 5140 Lecture 1 Chapter 1
 ATMOS 5140 Lecture 1 Chapter 1 Atmospheric Radiation Relevance for Weather and Climate Solar Radiation Thermal Infrared Radiation Global Heat Engine Components of the Earth s Energy Budget Relevance for
ATMOS 5140 Lecture 1 Chapter 1 Atmospheric Radiation Relevance for Weather and Climate Solar Radiation Thermal Infrared Radiation Global Heat Engine Components of the Earth s Energy Budget Relevance for
Fundamentals of Atmospheric Radiation and its Parameterization
 Source Materials Fundamentals of Atmospheric Radiation and its Parameterization The following notes draw extensively from Fundamentals of Atmospheric Physics by Murry Salby and Chapter 8 of Parameterization
Source Materials Fundamentals of Atmospheric Radiation and its Parameterization The following notes draw extensively from Fundamentals of Atmospheric Physics by Murry Salby and Chapter 8 of Parameterization
Influence of Clouds and Aerosols on the Earth s Radiation Budget Using Clouds and the Earth s Radiant Energy System (CERES) Measurements
 Influence of Clouds and Aerosols on the Earth s Radiation Budget Using Clouds and the Earth s Radiant Energy System (CERES) Measurements Norman G. Loeb Hampton University/NASA Langley Research Center Bruce
Influence of Clouds and Aerosols on the Earth s Radiation Budget Using Clouds and the Earth s Radiant Energy System (CERES) Measurements Norman G. Loeb Hampton University/NASA Langley Research Center Bruce
Electromagnetic Radiation. Radiation and the Planetary Energy Balance. Electromagnetic Spectrum of the Sun
 Radiation and the Planetary Energy Balance Electromagnetic Radiation Solar radiation warms the planet Conversion of solar energy at the surface Absorption and emission by the atmosphere The greenhouse
Radiation and the Planetary Energy Balance Electromagnetic Radiation Solar radiation warms the planet Conversion of solar energy at the surface Absorption and emission by the atmosphere The greenhouse
Climate Change: Moonshine, Millions of Models, & Billions of Data New Ways to Sort Fact from Fiction
 Climate Change: Moonshine, Millions of Models, & Billions of Data New Ways to Sort Fact from Fiction Bruce Wielicki NASA Langley Research Center June 5, 2008 VIMS Lecture Outline Is that earthshine or
Climate Change: Moonshine, Millions of Models, & Billions of Data New Ways to Sort Fact from Fiction Bruce Wielicki NASA Langley Research Center June 5, 2008 VIMS Lecture Outline Is that earthshine or
McIDAS support of Suomi-NPP /JPSS and GOES-R L2
 McIDAS support of Suomi-NPP /JPSS and GOES-R L2 William Straka III 1 Tommy Jasmin 1, Bob Carp 1 1 Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies, Space Science and Engineering Center, University
McIDAS support of Suomi-NPP /JPSS and GOES-R L2 William Straka III 1 Tommy Jasmin 1, Bob Carp 1 1 Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies, Space Science and Engineering Center, University
Arctic System Reanalysis Provides Highresolution Accuracy for Arctic Studies
 Arctic System Reanalysis Provides Highresolution Accuracy for Arctic Studies David H. Bromwich, Aaron Wilson, Lesheng Bai, Zhiquan Liu POLAR2018 Davos, Switzerland Arctic System Reanalysis Regional reanalysis
Arctic System Reanalysis Provides Highresolution Accuracy for Arctic Studies David H. Bromwich, Aaron Wilson, Lesheng Bai, Zhiquan Liu POLAR2018 Davos, Switzerland Arctic System Reanalysis Regional reanalysis
The Ocean-Atmosphere System II: Oceanic Heat Budget
 The Ocean-Atmosphere System II: Oceanic Heat Budget C. Chen General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth MAR 555 Lecture 2: The Oceanic Heat Budget Q
The Ocean-Atmosphere System II: Oceanic Heat Budget C. Chen General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth MAR 555 Lecture 2: The Oceanic Heat Budget Q
Monday 9 September, :30-11:30 Class#03
 Monday 9 September, 2013 10:30-11:30 Class#03 Topics for the hour Solar zenith angle & relationship to albedo Blackbody spectra Stefan-Boltzman Relationship Layer model of atmosphere OLR, Outgoing longwave
Monday 9 September, 2013 10:30-11:30 Class#03 Topics for the hour Solar zenith angle & relationship to albedo Blackbody spectra Stefan-Boltzman Relationship Layer model of atmosphere OLR, Outgoing longwave
1) The energy balance at the TOA is: 4 (1 α) = σt (1 0.3) = ( ) 4. (1 α) 4σ = ( S 0 = 255 T 1
 EAS488/B8800 Climate & Climate Change Homework 2: Atmospheric Radiation and Climate, surface energy balance, and atmospheric general circulation Posted: 3/12/18; due: 3/26/18 Answer keys 1. (10 points)
EAS488/B8800 Climate & Climate Change Homework 2: Atmospheric Radiation and Climate, surface energy balance, and atmospheric general circulation Posted: 3/12/18; due: 3/26/18 Answer keys 1. (10 points)
The Energy Balance Model
 1 The Energy Balance Model 2 D.S. Battisti 3 Dept. of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington, Seattle Generated using v.3.2 of the AMS LATEX template 1 ABSTRACT 5 ad 2 6 1. Zero-order climatological
1 The Energy Balance Model 2 D.S. Battisti 3 Dept. of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington, Seattle Generated using v.3.2 of the AMS LATEX template 1 ABSTRACT 5 ad 2 6 1. Zero-order climatological
Evaluation of Satellite and Reanalysis Products of Downward Surface Solar Radiation over East Asia
 International Workshop on Land Use/Cover Changes and Air Pollution in Asia August 4-7th, 2015, Bogor, Indonesia Evaluation of Satellite and Reanalysis Products of Downward Surface Solar Radiation over
International Workshop on Land Use/Cover Changes and Air Pollution in Asia August 4-7th, 2015, Bogor, Indonesia Evaluation of Satellite and Reanalysis Products of Downward Surface Solar Radiation over
NEAR REAL TIME GLOBAL RADIATION AND METEOROLOGY WEB SERVICES AVAILABLE FROM NASA
 NEARREAL TIMEGLOBALRADIATIONANDMETEOROLOGYWEBSERVICESAVAILABLE FROMNASA ABSTRACT WilliamS.Chandler JamesM.Hoell DavidWestberg CharlesH.Whitlock TaipingZhang ScienceSystems&Applications,Inc. OneEnterpriseParkway,Suite200
NEARREAL TIMEGLOBALRADIATIONANDMETEOROLOGYWEBSERVICESAVAILABLE FROMNASA ABSTRACT WilliamS.Chandler JamesM.Hoell DavidWestberg CharlesH.Whitlock TaipingZhang ScienceSystems&Applications,Inc. OneEnterpriseParkway,Suite200
Assessing the Radiative Impact of Clouds of Low Optical Depth
 Assessing the Radiative Impact of Clouds of Low Optical Depth W. O'Hirok and P. Ricchiazzi Institute for Computational Earth System Science University of California Santa Barbara, California C. Gautier
Assessing the Radiative Impact of Clouds of Low Optical Depth W. O'Hirok and P. Ricchiazzi Institute for Computational Earth System Science University of California Santa Barbara, California C. Gautier
Antarctic Cloud Radiative Forcing at the Surface Estimated from the AVHRR Polar Pathfinder and ISCCP D1 Datasets,
 JUNE 2003 PAVOLONIS AND KEY 827 Antarctic Cloud Radiative Forcing at the Surface Estimated from the AVHRR Polar Pathfinder and ISCCP D1 Datasets, 1985 93 MICHAEL J. PAVOLONIS Cooperative Institute for
JUNE 2003 PAVOLONIS AND KEY 827 Antarctic Cloud Radiative Forcing at the Surface Estimated from the AVHRR Polar Pathfinder and ISCCP D1 Datasets, 1985 93 MICHAEL J. PAVOLONIS Cooperative Institute for
A new diagram of Earth s global energy budget
 Acta Geod Geophys (2016) 51:481 492 DOI 10.1007/s40328-015-0138-0 A new diagram of Earth s global energy budget Miklos Zagoni 1 Received: 26 November 2014 / Accepted: 23 July 2015 / Published online: 19
Acta Geod Geophys (2016) 51:481 492 DOI 10.1007/s40328-015-0138-0 A new diagram of Earth s global energy budget Miklos Zagoni 1 Received: 26 November 2014 / Accepted: 23 July 2015 / Published online: 19
Variability in the Characteristics of Precipitation Systems in the Tropical Pacific. Part II: Implications for Atmospheric Heating
 1388 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 19 Variability in the Characteristics of Precipitation Systems in the Tropical Pacific. Part II: Implications for Atmospheric Heating TRISTAN S. L ECUYER, HIROHIKO
1388 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 19 Variability in the Characteristics of Precipitation Systems in the Tropical Pacific. Part II: Implications for Atmospheric Heating TRISTAN S. L ECUYER, HIROHIKO
Observational Needs for Polar Atmospheric Science
 Observational Needs for Polar Atmospheric Science John J. Cassano University of Colorado with contributions from: Ed Eloranta, Matthew Lazzara, Julien Nicolas, Ola Persson, Matthew Shupe, and Von Walden
Observational Needs for Polar Atmospheric Science John J. Cassano University of Colorado with contributions from: Ed Eloranta, Matthew Lazzara, Julien Nicolas, Ola Persson, Matthew Shupe, and Von Walden
Earth Systems Science Chapter 3
 Earth Systems Science Chapter 3 ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION: WAVES I. Global Energy Balance and the Greenhouse Effect: The Physics of the Radiation Balance of the Earth 1. Electromagnetic Radiation: waves,
Earth Systems Science Chapter 3 ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION: WAVES I. Global Energy Balance and the Greenhouse Effect: The Physics of the Radiation Balance of the Earth 1. Electromagnetic Radiation: waves,
Radiation in the atmosphere
 Radiation in the atmosphere Flux and intensity Blackbody radiation in a nutshell Solar constant Interaction of radiation with matter Absorption of solar radiation Scattering Radiative transfer Irradiance
Radiation in the atmosphere Flux and intensity Blackbody radiation in a nutshell Solar constant Interaction of radiation with matter Absorption of solar radiation Scattering Radiative transfer Irradiance
Surface Fluxes from In Situ Observations
 Surface Fluxes from In Situ Observations Outline: Background / Sampling Problem Use of In Situ Observations to Produce Flux Datasets Use of In Situ Observations For Flux Dataset Evaluations Evaluation
Surface Fluxes from In Situ Observations Outline: Background / Sampling Problem Use of In Situ Observations to Produce Flux Datasets Use of In Situ Observations For Flux Dataset Evaluations Evaluation
Improved Fields of Satellite-Derived Ocean Surface Turbulent Fluxes of Energy and Moisture
 Improved Fields of Satellite-Derived Ocean Surface Turbulent Fluxes of Energy and Moisture First year report on NASA grant NNX09AJ49G PI: Mark A. Bourassa Co-Is: Carol Anne Clayson, Shawn Smith, and Gary
Improved Fields of Satellite-Derived Ocean Surface Turbulent Fluxes of Energy and Moisture First year report on NASA grant NNX09AJ49G PI: Mark A. Bourassa Co-Is: Carol Anne Clayson, Shawn Smith, and Gary
Variability in clear-sky longwave radiative cooling of the atmosphere
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2006jd007304, 2006 Variability in clear-sky longwave radiative cooling of the atmosphere Richard P. Allan 1 Received
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2006jd007304, 2006 Variability in clear-sky longwave radiative cooling of the atmosphere Richard P. Allan 1 Received
P1.6 DIURNAL CYCLES OF THE SURFACE RADIATION BUDGET DATA SET
 P1.6 DIURNAL CYCLES OF THE SURFACE RADIATION BUDGET DATA SET Pamela E. Mlynczak Science Applications International Corporation, Hampton, VA G. Louis Smith National Institute of Aerospace, Hampton, VA Paul
P1.6 DIURNAL CYCLES OF THE SURFACE RADIATION BUDGET DATA SET Pamela E. Mlynczak Science Applications International Corporation, Hampton, VA G. Louis Smith National Institute of Aerospace, Hampton, VA Paul
ATMOS 5140 Lecture 7 Chapter 6
 ATMOS 5140 Lecture 7 Chapter 6 Thermal Emission Blackbody Radiation Planck s Function Wien s Displacement Law Stefan-Bolzmann Law Emissivity Greybody Approximation Kirchhoff s Law Brightness Temperature
ATMOS 5140 Lecture 7 Chapter 6 Thermal Emission Blackbody Radiation Planck s Function Wien s Displacement Law Stefan-Bolzmann Law Emissivity Greybody Approximation Kirchhoff s Law Brightness Temperature
The SeaFlux Turbulent Flux Dataset Version 1.0 Documentation
 The SeaFlux Turbulent Flux Dataset The SeaFlux Turbulent Flux Dataset Version 1.0 Documentation Carol Anne Clayson1 J. Brent Roberts2 Alec S. Bogdanoff1,3 1. Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods
The SeaFlux Turbulent Flux Dataset The SeaFlux Turbulent Flux Dataset Version 1.0 Documentation Carol Anne Clayson1 J. Brent Roberts2 Alec S. Bogdanoff1,3 1. Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods
Climate Roles of Land Surface
 Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Climate Roles Surface Energy Balance Surface Water Balance Sea Ice Land Ice (from Our Changing Planet) Surface Albedo Climate Roles of Land Surface greenhouse
Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Climate Roles Surface Energy Balance Surface Water Balance Sea Ice Land Ice (from Our Changing Planet) Surface Albedo Climate Roles of Land Surface greenhouse
On the use of satellite remote sensing to determine direct aerosol radiative effect over land : A case study over China
 On the use of satellite remote sensing to determine direct aerosol radiative effect over land : A case study over China Anu-Maija Sundström, Antti Arola, Pekka Kolmonen, Gerrit de Leeuw, and Markku Kulmala
On the use of satellite remote sensing to determine direct aerosol radiative effect over land : A case study over China Anu-Maija Sundström, Antti Arola, Pekka Kolmonen, Gerrit de Leeuw, and Markku Kulmala
2nd Annual CICS-MD Science Meeting November 6-7, 2013 Earth System Science Interdisciplinary Center University of Maryland, College Park, MD
 Development of Algorithms for Shortwave Radiation Budget from GOES-R R. T. Pinker, M. M. Wonsick GOES-R Algorithm Working Group Radiation Budget Application Team John A. Augustine (NOAA); Hye-Yun Kim (IMSG);
Development of Algorithms for Shortwave Radiation Budget from GOES-R R. T. Pinker, M. M. Wonsick GOES-R Algorithm Working Group Radiation Budget Application Team John A. Augustine (NOAA); Hye-Yun Kim (IMSG);
Modeling the Arctic Climate System
 Modeling the Arctic Climate System General model types Single-column models: Processes in a single column Land Surface Models (LSMs): Interactions between the land surface, atmosphere and underlying surface
Modeling the Arctic Climate System General model types Single-column models: Processes in a single column Land Surface Models (LSMs): Interactions between the land surface, atmosphere and underlying surface
Radiation Quantities in the ECMWF model and MARS
 Radiation Quantities in the ECMWF model and MARS Contact: Robin Hogan (r.j.hogan@ecmwf.int) This document is correct until at least model cycle 40R3 (October 2014) Abstract Radiation quantities are frequently
Radiation Quantities in the ECMWF model and MARS Contact: Robin Hogan (r.j.hogan@ecmwf.int) This document is correct until at least model cycle 40R3 (October 2014) Abstract Radiation quantities are frequently
Key Feedbacks in the Climate System
 Key Feedbacks in the Climate System With a Focus on Climate Sensitivity SOLAS Summer School 12 th of August 2009 Thomas Schneider von Deimling, Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research Why do Climate
Key Feedbacks in the Climate System With a Focus on Climate Sensitivity SOLAS Summer School 12 th of August 2009 Thomas Schneider von Deimling, Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research Why do Climate
The effect of ocean mixed layer depth on climate in slab ocean aquaplanet ABSTRACT
 Climate Dynamics manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) 1 2 The effect of ocean mixed layer depth on climate in slab ocean aquaplanet experiments. 3 Aaron Donohoe Dargan Frierson 4 5 Manuscript
Climate Dynamics manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) 1 2 The effect of ocean mixed layer depth on climate in slab ocean aquaplanet experiments. 3 Aaron Donohoe Dargan Frierson 4 5 Manuscript
Atmospheric "greenhouse effect" - How the presence of an atmosphere makes Earth's surface warmer
 Atmospheric "greenhouse effect" - How the presence of an atmosphere makes Earth's surface warmer Some relevant parameters and facts (see previous slide sets) (So/) 32 W m -2 is the average incoming solar
Atmospheric "greenhouse effect" - How the presence of an atmosphere makes Earth's surface warmer Some relevant parameters and facts (see previous slide sets) (So/) 32 W m -2 is the average incoming solar
Shortwave Radiative Transfer in the Earth s Atmosphere: Current Models and Validation
 Shortwave Radiative Transfer in the Earth s Atmosphere: Current Models and Validation Jennifer Delamere, Eli Mlawer, and Tony Clough Atmospheric & Environmental Research, Inc. Summary AER builds radiative
Shortwave Radiative Transfer in the Earth s Atmosphere: Current Models and Validation Jennifer Delamere, Eli Mlawer, and Tony Clough Atmospheric & Environmental Research, Inc. Summary AER builds radiative
An Interconnected Planet
 An Interconnected Planet How Clouds, Aerosols, and the Ocean Cause Distant Rainfall Anomalies Dargan M. W. Frierson University of Washington CESM Workshop, 6-15-15 New Connections Recent research has uncovered
An Interconnected Planet How Clouds, Aerosols, and the Ocean Cause Distant Rainfall Anomalies Dargan M. W. Frierson University of Washington CESM Workshop, 6-15-15 New Connections Recent research has uncovered
9/5/16. Section 3-4: Radiation, Energy, Climate. Common Forms of Energy Transfer in Climate. Electromagnetic radiation.
 Section 3-4: Radiation, Energy, Climate Learning outcomes types of energy important to the climate system Earth energy balance (top of atm., surface) greenhouse effect natural and anthropogenic forcings
Section 3-4: Radiation, Energy, Climate Learning outcomes types of energy important to the climate system Earth energy balance (top of atm., surface) greenhouse effect natural and anthropogenic forcings
Global Energy and Water Budgets
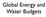 Global Energy and Water Budgets 1 40 10 30 Pressure (hpa) 100 Pure radiative equilibrium Dry adiabatic adjustment 20 Altitude (km) 6.5 C/km adjustment 10 1000 0 180 220 260 300 340 Temperature (K)
Global Energy and Water Budgets 1 40 10 30 Pressure (hpa) 100 Pure radiative equilibrium Dry adiabatic adjustment 20 Altitude (km) 6.5 C/km adjustment 10 1000 0 180 220 260 300 340 Temperature (K)
Seasonal and interannual variations of top-of-atmosphere irradiance and cloud cover over polar regions derived from the CERES data set
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L19804, doi:10.1029/2006gl026685, 2006 Seasonal and interannual variations of top-of-atmosphere irradiance and cloud cover over polar
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L19804, doi:10.1029/2006gl026685, 2006 Seasonal and interannual variations of top-of-atmosphere irradiance and cloud cover over polar
Flux Tower Data Quality Analysis in the North American Monsoon Region
 Flux Tower Data Quality Analysis in the North American Monsoon Region 1. Motivation The area of focus in this study is mainly Arizona, due to data richness and availability. Monsoon rains in Arizona usually
Flux Tower Data Quality Analysis in the North American Monsoon Region 1. Motivation The area of focus in this study is mainly Arizona, due to data richness and availability. Monsoon rains in Arizona usually
Lecture 2 Global and Zonal-mean Energy Balance
 Lecture 2 Global and Zonal-mean Energy Balance A zero-dimensional view of the planet s energy balance RADIATIVE BALANCE Roughly 70% of the radiation received from the Sun at the top of Earth s atmosphere
Lecture 2 Global and Zonal-mean Energy Balance A zero-dimensional view of the planet s energy balance RADIATIVE BALANCE Roughly 70% of the radiation received from the Sun at the top of Earth s atmosphere
The role of soil moisture in influencing climate and terrestrial ecosystem processes
 1of 18 The role of soil moisture in influencing climate and terrestrial ecosystem processes Vivek Arora Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis Meteorological Service of Canada Outline 2of 18
1of 18 The role of soil moisture in influencing climate and terrestrial ecosystem processes Vivek Arora Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis Meteorological Service of Canada Outline 2of 18
Operational Uses of Bands on the GOES-R Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI) Presented by: Kaba Bah
 Operational Uses of Bands on the GOES-R Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI) Presented by: Kaba Bah Topics: Introduction to GOES-R & ABI ABI individual bands Use of band differences ABI derived products Conclusions
Operational Uses of Bands on the GOES-R Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI) Presented by: Kaba Bah Topics: Introduction to GOES-R & ABI ABI individual bands Use of band differences ABI derived products Conclusions
Related Improvements. A DFS Application. Mark A. Bourassa
 Related Improvements in Surface Turbulent Heat Fluxes A DFS Application Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies & Department of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences, The Florida State University,
Related Improvements in Surface Turbulent Heat Fluxes A DFS Application Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies & Department of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences, The Florida State University,
Dependence of Radiative Forcing on Mineralogy in the Community Atmosphere Model
 Dependence of Radiative Forcing on Mineralogy in the Community Atmosphere Model Rachel Scanza 1, Natalie Mahowald 1, Jasper Kok 2, Steven Ghan 3, Charles Zender 4, Xiaohong Liu 5, Yan Zhang 6 February
Dependence of Radiative Forcing on Mineralogy in the Community Atmosphere Model Rachel Scanza 1, Natalie Mahowald 1, Jasper Kok 2, Steven Ghan 3, Charles Zender 4, Xiaohong Liu 5, Yan Zhang 6 February
Sun and Earth s Climate
 Kevin E Trenberth Sun and Earth s Climate BAMS cover March 2009 NCAR Here comes the sun So where does all that solar radiation go? If the sun keeps shining why don t we continue to get warmer? Aaagh! But
Kevin E Trenberth Sun and Earth s Climate BAMS cover March 2009 NCAR Here comes the sun So where does all that solar radiation go? If the sun keeps shining why don t we continue to get warmer? Aaagh! But
How surface latent heat flux is related to lower-tropospheric stability in southern subtropical marine stratus and stratocumulus regions
 Cent. Eur. J. Geosci. 1(3) 2009 368-375 DOI: 10.2478/v10085-009-0028-1 Central European Journal of Geosciences How surface latent heat flux is related to lower-tropospheric stability in southern subtropical
Cent. Eur. J. Geosci. 1(3) 2009 368-375 DOI: 10.2478/v10085-009-0028-1 Central European Journal of Geosciences How surface latent heat flux is related to lower-tropospheric stability in southern subtropical
Understanding land-surfaceatmosphere. observations and models
 Understanding land-surfaceatmosphere coupling in observations and models Alan K. Betts Atmospheric Research akbetts@aol.com MERRA Workshop AMS Conference, Phoenix January 11, 2009 Land-surface-atmosphere
Understanding land-surfaceatmosphere coupling in observations and models Alan K. Betts Atmospheric Research akbetts@aol.com MERRA Workshop AMS Conference, Phoenix January 11, 2009 Land-surface-atmosphere
GERB/CERES Comparisons Update
 GERB/CERES Comparisons Update N. Clerbaux, S. Dewitte, A. Ipe, P.-J. Baeck, A. Velazquez, I. Decoster Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium, Department of Observations, Section Remote Sensing from
GERB/CERES Comparisons Update N. Clerbaux, S. Dewitte, A. Ipe, P.-J. Baeck, A. Velazquez, I. Decoster Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium, Department of Observations, Section Remote Sensing from
