THE OPPOSITION CYCLE OF MARS By: Jeffrey D. Beish (Revised 14 October 2010)
|
|
|
- Isabel Fisher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE OPPOSITION CYCLE OF MARS By: Jeffrey D. Beish (Revised 14 October 2010) The orbits of Earth and Mars are elliptical with Mars having a more eccentric orbit that our planet. The distance between the Earth and Mars varies from 248,700,000 miles, when Mars is in conjunction with the Sun, and may approach within 34,650,000 miles during Perihelic apparitions, or 63,000,000 miles during Aphelic apparitions. When Mars is in Conjunction the Sun is between Mars and Earth. Opposition, or when the Mars is on opposite side of the Earth from the Sun, will occur approximately 390 days after conjunction. At opposition the Earth and Mars will be nearly in a straight line from the Sun. The physical diameter of Mars is about 53% that of Earth and has a polar diameter of 4,194 miles ( km) and an equatorial diameter of 4,217 miles ( km). So, the apparent size of Mars, as viewed through a telescope from Earth, will vary from as small as 13.8 seconds of arc during Aphelic apparitions, and as large as 25.1 seconds of arc during Perihelic apparitions. The Martian year is 1.88 tropical Earth years consisting of Martian days (sols) or Earth days. The mean synodic period is mean days. We find the synodic period from the mathematical expression: 1/s = 1/Pe - 1/Pm, where Pe = days and Pm = days A general rule for predicting oppositions of the Red Planet; Mars has average 15.8-year seasonal opposition cycle, which consists of three or four Aphelic oppositions and three consecutive Perihelic oppositions [Capen, 1984, Capen, 1984]. We sometimes refer to this as the seven Martian synodic periods. This cycle repeats after every 79 years, with an error of several days (4 to 5 days), and if one would live long enough they may see this cycle nearly replicated in 284 years [Frommert, 2008] (See Table 1).
2 Table 1. A list of dates when the apparent diameter of Mars was and will be over 25 seconds of arc over a period of plus and minus 284 years from the next apparition in IN 2003 MARS WAS CLOSER TO EARTH SINCE TELESCOPES USED During a conversation with syndicated television personality and astronomer Jack Horkheimer asked the ALPO Mars Section to compute the date when Mars last came as close to Earth as it is predicted to approach Earth during the 2003 Perihelic apparition [Horkheimer, 2001]. He posed an interesting question and one that the answer was not readily available. Since our computer programs are written to calculate the physical Epemerides of Mars for the life span of a typical observer there was no practical reason to compute the orbits and other aspects of Earth and Mars for more than a hundred years or so. Several computer runs were made using this author s PC and it soon became clear that this problem was too much for a home computer to solve in a timely manner. So, we enlisted the aid of a Jim DeYoung, a former coworker and employee of the U.S. Naval Observatory Time Service, for his expert help to answer this most intriguing question. The problem that was posed to Jim: when was Mars as close or closer to Earth as it will be during the 2003 apparition? Jim is a mathematician and computer specialist by trade and is interested in astronomical calculations. This was just the problem for Jim to help us solve. He prepared a computer program using the integration method used was the Burlirsch-Stoer method to calculate the orbits of and perturbations of all nine-planets [James DeYoung, 2002]. This included the major perturbations and effects of the Moon and the four major asteroids to plot the results. During Jim's off duty hours he ran the program constantly until a plot of each time Mars was near opposition at the closest approach to Earth. We arbitrarily chose a limit of +/- 100,000 years starting with this author's last birthday on October 17, 2001 (JD ). Amazingly, we found that Mars will be closer during the 2003 apparition than at any time since the year -57,537! At that time Mars was AU (apparent diameter of seconds of arc). Competing calculations have been found that the year -57,617 was the closest approach of
3 Mars to Earth, or 79 years further back in time, according to Aldo Vitagliano of the Universitá di Napoli Federico II in Naples, Italy [Meeus, 2003]. NOTE: Upon further investigation I discovered that by using my last birthday it skipped the August 27 date and added 79 years to our initial computations. Must be a quirk in the integration method we used. In a second computation the results matched Vitagliano s values. Additional results were gleaned from this experiment and we include some interesting points: First, during the year -79,241 Mars and Earth were AU apart and subtended an apparent diameter of seconds of arc! It should be noted that these values are Earth-Moon barycenter to Mars distances where slightly different values can result from using the methods used for predicting the Solar System Ephemerides in the short run -- say 100 years or so. A plot established several interesting points when Mars was as close to or closer to Earth than it will be during The integration output was printed steps to maintain the 1x10-15 accuracy. The integration should have maintained 5 to 6 digits of precision over this number of steps, mostly round off error accumulation and a smaller amount from truncation errors (See Figure 1). NOTE: Predicting harmonic errors of the perihelion date for Mars coincident with the date Earth is at or near aphelion would be difficult to calculate because of the long precession periods for both planets. The axis of rotational precession for is over a period of ~175,000 years [~173,000, Kieffer et al, 1992]. Additionally, Mars orbit also precesses causing the line of apsides (a line bisecting aphelion and perihelion) to rotate. This cycle is completed in 72,000 years that results in a gradual shift in the position of perihelion with respect to the space that the Solar System occupies [Chattermole, 1992]. The axis of rotational for Earth precesses over a period of ~25,800 years therefore Compounding this problems of predicting their reoccurrence of this coincidental meeting of the Red Planet and Earth.
4 Figure 1. A plot from numerical integration for the orbits of Earth and Mars during the points of closest approach for a period of +/- 100,000 years from JD Left, or the red points, indicate pre-2001 and right, or green points, are after The ordinate axis indicates the Julian day in millions of days and the coordinate shows the apparent diameter of Mars as seen form Earth during a particular closest approach. The results published in this paper has come under scrutiny since first published and upon further examination we have found that our integration method calculations were correct; however, by arbitrarily choosing this author s birthday on October 17, 2001 (JD ) with a limit of +/- 100,000 years the integration skipped one 79 year repetitive cycle (for reasons hover this author s head). Our quest to find the last time Mars and Earth was as close as it was in 2003 was off by 79 years. This has been corrected as stated above by a second computation. First to publish anything on this problem was Belgian author and mathematician Jean Meeus. He calculated that Mars has not been closer to Earth since the year 73,000 B.C.. However, Meeus based his initial calculations on the work of French astronomer Pierre Bretagnon and was off by more than 20,000 years. After Jean s book was published, he contacted Italian mathematician Aldo Vitagliano (Naples University, Italy) and asked him to investigate the motion of Mars by numerical integration. Vitagliano reported back that the last time Mars was closer to Earth than during the 2003 opposition was on September 12 of the year 57,617 B.C.. This can be read on his web site at:
5 DISCUSSION We are thankful to the late astronomer Jack Horkheimer for asking the question and hopefully the answer was satisfactory. While it is of interest to observers to know how close Mars will approach Earth during any particular apparition we pay little attention to exact details of the apparition characteristics. To many it would be only a passing interest to know that Mars will reach some historic distance from Earth or be higher in the sky, etc., but to relate to orbital elements is not very exciting to most Mars watchers. In other words, most of us like to look at Mars without all the mathematical fuss. At the times when Mars approaches very close to the Earth we know observers will likely want to get out their telescopes and record what the see of the Red Planet, and we in the Mars Section are more than happy to encourage them to do so. One way is to make upcoming apparition sound exciting and to interest observers to participate in our observing programs. However, in 2003 Mars came closer to Earth than at any time since we can remember, or at least for anyone alive today. While we usually do not take the time to compute the orbit of Mars so far in the past or future it was never the less a fun project for our friend Jack Horkheimer and his TV audience. It shows us the unusual nature of the orbital relationship of Mars and Earth and hopefully to help us realize how erratic our Solar System really is. The Solar System is always in a state of change! REFERENCES Capen, C.F., "A Guide to Observing Mars - I", Journal of the Association of Lunar and Planetary Observers (J.A.L.P.O.),Vol. 30, Nos. 7-8, April 1984, pp Capen, C.F., "A Guide to Observing Mars - II", Journal of the Association of Lunar and Planetary Observers (J.A.L.P.O.), Vol 30, Nos. 9-10, August 1984, pp Chattermole, P., (1992), Mars: The Story of the Red Planet, Chapman & Hall, Chapter 1.3, "The Martian Seasons," pp DeYoung, James, personal communications, December Frommert, Hartmut (2008), "Mars Oppositions," spider at seds.org, Horkheimer, Jack, "Star Gazer Celebrates its 25th Anniversary! The Leonid Meteor Shower May Turn Into A Meteor Storm And An Announcement About Mars You Won't Believe!" STAR GAZER Episode # 01-45, 1248th Show, Aired: Monday 11/05/2001 through Sunday 11/11/2001 Kieffer, H.H., B. M. Jakosky, C.W. Snyder, and M.S. Matthews, Editors (1992), Chapter 9, "Long- Term Orbital and Spin Dynamics," Mars, University of Arizona Press, pp Meeus, Jean, (2003), "When Was Mars Last This Close?" The Planetarian (Journal of the International Planetarium Society), March
Astronomy Notes Chapter 02.notebook April 11, 2014 Pythagoras Aristotle geocentric retrograde motion epicycles deferents Aristarchus, heliocentric
 Around 2500 years ago, Pythagoras began to use math to describe the world around him. Around 200 years later, Aristotle stated that the Universe is understandable and is governed by regular laws. Most
Around 2500 years ago, Pythagoras began to use math to describe the world around him. Around 200 years later, Aristotle stated that the Universe is understandable and is governed by regular laws. Most
(BASED ON SG 1609 JUPITER AT OPPOSITION AND SG 1713 ROYAL OPPOSITION! )
 STAR GAZERS SG 1817-5 MINUTE (APRIL 23-29, 2018) (BASED ON SG 1609 JUPITER AT OPPOSITION AND SG 1713 ROYAL OPPOSITION! ) THE FIFTH PLANET FROM THE SUN! WELCOME TO STAR GAZERS. I'M JAMES ALBURY, DIRECTOR
STAR GAZERS SG 1817-5 MINUTE (APRIL 23-29, 2018) (BASED ON SG 1609 JUPITER AT OPPOSITION AND SG 1713 ROYAL OPPOSITION! ) THE FIFTH PLANET FROM THE SUN! WELCOME TO STAR GAZERS. I'M JAMES ALBURY, DIRECTOR
PTYS/ASTR 206 Section 2 Spring 2007 Homework #1 (Page 1/4)
 PTYS/ASTR 206 Section 2 Spring 2007 Homework #1 (Page 1/4) NAME: KEY Due Date: start of class 1/25/2007 5 pts extra credit if turned in before 9:00AM (early!) (To get the extra credit, the assignment must
PTYS/ASTR 206 Section 2 Spring 2007 Homework #1 (Page 1/4) NAME: KEY Due Date: start of class 1/25/2007 5 pts extra credit if turned in before 9:00AM (early!) (To get the extra credit, the assignment must
2. See FIGURE B. This person in the FIGURE discovered that this planet had phases (name the planet)?
 ASTRONOMY 2 MIDTERM EXAM PART I SPRING 2019 60 QUESTIONS 50 POINTS: Part I of the midterm constitutes the Take-Home part of the entire Midterm Exam. Additionally, this Take-Home part is divided into two
ASTRONOMY 2 MIDTERM EXAM PART I SPRING 2019 60 QUESTIONS 50 POINTS: Part I of the midterm constitutes the Take-Home part of the entire Midterm Exam. Additionally, this Take-Home part is divided into two
John Hopkins, Editor. Index
 John Hopkins, Editor Index Abraham Lincoln and the Almanac Defense Volume 13, Issue 4 October December, 2013 Amateur Astronomer Makes a Discovery, an Impact Spot on Jupiter Volume 9, Issue 4 October December,
John Hopkins, Editor Index Abraham Lincoln and the Almanac Defense Volume 13, Issue 4 October December, 2013 Amateur Astronomer Makes a Discovery, an Impact Spot on Jupiter Volume 9, Issue 4 October December,
Astronomy Club of Asheville January 2016 Sky Events
 January 2016 Sky Events The Planets this Month - page 2 Planet Highlights - page 7 All 5 Naked-Eye Planets in the Dawn Sky - page 10 Moon Phases - page 11 Earth Reaches Perihelion on Jan. 4 - page 12 Quadrantid
January 2016 Sky Events The Planets this Month - page 2 Planet Highlights - page 7 All 5 Naked-Eye Planets in the Dawn Sky - page 10 Moon Phases - page 11 Earth Reaches Perihelion on Jan. 4 - page 12 Quadrantid
PHSC 1053: Astronomy Time and Coordinates
 PHSC 1053: Astronomy Time and Coordinates Astronomical Clocks Earth s Rotation on its Axis Time between two successive meridian transits of the sun 1 solar day (our adopted clock time) 24 hours (86,400
PHSC 1053: Astronomy Time and Coordinates Astronomical Clocks Earth s Rotation on its Axis Time between two successive meridian transits of the sun 1 solar day (our adopted clock time) 24 hours (86,400
Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens
 Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens Origins of Modern Astronomy Earth Science, 13e Chapter 21 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Early history of astronomy Ancient Greeks Used philosophical
Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens Origins of Modern Astronomy Earth Science, 13e Chapter 21 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Early history of astronomy Ancient Greeks Used philosophical
18. Kepler as a young man became the assistant to A) Nicolaus Copernicus. B) Ptolemy. C) Tycho Brahe. D) Sir Isaac Newton.
 Name: Date: 1. The word planet is derived from a Greek term meaning A) bright nighttime object. B) astrological sign. C) wanderer. D) nontwinkling star. 2. The planets that were known before the telescope
Name: Date: 1. The word planet is derived from a Greek term meaning A) bright nighttime object. B) astrological sign. C) wanderer. D) nontwinkling star. 2. The planets that were known before the telescope
Earth Science, 11e. Origin of Modern Astronomy Chapter 21. Early history of astronomy. Early history of astronomy. Early history of astronomy
 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 21 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
2006 Pearson Prentice Hall Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 21 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
What is a Satellite? A satellite is an object that orbits another object. Ex. Radio satellite, moons, planets
 Planetary Orbit Planetary Orbits What shape do planets APPEAR to orbit the sun? Planets APPEAR to orbit in a circle. What shape do the planets orbit the sun??? Each planet Orbits the Sun in an ellipse
Planetary Orbit Planetary Orbits What shape do planets APPEAR to orbit the sun? Planets APPEAR to orbit in a circle. What shape do the planets orbit the sun??? Each planet Orbits the Sun in an ellipse
Name Period Date Earth and Space Science. Solar System Review
 Name Period Date Earth and Space Science Solar System Review 1. is the spinning a planetary object on its axis. 2. is the backward motion of planets. 3. The is a unit less number between 0 and 1 that describes
Name Period Date Earth and Space Science Solar System Review 1. is the spinning a planetary object on its axis. 2. is the backward motion of planets. 3. The is a unit less number between 0 and 1 that describes
EXAM #2. ANSWERS ASTR , Spring 2008
 EXAM #2. ANSWERS ASTR 1101-001, Spring 2008 1. In Copernicus s heliocentric model of the universe, which of the following astronomical objects was placed in an orbit around the Earth? The Moon 2. In his
EXAM #2. ANSWERS ASTR 1101-001, Spring 2008 1. In Copernicus s heliocentric model of the universe, which of the following astronomical objects was placed in an orbit around the Earth? The Moon 2. In his
- ( ). 1. THE PLANETARY GAMBLING MACHINE.
 There is no dark side of the Moon really, as a matter of fact it is all dark, - Pink Floyd ( The Dark Side of the Moon ). 1. THE PLANETARY GAMBLING MACHINE. Everybody living on this planet must have heard
There is no dark side of the Moon really, as a matter of fact it is all dark, - Pink Floyd ( The Dark Side of the Moon ). 1. THE PLANETARY GAMBLING MACHINE. Everybody living on this planet must have heard
How big is the Universe and where are we in it?
 Announcements Results of clicker questions from Monday are on ICON. First homework is graded on ICON. Next homework due one minute before midnight on Tuesday, September 6. Labs start this week. All lab
Announcements Results of clicker questions from Monday are on ICON. First homework is graded on ICON. Next homework due one minute before midnight on Tuesday, September 6. Labs start this week. All lab
Basics of Kepler and Newton. Orbits of the planets, moons,
 Basics of Kepler and Newton Orbits of the planets, moons, Kepler s Laws, as derived by Newton. Kepler s Laws Universal Law of Gravity Three Laws of Motion Deriving Kepler s Laws Recall: The Copernican
Basics of Kepler and Newton Orbits of the planets, moons, Kepler s Laws, as derived by Newton. Kepler s Laws Universal Law of Gravity Three Laws of Motion Deriving Kepler s Laws Recall: The Copernican
PHYS 155 Introductory Astronomy
 PHYS 155 Introductory Astronomy - observing sessions: Sunday Thursday, 9pm, weather permitting http://www.phys.uconn.edu/observatory - Exam - Tuesday March 20, - Review Monday 6:30-9pm, PB 38 Marek Krasnansky
PHYS 155 Introductory Astronomy - observing sessions: Sunday Thursday, 9pm, weather permitting http://www.phys.uconn.edu/observatory - Exam - Tuesday March 20, - Review Monday 6:30-9pm, PB 38 Marek Krasnansky
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 4, Week 5, Day 1
 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 4, Week 5, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: Earth Sciences 1.d students know the evidence indicating that the planets are much closer to Earth than are the stars
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 4, Week 5, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: Earth Sciences 1.d students know the evidence indicating that the planets are much closer to Earth than are the stars
Astronomy Section 2 Solar System Test
 is really cool! 1. The diagram below shows one model of a portion of the universe. Astronomy Section 2 Solar System Test 4. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high
is really cool! 1. The diagram below shows one model of a portion of the universe. Astronomy Section 2 Solar System Test 4. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high
October 19, NOTES Solar System Data Table.notebook. Which page in the ESRT???? million km million. average.
 Celestial Object: Naturally occurring object that exists in space. NOT spacecraft or man-made satellites Which page in the ESRT???? Mean = average Units = million km How can we find this using the Solar
Celestial Object: Naturally occurring object that exists in space. NOT spacecraft or man-made satellites Which page in the ESRT???? Mean = average Units = million km How can we find this using the Solar
Unit 2: Celestial Mechanics
 Unit 2: Celestial Mechanics The position of the Earth Ptolemy (90 168 AD) Made tables that allowed a user to locate the position of a planet at any past, present, or future date. In order to maintain circular
Unit 2: Celestial Mechanics The position of the Earth Ptolemy (90 168 AD) Made tables that allowed a user to locate the position of a planet at any past, present, or future date. In order to maintain circular
SKYCAL - Sky Events Calendar
 SKYCAL - Sky Events Calendar Your web browser must have Javascript turned on. The following browsers have been successfully tested: Macintosh - Firefox 3.0 (Safari NOT supported) Windows - Firefox 3.0,
SKYCAL - Sky Events Calendar Your web browser must have Javascript turned on. The following browsers have been successfully tested: Macintosh - Firefox 3.0 (Safari NOT supported) Windows - Firefox 3.0,
You should have finished reading Chapter 3, and started on chapter 4 for next week.
 Announcements Homework due on Sunday at 11:45pm. Thank your classmate! You should have finished reading Chapter 3, and started on chapter 4 for next week. Don t forget your out of class planetarium show
Announcements Homework due on Sunday at 11:45pm. Thank your classmate! You should have finished reading Chapter 3, and started on chapter 4 for next week. Don t forget your out of class planetarium show
Origin of Modern Astronomy Chapter 21
 Origin of Modern Astronomy Chapter 21 Early history of astronomy Ancient Greeks Used philosophical arguments to explain natural phenomena Also used some observa:onal data (looking at the night sky) Ancient
Origin of Modern Astronomy Chapter 21 Early history of astronomy Ancient Greeks Used philosophical arguments to explain natural phenomena Also used some observa:onal data (looking at the night sky) Ancient
1. The bar graph below shows one planetary characteristic, identified as X, plotted for the planets of our solar system.
 1. The bar graph below shows one planetary characteristic, identified as X, plotted for the planets of our solar system. Which characteristic of the planets in our solar system is represented by X? A)
1. The bar graph below shows one planetary characteristic, identified as X, plotted for the planets of our solar system. Which characteristic of the planets in our solar system is represented by X? A)
6 The Orbit of Mercury
 6 The Orbit of Mercury Name: Date: Of the five planets known since ancient times (Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn), Mercury is the most difficult to see. In fact, of the 6 billion people on the
6 The Orbit of Mercury Name: Date: Of the five planets known since ancient times (Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn), Mercury is the most difficult to see. In fact, of the 6 billion people on the
Planets in the Sky ASTR 101 2/16/2018
 Planets in the Sky ASTR 101 2/16/2018 1 Planets in the Sky 2018 paths of Jupiter among stars (2017/2018) Unlike stars which have fixed positions in the sky (celestial sphere), planets seem to move with
Planets in the Sky ASTR 101 2/16/2018 1 Planets in the Sky 2018 paths of Jupiter among stars (2017/2018) Unlike stars which have fixed positions in the sky (celestial sphere), planets seem to move with
Mars Opposition Friday 27 th July 2018
 Mars Opposition Friday 27 th July 2018 Mars is about 6,780 kilometres in diameter or roughly half the size of the Earth whose diameter is 12,742km. As they orbit the Sun, the minimum distance between the
Mars Opposition Friday 27 th July 2018 Mars is about 6,780 kilometres in diameter or roughly half the size of the Earth whose diameter is 12,742km. As they orbit the Sun, the minimum distance between the
What's Up? 2018 December 10 to 2019 January 28. Bill Barton, FRAS
 What's Up? 2018 December 10 to 2019 January 28 Bill Barton, FRAS The Sky 21:00 Tonight The Sky 07:00 Tomorrow Inner Solar System Sun Declination decreasing until Solstice December 21, perihelion January
What's Up? 2018 December 10 to 2019 January 28 Bill Barton, FRAS The Sky 21:00 Tonight The Sky 07:00 Tomorrow Inner Solar System Sun Declination decreasing until Solstice December 21, perihelion January
Astronomy 291. Professor Bradley M. Peterson
 Astronomy 291 Professor Bradley M. Peterson The Sky As a first step, we need to understand the appearance of the sky. Important points (to be explained): The relative positions of stars remain the same
Astronomy 291 Professor Bradley M. Peterson The Sky As a first step, we need to understand the appearance of the sky. Important points (to be explained): The relative positions of stars remain the same
ASTRONOMY Merit Badge Requirements
 ASTRONOMY Merit Badge Requirements 1) Do the following: A) Sketch the face of the moon, indicating on it the locations of at least five seas and five craters. B) Within a single week, sketch the position
ASTRONOMY Merit Badge Requirements 1) Do the following: A) Sketch the face of the moon, indicating on it the locations of at least five seas and five craters. B) Within a single week, sketch the position
Jan. 12th SMAS Meeting PSTCC, Main Campus Hardin Valley Road 7:30 pm, Alexander Bldg, Room 223
 Smoky S.C.R.A.P.S. Mountain Astronomical Society Page 1 S.C.R.A.P.S. Society s ChRonological Astronomical PaperS Jan. 12th SMAS Meeting PSTCC, Main Campus Hardin Valley Road 7:30 pm, Alexander Bldg, Room
Smoky S.C.R.A.P.S. Mountain Astronomical Society Page 1 S.C.R.A.P.S. Society s ChRonological Astronomical PaperS Jan. 12th SMAS Meeting PSTCC, Main Campus Hardin Valley Road 7:30 pm, Alexander Bldg, Room
Schedule of public programs on last page!
 The Observer February 2016 (#39) Schedule of public programs on last page! CELEBRATE PERIHELION DAY! There are many holidays that people celebrate around the end of December and the beginning of January.
The Observer February 2016 (#39) Schedule of public programs on last page! CELEBRATE PERIHELION DAY! There are many holidays that people celebrate around the end of December and the beginning of January.
Orbital Mechanics. CTLA Earth & Environmental Science
 Orbital Mechanics CTLA Earth & Environmental Science The Earth Spherical body that is flattened near the poles due to centrifugal force (rotation of the Earth) 40,074 KM across at the Equator 40,0007 KM
Orbital Mechanics CTLA Earth & Environmental Science The Earth Spherical body that is flattened near the poles due to centrifugal force (rotation of the Earth) 40,074 KM across at the Equator 40,0007 KM
Gravity. Newton s Law of Gravitation Kepler s Laws of Planetary Motion Gravitational Fields
 Gravity Newton s Law of Gravitation Kepler s Laws of Planetary Motion Gravitational Fields Simulation Synchronous Rotation https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ozib_l eg75q Sun-Earth-Moon System https://vimeo.com/16015937
Gravity Newton s Law of Gravitation Kepler s Laws of Planetary Motion Gravitational Fields Simulation Synchronous Rotation https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ozib_l eg75q Sun-Earth-Moon System https://vimeo.com/16015937
Venus Project Book, the Galileo Project, GEAR
 1 Venus Project Book, the Galileo Project, GEAR Jeffrey La Favre November, 2013 Updated March 31, 2016 You have already learned about Galileo and his telescope. Recall that he built his first telescopes
1 Venus Project Book, the Galileo Project, GEAR Jeffrey La Favre November, 2013 Updated March 31, 2016 You have already learned about Galileo and his telescope. Recall that he built his first telescopes
Chapter 22 Exam Study Guide
 Chapter 22 Exam Study Guide Name: Hour: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Write the letter that best answers the question or completes
Chapter 22 Exam Study Guide Name: Hour: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Write the letter that best answers the question or completes
Exercise 4.0 PLANETARY ORBITS AND CONFIGURATIONS
 Exercise 4.0 PLANETARY ORBITS AND CONFIGURATIONS I. Introduction The planets revolve around the Sun in orbits that lie nearly in the same plane. Therefore, the planets, with the exception of Pluto, are
Exercise 4.0 PLANETARY ORBITS AND CONFIGURATIONS I. Introduction The planets revolve around the Sun in orbits that lie nearly in the same plane. Therefore, the planets, with the exception of Pluto, are
Boy Scout Badge Workshop ASTRONOMY
 Boy Scout Badge Workshop ASTRONOMY Welcome to the Schenectady Museum & Suits-Bueche Planetarium! During this workshop, you will explore the museum, see a show in the planetarium, and try out some other
Boy Scout Badge Workshop ASTRONOMY Welcome to the Schenectady Museum & Suits-Bueche Planetarium! During this workshop, you will explore the museum, see a show in the planetarium, and try out some other
Chapter 22.2 The Earth- Moon-Sun System. Chapter 22.3: Earth s Moon
 Chapter 22.2 The Earth- Moon-Sun System Chapter 22.3: Earth s Moon Chapter 22.2 The Earth- Moon-Sun System Motions of the Earth The two main motions of the Earth are rotation and revolution Rotation
Chapter 22.2 The Earth- Moon-Sun System Chapter 22.3: Earth s Moon Chapter 22.2 The Earth- Moon-Sun System Motions of the Earth The two main motions of the Earth are rotation and revolution Rotation
Kepler's Laws and Newton's Laws
 Kepler's Laws and Newton's Laws Kepler's Laws Johannes Kepler (1571-1630) developed a quantitative description of the motions of the planets in the solar system. The description that he produced is expressed
Kepler's Laws and Newton's Laws Kepler's Laws Johannes Kepler (1571-1630) developed a quantitative description of the motions of the planets in the solar system. The description that he produced is expressed
Mercury Data (Table 11-1) 11a. Sun-Scorched Mercury. Mercury Data: Numbers
 11a. Sun-Scorched Mercury Earth-based observations of Mercury Mercury s rotation & year Mariner 10 s images of Mercury Mercury s interior Mercury Data (Table 11-1) Mercury Data: Numbers Diameter: 4,878.km
11a. Sun-Scorched Mercury Earth-based observations of Mercury Mercury s rotation & year Mariner 10 s images of Mercury Mercury s interior Mercury Data (Table 11-1) Mercury Data: Numbers Diameter: 4,878.km
The following terms are some of the vocabulary that students should be familiar with in order to fully master this lesson.
 Lesson 211: EARTH'S SEASONS Students learn the complex geometry and planetary motions that cause Earth to have four distinct seasons. Fundamental Questions Attempting to give thorough and reasonable answers
Lesson 211: EARTH'S SEASONS Students learn the complex geometry and planetary motions that cause Earth to have four distinct seasons. Fundamental Questions Attempting to give thorough and reasonable answers
Earth & Beyond Teacher Newsletter
 Paul Floyd s Astronomy & Space Website Earth & Beyond Teacher Newsletter www.nightskyonline.info Earth & Beyond Teaching opportunities for 2012 This special edition has been prepared to assist you with
Paul Floyd s Astronomy & Space Website Earth & Beyond Teacher Newsletter www.nightskyonline.info Earth & Beyond Teaching opportunities for 2012 This special edition has been prepared to assist you with
Review of previous concepts!! Earth s orbit: Year, seasons, observed constellations, Polaris (North star), day/night lengths, equinoxes
 Review of previous concepts!! Earth s orbit: Year, seasons, observed constellations, Polaris (North star), day/night lengths, equinoxes Celestial poles, celestial equator, ecliptic, ecliptic plane (Fig
Review of previous concepts!! Earth s orbit: Year, seasons, observed constellations, Polaris (North star), day/night lengths, equinoxes Celestial poles, celestial equator, ecliptic, ecliptic plane (Fig
Eclipses and Forces. Jan 21, ) Review 2) Eclipses 3) Kepler s Laws 4) Newton s Laws
 Eclipses and Forces Jan 21, 2004 1) Review 2) Eclipses 3) Kepler s Laws 4) Newton s Laws Review Lots of motion The Moon revolves around the Earth Eclipses Solar Lunar the Sun, Earth and Moon must all be
Eclipses and Forces Jan 21, 2004 1) Review 2) Eclipses 3) Kepler s Laws 4) Newton s Laws Review Lots of motion The Moon revolves around the Earth Eclipses Solar Lunar the Sun, Earth and Moon must all be
Astronomy Regents Review
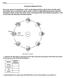 Name Astronomy Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows s orbit around the un as viewed from space. is shown at eight different positions labeled A through
Name Astronomy Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows s orbit around the un as viewed from space. is shown at eight different positions labeled A through
Astronomy Club of Asheville April 2017 Sky Events
 April 2017 Sky Events The Planets this Month page 2 April 6 th - Regulus and the Gibbous Moon page 5 April 10 th -The Full Moon Joins Jupiter and Spica page 6 Planet Highlights page 7 Moon Phases page
April 2017 Sky Events The Planets this Month page 2 April 6 th - Regulus and the Gibbous Moon page 5 April 10 th -The Full Moon Joins Jupiter and Spica page 6 Planet Highlights page 7 Moon Phases page
Directed Reading. Section: Viewing the Universe THE VALUE OF ASTRONOMY. Skills Worksheet. 1. How did observations of the sky help farmers in the past?
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe 1. How did observations of the sky help farmers in the past? 2. How did observations of the sky help sailors in the past? 3. What is the
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe 1. How did observations of the sky help farmers in the past? 2. How did observations of the sky help sailors in the past? 3. What is the
Physical Science 1 Chapter 16 INTRODUCTION. Astronomy is the study of the universe, which includes all matter, energy, space and time.
 INTRODUCTION Astronomy is the study of the universe, which includes all matter, energy, space and time. Although the universe is vast and almost beyond imagination, much is known about its make-up and
INTRODUCTION Astronomy is the study of the universe, which includes all matter, energy, space and time. Although the universe is vast and almost beyond imagination, much is known about its make-up and
Venus Transits Sun for Last Time This Century
 4 June 2012 MP3 at voaspecialenglish.com Venus Transits Sun for Last Time This Century JUNE SIMMS: This is SCIENCE IN THE NEWS, in VOA Special English. I m June Simms. SHIRLEY GRIFFITH: And I m Shirley
4 June 2012 MP3 at voaspecialenglish.com Venus Transits Sun for Last Time This Century JUNE SIMMS: This is SCIENCE IN THE NEWS, in VOA Special English. I m June Simms. SHIRLEY GRIFFITH: And I m Shirley
Astronomy A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE UNIVERSE EIGHTH EDITION
 Astronomy A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE UNIVERSE EIGHTH EDITION CHAPTER 4 The Solar System Lecture Presentation 4.0 What can be seen with the naked eye? Early astronomers knew about the Sun, Moon, stars, Mercury,
Astronomy A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE UNIVERSE EIGHTH EDITION CHAPTER 4 The Solar System Lecture Presentation 4.0 What can be seen with the naked eye? Early astronomers knew about the Sun, Moon, stars, Mercury,
JAMES: HEY THERE STAR GAZERS. I'M JAMES ALBURY, DIRECTOR OF THE KIKA SILVA PLA PLANETARIUM IN GAINESVILLE, FLORIDA.
 STAR GAZERS SG 1745 5-MINUTE "THE LEONID METEOR SHOWER" HEY THERE STAR GAZERS. I'M JAMES ALBURY, DIRECTOR OF THE KIKA SILVA PLA PLANETARIUM IN GAINESVILLE, FLORIDA. AND I'M DEAN REGAS, ASTRONOMER FOR THE
STAR GAZERS SG 1745 5-MINUTE "THE LEONID METEOR SHOWER" HEY THERE STAR GAZERS. I'M JAMES ALBURY, DIRECTOR OF THE KIKA SILVA PLA PLANETARIUM IN GAINESVILLE, FLORIDA. AND I'M DEAN REGAS, ASTRONOMER FOR THE
by Jeffrey S. Keen BSc Hons ARCS MInstP CPhys CEng
 Variation in Dowsing Measurements due to the Combined Vorticity in the Ecliptic Plane of the Earth s Orbit around the Sun, and the Spin of the Earth around its Tilted Axis by Jeffrey S. Keen BSc Hons ARCS
Variation in Dowsing Measurements due to the Combined Vorticity in the Ecliptic Plane of the Earth s Orbit around the Sun, and the Spin of the Earth around its Tilted Axis by Jeffrey S. Keen BSc Hons ARCS
Comets, quasi-comets and the Comet Section. Jonathan Shanklin Director, BAA Comet Section
 Comets, quasi-comets and the Comet Section Jonathan Shanklin Director, BAA Comet Section BAA founded 1890 Comet Section formed 1891 Around 40,000 observations Virtually all extant observations are post
Comets, quasi-comets and the Comet Section Jonathan Shanklin Director, BAA Comet Section BAA founded 1890 Comet Section formed 1891 Around 40,000 observations Virtually all extant observations are post
I'M DEAN REGAS, ASTRONOMER FROM THE CINCINNATI OBSERVATORY. AND I'M JAMES ALBURY, DIRECTOR OF THE KIKA SILVA PLA PLANETARIUM IN GAINESVILLE, FLORIDA.
 STAR GAZERS SG 1815-5 MINUTE (APRIL 9-15, 2018) (REPEAT OF SG 1645 - VENUS ) THE SECOND PLANET FROM THE SUN WELCOME TO STAR GAZERS! I'M DEAN REGAS, ASTRONOMER FROM THE CINCINNATI OBSERVATORY. AND I'M JAMES
STAR GAZERS SG 1815-5 MINUTE (APRIL 9-15, 2018) (REPEAT OF SG 1645 - VENUS ) THE SECOND PLANET FROM THE SUN WELCOME TO STAR GAZERS! I'M DEAN REGAS, ASTRONOMER FROM THE CINCINNATI OBSERVATORY. AND I'M JAMES
Name: Earth and Space Assessment Study Guide. Assessment Date : Term Rotation Revolution
 Name: Earth and Space Assessment Study Guide Assessment Date : Earth s Rotation and Revolution Term Rotation Revolution Brief Definition Earth s Time to Complete One complete spin on an axis 24 hours (or
Name: Earth and Space Assessment Study Guide Assessment Date : Earth s Rotation and Revolution Term Rotation Revolution Brief Definition Earth s Time to Complete One complete spin on an axis 24 hours (or
Astronomical Time Periods 9/18/2009
 Astronomical Time Periods 9/18/2009 Opening Discussion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kmegyngwwyc Have you see anything interesting in the news? What did we talk about last class? Checking grades. Minute
Astronomical Time Periods 9/18/2009 Opening Discussion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kmegyngwwyc Have you see anything interesting in the news? What did we talk about last class? Checking grades. Minute
Practice Test DeAnza College Astronomy 04 Test 1 Spring Quarter 2009
 Practice Test DeAnza College Astronomy 04 Test 1 Spring Quarter 2009 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Mark answer on Scantron.
Practice Test DeAnza College Astronomy 04 Test 1 Spring Quarter 2009 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Mark answer on Scantron.
ASTR 1010 Astronomy of the Solar System. Course Info. Course Info. Fall 2006 Mon/Wed/Fri 11:00-11:50AM 430 Aderhold Learning Center
 ASTR 1010 Astronomy of the Solar System Fall 2006 Mon/Wed/Fri 11:00-11:50AM 430 Aderhold Learning Center Instructor: Wes Ryle Course Info In-class Activities/Quizzes (10%) 4 Homework Assignments (15%)
ASTR 1010 Astronomy of the Solar System Fall 2006 Mon/Wed/Fri 11:00-11:50AM 430 Aderhold Learning Center Instructor: Wes Ryle Course Info In-class Activities/Quizzes (10%) 4 Homework Assignments (15%)
Observational Astronomy - Lecture 4 Orbits, Motions, Kepler s and Newton s Laws
 Observational Astronomy - Lecture 4 Orbits, Motions, Kepler s and Newton s Laws Craig Lage New York University - Department of Physics craig.lage@nyu.edu February 24, 2014 1 / 21 Tycho Brahe s Equatorial
Observational Astronomy - Lecture 4 Orbits, Motions, Kepler s and Newton s Laws Craig Lage New York University - Department of Physics craig.lage@nyu.edu February 24, 2014 1 / 21 Tycho Brahe s Equatorial
ASTRONOMY COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL
 I ASTRONOMY COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 1 Line Up Make a Model of the Solar System! Celestial bodies are natural things in the sky, such as stars (bodies made of gases that are so hot they give off light), planets
I ASTRONOMY COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 1 Line Up Make a Model of the Solar System! Celestial bodies are natural things in the sky, such as stars (bodies made of gases that are so hot they give off light), planets
The celestial sphere, the coordinates system, seasons, phases of the moon and eclipses. Chapters 2 and S1
 The celestial sphere, the coordinates system, seasons, phases of the moon and eclipses Chapters 2 and S1 The celestial sphere and the coordinates system Chapter S1 How to find our way in the sky? Let s
The celestial sphere, the coordinates system, seasons, phases of the moon and eclipses Chapters 2 and S1 The celestial sphere and the coordinates system Chapter S1 How to find our way in the sky? Let s
Some remarks concerning solar eclipse data predictions
 Some remarks concerning solar eclipse data predictions Robert Nufer, Switzerland (Robert.Nufer@Bluewin.ch) Computing solar eclipse predictions consists of two main "steps": 1.) Accurate computing of the
Some remarks concerning solar eclipse data predictions Robert Nufer, Switzerland (Robert.Nufer@Bluewin.ch) Computing solar eclipse predictions consists of two main "steps": 1.) Accurate computing of the
Name: Exam 1, 9/30/05
 Multiple Choice: Select the choice that best answers each question. Write your choice in the blank next to each number. (2 points each) 1. At the North Pole in mid-november, the sun rises at a. North of
Multiple Choice: Select the choice that best answers each question. Write your choice in the blank next to each number. (2 points each) 1. At the North Pole in mid-november, the sun rises at a. North of
Astronomy 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 1
 Astronomy 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 1 Chapter 1 1. A scientific hypothesis is a) a wild, baseless guess about how something works. b) a collection of ideas that seems to explain
Astronomy 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 1 Chapter 1 1. A scientific hypothesis is a) a wild, baseless guess about how something works. b) a collection of ideas that seems to explain
Gravitation and the Waltz of the Planets
 Gravitation and the Waltz of the Planets Chapter Four Guiding Questions 1. How did ancient astronomers explain the motions of the planets? 2. Why did Copernicus think that the Earth and the other planets
Gravitation and the Waltz of the Planets Chapter Four Guiding Questions 1. How did ancient astronomers explain the motions of the planets? 2. Why did Copernicus think that the Earth and the other planets
Gravitation and the Waltz of the Planets. Chapter Four
 Gravitation and the Waltz of the Planets Chapter Four Guiding Questions 1. How did ancient astronomers explain the motions of the planets? 2. Why did Copernicus think that the Earth and the other planets
Gravitation and the Waltz of the Planets Chapter Four Guiding Questions 1. How did ancient astronomers explain the motions of the planets? 2. Why did Copernicus think that the Earth and the other planets
DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST PACKET. Test Booklet NSCD Invitational 2010
 Solar System Science Olympiad Test Booklet NSCD Invitational 2010 Multiple Choice: On the answer sheet, write the letter of the choice that best answers each question. No credit will be given for answers
Solar System Science Olympiad Test Booklet NSCD Invitational 2010 Multiple Choice: On the answer sheet, write the letter of the choice that best answers each question. No credit will be given for answers
DeAnza College Winter First Midterm Exam MAKE ALL MARKS DARK AND COMPLETE.
 FAMILY NAME : (Please PRINT!) GIVEN NAME : (Please PRINT!) Signature: ASTRONOMY 4 DeAnza College Winter 2018 First Midterm Exam MAKE ALL MARKS DARK AND COMPLETE. Instructions: 1. On your Parscore sheet
FAMILY NAME : (Please PRINT!) GIVEN NAME : (Please PRINT!) Signature: ASTRONOMY 4 DeAnza College Winter 2018 First Midterm Exam MAKE ALL MARKS DARK AND COMPLETE. Instructions: 1. On your Parscore sheet
At this point of its orbit, any solar satellite such as a comet or a planet is farthest away from the sun. What is the aphelion?
 At this point of its orbit, any solar satellite such as a comet or a planet is farthest away from the sun. What is the aphelion? These small, rocky worlds orbit the sun generally between the orbits of
At this point of its orbit, any solar satellite such as a comet or a planet is farthest away from the sun. What is the aphelion? These small, rocky worlds orbit the sun generally between the orbits of
The Solar System. Name Test Date Hour
 Name Test Date Hour Astronomy#3 - Notebook The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the objects that make up our solar system. I can identify the inner and outer planets. I can explain the difference
Name Test Date Hour Astronomy#3 - Notebook The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the objects that make up our solar system. I can identify the inner and outer planets. I can explain the difference
November 20, NOTES ES Rotation, Rev, Tilt.notebook. vertically. night. night. counterclockwise. counterclockwise. East. Foucault.
 NOTES ES, Rev,.notebook, and Rotates on an imaginary axis that runs from the to the South North Pole Pole vertically North The of the axis points to a point in space near day Pole Polaris night Responsible
NOTES ES, Rev,.notebook, and Rotates on an imaginary axis that runs from the to the South North Pole Pole vertically North The of the axis points to a point in space near day Pole Polaris night Responsible
Chapter 3 Cycles of the Moon
 Chapter 3 Cycles of the Moon Guidepost In the previous chapter, you studied the cycle of day and night and the cycle of the seasons. Now you are ready to study the brightest object in the night sky. The
Chapter 3 Cycles of the Moon Guidepost In the previous chapter, you studied the cycle of day and night and the cycle of the seasons. Now you are ready to study the brightest object in the night sky. The
PHYS 162 Elementary Astronomy
 PHYS 162 Elementary Astronomy Instructor: Mary Anne Cummings, macc@niu.edu Book: Discovering the Essential Universe, Neil Comins (5 th edition but can use 4 th Ed.) Recommended: The Cosmic Perspective
PHYS 162 Elementary Astronomy Instructor: Mary Anne Cummings, macc@niu.edu Book: Discovering the Essential Universe, Neil Comins (5 th edition but can use 4 th Ed.) Recommended: The Cosmic Perspective
Astronomy 103: First Exam
 Name: Astronomy 103: First Exam Stephen Lepp September 21, 2010 Each question is worth 2 points. Write your name on this exam and on the scantron. Short Answer Mercury What is the closest Planet to the
Name: Astronomy 103: First Exam Stephen Lepp September 21, 2010 Each question is worth 2 points. Write your name on this exam and on the scantron. Short Answer Mercury What is the closest Planet to the
astronomy A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times.
 astronomy 2008 1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. 5. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun were
astronomy 2008 1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. 5. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun were
Introduction To Modern Astronomy II
 ASTR 111 003 Fall 2006 Lecture 03 Sep. 18, 2006 Introduction To Modern Astronomy II Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-17) Ch1: Astronomy and the Universe Ch2: Knowing the Heavens
ASTR 111 003 Fall 2006 Lecture 03 Sep. 18, 2006 Introduction To Modern Astronomy II Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-17) Ch1: Astronomy and the Universe Ch2: Knowing the Heavens
Gravitation and the Motion of the Planets
 Gravitation and the Motion of the Planets 1 Guiding Questions 1. How did ancient astronomers explain the motions of the planets? 2. Why did Copernicus think that the Earth and the other planets go around
Gravitation and the Motion of the Planets 1 Guiding Questions 1. How did ancient astronomers explain the motions of the planets? 2. Why did Copernicus think that the Earth and the other planets go around
Introduction to Astronomy
 Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
Physics Lab #6:! Mercury!
 Physics 10293 Lab #6: Mercury Introduction Today we will explore the motions in the sky of the innermost planet in our solar system: Mercury. Both Mercury and Venus were easily visible to the naked eye
Physics 10293 Lab #6: Mercury Introduction Today we will explore the motions in the sky of the innermost planet in our solar system: Mercury. Both Mercury and Venus were easily visible to the naked eye
Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky. The sky is divided into 88 unequal areas that we call constellations.
 Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky Constellations: Recognizable patterns of the brighter stars that have been derived from ancient legends. Different cultures have associated the patterns with their
Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky Constellations: Recognizable patterns of the brighter stars that have been derived from ancient legends. Different cultures have associated the patterns with their
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #1 Fall 2017 Version B
 PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #1 Fall 2017 Version B 1 I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. An object has the same weight,
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #1 Fall 2017 Version B 1 I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. An object has the same weight,
JAMES: GREETINGS STAR GAZERS, I M JAMES ALBURY, DIRECTOR OF THE KIKA SILVA PLA PLANETARIUM IN GAINESVILLE, FLORIDA.
 STAR GAZERS SG 1750-5M DECEMBER 11-17, 2017 LIFE AND DEATH OF TYCHO BRAHE GREETINGS STAR GAZERS, I M JAMES ALBURY, DIRECTOR OF THE KIKA SILVA PLA PLANETARIUM IN GAINESVILLE, FLORIDA. AND I M DEAN REGAS,
STAR GAZERS SG 1750-5M DECEMBER 11-17, 2017 LIFE AND DEATH OF TYCHO BRAHE GREETINGS STAR GAZERS, I M JAMES ALBURY, DIRECTOR OF THE KIKA SILVA PLA PLANETARIUM IN GAINESVILLE, FLORIDA. AND I M DEAN REGAS,
Earth s Motions. Rotation -!! Period of Rotation - amount of time to make one complete rotation Example: Earth rotates in hours.
 Name: Date: Period: Earth In the Solar System The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES! Rotation -! Period of Rotation - amount of time to make one complete rotation Example: Earth rotates in hours
Name: Date: Period: Earth In the Solar System The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES! Rotation -! Period of Rotation - amount of time to make one complete rotation Example: Earth rotates in hours
State Vector Reference Body Transformations Throughout The Solar System
 Introduction One of the more mind-boggling programming challenges encountered during interplanetary trajectory design software development is how to transform a specified inertial position and velocity
Introduction One of the more mind-boggling programming challenges encountered during interplanetary trajectory design software development is how to transform a specified inertial position and velocity
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Astro Quiz 2 (ch2) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Star A has an apparent visual magnitude of 13.4 and star B has
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Astro Quiz 2 (ch2) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Star A has an apparent visual magnitude of 13.4 and star B has
3) During retrograde motion a planet appears to be A) dimmer than usual. B) the same brightness as usual C) brighter than usual.
 Descriptive Astronomy (ASTR 108) Exam 1 B February 17, 2010 Name: In each of the following multiple choice questions, select the best possible answer. In the line on the scan sheet corresponding to the
Descriptive Astronomy (ASTR 108) Exam 1 B February 17, 2010 Name: In each of the following multiple choice questions, select the best possible answer. In the line on the scan sheet corresponding to the
1) Kepler's third law allows us to find the average distance to a planet from observing its period of rotation on its axis.
 Descriptive Astronomy (ASTR 108) Exam 1 A February 17, 2010 Name: In each of the following multiple choice questions, select the best possible answer. In the line on the scan sheet corresponding to the
Descriptive Astronomy (ASTR 108) Exam 1 A February 17, 2010 Name: In each of the following multiple choice questions, select the best possible answer. In the line on the scan sheet corresponding to the
Physical Science. Chapter 22 The Earth in Space. Earth s Rotation
 Physical Science Chapter 22 The Earth in Space Earth s Rotation Axis imaginary line passing through the North and South Pole Earth s axis is tilted at 23 ½ degrees Rotation: the Earth spinning on its axis
Physical Science Chapter 22 The Earth in Space Earth s Rotation Axis imaginary line passing through the North and South Pole Earth s axis is tilted at 23 ½ degrees Rotation: the Earth spinning on its axis
Unlocking the Solar System
 Unlocking the Solar System Grade 5 Pre-Visit Activities Howard B. Owens Science Center Unlocking the Solar System (5 th grade) DESCRIPTION What *IS* a solar system? What does it look like? What SHOULD
Unlocking the Solar System Grade 5 Pre-Visit Activities Howard B. Owens Science Center Unlocking the Solar System (5 th grade) DESCRIPTION What *IS* a solar system? What does it look like? What SHOULD
Paper Reference. Paper Reference(s) 1627/01 Edexcel GCSE Astronomy Paper 01. Friday 15 May 2009 Morning Time: 2 hours
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1627/01 Edexcel GCSE Astronomy Paper 01 Friday 15 May 2009 Morning Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Calculator Items included with question papers
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1627/01 Edexcel GCSE Astronomy Paper 01 Friday 15 May 2009 Morning Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Calculator Items included with question papers
Physical Science. Chapter 22 The Earth in Space
 Physical Science Chapter 22 The Earth in Space Earth s Rotation Axis imaginary line passing through the North and South Pole Earth s axis is tilted at 23 ½ degrees Rotation: the Earth spinning on its axis
Physical Science Chapter 22 The Earth in Space Earth s Rotation Axis imaginary line passing through the North and South Pole Earth s axis is tilted at 23 ½ degrees Rotation: the Earth spinning on its axis
The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS. Scientific Language. Name Test Date Hour
 Name Test Date Hour Astronomy#3 - Notebook The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the objects that make up our solar system. I can identify the inner and outer planets. I can explain the difference
Name Test Date Hour Astronomy#3 - Notebook The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the objects that make up our solar system. I can identify the inner and outer planets. I can explain the difference
DEAN: HEY THERE STARGAZERS, I'M DEAN REGAS, ASTRONOMER FOR THE CINCINNATI OBSERVATORY.
 STAR GAZERS SG 1828-5M JULY 9-15, 2018 MOON CONJUNCTION JUNCTION HEY THERE STARGAZERS, I'M DEAN REGAS, ASTRONOMER FOR THE CINCINNATI OBSERVATORY. AND IM JAMES ALBURY DIRECTOR OF THE KIKA SILVA PLA PLANETARIUM
STAR GAZERS SG 1828-5M JULY 9-15, 2018 MOON CONJUNCTION JUNCTION HEY THERE STARGAZERS, I'M DEAN REGAS, ASTRONOMER FOR THE CINCINNATI OBSERVATORY. AND IM JAMES ALBURY DIRECTOR OF THE KIKA SILVA PLA PLANETARIUM
Chapter 16 The Solar System
 Chapter 16 The Solar System Finding the Standard Time and Date at Another Location Example When it is 12 noon in London, what is the standard time in Denver, Colorado (40 N, 105 W)? Section 15.3 Finding
Chapter 16 The Solar System Finding the Standard Time and Date at Another Location Example When it is 12 noon in London, what is the standard time in Denver, Colorado (40 N, 105 W)? Section 15.3 Finding
Unit 1 Astronomy: Kepler s Laws Of Planetary Motion Assessed Activity (66 marks total)
 Name: Solutions & Marking Scheme 2009 TG: PF Unit 1 Astronomy: Kepler s Laws Of Planetary Motion Assessed Activity (66 marks total) Aim: To investigate Kepler s three laws planetary motion. Apparatus:
Name: Solutions & Marking Scheme 2009 TG: PF Unit 1 Astronomy: Kepler s Laws Of Planetary Motion Assessed Activity (66 marks total) Aim: To investigate Kepler s three laws planetary motion. Apparatus:
Planetary Orbits: Kepler s Laws 1/18/07
 Planetary Orbits: Kepler s Laws Announcements The correct link for the course webpage http://www.lpl.arizona.edu/undergrad/classes/spring2007/giacalone_206-2 The first homework due Jan 25 (available for
Planetary Orbits: Kepler s Laws Announcements The correct link for the course webpage http://www.lpl.arizona.edu/undergrad/classes/spring2007/giacalone_206-2 The first homework due Jan 25 (available for
CHAPTER 8 PLANETARY MOTIONS
 1 CHAPTER 8 PLANETARY MOTIONS 8.1 Introduction The word planet means wanderer (πλάνητες αστέρες wandering stars); in contrast to the fixed stars, the planets wander around on the celestial sphere, sometimes
1 CHAPTER 8 PLANETARY MOTIONS 8.1 Introduction The word planet means wanderer (πλάνητες αστέρες wandering stars); in contrast to the fixed stars, the planets wander around on the celestial sphere, sometimes
Q25: Record the wavelength of each colored line according to the scale given.
 C. Measurement Errors and Uncertainties The term "error" signifies a deviation of the result from some "true" value. Often in science, we cannot know what the true value is, and we can only determine estimates
C. Measurement Errors and Uncertainties The term "error" signifies a deviation of the result from some "true" value. Often in science, we cannot know what the true value is, and we can only determine estimates
