LECTURE TWO BLOCK DIAGRAM REDUCTION
|
|
|
- Agatha Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 3rd Yearomputer ommunication EngineeringU ontrol Theory LETUE TWO BLOK DIAGAM EDUTION Block diagram is a pictorial representation of a control system showing interrelation between the transfer function of various components. The block diagram is obtained after obtaining the differential and transfer function of all components of a control system. Figure 2.1 shows an element of the block diagram. The arrowhead pointing toward the block indicates the input and the one pointing away from the block indicates the output. Figure 2.1 Single block diagram system may be written as; ( ) ( ) ( ) After obtaining the block diagram for each and every components, all blocks are combined to obtain a complete representation. It is then reduced using some rules to a more simple form with the help of block diagram algebra. Dr. Mohammed Saheb Khesbak Page 7
2 3rd Yearomputer ommunication EngineeringU ontrol Theory 2.1 ules for Block Diagram eduction: Now the following block diagram algebra is often used to describe rules for reduction: ule 1: Blocks in cascade Two or more blocks in cascade may be combined in one block. G 1 (s) G 2 (s) G 1 (s) G 2 (s) ule 2: ombining Blocks in Parallel Two blocks or more in parallel may be combined in one block as the algebraic sum. G 2 (s) G 1 (s) G 1 (s)g 2 (s) Dr. Mohammed Saheb Khesbak Page 8
3 3rd Yearomputer ommunication EngineeringU ontrol Theory ule 3: Eliminating a Feedback Loop Each feedback combination may be replaced by one block with its corresponding beedback equation. H(s) 1 H(s) ule 4: Moving a Summing Point Beyond a Block ule 5: Moving a Summing Point Ahead of a Block 1 Dr. Mohammed Saheb Khesbak Page 9
4 3rd Yearomputer ommunication EngineeringU ontrol Theory ule 6: Moving a Take off Point Beyond a Block X (s) X (s) 1 ule 7: Moving a Take off Point Ahead of a Block Y (s) Y (s) ule 8: earranging Summing point X3(s) X3(s) X3(s) Dr. Mohammed Saheb Khesbak Page 10
5 3rd Yearomputer ommunication EngineeringU ontrol Theory ule 9: Moving a Takeoff point beyond a Summing point X (s) Z(s) Z(s) X (s) Z(s) Example 2.1: Obtain the transfer function of the block diagram control system using block diagram reduction method. Dr. Mohammed Saheb Khesbak Page 11
6 3rd Yearomputer ommunication EngineeringU ontrol Theory The solution of this type of problems will be based on detecting the combinations that match one or more of the rules previously explained. ( ) 1 ( ) 1 ( ) 1 ( ) ( ) ( ) 1 ( ) ( ) 1 ( ) ( ) Dr. Mohammed Saheb Khesbak Page 12
7 3rd Yearomputer ommunication EngineeringU ontrol Theory Example 2.2: Obtain the transfer function of the block diagram control system using block diagram reduction method. Using the previously explained rules: 1 Dr. Mohammed Saheb Khesbak Page 13
8 3rd Yearomputer ommunication EngineeringU ontrol Theory Dr. Mohammed Saheb Khesbak Page 14
9 3rd Yearomputer ommunication EngineeringU ontrol Theory 1 Exercises: Obtain the transfer function of the following block diagram control systems using block diagram reduction method. 1 H3 2 H3 Dr. Mohammed Saheb Khesbak Page 15
10 3rd Yearomputer ommunication EngineeringU ontrol Theory 3 G5 4 G5 G6 Dr. Mohammed Saheb Khesbak Page 16
11 3rd Yearomputer ommunication EngineeringU ontrol Theory 5 6 G5 G6 G7 H8 7 Dr. Mohammed Saheb Khesbak Page 17
12 3rd Yearomputer ommunication EngineeringU ontrol Theory 8 H3 9 H3 10 Dr. Mohammed Saheb Khesbak Page 18
Fourier Series : Dr. Mohammed Saheb Khesbak Page 34
 Fourier Series : Dr. Mohammed Saheb Khesbak Page 34 Dr. Mohammed Saheb Khesbak Page 35 Example 1: Dr. Mohammed Saheb Khesbak Page 36 Dr. Mohammed Saheb Khesbak Page 37 Dr. Mohammed Saheb Khesbak Page 38
Fourier Series : Dr. Mohammed Saheb Khesbak Page 34 Dr. Mohammed Saheb Khesbak Page 35 Example 1: Dr. Mohammed Saheb Khesbak Page 36 Dr. Mohammed Saheb Khesbak Page 37 Dr. Mohammed Saheb Khesbak Page 38
in a given order. Each of and so on represents a number. These are the terms of the sequence. For example the sequence
 INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES Infinite series sometimes have a finite sum, as in Other infinite series do not have a finite sum, as with The sum of the first few terms gets larger and larger as we add
INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES Infinite series sometimes have a finite sum, as in Other infinite series do not have a finite sum, as with The sum of the first few terms gets larger and larger as we add
Fig R 1fGH E 1 -=- R 1kGH B GH DGH k NGH = 0 (7.6)
 156 BLOCK DIAGRAM ALGEBRA AND TRANSFER FUNCTIONS OF SYSTEMS [CHAP. 7 7.4 CANONICAL FORM OF A FEEDBACK CONTROL SYSTEM The two blocks in the forward path of the feedback system of Fig. 7-2 may be combined.
156 BLOCK DIAGRAM ALGEBRA AND TRANSFER FUNCTIONS OF SYSTEMS [CHAP. 7 7.4 CANONICAL FORM OF A FEEDBACK CONTROL SYSTEM The two blocks in the forward path of the feedback system of Fig. 7-2 may be combined.
Stability Analysis Techniques
 Stability Analysis Techniques In this section the stability analysis techniques for the Linear Time-Invarient (LTI) discrete system are emphasized. In general the stability techniques applicable to LTI
Stability Analysis Techniques In this section the stability analysis techniques for the Linear Time-Invarient (LTI) discrete system are emphasized. In general the stability techniques applicable to LTI
feedback cannot be maintained. If loop 2 is reduced, the signal between G
 ME 3600 Control Systems Block Diagram eduction Examples Example :.C. Dorf and.h. Bishop, Modern Control Systems, th Ed., Pearson Prentice-Hall, 008. Given: The system shown in the block diagram has one
ME 3600 Control Systems Block Diagram eduction Examples Example :.C. Dorf and.h. Bishop, Modern Control Systems, th Ed., Pearson Prentice-Hall, 008. Given: The system shown in the block diagram has one
CHAPTER 5 : REDUCTION OF MULTIPLE SUBSYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 5 : REDUCTION OF MULTIPLE SUBSYSTEMS Objectives Students should be able to: Reduce a block diagram of multiple subsystems to a single block representing the transfer function from input to output
CHAPTER 5 : REDUCTION OF MULTIPLE SUBSYSTEMS Objectives Students should be able to: Reduce a block diagram of multiple subsystems to a single block representing the transfer function from input to output
CHAP. 7] BLOCK DIAGRAM ALGEBRA AND TRANSFER FUNCTIONS OF SYSTEMS 157
![CHAP. 7] BLOCK DIAGRAM ALGEBRA AND TRANSFER FUNCTIONS OF SYSTEMS 157 CHAP. 7] BLOCK DIAGRAM ALGEBRA AND TRANSFER FUNCTIONS OF SYSTEMS 157](/thumbs/86/93955208.jpg) CHAP. 7] BLOCK DIAGAM ALGEBA AND TANSFE FUNCTIONS OF SYSTEMS 157 Transformation Equation Block Diagram Equivalent Block Diagram Combining Blocks in Cascade Y = (P1Pz)X Combining Blocks in Parallel; or
CHAP. 7] BLOCK DIAGAM ALGEBA AND TANSFE FUNCTIONS OF SYSTEMS 157 Transformation Equation Block Diagram Equivalent Block Diagram Combining Blocks in Cascade Y = (P1Pz)X Combining Blocks in Parallel; or
Fundamental of Control Systems Steady State Error Lecturer: Dr. Wahidin Wahab M.Sc. Aries Subiantoro, ST. MSc.
 Fundamental of Control Systems Steady State Error Lecturer: Dr. Wahidin Wahab M.Sc. Aries Subiantoro, ST. MSc. Electrical Engineering Department University of Indonesia 2 Steady State Error How well can
Fundamental of Control Systems Steady State Error Lecturer: Dr. Wahidin Wahab M.Sc. Aries Subiantoro, ST. MSc. Electrical Engineering Department University of Indonesia 2 Steady State Error How well can
20.6. Transfer Functions. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Transfer Functions 2.6 Introduction In this Section we introduce the concept of a transfer function and then use this to obtain a Laplace transform model of a linear engineering system. (A linear engineering
Transfer Functions 2.6 Introduction In this Section we introduce the concept of a transfer function and then use this to obtain a Laplace transform model of a linear engineering system. (A linear engineering
Discrete State Space Models
 Discrete State Space Models In this lecture we will discuss the relation between transfer function and state space model for a discrete time system and various standard or canonical state variable models.
Discrete State Space Models In this lecture we will discuss the relation between transfer function and state space model for a discrete time system and various standard or canonical state variable models.
MECHATRONICS CONTROL SYSTEM UNIT II
 MECHATRONICS UNIT II CONTROL SYSTEM Prepared By Prof. Shinde Vishal Vasant Dept. of Mechanical Engg. NDMVP S Karmaveer Baburao Thakare College of Engg. Nashik Contact No- 8928461713 E mail:- nilvasant22@gmail.com
MECHATRONICS UNIT II CONTROL SYSTEM Prepared By Prof. Shinde Vishal Vasant Dept. of Mechanical Engg. NDMVP S Karmaveer Baburao Thakare College of Engg. Nashik Contact No- 8928461713 E mail:- nilvasant22@gmail.com
Automatic Control Systems
 Automatic Control Sytem Lecture- Block Diagram Reduction Emam Fathy Department of Electrical and Control Engineering email: emfmz@yahoo.com Introduction A Block Diagram i a horthand pictorial repreentation
Automatic Control Sytem Lecture- Block Diagram Reduction Emam Fathy Department of Electrical and Control Engineering email: emfmz@yahoo.com Introduction A Block Diagram i a horthand pictorial repreentation
MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF CONTROL SYSTEMS
 1 MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF CONTROL SYSTEMS Sep-14 Dr. Mohammed Morsy Outline Introduction Transfer function and impulse response function Laplace Transform Review Automatic control systems Signal Flow
1 MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF CONTROL SYSTEMS Sep-14 Dr. Mohammed Morsy Outline Introduction Transfer function and impulse response function Laplace Transform Review Automatic control systems Signal Flow
1st Year-Computer Communication Engineering-RUC. 4- P-N Junction
 4- P-N Junction We begin our study of semiconductor devices with the junction for three reasons. (1) The device finds application in many electronic systems, e.g., in adapters that charge the batteries
4- P-N Junction We begin our study of semiconductor devices with the junction for three reasons. (1) The device finds application in many electronic systems, e.g., in adapters that charge the batteries
A linear equation in two variables is generally written as follows equation in three variables can be written as
 System of Equations A system of equations is a set of equations considered simultaneously. In this course, we will discuss systems of equation in two or three variables either linear or quadratic or a
System of Equations A system of equations is a set of equations considered simultaneously. In this course, we will discuss systems of equation in two or three variables either linear or quadratic or a
MATHEMATICS Lecture. 4 Chapter.8 TECHNIQUES OF INTEGRATION By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh
 MATHEMATICS Lecture. 4 Chapter.8 TECHNIQUES OF INTEGRATION By TECHNIQUES OF INTEGRATION OVERVIEW The Fundamental Theorem connects antiderivatives and the definite integral. Evaluating the indefinite integral,
MATHEMATICS Lecture. 4 Chapter.8 TECHNIQUES OF INTEGRATION By TECHNIQUES OF INTEGRATION OVERVIEW The Fundamental Theorem connects antiderivatives and the definite integral. Evaluating the indefinite integral,
Test 2 SOLUTIONS. ENGI 5821: Control Systems I. March 15, 2010
 Test 2 SOLUTIONS ENGI 5821: Control Systems I March 15, 2010 Total marks: 20 Name: Student #: Answer each question in the space provided or on the back of a page with an indication of where to find the
Test 2 SOLUTIONS ENGI 5821: Control Systems I March 15, 2010 Total marks: 20 Name: Student #: Answer each question in the space provided or on the back of a page with an indication of where to find the
Analysis and Design of Control Systems in the Time Domain
 Chapter 6 Analysis and Design of Control Systems in the Time Domain 6. Concepts of feedback control Given a system, we can classify it as an open loop or a closed loop depends on the usage of the feedback.
Chapter 6 Analysis and Design of Control Systems in the Time Domain 6. Concepts of feedback control Given a system, we can classify it as an open loop or a closed loop depends on the usage of the feedback.
Essence of the Root Locus Technique
 Essence of the Root Locus Technique In this chapter we study a method for finding locations of system poles. The method is presented for a very general set-up, namely for the case when the closed-loop
Essence of the Root Locus Technique In this chapter we study a method for finding locations of system poles. The method is presented for a very general set-up, namely for the case when the closed-loop
Chapter 30 Minimality and Stability of Interconnected Systems 30.1 Introduction: Relating I/O and State-Space Properties We have already seen in Chapt
 Lectures on Dynamic Systems and Control Mohammed Dahleh Munther A. Dahleh George Verghese Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachuasetts Institute of Technology 1 1 c Chapter
Lectures on Dynamic Systems and Control Mohammed Dahleh Munther A. Dahleh George Verghese Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachuasetts Institute of Technology 1 1 c Chapter
MODELING OF CONTROL SYSTEMS
 1 MODELING OF CONTROL SYSTEMS Feb-15 Dr. Mohammed Morsy Outline Introduction Differential equations and Linearization of nonlinear mathematical models Transfer function and impulse response function Laplace
1 MODELING OF CONTROL SYSTEMS Feb-15 Dr. Mohammed Morsy Outline Introduction Differential equations and Linearization of nonlinear mathematical models Transfer function and impulse response function Laplace
Factoring and Algebraic Fractions
 Worksheet. Algebraic Fractions Section Factoring and Algebraic Fractions As pointed out in worksheet., we can use factoring to simplify algebraic expressions, and in particular we can use it to simplify
Worksheet. Algebraic Fractions Section Factoring and Algebraic Fractions As pointed out in worksheet., we can use factoring to simplify algebraic expressions, and in particular we can use it to simplify
Part 1: You are given the following system of two equations: x + 2y = 16 3x 4y = 2
 Solving Systems of Equations Algebraically Teacher Notes Comment: As students solve equations throughout this task, have them continue to explain each step using properties of operations or properties
Solving Systems of Equations Algebraically Teacher Notes Comment: As students solve equations throughout this task, have them continue to explain each step using properties of operations or properties
Today s Lecture. Block Diagrams. Block Diagrams: Examples. Block Diagrams: Examples. Closed Loop System 06/03/2017
 06/0/07 UW Britol Indutrial ontrol UFMF6W-0- ontrol Sytem ngineering UFMUY-0- Lecture 5: Block Diagram and Steady State rror Today Lecture Block diagram to repreent control ytem Block diagram manipulation
06/0/07 UW Britol Indutrial ontrol UFMF6W-0- ontrol Sytem ngineering UFMUY-0- Lecture 5: Block Diagram and Steady State rror Today Lecture Block diagram to repreent control ytem Block diagram manipulation
FREQUENCY RESPONSE ANALYSIS Closed Loop Frequency Response
 Closed Loop Frequency Response The Bode plot is generally constructed for an open loop transfer function of a system. In order to draw the Bode plot for a closed loop system, the transfer function has
Closed Loop Frequency Response The Bode plot is generally constructed for an open loop transfer function of a system. In order to draw the Bode plot for a closed loop system, the transfer function has
Factorizing Algebraic Expressions
 1 of 60 Factorizing Algebraic Expressions 2 of 60 Factorizing expressions Factorizing an expression is the opposite of expanding it. Expanding or multiplying out a(b + c) ab + ac Factorizing Often: When
1 of 60 Factorizing Algebraic Expressions 2 of 60 Factorizing expressions Factorizing an expression is the opposite of expanding it. Expanding or multiplying out a(b + c) ab + ac Factorizing Often: When
Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) Operational Amplifiers. OP-Amp: Components. Internal Design of LM741
 (Op-Amp) s Prof. Dr. M. Zahurul Haq zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd http://teacher.buet.ac.bd/zahurul/ Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology ME 475: Mechatronics
(Op-Amp) s Prof. Dr. M. Zahurul Haq zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd http://teacher.buet.ac.bd/zahurul/ Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology ME 475: Mechatronics
Digital Control Engineering Analysis and Design
 Digital Control Engineering Analysis and Design M. Sami Fadali Antonio Visioli AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO Academic Press is
Digital Control Engineering Analysis and Design M. Sami Fadali Antonio Visioli AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO Academic Press is
SECTION 2: BLOCK DIAGRAMS & SIGNAL FLOW GRAPHS
 SECTION 2: BLOCK DIAGRAMS & SIGNAL FLOW GRAPHS MAE 4421 Control of Aerospace & Mechanical Systems 2 Block Diagram Manipulation Block Diagrams 3 In the introductory section we saw examples of block diagrams
SECTION 2: BLOCK DIAGRAMS & SIGNAL FLOW GRAPHS MAE 4421 Control of Aerospace & Mechanical Systems 2 Block Diagram Manipulation Block Diagrams 3 In the introductory section we saw examples of block diagrams
MATHEMATICAL MODELS OF PHYSICAL SYSTEMS
 hapter MATHEMATIAL MODELS OF PHYSIAL SYSTEMS.. INTODUTION For the analyi and deign of control ytem, we need to formulate a mathematical decription of the ytem. The proce of obtaining the deired mathematical
hapter MATHEMATIAL MODELS OF PHYSIAL SYSTEMS.. INTODUTION For the analyi and deign of control ytem, we need to formulate a mathematical decription of the ytem. The proce of obtaining the deired mathematical
R a) Compare open loop and closed loop control systems. b) Clearly bring out, from basics, Force-current and Force-Voltage analogies.
 SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations Dec 01 1. a) Compare open loop and closed loop control systems. b) Clearly bring out, from basics, Force-current and Force-Voltage analogies..
SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations Dec 01 1. a) Compare open loop and closed loop control systems. b) Clearly bring out, from basics, Force-current and Force-Voltage analogies..
Automatic Control (TSRT15): Lecture 7
 Automatic Control (TSRT15): Lecture 7 Tianshi Chen Division of Automatic Control Dept. of Electrical Engineering Email: tschen@isy.liu.se Phone: 13-282226 Office: B-house extrance 25-27 Outline 2 Feedforward
Automatic Control (TSRT15): Lecture 7 Tianshi Chen Division of Automatic Control Dept. of Electrical Engineering Email: tschen@isy.liu.se Phone: 13-282226 Office: B-house extrance 25-27 Outline 2 Feedforward
12/31/2010. Overview. 10-Combinational Circuit Design Text: Unit 8. Limited Fan-in. Limited Fan-in. Limited Fan-in. Limited Fan-in
 Overview 10-ombinational ircuit esign Text: Unit 8 Gates with elays and Timing Other Hazards GR/ISS 201 igital Operations and omputations Winter 2011 r. Louie 2 Practical logic gates are limited by the
Overview 10-ombinational ircuit esign Text: Unit 8 Gates with elays and Timing Other Hazards GR/ISS 201 igital Operations and omputations Winter 2011 r. Louie 2 Practical logic gates are limited by the
Chapter 1.6. Perform Operations with Complex Numbers
 Chapter 1.6 Perform Operations with Complex Numbers EXAMPLE Warm-Up 1 Exercises Solve a quadratic equation Solve 2x 2 + 11 = 37. 2x 2 + 11 = 37 2x 2 = 48 Write original equation. Subtract 11 from each
Chapter 1.6 Perform Operations with Complex Numbers EXAMPLE Warm-Up 1 Exercises Solve a quadratic equation Solve 2x 2 + 11 = 37. 2x 2 + 11 = 37 2x 2 = 48 Write original equation. Subtract 11 from each
Lecture 19 IIR Filters
 Lecture 19 IIR Filters Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing Spring, 2012 Wei-Ta Chu 2012/5/10 1 General IIR Difference Equation IIR system: infinite-impulse response system The most general class
Lecture 19 IIR Filters Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing Spring, 2012 Wei-Ta Chu 2012/5/10 1 General IIR Difference Equation IIR system: infinite-impulse response system The most general class
(a) Torsional spring-mass system. (b) Spring element.
 m v s T s v a (a) T a (b) T a FIGURE 2.1 (a) Torsional spring-mass system. (b) Spring element. by ky Wall friction, b Mass M k y M y r(t) Force r(t) (a) (b) FIGURE 2.2 (a) Spring-mass-damper system. (b)
m v s T s v a (a) T a (b) T a FIGURE 2.1 (a) Torsional spring-mass system. (b) Spring element. by ky Wall friction, b Mass M k y M y r(t) Force r(t) (a) (b) FIGURE 2.2 (a) Spring-mass-damper system. (b)
Chapter 6 Steady-State Analysis of Continuous-Time Systems
 Chapter 6 Steady-State Analysis of Continuous-Time Systems 6.1 INTRODUCTION One of the objectives of a control systems engineer is to minimize the steady-state error of the closed-loop system response
Chapter 6 Steady-State Analysis of Continuous-Time Systems 6.1 INTRODUCTION One of the objectives of a control systems engineer is to minimize the steady-state error of the closed-loop system response
WHITE PAPER: SLOA011 Author: Jim Karki Digital Signal Processing Solutions April 1998
 OPerational AMPlifier lifiers Source: Understanding Operational Amplifier Specifications Source: Understanding Operational Amplifier Specifications WHITE PAPE: SLOA0 Author: Jim Karki Digital Signal Processing
OPerational AMPlifier lifiers Source: Understanding Operational Amplifier Specifications Source: Understanding Operational Amplifier Specifications WHITE PAPE: SLOA0 Author: Jim Karki Digital Signal Processing
Chapter 6 Introduction to state machines
 9..7 hapter 6 Introduction to state machines Dr.-Ing. Stefan Werner Table of content hapter : Switching Algebra hapter : Logical Levels, Timing & Delays hapter 3: Karnaugh-Veitch-Maps hapter 4: ombinational
9..7 hapter 6 Introduction to state machines Dr.-Ing. Stefan Werner Table of content hapter : Switching Algebra hapter : Logical Levels, Timing & Delays hapter 3: Karnaugh-Veitch-Maps hapter 4: ombinational
TWO-PORT. C.T. Pan 1. C.T. Pan
 TWO-PORT CRCUTS C.T. Pan 5. Definition of Two-Port Circuits 5. Classification of Two-Port Parameters 5.3 Finding Two-Port Parameters 5.4 Analysis of the Terminated Two-Port Circuit 5.5 nterconnected Two-Port
TWO-PORT CRCUTS C.T. Pan 5. Definition of Two-Port Circuits 5. Classification of Two-Port Parameters 5.3 Finding Two-Port Parameters 5.4 Analysis of the Terminated Two-Port Circuit 5.5 nterconnected Two-Port
Procedure for sketching bode plots (mentioned on Oct 5 th notes, Pg. 20)
 Procedure for sketching bode plots (mentioned on Oct 5 th notes, Pg. 20) 1. Rewrite the transfer function in proper p form. 2. Separate the transfer function into its constituent parts. 3. Draw the Bode
Procedure for sketching bode plots (mentioned on Oct 5 th notes, Pg. 20) 1. Rewrite the transfer function in proper p form. 2. Separate the transfer function into its constituent parts. 3. Draw the Bode
Week 1 Factor & Remainder Past Paper Questions - SOLUTIONS
 Question Solution Marks C2 JUNE 2010 Q2 f(3) = 3(3) 3 5(3) 2 58(3) + 40 f(3) = 98 So, the remainder is 98 Substitute x = 3 into 98 (If it is not stated that 98 is the remainder, do not give this C2 JUNE
Question Solution Marks C2 JUNE 2010 Q2 f(3) = 3(3) 3 5(3) 2 58(3) + 40 f(3) = 98 So, the remainder is 98 Substitute x = 3 into 98 (If it is not stated that 98 is the remainder, do not give this C2 JUNE
Direct-Current Circuits. Physics 231 Lecture 6-1
 Direct-Current Circuits Physics 231 Lecture 6-1 esistors in Series and Parallel As with capacitors, resistors are often in series and parallel configurations in circuits Series Parallel The question then
Direct-Current Circuits Physics 231 Lecture 6-1 esistors in Series and Parallel As with capacitors, resistors are often in series and parallel configurations in circuits Series Parallel The question then
An Introduction to Control Systems
 An Introduction to Control Systems Signals and Systems: 3C1 Control Systems Handout 1 Dr. David Corrigan Electronic and Electrical Engineering corrigad@tcd.ie November 21, 2012 Recall the concept of a
An Introduction to Control Systems Signals and Systems: 3C1 Control Systems Handout 1 Dr. David Corrigan Electronic and Electrical Engineering corrigad@tcd.ie November 21, 2012 Recall the concept of a
Section 1.1 System of Linear Equations. Dr. Abdulla Eid. College of Science. MATHS 211: Linear Algebra
 Section 1.1 System of Linear Equations College of Science MATHS 211: Linear Algebra (University of Bahrain) Linear System 1 / 33 Goals:. 1 Define system of linear equations and their solutions. 2 To represent
Section 1.1 System of Linear Equations College of Science MATHS 211: Linear Algebra (University of Bahrain) Linear System 1 / 33 Goals:. 1 Define system of linear equations and their solutions. 2 To represent
1 Chapter 9: Design via Root Locus
 1 Figure 9.1 a. Sample root locus, showing possible design point via gain adjustment (A) and desired design point that cannot be met via simple gain adjustment (B); b. responses from poles at A and B 2
1 Figure 9.1 a. Sample root locus, showing possible design point via gain adjustment (A) and desired design point that cannot be met via simple gain adjustment (B); b. responses from poles at A and B 2
Time Response Analysis (Part II)
 Time Response Analysis (Part II). A critically damped, continuous-time, second order system, when sampled, will have (in Z domain) (a) A simple pole (b) Double pole on real axis (c) Double pole on imaginary
Time Response Analysis (Part II). A critically damped, continuous-time, second order system, when sampled, will have (in Z domain) (a) A simple pole (b) Double pole on real axis (c) Double pole on imaginary
Automatic Control Systems (FCS) Lecture- 8 Steady State Error
 Automatic Control Systems (FCS) Lecture- 8 Steady State Error Introduction Any physical control system inherently suffers steady-state error in response to certain types of inputs. A system may have no
Automatic Control Systems (FCS) Lecture- 8 Steady State Error Introduction Any physical control system inherently suffers steady-state error in response to certain types of inputs. A system may have no
Lecture IV: LTI models of physical systems
 BME 171: Signals and Systems Duke University September 5, 2008 This lecture Plan for the lecture: 1 Interconnections of linear systems 2 Differential equation models of LTI systems 3 eview of linear circuit
BME 171: Signals and Systems Duke University September 5, 2008 This lecture Plan for the lecture: 1 Interconnections of linear systems 2 Differential equation models of LTI systems 3 eview of linear circuit
EEE 184 Project: Option 1
 EEE 184 Project: Option 1 Date: November 16th 2012 Due: December 3rd 2012 Work Alone, show your work, and comment your results. Comments, clarity, and organization are important. Same wrong result or same
EEE 184 Project: Option 1 Date: November 16th 2012 Due: December 3rd 2012 Work Alone, show your work, and comment your results. Comments, clarity, and organization are important. Same wrong result or same
UNIT III Design of Combinational Logic Circuits. Department of Computer Science SRM UNIVERSITY
 UNIT III Design of ombinational Logic ircuits Department of omputer Science SRM UNIVERSITY Introduction to ombinational ircuits Logic circuits for digital systems may be ombinational Sequential combinational
UNIT III Design of ombinational Logic ircuits Department of omputer Science SRM UNIVERSITY Introduction to ombinational ircuits Logic circuits for digital systems may be ombinational Sequential combinational
Chapter 7 Interconnected Systems and Feedback: Well-Posedness, Stability, and Performance 7. Introduction Feedback control is a powerful approach to o
 Lectures on Dynamic Systems and Control Mohammed Dahleh Munther A. Dahleh George Verghese Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachuasetts Institute of Technology c Chapter 7 Interconnected
Lectures on Dynamic Systems and Control Mohammed Dahleh Munther A. Dahleh George Verghese Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachuasetts Institute of Technology c Chapter 7 Interconnected
z x = f x (x, y, a, b), z y = f y (x, y, a, b). F(x, y, z, z x, z y ) = 0. This is a PDE for the unknown function of two independent variables.
 Chapter 2 First order PDE 2.1 How and Why First order PDE appear? 2.1.1 Physical origins Conservation laws form one of the two fundamental parts of any mathematical model of Continuum Mechanics. These
Chapter 2 First order PDE 2.1 How and Why First order PDE appear? 2.1.1 Physical origins Conservation laws form one of the two fundamental parts of any mathematical model of Continuum Mechanics. These
Experiment 7: Magnitude comparators
 Module: Logic Design Lab Name:... University no:.. Group no: Lab Partner Name: Experiment 7: Magnitude comparators Mr. Mohamed El-Saied Objective: Realization of -bit comparator using logic gates. Realization
Module: Logic Design Lab Name:... University no:.. Group no: Lab Partner Name: Experiment 7: Magnitude comparators Mr. Mohamed El-Saied Objective: Realization of -bit comparator using logic gates. Realization
Kinematics Introduction
 Kinematics Introduction Kinematics is the study of the motion of bodies. As such it deals with the distance/displacement, speed/velocity, and the acceleration of bodies. Although we are familiar with the
Kinematics Introduction Kinematics is the study of the motion of bodies. As such it deals with the distance/displacement, speed/velocity, and the acceleration of bodies. Although we are familiar with the
Solving Systems of Linear Equations with Linear Combinations (The Elimination Method)
 Student Handout Name Solving Systems of Linear Equations with Linear Combinations (The Elimination Method) Problem 1 Launch the Activity (Multiplying an Equation by a Constant) When asked to graph the
Student Handout Name Solving Systems of Linear Equations with Linear Combinations (The Elimination Method) Problem 1 Launch the Activity (Multiplying an Equation by a Constant) When asked to graph the
6.302 Feedback Systems Recitation 7: Root Locus Prof. Joel L. Dawson
 To start with, let s mae sure we re clear on exactly what we mean by the words root locus plot. Webster can help us with this: ROOT: A number that reduces and equation to an identity when it is substituted
To start with, let s mae sure we re clear on exactly what we mean by the words root locus plot. Webster can help us with this: ROOT: A number that reduces and equation to an identity when it is substituted
Lecture 2: Discrete-time Linear Quadratic Optimal Control
 ME 33, U Berkeley, Spring 04 Xu hen Lecture : Discrete-time Linear Quadratic Optimal ontrol Big picture Example onvergence of finite-time LQ solutions Big picture previously: dynamic programming and finite-horizon
ME 33, U Berkeley, Spring 04 Xu hen Lecture : Discrete-time Linear Quadratic Optimal ontrol Big picture Example onvergence of finite-time LQ solutions Big picture previously: dynamic programming and finite-horizon
CDS 110b: Lecture 2-1 Linear Quadratic Regulators
 CDS 110b: Lecture 2-1 Linear Quadratic Regulators Richard M. Murray 11 January 2006 Goals: Derive the linear quadratic regulator and demonstrate its use Reading: Friedland, Chapter 9 (different derivation,
CDS 110b: Lecture 2-1 Linear Quadratic Regulators Richard M. Murray 11 January 2006 Goals: Derive the linear quadratic regulator and demonstrate its use Reading: Friedland, Chapter 9 (different derivation,
Last week: analysis of pinion-rack w velocity feedback
 Last week: analysis of pinion-rack w velocity feedback Calculation of the steady state error Transfer function: V (s) V ref (s) = 0.362K s +2+0.362K Step input: V ref (s) = s Output: V (s) = s 0.362K s
Last week: analysis of pinion-rack w velocity feedback Calculation of the steady state error Transfer function: V (s) V ref (s) = 0.362K s +2+0.362K Step input: V ref (s) = s Output: V (s) = s 0.362K s
EE3CL4: Introduction to Linear Control Systems
 1 / 17 EE3CL4: Introduction to Linear Control Systems Section 7: McMaster University Winter 2018 2 / 17 Outline 1 4 / 17 Cascade compensation Throughout this lecture we consider the case of H(s) = 1. We
1 / 17 EE3CL4: Introduction to Linear Control Systems Section 7: McMaster University Winter 2018 2 / 17 Outline 1 4 / 17 Cascade compensation Throughout this lecture we consider the case of H(s) = 1. We
Dynamics and control of mechanical systems
 Dynamics and control of mechanical systems Date Day 1 (03/05) - 05/05 Day 2 (07/05) Day 3 (09/05) Day 4 (11/05) Day 5 (14/05) Day 6 (16/05) Content Review of the basics of mechanics. Kinematics of rigid
Dynamics and control of mechanical systems Date Day 1 (03/05) - 05/05 Day 2 (07/05) Day 3 (09/05) Day 4 (11/05) Day 5 (14/05) Day 6 (16/05) Content Review of the basics of mechanics. Kinematics of rigid
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science : Dynamic Systems Spring 2011
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.4: Dynamic Systems Spring Homework Solutions Exercise 3. a) We are given the single input LTI system: [
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.4: Dynamic Systems Spring Homework Solutions Exercise 3. a) We are given the single input LTI system: [
ECE317 : Feedback and Control
 ECE317 : Feedback and Control Lecture : Steady-state error Dr. Richard Tymerski Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Portland State University 1 Course roadmap Modeling Analysis Design Laplace
ECE317 : Feedback and Control Lecture : Steady-state error Dr. Richard Tymerski Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Portland State University 1 Course roadmap Modeling Analysis Design Laplace
Lesson 2: Introduction to Variables
 In this lesson we begin our study of algebra by introducing the concept of a variable as an unknown or varying quantity in an algebraic expression. We then take a closer look at algebraic expressions to
In this lesson we begin our study of algebra by introducing the concept of a variable as an unknown or varying quantity in an algebraic expression. We then take a closer look at algebraic expressions to
ACTIVITY: Finding Quotients of Powers. Quotient Repeated Multiplication Form Power
 10. the same base? How can you divide two powers that have 1 ACTIVITY: Finding Quotients of Powers Work with a partner. a. Copy and complete the table. Quotient Repeated Multiplication Form Power 4 ( 4)
10. the same base? How can you divide two powers that have 1 ACTIVITY: Finding Quotients of Powers Work with a partner. a. Copy and complete the table. Quotient Repeated Multiplication Form Power 4 ( 4)
Chapter Stability Robustness Introduction Last chapter showed how the Nyquist stability criterion provides conditions for the stability robustness of
 Lectures on Dynamic Systems and Control Mohammed Dahleh Munther A Dahleh George Verghese Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachuasetts Institute of Technology c Chapter Stability
Lectures on Dynamic Systems and Control Mohammed Dahleh Munther A Dahleh George Verghese Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachuasetts Institute of Technology c Chapter Stability
Lecture 12. AO Control Theory
 Lecture 12 AO Control Theory Claire Max with many thanks to Don Gavel and Don Wiberg UC Santa Cruz February 18, 2016 Page 1 What are control systems? Control is the process of making a system variable
Lecture 12 AO Control Theory Claire Max with many thanks to Don Gavel and Don Wiberg UC Santa Cruz February 18, 2016 Page 1 What are control systems? Control is the process of making a system variable
Lesson 28: Another Computational Method of Solving a Linear System
 Lesson 28: Another Computational Method of Solving a Linear System Student Outcomes Students learn the elimination method for solving a system of linear equations. Students use properties of rational numbers
Lesson 28: Another Computational Method of Solving a Linear System Student Outcomes Students learn the elimination method for solving a system of linear equations. Students use properties of rational numbers
Control Systems, Lecture 05
 Control Systems, Lecture 05 İbrahim Beklan Küçükdemiral Yıldız Teknik Üniversitesi 2015 1 / 33 Laplace Transform Solution of State Equations In previous sections, systems were modeled in state space, where
Control Systems, Lecture 05 İbrahim Beklan Küçükdemiral Yıldız Teknik Üniversitesi 2015 1 / 33 Laplace Transform Solution of State Equations In previous sections, systems were modeled in state space, where
Selamat Kembali Ke Parit Raja.. BDA30703 Kejuruteraan Kawalan Seksyen S5
 PROFESOR MADYA DR. ZAMRI BIN OMAR Timbalan Dekan (Hal Ehwal Pelajar & Alumni) Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal & Pembuatan Selamat Kembali Ke Parit Raja.. BDA30703 Kejuruteraan Kawalan Seksyen S5 Email :
PROFESOR MADYA DR. ZAMRI BIN OMAR Timbalan Dekan (Hal Ehwal Pelajar & Alumni) Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal & Pembuatan Selamat Kembali Ke Parit Raja.. BDA30703 Kejuruteraan Kawalan Seksyen S5 Email :
(a) Find the transfer function of the amplifier. Ans.: G(s) =
 126 INTRDUCTIN T CNTR ENGINEERING 10( s 1) (a) Find the transfer function of the amplifier. Ans.: (. 02s 1)(. 001s 1) (b) Find the expected percent overshoot for a step input for the closed-loop system
126 INTRDUCTIN T CNTR ENGINEERING 10( s 1) (a) Find the transfer function of the amplifier. Ans.: (. 02s 1)(. 001s 1) (b) Find the expected percent overshoot for a step input for the closed-loop system
Mathematical modeling of control systems. Laith Batarseh. Mathematical modeling of control systems
 Chapter two Laith Batareh Mathematical modeling The dynamic of many ytem, whether they are mechanical, electrical, thermal, economic, biological, and o on, may be decribed in term of differential equation
Chapter two Laith Batareh Mathematical modeling The dynamic of many ytem, whether they are mechanical, electrical, thermal, economic, biological, and o on, may be decribed in term of differential equation
Big Ideas Math 2015 HS Algebra 1: Common Core Edition Chapter 10 Test
 Big Ideas Math 2015 HS Algebra 1: Common Core Edition Chapter 10 Test Exercise 1 Plot the points on the graph of x 0 1 4 9 16 f (x)????? f (x) = x + 5 that correspond to the x-values shown in the table.
Big Ideas Math 2015 HS Algebra 1: Common Core Edition Chapter 10 Test Exercise 1 Plot the points on the graph of x 0 1 4 9 16 f (x)????? f (x) = x + 5 that correspond to the x-values shown in the table.
EE Experiment 11 The Laplace Transform and Control System Characteristics
 EE216:11 1 EE 216 - Experiment 11 The Laplace Transform and Control System Characteristics Objectives: To illustrate computer usage in determining inverse Laplace transforms. Also to determine useful signal
EE216:11 1 EE 216 - Experiment 11 The Laplace Transform and Control System Characteristics Objectives: To illustrate computer usage in determining inverse Laplace transforms. Also to determine useful signal
CHAPTER 15: FEEDFORWARD CONTROL
 CHAPER 5: EEDORWARD CONROL When I complete this chapter, I want to be able to do the following. Identify situations for which feedforward is a good control enhancement Design feedforward control using
CHAPER 5: EEDORWARD CONROL When I complete this chapter, I want to be able to do the following. Identify situations for which feedforward is a good control enhancement Design feedforward control using
Lecture 38 Insulated Boundary Conditions
 Lecture 38 Insulated Boundary Conditions Insulation In many of the previous sections we have considered fixed boundary conditions, i.e. u(0) = a, u(l) = b. We implemented these simply by assigning u j
Lecture 38 Insulated Boundary Conditions Insulation In many of the previous sections we have considered fixed boundary conditions, i.e. u(0) = a, u(l) = b. We implemented these simply by assigning u j
23.1 Tuning controllers, in the large view Quoting from Section 16.7:
 Lesson 23. Tuning a real ontroller - modeling, proess identifiation, fine tuning 23.0 Context We have learned to view proesses as dynami systems, taking are to identify their input, intermediate, and output
Lesson 23. Tuning a real ontroller - modeling, proess identifiation, fine tuning 23.0 Context We have learned to view proesses as dynami systems, taking are to identify their input, intermediate, and output
6.302 Feedback Systems Recitation 17: Black s Formula Revisited, and Lead Compensation Prof. Joel L. Dawson
 Recitation 7: Black s Formula Revisited, and Lead Compensation By now, applying Black s Formula to a feedback system is almost a reflex: x(s) G(s) Y(s) H(s) This formula actually lends itself rather naturally
Recitation 7: Black s Formula Revisited, and Lead Compensation By now, applying Black s Formula to a feedback system is almost a reflex: x(s) G(s) Y(s) H(s) This formula actually lends itself rather naturally
CONTROL SYSTEMS LECTURE NOTES B.TECH (II YEAR II SEM) ( ) Prepared by: Mrs.P.ANITHA, Associate Professor Mr.V.KIRAN KUMAR, Assistant Professor
 LECTURE NOTES B.TECH (II YEAR II SEM) (2017-18) Prepared by: Mrs.P.ANITHA, Associate Professor Mr.V.KIRAN KUMAR, Assistant Professor Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering MALLA REDDY
LECTURE NOTES B.TECH (II YEAR II SEM) (2017-18) Prepared by: Mrs.P.ANITHA, Associate Professor Mr.V.KIRAN KUMAR, Assistant Professor Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering MALLA REDDY
Lesson 30: Linear Systems in Three Variables
 Lesson 30: Linear Systems in Three Variables Student Outcomes Students solve linear systems in three variables algebraically. Lesson Notes Students solved systems of linear equations in two variables using
Lesson 30: Linear Systems in Three Variables Student Outcomes Students solve linear systems in three variables algebraically. Lesson Notes Students solved systems of linear equations in two variables using
Lesson 2: Introduction to Variables
 Lesson 2: Introduction to Variables Topics and Objectives: Evaluating Algebraic Expressions Some Vocabulary o Variable o Term o Coefficient o Constant o Factor Like Terms o Identifying Like Terms o Combining
Lesson 2: Introduction to Variables Topics and Objectives: Evaluating Algebraic Expressions Some Vocabulary o Variable o Term o Coefficient o Constant o Factor Like Terms o Identifying Like Terms o Combining
Module 4 : Laplace and Z Transform Problem Set 4
 Module 4 : Laplace and Z Transform Problem Set 4 Problem 1 The input x(t) and output y(t) of a causal LTI system are related to the block diagram representation shown in the figure. (a) Determine a differential
Module 4 : Laplace and Z Transform Problem Set 4 Problem 1 The input x(t) and output y(t) of a causal LTI system are related to the block diagram representation shown in the figure. (a) Determine a differential
Hydraulic (Fluid) Systems
 Hydraulic (Fluid) Systems Basic Modeling Elements Resistance apacitance Inertance Pressure and Flow Sources Interconnection Relationships ompatibility Law ontinuity Law Derive Input/Output Models ME375
Hydraulic (Fluid) Systems Basic Modeling Elements Resistance apacitance Inertance Pressure and Flow Sources Interconnection Relationships ompatibility Law ontinuity Law Derive Input/Output Models ME375
Word Search - Unit Name: Class: Date: Z C L O S E D L O O P K F K M Y O F M P S A D J U S T M E N T S Y M S Y G V U K
 Word Search - Unit 3.2.1 Name: Class: Date: Try to find the hidden words. Z C L O S E D L O O P K F K M Y O F M P S A D J U S T M E N T S Y M S Y G V U K D K P S M A N A G E M E N T N T C J J E G I N M
Word Search - Unit 3.2.1 Name: Class: Date: Try to find the hidden words. Z C L O S E D L O O P K F K M Y O F M P S A D J U S T M E N T S Y M S Y G V U K D K P S M A N A G E M E N T N T C J J E G I N M
2 Problem formulation. Fig. 1 Unity-feedback system. where A(s) and B(s) are coprime polynomials. The reference input is.
 Synthesis of pole-zero assignment control law with minimum control input M.-H. TU C.-M. Lin Indexiny ferms: Control systems, Pules and zeros. Internal stability Abstract: A new method of control system
Synthesis of pole-zero assignment control law with minimum control input M.-H. TU C.-M. Lin Indexiny ferms: Control systems, Pules and zeros. Internal stability Abstract: A new method of control system
Study Material. CONTROL SYSTEM ENGINEERING (As per SCTE&VT,Odisha new syllabus) 4th Semester Electronics & Telecom Engineering
 Study Material CONTROL SYSTEM ENGINEERING (As per SCTE&VT,Odisha new syllabus) 4th Semester Electronics & Telecom Engineering By Sri Asit Kumar Acharya, Lecturer ETC, Govt. Polytechnic Dhenkanal & Sri
Study Material CONTROL SYSTEM ENGINEERING (As per SCTE&VT,Odisha new syllabus) 4th Semester Electronics & Telecom Engineering By Sri Asit Kumar Acharya, Lecturer ETC, Govt. Polytechnic Dhenkanal & Sri
U1 is zero based because its noninverting terminal is connected to circuit common. Therefore, the circuit reference voltage is 0 V.
 When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to operate a zener-clamped op amp comparator circuit using dc and ac voltages. You will verify your results with an oscilloscope. U1 is zero based
When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to operate a zener-clamped op amp comparator circuit using dc and ac voltages. You will verify your results with an oscilloscope. U1 is zero based
Root Locus. Motivation Sketching Root Locus Examples. School of Mechanical Engineering Purdue University. ME375 Root Locus - 1
 Root Locus Motivation Sketching Root Locus Examples ME375 Root Locus - 1 Servo Table Example DC Motor Position Control The block diagram for position control of the servo table is given by: D 0.09 Position
Root Locus Motivation Sketching Root Locus Examples ME375 Root Locus - 1 Servo Table Example DC Motor Position Control The block diagram for position control of the servo table is given by: D 0.09 Position
Dynamic Systems. Simulation of. with MATLAB and Simulink. Harold Klee. Randal Allen SECOND EDITION. CRC Press. Taylor & Francis Group
 SECOND EDITION Simulation of Dynamic Systems with MATLAB and Simulink Harold Klee Randal Allen CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis
SECOND EDITION Simulation of Dynamic Systems with MATLAB and Simulink Harold Klee Randal Allen CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis
School of Engineering Faculty of Built Environment, Engineering, Technology & Design
 Module Name and Code : ENG60803 Real Time Instrumentation Semester and Year : Semester 5/6, Year 3 Lecture Number/ Week : Lecture 3, Week 3 Learning Outcome (s) : LO5 Module Co-ordinator/Tutor : Dr. Phang
Module Name and Code : ENG60803 Real Time Instrumentation Semester and Year : Semester 5/6, Year 3 Lecture Number/ Week : Lecture 3, Week 3 Learning Outcome (s) : LO5 Module Co-ordinator/Tutor : Dr. Phang
3.1 Overview 3.2 Process and control-loop interactions
 3. Multivariable 3.1 Overview 3.2 and control-loop interactions 3.2.1 Interaction analysis 3.2.2 Closed-loop stability 3.3 Decoupling control 3.3.1 Basic design principle 3.3.2 Complete decoupling 3.3.3
3. Multivariable 3.1 Overview 3.2 and control-loop interactions 3.2.1 Interaction analysis 3.2.2 Closed-loop stability 3.3 Decoupling control 3.3.1 Basic design principle 3.3.2 Complete decoupling 3.3.3
School of Mechanical Engineering Purdue University. DC Motor Position Control The block diagram for position control of the servo table is given by:
 Root Locus Motivation Sketching Root Locus Examples ME375 Root Locus - 1 Servo Table Example DC Motor Position Control The block diagram for position control of the servo table is given by: θ D 0.09 See
Root Locus Motivation Sketching Root Locus Examples ME375 Root Locus - 1 Servo Table Example DC Motor Position Control The block diagram for position control of the servo table is given by: θ D 0.09 See
Block Diagrams and VisSim
 Block iagrams Block iagrams and VisSim Block iagrams are a graphical way to describe how dynamic systems are interconnected. They help explain how a control system will be built and how the signals flow
Block iagrams Block iagrams and VisSim Block iagrams are a graphical way to describe how dynamic systems are interconnected. They help explain how a control system will be built and how the signals flow
Chapter 6 Page 1 of 10. Lecture Guide. Math College Algebra Chapter 6. to accompany. College Algebra by Julie Miller
 Chapter 6 Page 1 of 10 Lecture Guide Math 105 - College Algebra Chapter 6 to accompany College Algebra by Julie Miller Corresponding Lecture Videos can be found at Prepared by Stephen Toner & Nichole DuBal
Chapter 6 Page 1 of 10 Lecture Guide Math 105 - College Algebra Chapter 6 to accompany College Algebra by Julie Miller Corresponding Lecture Videos can be found at Prepared by Stephen Toner & Nichole DuBal
Mathematics Lecture. 6 Chapter. 4 APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES. By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh
 Mathematics Lecture. 6 Chapter. 4 APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh OVERVIEW: This chapter studies some of the important applications of derivatives. We learn how derivatives are used
Mathematics Lecture. 6 Chapter. 4 APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh OVERVIEW: This chapter studies some of the important applications of derivatives. We learn how derivatives are used
Statistics for Financial Engineering Session 2: Basic Set Theory March 19 th, 2006
 Statistics for Financial Engineering Session 2: Basic Set Theory March 19 th, 2006 Topics What is a set? Notations for sets Empty set Inclusion/containment and subsets Sample spaces and events Operations
Statistics for Financial Engineering Session 2: Basic Set Theory March 19 th, 2006 Topics What is a set? Notations for sets Empty set Inclusion/containment and subsets Sample spaces and events Operations
Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 6
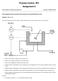 Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 6 Kevin Dunn, kevin.dunn@mcmaster.ca Due date: 28 March 204 This assignment gives you practice with cascade control and feedforward control. Question [0 = 6 + 4] The outlet
Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 6 Kevin Dunn, kevin.dunn@mcmaster.ca Due date: 28 March 204 This assignment gives you practice with cascade control and feedforward control. Question [0 = 6 + 4] The outlet
ẋ n = f n (x 1,...,x n,u 1,...,u m ) (5) y 1 = g 1 (x 1,...,x n,u 1,...,u m ) (6) y p = g p (x 1,...,x n,u 1,...,u m ) (7)
 EEE582 Topical Outline A.A. Rodriguez Fall 2007 GWC 352, 965-3712 The following represents a detailed topical outline of the course. It attempts to highlight most of the key concepts to be covered and
EEE582 Topical Outline A.A. Rodriguez Fall 2007 GWC 352, 965-3712 The following represents a detailed topical outline of the course. It attempts to highlight most of the key concepts to be covered and
Chapter 3 MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF DYNAMIC SYSTEMS
 Chapter 3 MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF DYNAMIC SYSTEMS 3. System Modeling Mathematical Modeling In designing control systems we mst be able to model engineered system dynamics. The model of a dynamic system
Chapter 3 MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF DYNAMIC SYSTEMS 3. System Modeling Mathematical Modeling In designing control systems we mst be able to model engineered system dynamics. The model of a dynamic system
