Rate Maps and Smoothing
|
|
|
- Hubert Carson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Rate Maps and Smoothing Luc Anselin Spatial Analysis Laboratory Dept. Agricultural and Consumer Economics University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign
2 Outline Mapping Rates Risk and Excess Risk Empirical Bayes Smoothing Spatial Smoothing
3 Mapping Rates
4 Events Locations individual points point pattern analysis areal aggregates counts of events rate = # events / # population at risk raw rate is ML estimate of risk Probability Surface or Risk Surface probability that event will happen at any given location, in any given area
5 Event and Base
6 Kernel Estimation Creating a Continuous Surface for Discrete Events typical application = point density surface e.g. location of homicides yields a crime surface weighted average of values around points locate a grid over data center kernel at each grid point and compute average of points within the range kernel parameters (bandwidth, slope, etc.) different kernels simple average, inverse distance, gaussian
7 data points kernel smoother Kernel Estimation - Density Surface Source: Longley et al (2001)
8 Risk and Excess Risk
9 Problems with Rates Risk rate as an estimate of underlying risk Issues expected events = risk x population at risk intrinsic heterogeneity variance depends on mean variance depends on base variance instability spurious outliers
10 Events and Expected Events << number of strokes for 65+ African- American males, NC and SC (yellow = zero) expected # strokes using average risk for state, not average of county risks (risk = total deaths / pop at risk) >>
11 Expected Events Number of Events if Average Risk Applied control for age/sex structure of population at risk different rates for different age groups apply estimated risk, a prior estimated risk = average for reference population expected events = Σ k r k x p k for k groups r k risk for group k p k population in group k
12 Relative Risk Compare Observed to Expected observed = number of events expected = number of events if average risk applied to population Relative Risk ratio of observed events over expected events > 1: higher (excess) risk < 1: lower risk SMR = standardized mortality ratio use age/gender specific rates
13 Excess Risk Map - Strokes ratio of observed stroke deaths over expected, blue <1 red > 1 (darkest > 3)
14 Excess Risk St. Louis Homicides
15 Empirical Bayes Smoothing
16 Variance Instability in Rates Rates as Binomial r.v. x/p: x count, P population at risk E[x/P] = π Var[x/P] = π(1-π)/p with π as unknown Unknown mean in variance non-standard assumption Variance depends inversely on base P smaller areas have larger variance example: π = 0.1 P 1 =500 P 2 =100,000 SD 1 = SD 2 =
17 Shrinkage Principle use prior information on unknown π i to smooth (shrink) rate estimate r i = x i /P i shrinkage inverse function of variance smaller variance gives higher weight to observed rate larger variance gives higher weight to prior prior θ i with mean γ i and variance φ i
18 Bayesian Estimate Bayesian Principle combine prior distribution with information provided by the data Empirical Bayes (EB) prior comes from the data est π i = w i r i + (1 - w i )θ i is weighted average of r and prior w i = φ i / [φ i + (θ i /P i ) ] for large P weight w is 1 (no weight given to prior)
19 EB Transformation Estimate Mean (θ) and Variance (φ) Method of Moments overall mean θ θ = Σ i x i / Σ i P i P av = Σ i P i / R (R = # areas) overall variance φ φ ={ [ Σ i P i (r i - θ) 2 ] / [ Σ i P i ]} - (θ / P av )
20 Raw Rate Map
21 EB Smoothed Map
22 EB Rates vs. Raw Rates
23 Regional EB Smoothing
24 Spatial Smoothing
25 Spatial Window Smoother Replace raw rate by window average define reference neighbors S i use window around area spatial window average Σ j x j / Σ j P j = average for window smoothes out the peaks in the data fewer outliers highlights broad spatial trends the highs and the lows
26 Spatial Rate Smoother
27 Spatial Rate Smoothing
28
Mapping and Analysis for Spatial Social Science
 Mapping and Analysis for Spatial Social Science Luc Anselin Spatial Analysis Laboratory Dept. Agricultural and Consumer Economics University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign http://sal.agecon.uiuc.edu Outline
Mapping and Analysis for Spatial Social Science Luc Anselin Spatial Analysis Laboratory Dept. Agricultural and Consumer Economics University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign http://sal.agecon.uiuc.edu Outline
Luc Anselin Spatial Analysis Laboratory Dept. Agricultural and Consumer Economics University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign
 GIS and Spatial Analysis Luc Anselin Spatial Analysis Laboratory Dept. Agricultural and Consumer Economics University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign http://sal.agecon.uiuc.edu Outline GIS and Spatial Analysis
GIS and Spatial Analysis Luc Anselin Spatial Analysis Laboratory Dept. Agricultural and Consumer Economics University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign http://sal.agecon.uiuc.edu Outline GIS and Spatial Analysis
OPEN GEODA WORKSHOP / CRASH COURSE FACILITATED BY M. KOLAK
 OPEN GEODA WORKSHOP / CRASH COURSE FACILITATED BY M. KOLAK WHAT IS GEODA? Software program that serves as an introduction to spatial data analysis Free Open Source Source code is available under GNU license
OPEN GEODA WORKSHOP / CRASH COURSE FACILITATED BY M. KOLAK WHAT IS GEODA? Software program that serves as an introduction to spatial data analysis Free Open Source Source code is available under GNU license
Spatial Clusters of Rates
 Spatial Clusters of Rates Luc Anselin http://spatial.uchicago.edu concepts EBI local Moran scan statistics Concepts Rates as Risk from counts (spatially extensive) to rates (spatially intensive) rate =
Spatial Clusters of Rates Luc Anselin http://spatial.uchicago.edu concepts EBI local Moran scan statistics Concepts Rates as Risk from counts (spatially extensive) to rates (spatially intensive) rate =
Kriging Luc Anselin, All Rights Reserved
 Kriging Luc Anselin Spatial Analysis Laboratory Dept. Agricultural and Consumer Economics University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign http://sal.agecon.uiuc.edu Outline Principles Kriging Models Spatial Interpolation
Kriging Luc Anselin Spatial Analysis Laboratory Dept. Agricultural and Consumer Economics University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign http://sal.agecon.uiuc.edu Outline Principles Kriging Models Spatial Interpolation
Spatial Autocorrelation (2) Spatial Weights
 Spatial Autocorrelation (2) Spatial Weights Luc Anselin Spatial Analysis Laboratory Dept. Agricultural and Consumer Economics University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign http://sal.agecon.uiuc.edu Outline
Spatial Autocorrelation (2) Spatial Weights Luc Anselin Spatial Analysis Laboratory Dept. Agricultural and Consumer Economics University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign http://sal.agecon.uiuc.edu Outline
Outline ESDA. Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis ESDA. Luc Anselin
 Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis ESDA Luc Anselin University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign http://www.spacestat.com Outline ESDA Exploring Spatial Patterns Global Spatial Autocorrelation Local Spatial
Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis ESDA Luc Anselin University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign http://www.spacestat.com Outline ESDA Exploring Spatial Patterns Global Spatial Autocorrelation Local Spatial
Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis Using GeoDA: : An Introduction
 Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis Using GeoDA: : An Introduction Prepared by Professor Ravi K. Sharma, University of Pittsburgh Modified for NBDPN 2007 Conference Presentation by Professor Russell S. Kirby,
Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis Using GeoDA: : An Introduction Prepared by Professor Ravi K. Sharma, University of Pittsburgh Modified for NBDPN 2007 Conference Presentation by Professor Russell S. Kirby,
Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis and GeoDa
 Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis and GeoDa Luc Anselin Spatial Analysis Laboratory Dept. Agricultural and Consumer Economics University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign http://sal.agecon.uiuc.edu Outline
Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis and GeoDa Luc Anselin Spatial Analysis Laboratory Dept. Agricultural and Consumer Economics University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign http://sal.agecon.uiuc.edu Outline
Bayesian Hierarchical Models
 Bayesian Hierarchical Models Gavin Shaddick, Millie Green, Matthew Thomas University of Bath 6 th - 9 th December 2016 1/ 34 APPLICATIONS OF BAYESIAN HIERARCHICAL MODELS 2/ 34 OUTLINE Spatial epidemiology
Bayesian Hierarchical Models Gavin Shaddick, Millie Green, Matthew Thomas University of Bath 6 th - 9 th December 2016 1/ 34 APPLICATIONS OF BAYESIAN HIERARCHICAL MODELS 2/ 34 OUTLINE Spatial epidemiology
Quantitative Methods Chapter 0: Review of Basic Concepts 0.1 Business Applications (II) 0.2 Business Applications (III)
 Quantitative Methods Chapter 0: Review of Basic Concepts 0.1 Business Applications (II) 0.1.1 Simple Interest 0.2 Business Applications (III) 0.2.1 Expenses Involved in Buying a Car 0.2.2 Expenses Involved
Quantitative Methods Chapter 0: Review of Basic Concepts 0.1 Business Applications (II) 0.1.1 Simple Interest 0.2 Business Applications (III) 0.2.1 Expenses Involved in Buying a Car 0.2.2 Expenses Involved
Multi-level Models: Idea
 Review of 140.656 Review Introduction to multi-level models The two-stage normal-normal model Two-stage linear models with random effects Three-stage linear models Two-stage logistic regression with random
Review of 140.656 Review Introduction to multi-level models The two-stage normal-normal model Two-stage linear models with random effects Three-stage linear models Two-stage logistic regression with random
Spatio-Temporal Models for Areal Data
 Spatio-Temporal Models for Areal Data Juan C. Vivar (jcvivar@dme.ufrj.br) and Marco A. R. Ferreira (marco@im.ufrj.br) Departamento de Métodos Estatísticos - IM Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ)
Spatio-Temporal Models for Areal Data Juan C. Vivar (jcvivar@dme.ufrj.br) and Marco A. R. Ferreira (marco@im.ufrj.br) Departamento de Métodos Estatísticos - IM Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ)
PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHAPTER 2: PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS
 PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHAPTER 2: PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Parametric Distributions Basic building blocks: Need to determine given Representation: or? Recall Curve Fitting Binary Variables
PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHAPTER 2: PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Parametric Distributions Basic building blocks: Need to determine given Representation: or? Recall Curve Fitting Binary Variables
Points. Luc Anselin. Copyright 2017 by Luc Anselin, All Rights Reserved
 Points Luc Anselin http://spatial.uchicago.edu 1 classic point pattern analysis spatial randomness intensity distance-based statistics points on networks 2 Classic Point Pattern Analysis 3 Classic Examples
Points Luc Anselin http://spatial.uchicago.edu 1 classic point pattern analysis spatial randomness intensity distance-based statistics points on networks 2 Classic Point Pattern Analysis 3 Classic Examples
Web-Based Analytical Tools for the Exploration of Spatial Data
 Web-Based Analytical Tools for the Exploration of Spatial Data Luc Anselin, Yong Wook Kim and Ibnu Syabri Spatial Analysis Laboratory Department of Agricultural and Consumer Economics University of Illinois,
Web-Based Analytical Tools for the Exploration of Spatial Data Luc Anselin, Yong Wook Kim and Ibnu Syabri Spatial Analysis Laboratory Department of Agricultural and Consumer Economics University of Illinois,
12 - Nonparametric Density Estimation
 ST 697 Fall 2017 1/49 12 - Nonparametric Density Estimation ST 697 Fall 2017 University of Alabama Density Review ST 697 Fall 2017 2/49 Continuous Random Variables ST 697 Fall 2017 3/49 1.0 0.8 F(x) 0.6
ST 697 Fall 2017 1/49 12 - Nonparametric Density Estimation ST 697 Fall 2017 University of Alabama Density Review ST 697 Fall 2017 2/49 Continuous Random Variables ST 697 Fall 2017 3/49 1.0 0.8 F(x) 0.6
Cluster investigations using Disease mapping methods International workshop on Risk Factors for Childhood Leukemia Berlin May
 Cluster investigations using Disease mapping methods International workshop on Risk Factors for Childhood Leukemia Berlin May 5-7 2008 Peter Schlattmann Institut für Biometrie und Klinische Epidemiologie
Cluster investigations using Disease mapping methods International workshop on Risk Factors for Childhood Leukemia Berlin May 5-7 2008 Peter Schlattmann Institut für Biometrie und Klinische Epidemiologie
Global Spatial Autocorrelation Clustering
 Global Spatial Autocorrelation Clustering Luc Anselin http://spatial.uchicago.edu join count statistics Moran s I Moran scatter plot non-parametric spatial autocorrelation Join Count Statistics Recap -
Global Spatial Autocorrelation Clustering Luc Anselin http://spatial.uchicago.edu join count statistics Moran s I Moran scatter plot non-parametric spatial autocorrelation Join Count Statistics Recap -
Bayesian SAE using Complex Survey Data Lecture 4A: Hierarchical Spatial Bayes Modeling
 Bayesian SAE using Complex Survey Data Lecture 4A: Hierarchical Spatial Bayes Modeling Jon Wakefield Departments of Statistics and Biostatistics University of Washington 1 / 37 Lecture Content Motivation
Bayesian SAE using Complex Survey Data Lecture 4A: Hierarchical Spatial Bayes Modeling Jon Wakefield Departments of Statistics and Biostatistics University of Washington 1 / 37 Lecture Content Motivation
Disease mapping with Gaussian processes
 EUROHEIS2 Kuopio, Finland 17-18 August 2010 Aki Vehtari (former Helsinki University of Technology) Department of Biomedical Engineering and Computational Science (BECS) Acknowledgments Researchers - Jarno
EUROHEIS2 Kuopio, Finland 17-18 August 2010 Aki Vehtari (former Helsinki University of Technology) Department of Biomedical Engineering and Computational Science (BECS) Acknowledgments Researchers - Jarno
Lattice Data. Tonglin Zhang. Spatial Statistics for Point and Lattice Data (Part III)
 Title: Spatial Statistics for Point Processes and Lattice Data (Part III) Lattice Data Tonglin Zhang Outline Description Research Problems Global Clustering and Local Clusters Permutation Test Spatial
Title: Spatial Statistics for Point Processes and Lattice Data (Part III) Lattice Data Tonglin Zhang Outline Description Research Problems Global Clustering and Local Clusters Permutation Test Spatial
Signal detection theory
 Signal detection theory z p[r -] p[r +] - + Role of priors: Find z by maximizing P[correct] = p[+] b(z) + p[-](1 a(z)) Is there a better test to use than r? z p[r -] p[r +] - + The optimal
Signal detection theory z p[r -] p[r +] - + Role of priors: Find z by maximizing P[correct] = p[+] b(z) + p[-](1 a(z)) Is there a better test to use than r? z p[r -] p[r +] - + The optimal
Bayesian Semiparametric GARCH Models
 Bayesian Semiparametric GARCH Models Xibin (Bill) Zhang and Maxwell L. King Department of Econometrics and Business Statistics Faculty of Business and Economics xibin.zhang@monash.edu Quantitative Methods
Bayesian Semiparametric GARCH Models Xibin (Bill) Zhang and Maxwell L. King Department of Econometrics and Business Statistics Faculty of Business and Economics xibin.zhang@monash.edu Quantitative Methods
Bayesian Semiparametric GARCH Models
 Bayesian Semiparametric GARCH Models Xibin (Bill) Zhang and Maxwell L. King Department of Econometrics and Business Statistics Faculty of Business and Economics xibin.zhang@monash.edu Quantitative Methods
Bayesian Semiparametric GARCH Models Xibin (Bill) Zhang and Maxwell L. King Department of Econometrics and Business Statistics Faculty of Business and Economics xibin.zhang@monash.edu Quantitative Methods
Approaches for Multiple Disease Mapping: MCAR and SANOVA
 Approaches for Multiple Disease Mapping: MCAR and SANOVA Dipankar Bandyopadhyay Division of Biostatistics, University of Minnesota SPH April 22, 2015 1 Adapted from Sudipto Banerjee s notes SANOVA vs MCAR
Approaches for Multiple Disease Mapping: MCAR and SANOVA Dipankar Bandyopadhyay Division of Biostatistics, University of Minnesota SPH April 22, 2015 1 Adapted from Sudipto Banerjee s notes SANOVA vs MCAR
Gaussian Multiscale Spatio-temporal Models for Areal Data
 Gaussian Multiscale Spatio-temporal Models for Areal Data (University of Missouri) Scott H. Holan (University of Missouri) Adelmo I. Bertolde (UFES) Outline Motivation Multiscale factorization The multiscale
Gaussian Multiscale Spatio-temporal Models for Areal Data (University of Missouri) Scott H. Holan (University of Missouri) Adelmo I. Bertolde (UFES) Outline Motivation Multiscale factorization The multiscale
Local Likelihood Bayesian Cluster Modeling for small area health data. Andrew Lawson Arnold School of Public Health University of South Carolina
 Local Likelihood Bayesian Cluster Modeling for small area health data Andrew Lawson Arnold School of Public Health University of South Carolina Local Likelihood Bayesian Cluster Modelling for Small Area
Local Likelihood Bayesian Cluster Modeling for small area health data Andrew Lawson Arnold School of Public Health University of South Carolina Local Likelihood Bayesian Cluster Modelling for Small Area
Lecture 3: Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis (ESDA) Prof. Eduardo A. Haddad
 Lecture 3: Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis (ESDA) Prof. Eduardo A. Haddad Key message Spatial dependence First Law of Geography (Waldo Tobler): Everything is related to everything else, but near things
Lecture 3: Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis (ESDA) Prof. Eduardo A. Haddad Key message Spatial dependence First Law of Geography (Waldo Tobler): Everything is related to everything else, but near things
Measures of Spatial Dependence
 Measures of Spatial Dependence Carlos Hurtado Department of Economics University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign hrtdmrt2@illinois.edu Junel 30th, 2016 C. Hurtado (UIUC - Economics) Spatial Econometrics
Measures of Spatial Dependence Carlos Hurtado Department of Economics University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign hrtdmrt2@illinois.edu Junel 30th, 2016 C. Hurtado (UIUC - Economics) Spatial Econometrics
Appendix A. Numeric example of Dimick Staiger Estimator and comparison between Dimick-Staiger Estimator and Hierarchical Poisson Estimator
 Appendix A. Numeric example of Dimick Staiger Estimator and comparison between Dimick-Staiger Estimator and Hierarchical Poisson Estimator As described in the manuscript, the Dimick-Staiger (DS) estimator
Appendix A. Numeric example of Dimick Staiger Estimator and comparison between Dimick-Staiger Estimator and Hierarchical Poisson Estimator As described in the manuscript, the Dimick-Staiger (DS) estimator
Point Pattern Analysis
 Point Pattern Analysis Nearest Neighbor Statistics Luc Anselin http://spatial.uchicago.edu principle G function F function J function Principle Terminology events and points event: observed location of
Point Pattern Analysis Nearest Neighbor Statistics Luc Anselin http://spatial.uchicago.edu principle G function F function J function Principle Terminology events and points event: observed location of
Statistics: Learning models from data
 DS-GA 1002 Lecture notes 5 October 19, 2015 Statistics: Learning models from data Learning models from data that are assumed to be generated probabilistically from a certain unknown distribution is a crucial
DS-GA 1002 Lecture notes 5 October 19, 2015 Statistics: Learning models from data Learning models from data that are assumed to be generated probabilistically from a certain unknown distribution is a crucial
Habilitationsvortrag: Machine learning, shrinkage estimation, and economic theory
 Habilitationsvortrag: Machine learning, shrinkage estimation, and economic theory Maximilian Kasy May 25, 218 1 / 27 Introduction Recent years saw a boom of machine learning methods. Impressive advances
Habilitationsvortrag: Machine learning, shrinkage estimation, and economic theory Maximilian Kasy May 25, 218 1 / 27 Introduction Recent years saw a boom of machine learning methods. Impressive advances
Nonparametric Methods
 Nonparametric Methods Michael R. Roberts Department of Finance The Wharton School University of Pennsylvania July 28, 2009 Michael R. Roberts Nonparametric Methods 1/42 Overview Great for data analysis
Nonparametric Methods Michael R. Roberts Department of Finance The Wharton School University of Pennsylvania July 28, 2009 Michael R. Roberts Nonparametric Methods 1/42 Overview Great for data analysis
Topic 12 Overview of Estimation
 Topic 12 Overview of Estimation Classical Statistics 1 / 9 Outline Introduction Parameter Estimation Classical Statistics Densities and Likelihoods 2 / 9 Introduction In the simplest possible terms, the
Topic 12 Overview of Estimation Classical Statistics 1 / 9 Outline Introduction Parameter Estimation Classical Statistics Densities and Likelihoods 2 / 9 Introduction In the simplest possible terms, the
Modelling geoadditive survival data
 Modelling geoadditive survival data Thomas Kneib & Ludwig Fahrmeir Department of Statistics, Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich 1. Leukemia survival data 2. Structured hazard regression 3. Mixed model
Modelling geoadditive survival data Thomas Kneib & Ludwig Fahrmeir Department of Statistics, Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich 1. Leukemia survival data 2. Structured hazard regression 3. Mixed model
Research Note: A more powerful test statistic for reasoning about interference between units
 Research Note: A more powerful test statistic for reasoning about interference between units Jake Bowers Mark Fredrickson Peter M. Aronow August 26, 2015 Abstract Bowers, Fredrickson and Panagopoulos (2012)
Research Note: A more powerful test statistic for reasoning about interference between units Jake Bowers Mark Fredrickson Peter M. Aronow August 26, 2015 Abstract Bowers, Fredrickson and Panagopoulos (2012)
Spatial Analysis I. Spatial data analysis Spatial analysis and inference
 Spatial Analysis I Spatial data analysis Spatial analysis and inference Roadmap Outline: What is spatial analysis? Spatial Joins Step 1: Analysis of attributes Step 2: Preparing for analyses: working with
Spatial Analysis I Spatial data analysis Spatial analysis and inference Roadmap Outline: What is spatial analysis? Spatial Joins Step 1: Analysis of attributes Step 2: Preparing for analyses: working with
Introduction to Machine Learning
 Introduction to Machine Learning 3. Instance Based Learning Alex Smola Carnegie Mellon University http://alex.smola.org/teaching/cmu2013-10-701 10-701 Outline Parzen Windows Kernels, algorithm Model selection
Introduction to Machine Learning 3. Instance Based Learning Alex Smola Carnegie Mellon University http://alex.smola.org/teaching/cmu2013-10-701 10-701 Outline Parzen Windows Kernels, algorithm Model selection
Lecture 3: Statistical Decision Theory (Part II)
 Lecture 3: Statistical Decision Theory (Part II) Hao Helen Zhang Hao Helen Zhang Lecture 3: Statistical Decision Theory (Part II) 1 / 27 Outline of This Note Part I: Statistics Decision Theory (Classical
Lecture 3: Statistical Decision Theory (Part II) Hao Helen Zhang Hao Helen Zhang Lecture 3: Statistical Decision Theory (Part II) 1 / 27 Outline of This Note Part I: Statistics Decision Theory (Classical
Neutral Bayesian reference models for incidence rates of (rare) clinical events
 Neutral Bayesian reference models for incidence rates of (rare) clinical events Jouni Kerman Statistical Methodology, Novartis Pharma AG, Basel BAYES2012, May 10, Aachen Outline Motivation why reference
Neutral Bayesian reference models for incidence rates of (rare) clinical events Jouni Kerman Statistical Methodology, Novartis Pharma AG, Basel BAYES2012, May 10, Aachen Outline Motivation why reference
Density Estimation. Seungjin Choi
 Density Estimation Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr http://mlg.postech.ac.kr/
Density Estimation Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr http://mlg.postech.ac.kr/
Practice Exam 1. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) You are given the following data on loss sizes:
 Practice Exam 1 1. Losses for an insurance coverage have the following cumulative distribution function: F(0) = 0 F(1,000) = 0.2 F(5,000) = 0.4 F(10,000) = 0.9 F(100,000) = 1 with linear interpolation
Practice Exam 1 1. Losses for an insurance coverage have the following cumulative distribution function: F(0) = 0 F(1,000) = 0.2 F(5,000) = 0.4 F(10,000) = 0.9 F(100,000) = 1 with linear interpolation
Lecture 16: Small Sample Size Problems (Covariance Estimation) Many thanks to Carlos Thomaz who authored the original version of these slides
 Lecture 16: Small Sample Size Problems (Covariance Estimation) Many thanks to Carlos Thomaz who authored the original version of these slides Intelligent Data Analysis and Probabilistic Inference Lecture
Lecture 16: Small Sample Size Problems (Covariance Estimation) Many thanks to Carlos Thomaz who authored the original version of these slides Intelligent Data Analysis and Probabilistic Inference Lecture
Intensity Analysis of Spatial Point Patterns Geog 210C Introduction to Spatial Data Analysis
 Intensity Analysis of Spatial Point Patterns Geog 210C Introduction to Spatial Data Analysis Chris Funk Lecture 4 Spatial Point Patterns Definition Set of point locations with recorded events" within study
Intensity Analysis of Spatial Point Patterns Geog 210C Introduction to Spatial Data Analysis Chris Funk Lecture 4 Spatial Point Patterns Definition Set of point locations with recorded events" within study
Spatial Statistics or Why Spatial is Special?
 Spatial Statistics or Why Spatial is Special? Curdin Derungs, GISLab 20.10.2017 Seite 1 Spatial is special Spatial is special Longley et al s (2011) spatial is special -list: 20.10.2017 Seite 3 Spatial
Spatial Statistics or Why Spatial is Special? Curdin Derungs, GISLab 20.10.2017 Seite 1 Spatial is special Spatial is special Longley et al s (2011) spatial is special -list: 20.10.2017 Seite 3 Spatial
Time Series Models for Measuring Market Risk
 Time Series Models for Measuring Market Risk José Miguel Hernández Lobato Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Computer Science Department June 28, 2007 1/ 32 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Competitive and collaborative
Time Series Models for Measuring Market Risk José Miguel Hernández Lobato Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Computer Science Department June 28, 2007 1/ 32 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Competitive and collaborative
Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5
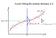 Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5 Maximum Likelihood Bishop 1.2.5 Model Likelihood differentiation p(t x, w, β) = Maximum Likelihood N N ( t n y(x n, w), β 1). (1.61) n=1 As we did in the case of the
Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5 Maximum Likelihood Bishop 1.2.5 Model Likelihood differentiation p(t x, w, β) = Maximum Likelihood N N ( t n y(x n, w), β 1). (1.61) n=1 As we did in the case of the
Econ 582 Nonparametric Regression
 Econ 582 Nonparametric Regression Eric Zivot May 28, 2013 Nonparametric Regression Sofarwehaveonlyconsideredlinearregressionmodels = x 0 β + [ x ]=0 [ x = x] =x 0 β = [ x = x] [ x = x] x = β The assume
Econ 582 Nonparametric Regression Eric Zivot May 28, 2013 Nonparametric Regression Sofarwehaveonlyconsideredlinearregressionmodels = x 0 β + [ x ]=0 [ x = x] =x 0 β = [ x = x] [ x = x] x = β The assume
Spatial Inference of Nitrate Concentrations in Groundwater
 Spatial Inference of Nitrate Concentrations in Groundwater Dawn Woodard Operations Research & Information Engineering Cornell University joint work with Robert Wolpert, Duke Univ. Dept. of Statistical
Spatial Inference of Nitrate Concentrations in Groundwater Dawn Woodard Operations Research & Information Engineering Cornell University joint work with Robert Wolpert, Duke Univ. Dept. of Statistical
Frailty Modeling for Spatially Correlated Survival Data, with Application to Infant Mortality in Minnesota By: Sudipto Banerjee, Mela. P.
 Frailty Modeling for Spatially Correlated Survival Data, with Application to Infant Mortality in Minnesota By: Sudipto Banerjee, Melanie M. Wall, Bradley P. Carlin November 24, 2014 Outlines of the talk
Frailty Modeling for Spatially Correlated Survival Data, with Application to Infant Mortality in Minnesota By: Sudipto Banerjee, Melanie M. Wall, Bradley P. Carlin November 24, 2014 Outlines of the talk
Least Absolute Shrinkage is Equivalent to Quadratic Penalization
 Least Absolute Shrinkage is Equivalent to Quadratic Penalization Yves Grandvalet Heudiasyc, UMR CNRS 6599, Université de Technologie de Compiègne, BP 20.529, 60205 Compiègne Cedex, France Yves.Grandvalet@hds.utc.fr
Least Absolute Shrinkage is Equivalent to Quadratic Penalization Yves Grandvalet Heudiasyc, UMR CNRS 6599, Université de Technologie de Compiègne, BP 20.529, 60205 Compiègne Cedex, France Yves.Grandvalet@hds.utc.fr
Semiparametric Generalized Linear Models
 Semiparametric Generalized Linear Models North American Stata Users Group Meeting Chicago, Illinois Paul Rathouz Department of Health Studies University of Chicago prathouz@uchicago.edu Liping Gao MS Student
Semiparametric Generalized Linear Models North American Stata Users Group Meeting Chicago, Illinois Paul Rathouz Department of Health Studies University of Chicago prathouz@uchicago.edu Liping Gao MS Student
Confidence intervals for kernel density estimation
 Stata User Group - 9th UK meeting - 19/20 May 2003 Confidence intervals for kernel density estimation Carlo Fiorio c.fiorio@lse.ac.uk London School of Economics and STICERD Stata User Group - 9th UK meeting
Stata User Group - 9th UK meeting - 19/20 May 2003 Confidence intervals for kernel density estimation Carlo Fiorio c.fiorio@lse.ac.uk London School of Economics and STICERD Stata User Group - 9th UK meeting
SYDE 372 Introduction to Pattern Recognition. Probability Measures for Classification: Part I
 SYDE 372 Introduction to Pattern Recognition Probability Measures for Classification: Part I Alexander Wong Department of Systems Design Engineering University of Waterloo Outline 1 2 3 4 Why use probability
SYDE 372 Introduction to Pattern Recognition Probability Measures for Classification: Part I Alexander Wong Department of Systems Design Engineering University of Waterloo Outline 1 2 3 4 Why use probability
STA 4273H: Sta-s-cal Machine Learning
 STA 4273H: Sta-s-cal Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Computer Science! Department of Statistical Sciences! rsalakhu@cs.toronto.edu! h0p://www.cs.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Lecture 2 In our
STA 4273H: Sta-s-cal Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Computer Science! Department of Statistical Sciences! rsalakhu@cs.toronto.edu! h0p://www.cs.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Lecture 2 In our
CS-E3210 Machine Learning: Basic Principles
 CS-E3210 Machine Learning: Basic Principles Lecture 4: Regression II slides by Markus Heinonen Department of Computer Science Aalto University, School of Science Autumn (Period I) 2017 1 / 61 Today s introduction
CS-E3210 Machine Learning: Basic Principles Lecture 4: Regression II slides by Markus Heinonen Department of Computer Science Aalto University, School of Science Autumn (Period I) 2017 1 / 61 Today s introduction
Frequency Based Fatigue
 Frequency Based Fatigue Professor Darrell F. Socie Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 001-01 Darrell Socie, All Rights Reserved Deterministic versus
Frequency Based Fatigue Professor Darrell F. Socie Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 001-01 Darrell Socie, All Rights Reserved Deterministic versus
Multivariate Survival Analysis
 Multivariate Survival Analysis Previously we have assumed that either (X i, δ i ) or (X i, δ i, Z i ), i = 1,..., n, are i.i.d.. This may not always be the case. Multivariate survival data can arise in
Multivariate Survival Analysis Previously we have assumed that either (X i, δ i ) or (X i, δ i, Z i ), i = 1,..., n, are i.i.d.. This may not always be the case. Multivariate survival data can arise in
Spatial Analysis and Modeling (GIST 4302/5302) Guofeng Cao Department of Geosciences Texas Tech University
 Spatial Analysis and Modeling (GIST 4302/5302) Guofeng Cao Department of Geosciences Texas Tech University Outline of This Week Last week, we learned: Data representation: Object vs. Fieldbased approaches
Spatial Analysis and Modeling (GIST 4302/5302) Guofeng Cao Department of Geosciences Texas Tech University Outline of This Week Last week, we learned: Data representation: Object vs. Fieldbased approaches
Right-truncated data. STAT474/STAT574 February 7, / 44
 Right-truncated data For this data, only individuals for whom the event has occurred by a given date are included in the study. Right truncation can occur in infectious disease studies. Let T i denote
Right-truncated data For this data, only individuals for whom the event has occurred by a given date are included in the study. Right truncation can occur in infectious disease studies. Let T i denote
Aggregated cancer incidence data: spatial models
 Aggregated cancer incidence data: spatial models 5 ième Forum du Cancéropôle Grand-est - November 2, 2011 Erik A. Sauleau Department of Biostatistics - Faculty of Medicine University of Strasbourg ea.sauleau@unistra.fr
Aggregated cancer incidence data: spatial models 5 ième Forum du Cancéropôle Grand-est - November 2, 2011 Erik A. Sauleau Department of Biostatistics - Faculty of Medicine University of Strasbourg ea.sauleau@unistra.fr
Kernel density estimation in R
 Kernel density estimation in R Kernel density estimation can be done in R using the density() function in R. The default is a Guassian kernel, but others are possible also. It uses it s own algorithm to
Kernel density estimation in R Kernel density estimation can be done in R using the density() function in R. The default is a Guassian kernel, but others are possible also. It uses it s own algorithm to
Minimum Message Length Analysis of the Behrens Fisher Problem
 Analysis of the Behrens Fisher Problem Enes Makalic and Daniel F Schmidt Centre for MEGA Epidemiology The University of Melbourne Solomonoff 85th Memorial Conference, 2011 Outline Introduction 1 Introduction
Analysis of the Behrens Fisher Problem Enes Makalic and Daniel F Schmidt Centre for MEGA Epidemiology The University of Melbourne Solomonoff 85th Memorial Conference, 2011 Outline Introduction 1 Introduction
Bayesian Learning (II)
 Universität Potsdam Institut für Informatik Lehrstuhl Maschinelles Lernen Bayesian Learning (II) Niels Landwehr Overview Probabilities, expected values, variance Basic concepts of Bayesian learning MAP
Universität Potsdam Institut für Informatik Lehrstuhl Maschinelles Lernen Bayesian Learning (II) Niels Landwehr Overview Probabilities, expected values, variance Basic concepts of Bayesian learning MAP
Intensity Analysis of Spatial Point Patterns Geog 210C Introduction to Spatial Data Analysis
 Intensity Analysis of Spatial Point Patterns Geog 210C Introduction to Spatial Data Analysis Chris Funk Lecture 5 Topic Overview 1) Introduction/Unvariate Statistics 2) Bootstrapping/Monte Carlo Simulation/Kernel
Intensity Analysis of Spatial Point Patterns Geog 210C Introduction to Spatial Data Analysis Chris Funk Lecture 5 Topic Overview 1) Introduction/Unvariate Statistics 2) Bootstrapping/Monte Carlo Simulation/Kernel
Robustness to Parametric Assumptions in Missing Data Models
 Robustness to Parametric Assumptions in Missing Data Models Bryan Graham NYU Keisuke Hirano University of Arizona April 2011 Motivation Motivation We consider the classic missing data problem. In practice
Robustness to Parametric Assumptions in Missing Data Models Bryan Graham NYU Keisuke Hirano University of Arizona April 2011 Motivation Motivation We consider the classic missing data problem. In practice
Small Area Modeling of County Estimates for Corn and Soybean Yields in the US
 Small Area Modeling of County Estimates for Corn and Soybean Yields in the US Matt Williams National Agricultural Statistics Service United States Department of Agriculture Matt.Williams@nass.usda.gov
Small Area Modeling of County Estimates for Corn and Soybean Yields in the US Matt Williams National Agricultural Statistics Service United States Department of Agriculture Matt.Williams@nass.usda.gov
An example of Bayesian reasoning Consider the one-dimensional deconvolution problem with various degrees of prior information.
 An example of Bayesian reasoning Consider the one-dimensional deconvolution problem with various degrees of prior information. Model: where g(t) = a(t s)f(s)ds + e(t), a(t) t = (rapidly). The problem,
An example of Bayesian reasoning Consider the one-dimensional deconvolution problem with various degrees of prior information. Model: where g(t) = a(t s)f(s)ds + e(t), a(t) t = (rapidly). The problem,
Previous lecture. P-value based combination. Fixed vs random effects models. Meta vs. pooled- analysis. New random effects testing.
 Previous lecture P-value based combination. Fixed vs random effects models. Meta vs. pooled- analysis. New random effects testing. Interaction Outline: Definition of interaction Additive versus multiplicative
Previous lecture P-value based combination. Fixed vs random effects models. Meta vs. pooled- analysis. New random effects testing. Interaction Outline: Definition of interaction Additive versus multiplicative
Spatial analysis of a designed experiment. Uniformity trials. Blocking
 Spatial analysis of a designed experiment RA Fisher s 3 principles of experimental design randomization unbiased estimate of treatment effect replication unbiased estimate of error variance blocking =
Spatial analysis of a designed experiment RA Fisher s 3 principles of experimental design randomization unbiased estimate of treatment effect replication unbiased estimate of error variance blocking =
Estimation Theory. as Θ = (Θ 1,Θ 2,...,Θ m ) T. An estimator
 Estimation Theory Estimation theory deals with finding numerical values of interesting parameters from given set of data. We start with formulating a family of models that could describe how the data were
Estimation Theory Estimation theory deals with finding numerical values of interesting parameters from given set of data. We start with formulating a family of models that could describe how the data were
Terminology for Statistical Data
 Terminology for Statistical Data variables - features - attributes observations - cases (consist of multiple values) In a standard data matrix, variables or features correspond to columns observations
Terminology for Statistical Data variables - features - attributes observations - cases (consist of multiple values) In a standard data matrix, variables or features correspond to columns observations
Areal data. Infant mortality, Auckland NZ districts. Number of plant species in 20cm x 20 cm patches of alpine tundra. Wheat yield
 Areal data Reminder about types of data Geostatistical data: Z(s) exists everyhere, varies continuously Can accommodate sudden changes by a model for the mean E.g., soil ph, two soil types with different
Areal data Reminder about types of data Geostatistical data: Z(s) exists everyhere, varies continuously Can accommodate sudden changes by a model for the mean E.g., soil ph, two soil types with different
Chapter 9. Non-Parametric Density Function Estimation
 9-1 Density Estimation Version 1.2 Chapter 9 Non-Parametric Density Function Estimation 9.1. Introduction We have discussed several estimation techniques: method of moments, maximum likelihood, and least
9-1 Density Estimation Version 1.2 Chapter 9 Non-Parametric Density Function Estimation 9.1. Introduction We have discussed several estimation techniques: method of moments, maximum likelihood, and least
SPATIAL ANALYSIS & MORE
 SPATIAL ANALYSIS & MORE Thomas A. Louis, PhD Department of Biostatistics Johns Hopins Bloomberg School of Public Health www.biostat.jhsph.edu/ tlouis/ tlouis@jhu.edu 1/28 Outline Prediction vs Inference
SPATIAL ANALYSIS & MORE Thomas A. Louis, PhD Department of Biostatistics Johns Hopins Bloomberg School of Public Health www.biostat.jhsph.edu/ tlouis/ tlouis@jhu.edu 1/28 Outline Prediction vs Inference
Analysis of Violent Crime in Los Angeles County
 Analysis of Violent Crime in Los Angeles County Xiaohong Huang UID: 004693375 March 20, 2017 Abstract Violent crime can have a negative impact to the victims and the neighborhoods. It can affect people
Analysis of Violent Crime in Los Angeles County Xiaohong Huang UID: 004693375 March 20, 2017 Abstract Violent crime can have a negative impact to the victims and the neighborhoods. It can affect people
Penalized Splines, Mixed Models, and Recent Large-Sample Results
 Penalized Splines, Mixed Models, and Recent Large-Sample Results David Ruppert Operations Research & Information Engineering, Cornell University Feb 4, 2011 Collaborators Matt Wand, University of Wollongong
Penalized Splines, Mixed Models, and Recent Large-Sample Results David Ruppert Operations Research & Information Engineering, Cornell University Feb 4, 2011 Collaborators Matt Wand, University of Wollongong
A primer on Bayesian statistics, with an application to mortality rate estimation
 A primer on Bayesian statistics, with an application to mortality rate estimation Peter off University of Washington Outline Subjective probability Practical aspects Application to mortality rate estimation
A primer on Bayesian statistics, with an application to mortality rate estimation Peter off University of Washington Outline Subjective probability Practical aspects Application to mortality rate estimation
Analytical Graphing. lets start with the best graph ever made
 Analytical Graphing lets start with the best graph ever made Probably the best statistical graphic ever drawn, this map by Charles Joseph Minard portrays the losses suffered by Napoleon's army in the Russian
Analytical Graphing lets start with the best graph ever made Probably the best statistical graphic ever drawn, this map by Charles Joseph Minard portrays the losses suffered by Napoleon's army in the Russian
Chapter 9. Non-Parametric Density Function Estimation
 9-1 Density Estimation Version 1.1 Chapter 9 Non-Parametric Density Function Estimation 9.1. Introduction We have discussed several estimation techniques: method of moments, maximum likelihood, and least
9-1 Density Estimation Version 1.1 Chapter 9 Non-Parametric Density Function Estimation 9.1. Introduction We have discussed several estimation techniques: method of moments, maximum likelihood, and least
Gaussian processes. Chuong B. Do (updated by Honglak Lee) November 22, 2008
 Gaussian processes Chuong B Do (updated by Honglak Lee) November 22, 2008 Many of the classical machine learning algorithms that we talked about during the first half of this course fit the following pattern:
Gaussian processes Chuong B Do (updated by Honglak Lee) November 22, 2008 Many of the classical machine learning algorithms that we talked about during the first half of this course fit the following pattern:
Nonparametric Methods Lecture 5
 Nonparametric Methods Lecture 5 Jason Corso SUNY at Buffalo 17 Feb. 29 J. Corso (SUNY at Buffalo) Nonparametric Methods Lecture 5 17 Feb. 29 1 / 49 Nonparametric Methods Lecture 5 Overview Previously,
Nonparametric Methods Lecture 5 Jason Corso SUNY at Buffalo 17 Feb. 29 J. Corso (SUNY at Buffalo) Nonparametric Methods Lecture 5 17 Feb. 29 1 / 49 Nonparametric Methods Lecture 5 Overview Previously,
Generalized common spatial factor model
 Biostatistics (2003), 4, 4,pp. 569 582 Printed in Great Britain Generalized common spatial factor model FUJUN WANG Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, IN 46285, USA MELANIE M. WALL Division of Biostatistics,
Biostatistics (2003), 4, 4,pp. 569 582 Printed in Great Britain Generalized common spatial factor model FUJUN WANG Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, IN 46285, USA MELANIE M. WALL Division of Biostatistics,
Models for Count and Binary Data. Poisson and Logistic GWR Models. 24/07/2008 GWR Workshop 1
 Models for Count and Binary Data Poisson and Logistic GWR Models 24/07/2008 GWR Workshop 1 Outline I: Modelling counts Poisson regression II: Modelling binary events Logistic Regression III: Poisson Regression
Models for Count and Binary Data Poisson and Logistic GWR Models 24/07/2008 GWR Workshop 1 Outline I: Modelling counts Poisson regression II: Modelling binary events Logistic Regression III: Poisson Regression
NONINFORMATIVE NONPARAMETRIC BAYESIAN ESTIMATION OF QUANTILES
 NONINFORMATIVE NONPARAMETRIC BAYESIAN ESTIMATION OF QUANTILES Glen Meeden School of Statistics University of Minnesota Minneapolis, MN 55455 Appeared in Statistics & Probability Letters Volume 16 (1993)
NONINFORMATIVE NONPARAMETRIC BAYESIAN ESTIMATION OF QUANTILES Glen Meeden School of Statistics University of Minnesota Minneapolis, MN 55455 Appeared in Statistics & Probability Letters Volume 16 (1993)
Statistical Learning Theory and the C-Loss cost function
 Statistical Learning Theory and the C-Loss cost function Jose Principe, Ph.D. Distinguished Professor ECE, BME Computational NeuroEngineering Laboratory and principe@cnel.ufl.edu Statistical Learning Theory
Statistical Learning Theory and the C-Loss cost function Jose Principe, Ph.D. Distinguished Professor ECE, BME Computational NeuroEngineering Laboratory and principe@cnel.ufl.edu Statistical Learning Theory
Concepts and Applications of Kriging. Eric Krause Konstantin Krivoruchko
 Concepts and Applications of Kriging Eric Krause Konstantin Krivoruchko Outline Introduction to interpolation Exploratory spatial data analysis (ESDA) Using the Geostatistical Wizard Validating interpolation
Concepts and Applications of Kriging Eric Krause Konstantin Krivoruchko Outline Introduction to interpolation Exploratory spatial data analysis (ESDA) Using the Geostatistical Wizard Validating interpolation
DIFFERENT INFLUENCES OF SOCIOECONOMIC FACTORS ON THE HUNTING AND FISHING LICENSE SALES IN COOK COUNTY, IL
 DIFFERENT INFLUENCES OF SOCIOECONOMIC FACTORS ON THE HUNTING AND FISHING LICENSE SALES IN COOK COUNTY, IL Xiaohan Zhang and Craig Miller Illinois Natural History Survey University of Illinois at Urbana
DIFFERENT INFLUENCES OF SOCIOECONOMIC FACTORS ON THE HUNTING AND FISHING LICENSE SALES IN COOK COUNTY, IL Xiaohan Zhang and Craig Miller Illinois Natural History Survey University of Illinois at Urbana
New Statistical Methods That Improve on MLE and GLM Including for Reserve Modeling GARY G VENTER
 New Statistical Methods That Improve on MLE and GLM Including for Reserve Modeling GARY G VENTER MLE Going the Way of the Buggy Whip Used to be gold standard of statistical estimation Minimum variance
New Statistical Methods That Improve on MLE and GLM Including for Reserve Modeling GARY G VENTER MLE Going the Way of the Buggy Whip Used to be gold standard of statistical estimation Minimum variance
Hierarchical modelling of performance indicators, with application to MRSA & teenage conception rates
 Hierarchical modelling of performance indicators, with application to MRSA & teenage conception rates Hayley E Jones School of Social and Community Medicine, University of Bristol, UK Thanks to David Spiegelhalter,
Hierarchical modelling of performance indicators, with application to MRSA & teenage conception rates Hayley E Jones School of Social and Community Medicine, University of Bristol, UK Thanks to David Spiegelhalter,
Spatial Tools for Econometric and Exploratory Analysis
 Spatial Tools for Econometric and Exploratory Analysis Michael F. Goodchild University of California, Santa Barbara Luc Anselin University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign http://csiss.org Outline A Quick
Spatial Tools for Econometric and Exploratory Analysis Michael F. Goodchild University of California, Santa Barbara Luc Anselin University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign http://csiss.org Outline A Quick
Technical Vignette 5: Understanding intrinsic Gaussian Markov random field spatial models, including intrinsic conditional autoregressive models
 Technical Vignette 5: Understanding intrinsic Gaussian Markov random field spatial models, including intrinsic conditional autoregressive models Christopher Paciorek, Department of Statistics, University
Technical Vignette 5: Understanding intrinsic Gaussian Markov random field spatial models, including intrinsic conditional autoregressive models Christopher Paciorek, Department of Statistics, University
STAT5044: Regression and Anova
 STAT5044: Regression and Anova Inyoung Kim 1 / 18 Outline 1 Logistic regression for Binary data 2 Poisson regression for Count data 2 / 18 GLM Let Y denote a binary response variable. Each observation
STAT5044: Regression and Anova Inyoung Kim 1 / 18 Outline 1 Logistic regression for Binary data 2 Poisson regression for Count data 2 / 18 GLM Let Y denote a binary response variable. Each observation
Efficient and Robust Scale Estimation
 Efficient and Robust Scale Estimation Garth Tarr, Samuel Müller and Neville Weber School of Mathematics and Statistics THE UNIVERSITY OF SYDNEY Outline Introduction and motivation The robust scale estimator
Efficient and Robust Scale Estimation Garth Tarr, Samuel Müller and Neville Weber School of Mathematics and Statistics THE UNIVERSITY OF SYDNEY Outline Introduction and motivation The robust scale estimator
This lab exercise will try to answer these questions using spatial statistics in a geographic information system (GIS) context.
 by Introduction Problem Do the patterns of forest fires change over time? Do forest fires occur in clusters, and do the clusters change over time? Is this information useful in fighting forest fires? This
by Introduction Problem Do the patterns of forest fires change over time? Do forest fires occur in clusters, and do the clusters change over time? Is this information useful in fighting forest fires? This
Bayesian Spatial Health Surveillance
 Bayesian Spatial Health Surveillance Allan Clark and Andrew Lawson University of South Carolina 1 Two important problems Clustering of disease: PART 1 Development of Space-time models Modelling vs Testing
Bayesian Spatial Health Surveillance Allan Clark and Andrew Lawson University of South Carolina 1 Two important problems Clustering of disease: PART 1 Development of Space-time models Modelling vs Testing
Mixture distributions in Exams MLC/3L and C/4
 Making sense of... Mixture distributions in Exams MLC/3L and C/4 James W. Daniel Jim Daniel s Actuarial Seminars www.actuarialseminars.com February 1, 2012 c Copyright 2012 by James W. Daniel; reproduction
Making sense of... Mixture distributions in Exams MLC/3L and C/4 James W. Daniel Jim Daniel s Actuarial Seminars www.actuarialseminars.com February 1, 2012 c Copyright 2012 by James W. Daniel; reproduction
Spatial Variation in Infant Mortality with Geographically Weighted Poisson Regression (GWPR) Approach
 Spatial Variation in Infant Mortality with Geographically Weighted Poisson Regression (GWPR) Approach Kristina Pestaria Sinaga, Manuntun Hutahaean 2, Petrus Gea 3 1, 2, 3 University of Sumatera Utara,
Spatial Variation in Infant Mortality with Geographically Weighted Poisson Regression (GWPR) Approach Kristina Pestaria Sinaga, Manuntun Hutahaean 2, Petrus Gea 3 1, 2, 3 University of Sumatera Utara,
