Structure of a Typical Digital System Data Inputs
|
|
|
- Ira Hood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ecture RT Desig Methodology Trasitio from the & Iterface to a Correspodig Block Diagram Structure of a Typical Digital System Data Iputs Datapath (Executio Uit) Data Outputs Cotrol Sigals Status Sigals Cotrol & Status Iputs Cotroller (Cotrol Uit) Cotrol & Status Outputs Hardware Desig with RT VHD Datapath Block diagram VHD code Iterface ASM chart Cotroller VHD code 3 Steps of the Desig Process 1. Text descriptio. Iterface Block diagram of the Datapath 5. Iterface divided ito the Datapath ad Cotroller 6. ASM chart of the Cotroller 7. RT VHD code of the Datapath, Cotroller, ad Top-evel Uit 8. Testbech for the Datapath, Cotroller, ad Top-evel Uit 9. Fuctioal simulatio ad debuggig 1. Sythesis ad post-sythesis simulatio 11. Implemetatio ad timig simulatio 1. Experimetal testig usig FPGA board 4 Steps of the Desig Process Itroduced i Class Today 1. Text descriptio. Iterface Block diagram of the Datapath 5. Iterface divided ito the Datapath ad Cotroller 6. ASM chart of the Cotroller 7. RT VHD code of the Datapath, Cotroller, ad Toplevel Uit 8. Testbech for the Datapath, Cotroller, ad Top-evel Uit 9. Fuctioal simulatio ad debuggig 1. Sythesis ad post-sythesis simulatio 11. Implemetatio ad timig simulatio 1. Experimetal testig usig FPGA board 5 Class Exercise 1 STATISTICS 6 1
2 Circuit Iterface o_1 = o_ = o_3 = sum = for i= to k-1 do sum = sum + di if di > o_1 the o_3 = o_ o_ = o_1 o_1 = di elseif (di > o_) the o_3 = o_ o_ = di elseif (di > o_3) the o_3 = di ed if ed for avr = sum / k 7 di go Statistics doe dout dout_mode 8 Iterface Table Port Width Meaig 1 System clock. 1 System. di Iput Data. go 1 Cotrol sigal idicatig that the first iput is ready. Active for oe clock cycle. doe 1 Sigal set to high after the output is ready. dout Output depedet o the dout_mode iput. dout_mode Cotrol sigal determiig value available at the output. : avr, 1: o_1, 1: o_, 11: o_3. STATISTICS: Solutios 9 1 di Alterative Couters +m esum e +m sum +m +m rst e1 e e rst 1 s e o_1 rst o_ 1 s3 A A>B B A A>B B gt1 gt ec e rst m i m >> m avr o_1 o_ o_ e3 dout_mode e rst o_3 A A>B B gt3 == k-1 zi dout Block diagram of the Datapath 1
3 Iterface with the divisio ito the Datapath ad Cotroller di dout_mode go Datapath gt1 gt gt3 zi e1 e e3 Cotroller Class Exercise CIPHER esum ec s s3 dout doe 13 (Rivest Cipher 6) - symmetric key block cipher Security Margi IST Report: Security Desigers: Ro Rivest, Matt Robshaw, Ray Sidey, ad Yiqu isa Yi Oe of five fialists of the cotest for the Advaced Ecryptio Stadard (AES) Cadidate algorithm i the followig other cotests: ESSIE for Europea stadards (-3) CRYPTREC for Japaese stadards (-3) 15 High Adequate Serpet Rijdael Simple MARS Twofish Complex Complexity high medium low IST Report: Software Efficiecy Ecryptio ad Decryptio Speed 3-bit processors Rijdael Mars Twofish Serpet 64-bit processors Rijdael Twofish Mars Serpet DSPs Rijdael Twofish Mars Serpet Efficiecy i hardware: FPGA Virtex 1: Speed Throughput [Mbit/s] Serpet I George Maso Uiversity Uiversity of Souther Califoria Worcester Polytechic Istitute 149 Rijdael Twofish Serpet Mars I
4 Split iput I ito four words, I3, I, I1, I, of the size of w bits each A = I3; B = I; C = I1; D=I B = B + S[] D = D + S[1] for i = 1 to r do { T = (B*(B + 1)) <<< k U = (D*(D + 1)) <<< k A = ((A T) <<< U) + S[i] C = ((C U) <<< T) + S[i + 1] (A, B, C, D) = (B, C, D, A) } A = A + S[r + ] C = C + S[r + 3] O = (A, B, C, D) otatio w: word size, e.g., w=3 (costat) k: log (w) (costat) A, B, C, D, U, T: w-bit variables I3, I, I1, I: Four w-bit words of the iput I r: umber of rouds (costat) O: output of the size of 4w bits S[j] : r+4 roud keys stored i two RAMs. Each key is a w-bit word. The first RAM stores values of S[j=i], i.e., oly roud keys with eve idices. The secod memory stores values of S[j=i+1], i.e., oly roud keys with odd idices. 19 Operatios Modular Arithmetic : XOR + : additio modulo w : subtractio modulo w * : multiplicatio modulo w X <<< Y : rotatio of X to the left by the umber of positios give i Y X >>> Y : rotatio of X to the right by the umber of positios give i Y (A, B, C, D) : Cocateatio of A, B, C, ad D mod 1 = 3 Circuit Iterface Iterface Table I write_i 4w CIPHER 4w O DOE Sj w Write_Sj j m ote: m is a size of idex j. It is a miimum iteger, such that m -1 ³ r
5 Protocol (1) A exteral circuit first loads all roud keys S[], S[1], S[],, S[r+], [r+3] to the two iteral memories of the CIPHER uit. The first memory stores values of S[j=i], i.e., oly roud keys with eve idices. The secod memory stores values of S[j=i+1], i.e. oly roud keys with odd idices. Protocol () Whe the ecryptio is completed, sigal DOE becomes active, ad the output O chages to the ew value of the ciphertext. The output O keeps the last value of the ciphertext at the output, util the ext ecryptio is completed. Before the first ecryptio is completed, this output should be equal to zero. oadig roud keys is performed usig iputs: Sj, j, write_sj,. The, the exteral circuits, loads a iput block I to the CIPHER uit, usig iputs: I, write_i,. After the iput block I is loaded to the CIPHER uit, the ecryptio starts automatically. 5 6 Assumptios r+4 clock cycles are used to load roud keys to iteral RAMs oe roud of the mai for loop of the pseudocode executes i oe clock cycle you ca access oly oe positio of each iteral memory of roud keys per clock cycle CIPHER: Buildig Blocks As a result, the ecryptio of a sigle iput block I should last r+ clock cycles. 7 8 Additio mod w XOR Multiplicatio mod w 9 3 5
6 Variable Rotatio X<<<Y CIPHER Solutios 31 Datapath Iitializatio & Mai oop 3 Datapath PostProcessig & oop Couter 33 Memories of Roud Keys Cotets 34 Datapath Memories of Roud Keys
7 Iterface with the Divisio ito the Datapath ad Cotroller Timig Aalysis Key Setup & Ecryptio otatio: T CK clock period i s M umber of ecrypted message blocks I T KeySetup[cycles] = r+4 T KeySetup[s] = (r+4) T CK T Ecryptio( M)[cycles] = (r+) M T Ecryptio( M)[s] = (r+) M T CK Timig Aalysis - Throughput otatio: T CK clock period i s M umber of ecrypted message blocks I w word size Thr Ecryptio( M)[Gbit/s] = (r+) M T CK 4 w 4 w M = (r+) TCK r & w costats, determied by the security aalysis of the cipher For the security equivalet to AES-18, r= & w=3 Timig Aalysis Critical Path T CK-mi = d R + d logic-max + t setup Critical Path a path from a output of a register to a iput of a register with the maximum value of the delay (deoted as d logic-max) d R delay of a register t setup setup time of a register T CK depedet o w, retured by the FPGA tools based o the static timig aalysis of the critical path 39 4 Setup & Hold Time of a Register Datapath Critical Path tsetup dr Setup time - the amout of time the data at the sychroous iput must be stable before the ext active edge of clock Hold time - the amout of time the data at the sychroous iput must be stable after the last active edge of clock 41 dlogic-max Critical Path marked i red 4 7
8 Sortig - Required Iterface Class Exercise 3 SORTIG Reset DataI RAdd WrIit Sort DataOut Doe S (=iitializatio 1=computatios) Rd Sortig - Required Iterface Simulatio results for the sort operatio (1) oadig memory ad startig sortig Simulatio results for the sort operatio () Completig sortig ad readig out memory Address 1 3 Before sortig Sortig - Example Durig Sortig i= i= i= i=1 i=1 i= j=1 j= j=3 j= j=3 j=3 After sortig eged: positio of memory idexed by i M i positio of memory idexed by j M j
9 [load iput data] wait for s=1 for i = to do A = Mi ; for j = i + 1 to 3 do B = M j ; if B < A the Mi = B ; Mj = A ; A = Mi ; edif ; edfor; edfor; Doe wait for s= [read output data] go to the begiig FOR k = 4 FOR ay k [load iput data] wait for s=1 for i = to k - do A = Mi ; for j = i + 1 to k 1 do B = Mj ; if B < A the Mi = B ; Mj = A ; A = Mi ; edif ; edfor; edfor; Doe wait for s= [read output data] go to the begiig 49 wait for s=1 for i= to k- do A = M i for j=i+1 to k-1 do B = M j if A > B the M i = B M j = A A = M i ed if ed for ed for Doe wait for s= go to the begiig 5 SORTIG Solutios ABMux WrIit Wr We WE CK 1 s DI DOUT Addr ADDR EA EB E CK RST Reset E CK RST Reset 1 Bout A A>B DataI Di Mij B s 1 RAdd Csel 1 i D Ei E CK Rd i j DataOut RST Reset j Ej D E CK = k- = k-1 zi +1 zj RST Reset AgtB Block diagram of the Datapath 51 Iterface divided ito the Datapath ad Cotroller DataI RAddr WrIit Rd Reset s AgtB zi Datapath zj Wr i Cotroller Ei j Ej EA EB Bout Csel DataOut Doe 53 9
Chapter 9 Computer Design Basics
 Logic ad Computer Desig Fudametals Chapter 9 Computer Desig Basics Part 1 Datapaths Overview Part 1 Datapaths Itroductio Datapath Example Arithmetic Logic Uit (ALU) Shifter Datapath Represetatio Cotrol
Logic ad Computer Desig Fudametals Chapter 9 Computer Desig Basics Part 1 Datapaths Overview Part 1 Datapaths Itroductio Datapath Example Arithmetic Logic Uit (ALU) Shifter Datapath Represetatio Cotrol
Chapter 9 Computer Design Basics
 Logic ad Computer Desig Fudametals Chapter 9 Computer Desig asics Part Datapaths Charles Kime & Thomas Kamiski 008 Pearso Educatio, Ic. (Hyperliks are active i View Show mode) Overview Part Datapaths Itroductio
Logic ad Computer Desig Fudametals Chapter 9 Computer Desig asics Part Datapaths Charles Kime & Thomas Kamiski 008 Pearso Educatio, Ic. (Hyperliks are active i View Show mode) Overview Part Datapaths Itroductio
Load. Load. Load 1 0 MUX B. MB select. Bus A. A B n H select S 2:0 C S. G select 4 V C N Z. unit (ALU) G. Zero Detect.
 9- Write D data Load eable A address A select B address B select Load R 2 2 Load Load R R2 UX 2 3 UX 2 3 2 3 Decoder D address 2 Costat i Destiatio select 28 Pearso Educatio, Ic.. orris ao & Charles R.
9- Write D data Load eable A address A select B address B select Load R 2 2 Load Load R R2 UX 2 3 UX 2 3 2 3 Decoder D address 2 Costat i Destiatio select 28 Pearso Educatio, Ic.. orris ao & Charles R.
EE260: Digital Design, Spring n Binary Addition. n Complement forms. n Subtraction. n Multiplication. n Inputs: A 0, B 0. n Boolean equations:
 EE260: Digital Desig, Sprig 2018 EE 260: Itroductio to Digital Desig Arithmetic Biary Additio Complemet forms Subtractio Multiplicatio Overview Yao Zheg Departmet of Electrical Egieerig Uiversity of Hawaiʻi
EE260: Digital Desig, Sprig 2018 EE 260: Itroductio to Digital Desig Arithmetic Biary Additio Complemet forms Subtractio Multiplicatio Overview Yao Zheg Departmet of Electrical Egieerig Uiversity of Hawaiʻi
Fig. 7-6 Single Bus versus Dedicated Multiplexers
 7- Select SSS2 LLL2 LLL2 S 2 to MUX R R Select S 2 to MUX R S S 3 to MUX 2 us R S 2 to MUX R2 R2 (a) Dedicated multiplexers (b) Sigle us Fig. 7-6 Sigle us versus Dedicated Multiplexers 2 Pretice Hall,
7- Select SSS2 LLL2 LLL2 S 2 to MUX R R Select S 2 to MUX R S S 3 to MUX 2 us R S 2 to MUX R2 R2 (a) Dedicated multiplexers (b) Sigle us Fig. 7-6 Sigle us versus Dedicated Multiplexers 2 Pretice Hall,
Algorithm Analysis. Chapter 3
 Data Structures Dr Ahmed Rafat Abas Computer Sciece Dept, Faculty of Computer ad Iformatio, Zagazig Uiversity arabas@zu.edu.eg http://www.arsaliem.faculty.zu.edu.eg/ Algorithm Aalysis Chapter 3 3. Itroductio
Data Structures Dr Ahmed Rafat Abas Computer Sciece Dept, Faculty of Computer ad Iformatio, Zagazig Uiversity arabas@zu.edu.eg http://www.arsaliem.faculty.zu.edu.eg/ Algorithm Aalysis Chapter 3 3. Itroductio
Design and Analysis of ALGORITHM (Topic 2)
 DR. Gatot F. Hertoo, MSc. Desig ad Aalysis of ALGORITHM (Topic 2) Algorithms + Data Structures = Programs Lessos Leared 1 Our Machie Model: Assumptios Geeric Radom Access Machie (RAM) Executes operatios
DR. Gatot F. Hertoo, MSc. Desig ad Aalysis of ALGORITHM (Topic 2) Algorithms + Data Structures = Programs Lessos Leared 1 Our Machie Model: Assumptios Geeric Radom Access Machie (RAM) Executes operatios
A Block Cipher Using Linear Congruences
 Joural of Computer Sciece 3 (7): 556-560, 2007 ISSN 1549-3636 2007 Sciece Publicatios A Block Cipher Usig Liear Cogrueces 1 V.U.K. Sastry ad 2 V. Jaaki 1 Academic Affairs, Sreeidhi Istitute of Sciece &
Joural of Computer Sciece 3 (7): 556-560, 2007 ISSN 1549-3636 2007 Sciece Publicatios A Block Cipher Usig Liear Cogrueces 1 V.U.K. Sastry ad 2 V. Jaaki 1 Academic Affairs, Sreeidhi Istitute of Sciece &
Advanced Course of Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Differet complexity measures Advaced Course of Algorithm Desig ad Aalysis Asymptotic complexity Big-Oh otatio Properties of O otatio Aalysis of simple algorithms A algorithm may may have differet executio
Differet complexity measures Advaced Course of Algorithm Desig ad Aalysis Asymptotic complexity Big-Oh otatio Properties of O otatio Aalysis of simple algorithms A algorithm may may have differet executio
Test One (Answer Key)
 CS395/Ma395 (Sprig 2005) Test Oe Name: Page 1 Test Oe (Aswer Key) CS395/Ma395: Aalysis of Algorithms This is a closed book, closed otes, 70 miute examiatio. It is worth 100 poits. There are twelve (12)
CS395/Ma395 (Sprig 2005) Test Oe Name: Page 1 Test Oe (Aswer Key) CS395/Ma395: Aalysis of Algorithms This is a closed book, closed otes, 70 miute examiatio. It is worth 100 poits. There are twelve (12)
CHAPTER XI DATAPATH ELEMENTS
 CHAPTER XI- CHAPTER XI CHAPTER XI READ REE-DOC ON COURSE WEBPAGE CHAPTER XI-2 INTRODUCTION -INTRODUCTION So far we have discussed may small compoets ad buildig blocks. Oe fial step i our buildig blocks
CHAPTER XI- CHAPTER XI CHAPTER XI READ REE-DOC ON COURSE WEBPAGE CHAPTER XI-2 INTRODUCTION -INTRODUCTION So far we have discussed may small compoets ad buildig blocks. Oe fial step i our buildig blocks
DESCRIPTION OF THE SYSTEM
 Sychroous-Serial Iterface for absolute Ecoders SSI 1060 BE 10 / 01 DESCRIPTION OF THE SYSTEM TWK-ELEKTRONIK GmbH D-001 Düsseldorf PB 1006 Heirichstr. Tel +9/11/6067 Fax +9/11/6770 e-mail: ifo@twk.de Page
Sychroous-Serial Iterface for absolute Ecoders SSI 1060 BE 10 / 01 DESCRIPTION OF THE SYSTEM TWK-ELEKTRONIK GmbH D-001 Düsseldorf PB 1006 Heirichstr. Tel +9/11/6067 Fax +9/11/6770 e-mail: ifo@twk.de Page
CS 270 Algorithms. Oliver Kullmann. Growth of Functions. Divide-and- Conquer Min-Max- Problem. Tutorial. Reading from CLRS for week 2
 Geeral remarks Week 2 1 Divide ad First we cosider a importat tool for the aalysis of algorithms: Big-Oh. The we itroduce a importat algorithmic paradigm:. We coclude by presetig ad aalysig two examples.
Geeral remarks Week 2 1 Divide ad First we cosider a importat tool for the aalysis of algorithms: Big-Oh. The we itroduce a importat algorithmic paradigm:. We coclude by presetig ad aalysig two examples.
1. ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS IN OBSERVER'S MATHEMATICS
 1. ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS IN OBSERVER'S MATHEMATICS We cosider a ite well-ordered system of observers, where each observer sees the real umbers as the set of all iite decimal fractios. The observers are
1. ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS IN OBSERVER'S MATHEMATICS We cosider a ite well-ordered system of observers, where each observer sees the real umbers as the set of all iite decimal fractios. The observers are
ECE-S352 Introduction to Digital Signal Processing Lecture 3A Direct Solution of Difference Equations
 ECE-S352 Itroductio to Digital Sigal Processig Lecture 3A Direct Solutio of Differece Equatios Discrete Time Systems Described by Differece Equatios Uit impulse (sample) respose h() of a DT system allows
ECE-S352 Itroductio to Digital Sigal Processig Lecture 3A Direct Solutio of Differece Equatios Discrete Time Systems Described by Differece Equatios Uit impulse (sample) respose h() of a DT system allows
Oblivious Transfer using Elliptic Curves
 Oblivious Trasfer usig Elliptic Curves bhishek Parakh Louisiaa State Uiversity, ato Rouge, L May 4, 006 bstract: This paper proposes a algorithm for oblivious trasfer usig elliptic curves lso, we preset
Oblivious Trasfer usig Elliptic Curves bhishek Parakh Louisiaa State Uiversity, ato Rouge, L May 4, 006 bstract: This paper proposes a algorithm for oblivious trasfer usig elliptic curves lso, we preset
End-of-Year Contest. ERHS Math Club. May 5, 2009
 Ed-of-Year Cotest ERHS Math Club May 5, 009 Problem 1: There are 9 cois. Oe is fake ad weighs a little less tha the others. Fid the fake coi by weighigs. Solutio: Separate the 9 cois ito 3 groups (A, B,
Ed-of-Year Cotest ERHS Math Club May 5, 009 Problem 1: There are 9 cois. Oe is fake ad weighs a little less tha the others. Fid the fake coi by weighigs. Solutio: Separate the 9 cois ito 3 groups (A, B,
A New Solution Method for the Finite-Horizon Discrete-Time EOQ Problem
 This is the Pre-Published Versio. A New Solutio Method for the Fiite-Horizo Discrete-Time EOQ Problem Chug-Lu Li Departmet of Logistics The Hog Kog Polytechic Uiversity Hug Hom, Kowloo, Hog Kog Phoe: +852-2766-7410
This is the Pre-Published Versio. A New Solutio Method for the Fiite-Horizo Discrete-Time EOQ Problem Chug-Lu Li Departmet of Logistics The Hog Kog Polytechic Uiversity Hug Hom, Kowloo, Hog Kog Phoe: +852-2766-7410
ITEC 360 Data Structures and Analysis of Algorithms Spring for n 1
 ITEC 360 Data Structures ad Aalysis of Algorithms Sprig 006 1. Prove that f () = 60 + 5 + 1 is Θ ( ). 60 + 5 + 1 60 + 5 + = 66 for 1 Take C 1 = 66 f () = 60 + 5 + 1 is O( ) Sice 60 + 5 + 1 60 for 1 If
ITEC 360 Data Structures ad Aalysis of Algorithms Sprig 006 1. Prove that f () = 60 + 5 + 1 is Θ ( ). 60 + 5 + 1 60 + 5 + = 66 for 1 Take C 1 = 66 f () = 60 + 5 + 1 is O( ) Sice 60 + 5 + 1 60 for 1 If
CSI 5163 (95.573) ALGORITHM ANALYSIS AND DESIGN
 CSI 5163 (95.573) ALGORITHM ANALYSIS AND DESIGN CSI 5163 (95.5703) ALGORITHM ANALYSIS AND DESIGN (3 cr.) (T) Topics of curret iterest i the desig ad aalysis of computer algorithms for graphtheoretical
CSI 5163 (95.573) ALGORITHM ANALYSIS AND DESIGN CSI 5163 (95.5703) ALGORITHM ANALYSIS AND DESIGN (3 cr.) (T) Topics of curret iterest i the desig ad aalysis of computer algorithms for graphtheoretical
Hashing. Algorithm : Design & Analysis [09]
![Hashing. Algorithm : Design & Analysis [09] Hashing. Algorithm : Design & Analysis [09]](/thumbs/82/84955480.jpg) Hashig Algorithm : Desig & Aalysis [09] I the last class Implemetig Dictioary ADT Defiitio of red-black tree Black height Isertio ito a red-black tree Deletio from a red-black tree Hashig Hashig Collisio
Hashig Algorithm : Desig & Aalysis [09] I the last class Implemetig Dictioary ADT Defiitio of red-black tree Black height Isertio ito a red-black tree Deletio from a red-black tree Hashig Hashig Collisio
Generic datapath. Generic datapath architecture. Register file. Register file. Calcolatori Elettronici e Sistemi Operativi.
 alcolatori Elettroici e Sistei Operativi Geeric datapath architecture Set of registers Geeric datapath uber, size. addressig R[0], R[1],... Set of operatios arithetic, logic, shift Addressig (uber of operads,
alcolatori Elettroici e Sistei Operativi Geeric datapath architecture Set of registers Geeric datapath uber, size. addressig R[0], R[1],... Set of operatios arithetic, logic, shift Addressig (uber of operads,
6.003 Homework #3 Solutions
 6.00 Homework # Solutios Problems. Complex umbers a. Evaluate the real ad imagiary parts of j j. π/ Real part = Imagiary part = 0 e Euler s formula says that j = e jπ/, so jπ/ j π/ j j = e = e. Thus the
6.00 Homework # Solutios Problems. Complex umbers a. Evaluate the real ad imagiary parts of j j. π/ Real part = Imagiary part = 0 e Euler s formula says that j = e jπ/, so jπ/ j π/ j j = e = e. Thus the
Model of Computation and Runtime Analysis
 Model of Computatio ad Rutime Aalysis Model of Computatio Model of Computatio Specifies Set of operatios Cost of operatios (ot ecessarily time) Examples Turig Machie Radom Access Machie (RAM) PRAM Map
Model of Computatio ad Rutime Aalysis Model of Computatio Model of Computatio Specifies Set of operatios Cost of operatios (ot ecessarily time) Examples Turig Machie Radom Access Machie (RAM) PRAM Map
7. Modern Techniques. Data Encryption Standard (DES)
 7. Moder Techiques. Data Ecryptio Stadard (DES) The objective of this chapter is to illustrate the priciples of moder covetioal ecryptio. For this purpose, we focus o the most widely used covetioal ecryptio
7. Moder Techiques. Data Ecryptio Stadard (DES) The objective of this chapter is to illustrate the priciples of moder covetioal ecryptio. For this purpose, we focus o the most widely used covetioal ecryptio
Fortgeschrittene Datenstrukturen Vorlesung 11
 Fortgeschrittee Datestruture Vorlesug 11 Schriftführer: Marti Weider 19.01.2012 1 Succict Data Structures (ctd.) 1.1 Select-Queries A slightly differet approach, compared to ra, is used for select. B represets
Fortgeschrittee Datestruture Vorlesug 11 Schriftführer: Marti Weider 19.01.2012 1 Succict Data Structures (ctd.) 1.1 Select-Queries A slightly differet approach, compared to ra, is used for select. B represets
Lecture 12: Spiral: Domain Specific HLS. James C. Hoe Department of ECE Carnegie Mellon University
 8 643 Lecture : Spiral: Domai Specific HLS James C. Hoe Departmet of ECE Caregie Mello Uiversity 8 643 F7 L S, James C. Hoe, CMU/ECE/CALCM, 07 Houseeepig Your goal today: see a eample of really highlevel
8 643 Lecture : Spiral: Domai Specific HLS James C. Hoe Departmet of ECE Caregie Mello Uiversity 8 643 F7 L S, James C. Hoe, CMU/ECE/CALCM, 07 Houseeepig Your goal today: see a eample of really highlevel
Inverse Matrix. A meaning that matrix B is an inverse of matrix A.
 Iverse Matrix Two square matrices A ad B of dimesios are called iverses to oe aother if the followig holds, AB BA I (11) The otio is dual but we ofte write 1 B A meaig that matrix B is a iverse of matrix
Iverse Matrix Two square matrices A ad B of dimesios are called iverses to oe aother if the followig holds, AB BA I (11) The otio is dual but we ofte write 1 B A meaig that matrix B is a iverse of matrix
Arithmetic Circuits. (Part I) Randy H. Katz University of California, Berkeley. Spring 2007
 rithmetic Circuits (Part I) Rady H. Katz Uiversity of Califoria, erkeley prig 27 Lecture #23: rithmetic Circuits- Motivatio rithmetic circuits are excellet examples of comb. logic desig Time vs. pace Trade-offs
rithmetic Circuits (Part I) Rady H. Katz Uiversity of Califoria, erkeley prig 27 Lecture #23: rithmetic Circuits- Motivatio rithmetic circuits are excellet examples of comb. logic desig Time vs. pace Trade-offs
4.3 Growth Rates of Solutions to Recurrences
 4.3. GROWTH RATES OF SOLUTIONS TO RECURRENCES 81 4.3 Growth Rates of Solutios to Recurreces 4.3.1 Divide ad Coquer Algorithms Oe of the most basic ad powerful algorithmic techiques is divide ad coquer.
4.3. GROWTH RATES OF SOLUTIONS TO RECURRENCES 81 4.3 Growth Rates of Solutios to Recurreces 4.3.1 Divide ad Coquer Algorithms Oe of the most basic ad powerful algorithmic techiques is divide ad coquer.
Model of Computation and Runtime Analysis
 Model of Computatio ad Rutime Aalysis Model of Computatio Model of Computatio Specifies Set of operatios Cost of operatios (ot ecessarily time) Examples Turig Machie Radom Access Machie (RAM) PRAM Map
Model of Computatio ad Rutime Aalysis Model of Computatio Model of Computatio Specifies Set of operatios Cost of operatios (ot ecessarily time) Examples Turig Machie Radom Access Machie (RAM) PRAM Map
Review of Elementary Cryptography. For more material, see my notes of CSE 5351, available on my webpage
 Review of Elemetary Cryptography For more material, see my otes of CSE 5351, available o my webpage Outlie Security (CPA, CCA, sematic security, idistiguishability) RSA ElGamal Homomorphic ecryptio 2 Two
Review of Elemetary Cryptography For more material, see my otes of CSE 5351, available o my webpage Outlie Security (CPA, CCA, sematic security, idistiguishability) RSA ElGamal Homomorphic ecryptio 2 Two
Parallel Vector Algorithms David A. Padua
 Parallel Vector Algorithms 1 of 32 Itroductio Next, we study several algorithms where parallelism ca be easily expressed i terms of array operatios. We will use Fortra 90 to represet these algorithms.
Parallel Vector Algorithms 1 of 32 Itroductio Next, we study several algorithms where parallelism ca be easily expressed i terms of array operatios. We will use Fortra 90 to represet these algorithms.
ECE 308 Discrete-Time Signals and Systems
 ECE 38-5 ECE 38 Discrete-Time Sigals ad Systems Z. Aliyazicioglu Electrical ad Computer Egieerig Departmet Cal Poly Pomoa ECE 38-5 1 Additio, Multiplicatio, ad Scalig of Sequeces Amplitude Scalig: (A Costat
ECE 38-5 ECE 38 Discrete-Time Sigals ad Systems Z. Aliyazicioglu Electrical ad Computer Egieerig Departmet Cal Poly Pomoa ECE 38-5 1 Additio, Multiplicatio, ad Scalig of Sequeces Amplitude Scalig: (A Costat
Overview EECS Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Lec 15 Addition, Subtraction, and Negative Numbers. Positional Notation
 Overview EEC 5 Compoets ad Desig Techiques for Digital ystems Lec 5 dditio, ubtractio, ad Negative Numbers David Culler Electrical Egieerig ad Computer cieces Uiversity of Califoria, erkeley Recall basic
Overview EEC 5 Compoets ad Desig Techiques for Digital ystems Lec 5 dditio, ubtractio, ad Negative Numbers David Culler Electrical Egieerig ad Computer cieces Uiversity of Califoria, erkeley Recall basic
Message Authentication Codes. Reading: Chapter 4 of Katz & Lindell
 Message Autheticatio Codes Readig: Chapter 4 of Katz & Lidell 1 Message autheticatio Bob receives a message m from Alice, he wats to ow (Data origi autheticatio) whether the message was really set by Alice.
Message Autheticatio Codes Readig: Chapter 4 of Katz & Lidell 1 Message autheticatio Bob receives a message m from Alice, he wats to ow (Data origi autheticatio) whether the message was really set by Alice.
EE260: Digital Design, Spring n MUX Gate n Rudimentary functions n Binary Decoders. n Binary Encoders n Priority Encoders
 EE260: Digital Desig, Sprig 2018 EE 260: Itroductio to Digital Desig MUXs, Ecoders, Decoders Yao Zheg Departmet of Electrical Egieerig Uiversity of Hawaiʻi at Māoa Overview of Ecoder ad Decoder MUX Gate
EE260: Digital Desig, Sprig 2018 EE 260: Itroductio to Digital Desig MUXs, Ecoders, Decoders Yao Zheg Departmet of Electrical Egieerig Uiversity of Hawaiʻi at Māoa Overview of Ecoder ad Decoder MUX Gate
Arithmetic Circuits. (Part I) Randy H. Katz University of California, Berkeley. Spring Time vs. Space Trade-offs. Arithmetic Logic Units
 rithmetic rcuits (art I) Rady H. Katz Uiversity of Califoria, erkeley otivatio rithmetic circuits are excellet examples of comb. logic desig Time vs. pace Trade-offs Doig thigs fast requires more logic
rithmetic rcuits (art I) Rady H. Katz Uiversity of Califoria, erkeley otivatio rithmetic circuits are excellet examples of comb. logic desig Time vs. pace Trade-offs Doig thigs fast requires more logic
Lecture 11: Pseudorandom functions
 COM S 6830 Cryptography Oct 1, 2009 Istructor: Rafael Pass 1 Recap Lecture 11: Pseudoradom fuctios Scribe: Stefao Ermo Defiitio 1 (Ge, Ec, Dec) is a sigle message secure ecryptio scheme if for all uppt
COM S 6830 Cryptography Oct 1, 2009 Istructor: Rafael Pass 1 Recap Lecture 11: Pseudoradom fuctios Scribe: Stefao Ermo Defiitio 1 (Ge, Ec, Dec) is a sigle message secure ecryptio scheme if for all uppt
4.1 Sigma Notation and Riemann Sums
 0 the itegral. Sigma Notatio ad Riema Sums Oe strategy for calculatig the area of a regio is to cut the regio ito simple shapes, calculate the area of each simple shape, ad the add these smaller areas
0 the itegral. Sigma Notatio ad Riema Sums Oe strategy for calculatig the area of a regio is to cut the regio ito simple shapes, calculate the area of each simple shape, ad the add these smaller areas
OPTIMAL ALGORITHMS -- SUPPLEMENTAL NOTES
 OPTIMAL ALGORITHMS -- SUPPLEMENTAL NOTES Peter M. Maurer Why Hashig is θ(). As i biary search, hashig assumes that keys are stored i a array which is idexed by a iteger. However, hashig attempts to bypass
OPTIMAL ALGORITHMS -- SUPPLEMENTAL NOTES Peter M. Maurer Why Hashig is θ(). As i biary search, hashig assumes that keys are stored i a array which is idexed by a iteger. However, hashig attempts to bypass
Basic Sets. Functions. MTH299 - Examples. Example 1. Let S = {1, {2, 3}, 4}. Indicate whether each statement is true or false. (a) S = 4. (e) 2 S.
 Basic Sets Example 1. Let S = {1, {2, 3}, 4}. Idicate whether each statemet is true or false. (a) S = 4 (b) {1} S (c) {2, 3} S (d) {1, 4} S (e) 2 S. (f) S = {1, 4, {2, 3}} (g) S Example 2. Compute the
Basic Sets Example 1. Let S = {1, {2, 3}, 4}. Idicate whether each statemet is true or false. (a) S = 4 (b) {1} S (c) {2, 3} S (d) {1, 4} S (e) 2 S. (f) S = {1, 4, {2, 3}} (g) S Example 2. Compute the
Applications of Distributed Arithmetic to Digital Signal Processing: A Tutorial Review
 pplicatios of Distriuted rithmetic to Digital Sigal Processig: Tutorial Review Ref: Staley. White, pplicatios of Distriuted rithmetic to Digital Sigal Processig: Tutorial Review, IEEE SSP Magazie, July,
pplicatios of Distriuted rithmetic to Digital Sigal Processig: Tutorial Review Ref: Staley. White, pplicatios of Distriuted rithmetic to Digital Sigal Processig: Tutorial Review, IEEE SSP Magazie, July,
COMPARISON OF FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF THE MOD M REDUCTION
 Lati America Applied Research 37:93-97 (2007) COMPARISON OF FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF THE MOD M REDUCTION J-P. DESCHAMPS ad G. SUTTER Escola Tècica Superior d Egiyeria, Uiversitat Rovira i Virgili, Tarragoa,
Lati America Applied Research 37:93-97 (2007) COMPARISON OF FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF THE MOD M REDUCTION J-P. DESCHAMPS ad G. SUTTER Escola Tècica Superior d Egiyeria, Uiversitat Rovira i Virgili, Tarragoa,
Lecture 2: Uncomputability and the Haling Problem
 CSE 200 Computability ad Complexity Wedesday, April 3, 2013 Lecture 2: Ucomputability ad the Halig Problem Istructor: Professor Shachar Lovett Scribe: Dogcai She 1 The Uiversal Turig Machie I the last
CSE 200 Computability ad Complexity Wedesday, April 3, 2013 Lecture 2: Ucomputability ad the Halig Problem Istructor: Professor Shachar Lovett Scribe: Dogcai She 1 The Uiversal Turig Machie I the last
Analysis of Algorithms. Introduction. Contents
 Itroductio The focus of this module is mathematical aspects of algorithms. Our mai focus is aalysis of algorithms, which meas evaluatig efficiecy of algorithms by aalytical ad mathematical methods. We
Itroductio The focus of this module is mathematical aspects of algorithms. Our mai focus is aalysis of algorithms, which meas evaluatig efficiecy of algorithms by aalytical ad mathematical methods. We
6.111 Lecture 6 Today: 1.Blocking vs. non-blocking assignments 2.Single clock synchronous circuits 3.Finite State Machines
 6. Lecture 6 Today:.Blockig vs. o-blockig assigmets 2.Sigle clock sychroous circuits 3.Fiite State Machies 6. Fall 25 Lecture 6, Slide I. Blockig vs. Noblockig Assigmets Coceptual eed for two kids of assigmet
6. Lecture 6 Today:.Blockig vs. o-blockig assigmets 2.Sigle clock sychroous circuits 3.Fiite State Machies 6. Fall 25 Lecture 6, Slide I. Blockig vs. Noblockig Assigmets Coceptual eed for two kids of assigmet
CSI 2101 Discrete Structures Winter Homework Assignment #4 (100 points, weight 5%) Due: Thursday, April 5, at 1:00pm (in lecture)
 CSI 101 Discrete Structures Witer 01 Prof. Lucia Moura Uiversity of Ottawa Homework Assigmet #4 (100 poits, weight %) Due: Thursday, April, at 1:00pm (i lecture) Program verificatio, Recurrece Relatios
CSI 101 Discrete Structures Witer 01 Prof. Lucia Moura Uiversity of Ottawa Homework Assigmet #4 (100 poits, weight %) Due: Thursday, April, at 1:00pm (i lecture) Program verificatio, Recurrece Relatios
Ch3. Asymptotic Notation
 Ch. Asymptotic Notatio copyright 006 Preview of Chapters Chapter How to aalyze the space ad time complexities of program Chapter Review asymptotic otatios such as O, Ω, Θ, o for simplifyig the aalysis
Ch. Asymptotic Notatio copyright 006 Preview of Chapters Chapter How to aalyze the space ad time complexities of program Chapter Review asymptotic otatios such as O, Ω, Θ, o for simplifyig the aalysis
Dr. Maddah ENMG 617 EM Statistics 11/26/12. Multiple Regression (2) (Chapter 15, Hines)
 Dr Maddah NMG 617 M Statistics 11/6/1 Multiple egressio () (Chapter 15, Hies) Test for sigificace of regressio This is a test to determie whether there is a liear relatioship betwee the depedet variable
Dr Maddah NMG 617 M Statistics 11/6/1 Multiple egressio () (Chapter 15, Hies) Test for sigificace of regressio This is a test to determie whether there is a liear relatioship betwee the depedet variable
n m CHAPTER 3 RATIONAL EXPONENTS AND RADICAL FUNCTIONS 3-1 Evaluate n th Roots and Use Rational Exponents Real nth Roots of a n th Root of a
 CHAPTER RATIONAL EXPONENTS AND RADICAL FUNCTIONS Big IDEAS: 1) Usig ratioal expoets ) Performig fuctio operatios ad fidig iverse fuctios ) Graphig radical fuctios ad solvig radical equatios Sectio: Essetial
CHAPTER RATIONAL EXPONENTS AND RADICAL FUNCTIONS Big IDEAS: 1) Usig ratioal expoets ) Performig fuctio operatios ad fidig iverse fuctios ) Graphig radical fuctios ad solvig radical equatios Sectio: Essetial
Olli Simula T / Chapter 1 3. Olli Simula T / Chapter 1 5
 Sigals ad Systems Sigals ad Systems Sigals are variables that carry iformatio Systemstake sigals as iputs ad produce sigals as outputs The course deals with the passage of sigals through systems T-6.4
Sigals ad Systems Sigals ad Systems Sigals are variables that carry iformatio Systemstake sigals as iputs ad produce sigals as outputs The course deals with the passage of sigals through systems T-6.4
Statistical Properties of the Square Map Modulo a Power of Two
 Statistical Properties of the Square Map Modulo a Power of Two S. M. Dehavi, A. Mahmoodi Rishakai, M. R. Mirzee Shamsabad 3, Hamidreza Maimai, Eiollah Pasha Kharazmi Uiversity, Faculty of Mathematical
Statistical Properties of the Square Map Modulo a Power of Two S. M. Dehavi, A. Mahmoodi Rishakai, M. R. Mirzee Shamsabad 3, Hamidreza Maimai, Eiollah Pasha Kharazmi Uiversity, Faculty of Mathematical
Data Structures Lecture 9
 Fall 2017 Fag Yu Software Security Lab. Dept. Maagemet Iformatio Systems, Natioal Chegchi Uiversity Data Structures Lecture 9 Midterm o Dec. 7 (9:10-12:00am, 106) Lec 1-9, TextBook Ch1-8, 11,12 How to
Fall 2017 Fag Yu Software Security Lab. Dept. Maagemet Iformatio Systems, Natioal Chegchi Uiversity Data Structures Lecture 9 Midterm o Dec. 7 (9:10-12:00am, 106) Lec 1-9, TextBook Ch1-8, 11,12 How to
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
 6.0/6.3: Probabilistic Systems Aalysis (Fall 00) Problem Set 8: Solutios. (a) We cosider a Markov chai with states 0,,, 3,, 5, where state i idicates that there are i shoes available at the frot door i
6.0/6.3: Probabilistic Systems Aalysis (Fall 00) Problem Set 8: Solutios. (a) We cosider a Markov chai with states 0,,, 3,, 5, where state i idicates that there are i shoes available at the frot door i
Principle Of Superposition
 ecture 5: PREIMINRY CONCEP O RUCUR NYI Priciple Of uperpositio Mathematically, the priciple of superpositio is stated as ( a ) G( a ) G( ) G a a or for a liear structural system, the respose at a give
ecture 5: PREIMINRY CONCEP O RUCUR NYI Priciple Of uperpositio Mathematically, the priciple of superpositio is stated as ( a ) G( a ) G( ) G a a or for a liear structural system, the respose at a give
Quantum Computing Lecture 7. Quantum Factoring
 Quatum Computig Lecture 7 Quatum Factorig Maris Ozols Quatum factorig A polyomial time quatum algorithm for factorig umbers was published by Peter Shor i 1994. Polyomial time meas that the umber of gates
Quatum Computig Lecture 7 Quatum Factorig Maris Ozols Quatum factorig A polyomial time quatum algorithm for factorig umbers was published by Peter Shor i 1994. Polyomial time meas that the umber of gates
Summary: Congruences. j=1. 1 Here we use the Mathematica syntax for the function. In Maple worksheets, the function
 Summary: Cogrueces j whe divided by, ad determiig the additive order of a iteger mod. As described i the Prelab sectio, cogrueces ca be thought of i terms of coutig with rows, ad for some questios this
Summary: Cogrueces j whe divided by, ad determiig the additive order of a iteger mod. As described i the Prelab sectio, cogrueces ca be thought of i terms of coutig with rows, ad for some questios this
Discrete-Time Signals and Systems. Discrete-Time Signals and Systems. Signal Symmetry. Elementary Discrete-Time Signals.
 Discrete-ime Sigals ad Systems Discrete-ime Sigals ad Systems Dr. Deepa Kudur Uiversity of oroto Referece: Sectios. -.5 of Joh G. Proakis ad Dimitris G. Maolakis, Digital Sigal Processig: Priciples, Algorithms,
Discrete-ime Sigals ad Systems Discrete-ime Sigals ad Systems Dr. Deepa Kudur Uiversity of oroto Referece: Sectios. -.5 of Joh G. Proakis ad Dimitris G. Maolakis, Digital Sigal Processig: Priciples, Algorithms,
CS161 Design and Analysis of Algorithms. Administrative
 CS161 Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms Da Boeh 1 Admiistrative Lecture 1, April 3, 1 Web page http://theory.staford.edu/~dabo/cs161» Hadouts» Aoucemets» Late breakig ews Gradig ad course requiremets» Midterm/fial/hw»
CS161 Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms Da Boeh 1 Admiistrative Lecture 1, April 3, 1 Web page http://theory.staford.edu/~dabo/cs161» Hadouts» Aoucemets» Late breakig ews Gradig ad course requiremets» Midterm/fial/hw»
Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms Probabilistic aalysis ad Radomized algorithms Referece: CLRS Chapter 5 Topics: Hirig problem Idicatio radom variables Radomized algorithms Huo Hogwei 1 The hirig problem
Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms Probabilistic aalysis ad Radomized algorithms Referece: CLRS Chapter 5 Topics: Hirig problem Idicatio radom variables Radomized algorithms Huo Hogwei 1 The hirig problem
Mechatronics. Time Response & Frequency Response 2 nd -Order Dynamic System 2-Pole, Low-Pass, Active Filter
 Time Respose & Frequecy Respose d -Order Dyamic System -Pole, Low-Pass, Active Filter R 4 R 7 C 5 e i R 1 C R 3 - + R 6 - + e out Assigmet: Perform a Complete Dyamic System Ivestigatio of the Two-Pole,
Time Respose & Frequecy Respose d -Order Dyamic System -Pole, Low-Pass, Active Filter R 4 R 7 C 5 e i R 1 C R 3 - + R 6 - + e out Assigmet: Perform a Complete Dyamic System Ivestigatio of the Two-Pole,
Discrete-Time Systems, LTI Systems, and Discrete-Time Convolution
 EEL5: Discrete-Time Sigals ad Systems. Itroductio I this set of otes, we begi our mathematical treatmet of discrete-time s. As show i Figure, a discrete-time operates or trasforms some iput sequece x [
EEL5: Discrete-Time Sigals ad Systems. Itroductio I this set of otes, we begi our mathematical treatmet of discrete-time s. As show i Figure, a discrete-time operates or trasforms some iput sequece x [
Numerical Methods in Fourier Series Applications
 Numerical Methods i Fourier Series Applicatios Recall that the basic relatios i usig the Trigoometric Fourier Series represetatio were give by f ( x) a o ( a x cos b x si ) () where the Fourier coefficiets
Numerical Methods i Fourier Series Applicatios Recall that the basic relatios i usig the Trigoometric Fourier Series represetatio were give by f ( x) a o ( a x cos b x si ) () where the Fourier coefficiets
ENGI 4421 Probability and Statistics Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 1 Solutions Descriptive Statistics. None at all!
 ENGI 44 Probability ad Statistics Faculty of Egieerig ad Applied Sciece Problem Set Solutios Descriptive Statistics. If, i the set of values {,, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 } a error causes the value 5 to be replaced
ENGI 44 Probability ad Statistics Faculty of Egieerig ad Applied Sciece Problem Set Solutios Descriptive Statistics. If, i the set of values {,, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 } a error causes the value 5 to be replaced
Lecture 3: Divide and Conquer: Fast Fourier Transform
 Lecture 3: Divide ad Coquer: Fast Fourier Trasform Polyomial Operatios vs. Represetatios Divide ad Coquer Algorithm Collapsig Samples / Roots of Uity FFT, IFFT, ad Polyomial Multiplicatio Polyomial operatios
Lecture 3: Divide ad Coquer: Fast Fourier Trasform Polyomial Operatios vs. Represetatios Divide ad Coquer Algorithm Collapsig Samples / Roots of Uity FFT, IFFT, ad Polyomial Multiplicatio Polyomial operatios
Last time, we talked about how Equation (1) can simulate Equation (2). We asserted that Equation (2) can also simulate Equation (1).
 6896 Quatum Complexity Theory Sept 23, 2008 Lecturer: Scott Aaroso Lecture 6 Last Time: Quatum Error-Correctio Quatum Query Model Deutsch-Jozsa Algorithm (Computes x y i oe query) Today: Berstei-Vazirii
6896 Quatum Complexity Theory Sept 23, 2008 Lecturer: Scott Aaroso Lecture 6 Last Time: Quatum Error-Correctio Quatum Query Model Deutsch-Jozsa Algorithm (Computes x y i oe query) Today: Berstei-Vazirii
Algebra II Notes Unit Seven: Powers, Roots, and Radicals
 Syllabus Objectives: 7. The studets will use properties of ratioal epoets to simplify ad evaluate epressios. 7.8 The studet will solve equatios cotaiig radicals or ratioal epoets. b a, the b is the radical.
Syllabus Objectives: 7. The studets will use properties of ratioal epoets to simplify ad evaluate epressios. 7.8 The studet will solve equatios cotaiig radicals or ratioal epoets. b a, the b is the radical.
Chemical Kinetics CHAPTER 14. Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter, 6 th edition By Jesperson, Brady, & Hyslop. CHAPTER 14 Chemical Kinetics
 Chemical Kietics CHAPTER 14 Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter, 6 th editio By Jesperso, Brady, & Hyslop CHAPTER 14 Chemical Kietics Learig Objectives: Factors Affectig Reactio Rate: o Cocetratio
Chemical Kietics CHAPTER 14 Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter, 6 th editio By Jesperso, Brady, & Hyslop CHAPTER 14 Chemical Kietics Learig Objectives: Factors Affectig Reactio Rate: o Cocetratio
Annotations to the assignments and the solution sheet. Note the following points
 WS 26/7 Trial Exam: Fudametals of Computer Egieerig Seite: Aotatios to the assigmets ad the solutio sheet This is a multiple choice examiatio, that meas: Solutio approaches are ot assessed. For each sub-task
WS 26/7 Trial Exam: Fudametals of Computer Egieerig Seite: Aotatios to the assigmets ad the solutio sheet This is a multiple choice examiatio, that meas: Solutio approaches are ot assessed. For each sub-task
Internal Information Representation and Processing
 Iteral Iformatio Represetatio ad Processig CSCE 16 - Fudametals of Computer Sciece Dr. Awad Khalil Computer Sciece & Egieerig Departmet The America Uiversity i Cairo Decimal Number System We are used to
Iteral Iformatio Represetatio ad Processig CSCE 16 - Fudametals of Computer Sciece Dr. Awad Khalil Computer Sciece & Egieerig Departmet The America Uiversity i Cairo Decimal Number System We are used to
Randomized Algorithms I, Spring 2018, Department of Computer Science, University of Helsinki Homework 1: Solutions (Discussed January 25, 2018)
 Radomized Algorithms I, Sprig 08, Departmet of Computer Sciece, Uiversity of Helsiki Homework : Solutios Discussed Jauary 5, 08). Exercise.: Cosider the followig balls-ad-bi game. We start with oe black
Radomized Algorithms I, Sprig 08, Departmet of Computer Sciece, Uiversity of Helsiki Homework : Solutios Discussed Jauary 5, 08). Exercise.: Cosider the followig balls-ad-bi game. We start with oe black
FLC Ch 8 & 9. Evaluate. Check work. a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) i) j) k) l) m) n) o) 3. p) q) r) s) t) 3.
 Math 100 Elemetary Algebra Sec 8.1: Radical Expressios List perfect squares ad evaluate their square root. Kow these perfect squares for test. Def The positive (pricipal) square root of x, writte x, is
Math 100 Elemetary Algebra Sec 8.1: Radical Expressios List perfect squares ad evaluate their square root. Kow these perfect squares for test. Def The positive (pricipal) square root of x, writte x, is
1. Hilbert s Grand Hotel. The Hilbert s Grand Hotel has infinite many rooms numbered 1, 2, 3, 4
 . Hilbert s Grad Hotel The Hilbert s Grad Hotel has ifiite may rooms umbered,,,.. Situatio. The Hotel is full ad a ew guest arrives. Ca the mager accommodate the ew guest? - Yes, he ca. There is a simple
. Hilbert s Grad Hotel The Hilbert s Grad Hotel has ifiite may rooms umbered,,,.. Situatio. The Hotel is full ad a ew guest arrives. Ca the mager accommodate the ew guest? - Yes, he ca. There is a simple
10.2 Infinite Series Contemporary Calculus 1
 10. Ifiite Series Cotemporary Calculus 1 10. INFINITE SERIES Our goal i this sectio is to add together the umbers i a sequece. Sice it would take a very log time to add together the ifiite umber of umbers,
10. Ifiite Series Cotemporary Calculus 1 10. INFINITE SERIES Our goal i this sectio is to add together the umbers i a sequece. Sice it would take a very log time to add together the ifiite umber of umbers,
SECTION 1.5 : SUMMATION NOTATION + WORK WITH SEQUENCES
 SECTION 1.5 : SUMMATION NOTATION + WORK WITH SEQUENCES Read Sectio 1.5 (pages 5 9) Overview I Sectio 1.5 we lear to work with summatio otatio ad formulas. We will also itroduce a brief overview of sequeces,
SECTION 1.5 : SUMMATION NOTATION + WORK WITH SEQUENCES Read Sectio 1.5 (pages 5 9) Overview I Sectio 1.5 we lear to work with summatio otatio ad formulas. We will also itroduce a brief overview of sequeces,
We are mainly going to be concerned with power series in x, such as. (x)} converges - that is, lims N n
 Review of Power Series, Power Series Solutios A power series i x - a is a ifiite series of the form c (x a) =c +c (x a)+(x a) +... We also call this a power series cetered at a. Ex. (x+) is cetered at
Review of Power Series, Power Series Solutios A power series i x - a is a ifiite series of the form c (x a) =c +c (x a)+(x a) +... We also call this a power series cetered at a. Ex. (x+) is cetered at
Optimally Sparse SVMs
 A. Proof of Lemma 3. We here prove a lower boud o the umber of support vectors to achieve geeralizatio bouds of the form which we cosider. Importatly, this result holds ot oly for liear classifiers, but
A. Proof of Lemma 3. We here prove a lower boud o the umber of support vectors to achieve geeralizatio bouds of the form which we cosider. Importatly, this result holds ot oly for liear classifiers, but
1 Hash tables. 1.1 Implementation
 Lecture 8 Hash Tables, Uiversal Hash Fuctios, Balls ad Bis Scribes: Luke Johsto, Moses Charikar, G. Valiat Date: Oct 18, 2017 Adapted From Virgiia Williams lecture otes 1 Hash tables A hash table is a
Lecture 8 Hash Tables, Uiversal Hash Fuctios, Balls ad Bis Scribes: Luke Johsto, Moses Charikar, G. Valiat Date: Oct 18, 2017 Adapted From Virgiia Williams lecture otes 1 Hash tables A hash table is a
Skip Lists. Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 S 3 S S 1
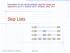 Presetatio for use with the textbook, Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Skip Lists S 3 15 15 23 10 15 23 36 Skip Lists 1 What is a Skip List A skip list for
Presetatio for use with the textbook, Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Skip Lists S 3 15 15 23 10 15 23 36 Skip Lists 1 What is a Skip List A skip list for
In number theory we will generally be working with integers, though occasionally fractions and irrationals will come into play.
 Number Theory Math 5840 otes. Sectio 1: Axioms. I umber theory we will geerally be workig with itegers, though occasioally fractios ad irratioals will come ito play. Notatio: Z deotes the set of all itegers
Number Theory Math 5840 otes. Sectio 1: Axioms. I umber theory we will geerally be workig with itegers, though occasioally fractios ad irratioals will come ito play. Notatio: Z deotes the set of all itegers
Department of Informatics Prof. Dr. Michael Böhlen Binzmühlestrasse Zurich Phone:
 Departmet of Iformatics Prof. Dr. Michael Böhle Bizmühlestrasse 14 8050 Zurich Phoe: +41 44 635 4333 Email: boehle@ifi.uzh.ch Iformatik II Midterm1 Sprig 018 3.03.018 Advice You have 90 miutes to complete
Departmet of Iformatics Prof. Dr. Michael Böhle Bizmühlestrasse 14 8050 Zurich Phoe: +41 44 635 4333 Email: boehle@ifi.uzh.ch Iformatik II Midterm1 Sprig 018 3.03.018 Advice You have 90 miutes to complete
Universal Subsets of Z n, Linear Integer Optimization, and Integer Factorization
 DIMACS Techical Report 005-9 Jauary 006 Uiversal Subsets of Z, Liear Iteger Optimizatio, ad Iteger Factorizatio by Zhivko Nedev 1 1 Uiv. of Victoria, zedev@math.uvic.ca. Part of the work was doe while
DIMACS Techical Report 005-9 Jauary 006 Uiversal Subsets of Z, Liear Iteger Optimizatio, ad Iteger Factorizatio by Zhivko Nedev 1 1 Uiv. of Victoria, zedev@math.uvic.ca. Part of the work was doe while
POWER SERIES SOLUTION OF FIRST ORDER MATRIX DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 Joural of Applied Mathematics ad Computatioal Mechaics 4 3(3) 3-8 POWER SERIES SOLUION OF FIRS ORDER MARIX DIFFERENIAL EQUAIONS Staisław Kukla Izabela Zamorska Istitute of Mathematics Czestochowa Uiversity
Joural of Applied Mathematics ad Computatioal Mechaics 4 3(3) 3-8 POWER SERIES SOLUION OF FIRS ORDER MARIX DIFFERENIAL EQUAIONS Staisław Kukla Izabela Zamorska Istitute of Mathematics Czestochowa Uiversity
Efficient Hashing using the AES Instruction Set
 Efficiet Hashig usig the AES Istructio Set Joppe Bos 1 Our Öze 1 Martij Stam 2 1 Ecole Polytechique Fédérale de Lausae 2 Uiversity of Bristol Nara, 1 October 2011 Outlie 1 Itroductio AES ad Hash Fuctios
Efficiet Hashig usig the AES Istructio Set Joppe Bos 1 Our Öze 1 Martij Stam 2 1 Ecole Polytechique Fédérale de Lausae 2 Uiversity of Bristol Nara, 1 October 2011 Outlie 1 Itroductio AES ad Hash Fuctios
1 Summary: Binary and Logic
 1 Summary: Biary ad Logic Biary Usiged Represetatio : each 1-bit is a power of two, the right-most is for 2 0 : 0110101 2 = 2 5 + 2 4 + 2 2 + 2 0 = 32 + 16 + 4 + 1 = 53 10 Usiged Rage o bits is [0...2
1 Summary: Biary ad Logic Biary Usiged Represetatio : each 1-bit is a power of two, the right-most is for 2 0 : 0110101 2 = 2 5 + 2 4 + 2 2 + 2 0 = 32 + 16 + 4 + 1 = 53 10 Usiged Rage o bits is [0...2
ADVANCED SOFTWARE ENGINEERING
 ADVANCED SOFTWARE ENGINEERING COMP 3705 Exercise Usage-based Testig ad Reliability Versio 1.0-040406 Departmet of Computer Ssciece Sada Narayaappa, Aeliese Adrews Versio 1.1-050405 Departmet of Commuicatio
ADVANCED SOFTWARE ENGINEERING COMP 3705 Exercise Usage-based Testig ad Reliability Versio 1.0-040406 Departmet of Computer Ssciece Sada Narayaappa, Aeliese Adrews Versio 1.1-050405 Departmet of Commuicatio
EE422G Homework #13 (12 points)
 EE422G Homework #1 (12 poits) 1. (5 poits) I this problem, you are asked to explore a importat applicatio of FFT: efficiet computatio of covolutio. The impulse respose of a system is give by h(t) (.9),1,2,,1
EE422G Homework #1 (12 poits) 1. (5 poits) I this problem, you are asked to explore a importat applicatio of FFT: efficiet computatio of covolutio. The impulse respose of a system is give by h(t) (.9),1,2,,1
4755 Mark Scheme June Question Answer Marks Guidance M1* Attempt to find M or 108M -1 M 108 M1 A1 [6] M1 A1
![4755 Mark Scheme June Question Answer Marks Guidance M1* Attempt to find M or 108M -1 M 108 M1 A1 [6] M1 A1 4755 Mark Scheme June Question Answer Marks Guidance M1* Attempt to find M or 108M -1 M 108 M1 A1 [6] M1 A1](/thumbs/86/94560574.jpg) 4755 Mark Scheme Jue 05 * Attempt to fid M or 08M - M 08 8 4 * Divide by their determiat,, at some stage Correct determiat, (A0 for det M= 08 stated, all other OR 08 8 4 5 8 7 5 x, y,oe 8 7 4xy 8xy dep*
4755 Mark Scheme Jue 05 * Attempt to fid M or 08M - M 08 8 4 * Divide by their determiat,, at some stage Correct determiat, (A0 for det M= 08 stated, all other OR 08 8 4 5 8 7 5 x, y,oe 8 7 4xy 8xy dep*
Sigma notation. 2.1 Introduction
 Sigma otatio. Itroductio We use sigma otatio to idicate the summatio process whe we have several (or ifiitely may) terms to add up. You may have see sigma otatio i earlier courses. It is used to idicate
Sigma otatio. Itroductio We use sigma otatio to idicate the summatio process whe we have several (or ifiitely may) terms to add up. You may have see sigma otatio i earlier courses. It is used to idicate
Filter banks. Separately, the lowpass and highpass filters are not invertible. removes the highest frequency 1/ 2and
 Filter bas Separately, the lowpass ad highpass filters are ot ivertible T removes the highest frequecy / ad removes the lowest frequecy Together these filters separate the sigal ito low-frequecy ad high-frequecy
Filter bas Separately, the lowpass ad highpass filters are ot ivertible T removes the highest frequecy / ad removes the lowest frequecy Together these filters separate the sigal ito low-frequecy ad high-frequecy
ECE 448 Lecture 6. Finite State Machines. State Diagrams, State Tables, Algorithmic State Machine (ASM) Charts, and VHDL Code. George Mason University
 ECE 448 Lecture 6 Finite State Machines State Diagrams, State Tables, Algorithmic State Machine (ASM) Charts, and VHDL Code George Mason University Required reading P. Chu, FPGA Prototyping by VHDL Examples
ECE 448 Lecture 6 Finite State Machines State Diagrams, State Tables, Algorithmic State Machine (ASM) Charts, and VHDL Code George Mason University Required reading P. Chu, FPGA Prototyping by VHDL Examples
CSE 202 Homework 1 Matthias Springer, A Yes, there does always exist a perfect matching without a strong instability.
 CSE 0 Homework 1 Matthias Spriger, A9950078 1 Problem 1 Notatio a b meas that a is matched to b. a < b c meas that b likes c more tha a. Equality idicates a tie. Strog istability Yes, there does always
CSE 0 Homework 1 Matthias Spriger, A9950078 1 Problem 1 Notatio a b meas that a is matched to b. a < b c meas that b likes c more tha a. Equality idicates a tie. Strog istability Yes, there does always
6.3 Testing Series With Positive Terms
 6.3. TESTING SERIES WITH POSITIVE TERMS 307 6.3 Testig Series With Positive Terms 6.3. Review of what is kow up to ow I theory, testig a series a i for covergece amouts to fidig the i= sequece of partial
6.3. TESTING SERIES WITH POSITIVE TERMS 307 6.3 Testig Series With Positive Terms 6.3. Review of what is kow up to ow I theory, testig a series a i for covergece amouts to fidig the i= sequece of partial
ANALYSIS OF EXPERIMENTAL ERRORS
 ANALYSIS OF EXPERIMENTAL ERRORS All physical measuremets ecoutered i the verificatio of physics theories ad cocepts are subject to ucertaities that deped o the measurig istrumets used ad the coditios uder
ANALYSIS OF EXPERIMENTAL ERRORS All physical measuremets ecoutered i the verificatio of physics theories ad cocepts are subject to ucertaities that deped o the measurig istrumets used ad the coditios uder
6 Integers Modulo n. integer k can be written as k = qn + r, with q,r, 0 r b. So any integer.
 6 Itegers Modulo I Example 2.3(e), we have defied the cogruece of two itegers a,b with respect to a modulus. Let us recall that a b (mod ) meas a b. We have proved that cogruece is a equivalece relatio
6 Itegers Modulo I Example 2.3(e), we have defied the cogruece of two itegers a,b with respect to a modulus. Let us recall that a b (mod ) meas a b. We have proved that cogruece is a equivalece relatio
The Mathematical Model and the Simulation Modelling Algoritm of the Multitiered Mechanical System
 The Mathematical Model ad the Simulatio Modellig Algoritm of the Multitiered Mechaical System Demi Aatoliy, Kovalev Iva Dept. of Optical Digital Systems ad Techologies, The St. Petersburg Natioal Research
The Mathematical Model ad the Simulatio Modellig Algoritm of the Multitiered Mechaical System Demi Aatoliy, Kovalev Iva Dept. of Optical Digital Systems ad Techologies, The St. Petersburg Natioal Research
5. Fast NLMS-OCF Algorithm
 5. Fast LMS-OCF Algorithm The LMS-OCF algorithm preseted i Chapter, which relies o Gram-Schmidt orthogoalizatio, has a compleity O ( M ). The square-law depedece o computatioal requiremets o the umber
5. Fast LMS-OCF Algorithm The LMS-OCF algorithm preseted i Chapter, which relies o Gram-Schmidt orthogoalizatio, has a compleity O ( M ). The square-law depedece o computatioal requiremets o the umber
MAT1026 Calculus II Basic Convergence Tests for Series
 MAT026 Calculus II Basic Covergece Tests for Series Egi MERMUT 202.03.08 Dokuz Eylül Uiversity Faculty of Sciece Departmet of Mathematics İzmir/TURKEY Cotets Mootoe Covergece Theorem 2 2 Series of Real
MAT026 Calculus II Basic Covergece Tests for Series Egi MERMUT 202.03.08 Dokuz Eylül Uiversity Faculty of Sciece Departmet of Mathematics İzmir/TURKEY Cotets Mootoe Covergece Theorem 2 2 Series of Real
Recursive Algorithm for Generating Partitions of an Integer. 1 Preliminary
 Recursive Algorithm for Geeratig Partitios of a Iteger Sug-Hyuk Cha Computer Sciece Departmet, Pace Uiversity 1 Pace Plaza, New York, NY 10038 USA scha@pace.edu Abstract. This article first reviews the
Recursive Algorithm for Geeratig Partitios of a Iteger Sug-Hyuk Cha Computer Sciece Departmet, Pace Uiversity 1 Pace Plaza, New York, NY 10038 USA scha@pace.edu Abstract. This article first reviews the
