ADAPTIVE EQUALIZATION AT MULTI-GHZ DATARATES
|
|
|
- Meagan Townsend
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ADAPTIVE EQUALIZATION AT MULTI-GHZ DATARATES Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras 1st February 2007
2 Outline Introduction. Approaches to electronic mitigation - ADC & Digital FIR Filter. - Analog Traveling Wave and Transversal Equalizers. Problems and prospects of analog adaptive filters. Conclusions
3 Non-Return-to-Zero (NRZ) Data Transmission bit period NRZ Pulse At 10 Gbps, 1 Bit period is 100 picoseconds
4 What is Inter-Symbol-Interference? Tx Ch 1 Ch 2
5 Why is ISI Bad? Smaller "Distance" Smaller separation, more likely to make an error
6 What is an Eye Diagram? Graphics Source : Electronic Design Magazine
7 Eye Diagram : No ISI, no noise Amplitude Time (ps)
8 Eye Diagram : No ISI, with noise Amplitude Time (ps)
9 Eye Diagram : With ISI, no noise Amplitude Time (ps)
10 Eye Diagram : With ISI, with noise Amplitude Time (ps)
11 Typical Optical Fiber Data Link Photodiode Receiver Transmitter Fiber
12 Typical Optical Fiber Data Link Photodiode Receiver Transmitter Fiber TIA Transimpedance Amplifier LA Limiting Amplifier CDR Clock/Data Recovery Data
13 Typical Optical Fiber Data Link Transimpedance Amplifier TIA Limiting Amplifier LA Clock/Data Recovery CDR Data
14 ISI in Optical Links Dispersion in fiber due to manufacturing tolerances Polarization Mode Dispersion in Single Mode Fiber Impulse Response : αδ(t) + (1 α)δ(t T d ) α is called the Power Split T d is called the Differential Group Delay (DGD) Two paths with different delays and gains Much worse (many more paths, greater spread) in multi-mode fibers
15 Example Eye : No ISI, Finite Tx Bandwidth Amplitude Time (ps)
16 PMD, Finite Tx BW, DGD = 75 ps Amplitude Time (ps)
17 PMD, Finite Tx BW, DGD = 75 ps & Noise
18 Mitigating ISI Input Channel Output 1 β y(t) y(t) - βy(t-t b ) + β 2 y(t-2t b ) 1 1 β y(t) y(t-t b ) β 1 β 1 y(t-2t b ) y(t) β βy(t-t b ) β β 2 + β 2 y(t-2t b ) β 2 β 3 1 β 3
19 Mitigating ISI : Equalization 1/T b Input Channel Output T b T b T b w 1 w 2 w 3 w 4 Output(nT b ) = k=n 1 k=0 Σ Output w k y(nt b kt b ) (1) Tapped-delay line Equalizer Weights need to be adaptive, since channel is varying (slowly) with time
20 Mitigating ISI : Equalization 1/T b Channel Filter T Input b T b T b w 1 w 2 w 3 w 4 Σ Output 4 tap" adaptive equalizer Need a filter before sampling Called the matched filter"
21 Digital Receiver : Baud Spaced Equalizer (BSE) TIA/VGA FILTER ADC 10 Gbps 6-bit Timing Phase sensitivity in a BSE High speed (10 Gbps), 6-bit ADC Digital FIR LMS ENGINE Data Example : Bell Labs (2003) - 6-bit 10 G ADC W and yields 4 effective bits in 0.18µm SiGe BiCMOS Technology (state of the art) Parallelism in the equalizer - more area
22 Digital Receiver : Baud Spaced Equalizer (BSE) 10 Gbps 6-bit Digital FIR ADC Data FILTER TIA/VGA LMS ENGINE Too much power / area ADC is a big project in itself
23 Digital Receiver : Fractionally Spaced Equalizer (FSE) 20 Gbps 6-bit Digital FIR ADC Data FILTER TIA/VGA LMS ENGINE Insensitive to timing phase High speed (20 Gbps), 6-bit ADC! Parallelism in the equalizer
24 Digital Implementation : Summary Power hungry! ADC may be doable 10Gbps Solution doesnt scale well to higher speeds (40 Gbps)
25 Analog Implementation Analog Input Channel Filter T b T b T b w 1 w 2 w 3 w 4 Σ 1/T b Output Sampling after equalization Delays implemented using transmission lines FSE 10Gbps : Each delay line is 50 ps long
26 System Model b n ε { 0, 1} Σ b n δ(t - nt) IID BIT SOURCE Tx FILTER αδ(t) + (1-α)δ(t-τ) PMD CHANNEL FIBER LOSS (β) 1/β 4th Order Butterworth + TIA & VGA + EQUALIZER AA FILTER f s OUT Offset Correct AWGN
27 System Model a n ε { 1/2, 1/2} Σ a n δ(t - nt) αδ(t) + (1-α)δ(t-τ) 4th Order Butterworth IID BIT SOURCE Tx FILTER PMD CHANNEL + EQUALIZER AA FILTER f s OUT AWGN (b) w 1 x 1 (t) IID BIT SOURCE a n ε { 1/2, 1/2} Σa n δ(t - nt) p(t) Tx Filter & Channel + n(t) x 2 (t) w 2 AA Filter v ncir v i v r(t) out w N-1 y(t) x (N-1) (t) x N (t) w N f s y(n) OUT EQUALIZER (c)
28 System Model a n ε { 1/2, 1/2} Σa n δ(t - nt) x 1 (t) w 1 IID BIT SOURCE p(t) Tx Filter & Channel + n(t) v i x N (t) f s v out y(t) y(n) OUT w N EQUALIZER
29 MMSE solution a n ε { 1/2, 1/2} Σa n δ(t - nt) IID BIT SOURCE p(t) Tx Filter & Channel + n(t) v i x 1 (t) x N (t) w 1 f s vout y(t) y(n) OUT w N EQUALIZER c i (t) = p(t) x i (t) N y(t) = w i a(k) c i (t kt ) + i=1 k= N w i n(t) x i (t) N n N y(n) = w i a(k) c i (nt kt ) + w i (n(t) x i (t)) t=nt i=1 i=1 k= i=1
30 MMSE solution y(n) = N n i=1 k= w i a(k) c i (nt kt ) + N w i (n(t) x i (t)) t=nt i=1 c 1 (0.T ) c 2 (0.T )... c N (0.T ) y(n) = a T c 1 (T ) c 2 (T )... c N (T ) (n) c 1 (L.T ) c 2 (L.T )... c N (L.T ) w 1 w 2. w N +ηt (n) w 1 w 2. w N a T (n) = [a(n) a(n 1) a(n L)] η T (n) = [ (n(t) x 1 (t)) t=nt (n(t) x 2 (t)) t=nt (n(t) x N (t)) t=nt ] Equalizer output is y(n) = a T (n)cw + η T (n)w
31 MMSE solution Equalizer output & desired outputs are y(n) = a T (n)cw + η T (n)w y d (n) = a(n δ) = a T (n) h δ The error at the output of the equalizer is e(n) = y(n) a T (n)h δ = a T (n) (Cw h δ ) + η T (n)w [ e(n) 2] [ ] = (Cw h δ ) T E a(n) T a(n) (CW h δ )+w T E E [ a(n) T a(n) ] = σ 2 a I, where σ 2 a = E[ a(n) 2 ]. [ ] η T (n)η(n) w
32 MMSE solution E [ ] η T (n)η(n) = M = N o 2 0 x 1(t)x 1 (t)dt... 0 x 1(t)x N (t)dt 0 x 2(t)x 1 (t)dt... 0 x 2(t)x N (t)dt x N(t)x 1 (t)dt... x N(t)x N (t)dt so that [ E e(n) 2] = σa 2 (Cw h δ ) T (Cw h δ ) + w T Mw 0 It can be shown that w opt = A 1 C T h δ MMSE = σa 2 h T δ (I CA 1 C T )h δ where A = C T C + M/σa 2
33 Tapped Delay Line Filters : Transversal G R T R T Z o, T Z o, T v i v 1 v 2 v 3 w 1 w 2 w 3 v g i v out R T /2 i = gv Delay Elements are passive Tap weights : variable gain amplifiers (Differential pair) Summation : Kirchoffs Current Law
34 Choices for On-chip Delay Lines : Microstrip Wideband Need 50 ps delay Velocity of light 150 µm/ps 50 ps 7.5 mm! (and we need several of them) Conclusion : No good What can we do to make the delay line smaller?
35 Spiral Delay Lines Metal 1 Metal 5 Spiral : reduces size Use metal interconnect layers Mutual coupling results in increased inductance
36 Spiral Delay Lines Metal 1 Metal 5 Ground plane is broken to avoid image currents Attempt to distribute capacitance uniformly across the inductor Typical size - 300µm on a side Accurate model through EM Simulations
37 Tunable Weights om op Vdd Sign S Q5,6 S Q7,8 S Vdd ip Q1 Q4 im Q2 Q3 Magnitude Example of a tunable tap weight implementation
38 Problems with Transversal Filters G R T Z o, T Z o, T R T v i v 1 v+ v+(t-2t) 1 >> Γ Τ >> Γ 2 Τ... h v1 (t) 1 Γ T v+(t-4t) Γ T v+(t-2t) Exponential tails due to series losses Components due to reflection Γ T Equalizer Span t/t Mistermination & Loss in the delay lines Tap responses have components outside equalizer span ISI" within the equalizer! Degrades performance
39 Problems with Transversal Filters Normalized Filter Output time (ps) Eye diagram at the first tap output
40 Traveling Wave Amplifier (TWA) FIR Filter G R T Z o, T/2 Z o, T/2 R T v i v 1 v 2 v 3 w 1 w 2 w 3 Z o, T/2 Z o, T/2 v g i v out R T R T i = gv
41 Traveling Wave Amplifier (TWA) FIR Filter v i G R T Z o, T/2 Z o, T/2 R T v 1 v 2 v 3 h v1 (t) k 1 Γ T k=gz o (1+Γ Τ )/ t/t v out w 1 w 2 w 3 Z o, T/2 Z o, T/2 h w1 (t) 1 k1 k1=k 2 /G 2Γ T t/t R T R T
42 TWA FIR Filters : Comments Improvement over a transversal filter Robust with mistermination and series loss Used in several commerical equalizer ICs Two doubly terminated lines - Tap weights need to be larger by a factor of 2
43 Traveling Wave versus Transversal Equalizers NRZ response (V) 0.3 Tap 1 (a) Tap t / T b NRZ response (V) Tap 1 Tap 10 (b) t / T b
44 Traveling Wave versus Transversal Equalizers Equalizer Output Receiver Input e Receiver Input time (ps) MSE = time (ps) 10 Tap Transversal Equalizer Equalizer Input Equalizer Output Equalizer Input time (ps) MSE = time (ps) 10 Tap TW Equalizer
45 Summary-1 TWA FIR Filters represent the state-of-the-art in high speed equalization Signal attenuation due to double termination Need for an anti-alias" filter Delay cells are large and occupy space Example : A fully differential 10 tap TWA equalizer has 36 inductors! (each being about 300µm on a side Capacitive loading of lines reduces cut-off frequency of the delay lines TWA filters are not amenable to LMS adaptation
46 Summary-2 DFE used alongwith an FFE in tough channels - e.g. multimode channels. Timing recovery is an important issue. In simple channels, common to use an upfront timing recovery module that works with the receiver input. In more complicated channels, the FFE output can be used to derive the timing error. Joint timing recovery/equalization without a training sequence is a challenge.
47 Conclusions High speed equalization at multi-ghz datarates involves signal processing, circuit design and electromagnetics. The challenge is to implement well known signal processing techniques at such high data rates. Many problems to be solved - e.g. efficient LMS implementation at several GHz speeds. Lots of work to do!
48 Selected References Wu et. al, Integrated transversal equalizers in high-speed fiber-optic systems, IEEE JSSC, December Sewter et. al, A 3-tap FIR filter with cascaded distributed tap amplifiers for equalization up to 40 Gb/s, IEEE JSSC, August Pavan et. al, Nonidealities in Traveling Wave and Transversal FIR Filters Operating at Microwave Frequencies, IEEE TCAS-1, January 2006.
Similarities of PMD and DMD for 10Gbps Equalization
 Similarities of PMD and DMD for 10Gbps Equalization Moe Win Jack Winters win/jhw@research.att.com AT&T Labs-Research (Some viewgraphs and results curtesy of Julien Porrier) Outline Polarization Mode Dispersion
Similarities of PMD and DMD for 10Gbps Equalization Moe Win Jack Winters win/jhw@research.att.com AT&T Labs-Research (Some viewgraphs and results curtesy of Julien Porrier) Outline Polarization Mode Dispersion
Principles of Communications Lecture 8: Baseband Communication Systems. Chih-Wei Liu 劉志尉 National Chiao Tung University
 Principles of Communications Lecture 8: Baseband Communication Systems Chih-Wei Liu 劉志尉 National Chiao Tung University cwliu@twins.ee.nctu.edu.tw Outlines Introduction Line codes Effects of filtering Pulse
Principles of Communications Lecture 8: Baseband Communication Systems Chih-Wei Liu 劉志尉 National Chiao Tung University cwliu@twins.ee.nctu.edu.tw Outlines Introduction Line codes Effects of filtering Pulse
Weiyao Lin. Shanghai Jiao Tong University. Chapter 5: Digital Transmission through Baseband slchannels Textbook: Ch
 Principles of Communications Weiyao Lin Shanghai Jiao Tong University Chapter 5: Digital Transmission through Baseband slchannels Textbook: Ch 10.1-10.5 2009/2010 Meixia Tao @ SJTU 1 Topics to be Covered
Principles of Communications Weiyao Lin Shanghai Jiao Tong University Chapter 5: Digital Transmission through Baseband slchannels Textbook: Ch 10.1-10.5 2009/2010 Meixia Tao @ SJTU 1 Topics to be Covered
Square Root Raised Cosine Filter
 Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Square Root Raised Cosine Filter Institute of Communications Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Introduction We consider the problem of signal design
Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Square Root Raised Cosine Filter Institute of Communications Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Introduction We consider the problem of signal design
14 Gb/s AC Coupled Receiver in 90 nm CMOS. Masum Hossain & Tony Chan Carusone University of Toronto
 14 Gb/s AC Coupled Receiver in 90 nm CMOS Masum Hossain & Tony Chan Carusone University of Toronto masum@eecg.utoronto.ca OUTLINE Chip-to-Chip link overview AC interconnects Link modelling ISI & sensitivity
14 Gb/s AC Coupled Receiver in 90 nm CMOS Masum Hossain & Tony Chan Carusone University of Toronto masum@eecg.utoronto.ca OUTLINE Chip-to-Chip link overview AC interconnects Link modelling ISI & sensitivity
ECEN689: Special Topics in High-Speed Links Circuits and Systems Spring 2012
 ECEN689: pecial Topics in High-peed Links Circuits and ystems pring 01 Lecture 3: Time-Domain Reflectometry & -Parameter Channel Models am Palermo Analog & Mixed-ignal Center Texas A&M University Announcements
ECEN689: pecial Topics in High-peed Links Circuits and ystems pring 01 Lecture 3: Time-Domain Reflectometry & -Parameter Channel Models am Palermo Analog & Mixed-ignal Center Texas A&M University Announcements
EE4601 Communication Systems
 EE4601 Communication Systems Week 13 Linear Zero Forcing Equalization 0 c 2012, Georgia Institute of Technology (lect13 1) Equalization The cascade of the transmit filter g(t), channel c(t), receiver filter
EE4601 Communication Systems Week 13 Linear Zero Forcing Equalization 0 c 2012, Georgia Institute of Technology (lect13 1) Equalization The cascade of the transmit filter g(t), channel c(t), receiver filter
EE4061 Communication Systems
 EE4061 Communication Systems Week 11 Intersymbol Interference Nyquist Pulse Shaping 0 c 2015, Georgia Institute of Technology (lect10 1) Intersymbol Interference (ISI) Tx filter channel Rx filter a δ(t-nt)
EE4061 Communication Systems Week 11 Intersymbol Interference Nyquist Pulse Shaping 0 c 2015, Georgia Institute of Technology (lect10 1) Intersymbol Interference (ISI) Tx filter channel Rx filter a δ(t-nt)
EE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications
 EE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications Week 12, 13: Inter Symbol Interference (ISI) Nyquist Criteria for ISI Pulse Shaping and Raised-Cosine Filter Eye Pattern Equalization (On Board) 20-May-15 Muhammad
EE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications Week 12, 13: Inter Symbol Interference (ISI) Nyquist Criteria for ISI Pulse Shaping and Raised-Cosine Filter Eye Pattern Equalization (On Board) 20-May-15 Muhammad
Adaptive Polarization Mode Dispersion Compensation at 40Gb/s with Integrated Optical Finite Impulse Response (FIR) Filters
 Adaptive Polarization Mode Dispersion Compensation at 40Gb/s with Integrated Optical Finite Impulse Response (FIR) Filters Marc Bohn, Werner Rosenkranz Chair for Communications, University of Kiel, Kaiserstr.
Adaptive Polarization Mode Dispersion Compensation at 40Gb/s with Integrated Optical Finite Impulse Response (FIR) Filters Marc Bohn, Werner Rosenkranz Chair for Communications, University of Kiel, Kaiserstr.
Leistungsfähigkeit von elektronischen Entzerrer in hochbitratigen optischen Übertragungsystemen. S. Otte, W. Rosenkranz. chair for communications,
 Leistungsfähigkeit von elektronischen Entzerrer in hochbitratigen optischen Übertragungsystemen S. Otte, W. Rosenkranz chair for communications, Sven Otte, DFG-Kolloquium, 6. 11. 001, 1 Outline 1. Motivation.
Leistungsfähigkeit von elektronischen Entzerrer in hochbitratigen optischen Übertragungsystemen S. Otte, W. Rosenkranz chair for communications, Sven Otte, DFG-Kolloquium, 6. 11. 001, 1 Outline 1. Motivation.
Revision of Lecture 4
 Revision of Lecture 4 We have discussed all basic components of MODEM Pulse shaping Tx/Rx filter pair Modulator/demodulator Bits map symbols Discussions assume ideal channel, and for dispersive channel
Revision of Lecture 4 We have discussed all basic components of MODEM Pulse shaping Tx/Rx filter pair Modulator/demodulator Bits map symbols Discussions assume ideal channel, and for dispersive channel
Digital Baseband Systems. Reference: Digital Communications John G. Proakis
 Digital Baseband Systems Reference: Digital Communications John G. Proais Baseband Pulse Transmission Baseband digital signals - signals whose spectrum extend down to or near zero frequency. Model of the
Digital Baseband Systems Reference: Digital Communications John G. Proais Baseband Pulse Transmission Baseband digital signals - signals whose spectrum extend down to or near zero frequency. Model of the
Analog Electronics 2 ICS905
 Analog Electronics 2 ICS905 G. Rodriguez-Guisantes Dépt. COMELEC http://perso.telecom-paristech.fr/ rodrigez/ens/cycle_master/ November 2016 2/ 67 Schedule Radio channel characteristics ; Analysis and
Analog Electronics 2 ICS905 G. Rodriguez-Guisantes Dépt. COMELEC http://perso.telecom-paristech.fr/ rodrigez/ens/cycle_master/ November 2016 2/ 67 Schedule Radio channel characteristics ; Analysis and
CMOS Cross Section. EECS240 Spring Today s Lecture. Dimensions. CMOS Process. Devices. Lecture 2: CMOS Technology and Passive Devices
 EECS240 Spring 2008 CMOS Cross Section Metal p - substrate p + diffusion Lecture 2: CMOS echnology and Passive Devices Poly n - well n + diffusion Elad Alon Dept. of EECS EECS240 Lecture 2 4 oday s Lecture
EECS240 Spring 2008 CMOS Cross Section Metal p - substrate p + diffusion Lecture 2: CMOS echnology and Passive Devices Poly n - well n + diffusion Elad Alon Dept. of EECS EECS240 Lecture 2 4 oday s Lecture
RADIO SYSTEMS ETIN15. Lecture no: Equalization. Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology
 RADIO SYSTEMS ETIN15 Lecture no: 8 Equalization Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology Ove.Edfors@eit.lth.se Contents Inter-symbol interference Linear equalizers Decision-feedback
RADIO SYSTEMS ETIN15 Lecture no: 8 Equalization Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology Ove.Edfors@eit.lth.se Contents Inter-symbol interference Linear equalizers Decision-feedback
IEEE 802.3ap Task Force Ottawa Sept 27-29, 2004
 Edge-Equalized NRZ and Duobinary IEEE 82.3ap Task Force Ottawa Sept 27-29, 24 Brian Brunn, Xilinx Intro It appears the equalization algorithm for EE-NRZ and Duobinary are the same. Both want to zero-force
Edge-Equalized NRZ and Duobinary IEEE 82.3ap Task Force Ottawa Sept 27-29, 24 Brian Brunn, Xilinx Intro It appears the equalization algorithm for EE-NRZ and Duobinary are the same. Both want to zero-force
Motivation for CDR: Deserializer (1)
 Motivation for CDR: Deserializer (1) Input data 1:2 DMUX 1:2 DMUX channel 1:2 DMUX Input clock 2 2 If input data were accompanied by a well-synchronized clock, deserialization could be done directly. EECS
Motivation for CDR: Deserializer (1) Input data 1:2 DMUX 1:2 DMUX channel 1:2 DMUX Input clock 2 2 If input data were accompanied by a well-synchronized clock, deserialization could be done directly. EECS
Signal Design for Band-Limited Channels
 Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Signal Design for Band-Limited Channels Institute of Communications Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Introduction We consider the problem of signal
Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Signal Design for Band-Limited Channels Institute of Communications Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Introduction We consider the problem of signal
LECTURE 16 AND 17. Digital signaling on frequency selective fading channels. Notes Prepared by: Abhishek Sood
 ECE559:WIRELESS COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES LECTURE 16 AND 17 Digital signaling on frequency selective fading channels 1 OUTLINE Notes Prepared by: Abhishek Sood In section 2 we discuss the receiver design
ECE559:WIRELESS COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES LECTURE 16 AND 17 Digital signaling on frequency selective fading channels 1 OUTLINE Notes Prepared by: Abhishek Sood In section 2 we discuss the receiver design
Polarization division multiplexing system quality in the presence of polarization effects
 Opt Quant Electron (2009) 41:997 1006 DOI 10.1007/s11082-010-9412-0 Polarization division multiplexing system quality in the presence of polarization effects Krzysztof Perlicki Received: 6 January 2010
Opt Quant Electron (2009) 41:997 1006 DOI 10.1007/s11082-010-9412-0 Polarization division multiplexing system quality in the presence of polarization effects Krzysztof Perlicki Received: 6 January 2010
ELECTRONIC EQUALIZATION OF HIGH-SPEED MULTI-MODE FIBER LINKS
 ELECTRONIC EQUALIZATION OF HIGH-SPEED MULTI-MODE FIBER LINKS A Thesis Presented to The Academic Faculty by Kasyapa Balemarthy In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Philosophy
ELECTRONIC EQUALIZATION OF HIGH-SPEED MULTI-MODE FIBER LINKS A Thesis Presented to The Academic Faculty by Kasyapa Balemarthy In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Philosophy
that efficiently utilizes the total available channel bandwidth W.
 Signal Design for Band-Limited Channels Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Institute of Communications Engineering g National Sun Yat-sen University Introduction We consider the problem of signal
Signal Design for Band-Limited Channels Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Institute of Communications Engineering g National Sun Yat-sen University Introduction We consider the problem of signal
Propagation losses in optical fibers
 Chapter Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers 1-Fev-017 Propagation losses in optical fibers Charles Kao, Nobel Laureate (009) Courtesy of the Chinese University of Hong Kong S.O. Kasap, Optoelectronics
Chapter Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers 1-Fev-017 Propagation losses in optical fibers Charles Kao, Nobel Laureate (009) Courtesy of the Chinese University of Hong Kong S.O. Kasap, Optoelectronics
Preliminary Studies on DFE Error Propagation, Precoding, and their Impact on KP4 FEC Performance for PAM4 Signaling Systems
 Preliminary Studies on DFE Error Propagation, Precoding, and their Impact on KP4 FEC Performance for PAM4 Signaling Systems Geoff Zhang September, 2018 Outline 1/(1+D) precoding for PAM4 link systems 1/(1+D)
Preliminary Studies on DFE Error Propagation, Precoding, and their Impact on KP4 FEC Performance for PAM4 Signaling Systems Geoff Zhang September, 2018 Outline 1/(1+D) precoding for PAM4 link systems 1/(1+D)
CMOS Cross Section. EECS240 Spring Dimensions. Today s Lecture. Why Talk About Passives? EE240 Process
 EECS240 Spring 202 CMOS Cross Section Metal p - substrate p + diffusion Lecture 2: CMOS Technology and Passive Devices Poly n - well n + diffusion Elad Alon Dept. of EECS EECS240 Lecture 2 4 Today s Lecture
EECS240 Spring 202 CMOS Cross Section Metal p - substrate p + diffusion Lecture 2: CMOS Technology and Passive Devices Poly n - well n + diffusion Elad Alon Dept. of EECS EECS240 Lecture 2 4 Today s Lecture
Principles of Communications
 Principles of Communications Chapter V: Representation and Transmission of Baseband Digital Signal Yongchao Wang Email: ychwang@mail.xidian.edu.cn Xidian University State Key Lab. on ISN November 18, 2012
Principles of Communications Chapter V: Representation and Transmission of Baseband Digital Signal Yongchao Wang Email: ychwang@mail.xidian.edu.cn Xidian University State Key Lab. on ISN November 18, 2012
SerDes_Channel_Impulse_Modeling_with_Rambus
 SerDes_Channel_Impulse_Modeling_with_Rambus Author: John Baprawski; John Baprawski Inc. (JB) Email: John.baprawski@gmail.com Web sites: https://www.johnbaprawski.com; https://www.serdesdesign.com Date:
SerDes_Channel_Impulse_Modeling_with_Rambus Author: John Baprawski; John Baprawski Inc. (JB) Email: John.baprawski@gmail.com Web sites: https://www.johnbaprawski.com; https://www.serdesdesign.com Date:
II - Baseband pulse transmission
 II - Baseband pulse transmission 1 Introduction We discuss how to transmit digital data symbols, which have to be converted into material form before they are sent or stored. In the sequel, we associate
II - Baseband pulse transmission 1 Introduction We discuss how to transmit digital data symbols, which have to be converted into material form before they are sent or stored. In the sequel, we associate
Projects in Wireless Communication Lecture 1
 Projects in Wireless Communication Lecture 1 Fredrik Tufvesson/Fredrik Rusek Department of Electrical and Information Technology Lund University, Sweden Lund, Sept 2018 Outline Introduction to the course
Projects in Wireless Communication Lecture 1 Fredrik Tufvesson/Fredrik Rusek Department of Electrical and Information Technology Lund University, Sweden Lund, Sept 2018 Outline Introduction to the course
EE290C Spring Motivation. Lecture 6: Link Performance Analysis. Elad Alon Dept. of EECS. Does eqn. above predict everything? EE290C Lecture 5 2
 EE29C Spring 2 Lecture 6: Link Performance Analysis Elad Alon Dept. of EECS Motivation V in, ampl Voff BER = 2 erfc 2σ noise Does eqn. above predict everything? EE29C Lecture 5 2 Traditional Approach Borrowed
EE29C Spring 2 Lecture 6: Link Performance Analysis Elad Alon Dept. of EECS Motivation V in, ampl Voff BER = 2 erfc 2σ noise Does eqn. above predict everything? EE29C Lecture 5 2 Traditional Approach Borrowed
Asymptotic Capacity Bounds for Magnetic Recording. Raman Venkataramani Seagate Technology (Joint work with Dieter Arnold)
 Asymptotic Capacity Bounds for Magnetic Recording Raman Venkataramani Seagate Technology (Joint work with Dieter Arnold) Outline Problem Statement Signal and Noise Models for Magnetic Recording Capacity
Asymptotic Capacity Bounds for Magnetic Recording Raman Venkataramani Seagate Technology (Joint work with Dieter Arnold) Outline Problem Statement Signal and Noise Models for Magnetic Recording Capacity
Decision-Point Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR)
 Decision-Point Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) Receiver Decision ^ SNR E E e y z Matched Filter Bound error signal at input to decision device Performance upper-bound on ISI channels Achieved on memoryless
Decision-Point Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) Receiver Decision ^ SNR E E e y z Matched Filter Bound error signal at input to decision device Performance upper-bound on ISI channels Achieved on memoryless
Nonlinearity Equalization Techniques for DML- Transmission Impairments
 Nonlinearity Equalization Techniques for DML- Transmission Impairments Johannes von Hoyningen-Huene jhh@tf.uni-kiel.de Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel Workshop on Optical Communication Systems
Nonlinearity Equalization Techniques for DML- Transmission Impairments Johannes von Hoyningen-Huene jhh@tf.uni-kiel.de Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel Workshop on Optical Communication Systems
Direct-Sequence Spread-Spectrum
 Chapter 3 Direct-Sequence Spread-Spectrum In this chapter we consider direct-sequence spread-spectrum systems. Unlike frequency-hopping, a direct-sequence signal occupies the entire bandwidth continuously.
Chapter 3 Direct-Sequence Spread-Spectrum In this chapter we consider direct-sequence spread-spectrum systems. Unlike frequency-hopping, a direct-sequence signal occupies the entire bandwidth continuously.
PMD Compensator and PMD Emulator
 by Yu Mimura *, Kazuhiro Ikeda *, Tatsuya Hatano *, Takeshi Takagi *, Sugio Wako * and Hiroshi Matsuura * As a technology for increasing the capacity to meet the growing demand ABSTRACT for communications
by Yu Mimura *, Kazuhiro Ikeda *, Tatsuya Hatano *, Takeshi Takagi *, Sugio Wako * and Hiroshi Matsuura * As a technology for increasing the capacity to meet the growing demand ABSTRACT for communications
Optical Component Characterization: A Linear Systems Approach
 Optical Component Characterization: A Linear Systems Approach Authors: Mark Froggatt, Brian Soller, Eric Moore, Matthew Wolfe Email: froggattm@lunatechnologies.com Luna Technologies, 2020 Kraft Drive,
Optical Component Characterization: A Linear Systems Approach Authors: Mark Froggatt, Brian Soller, Eric Moore, Matthew Wolfe Email: froggattm@lunatechnologies.com Luna Technologies, 2020 Kraft Drive,
Pulse Shaping and ISI (Proakis: chapter 10.1, 10.3) EEE3012 Spring 2018
 Pulse Shaping and ISI (Proakis: chapter 10.1, 10.3) EEE3012 Spring 2018 Digital Communication System Introduction Bandlimited channels distort signals the result is smeared pulses intersymol interference
Pulse Shaping and ISI (Proakis: chapter 10.1, 10.3) EEE3012 Spring 2018 Digital Communication System Introduction Bandlimited channels distort signals the result is smeared pulses intersymol interference
FBMC/OQAM transceivers for 5G mobile communication systems. François Rottenberg
 FBMC/OQAM transceivers for 5G mobile communication systems François Rottenberg Modulation Wikipedia definition: Process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the carrier signal,
FBMC/OQAM transceivers for 5G mobile communication systems François Rottenberg Modulation Wikipedia definition: Process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the carrier signal,
EECS240 Spring Today s Lecture. Lecture 2: CMOS Technology and Passive Devices. Lingkai Kong EECS. EE240 CMOS Technology
 EECS240 Spring 2013 Lecture 2: CMOS Technology and Passive Devices Lingkai Kong EECS Today s Lecture EE240 CMOS Technology Passive devices Motivation Resistors Capacitors (Inductors) Next time: MOS transistor
EECS240 Spring 2013 Lecture 2: CMOS Technology and Passive Devices Lingkai Kong EECS Today s Lecture EE240 CMOS Technology Passive devices Motivation Resistors Capacitors (Inductors) Next time: MOS transistor
OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS S
 OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS S-108.3110 1 Course program 1. Introduction and Optical Fibers 2. Nonlinear Effects in Optical Fibers 3. Fiber-Optic Components I 4. Transmitters and Receivers 5. Fiber-Optic Measurements
OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS S-108.3110 1 Course program 1. Introduction and Optical Fibers 2. Nonlinear Effects in Optical Fibers 3. Fiber-Optic Components I 4. Transmitters and Receivers 5. Fiber-Optic Measurements
THE IMPACT POLARIZATION MODE DISPERSION OPTICAL DUOBINARY TRANSMISSION
 THE IMPACT of POLARIZATION MODE DISPERSION on OPTICAL DUOBINARY TRANSMISSION A. Carena, V. Curri, R. Gaudino, P. Poggiolini Optical Communications Group - Politecnico di Torino Torino - ITALY OptCom@polito.it
THE IMPACT of POLARIZATION MODE DISPERSION on OPTICAL DUOBINARY TRANSMISSION A. Carena, V. Curri, R. Gaudino, P. Poggiolini Optical Communications Group - Politecnico di Torino Torino - ITALY OptCom@polito.it
Imperfect Sampling Moments and Average SINR
 Engineering Notes Imperfect Sampling Moments and Average SINR Dragan Samardzija Wireless Research Laboratory, Bell Labs, Lucent Technologies, 791 Holmdel-Keyport Road, Holmdel, NJ 07733, USA dragan@lucent.com
Engineering Notes Imperfect Sampling Moments and Average SINR Dragan Samardzija Wireless Research Laboratory, Bell Labs, Lucent Technologies, 791 Holmdel-Keyport Road, Holmdel, NJ 07733, USA dragan@lucent.com
Chapter 10. Timing Recovery. March 12, 2008
 Chapter 10 Timing Recovery March 12, 2008 b[n] coder bit/ symbol transmit filter, pt(t) Modulator Channel, c(t) noise interference form other users LNA/ AGC Demodulator receive/matched filter, p R(t) sampler
Chapter 10 Timing Recovery March 12, 2008 b[n] coder bit/ symbol transmit filter, pt(t) Modulator Channel, c(t) noise interference form other users LNA/ AGC Demodulator receive/matched filter, p R(t) sampler
Information Theory for Dispersion-Free Fiber Channels with Distributed Amplification
 Information Theory for Dispersion-Free Fiber Channels with Distributed Amplification Gerhard Kramer Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Technical University of Munich CLEO-PR, OECC & PGC
Information Theory for Dispersion-Free Fiber Channels with Distributed Amplification Gerhard Kramer Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Technical University of Munich CLEO-PR, OECC & PGC
Preamplifier in 0.5µm CMOS
 A 2.125 Gbaud 1.6kΩ Transimpedance Preamplifier in 0.5µm CMOS Sunderarajan S. Mohan Thomas H. Lee Center for Integrated Systems Stanford University OUTLINE Motivation Shunt-peaked Amplifier Inductor Modeling
A 2.125 Gbaud 1.6kΩ Transimpedance Preamplifier in 0.5µm CMOS Sunderarajan S. Mohan Thomas H. Lee Center for Integrated Systems Stanford University OUTLINE Motivation Shunt-peaked Amplifier Inductor Modeling
Lecture 2. Fading Channel
 1 Lecture 2. Fading Channel Characteristics of Fading Channels Modeling of Fading Channels Discrete-time Input/Output Model 2 Radio Propagation in Free Space Speed: c = 299,792,458 m/s Isotropic Received
1 Lecture 2. Fading Channel Characteristics of Fading Channels Modeling of Fading Channels Discrete-time Input/Output Model 2 Radio Propagation in Free Space Speed: c = 299,792,458 m/s Isotropic Received
8.1 Circuit Parameters
 8.1 Circuit Parameters definition of decibels using decibels transfer functions impulse response rise time analysis Gaussian amplifier transfer function RC circuit transfer function analog-to-digital conversion
8.1 Circuit Parameters definition of decibels using decibels transfer functions impulse response rise time analysis Gaussian amplifier transfer function RC circuit transfer function analog-to-digital conversion
A Family of Nyquist Filters Based on Generalized Raised-Cosine Spectra
 Proc. Biennial Symp. Commun. (Kingston, Ont.), pp. 3-35, June 99 A Family of Nyquist Filters Based on Generalized Raised-Cosine Spectra Nader Sheikholeslami Peter Kabal Department of Electrical Engineering
Proc. Biennial Symp. Commun. (Kingston, Ont.), pp. 3-35, June 99 A Family of Nyquist Filters Based on Generalized Raised-Cosine Spectra Nader Sheikholeslami Peter Kabal Department of Electrical Engineering
ELEC E7210: Communication Theory. Lecture 4: Equalization
 ELEC E7210: Communication Theory Lecture 4: Equalization Equalization Delay sprea ISI irreucible error floor if the symbol time is on the same orer as the rms elay sprea. DF: Equalization a receiver signal
ELEC E7210: Communication Theory Lecture 4: Equalization Equalization Delay sprea ISI irreucible error floor if the symbol time is on the same orer as the rms elay sprea. DF: Equalization a receiver signal
Electronic Circuits Summary
 Electronic Circuits Summary Andreas Biri, D-ITET 6.06.4 Constants (@300K) ε 0 = 8.854 0 F m m 0 = 9. 0 3 kg k =.38 0 3 J K = 8.67 0 5 ev/k kt q = 0.059 V, q kt = 38.6, kt = 5.9 mev V Small Signal Equivalent
Electronic Circuits Summary Andreas Biri, D-ITET 6.06.4 Constants (@300K) ε 0 = 8.854 0 F m m 0 = 9. 0 3 kg k =.38 0 3 J K = 8.67 0 5 ev/k kt q = 0.059 V, q kt = 38.6, kt = 5.9 mev V Small Signal Equivalent
Optical Fiber Signal Degradation
 Optical Fiber Signal Degradation Effects Pulse Spreading Dispersion (Distortion) Causes the optical pulses to broaden as they travel along a fiber Overlap between neighboring pulses creates errors Resulting
Optical Fiber Signal Degradation Effects Pulse Spreading Dispersion (Distortion) Causes the optical pulses to broaden as they travel along a fiber Overlap between neighboring pulses creates errors Resulting
Non-Sinusoidal Waves on (Mostly Lossless)Transmission Lines
 Non-Sinusoidal Waves on (Mostly Lossless)Transmission Lines Don Estreich Salazar 21C Adjunct Professor Engineering Science October 212 https://www.iol.unh.edu/services/testing/sas/tools.php 1 Outline of
Non-Sinusoidal Waves on (Mostly Lossless)Transmission Lines Don Estreich Salazar 21C Adjunct Professor Engineering Science October 212 https://www.iol.unh.edu/services/testing/sas/tools.php 1 Outline of
Optimal Placement of Training Symbols for Frequency Acquisition: A Cramér-Rao Bound Approach
 1 Optimal Placement of Training Symbols for Frequency Acquisition: A Cramér-Rao Bound Approach Aravind R. Nayak, Member, IEEE, John R. Barry, Senior Member, IEEE, and Steven W. McLaughlin, Senior Member,
1 Optimal Placement of Training Symbols for Frequency Acquisition: A Cramér-Rao Bound Approach Aravind R. Nayak, Member, IEEE, John R. Barry, Senior Member, IEEE, and Steven W. McLaughlin, Senior Member,
ELEN E4810: Digital Signal Processing Topic 11: Continuous Signals. 1. Sampling and Reconstruction 2. Quantization
 ELEN E4810: Digital Signal Processing Topic 11: Continuous Signals 1. Sampling and Reconstruction 2. Quantization 1 1. Sampling & Reconstruction DSP must interact with an analog world: A to D D to A x(t)
ELEN E4810: Digital Signal Processing Topic 11: Continuous Signals 1. Sampling and Reconstruction 2. Quantization 1 1. Sampling & Reconstruction DSP must interact with an analog world: A to D D to A x(t)
Line Codes and Pulse Shaping Review. Intersymbol interference (ISI) Pulse shaping to reduce ISI Embracing ISI
 Line Codes and Pulse Shaping Review Line codes Pulse width and polarity Power spectral density Intersymbol interference (ISI) Pulse shaping to reduce ISI Embracing ISI Line Code Examples (review) on-off
Line Codes and Pulse Shaping Review Line codes Pulse width and polarity Power spectral density Intersymbol interference (ISI) Pulse shaping to reduce ISI Embracing ISI Line Code Examples (review) on-off
a) Find the compact (i.e. smallest) basis set required to ensure sufficient statistics.
 Digital Modulation and Coding Tutorial-1 1. Consider the signal set shown below in Fig.1 a) Find the compact (i.e. smallest) basis set required to ensure sufficient statistics. b) What is the minimum Euclidean
Digital Modulation and Coding Tutorial-1 1. Consider the signal set shown below in Fig.1 a) Find the compact (i.e. smallest) basis set required to ensure sufficient statistics. b) What is the minimum Euclidean
Revision of Lecture 4
 Revision of Lecture 4 We have completed studying digital sources from information theory viewpoint We have learnt all fundamental principles for source coding, provided by information theory Practical
Revision of Lecture 4 We have completed studying digital sources from information theory viewpoint We have learnt all fundamental principles for source coding, provided by information theory Practical
Computation of Bit-Error Rate of Coherent and Non-Coherent Detection M-Ary PSK With Gray Code in BFWA Systems
 Computation of Bit-Error Rate of Coherent and Non-Coherent Detection M-Ary PSK With Gray Code in BFWA Systems Department of Electrical Engineering, College of Engineering, Basrah University Basrah Iraq,
Computation of Bit-Error Rate of Coherent and Non-Coherent Detection M-Ary PSK With Gray Code in BFWA Systems Department of Electrical Engineering, College of Engineering, Basrah University Basrah Iraq,
Performance Analysis of Spread Spectrum CDMA systems
 1 Performance Analysis of Spread Spectrum CDMA systems 16:33:546 Wireless Communication Technologies Spring 5 Instructor: Dr. Narayan Mandayam Summary by Liang Xiao lxiao@winlab.rutgers.edu WINLAB, Department
1 Performance Analysis of Spread Spectrum CDMA systems 16:33:546 Wireless Communication Technologies Spring 5 Instructor: Dr. Narayan Mandayam Summary by Liang Xiao lxiao@winlab.rutgers.edu WINLAB, Department
Lecture 7: Wireless Channels and Diversity Advanced Digital Communications (EQ2410) 1
 Wireless : Wireless Advanced Digital Communications (EQ2410) 1 Thursday, Feb. 11, 2016 10:00-12:00, B24 1 Textbook: U. Madhow, Fundamentals of Digital Communications, 2008 1 / 15 Wireless Lecture 1-6 Equalization
Wireless : Wireless Advanced Digital Communications (EQ2410) 1 Thursday, Feb. 11, 2016 10:00-12:00, B24 1 Textbook: U. Madhow, Fundamentals of Digital Communications, 2008 1 / 15 Wireless Lecture 1-6 Equalization
ARCC Workshop on Time-reversal communications in richly scattering environments. Large-Delay-Spread Channels: Mathematical models and fast algorithms
 ARCC Workshop on Time-reversal communications in richly scattering environments Large-Delay-Spread Channels: Mathematical models and fast algorithms Thomas Strohmer Department of Mathematics University
ARCC Workshop on Time-reversal communications in richly scattering environments Large-Delay-Spread Channels: Mathematical models and fast algorithms Thomas Strohmer Department of Mathematics University
UNIT 1. SIGNALS AND SYSTEM
 Page no: 1 UNIT 1. SIGNALS AND SYSTEM INTRODUCTION A SIGNAL is defined as any physical quantity that changes with time, distance, speed, position, pressure, temperature or some other quantity. A SIGNAL
Page no: 1 UNIT 1. SIGNALS AND SYSTEM INTRODUCTION A SIGNAL is defined as any physical quantity that changes with time, distance, speed, position, pressure, temperature or some other quantity. A SIGNAL
Timing Recovery at Low SNR Cramer-Rao bound, and outperforming the PLL
 T F T I G E O R G A I N S T I T U T E O H E O F E A L P R O G R ESS S A N D 1 8 8 5 S E R V L O G Y I C E E C H N O Timing Recovery at Low SNR Cramer-Rao bound, and outperforming the PLL Aravind R. Nayak
T F T I G E O R G A I N S T I T U T E O H E O F E A L P R O G R ESS S A N D 1 8 8 5 S E R V L O G Y I C E E C H N O Timing Recovery at Low SNR Cramer-Rao bound, and outperforming the PLL Aravind R. Nayak
Optoelectronic Applications. Injection Locked Oscillators. Injection Locked Oscillators. Q 2, ω 2. Q 1, ω 1
 Injection Locked Oscillators Injection Locked Oscillators Optoelectronic Applications Q, ω Q, ω E. Shumakher, J. Lasri,, B. Sheinman, G. Eisenstein, D. Ritter Electrical Engineering Dept. TECHNION Haifa
Injection Locked Oscillators Injection Locked Oscillators Optoelectronic Applications Q, ω Q, ω E. Shumakher, J. Lasri,, B. Sheinman, G. Eisenstein, D. Ritter Electrical Engineering Dept. TECHNION Haifa
Example: Bipolar NRZ (non-return-to-zero) signaling
 Baseand Data Transmission Data are sent without using a carrier signal Example: Bipolar NRZ (non-return-to-zero signaling is represented y is represented y T A -A T : it duration is represented y BT. Passand
Baseand Data Transmission Data are sent without using a carrier signal Example: Bipolar NRZ (non-return-to-zero signaling is represented y is represented y T A -A T : it duration is represented y BT. Passand
Blind phase/frequency synchronization with low-precision ADC: a Bayesian approach
 Blind phase/frequency synchronization with low-precision ADC: a Bayesian approach Aseem Wadhwa, Upamanyu Madhow Department of ECE, UCSB 1/26 Modern Communication Receiver Architecture Analog Digital TX
Blind phase/frequency synchronization with low-precision ADC: a Bayesian approach Aseem Wadhwa, Upamanyu Madhow Department of ECE, UCSB 1/26 Modern Communication Receiver Architecture Analog Digital TX
ANALYSIS OF A PARTIAL DECORRELATOR IN A MULTI-CELL DS/CDMA SYSTEM
 ANAYSIS OF A PARTIA DECORREATOR IN A MUTI-CE DS/CDMA SYSTEM Mohammad Saquib ECE Department, SU Baton Rouge, A 70803-590 e-mail: saquib@winlab.rutgers.edu Roy Yates WINAB, Rutgers University Piscataway
ANAYSIS OF A PARTIA DECORREATOR IN A MUTI-CE DS/CDMA SYSTEM Mohammad Saquib ECE Department, SU Baton Rouge, A 70803-590 e-mail: saquib@winlab.rutgers.edu Roy Yates WINAB, Rutgers University Piscataway
Optical solitons and its applications
 Physics 568 (Nonlinear optics) 04/30/007 Final report Optical solitons and its applications 04/30/007 1 1 Introduction to optical soliton. (temporal soliton) The optical pulses which propagate in the lossless
Physics 568 (Nonlinear optics) 04/30/007 Final report Optical solitons and its applications 04/30/007 1 1 Introduction to optical soliton. (temporal soliton) The optical pulses which propagate in the lossless
Estimation of the Capacity of Multipath Infrared Channels
 Estimation of the Capacity of Multipath Infrared Channels Jeffrey B. Carruthers Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Boston University jbc@bu.edu Sachin Padma Department of Electrical and
Estimation of the Capacity of Multipath Infrared Channels Jeffrey B. Carruthers Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Boston University jbc@bu.edu Sachin Padma Department of Electrical and
ADAPTIVE FILTER ALGORITHMS. Prepared by Deepa.T, Asst.Prof. /TCE
 ADAPTIVE FILTER ALGORITHMS Prepared by Deepa.T, Asst.Prof. /TCE Equalization Techniques Fig.3 Classification of equalizers Equalizer Techniques Linear transversal equalizer (LTE, made up of tapped delay
ADAPTIVE FILTER ALGORITHMS Prepared by Deepa.T, Asst.Prof. /TCE Equalization Techniques Fig.3 Classification of equalizers Equalizer Techniques Linear transversal equalizer (LTE, made up of tapped delay
Channel Estimation with Low-Precision Analog-to-Digital Conversion
 Channel Estimation with Low-Precision Analog-to-Digital Conversion Onkar Dabeer School of Technology and Computer Science Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai India Email: onkar@tcs.tifr.res.in
Channel Estimation with Low-Precision Analog-to-Digital Conversion Onkar Dabeer School of Technology and Computer Science Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai India Email: onkar@tcs.tifr.res.in
CS6956: Wireless and Mobile Networks Lecture Notes: 2/4/2015
 CS6956: Wireless and Mobile Networks Lecture Notes: 2/4/2015 [Most of the material for this lecture has been taken from the Wireless Communications & Networks book by Stallings (2 nd edition).] Effective
CS6956: Wireless and Mobile Networks Lecture Notes: 2/4/2015 [Most of the material for this lecture has been taken from the Wireless Communications & Networks book by Stallings (2 nd edition).] Effective
Digital Communications
 Digital Communications Chapter 9 Digital Communications Through Band-Limited Channels Po-Ning Chen, Professor Institute of Communications Engineering National Chiao-Tung University, Taiwan Digital Communications:
Digital Communications Chapter 9 Digital Communications Through Band-Limited Channels Po-Ning Chen, Professor Institute of Communications Engineering National Chiao-Tung University, Taiwan Digital Communications:
Data Detection for Controlled ISI. h(nt) = 1 for n=0,1 and zero otherwise.
 Data Detection for Controlled ISI *Symbol by symbol suboptimum detection For the duobinary signal pulse h(nt) = 1 for n=0,1 and zero otherwise. The samples at the output of the receiving filter(demodulator)
Data Detection for Controlled ISI *Symbol by symbol suboptimum detection For the duobinary signal pulse h(nt) = 1 for n=0,1 and zero otherwise. The samples at the output of the receiving filter(demodulator)
High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 4 Generalized Reflection Coefficient, Smith Chart, Integrated Passive Components
 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 4 Generalized Reflection Coefficient, Smith Chart, Integrated Passive Components Michael H. Perrott February 11, 2004 Copyright 2004 by Michael H.
High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 4 Generalized Reflection Coefficient, Smith Chart, Integrated Passive Components Michael H. Perrott February 11, 2004 Copyright 2004 by Michael H.
Advantages of Using CMOS
 Advantages of Using CMOS Compact (shared diffusion regions) Very low static power dissipation High noise margin (nearly ideal inverter voltage transfer characteristic) Very well modeled and characterized
Advantages of Using CMOS Compact (shared diffusion regions) Very low static power dissipation High noise margin (nearly ideal inverter voltage transfer characteristic) Very well modeled and characterized
Broadband material model identification with GMS-parameters
 Broadband material model identification with GMS-parameters Yuriy Olegovich Shlepnev Simberian Inc. shlepnev@simberian.com 2015 EPEPS Conference, October 27, 2015 2015 Simberian Inc. Outline Introduction
Broadband material model identification with GMS-parameters Yuriy Olegovich Shlepnev Simberian Inc. shlepnev@simberian.com 2015 EPEPS Conference, October 27, 2015 2015 Simberian Inc. Outline Introduction
Effect of Nonlinearity on PMD Compensation in a Single-Channel 10-Gb/s NRZ System
 The Open Optics Journal, 28, 2, 53-6 53 Open Access Effect of Nonlinearity on PMD Compensation in a Single-Channel -Gb/s NRZ System John Cameron *,,2, Xiaoyi Bao and Liang Chen Physics Department, University
The Open Optics Journal, 28, 2, 53-6 53 Open Access Effect of Nonlinearity on PMD Compensation in a Single-Channel -Gb/s NRZ System John Cameron *,,2, Xiaoyi Bao and Liang Chen Physics Department, University
Feedback Transimpedance & Current Amplifiers
 Feedback Transimpedance & Current Amplifiers Willy Sansen KULeuven, ESATMICAS Leuven, Belgium willy.sansen@esat.kuleuven.be Willy Sansen 1005 141 Table of contents Introduction Shuntshunt FB for Transimpedance
Feedback Transimpedance & Current Amplifiers Willy Sansen KULeuven, ESATMICAS Leuven, Belgium willy.sansen@esat.kuleuven.be Willy Sansen 1005 141 Table of contents Introduction Shuntshunt FB for Transimpedance
Summary: ISI. No ISI condition in time. II Nyquist theorem. Ideal low pass filter. Raised cosine filters. TX filters
 UORIAL ON DIGIAL MODULAIONS Part 7: Intersymbol interference [last modified: 200--23] Roberto Garello, Politecnico di orino Free download at: www.tlc.polito.it/garello (personal use only) Part 7: Intersymbol
UORIAL ON DIGIAL MODULAIONS Part 7: Intersymbol interference [last modified: 200--23] Roberto Garello, Politecnico di orino Free download at: www.tlc.polito.it/garello (personal use only) Part 7: Intersymbol
Lecture 15: Thu Feb 28, 2019
 Lecture 15: Thu Feb 28, 2019 Announce: HW5 posted Lecture: The AWGN waveform channel Projecting temporally AWGN leads to spatially AWGN sufficiency of projection: irrelevancy theorem in waveform AWGN:
Lecture 15: Thu Feb 28, 2019 Announce: HW5 posted Lecture: The AWGN waveform channel Projecting temporally AWGN leads to spatially AWGN sufficiency of projection: irrelevancy theorem in waveform AWGN:
Data-aided and blind synchronization
 PHYDYAS Review Meeting 2009-03-02 Data-aided and blind synchronization Mario Tanda Università di Napoli Federico II Dipartimento di Ingegneria Biomedica, Elettronicae delle Telecomunicazioni Via Claudio
PHYDYAS Review Meeting 2009-03-02 Data-aided and blind synchronization Mario Tanda Università di Napoli Federico II Dipartimento di Ingegneria Biomedica, Elettronicae delle Telecomunicazioni Via Claudio
Mobile Communications (KECE425) Lecture Note Prof. Young-Chai Ko
 Mobile Communications (KECE425) Lecture Note 20 5-19-2014 Prof Young-Chai Ko Summary Complexity issues of diversity systems ADC and Nyquist sampling theorem Transmit diversity Channel is known at the transmitter
Mobile Communications (KECE425) Lecture Note 20 5-19-2014 Prof Young-Chai Ko Summary Complexity issues of diversity systems ADC and Nyquist sampling theorem Transmit diversity Channel is known at the transmitter
Efficient Semi-Blind Channel Estimation and Equalization Based on a Parametric Channel Representation
 Efficient Semi-Blind Channel Estimation and Equalization Based on a Parametric Channel Representation Presenter: Kostas Berberidis University of Patras Computer Engineering & Informatics Department Signal
Efficient Semi-Blind Channel Estimation and Equalization Based on a Parametric Channel Representation Presenter: Kostas Berberidis University of Patras Computer Engineering & Informatics Department Signal
Single-Carrier Block Transmission With Frequency-Domain Equalisation
 ELEC6014 RCNSs: Additional Topic Notes Single-Carrier Block Transmission With Frequency-Domain Equalisation Professor Sheng Chen School of Electronics and Computer Science University of Southampton Southampton
ELEC6014 RCNSs: Additional Topic Notes Single-Carrier Block Transmission With Frequency-Domain Equalisation Professor Sheng Chen School of Electronics and Computer Science University of Southampton Southampton
This examination consists of 11 pages. Please check that you have a complete copy. Time: 2.5 hrs INSTRUCTIONS
 THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EECE 564 Detection and Estimation of Signals in Noise Final Examination 6 December 2006 This examination consists of
THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EECE 564 Detection and Estimation of Signals in Noise Final Examination 6 December 2006 This examination consists of
Raman Amplification for Telecom Optical Networks. Dominique Bayart Alcatel Lucent Bell Labs France, Research Center of Villarceaux
 Raman Amplification for Telecom Optical Networks Dominique Bayart Alcatel Lucent Bell Labs France, Research Center of Villarceaux Training day www.brighter.eu project Cork, June 20th 2008 Outline of the
Raman Amplification for Telecom Optical Networks Dominique Bayart Alcatel Lucent Bell Labs France, Research Center of Villarceaux Training day www.brighter.eu project Cork, June 20th 2008 Outline of the
On VDSL Performance and Hardware Implications for Single Carrier Modulation Transceivers
 On VDSL Performance and ardware Implications for Single Carrier Modulation Transceivers S. AAR, R.ZUKUNFT, T.MAGESACER Institute for Integrated Circuits - BRIDGELAB Munich University of Technology Arcisstr.
On VDSL Performance and ardware Implications for Single Carrier Modulation Transceivers S. AAR, R.ZUKUNFT, T.MAGESACER Institute for Integrated Circuits - BRIDGELAB Munich University of Technology Arcisstr.
Self-Phase Modulation in Optical Fiber Communications: Good or Bad?
 1/100 Self-Phase Modulation in Optical Fiber Communications: Good or Bad? Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Historical Introduction
1/100 Self-Phase Modulation in Optical Fiber Communications: Good or Bad? Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Historical Introduction
EE4512 Analog and Digital Communications Chapter 4. Chapter 4 Receiver Design
 Chapter 4 Receiver Design Chapter 4 Receiver Design Probability of Bit Error Pages 124-149 149 Probability of Bit Error The low pass filtered and sampled PAM signal results in an expression for the probability
Chapter 4 Receiver Design Chapter 4 Receiver Design Probability of Bit Error Pages 124-149 149 Probability of Bit Error The low pass filtered and sampled PAM signal results in an expression for the probability
Digital Band-pass Modulation PROF. MICHAEL TSAI 2011/11/10
 Digital Band-pass Modulation PROF. MICHAEL TSAI 211/11/1 Band-pass Signal Representation a t g t General form: 2πf c t + φ t g t = a t cos 2πf c t + φ t Envelope Phase Envelope is always non-negative,
Digital Band-pass Modulation PROF. MICHAEL TSAI 211/11/1 Band-pass Signal Representation a t g t General form: 2πf c t + φ t g t = a t cos 2πf c t + φ t Envelope Phase Envelope is always non-negative,
Communication Theory Summary of Important Definitions and Results
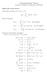 Signal and system theory Convolution of signals x(t) h(t) = y(t): Fourier Transform: Communication Theory Summary of Important Definitions and Results X(ω) = X(ω) = y(t) = X(ω) = j x(t) e jωt dt, 0 Properties
Signal and system theory Convolution of signals x(t) h(t) = y(t): Fourier Transform: Communication Theory Summary of Important Definitions and Results X(ω) = X(ω) = y(t) = X(ω) = j x(t) e jωt dt, 0 Properties
Electronic Circuits. Prof. Dr. Qiuting Huang Integrated Systems Laboratory
 Electronic Circuits Prof. Dr. Qiuting Huang 6. Transimpedance Amplifiers, Voltage Regulators, Logarithmic Amplifiers, Anti-Logarithmic Amplifiers Transimpedance Amplifiers Sensing an input current ii in
Electronic Circuits Prof. Dr. Qiuting Huang 6. Transimpedance Amplifiers, Voltage Regulators, Logarithmic Amplifiers, Anti-Logarithmic Amplifiers Transimpedance Amplifiers Sensing an input current ii in
RFIC2017 MO2B-2. A Simplified CMOS FET Model using Surface Potential Equations For Inter-modulation Simulations of Passive-Mixer-Like Circuits
 A Simplified CMOS FET Model using Surface Potential Equations For Inter-modulation Simulations of Passive-Mixer-Like Circuits M. Baraani Dastjerdi and H. Krishnaswamy CoSMIC Lab, Columbia University, New
A Simplified CMOS FET Model using Surface Potential Equations For Inter-modulation Simulations of Passive-Mixer-Like Circuits M. Baraani Dastjerdi and H. Krishnaswamy CoSMIC Lab, Columbia University, New
LOPE3202: Communication Systems 10/18/2017 2
 By Lecturer Ahmed Wael Academic Year 2017-2018 LOPE3202: Communication Systems 10/18/2017 We need tools to build any communication system. Mathematics is our premium tool to do work with signals and systems.
By Lecturer Ahmed Wael Academic Year 2017-2018 LOPE3202: Communication Systems 10/18/2017 We need tools to build any communication system. Mathematics is our premium tool to do work with signals and systems.
Approximate Best Linear Unbiased Channel Estimation for Frequency Selective Channels with Long Delay Spreads: Robustness to Timing and Carrier Offsets
 Approximate Best Linear Unbiased Channel Estimation for Frequency Selective Channels with Long Delay Spreads: Robustness to Timing and Carrier Offsets Serdar Özen,SMNerayanuru, Christopher Pladdy, and
Approximate Best Linear Unbiased Channel Estimation for Frequency Selective Channels with Long Delay Spreads: Robustness to Timing and Carrier Offsets Serdar Özen,SMNerayanuru, Christopher Pladdy, and
Lecture 3 Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 3, Slide 1
 Lecture 3 Optical fibers as waveguides Maxwell s equations The wave equation Fiber modes Phase velocity, group velocity Dispersion Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 3, Slide 1 Maxwell s equations in
Lecture 3 Optical fibers as waveguides Maxwell s equations The wave equation Fiber modes Phase velocity, group velocity Dispersion Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 3, Slide 1 Maxwell s equations in
Lecture 9. PMTs and Laser Noise. Lecture 9. Photon Counting. Photomultiplier Tubes (PMTs) Laser Phase Noise. Relative Intensity
 s and Laser Phase Phase Density ECE 185 Lasers and Modulators Lab - Spring 2018 1 Detectors Continuous Output Internal Photoelectron Flux Thermal Filtered External Current w(t) Sensor i(t) External System
s and Laser Phase Phase Density ECE 185 Lasers and Modulators Lab - Spring 2018 1 Detectors Continuous Output Internal Photoelectron Flux Thermal Filtered External Current w(t) Sensor i(t) External System
Lecture 4 Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 4, Slide 1
 ecture 4 Dispersion in single-mode fibers Material dispersion Waveguide dispersion imitations from dispersion Propagation equations Gaussian pulse broadening Bit-rate limitations Fiber losses Fiber Optical
ecture 4 Dispersion in single-mode fibers Material dispersion Waveguide dispersion imitations from dispersion Propagation equations Gaussian pulse broadening Bit-rate limitations Fiber losses Fiber Optical
