EE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications
|
|
|
- Jessica Hamilton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications Week 12, 13: Inter Symbol Interference (ISI) Nyquist Criteria for ISI Pulse Shaping and Raised-Cosine Filter Eye Pattern Equalization (On Board) 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713) 1
2 Baseband Communication System We have been considering the following baseband system he transmitted signal is created by the line coder according to s ( t) = a g ( t ) n= where a n is the symbol mapping and g(t) is the pulse shape Problems with Line Codes n n b One big problem with the line codes is that they are not bandlimited he absolute bandwidth is infinite he power outside the 1st null bandwidth is not negligible. hat is, the power in the sidelobes can be quite high 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713) 2
3 Intersymbol Interference (ISI) If the transmission channel is bandlimited, then high frequency components will be cut off Hence, the pulses will spread out If the pulse spread out into the adjacent symbol periods, then it is said that intersymbol interference (ISI) has occurred Intersymbol Interference (ISI) Intersymbol interference (ISI) occurs when a pulse spreads out in such a way that it interferes with adjacent pulses at the sample instant Causes Channel induced distortion which spreads or disperses the pulses Multipath effects (echo) 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713) 3
4 Pulse spreading Due to improper filtering x and/or Rx), the received pulses overlap one another thus making detection difficult Example of ISI Assume polar NRZ line code 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713) 4
5 Inter Symbol Interference Input data stream and bit superposition he channel output is the sum of the contributions from each bit 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713) 5
6 ISI Note: ISI can occur whenever a non-bandlimited line code is used over a bandlimited channel ISI can occur only at the sampling instants Overlapping pulses will not cause ISI if they have zero amplitude at the time the signal is sampled 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713) 6
7 ISI Baseband Communication System Model where h h C h R ( t) = Impulse response of the transmitter, ( t) = Impulse response of the channel, ( t) = Impulse response of the receiver s ( t) = a h ( t n ), n n= r( t) = a n n = n e n= g ( t n ) + y t) = a h ( t n) + n ( t) e n( t), where g ( t) = h ( t) * h C ( t), = 1 / f ( where h ( t) h ( t)* h ( t)* h ( t), n e = ( t) n( t) * h ( t) * h ( t) e = C C R R s 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713) 7
8 ISI Baseband Communication System Model Note that h e (t) is the equivalent impulse response of the receiving filter o recover the information sequence {a n }, the output y(t) is sampled at t = k, k = 0, 1, 2, he sampled sequence is n= = y ( k) = a h ( k n) + n ( k) or equivalently n e e AWGN term y k = n= a n h k n + nk = h0ak + anhk n + n=, n k n k where h = h ( k), n = n ( k), k = 0, ± 1, ± 2,.. k Desired symbol scaled by gain parameters h 0 e h 0 is an arbitrary constant k e Effect of other symbols at the sampling instants t=k 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713) 8
9 Signal Design for Bandlimited Channel Zero ISI y( k ) = h 0 ak + anhe ( k n ) + ne ( k ) n=, n k o remove ISI, it is necessary and sufficient to make the term h e Nyquist Criterion ( k n ) = 0, for n k and h 0 0 Pulse amplitudes can be detected correctly despite pulse spreading or overlapping, if there is no ISI at the decisionmaking instants 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713) 9
10 Nyquist s three criteria Nyquist Criteria Pulse amplitudes can be detected correctly despite pulse spreading or overlapping, if there is no ISI at the decisionmaking instants 1: At sampling points, no ISI 2: At threshold, no ISI 3: Areas within symbol period is zero, then no ISI Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713)
11 1st Nyquist Criterion: ime domain p(t): impulse response of a transmission system (infinite length) p(t) 1 shaping function 0 1 = 2 f N t 0 2t 0 t no ISI! -1 Equally spaced zeros, interval 1 = 2 f n Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713)
12 1st Nyquist Criterion: ime domain Suppose 1/ is the sample rate he necessary and sufficient condition for p(t) to satisfy p ( n ) = 1, 0, ( n = 0) ( n 0) Is that its Fourier transform P(f) satisfy m= P( f + m ) = Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713)
13 1st Nyquist Criterion: Frequency domain m= P ( f + m ) = 0 fa = 2 fn 4 f N (limited bandwidth) f Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713)
14 Fourier ransform At t= p = = = p ( 2m+ 1) Proof ( n ) = P( f ) exp( j2πfn ) m= m = ( 2m 1) p ( t) P( f ) exp( j2πft ) 2 2 = df ( n ) P( f ) exp( j2πfn ) 2 m = B 2 P P = df ( f + m ) exp( j2πfn ) ( f + m ) exp( j2πfn ) ( f ) exp( j2πfn ) df B df df df ( f ) = P( f + m ) m= Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713)
15 Proof B ( f ) = P( f + m ) m= B b n ( f ) = b exp( j2πnf ) = n= n B ( f ) exp( j2πnf ) b n ( n ) = p ( n 0) b n = = 0 n 0 ( ) ( f ) B = P( f + m ) = m= Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713)
16 Nyquist Criterion: ime domain Pulse shape that satisfy this criteria is Sinc(.) function, e.g., t h e ( t) or p( t) = sinc = sinc(2wt ) he smallest value of for which transmission with zero ISI is possible is Problems with Sinc(.) function It is not possible to create Sinc pulses due to 1 = 2 W Infinite time duration Sharp transition band in the frequency domain Sinc(.) pulse shape can cause ISI in the presence of timing errors If the received signal is not sampled at exactly the bit instant, then ISI will occur 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713) 16
17 Nyquist Criterion: ime domain p(t) 1 shaping function 0 1 = 2 f s t 0 2t 0 t no ISI! -1 Equally spaced zeros, 1 interval = 2 f s 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713) 17
18 Sample rate vs. bandwidth W is the channel bandwidth for P(f) When 1/ > 2W, there is no way, we can design a system with no ISI P(f) 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713) 18
19 Sample rate vs. bandwidth When 1/ = 2W (he Nyquist Rate), rectangular function satisfy Nyquist condition sinπt πt, ( f < W ) p( t) = = sinc ; P( f ) = π t ( f ) = rect rect ( f ); 1 f P = 2W 2W 0, ( otherwise), W 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713) 19
20 Sample rate vs. bandwidth When 1/ < 2W, numbers of choices to satisfy Nyquist condition Raised Cosine Filter Duobinary Signaling (Partial Response Signals) Gaussian Filter Approximation he most typical one is the raised cosine function 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713) 20
21 Raised Cosine Pulse he following pulse shape satisfies Nyquist s method for zero ISI he Fourier ransform of this pulse shape is cos sinc 4 1 cos sin ) ( t r t r t t r t r t r t r t p = = π π π π 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713) 21 he Fourier ransform of this pulse shape is where r is the roll-off factor that determines the bandwidth = r f r f r r f r r f f P 2 1 0, , 2 1 cos / , ) ( π
22 Responses for different roll-off factors (a) Frequency response. (b) ime response
23 Rolloff and bandwidth Bandwidth occupied beyond 1/2 is called the excess bandwidth (EB) EB is usually expressed as a %tage of the Nyquist frequency, e.g., Rolloff factor, r = 1/2 ===> excess bandwidth is 50 % Rolloff factor, r = 1 ===> excess bandwidth is 100 % RC filter is used to realized Nyquist filter since the transition band can be changed using the roll-off factor he sharpness of the filter is controlled by the parameter r When r = 0 this corresponds to an ideal rectangular function Bandwidth B occupied by a RC filtered signal is increased from its minimum value B 1 2 So the bandwidth becomes: s = min B = B ( 1+ r) 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713) 23 min
24 Rolloff and bandwidth Benefits of large roll off factor Simpler filter fewer stages (taps) hence easier to implement with less processing delay Less signal overshoot, resulting in lower peak to mean excursions of the transmitted signal Less sensitivity to symbol timing accuracy wider eye opening r = 0 corresponds to Sinc(.) function 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713) 24
25 Partial Response Signals o improve the bandwidth efficiency Widen the pulse, the smaller the bandwidth. But there is ISI. For binary case with two symbols, there is only few possible interference patterns. By adding ISI in a controlled manner, it is possible to achieve a signaling rate equal to the Nyquist rate i.e. Duobinary and Polibinary Signaling (Covered in the previous lectures) 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713) 25
26 2 nd Nyquist Criterion Values at the pulse edge are distortion-less
27 Nyquist s hree Criteria Nyquist hree Criteria Pulse amplitudes can be detected correctly despite pulse spreading or overlapping, if there is no ISI at the decisionmaking instants 1: At sampling points, no ISI 2: At threshold, no ISI 3: Areas within symbol period from other symbols is zero, then no ISI Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713)
28 Example (wo Criteria)
29 3 rd Nyquist Criterion Within each symbol period, the integration of signal (area) is proportional to the integration of the transmit signal (area) A 1, p( t) dt= 0, = 2 n n 2 1 n n= 0 0
30 Eye Patterns An eye pattern is obtained by superimposing the actual waveforms for large numbers of transmitted or received symbols Perfect eye pattern for noise-free, bandwidth-limited transmission of an alphabet of two digital waveforms encoding a binary signal (1 s and 0 s) Actual eye patterns are used to estimate the bit error rate and the signal to- noise ratio 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713) 30
31 Eye Patterns Concept of the eye pattern 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713) 31
32 Eye Diagram he eye diagram is created by taking the time domain signal and overlapping the traces for a certain number of symbols. he open part of the signal represents the time that we can safely sample the signal with fidelity
33 Vertical and Horizontal Eye Openings he vertical eye opening or noise margin is related to the SNR, and thus the BER A large eye opening corresponds to a low BER he horizontal eye opening relates the jitter and the sensitivity of the sampling instant to jitter he red brace indicates the range of sample instants with good eye opening At other sample instants, the eye opening is greatly reduced, as governed by the indicated slope
34 Interpretation of Eye Diagram
35 Cosine rolloff filter: Eye pattern 2nd Nyquist 1st Nyquist: 2nd Nyquist: 1st Nyquist: 2nd Nyquist: 1st Nyquist 1st Nyquist: 2nd Nyquist: 1st Nyquist: 2nd Nyquist: 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Advanced Digital Communications (EE5713) 35
Digital Baseband Systems. Reference: Digital Communications John G. Proakis
 Digital Baseband Systems Reference: Digital Communications John G. Proais Baseband Pulse Transmission Baseband digital signals - signals whose spectrum extend down to or near zero frequency. Model of the
Digital Baseband Systems Reference: Digital Communications John G. Proais Baseband Pulse Transmission Baseband digital signals - signals whose spectrum extend down to or near zero frequency. Model of the
Square Root Raised Cosine Filter
 Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Square Root Raised Cosine Filter Institute of Communications Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Introduction We consider the problem of signal design
Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Square Root Raised Cosine Filter Institute of Communications Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Introduction We consider the problem of signal design
Digital Communications
 Digital Communications Chapter 9 Digital Communications Through Band-Limited Channels Po-Ning Chen, Professor Institute of Communications Engineering National Chiao-Tung University, Taiwan Digital Communications:
Digital Communications Chapter 9 Digital Communications Through Band-Limited Channels Po-Ning Chen, Professor Institute of Communications Engineering National Chiao-Tung University, Taiwan Digital Communications:
Weiyao Lin. Shanghai Jiao Tong University. Chapter 5: Digital Transmission through Baseband slchannels Textbook: Ch
 Principles of Communications Weiyao Lin Shanghai Jiao Tong University Chapter 5: Digital Transmission through Baseband slchannels Textbook: Ch 10.1-10.5 2009/2010 Meixia Tao @ SJTU 1 Topics to be Covered
Principles of Communications Weiyao Lin Shanghai Jiao Tong University Chapter 5: Digital Transmission through Baseband slchannels Textbook: Ch 10.1-10.5 2009/2010 Meixia Tao @ SJTU 1 Topics to be Covered
Line Codes and Pulse Shaping Review. Intersymbol interference (ISI) Pulse shaping to reduce ISI Embracing ISI
 Line Codes and Pulse Shaping Review Line codes Pulse width and polarity Power spectral density Intersymbol interference (ISI) Pulse shaping to reduce ISI Embracing ISI Line Code Examples (review) on-off
Line Codes and Pulse Shaping Review Line codes Pulse width and polarity Power spectral density Intersymbol interference (ISI) Pulse shaping to reduce ISI Embracing ISI Line Code Examples (review) on-off
Principles of Communications Lecture 8: Baseband Communication Systems. Chih-Wei Liu 劉志尉 National Chiao Tung University
 Principles of Communications Lecture 8: Baseband Communication Systems Chih-Wei Liu 劉志尉 National Chiao Tung University cwliu@twins.ee.nctu.edu.tw Outlines Introduction Line codes Effects of filtering Pulse
Principles of Communications Lecture 8: Baseband Communication Systems Chih-Wei Liu 劉志尉 National Chiao Tung University cwliu@twins.ee.nctu.edu.tw Outlines Introduction Line codes Effects of filtering Pulse
EE4061 Communication Systems
 EE4061 Communication Systems Week 11 Intersymbol Interference Nyquist Pulse Shaping 0 c 2015, Georgia Institute of Technology (lect10 1) Intersymbol Interference (ISI) Tx filter channel Rx filter a δ(t-nt)
EE4061 Communication Systems Week 11 Intersymbol Interference Nyquist Pulse Shaping 0 c 2015, Georgia Institute of Technology (lect10 1) Intersymbol Interference (ISI) Tx filter channel Rx filter a δ(t-nt)
Lecture 5b: Line Codes
 Lecture 5b: Line Codes Dr. Mohammed Hawa Electrical Engineering Department University of Jordan EE421: Communications I Digitization Sampling (discrete analog signal). Quantization (quantized discrete
Lecture 5b: Line Codes Dr. Mohammed Hawa Electrical Engineering Department University of Jordan EE421: Communications I Digitization Sampling (discrete analog signal). Quantization (quantized discrete
Pulse Shaping and ISI (Proakis: chapter 10.1, 10.3) EEE3012 Spring 2018
 Pulse Shaping and ISI (Proakis: chapter 10.1, 10.3) EEE3012 Spring 2018 Digital Communication System Introduction Bandlimited channels distort signals the result is smeared pulses intersymol interference
Pulse Shaping and ISI (Proakis: chapter 10.1, 10.3) EEE3012 Spring 2018 Digital Communication System Introduction Bandlimited channels distort signals the result is smeared pulses intersymol interference
Example: Bipolar NRZ (non-return-to-zero) signaling
 Baseand Data Transmission Data are sent without using a carrier signal Example: Bipolar NRZ (non-return-to-zero signaling is represented y is represented y T A -A T : it duration is represented y BT. Passand
Baseand Data Transmission Data are sent without using a carrier signal Example: Bipolar NRZ (non-return-to-zero signaling is represented y is represented y T A -A T : it duration is represented y BT. Passand
Signal Design for Band-Limited Channels
 Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Signal Design for Band-Limited Channels Institute of Communications Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Introduction We consider the problem of signal
Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Signal Design for Band-Limited Channels Institute of Communications Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Introduction We consider the problem of signal
Summary: ISI. No ISI condition in time. II Nyquist theorem. Ideal low pass filter. Raised cosine filters. TX filters
 UORIAL ON DIGIAL MODULAIONS Part 7: Intersymbol interference [last modified: 200--23] Roberto Garello, Politecnico di orino Free download at: www.tlc.polito.it/garello (personal use only) Part 7: Intersymbol
UORIAL ON DIGIAL MODULAIONS Part 7: Intersymbol interference [last modified: 200--23] Roberto Garello, Politecnico di orino Free download at: www.tlc.polito.it/garello (personal use only) Part 7: Intersymbol
Principles of Communications
 Principles of Communications Chapter V: Representation and Transmission of Baseband Digital Signal Yongchao Wang Email: ychwang@mail.xidian.edu.cn Xidian University State Key Lab. on ISN November 18, 2012
Principles of Communications Chapter V: Representation and Transmission of Baseband Digital Signal Yongchao Wang Email: ychwang@mail.xidian.edu.cn Xidian University State Key Lab. on ISN November 18, 2012
that efficiently utilizes the total available channel bandwidth W.
 Signal Design for Band-Limited Channels Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Institute of Communications Engineering g National Sun Yat-sen University Introduction We consider the problem of signal
Signal Design for Band-Limited Channels Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Institute of Communications Engineering g National Sun Yat-sen University Introduction We consider the problem of signal
II - Baseband pulse transmission
 II - Baseband pulse transmission 1 Introduction We discuss how to transmit digital data symbols, which have to be converted into material form before they are sent or stored. In the sequel, we associate
II - Baseband pulse transmission 1 Introduction We discuss how to transmit digital data symbols, which have to be converted into material form before they are sent or stored. In the sequel, we associate
A Family of Nyquist Filters Based on Generalized Raised-Cosine Spectra
 Proc. Biennial Symp. Commun. (Kingston, Ont.), pp. 3-35, June 99 A Family of Nyquist Filters Based on Generalized Raised-Cosine Spectra Nader Sheikholeslami Peter Kabal Department of Electrical Engineering
Proc. Biennial Symp. Commun. (Kingston, Ont.), pp. 3-35, June 99 A Family of Nyquist Filters Based on Generalized Raised-Cosine Spectra Nader Sheikholeslami Peter Kabal Department of Electrical Engineering
EE 661: Modulation Theory Solutions to Homework 6
 EE 66: Modulation Theory Solutions to Homework 6. Solution to problem. a) Binary PAM: Since 2W = 4 KHz and β = 0.5, the minimum T is the solution to (+β)/(2t ) = W = 2 0 3 Hz. Thus, we have the maximum
EE 66: Modulation Theory Solutions to Homework 6. Solution to problem. a) Binary PAM: Since 2W = 4 KHz and β = 0.5, the minimum T is the solution to (+β)/(2t ) = W = 2 0 3 Hz. Thus, we have the maximum
a) Find the compact (i.e. smallest) basis set required to ensure sufficient statistics.
 Digital Modulation and Coding Tutorial-1 1. Consider the signal set shown below in Fig.1 a) Find the compact (i.e. smallest) basis set required to ensure sufficient statistics. b) What is the minimum Euclidean
Digital Modulation and Coding Tutorial-1 1. Consider the signal set shown below in Fig.1 a) Find the compact (i.e. smallest) basis set required to ensure sufficient statistics. b) What is the minimum Euclidean
Data Detection for Controlled ISI. h(nt) = 1 for n=0,1 and zero otherwise.
 Data Detection for Controlled ISI *Symbol by symbol suboptimum detection For the duobinary signal pulse h(nt) = 1 for n=0,1 and zero otherwise. The samples at the output of the receiving filter(demodulator)
Data Detection for Controlled ISI *Symbol by symbol suboptimum detection For the duobinary signal pulse h(nt) = 1 for n=0,1 and zero otherwise. The samples at the output of the receiving filter(demodulator)
ELEN E4810: Digital Signal Processing Topic 11: Continuous Signals. 1. Sampling and Reconstruction 2. Quantization
 ELEN E4810: Digital Signal Processing Topic 11: Continuous Signals 1. Sampling and Reconstruction 2. Quantization 1 1. Sampling & Reconstruction DSP must interact with an analog world: A to D D to A x(t)
ELEN E4810: Digital Signal Processing Topic 11: Continuous Signals 1. Sampling and Reconstruction 2. Quantization 1 1. Sampling & Reconstruction DSP must interact with an analog world: A to D D to A x(t)
EE303: Communication Systems
 EE303: Communication Systems Professor A. Manikas Chair of Communications and Array Processing Imperial College London Introductory Concepts Prof. A. Manikas (Imperial College) EE303: Introductory Concepts
EE303: Communication Systems Professor A. Manikas Chair of Communications and Array Processing Imperial College London Introductory Concepts Prof. A. Manikas (Imperial College) EE303: Introductory Concepts
Direct-Sequence Spread-Spectrum
 Chapter 3 Direct-Sequence Spread-Spectrum In this chapter we consider direct-sequence spread-spectrum systems. Unlike frequency-hopping, a direct-sequence signal occupies the entire bandwidth continuously.
Chapter 3 Direct-Sequence Spread-Spectrum In this chapter we consider direct-sequence spread-spectrum systems. Unlike frequency-hopping, a direct-sequence signal occupies the entire bandwidth continuously.
BASICS OF DETECTION AND ESTIMATION THEORY
 BASICS OF DETECTION AND ESTIMATION THEORY 83050E/158 In this chapter we discuss how the transmitted symbols are detected optimally from a noisy received signal (observation). Based on these results, optimal
BASICS OF DETECTION AND ESTIMATION THEORY 83050E/158 In this chapter we discuss how the transmitted symbols are detected optimally from a noisy received signal (observation). Based on these results, optimal
EE4601 Communication Systems
 EE4601 Communication Systems Week 13 Linear Zero Forcing Equalization 0 c 2012, Georgia Institute of Technology (lect13 1) Equalization The cascade of the transmit filter g(t), channel c(t), receiver filter
EE4601 Communication Systems Week 13 Linear Zero Forcing Equalization 0 c 2012, Georgia Institute of Technology (lect13 1) Equalization The cascade of the transmit filter g(t), channel c(t), receiver filter
Es e j4φ +4N n. 16 KE s /N 0. σ 2ˆφ4 1 γ s. p(φ e )= exp 1 ( 2πσ φ b cos N 2 φ e 0
 Problem 6.15 : he received signal-plus-noise vector at the output of the matched filter may be represented as (see (5-2-63) for example) : r n = E s e j(θn φ) + N n where θ n =0,π/2,π,3π/2 for QPSK, and
Problem 6.15 : he received signal-plus-noise vector at the output of the matched filter may be represented as (see (5-2-63) for example) : r n = E s e j(θn φ) + N n where θ n =0,π/2,π,3π/2 for QPSK, and
Digital Band-pass Modulation PROF. MICHAEL TSAI 2011/11/10
 Digital Band-pass Modulation PROF. MICHAEL TSAI 211/11/1 Band-pass Signal Representation a t g t General form: 2πf c t + φ t g t = a t cos 2πf c t + φ t Envelope Phase Envelope is always non-negative,
Digital Band-pass Modulation PROF. MICHAEL TSAI 211/11/1 Band-pass Signal Representation a t g t General form: 2πf c t + φ t g t = a t cos 2πf c t + φ t Envelope Phase Envelope is always non-negative,
References Ideal Nyquist Channel and Raised Cosine Spectrum Chapter 4.5, 4.11, S. Haykin, Communication Systems, Wiley.
 Baseand Data Transmission III Reerences Ideal yquist Channel and Raised Cosine Spectrum Chapter 4.5, 4., S. Haykin, Communication Systems, iley. Equalization Chapter 9., F. G. Stremler, Communication Systems,
Baseand Data Transmission III Reerences Ideal yquist Channel and Raised Cosine Spectrum Chapter 4.5, 4., S. Haykin, Communication Systems, iley. Equalization Chapter 9., F. G. Stremler, Communication Systems,
EE4512 Analog and Digital Communications Chapter 4. Chapter 4 Receiver Design
 Chapter 4 Receiver Design Chapter 4 Receiver Design Probability of Bit Error Pages 124-149 149 Probability of Bit Error The low pass filtered and sampled PAM signal results in an expression for the probability
Chapter 4 Receiver Design Chapter 4 Receiver Design Probability of Bit Error Pages 124-149 149 Probability of Bit Error The low pass filtered and sampled PAM signal results in an expression for the probability
EE401: Advanced Communication Theory
 EE401: Advanced Communication Theory Professor A. Manikas Chair of Communications and Array Processing Imperial College London Introductory Concepts Prof. A. Manikas (Imperial College) EE.401: Introductory
EE401: Advanced Communication Theory Professor A. Manikas Chair of Communications and Array Processing Imperial College London Introductory Concepts Prof. A. Manikas (Imperial College) EE.401: Introductory
ECS 332: Principles of Communications 2012/1. HW 4 Due: Sep 7
 ECS 332: Principles of Communications 2012/1 HW 4 Due: Sep 7 Lecturer: Prapun Suksompong, Ph.D. Instructions (a) ONE part of a question will be graded (5 pt). Of course, you do not know which part will
ECS 332: Principles of Communications 2012/1 HW 4 Due: Sep 7 Lecturer: Prapun Suksompong, Ph.D. Instructions (a) ONE part of a question will be graded (5 pt). Of course, you do not know which part will
This examination consists of 11 pages. Please check that you have a complete copy. Time: 2.5 hrs INSTRUCTIONS
 THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EECE 564 Detection and Estimation of Signals in Noise Final Examination 6 December 2006 This examination consists of
THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EECE 564 Detection and Estimation of Signals in Noise Final Examination 6 December 2006 This examination consists of
3.2 Complex Sinusoids and Frequency Response of LTI Systems
 3. Introduction. A signal can be represented as a weighted superposition of complex sinusoids. x(t) or x[n]. LTI system: LTI System Output = A weighted superposition of the system response to each complex
3. Introduction. A signal can be represented as a weighted superposition of complex sinusoids. x(t) or x[n]. LTI system: LTI System Output = A weighted superposition of the system response to each complex
Analog Electronics 2 ICS905
 Analog Electronics 2 ICS905 G. Rodriguez-Guisantes Dépt. COMELEC http://perso.telecom-paristech.fr/ rodrigez/ens/cycle_master/ November 2016 2/ 67 Schedule Radio channel characteristics ; Analysis and
Analog Electronics 2 ICS905 G. Rodriguez-Guisantes Dépt. COMELEC http://perso.telecom-paristech.fr/ rodrigez/ens/cycle_master/ November 2016 2/ 67 Schedule Radio channel characteristics ; Analysis and
LOPE3202: Communication Systems 10/18/2017 2
 By Lecturer Ahmed Wael Academic Year 2017-2018 LOPE3202: Communication Systems 10/18/2017 We need tools to build any communication system. Mathematics is our premium tool to do work with signals and systems.
By Lecturer Ahmed Wael Academic Year 2017-2018 LOPE3202: Communication Systems 10/18/2017 We need tools to build any communication system. Mathematics is our premium tool to do work with signals and systems.
This examination consists of 10 pages. Please check that you have a complete copy. Time: 2.5 hrs INSTRUCTIONS
 THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EECE 564 Detection and Estimation of Signals in Noise Final Examination 08 December 2009 This examination consists of
THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EECE 564 Detection and Estimation of Signals in Noise Final Examination 08 December 2009 This examination consists of
Revision of Lecture 4
 Revision of Lecture 4 We have discussed all basic components of MODEM Pulse shaping Tx/Rx filter pair Modulator/demodulator Bits map symbols Discussions assume ideal channel, and for dispersive channel
Revision of Lecture 4 We have discussed all basic components of MODEM Pulse shaping Tx/Rx filter pair Modulator/demodulator Bits map symbols Discussions assume ideal channel, and for dispersive channel
Contents Equalization 148
 Contents 3 Equalization 48 3. Intersymbol Interference and Receivers for Successive Message ransmission........ 50 3.. ransmission of Successive Messages.......................... 50 3.. Bandlimited Channels..................................
Contents 3 Equalization 48 3. Intersymbol Interference and Receivers for Successive Message ransmission........ 50 3.. ransmission of Successive Messages.......................... 50 3.. Bandlimited Channels..................................
Optimized Impulses for Multicarrier Offset-QAM
 Optimized Impulses for ulticarrier Offset-QA Stephan Pfletschinger, Joachim Speidel Institut für Nachrichtenübertragung Universität Stuttgart, Pfaffenwaldring 47, D-7469 Stuttgart, Germany Abstract The
Optimized Impulses for ulticarrier Offset-QA Stephan Pfletschinger, Joachim Speidel Institut für Nachrichtenübertragung Universität Stuttgart, Pfaffenwaldring 47, D-7469 Stuttgart, Germany Abstract The
3.9 Diversity Equalization Multiple Received Signals and the RAKE Infinite-length MMSE Equalization Structures
 Contents 3 Equalization 57 3. Intersymbol Interference and Receivers for Successive Message ransmission........ 59 3.. ransmission of Successive Messages.......................... 59 3.. Bandlimited Channels..................................
Contents 3 Equalization 57 3. Intersymbol Interference and Receivers for Successive Message ransmission........ 59 3.. ransmission of Successive Messages.......................... 59 3.. Bandlimited Channels..................................
Digital Transmission Methods S
 Digital ransmission ethods S-7.5 Second Exercise Session Hypothesis esting Decision aking Gram-Schmidt method Detection.K.K. Communication Laboratory 5//6 Konstantinos.koufos@tkk.fi Exercise We assume
Digital ransmission ethods S-7.5 Second Exercise Session Hypothesis esting Decision aking Gram-Schmidt method Detection.K.K. Communication Laboratory 5//6 Konstantinos.koufos@tkk.fi Exercise We assume
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATIONS DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS
 EC 32 (CR) Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 02 III/IV B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, APRIL/MAY- 207 Second Semester ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATIONS DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS Time: Three Hours
EC 32 (CR) Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 02 III/IV B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, APRIL/MAY- 207 Second Semester ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATIONS DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS Time: Three Hours
Physical Layer and Coding
 Physical Layer and Coding Muriel Médard Professor EECS Overview A variety of physical media: copper, free space, optical fiber Unified way of addressing signals at the input and the output of these media:
Physical Layer and Coding Muriel Médard Professor EECS Overview A variety of physical media: copper, free space, optical fiber Unified way of addressing signals at the input and the output of these media:
IEEE 802.3ap Task Force Ottawa Sept 27-29, 2004
 Edge-Equalized NRZ and Duobinary IEEE 82.3ap Task Force Ottawa Sept 27-29, 24 Brian Brunn, Xilinx Intro It appears the equalization algorithm for EE-NRZ and Duobinary are the same. Both want to zero-force
Edge-Equalized NRZ and Duobinary IEEE 82.3ap Task Force Ottawa Sept 27-29, 24 Brian Brunn, Xilinx Intro It appears the equalization algorithm for EE-NRZ and Duobinary are the same. Both want to zero-force
Summary II: Modulation and Demodulation
 Summary II: Modulation and Demodulation Instructor : Jun Chen Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, McMaster University Room: ITB A1, ext. 0163 Email: junchen@mail.ece.mcmaster.ca Website:
Summary II: Modulation and Demodulation Instructor : Jun Chen Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, McMaster University Room: ITB A1, ext. 0163 Email: junchen@mail.ece.mcmaster.ca Website:
MATHEMATICAL TOOLS FOR DIGITAL TRANSMISSION ANALYSIS
 ch03.qxd 1/9/03 09:14 AM Page 35 CHAPTER 3 MATHEMATICAL TOOLS FOR DIGITAL TRANSMISSION ANALYSIS 3.1 INTRODUCTION The study of digital wireless transmission is in large measure the study of (a) the conversion
ch03.qxd 1/9/03 09:14 AM Page 35 CHAPTER 3 MATHEMATICAL TOOLS FOR DIGITAL TRANSMISSION ANALYSIS 3.1 INTRODUCTION The study of digital wireless transmission is in large measure the study of (a) the conversion
SerDes_Channel_Impulse_Modeling_with_Rambus
 SerDes_Channel_Impulse_Modeling_with_Rambus Author: John Baprawski; John Baprawski Inc. (JB) Email: John.baprawski@gmail.com Web sites: https://www.johnbaprawski.com; https://www.serdesdesign.com Date:
SerDes_Channel_Impulse_Modeling_with_Rambus Author: John Baprawski; John Baprawski Inc. (JB) Email: John.baprawski@gmail.com Web sites: https://www.johnbaprawski.com; https://www.serdesdesign.com Date:
GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING Final Examination - Fall 2015 EE 4601: Communication Systems
 GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING Final Examination - Fall 2015 EE 4601: Communication Systems Aids Allowed: 2 8 1/2 X11 crib sheets, calculator DATE: Tuesday
GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING Final Examination - Fall 2015 EE 4601: Communication Systems Aids Allowed: 2 8 1/2 X11 crib sheets, calculator DATE: Tuesday
ECE 546 Lecture 23 Jitter Basics
 ECE 546 Lecture 23 Jitter Basics Spring 2018 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu ECE 546 Jose Schutt Aine 1 Probe Further D. Derickson and M.
ECE 546 Lecture 23 Jitter Basics Spring 2018 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu ECE 546 Jose Schutt Aine 1 Probe Further D. Derickson and M.
Principles of Communications
 Principles of Communications Weiyao Lin, PhD Shanghai Jiao Tong University Chapter 4: Analog-to-Digital Conversion Textbook: 7.1 7.4 2010/2011 Meixia Tao @ SJTU 1 Outline Analog signal Sampling Quantization
Principles of Communications Weiyao Lin, PhD Shanghai Jiao Tong University Chapter 4: Analog-to-Digital Conversion Textbook: 7.1 7.4 2010/2011 Meixia Tao @ SJTU 1 Outline Analog signal Sampling Quantization
EE (082) Ch. II: Intro. to Signals Lecture 2 Dr. Wajih Abu-Al-Saud
 Classification of Signals Some important classifications of signals Analog vs. Digital signals: as stated in the previous lecture, a signal with a magnitude that may take any real value in a specific range
Classification of Signals Some important classifications of signals Analog vs. Digital signals: as stated in the previous lecture, a signal with a magnitude that may take any real value in a specific range
Lecture 4. Capacity of Fading Channels
 1 Lecture 4. Capacity of Fading Channels Capacity of AWGN Channels Capacity of Fading Channels Ergodic Capacity Outage Capacity Shannon and Information Theory Claude Elwood Shannon (April 3, 1916 February
1 Lecture 4. Capacity of Fading Channels Capacity of AWGN Channels Capacity of Fading Channels Ergodic Capacity Outage Capacity Shannon and Information Theory Claude Elwood Shannon (April 3, 1916 February
Revision of Lecture 4
 Revision of Lecture 4 We have completed studying digital sources from information theory viewpoint We have learnt all fundamental principles for source coding, provided by information theory Practical
Revision of Lecture 4 We have completed studying digital sources from information theory viewpoint We have learnt all fundamental principles for source coding, provided by information theory Practical
Estimation of the Capacity of Multipath Infrared Channels
 Estimation of the Capacity of Multipath Infrared Channels Jeffrey B. Carruthers Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Boston University jbc@bu.edu Sachin Padma Department of Electrical and
Estimation of the Capacity of Multipath Infrared Channels Jeffrey B. Carruthers Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Boston University jbc@bu.edu Sachin Padma Department of Electrical and
Imperfect Sampling Moments and Average SINR
 Engineering Notes Imperfect Sampling Moments and Average SINR Dragan Samardzija Wireless Research Laboratory, Bell Labs, Lucent Technologies, 791 Holmdel-Keyport Road, Holmdel, NJ 07733, USA dragan@lucent.com
Engineering Notes Imperfect Sampling Moments and Average SINR Dragan Samardzija Wireless Research Laboratory, Bell Labs, Lucent Technologies, 791 Holmdel-Keyport Road, Holmdel, NJ 07733, USA dragan@lucent.com
Sensors. Chapter Signal Conditioning
 Chapter 2 Sensors his chapter, yet to be written, gives an overview of sensor technology with emphasis on how to model sensors. 2. Signal Conditioning Sensors convert physical measurements into data. Invariably,
Chapter 2 Sensors his chapter, yet to be written, gives an overview of sensor technology with emphasis on how to model sensors. 2. Signal Conditioning Sensors convert physical measurements into data. Invariably,
Communication Theory Summary of Important Definitions and Results
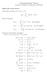 Signal and system theory Convolution of signals x(t) h(t) = y(t): Fourier Transform: Communication Theory Summary of Important Definitions and Results X(ω) = X(ω) = y(t) = X(ω) = j x(t) e jωt dt, 0 Properties
Signal and system theory Convolution of signals x(t) h(t) = y(t): Fourier Transform: Communication Theory Summary of Important Definitions and Results X(ω) = X(ω) = y(t) = X(ω) = j x(t) e jωt dt, 0 Properties
Multi User Detection I
 January 12, 2005 Outline Overview Multiple Access Communication Motivation: What is MU Detection? Overview of DS/CDMA systems Concept and Codes used in CDMA CDMA Channels Models Synchronous and Asynchronous
January 12, 2005 Outline Overview Multiple Access Communication Motivation: What is MU Detection? Overview of DS/CDMA systems Concept and Codes used in CDMA CDMA Channels Models Synchronous and Asynchronous
One Lesson of Information Theory
 Institut für One Lesson of Information Theory Prof. Dr.-Ing. Volker Kühn Institute of Communications Engineering University of Rostock, Germany Email: volker.kuehn@uni-rostock.de http://www.int.uni-rostock.de/
Institut für One Lesson of Information Theory Prof. Dr.-Ing. Volker Kühn Institute of Communications Engineering University of Rostock, Germany Email: volker.kuehn@uni-rostock.de http://www.int.uni-rostock.de/
Sample Problems for the 9th Quiz
 Sample Problems for the 9th Quiz. Draw the line coded signal waveform of the below line code for 0000. (a Unipolar nonreturn-to-zero (NRZ signaling (b Polar nonreturn-to-zero (NRZ signaling (c Unipolar
Sample Problems for the 9th Quiz. Draw the line coded signal waveform of the below line code for 0000. (a Unipolar nonreturn-to-zero (NRZ signaling (b Polar nonreturn-to-zero (NRZ signaling (c Unipolar
Information Sources. Professor A. Manikas. Imperial College London. EE303 - Communication Systems An Overview of Fundamentals
 Information Sources Professor A. Manikas Imperial College London EE303 - Communication Systems An Overview of Fundamentals Prof. A. Manikas (Imperial College) EE303: Information Sources 24 Oct. 2011 1
Information Sources Professor A. Manikas Imperial College London EE303 - Communication Systems An Overview of Fundamentals Prof. A. Manikas (Imperial College) EE303: Information Sources 24 Oct. 2011 1
Consider a 2-D constellation, suppose that basis signals =cosine and sine. Each constellation symbol corresponds to a vector with two real components
 TUTORIAL ON DIGITAL MODULATIONS Part 3: 4-PSK [2--26] Roberto Garello, Politecnico di Torino Free download (for personal use only) at: www.tlc.polito.it/garello Quadrature modulation Consider a 2-D constellation,
TUTORIAL ON DIGITAL MODULATIONS Part 3: 4-PSK [2--26] Roberto Garello, Politecnico di Torino Free download (for personal use only) at: www.tlc.polito.it/garello Quadrature modulation Consider a 2-D constellation,
Summary: SER formulation. Binary antipodal constellation. Generic binary constellation. Constellation gain. 2D constellations
 TUTORIAL ON DIGITAL MODULATIONS Part 8a: Error probability A [2011-01-07] 07] Roberto Garello, Politecnico di Torino Free download (for personal use only) at: www.tlc.polito.it/garello 1 Part 8a: Error
TUTORIAL ON DIGITAL MODULATIONS Part 8a: Error probability A [2011-01-07] 07] Roberto Garello, Politecnico di Torino Free download (for personal use only) at: www.tlc.polito.it/garello 1 Part 8a: Error
s o (t) = S(f)H(f; t)e j2πft df,
 Sample Problems for Midterm. The sample problems for the fourth and fifth quizzes as well as Example on Slide 8-37 and Example on Slides 8-39 4) will also be a key part of the second midterm.. For a causal)
Sample Problems for Midterm. The sample problems for the fourth and fifth quizzes as well as Example on Slide 8-37 and Example on Slides 8-39 4) will also be a key part of the second midterm.. For a causal)
Lecture 12. Block Diagram
 Lecture 12 Goals Be able to encode using a linear block code Be able to decode a linear block code received over a binary symmetric channel or an additive white Gaussian channel XII-1 Block Diagram Data
Lecture 12 Goals Be able to encode using a linear block code Be able to decode a linear block code received over a binary symmetric channel or an additive white Gaussian channel XII-1 Block Diagram Data
CS6956: Wireless and Mobile Networks Lecture Notes: 2/4/2015
 CS6956: Wireless and Mobile Networks Lecture Notes: 2/4/2015 [Most of the material for this lecture has been taken from the Wireless Communications & Networks book by Stallings (2 nd edition).] Effective
CS6956: Wireless and Mobile Networks Lecture Notes: 2/4/2015 [Most of the material for this lecture has been taken from the Wireless Communications & Networks book by Stallings (2 nd edition).] Effective
EE456 Digital Communications
 EE456 Digital Communications Professor Ha Nguyen September 5 EE456 Digital Communications Block Diagram of Binary Communication Systems m ( t { b k } b k = s( t b = s ( t k m ˆ ( t { bˆ } k r( t Bits in
EE456 Digital Communications Professor Ha Nguyen September 5 EE456 Digital Communications Block Diagram of Binary Communication Systems m ( t { b k } b k = s( t b = s ( t k m ˆ ( t { bˆ } k r( t Bits in
RADIO SYSTEMS ETIN15. Lecture no: Equalization. Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology
 RADIO SYSTEMS ETIN15 Lecture no: 8 Equalization Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology Ove.Edfors@eit.lth.se Contents Inter-symbol interference Linear equalizers Decision-feedback
RADIO SYSTEMS ETIN15 Lecture no: 8 Equalization Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology Ove.Edfors@eit.lth.se Contents Inter-symbol interference Linear equalizers Decision-feedback
Functions not limited in time
 Functions not limited in time We can segment an arbitrary L 2 function into segments of width T. The mth segment is u m (t) = u(t)rect(t/t m). We then have m 0 u(t) =l.i.m. m0 u m (t) m= m 0 This wors
Functions not limited in time We can segment an arbitrary L 2 function into segments of width T. The mth segment is u m (t) = u(t)rect(t/t m). We then have m 0 u(t) =l.i.m. m0 u m (t) m= m 0 This wors
Basic information theory
 Basic information theory Communication system performance is limited by Available signal power Background noise Bandwidth limits. Can we postulate an ideal system based on physical principles, against
Basic information theory Communication system performance is limited by Available signal power Background noise Bandwidth limits. Can we postulate an ideal system based on physical principles, against
Lecture 7: Wireless Channels and Diversity Advanced Digital Communications (EQ2410) 1
 Wireless : Wireless Advanced Digital Communications (EQ2410) 1 Thursday, Feb. 11, 2016 10:00-12:00, B24 1 Textbook: U. Madhow, Fundamentals of Digital Communications, 2008 1 / 15 Wireless Lecture 1-6 Equalization
Wireless : Wireless Advanced Digital Communications (EQ2410) 1 Thursday, Feb. 11, 2016 10:00-12:00, B24 1 Textbook: U. Madhow, Fundamentals of Digital Communications, 2008 1 / 15 Wireless Lecture 1-6 Equalization
Lecture 27 Frequency Response 2
 Lecture 27 Frequency Response 2 Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing Spring, 2012 Wei-Ta Chu 2012/6/12 1 Application of Ideal Filters Suppose we can generate a square wave with a fundamental period
Lecture 27 Frequency Response 2 Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing Spring, 2012 Wei-Ta Chu 2012/6/12 1 Application of Ideal Filters Suppose we can generate a square wave with a fundamental period
LECTURE 16 AND 17. Digital signaling on frequency selective fading channels. Notes Prepared by: Abhishek Sood
 ECE559:WIRELESS COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES LECTURE 16 AND 17 Digital signaling on frequency selective fading channels 1 OUTLINE Notes Prepared by: Abhishek Sood In section 2 we discuss the receiver design
ECE559:WIRELESS COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES LECTURE 16 AND 17 Digital signaling on frequency selective fading channels 1 OUTLINE Notes Prepared by: Abhishek Sood In section 2 we discuss the receiver design
EE Introduction to Digital Communications Homework 8 Solutions
 EE 2 - Introduction to Digital Communications Homework 8 Solutions May 7, 2008. (a) he error probability is P e = Q( SNR). 0 0 0 2 0 4 0 6 P e 0 8 0 0 0 2 0 4 0 6 0 5 0 5 20 25 30 35 40 SNR (db) (b) SNR
EE 2 - Introduction to Digital Communications Homework 8 Solutions May 7, 2008. (a) he error probability is P e = Q( SNR). 0 0 0 2 0 4 0 6 P e 0 8 0 0 0 2 0 4 0 6 0 5 0 5 20 25 30 35 40 SNR (db) (b) SNR
Copyright license. Exchanging Information with the Stars. The goal. Some challenges
 Copyright license Exchanging Information with the Stars David G Messerschmitt Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley messer@eecs.berkeley.edu Talk
Copyright license Exchanging Information with the Stars David G Messerschmitt Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley messer@eecs.berkeley.edu Talk
Channel capacity. Outline : 1. Source entropy 2. Discrete memoryless channel 3. Mutual information 4. Channel capacity 5.
 Channel capacity Outline : 1. Source entropy 2. Discrete memoryless channel 3. Mutual information 4. Channel capacity 5. Exercices Exercise session 11 : Channel capacity 1 1. Source entropy Given X a memoryless
Channel capacity Outline : 1. Source entropy 2. Discrete memoryless channel 3. Mutual information 4. Channel capacity 5. Exercices Exercise session 11 : Channel capacity 1 1. Source entropy Given X a memoryless
ADAPTIVE EQUALIZATION AT MULTI-GHZ DATARATES
 ADAPTIVE EQUALIZATION AT MULTI-GHZ DATARATES Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras 1st February 2007 Outline Introduction. Approaches to electronic mitigation - ADC
ADAPTIVE EQUALIZATION AT MULTI-GHZ DATARATES Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras 1st February 2007 Outline Introduction. Approaches to electronic mitigation - ADC
ENSC327 Communications Systems 2: Fourier Representations. Jie Liang School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University
 ENSC327 Communications Systems 2: Fourier Representations Jie Liang School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University 1 Outline Chap 2.1 2.5: Signal Classifications Fourier Transform Dirac Delta Function
ENSC327 Communications Systems 2: Fourier Representations Jie Liang School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University 1 Outline Chap 2.1 2.5: Signal Classifications Fourier Transform Dirac Delta Function
Shallow Water Fluctuations and Communications
 Shallow Water Fluctuations and Communications H.C. Song Marine Physical Laboratory Scripps Institution of oceanography La Jolla, CA 92093-0238 phone: (858) 534-0954 fax: (858) 534-7641 email: hcsong@mpl.ucsd.edu
Shallow Water Fluctuations and Communications H.C. Song Marine Physical Laboratory Scripps Institution of oceanography La Jolla, CA 92093-0238 phone: (858) 534-0954 fax: (858) 534-7641 email: hcsong@mpl.ucsd.edu
ANALYSIS OF A PARTIAL DECORRELATOR IN A MULTI-CELL DS/CDMA SYSTEM
 ANAYSIS OF A PARTIA DECORREATOR IN A MUTI-CE DS/CDMA SYSTEM Mohammad Saquib ECE Department, SU Baton Rouge, A 70803-590 e-mail: saquib@winlab.rutgers.edu Roy Yates WINAB, Rutgers University Piscataway
ANAYSIS OF A PARTIA DECORREATOR IN A MUTI-CE DS/CDMA SYSTEM Mohammad Saquib ECE Department, SU Baton Rouge, A 70803-590 e-mail: saquib@winlab.rutgers.edu Roy Yates WINAB, Rutgers University Piscataway
EE538 Final Exam Fall :20 pm -5:20 pm PHYS 223 Dec. 17, Cover Sheet
 EE538 Final Exam Fall 005 3:0 pm -5:0 pm PHYS 3 Dec. 17, 005 Cover Sheet Test Duration: 10 minutes. Open Book but Closed Notes. Calculators ARE allowed!! This test contains five problems. Each of the five
EE538 Final Exam Fall 005 3:0 pm -5:0 pm PHYS 3 Dec. 17, 005 Cover Sheet Test Duration: 10 minutes. Open Book but Closed Notes. Calculators ARE allowed!! This test contains five problems. Each of the five
Computation of Bit-Error Rate of Coherent and Non-Coherent Detection M-Ary PSK With Gray Code in BFWA Systems
 Computation of Bit-Error Rate of Coherent and Non-Coherent Detection M-Ary PSK With Gray Code in BFWA Systems Department of Electrical Engineering, College of Engineering, Basrah University Basrah Iraq,
Computation of Bit-Error Rate of Coherent and Non-Coherent Detection M-Ary PSK With Gray Code in BFWA Systems Department of Electrical Engineering, College of Engineering, Basrah University Basrah Iraq,
ω 0 = 2π/T 0 is called the fundamental angular frequency and ω 2 = 2ω 0 is called the
 he ime-frequency Concept []. Review of Fourier Series Consider the following set of time functions {3A sin t, A sin t}. We can represent these functions in different ways by plotting the amplitude versus
he ime-frequency Concept []. Review of Fourier Series Consider the following set of time functions {3A sin t, A sin t}. We can represent these functions in different ways by plotting the amplitude versus
Representation of Signals and Systems. Lecturer: David Shiung
 Representation of Signals and Systems Lecturer: David Shiung 1 Abstract (1/2) Fourier analysis Properties of the Fourier transform Dirac delta function Fourier transform of periodic signals Fourier-transform
Representation of Signals and Systems Lecturer: David Shiung 1 Abstract (1/2) Fourier analysis Properties of the Fourier transform Dirac delta function Fourier transform of periodic signals Fourier-transform
NORWEGIAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS
 page 1 of 5 (+ appendix) NORWEGIAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS Contact during examination: Name: Magne H. Johnsen Tel.: 73 59 26 78/930 25 534
page 1 of 5 (+ appendix) NORWEGIAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS Contact during examination: Name: Magne H. Johnsen Tel.: 73 59 26 78/930 25 534
Solutions to Selected Problems
 Solutions to Selected Problems from Madhow: Fundamentals of Digital Communication and from Johannesson & Zigangirov: Fundamentals of Convolutional Coding Saif K. Mohammed Department of Electrical Engineering
Solutions to Selected Problems from Madhow: Fundamentals of Digital Communication and from Johannesson & Zigangirov: Fundamentals of Convolutional Coding Saif K. Mohammed Department of Electrical Engineering
encoding without prediction) (Server) Quantization: Initial Data 0, 1, 2, Quantized Data 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256
 General Models for Compression / Decompression -they apply to symbols data, text, and to image but not video 1. Simplest model (Lossless ( encoding without prediction) (server) Signal Encode Transmit (client)
General Models for Compression / Decompression -they apply to symbols data, text, and to image but not video 1. Simplest model (Lossless ( encoding without prediction) (server) Signal Encode Transmit (client)
Determining the Optimal Decision Delay Parameter for a Linear Equalizer
 International Journal of Automation and Computing 1 (2005) 20-24 Determining the Optimal Decision Delay Parameter for a Linear Equalizer Eng Siong Chng School of Computer Engineering, Nanyang Technological
International Journal of Automation and Computing 1 (2005) 20-24 Determining the Optimal Decision Delay Parameter for a Linear Equalizer Eng Siong Chng School of Computer Engineering, Nanyang Technological
E303: Communication Systems
 E303: Communication Systems Professor A. Manikas Chair of Communications and Array Processing Imperial College London Principles of PCM Prof. A. Manikas (Imperial College) E303: Principles of PCM v.17
E303: Communication Systems Professor A. Manikas Chair of Communications and Array Processing Imperial College London Principles of PCM Prof. A. Manikas (Imperial College) E303: Principles of PCM v.17
Data Converter Fundamentals
 Data Converter Fundamentals David Johns and Ken Martin (johns@eecg.toronto.edu) (martin@eecg.toronto.edu) slide 1 of 33 Introduction Two main types of converters Nyquist-Rate Converters Generate output
Data Converter Fundamentals David Johns and Ken Martin (johns@eecg.toronto.edu) (martin@eecg.toronto.edu) slide 1 of 33 Introduction Two main types of converters Nyquist-Rate Converters Generate output
Chapter 8. Conclusions and Further Work Overview of Findings
 8.1. Overview of Findings The aim of this thesis was to analyse, theoretically and experimentally, the signal and noise aspects of digital magnetic recording on longitudinal thin-film disk media. This
8.1. Overview of Findings The aim of this thesis was to analyse, theoretically and experimentally, the signal and noise aspects of digital magnetic recording on longitudinal thin-film disk media. This
GATE EE Topic wise Questions SIGNALS & SYSTEMS
 www.gatehelp.com GATE EE Topic wise Questions YEAR 010 ONE MARK Question. 1 For the system /( s + 1), the approximate time taken for a step response to reach 98% of the final value is (A) 1 s (B) s (C)
www.gatehelp.com GATE EE Topic wise Questions YEAR 010 ONE MARK Question. 1 For the system /( s + 1), the approximate time taken for a step response to reach 98% of the final value is (A) 1 s (B) s (C)
SEISMIC WAVE PROPAGATION. Lecture 2: Fourier Analysis
 SEISMIC WAVE PROPAGATION Lecture 2: Fourier Analysis Fourier Series & Fourier Transforms Fourier Series Review of trigonometric identities Analysing the square wave Fourier Transform Transforms of some
SEISMIC WAVE PROPAGATION Lecture 2: Fourier Analysis Fourier Series & Fourier Transforms Fourier Series Review of trigonometric identities Analysing the square wave Fourier Transform Transforms of some
Module 4. Signal Representation and Baseband Processing. Version 2 ECE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module Signal Representation and Baseband Processing Version ECE II, Kharagpur Lesson 8 Response of Linear System to Random Processes Version ECE II, Kharagpur After reading this lesson, you will learn
Module Signal Representation and Baseband Processing Version ECE II, Kharagpur Lesson 8 Response of Linear System to Random Processes Version ECE II, Kharagpur After reading this lesson, you will learn
Issues with sampling time and jitter in Annex 93A. Adam Healey IEEE P802.3bj Task Force May 2013
 Issues with sampling time and jitter in Annex 93A Adam Healey IEEE P802.3bj Task Force May 2013 Part 1: Jitter (comment #157) 2 Treatment of jitter in COM Draft 2.0 h (0) (t s ) slope h(0) (t s ) 1 UI
Issues with sampling time and jitter in Annex 93A Adam Healey IEEE P802.3bj Task Force May 2013 Part 1: Jitter (comment #157) 2 Treatment of jitter in COM Draft 2.0 h (0) (t s ) slope h(0) (t s ) 1 UI
Fourier Series and Transform KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #7, March 24, Prof. Young-Chai Ko
 Fourier Series and Transform KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #7, March 24, 20 Prof. Young-Chai Ko koyc@korea.ac.kr Summary Fourier transform Properties Fourier transform of special function Fourier
Fourier Series and Transform KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #7, March 24, 20 Prof. Young-Chai Ko koyc@korea.ac.kr Summary Fourier transform Properties Fourier transform of special function Fourier
INFLUENCE OF EVEN ORDER DISPERSION ON SOLITON TRANSMISSION QUALITY WITH COHERENT INTERFERENCE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 3, 63 72, 2008 INFLUENCE OF EVEN ORDER DISPERSION ON SOLITON TRANSMISSION QUALITY WITH COHERENT INTERFERENCE A. Panajotovic and D. Milovic Faculty of Electronic
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 3, 63 72, 2008 INFLUENCE OF EVEN ORDER DISPERSION ON SOLITON TRANSMISSION QUALITY WITH COHERENT INTERFERENCE A. Panajotovic and D. Milovic Faculty of Electronic
DCSP-2: Fourier Transform
 DCSP-2: Fourier Transform Jianfeng Feng Department of Computer Science Warwick Univ., UK Jianfeng.feng@warwick.ac.uk http://www.dcs.warwick.ac.uk/~feng/dcsp.html Data transmission Channel characteristics,
DCSP-2: Fourier Transform Jianfeng Feng Department of Computer Science Warwick Univ., UK Jianfeng.feng@warwick.ac.uk http://www.dcs.warwick.ac.uk/~feng/dcsp.html Data transmission Channel characteristics,
2. SPECTRAL ANALYSIS APPLIED TO STOCHASTIC PROCESSES
 2. SPECTRAL ANALYSIS APPLIED TO STOCHASTIC PROCESSES 2.0 THEOREM OF WIENER- KHINTCHINE An important technique in the study of deterministic signals consists in using harmonic functions to gain the spectral
2. SPECTRAL ANALYSIS APPLIED TO STOCHASTIC PROCESSES 2.0 THEOREM OF WIENER- KHINTCHINE An important technique in the study of deterministic signals consists in using harmonic functions to gain the spectral
Digital Modulation 1
 Digital Modulation 1 Lecture Notes Ingmar Land and Bernard H. Fleury Navigation and Communications () Department of Electronic Systems Aalborg University, DK Version: February 5, 27 i Contents I Basic
Digital Modulation 1 Lecture Notes Ingmar Land and Bernard H. Fleury Navigation and Communications () Department of Electronic Systems Aalborg University, DK Version: February 5, 27 i Contents I Basic
Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 41 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) So, if you remember we have been talking
Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 41 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) So, if you remember we have been talking
