U.S. Army Injury Surveillance Summary 2014
|
|
|
- Tamsyn Susanna Norton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 U.S. Army Injury Surveillance Summary 2014 Epidemiology and Disease Surveillance Portfolio Injury Prevention Program Website: Approved for Public Release Distribution Unlimited
2 Injury Pyramid, U.S. Army Active Duty, 2014 Frequency 180 Death Ratio 1 3,000 Hospitalizations ,000 Ambulatory/Outpatient 3,489 Frequencies are rounded 2
3 Relative Burden of Injuries and Diseases, U.S. Army Active Duty, 2014 ICD-9-CM Code Groups Injury Mental Ill-defined conditions Musculoskeletal Resp infections Sense organ Skin Genitourinary Resp disease Digestive Infect/Parasite Other* Medical encounters Individuals affected Hospital bed days Medical Encounters/Individuals Affected *Includes all ICD-9-CM code groups with less than 80,000 medical encounters Diagnosis group Injury contains both injury and injury-related musculoskeletal conditions 3
4 U.S. Army Active Duty vs. Trainee Overall Injury Visit Rates, Rate per 1,000 PY Trainee Active Duty Active Duty injury adjusted to remove deployed injury and deployed person-time 4
5 U.S. Army Active Duty Injury and Overuse Injury Visit Rates, Rates per 1,000 PY All Injuries Overuse Injuries Active Duty injury adjusted to remove deployed injury and deployed person-time Overuse injuries of the lower extremity 5
6 U.S. Army Trainee Injury and Overuse Injury Visit Rates, Rates per 1,000 PY All Injuries Overuse Injuries Overuse injury of the lower extremity 6
7 Conditions Resulting in Hospitalization Top 10 ICD-9 Categories, U.S. Army Active Duty, 2014 Mental 24.6 Percent (%) of Hospitalizations Pregnancy Injury & Msk Gastrointestinal Ill-defined Msk (non-injury) Circulatory Genitourinary Respiratory Nervous Total number of incident hospitalizations = 30,840 7
8 Injuries vs. Illnesses Resulting in Outpatient Visits, Top 10 ICD-9 Categories, U.S. Army Active Duty, 2014 Injury & Msk 27.2 Percent (%) of Outpatient Visits Ill-defined Nervous Mental Msk (non-injury) Respiratory Skin & Subcut Gastrointestinal Genitourinary Infect/Parasite Total number of incident outpatient visits = 2,307,011 8
9 Leading Causes of Unintentional Hospitalizations by Cause, U.S. Army Active Duty, Percent (%) of All Causes Total number of cause-coded unintentional injury hospitalizations = 963 Land transport includes both traffic and nontraffic related and military and nonmilitary related incidents 9
10 Leading Causes of Unintentional Injury Outpatient Visits by Cause, U.S. Army Active Duty, Percent (%) of All Causes Overexertion Fall Struck by/against Transport Cut/Pierce Natural/Environ Total number of cause-coded unintentional outpatient visits = 73,379 10
11 Frequency of Acute Injuries by Location and Diagnosis (Barell Matrix) Hospitalizations, U.S. Army Active Duty, 2014 BODY REGION Head and Neck Spine and Back Torso Extremities Unclass. by Site Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Other Head, Face, Neck Spinal Cord (SCI) Vertebral Column (VCI) Torso Upper Lower Other, Unspecified DIAGNOSIS Fracture Dislocation Sprains/ Strains Internal Open Wound Amputations Blood Vessel Contusion/ Superficial Crush Burns Nerves Unspec Total Type 1 TBI Type 2 TBI Type 3 TBI TBI Unspec Other head Face Eye Neck Head, Face, Neck Unspec Cervical SCI Thoracic/Dorsal SCI Lumbar SCI Sacrum Coccyx SCI Spine, Back Unspec. SCI Cervical VCI Thoracic/Dorsal VCI Lumbar VCI Sacrum Coccyx VCI Spine, Back Unspec. VCI Chest (thorax) Abdomen Pelvis, Urogenital Trunk Back, Buttock Shoulder, Upper Arm Forearm, Elbow Wrist, Hand, Fingers Other & Unspec Hip Upper leg, Thigh Knee Lower leg, Ankle Foot, toes Other & Unspec Systemwide & late effects 29.4% Other/Multiple % Unspec. Site % System-wide & late effects % Total , % % Total 44.7% 3.5% 7.4% 13.2% 8.2% 0.4% 0.5% 3.5% 0.6% 2.7% 0.4% 4.1% 10.6% 100% % by body region 12.8% 10.3% 0.8% 4.5% 10.5% 18.3% 11
12 Frequency of Acute Injuries by Location and Diagnosis (Barell Matrix) Outpatient Visits, U.S. Army Active Duty, 2014 BODY REGION Head and Neck Spine and Back Torso Extremities Unclass. by Site Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Other Head, Face, Neck Spinal Cord (SCI) Vertebral Column (VCI) Torso Upper Lower DIAGNOSIS Fracture Dislocation Sprains/ Strains Internal Open Wound Amputations Blood Vessel Contusion/ Superficial Crush Burns Nerves Unspec Total Type 1 TBI , ,846 Type 2 TBI , ,335 Type 3 TBI , ,638 TBI Unspec Other head , ,140 Face 1, , ,268 Eye , ,953 Neck Head, Face, Neck Unspec , , ,133 Cervical SCI Thoracic/Dorsal SCI Lumbar SCI Sacrum Coccyx SCI Spine, Back Unspec. SCI Cervical VCI , ,668 Thoracic/Dorsal VCI , ,833 Lumbar VCI , ,900 Sacrum Coccyx VCI Spine, Back Unspec. VCI Chest (thorax) , , ,758 Abdomen Pelvis, Urogenital , ,379 Trunk , , ,049 Back, Buttock 0 0 2, ,757 Shoulder, Upper Arm 899 1,927 15, , ,694 Forearm, Elbow 1, ,642 Wrist, Hand, Fingers 5, , , , , ,719 Other & Unspec , ,020 Hip , ,186 Upper leg, Thigh Knee 166 3,843 3, , ,268 Lower leg, Ankle 2, , ,366 Foot, toes 3, , , , ,770 Other & Unspec , , , , ,352 Systemwide & late effects 38.7% Other, Other/Multiple % Unspecified Unspec. Site , , , , , % System-wide & late effects ,723 5, % Total 18,431 7,009 96,695 7,380 17, , , ,929 5, , % % Total 8.8% 3.3% 46.0% 3.5% 8.2% 0.2% 0.1% 15.1% 0.4% 0.9% 0.4% 10.4% 2.7% 100% % by body region 4.7% 6.5% 0.1% 6.6% 7.8% 26.2% 12
13 Frequency of Injury-related Musculoskeletal Conditions by Location and Diagnosis Hospitalizations, U.S. Army Active Duty, 2014 DIAGNOSIS Injury Location Inflammation and Pain (Overuse) Joint Derangement Joint Derangement with Neurological Involvement Stress Fracture Sprains/ Strains/ Rupture Dislocation Total % by body region Cervical Thoracic/Dorsal Vertebral Column Lumbar % Sacrum, Coccyx Spine, Back Unspecified Shoulder BODY REGION Extremities Upper Lower Upper arm, Elbow Forearm, Wrist Hand Pelvis, Hip, Thigh Knee, Lower leg % 26.3% Unclassified by Site Others and Unspecified Ankle, Foot Other specified/multiple Unspecified Site Total , % 3.0% % Total
14 Frequency of Injury-related Musculoskeletal Conditions by Location and Diagnosis Outpatient Visits, U.S. Army Active Duty, 2014 DIAGNOSIS Injury Location Inflammation and Pain (Overuse) Joint Derangement Joint Derangement with Neurological Involvement Stress Fracture Sprains/ Strains/ Rupture Dislocation Total % by body region Cervical 20,587 2,280 3, ,056 Thoracic/Dorsal , ,799 Vertebral Column Lumbar 73,862 9,577 2, ,085 Sacrum, Coccyx 3, ,848 Spine, Back Unspecified 11,994 1, , % Shoulder 52,280 4, ,874 BODY REGION Extremities Upper Lower Upper arm, Elbow 8, ,676 Forearm, Wrist 9, ,297 Hand 4, , % Pelvis, Hip, Thigh 22, ,861 Knee, Lower leg 82,335 6, ,730 3, ,436 Unclassified by Site Others and Unspecified Ankle, Foot 57,215 3, , % Other specified/multiple 1, ,401 Unspecified Site 10, , , % Total 359,498 29,315 11,843 3,058 4, , % % Total
15 Disclaimer The views expressed in this presentation are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the official policy of the Department of Defense, Department of the Army, U.S. Army Medical Department or the U.S. 15
RENCO ELECTRONICS, INC.
 Directions: Complete sections 1, 2, and 3 for all accidents and incidents. Accidents or incidents that require medical attention or lost or restricted work require the signature of Human Resources. Attach
Directions: Complete sections 1, 2, and 3 for all accidents and incidents. Accidents or incidents that require medical attention or lost or restricted work require the signature of Human Resources. Attach
US ARMY ACTIVE DUTY EYE INJURY SUMMARY CALENDAR YEAR Approved for public release, distribution unlimited
 U.S. Army Public Health Command US ARMY ACTIVE DUTY EYE INJURY SUMMARY CALENDAR YEAR 2013 Approved for public release, distribution unlimited 2014 INTRODUCTION: In 2010 the Armed Forces Health Surveillance
U.S. Army Public Health Command US ARMY ACTIVE DUTY EYE INJURY SUMMARY CALENDAR YEAR 2013 Approved for public release, distribution unlimited 2014 INTRODUCTION: In 2010 the Armed Forces Health Surveillance
Accident/Incident Report and Investigation Form
 Accident/Incident Report and Investigation Form EMPLOYEE INFORMATION Name: First MI Last Social Security#: Dept.: Job Title: Full Time Part Time Student Worker Other ACCIDENT/INCIDENT INFORMATION Date
Accident/Incident Report and Investigation Form EMPLOYEE INFORMATION Name: First MI Last Social Security#: Dept.: Job Title: Full Time Part Time Student Worker Other ACCIDENT/INCIDENT INFORMATION Date
II. Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy is. B. Physiology is.
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Human Anatomy and Physiology, 13 th ed. Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. The
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Human Anatomy and Physiology, 13 th ed. Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. The
18. Which body system is needed for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide? A. Respiratory B. Integumentary C. Digestive D. Urinary 19.
 1 Student: 1. Which of the following is NOT a part of the study of anatomy? A. The structure of body parts B. Predicting the body's responses to stimuli C. Microscopic organization D. The relationship
1 Student: 1. Which of the following is NOT a part of the study of anatomy? A. The structure of body parts B. Predicting the body's responses to stimuli C. Microscopic organization D. The relationship
Name: Period: Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Study Outline
 Name: Period: Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Study Outline I. Introduction A. The interests of our earliest ancestors most likely concerned. B. Primitive people certainly suffered
Name: Period: Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Study Outline I. Introduction A. The interests of our earliest ancestors most likely concerned. B. Primitive people certainly suffered
Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology. I. Introduction A. The interests of our earliest ancestors most likely concerned
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11 th ed. Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. The
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11 th ed. Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. The
Applegate: The Anatomy and Physiology Learning System, 3 rd Edition
 Applegate: The Anatomy and Physiology Learning System, 3 rd Edition Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body TRUE/FALSE 1. The cell is the simplest living unit of organization within the human body. T
Applegate: The Anatomy and Physiology Learning System, 3 rd Edition Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body TRUE/FALSE 1. The cell is the simplest living unit of organization within the human body. T
Chapter 01: Organization of the Body Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition
 Chapter 01: Organization of the Body Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following describes anatomy? a. Using devices to investigate parameters such as heart rate
Chapter 01: Organization of the Body Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following describes anatomy? a. Using devices to investigate parameters such as heart rate
TABLE 1a. Wisconsin Codes Project Inpatient Hospital Injury Report Major Cause of Injury StCroix County 2011
 TABLE 1a. Inpatient Hospital Injury Report Major Cause of Injury Injured Inpatients Hospital Inpatients Length of Stay Maximum Injury Severity Major Cause Number Percent 100,000 Pop Average Sum Average
TABLE 1a. Inpatient Hospital Injury Report Major Cause of Injury Injured Inpatients Hospital Inpatients Length of Stay Maximum Injury Severity Major Cause Number Percent 100,000 Pop Average Sum Average
TABLE 1a. Wisconsin Codes Project Inpatient Hospital Injury Report Major Cause of Injury City of River Falls 2006
 TABLE 1a. Inpatient Hospital Injury Report Major Cause of Injury Injured Inpatients Hospital Inpatients Length of Stay Maximum Injury Severity Major Cause Number Percent 100,000 Pop Average Sum Average
TABLE 1a. Inpatient Hospital Injury Report Major Cause of Injury Injured Inpatients Hospital Inpatients Length of Stay Maximum Injury Severity Major Cause Number Percent 100,000 Pop Average Sum Average
TABLE 1a. Wisconsin Codes Project Inpatient Hospital Injury Report Major Cause of Injury City of Chippewa Falls 2006
 TABLE 1a. Inpatient Hospital Injury Report Major Cause of Injury Injured Inpatients Hospital Inpatients Length of Stay Maximum Injury Severity Major Cause Number Percent 100,000 Pop Average Sum Average
TABLE 1a. Inpatient Hospital Injury Report Major Cause of Injury Injured Inpatients Hospital Inpatients Length of Stay Maximum Injury Severity Major Cause Number Percent 100,000 Pop Average Sum Average
TABLE 1a. Wisconsin Codes Project Inpatient Hospital Injury Report Major Cause of Injury City of Sun Prairie 2006
 TABLE 1a. Inpatient Hospital Injury Report Major Cause of Injury Injured Inpatients Hospital Inpatients Length of Stay Maximum Injury Severity Major Cause Number Percent 100,000 Pop Average Sum Average
TABLE 1a. Inpatient Hospital Injury Report Major Cause of Injury Injured Inpatients Hospital Inpatients Length of Stay Maximum Injury Severity Major Cause Number Percent 100,000 Pop Average Sum Average
SERIOUS AND/OR CATASTROPHIC HEAD, NECK AND SPINE RUGBY INJURIES IN SOUTH AFRICA (INCLUDING CARDIAC EVENTS) (LAST UPDATED 16 JANUARY 2017)
 SERIOUS AND/OR CATASTROPHIC HEAD, NECK AND SPINE RUGBY INJURIES IN SOUTH AFRICA (INCLUDING CARDIAC EVENTS) (LAST UPDATED 16 JANUARY 2017) Tables 1, 2 and 3 represent the current and most accurate statistics
SERIOUS AND/OR CATASTROPHIC HEAD, NECK AND SPINE RUGBY INJURIES IN SOUTH AFRICA (INCLUDING CARDIAC EVENTS) (LAST UPDATED 16 JANUARY 2017) Tables 1, 2 and 3 represent the current and most accurate statistics
AUBURN UNIVERSITY ATHLETIC DEPARTMENT MEDICAL HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE
 AUBURN UNIVERSITY ATHLETIC DEPARTMENT MEDICAL HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE NAME: SPORT: SOCIAL SECURITY #: SEX: BIRTHDATE: / / Please circle any of the following that you have, have had, or are now undergoing
AUBURN UNIVERSITY ATHLETIC DEPARTMENT MEDICAL HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE NAME: SPORT: SOCIAL SECURITY #: SEX: BIRTHDATE: / / Please circle any of the following that you have, have had, or are now undergoing
What is a Skeleton? SKELETONS: Museum of Osteology Lesson Curriculum K 5 th Grade 55 Minute Program
 Kindergarten: SC.K.N.1.2 Make observations of the natural world and know that they are descriptors collected using the five senses. SC.K.N.1.4 Observe and create a visual representation of an object which
Kindergarten: SC.K.N.1.2 Make observations of the natural world and know that they are descriptors collected using the five senses. SC.K.N.1.4 Observe and create a visual representation of an object which
Applications of Fresnel-Kirchhoff diffraction theory in the analysis of human-motion Doppler sonar grams
 Applications of Fresnel-Kirchhoff diffraction theory in the analysis of human-motion Doppler sonar grams Marshall Bradley a) National Center for Physical Acoustics, The University of Mississippi, 1 Coliseum
Applications of Fresnel-Kirchhoff diffraction theory in the analysis of human-motion Doppler sonar grams Marshall Bradley a) National Center for Physical Acoustics, The University of Mississippi, 1 Coliseum
Phone number: When and how did your pain begin? (a date is required for Medicare and some insurance policies) Date of onset:
 C H I R O P R A C T I C O R T H O P E D I C S A N D R E H A B I L I T A T I O N ILJXAi Pain Relief Clinics Please complete all sections. Full Name: Nickname: Gender: M F Age: Race: Date of Birth: I I Family
C H I R O P R A C T I C O R T H O P E D I C S A N D R E H A B I L I T A T I O N ILJXAi Pain Relief Clinics Please complete all sections. Full Name: Nickname: Gender: M F Age: Race: Date of Birth: I I Family
H E A LT H H I S T O RY
 H E A LT H H I S T O RY Name: : List All Current Health Problems: List Any Other Doctors Seen, Treatments And Results Obtained: Your Current Physician(s)/Therapist(s): List All Surgeries And Their s: List
H E A LT H H I S T O RY Name: : List All Current Health Problems: List Any Other Doctors Seen, Treatments And Results Obtained: Your Current Physician(s)/Therapist(s): List All Surgeries And Their s: List
Year 2016 HSE/ Accident Report
 Year 2016 HSE/ Accident Report Monthly Accident Record JAN FEB MAR APR MAY JUN JUL AUG SEP OCT NOV DEC T O T A L Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Accident Data Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul
Year 2016 HSE/ Accident Report Monthly Accident Record JAN FEB MAR APR MAY JUN JUL AUG SEP OCT NOV DEC T O T A L Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Accident Data Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul
Address: City: State: Zip: Age: Birth Date: Marital Status: M S W D No. of Children. Your Employer: Occupation: Years on Job:
 C O N F I D E N T I A L PAT I E N T I N F O R M AT I O N The following information is needed in order to better serve you. Please complete all questions. If you need help, please ask the receptionist.
C O N F I D E N T I A L PAT I E N T I N F O R M AT I O N The following information is needed in order to better serve you. Please complete all questions. If you need help, please ask the receptionist.
16. Why are many anatomical terms based on Greek and Latin roots? A. because they are easy to spell B. because many terms are based on the names of
 1 Student: 1. Which of the following is NOT true? A. Anatomy is the study of the structure of the body. B. Gross anatomy is the study of tissues and cells. C. Comparative anatomy is the study of more than
1 Student: 1. Which of the following is NOT true? A. Anatomy is the study of the structure of the body. B. Gross anatomy is the study of tissues and cells. C. Comparative anatomy is the study of more than
Low-level Fall Simulation: Toddler Falling From Chair
 Low-level Fall Simulation: Toddler Falling From Chair R. J. Reimann Professor Emeritus of Physics Boise State University 11 June 2012 (rev. 7/9/2013) This simulation was generated using Working Model software
Low-level Fall Simulation: Toddler Falling From Chair R. J. Reimann Professor Emeritus of Physics Boise State University 11 June 2012 (rev. 7/9/2013) This simulation was generated using Working Model software
BIO130 Lab Practice Exam 1 Questions
 BIO130 Lab Practice Exam 1 Questions 1. Refer to Figure 1.1 or Figure 1.2 and answer the following: A. Name the heavy bottom part labeled A. B. Name the circular part indicated by the arrow B. C. Name
BIO130 Lab Practice Exam 1 Questions 1. Refer to Figure 1.1 or Figure 1.2 and answer the following: A. Name the heavy bottom part labeled A. B. Name the circular part indicated by the arrow B. C. Name
Heat and Cold in Medicine
 Heat and Cold in Medicine Physical Basis of Heat and Temperature Matter is composed of molecules that are in motion, In gas or liquid the molecules move about hitting one another or the walls of the container;
Heat and Cold in Medicine Physical Basis of Heat and Temperature Matter is composed of molecules that are in motion, In gas or liquid the molecules move about hitting one another or the walls of the container;
physical interaction enhance performance minimizing the risk
 Kin 420 Midterm 1 review What are Tichauer s 15 principles o Keep elbows in o Minimize spine moments o Avoid covert lifting tasks o Gender differences o Optimize joint position for max muscle force o Reduce
Kin 420 Midterm 1 review What are Tichauer s 15 principles o Keep elbows in o Minimize spine moments o Avoid covert lifting tasks o Gender differences o Optimize joint position for max muscle force o Reduce
1. Medical History - This will let us know about any previous medical problems and hopefully prevent any further problems.
 Dear AU Tiger and Parents, Welcome to Auburn University! We are glad to have you join the Auburn family. We would like to ask that you review and complete the enclosed forms listed on the checklist below.
Dear AU Tiger and Parents, Welcome to Auburn University! We are glad to have you join the Auburn family. We would like to ask that you review and complete the enclosed forms listed on the checklist below.
Illustrative exercises for the lectures
 Biomechanics, LTH, 2013 Biomechanics Illustrative exercises for the lectures Ingrid Svensson 2013 1 1. To practise the use of free-body diagram, consider the problem of analyzing the stress in man s back
Biomechanics, LTH, 2013 Biomechanics Illustrative exercises for the lectures Ingrid Svensson 2013 1 1. To practise the use of free-body diagram, consider the problem of analyzing the stress in man s back
MultimediaContent PrimalPictures3DAnatomySoftware
 MultimediaContent PrimalPictures3DAnatomySoftware onanatomy.tv P a g e 2 Human Anatomy: Regional Edition Human Anatomy: Regional Edition total 257 individual 3D views, with 67,541 images 33 cross-sectional
MultimediaContent PrimalPictures3DAnatomySoftware onanatomy.tv P a g e 2 Human Anatomy: Regional Edition Human Anatomy: Regional Edition total 257 individual 3D views, with 67,541 images 33 cross-sectional
Biomechanical Modelling of Musculoskeletal Systems
 Biomechanical Modelling of Musculoskeletal Systems Lecture 6 Presented by Phillip Tran AMME4981/9981 Semester 1, 2016 The University of Sydney Slide 1 The Musculoskeletal System The University of Sydney
Biomechanical Modelling of Musculoskeletal Systems Lecture 6 Presented by Phillip Tran AMME4981/9981 Semester 1, 2016 The University of Sydney Slide 1 The Musculoskeletal System The University of Sydney
The following information is needed in order to better serve you. Please complete all questions.
 C O N F I D E N T I A L PAT I E N T I N F O R M AT I O N The following information is needed in order to better serve you. Please complete all questions. If you need help, please ask the receptionist.
C O N F I D E N T I A L PAT I E N T I N F O R M AT I O N The following information is needed in order to better serve you. Please complete all questions. If you need help, please ask the receptionist.
Human Anatomy, 7e (Martini/Timmons/Tallitsch) Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy. 1.1 Multiple-Choice Questions
 Human Anatomy, 7e (Martini/Timmons/Tallitsch) Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy 1.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which is the most accurate statement? A) Historically, the relationship
Human Anatomy, 7e (Martini/Timmons/Tallitsch) Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy 1.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which is the most accurate statement? A) Historically, the relationship
CHAPTER 1. Quick Check and Active Learning Answer Keys QUICK CHECK
 CHAPTER 1 QUICK CHECK Page 9 1. Anatomy is the study of the structure of an organism and the relationships of its parts. Physiology is the study of the functions of living organisms and their parts. Pathology
CHAPTER 1 QUICK CHECK Page 9 1. Anatomy is the study of the structure of an organism and the relationships of its parts. Physiology is the study of the functions of living organisms and their parts. Pathology
Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education
 Orthopaedic Surgery Case Logs National Data Report Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education Prepared by: Department of Applications and Data Analysis I. National ident Statistics Main Table
Orthopaedic Surgery Case Logs National Data Report Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education Prepared by: Department of Applications and Data Analysis I. National ident Statistics Main Table
Road vehicles Dummies for restraint system testing Part 1: Adult dummies
 ISO 2013 All rights reserved ISO TC 22/SC 12/WG 5 N1019 Date: 2013-02-20 ISO/PDTR 12349-1/WD 12349-1 ISO TC 22/SC 12/WG 5 Secretariat: AFNOR Road vehicles Dummies for restraint system testing Part 1: Adult
ISO 2013 All rights reserved ISO TC 22/SC 12/WG 5 N1019 Date: 2013-02-20 ISO/PDTR 12349-1/WD 12349-1 ISO TC 22/SC 12/WG 5 Secretariat: AFNOR Road vehicles Dummies for restraint system testing Part 1: Adult
These are just basic training slides, may vary from standards. Basic First Aid. 1
 These are just basic training slides, may vary from standards Basic First Aid www.askmaaz.com 1 What is 1 st Aid First Aid is an immediate and temporary care given to a victim of an accident or sudden
These are just basic training slides, may vary from standards Basic First Aid www.askmaaz.com 1 What is 1 st Aid First Aid is an immediate and temporary care given to a victim of an accident or sudden
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: Covers the basics of human anatomy and physiology including anatomical terminology, basic biochemistry, cells and tissues, and the integumentary,
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: Covers the basics of human anatomy and physiology including anatomical terminology, basic biochemistry, cells and tissues, and the integumentary,
1. Why Dissect. Why are frogs a good model to use when studying the digestive system (as well as other systems)?
 Name: Date: Period: Frog Dissection Virtual Lab Use the frog Dissection link that follows to answer the questions. http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/virtual_labs/bl_16/bl_16.html Introduction 1. Why Dissect.
Name: Date: Period: Frog Dissection Virtual Lab Use the frog Dissection link that follows to answer the questions. http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/virtual_labs/bl_16/bl_16.html Introduction 1. Why Dissect.
Skeletal 2 - joints. Puzzle 1 bones
 Puzzle 1 bones Listed below are the names of some of the bones that make up your skeletal system. But the names have been encrypted using a secret code. Can you decipher this code to find out what they
Puzzle 1 bones Listed below are the names of some of the bones that make up your skeletal system. But the names have been encrypted using a secret code. Can you decipher this code to find out what they
Mesoderm Development
 Quiz rules: Spread out across available tables No phones, text books, or (lecture) notes on your desks No consultation with your colleagues No websites open other than the Quiz page No screen snap shots
Quiz rules: Spread out across available tables No phones, text books, or (lecture) notes on your desks No consultation with your colleagues No websites open other than the Quiz page No screen snap shots
Levels of Organization
 Levels of Organization MADE UP OF CELLS REPRO- DUCE 5 CHARACH- TERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS RESPOND TO CHANGES GROW AND DEVELOP USE ENERGY cells the basic units of structure and function of all living
Levels of Organization MADE UP OF CELLS REPRO- DUCE 5 CHARACH- TERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS RESPOND TO CHANGES GROW AND DEVELOP USE ENERGY cells the basic units of structure and function of all living
human cell Smallest living structure and constituent unit of human beings; the sizes and shapes of cells vary according to their function.
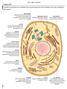 human cell CELL AND TISSUES Smallest living structure and constituent unit of human beings; the sizes and shapes of cells vary according to their function. Golgi apparatus Organelle composed of a series
human cell CELL AND TISSUES Smallest living structure and constituent unit of human beings; the sizes and shapes of cells vary according to their function. Golgi apparatus Organelle composed of a series
Test Bank forprinciples of Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition by Tortora
 Test Bank forprinciples of Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition by Tortora Chapter Number: 01 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) Which term describes the study of the functions of body structures? a) anatomy
Test Bank forprinciples of Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition by Tortora Chapter Number: 01 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) Which term describes the study of the functions of body structures? a) anatomy
Kelley: Sectional Anatomy for Imaging Professionals, 3rd Edition
 Kelley: Sectional Anatomy for Imaging Professionals, 3rd Edition Chapter 1: Introduction to Sectional Anatomy Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A vertical plane that passes through the body, dividing it into
Kelley: Sectional Anatomy for Imaging Professionals, 3rd Edition Chapter 1: Introduction to Sectional Anatomy Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A vertical plane that passes through the body, dividing it into
Introduction Chpt 1. Study Slides
 Introduction Chpt 1 Study Slides A group of molecules working together toward a common function is a: A. Cell B. Atom C. Organelle D. Tissue E. Organ ANSWER A group of molecules working together toward
Introduction Chpt 1 Study Slides A group of molecules working together toward a common function is a: A. Cell B. Atom C. Organelle D. Tissue E. Organ ANSWER A group of molecules working together toward
Forces on and in the Body
 Forces on and in the Body Physicists recognize four fundamental forces. In order of their relative strength from weakest to strongest. They are: 1- Gravitational force 2- Electrical force 3- Weak nuclear
Forces on and in the Body Physicists recognize four fundamental forces. In order of their relative strength from weakest to strongest. They are: 1- Gravitational force 2- Electrical force 3- Weak nuclear
1. Anatomy is. 2. Which subdivision of anatomy involves the study of organs that function together?
 1 of 19 1 Student: 1. Anatomy is A. the study of function. B. a branch of physiology. C. the study of structure. D. the study of living organisms. E. the study of homeostasis. 2. Which subdivision of anatomy
1 of 19 1 Student: 1. Anatomy is A. the study of function. B. a branch of physiology. C. the study of structure. D. the study of living organisms. E. the study of homeostasis. 2. Which subdivision of anatomy
Chapter 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The anatomic term means toward the midline. a. anterior b. posterior c. medial d. cranial The term medial indicates an anatomic direction
Chapter 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The anatomic term means toward the midline. a. anterior b. posterior c. medial d. cranial The term medial indicates an anatomic direction
BASIC TAPPING SCRIPT LEARN HOW TO TAP
 BASIC TAPPING SCRIPT LEARN HOW TO TAP meridianvitality.com 2010 To familiarize yourself with Meridian Tapping we introduce to you the basic tapping script. OVERVIEW Give the problem a subjective rating
BASIC TAPPING SCRIPT LEARN HOW TO TAP meridianvitality.com 2010 To familiarize yourself with Meridian Tapping we introduce to you the basic tapping script. OVERVIEW Give the problem a subjective rating
October 2017 Testimonies
 October 2017 Testimonies In Florida: Prayed for a woman with right hip pain. Checked her legs and Jesus grew one out about one-half inch. Commanded the pain to go and for complete healing of the hip flexor.
October 2017 Testimonies In Florida: Prayed for a woman with right hip pain. Checked her legs and Jesus grew one out about one-half inch. Commanded the pain to go and for complete healing of the hip flexor.
ICD-10-CM EXTERNAL CAUSE of INJURIES INDEX Addenda
 ICD-10-CM EXTERNAL CAUSE of INJURIES INDEX A 2017 enda Accident (to) X58 - caused by, due to - - corrosive liquid, substance - see Table of drugs and chemicals - - corrosive liquid, substance - see Table
ICD-10-CM EXTERNAL CAUSE of INJURIES INDEX A 2017 enda Accident (to) X58 - caused by, due to - - corrosive liquid, substance - see Table of drugs and chemicals - - corrosive liquid, substance - see Table
LABORATORY 11. Kinetics. Objectives. Background. Equipment
 LABORATORY 11 Kinetics Objectives 1. State Newton's laws as they apply to both linear and angular motion. 2. Explain the cause and effect relationship between the forces responsible for linear motion and
LABORATORY 11 Kinetics Objectives 1. State Newton's laws as they apply to both linear and angular motion. 2. Explain the cause and effect relationship between the forces responsible for linear motion and
Sioux Falls School District Anatomy and Physiology Holes Anatomy and Physiology Authors: Shier, Butler, and Lewis Glencoe/ McGraw hill
 Sioux Falls School District Anatomy and Physiology Holes Anatomy and Physiology Authors: Shier, Butler, and Lewis Glencoe/ McGraw hill Semester 1 Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Sioux Falls School District Anatomy and Physiology Holes Anatomy and Physiology Authors: Shier, Butler, and Lewis Glencoe/ McGraw hill Semester 1 Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Technical Note Series
 Technical Note Series INCLINOTRAC (T7650) & DUAL-INCLINOTRAC (T7655) S TN0011-0 0 I n c l i n o T r a c / D u a l - I n c l i n o T r a c Page 2 IMPORTANT OPERATION INFORMATION Type BF Equipment Internally
Technical Note Series INCLINOTRAC (T7650) & DUAL-INCLINOTRAC (T7655) S TN0011-0 0 I n c l i n o T r a c / D u a l - I n c l i n o T r a c Page 2 IMPORTANT OPERATION INFORMATION Type BF Equipment Internally
Organization of the Body
 Name: Hmwk # 1 - Chapter 1 Organization of the Body The study of human anatomy and physiology the structure and function of an organism and the relationship of its parts. It begins with a basic organization
Name: Hmwk # 1 - Chapter 1 Organization of the Body The study of human anatomy and physiology the structure and function of an organism and the relationship of its parts. It begins with a basic organization
PHYSICS & BIOLOGY IN MEDICINE 218 RADIOLOGIC FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY. Fall 2017
 PHYSICS & BIOLOGY IN MEDICINE 218 RADIOLOGIC FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY Fall 2017 INSTRUCTORS Allan MacKenzie-Graham, PhD Jeff Alger, PhD Neuroscience Research Building 225Z 635 Charles Young Drive Email: amg@ucla.edu
PHYSICS & BIOLOGY IN MEDICINE 218 RADIOLOGIC FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY Fall 2017 INSTRUCTORS Allan MacKenzie-Graham, PhD Jeff Alger, PhD Neuroscience Research Building 225Z 635 Charles Young Drive Email: amg@ucla.edu
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION. Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 Anatomy and Physiology Four basic properties of life: Reception The ability of the organism to control its actions
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 Anatomy and Physiology Four basic properties of life: Reception The ability of the organism to control its actions
Levels of Organization. Monday, December 5, 16
 Levels of Organization The human body is structured into systems. Cells are the smallest unit of life. Calls similar in shape and function work together as tissues. Different types of tissues form organs
Levels of Organization The human body is structured into systems. Cells are the smallest unit of life. Calls similar in shape and function work together as tissues. Different types of tissues form organs
METHODOLOGY FOR ESTIMATING THORACIC IMPACT RESPONSE IN FRONTAL CRASH TESTS
 METHODOLOGY FOR ESTIMATING THORACIC IMPACT RESPONSE IN FRONTAL CRASH TESTS Craig P. Thor, Hampton C. Gabler Virginia Tech-Wake Forest, Center for Injury Biomechanics ABSTRACT This study has investigated
METHODOLOGY FOR ESTIMATING THORACIC IMPACT RESPONSE IN FRONTAL CRASH TESTS Craig P. Thor, Hampton C. Gabler Virginia Tech-Wake Forest, Center for Injury Biomechanics ABSTRACT This study has investigated
28.1. Levels of Organization. > Virginia standards
 28.1 Levels of Organization vocabulary determination differentiation tissue organ organ system > Virginia standards BIO.4 The student will investigate and understand life functions of Archaea, Bacteria
28.1 Levels of Organization vocabulary determination differentiation tissue organ organ system > Virginia standards BIO.4 The student will investigate and understand life functions of Archaea, Bacteria
Angular Motion Maximum Hand, Foot, or Equipment Linear Speed
 Motion Maximum Hand, Foot, or Equipment Linear Speed Biomechanical Model: Mo3on Maximum Hand, Foot, or Equipment Linear Speed Hand, Foot, or Equipment Linear Speed Sum of Joint Linear Speeds Principle
Motion Maximum Hand, Foot, or Equipment Linear Speed Biomechanical Model: Mo3on Maximum Hand, Foot, or Equipment Linear Speed Hand, Foot, or Equipment Linear Speed Sum of Joint Linear Speeds Principle
Rad Tech 4912 MRI Registry Review. Outline of the Registry Exam: Certification Fees
 Rad Tech 4912 MRI Registry Review Outline of the Registry Exam: Category: # of questions: A. Patient Care 30 B. Imaging Procedures 62 C. Data Acquisition and Processing 65 D. Physical Principles of Image
Rad Tech 4912 MRI Registry Review Outline of the Registry Exam: Category: # of questions: A. Patient Care 30 B. Imaging Procedures 62 C. Data Acquisition and Processing 65 D. Physical Principles of Image
2 Statics of the Body
 2 Statics of the Body The study of the force balance of an object at rest is called statics. Moreover, the study of very slow motion can usually be treated as a series of static conditions as if there
2 Statics of the Body The study of the force balance of an object at rest is called statics. Moreover, the study of very slow motion can usually be treated as a series of static conditions as if there
Downloaded from
 INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH SCIENCE WORKSHEET SA2 STD. V 2012-13 L-6 Nervous System (FA3 + SA2) I Fill in the blanks:- 1. The brain gets its signals from various parts of the body through the 2.
INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH SCIENCE WORKSHEET SA2 STD. V 2012-13 L-6 Nervous System (FA3 + SA2) I Fill in the blanks:- 1. The brain gets its signals from various parts of the body through the 2.
EMF exposure of the skin at the mmw
 Session PW1 Workshop: EMF exposure from 5G equipment: the state of art of research and standardization EMF exposure of the skin at the mmw (Marvin C. Ziskin, M.D. Temple University Medical School) Slide
Session PW1 Workshop: EMF exposure from 5G equipment: the state of art of research and standardization EMF exposure of the skin at the mmw (Marvin C. Ziskin, M.D. Temple University Medical School) Slide
BTECFIRST. Sport. Teacher Resource Pack Answers to Section 2 Activities
 BTEC 1st SPORT TRP ANS q8_layout 1 28/07/2010 17:25 Page 1 BTECFIRST Sport Teacher Resource Pack Answers to Section 2 Activities The following are the answers to the Stepping Stone and Challenge activities
BTEC 1st SPORT TRP ANS q8_layout 1 28/07/2010 17:25 Page 1 BTECFIRST Sport Teacher Resource Pack Answers to Section 2 Activities The following are the answers to the Stepping Stone and Challenge activities
Development of an anthropomorphic model for vehicle-pedestrian crash test
 NMV0728 Development of an anthropomorphic model for vehicle-pedestrian crash test Gaetano Bellavia, Gabriele Virzì Mariotti Dipartimento di Meccanica, Università di Palermo, Italy Abstract The purpose
NMV0728 Development of an anthropomorphic model for vehicle-pedestrian crash test Gaetano Bellavia, Gabriele Virzì Mariotti Dipartimento di Meccanica, Università di Palermo, Italy Abstract The purpose
Calculating the Lyapunov Exponent Time Series Analysis of Human Gait Data. Rodney Gaines Anthony Zittle. Louisiana State University
 Calculating the Lyapunov Exponent Time Series Analysis of Human Gait Data Rodney Gaines Anthony Zittle Louisiana State University 1 1. Introduction Peripheral neuropathy causes pain and numbness in your
Calculating the Lyapunov Exponent Time Series Analysis of Human Gait Data Rodney Gaines Anthony Zittle Louisiana State University 1 1. Introduction Peripheral neuropathy causes pain and numbness in your
ADULT INTAKE FORM (13 and older) Name Date of First Visit Address City State Zip Code Telephone (home) (work) (cell) Is it ok to leave a message?
 ADULT INTAKE FORM (13 and older) Name Date of First Visit Address City State Zip Code Telephone (home) (work) (cell) Is it ok to leave a message? Age Date of Birth Gender Identity Relationship: Single
ADULT INTAKE FORM (13 and older) Name Date of First Visit Address City State Zip Code Telephone (home) (work) (cell) Is it ok to leave a message? Age Date of Birth Gender Identity Relationship: Single
Chapter 6 General Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 6 General Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The study of the human body structures that can be seen with the naked eye is. a. anatomy c. biology b. physiology d. pathology Anatomy is the
Chapter 6 General Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The study of the human body structures that can be seen with the naked eye is. a. anatomy c. biology b. physiology d. pathology Anatomy is the
CN Cell Differentiation #69
 Questions: Five study Questions EQ: What factors influence how and when cells differentiate within different organisms? Cell theory states that living things are made of cells some are unicellular (one
Questions: Five study Questions EQ: What factors influence how and when cells differentiate within different organisms? Cell theory states that living things are made of cells some are unicellular (one
Anatomy & Physiology Standards and Benchmarks
 Anatomy & Standards and Standard 1: Understands and applies principles of scientific inquiry Power : Identifies questions and concepts that guide science investigations Uses technology and mathematics
Anatomy & Standards and Standard 1: Understands and applies principles of scientific inquiry Power : Identifies questions and concepts that guide science investigations Uses technology and mathematics
Name: Grade 5 ( ) Date:
 SCIENCE REVISION ANSWER KEY. QA: KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING. a. Fill in the blanks by choosing the words from the box below: 1. Mollusks 2. Vertebrates 3. Invertebrates 4. Arthropods 5. Archaebacterial
SCIENCE REVISION ANSWER KEY. QA: KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING. a. Fill in the blanks by choosing the words from the box below: 1. Mollusks 2. Vertebrates 3. Invertebrates 4. Arthropods 5. Archaebacterial
Introduction to Humanoid Robot Kinematics with the NAO H25 technical report
 Research Collection Report Introduction to Humanoid Robot Kinematics with the NAO H technical report Author(s): Wadehn, Federico; Diether, Salomon Publication Date: 01 Permanent Link: https://doi.org/10.99/ethz-a-01044667
Research Collection Report Introduction to Humanoid Robot Kinematics with the NAO H technical report Author(s): Wadehn, Federico; Diether, Salomon Publication Date: 01 Permanent Link: https://doi.org/10.99/ethz-a-01044667
Biomechanics 1. Péter Makra Department of Medical Physics and Informatics University of Szeged 13 th September 2018
 Biomechanics 1 Péter Makra Department of Medical Physics and Informatics University of Szeged 13 th September 2018 Péter Makra (SZTE OFOII) Biomechanics 1 13 th September 2018 1 59 Contents 1 Velocity
Biomechanics 1 Péter Makra Department of Medical Physics and Informatics University of Szeged 13 th September 2018 Péter Makra (SZTE OFOII) Biomechanics 1 13 th September 2018 1 59 Contents 1 Velocity
Introduction to the Human Body. Cells. Body Functions. Tissues. Organs. Systems. Body Functions & Life Process
 complex functions for the body. Ten major systems compose the human body: Introduction to the Human Body Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic
complex functions for the body. Ten major systems compose the human body: Introduction to the Human Body Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic
Radiation Dose Limits. Radiation Safety Training Module 3
 Module 3 This module will address Western Kentucky University radiation dose limits. Basis for WKU limits Kentucky Administrative Regulations, specifically 902 KAR 100:019 Overview Module 3, Page 2 Annual
Module 3 This module will address Western Kentucky University radiation dose limits. Basis for WKU limits Kentucky Administrative Regulations, specifically 902 KAR 100:019 Overview Module 3, Page 2 Annual
HUMAN BODY THE SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS REM 653 A TEACHING RESOURCE FROM...
 THE HUMAN BODY SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS A TEACHING RESOURCE FROM... REM 653 AUTHOR Melba Callender 1987, 2001 Copyright by Remedia Publications, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Printed in the U.S.A. The
THE HUMAN BODY SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS A TEACHING RESOURCE FROM... REM 653 AUTHOR Melba Callender 1987, 2001 Copyright by Remedia Publications, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Printed in the U.S.A. The
Report Documentation Page
 Report Documentation Page Report Date 14 Jul 2000 Title and Subtitle Army Ergonomics Program Author(s) Report Type N/A Dates Covered (from... to) - Contract Number Grant Number Program Element Number Project
Report Documentation Page Report Date 14 Jul 2000 Title and Subtitle Army Ergonomics Program Author(s) Report Type N/A Dates Covered (from... to) - Contract Number Grant Number Program Element Number Project
1. The basic vocabulary used in anatomy is primarily derived from. A. Greek. B. Hebrew. C. Latin. D. German. E. Greek and Latin
 Page 1 of 28 1. The basic vocabulary used in anatomy is primarily derived from A. Greek B. Hebrew C. Latin D. German E. Greek and Latin 1 Student: 2. The early anatomist known as the "Prince of Physicians"
Page 1 of 28 1. The basic vocabulary used in anatomy is primarily derived from A. Greek B. Hebrew C. Latin D. German E. Greek and Latin 1 Student: 2. The early anatomist known as the "Prince of Physicians"
BIO 115 SP 2012 Homework 1: Introduction to A&P and Chemistry Please note that this is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 BIO 115 SP 2012 Homework 1: Introduction to A&P and Chemistry Please note that this is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. When a body is in the anatomical position, it is A. Standing erect,
BIO 115 SP 2012 Homework 1: Introduction to A&P and Chemistry Please note that this is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. When a body is in the anatomical position, it is A. Standing erect,
Development and Validation of the FAT Finite Element Model for the Side Impact Dummy EUROSID-1
 Development and Validation of the FAT Finite Element Model for the Side Impact Dummy EUROSID-1 Thomas Pyttel* *ESI GmbH, 65760 Eschborn, Frankfurter Str. 13-15, Germany ABSTRACT A new deformable model
Development and Validation of the FAT Finite Element Model for the Side Impact Dummy EUROSID-1 Thomas Pyttel* *ESI GmbH, 65760 Eschborn, Frankfurter Str. 13-15, Germany ABSTRACT A new deformable model
The STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN BODY
 The STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN BODY The topography of organs and organ systems 1. The organs are: a. clusters of identical tissues; b. different tissue groups; c. morphological units that fulfill the function
The STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN BODY The topography of organs and organ systems 1. The organs are: a. clusters of identical tissues; b. different tissue groups; c. morphological units that fulfill the function
CH. 4 Heat & Cold In Medicine
 CH. 4 Heat & Cold In Medicine Matter is composed of molecules that are in motion (This means have KE, it related to Temp : KE Temp). أ.م.د. رجاء سهيل جنم Heat : It is the energy transferred from the hot
CH. 4 Heat & Cold In Medicine Matter is composed of molecules that are in motion (This means have KE, it related to Temp : KE Temp). أ.م.د. رجاء سهيل جنم Heat : It is the energy transferred from the hot
Reading. Realistic Character Animation. Modeling Realistic Motion. Two Approaches
 Realistic Character Animation Reading Jessica Hodgins,,et.al,Animating Human Athletics,, SIGGRAPH 95 Zoran Popović, Changing Physics for Character Animation,, SIGGRAPH 00 2 Modeling Realistic Motion Model
Realistic Character Animation Reading Jessica Hodgins,,et.al,Animating Human Athletics,, SIGGRAPH 95 Zoran Popović, Changing Physics for Character Animation,, SIGGRAPH 00 2 Modeling Realistic Motion Model
Flips are Fun: A Study in the Conservation of Angular Momentum of a Non-Rigid Human Body
 Flips are Fun: A Study in the Conservation of Angular Momentum of a Non-Rigid Human Body Benjamin Jenkins Physics Department, The College of Wooster, Wooster, Ohio 44691, USA May 10, 2018 Abstract In this
Flips are Fun: A Study in the Conservation of Angular Momentum of a Non-Rigid Human Body Benjamin Jenkins Physics Department, The College of Wooster, Wooster, Ohio 44691, USA May 10, 2018 Abstract In this
skin, and recourse was had to the prediction previously made by Machle &
 156 J. Physiol. (I958) I4V, I56-I63 THE HEAT EXCHANGES OF WET SKIN By D. McK. KERSLAKE AND J. L. WADDELL From the R.A.F. Institute of Aviation Medicine, Farnborough, Hants (Received 29 October 1957) Machle
156 J. Physiol. (I958) I4V, I56-I63 THE HEAT EXCHANGES OF WET SKIN By D. McK. KERSLAKE AND J. L. WADDELL From the R.A.F. Institute of Aviation Medicine, Farnborough, Hants (Received 29 October 1957) Machle
Name Class Date. After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 14 3 Invertebrates SECTION Introduction to Animals BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What structures and systems perform basic life functions
CHAPTER 14 3 Invertebrates SECTION Introduction to Animals BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What structures and systems perform basic life functions
Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education
 Orthopaedic Surgery Case Logs National Data Report Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education Prepared by: Department of Applications and Data Analysis I. National ident Statistics Main Table
Orthopaedic Surgery Case Logs National Data Report Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education Prepared by: Department of Applications and Data Analysis I. National ident Statistics Main Table
The simulation of aerial movementii. A mathematical inertia model of the human body
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository The simulation of aerial movementii. A mathematical inertia model of the human body This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository
Loughborough University Institutional Repository The simulation of aerial movementii. A mathematical inertia model of the human body This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository
Initial Certification
 Initial Certification Medical Physics Part 1 Content Guide Part 1 Content Guides and Sample Questions PLEASE NOTE: List of Constants and Physical Values for Use on the Part 1 Physics Exam The ABR provides
Initial Certification Medical Physics Part 1 Content Guide Part 1 Content Guides and Sample Questions PLEASE NOTE: List of Constants and Physical Values for Use on the Part 1 Physics Exam The ABR provides
Grade7 (Grade7) 1. Which of the following symbiotic relationships is considered parasitic? A. ticks feeding on a dog
 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following symbiotic relationships is considered parasitic? A. ticks feeding on a dog B. bees transporting pollen from flowers C. pilotfish swimming under sharks D. birds eating
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following symbiotic relationships is considered parasitic? A. ticks feeding on a dog B. bees transporting pollen from flowers C. pilotfish swimming under sharks D. birds eating
Unit 1: Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems
 Unit 1: Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems Big Ideas The cell is the basic scientific unit of all living things. Cells must interact with the external environment to meet their basic needs. Your health
Unit 1: Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems Big Ideas The cell is the basic scientific unit of all living things. Cells must interact with the external environment to meet their basic needs. Your health
3) Using your fingers to find your pulse on your wrist is an example of
 Package Title: Testbank Course Title: PAP13 Chapter Number: 01 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) This is the study of the functions of body structures. a) anatomy b) physiology c) endocrinology d) histology
Package Title: Testbank Course Title: PAP13 Chapter Number: 01 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) This is the study of the functions of body structures. a) anatomy b) physiology c) endocrinology d) histology
Pericardial Abdominal Pelvic
 1. A mid-sagittal section of the human body would contain which of the following? Write the name of the smallest body cavity that each of the organs in your first answer here would be located within. a)
1. A mid-sagittal section of the human body would contain which of the following? Write the name of the smallest body cavity that each of the organs in your first answer here would be located within. a)
τ = F d Angular Kinetics Components of Torque (review from Systems FBD lecture Muscles Create Torques Torque is a Vector Work versus Torque
 Components of Torque (review from Systems FBD lecture Angular Kinetics Hamill & Knutzen (Ch 11) Hay (Ch. 6), Hay & Ried (Ch. 12), Kreighbaum & Barthels (Module I & J) or Hall (Ch. 13 & 14) axis of rotation
Components of Torque (review from Systems FBD lecture Angular Kinetics Hamill & Knutzen (Ch 11) Hay (Ch. 6), Hay & Ried (Ch. 12), Kreighbaum & Barthels (Module I & J) or Hall (Ch. 13 & 14) axis of rotation
External Dosimetry at NPPs; NVLAP, Noble Gas, and TEDE
 External Dosimetry at NPPs; NVLAP, Noble Gas, and TEDE Joseph L Danek - CHP 2018 Fall Meeting FLORIDA CHAPTER HEALTH PHYSICS SOCIETY 1 Part 1 National Voluntary Laboratory Accreditation Program (NVLAP)
External Dosimetry at NPPs; NVLAP, Noble Gas, and TEDE Joseph L Danek - CHP 2018 Fall Meeting FLORIDA CHAPTER HEALTH PHYSICS SOCIETY 1 Part 1 National Voluntary Laboratory Accreditation Program (NVLAP)
» APPLICATIONS OF CONTROL
 » APPLICATIONS OF CONTROL A PID Model of Human Balance Keeping KIMURA HIDENORI and YIFA JIANG The basic requirement of biped (two-legged) motion is apparatus records what we know today as the center of
» APPLICATIONS OF CONTROL A PID Model of Human Balance Keeping KIMURA HIDENORI and YIFA JIANG The basic requirement of biped (two-legged) motion is apparatus records what we know today as the center of
WORKERS COMPENSATION HISTORY
 WORKERS COMPENSATION HISTORY PATIENT NAME PHONE NUMBER ADDRESS CITY STATE ZIP CODE AGE BIRTHDATE ( ) MALE ( ) FEMALE SSN NAME OF COMPENSATION CARRIER (if known) PHONE EMPLOYER S NAME PHONE EMPLOYER S ADDRESS
WORKERS COMPENSATION HISTORY PATIENT NAME PHONE NUMBER ADDRESS CITY STATE ZIP CODE AGE BIRTHDATE ( ) MALE ( ) FEMALE SSN NAME OF COMPENSATION CARRIER (if known) PHONE EMPLOYER S NAME PHONE EMPLOYER S ADDRESS
Neural development its all connected
 Neural development its all connected How do you build a complex nervous system? How do you build a complex nervous system? 1. Learn how tissue is instructed to become nervous system. Neural induction 2.
Neural development its all connected How do you build a complex nervous system? How do you build a complex nervous system? 1. Learn how tissue is instructed to become nervous system. Neural induction 2.
