Organization of the Body
|
|
|
- Dana Dennis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Hmwk # 1 - Chapter 1 Organization of the Body The study of human anatomy and physiology the structure and function of an organism and the relationship of its parts. It begins with a basic organization of the body into different structural levels. Beginning with the smallest level (the cell) and progressing to the largest, most complex level (the system), this chapter familiarizes you with the terminology and the levels of organization needed to facilitate the study of the body in parts or as a whole. It is also important to be able to identify and describe specific body areas or regions as we progress in this field. The anatomical position is used as a reference when dissecting the body into planes, regions, or cavities. The terminology defined in this chapter allows you to describe the areas efficiently and accurately. Finally, the process of homeostasis is reviewed. This state of relative constancy in the chemical composition of body fluids is necessary for good health. In fact, the very survival of the body depends on the successful maintenance of homeostasis. Anatomy and Physiology and Characteristics of Life 1. Anatomy refers to: A. Using devices to investigate parameters such as heart rate and blood pressure B. Investigating human structure via dissection and other methods C. Studying the unusual manner in which an organism responds to painful stimuli D. Examining the chemistry of life 2. Systemic anatomy refers to anatomical investigation: A. At a microscopic level B. That begins in the head and neck and concludes at the feet C. That approaches the study of the body by systems: groups of organs having a common function D. At the cellular level 3. Physiology refers to the: A. Nature of human function B. Structure of the human form C. Evolution of human thought D. Accuracy of measuring the human physique 4. The removal of waste products in the body is achieved by a process known as: A. Secretion B. Excretion C. Circulation D. Conductivity 1
2 Chapter 1 5. Metabolism is the: A. Exchange of gases in the blood B. Formation of new cells in the body to permit growth C. Sum total of all physical and chemical reactions occurring in the body D. Production and delivery of specialized substances for diverse body functions Levels of Organization If you had difficulty with this section, review pages Beginning with the smallest level, the levels of organization of the body are: A. Cellular, chemical, tissue, organelle, organ, system, organism B. Cellular, chemical, organelle, organ, tissue, organism, system C. Chemical, cellular, organelle, organ, system, organism D. Chemical, organelle, cellular, tissue, organ, system, organism 7. Molecules are: A. Combinations of atoms forming larger chemical aggregates B. Electrons orbiting a nucleus C. A complex of electrons arranged in orderly shells D. Composed of cellular organelles 8. Mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, and Endoplasmic reticulum are examples of: A. Macromolecules B. Cytoplasm C. Organelles D. Nuclei 9. Blood production is a function of which system? A. Circulatory B. Respiratory C. Skeletal D. Urinary 10. Support and movement are functions of which systems? A. Respiratory, digestive, and urinary systems B. Reproductive and urinary systems C. Skeletal and muscular systems D. Cardiovascular and lymphatic / immune systems Matching 11. Organelle 12. Cells 13. Tissue 14. Organ 15. Systems A. Many similar cells that act together to perform a common function B. The most complex units that make up the body C. A group of several different kinds of tissues arranged to perform a special function D. Collections of molecules that perform a function E. The smallest living units of structure and function 2
3 Chapter 1 Matching 16. Integumentary System 17. Skeletal System 18. Muscular System 19. Nervous System 20. Endocrine System 21. Digestive System 22. Respiratory System 23. Cardiovascular System 24. Lymphatic System 25. Urinary System 26. Reproductive System A. Support and Movement B. Communication, control and integration C. Reproduction and development D. Transportation and defense E. Respiration, nutrition, and excretion If you had difficulty with this section, review pages 7-9 Anatomical Position, Body Cavities, Body Regions, Anatomical Terms, & Body Planes 27. In the anatomical position the subject is: A. Seated with the head facing forward B. Standing with the arms at the sides and palms facing forward C. Seated with arms parallel to the ground D. Standing with the arms at the sides and palms facing backward 28. The dorsal body cavity contains the: A. Brain and spinal cord B. Abdominal organs C. Pelvic organs D. Thoracic organs 29. The ventral body cavity contains the: A. Thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities B. Thoracic cavity only C. Abdominopelvic cavity only D. Brain and spinal cord 30. The axial portion of the body consists of: A. Arms, neck, and torso B. Neck, torso, and legs C. Torso, arms, and legs D. Head, neck and torso 31. The abdominopelvic cavity contains all of the following EXCEPT the: A. Kidneys B. Pancreas C. Lungs D. Urinary bladder 3
4 Chapter The mediastinum contains all of the following EXCEPT the: A. Esophagus B. Aorta C. Lungs D. Trachea 33. Visceral peritoneum would cover which of the following organs? A. Heart B. Liver C. Lungs D. Brain 34. A sagittal section would divide the body into: A. Upper and lover parts B. Right and left sides C. Front and back portions D. None of the above 35. A coronal section would divide the body into: A. Upper and lower parts B. Right and left sides C. Front and back portions D. None of the above 36. Inguinal is a term referring to which body region? A. Anterior portion of elbow B. Armpit C. Posterior knee D. Groin Circle the correct answer 37. The stomach is (superior or inferior) to the diaphragm. 38. The nose is located on the (anterior or posterior) surface of the body. 39. The lungs lie (medial or lateral) to the heart. 40. The elbow lies (proximal or distal) to the forearm. 41. The skin is (superficial or deep) to the muscles below it. 42. A midsagittal plane divides the body into (equal or unequal) parts. 43. A frontal plane divides the body into (anterior and posterior or superior and inferior) sections. 44. A transverse plane divides the body into (right and left or upper and lower) sections. 45. A coronal plane may also be referred to as a (sagittal or frontal) plane. 4
5 1 Chapter 1 Matching 46. Thoracic 47. Cranial 48. Abdominal 49. Pelvic 50. Mediastinum 51. Pleural A. Ventral Cavity B. Dorsal Cavity Labeling- using the terms provided, label the anatomical directions on the illustration below Anterior Distal Lateral Coronal plane Posterior Proximal Medial Frontal plane Ventral Superior Midline Transverse plane Dorsal Inferior Sagittal plane Cross section 5
6 Chapter 1 Labeling- label the various body cavities on the diagram below If you had difficulty with this section, review pages Homeostasis and Homeostatic Mechanisms of Control 52. Homeostasis can be defined as the: A. Relatively constant state maintained by the body B. Overall contribution of an organ system C. External stimuli that evoke a disruption to an organism D. Lack of cytoplasm within a plasma membrane 53. Which of the following is NOT a component of a feedback control loop? A. Sensory mechanism B. Integrating, or control center C. Effector mechanism D. Stressor stimulator 54. negative feedback control systems: A. Oppose a change B. Accelerate a change C. Ignore a change D. None of the above 6
7 Chapter Positive feedback control systems: A. Oppose a change B. Accelerate a change C. Ignore a change D. None of the above True or False 56. Any given physiological parameter will never deviate beyond the set point. 57. In the thermostatically regulated furnace example of negative feedback, the furnace functions as the sensor. 58. Negative feedback systems are inhibitory. 59. The process of childbirth, in which the baby s head causes increased stretching of the reproductive tract, which in turn feeds back to the brain, thus triggering the release of oxytocin, is an example of positive feedback. If you had difficulty with this section, review pages Health Matters Matching 60. Pathology 61. Signs 62. Symptoms 63. Etiology 64. Syndrome 65. Idiopathic 66. Acute 67. Pandemic 68. Endemic 69. Pathogenesis A. Subjective abnormalities B. Study of disease C. Collection of different signs and symptoms that present a clear picture of a pathological condition D. Study of factors involved in causing a disease E. Objective abnormalities F. Undetermined causes G. Disease native to a local region H. Symptoms appear suddenly and for a short period I. Affects large geographic regions J. Actual pattern of a disease s development Fill in the blanks 70. is the organized study of the underlying physiological processes associated with disease. 71. Many diseases are best understood as disturbances of. 72. Altered or genes can cause abnormal proteins to be made. 73. An organism that lives in or on another organism to obtain its nutrients is call a. 74. Abnormal tissue growths may also be referred to as. 75. Autoimmunity literally means. If you had difficulty with this section, review pages
8 Chapter 1 Crossword Puzzle Across 1. Study of body function 5. Staying the same 9. feedback in inhibitory 10. Total of chemical and physical reactions 11. Divides the body into sections 12. Group of similar cells 9 10 Down 2. Heart is an example 3. Organs arranged to perform a function 4. Basic unit of the body 6. Sum of its parts 7. Physique Study of body systems. 12 Applying What You Know 76. Laurie has had an appendectomy. The nurse is preparing to change the dressing. She knows that the appendix is located in the right iliac inguinal region, the distal portion extending at an angle into the hypogastric region. Place an X on the diagram where the nurse will place the dressing. 77. Penny noticed a lump in her breast. Dr. Reeder noted on her chart that a small mass was located in the left breast medial to the nipple. Place an X where Penny s lump would be located. 78. Madison was injured in a bicycle accident. X-ray films revealed that she had a fracture of the right patella. A cast was applied beginning at the distal femoral region and extending to the pedal region. Place an line where Madison s cast begins and ends. Did You Know? Many animals produce tears but only humans weep as a result of emotional stress. 8
9 Chapter 1 One Last Quick Check 79. The body s ability to continuously respond to changes in the environment and maintain consistency in the internal environment is called: A. Homeostasis B. Superficial C. Structural levels D. None of the above 80. The regions frequently used by health professionals to locate pain or tumors divide the abdomen into four basic areas called: A. Planes B. Cavitites C. Pleural D. Quadrants 81. A lengthwise plane running from front to back that divides the body into right and left sides is called: A. Transverse B. Coronal C. Frontal D. Sagittal 82. A study of the functions of living organisms and their parts is called: A. Physiology B. Chemistry C. Biology D. None of the above 83. Which of the following structures does not lie within the abdominopelvic cavity? A. Right iliac region B. Left antecubital region C. Left lumbar region D. Hypogastric region 84. The dorsal body cavity contains components of the: A. Reproductive system B. Digestive system C. Respiratory system D. Nervous system 9
10 Chapter If your reference point is nearest the trunk of the body versus farthest from the trunk of the body, where does the elbow lie in relation to the wrist? A. Anterior B. Posterior C. Distal D. Proximal 86. The buttocks are often used as injection sites. This region can also be called: A. Sacral B. Buccal C. Cutaneous D. Gluteal 87. Which of the following is not a component of the axial subdivision of the body? A. Upper extremity B. Neck C. Trunk D. Head 88. The synonym for medial is: A. Toward the side B. In front of C. Midline D. Anterior 10
11 Chapter 2 The Chemical basis of Life Although anatomy can be studied without knowledge of chemistry, it is hard to imagine an understanding of physiology without a basic comprehension of chemical reactions in the body. Trillions of cells make up the various levels or organization in the body. Our health and survival depend upon the proper chemical maintenance in the cytoplasm of our cells. Chemists use the terms elements or compounds to describe all of the substances (matter) in and around us. Distinguishing these two terms is the fact that an element cannot be broken down. A compound, on the other hand, is made up of two or more elements and has the ability to be broken down into the elements that form it. Organic and inorganic compounds are equally important to us. Without organic compounds such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, and inorganic compounds such as water, we could not sustain life. Because we cannot see many of the chemical reactions that take place daily in our bodies, it is sometimes difficult to comprehend the principles involved in initiating them. Chemicals are responsible for directing virtually all of our bodily functions. It is therefore important to master the fundamental concepts of chemistry Basic Chemistry 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the major elements present in the human body: A. Oxygen B. Carbon C. Iron D. Hydrogen 2. Which of the following NOT a subatomic particle: A. Proton B. Electron C. Isotope D. Neutron 3. The total number of electrons in an atom equals the number of: A. Neutrons in its nucleus B. Electrons in its nucleus C. Protons in its nucleus D. Ions in its nucleus 4. An atom can be described a chemically inert if its outermost electron shell contains: A. Three electrons B. Five electrons C. Six electrons D. Eight electrons 11
12 Chapter 2 5. Isotopes are atoms of elements that differ in their number of: A. Protons B. Electrons C. Neutrons D. Nuclei 6. Ionic bonds are chemical bonds formed by the: A. Sharing of electrons between atoms B. Donation of protons from one atom to another C. Transfer of electrons from one atom to another D. Acceptance of protons from one atom to another 7. Chemical bonds formed by the sharing of electrons are called: A. Ionic B. Covalent C. Hydrogen E. Electronic 8. A chemical reaction in which substances combine to form more complex substances is called: A. Synthesis B. Decomposition C. Exchange D. Reversible True or False 9. Matter is a term used by chemists to describe all the materials or substances around us. 10. Atomic weight refers to the number of protons plus the number of neutrons in an atom. 11. Sodium chloride is an example of a covalent bond. 12. Hydrogen bonds form from an equal charge distribution within a molecule. 13. The digestion of food is an example of a decomposition reaction. Identify the following elements 14. O 15. Ca 16. K 17. Na 18. Mg 19. Fe 20. Se If you had difficulty with this section, review pages
13 Chapter 2 Metabolism Matching 21. Catabolism 22. Anabolism 23. ATP 24. Metabolism 25. Dehydration synthesis A. Breaks down larger food molecules into smaller units B. The form of energy that cells generally use C. All the chemical reactions that occur in body cells D. Joins simple molecules together to form more complex ones E. Key reaction during anabolism If you had difficulty with this section, review pages Inorganic Molecules 26. Water plays a key role in such processes as: A. Cell permeability B. Active transport of materials C. Secretion D. All of the above 27. Which of the following is NOT a property of water? A. Strong polarity B. High specific heat C. High heat of vaporization D. Strong acidity 28. Acids: A. Are proton receptors B. Dye litmus blue C. Release hydrogen ions when in an aqueous solution D. Accept electrons when in an aqueous solution 29. Substances that accept hydrogen ions are referred to as: A. Acids B. Bases C. Buffers D. Salts 30. The constancy of the ph homeostatic mechanism is caused by the presence of substances called: A. Salts B. Bases C. Buffers D. Acids 13
14 Chapter 2 True or False 31. The ph scale indicates the degree of acidity or alkalinity of a solution. 32. Milk is acid on the ph scale. 33. Litmus will turn red in the presences of an acid. 34. The basic substance of each cell is water. 35. Oxygen and carbon dioxide are examples of organic compounds. Organic Molecules If you had difficulty with this section, review pages Which of the following in NOT a type of carbohydrate? A. Monosaccharides B. Disaccharides C. Megasaccharides D. Polysaccharides 37. Which of the following is INCORRECT in reference to carbohydrates? A. They include substances referred to as sugars B. They serve critical structural roles in RNA and DNA C. They represent a primary source of chemical energy for body cells D. They are replete with nitrogen atoms 38. Proteins are composed of commonly occurring amino acids. A. 8 B. 12 C. 20 D Amino acids frequently become joined by: A. Peptide bonds B. Phospholipid reactions C. Degradation synthesis D. None of the above 40. Which of the following is NOT an example of proteins? A. Hormones B. Antibodies C. Urine D. Enzymes 14
15 Chapter A structural lipid found in a cell membrane is: A. Triglyceride B. Phospholipids C. Steroid D. Prostaglandin 42. Which of the following is the correct example of DNA base pairing? A. Adenine-Cytosine B. Guanine- Adenine C. Adenine-Thymine D. Guanine- Thymine 43. A DNA molecule contains each of the following EXCEPT: A. Sugar B. Nitrogenous base C. Phosphate D. Lipid 44. DNA differs from RNA in that: A. RNA contains ribose instead of deoxyribose B. RNA contains thymine instead of uracil C. RNA contain a double polynucleotide strand D. There is no structural difference between DNA and RNA True or False 45. Steroids are poorly distributed throughout the body. 46. High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is also called the good cholesterol. 47. Protein compounds have no role in defending the body against harmful agents. 48. The nonessential amino acids can be produced from the other amino acids or from simple organic molecules. 49. Enzymes are proteins that function by the lock and key model. 50. Prostaglandins are tissue hormones. If you had difficulty with this section, review pages
16 Chapter 2 Crossword Puzzle Across 1. Acts as a reservoir for H + ions 5. DNA or RNA (two words) 9. Small particle of an element 10. Simple form of matter 12. Amino acid 14. Tastes bitter Down 2. Dissociates in solution to form ions 3. Releases hydrogen when in solution 4. bond / electrocovalent bond 6. Sugar or starch 7. Chemical catalysts 8. bond shares electron pairs between atoms 11. Fat 13. Electrically charged atom 14 Applying What You Know 51. Amanda and Bill own a home that was recently discovered to contain very high levels of radon. Where in the house would these levels be greatest? What could be done to eliminate the radon? What is the family at greatest risk for? 52. Kim just finished preparing a meal of pan-fried hamburgers for her family. While the frying pan was still hot, she poured the liquid grease into a metal container to cool. Later she noticed that the liquid oil had solidified as it cooled. Explain the chemistry of why the now room-temperature fat was solid. Did You Know? After a vigorous workout, your triglycerides fall % and your HDL increases by the same percentage for 2-3 hours. The only letter not appearing on the Periodic Table is the letter J Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe (75%) 16
17 Chapter 2 One Last Quick Check Matching 53. Atoms of the same element but with different atomic weights (because their nuclei contain different numbers of neutrons). 54. Adenine-thymine and guanine-cytosine are examples of present in DNA. 55. Atoms with fewer than eight electrons in their valence shell will attempt to lose, gain, or share electrons with other atoms to achieve stability. 56. The number of protons in an atom s nucleus. 57. Any large molecule made up of many identical small molecules. 58. components of DNA and RNA that are composed of sugar, a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group. 59. Chemical property that allows water to act as a effective solvent. 60. Large group of inorganic compounds including acids, bases, and salts. A. Atomic number B. Base pairs C. Electrolyte D. High-energy bonds E. Isotopes F. Nucleotide G. Octet rule H. Polarity I. Polymers Matching 61. Ribose 62. Steroids 63. Amino acid 64. Glycerol 65. Monosaccharides 66. Phospholipids 67. Enzymes A. Protein B. Carbohydrate C. Lipid Matching 68. Litmus turns blue 69. Proton donor 70. Bitter taste 71. Proton acceptor 72. Releases a hydrogen ion A. Acid B. Base 17
BIO 115 SP 2012 Homework 1: Introduction to A&P and Chemistry Please note that this is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 BIO 115 SP 2012 Homework 1: Introduction to A&P and Chemistry Please note that this is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. When a body is in the anatomical position, it is A. Standing erect,
BIO 115 SP 2012 Homework 1: Introduction to A&P and Chemistry Please note that this is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. When a body is in the anatomical position, it is A. Standing erect,
Applegate: The Anatomy and Physiology Learning System, 3 rd Edition
 Applegate: The Anatomy and Physiology Learning System, 3 rd Edition Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body TRUE/FALSE 1. The cell is the simplest living unit of organization within the human body. T
Applegate: The Anatomy and Physiology Learning System, 3 rd Edition Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body TRUE/FALSE 1. The cell is the simplest living unit of organization within the human body. T
18. Which body system is needed for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide? A. Respiratory B. Integumentary C. Digestive D. Urinary 19.
 1 Student: 1. Which of the following is NOT a part of the study of anatomy? A. The structure of body parts B. Predicting the body's responses to stimuli C. Microscopic organization D. The relationship
1 Student: 1. Which of the following is NOT a part of the study of anatomy? A. The structure of body parts B. Predicting the body's responses to stimuli C. Microscopic organization D. The relationship
CHAPTER 1. Quick Check and Active Learning Answer Keys QUICK CHECK
 CHAPTER 1 QUICK CHECK Page 9 1. Anatomy is the study of the structure of an organism and the relationships of its parts. Physiology is the study of the functions of living organisms and their parts. Pathology
CHAPTER 1 QUICK CHECK Page 9 1. Anatomy is the study of the structure of an organism and the relationships of its parts. Physiology is the study of the functions of living organisms and their parts. Pathology
Chapter 01: Organization of the Body Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition
 Chapter 01: Organization of the Body Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following describes anatomy? a. Using devices to investigate parameters such as heart rate
Chapter 01: Organization of the Body Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following describes anatomy? a. Using devices to investigate parameters such as heart rate
Introduction Chpt 1. Study Slides
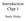 Introduction Chpt 1 Study Slides A group of molecules working together toward a common function is a: A. Cell B. Atom C. Organelle D. Tissue E. Organ ANSWER A group of molecules working together toward
Introduction Chpt 1 Study Slides A group of molecules working together toward a common function is a: A. Cell B. Atom C. Organelle D. Tissue E. Organ ANSWER A group of molecules working together toward
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION. Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 Anatomy and Physiology Four basic properties of life: Reception The ability of the organism to control its actions
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 Anatomy and Physiology Four basic properties of life: Reception The ability of the organism to control its actions
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Prepared by Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar
The Human Body: An Orientation Prepared by Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar
Unit 1: Body Plan & Organization Test Review 1. Define anatomy and contrast it with physiology.
 Name: Period: Unit 1: Body Plan & Organization Test Review 1. Define anatomy and contrast it with physiology. 2. Arrange and identify, in order, the six levels of structural organization of the human body.
Name: Period: Unit 1: Body Plan & Organization Test Review 1. Define anatomy and contrast it with physiology. 2. Arrange and identify, in order, the six levels of structural organization of the human body.
Name: Period: Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Study Outline
 Name: Period: Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Study Outline I. Introduction A. The interests of our earliest ancestors most likely concerned. B. Primitive people certainly suffered
Name: Period: Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Study Outline I. Introduction A. The interests of our earliest ancestors most likely concerned. B. Primitive people certainly suffered
Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology. I. Introduction A. The interests of our earliest ancestors most likely concerned
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11 th ed. Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. The
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11 th ed. Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. The
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body NOTES
 Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body NOTES Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body NOTES Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable
Chapter 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The anatomic term means toward the midline. a. anterior b. posterior c. medial d. cranial The term medial indicates an anatomic direction
Chapter 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The anatomic term means toward the midline. a. anterior b. posterior c. medial d. cranial The term medial indicates an anatomic direction
Chapter 1. The Human Organism 1-1
 Chapter 1 The Human Organism 1-1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: Scientific discipline that investigates the body s structure Physiology: Scientific investigation of the processes or functions
Chapter 1 The Human Organism 1-1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: Scientific discipline that investigates the body s structure Physiology: Scientific investigation of the processes or functions
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Chapter 2
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 2 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CHAPTER 2 CHEMICAL BASIS OF
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 2 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CHAPTER 2 CHEMICAL BASIS OF
Unit 2: Basic Chemistry
 Unit 2: Basic Chemistry I. Matter and Energy A. Matter anything that occupies space and has mass (weight) B. Energy the ability to do work 1. Chemical 2. Electrical 3. Mechanical 4. Radiant C. Composition
Unit 2: Basic Chemistry I. Matter and Energy A. Matter anything that occupies space and has mass (weight) B. Energy the ability to do work 1. Chemical 2. Electrical 3. Mechanical 4. Radiant C. Composition
UNIT 2 CHEMISTRY. Atomic Structure: Ionic Bond: Covalent Bond: Hydrogen Bond:
 UNIT 2 CHEMISTRY Atomic Structure: Ionic Bond: Hydrogen Bond: Covalent Bond: 1 Carbohydrates: >energy yield- >elements- >monomers- >functions- >examples- >misc- Lipids: Proteins: Nucleic Acids: I. Energy
UNIT 2 CHEMISTRY Atomic Structure: Ionic Bond: Hydrogen Bond: Covalent Bond: 1 Carbohydrates: >energy yield- >elements- >monomers- >functions- >examples- >misc- Lipids: Proteins: Nucleic Acids: I. Energy
UNIT 2 CHEMISTRY. Atomic Structure: Ionic Bond: Covalent Bond: Hydrogen Bond:
 UNIT 2 CHEMISTRY Atomic Structure: Ionic Bond: Hydrogen Bond: Covalent Bond: 1 Carbohydrates: >energy yield- >elements- >monomers- >functions- >examples- >misc- Lipids: Proteins: Nucleic Acids: I. Energy
UNIT 2 CHEMISTRY Atomic Structure: Ionic Bond: Hydrogen Bond: Covalent Bond: 1 Carbohydrates: >energy yield- >elements- >monomers- >functions- >examples- >misc- Lipids: Proteins: Nucleic Acids: I. Energy
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition. Chapter 2
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition Shier w Butler w Lewis Chapter 2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition Shier w Butler w Lewis Chapter 2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
A Brief Overview of Biochemistry. And I mean BRIEF!
 A Brief Overview of Biochemistry And I mean BRIEF! Introduction A. Chemistry deals with the composition of substances and how they change. B. A knowledge of chemistry is necessary for the understanding
A Brief Overview of Biochemistry And I mean BRIEF! Introduction A. Chemistry deals with the composition of substances and how they change. B. A knowledge of chemistry is necessary for the understanding
Chapter 2 Chemical Aspects of Life
 Chapter 2 Chemical Aspects of Life Multiple Choice Questions 1. Anything that has weight and occupies space can be described as A. an atom. B. matter. C. a compound. D. a molecule. #1 Learning Outcome:
Chapter 2 Chemical Aspects of Life Multiple Choice Questions 1. Anything that has weight and occupies space can be described as A. an atom. B. matter. C. a compound. D. a molecule. #1 Learning Outcome:
Chapter 2. Introduction: Chapter Chemical Basis of Life. Structure of Matter:
 Chapter 2.1-2.2 Read text 2.1 and describe why chemistry is important in understanding life. Read text 2.2 and discuss how atomic structure determines how atoms interact. Also describe the types of chemical
Chapter 2.1-2.2 Read text 2.1 and describe why chemistry is important in understanding life. Read text 2.2 and discuss how atomic structure determines how atoms interact. Also describe the types of chemical
Figure ) Letter E represents a nucleic acid building block known as a. Answer: nucleotide Diff: 3 Page Ref: 54
 Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10e (Marieb) Chapter 2 Basic Chemistry 2.1 Short Answer Figure 2.1 Using Figure 2.1, identify the following: 1) Which letter represents a carbohydrate polymer?
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10e (Marieb) Chapter 2 Basic Chemistry 2.1 Short Answer Figure 2.1 Using Figure 2.1, identify the following: 1) Which letter represents a carbohydrate polymer?
Chemical Basis of Life
 Chemical Basis of Life Jan 30 11:42 AM In order to understand digestion and nutrition, we need some basic biochemistry Chemistry studies the composition of matter and its changes as well as the change
Chemical Basis of Life Jan 30 11:42 AM In order to understand digestion and nutrition, we need some basic biochemistry Chemistry studies the composition of matter and its changes as well as the change
Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life
 Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life Chemistry is the scientific study of the composition of matter and how composition changes. In order to understand human physiological processes, it is important to understand
Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life Chemistry is the scientific study of the composition of matter and how composition changes. In order to understand human physiological processes, it is important to understand
Journal #1: How might an Anatomist and Physiologist see a computer differently?
 Journal #1: How might an Anatomist and Physiologist see a computer differently? Objective #1: Define Anatomy and Physiology and describe various specialties of each discipline. Identify the major levels
Journal #1: How might an Anatomist and Physiologist see a computer differently? Objective #1: Define Anatomy and Physiology and describe various specialties of each discipline. Identify the major levels
CURRICULUM MAP. TIME CONTENT PAGE REF. SKILLS ASSESSMENT/ACTIVITIES Day 1-3
 CURRICULUM MAP COURSE TITLE: Anatomy and Physiology DESCRIPTION TEXTBOOK Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology OF COURSE: 8 th ed: Elaine Marieb Integrated approach to human anatomy. Performance and lab
CURRICULUM MAP COURSE TITLE: Anatomy and Physiology DESCRIPTION TEXTBOOK Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology OF COURSE: 8 th ed: Elaine Marieb Integrated approach to human anatomy. Performance and lab
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 ch 2 chemical basis of life Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Fill in the blank or provide a short answer: 1) When a change in matter
ch 2 chemical basis of life Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Fill in the blank or provide a short answer: 1) When a change in matter
Chapter 2: Fundamentals of Chemistry. Question Type: Multiple Choice. 1) Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
 Microbiology Principles and Explorations 9th Edition Black TEST BANK Full clear download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/microbiology-principles-explorations- 9th-edition-black-test-bank/ Microbiology
Microbiology Principles and Explorations 9th Edition Black TEST BANK Full clear download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/microbiology-principles-explorations- 9th-edition-black-test-bank/ Microbiology
Chapter 2 Concepts of Chemistry
 Anatomy Physiology and Disease for the Health Professions 3rd Edition Booth Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/anatomy-physiology-and-disease-for-the-health-professions-3rd-edition-booth-te
Anatomy Physiology and Disease for the Health Professions 3rd Edition Booth Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/anatomy-physiology-and-disease-for-the-health-professions-3rd-edition-booth-te
Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life I. Introduction A. The study of chemistry is essential for the study of physiology because
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11 th ed. Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life I. Introduction A. The study of chemistry is essential for the
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11 th ed. Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life I. Introduction A. The study of chemistry is essential for the
Anatomy and Physiology. Science Curriculum Framework
 Anatomy and Physiology Science Curriculum Framework Revised 005 Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology should develop an understanding of the organization of the human body through studies of body
Anatomy and Physiology Science Curriculum Framework Revised 005 Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology should develop an understanding of the organization of the human body through studies of body
Full file at Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology (Martini/ Bartholomew) Chapter 2 The Chemical Level of Organization
 Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology (Martini/ Bartholomew) Chapter 2 The Chemical Level of Organization Multiple Choice 1) An unstable isotope that emits subatomic particles spontaneously is called A) a
Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology (Martini/ Bartholomew) Chapter 2 The Chemical Level of Organization Multiple Choice 1) An unstable isotope that emits subatomic particles spontaneously is called A) a
Teacher Instructions
 Teacher Instructions To print handouts for students Go to File print, change Print what: to handouts, change # per page if desired to enlarge slides on page Change Print range to slides and type in slide
Teacher Instructions To print handouts for students Go to File print, change Print what: to handouts, change # per page if desired to enlarge slides on page Change Print range to slides and type in slide
1. Anatomy is. 2. Which subdivision of anatomy involves the study of organs that function together?
 1 of 19 1 Student: 1. Anatomy is A. the study of function. B. a branch of physiology. C. the study of structure. D. the study of living organisms. E. the study of homeostasis. 2. Which subdivision of anatomy
1 of 19 1 Student: 1. Anatomy is A. the study of function. B. a branch of physiology. C. the study of structure. D. the study of living organisms. E. the study of homeostasis. 2. Which subdivision of anatomy
BIOCHEMISTRY 10/9/17 CHEMISTRY OF LIFE. Elements: simplest form of a substance - cannot be broken down any further without changing what it is
 BIOCHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY OF LIFE Elements: simplest form of a substance - cannot be broken down any further without changing what it is THE ATOM Just like cells are the basic unit of life, the ATOM is the
BIOCHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY OF LIFE Elements: simplest form of a substance - cannot be broken down any further without changing what it is THE ATOM Just like cells are the basic unit of life, the ATOM is the
Full file at
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following is an uncharged particle found in the nucleus of 1) an atom and which has
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following is an uncharged particle found in the nucleus of 1) an atom and which has
Ch. 2 BASIC CHEMISTRY. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Ch. 2 BASIC CHEMISTRY Matter and Composition of Matter Definition: Anything that has mass and occupies space Matter is made up of elements An element cannot be broken down by ordinary chemical means Atoms
Ch. 2 BASIC CHEMISTRY Matter and Composition of Matter Definition: Anything that has mass and occupies space Matter is made up of elements An element cannot be broken down by ordinary chemical means Atoms
2/25/2013. Electronic Configurations
 1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 2 Chemical Principles The Structure of Atoms Chemistry is the study of interactions between atoms and molecules The atom is the smallest unit of matter that enters into chemical reactions
1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 2 Chemical Principles The Structure of Atoms Chemistry is the study of interactions between atoms and molecules The atom is the smallest unit of matter that enters into chemical reactions
Chapter 02 Chemistry of Life
 Chapter 02 Chemistry of Life Multiple Choice Questions 1. The smallest unit of matter is the A. molecule. B. atom. C. compound. D. isotope. HAPS Objective: C.01.03 Compare and contrast the terms atoms,
Chapter 02 Chemistry of Life Multiple Choice Questions 1. The smallest unit of matter is the A. molecule. B. atom. C. compound. D. isotope. HAPS Objective: C.01.03 Compare and contrast the terms atoms,
Pericardial Abdominal Pelvic
 1. A mid-sagittal section of the human body would contain which of the following? Write the name of the smallest body cavity that each of the organs in your first answer here would be located within. a)
1. A mid-sagittal section of the human body would contain which of the following? Write the name of the smallest body cavity that each of the organs in your first answer here would be located within. a)
McKinley/O Loughlin/Bidle Anatomy and Physiology: An Integrative Approach, 1/e Answer Key
 Chapter 1 Answers to What Did You Learn? 1. Comparative anatomy McKinley/O Loughlin/Bidle Anatomy and Physiology: An Integrative Approach, 1/e Answer Key 2. Anatomy is the study of structure and form.
Chapter 1 Answers to What Did You Learn? 1. Comparative anatomy McKinley/O Loughlin/Bidle Anatomy and Physiology: An Integrative Approach, 1/e Answer Key 2. Anatomy is the study of structure and form.
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e (Marieb) Chapter 2 Basic Chemistry. 2.1 Multiple Choice Part I Questions
 Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e (Marieb) Chapter 2 Basic Chemistry 2.1 Multiple Choice Part I Questions Using Figure 2.1, identify the following: 1) Which letter represents a carbohydrate
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e (Marieb) Chapter 2 Basic Chemistry 2.1 Multiple Choice Part I Questions Using Figure 2.1, identify the following: 1) Which letter represents a carbohydrate
Chapter 2. Chemical Basis of Life
 hapter 2 hemical Basis of Life opyright The McGrawill ompanies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction: A. hemistry deals with the composition of matter and how it changes.
hapter 2 hemical Basis of Life opyright The McGrawill ompanies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction: A. hemistry deals with the composition of matter and how it changes.
Microbiology with Diseases by Taxonomy, 5e (Bauman) Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Microbiology. 2.1 Multiple Choice Questions
 Microbiology with Diseases by Taxonomy, 5e (Bauman) Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Microbiology 2.1 Multiple Choice Questions 1) Which of the following does not contribute significantly to the mass of an atom?
Microbiology with Diseases by Taxonomy, 5e (Bauman) Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Microbiology 2.1 Multiple Choice Questions 1) Which of the following does not contribute significantly to the mass of an atom?
Objectives continued- Answer each of the objectives on a separate sheet of paper to demonstrate content mastery. Attach answers to back of packet.
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 2: Basic Chemistry Name: Objectives- By the end of this chapter I will be able to: 1. Differentiate between matter and energy. 2. Define chemical element, and list the four
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 2: Basic Chemistry Name: Objectives- By the end of this chapter I will be able to: 1. Differentiate between matter and energy. 2. Define chemical element, and list the four
2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules
 2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules Living things consist of atoms of different elements. An atom is the smallest basic unit of matter. An element is one type of atom. 6 elements make up 99% of all living things
2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules Living things consist of atoms of different elements. An atom is the smallest basic unit of matter. An element is one type of atom. 6 elements make up 99% of all living things
Basic Chemistry. Chapter 2 BIOL1000 Dr. Mohamad H. Termos
 Basic Chemistry Chapter 2 BIOL1000 Dr. Mohamad H. Termos Chapter 2 Objectives Following this chapter, you should be able to describe: - Atoms, molecules, and ions - Composition and properties - Types of
Basic Chemistry Chapter 2 BIOL1000 Dr. Mohamad H. Termos Chapter 2 Objectives Following this chapter, you should be able to describe: - Atoms, molecules, and ions - Composition and properties - Types of
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 12e (Marieb) Chapter 2 Basic Chemistry. 2.1 Multiple Choice Part I Questions
 Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology 12th Edition Marieb TEST BANK Full download at: https://testbankrealcom/download/essentialshuman-anatomy-physiology-12th-edition-mariebtest-bank/ Essentials of
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology 12th Edition Marieb TEST BANK Full download at: https://testbankrealcom/download/essentialshuman-anatomy-physiology-12th-edition-mariebtest-bank/ Essentials of
Test Bank forprinciples of Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition by Tortora
 Test Bank forprinciples of Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition by Tortora Chapter Number: 01 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) Which term describes the study of the functions of body structures? a) anatomy
Test Bank forprinciples of Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition by Tortora Chapter Number: 01 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) Which term describes the study of the functions of body structures? a) anatomy
Chapter 02 Chemistry of Life
 Maders Understanding Human Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Longenbaker Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/maders-understanding-human-anatomy-and-physiology-9th-edition-longenbaker
Maders Understanding Human Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Longenbaker Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/maders-understanding-human-anatomy-and-physiology-9th-edition-longenbaker
Chemistry Basics. Matter anything that occupies space and has mass Energy the ability to do work. Chemical Electrical Mechanical Radiant. Slide 2.
 Chemistry Basics Matter anything that occupies space and has mass Energy the ability to do work Chemical Electrical Mechanical Radiant Slide 2.1 Composition of Matter Elements Fundamental units of matter
Chemistry Basics Matter anything that occupies space and has mass Energy the ability to do work Chemical Electrical Mechanical Radiant Slide 2.1 Composition of Matter Elements Fundamental units of matter
East Poinsett County School District Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Guide Revised August 2011
 East Poinsett County School District Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Guide Revised August 0 Ongoing Strand: Nature of Science Standard 6: Students shall demonstrate an understanding that science is a
East Poinsett County School District Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Guide Revised August 0 Ongoing Strand: Nature of Science Standard 6: Students shall demonstrate an understanding that science is a
2.1 Basic Chemistry 1
 2.1 Basic Chemistry 1 A. Introduction 1. Matter anything that takes up space and has mass 2. States of matter a. Solid b. Liquid c. Gas 2 B. Elements and Atoms 1. Elements basic substances that make up
2.1 Basic Chemistry 1 A. Introduction 1. Matter anything that takes up space and has mass 2. States of matter a. Solid b. Liquid c. Gas 2 B. Elements and Atoms 1. Elements basic substances that make up
An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 C h a p t e r 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris 1-1 The common functions of all living things include responsiveness,
C h a p t e r 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris 1-1 The common functions of all living things include responsiveness,
1. The basic vocabulary used in anatomy is primarily derived from. A. Greek. B. Hebrew. C. Latin. D. German. E. Greek and Latin
 Page 1 of 28 1. The basic vocabulary used in anatomy is primarily derived from A. Greek B. Hebrew C. Latin D. German E. Greek and Latin 1 Student: 2. The early anatomist known as the "Prince of Physicians"
Page 1 of 28 1. The basic vocabulary used in anatomy is primarily derived from A. Greek B. Hebrew C. Latin D. German E. Greek and Latin 1 Student: 2. The early anatomist known as the "Prince of Physicians"
The Chemistry of Microbiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 2 The Chemistry of Microbiology Atoms Matter anything that takes up space and has mass
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 2 The Chemistry of Microbiology Atoms Matter anything that takes up space and has mass
Chemistry of Life. Chapter 2
 Chemistry of Life Chapter 2 Elements Simplest form of matter Made of atoms of one type Cannot be chemically broken down into simpler substances About 117 known elements The Periodic Table of Elements Each
Chemistry of Life Chapter 2 Elements Simplest form of matter Made of atoms of one type Cannot be chemically broken down into simpler substances About 117 known elements The Periodic Table of Elements Each
Chapter 002 The Chemistry of Biology
 Chapter 002 The Chemistry of Biology Multiple Choice Questions 1. Anything that occupies space and has mass is called A. Atomic B. Living C. Matter D. Energy E. Space 2. The electrons of an atom are A.
Chapter 002 The Chemistry of Biology Multiple Choice Questions 1. Anything that occupies space and has mass is called A. Atomic B. Living C. Matter D. Energy E. Space 2. The electrons of an atom are A.
Basic Chemistry. Chemistry Review. Bio 250: Anatomy & Physiology
 Basic Chemistry Bio 250: Anatomy & Physiology Chemistry Review It is going to be your responsibility to review the basic principles of chemistry you learned in BIO 101 This basic set of notes will help
Basic Chemistry Bio 250: Anatomy & Physiology Chemistry Review It is going to be your responsibility to review the basic principles of chemistry you learned in BIO 101 This basic set of notes will help
The Chemical Level of Organization
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 2 The Chemical Level of Organization Chapter 2 Learning Outcomes 2-1 2-2 2-3 2-4 Describe an atom and how atomic
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 2 The Chemical Level of Organization Chapter 2 Learning Outcomes 2-1 2-2 2-3 2-4 Describe an atom and how atomic
Chapter 02 Chemical Basis of Life. Multiple Choice Questions
 Seeleys Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 8th Edition VanPutte Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/seeleys-essentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology-8th-edition-vanputte-test-bank/
Seeleys Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 8th Edition VanPutte Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/seeleys-essentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology-8th-edition-vanputte-test-bank/
BIOLOGY II ORGANIC CHEMISTRY UNIT
 BIOLOGY II ORGANIC CHEMISTRY UNIT ELEMENTS AND ATOMS Matter Anything that takes up space. Three classes of matter: Elements contain only 1 type of atom Compounds 2 or more elements combined in a chemical
BIOLOGY II ORGANIC CHEMISTRY UNIT ELEMENTS AND ATOMS Matter Anything that takes up space. Three classes of matter: Elements contain only 1 type of atom Compounds 2 or more elements combined in a chemical
Chapter 2. Chemical Principles
 Chapter 2 Chemical Principles Insert Fig CO 2 The Structure of Atoms Chemistry is the study of interactions between atoms and molecules The atom is the smallest unit of matter that enters into chemical
Chapter 2 Chemical Principles Insert Fig CO 2 The Structure of Atoms Chemistry is the study of interactions between atoms and molecules The atom is the smallest unit of matter that enters into chemical
Chapter 01 The Sciences of Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 01 The Sciences of Anatomy and Physiology Multiple Choice Questions 1. The word "anatomy" comes from A. Latin and means "to be born." B. Hebrew and means "shape." C. Greek and means "to cut apart."
Chapter 01 The Sciences of Anatomy and Physiology Multiple Choice Questions 1. The word "anatomy" comes from A. Latin and means "to be born." B. Hebrew and means "shape." C. Greek and means "to cut apart."
Introduction to the Human Body, 10th Edition Tortora Test Bank TEST BANK for Introduction to the Human Body, 10th Edition by Gerard J.
 Introduction to the Human Body, 10th Edition Tortora Test Bank TEST BANK for Introduction to the Human Body, 10th Edition by Gerard J. Tortora Test Bank for all chapters are included. Download link: https://testbankreal.com/download/introduction-human-body-10thedition-kindle-edition-test-bank-tortora/
Introduction to the Human Body, 10th Edition Tortora Test Bank TEST BANK for Introduction to the Human Body, 10th Edition by Gerard J. Tortora Test Bank for all chapters are included. Download link: https://testbankreal.com/download/introduction-human-body-10thedition-kindle-edition-test-bank-tortora/
PRESENTATION TITLE. Chemistry. Chemistry
 PRESENTATION TITLE Chemistry Chemistry Chemistry is the study of the smallest forms of matter and their interactions. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Generally, chemistry deals with
PRESENTATION TITLE Chemistry Chemistry Chemistry is the study of the smallest forms of matter and their interactions. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Generally, chemistry deals with
2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules. 2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules. 2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules. 2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules
 All living things are based on atoms and their interactions. Living things consist of atoms of different elements. An atom is the smallest basic unit of matter. An element is one type of atom. ydrogen
All living things are based on atoms and their interactions. Living things consist of atoms of different elements. An atom is the smallest basic unit of matter. An element is one type of atom. ydrogen
3) Using your fingers to find your pulse on your wrist is an example of
 Package Title: Testbank Course Title: PAP13 Chapter Number: 01 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) This is the study of the functions of body structures. a) anatomy b) physiology c) endocrinology d) histology
Package Title: Testbank Course Title: PAP13 Chapter Number: 01 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) This is the study of the functions of body structures. a) anatomy b) physiology c) endocrinology d) histology
Biology Unit 2 Chemistry of Life (Ch. 6) Guided Notes
 Name Biology Unit 2 Chemistry of Life (Ch. 6) Guided Notes Atoms, Elements, and Chemical Bonding I can draw atom models and identify the # protons, # neutrons, and # electrons in an atom. I can identify
Name Biology Unit 2 Chemistry of Life (Ch. 6) Guided Notes Atoms, Elements, and Chemical Bonding I can draw atom models and identify the # protons, # neutrons, and # electrons in an atom. I can identify
16. Why are many anatomical terms based on Greek and Latin roots? A. because they are easy to spell B. because many terms are based on the names of
 1 Student: 1. Which of the following is NOT true? A. Anatomy is the study of the structure of the body. B. Gross anatomy is the study of tissues and cells. C. Comparative anatomy is the study of more than
1 Student: 1. Which of the following is NOT true? A. Anatomy is the study of the structure of the body. B. Gross anatomy is the study of tissues and cells. C. Comparative anatomy is the study of more than
Chemical Principles. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 2 Chemical Principles The Structure of Atoms Learning Objective 2-1 Describe the structure of
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 2 Chemical Principles The Structure of Atoms Learning Objective 2-1 Describe the structure of
2. Anatomy is the study of structure and form. Physiology is the study of how the structures function.
 McKinley/O Loughlin/Bidle Anatomy and Physiology: An Integrative Approach, 2/e Instructor Answer Key to In-chapter and End-of-chapter Questions Completed download Solutions Manual, Instructor Manual, Case
McKinley/O Loughlin/Bidle Anatomy and Physiology: An Integrative Approach, 2/e Instructor Answer Key to In-chapter and End-of-chapter Questions Completed download Solutions Manual, Instructor Manual, Case
BIOCHEMISTRY GUIDED NOTES - AP BIOLOGY-
 BIOCHEMISTRY GUIDED NOTES - AP BIOLOGY- ELEMENTS AND COMPOUNDS - anything that has mass and takes up space. - cannot be broken down to other substances. - substance containing two or more different elements
BIOCHEMISTRY GUIDED NOTES - AP BIOLOGY- ELEMENTS AND COMPOUNDS - anything that has mass and takes up space. - cannot be broken down to other substances. - substance containing two or more different elements
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: Covers the basics of human anatomy and physiology including anatomical terminology, basic biochemistry, cells and tissues, and the integumentary,
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: Covers the basics of human anatomy and physiology including anatomical terminology, basic biochemistry, cells and tissues, and the integumentary,
Biology 30 The Chemistry of Living Things
 Biology 30 The Chemistry of Living Things Hierarchy of organization: Chemistry: MATTER: Periodic Table: ELEMENT: Ex. oxygen, gold, copper, carbon COMPOUND: Ex. salt (NaCl), H 2 O ELEMENTS ESSENTIAL TO
Biology 30 The Chemistry of Living Things Hierarchy of organization: Chemistry: MATTER: Periodic Table: ELEMENT: Ex. oxygen, gold, copper, carbon COMPOUND: Ex. salt (NaCl), H 2 O ELEMENTS ESSENTIAL TO
Chemistry of Life. Chapters 2 & 3. Credit: Larry Stepanowicz. Learning Objectives
 Chemistry of Life Chapters 2 & 3 Credit: Larry Stepanowicz Learning Objectives 1. Differentiate between the definitions of an atom, element, ion, and molecule. 2. Describe why and how atoms react chemically.
Chemistry of Life Chapters 2 & 3 Credit: Larry Stepanowicz Learning Objectives 1. Differentiate between the definitions of an atom, element, ion, and molecule. 2. Describe why and how atoms react chemically.
1/23/2012. Atoms. Atoms Atoms - Electron Shells. Chapter 2 Outline. Planetary Models of Elements Chemical Bonds
 Chapter 2 Outline Atoms Chemical Bonds Acids, Bases and the p Scale Organic Molecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Are smallest units of the chemical elements Composed of protons, neutrons
Chapter 2 Outline Atoms Chemical Bonds Acids, Bases and the p Scale Organic Molecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Are smallest units of the chemical elements Composed of protons, neutrons
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 2 Basic Chemistry. Short Answer. Figure 2.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 2 Basic Chemistry Short Answer Figure 2.1 Using Figure 2.1, identify the following: 1) The structure of the functional protein is. Diff: 3 Page
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 2 Basic Chemistry Short Answer Figure 2.1 Using Figure 2.1, identify the following: 1) The structure of the functional protein is. Diff: 3 Page
Chapter 2: Chemistry. What does chemistry have to do with biology? Vocabulary BIO 105
 Chapter 2: Chemistry What does chemistry have to do with biology? BIO 105 Vocabulary 1. Matter anything that takes up space and has mass Atoms are the smallest units of matter that can participate in chemical
Chapter 2: Chemistry What does chemistry have to do with biology? BIO 105 Vocabulary 1. Matter anything that takes up space and has mass Atoms are the smallest units of matter that can participate in chemical
An atom is the smallest unit of an element. It has: A general understanding of chemistry is necessary for understanding human physiology.
 8/29/11 Chapter 2 I. Atoms, Ions, and Chemical Bonds Chemical Composition of the Body Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Body
8/29/11 Chapter 2 I. Atoms, Ions, and Chemical Bonds Chemical Composition of the Body Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Body
Chapter 2. The Chemistry of Life
 Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Introduction Cells, tissues and organs composed of chemicals Chemical reactions important for function Chemistry is the study of elements, compounds, chemical reactions,
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Introduction Cells, tissues and organs composed of chemicals Chemical reactions important for function Chemistry is the study of elements, compounds, chemical reactions,
Chapter 02 Testbank. 1. Anything that occupies space and has mass is called. A. an electron. B. living. C. matter. D. energy. E. space.
 Chapter 02 Testbank Student: 1. Anything that occupies space and has mass is called A. an electron. B. living. C. matter. D. energy. E. space. 2. The electrons of an atom are A. always equal to the number
Chapter 02 Testbank Student: 1. Anything that occupies space and has mass is called A. an electron. B. living. C. matter. D. energy. E. space. 2. The electrons of an atom are A. always equal to the number
W2. Chemical structures of protein and DNA
 W2. Chemical structures of protein and DNA Copyright Kang, Lin-Woo, Ph.D. Professor Department of Biological Sciences Konkuk University Seoul, Korea Lectures prepared by Christine L. Case The Structure
W2. Chemical structures of protein and DNA Copyright Kang, Lin-Woo, Ph.D. Professor Department of Biological Sciences Konkuk University Seoul, Korea Lectures prepared by Christine L. Case The Structure
Biology of Humans: Concepts, Applications, and Issues, 6e (Goodenough) Chapter 2 Chemistry Comes to Life
 Biology of Humans: Concepts, Applications, and Issues, 6e (Goodenough) Chapter 2 Chemistry Comes to Life 2.1 Multiple Choice Questions 1) A neutral atom must contain. A) an equal number of protons and
Biology of Humans: Concepts, Applications, and Issues, 6e (Goodenough) Chapter 2 Chemistry Comes to Life 2.1 Multiple Choice Questions 1) A neutral atom must contain. A) an equal number of protons and
**Refer to your pre-lecture notes for all the sections we will be covering to help you keep an eye on the big picture
 Section 1: Human Organization and the chemistry of life **Refer to your pre-lecture notes for all the sections we will be covering to help you keep an eye on the big picture Biology Bio = life ology =
Section 1: Human Organization and the chemistry of life **Refer to your pre-lecture notes for all the sections we will be covering to help you keep an eye on the big picture Biology Bio = life ology =
Name Date. Chapter 2 - Chemistry Guide Microbiology (MCB 2010C) Part 1
 Name Date Chapter 2 - Chemistry Guide Microbiology (MCB 2010C) Part 1 The study of biology in the 21 st century is actually the study of biochemistry. In order to be successful in this course, it is important
Name Date Chapter 2 - Chemistry Guide Microbiology (MCB 2010C) Part 1 The study of biology in the 21 st century is actually the study of biochemistry. In order to be successful in this course, it is important
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Biology. Dr. Ramos BIO 370
 Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Biology Dr. Ramos BIO 370 2 Atoms, Bonds, and Molecules Matter - all materials that occupy space and have mass Matter is composed of atoms. Atom simplest form of matter not divisible
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Biology Dr. Ramos BIO 370 2 Atoms, Bonds, and Molecules Matter - all materials that occupy space and have mass Matter is composed of atoms. Atom simplest form of matter not divisible
Human Biology. The Chemistry of Living Things. Concepts and Current Issues. All Matter Consists of Elements Made of Atoms
 2 The Chemistry of Living Things PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation Robert J. Sullivan, Marist College Michael D. Johnson Human Biology Concepts and Current Issues THIRD EDITION Copyright 2006 Pearson
2 The Chemistry of Living Things PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation Robert J. Sullivan, Marist College Michael D. Johnson Human Biology Concepts and Current Issues THIRD EDITION Copyright 2006 Pearson
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Using Figure 2.1, match the following: 1) Lipid. 2) Functional protein. 3) Nucleotide.
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Using Figure 2.1, match the following: 1) Lipid. 2) Functional protein. 3) Nucleotide.
Chapter 02 Testbank. 1. Anything that occupies space and has mass is called. A. an electron. B. living. C. matter. D. energy. E. space.
 Chapter 02 Testbank Student: 1. Anything that occupies space and has mass is called A. an electron. B. living. C. matter. D. energy. E. space. 2. The electrons of an atom are A. always equal to the number
Chapter 02 Testbank Student: 1. Anything that occupies space and has mass is called A. an electron. B. living. C. matter. D. energy. E. space. 2. The electrons of an atom are A. always equal to the number
Microbiology: A Systems Approach, 2 nd ed. Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Biology
 Microbiology: A Systems Approach, 2 nd ed. Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Biology 2.1 Atoms, Bonds, and Molecules: Fundamental Building Blocks Matter: anything that occupies space and has mass Can be liquid,
Microbiology: A Systems Approach, 2 nd ed. Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Biology 2.1 Atoms, Bonds, and Molecules: Fundamental Building Blocks Matter: anything that occupies space and has mass Can be liquid,
ATom,ion, molwcul in the dily live
 ATom,ion, molwcul in the dily live Chemistry of Life All matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms. There are 109 types of atoms. A substance made up of one kind of atom is called an element. An
ATom,ion, molwcul in the dily live Chemistry of Life All matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms. There are 109 types of atoms. A substance made up of one kind of atom is called an element. An
CHAPTER 2 The Chemical Level of Organization
 The objectives of tonight's lecture is to: 4. Explain the structure of the atom, including the subatomic particles. Define isotope ion, anion,cation and electrolytes. 5. Differentiate among elements, molecules
The objectives of tonight's lecture is to: 4. Explain the structure of the atom, including the subatomic particles. Define isotope ion, anion,cation and electrolytes. 5. Differentiate among elements, molecules
Full file at https://fratstock.eu
 VanMeter: Microbiology for the Healthcare Professional Chapter 02: Chemistry of Life Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The atomic number equals the number of a. Protons b. Neutrons c. Electrons d. Protons and
VanMeter: Microbiology for the Healthcare Professional Chapter 02: Chemistry of Life Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The atomic number equals the number of a. Protons b. Neutrons c. Electrons d. Protons and
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Circle the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Summer Work Quiz - Molecules and Chemistry Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Circle the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The four most common elements in living organisms
Summer Work Quiz - Molecules and Chemistry Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Circle the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The four most common elements in living organisms
The Chemical Level of Organization
 Scuola di Ingegneria Industriale e dell Informazione Course 096125 (095857) Introduction to Green and Sustainable Chemistry The Chemical Level of Organization Prof. (and Ada Truscello) Dept. CMIC http://iscamap.chem.polimi.it/citterio/education/course-topics/
Scuola di Ingegneria Industriale e dell Informazione Course 096125 (095857) Introduction to Green and Sustainable Chemistry The Chemical Level of Organization Prof. (and Ada Truscello) Dept. CMIC http://iscamap.chem.polimi.it/citterio/education/course-topics/
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A neutral atom must contain. A) an equal number of protons, neutrons, and electrons B) an equal
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A neutral atom must contain. A) an equal number of protons, neutrons, and electrons B) an equal
Objectives. in living cells.
 Objectives The studient will know the definition of matter, energy potential energy and kinetic energy. the student will be able to define element and be able to list the elements that make up most of
Objectives The studient will know the definition of matter, energy potential energy and kinetic energy. the student will be able to define element and be able to list the elements that make up most of
Chapter 2. The Structure of Atoms. The Structure of Atoms. The Structure of Atoms
 1 The Structure of Atoms 2 Chapter 2 Chemical Principles Chemistry is the study of interactions between atoms and molecules The atom is the smallest unit of matter that enters into chemical reactions Atoms
1 The Structure of Atoms 2 Chapter 2 Chemical Principles Chemistry is the study of interactions between atoms and molecules The atom is the smallest unit of matter that enters into chemical reactions Atoms
