An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
|
|
|
- Winifred McLaughlin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 C h a p t e r 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris
2 1-1 The common functions of all living things include responsiveness, growth, reproduction,movement, and metabolism
3 Living Things All living organisms share the following characteristics Responsiveness Growth Reproduction Movement Metabolism
4 1-2 Anatomy is structure, and physiology is function
5 Anatomy Describes the structures of the body What they are made of Where they are located Associated structures
6 Anatomy Gross anatomy, or macroscopic anatomy, examines large, visible structures Surface anatomy: exterior features Regional anatomy: body areas Systemic anatomy: groups of organs working together
7 Anatomy Microscopic anatomy examines cells and molecules Cytology: study of cells and their structures: cyt- = cell Histology: study of tissues and their structures
8 Physiology Is the study of Functions of anatomical structures Individual and cooperative functions
9 Physiology Cell physiology: processes within and between cells Special physiology: functions of specific organs Systemic physiology: functions of an organ system Pathological physiology: effects of diseases
10 1-3 Levels of organization progress from molecules to a complete organism
11 Levels of Organization The Chemical (or Molecular) Level Atoms are the smallest chemical units Molecules are a group of atoms working together The Cellular Level Cells are a group of atoms, molecules, and organelles working together The Tissue Level Tissues are a group of similar cells working together The Organ Level An organ is a group of different tissues working together
12 Levels of Organization The Organ System Level Organ systems are a group of organs working together Humans have 11 organ systems The Organism Level A human is an organism Levels of Organization Organ Systems
13 Levels of Organization Figure 1-1
14 1-4 The human body consists of 11 organ systems
15 Organ Systems
16 Organ Systems
17 Organ Systems
18 Organ Systems
19 Organ Systems
20 Organ Systems
21 Organ Systems
22 Organ Systems
23 Organ Systems
24 Organ Systems
25 Organ Systems
26 Organ Systems
27 1-5 Homeostasis is the tendency toward internal balance
28 Homeostasis Homeostasis: all body systems working together to maintain a stable internal environment Systems respond to external and internal changes to function within a normal range (body temperature, fluid balance)
29 Homeostasis Receptor Receives the stimulus Control Center Processes the signal and sends instructions Effector Carries out instructions
30 The Control of Room Temperature Figure 1-3
31 1-6 Negative feedback opposes variations from normal, whereas positive feedback exaggerates them
32 Negative Feedback The Role of Negative Feedback The response of the effector negates the stimulus Body is brought back into homeostasis Normal range is achieved
33 Negative Feedback in Thermoregulation Figure 1-4
34 Positive Feedback The Role of Positive Feedback The response of the effector increases change of the stimulus Body is moved away from homeostasis Normal range is lost Used to speed up processes
35 Positive Feedback Figure 1-5
36 The Big Picture Systems integration Systems work together to maintain homeostasis Homeostasis is a state of equilibrium Opposing forces are in balance Physiological systems work to restore balance Failure results in disease or death
37 1-7 Anatomical terms describe body regions, anatomical positions and directions, and body sections
38 Surface Anatomy Anatomical Landmarks Anatomical position: hands at sides, palms forward Supine: lying down, face up Prone: lying down, face down Anatomical Regions Body regions Abdominopelvic quadrants Abdominopelvic regions Anatomical Directions Reference terms based on subject
39 Anatomical Landmarks. Anterior Figure 1-6
40 Anatomical Landmarks. Anterior Figure 1-6
41 Anatomical Landmarks. Posterior Figure 1-6
42 Anatomical Landmarks. Posterior Figure 1-6
43
44
45 Abdominopelvic Quadrants Figure 1-7
46 Abdominopelvic Regions Figure 1-7
47 Abdominopelvic Relationships Figure 1-7
48 Directional References. A Lateral View Figure 1-8
49 Directional References. A Lateral View Figure 1-8
50
51 Sectional Anatomy Planes and sections Plane: a three-dimensional axis Section: a slice parallel to a plane Used to visualize internal organization and structure Important in radiological techniques: MRI PET CT
52 Plane of Section Figure 1-9
53
54 1-8 Body cavities protect internal organs and allow them to change shape
55 Body Cavities Body cavities have two essential functions Protect organs from accidental shocks Permit changes in size and shape of internal organs Ventral body cavity (coelom) Divided by the diaphragm: Thoracic cavity Abdominopelvic cavity
56 Body Cavities Serous Membranes Line body cavities and cover organs Consist of parietal layer and visceral layer Parietal layer lines cavity Visceral layer covers organ
57 The Thoracic Cavity Separated into regions Right and left pleural cavities: Contain right and left lungs Mediastinum Upper portion filled with blood vessels, trachea, esophagus, and thymus Lower portion contains pericardial cavity: The heart is located within the pericardial cavity
58 The Ventral Body Cavity and Its Subdivisions Figure 1-10
59 The Abdominopelvic Cavity Peritoneal cavity chamber within abdominopelvic cavity Parietal peritoneum lines the internal body wall Visceral peritoneum covers the organs
60 The Abdominopelvic Cavity Abdominal cavity superior portion Diaphragm to top of pelvic bones Contains digestive organs Pelvic cavity inferior portion Within pelvic bones Contains reproductive organs, rectum, and bladder
61 X-Rays Figure 1-11
62 Figure 1-12
Journal #1: How might an Anatomist and Physiologist see a computer differently?
 Journal #1: How might an Anatomist and Physiologist see a computer differently? Objective #1: Define Anatomy and Physiology and describe various specialties of each discipline. Identify the major levels
Journal #1: How might an Anatomist and Physiologist see a computer differently? Objective #1: Define Anatomy and Physiology and describe various specialties of each discipline. Identify the major levels
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body NOTES
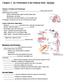 Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body NOTES Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body NOTES Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable
Chapter 1. The Human Organism 1-1
 Chapter 1 The Human Organism 1-1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: Scientific discipline that investigates the body s structure Physiology: Scientific investigation of the processes or functions
Chapter 1 The Human Organism 1-1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: Scientific discipline that investigates the body s structure Physiology: Scientific investigation of the processes or functions
Introduction Chpt 1. Study Slides
 Introduction Chpt 1 Study Slides A group of molecules working together toward a common function is a: A. Cell B. Atom C. Organelle D. Tissue E. Organ ANSWER A group of molecules working together toward
Introduction Chpt 1 Study Slides A group of molecules working together toward a common function is a: A. Cell B. Atom C. Organelle D. Tissue E. Organ ANSWER A group of molecules working together toward
Unit 1: Body Plan & Organization Test Review 1. Define anatomy and contrast it with physiology.
 Name: Period: Unit 1: Body Plan & Organization Test Review 1. Define anatomy and contrast it with physiology. 2. Arrange and identify, in order, the six levels of structural organization of the human body.
Name: Period: Unit 1: Body Plan & Organization Test Review 1. Define anatomy and contrast it with physiology. 2. Arrange and identify, in order, the six levels of structural organization of the human body.
An Introduction to Anatomy
 C h a p t e r 1 An Introduction to Anatomy PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
C h a p t e r 1 An Introduction to Anatomy PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
18. Which body system is needed for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide? A. Respiratory B. Integumentary C. Digestive D. Urinary 19.
 1 Student: 1. Which of the following is NOT a part of the study of anatomy? A. The structure of body parts B. Predicting the body's responses to stimuli C. Microscopic organization D. The relationship
1 Student: 1. Which of the following is NOT a part of the study of anatomy? A. The structure of body parts B. Predicting the body's responses to stimuli C. Microscopic organization D. The relationship
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Prepared by Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar
The Human Body: An Orientation Prepared by Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar
Name: Period: Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Study Outline
 Name: Period: Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Study Outline I. Introduction A. The interests of our earliest ancestors most likely concerned. B. Primitive people certainly suffered
Name: Period: Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Study Outline I. Introduction A. The interests of our earliest ancestors most likely concerned. B. Primitive people certainly suffered
Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology. I. Introduction A. The interests of our earliest ancestors most likely concerned
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11 th ed. Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. The
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11 th ed. Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. The
1. Anatomy is. 2. Which subdivision of anatomy involves the study of organs that function together?
 1 of 19 1 Student: 1. Anatomy is A. the study of function. B. a branch of physiology. C. the study of structure. D. the study of living organisms. E. the study of homeostasis. 2. Which subdivision of anatomy
1 of 19 1 Student: 1. Anatomy is A. the study of function. B. a branch of physiology. C. the study of structure. D. the study of living organisms. E. the study of homeostasis. 2. Which subdivision of anatomy
Introductions. Biology 241: Human Anatomy and Physiology 1. Contact info. Syllabus highlights. Course website. Course website. Instructor: Joel Dahms
 Biology 241: Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Instructor: Joel Dahms Introductions Note cards Name Year you graduated HS and where Career goal List of classes you have taken that may help prepare you for
Biology 241: Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Instructor: Joel Dahms Introductions Note cards Name Year you graduated HS and where Career goal List of classes you have taken that may help prepare you for
1. The basic vocabulary used in anatomy is primarily derived from. A. Greek. B. Hebrew. C. Latin. D. German. E. Greek and Latin
 Page 1 of 28 1. The basic vocabulary used in anatomy is primarily derived from A. Greek B. Hebrew C. Latin D. German E. Greek and Latin 1 Student: 2. The early anatomist known as the "Prince of Physicians"
Page 1 of 28 1. The basic vocabulary used in anatomy is primarily derived from A. Greek B. Hebrew C. Latin D. German E. Greek and Latin 1 Student: 2. The early anatomist known as the "Prince of Physicians"
16. Why are many anatomical terms based on Greek and Latin roots? A. because they are easy to spell B. because many terms are based on the names of
 1 Student: 1. Which of the following is NOT true? A. Anatomy is the study of the structure of the body. B. Gross anatomy is the study of tissues and cells. C. Comparative anatomy is the study of more than
1 Student: 1. Which of the following is NOT true? A. Anatomy is the study of the structure of the body. B. Gross anatomy is the study of tissues and cells. C. Comparative anatomy is the study of more than
Chapter 01 The Sciences of Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 01 The Sciences of Anatomy and Physiology Multiple Choice Questions 1. The word "anatomy" comes from A. Latin and means "to be born." B. Hebrew and means "shape." C. Greek and means "to cut apart."
Chapter 01 The Sciences of Anatomy and Physiology Multiple Choice Questions 1. The word "anatomy" comes from A. Latin and means "to be born." B. Hebrew and means "shape." C. Greek and means "to cut apart."
BIO 115 SP 2012 Homework 1: Introduction to A&P and Chemistry Please note that this is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 BIO 115 SP 2012 Homework 1: Introduction to A&P and Chemistry Please note that this is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. When a body is in the anatomical position, it is A. Standing erect,
BIO 115 SP 2012 Homework 1: Introduction to A&P and Chemistry Please note that this is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. When a body is in the anatomical position, it is A. Standing erect,
Applegate: The Anatomy and Physiology Learning System, 3 rd Edition
 Applegate: The Anatomy and Physiology Learning System, 3 rd Edition Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body TRUE/FALSE 1. The cell is the simplest living unit of organization within the human body. T
Applegate: The Anatomy and Physiology Learning System, 3 rd Edition Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body TRUE/FALSE 1. The cell is the simplest living unit of organization within the human body. T
Test Bank forprinciples of Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition by Tortora
 Test Bank forprinciples of Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition by Tortora Chapter Number: 01 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) Which term describes the study of the functions of body structures? a) anatomy
Test Bank forprinciples of Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition by Tortora Chapter Number: 01 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) Which term describes the study of the functions of body structures? a) anatomy
Chapter 01: Organization of the Body Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition
 Chapter 01: Organization of the Body Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following describes anatomy? a. Using devices to investigate parameters such as heart rate
Chapter 01: Organization of the Body Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following describes anatomy? a. Using devices to investigate parameters such as heart rate
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION. Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 Anatomy and Physiology Four basic properties of life: Reception The ability of the organism to control its actions
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 Anatomy and Physiology Four basic properties of life: Reception The ability of the organism to control its actions
Chapter 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The anatomic term means toward the midline. a. anterior b. posterior c. medial d. cranial The term medial indicates an anatomic direction
Chapter 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The anatomic term means toward the midline. a. anterior b. posterior c. medial d. cranial The term medial indicates an anatomic direction
3) Using your fingers to find your pulse on your wrist is an example of
 Package Title: Testbank Course Title: PAP13 Chapter Number: 01 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) This is the study of the functions of body structures. a) anatomy b) physiology c) endocrinology d) histology
Package Title: Testbank Course Title: PAP13 Chapter Number: 01 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) This is the study of the functions of body structures. a) anatomy b) physiology c) endocrinology d) histology
Pericardial Abdominal Pelvic
 1. A mid-sagittal section of the human body would contain which of the following? Write the name of the smallest body cavity that each of the organs in your first answer here would be located within. a)
1. A mid-sagittal section of the human body would contain which of the following? Write the name of the smallest body cavity that each of the organs in your first answer here would be located within. a)
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY (FOR PARAMEDICAL STUDENTS) Poonam Bachheti Managing Director DPMI Aruna Singh Principal DPMI (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Company) Vayu Education of India 2/25, Ansari Road, Darya Ganj,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY (FOR PARAMEDICAL STUDENTS) Poonam Bachheti Managing Director DPMI Aruna Singh Principal DPMI (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Company) Vayu Education of India 2/25, Ansari Road, Darya Ganj,
Human Anatomy, 7e (Martini/Timmons/Tallitsch) Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy. 1.1 Multiple-Choice Questions
 Human Anatomy, 7e (Martini/Timmons/Tallitsch) Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy 1.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which is the most accurate statement? A) Historically, the relationship
Human Anatomy, 7e (Martini/Timmons/Tallitsch) Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy 1.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which is the most accurate statement? A) Historically, the relationship
Broken Arrow Public Schools Physiology Objectives
 1 st six weeks 1 Define anatomy and physiology. 2 Compare and contrast levels of structural organization. 3 Identify necessary life functions and essential needs and how they are related to homeostasis.
1 st six weeks 1 Define anatomy and physiology. 2 Compare and contrast levels of structural organization. 3 Identify necessary life functions and essential needs and how they are related to homeostasis.
II. Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy is. B. Physiology is.
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Human Anatomy and Physiology, 13 th ed. Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. The
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Human Anatomy and Physiology, 13 th ed. Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. The
CHAPTER 1. Quick Check and Active Learning Answer Keys QUICK CHECK
 CHAPTER 1 QUICK CHECK Page 9 1. Anatomy is the study of the structure of an organism and the relationships of its parts. Physiology is the study of the functions of living organisms and their parts. Pathology
CHAPTER 1 QUICK CHECK Page 9 1. Anatomy is the study of the structure of an organism and the relationships of its parts. Physiology is the study of the functions of living organisms and their parts. Pathology
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Faculty, Department of Natural Sciences College of Education, Arts and Sciences Ramon Magsaysay Technological University Human Anatomy & Physiology
Human Anatomy & Physiology Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Faculty, Department of Natural Sciences College of Education, Arts and Sciences Ramon Magsaysay Technological University Human Anatomy & Physiology
Bio 250 Anatomy & Physiology The Human Organism. Introduction to A & P. Why Anatomy & Physiology? Dr. Tom Rachow Rock-o Office: Agenstein Hall 201E
 Bio 250 Anatomy & Physiology The Human Organism Dr. Tom Rachow Rock-o Office: Agenstein Hall 201E Introduction to A & P Check out the A & P Website at: http://academic.missouriwestern.edu/rachow/ Office
Bio 250 Anatomy & Physiology The Human Organism Dr. Tom Rachow Rock-o Office: Agenstein Hall 201E Introduction to A & P Check out the A & P Website at: http://academic.missouriwestern.edu/rachow/ Office
4. Which of the following organelles digests waste using hydrolytic enzymes:
 Multichoice questions section. You must answer ALL questions. 1. A cell contains many organelles, each of which has a specific function. What is function of mitochondria? a) production of plasma membrane
Multichoice questions section. You must answer ALL questions. 1. A cell contains many organelles, each of which has a specific function. What is function of mitochondria? a) production of plasma membrane
Organization of the Body
 Name: Hmwk # 1 - Chapter 1 Organization of the Body The study of human anatomy and physiology the structure and function of an organism and the relationship of its parts. It begins with a basic organization
Name: Hmwk # 1 - Chapter 1 Organization of the Body The study of human anatomy and physiology the structure and function of an organism and the relationship of its parts. It begins with a basic organization
Anatomy and Physiology. Science Curriculum Framework
 Anatomy and Physiology Science Curriculum Framework Revised 005 Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology should develop an understanding of the organization of the human body through studies of body
Anatomy and Physiology Science Curriculum Framework Revised 005 Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology should develop an understanding of the organization of the human body through studies of body
Module A BODY PLAN & ORGANIZATION
 Module A BODY PLAN & ORGANIZATION Topic from Anatomical position Body planes & sections Body cavities & regions Directional terms Basic terminology Levels of organization Survey of body systems 1. Describe
Module A BODY PLAN & ORGANIZATION Topic from Anatomical position Body planes & sections Body cavities & regions Directional terms Basic terminology Levels of organization Survey of body systems 1. Describe
HTHS 1110 / Biomedical Core Module 1
 HTHS 1110 / Biomedical Core Module 1 Body Plan & Organization Homeostasis Disease: A Disruption in Homeostasis Measurement Systems and Calculations Used for the Human Body Body Plan & Organization Anatomy
HTHS 1110 / Biomedical Core Module 1 Body Plan & Organization Homeostasis Disease: A Disruption in Homeostasis Measurement Systems and Calculations Used for the Human Body Body Plan & Organization Anatomy
ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 01 INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. I. The Scope of Anatomy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 01 INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. I. The Scope of Anatomy
A) Collection of changing/dynamic information dealing with measurable phenomena. 2) study of matter and the energy changes that matter undergoes
 Human Biology 175 Lecture Notes: Introduction Part I Science and the Scientific Method A) Collection of changing/dynamic information dealing with measurable phenomena B) Disciplines of Science 1) study
Human Biology 175 Lecture Notes: Introduction Part I Science and the Scientific Method A) Collection of changing/dynamic information dealing with measurable phenomena B) Disciplines of Science 1) study
NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE. Cells, Tissues, and Membranes
 NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE Cells, Tissues, and Membranes I. Cell Types A. Prokaryote bacteria cells; a cell that does not have a nucleus in which to store its genetic material. B. Eukaryote plant or animal
NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE Cells, Tissues, and Membranes I. Cell Types A. Prokaryote bacteria cells; a cell that does not have a nucleus in which to store its genetic material. B. Eukaryote plant or animal
Anatomy & Physiology (Master)
 St. Michael-Albertville High School Teacher: Kay Nowell Anatomy & Physiology (Master) September 2014 Content Skills Learning Targets Assessment Resources & Technology CEQ 1. How do all the organ systems
St. Michael-Albertville High School Teacher: Kay Nowell Anatomy & Physiology (Master) September 2014 Content Skills Learning Targets Assessment Resources & Technology CEQ 1. How do all the organ systems
JEFFERSON COLLEGE VERTEBRATE ANATOMY
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO207 VERTEBRATE ANATOMY 4 Credit Hours Prepared by: Mr. Jim McCain Revised Date: November 2005 by Dr. Ken Balak Division of Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor,
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO207 VERTEBRATE ANATOMY 4 Credit Hours Prepared by: Mr. Jim McCain Revised Date: November 2005 by Dr. Ken Balak Division of Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor,
CURRICULUM MAP. TIME CONTENT PAGE REF. SKILLS ASSESSMENT/ACTIVITIES Day 1-3
 CURRICULUM MAP COURSE TITLE: Anatomy and Physiology DESCRIPTION TEXTBOOK Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology OF COURSE: 8 th ed: Elaine Marieb Integrated approach to human anatomy. Performance and lab
CURRICULUM MAP COURSE TITLE: Anatomy and Physiology DESCRIPTION TEXTBOOK Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology OF COURSE: 8 th ed: Elaine Marieb Integrated approach to human anatomy. Performance and lab
ERIN C. AMERMAN FLORIDA STATE COLLEGE AT JACKSONVILLE
 ERIN C. AMERMAN FLORIDA STATE COLLEGE AT JACKSONVILLE Lecture Presentation by Suzanne Pundt University of Texas at Tyler MODULE 1.1 HOW TO SUCCEED IN YOUR ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY COURSE HOW TO DEVELOP STUDY
ERIN C. AMERMAN FLORIDA STATE COLLEGE AT JACKSONVILLE Lecture Presentation by Suzanne Pundt University of Texas at Tyler MODULE 1.1 HOW TO SUCCEED IN YOUR ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY COURSE HOW TO DEVELOP STUDY
Full file at Test Bank. Agnes Yard Michael Yard INDIANA UNIVERSITY PURDUE UNIVERSITY AT INDIANAPOLIS (IUPUI)
 Test Bank Agnes Yard Michael Yard INDIANA UNIVERSITY PURDUE UNIVERSITY AT INDIANAPOLIS (IUPUI) Jason LaPres LONE STAR COLLEGE NORTH HARRIS Judi L. Nath LOURDES UNIVERSITY Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology
Test Bank Agnes Yard Michael Yard INDIANA UNIVERSITY PURDUE UNIVERSITY AT INDIANAPOLIS (IUPUI) Jason LaPres LONE STAR COLLEGE NORTH HARRIS Judi L. Nath LOURDES UNIVERSITY Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: Covers the basics of human anatomy and physiology including anatomical terminology, basic biochemistry, cells and tissues, and the integumentary,
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: Covers the basics of human anatomy and physiology including anatomical terminology, basic biochemistry, cells and tissues, and the integumentary,
Anatomy and Physiology of Domestic Animals. Second Edition COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL
 Anatomy and Physiology of Domestic Animals Second Edition COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 1 Introduction to a natomy and p hysiology Contents Anatomy and Physiology 3 Levels of Organization 4 Homeostasis 5 Homeostatic
Anatomy and Physiology of Domestic Animals Second Edition COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 1 Introduction to a natomy and p hysiology Contents Anatomy and Physiology 3 Levels of Organization 4 Homeostasis 5 Homeostatic
East Poinsett County School District Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Guide Revised August 2011
 East Poinsett County School District Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Guide Revised August 0 Ongoing Strand: Nature of Science Standard 6: Students shall demonstrate an understanding that science is a
East Poinsett County School District Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Guide Revised August 0 Ongoing Strand: Nature of Science Standard 6: Students shall demonstrate an understanding that science is a
Sneak Preview. The Human Body. Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology Black and white edition
 Sneak Preview The Human Body Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology Black and white edition By Bruce Wingerd Included in this preview: Copyrights Preface A Note to Students Table of Contents Chapter 1 For
Sneak Preview The Human Body Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology Black and white edition By Bruce Wingerd Included in this preview: Copyrights Preface A Note to Students Table of Contents Chapter 1 For
CHAPTER 01 INTRODUCTION
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I CHAPTER 01 1 Please wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click to advance. Arrow keys etc.also work. Hit ESCAPE Key to exit. INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I CHAPTER 01 1 Please wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click to advance. Arrow keys etc.also work. Hit ESCAPE Key to exit. INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY
McKinley/O Loughlin/Bidle Anatomy and Physiology: An Integrative Approach, 1/e Answer Key
 Chapter 1 Answers to What Did You Learn? 1. Comparative anatomy McKinley/O Loughlin/Bidle Anatomy and Physiology: An Integrative Approach, 1/e Answer Key 2. Anatomy is the study of structure and form.
Chapter 1 Answers to What Did You Learn? 1. Comparative anatomy McKinley/O Loughlin/Bidle Anatomy and Physiology: An Integrative Approach, 1/e Answer Key 2. Anatomy is the study of structure and form.
LABETTE COMMUNITY COLLEGE BRIEF SYLLABUS. ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY, lecture and lab
 LABETTE COMMUNITY COLLEGE BRIEF SYLLABUS SPECIAL NOTE: This brief syllabus is not intended to be a legal contract. A full syllabus will be distributed to students at the first class session. TEXT AND SUPPLEMENTARY
LABETTE COMMUNITY COLLEGE BRIEF SYLLABUS SPECIAL NOTE: This brief syllabus is not intended to be a legal contract. A full syllabus will be distributed to students at the first class session. TEXT AND SUPPLEMENTARY
Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record ANAT 125
 Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record ANAT 125 I. OVERVIEW The following information will appear in the 2010-2011 catalog ANAT 125 Human Anatomy 5 Units Prerequisite: Satisfactory completion
Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record ANAT 125 I. OVERVIEW The following information will appear in the 2010-2011 catalog ANAT 125 Human Anatomy 5 Units Prerequisite: Satisfactory completion
Kelley: Sectional Anatomy for Imaging Professionals, 3rd Edition
 Kelley: Sectional Anatomy for Imaging Professionals, 3rd Edition Chapter 1: Introduction to Sectional Anatomy Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A vertical plane that passes through the body, dividing it into
Kelley: Sectional Anatomy for Imaging Professionals, 3rd Edition Chapter 1: Introduction to Sectional Anatomy Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A vertical plane that passes through the body, dividing it into
Essential Question Content Skills Assessment Standards. Anatomical terms. Homeostatic mechanisms. Characteristics of Life. Requirements for life
 Honors Anatomy & Physiology 2012 Michael Harshaw, Melissa Castone Essential Question Content Skills Assessment Standards Month Introduction September- 1.5 weeks How do Anatomy and Physiology relate to
Honors Anatomy & Physiology 2012 Michael Harshaw, Melissa Castone Essential Question Content Skills Assessment Standards Month Introduction September- 1.5 weeks How do Anatomy and Physiology relate to
Standard 1: Students shall explore the organizational structures of the body from the molecular to the organism level. SE/TE: 1-2 SE/TE: 2
 Strand: Organization of the Human Body Standard 1: Students shall explore the organizational structures of the body from the molecular to the organism level. OHB.1.AP.1 Infer the relationship between anatomy
Strand: Organization of the Human Body Standard 1: Students shall explore the organizational structures of the body from the molecular to the organism level. OHB.1.AP.1 Infer the relationship between anatomy
2. Anatomy is the study of structure and form. Physiology is the study of how the structures function.
 McKinley/O Loughlin/Bidle Anatomy and Physiology: An Integrative Approach, 2/e Instructor Answer Key to In-chapter and End-of-chapter Questions Completed download Solutions Manual, Instructor Manual, Case
McKinley/O Loughlin/Bidle Anatomy and Physiology: An Integrative Approach, 2/e Instructor Answer Key to In-chapter and End-of-chapter Questions Completed download Solutions Manual, Instructor Manual, Case
Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true.
 Unit 4 Review Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 1. A stimulus is anything that threatens the
Unit 4 Review Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 1. A stimulus is anything that threatens the
Human Body Organization And Homeostasis Answer Key
 Organization And Homeostasis Answer Key Free PDF ebook Download: Organization And Homeostasis Answer Key Download or Read Online ebook human body organization and homeostasis answer key in PDF Format From
Organization And Homeostasis Answer Key Free PDF ebook Download: Organization And Homeostasis Answer Key Download or Read Online ebook human body organization and homeostasis answer key in PDF Format From
Study Guide for Bio101 Lecture Exam 1
 Study Guide for Bio101 Lecture Exam 1 Please note that this study guide is a listing of objectives that you are required to master for this course. However, items mentioned in class or in laboratory as
Study Guide for Bio101 Lecture Exam 1 Please note that this study guide is a listing of objectives that you are required to master for this course. However, items mentioned in class or in laboratory as
Physiology. Organization of the Body. Assumptions in Physiology. Chapter 1. Physiology is the study of how living organisms function
 Introduction to Physiology and Homeostasis Chapter 1 Physiology Physiology is the study of how living organisms function On the street explanations are in terms of meeting a bodily need Physiologic explanations
Introduction to Physiology and Homeostasis Chapter 1 Physiology Physiology is the study of how living organisms function On the street explanations are in terms of meeting a bodily need Physiologic explanations
Organization of Vertebrate Body. Organization of Vertebrate Body
 The Animal Body and Principles of Regulation Chapter 43 There are four levels of organization: 1. Cells 2. Tissues 3. Organs 4. Organ systems Bodies of vertebrates are composed of different cell types
The Animal Body and Principles of Regulation Chapter 43 There are four levels of organization: 1. Cells 2. Tissues 3. Organs 4. Organ systems Bodies of vertebrates are composed of different cell types
Overview of Physiology & Homeostasis. Biological explanations Levels of organization Homeostasis
 Overview of Physiology & Homeostasis 1 Biological explanations Levels of organization Homeostasis 2 Biological Explanations Proximate Proximate causation: an explanation of an animal's behavior based on
Overview of Physiology & Homeostasis 1 Biological explanations Levels of organization Homeostasis 2 Biological Explanations Proximate Proximate causation: an explanation of an animal's behavior based on
tissues are made of cells that work together, organs are )
 Study Guide Cells Unit Test Matching. Write the letter of the correct response on the line. You may use the responses more than once. A. proteins B. simple carbohydrates C. complex carbohydrates D. lipids
Study Guide Cells Unit Test Matching. Write the letter of the correct response on the line. You may use the responses more than once. A. proteins B. simple carbohydrates C. complex carbohydrates D. lipids
Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function
 Chapter 40 Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Big Ideas Physical laws and environment constrain
Chapter 40 Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Big Ideas Physical laws and environment constrain
Animal Form & Function Lecture 10 Winter 2014
 Animal Form & Function Lecture 10 Winter 2014 Physical Constraints on Form & Function 1 Anatomy & physiology (define) Environmental constraints on form Convergent evolution Larger organisms Need thicker
Animal Form & Function Lecture 10 Winter 2014 Physical Constraints on Form & Function 1 Anatomy & physiology (define) Environmental constraints on form Convergent evolution Larger organisms Need thicker
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Human Anatomy and Physiology I
 EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Human Anatomy and Physiology I Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number BIO 201 (SUN# BIO 2201) Title Human Anatomy and Physiology I Credits 4 Developed
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Human Anatomy and Physiology I Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number BIO 201 (SUN# BIO 2201) Title Human Anatomy and Physiology I Credits 4 Developed
UNIT 2- BODY ORGANIZATION AND HOMEOSTASIS M E L A N I E L O U L O U S I S
 UNIT 2- BODY ORGANIZATION AND HOMEOSTASIS M E L A N I E L O U L O U S I S ANCHORING PHENOMENON- DIABETES MELLITUS What is Diabetes mellitus Questions: UNIT 2.1 DRIVING QUESTION- HOW ARE LIVING THINGS ORGANIZED?
UNIT 2- BODY ORGANIZATION AND HOMEOSTASIS M E L A N I E L O U L O U S I S ANCHORING PHENOMENON- DIABETES MELLITUS What is Diabetes mellitus Questions: UNIT 2.1 DRIVING QUESTION- HOW ARE LIVING THINGS ORGANIZED?
Anatomy & Physiology Curriculum Map Date Content/Topics Objectives Activities/Assessments Aug. 7th- 21st
 Anatomy & Physiology Curriculum Map 2012-13 Date Content/Topics Objectives Activities/Assessments Aug. 7th- 21st Chapter 1 Body Regions/Cavities Directional Terms Homeostasis System Basics with introduction
Anatomy & Physiology Curriculum Map 2012-13 Date Content/Topics Objectives Activities/Assessments Aug. 7th- 21st Chapter 1 Body Regions/Cavities Directional Terms Homeostasis System Basics with introduction
Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function. Chapter 40
 Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function Chapter 40 Form and Function Anatomy- biological form of an organism. Physiology- biological function. Size and Shape Development of body plan and shape is
Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function Chapter 40 Form and Function Anatomy- biological form of an organism. Physiology- biological function. Size and Shape Development of body plan and shape is
Sioux Falls School District Anatomy and Physiology Holes Anatomy and Physiology Authors: Shier, Butler, and Lewis Glencoe/ McGraw hill
 Sioux Falls School District Anatomy and Physiology Holes Anatomy and Physiology Authors: Shier, Butler, and Lewis Glencoe/ McGraw hill Semester 1 Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Sioux Falls School District Anatomy and Physiology Holes Anatomy and Physiology Authors: Shier, Butler, and Lewis Glencoe/ McGraw hill Semester 1 Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
1. Why Dissect. Why are frogs a good model to use when studying the digestive system (as well as other systems)?
 Name: Date: Period: Frog Dissection Virtual Lab Use the frog Dissection link that follows to answer the questions. http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/virtual_labs/bl_16/bl_16.html Introduction 1. Why Dissect.
Name: Date: Period: Frog Dissection Virtual Lab Use the frog Dissection link that follows to answer the questions. http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/virtual_labs/bl_16/bl_16.html Introduction 1. Why Dissect.
Revision Based on Chapter 25 Grade 11
 Revision Based on Chapter 25 Grade 11 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
Revision Based on Chapter 25 Grade 11 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
Introduction to the Human Body. Cells. Body Functions. Tissues. Organs. Systems. Body Functions & Life Process
 complex functions for the body. Ten major systems compose the human body: Introduction to the Human Body Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic
complex functions for the body. Ten major systems compose the human body: Introduction to the Human Body Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic
Anatomy & Physiology Standards and Benchmarks
 Anatomy & Standards and Standard 1: Understands and applies principles of scientific inquiry Power : Identifies questions and concepts that guide science investigations Uses technology and mathematics
Anatomy & Standards and Standard 1: Understands and applies principles of scientific inquiry Power : Identifies questions and concepts that guide science investigations Uses technology and mathematics
BIOL Anatomy and Physiology I ( version L )
 BIOL 2113 - Anatomy and Physiology I ( version 213L ) Course Title Course Development Learning Support Anatomy and Physiology I Standard No Course Description Introduces the anatomy and physiology of the
BIOL 2113 - Anatomy and Physiology I ( version 213L ) Course Title Course Development Learning Support Anatomy and Physiology I Standard No Course Description Introduces the anatomy and physiology of the
Fairfield Public Schools Science Curriculum Human Anatomy and Physiology: Brains, Bones and Brawn
 Fairfield Public Schools Science Curriculum Human Anatomy and Physiology: Brains, Bones and Brawn BOE Approved 5/8/2018 1 Human Anatomy and Physiology Brains, Bones and Brawn: Description Human Anatomy
Fairfield Public Schools Science Curriculum Human Anatomy and Physiology: Brains, Bones and Brawn BOE Approved 5/8/2018 1 Human Anatomy and Physiology Brains, Bones and Brawn: Description Human Anatomy
BIOLOGY 374 MAMMALIAN CELL MICROANATOMY. Wayne L. Rickoll Phone:
 BIOLOGY 374 MAMMALIAN CELL MICROANATOMY Wayne L. Rickoll Phone: 879-3120 Thompson 257B email: rickoll@ups.edu OFFICE/LAB CHATS GENEROUSLY AVAILABLE. Just email me or send a voice mail as to when you would
BIOLOGY 374 MAMMALIAN CELL MICROANATOMY Wayne L. Rickoll Phone: 879-3120 Thompson 257B email: rickoll@ups.edu OFFICE/LAB CHATS GENEROUSLY AVAILABLE. Just email me or send a voice mail as to when you would
Bio 103 Introduction 13
 13 BIO 103 Lecture Outline Introduction/Organic Molecules/Cells/Cell Division Hole s Human Anatomy & Physiology [Chapters 1, 2 (p. 6169), 3, 4, 22 (p. 835837, 849852)] Introduction [Chapter 1] A. Anatomy
13 BIO 103 Lecture Outline Introduction/Organic Molecules/Cells/Cell Division Hole s Human Anatomy & Physiology [Chapters 1, 2 (p. 6169), 3, 4, 22 (p. 835837, 849852)] Introduction [Chapter 1] A. Anatomy
KRSN BIO 2030 Anatomy and Physiology - 8 credit hours KRSN BIO 2031 Anatomy and Physiology KRSN BIO 2032 Anatomy and Physiology Lab
 KRSN BIO 2030 Anatomy and Physiology - 8 credit hours KRSN BIO 2031 Anatomy and Physiology KRSN BIO 2032 Anatomy and Physiology Lab For institutional specific information, visit the University & College
KRSN BIO 2030 Anatomy and Physiology - 8 credit hours KRSN BIO 2031 Anatomy and Physiology KRSN BIO 2032 Anatomy and Physiology Lab For institutional specific information, visit the University & College
Warm # 15. A scientist wanted to test if playing video games increased a person's reflexes (reaction time).
 Warm # 15 A scientist wanted to test if playing video games increased a person's reflexes (reaction time). What are the independent and dependent variables? 7:53 AM Warm # 16 Give 2 characteristics of
Warm # 15 A scientist wanted to test if playing video games increased a person's reflexes (reaction time). What are the independent and dependent variables? 7:53 AM Warm # 16 Give 2 characteristics of
SPRINGFIELD TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE ACADEMIC AFFAIRS
 SPRINGFIELD TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE ACADEMIC AFFAIRS Course Number: BIOL 132 Department: Biological Sciences Course Title: Anatomy & Physiology 1 Semester: Spring Year: 1997 Objectives/ 1. Recognize
SPRINGFIELD TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE ACADEMIC AFFAIRS Course Number: BIOL 132 Department: Biological Sciences Course Title: Anatomy & Physiology 1 Semester: Spring Year: 1997 Objectives/ 1. Recognize
VOCABULARY. Cell Membrane Nucleus Cell Wall Chloroplast Vacuole Tissue Organ Organ System
 CELLS VOCABULARY Cell Membrane Nucleus Cell Wall Chloroplast Vacuole Tissue Organ Organ System THE IMPORTANCE OF CELLS Cells are the smallest unit of life in all living things They are organized structures
CELLS VOCABULARY Cell Membrane Nucleus Cell Wall Chloroplast Vacuole Tissue Organ Organ System THE IMPORTANCE OF CELLS Cells are the smallest unit of life in all living things They are organized structures
Next Generation Science Standards Life Science Performance Expectations
 A Correlation of Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology 12 th Edition, 2018 To the Life Science Performance Expectations HS-LS1 From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes HS-LS1-1. Construct
A Correlation of Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology 12 th Edition, 2018 To the Life Science Performance Expectations HS-LS1 From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes HS-LS1-1. Construct
Science 8 Unit 4: Cells, Tissues, Organs & Systems
 Science 8 Unit 4: Cells, Tissues, Organs & Systems How do you know when something is alive? How do we know when something is alive? All living things: Are made up of cells The smallest unit of life, often
Science 8 Unit 4: Cells, Tissues, Organs & Systems How do you know when something is alive? How do we know when something is alive? All living things: Are made up of cells The smallest unit of life, often
Syllabus. BIO 172 Human Anatomy and Physiology II
 General Information Syllabus BIO 172 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Date May 23rd, 2018 Author Christy Parker Department Science and Technology Course Prefix BIO Course Number 172 Course Title Human Anatomy
General Information Syllabus BIO 172 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Date May 23rd, 2018 Author Christy Parker Department Science and Technology Course Prefix BIO Course Number 172 Course Title Human Anatomy
Fairfield Public Schools Science Curriculum. Draft Units
 Fairfield Public Schools Science Curriculum Draft Units Human Anatomy and Physiology - Blood, Guts, Senses, and Defenses 1 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Blood, Guts, Senses, and Defenses: Description
Fairfield Public Schools Science Curriculum Draft Units Human Anatomy and Physiology - Blood, Guts, Senses, and Defenses 1 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Blood, Guts, Senses, and Defenses: Description
Specialized Cells, Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems. Chap 2, p. 67 Chap 9, p. 295 Chap 14, p
 Specialized Cells, Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems Chap 2, p. 67 Chap 9, p. 295 Chap 14, p. 468-471 2. I. Cell (Review) basic unit of structure and function in a living thing. They carry out the processes
Specialized Cells, Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems Chap 2, p. 67 Chap 9, p. 295 Chap 14, p. 468-471 2. I. Cell (Review) basic unit of structure and function in a living thing. They carry out the processes
Module 6 Note Taking Guide. Lesson 6.01:Organization of Life
 Module 6 Note Taking Guide Lesson 6.01:Organization of Life Lesson Page: Organization of Living Things The smallest level of organization for living things. Example: Oxygen, Hydrogen - A group of atoms
Module 6 Note Taking Guide Lesson 6.01:Organization of Life Lesson Page: Organization of Living Things The smallest level of organization for living things. Example: Oxygen, Hydrogen - A group of atoms
PUBLIC SCHOOLS OF EDISON TOWNSHIP OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. Length of Course: Student Eligibility: Grades 11, 12
 PUBLIC SCHOOLS OF EDISON TOWNSHIP OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Length of Course: Elective/Required: School: Term Elective High Schools Student Eligibility: Grades 11, 12
PUBLIC SCHOOLS OF EDISON TOWNSHIP OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Length of Course: Elective/Required: School: Term Elective High Schools Student Eligibility: Grades 11, 12
Introduction. The study of animal form and function is integrated by the common set of problems that all animals must solve.
 Introduction The study of animal form and function is integrated by the common set of problems that all animals must solve. These include how to extract oxygen from the environment, how to nourish themselves,
Introduction The study of animal form and function is integrated by the common set of problems that all animals must solve. These include how to extract oxygen from the environment, how to nourish themselves,
Initial Certification
 Initial Certification Medical Physics Part 1 Content Guide Part 1 Content Guides and Sample Questions PLEASE NOTE: List of Constants and Physical Values for Use on the Part 1 Physics Exam The ABR provides
Initial Certification Medical Physics Part 1 Content Guide Part 1 Content Guides and Sample Questions PLEASE NOTE: List of Constants and Physical Values for Use on the Part 1 Physics Exam The ABR provides
CUMBERLAND COUNTY SCHOOL DISTRICT BENCHMARK ASSESSMENT CURRICULUM PACING GUIDE Subject: Anatomy & Physiology Grade: 11-12
 Benchmark Assessment 1 Instructional Timeline: 8 weeks Topic(s): Introduction, Tissues, Integumentary System Describe the major components and functions of physiological systems, including skeletal, muscle,
Benchmark Assessment 1 Instructional Timeline: 8 weeks Topic(s): Introduction, Tissues, Integumentary System Describe the major components and functions of physiological systems, including skeletal, muscle,
B L U E V A L L E Y D I S T R I C T C U R R I C U L U M Science Anatomy & Physiology
 B L U E V A L L E Y D I S T R I C T C U R R I C U L U M Science Anatomy & Physiology UNIT 1: FUNDAMENTALS (optional) Body cavities and planes, Cancer, Cells, Directional and regional terms,, Life processes,
B L U E V A L L E Y D I S T R I C T C U R R I C U L U M Science Anatomy & Physiology UNIT 1: FUNDAMENTALS (optional) Body cavities and planes, Cancer, Cells, Directional and regional terms,, Life processes,
Anatomy and Physiology 4601
 Anatomy and Physiology 4601 Description Basic concepts of human anatomy and physiology will be explored in this health (life) sciencefocused course. Using a systems approach, students will learn about
Anatomy and Physiology 4601 Description Basic concepts of human anatomy and physiology will be explored in this health (life) sciencefocused course. Using a systems approach, students will learn about
Advanced Anatomy and Physiology
 Lakeshore Technical College 10806179 Advanced Anatomy and Physiology Course Outcome Summary Course Information Alternate Title Description Total Credits 4 Total Hours 90 Adv Anatomy & Physiology Advanced
Lakeshore Technical College 10806179 Advanced Anatomy and Physiology Course Outcome Summary Course Information Alternate Title Description Total Credits 4 Total Hours 90 Adv Anatomy & Physiology Advanced
PHYSICS & BIOLOGY IN MEDICINE 218 RADIOLOGIC FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY. Fall 2017
 PHYSICS & BIOLOGY IN MEDICINE 218 RADIOLOGIC FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY Fall 2017 INSTRUCTORS Allan MacKenzie-Graham, PhD Jeff Alger, PhD Neuroscience Research Building 225Z 635 Charles Young Drive Email: amg@ucla.edu
PHYSICS & BIOLOGY IN MEDICINE 218 RADIOLOGIC FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY Fall 2017 INSTRUCTORS Allan MacKenzie-Graham, PhD Jeff Alger, PhD Neuroscience Research Building 225Z 635 Charles Young Drive Email: amg@ucla.edu
Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit #4 Assessment
 Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit #4 Assessment 1. Which of these shows the correct hierarchical sequence? A. organs cells tissues organ systems B. cells tissues organs organ systems
Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit #4 Assessment 1. Which of these shows the correct hierarchical sequence? A. organs cells tissues organ systems B. cells tissues organs organ systems
1. Which of the cellular components listed above are part of the endomembrane system and surrounded by a double membrane?
 Anatomy and Physiology 141 Fall 2014: Exam IA Name: Use the following list to answer Question 1. 1 Golgi apparatus 2 Nuclear membrane 3 Mitochondria 4 Rough ER 5 Smooth ER 1. Which of the cellular components
Anatomy and Physiology 141 Fall 2014: Exam IA Name: Use the following list to answer Question 1. 1 Golgi apparatus 2 Nuclear membrane 3 Mitochondria 4 Rough ER 5 Smooth ER 1. Which of the cellular components
2. Skeletal muscle cells need large numbers of to make the many proteins they contain.
 BIOL 2010 Human Anatomy & Physiology I -- Exam 1 -Form A- Name: 1. Vesicles are formed from A. lysosomal membrane. B. nuclear membrane. C. cell membrane. D. endoplasmic reticulum. E. none of the above.
BIOL 2010 Human Anatomy & Physiology I -- Exam 1 -Form A- Name: 1. Vesicles are formed from A. lysosomal membrane. B. nuclear membrane. C. cell membrane. D. endoplasmic reticulum. E. none of the above.
BIOLOGY 374 MAMMALIAN CELL MICROANATOMY Spring Course Objectives and Organization
 BIOLOGY 374 MAMMALIAN CELL MICROANATOMY Spring 2014 Wayne L. Rickoll Phone: 879-3120 Thompson 257B email: rickoll@ups.edu Scheduled office hours: M 1-3; T 11-12; F 2-3. OTHER OFFICE HOURS GENEROUSLY AVAILABLE.
BIOLOGY 374 MAMMALIAN CELL MICROANATOMY Spring 2014 Wayne L. Rickoll Phone: 879-3120 Thompson 257B email: rickoll@ups.edu Scheduled office hours: M 1-3; T 11-12; F 2-3. OTHER OFFICE HOURS GENEROUSLY AVAILABLE.
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 120 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY. 5 Credit Hours. Prepared by: Deborah Allen. Revised date: July, 2014
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 120 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Deborah Allen Revised date: July, 2014 Ms. Linda Abernathy, Division Chair, Math, Science & Business Ms.
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 120 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Deborah Allen Revised date: July, 2014 Ms. Linda Abernathy, Division Chair, Math, Science & Business Ms.
