Compilation and validation of bathymetric data for the South China Sea with an emphasis on shallow region
|
|
|
- Stuart Powell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 九州大学大学院総合理工学府報告 Engineering Sciences Reports, Kyushu University 第 35 巻第 2 号 7-13 頁平成 26 年 2 月 Vol. 35, No. 2, pp. 7-13, FEB, 2014 Compilation and validation of bathymetric data for the South China Sea with an emphasis on shallow region Katsuto UEHARA *1, of corresponding author: uehara@riam.kyushu-u.ac.jp (Received January 20, 2014, accepted January 22, 2014) Bathymetric data with a resolution of 5 min called gbscs5 have been compiled for a shelf region shallower than 200 m in the South China Sea by referring to paper charts, electronic charts, and trackline sounding data. Through a comparison between the new dataset and existing datasets (etopo5, etopo1, gebco08), characteristics of each dataset, including the existence of artificial features derived from erroneous sounding data or a conversion error of depth units, were documented for each dataset. It was found that small-scale bathymetric features observed along the shelf edge in gebco08 bathymetry are bounded by survey lines and were likely to be a spurious figure generated when applying a high-order interpolation scheme. Tidal simulations conducted with changing bathymetries have shown that the newly compiled dataset will produce smaller deviation from observed values than the existing bathymetries. While all four datasets analyzed in this study were found to be suitable for estimating overall tidal features of the South China Sea, a care must be taken when applying the tidal model results to a particular coastal region. Key words: South China Sea, continental shelf, bathymetry, tidal model, internal tide generation 1. Introduction Ocean bathymetry is one of the major factors which control dynamical processes such as oceanic currents, coastal upwelling, tides, tsunamis, and internal waves. Accurate water depth is therefore essential when studying ocean dynamics. During the last 25 years, a number of digital terrain models (DTMs) covering global lands and oceans have been developed. While the quality and resolution of such datasets have improved greatly for open oceans as satellitealtimetry data become available in the late 1990s 1), large uncertainties still remain for bathymetries in shallow waters where the spatial scale of bottom features are small. Further refinement of bathymetric dataset for shallow regions is necessary to improve the overall performance of ocean models. In this study, bathymetry data of the South China Sea are compiled for depths shallower than 200 m and compared with existing bathymetry data. *1 Center for East Asian Ocean-Atmosphere Research, Research Institute for Applied Mechanics 2. Materials and methods 2.1 Existing bathymetry datasets Three existing DTMs, etopo5, etopo1, and gebco08, which contain land altitudes and ocean depths on a global longitude-latitude grid were used for analyses. The study area ranges from 99 E to 125 E and from 0 to 23 N (Fig. 1). Fig.1 Map of the study region. Circles denote locations of tide-gauge stations used for analyses.
2 8 Compilation of South China Sea bathymetric data Etopo5 (Fig.2a) is a 5 min resolution dataset developed in 1988 which is distributed by U.S. National Geophysical Data Center (NGDC) in National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Water depths of etopo5 are based on ship sounding data. This dataset was superseded by a 1 min resolution etopo1 in 2009 (Fig.2b) 2). Ocean depths in etopo1 are derived mostly by satellite altimetry technique. Gebco08 dataset was released in 2010 by British Oceanographic Data Centre (BODC) and has a spatial resolution of 0.5 min (Fig.2c). It was generated by combining ship depth sounding data with interpolation of sounding points guided by satellite derived gravity data. 2.2 Gbscs5 bathymetry The newly compiled 5 min resolution dataset (gbscs5; Fig.2d) was based on gebco08. Firstly, the 0.5 min resolution gebco08 was remapped onto a 5 min resolution grid compatible to that of etopo5 (cell-registered configuration, i.e., cell edges are along lines of latitude and longitude) by taking average of the second and third quadrants of 100 depth values allocated within the enlarged grid cell (Fig. 2e). Grid cell values were modified over an area shown in Fig.2f, which includes a wide shelf west of 110 E and an area along southern Chinese coasts. The water depth of the revised region was mostly shallower than 200 m, as our aim was to improve the data quality in shallow waters. The revision was made by overlaying (a) scanned paper charts issued by U.S., Russia, U.K., Vietnam, and Thailand, (b) electronic charts (ENCs) supplied as a part of U.K. Hydrographic Office (UKHO) Admiralty Vector Chart System (AVCS) and South China Sea Electronic Navigational Charts (SCS ENC) by East Asia Hydrographic Commission (EAHC), and (c) trackline bathymetry data distributed at NGDC website which contain serial sounding records along survey sections, and (d) depth contours generated from gebco08 bathymetry for every 10 m from 0 m to 200 m and for 500 m depth (displayed for reference purpose only and not used for depth estimation) on a single screen of a GIS software. A representative depth at a certain grid cell was estimated by referring to depth sounding values appear inside the cell, normally by taking an average of maximum and minimum depths found in the cell. Comparison between the depth sounding values derived from charts and trackline data with depth contours of gebco08 indicated that the number of depth points used to compile gbscs5 was larger than that for gebco08, which was probably because we employed large scale charts containing detailed bathymetry especially at nearshore regions. Horizontal datum of scanned paper charts were converted from local datum to WGS84 coordinates if necessary. Tidal correction was not applied here because we could not obtain appropriate offset values to make a correction at the current stage. We did not employ an automated method such as an interpolation scheme to obtain a gridded dataset mainly for two reasons. Firstly, it was found that navigational charts, especially small-scale ones, tend to indicate depth values at shallow shoals more frequently than those in deep troughs or those at a moderate depth, so that a simple interpolation of depth values without considering such bias often result in an underestimation of a representative depth. Another reason was that the distribution of available sounding points in the South China Sea are generally not dense enough for automated interpolation scheme to resolve subgrid scale anisotropic features such as narrow troughs and elongated ridges. The low spatial resolution of the new dataset (5 min) compared to the existing ones (up to 0.5 min) was also due to the overall sparseness of the depth sounding data, which is evident in regions south of Vietnam (especially in offshore area between 4 N and 8 N), central Gulf of Thailand, Gulf of Tonkin west of 108 E or south of 18 N, and southern Taiwan Strait 118 E E and 22 N-23 N (Fig. 3). 2.3 Tidal experiment A two dimensional finite difference model was introduced to verify the performance of the new bathymetry data. The model was forced by specifying harmonic constants (M2, S2, N2, K2, K1, O1, P1, and Q1 constituents) of a global tidal model TPXO7.2 3) along open boundaries and also by applying astronomical forcing (M2, S2, K1, and O1). A series of numerical experiments were conducted with different bathymetries (etopo5, etopo1, gebco08, and gbscs05; all datasets were converted into 5 min resolution) but other conditions were kept unchanged. Model results were compared against tidegauge data for M2 and K1 constituents at all stations listed in Zu et al. 4-5) (except for 5 stations situated north of 23 N) (see Fig. 1 for locations). Each numerical run was conducted for days with a time step of 12 sec and
3 平成 25 年度九州大学大学院総合理工学報告第 35 巻第 2 号 9 Fig.2 Depth contour of bathymetric datasets used in this study: (a) etopo5, (b) etopo1, (c) gebco08, (d) gbscs5, (e) gebco08 (converted to 5min resolution), and (f) difference between Figs. 2d and 2e. Contour lines are drawn for (a-e) depth 0, 20, 50, 75, 100, 500, 1000, 2000 and 4000m or (f) 0 and 200m. the last days were used for analyses. Quadratic bottom friction coefficient was set as and horizontal eddy viscosity coefficient was 100m/s 2. Details of the model formulation are found in other article 6).
4 10 Compilation of South China Sea bathymetric data locations, such as those north of Gulf of Thailand, in southwestern Sumatra Island, in the Mekong River delta, and along the northwestern coast of Gulf of Tonkin, grid point values were padded with 0 m and coastlines were not represented correctly. Furthermore, depths at some coastal regions, such as those along the east coast of Laizhou Peninsula (110.3 E, 21 N), off the Pearl River mouth, northeast and southwest of Palawan Island (120.5 E, 11 N and 117 E, 7.5 N), were padded with an erroneous value of 10 m. In offshore regions, there were three major differences between etopo5 and gbscs5: (1) depth of etopo5 in the central part of Gulf of Thailand was deeper than that of gbscs5, (2) an isolated shoal situated along the shelf edge in the southwestern South China Sea (109.8 E, 5.6 N) was existent only in etopo5, and (3) the depth of a shoal in the southeastern Taiwan Strait (118 E, 22.7 N) was much shallower in etopo5. We could not collect enough materials to make further discussion on this discrepancy because depth information was sparse in these three areas Etopo1 Fig.3 Screenshots of overlaid depth information derived from paper charts, encs (dots and blue lines), and trackline sounding data (thick brown lines) in northwestern (upper panel, 105 E-121 E and 15 N N) and southwestern (lower panel, 98.5 E-115 E and 0-14 N) South China Sea. Red lattices denote latitudes and longitudes in 0.5 degree interval, which are six times coarser than the resolution of gbscs5. Thin brown lines denote depth contour (every 10 m up to 200 m and 500 m) derived from gebco08 bathymetry. 3. Results 3.1 Comparison between depth datasets Figure 2 shows the water depth of three existing datasets as well as that of gbscs5 developed in this study. Though the overall features were similar among the four datasets, discrepancies were also evident. Here, we confine our view to areas shallower than 200 m Etopo5 The depth contour of etopo5 show patterns similar to those of gbscs5 at depths between 20 m and 100 m (Figs. 2a and 2d) except that the contour of etopo5 was generally smoother. The resemblance is probably because both datasets are based on ship sounding data. The contour of etopo5 is smooth because a smoothing filter was applied when producing the grid data. On the other hand, etopo5 seems to have problems with the coastline position and depth shallower than 20 m. At lowlands in several The position of coastline in etopo1 was improved significantly from that in etopo5 as the former incorporates Global Self-consistent, Hierarchical, High-resolution Shoreline data (GSHHS) published by NGDC in 2003 (Fig.2b). However, etopo1 still have small though systematic errors at around shorelines adjacent to lowlands such as Mekong and Pearl River deltas and the northern coast of Gulf of Tonkin, so that a care must be taken when the dataset is used with its original resolution. It was also found that bottom features in coastal areas shallower than 50 m were smoothed excessively and 20 m contour was located much farther from the coast than etopo5 and gbscs5. Anomalous shallow depths were also found at Paracel (114.5 E, 16 N) and Spratly (116.5 E, 11.5 N) islands located in the central South China Sea and at a region northwest of Palawan Island (120 E, 11 N). While undulating features observed in the Malacca Strait (102 E, 2 N) are obviously artificial, we could not acquire enough material to confirm the existence of two shoals observed in Gulf of Thailand (103.7 E, 6.5 N) and in Gulf of Tonkin (107.7 E, 19 ), which were not found in etopo5 and gbscs Gebco08 Depth contours shown in Fig.2c indicate that gebco08 bathymetry, which uses both sounding and altimetry information, has more realistic
5 平成 25 年度九州大学大学院総合理工学報告第 35 巻第 2 号 11 Fig.4 (a) Location of Figs.4(b-f). (b) Overlay of land area derived from gebco08 (dark green) and from a nautical chart (light green). (c) Anomalous depth (exceeding 2000m) observed in sounding data. Color contours indicating the depth of gebco08 in 10 m intserval from 0 m to 200 m as well as 500 m, and a series of anomalous sounding data exceeding 2000 m. (c) a circular 20 m contour of gebco08 crossing two points showing 17 fathom (31 m) and 25.6 m depths. Bold figures (e.g., 25.6 and 29.2) indicate depth in meters, obtained from different chart. (e) Depth contour of gebco08 (color contours) and sounding survey lines (thick brown lines) at a shelf edge south of Taiwan Strait (118 E E, 22 N- 23 N). (f) Same as (e) except for a shelf edge south of Vietnam in the southwestern South China Sea. coastline and higher resolution than etopo5 (Fig.2a) and has more accurate bathymetry at shallow regions than etopo1 (Fig.2b). Depth difference between gebco08 and gbscs5 was found mainly in areas where the depth sounding information was sparse (Fig.2f). Irrespective of overall improvements in the data quality, some erroneous values still remains in the depth data of gebco08 (Fig.4). For example, inaccurate coastline position were observed at several lowlands such as Mekong (Fig.4b) and Pearl River deltas, which seems to have inherited from etopo1. It was also found that gebco08 incorporates erroneous sounding data at a shallow shelf north of Brunei, which could be recognized by a series of isolated hollows deeper than 500 m (Fig.4c). Several small shoals appear in Gulf of Thailand in the gebco08 bathymetry seems to have made by a conversion error of depth units, i.e., depths indicated in fathoms (1.83 m) were regarded as meters and were underestimated (Fig.4d). It is
6 12 Compilation of South China Sea bathymetric data to be noted that many sounding data obtained in 1930s-1960s are still in use in the South China Sea and several paper charts represent depths in fathoms. Similar depth conversion failure was also observed in SCS ENC. In etopo1 and gebco08, spurious deep depths Dataset were often found in nearshore areas such as an inlet surrounded by high mountains and an intertidal zone where no depth information is specified. The erroneous values seem to have associated with an overshoot caused by the gebco_08 application of high-order interpolation scheme. gbscs5 Small-scale bathymetric features observed at the shelf edge (Figs.4e and 4f) might also be spurious features caused by the overshooting effect, as ridges and troughs seem to be bounded by the survey lines and the depth sounding points, and the features were more apparent at areas where the overall depth changes abruptly from 2000 m to 200 m. In the southern Taiwan Strait, the magnitude of depth variation along the shelf edge was smaller at region west of 119 E, where the depth point is distributed more densely than at areas east of 119 E, which is consistent with the overshooting hypothesis. We cannot present clear conclusion on whether the features are artificial or not, because the area where such feature is evident generally coincides with an area where depth information is extremely sparse. More detailed survey on the bathymetry of shelf-edge region in the South China Sea is anticipated, as the shelf edge is considered as major generation site of internal waves. 3.2 Tidal experiment The rms deviation between observed and simulated results indicates that the model outputs derived by using gebco08 and gbscs5 bathymetries show better performance than those derived by using etopo5 and etopo1 datasets (Table 1). Larger rms deviation in etopo5 and etopo1 cases were caused mainly by large discrepancies observed at several specific stations, which indicate that all four datasets analyzed in this study would be suitable to obtain overall tidal features in the South China Sea while a care must be taken when focusing on a specific coastal location. For example, etopo1 is not suitable to be used in a numerical model predicting tides in the upper Gulf of Thailand (station 26 in Fig.1) as the bathymetry is much shallower than observed and tides around the area are largely underestimated. Erroneous configuration of the Pearl River Estuary in etopo1 and gebco08 Table 1 Root-mean-squared (rms) deviation of tidal harmonic constants (ampliutde and phase) between model run output using different bathymetry and observed values at 49 tide-gauge stations listed in Fig.1. influenced tidal estimates along the coast of Guanxi Province in China (station 5). Though tidal simulation using gbscs5 produces optimal results in overall sense, the model tends to overestimate tidal amplitudes along peninsula Malaysia (stations 28-31) and at southwest Borneo (station 38). These large errors might be due partly to insufficient accuracy of model bathymetry in the central part of Gulf of Thailand and the area south of Vietnam, as the number of sounding data used for revision was small compared to other regions. In addition, usage of old sounding data may also have influenced the tidal output, because a recent study for the Bohai Sea in northern China indicates that a decadal shoreline change may alter M2 amplitude for more than 10 cm 7). 4. Summary and Conclusion New bathymetric dataset of the South China Sea shelf was compiled and compared with existing datasets. It was found that the new dataset, which refers to larger number of sounding data than in previous cases, seems to show better performance than the three existing datasets. Additional sounding data are necessary to compile more accurate bathymetry dataset of the South China Sea shelf, especially at regions such as the central Gulf of Thailand, offshore area south of Vietnam from 4 N to 8 N, and shelf edge in the southwestern South China Sea, southern Gulf of Tonkin, and southern Taiwan Strait (118 E -119 E ). Acknowledgments amp (cm) M2 phase (deg) This work was supported by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI ( ), JSPS G8 Research Councils Initiative, and Research Institute for East Asia Environments, Kyushu University. K1 amplitude (cm) phase (deg) etopo etopo
7 平成 25 年度九州大学大学院総合理工学報告第 35 巻第 2 号 13 References 1) W.H.F. Smith and D.T. Sandwell, Science 277 (1997) ) C. Amante and B.W. Eakins, NOAA Technical Memorandum NESDIS NGDC-24 (200) 19pp. 3) G.D. Egbert and S.Y. Erofeeva, J. Atmos Ocean. Tech. 19 (2002) ) T. Zu et al., Deep-Sea Res. I 55 (2008) ) G. Fang et al., Cont. Shelf Res. 19 (1999) ) K. Uehara, Rep. Res. Inst. Appl. Mech, Kyushu Univ. No.143 (2012) ) H.E. Pelling et al., J. Geophys. Res. 118 (2013) doi: /jgrc.20258, 11pp. Appendix A1. URL of the data source Etopo5 Etopo1 Gebco08 Trackline sounding data SCS ENC
Updating the GEBCO Grid
 Updating the GEBCO Grid PAULINE WEATHERALL, GEBCO DIGITAL ATLAS MANAGER, BRITISH OCEANOGRAPHIC DATA CENTRE (BODC), NATIONAL OCEANOGRAPHY CENTRE (NOC), LIVERPOOL, UK. GEBCO TSCOM and SCRUM meeting, Kuala
Updating the GEBCO Grid PAULINE WEATHERALL, GEBCO DIGITAL ATLAS MANAGER, BRITISH OCEANOGRAPHIC DATA CENTRE (BODC), NATIONAL OCEANOGRAPHY CENTRE (NOC), LIVERPOOL, UK. GEBCO TSCOM and SCRUM meeting, Kuala
Integrated Hydrodynamic Modeling System
 Integrated Hydrodynamic Modeling System Applied Science Associates, Inc. 70 Dean Knauss Drive Narragansett, RI USA 02882 www.asascience.com support@asascience.com 1 Introduction HYDROMAP is a globally
Integrated Hydrodynamic Modeling System Applied Science Associates, Inc. 70 Dean Knauss Drive Narragansett, RI USA 02882 www.asascience.com support@asascience.com 1 Introduction HYDROMAP is a globally
The route towards a new GEBCO grid
 The route towards a new GEBCO grid Pauline Weatherall, GEBCO Digital Atlas Manager British Oceanographic Data Centre (BODC) GEBCO TSCOM/SCRUM meeting, Monaco, October 2012 The route towards a new GEBCO
The route towards a new GEBCO grid Pauline Weatherall, GEBCO Digital Atlas Manager British Oceanographic Data Centre (BODC) GEBCO TSCOM/SCRUM meeting, Monaco, October 2012 The route towards a new GEBCO
Nested High- Resolu0on Data Assimila0on Modeling of Ocean Tides in Coastal and Shallow Seas
 Nested High- Resolu0on Data Assimila0on Modeling of Ocean Tides in Coastal and Shallow Seas Gary Egbert Lana Erofeeva College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences Oregon State University TPXO7.2- GOT4.7
Nested High- Resolu0on Data Assimila0on Modeling of Ocean Tides in Coastal and Shallow Seas Gary Egbert Lana Erofeeva College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences Oregon State University TPXO7.2- GOT4.7
A Study on Residual Flow in the Gulf of Tongking
 Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 56, pp. 59 to 68. 2000 A Study on Residual Flow in the Gulf of Tongking DINH-VAN MANH 1 and TETSUO YANAGI 2 1 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Ehime University,
Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 56, pp. 59 to 68. 2000 A Study on Residual Flow in the Gulf of Tongking DINH-VAN MANH 1 and TETSUO YANAGI 2 1 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Ehime University,
Bathymetry Data and Models: Best Practices
 Bathymetry Data and Models: Best Practices Barry Eakins & Lisa Taylor The NOAA National Geophysical Data Center Over 600 data types - from the core of the Earth to the surface of the Sun NGDC Bathymetry
Bathymetry Data and Models: Best Practices Barry Eakins & Lisa Taylor The NOAA National Geophysical Data Center Over 600 data types - from the core of the Earth to the surface of the Sun NGDC Bathymetry
Characterization of the Nigerian Shoreline using Publicly-Available Satellite Imagery
 University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Center for Coastal and Ocean Mapping Center for Coastal and Ocean Mapping 1-2014 Characterization of the Nigerian Shoreline
University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Center for Coastal and Ocean Mapping Center for Coastal and Ocean Mapping 1-2014 Characterization of the Nigerian Shoreline
京都大学防災研究所年報第 49 号 B 平成 18 年 4 月. Annuals of Disas. Prev. Res. Inst., Kyoto Univ., No. 49 B,
 京都大学防災研究所年報第 49 号 B 平成 18 年 4 月 Annuals of Disas. Prev. Res. Inst., Kyoto Univ., No. 49 B, 2006 170 1978 2003 26 30-60 10-20 :. 10 60 (Krishnamurti and Bhalme, 1976; Hartmann and Michelsen, 1989 )Hartmann
京都大学防災研究所年報第 49 号 B 平成 18 年 4 月 Annuals of Disas. Prev. Res. Inst., Kyoto Univ., No. 49 B, 2006 170 1978 2003 26 30-60 10-20 :. 10 60 (Krishnamurti and Bhalme, 1976; Hartmann and Michelsen, 1989 )Hartmann
Briefing on the work of GEBCO (GENERAL BATHYMETRIC CHART OF THE OCEANS)
 Briefing on the work of GEBCO (GENERAL BATHYMETRIC CHART OF THE OCEANS) 7th ROPME Sea Area Hydrographic Commission Meeting, Muscat, Oman 20-22 February 2017 What is GEBCO? The General Bathymetric Chart
Briefing on the work of GEBCO (GENERAL BATHYMETRIC CHART OF THE OCEANS) 7th ROPME Sea Area Hydrographic Commission Meeting, Muscat, Oman 20-22 February 2017 What is GEBCO? The General Bathymetric Chart
Digital Elevation Model of Tutuila, American Samoa: Procedures, Data Sources, and Analysis
 Digital Elevation Model of Tutuila, American Samoa: Procedures, Data Sources, and Analysis Prepared for the National Tsunami Hazard Mitigation Program (NTHMP) by the NOAA National Geophysical Data Center
Digital Elevation Model of Tutuila, American Samoa: Procedures, Data Sources, and Analysis Prepared for the National Tsunami Hazard Mitigation Program (NTHMP) by the NOAA National Geophysical Data Center
Numerical Simulation of Hydrodynamic for Abrupt Bathymetry in Palu River Estuary
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 10(29), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2017/v10i29/116502, August 2017 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Numerical Simulation of Hydrodynamic for Abrupt
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 10(29), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2017/v10i29/116502, August 2017 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Numerical Simulation of Hydrodynamic for Abrupt
Updating the GEBCO_08 Grid with regional compilations and surveys
 Updating the GEBCO_08 Grid with regional compilations and surveys Pauline Weatherall, GEBCO Digital Atlas Manager, British Oceanographic Data Centre (BODC) GEBCO TSCOM/iSCRUM meeting, SIO, October 2011
Updating the GEBCO_08 Grid with regional compilations and surveys Pauline Weatherall, GEBCO Digital Atlas Manager, British Oceanographic Data Centre (BODC) GEBCO TSCOM/iSCRUM meeting, SIO, October 2011
Not all bathymetry grids are created equal
 Bathymetry grids - 1 - Not all bathymetry grids are created equal K. M. Marks NOAA Laboratory for Satellite Altimetry, Silver Spring, MD 20910, USA W. H. F. Smith NOAA Laboratory for Satellite Altimetry,
Bathymetry grids - 1 - Not all bathymetry grids are created equal K. M. Marks NOAA Laboratory for Satellite Altimetry, Silver Spring, MD 20910, USA W. H. F. Smith NOAA Laboratory for Satellite Altimetry,
Cotidal Charts near Hawaii Derived from TOPEX/Poseidon Altimetry Data
 606 J O U R N A L O F A T M O S P H E R I C A N D O C E A N I C T E C H N O L O G Y VOLUME 28 Cotidal Charts near Hawaii Derived from TOPEX/Poseidon Altimetry Data LI-LI FAN, BIN WANG, AND XIAN-QING LV
606 J O U R N A L O F A T M O S P H E R I C A N D O C E A N I C T E C H N O L O G Y VOLUME 28 Cotidal Charts near Hawaii Derived from TOPEX/Poseidon Altimetry Data LI-LI FAN, BIN WANG, AND XIAN-QING LV
Spatial variability in annual sea level variations around the Korean peninsula
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L03603, doi:10.1029/2007gl032527, 2008 Spatial variability in annual sea level variations around the Korean peninsula Sok Kuh Kang, 1 Josef Y. Cherniawsky, 2 Michael
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L03603, doi:10.1029/2007gl032527, 2008 Spatial variability in annual sea level variations around the Korean peninsula Sok Kuh Kang, 1 Josef Y. Cherniawsky, 2 Michael
Assessing Shelf Sea Tides in Global HYCOM
 Assessing Shelf Sea Tides in Global HYCOM Patrick G. Timko 1, Patrick Hyder 2, Brian K. Arbic 3, and Luis Zamudio 4 1 Bangor University 2 UK Met. Office 3 University of Michigan 4 COAPS, Florida State
Assessing Shelf Sea Tides in Global HYCOM Patrick G. Timko 1, Patrick Hyder 2, Brian K. Arbic 3, and Luis Zamudio 4 1 Bangor University 2 UK Met. Office 3 University of Michigan 4 COAPS, Florida State
Tidal Constituents in the Persian Gulf, Gulf of Oman and Arabian Sea: a Numerical Study
 Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences Vol. 45(8), August 2016, pp. 1010-1016 Tidal Constituents in the Persian Gulf, Gulf of Oman and Arabian Sea: a Numerical Study P. Akbari 1 *, M. Sadrinasab 2, V. Chegini
Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences Vol. 45(8), August 2016, pp. 1010-1016 Tidal Constituents in the Persian Gulf, Gulf of Oman and Arabian Sea: a Numerical Study P. Akbari 1 *, M. Sadrinasab 2, V. Chegini
2 nd Tidal and Water Level Working Group Meeting
 2 nd Tidal and Water Level Working Group Meeting Norwegian Hydrographic Service, Stavanger, Norway 27 29 April 2010 Vertical Offshore Reference Framework (VORF) Chris Jones United Kingdom Hydrographic
2 nd Tidal and Water Level Working Group Meeting Norwegian Hydrographic Service, Stavanger, Norway 27 29 April 2010 Vertical Offshore Reference Framework (VORF) Chris Jones United Kingdom Hydrographic
Supplement of Scenario-based numerical modelling and the palaeo-historic record of tsunamis in Wallis and Futuna, Southwest Pacific
 Supplement of Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 15, 1763 1784, 2015 http://www.nat-hazards-earth-syst-sci.net/15/1763/2015/ doi:10.5194/nhess-15-1763-2015-supplement Author(s) 2015. CC Attribution 3.0 License.
Supplement of Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 15, 1763 1784, 2015 http://www.nat-hazards-earth-syst-sci.net/15/1763/2015/ doi:10.5194/nhess-15-1763-2015-supplement Author(s) 2015. CC Attribution 3.0 License.
VALIDATION OF TSUNAMI INUNDATION MODELING FOR THE 2004 SUMATRA-ANDAMAN EARTHQUAKE FOR MAKING HAZARD MAPS IN PENANG AND LANGKAWI, MALAYSIA
 Synopses of Master Papers Bulletin of IISEE, 47, 11-16, 013 VALIDATION OF TSUNAMI INUNDATION MODELING FOR THE 004 SUMATRA-ANDAMAN EARTHQUAKE FOR MAKING HAZARD MAPS IN PENANG AND LANGKAWI, MALAYSIA Noor
Synopses of Master Papers Bulletin of IISEE, 47, 11-16, 013 VALIDATION OF TSUNAMI INUNDATION MODELING FOR THE 004 SUMATRA-ANDAMAN EARTHQUAKE FOR MAKING HAZARD MAPS IN PENANG AND LANGKAWI, MALAYSIA Noor
APPENDIX B PHYSICAL BASELINE STUDY: NORTHEAST BAFFIN BAY 1
 APPENDIX B PHYSICAL BASELINE STUDY: NORTHEAST BAFFIN BAY 1 1 By David B. Fissel, Mar Martínez de Saavedra Álvarez, and Randy C. Kerr, ASL Environmental Sciences Inc. (Feb. 2012) West Greenland Seismic
APPENDIX B PHYSICAL BASELINE STUDY: NORTHEAST BAFFIN BAY 1 1 By David B. Fissel, Mar Martínez de Saavedra Álvarez, and Randy C. Kerr, ASL Environmental Sciences Inc. (Feb. 2012) West Greenland Seismic
A High-Resolution Future Wave Climate Projection for the Coastal Northwestern Atlantic
 A High-Resolution Future Wave Climate Projection for the Coastal Northwestern Atlantic Adrean WEBB 1, Tomoya SHIMURA 2 and Nobuhito MORI 3 1 Project Assistant professor, DPRI, Kyoto University (Gokasho,
A High-Resolution Future Wave Climate Projection for the Coastal Northwestern Atlantic Adrean WEBB 1, Tomoya SHIMURA 2 and Nobuhito MORI 3 1 Project Assistant professor, DPRI, Kyoto University (Gokasho,
Adapting NEMO for use as the UK operational storm surge forecasting model
 Adapting NEMO for use as the UK operational storm surge forecasting model Rachel Furner 1, Jane Williams 2, Kevin Horsburgh 2, Andy Saulter 1 1; Met Office 2; NOC Table of Contents Existing CS3 model Developments
Adapting NEMO for use as the UK operational storm surge forecasting model Rachel Furner 1, Jane Williams 2, Kevin Horsburgh 2, Andy Saulter 1 1; Met Office 2; NOC Table of Contents Existing CS3 model Developments
Charts and Chart Work with Poole Sailing
 with Poole Sailing Nautical charts are a mine of information but they need to be up to date. Corrections to charts are published by the Hydrographic Office monthly as Notices to Mariners both in print
with Poole Sailing Nautical charts are a mine of information but they need to be up to date. Corrections to charts are published by the Hydrographic Office monthly as Notices to Mariners both in print
Figure 3.1: Illustration showing the bathymetry s role for the tsunami propagation following the earth quake 26 December 2004 outside of Sumatra.
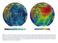 Figure 3.1: Illustration showing the bathymetry s role for the tsunami propagation following the earth quake 26 December 2004 outside of Sumatra. The left globe shows the seafloor bathymetry as portrayed
Figure 3.1: Illustration showing the bathymetry s role for the tsunami propagation following the earth quake 26 December 2004 outside of Sumatra. The left globe shows the seafloor bathymetry as portrayed
Chapter 27. Shelf sea modelling Test case bohai
 Chapter 27 Shelf sea modelling 27.1 Test case bohai The aim of this test case is to illustrate the use of COHERENS for tidal prediction studies, to show how an harmonic analysis can be performed and how
Chapter 27 Shelf sea modelling 27.1 Test case bohai The aim of this test case is to illustrate the use of COHERENS for tidal prediction studies, to show how an harmonic analysis can be performed and how
multibeam bathymetric data is often based on the local depth datum, which is the local lowest normal low sea level, see the Figure 1. Multibeam Bathym
 3D DYNAMIC TERRAIN VISUALIZATION OF ISLAND AREAS AI Bo a, *, TANG Xinming b, SHI Shaoyu c, WANG Hongyan d, YANG Fanlin e a Geomatics College, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao, China
3D DYNAMIC TERRAIN VISUALIZATION OF ISLAND AREAS AI Bo a, *, TANG Xinming b, SHI Shaoyu c, WANG Hongyan d, YANG Fanlin e a Geomatics College, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao, China
The Taiwan-Tsushima Warm Current System: Its Path and the Transformation of the Water Mass in the East China Sea
 Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 55, pp. 185 to 195. 1999 The Taiwan-Tsushima Warm Current System: Its Path and the Transformation of the Water Mass in the East China Sea ATSUHIKO ISOBE Department of Earth
Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 55, pp. 185 to 195. 1999 The Taiwan-Tsushima Warm Current System: Its Path and the Transformation of the Water Mass in the East China Sea ATSUHIKO ISOBE Department of Earth
British Colombia Knight Inlet Strait of Georgia Strait of Juan de Fuca
 An Atlas of Oceanic Internal Solitary Waves (February 2004) Knight Inlet Strait of Georgia Strait of Juan de Fuca Overview Knight Inlet, the Strait of Georgia and the Strait of Juan de Fuca are all shallow
An Atlas of Oceanic Internal Solitary Waves (February 2004) Knight Inlet Strait of Georgia Strait of Juan de Fuca Overview Knight Inlet, the Strait of Georgia and the Strait of Juan de Fuca are all shallow
UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (December 2017)
 UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (December 2017) 1. Review of Regional Weather Conditions for November 2017 1.1 In November 2017, Southeast Asia experienced inter-monsoon conditions in the first
UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (December 2017) 1. Review of Regional Weather Conditions for November 2017 1.1 In November 2017, Southeast Asia experienced inter-monsoon conditions in the first
The Ocean Floor THE VAST WORLD OCEAN
 OCEANOGRAPHY Name Color all water LIGHT BLUE. Color all land LIGHT GREEN. Label the 5 Oceans: Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic, Antarctic. Label the 7 Continents: N.America, S.America, Europe, Asia, Africa,
OCEANOGRAPHY Name Color all water LIGHT BLUE. Color all land LIGHT GREEN. Label the 5 Oceans: Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic, Antarctic. Label the 7 Continents: N.America, S.America, Europe, Asia, Africa,
ALGORITHM FOR DERIVING SEA SURFACE CURRE NT IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA
 ALGORITHM FOR DERIVING SEA SURFACE CURRE NT IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA Nurul Hazrina Idris a and Mohd Ibrahim Seeni Mohd b a Department of Remote Sensing, Faculty of Geoinformation Science and Engineering,
ALGORITHM FOR DERIVING SEA SURFACE CURRE NT IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA Nurul Hazrina Idris a and Mohd Ibrahim Seeni Mohd b a Department of Remote Sensing, Faculty of Geoinformation Science and Engineering,
7B.4 ASSESSMENT OF THE GROSS U.S. OFFSHORE WIND ENERGY POTENTIAL
 7B.4 ASSESSMENT OF THE GROSS U.S. OFFSHORE WIND ENERGY POTENTIAL Marc Schwartz, Donna Heimiller, Steve Haymes, and Walt Musial National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden, Colorado 1. INTRODUCTION Offshore
7B.4 ASSESSMENT OF THE GROSS U.S. OFFSHORE WIND ENERGY POTENTIAL Marc Schwartz, Donna Heimiller, Steve Haymes, and Walt Musial National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden, Colorado 1. INTRODUCTION Offshore
UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (February 2018)
 UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (February 2018) 1. Review of Regional Weather Conditions for January 2018 1.1 The prevailing Northeast monsoon conditions over Southeast Asia strengthened in January
UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (February 2018) 1. Review of Regional Weather Conditions for January 2018 1.1 The prevailing Northeast monsoon conditions over Southeast Asia strengthened in January
Established Global bathymetry yproducts. Undersea feature names. Capacity building
 IHO IOC Established 1903 Global bathymetry yproducts Undersea feature names Capacity building A GEBCO data GEBCO s d t sets t and d products d t Global bathymetric grids Global set of bathymetric contours
IHO IOC Established 1903 Global bathymetry yproducts Undersea feature names Capacity building A GEBCO data GEBCO s d t sets t and d products d t Global bathymetric grids Global set of bathymetric contours
Developing a Seabed Resurvey Strategy: A GIS approach to modelling seabed changes and resurvey risk
 Developing a Seabed Resurvey Strategy: A GIS approach to modelling seabed changes and resurvey risk A. M. Bakare, J. G. Morley, R. R. Simons Department of Geomatic Engineering, University College London,
Developing a Seabed Resurvey Strategy: A GIS approach to modelling seabed changes and resurvey risk A. M. Bakare, J. G. Morley, R. R. Simons Department of Geomatic Engineering, University College London,
SEDIMENT TRANSPORT AND GO-CONG MORPHOLOGICAL CHANGE MODELING BY TELEMAC MODEL SUITE
 SEDIMENT TRANSPORT AND GO-CONG MORPHOLOGICAL CHANGE MODELING BY TELEMAC MODEL SUITE TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION... 2 2. OBJECTIVES... 2 3. METHOLOGY... 2 4. MODEL CALIBRATION, VALIDATION OF SEDIMENT
SEDIMENT TRANSPORT AND GO-CONG MORPHOLOGICAL CHANGE MODELING BY TELEMAC MODEL SUITE TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION... 2 2. OBJECTIVES... 2 3. METHOLOGY... 2 4. MODEL CALIBRATION, VALIDATION OF SEDIMENT
Upgrades to the Operational Sea State Forecast System
 NMOC Operations Bulletin No. 53 Upgrades to the Operational Sea State Forecast System Introduction 25 August 2000 The WAM wave model (WAMDI, 1988, Komen et al., 1994) has been the operational sea state
NMOC Operations Bulletin No. 53 Upgrades to the Operational Sea State Forecast System Introduction 25 August 2000 The WAM wave model (WAMDI, 1988, Komen et al., 1994) has been the operational sea state
Effect of coastal resolution on global estimates of tidal energy dissipation
 Effect of coastal resolution on global estimates of tidal energy dissipation Maialen Irazoqui Apecechea, Martin Verlaan Contents The GTSMv2.0 model Characteristics Major developments Applications Coastal
Effect of coastal resolution on global estimates of tidal energy dissipation Maialen Irazoqui Apecechea, Martin Verlaan Contents The GTSMv2.0 model Characteristics Major developments Applications Coastal
NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS FOR TSUNAMI FORECASTING AT PADANG CITY USING OFFSHORE TSUNAMI SENSORS
 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS FOR TSUNAMI FORECASTING AT PADANG CITY USING OFFSHORE TSUNAMI SENSORS Setyoajie Prayoedhie Supervisor: Yushiro FUJII MEE10518 Bunichiro SHIBAZAKI ABSTRACT We conducted numerical simulations
NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS FOR TSUNAMI FORECASTING AT PADANG CITY USING OFFSHORE TSUNAMI SENSORS Setyoajie Prayoedhie Supervisor: Yushiro FUJII MEE10518 Bunichiro SHIBAZAKI ABSTRACT We conducted numerical simulations
Effect of the Emperor seamounts on trans-oceanic propagation of the 2006 Kuril Island earthquake tsunami
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L02611, doi:10.1029/2007gl032129, 2008 Effect of the Emperor seamounts on trans-oceanic propagation of the 2006 Kuril Island earthquake tsunami S. Koshimura, 1 Y.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L02611, doi:10.1029/2007gl032129, 2008 Effect of the Emperor seamounts on trans-oceanic propagation of the 2006 Kuril Island earthquake tsunami S. Koshimura, 1 Y.
Measuring the Flow through the Kerama Gap
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Measuring the Flow through the Kerama Gap Mark Wimbush & Jae-Hun Park Graduate School of Oceanography University of Rhode
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Measuring the Flow through the Kerama Gap Mark Wimbush & Jae-Hun Park Graduate School of Oceanography University of Rhode
Forecast of Nearshore Wave Parameters Using MIKE-21 Spectral Wave Model
 Forecast of Nearshore Wave Parameters Using MIKE-21 Spectral Wave Model Felix Jose 1 and Gregory W. Stone 2 1 Coastal Studies Institute, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA 70803 2 Coastal Studies
Forecast of Nearshore Wave Parameters Using MIKE-21 Spectral Wave Model Felix Jose 1 and Gregory W. Stone 2 1 Coastal Studies Institute, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA 70803 2 Coastal Studies
An Atlas of Oceanic Internal Solitary Waves (February 2004) by Global Ocean Associates Prepared for Office of Naval Research Code 322 PO
 Overview is located in the western Equatorial Pacific Ocean. The Island is immediately north of Queensland Australia and adjacent to the Bismark Archipelago. (Figure 1). The region is influenced by the
Overview is located in the western Equatorial Pacific Ocean. The Island is immediately north of Queensland Australia and adjacent to the Bismark Archipelago. (Figure 1). The region is influenced by the
SOUTH CHINA SEA OCEAN TIDE SIMULATOR
 Proceedings of the 7 th International Conference on Asian and Pacific Coasts (APAC 2013) Bali, Indonesia, September 24-26, 2013 SOUTH CHINA SEA OCEAN TIDE SIMULATOR B. H. Choi 1, K. O. Kim 2, J. H. Yuk
Proceedings of the 7 th International Conference on Asian and Pacific Coasts (APAC 2013) Bali, Indonesia, September 24-26, 2013 SOUTH CHINA SEA OCEAN TIDE SIMULATOR B. H. Choi 1, K. O. Kim 2, J. H. Yuk
Joint Hydrographic Center, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Durham, NH 03824, USA
 Future directions in hydrography using satellite-derived bathymetry Shachak Pe eri 1, Christopher Parrish 2, 3, Lee Alexander 1, Chukwuma Azuike 1, Andrew Armstrong 1,3 and Maryellen Sault 2 1 Center for
Future directions in hydrography using satellite-derived bathymetry Shachak Pe eri 1, Christopher Parrish 2, 3, Lee Alexander 1, Chukwuma Azuike 1, Andrew Armstrong 1,3 and Maryellen Sault 2 1 Center for
Final VRF grids Date: Aug 25, 2011 Author: R. Forsberg, G. Strykowski, O. Andersen
 Final VRF grids Date: Aug 25, 2011 Author: R. Forsberg, G. Strykowski, O. Andersen www.blast-project.eu 1 Authors Name Organisation Rene Forsberg National Space Institute, DTU G. Strykowski National Space
Final VRF grids Date: Aug 25, 2011 Author: R. Forsberg, G. Strykowski, O. Andersen www.blast-project.eu 1 Authors Name Organisation Rene Forsberg National Space Institute, DTU G. Strykowski National Space
Climate. Annual Temperature (Last 30 Years) January Temperature. July Temperature. Average Precipitation (Last 30 Years)
 Climate Annual Temperature (Last 30 Years) Average Annual High Temp. (F)70, (C)21 Average Annual Low Temp. (F)43, (C)6 January Temperature Average January High Temp. (F)48, (C)9 Average January Low Temp.
Climate Annual Temperature (Last 30 Years) Average Annual High Temp. (F)70, (C)21 Average Annual Low Temp. (F)43, (C)6 January Temperature Average January High Temp. (F)48, (C)9 Average January Low Temp.
(JONSMOD 2008 Paper) An intercomparison of tidal solutions computed. with a range of unstructured grid models of the. Irish and Celtic Sea Regions
 F: TLQUODVR1 Nov 7th 2008 Revised July 2009 Final Revision Aug 2009 (JONSMOD 2008 Paper) An intercomparison of tidal solutions computed with a range of unstructured grid models of the Irish and Celtic
F: TLQUODVR1 Nov 7th 2008 Revised July 2009 Final Revision Aug 2009 (JONSMOD 2008 Paper) An intercomparison of tidal solutions computed with a range of unstructured grid models of the Irish and Celtic
TECHNICAL DOCUMENT R 2 OF THE SPANISH BRAILLE COMMISSION GENERAL CRITERIA FOR PREPARING ADAPTED MAPS FOR VISUALLY IMPAIRED PERSONS
 TECHNICAL DOCUMENT R 2 OF THE SPANISH BRAILLE COMMISSION GENERAL CRITERIA FOR PREPARING ADAPTED MAPS FOR VISUALLY IMPAIRED PERSONS Updated on December 2013 (Version 1) First edition in English, March 2015
TECHNICAL DOCUMENT R 2 OF THE SPANISH BRAILLE COMMISSION GENERAL CRITERIA FOR PREPARING ADAPTED MAPS FOR VISUALLY IMPAIRED PERSONS Updated on December 2013 (Version 1) First edition in English, March 2015
Modeling New York in D-Flow FM
 Modeling New York in D-Flow FM Delft, 30 th of October 2013 Internship Tuinhof, T.J. (Taco) August - October 2013 Supervisors: Sander Post (Royal HaskoningDHV) Maarten van Ormondt (Deltares) Contents Introduction...
Modeling New York in D-Flow FM Delft, 30 th of October 2013 Internship Tuinhof, T.J. (Taco) August - October 2013 Supervisors: Sander Post (Royal HaskoningDHV) Maarten van Ormondt (Deltares) Contents Introduction...
Design and Implementation of a NOAA/NOS Cook Inlet and Shelikof Straits Circulation Modeling System
 Design and Implementation of a NOAA/NOS Cook Inlet and Shelikof Straits Circulation Modeling System Presented at a NOAA/AEA Stakeholders Meeting, August 24, 2011, Anchorage Alaska Richard Patchen and Lyon
Design and Implementation of a NOAA/NOS Cook Inlet and Shelikof Straits Circulation Modeling System Presented at a NOAA/AEA Stakeholders Meeting, August 24, 2011, Anchorage Alaska Richard Patchen and Lyon
Initiatives in Using Crowdsourcing, Satellite Derived Bathymetry, and Other Non-Traditional Hydrographic/Bathymetric Measurements
 University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Center for Coastal and Ocean Mapping Center for Coastal and Ocean Mapping 10-5-2015 Initiatives in Using Crowdsourcing, Satellite
University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Center for Coastal and Ocean Mapping Center for Coastal and Ocean Mapping 10-5-2015 Initiatives in Using Crowdsourcing, Satellite
EFFECTIVE TROPICAL CYCLONE WARNING IN BANGLADESH
 Country Report of Bangladesh On EFFECTIVE TROPICAL CYCLONE WARNING IN BANGLADESH Presented At JMA/WMO WORKSHOP ON EFFECTIVE TROPICAL CYCLONE WARNING IN SOUTHEAST ASIA Tokyo, Japan,11-14 March 2014 By Sayeed
Country Report of Bangladesh On EFFECTIVE TROPICAL CYCLONE WARNING IN BANGLADESH Presented At JMA/WMO WORKSHOP ON EFFECTIVE TROPICAL CYCLONE WARNING IN SOUTHEAST ASIA Tokyo, Japan,11-14 March 2014 By Sayeed
SCIENTIFIC COUNCIL MEETING JUNE B. Petrie, R. G. Pettipas, W. M. Petrie and V. V. Soukhovtsev
 NOT TO BE CITED WITHOUT PRIOR REFERENCE TO THE AUTHOR(S) Northwest Atlantic Fisheries Organization Serial No. N5361 NAFO SCR Doc. 07/14 SCIENTIFIC COUNCIL MEETING JUNE 2007 Physical Oceanographic Conditions
NOT TO BE CITED WITHOUT PRIOR REFERENCE TO THE AUTHOR(S) Northwest Atlantic Fisheries Organization Serial No. N5361 NAFO SCR Doc. 07/14 SCIENTIFIC COUNCIL MEETING JUNE 2007 Physical Oceanographic Conditions
Characteristics of Sea Surface Circulation and Eddy Field in the South China Sea Revealed by Satellite Altimetric Data
 Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 56, pp. 331 to 344, 2000 Characteristics of Sea Surface Circulation and Eddy Field in the South China Sea Revealed by Satellite Altimetric Data AKIHIKO MORIMOTO 1 *, KOICHI
Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 56, pp. 331 to 344, 2000 Characteristics of Sea Surface Circulation and Eddy Field in the South China Sea Revealed by Satellite Altimetric Data AKIHIKO MORIMOTO 1 *, KOICHI
Oceanography. Oceanography is the study of the deep sea and shallow coastal oceans.
 Oceanography Oceanography is the study of the deep sea and shallow coastal oceans. Studying the Ocean Floor To determine the shape and composition of the ocean floor, scientists use techniques such as
Oceanography Oceanography is the study of the deep sea and shallow coastal oceans. Studying the Ocean Floor To determine the shape and composition of the ocean floor, scientists use techniques such as
Bifurcation Current along the Southwest Coast of the Kii Peninsula
 Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 54, pp. 45 to 52. 1998 Bifurcation Current along the Southwest Coast of the Kii Peninsula JUNICHI TAKEUCHI 1, NAOTO HONDA 2, YOSHITAKA MORIKAWA 2, TAKASHI KOIKE 2 and YUTAKA
Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 54, pp. 45 to 52. 1998 Bifurcation Current along the Southwest Coast of the Kii Peninsula JUNICHI TAKEUCHI 1, NAOTO HONDA 2, YOSHITAKA MORIKAWA 2, TAKASHI KOIKE 2 and YUTAKA
Tidal stream atlases Reprinted by PC Maritime with kind permission of Proudman Laboratory
 The generation of UK tidal stream atlases from regularly gridded hydrodynamic modelled data by Colin Bell and Lisa Carlin Proudman Oceanographic Laboratory http://www.pol.ac.uk http://www.pcmaritime.co.uk
The generation of UK tidal stream atlases from regularly gridded hydrodynamic modelled data by Colin Bell and Lisa Carlin Proudman Oceanographic Laboratory http://www.pol.ac.uk http://www.pcmaritime.co.uk
The Application of POM to the Operational Tidal Forecast for the Sea around Taiwan
 The Application of POM to the Operational Tidal Forecast for the Sea around Taiwan Shan-Pei YEH 1 Hwa CHIEN Sen JAN 3 and Chia Chuen KAO 4 1 Coastal Ocean Monitoring Center, National Cheng Kung University,
The Application of POM to the Operational Tidal Forecast for the Sea around Taiwan Shan-Pei YEH 1 Hwa CHIEN Sen JAN 3 and Chia Chuen KAO 4 1 Coastal Ocean Monitoring Center, National Cheng Kung University,
5. Gravity. 5.1 Geoid Variations. The Australian Continent: A Geophysical Synthesis Gravity
 34 The Australian Continent: A Geophysical Synthesis Gravity 5. Gravity Gravity data map subtle changes in the Earth s gravitational field caused by variations in the density of the underlying materials.
34 The Australian Continent: A Geophysical Synthesis Gravity 5. Gravity Gravity data map subtle changes in the Earth s gravitational field caused by variations in the density of the underlying materials.
The Effect of Koshu Seamount on the Formation of the Kuroshio Large Meander South of Japan
 1624 J O U R N A L O F P H Y S I C A L O C E A N O G R A P H Y VOLUME 41 The Effect of Koshu Seamount on the Formation of the Kuroshio Large Meander South of Japan TAKAHIRO ENDOH Research Institute for
1624 J O U R N A L O F P H Y S I C A L O C E A N O G R A P H Y VOLUME 41 The Effect of Koshu Seamount on the Formation of the Kuroshio Large Meander South of Japan TAKAHIRO ENDOH Research Institute for
A Factor of 2-4 Improvement in Marine Gravity and Predicted Bathymetry from CryoSat, Jason-1, and Envisat Radar Altimetry: Arctic and Coastal Regions
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. A Factor of 2-4 Improvement in Marine Gravity and Predicted Bathymetry from CryoSat, Jason-1, and Envisat Radar Altimetry:
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. A Factor of 2-4 Improvement in Marine Gravity and Predicted Bathymetry from CryoSat, Jason-1, and Envisat Radar Altimetry:
Sam Bateman and. State Practice Regarding Straight Baselines In East Asia Legal, Technical and Political Issues in a
 State Practice Regarding Straight Baselines In East Asia Legal, Technical and Political Issues in a Changing Environment Sam Bateman and Clive Schofield The Australian National Centre for Ocean Resources
State Practice Regarding Straight Baselines In East Asia Legal, Technical and Political Issues in a Changing Environment Sam Bateman and Clive Schofield The Australian National Centre for Ocean Resources
Map shows 3 main features of ocean floor
 Map shows 3 main features of ocean floor 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 3 Marine Provinces 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Chapter 3 Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean
Map shows 3 main features of ocean floor 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 3 Marine Provinces 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Chapter 3 Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean
NUMERICAL SIMULATION AS GUIDANCE IN MAKING TSUNAMI HAZARD MAP FOR LABUAN ISLAND
 NUMERICAL SIMULATION AS GUIDANCE IN MAKING TSUNAMI HAZARD MAP FOR LABUAN ISLAND MOHD RIDZUAN bin Adam Supervisor: Fumihiko IMAMURA MEE09199 ABSTRACT At the northeast end of the South China Sea, tsunamis
NUMERICAL SIMULATION AS GUIDANCE IN MAKING TSUNAMI HAZARD MAP FOR LABUAN ISLAND MOHD RIDZUAN bin Adam Supervisor: Fumihiko IMAMURA MEE09199 ABSTRACT At the northeast end of the South China Sea, tsunamis
By Geri Flanary To accompany AP Human Geography: A Study Guide 3 rd edition By Ethel Wood
 Session 1 By Geri Flanary To accompany AP Human Geography: A Study Guide 3 rd edition By Ethel Wood WHAT IS DEMOGRAPHY? It is the scientific or statistical study of population. It comes from the Greek
Session 1 By Geri Flanary To accompany AP Human Geography: A Study Guide 3 rd edition By Ethel Wood WHAT IS DEMOGRAPHY? It is the scientific or statistical study of population. It comes from the Greek
Introduction After reviewing the classification of continental margins (not plate margins) in your textbook, answer the following questions:
 Investigating the continental margins of North America using GeoMapApp. This exercise is designed to familiarize you with the features of continental margins. Through the analysis of color-coded bathymetric
Investigating the continental margins of North America using GeoMapApp. This exercise is designed to familiarize you with the features of continental margins. Through the analysis of color-coded bathymetric
Circulation in the South China Sea in summer of 1998
 Circulation in the South China Sea in summer of 1998 LIU Yonggang, YUAN Yaochu, SU Jilan & JIANG Jingzhong Second Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration (SOA), Hangzhou 310012, China;
Circulation in the South China Sea in summer of 1998 LIU Yonggang, YUAN Yaochu, SU Jilan & JIANG Jingzhong Second Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration (SOA), Hangzhou 310012, China;
Digital Elevation Model (DEM) of Sable Island Bank and adjacent areas
 GEOLOGICAL SURVEY OF CANADA OPEN FILE 5348 Digital Elevation Model (DEM) of Sable Island Bank and adjacent areas K.J. Webb and E.L. King 2014 GEOLOGICAL SURVEY OF CANADA OPEN FILE 5348 Digital Elevation
GEOLOGICAL SURVEY OF CANADA OPEN FILE 5348 Digital Elevation Model (DEM) of Sable Island Bank and adjacent areas K.J. Webb and E.L. King 2014 GEOLOGICAL SURVEY OF CANADA OPEN FILE 5348 Digital Elevation
Use of a Large-Scale, Spectral Wave Generation Model to Define Input into Nearshore Wave Transformation Model
 Use of a Large-Scale, Spectral Wave Generation Model to Define Input into Nearshore Wave Transformation Model Brian A. Caufield and Kirk F. Bosma Woods Hole Group 81 Technology Park Drive East Falmouth,
Use of a Large-Scale, Spectral Wave Generation Model to Define Input into Nearshore Wave Transformation Model Brian A. Caufield and Kirk F. Bosma Woods Hole Group 81 Technology Park Drive East Falmouth,
Research of the Influential Factors on the Simulation of Storm Surge in the Bohai Sea
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 2014, 8, 151-156 151 Open Access Research of the Influential Factors on the Simulation of Storm Surge in
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 2014, 8, 151-156 151 Open Access Research of the Influential Factors on the Simulation of Storm Surge in
The Effect of Statistical Abyssal Hill Roughness on the Generation of Internal Waves
 The Effect of Statistical Abyssal Hill Roughness on the Generation of Internal Waves Patrick G. Timko 1, Brian K. Arbic 1 John A. Goff 1 Center for Atmospheric and Oceanic Prediction Studies, Florida State
The Effect of Statistical Abyssal Hill Roughness on the Generation of Internal Waves Patrick G. Timko 1, Brian K. Arbic 1 John A. Goff 1 Center for Atmospheric and Oceanic Prediction Studies, Florida State
Bathymetry Measures the vertical distance from the ocean surface to mountains, valleys, plains, and other sea floor features
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces Chapter Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces Chapter Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools.
Ocean Boundary Currents Guiding Question: How do western boundary currents influence climate and ocean productivity?
 Name: Date: TEACHER VERSION: Suggested Student Responses Included Ocean Boundary Currents Guiding Question: How do western boundary currents influence climate and ocean productivity? Introduction The circulation
Name: Date: TEACHER VERSION: Suggested Student Responses Included Ocean Boundary Currents Guiding Question: How do western boundary currents influence climate and ocean productivity? Introduction The circulation
Preliminary Information Indicative of the Outer Limits of the Continental Shelf Beyond 200 Nautical Miles of the People s Republic of China
 (Translation) Preliminary Information Indicative of the Outer Limits of the Continental Shelf Beyond 200 Nautical Miles of the People s Republic of China 1. The People s Republic of China ratified the
(Translation) Preliminary Information Indicative of the Outer Limits of the Continental Shelf Beyond 200 Nautical Miles of the People s Republic of China 1. The People s Republic of China ratified the
Earth Observation & forecasting Storm Surges in the North Western Pacific. Mr. Nadao Kohno Japan Meteorological Agency
 Earth Observation & forecasting Storm Surges in the North Western Pacific Mr. Nadao Kohno Japan Meteorological Agency Lesson Outline Introduction JMA s responsibility and work as a RSMC, Tokyo Typhoon
Earth Observation & forecasting Storm Surges in the North Western Pacific Mr. Nadao Kohno Japan Meteorological Agency Lesson Outline Introduction JMA s responsibility and work as a RSMC, Tokyo Typhoon
Positioning the Pacific: NOAA s Geospatial Activities. Juliana Blackwell, Director NOAA s National Geodetic Survey March 6, 2012
 Positioning the Pacific: NOAA s Geospatial Activities Juliana Blackwell, Director NOAA s National Geodetic Survey March 6, 2012 A Common Problem of the Early 19 th Century 1807 President Thomas Jefferson
Positioning the Pacific: NOAA s Geospatial Activities Juliana Blackwell, Director NOAA s National Geodetic Survey March 6, 2012 A Common Problem of the Early 19 th Century 1807 President Thomas Jefferson
2014/2/25. Earth Observation & forecasting Storm Surges in the North Western Pacific. Lesson Outline. RSMC Tokyo Typhoon Center.
 Earth Observation & forecasting Storm Surges in the North Western Pacific Mr. Nadao Kohno Japan Meteorological Agency Lesson Outline Introduction JMA s responsibility and work as a RSMC, Tokyo Typhoon
Earth Observation & forecasting Storm Surges in the North Western Pacific Mr. Nadao Kohno Japan Meteorological Agency Lesson Outline Introduction JMA s responsibility and work as a RSMC, Tokyo Typhoon
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF TSUNAMI PROPAGATION AND INUNDATION ALONG THE RAKHINE COAST AREAS IN MYANMAR
 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF TSUNAMI PROPAGATION AND INUNDATION ALONG THE RAKHINE COAST AREAS IN MYANMAR Su Hninn Htwe Supervisor: Bunichiro SHIBAZAKI MEE12619 Yushiro FUJII ABSTRACT This study aimed to assess
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF TSUNAMI PROPAGATION AND INUNDATION ALONG THE RAKHINE COAST AREAS IN MYANMAR Su Hninn Htwe Supervisor: Bunichiro SHIBAZAKI MEE12619 Yushiro FUJII ABSTRACT This study aimed to assess
CALIBRATION OF THERMAL INFRARED CHANNELS OF FENG YUN SATELLITE DATA. Wan Hazli Wan Kadir, Abd Wahid Rasib, Ab. Latif Ibrahim and Zawatil Azhani Zaini
 CALIBRATION OF THERMAL INFRARED CHANNELS OF FENG YUN SATELLITE DATA Wan Hazli Wan Kadir, Abd Wahid Rasib, Ab. Latif Ibrahim and Zawatil Azhani Zaini Department of Remote Sensing, Faculty of Geoinformation
CALIBRATION OF THERMAL INFRARED CHANNELS OF FENG YUN SATELLITE DATA Wan Hazli Wan Kadir, Abd Wahid Rasib, Ab. Latif Ibrahim and Zawatil Azhani Zaini Department of Remote Sensing, Faculty of Geoinformation
TSUNAMI HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN NORTHERN EGYPT USING NUMERICAL SIMULATION
 TSUNAMI HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN NORTHERN EGYPT USING NUMERICAL SIMULATION Abutaleb Ali Supervisor: Bunichiro SHIBAZAKI MEE16717 Yushiro FUJII ABSTRACT To investigate the tsunami hazard along the northern
TSUNAMI HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN NORTHERN EGYPT USING NUMERICAL SIMULATION Abutaleb Ali Supervisor: Bunichiro SHIBAZAKI MEE16717 Yushiro FUJII ABSTRACT To investigate the tsunami hazard along the northern
TIDAL SIMULATION USING REGIONAL OCEAN MODELING SYSTEM (ROMS)
 TIDAL SIMULATION USING REGIONAL OCEAN MODELING SYSTEM (ROMS) Xiaochun Wang 1,2, Yi Chao 1, Changming Dong 3, John Farrara 1,2, Zhijin Li 1,2, Koji Matsumoto 4, James C. McWilliams 3, Jeffrey D. Paduan
TIDAL SIMULATION USING REGIONAL OCEAN MODELING SYSTEM (ROMS) Xiaochun Wang 1,2, Yi Chao 1, Changming Dong 3, John Farrara 1,2, Zhijin Li 1,2, Koji Matsumoto 4, James C. McWilliams 3, Jeffrey D. Paduan
Prediction of changes in tidal system and deltas at Nakdong estuary due to construction of Busan new port
 Prediction of changes in tidal system and deltas at Nakdong estuary due to construction of Busan new port H. Gm1 & G.-Y. park2 l Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering, Kookmin University, Korea
Prediction of changes in tidal system and deltas at Nakdong estuary due to construction of Busan new port H. Gm1 & G.-Y. park2 l Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering, Kookmin University, Korea
Modeling the North West European Shelf using Delft3D Flexible Mesh
 Modeling the North West European Shelf using Delft3D Flexible Mesh 2nd JCOMM Scientific and Technical Symposium on Storm Surges, 8-13 Nov. 2015, Key West, USA; Firmijn Zijl Outline of this presentation
Modeling the North West European Shelf using Delft3D Flexible Mesh 2nd JCOMM Scientific and Technical Symposium on Storm Surges, 8-13 Nov. 2015, Key West, USA; Firmijn Zijl Outline of this presentation
Tides in the Sea of Okhotsk
 1389 Tides in the Sea of Okhotsk ZYGMUNT KOWALIK AND IGOR POLYAKOV Institute of Marine Science, University of Alaska, Fairbanks, Alaska (Manuscript received 8 October 1996, in final form 25 August 1997)
1389 Tides in the Sea of Okhotsk ZYGMUNT KOWALIK AND IGOR POLYAKOV Institute of Marine Science, University of Alaska, Fairbanks, Alaska (Manuscript received 8 October 1996, in final form 25 August 1997)
The surface of the ocean floor is as varied as the land. The five major oceans, from largest to smallest, are
 11.1 Ocean Basins The surface of the ocean floor is as varied as the land. The five major oceans, from largest to smallest, are w the Pacific w the Atlantic w the Indian w the Southern w the Arctic The
11.1 Ocean Basins The surface of the ocean floor is as varied as the land. The five major oceans, from largest to smallest, are w the Pacific w the Atlantic w the Indian w the Southern w the Arctic The
Chapter Overview. Bathymetry. Measuring Bathymetry. Measuring Bathymetry
 CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces Chapter Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces Chapter Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
A Study on Tsunami Wave Penetration and Storm Surge Impact after the Construction of Sethusamudram Ship Canal
 A Study on Tsunami Wave Penetration and Storm Surge Impact after the Construction of Sethusamudram Ship Canal C.Piruthevi 1,,, S.Sunthareswaran1 and H.P.V Vithana1 1 Department of Civil and Environmental
A Study on Tsunami Wave Penetration and Storm Surge Impact after the Construction of Sethusamudram Ship Canal C.Piruthevi 1,,, S.Sunthareswaran1 and H.P.V Vithana1 1 Department of Civil and Environmental
Progress in embedding global tides into HYCOM simulations. Brian K. Arbic Institute for Geophysics The University of Texas at Austin
 Progress in embedding global tides into HYCOM simulations Brian K. Arbic Institute for Geophysics The University of Texas at Austin Am working closely with Alan on global forward tide modeling with HYCOM.
Progress in embedding global tides into HYCOM simulations Brian K. Arbic Institute for Geophysics The University of Texas at Austin Am working closely with Alan on global forward tide modeling with HYCOM.
Cold air outbreak over the Kuroshio Extension Region
 Cold air outbreak over the Kuroshio Extension Region Jensen, T. G. 1, T. Campbell 1, T. A. Smith 1, R. J. Small 2 and R. Allard 1 1 Naval Research Laboratory, 2 Jacobs Engineering NRL, Code 7320, Stennis
Cold air outbreak over the Kuroshio Extension Region Jensen, T. G. 1, T. Campbell 1, T. A. Smith 1, R. J. Small 2 and R. Allard 1 1 Naval Research Laboratory, 2 Jacobs Engineering NRL, Code 7320, Stennis
Applying Gerris to Mixing and Sedimentation in Estuaries
 Applying Gerris to Mixing and Sedimentation in Estuaries Timothy R. Keen U.S. Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, Mississippi, U.S.A. 4 July 2011 Université Pierre et Marie Curie Paris, France
Applying Gerris to Mixing and Sedimentation in Estuaries Timothy R. Keen U.S. Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, Mississippi, U.S.A. 4 July 2011 Université Pierre et Marie Curie Paris, France
Performance of the Nortek Aquadopp Z-Cell Profiler on a NOAA Surface Buoy
 Performance of the Nortek Aquadopp Z-Cell Profiler on a NOAA Surface Buoy Eric Siegel NortekUSA Annapolis, USA Rodney Riley & Karen Grissom NOAA National Data Buoy Center Stennis Space Center, USA Abstract-Observations
Performance of the Nortek Aquadopp Z-Cell Profiler on a NOAA Surface Buoy Eric Siegel NortekUSA Annapolis, USA Rodney Riley & Karen Grissom NOAA National Data Buoy Center Stennis Space Center, USA Abstract-Observations
Topographic Maps and Landforms Geology Lab
 Topographic Maps and Landforms Geology Lab Ray Rector: Instructor Today s Lab Activities 1) Discussion of Last Week s Lab 2) Lecture on Topo Maps and Elevation Contours 3) Construct Topographic Maps and
Topographic Maps and Landforms Geology Lab Ray Rector: Instructor Today s Lab Activities 1) Discussion of Last Week s Lab 2) Lecture on Topo Maps and Elevation Contours 3) Construct Topographic Maps and
Measuring the Flow Through the Kerama Gap
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Measuring the Flow Through the Kerama Gap Mark Wimbush & Jae-Hun Park Graduate School of Oceanography University of Rhode
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Measuring the Flow Through the Kerama Gap Mark Wimbush & Jae-Hun Park Graduate School of Oceanography University of Rhode
Skewed Occurrence Frequency of Water Temperature and Salinity in the Subarctic Regions
 Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 59, pp. 9 to 99, 3 Skewed Occurrence Frequency of Water Temperature and Salinity in the Subarctic Regions SACHIKO OGUMA *, TORU SUZUKI, SYDNEY LEVITUS and YUTAKA NAGATA Marine
Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 59, pp. 9 to 99, 3 Skewed Occurrence Frequency of Water Temperature and Salinity in the Subarctic Regions SACHIKO OGUMA *, TORU SUZUKI, SYDNEY LEVITUS and YUTAKA NAGATA Marine
Enhancing predictability of the Loop Current variability using Gulf of Mexico Hycom
 Enhancing predictability of the Loop Current variability using Gulf of Mexico Hycom Matthieu Le Hénaff (1) Villy Kourafalou (1) Ashwanth Srinivasan (1) Collaborators: O. M. Smedstad (2), P. Hogan (2),
Enhancing predictability of the Loop Current variability using Gulf of Mexico Hycom Matthieu Le Hénaff (1) Villy Kourafalou (1) Ashwanth Srinivasan (1) Collaborators: O. M. Smedstad (2), P. Hogan (2),
2) re-positioning of the SSS data, 3) individuation of geomorphological features and morphometrical parameters correlated to instability phenomena.
 HIGH-RESOLUTION SIDE SCAN SONAR AND MULTIBEAM DATA PROCESSING AND MERGING TO STUDY SUBMARINE INSTABILITY PHENOMENA ON VOLCANIC ISLANDS (PONTINE, CAMPANIAN AND AEOLIAN ARCHIPELAGOS) A. BOSMAN Extended abstract:
HIGH-RESOLUTION SIDE SCAN SONAR AND MULTIBEAM DATA PROCESSING AND MERGING TO STUDY SUBMARINE INSTABILITY PHENOMENA ON VOLCANIC ISLANDS (PONTINE, CAMPANIAN AND AEOLIAN ARCHIPELAGOS) A. BOSMAN Extended abstract:
Boundary Expansion of Thunder Bay National Marine Sanctuary; Correction and Expansion of Fagatele Bay National Marine
 This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 12/23/2015 and available online at http://federalregister.gov/a/2015-32265, and on FDsys.gov Billing Code 3510-NK-P DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE
This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 12/23/2015 and available online at http://federalregister.gov/a/2015-32265, and on FDsys.gov Billing Code 3510-NK-P DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE

 (note: all X
(note: all X