VALIDATION OF TSUNAMI INUNDATION MODELING FOR THE 2004 SUMATRA-ANDAMAN EARTHQUAKE FOR MAKING HAZARD MAPS IN PENANG AND LANGKAWI, MALAYSIA
|
|
|
- Arnold Sparks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Synopses of Master Papers Bulletin of IISEE, 47, 11-16, 013 VALIDATION OF TSUNAMI INUNDATION MODELING FOR THE 004 SUMATRA-ANDAMAN EARTHQUAKE FOR MAKING HAZARD MAPS IN PENANG AND LANGKAWI, MALAYSIA Noor Azam Shaari MEE116 Supervisor: Yushiro FUJII Hideaki YANAGISAWA ABSTRACT We adopted three heterogeneous slip models estimated by inversion method from satellite altimetry data, tsunami waveform data at tide gauges and the joint data as tsunami source models. Non-Linear Shallow Water Equations (NSWE) by considering the effects of the earth s curvature were applied in the numerical simulation to evaluate the tsunami propagation and runup at the target areas in Penang and Langkawi, Malaysia. We applied a nesting grid system with four layers in the numerical modeling. The result shows that the locations in the study region, Pantai Acheh, Pantai Tengah, Pantai Chenang, Kuala Triang and Pantai Kok, are prone to the tsunamis, where the tsunami heights of about.5 m were calculated. The calculated tsunami waves from the all source models almost reproduce the observed ones at two tide gauges. Tsunami source models with larger slip amount over Nicobar and Andaman Islands contribute to the maximum tsunami runup as high as 4.0 m in Pantai Tengah and Pantai Chenang. These results are almost agreeable to the runup-height data by the field survey. Keywords: 004 Sumatra-Andaman earthquake, Tsunami Propagation, Runup, Inundation, Langkawi, Penang. 1. INTRODUCTION An earthquake that occurred at 00:58:49 (UTC) on December 6, 004 along the Sumatra Island and Andaman Islands has created a big impact after the giant tsunami waves and struck the world and Malaysia especially in the coastal areas. The 004 Sumatra-Andaman earthquake with a magnitude of M9.1 at epicenter N/ E (USGS) has generated the giant tsunami waves propagated to few states in the northwest of Peninsular Malaysia. It is recorded that about 68 people died, left 6 missing and 300 injured. The Northern States of the west coast of Peninsular Malaysia have been badly affected by tsunami. Among the state affected were Kedah, Penang, Perlis, Perak and Selangor. Tsunami simulations from three source models will be used to validate the tsunami propagation in whole inundated areas in Langkawi, Penang and Kedah. This study is also aimed to analyze the tsunami inundation to the target locations in Batu Feringghi (P1), Pantai Chenang (K) and Kuala Triang (K3). Neighboring location such as P, P4, K1 and K4 will also be analyzed as they are located inside the same computational domain. Malaysian Meteorological Department. International Institute of Seismology and Earthquake Engineering (IISEE), Building Research Institute (BRI), Japan. Tohoku-Gakuin University, Japan.
2 . DATA.1 Bathymetry and topography data We used the bathymetry data from General Bathymetric Chart of the Ocean (GEBCO) with spatial grid size at 30 arc-sec. Generic Mapping Tools (Wessel and Smith, 007) is used to process and draw the bathymetry data in the target area lies within 0 N to 15 N and 90 E to 105 E. For the calculation of the inundation, the topography data from Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) is applied.. Computational regions and settings to evaluate tsunami propagations In order to perform the numerical modeling to evaluate the tsunami wave propagation towards the target area the computational area is divided into three regions (Figure 1). The bathymetry and topography data for all the regions are interpolated from GEBCO 30 arc-sec. The calculation time for the computation is 8,800 s (8 hours) with computation time step ( t) of 3 s. The t is derived from the stability criterion x formula t. Maximum sea gh max depth (h max ) of the computation region 1 is 5,514 m and gravitational acceleration at 9.81 ms -. Numerical simulation with the nesting grid system is carried out for the evaluation of the tsunami propagations from source area. Figure 1. Location and boundary of each computational region..3 Computational regions and settings to evaluate tsunami inundations In order to evaluate the tsunami inundation at each target locations, the computational area is divided into four regions. The same computational regions as those in section. are applied to the regions 1 and, but slight changes are made to region 3 to avoid the numerical instability during the computation. The same calculation time for the computation at 8,800 s (8 hours) is used at t of 3 s. The computation region 3 at the target area in Penang (Figure ) and Langkawi (Figure 3) is divided into smaller region 4. Target locations of P1, K and K3 are located at their smaller region 4 to analyze the coastal wave amplification. The bathymetry and topography grids in inundation area are merged for getting finer sea bottom surface and elevation data. The bathymetry for the region 4 is interpolated from GEBCO 30 arc-sec, whereas the topography is from SRTM 3 arc-sec. Three different sets of numerical simulations are performed to analyze the coastal amplification over the respective target locations.
3 Figure. Location and boundary for computational region 3 for Penang. Figure 3. Location and boundary for computational region 3 for Langkawi..4 Tide gauge stations and tsunami waveform data There are four tide gauge systems that are now operated in the study area. Two of the systems are operated by Department of Survey and Mapping (JUPEM); one located in Penang (5 5 N/100 1 E) and the other in Langkawi (6 6 N/ E). The other two operated by Malaysian Meteorological Meteorology (MMD) is located in Penang (5 7 N/ E) and Langkawi (6 15 N/ E). Observed tsunami waveforms by JUPEM at sampling interval of 50 s will be used in the study. Figures 4 and 5 show the locations of the tide gauge stations at Penang and Langkawi. Figure 4. Location of tide gauge station at Penang. Figure 5. Same as Figure 4, but for Langkawi..5 Tsunami source region and source models In this study three heterogeneous slip models from Model 1 by Hirata et al. (006), Model by Fujii and Satake (007), and Model 3 by Tanioka et al. (006) will be used in the validation process. Initial sea surface heights from the slip models shown in Figure 6 are calculated by the Okada formulation (Okada, 1985). The different variation of tsunami propagations is expected to be produced from the different parameters and slip amount used in the simulation.
4 Figure 6. Seafloor deformations by Model 1 (left), Model (center) and Model 3 (right). Red and blue lines indicate the uplift and subsidence area, respectively, with the contour interval of 1.0 m. 3. THEORY AND METHODOLOGY 3.1 Non-linear shallow water and governing equations The original Tohoku University s Numerical Analysis Model for Investigation (TUNAMI-N) model neglects the earth s curvature (Dao and Tkalich, 007). To consider the effects of the earth s curvature, the NSWE model is reformulated in spherical coordinates (Yanagisawa, 01). The continuity and momentum equations are rewritten as follows; η 1 M + (cos ) = 0 cos + N θ t R θ λ θ M gd η 1 M 1 MN gn (cos ) + + cos cos θ M M N t R θ λ R θ λ cos 7 / 3 D R θ θ D D N gd 1 1 (cos ) N cos MN gn + θη + + ( ) + cos cos θ N M t R θ θ R θ λ cos 7 / 3 D R θ λ D D = 0 + N = 0 (1) () (3) Where η is wave amplitude, M is discharge fluxes in the λ (along a parallel of latitude) direction, N is discharge fluxes in the θ (along a circle of longitude) direction, R is radius of the earth at km, t is time and n is manning roughness coefficient (n = 0.05 in this study). 3. Runup and inundation height The main objective of this study is to investigate the onshore effects of a tsunami or runup. Runup and inundation height are referring to the maximum vertical tsunami height onshore and elevation of local watermark measured from the sea level at the time of tsunami attack.
5 4. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 4.1 Tsunami wave propagations The result of Model 1 shows that K1, K, K3 and K4 are facing large tsunami height from.4 m up to.9 m but it is slightly lower at P1, P and P4. Wave pattern of Model 3 is slightly similar to that of the Model 1 but the tsunami height at K4 is only 1.5 m which is about half of.9 m in Model 1. The calculated tsunami height of Model is relatively small compared with Models 1 and 3. The calculated tsunami height at P1, P and P4 from Model 1 is almost agreeable to the computation result reported in Koh et al. (009) by using an in-house Tsunami Numerical Simulation Model (TUNA). The pattern of maximum tsunami heights at all coastal points show that P5, K1, K, K3 and K4 have been hit by the high waves about.0 m from Model 1. Figure 7 shows the calculated tsunami waveforms at four tide gauge stations in Penang and Langkawi and the comparison with the observed waveforms at TG1 and TG3. The calculated waveforms and the observed data generally fit to each other. The waveforms by Model 1 almost reproduce the observed ones. Figure 7. Comparison between the calculated tsunami waveforms (blue lines) and the observe ones (red lines) at tide gauge stations by Model 1(left), Model (center) and Model 3(right). 4. Tsunami inundation analysis All the calculated runup heights in Penang are underestimated compared with the observation data. The observed maximum tsunami runup is at as high as 4.0 m at P (Figure 8). Maximum tsunami runup estimated at K1 and K was between 3. and 4.0 m for both Model 1 and 3, respectively (Figure 9). The calculated result is almost agreeable to the observed data which is recorded at the maximum height of 3.75 m at K. Tsunami runup at the target locations K3 and K4 seem to be overestimated, where the calculated result from Model 1 shows the maximum runup at 5.1 and 5.3 m, respectively (Figure 10). The maximum runup from the observed data is only between.5 and 3.09 m. The computed runup at K3 by Model 3 is almost agreeable to the observed data of 3.1 m. Figure 8. Comparison between the calculated maximum tsunami runup heights and observed ones at the target locations in Penang
6 Figure 9. Same as Figure 8, but in Pantai Chenang, Langkawi. Figure 10. Same as Figure 8, but in Kuala Triang, Langkawi. 5. CONCLUSIONS The result of the tsunami propagation analysis shows that about.5 m of tsunami waves approaching the coastal locations P5, K1, K, K3 and K4 may severely impact the area if there is no sufficient protection given by the authority. The calculated maximum runup heights at K1 and K are as high as 4.0 m which is almost agreeable to the field observation data. The elevation profile also suggests that the location P1, P4 and K are exposed to the tsunami threat as they are located at low land. It was also found that the tsunami generated by the source Models 1 and 3 with higher slip distributions in Nicobar and Andaman Islands contributed to the large tsunami heights and runups over the study region. The source parameters from historical earthquakes and tsunamis in the northern Sumatra especially at Nicobar and Andaman islands will be investigated in order to estimate the impact to the northwest Peninsular Malaysia. The inundation results from the numerical simulations will be suggested for making tsunami hazard maps in Penang and Langkawi. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT Special thanks to Mohd Yusof Bin Abu Bakar and Zulkifli Bin Mohamad, the officers at the Department of Survey and Mapping Malaysia (JUPEM) and Malaysian Meteorological Department (MMD) for their support to make this study successful. REFERENCES Dao, M.H., Tkalich, P., 007. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 7, Fujii, Y., Satake, K., 007. Bull. Seism. Soc. Am., Vol. 97, No. 1A, pp. S19-S07. Hirata, K., et al., 006. Earth Planets Space, 58, Koh, H.L., et al., 009. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 36(009) Okada, Y., B. Seism. Soc. Am. 75 (4), Tanioka Y., et al., 006. Earth Planet Science 58(006), pp Wessel, P. and W. H. F. Smith, 007, The Generic Mapping Tools, version Yanagisawa, H., May 01, Tsukuba, Lecture Note
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF TSUNAMI PROPAGATION AND INUNDATION ALONG THE RAKHINE COAST AREAS IN MYANMAR
 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF TSUNAMI PROPAGATION AND INUNDATION ALONG THE RAKHINE COAST AREAS IN MYANMAR Su Hninn Htwe Supervisor: Bunichiro SHIBAZAKI MEE12619 Yushiro FUJII ABSTRACT This study aimed to assess
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF TSUNAMI PROPAGATION AND INUNDATION ALONG THE RAKHINE COAST AREAS IN MYANMAR Su Hninn Htwe Supervisor: Bunichiro SHIBAZAKI MEE12619 Yushiro FUJII ABSTRACT This study aimed to assess
NUMERICAL SIMULATION AS GUIDANCE IN MAKING TSUNAMI HAZARD MAP FOR LABUAN ISLAND
 NUMERICAL SIMULATION AS GUIDANCE IN MAKING TSUNAMI HAZARD MAP FOR LABUAN ISLAND MOHD RIDZUAN bin Adam Supervisor: Fumihiko IMAMURA MEE09199 ABSTRACT At the northeast end of the South China Sea, tsunamis
NUMERICAL SIMULATION AS GUIDANCE IN MAKING TSUNAMI HAZARD MAP FOR LABUAN ISLAND MOHD RIDZUAN bin Adam Supervisor: Fumihiko IMAMURA MEE09199 ABSTRACT At the northeast end of the South China Sea, tsunamis
TSUNAMI HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN NORTHERN EGYPT USING NUMERICAL SIMULATION
 TSUNAMI HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN NORTHERN EGYPT USING NUMERICAL SIMULATION Abutaleb Ali Supervisor: Bunichiro SHIBAZAKI MEE16717 Yushiro FUJII ABSTRACT To investigate the tsunami hazard along the northern
TSUNAMI HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN NORTHERN EGYPT USING NUMERICAL SIMULATION Abutaleb Ali Supervisor: Bunichiro SHIBAZAKI MEE16717 Yushiro FUJII ABSTRACT To investigate the tsunami hazard along the northern
TSUNAMI PROPAGATION AND INUNDATION MODELINGS ALONG SOUTH-EAST COAST OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA
 TSUNAMI PROPAGATION AND INUNDATION MODELINGS ALONG SOUTH-EAST COAST OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA Martin WAREK Supervisor: Yushiro FUJII MEE12620 Bunichiro SHIBAZAKI ABSTRACT This study covers tsunami generation,
TSUNAMI PROPAGATION AND INUNDATION MODELINGS ALONG SOUTH-EAST COAST OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA Martin WAREK Supervisor: Yushiro FUJII MEE12620 Bunichiro SHIBAZAKI ABSTRACT This study covers tsunami generation,
NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS FOR TSUNAMI FORECASTING AT PADANG CITY USING OFFSHORE TSUNAMI SENSORS
 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS FOR TSUNAMI FORECASTING AT PADANG CITY USING OFFSHORE TSUNAMI SENSORS Setyoajie Prayoedhie Supervisor: Yushiro FUJII MEE10518 Bunichiro SHIBAZAKI ABSTRACT We conducted numerical simulations
NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS FOR TSUNAMI FORECASTING AT PADANG CITY USING OFFSHORE TSUNAMI SENSORS Setyoajie Prayoedhie Supervisor: Yushiro FUJII MEE10518 Bunichiro SHIBAZAKI ABSTRACT We conducted numerical simulations
SOURCE INVERSION AND INUNDATION MODELING TECHNOLOGIES FOR TSUNAMI HAZARD ASSESSMENT, CASE STUDY: 2001 PERU TSUNAMI
 Paper No. TS-4-1 SOURCE INVERSION AND INUNDATION MODELING TECHNOLOGIES FOR TSUNAMI HAZARD ASSESSMENT, CASE STUDY: 2001 PERU TSUNAMI Bruno Adriano 1, Shunichi Koshimura 2 and Yushiro Fujii 3 ABSTRACT The
Paper No. TS-4-1 SOURCE INVERSION AND INUNDATION MODELING TECHNOLOGIES FOR TSUNAMI HAZARD ASSESSMENT, CASE STUDY: 2001 PERU TSUNAMI Bruno Adriano 1, Shunichi Koshimura 2 and Yushiro Fujii 3 ABSTRACT The
DETERMINATION OF SLIP DISTRIBUTION OF THE 28 MARCH 2005 NIAS EARTHQUAKE USING JOINT INVERSION OF TSUNAMI WAVEFORM AND GPS DATA
 Synopses of Master Papers Bulletin of IISEE, 47, 115-10, 013 DETERMINATION OF SLIP DISTRIBUTION OF THE 8 MARCH 005 NIAS EARTHQUAKE USING JOINT INVERSION OF TSUNAMI WAVEFORM AND GPS DATA Tatok Yatimantoro
Synopses of Master Papers Bulletin of IISEE, 47, 115-10, 013 DETERMINATION OF SLIP DISTRIBUTION OF THE 8 MARCH 005 NIAS EARTHQUAKE USING JOINT INVERSION OF TSUNAMI WAVEFORM AND GPS DATA Tatok Yatimantoro
TSUNAMI HAZARD ASSESSMENT FOR THE CENTRAL COAST OF PERU USING NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS FOR THE 1974, 1966 AND 1746 EARTHQUAKES
 TSUNAMI HAZARD ASSESSMENT FOR THE CENTRAL COAST OF PERU USING NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS FOR THE 1974, 1966 AND 1746 EARTHQUAKES Sheila Yauri Supervisor: Yushiro FUJII MEE10521 Bunichiro SHIBAZAKI ABSTRACT
TSUNAMI HAZARD ASSESSMENT FOR THE CENTRAL COAST OF PERU USING NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS FOR THE 1974, 1966 AND 1746 EARTHQUAKES Sheila Yauri Supervisor: Yushiro FUJII MEE10521 Bunichiro SHIBAZAKI ABSTRACT
STUDY ON APPROPRIATE MODELING OF TSUNAMIS IN MALAYSIA FOR RISK EVALUATION
 STUDY ON APPROPRIATE MODELING OF TSUNAMIS IN MALAYSIA FOR RISK EVALUATION Zaty Aktar binti Mokhtar* Supervisor: Fumihiko Imamura** MEE06025 Shunichi Koshimura** ABSTRACT In order to design a tsunami warning
STUDY ON APPROPRIATE MODELING OF TSUNAMIS IN MALAYSIA FOR RISK EVALUATION Zaty Aktar binti Mokhtar* Supervisor: Fumihiko Imamura** MEE06025 Shunichi Koshimura** ABSTRACT In order to design a tsunami warning
TSUNAMI CHARACTERISTICS OF OUTER-RISE EARTHQUAKES ALONG THE PACIFIC COAST OF NICARAGUA - A CASE STUDY FOR THE 2016 NICARAGUA EVENT-
 TSUNAMI CHARACTERISTICS OF OUTER-RISE EARTHQUAKES ALONG THE PACIFIC COAST OF NICARAGUA - A CASE STUDY FOR THE 2016 NICARAGUA EVENT- Amilcar Cabrera Supervisor: Yuichiro TANIOKA MEE16718 ABSTRACT Nicaragua
TSUNAMI CHARACTERISTICS OF OUTER-RISE EARTHQUAKES ALONG THE PACIFIC COAST OF NICARAGUA - A CASE STUDY FOR THE 2016 NICARAGUA EVENT- Amilcar Cabrera Supervisor: Yuichiro TANIOKA MEE16718 ABSTRACT Nicaragua
A PROTOTYPE OF WEB-APPLICATION FOR TSUNAMI DATABASE ALONG SOUTHERN JAVA ISLAND COASTLINE
 A PROTOTYPE OF WEB-APPLICATION FOR TSUNAMI DATABASE ALONG SOUTHERN JAVA ISLAND COASTLINE Ariska Rudyanto MEE07170 Supervisor: Yohei HASEGAWA Yosuke IGARASHI Yushiro FUJII ABSTRACT Development of tsunami
A PROTOTYPE OF WEB-APPLICATION FOR TSUNAMI DATABASE ALONG SOUTHERN JAVA ISLAND COASTLINE Ariska Rudyanto MEE07170 Supervisor: Yohei HASEGAWA Yosuke IGARASHI Yushiro FUJII ABSTRACT Development of tsunami
Source of the July 2006 West Java tsunami estimated from tide gauge records
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L24317, doi:10.1029/2006gl028049, 2006 Source of the July 2006 West Java tsunami estimated from tide gauge records Yushiro Fujii 1 and Kenji Satake 2 Received 13
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L24317, doi:10.1029/2006gl028049, 2006 Source of the July 2006 West Java tsunami estimated from tide gauge records Yushiro Fujii 1 and Kenji Satake 2 Received 13
SIMULATION OF FUTURE ANDAMAN TSUNAMI INTO STRAITS OF MALACCA BY TUNA
 Journal of Earthquake and Tsunami, Vol. 3, No. 2 (29) 89 1 c World Scientific Publishing Company SIMULATION OF FUTURE ANDAMAN TSUNAMI INTO STRAITS OF MALACCA BY TUNA KOH HOCK LYE,, TEH SU YEAN,KEWLEEMING
Journal of Earthquake and Tsunami, Vol. 3, No. 2 (29) 89 1 c World Scientific Publishing Company SIMULATION OF FUTURE ANDAMAN TSUNAMI INTO STRAITS OF MALACCA BY TUNA KOH HOCK LYE,, TEH SU YEAN,KEWLEEMING
Tsunami waveform inversion of the 2007 Bengkulu, southern Sumatra, earthquake
 LETTER Earth Planets Space, 60, 993 998, 2008 Tsunami waveform inversion of the 2007 Bengkulu, southern Sumatra, earthquake Yushiro Fujii 1 and Kenji Satake 2 1 International Institute of Seismology and
LETTER Earth Planets Space, 60, 993 998, 2008 Tsunami waveform inversion of the 2007 Bengkulu, southern Sumatra, earthquake Yushiro Fujii 1 and Kenji Satake 2 1 International Institute of Seismology and
Tsunami Simulation of 2009 Dusky Sound Earthquake in New Zealand
 Tsunami Simulation of 2009 Dusky Sound Earthquake in New Zealand Polina Berezina 1 Institute of Geology, Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv, Kyiv, Ukraine Supervisor: Prof. Kenji Satake Earthquake
Tsunami Simulation of 2009 Dusky Sound Earthquake in New Zealand Polina Berezina 1 Institute of Geology, Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv, Kyiv, Ukraine Supervisor: Prof. Kenji Satake Earthquake
REAL-TIME TSUNAMI INUNDATION FORECAST FOR THE PACIFIC COAST OF NICARAGUA
 REAL-TIME TSUNAMI INUNDATION FORECAST FOR THE PACIFIC COAST OF NICARAGUA Ulbert Grillo Rodriguez Supervisor: Yuichiro TANIOKA MEE17719 ABSTRACT We constructed a pre-computed tsunami database for six areas
REAL-TIME TSUNAMI INUNDATION FORECAST FOR THE PACIFIC COAST OF NICARAGUA Ulbert Grillo Rodriguez Supervisor: Yuichiro TANIOKA MEE17719 ABSTRACT We constructed a pre-computed tsunami database for six areas
Modeling of the 2011 Tohoku-oki. oki Tsunami and it s s impacts to Hawaii
 WAVES 11, KONA HAWAI`I Modeling of the 2011 Tohoku-oki oki Tsunami and it s s impacts to Hawaii Yoshiki Yamazaki 1, Volker Roeber 1, Kwok Fai Cheung 1 and Thorne Lay 2 1 Department of Ocean and Resources
WAVES 11, KONA HAWAI`I Modeling of the 2011 Tohoku-oki oki Tsunami and it s s impacts to Hawaii Yoshiki Yamazaki 1, Volker Roeber 1, Kwok Fai Cheung 1 and Thorne Lay 2 1 Department of Ocean and Resources
REAL-TIME TSUNAMI INUNDATION FORECAST STUDY IN CHIMBOTE CITY, PERU
 REAL-TIME TSUNAMI INUNDATION FORECAST STUDY IN CHIMBOTE CITY, PERU Nabilt Moggiano Supervisor: Kenji SATAKE MEE16720 ABSTRACT For rapid forecast of tsunami inundation during a tsunamigenic event, we constructed
REAL-TIME TSUNAMI INUNDATION FORECAST STUDY IN CHIMBOTE CITY, PERU Nabilt Moggiano Supervisor: Kenji SATAKE MEE16720 ABSTRACT For rapid forecast of tsunami inundation during a tsunamigenic event, we constructed
Effect of the Emperor seamounts on trans-oceanic propagation of the 2006 Kuril Island earthquake tsunami
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L02611, doi:10.1029/2007gl032129, 2008 Effect of the Emperor seamounts on trans-oceanic propagation of the 2006 Kuril Island earthquake tsunami S. Koshimura, 1 Y.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L02611, doi:10.1029/2007gl032129, 2008 Effect of the Emperor seamounts on trans-oceanic propagation of the 2006 Kuril Island earthquake tsunami S. Koshimura, 1 Y.
Inversion of tsunami data. A. Sladen CNRS, Géoazur 1/35
 Inversion of tsunami data A. Sladen CNRS, Géoazur 1/35 DEFINITION Tsunami waves are gravity wave with a long period need a BIG source! 2/35 DEFINITION Krakatoa, 1883 Summer 2015, E.T. pers. comm. Lituya
Inversion of tsunami data A. Sladen CNRS, Géoazur 1/35 DEFINITION Tsunami waves are gravity wave with a long period need a BIG source! 2/35 DEFINITION Krakatoa, 1883 Summer 2015, E.T. pers. comm. Lituya
Numerical Tsunami Propagation of 1703 Kanto Earthquake
 Numerical Tsunami Propagation of 1703 Kanto Earthquake Wu Yifei Supervisor: Kenji Satake Introduction Near Tokyo Bay, the 1703 Genroku Kanto Earthquake is known to generate a tsunami which hit the nearby
Numerical Tsunami Propagation of 1703 Kanto Earthquake Wu Yifei Supervisor: Kenji Satake Introduction Near Tokyo Bay, the 1703 Genroku Kanto Earthquake is known to generate a tsunami which hit the nearby
Scaling relations of seismic moment, rupture area, average slip, and asperity size for M~9 subduction-zone earthquakes
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 4, 7 74, doi:1.12/grl.976, 213 Scaling relations of seismic moment, rupture area, average slip, and asperity size for M~9 subduction-zone earthquakes Satoko Murotani,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 4, 7 74, doi:1.12/grl.976, 213 Scaling relations of seismic moment, rupture area, average slip, and asperity size for M~9 subduction-zone earthquakes Satoko Murotani,
TSUNAMI PROPAGATION IN ARABIAN SEA AND ITS EFFECT ON DWARKA CITY OF GUJARAT, INDIA
 International Journal of Advanced Structural Engineering, Vol. 2, No. 2, Pages 163-174, December 2010 Islamic Azad University, South Tehran Branch Published online December 2010 at (http://journals.azad.ac.ir/ijase)
International Journal of Advanced Structural Engineering, Vol. 2, No. 2, Pages 163-174, December 2010 Islamic Azad University, South Tehran Branch Published online December 2010 at (http://journals.azad.ac.ir/ijase)
On the open sea propagation of 2004 global tsunami generated by the sea bed deformation
 On the open sea propagation of 00 global tsunami generated by the sea bed deformation Md. Fazlul Karim Principal Lecturer, Engineering Mathematics Unit, Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Brunei,
On the open sea propagation of 00 global tsunami generated by the sea bed deformation Md. Fazlul Karim Principal Lecturer, Engineering Mathematics Unit, Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Brunei,
Lessons from the 2004 Sumatra earthquake and the Asian tsunami
 Lessons from the 2004 Sumatra earthquake and the Asian tsunami Kenji Satake National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology Outline 1. The largest earthquake in the last 40 years 2. Tsunami
Lessons from the 2004 Sumatra earthquake and the Asian tsunami Kenji Satake National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology Outline 1. The largest earthquake in the last 40 years 2. Tsunami
1.3 Short Review: Preliminary results and observations of the December 2004 Great Sumatra Earthquake Kenji Hirata
 1.3 Short Review: Preliminary results and observations of the December 2004 Great Sumatra Earthquake Kenji Hirata We give a brief review about observations and preliminary results regarding the 2004 great
1.3 Short Review: Preliminary results and observations of the December 2004 Great Sumatra Earthquake Kenji Hirata We give a brief review about observations and preliminary results regarding the 2004 great
EARTHQUAKE SOURCE PARAMETERS FOR SUBDUCTION ZONE EVENTS CAUSING TSUNAMIS IN AND AROUND THE PHILIPPINES
 EARTHQUAKE SOURCE PARAMETERS FOR SUBDUCTION ZONE EVENTS CAUSING TSUNAMIS IN AND AROUND THE PHILIPPINES Joan Cruz SALCEDO Supervisor: Tatsuhiko HARA MEE09186 ABSTRACT We have made a set of earthquake source
EARTHQUAKE SOURCE PARAMETERS FOR SUBDUCTION ZONE EVENTS CAUSING TSUNAMIS IN AND AROUND THE PHILIPPINES Joan Cruz SALCEDO Supervisor: Tatsuhiko HARA MEE09186 ABSTRACT We have made a set of earthquake source
Method to Determine Appropriate Source Models of Large Earthquakes Including Tsunami Earthquakes for Tsunami Early Warning in Central America
 Pure Appl. Geophys. 174 (2017), 3237 3248 Ó 2017 The Author(s) This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com DOI 10.1007/s00024-017-1630-y Pure and Applied Geophysics Method to Determine
Pure Appl. Geophys. 174 (2017), 3237 3248 Ó 2017 The Author(s) This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com DOI 10.1007/s00024-017-1630-y Pure and Applied Geophysics Method to Determine
Riskscape module Documentation: Inundation Modelling in Bay of Plenty. X. Wang C. Mueller
 Riskscape module Documentation: Inundation Modelling in Bay of Plenty X. Wang C. Mueller CONTENTS 1.0 GENERAL INFORMATION... 2 1.1 SITE OF STUDY... 5 1.2 SOURCE SCENARIOS... 5 1.3 NUMERICAL MODEL... 5
Riskscape module Documentation: Inundation Modelling in Bay of Plenty X. Wang C. Mueller CONTENTS 1.0 GENERAL INFORMATION... 2 1.1 SITE OF STUDY... 5 1.2 SOURCE SCENARIOS... 5 1.3 NUMERICAL MODEL... 5
Three Dimensional Simulations of Tsunami Generation and Propagation
 Chapter 1 Earth Science Three Dimensional Simulations of Tsunami Generation and Propagation Project Representative Takashi Furumura Authors Tatsuhiko Saito Takashi Furumura Earthquake Research Institute,
Chapter 1 Earth Science Three Dimensional Simulations of Tsunami Generation and Propagation Project Representative Takashi Furumura Authors Tatsuhiko Saito Takashi Furumura Earthquake Research Institute,
Differentiating earthquake tsunamis from other sources; how do we tell the difference?
 Differentiating earthquake tsunamis from other sources; how do we tell the difference? David Tappin (1), Stephan Grilli (2), Jeffrey Harris (2), Timothy Masterlark (3), James Kirby (4), Fengyan Shi Shi
Differentiating earthquake tsunamis from other sources; how do we tell the difference? David Tappin (1), Stephan Grilli (2), Jeffrey Harris (2), Timothy Masterlark (3), James Kirby (4), Fengyan Shi Shi
SCIENCE OF TSUNAMI HAZARDS
 SCIENCE OF TSUNAMI HAZARDS ISSN 8755-6839 Journal of Tsunami Society International Volume 31 Number 1 2012 SIMULATION OF THE EFFECT OF FAR FIELD TSUNAMI THROUGH AN OPEN BOUNDARY CONDITION IN A BOUNDARY-FITTED
SCIENCE OF TSUNAMI HAZARDS ISSN 8755-6839 Journal of Tsunami Society International Volume 31 Number 1 2012 SIMULATION OF THE EFFECT OF FAR FIELD TSUNAMI THROUGH AN OPEN BOUNDARY CONDITION IN A BOUNDARY-FITTED
Amplification of Tsunami Heights by Delayed Rupture of Great Earthquakes along the Nankai Trough
 Amplification of Tsunami Heights by Delayed Rupture of Great Earthquakes along the Nankai Trough Kentaro Imai 1,2, Kenji Satake 2 and Takashi Furumura 1,2 1 Center for Integrated Disaster Information Research,
Amplification of Tsunami Heights by Delayed Rupture of Great Earthquakes along the Nankai Trough Kentaro Imai 1,2, Kenji Satake 2 and Takashi Furumura 1,2 1 Center for Integrated Disaster Information Research,
EMERGENCY PLANNING IN NORTHERN ALGERIA BASED ON REMOTE SENSING DATA IN RESPECT TO TSUNAMI HAZARD PREPAREDNESS
 EMERGENCY PLANNING IN NORTHERN ALGERIA BASED ON REMOTE SENSING DATA IN RESPECT TO TSUNAMI HAZARD PREPAREDNESS Barbara Theilen-Willige Technical University of Berlin, Institute of Applied Geosciences Department
EMERGENCY PLANNING IN NORTHERN ALGERIA BASED ON REMOTE SENSING DATA IN RESPECT TO TSUNAMI HAZARD PREPAREDNESS Barbara Theilen-Willige Technical University of Berlin, Institute of Applied Geosciences Department
Source Fault Model of the 1771 Yaeyama Tsunami, Southern Ryukyu Islands, Japan, Inferred from Numerical Simulation
 Pure appl. geophys. 163 (2006) 41 54 0033 4553/06/010041 14 DOI 10.1007/s00024-005-0007-9 Ó Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, 2006 Pure and Applied Geophysics Source Fault Model of the 1771 Yaeyama Tsunami, Southern
Pure appl. geophys. 163 (2006) 41 54 0033 4553/06/010041 14 DOI 10.1007/s00024-005-0007-9 Ó Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, 2006 Pure and Applied Geophysics Source Fault Model of the 1771 Yaeyama Tsunami, Southern
Numerical simulations for Investigation of the Coastline Erosion due to the 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami
 Numerical simulations for Investigation of the Coastline Erosion due to the 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami Syamsidik, Musa Al ala, Mirza Fahmi, and Tursina Tsunami Computation and Visualization Laboratory Tsunami
Numerical simulations for Investigation of the Coastline Erosion due to the 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami Syamsidik, Musa Al ala, Mirza Fahmi, and Tursina Tsunami Computation and Visualization Laboratory Tsunami
Slip distributions of the 1944 Tonankai and 1946 Nankai earthquakes including the horizontal movement effect on tsunami generation
 Slip distributions of the 1944 Tonankai and 1946 Nankai earthquakes including the horizontal movement effect on tsunami generation Toshitaka Baba Research Program for Plate Dynamics, Institute for Frontier
Slip distributions of the 1944 Tonankai and 1946 Nankai earthquakes including the horizontal movement effect on tsunami generation Toshitaka Baba Research Program for Plate Dynamics, Institute for Frontier
SCIENCE OF TSUNAMI HAZARDS
 SCIENCE OF TSUNAMI HAZARDS ISSN 8755-6839 Journal of Tsunami Society International Volume 30 Number 1 2011 OPEN BOUNDARY CONDITION FOR DISTANT TSUNAMI COMPUTATION A LINEAR CASE M. Ashaque Meah, M. Johurul
SCIENCE OF TSUNAMI HAZARDS ISSN 8755-6839 Journal of Tsunami Society International Volume 30 Number 1 2011 OPEN BOUNDARY CONDITION FOR DISTANT TSUNAMI COMPUTATION A LINEAR CASE M. Ashaque Meah, M. Johurul
Numerical Simulation of the December 26,2004: Indian Ocean Tsunami
 Numerical Simulation of the December 26,2004: Indian Ocean Tsunami J. Asavanant, 1 M. Ioualalen, 2 N. Kaewbanjak, 1 S.T. Grilli, 3 P. Watts, 4 J.T. Kirby, 5 and F. Shi 5 1 Advanced Virtual and Intelligent
Numerical Simulation of the December 26,2004: Indian Ocean Tsunami J. Asavanant, 1 M. Ioualalen, 2 N. Kaewbanjak, 1 S.T. Grilli, 3 P. Watts, 4 J.T. Kirby, 5 and F. Shi 5 1 Advanced Virtual and Intelligent
Tsunami propagation modelling a sensitivity study
 Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 7, 741 754, 2007 Author(s) 2007. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Tsunami propagation modelling a sensitivity
Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 7, 741 754, 2007 Author(s) 2007. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Tsunami propagation modelling a sensitivity
Integrated Approach to Assess the Impact of Tsunami Disaster
 Integrated Approach to Assess the Impact of Tsunami Disaster Shunichi Koshimura & Shintaro Kayaba Disaster Control Research Center, Graduate School of Engineering, Tohoku University, Japan Masashi Matsuoka
Integrated Approach to Assess the Impact of Tsunami Disaster Shunichi Koshimura & Shintaro Kayaba Disaster Control Research Center, Graduate School of Engineering, Tohoku University, Japan Masashi Matsuoka
SOURCE PROCESS OF THE 2003 PUERTO PLATA EARTHQUAKE USING TELESEISMIC DATA AND STRONG GROUND MOTION SIMULATION
 Synopses of Master Papers Bulletin of IISEE, 47, 19-24, 2013 SOURCE PROCESS OF THE 2003 PUERTO PLATA EARTHQUAKE USING TELESEISMIC DATA AND STRONG GROUND MOTION SIMULATION Fabricio Moquete Everth* Supervisor:
Synopses of Master Papers Bulletin of IISEE, 47, 19-24, 2013 SOURCE PROCESS OF THE 2003 PUERTO PLATA EARTHQUAKE USING TELESEISMIC DATA AND STRONG GROUND MOTION SIMULATION Fabricio Moquete Everth* Supervisor:
Predicting of Tsunami Inundation Area based on Propagation and Runup Numerical Model in Pacitan City
 Predicting of Tsunami Inundation Area based on Propagation and Runup Numerical Model in Pacitan City 1 Agus Suharyanto, 1 Alwafi Pujiraharjo, 2 Adipandang Yudono, 3 Keisuke Murakami, and 3 Chikashi Deguchi
Predicting of Tsunami Inundation Area based on Propagation and Runup Numerical Model in Pacitan City 1 Agus Suharyanto, 1 Alwafi Pujiraharjo, 2 Adipandang Yudono, 3 Keisuke Murakami, and 3 Chikashi Deguchi
Coseismic slip distribution of the 1946 Nankai earthquake and aseismic slips caused by the earthquake
 Earth Planets Space, 53, 235 241, 2001 Coseismic slip distribution of the 1946 Nankai earthquake and aseismic slips caused by the earthquake Yuichiro Tanioka 1 and Kenji Satake 2 1 Meteorological Research
Earth Planets Space, 53, 235 241, 2001 Coseismic slip distribution of the 1946 Nankai earthquake and aseismic slips caused by the earthquake Yuichiro Tanioka 1 and Kenji Satake 2 1 Meteorological Research
Tsunami Waveform Inversion based on Oceanographic Radar Data
 Research Institute for Applied Mechanics Workshop of Oceanographic Radar 12-13 December 2012 1 Tsunami Waveform Inversion based on Oceanographic Radar Data Ryotaro Fuji 1), Hirofumi Hinata 1), Tomoyuki
Research Institute for Applied Mechanics Workshop of Oceanographic Radar 12-13 December 2012 1 Tsunami Waveform Inversion based on Oceanographic Radar Data Ryotaro Fuji 1), Hirofumi Hinata 1), Tomoyuki
Numerical Modeling for the Propagation of Tsunami Wave and Corresponding Inundation
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 78-1684,p-ISSN: 30-334X, Volume 1, Issue Ver. IV (Mar - Apr. 015), PP 55-6 www.iosrjournals.org Numerical Modeling for the Propagation
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 78-1684,p-ISSN: 30-334X, Volume 1, Issue Ver. IV (Mar - Apr. 015), PP 55-6 www.iosrjournals.org Numerical Modeling for the Propagation
Earthquakes and Tsunamis
 Earthquakes and Tsunamis Kenji Satake Earthquake Research Institute University of Tokyo 1 Part I 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami 2 Fukushima Dai ichi NPP accident Earthquake ground motion Reactors automatically
Earthquakes and Tsunamis Kenji Satake Earthquake Research Institute University of Tokyo 1 Part I 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami 2 Fukushima Dai ichi NPP accident Earthquake ground motion Reactors automatically
The 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami: Tsunami source model from satellite altimetry
 Earth Planets Space,, 9, The Indian Ocean tsunami: Tsunami source model from satellite altimetry Kenji Hirata, Kenji Satake, Yuichiro Tanioka 3, Tsurane Kuragano, Yohei Hasegawa, Yutaka Hayashi, and Nobuo
Earth Planets Space,, 9, The Indian Ocean tsunami: Tsunami source model from satellite altimetry Kenji Hirata, Kenji Satake, Yuichiro Tanioka 3, Tsurane Kuragano, Yohei Hasegawa, Yutaka Hayashi, and Nobuo
A SENSIVITY TEST OF TSUNAMI MODELLING USING VARIOUS DATA: CASE STUDY IN CILACAP INDONESIA
 Bali, Indonesia, November 2-4, 28 A SENSIVITY TEST OF TSUNAMI MODELLING USING VARIOUS DATA: CASE STUDY IN CILACAP INDONESIA WIDJO KONGKO,4,5, STEFAN LESCHKA 2, OLE LARSEN 2 GERHARD GAYER 3, INGEBORG NÖHREN
Bali, Indonesia, November 2-4, 28 A SENSIVITY TEST OF TSUNAMI MODELLING USING VARIOUS DATA: CASE STUDY IN CILACAP INDONESIA WIDJO KONGKO,4,5, STEFAN LESCHKA 2, OLE LARSEN 2 GERHARD GAYER 3, INGEBORG NÖHREN
A Study of Open Boundary Conditions for Far Field Tsunami Computation MD. FAZLUL KARIM a, G D ROY b, AHMAD IZANI M ISMAIL a
 A Study of Open Boundary Conditions for Far Field Tsunami Computation MD. FAZLUL KARIM a, G D ROY b, AHMAD IZANI M ISMAIL a a School of Mathematical Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia, 8 Pulau Pinang,
A Study of Open Boundary Conditions for Far Field Tsunami Computation MD. FAZLUL KARIM a, G D ROY b, AHMAD IZANI M ISMAIL a a School of Mathematical Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia, 8 Pulau Pinang,
THE 2011 OFF THE PACIFIC COAST OF TOHOKU-OKI EARTHQUAKE AND TSUNAMI: INFLUENCE OF THE SOURCE CHARACTERISTICS ON THE MAXIMUM TSUNAMI HEIGHTS
 Proceedings of the International Symposium on Engineering Lessons Learned from the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake, March 1-4, 2012, Tokyo, Japan THE 2011 OFF THE PACIFIC COAST OF TOHOKU-OKI EARTHQUAKE
Proceedings of the International Symposium on Engineering Lessons Learned from the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake, March 1-4, 2012, Tokyo, Japan THE 2011 OFF THE PACIFIC COAST OF TOHOKU-OKI EARTHQUAKE
Updating the GEBCO Grid
 Updating the GEBCO Grid PAULINE WEATHERALL, GEBCO DIGITAL ATLAS MANAGER, BRITISH OCEANOGRAPHIC DATA CENTRE (BODC), NATIONAL OCEANOGRAPHY CENTRE (NOC), LIVERPOOL, UK. GEBCO TSCOM and SCRUM meeting, Kuala
Updating the GEBCO Grid PAULINE WEATHERALL, GEBCO DIGITAL ATLAS MANAGER, BRITISH OCEANOGRAPHIC DATA CENTRE (BODC), NATIONAL OCEANOGRAPHY CENTRE (NOC), LIVERPOOL, UK. GEBCO TSCOM and SCRUM meeting, Kuala
Supplement of Scenario-based numerical modelling and the palaeo-historic record of tsunamis in Wallis and Futuna, Southwest Pacific
 Supplement of Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 15, 1763 1784, 2015 http://www.nat-hazards-earth-syst-sci.net/15/1763/2015/ doi:10.5194/nhess-15-1763-2015-supplement Author(s) 2015. CC Attribution 3.0 License.
Supplement of Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 15, 1763 1784, 2015 http://www.nat-hazards-earth-syst-sci.net/15/1763/2015/ doi:10.5194/nhess-15-1763-2015-supplement Author(s) 2015. CC Attribution 3.0 License.
Tsunami potential and modeling
 Tsunami potential and modeling GEORGE PRIEST OREGON DEPT. OF GEOLOGY AND MINERAL INDUSTRIES NEWPORT COASTAL FIELD OFFICE April 7, 2012 GeoPRISMS Cascadia Workshop, Portland, Oregon What creates most uncertainty
Tsunami potential and modeling GEORGE PRIEST OREGON DEPT. OF GEOLOGY AND MINERAL INDUSTRIES NEWPORT COASTAL FIELD OFFICE April 7, 2012 GeoPRISMS Cascadia Workshop, Portland, Oregon What creates most uncertainty
Tsunami Hazard Assessment for the Arabian Gulf from Earthquakes and Surface Landslides
 土木学会論文集 B2( 海岸工学 ),Vol. 72, No. 2, I_1675 I_1680, 2016. Tsunami Hazard Assessment for the Arabian Gulf from Earthquakes and Surface Landslides Anawat SUPPASRI 1, Panon LATCHAROTE 2, Tanuspong POKAVANICH
土木学会論文集 B2( 海岸工学 ),Vol. 72, No. 2, I_1675 I_1680, 2016. Tsunami Hazard Assessment for the Arabian Gulf from Earthquakes and Surface Landslides Anawat SUPPASRI 1, Panon LATCHAROTE 2, Tanuspong POKAVANICH
Tsunami waveform analyses of the 2006 underthrust and 2007 outer-rise Kurile earthquakes
 Author(s) 2008. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Advances in Geosciences Tsunami waveform analyses of the 2006 underthrust and 2007 outer-rise Kurile earthquakes Y. Tanioka 1, Y.
Author(s) 2008. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Advances in Geosciences Tsunami waveform analyses of the 2006 underthrust and 2007 outer-rise Kurile earthquakes Y. Tanioka 1, Y.
DETERMINATION OF EARTHQUAKE PARAMETERS USING SINGLE STATION BROADBAND DATA IN SRI LANKA
 DETERMINATION OF EARTHQUAKE PARAMETERS USING SINGLE STATION BROADBAND DATA IN SRI LANKA S.W.M. SENEVIRATNE* MEE71 Supervisors: Yasuhiro YOSHIDA** Tatsuhiko HARA*** ABSTRACT We determined epicenters and
DETERMINATION OF EARTHQUAKE PARAMETERS USING SINGLE STATION BROADBAND DATA IN SRI LANKA S.W.M. SENEVIRATNE* MEE71 Supervisors: Yasuhiro YOSHIDA** Tatsuhiko HARA*** ABSTRACT We determined epicenters and
Analysis of the Tsunami Generated by the Great 1977 Sumba Earthquake that Occurred in Indonesia
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 99, No. 4, pp. 2169 2179, August 2009, doi: 10.1785/0120080324 Analysis of the Tsunami Generated by the Great 1977 Sumba Earthquake that Occurred
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 99, No. 4, pp. 2169 2179, August 2009, doi: 10.1785/0120080324 Analysis of the Tsunami Generated by the Great 1977 Sumba Earthquake that Occurred
Sumatra earthquake from tsunami tide gauge record inversion
 1 2 Source process of the September 12, 2007 M W 8.4 Southern Sumatra earthquake from tsunami tide gauge record inversion 3 4 Stefano Lorito, Fabrizio Romano, Alessio Piatanesi and Enzo Boschi 5 6 Istituto
1 2 Source process of the September 12, 2007 M W 8.4 Southern Sumatra earthquake from tsunami tide gauge record inversion 3 4 Stefano Lorito, Fabrizio Romano, Alessio Piatanesi and Enzo Boschi 5 6 Istituto
W phase inversion and tsunami inundation modeling for tsunami. early warning: case study for the 2011 Tohoku event
 Title W Phase Inversion and Tsunami Inundation Modeling fo Event Author(s)Gusman, Aditya Riadi; Tanioka, Yuichiro CitationPure and Applied Geophysics, 171(7): 149-1422 Issue Date 214-7-1 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/59428
Title W Phase Inversion and Tsunami Inundation Modeling fo Event Author(s)Gusman, Aditya Riadi; Tanioka, Yuichiro CitationPure and Applied Geophysics, 171(7): 149-1422 Issue Date 214-7-1 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/59428
DATA BASE DEVELOPMENT OF ETA (ESTIMATED TIME OF ARRIVAL) FOR TSUNAMI DISASTER MITIGATION AT SOUTHWESTERN CITIES OF ACEH, INDONESIA
 6 th South China Sea Tsunami Workshop Nanyang Technology University, Singapore, 6-8 November 2013 DATA BASE DEVELOPMENT OF ETA (ESTIMATED TIME OF ARRIVAL) FOR TSUNAMI DISASTER MITIGATION AT SOUTHWESTERN
6 th South China Sea Tsunami Workshop Nanyang Technology University, Singapore, 6-8 November 2013 DATA BASE DEVELOPMENT OF ETA (ESTIMATED TIME OF ARRIVAL) FOR TSUNAMI DISASTER MITIGATION AT SOUTHWESTERN
QUANTIFYING NUMERICAL MODEL ACCURACY AND VARIABILITY. Luis Montoya 1 and Patrick Lynett 1
 QUANTIFYING NUMERICAL MODEL ACCURACY AND VARIABILITY Luis Montoya 1 and Patrick Lynett 1 On March 11, 2011 the Tohoku tsunami event caused the death of thousands of people and generated billions of dollars
QUANTIFYING NUMERICAL MODEL ACCURACY AND VARIABILITY Luis Montoya 1 and Patrick Lynett 1 On March 11, 2011 the Tohoku tsunami event caused the death of thousands of people and generated billions of dollars
Tsunamis and ocean waves
 Department of Mathematics & Statistics AAAS Annual Meeting St. Louis Missouri February 19, 2006 Introduction Tsunami waves are generated relatively often, from various sources Serious tsunamis (serious
Department of Mathematics & Statistics AAAS Annual Meeting St. Louis Missouri February 19, 2006 Introduction Tsunami waves are generated relatively often, from various sources Serious tsunamis (serious
Detailed analysis of tsunami waveforms generated by the 1946 Aleutian tsunami earthquake
 Detailed analysis of tsunami waveforms generated by the 1946 Aleutian tsunami earthquake Y. Tanioka, T. Seno To cite this version: Y. Tanioka, T. Seno. Detailed analysis of tsunami waveforms generated
Detailed analysis of tsunami waveforms generated by the 1946 Aleutian tsunami earthquake Y. Tanioka, T. Seno To cite this version: Y. Tanioka, T. Seno. Detailed analysis of tsunami waveforms generated
Preliminary Study of Possible Tsunami Hazards in Taiwan Region
 Preliminary Study of Possible Tsunami Hazards in Taiwan Region Xiaoming Wang and Philip L.-F. Liu Cornell University (First Draft on May 25 2006) (Second Draft on June 1 2006) (Final Update on June 8 2006)
Preliminary Study of Possible Tsunami Hazards in Taiwan Region Xiaoming Wang and Philip L.-F. Liu Cornell University (First Draft on May 25 2006) (Second Draft on June 1 2006) (Final Update on June 8 2006)
Time and Space Distribution of Coseismic Slip of the 2011 Tohoku Earthquake as. Inferred from Tsunami Waveform Data
 1 2 Time and Space Distribution of Coseismic Slip of the 2011 Tohoku Earthquake as Inferred from Tsunami Waveform Data 3 4 Kenji Satake 1, Yushiro Fujii 2, Tomoya Harada 1 and Yuichi Namegaya 3 5 6 7 8
1 2 Time and Space Distribution of Coseismic Slip of the 2011 Tohoku Earthquake as Inferred from Tsunami Waveform Data 3 4 Kenji Satake 1, Yushiro Fujii 2, Tomoya Harada 1 and Yuichi Namegaya 3 5 6 7 8
Mechanism of tsunami generation,propagation and runup -sharing experiences with Japanese
 Mechanism of tsunami generation,propagation and runup -sharing experiences with Japanese Mechanism of tsunami generation Predicting the propagation, runup and inundation of tsunamis Near and far-field
Mechanism of tsunami generation,propagation and runup -sharing experiences with Japanese Mechanism of tsunami generation Predicting the propagation, runup and inundation of tsunamis Near and far-field
Predicting tsunami waves and currents on the West Coast of Canada: A case study for Ucluelet, BC
 Predicting tsunami waves and currents on the West Coast of Canada: A case study for Ucluelet, BC Josef Cherniawsky, Kelin Wang and Roy Walters Institute of Ocean Sciences, Fisheries & Oceans Canada Pacific
Predicting tsunami waves and currents on the West Coast of Canada: A case study for Ucluelet, BC Josef Cherniawsky, Kelin Wang and Roy Walters Institute of Ocean Sciences, Fisheries & Oceans Canada Pacific
General-Circulation- Model System for Global Tsunami Warning
 A Coupled Teleseismic Ocean-General General-Circulation- Model System for Global Tsunami Warning Y. Tony Song Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology Contents:. Tsunami formation
A Coupled Teleseismic Ocean-General General-Circulation- Model System for Global Tsunami Warning Y. Tony Song Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology Contents:. Tsunami formation
Advisors: Arcadii Grinshpan, Mathematics and Statistics Rocco Malservisi, School of Geosciences. Problem Suggested By: Rocco Malservisi
 Undergraduate Journal of Mathematical Modeling: One + Two Volume 8 2018 Spring 2018 Issue 2 Article 6 Tsunami Waves Samantha Pennino University of South Florida Advisors: Arcadii Grinshpan, Mathematics
Undergraduate Journal of Mathematical Modeling: One + Two Volume 8 2018 Spring 2018 Issue 2 Article 6 Tsunami Waves Samantha Pennino University of South Florida Advisors: Arcadii Grinshpan, Mathematics
History of International Training in Seismology and Earthquake Engineering at IISEE
 History of International Training in Seismology and Earthquake Engineering at IISEE Activities of International Institute of Seismology and Earthquake Engineering (IISEE), BRI - Training for young researchers/engineers
History of International Training in Seismology and Earthquake Engineering at IISEE Activities of International Institute of Seismology and Earthquake Engineering (IISEE), BRI - Training for young researchers/engineers
Did a submarine landslide contribute to the 2011 Tohoku tsunami?
 Press Release Did a submarine landslide contribute to the 2011 Tohoku tsunami? 1. Key points Large tsunami amplitudes in Northern Tohoku (Sanriku) suggest that a secondary tsunami source lies offshore
Press Release Did a submarine landslide contribute to the 2011 Tohoku tsunami? 1. Key points Large tsunami amplitudes in Northern Tohoku (Sanriku) suggest that a secondary tsunami source lies offshore
Assessment of tsunami threat to Sri Lanka from potential mega-thrust earthquakes in the Arakan subduction zone
 J.Natn.Sci.Foundation Sri Lanka 2010 38 (2): 101-108 RESEARCH ARTICLE Assessment of tsunami threat to Sri Lanka from potential mega-thrust earthquakes in the Arakan subduction zone Janaka J. Wijetunge
J.Natn.Sci.Foundation Sri Lanka 2010 38 (2): 101-108 RESEARCH ARTICLE Assessment of tsunami threat to Sri Lanka from potential mega-thrust earthquakes in the Arakan subduction zone Janaka J. Wijetunge
2. Tsunami Source Details
 2. Tsunami Source Details The Northland area faces a range of potential tsunamigenic sources that include several local and distant fault systems and underwater landslides. A NIWA study (Goff et al. 2006)
2. Tsunami Source Details The Northland area faces a range of potential tsunamigenic sources that include several local and distant fault systems and underwater landslides. A NIWA study (Goff et al. 2006)
Tsunami. Harry Yeh Oregon State University. Eastern Japan Earthquake Disaster Briefing at PEER: April 28, 2011
 Tsunami by Harry Yeh Oregon State University Eastern Japan Earthquake Disaster Briefing at PEER: April 28, 2011 Seismic Characteristics Rupture Model (Harvard Seismology) The fault rupture process was
Tsunami by Harry Yeh Oregon State University Eastern Japan Earthquake Disaster Briefing at PEER: April 28, 2011 Seismic Characteristics Rupture Model (Harvard Seismology) The fault rupture process was
Tsunami source area of the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake determined from tsunami arrival times at offshore observation stations
 LETTER Earth Planets Space, 63, 809 813, 2011 Tsunami source area of the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake determined from tsunami arrival times at offshore observation stations Yutaka Hayashi,
LETTER Earth Planets Space, 63, 809 813, 2011 Tsunami source area of the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake determined from tsunami arrival times at offshore observation stations Yutaka Hayashi,
SCIENCE OF TSUNAMI HAZARDS
 SCIENCE OF TSUNAMI HAZARDS ISSN 8755-6839 Journal of Tsunami Society International Volume 31 Number 4 2012 RESPONSE OF THE GDACS SYSTEM TO THE TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE AND TSUNAMI OF 11 MARCH 2011 Annunziato,
SCIENCE OF TSUNAMI HAZARDS ISSN 8755-6839 Journal of Tsunami Society International Volume 31 Number 4 2012 RESPONSE OF THE GDACS SYSTEM TO THE TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE AND TSUNAMI OF 11 MARCH 2011 Annunziato,
Coupled Simulation of Ground Shaking and Tsunami for Mega-thrust Subduction Earthquakes
 Coupled Simulation of Ground Shaking and Tsunami for Mega-thrust Subduction Earthquakes Katsuichiro Goda Senior Lecturer, Dept. of Civil Engineering, University of Bristol, Bristol, United Kingdom Raffaele
Coupled Simulation of Ground Shaking and Tsunami for Mega-thrust Subduction Earthquakes Katsuichiro Goda Senior Lecturer, Dept. of Civil Engineering, University of Bristol, Bristol, United Kingdom Raffaele
Seismic Characteristics and Energy Release of Aftershock Sequences of Two Giant Sumatran Earthquakes of 2004 and 2005
 P-168 Seismic Characteristics and Energy Release of Aftershock Sequences of Two Giant Sumatran Earthquakes of 004 and 005 R. K. Jaiswal*, Harish Naswa and Anoop Singh Oil and Natural Gas Corporation, Vadodara
P-168 Seismic Characteristics and Energy Release of Aftershock Sequences of Two Giant Sumatran Earthquakes of 004 and 005 R. K. Jaiswal*, Harish Naswa and Anoop Singh Oil and Natural Gas Corporation, Vadodara
BIBLIOGRAPHIC REFERENCE
 BIBLIOGRAPHIC REFERENCE Power, W. L.; Wang, X.; Barberopoulou, A.; Mueller, C. 2014. Validation of a deaggregation-based approach for tsunami evacuation mapping, GNS Science Report 2014/36. 56 p. W. L.
BIBLIOGRAPHIC REFERENCE Power, W. L.; Wang, X.; Barberopoulou, A.; Mueller, C. 2014. Validation of a deaggregation-based approach for tsunami evacuation mapping, GNS Science Report 2014/36. 56 p. W. L.
Overview of Consequences of the Tsunami in Thailand and Roles and Activities of the Department of Mineral Resources after the 26 December 2004 Tsunami
 Overview of Consequences of the Tsunami in Thailand and Roles and Activities of the after the 26 December 2004 Tsunami By Mr.Worawoot Tantiwanit, Thailand 1 Earthquake in NW of North Sumatra Island 580
Overview of Consequences of the Tsunami in Thailand and Roles and Activities of the after the 26 December 2004 Tsunami By Mr.Worawoot Tantiwanit, Thailand 1 Earthquake in NW of North Sumatra Island 580
Tsunami modeling from the seismic CMT solution considering the dispersive effect: a case of the 2013 Santa Cruz Islands tsunami
 Miyoshi et al. Earth, Planets and Space (2015) 67:4 DOI 10.1186/s40623-014-0179-6 LETTER Open Access Tsunami modeling from the seismic CMT solution considering the dispersive effect: a case of the 2013
Miyoshi et al. Earth, Planets and Space (2015) 67:4 DOI 10.1186/s40623-014-0179-6 LETTER Open Access Tsunami modeling from the seismic CMT solution considering the dispersive effect: a case of the 2013
University of Bristol - Explore Bristol Research. Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record
 Goda, K. (2015). Effects of seabed surface rupture versus buried rupture on tsunami wave modeling: A case study for the 2011 Tohoku, Japan earthquake. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America,
Goda, K. (2015). Effects of seabed surface rupture versus buried rupture on tsunami wave modeling: A case study for the 2011 Tohoku, Japan earthquake. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America,
Preparation for Future Earthquake and Tsunami Hazards: Lessons Learned from the 2004 Sumatra-Andaman Earthquake and the Asian Tsunami
 First International Conference of Aceh and Indian Ocean Studies Organized by Asia Research Institute, National University of Singapore & Rehabilitation and Construction Executing Agency for Aceh and Nias
First International Conference of Aceh and Indian Ocean Studies Organized by Asia Research Institute, National University of Singapore & Rehabilitation and Construction Executing Agency for Aceh and Nias
THE EFFECT OF THE LATEST SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE TO MALAYSIAN PENINSULAR
 JURNAL KEJURUTERAAN AWAM (JOURNAL OF CIVIL ENGINEERING) Vol. 15 No. 2, 2002 THE EFFECT OF THE LATEST SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE TO MALAYSIAN PENINSULAR Assoc. Prof. Dr. Azlan Adnan Hendriyawan Structural Earthquake
JURNAL KEJURUTERAAN AWAM (JOURNAL OF CIVIL ENGINEERING) Vol. 15 No. 2, 2002 THE EFFECT OF THE LATEST SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE TO MALAYSIAN PENINSULAR Assoc. Prof. Dr. Azlan Adnan Hendriyawan Structural Earthquake
EFFECTIVE TROPICAL CYCLONE WARNING IN BANGLADESH
 Country Report of Bangladesh On EFFECTIVE TROPICAL CYCLONE WARNING IN BANGLADESH Presented At JMA/WMO WORKSHOP ON EFFECTIVE TROPICAL CYCLONE WARNING IN SOUTHEAST ASIA Tokyo, Japan,11-14 March 2014 By Sayeed
Country Report of Bangladesh On EFFECTIVE TROPICAL CYCLONE WARNING IN BANGLADESH Presented At JMA/WMO WORKSHOP ON EFFECTIVE TROPICAL CYCLONE WARNING IN SOUTHEAST ASIA Tokyo, Japan,11-14 March 2014 By Sayeed
JMA Tsunami Warning Services. Takeshi KOIZUMI Senior Coordinator for International Earthquake and Tsunami Information Japan Meteorological Agency
 JMA Tsunami Warning Services Takeshi KOIZUMI Senior Coordinator for International Earthquake and Tsunami Information Japan Meteorological Agency Tectonic Setting of Japan (Headquarters for Earthquake Research
JMA Tsunami Warning Services Takeshi KOIZUMI Senior Coordinator for International Earthquake and Tsunami Information Japan Meteorological Agency Tectonic Setting of Japan (Headquarters for Earthquake Research
Groundwater and Coastal Phenomena Preceding the 1944 Tsunami (Tonankai Earthquake)
 Groundwater and Coastal Phenomena Preceding the 1944 Tsunami (Tonankai Earthquake) Masataka Ando Institute of Earth Sciences, Academia Sinica ando@earth.sinica.edu.tw Study Area Characteristics of large
Groundwater and Coastal Phenomena Preceding the 1944 Tsunami (Tonankai Earthquake) Masataka Ando Institute of Earth Sciences, Academia Sinica ando@earth.sinica.edu.tw Study Area Characteristics of large
Developing fragility functions for tsunami damage estimation using the numerical model and satellite imagery
 Developing fragility functions for tsunami damage estimation using the numerical model and satellite imagery Shunichi KOSHIMURA 1 and Hideaki YANAGISAWA 2 1 Associate Professor, Disaster Control Research
Developing fragility functions for tsunami damage estimation using the numerical model and satellite imagery Shunichi KOSHIMURA 1 and Hideaki YANAGISAWA 2 1 Associate Professor, Disaster Control Research
FLOOD HAZARD AND RISK ASSESSMENT IN MID- EASTERN PART OF DHAKA, BANGLADESH
 FLOOD HAZARD AND RISK ASSESSMENT IN MID- EASTERN PART OF DHAKA, BANGLADESH Muhammad MASOOD MEE07180 Supervisor: Prof. Kuniyoshi TAKEUCHI ABSTRACT An inundation simulation has been done for the mid-eastern
FLOOD HAZARD AND RISK ASSESSMENT IN MID- EASTERN PART OF DHAKA, BANGLADESH Muhammad MASOOD MEE07180 Supervisor: Prof. Kuniyoshi TAKEUCHI ABSTRACT An inundation simulation has been done for the mid-eastern
GROUND MOTION SPECTRAL INTENSITY PREDICTION WITH STOCHASTIC GREEN S FUNCTION METHOD FOR HYPOTHETICAL GREAT EARTHQUAKES ALONG THE NANKAI TROUGH, JAPAN
 GROUND MOTION SPECTRAL INTENSITY PREDICTION WITH STOCHASTIC GREEN S FUNCTION METHOD FOR HYPOTHETICAL GREAT EARTHQUAKES ALONG THE NANKAI TROUGH, JAPAN Masayuki YOSHIMI 1, Yasuto KUWAHARA 2, Masayuki YAMADA
GROUND MOTION SPECTRAL INTENSITY PREDICTION WITH STOCHASTIC GREEN S FUNCTION METHOD FOR HYPOTHETICAL GREAT EARTHQUAKES ALONG THE NANKAI TROUGH, JAPAN Masayuki YOSHIMI 1, Yasuto KUWAHARA 2, Masayuki YAMADA
SMR/ May Simulation Analyses of Tsunami caused by Chilean and Nihon-Kai Chubu Earthquakes at Nuclear Power Plant Sites in Japan
 SMR/1839-2 Workshop on the Physics of Tsunami, Hazard Assessment Methods and Disaster Risk Management (Theories and Practices for Implementing Proactive Countermeasures) 14-18 May 2007 Simulation Analyses
SMR/1839-2 Workshop on the Physics of Tsunami, Hazard Assessment Methods and Disaster Risk Management (Theories and Practices for Implementing Proactive Countermeasures) 14-18 May 2007 Simulation Analyses
Tsunami source of the 2004 off the Kii Peninsula earthquakes inferred from offshore tsunami and coastal tide gauges
 LETTER Earth Planets Space, 57, 173 178, 2005 Tsunami source of the 2004 off the Kii Peninsula earthquakes inferred from offshore tsunami and coastal tide gauges Kenji Satake 1, Toshitaka Baba 2, Kenji
LETTER Earth Planets Space, 57, 173 178, 2005 Tsunami source of the 2004 off the Kii Peninsula earthquakes inferred from offshore tsunami and coastal tide gauges Kenji Satake 1, Toshitaka Baba 2, Kenji
PROOF COPY [WW/2006/022653] QWW
![PROOF COPY [WW/2006/022653] QWW PROOF COPY [WW/2006/022653] QWW](/thumbs/96/127946363.jpg) 1 2 3 4 Source Constraints and Model Simulation of the December 26, 2004, Indian Ocean Tsunami Stéphan T. Grilli, M.ASCE 1 ; Mansour Ioualalen 2 ; Jack Asavanant 3 ; Fengyan Shi 4 ; James T. Kirby, M.ASCE
1 2 3 4 Source Constraints and Model Simulation of the December 26, 2004, Indian Ocean Tsunami Stéphan T. Grilli, M.ASCE 1 ; Mansour Ioualalen 2 ; Jack Asavanant 3 ; Fengyan Shi 4 ; James T. Kirby, M.ASCE
RELATION BETWEEN RAYLEIGH WAVES AND UPLIFT OF THE SEABED DUE TO SEISMIC FAULTING
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 1359 RELATION BETWEEN RAYLEIGH WAVES AND UPLIFT OF THE SEABED DUE TO SEISMIC FAULTING Shusaku INOUE 1,
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 1359 RELATION BETWEEN RAYLEIGH WAVES AND UPLIFT OF THE SEABED DUE TO SEISMIC FAULTING Shusaku INOUE 1,
Figure 3.1: Illustration showing the bathymetry s role for the tsunami propagation following the earth quake 26 December 2004 outside of Sumatra.
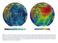 Figure 3.1: Illustration showing the bathymetry s role for the tsunami propagation following the earth quake 26 December 2004 outside of Sumatra. The left globe shows the seafloor bathymetry as portrayed
Figure 3.1: Illustration showing the bathymetry s role for the tsunami propagation following the earth quake 26 December 2004 outside of Sumatra. The left globe shows the seafloor bathymetry as portrayed
RELOCATION OF LARGE EARTHQUAKES ALONG THE SUMATRAN FAULT AND THEIR FAULT PLANES
 Synopses of Master Papers Bulletin of IISEE, 47, 25-30, 2013 RELOCATION OF LARGE EARTHQUAKES ALONG THE SUMATRAN FAULT AND THEIR FAULT PLANES Biana Rahayu Wulandari MEE11605 Supervisor: Nobuo HURUKAWA ABSTRACT
Synopses of Master Papers Bulletin of IISEE, 47, 25-30, 2013 RELOCATION OF LARGE EARTHQUAKES ALONG THE SUMATRAN FAULT AND THEIR FAULT PLANES Biana Rahayu Wulandari MEE11605 Supervisor: Nobuo HURUKAWA ABSTRACT
THE DEPOSITS OF TSUNAMIS WESLEY PESANTEZ, CATHERINE NIELD, COLIN WINTER
 THE DEPOSITS OF TSUNAMIS WESLEY PESANTEZ, CATHERINE NIELD, COLIN WINTER AN OVERVIEW OF OUR SEMINAR WHAT IS A TSUNAMI WHY STUDY TSUNAMIS PROPERTIES OF TSUNAMIS TSUNAMI HYDRODYNAMICS IDEALIZED DEPOSITS SEDIMENT
THE DEPOSITS OF TSUNAMIS WESLEY PESANTEZ, CATHERINE NIELD, COLIN WINTER AN OVERVIEW OF OUR SEMINAR WHAT IS A TSUNAMI WHY STUDY TSUNAMIS PROPERTIES OF TSUNAMIS TSUNAMI HYDRODYNAMICS IDEALIZED DEPOSITS SEDIMENT
News Release December 30, 2004 The Science behind the Aceh Earthquake
 News Release December 30, 2004 The Science behind the Aceh Earthquake PASADENA, Calif. - Kerry Sieh, the Robert P. Sharp Professor of Geology at the California Institute of Technology and a member of Caltech's
News Release December 30, 2004 The Science behind the Aceh Earthquake PASADENA, Calif. - Kerry Sieh, the Robert P. Sharp Professor of Geology at the California Institute of Technology and a member of Caltech's
Tsunami risk assessment in the Marquesas Islands (French Polynesia) through numerical modeling of generic far-field events
 Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences (2001) 1: 233 242 c European Geophysical Society 2001 Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Tsunami risk assessment in the Marquesas Islands (French Polynesia)
Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences (2001) 1: 233 242 c European Geophysical Society 2001 Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Tsunami risk assessment in the Marquesas Islands (French Polynesia)
