Improvements in research knowledge: a challenge for engineering
|
|
|
- Hilda Newton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Improvements in research knowledge: a challenge for engineering R. K. H. Falconer Group Manager Natural Hazards Group, Institute of Geological and Nuclear Sciences Ltd NZSEE 2002 Conference ABSTRACT: Research on hazard and risk provides continual improvements in knowledge of processes and associated risks. This provides a challenge for engineering as the lifetimes of many structures will be significantly longer than the lifetime of state of the art research knowledge. For example we now understand a lot about near fault effects that mean some structures built near faults are not safe according to current knowledge even though they were state of the art structures at the time of construction. We must not feel uncomfortable about new knowledge but we must acknowledge it. We need to consider: How do we cope with the changes in research knowledge for structures that are already built? How do we respond to the fact that research knowledge will undoubtedly change our views in the future for structures that we are designing now? 1 INTRODUCTION Research on hazard and risk produces continual improvements in knowledge of hazard processes and the consequent risks. This provides a significant challenge for the engineering community as the lifetimes of many built systems and structures are significantly longer than the lifetime of state of the art research knowledge. Take the example of building of structures near fault lines. Engineers have long recognized the hazards of fault rupture ground displacement and high shaking near faults and have taken precautions. However, in the last decade or so the importance of fault rupture directivity and fault fling have become more significant as data have been obtained close to faults in actual events. In the 1999 Taiwan earthquake ground velocities were measured that were at least twice those previously recorded anywhere. How do we cope with this given that there are structures that will be expected to last 50 years or more that are either already in existence near fault lines or are currently being designed? The problems are probably more severe for the engineering community that any others. Designers of computer hard disks or laser printers are scarcely required to consider issues of how those pieces of equipment may perform in 25 years time, or probably even 5 or 10 years. Engineers must consider the long term. 2 PRESENT KNOWLEDGE: EXAMPLES To explore further it is interesting to consider some examples from New Zealand where changes
2 in knowledge have impacted built structures. Notwithstanding this being the Earthquake Engineering Society I will give some examples that relate to hazards other than earthquakes. I refer just to natural hazards but clearly technological and social hazards should also be considered. New Zealand has a large number of natural hazards and the engineering community is involved with the issues of all of them. Frequently decisions relating to planning or the economics of building or retrofitting structures involve choices between expenditure on several competing issues. Decision-makers have to balance all risks in many cases. My choice of examples is not particularly systematic and they vary in the scale of the issues. They are just some interesting examples. Photos and figures for each example are available. Matahina Dam: Matahina Dam, an 80 metre high 400 metre long earth core dam in the Bay of Plenty was displaced and significantly damaged in the 1987 Edgecumbe earthquake. Repairs to the dam were made during the following two years. In the course of the work it was learned that some of the materials in the core of the dam might be more subject to failure than had been intended in the design. Studies associated with the repairs also looked at the geology around the area. Those and more regional geological studies done on a research basis for understanding New Zealand tectonics led to the conclusion that the potential for significant earthquake fault displacement through the dam site was much higher than had been previously thought. This led to a very major rebuild of the dam in the late 1990s. This was probably one of the most significant dam rebuilds anywhere in the world. Our present state of knowledge of faulting hazard in the area simply was not known at the time the dam was built in the 1950s and the designers built to what was then best practice. There can be no criticism of them, and only praise for those who have taken the decision to invest in the recent upgrade. Haywards Electricity substation: The Haywards substation in the Hutt Valley is the North Island terminal of the Cook Strait DC power cable and a major substation for the whole New Zealand electricity grid system. It is built only 150 metres from the Wellington fault line. The existence of the fault line was known when the substation was built more than 40 years ago and it was designed for what were assumed to be reasonable ground accelerations. Data from earthquakes over the last few decades have progressively increased expected accelerations close to faults and much work has been done retrofitting the substation. Retrofitting has been ongoing as knowledge has increased. For this structure it has been possible to do this type of retrofitting and so keep up with knowledge. Cook Strait Ferry Terminal: The Cook Strait Ferry Terminal in Wellington is built on reclaimed land and is right over the trace of the Wellington fault. Geological information now gives us an estimate of a return period for a rupture on the Wellington fault of years with the last rupture around 600 years ago. It is interesting to consider whether a ferry terminal would be built there with today s understanding. Are we, should we be, concerned enough to consider possible relocation? Active Subsurface Faults: The Institute of Geological & Nuclear Sciences (GNS) has a database of active faults in New Zealand. The database is built from GNS and other organization s research and is continually updated. Examination of this database and some of the latest geological maps will show for example that there is no significant active fault identified in NW Nelson. However, a very detailed deployment of earthquake monitoring equipment for a research experiment covering the central part of New Zealand in the mid 1990s clearly detected earthquakes that indicate an active fault in NW Nelson that links with the Taranaki fault system to the north and other faults to the south. The faults database and the geological mapping both are state of the art, so how do we have this apparent contradiction? The problem arises because the database is focused on surface faults and this particular one doesn t have an obvious surface expression. In the NW Nelson case there are no major engineering structures of concern but one can expect that this type of increase in knowledge will occur in many other places where there may be structures of concern.
3 Maui Gas Field: The Maui A Platform was built in the 1970s. Its location and indeed the existence of the oil are related to the Cape Egmont Fault zone. It wasn t however, until investigation works started for the building of the Maui B platform in the 1990s that it was realized that the fault extends right to the seabed and indeed there is a seafloor offset that can be seen. Maui B and the pipeline from it were designed for this but Maui A was not. In this case it is probably not of concern because the design was conservative for earthquakes given many other hazards of the site. National Earthquake Hazard Model: The current loadings code takes into account earthquakes and to a large extent was based on hazard maps prepared in the 1980s. New probabilistic seismic hazard assessments carried out in the 1990s dramatically change the expected ground shaking in some areas, particularly around the Alpine fault. New loadings codes being developed now take account of the new data but of course there are many structures built to old codes. They were built to state of the art knowledge then but now the knowledge is different. Retrofitting Buildings: In New Zealand buildings have generally been built according to the building codes of the time. With respect to earthquake resistance codes have altered several times. There is no discredit to people having built buildings to the codes that nowadays we consider to be insufficient. However, I know it is a source of much concern particularly to many members of this Society, that in spite of intense lobbying some local councils will not put adequate pressure on building owners to upgrade their buildings. Abbotsford Landslide: The Abbottsford, Dunedin, landslide of 1979 did not injure anyone but destroyed or damaged over 25 houses. The social and political impact was substantial and led to important revisions of the Building Act and application of new measures in many urban plans. It appears to be an unfortunate fact that major changes in codes and regulations often only come about when there are critical incidents. Clyde Dam: The Clyde Dam was a large hydro-electric dam expected to cost around $500M when construction commenced in the early 1980s. It was only after construction was well underway that it was realized that the filling of the lake behind the dam could create instability in rock slopes that might produce catastrophic landslides into the lake. Stabilization work done on these landslides alone cost more than $500M and delayed the project by two years. The nature of the landslides was simply not understood at the time the project started. Research knowledge dramatically changed about that time and led to the major engineering issues. It is interesting to speculate what might have been done if the landslide issue had not become apparent until after the dam and lake had been completed. Auckland Volcanic Risk: Geological research in the Auckland region and the central North Island in the last few years provides significant new information on the frequency of eruptions and the dispersal of ash. The probability of significant volcanic impact on Auckland City from either a local event or ash from a distant event is now known to be comparable to the probability of major earthquake impact in Wellington; about 10% in 50 years. It is surely fair to say that engineering projects in Auckland do not give the same attention to volcanic impact as engineering projects in Wellington give to earthquake impact. Tsunami Risk: The majority of New Zealanders probably think that the major tsunami risk in New Zealand arises from earthquakes far away on the Pacific Rim, for example those from Chile in However, there is significant risk from local earthquakes. In 1947 there was seaweed in the power lines on the main highway north of Gisborne from a tsunami. Such an event today, particularly on a summer surfing day, would have a significant social if not physical impact. Yet only last year we had Gisborne people driving down to the coast to look for a possible tsunami from an earthquake that occurred offshore. We suspect that ongoing geological research may reveal that the tsunami hazard in some coastal areas is
4 comparable to the volcanic and earthquake hazard. What of the risk to structures? Flood Risk: Visibility of risk also seems to influence decisions on planning and mitigation. For example the Wellington Region is happy to spend $100M over 10 years for stop bank strengthening in the Hutt Valley for the 450-year level flood. However, it has not been possible to get acceptance for even a $10,000 study of the fact that the 450-year earthquake will likely alter the level of the land by up to 1.5m, a more than insignificant effect on the river drainage. Is it that the small but frequent and visible floods raise the consciousness far more than small earthquakes? 3 FUTURE KNOWLEDGE The above examples are for existing structures and known hazards today. How do we cope with the fact that research knowledge is continually improving and may change the future risks for structures that exist now or even for those that we have yet to design? Some hints of significant in current research are as follows: A four-month deployment of over 100 earthquake-monitoring systems across the central North Island provides far greater detail on earthquake activity than we have known previously. We have known that there was persistent earthquake activity in the Waiouru area but we now see a much clearer picture of it. It is possible that the activity relates to ongoing deformation from the load of Mt Ruapehu. Will it change our thinking about the Rangipo Power Scheme tunnels, dams and aqueducts? Earth deformation measurement with GPS enables us to measure the buildup of strain throughout the country. We can see a very high concentration of strain in the central South Island and to a lesser extent southern North Island. Will we reach the point where we can forecast earthquakes, even if only their high probability in the next months or year rather than shorter term forecasts? Would that have an impact on decisions about the siting or construction of major engineering projects? Basin resonance advances in computing power now enable us to model the 3-D time sequence response of basins to earthquakes. A model of rupture on the Wellington fault shows that the subsurface configuration of the harbour basin produces marked amplification and resonance in earthquake shaking at some areas of the Wellington and Hutt Valley urban centres. The results are not yet fully calibrated but what if they show that possible forces exceed the codes to which existing buildings have been built? Modelling of urban fire spread is expected to reveal localities that may be particularly at risk of conflagration following a major earthquake. Will individuals and local authorities take steps to mitigate the risks? 4 COMMENT Research knowledge is always going to increase. We must not feel uncomfortable about new knowledge but we must acknowledge it. The engineering community understands that structures built as state of the art at the time they were built may not be adequate with today s knowledge. However, many planners, business leaders and decision-makers do not have the same level of understanding. There is a real challenge for the engineering community to bridge the gap in order to have good risk assessments done and acted upon. Designing today for risks that we don t yet understand or even recognize but may do in the future, is even more of a challenge. Risk assessment for future risk undoubtedly is difficult. GNS is commencing a FRST funded research programme on decision support modeling for risk assessment. There will be challenge in working on the present day decision making but it is hoped to also consider future decision-making.
5
Interpretive Map Series 24
 Oregon Department of Geology and Mineral Industries Interpretive Map Series 24 Geologic Hazards, and Hazard Maps, and Future Damage Estimates for Six Counties in the Mid/Southern Willamette Valley Including
Oregon Department of Geology and Mineral Industries Interpretive Map Series 24 Geologic Hazards, and Hazard Maps, and Future Damage Estimates for Six Counties in the Mid/Southern Willamette Valley Including
Update on the It s Our Fault project
 Report 12.552 Date 29 October 2012 File 12/01/01 Committee Author CDEM Group Bruce Pepperell, Regional Manager, WREMO Update on the It s Our Fault project 1. Purpose To inform the CDEM Group of progress
Report 12.552 Date 29 October 2012 File 12/01/01 Committee Author CDEM Group Bruce Pepperell, Regional Manager, WREMO Update on the It s Our Fault project 1. Purpose To inform the CDEM Group of progress
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Measuring Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the power or strength of an earthquake are: Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale based
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Measuring Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the power or strength of an earthquake are: Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale based
Wainui Beach Management Strategy (WBMS) Summary of Existing Documents. GNS Tsunami Reports
 Wainui Beach Management Strategy (WBMS) Summary of Existing Documents GNS Tsunami Reports a) Review of Tsunami Hazard and Risk in New Zealand ( National Risk Report ) b) Review of New Zealand s Preparedness
Wainui Beach Management Strategy (WBMS) Summary of Existing Documents GNS Tsunami Reports a) Review of Tsunami Hazard and Risk in New Zealand ( National Risk Report ) b) Review of New Zealand s Preparedness
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative
 Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative VANUATU September 211 Country Risk Profile: VANUATU is expected to incur, on average, 48 million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative VANUATU September 211 Country Risk Profile: VANUATU is expected to incur, on average, 48 million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative
 Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative TIMOR-LESTE September Timor-Leste is expected to incur, on average, 5.9 million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and tropical cyclones.
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative TIMOR-LESTE September Timor-Leste is expected to incur, on average, 5.9 million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and tropical cyclones.
Seismic Hazard Abatement Program
 Seismic Hazard Abatement Program Recommendations To take the first steps toward a seismic mitigation program for older existing buildings To improve our current regulatory system for implementation of
Seismic Hazard Abatement Program Recommendations To take the first steps toward a seismic mitigation program for older existing buildings To improve our current regulatory system for implementation of
BUILDING STRUCTURES ON OR NEAR STEEP SLOPES
 BUILDING STRUCTURES ON OR NEAR STEEP SLOPES Benefits of Building Structures on or Near Steep Slopes Why would you ever do this? In some instances, it is the steep slope that people want to be near. Like
BUILDING STRUCTURES ON OR NEAR STEEP SLOPES Benefits of Building Structures on or Near Steep Slopes Why would you ever do this? In some instances, it is the steep slope that people want to be near. Like
Natural Disasters Spring, LECTURE #8: Earthquake Disasters: Monitoring & Mitigation. Date: 1 Feb 2018 (lecturer: Dr.
 GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #8: Earthquake Disasters: Monitoring & Mitigation Date: 1 Feb 2018 (lecturer: Dr. Shawn Wright) I. Exam I - Reminder Feb 6 th next class details:
GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #8: Earthquake Disasters: Monitoring & Mitigation Date: 1 Feb 2018 (lecturer: Dr. Shawn Wright) I. Exam I - Reminder Feb 6 th next class details:
2. Tsunami Source Details
 2. Tsunami Source Details The Northland area faces a range of potential tsunamigenic sources that include several local and distant fault systems and underwater landslides. A NIWA study (Goff et al. 2006)
2. Tsunami Source Details The Northland area faces a range of potential tsunamigenic sources that include several local and distant fault systems and underwater landslides. A NIWA study (Goff et al. 2006)
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative
 Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative TUVALU is expected to incur, on average,. million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and tropical cyclones. In the next 5 years, has
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative TUVALU is expected to incur, on average,. million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and tropical cyclones. In the next 5 years, has
Hazard Resilience Index (HRI) Earthquakes, Tsunamis, and Volcanoes
 Hazard Index (HRI) Earthquakes, Tsunamis, and Volcanoes Earthquakes Tsunamis Volcano-Ash Falls, Projectiles and Lateral Blasts, Pyroclastic Flows and Lava Flows Earthquakes, Tsunamis and Volcanoes Please
Hazard Index (HRI) Earthquakes, Tsunamis, and Volcanoes Earthquakes Tsunamis Volcano-Ash Falls, Projectiles and Lateral Blasts, Pyroclastic Flows and Lava Flows Earthquakes, Tsunamis and Volcanoes Please
Slide 1: Earthquake sequence (with colour coding around big events and subsequent period). Illustrates migration to the east initially into
 Slide 1: Earthquake sequence (with colour coding around big events and subsequent period). Illustrates migration to the east initially into Christchurch, but now moving away (23 December in particular).
Slide 1: Earthquake sequence (with colour coding around big events and subsequent period). Illustrates migration to the east initially into Christchurch, but now moving away (23 December in particular).
The Seismic Hazardscape of New Zealand
 The Seismic Hazardscape of New Zealand Mark Stirling Professor of Earthquake Science Introduction Plate tectonic setting of New Zealand Seismic hazards for University of Otago campuses Kaikoura earthquake
The Seismic Hazardscape of New Zealand Mark Stirling Professor of Earthquake Science Introduction Plate tectonic setting of New Zealand Seismic hazards for University of Otago campuses Kaikoura earthquake
Hawke s Bay Liquefaction Hazard Report - Frequently Asked Questions
 Hawke s Bay Liquefaction Hazard Report - Frequently Asked Questions What is liquefaction? Liquefaction occurs when an earthquake shakes up water-logged sediments. As a result, the soil behaves like a liquid
Hawke s Bay Liquefaction Hazard Report - Frequently Asked Questions What is liquefaction? Liquefaction occurs when an earthquake shakes up water-logged sediments. As a result, the soil behaves like a liquid
New Zealand s Next Top Model: integrating tsunami modelling into land use planning
 New Zealand s Next Top Model: integrating tsunami modelling into land use planning Wendy Saunders (MZNZPI), Gegar Prasetya, Graham Leonard GNS Science, Lower Hutt, w.saunders@gns.cri.nz In April 2011 a
New Zealand s Next Top Model: integrating tsunami modelling into land use planning Wendy Saunders (MZNZPI), Gegar Prasetya, Graham Leonard GNS Science, Lower Hutt, w.saunders@gns.cri.nz In April 2011 a
Yev Kontar. Illinois State Geological Survey, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 Addressing Caribbean Geophysical Hazards through the Continuously Operating Caribbean GPS Observational Network (COCONet) and International Ocean Drilling Program (IODP) Yev Kontar Illinois State Geological
Addressing Caribbean Geophysical Hazards through the Continuously Operating Caribbean GPS Observational Network (COCONet) and International Ocean Drilling Program (IODP) Yev Kontar Illinois State Geological
New A-Level Physical Geography
 Half Term 1 3.1 Physical Geography: 3.1.5 Hazards: Plate Tectonics This optional section of our specification focuses on the lithosphere and the atmosphere, which intermittently but regularly present natural
Half Term 1 3.1 Physical Geography: 3.1.5 Hazards: Plate Tectonics This optional section of our specification focuses on the lithosphere and the atmosphere, which intermittently but regularly present natural
Earthquakes. Earthquake Magnitudes 10/1/2013. Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena
 Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena Fall 2013 Northridge 1994 Kobe 1995 Mexico City 1985 China 2008 Earthquakes Earthquake Magnitudes Earthquake Magnitudes Richter Magnitude
Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena Fall 2013 Northridge 1994 Kobe 1995 Mexico City 1985 China 2008 Earthquakes Earthquake Magnitudes Earthquake Magnitudes Richter Magnitude
Initiative. Country Risk Profile: papua new guinea. Better Risk Information for Smarter Investments PAPUA NEW GUINEA.
 Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative PAPUA NEW GUINEA September 211 Country Risk Profile: papua new is expected to incur, on average, 85 million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative PAPUA NEW GUINEA September 211 Country Risk Profile: papua new is expected to incur, on average, 85 million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes
This article is provided courtesy of the American Museum of Natural History.
 Avoiding Earthquake Surprises in the Pacific Northwest This article is provided courtesy of the American Museum of Natural History. How Vulnerable Is the Pacific Northwest? Cascadia is a region in the
Avoiding Earthquake Surprises in the Pacific Northwest This article is provided courtesy of the American Museum of Natural History. How Vulnerable Is the Pacific Northwest? Cascadia is a region in the
How to communicate Cascadia Subduction Zone earthquake hazards
 How to communicate Cascadia Subduction Zone earthquake hazards Tom Brocher Research Geophysicist Earthquake Science Center U.S. Geological Survey Menlo Park, California Seattle Post-Intelligencer Lessons
How to communicate Cascadia Subduction Zone earthquake hazards Tom Brocher Research Geophysicist Earthquake Science Center U.S. Geological Survey Menlo Park, California Seattle Post-Intelligencer Lessons
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative
 Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative PALAU September is expected to incur, on average,.7 million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and tropical cyclones. In the next 5 years,
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative PALAU September is expected to incur, on average,.7 million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and tropical cyclones. In the next 5 years,
3l NATURAL HAZARDS AND UNSTABLE GROUND
 Page 1 of Section 3l 3l NATURAL HAZARDS AND UNSTABLE GROUND 3l.1 Introduction A natural hazard is the result of natural processes that form, shape and change the environment and interact or potentially
Page 1 of Section 3l 3l NATURAL HAZARDS AND UNSTABLE GROUND 3l.1 Introduction A natural hazard is the result of natural processes that form, shape and change the environment and interact or potentially
The Impact of the 2010 Darfield (Canterbury) Earthquake on the Geodetic Infrastructure in New Zealand 1
 The Impact of the 2010 Darfield (Canterbury) Earthquake on the Geodetic Infrastructure in New Zealand 1 Graeme BLICK, John BEAVAN, Chris CROOK, Nic DONNELLY Keywords: Darfield Earthquake, control, survey,
The Impact of the 2010 Darfield (Canterbury) Earthquake on the Geodetic Infrastructure in New Zealand 1 Graeme BLICK, John BEAVAN, Chris CROOK, Nic DONNELLY Keywords: Darfield Earthquake, control, survey,
VULNERABILITY OF WATER SUPPLY TO NATURAL HAZARDS IN JAMAICA
 VULNERABILITY OF WATER SUPPLY TO NATURAL HAZARDS IN JAMAICA RAFI AHMAD rafi.ahmad@uwimona.edu.jm Unit for disaster studies, Department of Geography & Geology, The University of the West Indies, Mona Kingston
VULNERABILITY OF WATER SUPPLY TO NATURAL HAZARDS IN JAMAICA RAFI AHMAD rafi.ahmad@uwimona.edu.jm Unit for disaster studies, Department of Geography & Geology, The University of the West Indies, Mona Kingston
This page answers some of the questions people have been asking about the earthquakes in Christchurch and Canterbury since September 2010.
 1 of 5 04/12/2012 11:05 a.m. This page answers some of the questions people have been asking about the earthquakes in Christchurch and Canterbury since September 2010. Why are we getting so many earthquakes?
1 of 5 04/12/2012 11:05 a.m. This page answers some of the questions people have been asking about the earthquakes in Christchurch and Canterbury since September 2010. Why are we getting so many earthquakes?
Geotechnical issues in seismic assessments: When do I need a geotechnical specialist?
 Geotechnical issues in seismic assessments: When do I need a geotechnical specialist? B.H. Rama & S.J. Palmer Tonkin & Taylor Ltd (T+T), Wellington, New Zealand. 2016 NZSEE Conference ABSTRACT: The Canterbury
Geotechnical issues in seismic assessments: When do I need a geotechnical specialist? B.H. Rama & S.J. Palmer Tonkin & Taylor Ltd (T+T), Wellington, New Zealand. 2016 NZSEE Conference ABSTRACT: The Canterbury
Natural hazards in Glenorchy Summary Report May 2010
 Natural hazards in Glenorchy Summary Report May 2010 Contents Glenorchy s hazardscape Environment setting Flood hazard Earthquakes and seismic hazards Hazards Mass movement Summary Glossary Introduction
Natural hazards in Glenorchy Summary Report May 2010 Contents Glenorchy s hazardscape Environment setting Flood hazard Earthquakes and seismic hazards Hazards Mass movement Summary Glossary Introduction
Earthquake Risk Assessment of Flood Protection Assets in the Wellington Region
 Earthquake Risk Assessment of Flood Protection Assets in the Wellington Region A. K. Murashev, R Davey, P. Brabhaharan & B. Curley Opus International Consultants Limited, Wellington, New Zealand. 2006
Earthquake Risk Assessment of Flood Protection Assets in the Wellington Region A. K. Murashev, R Davey, P. Brabhaharan & B. Curley Opus International Consultants Limited, Wellington, New Zealand. 2006
Level 2 Earth and Space Science, 2017
 91191 911910 2SUPERVISOR S Level 2 Earth and Space Science, 2017 91191 Demonstrate understanding of the causes of extreme Earth events in New Zealand 9.30 a.m. Thursday 30 November 2017 Credits: Four Achievement
91191 911910 2SUPERVISOR S Level 2 Earth and Space Science, 2017 91191 Demonstrate understanding of the causes of extreme Earth events in New Zealand 9.30 a.m. Thursday 30 November 2017 Credits: Four Achievement
Guidelines for Site-Specific Seismic Hazard Reports for Essential and Hazardous Facilities and Major and Special-Occupancy Structures in Oregon
 Guidelines for Site-Specific Seismic Hazard Reports for Essential and Hazardous Facilities and Major and Special-Occupancy Structures in Oregon By the Oregon Board of Geologist Examiners and the Oregon
Guidelines for Site-Specific Seismic Hazard Reports for Essential and Hazardous Facilities and Major and Special-Occupancy Structures in Oregon By the Oregon Board of Geologist Examiners and the Oregon
An entire branch of Earth science, called, is devoted to the study of earthquakes.
 Lesson One Essential Question Where do earthquakes take place? What causes earthquakes? What are three different types of faults that occur at plate boundaries? How does energy from earthquakes travels
Lesson One Essential Question Where do earthquakes take place? What causes earthquakes? What are three different types of faults that occur at plate boundaries? How does energy from earthquakes travels
Tectonic Processes and Hazards Enquiry Question 1: Why are some locations more at risk from tectonic hazards?
 Tectonic Processes and Hazards Enquiry Question 1: Why are some locations more at risk from tectonic hazards? Key words Basalt Andesite Rhyolite Benioff Zone Subduction zone Crustal fracturing Definition
Tectonic Processes and Hazards Enquiry Question 1: Why are some locations more at risk from tectonic hazards? Key words Basalt Andesite Rhyolite Benioff Zone Subduction zone Crustal fracturing Definition
Application of a GIS for Earthquake Hazard Assessment and Risk Mitigation in Vietnam
 Application of a GIS for Earthquake Hazard Assessment and Risk Mitigation in Vietnam Nguyen Hong Phuong Earthquake Information and Tsunami Warning Centre, VAST OUTLINE Introduction Fault Source Model and
Application of a GIS for Earthquake Hazard Assessment and Risk Mitigation in Vietnam Nguyen Hong Phuong Earthquake Information and Tsunami Warning Centre, VAST OUTLINE Introduction Fault Source Model and
The Canterbury Earthquakes: Scientific answers to critical questions
 OFFICE OF THE PRIME MINISTER S SCIENCE ADVISORY COMMITTEE The Canterbury Earthquakes: Scientific answers to critical questions The Canterbury region has had six months of unexpected and extremely difficult
OFFICE OF THE PRIME MINISTER S SCIENCE ADVISORY COMMITTEE The Canterbury Earthquakes: Scientific answers to critical questions The Canterbury region has had six months of unexpected and extremely difficult
The Cascading Hazards from Cascadia s Earthquakes
 Tsunamis The Cascading Hazards from Cascadia s Earthquakes Earthquakes (Nisqually earthquake, Seattle, WA) Volcanoes (Mt St Helens eruption, WA) Joan Gomberg gomberg@usgs.gov Landslides (Oso landslide,
Tsunamis The Cascading Hazards from Cascadia s Earthquakes Earthquakes (Nisqually earthquake, Seattle, WA) Volcanoes (Mt St Helens eruption, WA) Joan Gomberg gomberg@usgs.gov Landslides (Oso landslide,
Word Cards. 2 map. 1 geographic representation. a description or portrayal of the Earth or parts of the Earth. a visual representation of an area
 Name: Date: Hour: Word Cards 1 geographic representation a description or portrayal of the Earth or parts of the Earth Example: A map is a representation of an actual location or place. 2 map a visual
Name: Date: Hour: Word Cards 1 geographic representation a description or portrayal of the Earth or parts of the Earth Example: A map is a representation of an actual location or place. 2 map a visual
Elastic Rebound Theory
 Earthquakes Elastic Rebound Theory Earthquakes occur when strain exceeds the strength of the rock and the rock fractures. The arrival of earthquakes waves is recorded by a seismograph. The amplitude of
Earthquakes Elastic Rebound Theory Earthquakes occur when strain exceeds the strength of the rock and the rock fractures. The arrival of earthquakes waves is recorded by a seismograph. The amplitude of
KNOWLEDGE NOTE 5-1. Risk Assessment and Hazard Mapping. CLUSTER 5: Hazard and Risk Information and Decision Making. Public Disclosure Authorized
 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized KNOWLEDGE NOTE 5-1 CLUSTER 5: Hazard and Risk Information and Decision Making Risk Assessment
Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized KNOWLEDGE NOTE 5-1 CLUSTER 5: Hazard and Risk Information and Decision Making Risk Assessment
b. Why is the area affected by each earthquake circular or nearly circular? Where is the epicenter of each quake located?
 Name: Skill Sheet 29-A Interpreting Geologic Hazard Maps Plate tectonics and the weather are often the cause of geologic hazards such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and flooding. Geologic hazard events
Name: Skill Sheet 29-A Interpreting Geologic Hazard Maps Plate tectonics and the weather are often the cause of geologic hazards such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and flooding. Geologic hazard events
Seismic Hazard Switzerland. When, where, and how often does certain shaking occur in Switzerland?
 Seismic Hazard Switzerland When, where, and how often does certain shaking occur in Switzerland? Hazard The hazard map shows where and how often certain incidents of horizontal acceleration are likely.
Seismic Hazard Switzerland When, where, and how often does certain shaking occur in Switzerland? Hazard The hazard map shows where and how often certain incidents of horizontal acceleration are likely.
Disaster Management and Spatial Data An Experience of Sri Lanka for Joint project team meeting 2012
 Disaster Management and Spatial Data An Experience of Sri Lanka for Joint project team meeting 2012 1 by Padma Kumara Withana Provincial Surveyor General Uva Province 2 Out line ü Introduction ü Natural
Disaster Management and Spatial Data An Experience of Sri Lanka for Joint project team meeting 2012 1 by Padma Kumara Withana Provincial Surveyor General Uva Province 2 Out line ü Introduction ü Natural
2016 Kaikoura Earthquake (NZ) Effects & Phenomena. Trevor Matuschka With special acknowledgement Dan Forster (Damsafety Intelligence)
 2016 Kaikoura Earthquake (NZ) Effects & Phenomena Trevor Matuschka With special acknowledgement Dan Forster (Damsafety Intelligence) Contents 1. Kaikoura Earthquake where and what happened 2. Seismic and
2016 Kaikoura Earthquake (NZ) Effects & Phenomena Trevor Matuschka With special acknowledgement Dan Forster (Damsafety Intelligence) Contents 1. Kaikoura Earthquake where and what happened 2. Seismic and
This seminar is jointly presented by the Body Corporate Chairs Group, the Wellington Inner City Associa>on and the Wellington City Council.
 This seminar is jointly presented by the Body Corporate Chairs Group, the Wellington Inner City Associa>on and the Wellington City Council. Please note that these slides do not represent legal advice but
This seminar is jointly presented by the Body Corporate Chairs Group, the Wellington Inner City Associa>on and the Wellington City Council. Please note that these slides do not represent legal advice but
Three Fs of earthquakes: forces, faults, and friction. Slow accumulation and rapid release of elastic energy.
 Earthquake Machine Stick-slip: Elastic Rebound Theory Jerky motions on faults produce EQs Three Fs of earthquakes: forces, faults, and friction. Slow accumulation and rapid release of elastic energy. Three
Earthquake Machine Stick-slip: Elastic Rebound Theory Jerky motions on faults produce EQs Three Fs of earthquakes: forces, faults, and friction. Slow accumulation and rapid release of elastic energy. Three
Land-use planning and volcanic hazards: Opportunities for New Zealand
 Land-use planning and volcanic hazards: Opportunities for New Zealand Julia Becker, Wendy Saunders, Graham Leonard, David Johnston, Lower Hutt Clare Robertson, Massey University, Palmerston North Presentation
Land-use planning and volcanic hazards: Opportunities for New Zealand Julia Becker, Wendy Saunders, Graham Leonard, David Johnston, Lower Hutt Clare Robertson, Massey University, Palmerston North Presentation
#13 Earthquake Prediction
 #13 Earthquake Prediction Obvious importance Earthquake Prediction Save lives, reduce damage Earthquake Prediction - Types Long-range prediction - involves EQ probability over long time period (years to
#13 Earthquake Prediction Obvious importance Earthquake Prediction Save lives, reduce damage Earthquake Prediction - Types Long-range prediction - involves EQ probability over long time period (years to
Lifelines mitigation in Hawke s Bay
 Lifelines mitigation in Hawke s Bay N.L. Evans Opus International Consultants (Member) NZSEE 2002 Conference ABSTRACT: This paper summarizes the findings of the recently completed Hawke s Bay Engineering
Lifelines mitigation in Hawke s Bay N.L. Evans Opus International Consultants (Member) NZSEE 2002 Conference ABSTRACT: This paper summarizes the findings of the recently completed Hawke s Bay Engineering
I. Locations of Earthquakes. Announcements. Earthquakes Ch. 5. video Northridge, California earthquake, lecture on Chapter 5 Earthquakes!
 51-100-21 Environmental Geology Summer 2006 Tuesday & Thursday 6-9:20 p.m. Dr. Beyer Earthquakes Ch. 5 I. Locations of Earthquakes II. Earthquake Processes III. Effects of Earthquakes IV. Earthquake Risk
51-100-21 Environmental Geology Summer 2006 Tuesday & Thursday 6-9:20 p.m. Dr. Beyer Earthquakes Ch. 5 I. Locations of Earthquakes II. Earthquake Processes III. Effects of Earthquakes IV. Earthquake Risk
Earthquake hazards. Aims 1. To know how hazards are classified 2. To be able to explain how the hazards occur 3. To be able to rank order hazards
 Earthquake hazards Aims 1. To know how hazards are classified 2. To be able to explain how the hazards occur 3. To be able to rank order hazards Types of hazard Primary A direct result of the earthquake
Earthquake hazards Aims 1. To know how hazards are classified 2. To be able to explain how the hazards occur 3. To be able to rank order hazards Types of hazard Primary A direct result of the earthquake
USING 3D GIS TO ASSESS ENVIRONMENTAL FLOOD HAZARDS IN MINA
 King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals College of Environmental Design Geographical Information system USING 3D GIS TO ASSESS ENVIRONMENTAL FLOOD HAZARDS IN MINA Prepared by : Ali AL-Zahrani OUTLINE
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals College of Environmental Design Geographical Information system USING 3D GIS TO ASSESS ENVIRONMENTAL FLOOD HAZARDS IN MINA Prepared by : Ali AL-Zahrani OUTLINE
DEPARTMENT OF GEOLOGY AND MINERAL INDUSTRIES WAYS & MEANS SUBCOMMITTEE ON NATURAL RESOURCES MARCH 2, 2017
 DEPARTMENT OF GEOLOGY AND MINERAL INDUSTRIES WAYS & MEANS SUBCOMMITTEE ON NATURAL RESOURCES MARCH 2, 2017 1 ABOUT DOGAMI AGENCY MISSION, VISION & GOALS 2 Lidar image of a stream network along the Umpqua
DEPARTMENT OF GEOLOGY AND MINERAL INDUSTRIES WAYS & MEANS SUBCOMMITTEE ON NATURAL RESOURCES MARCH 2, 2017 1 ABOUT DOGAMI AGENCY MISSION, VISION & GOALS 2 Lidar image of a stream network along the Umpqua
Disclaimer. This report was compiled by an ADRC visiting researcher (VR) from ADRC member countries.
 Disclaimer This report was compiled by an ADRC visiting researcher (VR) from ADRC member countries. The views expressed in the report do not necessarily reflect the views of the ADRC. The boundaries and
Disclaimer This report was compiled by an ADRC visiting researcher (VR) from ADRC member countries. The views expressed in the report do not necessarily reflect the views of the ADRC. The boundaries and
Year 8 Practice Questions for Summative Assessment. NAME:...
 Year 8 Practice Questions for Summative Assessment. NAME:... Earthquakes and Volcanoes 1. (a) The diagram below shows a simple cross section of the Earth. Complete the labels. (b) Name an earthquake you
Year 8 Practice Questions for Summative Assessment. NAME:... Earthquakes and Volcanoes 1. (a) The diagram below shows a simple cross section of the Earth. Complete the labels. (b) Name an earthquake you
Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Case History: Indonesian Tsunami Indonesian Tsunami (2) Introduction Historic Tsunamis
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Chapter 7 Tsunami Case History: Indonesian Tsunami December 26, 2004, within a few hours, close to 250,000 people were killed With no warning
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Chapter 7 Tsunami Case History: Indonesian Tsunami December 26, 2004, within a few hours, close to 250,000 people were killed With no warning
Assessing Hazards and Risk
 Page 1 of 6 EENS 204 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Assessing Hazards and Risk This page last updated on 07-Jan-2004 As discussed before, natural disasters are produced by
Page 1 of 6 EENS 204 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Assessing Hazards and Risk This page last updated on 07-Jan-2004 As discussed before, natural disasters are produced by
Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number CHANGING PHYSICAL AND HUMAN LANDSCAPES SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS
 GCSE GEOGRAPHY Sample Assessment Materials 5 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE GEOGRAPHY UNIT 1 CHANGING PHYSICAL AND HUMAN LANDSCAPES SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS 1 hour 30 minutes Section
GCSE GEOGRAPHY Sample Assessment Materials 5 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE GEOGRAPHY UNIT 1 CHANGING PHYSICAL AND HUMAN LANDSCAPES SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS 1 hour 30 minutes Section
Geography GCSE. Year 9 Term and Topic Unit Content Homework Opportunities
 Geography GCSE Year 9 Term and Topic Unit Content Homework Opportunities Autumn Term 1: Geographical Skills Autumn Term 2: Tectonic Hazards Spring Term 1: Ecosystems Rainforest Students are required to
Geography GCSE Year 9 Term and Topic Unit Content Homework Opportunities Autumn Term 1: Geographical Skills Autumn Term 2: Tectonic Hazards Spring Term 1: Ecosystems Rainforest Students are required to
I. What are Earthquakes?
 I. What are Earthquakes? A. There is more to earthquakes than just the shaking of the ground. An entire branch of Earth science, called seismology, is devoted to the study of earthquakes. B. Earthquakes
I. What are Earthquakes? A. There is more to earthquakes than just the shaking of the ground. An entire branch of Earth science, called seismology, is devoted to the study of earthquakes. B. Earthquakes
General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition 8 Plate Boundaries Beneath the Sea Complete by Thursday at 11:00 PM
 General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition 8 Plate Boundaries Beneath the Sea Complete by Thursday at 11:00 PM Name Expedition Objectives Learn about the types of plate boundaries and their key characteristics
General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition 8 Plate Boundaries Beneath the Sea Complete by Thursday at 11:00 PM Name Expedition Objectives Learn about the types of plate boundaries and their key characteristics
Year 4 Geography Revision Pack Summer 2018 Name
 Year 4 Geography Revision Pack Summer 2018 Name Welcome to your geography revision pack for the upcoming Summer exams. Everything that we have been working on in lessons since Christmas will be covered
Year 4 Geography Revision Pack Summer 2018 Name Welcome to your geography revision pack for the upcoming Summer exams. Everything that we have been working on in lessons since Christmas will be covered
Important Concepts. Earthquake hazards can be categorized as:
 Lecture 1 Page 1 Important Concepts Monday, August 17, 2009 1:05 PM Earthquake Engineering is a branch of Civil Engineering that requires expertise in geology, seismology, civil engineering and risk assessment.
Lecture 1 Page 1 Important Concepts Monday, August 17, 2009 1:05 PM Earthquake Engineering is a branch of Civil Engineering that requires expertise in geology, seismology, civil engineering and risk assessment.
Appendix 2. Extracts from Ministry for the Environment Active Fault Guidelines 2003
 Extracts from Ministry for the Environment Active Fault Guidelines 2003 Published in July 2003 by the Ministry for the Environment Manatu Mo Te Taiao PO Box 10-362, Wellington, New Zealand ISBN: 0-478-18901
Extracts from Ministry for the Environment Active Fault Guidelines 2003 Published in July 2003 by the Ministry for the Environment Manatu Mo Te Taiao PO Box 10-362, Wellington, New Zealand ISBN: 0-478-18901
Surviving the Big One: Understanding and Preparing for a Major Earthquake in Western Oregon
 Surviving the Big One: Understanding and Preparing for a Major Earthquake in Western Oregon May 21, 2013 City of Salem Salem Public Library Althea Rizzo, Geological Hazards Program Coordinator Oregon Emergency
Surviving the Big One: Understanding and Preparing for a Major Earthquake in Western Oregon May 21, 2013 City of Salem Salem Public Library Althea Rizzo, Geological Hazards Program Coordinator Oregon Emergency
Final Presentation on Disaster Risk Management in Japan. Through ADRC V. R Programme. Main Findings and Action Plan:
 Final Presentation on Disaster Risk Management in Japan Through ADRC V. R Programme Main Findings and Action Plan: Problem/Hazard and Disaster in Japan Good Practiced on Disaster Risk Management in Japan
Final Presentation on Disaster Risk Management in Japan Through ADRC V. R Programme Main Findings and Action Plan: Problem/Hazard and Disaster in Japan Good Practiced on Disaster Risk Management in Japan
MANAGING VOLCANIC IMPACTS IN CANTERBURY. Tom Wilson University of Canterbury & Natural Hazard Research Platform
 MANAGING VOLCANIC IMPACTS IN CANTERBURY Tom Wilson University of Canterbury & Natural Hazard Research Platform Talk Outline Risk of a Volcanic eruption affecting Canterbury Putting it in context (likelihood/consequence)
MANAGING VOLCANIC IMPACTS IN CANTERBURY Tom Wilson University of Canterbury & Natural Hazard Research Platform Talk Outline Risk of a Volcanic eruption affecting Canterbury Putting it in context (likelihood/consequence)
Plates & Boundaries The earth's continents are constantly moving due to the motions of the tectonic plates.
 Plates & Boundaries The earth's continents are constantly moving due to the motions of the tectonic plates. As you can see, some of the plates contain continents and others are mostly under the ocean.
Plates & Boundaries The earth's continents are constantly moving due to the motions of the tectonic plates. As you can see, some of the plates contain continents and others are mostly under the ocean.
Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 27. Earthquake Engineering (Reference West, Ch. 18)
 Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 27 Earthquake Engineering (Reference West, Ch. 18) Earthquake Engineering 1. General introduction of earthquakes 2. Seismic Hazards 3. Strong ground motion Exactly
Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 27 Earthquake Engineering (Reference West, Ch. 18) Earthquake Engineering 1. General introduction of earthquakes 2. Seismic Hazards 3. Strong ground motion Exactly
Natural Disasters & Assessing Hazards and Risk. Natural Hazards and Natural Disasters
 Page 1 of 9 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Natural Disasters & Assessing Hazards and Risk This page last updated on 09-Jan-2018 Natural Hazards and Natural Disasters
Page 1 of 9 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Natural Disasters & Assessing Hazards and Risk This page last updated on 09-Jan-2018 Natural Hazards and Natural Disasters
Lesson 8. Natural Disasters
 Lesson 8 Natural Disasters 1 Reading is NOT a spectator sport! 2 Reading requires active participation! 3 PREDICT Try to figure out what information will come next and how the selection might end. 4 Natural
Lesson 8 Natural Disasters 1 Reading is NOT a spectator sport! 2 Reading requires active participation! 3 PREDICT Try to figure out what information will come next and how the selection might end. 4 Natural
GeoNet Project Update: Strong Ground Motion and Structural Monitoring in New Zealand
 GeoNet Project Update: Strong Ground Motion and Structural Monitoring in New Zealand Ken Gledhill and the GeoNet Team GNS Science 2007 NZSEE Conference ABSTRACT: The GeoNet project, which is now in its
GeoNet Project Update: Strong Ground Motion and Structural Monitoring in New Zealand Ken Gledhill and the GeoNet Team GNS Science 2007 NZSEE Conference ABSTRACT: The GeoNet project, which is now in its
General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition 8 Plate Boundaries Beneath the Sea
 General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition 8 Plate Boundaries Beneath the Sea Name Not attempting to answer questions on expeditions will result in point deductions on course workbook (two or more blank
General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition 8 Plate Boundaries Beneath the Sea Name Not attempting to answer questions on expeditions will result in point deductions on course workbook (two or more blank
3/3/2013. The hydro cycle water returns from the sea. All "toilet to tap." Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e
 Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Running Water: summary in haiku form Edward A. Keller Chapter 9 Rivers and Flooding Lecture Presentation prepared by X. Mara Chen, Salisbury University The hydro
Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Running Water: summary in haiku form Edward A. Keller Chapter 9 Rivers and Flooding Lecture Presentation prepared by X. Mara Chen, Salisbury University The hydro
What Drives Seismic Risk in New Zealand? Insights from a nextgeneration
 Proceedings of the Tenth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering Building an Earthquake-Resilient Pacific 6-8 November 2015, Sydney, Australia What Drives Seismic Risk in New Zealand? Insights from
Proceedings of the Tenth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering Building an Earthquake-Resilient Pacific 6-8 November 2015, Sydney, Australia What Drives Seismic Risk in New Zealand? Insights from
Landslide Disaster Management in Sri Lanka and Nichola Oya as a Case study. Group 16 Gamini Jayathissa Udeni Nawagamuwa
 Landslide Disaster Management in Sri Lanka and Nichola Oya as a Case study Group 16 Gamini Jayathissa Udeni Nawagamuwa Taiwan Sri lanka >2582 mm, max >5000mm NE= Nov. to Feb 1750 2500 mm >2500 mm Central
Landslide Disaster Management in Sri Lanka and Nichola Oya as a Case study Group 16 Gamini Jayathissa Udeni Nawagamuwa Taiwan Sri lanka >2582 mm, max >5000mm NE= Nov. to Feb 1750 2500 mm >2500 mm Central
Illustrations of historic and pre-historic surface rupture of active faults in New Zealand
 Illustrations of historic and pre-historic surface rupture of active faults in New Zealand R. Van Dissen, P.R., Wood, K. erryman, & S. Nathan Institute of Geological & Nuclear Sciences, Lower Hutt, New
Illustrations of historic and pre-historic surface rupture of active faults in New Zealand R. Van Dissen, P.R., Wood, K. erryman, & S. Nathan Institute of Geological & Nuclear Sciences, Lower Hutt, New
Earthquakes.
 Earthquakes http://thismodernworld.com/comic-archive Elastic rebound http://projects.crustal.ucsb.edu/understanding/elastic/rebound.html Elastic rebound Rocks store energy elastically When stored stress
Earthquakes http://thismodernworld.com/comic-archive Elastic rebound http://projects.crustal.ucsb.edu/understanding/elastic/rebound.html Elastic rebound Rocks store energy elastically When stored stress
TEGAM s Connection to the EarthScope Project
 TEGAM s Connection to the EarthScope Project Introduction The EarthScope Project is an undertaking funded by the National Science Foundation in partnership with the United States Geological Survey and
TEGAM s Connection to the EarthScope Project Introduction The EarthScope Project is an undertaking funded by the National Science Foundation in partnership with the United States Geological Survey and
Volcanoes. Introduction
 Volcanoes Introduction Display Slide V-0 Explain that a volcano is a vent through which molten rock escapes to the Earth s surface. Unlike other mountains, which are pushed up from below, volcanoes are
Volcanoes Introduction Display Slide V-0 Explain that a volcano is a vent through which molten rock escapes to the Earth s surface. Unlike other mountains, which are pushed up from below, volcanoes are
Modeling Great Britain s Flood Defenses. Flood Defense in Great Britain. By Dr. Yizhong Qu
 Modeling Great Britain s Flood Defenses AIRCurrents Editor s note: AIR launched its Inland Flood Model for Great Britain in December 2008. The hazard module captures the physical processes of rainfall-runoff
Modeling Great Britain s Flood Defenses AIRCurrents Editor s note: AIR launched its Inland Flood Model for Great Britain in December 2008. The hazard module captures the physical processes of rainfall-runoff
Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model
 Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model The Cascadia tectonic margin is caught between several tectonic forces, during the relentless motions of the giant Pacific Plate, the smaller subducting
Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model The Cascadia tectonic margin is caught between several tectonic forces, during the relentless motions of the giant Pacific Plate, the smaller subducting
What Are Disasters? The Rescue Kids Trio!
 The Rescue Kids Trio! What Are Disasters? This manual was made possible through funding by the Council of Local Authorities for International Relations. Disasters and emergency preparedness Emergency preparedness
The Rescue Kids Trio! What Are Disasters? This manual was made possible through funding by the Council of Local Authorities for International Relations. Disasters and emergency preparedness Emergency preparedness
AIRCURRENTS THE TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE AND STRESS TRANSFER STRESS TRANSFER
 THE TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE AND STRESS TRANSFER AIRCURRENTS 11.2011 Edited Editor s Note: The March 11th Tohoku Earthquake was unprecedented in Japan s recorded history. In April, AIR Currents described the
THE TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE AND STRESS TRANSFER AIRCURRENTS 11.2011 Edited Editor s Note: The March 11th Tohoku Earthquake was unprecedented in Japan s recorded history. In April, AIR Currents described the
Impacts of Climate Change and Water-Related Disaster Reduction Management in the Asia-Pacific Region
 Impacts of Climate Change and Water-Related Disaster Reduction Management in the Asia-Pacific Region Katumi MUSIAKE Professor, Fukushima University Secretary General, Asia Pacific Association of Hydrology
Impacts of Climate Change and Water-Related Disaster Reduction Management in the Asia-Pacific Region Katumi MUSIAKE Professor, Fukushima University Secretary General, Asia Pacific Association of Hydrology
Effect of explicitly representing buildings on tsunami inundation: a pilot study of Wellington CBD
 Effect of explicitly representing buildings on tsunami inundation: a pilot study of Wellington CBD X. Wang Department of Tectonophysics, GNS Science, Lower Hutt, New Zealand W.L. Power, B. Lukovic & C.
Effect of explicitly representing buildings on tsunami inundation: a pilot study of Wellington CBD X. Wang Department of Tectonophysics, GNS Science, Lower Hutt, New Zealand W.L. Power, B. Lukovic & C.
Usually, only a couple of centuries of earthquake data is available, much shorter than the complete seismic cycle for most plate motions.
 Earthquake Hazard Analysis estimate the hazard presented by earthquakes in a given region Hazard analysis is related to long term prediction and provides a basis to expressed hazard in probabilistic terms.
Earthquake Hazard Analysis estimate the hazard presented by earthquakes in a given region Hazard analysis is related to long term prediction and provides a basis to expressed hazard in probabilistic terms.
Seth J. Wittke Wyoming State Geological Survey
 Seth J. Wittke Wyoming State Geological Survey Project initiation Data manipulation Scenarios Creating the IMS Lessons learned County-wide block level probabilistic models created in 2004 for state mitigation
Seth J. Wittke Wyoming State Geological Survey Project initiation Data manipulation Scenarios Creating the IMS Lessons learned County-wide block level probabilistic models created in 2004 for state mitigation
Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e
 Lecture Presentation prepared by X. Mara Chen, Salisbury University Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Edward A. Keller Chapter 7 Tsunami Case History: Indonesian Tsunami December 26, 2004, within
Lecture Presentation prepared by X. Mara Chen, Salisbury University Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Edward A. Keller Chapter 7 Tsunami Case History: Indonesian Tsunami December 26, 2004, within
Cascadia megathrust earthquakes: reducing risk through science, engineering, and planning
 Cascadia megathrust earthquakes: reducing risk through science, engineering, and planning NSF Hazards SEES EAR-1331412 Urban Science and Engineering Workshop 21 July 2014 Everything to do with M9 Cascadia
Cascadia megathrust earthquakes: reducing risk through science, engineering, and planning NSF Hazards SEES EAR-1331412 Urban Science and Engineering Workshop 21 July 2014 Everything to do with M9 Cascadia
Lessons learnt from 2014 Mt Ontake and 2000 Mt Usu eruptions: findings from a post-eruption ballistic impact assessment trip to Japan
 Lessons learnt from 2014 Mt Ontake and 2000 Mt Usu eruptions: findings from a post-eruption ballistic impact assessment trip to Japan Rebecca Fitzgerald, Ben Kennedy, Thomas Wilson, Graham Leonard, Kae
Lessons learnt from 2014 Mt Ontake and 2000 Mt Usu eruptions: findings from a post-eruption ballistic impact assessment trip to Japan Rebecca Fitzgerald, Ben Kennedy, Thomas Wilson, Graham Leonard, Kae
Tsunami hazard risk and early warning projects at Global Geophysics Institute, Vietnam
 Tsunami hazard risk and early warning projects at Global Geophysics Institute, Vietnam presented by Dr Kelvin Berryman, GNS Science, New Zealand k.berryman@gns.cri.nz on behalf of Prof. Bui C. Que,, Director
Tsunami hazard risk and early warning projects at Global Geophysics Institute, Vietnam presented by Dr Kelvin Berryman, GNS Science, New Zealand k.berryman@gns.cri.nz on behalf of Prof. Bui C. Que,, Director
The Tectonic Setting of New Zealand
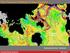 The Tectonic Setting of New Zealand we are here Subduction-driven tectonics The New Zealand continent Papua New Guinea Australia 3,000,000 sq km micro-continent back-arc basin trench volcanism faults accretionary
The Tectonic Setting of New Zealand we are here Subduction-driven tectonics The New Zealand continent Papua New Guinea Australia 3,000,000 sq km micro-continent back-arc basin trench volcanism faults accretionary
crustal structure experiment beneath Wairarapa - Wellington area: results from SAHKE
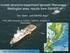 crustal structure experiment beneath Wairarapa - Wellington area: results from SAHKE Tim Stern and SAHKE team* * VUW, GNS, University of Southern California, University of Tokyo(Japan) SAHKE = Seismic
crustal structure experiment beneath Wairarapa - Wellington area: results from SAHKE Tim Stern and SAHKE team* * VUW, GNS, University of Southern California, University of Tokyo(Japan) SAHKE = Seismic
LECTURE #11: Volcanoes: Monitoring & Mitigation
 GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #11: Volcanoes: Monitoring & Mitigation Date: 15 February 2018 I. What is volcanic monitoring? the continuous collection of one or more data sources
GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #11: Volcanoes: Monitoring & Mitigation Date: 15 February 2018 I. What is volcanic monitoring? the continuous collection of one or more data sources
Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating.
 CH Earthquakes Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating Earthquakes Section 19.4: Earthquakes and Society Section 19.1 Forces
CH Earthquakes Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating Earthquakes Section 19.4: Earthquakes and Society Section 19.1 Forces
STRESS IN THE SYSTEM? INSIGHTS INTO MODELLING IN THE WAKE OF TOHOKU
 STRESS IN THE SYSTEM? INSIGHTS INTO MODELLING IN THE WAKE OF TOHOKU Aspen Re June 13, 2012 James Few President, Aspen Re Aspen Insurance Holdings Limited AGENDA Do we need near-term quake rates? Lessons
STRESS IN THE SYSTEM? INSIGHTS INTO MODELLING IN THE WAKE OF TOHOKU Aspen Re June 13, 2012 James Few President, Aspen Re Aspen Insurance Holdings Limited AGENDA Do we need near-term quake rates? Lessons
Subject Area: Geography
 Long Term Planning Overview Key Stage 3 Subject Area: Geography Academic : 08-9 7 Assessment Your Island Home the physical and human geography of the UK and will investigate weather patterns, population
Long Term Planning Overview Key Stage 3 Subject Area: Geography Academic : 08-9 7 Assessment Your Island Home the physical and human geography of the UK and will investigate weather patterns, population
