Groundwater Flow beneath Volcanoes Inferred from Electric Self-Potential and Magnetotellurics
|
|
|
- Allison Perry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 // (,*+*) 0,/+,/3 Groundwater Flow beneath Volcanoes Inferred from Electric Self-Potential and Magnetotellurics Koki A IZAWA + / (Kagiyama et al, +333 ; Hurwitz et al,,**1) (Lopez SiO -H O and Williams, +33- ; Reid,,**) OH Si-O +33/ ; Revil et al, +333,+ H K Na (Fig + a), - / 0 (convection current) (conduction current) (slipping plane) z, z,+ SP: Self Potential Spontaneous Potential,, ++- **-, Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo, Yayoi + + +, Bunkyo-ku, Toky, ++- **-,, Japan Corresponding author: Koki Aizawa a-zawa@eriu-tokyoacjp
2 252 Fig + (a) Microscopic view of convection current generation by electrokinetic phenomenon (b) Schematic illustration of negative correlation between self potential and elevation In the porous rock, electric charge is conveyed by convection (convection current) ; however no charge is conveyed outside the porous media Therefore, the charge accumulation occurs on the recharge and discharge zone The conduction current (Ohmic current) flows to cancel this charge separation ph,, MT (Ishido and Mizutani, +32+ ; Hase et al,,**- ; Aizawa et al,,**2b) (Morgan et al, +323 ; Tosha et al,,**-) + +* z ( -m),*** (Gaillard and Marziano,,**/) (Sill, +32-) (Fig + a) (Fig + b),*** MT MT (Fig,) (Aizawa,,**) MT (Michel (,**3) and Zlotnicki, +332 ; Aizawa et al,,**/ ; Revil et al,,**2) MT (Static shift) (Ishido,,** ; Aizawa,,**2 ; Aizawa et al,,**3a) Static shift
3 253 Fig, (a) Self-potential distribution around the summit of Mt Fuji volcano Contour interval is *,/ V Star shows the reference point (* V in the map) Thick lines indicate the locations of the summit crater and the Hoei crater (b) The self-potential data for the long profile (site locations are shown in Aizawa,,**) Horizontal axis of the figure is the horizontal distance from the center of the summit crater (c) Topographic profile for the data shown in Fig, b A B Seal- (Ogawa and Uchida, +330 ; Sasaki,,**) ing zone,** - (Hyndman et al, +331 ; Lee et al,,*+*) Aizawa et al (,**3 a),** / + km Sealing Cap (Fig - and Table + ) rock ( + +* -m) +** m A +* +* -m,** B A +323 ; Pellerin,,**, ( + +* -m) Aizawa et al (,**3a) Sealing zone Fig - Fig (Fig ) + +* ( -m),** + km,**,** Sealing zone (Zablocki Sealing zone et al, +31 ; Fitterman et al, +322 ; Sakuma et al,,**2 ; Sealing zone Hurwitz et al,,*+*),** Sealing
4 254 Table + Relationship between SP profile, resistivity structure and surface features Fig - Resistivity models and corresponding SP profiles for the Iwate, Iwaki, Nasu, Nantai, and Nikko-Shirane volcanoes, respectively (Aizawa et al,,**3a) Inverted triangles indicate MT measurement sites The horizontal axes are set as the projected distances along the MT survey lines Surface geothermal activity is shown by blue arrows (solid: hot spring, dashed: fumarole) Pronounced SP minima on the flanks of Type B (Fig ) are marked by dashed vertical lines Sealing zone B,**/ ; +313 (Fig,),3** Aizawa et al (,**3a) A B +322 A (Lopez and Williams, +33- ; Finn et B al,,**+) A B Fig -
5 255 Aizawa et al (,**3b) / MT km, Fig (Fig /) (Fig,) (Fig -a) (Aizawa et al, - He He,**2 a) ,**0 ;,*+* Sealing zone Aizawa et al (,*+*) + MT 0 +** +*** (m/day) Aizawa et al (,**3 a) + km Sealing zone Fournier ( +333) 2* Fracture ** Brittle- Fig Schematic model of a groundwater flow within a volcanic edifice Solid and dashed arrows represent the flow directions of liquid and vapor, respectively The top of the hydrothermal system is sealed by a low permeability and electrically conductive clay-rich layer, which is shown as thick gray line in the figure Conductive clay minerals (smectite) exist in the gray zone, whose bottom corresponds to the,** isotherm The hydrothermal zone below,** within the volcanic edifice is largely constrained to the volcano side of the SP minimum The hydrothermal zone is extensive beneath the flat part of the SP profile The two-phase zone may occur around the active conduit, but is not needed to explain the observations Note that the deep hydrothermal system, which may exist beneath the volcanic basement, is not determined by Aizawa et al,**3a
6 256 Fig / Resistivity structure of Iwate volcano combined with seismicity and geodetic model (Aizawa et al,,**3b) Black circles and white stars represent volcano-tectonic and low-frequency earthquakes, respectively Open rectangles show the temporal evolution of the location of dike-shaped pressures source (Sato and Hamaguchi,,**0) The numbers ( ) shown at the center of each rectangle (dike) represent the order of the estimated periods Ductile transition zone MT Sealing zone (Fig 0) ( / km) + +* ( -m) Sealing,** Sealing ** - He He, Sealing zone Fournier ( +333) Aizawa et al (,**3a) Fournier ( +333 ) ** Brittle- Ductile transition zone Sealing (Ohba et al,,**2) MT Sealing Reid (,**) Hurwitz et al (,**1) (Ogawa et al,,**+ ; Wannamaker et al,,**3) (Etheridge et al, +32- ; Jones, +321) Sealing Sealing Sealing Sibson, Becken et al (,**2) San-Andreas +33, ;,**-
7 257 Fig 0 Schematic model of groundwater flow (Fournier, +333) Self sealing by silica precipitation occur at about -1* to **, which correspond to the brittle-ductile transition zone Note that the sealing zone by clay minerals (Aizawa et al,,**3) occur at shallower level, Sealing zone,+ -, Aizawa, K (,**) A large self-potential anomaly and its changes on the quiet Mt Fuji, Japan Geophys Res Lett, -+,doi:l*/0+,+* +*,3 /,** gl *+30, Aizawa, K, et al (,**/) Hydrothermal system beneath Mt Fuji volcano inferred from magnetotellurics and electric self-potential Earth Planet Sci Lett,,-/, -- -//, doi: +* +*+0 /jepsl,**/*-*,- Aizawa, K (,**2) Classification of self-potential anomalies on volcanoes and possible interpretations for their subsurface structure J Volcanol Geotherm Res, +1/,,/-,02, doi: +* +*+0 /jjvolgeores,**2*-*++ Aizawa, K, Ogawa, Y, Hashimoto, T, Koyama, T, Kanda, W, Yamaya, Y, Mishina, M and Kagiyama, T (,**2a) Shallow resistivity structure of Asama Volcano and its implications for magma ascent process in the,** eruption J Volcanol Geotherm Res, +1-, +0/ +11, doi : +* +*+0 /jjvolgeores,**2*+*+0 Aizawa, K, Uyeshima, M and Nogami, K (,**2b) Zeta potential estimation of volcanic rocks on ++ island arctype volcanoes in Japan : Implication for the generation of local self-potential anomalies J Geophys Res, ++-, doi: B *,,*++* +*,3 /,**1 jb **/*/2 Aizawa, K, Ogawa, Y and Ishido, T (,**3a) Groundwater flow and hydrothermal systems within volcanic edifices : Delineation by electric self-potential and magnetotellurics J Geophys Res, ++, doi : B *+,*2+* +*,3 /,**2 jb **/3+* Aizawa, K, Ogawa, Y, Mishina, M, Takahashi, K, Nagaoka, S, Takagi, N, Sakanaka, S and Miura, T (,**3 b) Structural controls on the +332 volcanic unrest
8 258 at Iwate volcano: Relationship between a shallow, elec- Jones, AG ( +321) MT and reflection - an essential combitrically resistive body and the possible ascent route of nation Geophys J Int, 23, 1+1 magmatic fluid J Volcanol Geotherm Res, +21, +-+ Kagiyama, T, Utada, H and Yamamoto, T ( +333) Magma +-3, doi: +* +*+0 /jjvolgeores,**3*2**3 ascent beneath Unzen Volcano, SW Japan, deduced from Aizawa, K, Kanda, W, Ogawa, Y, Iguchi, M, Yokoo, A, the electrical resistivity structure J Volcanol Geotherm Yakiwara, H and Sugano, T (,*+*) Temporal Changes Res, 23, -/, in Electrical Resistivity at Sakurajima Volcano from Lee, JO, Kang, IM and Cho, W J (,*+*) Smectite Continuous Magnetotelluric Observations J Volcanol alteration and its influence on the barrier properties of Geotherm Res, doi: +* +*+0 /jjvolgeores,*+* ++ **- smectite clay for a repository Applied Clay Science, 1, (in press) 33 +*, doi: +* +*+0 /jclay,**2 +* **1 Becken, M, Ritter, O, Park, SK, Bedrosian, PA, Lopez, DL and Williams, SN ( +33-) Catastrophic vol- Weckmann, U and Weber, M (,**2) A deep crustal canic collapse - relation to hydrothermal processes Science, fluid channel into the San Andreas Fault System near,0*, Parkfield, California Geophys J Int, +1-, 1+21-,, doi : Michel, S and Zlotnicki, J ( +332) Self-potential and magfluid +* ++++ /j +-0/ -,0 X,**2*-1/x netic surveying of La Fournaise volcano (Reunion Etheridge, MA, Wall, V J and Vernon, RH ( +32-) The Island): Correlations with faulting, fluid circulation, and role of the fluid phase during regional metamorphism and eruption J Geophys Res, +*-, +12/ +12/1 deformation Journal of Metamorphic Geology, +,,*/ Morgan, FD, Williams, ER and Madden, TR ( +323),,0 Streaming potential properties of Westerly granite with Finn, CA, Sisson, TW and Deszcz-Pan, M (,**+) applications J Geophys Res, 3, +,3 +,0+ Aerogeophysical measurements of collapse-prone hydro- Ogawa, Y and Uchida, T ( +330) A two-dimensional thermally altered zones at Mount Rainier volcano Nature, magnetotelluric inversion assuming Gaussian static shift *3, 0** 0*- Geophys J Int, +,0, 0310 Fitterman, DV, Stanley, WD and Bisdorf, R J ( +322 ) Ogawa, Y, et al (,**+) Magnetotelluric imaging of fluids Electrical structure of Newberry volcano, Oregon J in intraplate earthquake zones, NE Japan back arc Geophy Res, 3-, +*++3 +*+- Geophys Res Lett,,2, Fournier, RO ( +333 ) Hydrothermal processes related to Ohba, T, Hirabayashi, J and Nogami, K (,**2) Tempomovement of fluid from plastic into brittle rock in the ral changes in the chemistry of lake water within Yugama magmatic-epithermal environment Economic Geology, Crater, Kusatsu-Shirane Volcano, Japan : Implications 3, ,++ for the evolution of the magmatic hydrothermal system Gaillard, F and Marziano, GI (,**/) Electrical conduc- J Volcanol Geotherm Res, +12, +-+ +, doi: +* +*+0/ tivity of magma in the course of crystallization controlled jjvolgeores,**2*0*+/ by their residual liquid composition J Geophys Res, Pellerin, L (,**,) Applications of electrical and electro- ++*, doi: +* +*,3 /,** jb **-,2, magnetic methods for environmental and geotechnical Hase, H, Ishido, T, Takakura, S, Hashimoto, T, Sato, K investigations Surveys in Geophysics,,-, +*+ +-, and Tanaka, Y (,**-) Zeta potential measurement of Reid, ME (,**) Massive collapse of volcano edifices volcanic rocks from Aso caldera Geophys Res Lett, -*, triggered by hydrothermal pressurization Geology, -,,,,+*,doi: +* +*,3 /,**- GL * ,doi: +* ++ -*/g*,-** + Hurwitz, S, Christiansen, LB and Hsieh, PA (,**1) Revil, A, Pezard, PA and Glover, PWJ ( +333) Stream- Hydrothermal fluid flow and deformation in large calderas ing potential in porous media + Theory of the zeta : Inferences from numerical simulations J Geophys potential, J Geophys Res, +*,,**,+,**-+ Res, ++,,doi:b*,,*0+* +*,3 /,**0 jb **023 Revil, A, et al (,**2) Inner structure of La Fossa di Hurwitz, S, Farrar, CD and Williams, CF, (,*+*) The thermal regime in the resurgent dome of Long Valley Caldera, California: Inferences from precision temperature logs in deep wells, J Volcanol Geotherm Res, doi: +* +*+0 /jjvolgeores,*+**2*,- (in press) Vulcano (Vulcano Island, southern Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy) revealed by high-resolution electric resistivity tomography coupled with self-potential, temperature, and CO, di# use degassing measurements J Geophys Res, ++-, doi: B *1,*1+* +*,3 /,**1 jb **/-3 Hyndman, RD, Yamano, M and Oleskevich, DA ( +331) Sakuma, S, Kajiwara, T, Nakada, S, Uto, K and Shimizu, The seismogenic zone of subduction thrust faults Isl H (,**2) Drilling and logging results of USDP- - Arc, 0,,,0* Penetration into the volcanic conduit of Unzen Volcano, Ishido, T and Mizutani, H ( +32+ ) Experimental and Japan J Volcanol Geotherm Res, +1/, ++,, doi: theoretical basis of electrokinetic phenomena in rockwater +* +*+0 /jjvolgeores,**2*-*-3 systems and its applications to geophysics J Sasaki, Y (,**) Three-dimensional inversion of static- Geophy Res, 20, / Ishido, T (,**) Electrokinetic mechanism for the W shifted magnetotelluric data,-3,2 Earth Planets Space, /0, -shaped self-potential profile on volcanoes Geophys Res Lett, -+,doi:l +/0+0+* +*,3 /,** gl *,**3 Sato, M and Hamaguchi, H (,**0) Weak long-lived ground deformation related to Iwate volcanism revealed
9 259 by Bayesian decomposition of strain, tilt and positioning (,**/) data J Volcanol Geotherm Res, +//,,,0,, doi: +* +*+0 /jjvolgeores,**0*-*-+ (,**3) MT Sibson, RH ( +33, ) Implications of fault-valve behavior 0+ S,,/ S,-2 for rupture nucleation and recurrence Tectonophysics, ( +323),++,,2-,3- Sill, WR ( +32-) Self-potential modeling from primary, flows Geophysics, 2, 1020 Tosha, T, Matsushima, N and Ishido, T (,**-) Zeta potential measured for an intact granite sample at temperatures to,** degrees C Geophys Res Lett, -*, doi:,**0 +,3/+* +*,3 /,**, gl *+00*2 Wannamaker, PE, Caldwell, TG, Jiracek, GR, Maris, V, Hill, G J, Ogawa, Y, Bibby, HM, Bennie, SL and,**- +, Heise, W (,**3) Fluid and deformation regime of an advancing subduction system at Marlborough, New Zealand Nature, 0*, 1---U 13*, doi: +* +*-2 /nature*2,* +33/ +2- Zablocki, C J, Tilling, RI, Peterson, DW and Christiansen, RL ( +31 ) : A deep research drill hole at the summit of (,***) /- +/,0 an active volcano, Kilauea, Hawaii, Geophys Res Lett, +, -,--,0 ( +313) -* ( +322) 3,*+*,*+*/ -- /,
Groundwater flow and hydrothermal systems within volcanic edifices: Delineation by electric self-potential and magnetotellurics
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jb005910, 2009 Groundwater flow and hydrothermal systems within volcanic edifices: Delineation by electric self-potential and magnetotellurics
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jb005910, 2009 Groundwater flow and hydrothermal systems within volcanic edifices: Delineation by electric self-potential and magnetotellurics
Haruhisa N. (Fig. + ) *+ Graduate School of Environmental Studies, Nagoya University, Furo-cho, Chikusa-ku, Nagoya.0. 20*+ Japan.
 /- (,**2) 0,+/,,+ Source Mechanism and Seismic Velocity Structure of Source Region of Deep Low-frequency Earthquakes beneath Volcanoes: Case Studies of Mt Iwate and Mt Fuji Haruhisa N AKAMICHI + +3 (Fig
/- (,**2) 0,+/,,+ Source Mechanism and Seismic Velocity Structure of Source Region of Deep Low-frequency Earthquakes beneath Volcanoes: Case Studies of Mt Iwate and Mt Fuji Haruhisa N AKAMICHI + +3 (Fig
VLF -MT Survey around Nakadake crater at Aso Volcano
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science OPEN ACCESS VLF -MT Survey around Nakadake crater at Aso Volcano To cite this article: A Harja et al 2016 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci. 29 012016
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science OPEN ACCESS VLF -MT Survey around Nakadake crater at Aso Volcano To cite this article: A Harja et al 2016 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci. 29 012016
Self-potential anomaly of Satsuma-Iwojima volcano
 Earth Planets Space, 54, 231 237, 22 Self-potential anomaly of Satsuma-Iwojima volcano Wataru Kanda and Sin yo Mori Sakurajima Volcano Research Center, Disaster Prevention Research Institute, Kyoto University,
Earth Planets Space, 54, 231 237, 22 Self-potential anomaly of Satsuma-Iwojima volcano Wataru Kanda and Sin yo Mori Sakurajima Volcano Research Center, Disaster Prevention Research Institute, Kyoto University,
Introduction Theory Vulcano Model Results Conclusions Acknowledgements. Introduction Theory Vulcano Model Results Conclusions Acknowledgements
 Time-dependent modelling of the electric and magnetic fields caused by fluid flow in Vulcano, Italy Emilie Walker & Paul Glover Université Laval, Québec, Canada Plan Introduction Theory Vulcano Model Results
Time-dependent modelling of the electric and magnetic fields caused by fluid flow in Vulcano, Italy Emilie Walker & Paul Glover Université Laval, Québec, Canada Plan Introduction Theory Vulcano Model Results
Integrated Geophysical Model for Suswa Geothermal Prospect using Resistivity, Seismics and Gravity Survey Data in Kenya
 Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2015 Melbourne, Australia, 19-25 April 2015 Integrated Geophysical Model for Suswa Geothermal Prospect using Resistivity, Seismics and Gravity Survey Data in Kenya
Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2015 Melbourne, Australia, 19-25 April 2015 Integrated Geophysical Model for Suswa Geothermal Prospect using Resistivity, Seismics and Gravity Survey Data in Kenya
Self-Potential Studies in Volcanic Areas (5) -Rishiri, Kusatsu-Shirane, and White Island-
 Jour. Fac. Sci., Hokkaido Univ., Ser. VII (Geophysics), Vol. 12, No. 2, 97-113, 2004. Self-Potential Studies in Volcanic Areas (5) -Rishiri, Kusatsu-Shirane, and White Island- Takeshi Hashimoto 1), Tohru
Jour. Fac. Sci., Hokkaido Univ., Ser. VII (Geophysics), Vol. 12, No. 2, 97-113, 2004. Self-Potential Studies in Volcanic Areas (5) -Rishiri, Kusatsu-Shirane, and White Island- Takeshi Hashimoto 1), Tohru
Self-potential distribution on active volcano controlled by three-dimensional resistivity structure in Izu-Oshima, Japan
 Geophys. J. Int. (2009) 178, 1164 1181 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04203.x Self-potential distribution on active volcano controlled by three-dimensional resistivity structure in Izu-Oshima, Japan Shin
Geophys. J. Int. (2009) 178, 1164 1181 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04203.x Self-potential distribution on active volcano controlled by three-dimensional resistivity structure in Izu-Oshima, Japan Shin
Numerical Evidences of Unrest Related Electromagnetic Effects in the Campi Flegrei Caldera
 Numerical Evidences of Unrest Related Electromagnetic Effects in the Campi Flegrei Caldera Antonio Troiano*, Maria Giulia Di Giuseppe*, Claudia Troise*, Giuseppe De Natale*, Giovanni Perillo *INGV Osservatorio
Numerical Evidences of Unrest Related Electromagnetic Effects in the Campi Flegrei Caldera Antonio Troiano*, Maria Giulia Di Giuseppe*, Claudia Troise*, Giuseppe De Natale*, Giovanni Perillo *INGV Osservatorio
Self-potential, soil CO 2 flux, and temperature on Masaya volcano, Nicaragua
 1 Self-potential, soil CO 2 flux, and temperature on Masaya volcano, Nicaragua J. L. Lewicki 1,2, C. Connor 1, K. St-Amand 3, J. Stix 4, and W. Spinner 1 Short title: SELF-POTENTIAL ON MASAYA VOLCANO 1
1 Self-potential, soil CO 2 flux, and temperature on Masaya volcano, Nicaragua J. L. Lewicki 1,2, C. Connor 1, K. St-Amand 3, J. Stix 4, and W. Spinner 1 Short title: SELF-POTENTIAL ON MASAYA VOLCANO 1
Two-dimensional resistivity structure of Unzen Volcano revealed by AMT and MT surveys
 Earth Planets Space, 65, 759 766, 2013 Two-dimensional resistivity structure of Unzen Volcano revealed by AMT and MT surveys Shogo Komori 1, Tsuneomi Kagiyama 2, Mitsuru Utsugi 2, Hiroyuki Inoue 2, and
Earth Planets Space, 65, 759 766, 2013 Two-dimensional resistivity structure of Unzen Volcano revealed by AMT and MT surveys Shogo Komori 1, Tsuneomi Kagiyama 2, Mitsuru Utsugi 2, Hiroyuki Inoue 2, and
HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER PROCESSES AFTER 1995 PHREATIC ERUPTION OF KUJU VOLCANO, CENTRAL KYUSHU, JAPAN
 HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER PROCESSES AFTER 1995 PHREATIC ERUPTION OF KUJU VOLCANO, CENTRAL KYUSHU, JAPAN Sachio Ehara 1,Yasuhiro Fujimitsu 1, Jun Nishijima 1,Akira Ono 1 and Yuichi Nakano 1 1 Laboratory of
HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER PROCESSES AFTER 1995 PHREATIC ERUPTION OF KUJU VOLCANO, CENTRAL KYUSHU, JAPAN Sachio Ehara 1,Yasuhiro Fujimitsu 1, Jun Nishijima 1,Akira Ono 1 and Yuichi Nakano 1 1 Laboratory of
EAS 116 Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 EAS 116 Earthquakes and Volcanoes J. Haase Forecasting Volcanic Eruptions Assessment of Volcanic Hazard Is that volcano active? Mount Lassen: 12000 BP and 1915 Santorini, IT: 180,000 BP, 70,000 BP, 21000
EAS 116 Earthquakes and Volcanoes J. Haase Forecasting Volcanic Eruptions Assessment of Volcanic Hazard Is that volcano active? Mount Lassen: 12000 BP and 1915 Santorini, IT: 180,000 BP, 70,000 BP, 21000
The Tectonic Setting of New Zealand
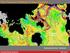 The Tectonic Setting of New Zealand we are here Subduction-driven tectonics The New Zealand continent Papua New Guinea Australia 3,000,000 sq km micro-continent back-arc basin trench volcanism faults accretionary
The Tectonic Setting of New Zealand we are here Subduction-driven tectonics The New Zealand continent Papua New Guinea Australia 3,000,000 sq km micro-continent back-arc basin trench volcanism faults accretionary
The importance of understanding coupled processes in geothermal reservoirs. Thomas Driesner October 19, 2016
 The importance of understanding coupled processes in geothermal reservoirs Thomas Driesner October 19, 2016 Findings from natural hydrothermal systems Interaction of permeability and fluid properties The
The importance of understanding coupled processes in geothermal reservoirs Thomas Driesner October 19, 2016 Findings from natural hydrothermal systems Interaction of permeability and fluid properties The
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa
 Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Fires Within: Igneous Activity Foundations, 6e - Chapter 7 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The nature of volcanic eruptions Characteristics
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Fires Within: Igneous Activity Foundations, 6e - Chapter 7 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The nature of volcanic eruptions Characteristics
Fig. 1. Joint volcanological experiment on volcanic structure and magma supply system in Japan.
 2. Joint Volcanological Experiment on Volcanic Structure and Magma Supply System Since 1994, joint experiments have been conducted in several volcanoes in Japan to reveal the structure and the magma supply
2. Joint Volcanological Experiment on Volcanic Structure and Magma Supply System Since 1994, joint experiments have been conducted in several volcanoes in Japan to reveal the structure and the magma supply
12. The diagram below shows the collision of an oceanic plate and a continental plate.
 Review 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below, which shows the boundary between two lithospheric plates. Point X is a location in the continental lithosphere. The depth
Review 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below, which shows the boundary between two lithospheric plates. Point X is a location in the continental lithosphere. The depth
TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology
 Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms.
 Chapter 10 Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms. Reading Strategy Previewing Before you read the section,
Chapter 10 Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms. Reading Strategy Previewing Before you read the section,
Earthquakes. Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy
 Earthquakes Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy The amount of energy released determines the magnitude of the earthquake Seismic waves carry the energy away from its origin Fig. 18.1 Origin
Earthquakes Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy The amount of energy released determines the magnitude of the earthquake Seismic waves carry the energy away from its origin Fig. 18.1 Origin
The Role of Magnetotellurics in Geothermal Exploration
 The Role of Magnetotellurics in Geothermal Exploration Adele Manzella CNR - Via Moruzzi 1 56124 PISA, Italy manzella@igg.cnr.it Foreword MT is one of the most used geophysical methods for geothermal exploration.
The Role of Magnetotellurics in Geothermal Exploration Adele Manzella CNR - Via Moruzzi 1 56124 PISA, Italy manzella@igg.cnr.it Foreword MT is one of the most used geophysical methods for geothermal exploration.
Introduction to Volcanic Seismology
 Introduction to Volcanic Seismology Second edition Vyacheslav M. Zobin Observatorio Vulcanolo'gico, Universidad de Colima, Colima, Col., Mexico ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON * NEW YORK OXFORD
Introduction to Volcanic Seismology Second edition Vyacheslav M. Zobin Observatorio Vulcanolo'gico, Universidad de Colima, Colima, Col., Mexico ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON * NEW YORK OXFORD
Overview of Ch. 4. I. The nature of volcanic eruptions 9/19/2011. Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5
 Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Continuing deflation by fumaroles at Kuju Volcano, Japan
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 30, NO. 0, XXXX, doi:10.1029/2002gl016047, 2003 Continuing deflation by fumaroles at Kuju Volcano, Japan M. Nakaboh, H. Ono, M. Sako, Y. Sudo, T. Hashimoto, and A. W.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 30, NO. 0, XXXX, doi:10.1029/2002gl016047, 2003 Continuing deflation by fumaroles at Kuju Volcano, Japan M. Nakaboh, H. Ono, M. Sako, Y. Sudo, T. Hashimoto, and A. W.
3D MAGNETOTELLURIC SURVEY AT THE YANAIZU-NISHIYAMA GEOTHERMAL FIELD, NORTHERN JAPAN
 3D MAGNETOTELLURIC SURVEY AT THE YANAIZU-NISHIYAMA GEOTHERMAL FIELD, NORTHERN JAPAN Toshihiro Uchida 1, Shinichi Takakura 1, Takumi Ueda 1, Masaho Adachi 2, Hitoshi Ozeki 2, Kunikazu Kamada 3, Tatsuya
3D MAGNETOTELLURIC SURVEY AT THE YANAIZU-NISHIYAMA GEOTHERMAL FIELD, NORTHERN JAPAN Toshihiro Uchida 1, Shinichi Takakura 1, Takumi Ueda 1, Masaho Adachi 2, Hitoshi Ozeki 2, Kunikazu Kamada 3, Tatsuya
3.2 Notes: Volcanoes Form as Molten Rock Erupts
 3.2 Notes: Volcanoes Form as Molten Rock Erupts Think about What happens when a volcano erupts? Volcanoes erupt many types of material Earth s thin outer layer is, but most of Earth is extremely hot rock
3.2 Notes: Volcanoes Form as Molten Rock Erupts Think about What happens when a volcano erupts? Volcanoes erupt many types of material Earth s thin outer layer is, but most of Earth is extremely hot rock
INTERGRATED GEOPHYSICAL METHODS USED TO SITE HIGH PRODUCER GEOTHERMAL WELLS
 Presented at Short Course VII on Exploration for Geothermal Resources, organized by UNU-GTP, GDC and KenGen, at Lake Bogoria and Lake Naivasha, Kenya, Oct. 27 Nov. 18, 2012. GEOTHERMAL TRAINING PROGRAMME
Presented at Short Course VII on Exploration for Geothermal Resources, organized by UNU-GTP, GDC and KenGen, at Lake Bogoria and Lake Naivasha, Kenya, Oct. 27 Nov. 18, 2012. GEOTHERMAL TRAINING PROGRAMME
A resistivity cross-section of Usu volcano, Hokkaido, Japan, by audiomagnetotelluric soundings
 Earth Planets Space, 50, 339 346, 1998 A resistivity cross-section of Usu volcano, Hokkaido, Japan, by audiomagnetotelluric soundings Y. Ogawa 1, N. Matsushima 1, H. Oshima 2, S. Takakura 1, M. Utsugi
Earth Planets Space, 50, 339 346, 1998 A resistivity cross-section of Usu volcano, Hokkaido, Japan, by audiomagnetotelluric soundings Y. Ogawa 1, N. Matsushima 1, H. Oshima 2, S. Takakura 1, M. Utsugi
Visualizing Earth Science. Chapter Overview. Volcanoes and Eruption Types. By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner. Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other
 Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
Key words: seismic activity, permeability, heat source, Kakkonda Granite, Iwate Volcano, Japan 2. SEISMIC ACTIVITY IN HIGH PERMEABLE ZONE
 SEISMIC ACTIVITY IN THE KAKKONDA GEOTHERMAL SYSTEM CHARACTERIZED BY THE QUATERNARY KAKKONDA GRANITE, JAPAN Nobuo Doi 1, Satoshi Shigehara 1, Ken Ikeuchi 1, Osamu Kato 1, Masaki Takahashi 1, Takao Ominato
SEISMIC ACTIVITY IN THE KAKKONDA GEOTHERMAL SYSTEM CHARACTERIZED BY THE QUATERNARY KAKKONDA GRANITE, JAPAN Nobuo Doi 1, Satoshi Shigehara 1, Ken Ikeuchi 1, Osamu Kato 1, Masaki Takahashi 1, Takao Ominato
INTRODUCTION TO VOLCANIC SEISMOLOGY
 INTRODUCTION TO VOLCANIC SEISMOLOGY V.M. Zobin Observatorio Vulcanologico, Colima, Mexico ELSEVIER Amsterdam - Boston - Heidelberg - London - New York - Oxford Paris - San Diego - San Francisco - Singapore
INTRODUCTION TO VOLCANIC SEISMOLOGY V.M. Zobin Observatorio Vulcanologico, Colima, Mexico ELSEVIER Amsterdam - Boston - Heidelberg - London - New York - Oxford Paris - San Diego - San Francisco - Singapore
High-temperature fracture of magma
 High-temperature fracture of magma Hugh Tuffen Peter Sammonds Rosanna Smith Harry Pinkerton Don Dingwell Jon Castro Cracks, Fractures and Faults in the Earth Thursday 19 th June 2008 Montserrat (Sparks
High-temperature fracture of magma Hugh Tuffen Peter Sammonds Rosanna Smith Harry Pinkerton Don Dingwell Jon Castro Cracks, Fractures and Faults in the Earth Thursday 19 th June 2008 Montserrat (Sparks
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 2017-2016 Chapter (4) Volcanoes Chapter 4: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity cataclysmic relating to or denoting a violent natural even Eventually the entire
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 2017-2016 Chapter (4) Volcanoes Chapter 4: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity cataclysmic relating to or denoting a violent natural even Eventually the entire
MIGRATING SWARMS OF BRITTLE-FAILURE EARTHQUAKES IN THE LOWER CRUST BENEATH MAMMOTH MOUNTAIN, CALIFORNIA
 MIGRATING SWARMS OF BRITTLE-FAILURE EARTHQUAKES IN THE LOWER CRUST BENEATH MAMMOTH MOUNTAIN, CALIFORNIA David Shelly and David Hill GRL, October 2011 Contents Tectonic Setting Long Valley Caldera Mammoth
MIGRATING SWARMS OF BRITTLE-FAILURE EARTHQUAKES IN THE LOWER CRUST BENEATH MAMMOTH MOUNTAIN, CALIFORNIA David Shelly and David Hill GRL, October 2011 Contents Tectonic Setting Long Valley Caldera Mammoth
Depth estimation of fumarolic gas source deduced by fume pressure measurement
 LETTER Earth Planets Space, 60, 889 893, 2008 Depth estimation of fumarolic gas source deduced by fume pressure measurement Takehiko Mori 1, Takashi Suzuki 2, Jun ichi Hirabayashi 3, Kenji Nogami 3, Michiko
LETTER Earth Planets Space, 60, 889 893, 2008 Depth estimation of fumarolic gas source deduced by fume pressure measurement Takehiko Mori 1, Takashi Suzuki 2, Jun ichi Hirabayashi 3, Kenji Nogami 3, Michiko
Title. Issue Date Doc URL. Type. File Information. Anthony W.; UTSUGI, Mitsuru; TANAKA, Yoshikazu.
 Title Self-potential studies in volcanic areas(5) : Rishir HASHIMOTO, Takeshi; MOGI, Tohru; NISHIDA, Yasunori; Author(s) Mitsuhiro; SAITO, Masaki; Nurhasan; MIZUHASHI, Shoei Anthony W.; UTSUGI, Mitsuru;
Title Self-potential studies in volcanic areas(5) : Rishir HASHIMOTO, Takeshi; MOGI, Tohru; NISHIDA, Yasunori; Author(s) Mitsuhiro; SAITO, Masaki; Nurhasan; MIZUHASHI, Shoei Anthony W.; UTSUGI, Mitsuru;
COMPOSITION and PHYSICAL PROPERTIES GENERAL SUBJECTS. GEODESY and GRAVITY
 COMPOSITION and PHYSICAL PROPERTIES Composition and structure of the continental crust Composition and structure of the core Composition and structure of the mantle Composition and structure of the oceanic
COMPOSITION and PHYSICAL PROPERTIES Composition and structure of the continental crust Composition and structure of the core Composition and structure of the mantle Composition and structure of the oceanic
magnetotellurics and induction vect
 Hydrothermal system beneath the cra TitleJapan : 3-D resistivity structure r magnetotellurics and induction vect Author(s) Yamaya, Yusuke; Mogi, Toru; Hiroshi Hashimo Citation Journal of Volcanology and
Hydrothermal system beneath the cra TitleJapan : 3-D resistivity structure r magnetotellurics and induction vect Author(s) Yamaya, Yusuke; Mogi, Toru; Hiroshi Hashimo Citation Journal of Volcanology and
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards
 UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 5 Magma and Volcanism Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information: pasakyi@ug.edu.gh College
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 5 Magma and Volcanism Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information: pasakyi@ug.edu.gh College
Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Kagoshima University
 20 +- -,+ +. / +- Geochemical Interpretation on Hydrothermal Formation Mechanism of the Thermal Water in the Iwodani Region and the Vicinity of the Hayashida Region of the Kirishima Volcanic Area Shun-ichi
20 +- -,+ +. / +- Geochemical Interpretation on Hydrothermal Formation Mechanism of the Thermal Water in the Iwodani Region and the Vicinity of the Hayashida Region of the Kirishima Volcanic Area Shun-ichi
Name: Answer Key Date: Period:
 Name: Answer Key Date: Period: Earth Science Final Exam Study Guide Ch 1: Mapping 1. On the global grid, the equator is at 0 degrees. Is the equator a line of longitude or latitude? Latitude 2. What type
Name: Answer Key Date: Period: Earth Science Final Exam Study Guide Ch 1: Mapping 1. On the global grid, the equator is at 0 degrees. Is the equator a line of longitude or latitude? Latitude 2. What type
Exploration of Geothermal High Enthalpy Resources using Magnetotellurics an Example from Chile
 Exploration of Geothermal High Enthalpy Resources using Magnetotellurics an Example from Chile Ulrich Kalberkamp, Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR), Stilleweg 2, 30655 Hannover,
Exploration of Geothermal High Enthalpy Resources using Magnetotellurics an Example from Chile Ulrich Kalberkamp, Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR), Stilleweg 2, 30655 Hannover,
Geophysics for Geothermal Exploration
 Geophysics for Geothermal Exploration Dr. Hendra Grandis Geofisika - ITB Agenda Basic concept of Geophysics: : Review Geophysical signatures of a geothermal system Geophysical methods for geotermal exploration
Geophysics for Geothermal Exploration Dr. Hendra Grandis Geofisika - ITB Agenda Basic concept of Geophysics: : Review Geophysical signatures of a geothermal system Geophysical methods for geotermal exploration
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy)
 Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
Numerical Simulation Study of the Mori Geothermal Field, Japan
 Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2010 Bali, Indonesia, 25-29 April 2010 Numerical Simulation Study of the Mori Geothermal Field, Japan Kazuyoshi Osada 1, Mineyuki Hanano 2, Kei Sato 1, Tatsuya Kajiwara
Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2010 Bali, Indonesia, 25-29 April 2010 Numerical Simulation Study of the Mori Geothermal Field, Japan Kazuyoshi Osada 1, Mineyuki Hanano 2, Kei Sato 1, Tatsuya Kajiwara
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 volcano sample test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Volcanic belts form along a. islands in the Pacific Ocean. b. North American
volcano sample test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Volcanic belts form along a. islands in the Pacific Ocean. b. North American
ELECTROKINETIC GROUNDWATER EXPLORATION: A NEW GEOPHYSICAL TECHNIQUE
 181 ELECTROKINETIC GROUNDWATER EXPLORATION: A NEW GEOPHYSICAL TECHNIQUE Sukhyoun Kim, Graham Heinson & John Joseph CRC LEME, School of Earth and Environment Sciences, University of Adelaide, SA, 5005 ABSTRACT
181 ELECTROKINETIC GROUNDWATER EXPLORATION: A NEW GEOPHYSICAL TECHNIQUE Sukhyoun Kim, Graham Heinson & John Joseph CRC LEME, School of Earth and Environment Sciences, University of Adelaide, SA, 5005 ABSTRACT
Volcano: a weak spot in the crust where molten material or magma comes to the surface
 Chapter 7 Volcano: a weak spot in the crust where molten material or magma comes to the surface Magma: a molten mixture of rock forming substances, gases and H 2 O from the mantle Volcanic Belts: Form
Chapter 7 Volcano: a weak spot in the crust where molten material or magma comes to the surface Magma: a molten mixture of rock forming substances, gases and H 2 O from the mantle Volcanic Belts: Form
A) B) C) D) 4. Which diagram below best represents the pattern of magnetic orientation in the seafloor on the west (left) side of the ocean ridge?
 1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
Chapter 10: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Section 1: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions I. Factors Affecting Eruptions Group # Main Idea:
 Chapter 10: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Section 1: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions I. Factors Affecting Eruptions Group # A. Viscosity Group # B. Dissolved Gases Group # II. Volcanic Material
Chapter 10: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Section 1: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions I. Factors Affecting Eruptions Group # A. Viscosity Group # B. Dissolved Gases Group # II. Volcanic Material
Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research
 Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research 187 (2009) 272 277 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jvolgeores
Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research 187 (2009) 272 277 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jvolgeores
THREE DIMENSIONAL MODELING OF GEOELECTRICAL STRUCTURE BASED ON MT AND TDEM DATA IN MORI GEOTHERMAL FIELD, HOKKAIDO, JAPAN
 THREE DIMENSIONAL MODELING OF GEOELECTRICAL STRUCTURE BASED ON MT AND TDEM DATA IN MORI GEOTHERMAL FIELD, HOKKAIDO, JAPAN Tatsuya Kajiwara 1, Tohru Mogi 2, Elena Fomenko 3 and Sachio Ehara 4 1 JMC Geothermal
THREE DIMENSIONAL MODELING OF GEOELECTRICAL STRUCTURE BASED ON MT AND TDEM DATA IN MORI GEOTHERMAL FIELD, HOKKAIDO, JAPAN Tatsuya Kajiwara 1, Tohru Mogi 2, Elena Fomenko 3 and Sachio Ehara 4 1 JMC Geothermal
Volcanoes. Table of Contents Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Landforms
 Volcanoes Table of Contents Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Landforms What is a volcano? cone Conduit Or Pipe vent Side vent Central vent Crater A volcano is a vent or 'chimney'
Volcanoes Table of Contents Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Landforms What is a volcano? cone Conduit Or Pipe vent Side vent Central vent Crater A volcano is a vent or 'chimney'
NUMERICAL MODELING STUDY OF SIBAYAK GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR, NORTH SUMATRA, INDONESIA
 PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Sixth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 29-31, 21 SGP-TR-168 NUMERICAL MODELING STUDY OF SIBAYAK GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR,
PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Sixth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 29-31, 21 SGP-TR-168 NUMERICAL MODELING STUDY OF SIBAYAK GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR,
Global Tectonics. Kearey, Philip. Table of Contents ISBN-13: Historical perspective. 2. The interior of the Earth.
 Global Tectonics Kearey, Philip ISBN-13: 9781405107778 Table of Contents Preface. Acknowledgments. 1. Historical perspective. 1.1 Continental drift. 1.2 Sea floor spreading and the birth of plate tectonics.
Global Tectonics Kearey, Philip ISBN-13: 9781405107778 Table of Contents Preface. Acknowledgments. 1. Historical perspective. 1.1 Continental drift. 1.2 Sea floor spreading and the birth of plate tectonics.
Japan Engineering Consultants, Inc., Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization,Tokyo, Japan
 DEEP GEOTHERMAL STRUCTURE AND THE HYDROTHERMAL SYSTEM THE GEOTHERMAL FIELD, JAPAN M. H. K. MATSUDA', T. K. Japan Engineering Consultants, Inc., Japan Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization,Tokyo,
DEEP GEOTHERMAL STRUCTURE AND THE HYDROTHERMAL SYSTEM THE GEOTHERMAL FIELD, JAPAN M. H. K. MATSUDA', T. K. Japan Engineering Consultants, Inc., Japan Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization,Tokyo,
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 10 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Factors Affecting Eruptions Factors that determine the violence of an eruption
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 10 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Factors Affecting Eruptions Factors that determine the violence of an eruption
4-D Geodynamic Modeling With Data Assimilation: Subduction and Continental Evolution
 4-D Geodynamic Modeling With Data Assimilation: Subduction and Continental Evolution PI: Lijun Liu Department of Geology, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Corresponding author: Lijun Liu, ljliu@illinois.edu
4-D Geodynamic Modeling With Data Assimilation: Subduction and Continental Evolution PI: Lijun Liu Department of Geology, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Corresponding author: Lijun Liu, ljliu@illinois.edu
THERMAL THERMAL AND AND RHEOLOGIC SIGNATURES OF
 THERMAL THERMAL AND AND RHEOLOGIC SIGNATURES OF OF HIGH HIGH ENTHALPY ENTHALPY RESOURCES ENGINE ENGINE Workshop Workshop Exploring Exploring high high temperature temperature reservoirs: reservoirs: new
THERMAL THERMAL AND AND RHEOLOGIC SIGNATURES OF OF HIGH HIGH ENTHALPY ENTHALPY RESOURCES ENGINE ENGINE Workshop Workshop Exploring Exploring high high temperature temperature reservoirs: reservoirs: new
When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere.
 When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere. A volcano is a mountain that forms when magma reaches the
When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere. A volcano is a mountain that forms when magma reaches the
Dynamic Planet PUT ALL YOUR ANSWERS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. c) low temperature d) high volatile content
 School Name: Team #: Students Names: Dynamic Planet 2016 Science Olympiad Invitational University of Texas at Austin PUT ALL YOUR ANSWERS ON THE ANSWER SHEET 1) Low viscosity magmas have: a) high silica
School Name: Team #: Students Names: Dynamic Planet 2016 Science Olympiad Invitational University of Texas at Austin PUT ALL YOUR ANSWERS ON THE ANSWER SHEET 1) Low viscosity magmas have: a) high silica
LETTER Earth Planets Space, 60, , 2008
 LETTER Earth Planets Space, 60, 705 710, 2008 Precise remote-monitoring technique of water volume and temperature of a crater lake in Aso volcano, Japan: implications for a sensitive window of a volcanic
LETTER Earth Planets Space, 60, 705 710, 2008 Precise remote-monitoring technique of water volume and temperature of a crater lake in Aso volcano, Japan: implications for a sensitive window of a volcanic
Continental Margin Geology of Korea : Review and constraints on the opening of the East Sea (Japan Sea)
 Continental Margin Geology of Korea : Review and constraints on the opening of the East Sea (Japan Sea) Han-Joon Kim Marine Satellite & Observation Tech. Korea Ocean Research and Development Institute
Continental Margin Geology of Korea : Review and constraints on the opening of the East Sea (Japan Sea) Han-Joon Kim Marine Satellite & Observation Tech. Korea Ocean Research and Development Institute
PRESSURE PERTURBATIONS IN TWO PHASE GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR ASSOCIATED WITH SEISMISITY
 PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Eighth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 27-29, 2003 SGP-TR-173 PRESSURE PERTURBATIONS IN TWO PHASE GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR
PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Eighth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 27-29, 2003 SGP-TR-173 PRESSURE PERTURBATIONS IN TWO PHASE GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR
Yellowstone National Park: Regional Groundwater Dynamics in High-Temperature Geothermal Areas
 International Symposium on Regional Groundwater Flow: Theory, Applications and Future Development Yellowstone National Park: Regional Groundwater Dynamics in High-Temperature Geothermal Areas K. Udo Weyer
International Symposium on Regional Groundwater Flow: Theory, Applications and Future Development Yellowstone National Park: Regional Groundwater Dynamics in High-Temperature Geothermal Areas K. Udo Weyer
GEOTHERMAL ENERGY POTENTIAL FOR LONGONOT PROSPECT, KENYA. By Mariita N. O. Kenya Electricity Generating Company
 GEOTHERMAL ENERGY POTENTIAL FOR LONGONOT PROSPECT, KENYA By Mariita N. O. Kenya Electricity Generating Company PRESENTATION OUTLINE INTRODUCTION REGIONAL SETTING GEOLOGY GEOTHERMAL MANIFESTATIONS HYDROGEOLOGY
GEOTHERMAL ENERGY POTENTIAL FOR LONGONOT PROSPECT, KENYA By Mariita N. O. Kenya Electricity Generating Company PRESENTATION OUTLINE INTRODUCTION REGIONAL SETTING GEOLOGY GEOTHERMAL MANIFESTATIONS HYDROGEOLOGY
Magma vs. Lava. Molten rock below Earth s surface is called magma. The magma that reaches the surface and erupts out of a volcano is called lava.
 CH. 10.1 Be able to Explain the factors that determine the type of volcanic eruption. List the 3 types of volcanoes Describe the features of a volcano. What is a Volcano? Volcanoes are sites where molten
CH. 10.1 Be able to Explain the factors that determine the type of volcanic eruption. List the 3 types of volcanoes Describe the features of a volcano. What is a Volcano? Volcanoes are sites where molten
Geophysical Surveys of The Geothermal System of The Lakes District Rift, Ethiopia
 Geophysical Surveys of The Geothermal System of The Lakes District Rift, Ethiopia By: Befekadu Oluma By: Geophysics Department Geological Survey of Ethiopia The formation of the rift was preceded by a
Geophysical Surveys of The Geothermal System of The Lakes District Rift, Ethiopia By: Befekadu Oluma By: Geophysics Department Geological Survey of Ethiopia The formation of the rift was preceded by a
Study Guide: Unit 3. Density and Pressure: You should be able to answer the types of questions given in the end of module questions.
 IDS 102 Study Guide: Unit 3 The purpose of this study guide is to help you prepare for the third exam by focusing your studying and providing example essay questions. In the Focus On section you will find
IDS 102 Study Guide: Unit 3 The purpose of this study guide is to help you prepare for the third exam by focusing your studying and providing example essay questions. In the Focus On section you will find
STUDY GUIDE FOR MID-TERM EXAM KEY. Color, luster, cleavage, fracture, hardness, taste, smell, fluorescence, radioactivity, magnetism
 STUDY GUIDE FOR MID-TERM EXAM KEY 1. In which type of rock are fossils most likely to be found? Sedimentary Rocks 2. Which mineral is easily identified by smell? Sulfur 3. Which natural resource makes
STUDY GUIDE FOR MID-TERM EXAM KEY 1. In which type of rock are fossils most likely to be found? Sedimentary Rocks 2. Which mineral is easily identified by smell? Sulfur 3. Which natural resource makes
GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca:
 Name: Date: GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca: SiO 2 silicon dioxide. This is quartz when it crystallizes.
Name: Date: GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca: SiO 2 silicon dioxide. This is quartz when it crystallizes.
Plate Boundaries & Resulting Landforms
 Plate Boundaries & Resulting Landforms Divergent Plate Boundaries (plates being pulled apart) Type: oceanic plates Description: rising magma gently lifts the crust creating a ridge. The flow of convection
Plate Boundaries & Resulting Landforms Divergent Plate Boundaries (plates being pulled apart) Type: oceanic plates Description: rising magma gently lifts the crust creating a ridge. The flow of convection
Verification of the asperity model using seismogenic fault materials Abstract
 Verification of the asperity model using seismogenic fault materials Takehiro Hirose*, Wataru Tanikawa and Weiren Lin Kochi Institute for Core Sample Research/JAMSTEC, JAPAN * Corresponding author: hiroset@jamstec.go.jp
Verification of the asperity model using seismogenic fault materials Takehiro Hirose*, Wataru Tanikawa and Weiren Lin Kochi Institute for Core Sample Research/JAMSTEC, JAPAN * Corresponding author: hiroset@jamstec.go.jp
What is the Relationship between Pressure & Volume Change in a Magma Chamber and Surface Deformation at Active Volcanoes?
 SSAC-pv2007.QE522.PL1.1 What is the Relationship between Pressure & Volume Change in a Magma Chamber and Surface Deformation at Active Volcanoes? What factors control the magnitude of surface deformation?
SSAC-pv2007.QE522.PL1.1 What is the Relationship between Pressure & Volume Change in a Magma Chamber and Surface Deformation at Active Volcanoes? What factors control the magnitude of surface deformation?
Section 2: How Mountains Form
 Section 2: How Mountains Form Preview Objectives Mountain Ranges and Systems Plate Tectonics and Mountains Types of Mountains Objectives Identify the types of plate collisions that form mountains. Identify
Section 2: How Mountains Form Preview Objectives Mountain Ranges and Systems Plate Tectonics and Mountains Types of Mountains Objectives Identify the types of plate collisions that form mountains. Identify
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN GEOTHERMAL ACTIVITY AND GRAVITY ANOMALIES ON VULCANO ISLAND, ITALY
 Proceedings NZ Geothermal Workshop 2002 RLATIONSHIP BTWN GOTHRMAL ACTIVITY AND GRAVITY ANOMALIS ON VULCANO ISLAND, ITALY M. S.OKUMA', S.NAKANO', R. FURUKAWA', M. KOMAZAWA' & R. SUPPR 2 'Geological Survey
Proceedings NZ Geothermal Workshop 2002 RLATIONSHIP BTWN GOTHRMAL ACTIVITY AND GRAVITY ANOMALIS ON VULCANO ISLAND, ITALY M. S.OKUMA', S.NAKANO', R. FURUKAWA', M. KOMAZAWA' & R. SUPPR 2 'Geological Survey
Figure 1: Location of principal shallow conductors at Alpala (anomalies C0-C10; 5 Ohm/m surfaces, red) and shallow zones of electrical chargeability
 Figure 1: Location of principal shallow conductors at Alpala (anomalies C0-C10; 5 Ohm/m surfaces, red) and shallow zones of electrical chargeability (85 msecs, yellow-green) shown on iso-surfaces of MVI
Figure 1: Location of principal shallow conductors at Alpala (anomalies C0-C10; 5 Ohm/m surfaces, red) and shallow zones of electrical chargeability (85 msecs, yellow-green) shown on iso-surfaces of MVI
Plate Tectonics. entirely rock both and rock
 Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
HYDROGEOLOGIC MODEL OF GROUNDWATER FLOW WITHIN MOUNT ST. HELENS VOLCANO DETERMINED FROM SELF-POTENTIAL AND TIME- DOMAIN ELECTROMAGNETIC MEASUREMENTS
 HYDROGEOLOGIC MODEL OF GROUNDWATER FLOW WITHIN MOUNT ST. HELENS VOLCANO DETERMINED FROM SELF-POTENTIAL AND TIME- DOMAIN ELECTROMAGNETIC MEASUREMENTS by Alicia Hotovec A thesis submitted to the Faculty
HYDROGEOLOGIC MODEL OF GROUNDWATER FLOW WITHIN MOUNT ST. HELENS VOLCANO DETERMINED FROM SELF-POTENTIAL AND TIME- DOMAIN ELECTROMAGNETIC MEASUREMENTS by Alicia Hotovec A thesis submitted to the Faculty
Three Dimensional Inversions of MT Resistivity Data to Image Geothermal Systems: Case Study, Korosi Geothermal Prospect
 PROCEEDINGS, 42nd Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 13-15, 2017 SGP-TR-212 Three Dimensional Inversions of MT Resistivity Data to Image Geothermal
PROCEEDINGS, 42nd Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 13-15, 2017 SGP-TR-212 Three Dimensional Inversions of MT Resistivity Data to Image Geothermal
Plate Tectonics and the cycling of Earth materials
 Plate Tectonics and the cycling of Earth materials Plate tectonics drives the rock cycle: the movement of rocks (and the minerals that comprise them, and the chemical elements that comprise them) from
Plate Tectonics and the cycling of Earth materials Plate tectonics drives the rock cycle: the movement of rocks (and the minerals that comprise them, and the chemical elements that comprise them) from
Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift
 Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift Predecessor to modern plate tectonics Shape and fit of the continents was the initial evidence Snider-Pelligrini (1858) Taylor (1908) Wegner (1915) Fig.
Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift Predecessor to modern plate tectonics Shape and fit of the continents was the initial evidence Snider-Pelligrini (1858) Taylor (1908) Wegner (1915) Fig.
Dynamic Crust Practice
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Geology 300, Physical Geology Spring 2019 Quiz Chapter 18, Seafloor Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Abyssal fans are made
Geology 300, Physical Geology Spring 2019 Quiz Chapter 18, Seafloor Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Abyssal fans are made
Directed Reading. Section: How Mountains Form MOUNTAIN RANGES AND SYSTEMS. Skills Worksheet
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: How Mountains Form 1. How high is Mount Everest? a. about 1980 km above sea level b. more than 8 km below sea level c. more than 8 km above sea level d. more
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: How Mountains Form 1. How high is Mount Everest? a. about 1980 km above sea level b. more than 8 km below sea level c. more than 8 km above sea level d. more
Investigation of Sumatran Fault Aceh Segment derived from Magnetotelluric Data
 Investigation of Sumatran Fault Aceh Segment derived from Magnetotelluric Data Nurhasan 1, D. Sutarno 1, Y Ogawa 2, F. Kimata 3, D Sugiyanto 4 1 Physics Department, Bandung Institute of Technology, Bandung,
Investigation of Sumatran Fault Aceh Segment derived from Magnetotelluric Data Nurhasan 1, D. Sutarno 1, Y Ogawa 2, F. Kimata 3, D Sugiyanto 4 1 Physics Department, Bandung Institute of Technology, Bandung,
MODELLING GEOTHERMAL FLOW AND SILICA DEPOSITION ALONG AN ACTIVE FAULT
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Seventh Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 30 - February 1, 2012 SGP-TR-194 MODELLING GEOTHERMAL FLOW AND SILICA DEPOSITION
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Seventh Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 30 - February 1, 2012 SGP-TR-194 MODELLING GEOTHERMAL FLOW AND SILICA DEPOSITION
Hijiori HDR Reservoir Evaluation by Micro-Earthquake Observation
 GRC Transactions, Vol. 38, 2014 Hijiori HDR Reservoir Evaluation by Micro-Earthquake Observation Hideshi Kaieda Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry, Abiko, Chiba, Japan Keywords HDR,
GRC Transactions, Vol. 38, 2014 Hijiori HDR Reservoir Evaluation by Micro-Earthquake Observation Hideshi Kaieda Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry, Abiko, Chiba, Japan Keywords HDR,
6. In the diagram below, letters A and B represent locations near the edge of a continent.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
Estimation of deep fault geometry of the Nagamachi-Rifu fault from seismic array observations
 Earth Planets Space,,, Estimation of deep fault geometry of the Nagamachi-Rifu fault from seismic array observations Ayako Nakamura, Youichi Asano, and Akira Hasegawa Research Center for Prediction of
Earth Planets Space,,, Estimation of deep fault geometry of the Nagamachi-Rifu fault from seismic array observations Ayako Nakamura, Youichi Asano, and Akira Hasegawa Research Center for Prediction of
Open Access EXPRESS LETTER. Takuto Minami 1*, Mitsuru Utsugi 2, Hisashi Utada 1, Tsuneomi Kagiyama 2,3 and Hiroyuki Inoue 2
 https://doi.org/.86/s63-8-99- XPRSS LTTR Open Access Temporal variation in the resistivity structure of the first Nakadake crater, Aso volcano, Japan, during the magmatic eruptions from November to May
https://doi.org/.86/s63-8-99- XPRSS LTTR Open Access Temporal variation in the resistivity structure of the first Nakadake crater, Aso volcano, Japan, during the magmatic eruptions from November to May
MINERALOGICAL STUDY OF VOLCANIC SUBLIMATES FROM HALEMA UMA U CRATER, KILAUEA VOLCANO
 MINERALOGICAL STUDY OF VOLCANIC SUBLIMATES FROM HALEMA UMA U CRATER, KILAUEA VOLCANO Ryan A. Bishop College of Arts and Sciences University of Hawai i at Hilo Hilo, HI 96720 ABSTRACT Halema uma u Crater
MINERALOGICAL STUDY OF VOLCANIC SUBLIMATES FROM HALEMA UMA U CRATER, KILAUEA VOLCANO Ryan A. Bishop College of Arts and Sciences University of Hawai i at Hilo Hilo, HI 96720 ABSTRACT Halema uma u Crater
Plate Tectonics Tutoiral. Questions. Teacher: Mrs. Zimmerman. Plate Tectonics and Mountains Practice Test
 Teacher: Mrs. Zimmerman Print Close Plate Tectonics and Mountains Practice Test Plate Tectonics Tutoiral URL: http://www.hartrao.ac.za/geodesy/tectonics.html Questions 1. Fossils of organisms that lived
Teacher: Mrs. Zimmerman Print Close Plate Tectonics and Mountains Practice Test Plate Tectonics Tutoiral URL: http://www.hartrao.ac.za/geodesy/tectonics.html Questions 1. Fossils of organisms that lived
Preliminary results for a near surface 3D seismic survey of a geothermal system in Colorado
 Preliminary results for a near surface 3D seismic survey of a geothermal system in Colorado Andrew Lamb 1, Kasper van Wijk 1, Lee Liberty 1, Mike Batzle 2, André Revil 2, Kyle Richards 2 and Chuck Diggins
Preliminary results for a near surface 3D seismic survey of a geothermal system in Colorado Andrew Lamb 1, Kasper van Wijk 1, Lee Liberty 1, Mike Batzle 2, André Revil 2, Kyle Richards 2 and Chuck Diggins
Chapter 7: Volcanoes 8/18/2014. Section 1 (Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics) 8 th Grade. Ring of Fire
 Section 1 (Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics) Chapter 7: Volcanoes 8 th Grade Ring of Fire a major belt of es that rims the Pacific Ocean Volcanic belts form along the boundaries of Earth s plates as they
Section 1 (Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics) Chapter 7: Volcanoes 8 th Grade Ring of Fire a major belt of es that rims the Pacific Ocean Volcanic belts form along the boundaries of Earth s plates as they
Earth and Space Science Semester 2 Exam Review. Part 1. - Convection currents circulate in the Asthenosphere located in the Upper Mantle.
 Earth and Space Science 2015 Semester 2 Exam Review Part 1 Convection -A form of heat transfer. - Convection currents circulate in the Asthenosphere located in the Upper Mantle. - Source of heat is from
Earth and Space Science 2015 Semester 2 Exam Review Part 1 Convection -A form of heat transfer. - Convection currents circulate in the Asthenosphere located in the Upper Mantle. - Source of heat is from
Captain s Tryouts 2017
 Captain s Tryouts 2017 Dynamic Planet Test Written by: Araneesh Pratap (Chattahoochee High School) Name: Date: Answer all questions on the answer sheet. Point values are given next to each question or
Captain s Tryouts 2017 Dynamic Planet Test Written by: Araneesh Pratap (Chattahoochee High School) Name: Date: Answer all questions on the answer sheet. Point values are given next to each question or
Summary of geothermal setting in Geo-Caraïbes target islands
 Summary of geothermal setting in Geo-Caraïbes target islands Dr Simon R Young Consultant to OAS Presentation made at the Guadeloupe workshop, 27 April 2004 St Lucia - overview Only one broad target area
Summary of geothermal setting in Geo-Caraïbes target islands Dr Simon R Young Consultant to OAS Presentation made at the Guadeloupe workshop, 27 April 2004 St Lucia - overview Only one broad target area
Hydrothermal circulation at Mount St. Helens determined by self-potential measurements
 Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research 160 (2007) 137 146 www.elsevier.com/locate/jvolgeores Hydrothermal circulation at Mount St. Helens determined by self-potential measurements Paul A. Bedrosian
Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research 160 (2007) 137 146 www.elsevier.com/locate/jvolgeores Hydrothermal circulation at Mount St. Helens determined by self-potential measurements Paul A. Bedrosian
