Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
|
|
|
- Chloe Hamilton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens
2 Chapter 10 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity
3 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Factors Affecting Eruptions Factors that determine the violence of an eruption Composition of the magma Temperature of the magma Dissolved gases in the magma Viscosity Viscosity is the measure of a material's resistance to flow.
4 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Factors Affecting Eruptions Viscosity Factors affecting viscosity - Temperature (hotter magmas are less viscous) - Composition (silica content) 1. High silica high viscosity (e.g., rhyolitic lava) 2. Low silica more fluid (e.g., basaltic lava)
5 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Factors Affecting Eruptions Dissolved gases Mainly water vapor and carbon dioxide Gases expand near the surface A vent is an opening in the surface of Earth through which molten rock and gases are released. Provide the force to extrude lava
6 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Factors Affecting Eruptions Dissolved gases Violence of an eruption is related to how easily gases escape from magma - Gases escape easily from fluid magma. - Viscous magma produces a more violent eruption.
7 Magma Composition
8 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Material Lava Flows Basaltic lavas are more fluid. Types of lava - Pahoehoe lava (resembles braids in ropes) - Aa lava (rough, jagged blocks) Gases One to 5 percent of magma by weight Mainly water vapor and carbon dioxide
9 Pahoehoe (Ropy) Lava Flow
10 Slow-Moving Aa Flow
11 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Material Pyroclastic Materials Pyroclastic materials is the name given to particles produced in volcanic eruptions. The fragments ejected during eruptions range in size from very fine duct and volcanic ash (less than 2 millimeters) to pieces that weigh several tons.
12 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Material Pyroclastic Materials Types of pyroclastic material - Ash and dust fine, glassy fragments - Pumice frothy, air-filled lava - Lapilli walnut-sized particles - Cinders pea-sized particles Particles larger than lapilli - Blocks hardened lava - Bombs ejected as hot lava
13 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Types of Volcanoes The three main volcanic types are shield volcanoes, cinder cones, and composite cones. Anatomy of a Volcano A volcano is a mountain formed of lava and/or pyroclastic material. A crater is the depression at the summit of a volcano or that which is produced by a meteorite impact. A conduit, or pipe, carries gas-rich magma to the surface.
14 Anatomy of a Typical Volcano
15 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Types of Volcanoes Shield Volcanoes Shield volcanoes are broad, gently sloping volcanoes built from fluid basaltic lavas. Cinder Cones Cinder cones are small volcanoes built primarily of pyroclastic material ejected from a single vent. - Steep slope angle - Rather small in size - Frequently occur in groups
16 Shield Volcanoes
17 Cinder Cones
18 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Types of Volcanoes Composite Cones Composite cones are volcanoes composed of both lava flows and pyroclastic material. - Most are adjacent to the Pacific Ocean (e.g., Mt. Rainier). - Large size - Interbedded lavas and pyroclastics - Most violent type of activity
19 Composite Cones
20 Mount St. Helens Before and After the May 18, 1980, Eruption
21 Profiles of Volcanic Landforms
22 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Other Volcanic Landforms Calderas Calderas are large depressions in volcanoes. Nearly circular Formed by collapse Size exceeds one kilometer in diameter
23 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Other Volcanic Landforms Lava Plateaus Fluid basaltic lava extruded from crustal fractures called fissures.
24 10.2 Intrusive Igneous Activity Plutons Plutons are intrusive igneous structures that result from the cooling and hardening of magma beneath the surface of Earth. Intrusive igneous bodies, or plutons, are generally classified according to their shape, size, and relationship to the surrounding rock layers.
25 10.2 Intrusive Igneous Activity Plutons Sills and Laccoliths Sills and laccoliths are plutons that form when magma is intruded close to the surface. - Sills resemble buried lava flows and may exhibit columnar joints. - Laccoliths are lens-shaped masses that arch overlying strata upward.
26 Sill Sills
27 10.2 Intrusive Igneous Activity Plutons Dikes Dikes are tabular-shaped intrusive igneous features that cut across preexisting rock layers. Many dikes form when magma from a large magma chamber invades fractures in the surrounding rocks.
28 10.2 Intrusive Igneous Activity Plutons Batholiths Batholiths are large masses of igneous rock that formed when magma intruded at depth, became crystallized, and subsequently was exposed by erosion. An intrusive igneous body must have a surface exposure greater than 100 square kilometers to be considered a batholith.
29 Batholiths
30 Types of Igneous Plutons
31 10.2 Intrusive Igneous Activity Origin of Magma Geologists conclude that magma originates when essentially solid rock, located in the crust and upper mantle, partially melts. The most obvious way to generate magma from solid rock is to raise the temperature above the level at which the rock begins to melt.
32 10.2 Intrusive Igneous Activity Origin of Magma Role of Heat The geothermal gradient Earth s natural temperature increases with depth but is not sufficient to melt rock in the lower crust and upper mantle Additional heat is generated by - friction in subduction zones - crustal rocks heated during subduction - rising, hot mantle rocks
33 10.2 Intrusive Igneous Activity Origin of Magma Role of Water Causes rock to melt at a lower temperature Plays an important role in subducting ocean plates
34 Basaltic Magma at the Surface
35 10.3 Plate Tectonics and Igneous Activity Convergent Plate Boundaries The basic connection between plate tectonics and volcanism is that plate motions provide the mechanisms by which mantle rocks melt to generate magma. Ocean-Ocean Rising magma can form volcanic island arcs in an ocean (Aleutian Islands). Ocean-Continent Rising magma can form continental volcanic arcs (Andes Mountains).
36 Convergent Boundary Volcano
37 10.3 Plate Tectonics and Igneous Activity Divergent Plate Boundaries The greatest volume of volcanic rock is produced along the oceanic ridge system. Lithosphere pulls apart. Less pressure on underlying rocks Partial melting occurs Large quantities of fluid basaltic magma are produced.
38 10.3 Plate Tectonics and Igneous Activity Intraplate Igneous Activity Intraplate volcanism is igneous activity that occurs within a tectonic plate away from plate boundaries. Most intraplate volcanism occurs where a mass of hotter than normal mantle material called a mantle plume rises toward the surface. The activity forms localized volcanic regions called hot spots. Examples include the Hawaiian Islands and the Columbia Plateau.
39 Kilauea, an Intraplate Volcano
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa
 Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Fires Within: Igneous Activity Foundations, 6e - Chapter 7 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The nature of volcanic eruptions Characteristics
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Fires Within: Igneous Activity Foundations, 6e - Chapter 7 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The nature of volcanic eruptions Characteristics
Overview of Ch. 4. I. The nature of volcanic eruptions 9/19/2011. Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5
 Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 2017-2016 Chapter (4) Volcanoes Chapter 4: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity cataclysmic relating to or denoting a violent natural even Eventually the entire
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 2017-2016 Chapter (4) Volcanoes Chapter 4: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity cataclysmic relating to or denoting a violent natural even Eventually the entire
EARTH SCIENCE KESSEL
 EARTH SCIENCE KESSEL Bell Ringer List everything you KNOW about a volcano (at least 3 things). Then list everything you WANT to know about volcanoes (at least 2 things). Bell Ringer What evidence might
EARTH SCIENCE KESSEL Bell Ringer List everything you KNOW about a volcano (at least 3 things). Then list everything you WANT to know about volcanoes (at least 2 things). Bell Ringer What evidence might
Magma vs. Lava. Molten rock below Earth s surface is called magma. The magma that reaches the surface and erupts out of a volcano is called lava.
 CH. 10.1 Be able to Explain the factors that determine the type of volcanic eruption. List the 3 types of volcanoes Describe the features of a volcano. What is a Volcano? Volcanoes are sites where molten
CH. 10.1 Be able to Explain the factors that determine the type of volcanic eruption. List the 3 types of volcanoes Describe the features of a volcano. What is a Volcano? Volcanoes are sites where molten
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards
 UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 5 Magma and Volcanism Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information: pasakyi@ug.edu.gh College
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 5 Magma and Volcanism Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information: pasakyi@ug.edu.gh College
WHAT IS A MAGMA. Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth.
 UNIT - 8 VOLCANOES WHAT IS A MAGMA Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth. In some instances, it solidifies within the crust to form plutonic
UNIT - 8 VOLCANOES WHAT IS A MAGMA Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth. In some instances, it solidifies within the crust to form plutonic
Magma. Objectives. Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary.
 Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere.
 When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere. A volcano is a mountain that forms when magma reaches the
When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere. A volcano is a mountain that forms when magma reaches the
Chapter 10: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Section 1: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions I. Factors Affecting Eruptions Group # Main Idea:
 Chapter 10: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Section 1: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions I. Factors Affecting Eruptions Group # A. Viscosity Group # B. Dissolved Gases Group # II. Volcanic Material
Chapter 10: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Section 1: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions I. Factors Affecting Eruptions Group # A. Viscosity Group # B. Dissolved Gases Group # II. Volcanic Material
Magma. Objectives. Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary.
 Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity. Aka Volcano Under the City
 Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity Aka Volcano Under the City 18.1 Magma Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Temperature and pressure increase
Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity Aka Volcano Under the City 18.1 Magma Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Temperature and pressure increase
A Volcano is An opening in Earth s crust through
 Volcanoes A Volcano is An opening in Earth s crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt. Also, the landform that develops around this opening. Kinds of Eruptions Geologists classify volcanic
Volcanoes A Volcano is An opening in Earth s crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt. Also, the landform that develops around this opening. Kinds of Eruptions Geologists classify volcanic
Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms.
 Chapter 10 Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms. Reading Strategy Previewing Before you read the section,
Chapter 10 Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms. Reading Strategy Previewing Before you read the section,
Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere. Volcanic Activity
 Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere Volcanic Activity Lesson 3 Volcanoes, Part 1 Think About It What happens when you shake a can of soda and then open it? Focus Question How does the composition of magma
Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere Volcanic Activity Lesson 3 Volcanoes, Part 1 Think About It What happens when you shake a can of soda and then open it? Focus Question How does the composition of magma
Unit 4 Lesson 4 Volcanoes. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Magma Magic What is a volcano? A volcano is any place where gas, ash, or melted rock come out of the ground. Many volcanoes are dormant, meaning an eruption has not occurred in a long period of time. What
Magma Magic What is a volcano? A volcano is any place where gas, ash, or melted rock come out of the ground. Many volcanoes are dormant, meaning an eruption has not occurred in a long period of time. What
Chapter 7: Volcanoes 8/18/2014. Section 1 (Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics) 8 th Grade. Ring of Fire
 Section 1 (Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics) Chapter 7: Volcanoes 8 th Grade Ring of Fire a major belt of es that rims the Pacific Ocean Volcanic belts form along the boundaries of Earth s plates as they
Section 1 (Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics) Chapter 7: Volcanoes 8 th Grade Ring of Fire a major belt of es that rims the Pacific Ocean Volcanic belts form along the boundaries of Earth s plates as they
Part A GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET VOLCANOES. Name
 GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET VOLCANOES Name Part A 1. The rough, jumbled blocky or jagged surface of a lava flow is called a. pahoehoe b. lahar c. aa d. phreatic 2. The Cascade volcanoes like Mt. St.
GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET VOLCANOES Name Part A 1. The rough, jumbled blocky or jagged surface of a lava flow is called a. pahoehoe b. lahar c. aa d. phreatic 2. The Cascade volcanoes like Mt. St.
Study guide chapter 9
 Study guide chapter 9 1. What are the three ways solid mantle material can change phase to a liquid? Associate a boundary/hot spot to each way mantle material changes phase. 1. A decrease in pressure which
Study guide chapter 9 1. What are the three ways solid mantle material can change phase to a liquid? Associate a boundary/hot spot to each way mantle material changes phase. 1. A decrease in pressure which
Volcano: a weak spot in the crust where molten material or magma comes to the surface
 Chapter 7 Volcano: a weak spot in the crust where molten material or magma comes to the surface Magma: a molten mixture of rock forming substances, gases and H 2 O from the mantle Volcanic Belts: Form
Chapter 7 Volcano: a weak spot in the crust where molten material or magma comes to the surface Magma: a molten mixture of rock forming substances, gases and H 2 O from the mantle Volcanic Belts: Form
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. Some volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than a(n) a. hand grenade. b. earthquake. c. geyser. d. atomic bomb. 2. The cause
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. Some volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than a(n) a. hand grenade. b. earthquake. c. geyser. d. atomic bomb. 2. The cause
The Nature of Igneous Rocks
 The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
Chapter 7 Lecture Outline. Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity
 Chapter 7 Lecture Outline Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Mount St. Helens eruption (May 18,1980) Largest historic eruption in North America Lowered peak by more than 400 m Destroyed all trees in
Chapter 7 Lecture Outline Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Mount St. Helens eruption (May 18,1980) Largest historic eruption in North America Lowered peak by more than 400 m Destroyed all trees in
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 volcano sample test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Volcanic belts form along a. islands in the Pacific Ocean. b. North American
volcano sample test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Volcanic belts form along a. islands in the Pacific Ocean. b. North American
A bowl shaped depression formed by the collapse of a volcano is called a. Magma that has left the vent of a volcano is known as. Lava.
 Magma that has left the vent of a volcano is known as Lava A bowl shaped depression formed by the collapse of a volcano is called a Caldera This can form in a caldera when magma starts to come back up
Magma that has left the vent of a volcano is known as Lava A bowl shaped depression formed by the collapse of a volcano is called a Caldera This can form in a caldera when magma starts to come back up
Chapter 7 Lecture Outline. Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity
 Chapter 7 Lecture Outline Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Focus Question 7.1 How were the eruptions of Mount St. Helens and Hawaii s Kilauea volcano different? Mount St. Helens eruption (May 18,1980)
Chapter 7 Lecture Outline Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Focus Question 7.1 How were the eruptions of Mount St. Helens and Hawaii s Kilauea volcano different? Mount St. Helens eruption (May 18,1980)
Earth has more than 600 active volcanoes. An active volcano is one that has erupted within recorded history.
 Volcanoes A volcano is an opening in Earth s surface that erupts gases, ash, and lava. These materials pile up in layers around the opening, forming volcanic mountains. Earth has more than 600 active volcanoes.
Volcanoes A volcano is an opening in Earth s surface that erupts gases, ash, and lava. These materials pile up in layers around the opening, forming volcanic mountains. Earth has more than 600 active volcanoes.
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanic Eruptions. light in color is called a. felsic. b. oceanic. c. mantle. d. mafic. dark in color is called
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanic Eruptions 1. Lava provides an opportunity for scientists to study a. the nature of Earth s inner core. b. the nature of Earth s tectonic plates. c. temperatures
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanic Eruptions 1. Lava provides an opportunity for scientists to study a. the nature of Earth s inner core. b. the nature of Earth s tectonic plates. c. temperatures
NC Earth Science Essential Standards
 NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
Volcano - A Volcano is an opening in the Earth s surface through which molten material or volcanic gases are erupted.
 What is a Volcano? Volcano - A Volcano is an opening in the Earth s surface through which molten material or volcanic gases are erupted. A volcano can either be a classic volcanic cone.. Mt. St. Helens,
What is a Volcano? Volcano - A Volcano is an opening in the Earth s surface through which molten material or volcanic gases are erupted. A volcano can either be a classic volcanic cone.. Mt. St. Helens,
Visualizing Earth Science. Chapter Overview. Volcanoes and Eruption Types. By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner. Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other
 Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
Objectives: Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Describe conditions that cause volcanoes. Describe the relationship between volcanoes and Earth
 Objectives: Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Describe conditions that cause volcanoes. Describe the relationship between volcanoes and Earth s moving plates. Inside of Old Smokey, All covered
Objectives: Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Describe conditions that cause volcanoes. Describe the relationship between volcanoes and Earth s moving plates. Inside of Old Smokey, All covered
Effects of Eruptions. Most active in the world Kilauea, Hawaii.
 Inside of Old Smokey, All covered with snow, Lurk tons of hot magma, Getting ready to blow, Objectives: From deep in the chamber, Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Up a vent to the top, Describe
Inside of Old Smokey, All covered with snow, Lurk tons of hot magma, Getting ready to blow, Objectives: From deep in the chamber, Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Up a vent to the top, Describe
Chapter 5 Lecture. Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology. Twelfth Edition. Volcanic Hazards. Tarbuck and Lutgens Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 5 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Twelfth Edition Volcanoes and Volcanic Hazards Tarbuck and Lutgens Chapter 5 Volcanoes The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions All eruptions involve
Chapter 5 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Twelfth Edition Volcanoes and Volcanic Hazards Tarbuck and Lutgens Chapter 5 Volcanoes The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions All eruptions involve
Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!!
 Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!! Three Types of Volcanos Shield Cinder Cone Composite Shield Volcano Created by hot spots Gently sloping Cinder Volcano Steep Cone-shaped hill/ mountain Composite Volcano Tall,
Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!! Three Types of Volcanos Shield Cinder Cone Composite Shield Volcano Created by hot spots Gently sloping Cinder Volcano Steep Cone-shaped hill/ mountain Composite Volcano Tall,
GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca:
 Name: Date: GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca: SiO 2 silicon dioxide. This is quartz when it crystallizes.
Name: Date: GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca: SiO 2 silicon dioxide. This is quartz when it crystallizes.
FOUNDATIONS OF GEOLOGY CHAPTER 2
 FOUNDATIONS OF GEOLOGY CHAPTER 2 2.3A- VOLCANOES Volcanoes all share common characteristics. Vent- a central channel through which gases, ash and rock are ejected. Magma- molten rock which lies several
FOUNDATIONS OF GEOLOGY CHAPTER 2 2.3A- VOLCANOES Volcanoes all share common characteristics. Vent- a central channel through which gases, ash and rock are ejected. Magma- molten rock which lies several
Essentials of Geology, 11e
 Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Critical Thinking 1. Contrast How could you tell the difference between a mafic rock and a felsic rock by looking at them?
 CHAPTER 13 2 SECTION Volcanoes Volcanic Eruptions KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: How does the composition of magma affect volcanic eruptions and lava flow? What are the
CHAPTER 13 2 SECTION Volcanoes Volcanic Eruptions KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: How does the composition of magma affect volcanic eruptions and lava flow? What are the
Chapter 5 Volcanoes The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Chapter 5 Volcanoes All eruptions involve magma Magma is molten rock that usually contains some crystals and varying amounts of dissolved gases Lava is erupted magma The behavior
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Chapter 5 Volcanoes All eruptions involve magma Magma is molten rock that usually contains some crystals and varying amounts of dissolved gases Lava is erupted magma The behavior
Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!! VOLCANOES
 Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!! VOLCANOES VOLCANOS Three Types of Volcanos Shield Cinder Cone Composite LAND FORMATIONS FROM LAVA & ASH Shield Volcano Created by hot spots Gently sloping Cinder Volcano Steep
Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!! VOLCANOES VOLCANOS Three Types of Volcanos Shield Cinder Cone Composite LAND FORMATIONS FROM LAVA & ASH Shield Volcano Created by hot spots Gently sloping Cinder Volcano Steep
Volcanoes. Table of Contents Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Landforms
 Volcanoes Table of Contents Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Landforms What is a volcano? cone Conduit Or Pipe vent Side vent Central vent Crater A volcano is a vent or 'chimney'
Volcanoes Table of Contents Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Landforms What is a volcano? cone Conduit Or Pipe vent Side vent Central vent Crater A volcano is a vent or 'chimney'
Volcanoes. Volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than the explosion of an atomic bomb.
 Ch. 13 Volcanoes Volcanoes Volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than the explosion of an atomic bomb. Many of these eruptions are caused by the movement of tectonic plates. Volcanism Volcanism-any activity
Ch. 13 Volcanoes Volcanoes Volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than the explosion of an atomic bomb. Many of these eruptions are caused by the movement of tectonic plates. Volcanism Volcanism-any activity
Igneous Rocks. Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members:
 Igneous Rocks Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members: Types of Magma Basaltic, Basic or Mafic very hot (900-1200 C) very fluid
Igneous Rocks Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members: Types of Magma Basaltic, Basic or Mafic very hot (900-1200 C) very fluid
Volcanology. The study of volcanoes
 Volcanology The study of volcanoes Magma forms wherever temperature and pressure are high enough to melt rock. Some magma forms at the aesthenosphere Magma also forms at plate boundaries, where intense
Volcanology The study of volcanoes Magma forms wherever temperature and pressure are high enough to melt rock. Some magma forms at the aesthenosphere Magma also forms at plate boundaries, where intense
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12 Volcanoes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Plate tectonics explains the global pattern of volcanism. Key Figure 12.20 (page
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12 Volcanoes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Plate tectonics explains the global pattern of volcanism. Key Figure 12.20 (page
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanic Eruptions
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanic Eruptions 1. Lava provides an opportunity for scientists to study a. the nature of Earth s inner core. b. the nature of Earth s tectonic plates. c. temperatures
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanic Eruptions 1. Lava provides an opportunity for scientists to study a. the nature of Earth s inner core. b. the nature of Earth s tectonic plates. c. temperatures
Imagine the first rock and the cycles that it has been through.
 A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
Volcano. Magma. Lava. weak spot in crust where magma and gases come up. molten mixture of rockforming
 Volcanoes Volcano weak spot in crust where magma and gases come up Magma Lava molten mixture of rockforming substance, gases, water from the mantle Magma that flows onto earth surface forms solid rock
Volcanoes Volcano weak spot in crust where magma and gases come up Magma Lava molten mixture of rockforming substance, gases, water from the mantle Magma that flows onto earth surface forms solid rock
Physical Geology, 15/e
 Lecture Outlines Physical Geology, 15/e Plummer, Carlson & Hammersley Copyright McGraw-Hill Education, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Volcanism and Extrusive Rocks Physical Geology
Lecture Outlines Physical Geology, 15/e Plummer, Carlson & Hammersley Copyright McGraw-Hill Education, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Volcanism and Extrusive Rocks Physical Geology
Chapter 5 9/10/2011. Introduction. Volcanoes and Volcanism. Volcanism. Introduction. Introduction. Introduction
 Introduction Chapter 5 Volcanism is the eruption of magma, and associated gases at the surface. Some magma erupts explosively as pyroclastic (fire-broken) rock and other erupts as lava flows. Volcanoes
Introduction Chapter 5 Volcanism is the eruption of magma, and associated gases at the surface. Some magma erupts explosively as pyroclastic (fire-broken) rock and other erupts as lava flows. Volcanoes
Apr 20 2:26 PM. the opening in Earth's crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt. the landform that develops around this opening
 Volcanoes Cleveland Volcano, Alaska, May 2006 Taken from the ISS Apr 20 2:26 PM The term volcano can refer to two things: 1. the opening in Earth's crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt
Volcanoes Cleveland Volcano, Alaska, May 2006 Taken from the ISS Apr 20 2:26 PM The term volcano can refer to two things: 1. the opening in Earth's crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt
Chapter 18. Volcanism
 Chapter 18 Volcanism Ring of fire contains 66% of world s active volcanoes Convergent : Divergent: Icelandic Eruption Mount Etna Different Kinds of eruptions: Volcanic activity is controlled by plate tectonics,
Chapter 18 Volcanism Ring of fire contains 66% of world s active volcanoes Convergent : Divergent: Icelandic Eruption Mount Etna Different Kinds of eruptions: Volcanic activity is controlled by plate tectonics,
180 points. 1. Lava erupts through an opening in Earth s crust called a. 2. A bowl-shaped depression that forms around the vent of a volcano is a
 CHAPTER 18 Volcanism SECTION 18.1 Volcanoes In your textbook, read about the anatomy of a volcano and volcanic material. Completes each statement or answer the question. 25 points 180 points volcano. In
CHAPTER 18 Volcanism SECTION 18.1 Volcanoes In your textbook, read about the anatomy of a volcano and volcanic material. Completes each statement or answer the question. 25 points 180 points volcano. In
lava magma pyroclastic materials lava flow igneous rock volcanic (extrusive igneous) rock plutonic (intrusive igneous) rock felsic magma mafic magma
 magma lava lava flow pyroclastic materials igneous rock volcanic (extrusive igneous) rock plutonic (intrusive igneous) rock felsic magma mafic magma intermediate magma viscosity magma chamber Bowen s reaction
magma lava lava flow pyroclastic materials igneous rock volcanic (extrusive igneous) rock plutonic (intrusive igneous) rock felsic magma mafic magma intermediate magma viscosity magma chamber Bowen s reaction
3.2 Notes: Volcanoes Form as Molten Rock Erupts
 3.2 Notes: Volcanoes Form as Molten Rock Erupts Think about What happens when a volcano erupts? Volcanoes erupt many types of material Earth s thin outer layer is, but most of Earth is extremely hot rock
3.2 Notes: Volcanoes Form as Molten Rock Erupts Think about What happens when a volcano erupts? Volcanoes erupt many types of material Earth s thin outer layer is, but most of Earth is extremely hot rock
Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark
 Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Effusive: lavas (e.g., Kilauea) Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Explosive: pyroclastic rocks (e.g., Krakatau) Factors Governing
Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Effusive: lavas (e.g., Kilauea) Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Explosive: pyroclastic rocks (e.g., Krakatau) Factors Governing
6/26/2018. Volcanoes & Volcanic Hazards Earth, Chapter 5 Chapter 5 Volcanoes
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Volcanoes & Earth, Chapter 5 Chapter 5 Volcanoes From the VolcanoCam, 12 September 2007 All eruptions involve magma Magma is molten rock that usually contains some
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Volcanoes & Earth, Chapter 5 Chapter 5 Volcanoes From the VolcanoCam, 12 September 2007 All eruptions involve magma Magma is molten rock that usually contains some
Types of Volcanoes KEY CONCEPT: TECTONIC PLATE MOTIONS CAN RESULT IN VOLCANIC ACTIVITY AT PLATE BOUNDARIES.
 Types of Volcanoes KEY CONCEPT: TECTONIC PLATE MOTIONS CAN RESULT IN VOLCANIC ACTIVITY AT PLATE BOUNDARIES. Volcanoes How do volcanoes work? How do volcanoes work? Magma is forced onto Earth s surface.
Types of Volcanoes KEY CONCEPT: TECTONIC PLATE MOTIONS CAN RESULT IN VOLCANIC ACTIVITY AT PLATE BOUNDARIES. Volcanoes How do volcanoes work? How do volcanoes work? Magma is forced onto Earth s surface.
Vulcanicity. Objectives to identify the basic structure of volcanoes and understand how they form.
 Vulcanicity Objectives to identify the basic structure of volcanoes and understand how they form. Some key terms to start.. Viscosity how well a substance (lava) flows. Acid lavas have a high viscosity,
Vulcanicity Objectives to identify the basic structure of volcanoes and understand how they form. Some key terms to start.. Viscosity how well a substance (lava) flows. Acid lavas have a high viscosity,
Geology 1 st Semester Exam YSBAT
 1. What is the role of a geologist? Geology 1 st Semester Exam YSBAT 2016-2017 2. Earth is subdivided into three main layers based on what? 3. What features do you find at divergent boundaries? 4. Rock
1. What is the role of a geologist? Geology 1 st Semester Exam YSBAT 2016-2017 2. Earth is subdivided into three main layers based on what? 3. What features do you find at divergent boundaries? 4. Rock
Chapter 11 Section 2 VOLCANOES TB 337
 Chapter 11 Section 2 VOLCANOES TB 337 http://www.brainpop.com/science/earthsystem/volcanoes/ I. How do volcanoes form? Rising Magma leads to eruptions. Magma (solids and gases) are spewed out to form cone-shape
Chapter 11 Section 2 VOLCANOES TB 337 http://www.brainpop.com/science/earthsystem/volcanoes/ I. How do volcanoes form? Rising Magma leads to eruptions. Magma (solids and gases) are spewed out to form cone-shape
Convergent Plate Boundary Geologic Features
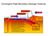 Convergent Plate Boundary Geologic Features Ocean Trench Mtn / Volcano New Ocean Crust Old Continenta l Crust Beadle, 2009 Convection cells provide the force to move the continents. The crust is carried
Convergent Plate Boundary Geologic Features Ocean Trench Mtn / Volcano New Ocean Crust Old Continenta l Crust Beadle, 2009 Convection cells provide the force to move the continents. The crust is carried
Dynamic Planet PUT ALL YOUR ANSWERS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. c) low temperature d) high volatile content
 School Name: Team #: Students Names: Dynamic Planet 2016 Science Olympiad Invitational University of Texas at Austin PUT ALL YOUR ANSWERS ON THE ANSWER SHEET 1) Low viscosity magmas have: a) high silica
School Name: Team #: Students Names: Dynamic Planet 2016 Science Olympiad Invitational University of Texas at Austin PUT ALL YOUR ANSWERS ON THE ANSWER SHEET 1) Low viscosity magmas have: a) high silica
1/31/2013 BASALTIC BASALTIC ANDESITIC RHYOLITIC
 Can you predict the location of volcanoes? What is causing this eruption? What factors influence its character? A volcano is any landform from which lava, gas, or ashes, escape from underground or have
Can you predict the location of volcanoes? What is causing this eruption? What factors influence its character? A volcano is any landform from which lava, gas, or ashes, escape from underground or have
! Profile of Mauna Loa in Hawaii. Mauna Loa is one of five huge shield volcanoes that make up the island of Hawaii.
 - Shield Volcanoes - Low, rounded profiles; slope angles 2-10 ; composed of numerous flows of mafic composition and little explosive activity - Largest of all volcanoes! Shield volcanoes consist of numerous
- Shield Volcanoes - Low, rounded profiles; slope angles 2-10 ; composed of numerous flows of mafic composition and little explosive activity - Largest of all volcanoes! Shield volcanoes consist of numerous
Types of Volcanoes. Key Concept: Tectonic plate motions can result in volcanic activity at plate boundaries.
 Types of Volcanoes Key Concept: Tectonic plate motions can result in volcanic activity at plate boundaries. Volcanoes How do volcanoes work? How do volcanoes work? Magma is forced onto Earth s surface.
Types of Volcanoes Key Concept: Tectonic plate motions can result in volcanic activity at plate boundaries. Volcanoes How do volcanoes work? How do volcanoes work? Magma is forced onto Earth s surface.
Igneous Rocks. Definition of Igneous Rocks. Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma
 Igneous Rocks Definition of Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma Magma molten rock within the Earth Lava molten rock on the Earth s s surface Igneous
Igneous Rocks Definition of Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma Magma molten rock within the Earth Lava molten rock on the Earth s s surface Igneous
Bellringer: What materials are ejected from volcanoes? Quote of the Day: "Science is not belief, but the will to find out.
 Bellringer: What materials are ejected from volcanoes? Quote of the Day: "Science is not belief, but the will to find out." ~Anonymous Sep 26 10:30 AM 1 Copy Directly into your notebook... 1. Pyro Latin
Bellringer: What materials are ejected from volcanoes? Quote of the Day: "Science is not belief, but the will to find out." ~Anonymous Sep 26 10:30 AM 1 Copy Directly into your notebook... 1. Pyro Latin
UNIT SIX: Earth s Structure. Chapter 18 Earth s History and Rocks Chapter 19 Changing Earth Chapter 20 Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 UNIT SIX: Earth s Structure Chapter 18 Earth s History and Rocks Chapter 19 Changing Earth Chapter 20 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Chapter Twenty: Earthquakes and Volcanoes 20.1 Earthquakes 20.2 Volcanoes
UNIT SIX: Earth s Structure Chapter 18 Earth s History and Rocks Chapter 19 Changing Earth Chapter 20 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Chapter Twenty: Earthquakes and Volcanoes 20.1 Earthquakes 20.2 Volcanoes
Week: Dates: 10/19 10/30 Unit: Volcanos
 clementaged.weebly.com Name: ODD Period: Week: 10 11 Dates: 10/19 10/30 Unit: Volcanos Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 19 E 20 O *Vocabulary *Frayer Vocab *Volcano Notes *Bill Nye Notes 21 E 22
clementaged.weebly.com Name: ODD Period: Week: 10 11 Dates: 10/19 10/30 Unit: Volcanos Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 19 E 20 O *Vocabulary *Frayer Vocab *Volcano Notes *Bill Nye Notes 21 E 22
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks
 Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Introduction to volcanoes. Volcano: an opening in the earth s surface through which lava, hot gases, and rock fragments erupt
 Introduction to volcanoes Volcano: an opening in the earth s surface through which lava, hot gases, and rock fragments erupt Origin of Volcanoes 1. Magma 50-100 miles below the earth s surface slowly begins
Introduction to volcanoes Volcano: an opening in the earth s surface through which lava, hot gases, and rock fragments erupt Origin of Volcanoes 1. Magma 50-100 miles below the earth s surface slowly begins
Volcano an opening in Earth s crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt and the landform that develops around this opening.
 Chapter 9 Volcano an opening in Earth s crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt and the landform that develops around this opening. 3 Conditions Allow Magma to Form: Decrease in pressure
Chapter 9 Volcano an opening in Earth s crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt and the landform that develops around this opening. 3 Conditions Allow Magma to Form: Decrease in pressure
IGNEOUS ROCKS AND IGNEOUS ACTIVITY
 DATE DUE: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 305 Name: Section: IGNEOUS ROCKS AND IGNEOUS ACTIVITY Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Use GEOLOGIC vocabulary where
DATE DUE: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 305 Name: Section: IGNEOUS ROCKS AND IGNEOUS ACTIVITY Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Use GEOLOGIC vocabulary where
Volcanoes. Presented by Kesler Science
 Presented by Kesler Science Essential Questions: 1. What are the parts of a volcano? 2. What are the four types? 3. What processes form volcanoes? 4. Where are volcanoes located on earth? What is a Volcano?
Presented by Kesler Science Essential Questions: 1. What are the parts of a volcano? 2. What are the four types? 3. What processes form volcanoes? 4. Where are volcanoes located on earth? What is a Volcano?
Geology 101. Reading Guide for Chapters 1, 4, and 5
 Geology 101 Name Reading Guide for Chapters 1, 4, and 5 The purpose of the Reading Guides is to help you sort out the most important ideas in the text. I recommend answering the questions as you read the
Geology 101 Name Reading Guide for Chapters 1, 4, and 5 The purpose of the Reading Guides is to help you sort out the most important ideas in the text. I recommend answering the questions as you read the
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore MAGMA For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources, visit:
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore MAGMA For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources, visit:
IGNEOUS ROCKS AND IGNEOUS ACTIVITY
 DATE DUE: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 300 Name: Section: IGNEOUS ROCKS AND IGNEOUS ACTIVITY Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Use GEOLOGIC vocabulary where
DATE DUE: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 300 Name: Section: IGNEOUS ROCKS AND IGNEOUS ACTIVITY Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Use GEOLOGIC vocabulary where
YORK CASTLE HIGH SCHOOL CHRISTMAS TERM EXAMINATIONS GEOGRAPHY Duration 1 1 /2 HRS.
 GRADE 9 YORK CASTLE HIGH SCHOOL CHRISTMAS TERM EXAMINATIONS GEOGRAPHY Duration 1 1 /2 HRS. Name: 1. Label the internal structure of the earth provided below. WRITE on the space provide. Oceanic Crust/Upper
GRADE 9 YORK CASTLE HIGH SCHOOL CHRISTMAS TERM EXAMINATIONS GEOGRAPHY Duration 1 1 /2 HRS. Name: 1. Label the internal structure of the earth provided below. WRITE on the space provide. Oceanic Crust/Upper
Week: Dates: 10/13 10/24 Unit: Volcanos
 clementaged.weebly.com Name: Period: 7 Week: 10 11 Dates: 10/13 10/24 Unit: Volcanos Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 13 No School 14 O *Greenhand Conference *Vocabulary *Volcano Movie 15 E *Volcano
clementaged.weebly.com Name: Period: 7 Week: 10 11 Dates: 10/13 10/24 Unit: Volcanos Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 13 No School 14 O *Greenhand Conference *Vocabulary *Volcano Movie 15 E *Volcano
Igneous Rocks. Igneous Rocks. Genetic Classification of
 Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
Volcano Vocabulary ROCK CYCLE. Igneous REMELTED REMELTED BURIED BURIED HEAT ERODED DEPOSITED. Metamorphic Sedimentary ERODED, TRANSPORTED DEPOSITED
 Volcano Vocabulary VOLCANISM VENT CRATER CALDERA QUIET ERUPTION EXPLOSIVE ERUPTION PYROCLASTIC DEBRIS CINDER CONE SHIELD VOLCANO COMPOSITE VOLCANO STRATO VOLCANO ACTIVE DORMANT EXTINCT INTRUSION DIKE SILL
Volcano Vocabulary VOLCANISM VENT CRATER CALDERA QUIET ERUPTION EXPLOSIVE ERUPTION PYROCLASTIC DEBRIS CINDER CONE SHIELD VOLCANO COMPOSITE VOLCANO STRATO VOLCANO ACTIVE DORMANT EXTINCT INTRUSION DIKE SILL
When magma is ejected by a volcano or other vent, the material is called lava. Magma that has cooled into a solid is called igneous rock.
 This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 4) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry magma For the
This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 4) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry magma For the
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. What can cause some of the most dramatic changes to Earth s surface? a. solar activity b. tides c. geysers d. volcanic eruptions
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. What can cause some of the most dramatic changes to Earth s surface? a. solar activity b. tides c. geysers d. volcanic eruptions
A. What is a volcano?
 VOLCANISM THE ROCK CYCLE I. Introduction From: Roman god of fire, Vulcan A. What is a volcano? A conical mountain formed around a vent where lava, pyroclastic materials, and gases are erupted. I. Introduction
VOLCANISM THE ROCK CYCLE I. Introduction From: Roman god of fire, Vulcan A. What is a volcano? A conical mountain formed around a vent where lava, pyroclastic materials, and gases are erupted. I. Introduction
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands
 Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 4 22 January 2004 Turn in Homework #1 Any Questions? IMPORTANT Big Island Field Trip We need a $162 payment for airfare BEFORE January 29 th Description of logistics,
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 4 22 January 2004 Turn in Homework #1 Any Questions? IMPORTANT Big Island Field Trip We need a $162 payment for airfare BEFORE January 29 th Description of logistics,
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals. Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane SGM 210_2013
 Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Intrusive and Effusive Rocks Effusive rocks: rapid cooling small crystalls or glas Lava & ash Magmatic
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Intrusive and Effusive Rocks Effusive rocks: rapid cooling small crystalls or glas Lava & ash Magmatic
3/24/2016. Geology 12 Mr. M. Gauthier 24 March 2016
 Geology 12 Mr. M. Gauthier 24 March 2016 Introduction: Mt. St. Helens Before 1980 Mt. St Helens, in Southern Washington State, had not erupted since 1857 On March 27,1980 minor ashand eruptions were due
Geology 12 Mr. M. Gauthier 24 March 2016 Introduction: Mt. St. Helens Before 1980 Mt. St Helens, in Southern Washington State, had not erupted since 1857 On March 27,1980 minor ashand eruptions were due
Volcanoes. I Types of Volcanoes II Plutonic Activity III Plate Tectonics and Igneous Activity IV Magma and Lava V Types of Lava Flows
 Volcanoes I Types of Volcanoes II Plutonic Activity III Plate Tectonics and Igneous Activity IV Magma and Lava V Types of Lava Flows 1 Some Definitions Igneous refers to processes and rocks involving or
Volcanoes I Types of Volcanoes II Plutonic Activity III Plate Tectonics and Igneous Activity IV Magma and Lava V Types of Lava Flows 1 Some Definitions Igneous refers to processes and rocks involving or
The locations of volcanoes are mostly determined by plate tectonics. convergent: tending to move toward one point or to approach each other
 Ch. 22.6 Volcanoes The locations of volcanoes are mostly determined by plate tectonics. Review Vocabulary convergent: tending to move toward one point or to approach each other IntroVolcanoes348 I. Zones
Ch. 22.6 Volcanoes The locations of volcanoes are mostly determined by plate tectonics. Review Vocabulary convergent: tending to move toward one point or to approach each other IntroVolcanoes348 I. Zones
Unit 5: Plate Tectonics
 Unit 5: Plate Tectonics A. Alfred Wegner 1. Continental drift hypothesis a. single supercontinent called Pangaea b. 200 million years ago Pangaea (all land) began to break up and started drifting to their
Unit 5: Plate Tectonics A. Alfred Wegner 1. Continental drift hypothesis a. single supercontinent called Pangaea b. 200 million years ago Pangaea (all land) began to break up and started drifting to their
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earthquakes Lesson 2 Volcanoes Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earthquakes Lesson 2 Volcanoes Chapter Wrap-Up What causes earthquakes and volcanic eruptions? What do you think? Before you begin, decide if you agree or disagree with each
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earthquakes Lesson 2 Volcanoes Chapter Wrap-Up What causes earthquakes and volcanic eruptions? What do you think? Before you begin, decide if you agree or disagree with each
Chapter 12 Vocabulary and Study Guide Volcanoes
 Chapter 12 Vocabulary and Study Guide Volcanoes 1) acid rain Moisture with a PH below 5.6 that falls to Earth as rain or snow and can damage forests, harm organisms, and corrode structures. Sulfurous gases
Chapter 12 Vocabulary and Study Guide Volcanoes 1) acid rain Moisture with a PH below 5.6 that falls to Earth as rain or snow and can damage forests, harm organisms, and corrode structures. Sulfurous gases
Igneous Rock. Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere
 Igneous Rock Magma Molten rock under the surface Temperature = 600 o 1400 o C Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere Magma chamber - most all magma consists of silicon and oxygen (silicate)
Igneous Rock Magma Molten rock under the surface Temperature = 600 o 1400 o C Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere Magma chamber - most all magma consists of silicon and oxygen (silicate)
VOLCANOES. Homework due Wed./Thurs. I have a few copies left, or get by moodle or webpage
 VOLCANOES Homework due Wed./Thurs. I have a few copies left, or get by moodle or webpage Bowen s Reaction Series Oceanic basin tectonics http://my.execpc.com/~acmelasr/mountains/geogramsnf.html Icelandic
VOLCANOES Homework due Wed./Thurs. I have a few copies left, or get by moodle or webpage Bowen s Reaction Series Oceanic basin tectonics http://my.execpc.com/~acmelasr/mountains/geogramsnf.html Icelandic
OIKOS > volcano > mechanism >types of volcanoes
 Main Types of Volcanoes Volcanologists have classified volcanoes into groups based on the shape of the volcano, the materials they are built of, and the way the volcano erupts. The main one can be described
Main Types of Volcanoes Volcanologists have classified volcanoes into groups based on the shape of the volcano, the materials they are built of, and the way the volcano erupts. The main one can be described
Introduction. Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth
 Introduction Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth Example: Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii Hot (~1,200 o C) lava pools around the volcanic vent. Hot, syrupy lava runs downhill as a lava flow. The
Introduction Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth Example: Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii Hot (~1,200 o C) lava pools around the volcanic vent. Hot, syrupy lava runs downhill as a lava flow. The
Folding. Faulting. Volcanoes
 Folding Faulting Volcanoes Most major global mountain ranges were formed by the collision of continental (tectonic) plates Fold mountains are actually formed by crust which have been uplifted and folded
Folding Faulting Volcanoes Most major global mountain ranges were formed by the collision of continental (tectonic) plates Fold mountains are actually formed by crust which have been uplifted and folded
Formation of the Hawaiian Islands. Volcanoes, Magma, and Hot Spots
 Formation of the Hawaiian Islands Volcanoes, Magma, and Hot Spots Topics Hawai i Ring of Fire Hot Spots Decompression Melting The Hawai i Hot Spot Topics Hawai i Ring of Fire Hot Spots Decompression Melting
Formation of the Hawaiian Islands Volcanoes, Magma, and Hot Spots Topics Hawai i Ring of Fire Hot Spots Decompression Melting The Hawai i Hot Spot Topics Hawai i Ring of Fire Hot Spots Decompression Melting
