Verification of the asperity model using seismogenic fault materials Abstract
|
|
|
- Hannah Cameron
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Verification of the asperity model using seismogenic fault materials Takehiro Hirose*, Wataru Tanikawa and Weiren Lin Kochi Institute for Core Sample Research/JAMSTEC, JAPAN * Corresponding author: hiroset@jamstec.go.jp Abstract The asperity model is an important conceptual framework for comprehensible understanding of a variety (heterogeneity in slip and moment) of earthquakes located in subduction zones. A significant advantage of the asperity model is that slip behavior in both the asperity area (strong coupling dominated by stick slip behavior) and the non-asperity area (weak coupling dominated by stable sliding) can be described by a single constitutive friction law with a few parameters (i.e., a-b, D c ). Therefore many numerical simulations for reproducing cycle and slip distribution of subduction earthquakes have been attempted based on the asperity model, resulting in several recent significant advances in understanding the origin of a variety of subduction zone earthquakes. However, whether the constitutive parameters used in such simulations represent realistic values determined from seismogenic fault materials by laboratory experiments have not been verified up until now. For instance, an asperity region is often described by the constitutive parameter, a-b<0 or larger D c, in numerical simulations, although we have not yet confirmed these mechanical properties in natural faults in seismogenic zones at depth. Moreover, we still do not fully understand what materials compose the asperity/non-asperity regions and what physical properties of the materials characterize the asperity/non-asperity. Detailed analyses of core materials collected from seismogenic fault drilling by the Chikyu in such actively deforming regions are essential, if we wish to (1) produce realistic constitutive parameters that can be incorporated into earthquake numerical simulations, and to (2) resolve the important question like what the asperity/non-asperity area is in terms of material sciences.
2 Introduction The slip heterogeneity revealed by recent geophysical studies is often characterized by terms such as asperities and non-asperities (barriers) which demonstrates the spatial diversity of seismic slip (Kanamori, 2008). Asperities are the portions on a fault at which large slip occurs, and non-asperities are patches where fault motion is impeded. Asperities and barriers reflect the heterogeneities of stress, the frictional properties of faults and geometries, and have a key role in the nucleation, growth and cessation of slip motion. Thus, the asperity/non-asperity model is an important conceptual framework for explaining regional variation of rupture patterns in subduction zone earthquakes by numerical simulations. However, it has not been verified up until now whether the constitutive parameters used in such simulations represent realistic values determined from seismogenic fault materials by laboratory experiments. In addition, it is not still poorly known what materials and their physical properties characterize an asperity and non-asperity. Here we propose three hypotheses that will be possibly confirmed by detailed analyses of core materials collected from seismogenic fault drilling by the Chikyu and by borehole monitoring in such actively deforming regions. (1) Depth variation of constitutive parameters in the framework of a rate and state friction law: Figure 1 shows a synoptic model for fault stability as a function of depth for subduction zones, summarized by Scholz (1998). This model implies that fault zone materials at asperity regions could show the velocity weakening behavior (one of the constitutive parameter, a-b, indicates negative value) at in-situ conditions. A critical slip weakening distance, D c, which is the slip over which fault strength breaks down during earthquake nucleation, is often used to define the asperity/non-asperity; shorter D c for asperity and longer D c for non-asperity. These hypotheses can be verified by determining the parameter by laboratory friction experiments on seismogenic fault materials collected from the asperity/non-asperity regions. (2) Strength profile along subducting plate boundaries: Figure 2 shows a conceptual model for the strength profile along subducting plate boundaries (Shimamoto et al., 1993). The diagram implies that intermediate seismogenic zone (region AB in the figure) could correspond to the asperity where earthquake ruptures nucleate and that the rocks in the region are possibly composed of strong materials which are able to accumulate the stress. The strength in the shallow and deep zone (region TA and BC) is low due to the massive solution-transfer processes and
3 to the fully-plastic deformation mechanisms operated. Thus the materials from non-asperity regions could show the characteristic microstructures formed by these deformation mechanisms. The strength of rocks along subduction plate boundaries is perhaps much weaker than the frictional strength of common rocks (i.e., Byerlee s law) due to the weakening effects of abundant H 2 O and chemical reactions on the strength of rocks. Core samples collected by ultra-deep drilling are required to verify these hypotheses and the model of strength profile along subducting plate boundaries. (3) Fluid pressure distribution along subduction fault zones: Evolution of pore-fluid pressure around fault zones is crucial for earthquake nucleation and recurrence intervals (i.e., a fault-valve model, proposed by Sibson, 1994). Elevated pore pressure reduces the effective normal stress on faults, leading to the initiation of failure or earthquake slip. On the other hand, a stable slip (fault creep) may be also enhanced by the existence of fluid. It is still unclear whether the distribution of fluid along faults could characterize the asperity/non-asperity. The distribution of fluid pressure within subduction zones can be estimated from 3D seismic reflection data (i.e., Tsuji et al., 2008, Figure 3) and should be calibrated by in-situ measurements. Establishing a correlation between distribution of microseismicity and fluid (or fluid pressure) along fault plane may help to understand the role of fluid to define the asperity/non-asperity
4 Figure 1. A conceptual model for fault stability as a function of depth for subduction zones (Scholz, 1998). The model implies that an asperity can be described as a constitutive parameter, a-b<0, in the framework of the rate and state friction law. Figure 2. A conceptual model for the strength profile along subducting plate boundaries (Shimamoto et al., 1993). AB, intermediate seismogenic zone, which could correspond to an asperity region. TA and BC, shallow and deep aseismic zones (non-asperity zones). Heavy dashed line indicates the frictional strength of many brittle rocks and the flow stress in the fully plastic regime. The strength of rocks along subduction plate boundaries is perhaps much weaker than the frictional strength due to the weakening effects of abundant H 2 O and chemical reactions on the strength of rocks. Figure 3. Pore pressure distribution at Nankai trough area estimated using a single
5 relationship between elastic property and porosity (Tsuji et al., 2008). Asperity or non-asperity at the plate boundary may be related with the pore pressure distribution. References Kanamori, H., Earthquake physics and real time-seismology, Nature, 451, Tsuji, T., Tokuyama, H., Pisani, P. C., and Moore, G., Effective stress and pore pressure in the Nankai accretionary prism off the Muroto Peninsula, southwestern Japan, J. Geophys. Res., 113, B11401, doi: /2007jb Shimamoto, T., Seno, T., and Ueda, S., A simple rheoligical framework for comparative subductology, in Relating Geophysical Structures and Processes: The Jeffreys Volume, Geophysical Monograph 76, IUGG 16, Scholz, C. H., Earthquakes and friction laws, Nature 391, 37-42
The Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 The Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Christopher H. Scholz Lamont-Doherty Geological Observatory and Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Columbia University 2nd edition CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY
The Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Christopher H. Scholz Lamont-Doherty Geological Observatory and Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Columbia University 2nd edition CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY
Hitoshi Hirose (1), and Kazuro Hirahara (2) Abstract. Introduction
 Three dimensional simulation for the earthquake cycle at a subduction zone based on a rate- and state-dependent friction law: Insight into a finiteness and a variety of dip-slip earthquakes Hitoshi Hirose
Three dimensional simulation for the earthquake cycle at a subduction zone based on a rate- and state-dependent friction law: Insight into a finiteness and a variety of dip-slip earthquakes Hitoshi Hirose
Seismic and aseismic processes in elastodynamic simulations of spontaneous fault slip
 Seismic and aseismic processes in elastodynamic simulations of spontaneous fault slip Most earthquake simulations study either one large seismic event with full inertial effects or long-term slip history
Seismic and aseismic processes in elastodynamic simulations of spontaneous fault slip Most earthquake simulations study either one large seismic event with full inertial effects or long-term slip history
I point out two possible paradoxical difficulties in the important target of the IODP in subduction zones, i.e.,
 Drilling the Seismogenic Zone: Some Paradoxes Tetsuzo Seno Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo (Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst., subumitted on January 16, 2003; accepted on July 22, 2003) Abstract
Drilling the Seismogenic Zone: Some Paradoxes Tetsuzo Seno Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo (Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst., subumitted on January 16, 2003; accepted on July 22, 2003) Abstract
Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics
 Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics Naoyuki Kato (1) and Tomowo Hirasawa (2) (1) Geological
Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics Naoyuki Kato (1) and Tomowo Hirasawa (2) (1) Geological
3D MODELING OF EARTHQUAKE CYCLES OF THE XIANSHUIHE FAULT, SOUTHWESTERN CHINA
 3D MODELING OF EARTHQUAKE CYCLES OF THE XIANSHUIHE FAULT, SOUTHWESTERN CHINA Li Xiaofan MEE09177 Supervisor: Bunichiro Shibazaki ABSTRACT We perform 3D modeling of earthquake generation of the Xianshuihe
3D MODELING OF EARTHQUAKE CYCLES OF THE XIANSHUIHE FAULT, SOUTHWESTERN CHINA Li Xiaofan MEE09177 Supervisor: Bunichiro Shibazaki ABSTRACT We perform 3D modeling of earthquake generation of the Xianshuihe
Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip Behaviors: What We Have and What We Need Nadia Lapusta. California Institute of Technology
 Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip Behaviors: What We Have and What We Need Nadia Lapusta California Institute of Technology Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip
Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip Behaviors: What We Have and What We Need Nadia Lapusta California Institute of Technology Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip
REGIONAL CHARACTERISTICS OF STRESS FIELD AND ITS DYNAMICS IN AND AROUND THE NANKAI TROUGH, JAPAN
 46 4 2003 7 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol. 46, No. 4 July, 2003 1 1 2 3 1, 100037 2, 920-1192 3, 237-0061,,, : -. (10 22 ), (60 85km) ; (40 ), (160km)..,. GPS,, -,,.,,,.. 0001-5733(2003) 04-0488 -
46 4 2003 7 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol. 46, No. 4 July, 2003 1 1 2 3 1, 100037 2, 920-1192 3, 237-0061,,, : -. (10 22 ), (60 85km) ; (40 ), (160km)..,. GPS,, -,,.,,,.. 0001-5733(2003) 04-0488 -
Qualitative modeling of earthquakes and aseismic slip in the Tohoku-Oki area. Nadia Lapusta, Caltech Hiroyuki Noda, JAMSTEC
 Qualitative modeling of earthquakes and aseismic slip in the Tohoku-Oki area Nadia Lapusta, Caltech Hiroyuki Noda, JAMSTEC Constitutive law on the fault: Rate-and-state friction at low slip rates + Potential
Qualitative modeling of earthquakes and aseismic slip in the Tohoku-Oki area Nadia Lapusta, Caltech Hiroyuki Noda, JAMSTEC Constitutive law on the fault: Rate-and-state friction at low slip rates + Potential
Megathrust Earthquakes
 Megathrust Earthquakes Susan Schwartz University of California Santa Cruz CIDER 2017 UC Berkeley July 5, 2017 The largest megathrust events are not uniformally distributed at all subduction zones. M>8
Megathrust Earthquakes Susan Schwartz University of California Santa Cruz CIDER 2017 UC Berkeley July 5, 2017 The largest megathrust events are not uniformally distributed at all subduction zones. M>8
Material is perfectly elastic until it undergoes brittle fracture when applied stress reaches σ f
 Material is perfectly elastic until it undergoes brittle fracture when applied stress reaches σ f Material undergoes plastic deformation when stress exceeds yield stress σ 0 Permanent strain results from
Material is perfectly elastic until it undergoes brittle fracture when applied stress reaches σ f Material undergoes plastic deformation when stress exceeds yield stress σ 0 Permanent strain results from
Depth variation of coseismic stress drop explains bimodal earthquake magnitude-frequency distribution
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L24301, doi:10.1029/2008gl036249, 2008 Depth variation of coseismic stress drop explains bimodal earthquake magnitude-frequency distribution
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L24301, doi:10.1029/2008gl036249, 2008 Depth variation of coseismic stress drop explains bimodal earthquake magnitude-frequency distribution
Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ).
 Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ). If sliding speeds up, the average lifespan of asperities decreases This means
Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ). If sliding speeds up, the average lifespan of asperities decreases This means
3D modeling of the cycle of a great Tohoku oki earthquake, considering frictional behavior at low to high slip velocities
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl049308, 2011 3D modeling of the cycle of a great Tohoku oki earthquake, considering frictional behavior at low to high slip velocities B. Shibazaki,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl049308, 2011 3D modeling of the cycle of a great Tohoku oki earthquake, considering frictional behavior at low to high slip velocities B. Shibazaki,
Coseismic slip distribution of the 1946 Nankai earthquake and aseismic slips caused by the earthquake
 Earth Planets Space, 53, 235 241, 2001 Coseismic slip distribution of the 1946 Nankai earthquake and aseismic slips caused by the earthquake Yuichiro Tanioka 1 and Kenji Satake 2 1 Meteorological Research
Earth Planets Space, 53, 235 241, 2001 Coseismic slip distribution of the 1946 Nankai earthquake and aseismic slips caused by the earthquake Yuichiro Tanioka 1 and Kenji Satake 2 1 Meteorological Research
A possible mechanism of M 9 earthquake generation cycles in the area of repeating M 7 8 earthquakes surrounded by aseismic sliding
 LETTER Earth Planets Space, 63, 773 777, 2011 A possible mechanism of M 9 earthquake generation cycles in the area of repeating M 7 8 earthquakes surrounded by aseismic sliding Takane Hori 1 and Shin ichi
LETTER Earth Planets Space, 63, 773 777, 2011 A possible mechanism of M 9 earthquake generation cycles in the area of repeating M 7 8 earthquakes surrounded by aseismic sliding Takane Hori 1 and Shin ichi
Study megathrust creep to understand megathrust earthquakes
 1 Study megathrust creep to understand megathrust earthquakes Kelin Wang Pacific Geoscience Centre, Geological Survey of Canada, kelin.wang@canada.ca Introduction Once upon a time, there was a belief that
1 Study megathrust creep to understand megathrust earthquakes Kelin Wang Pacific Geoscience Centre, Geological Survey of Canada, kelin.wang@canada.ca Introduction Once upon a time, there was a belief that
1/22/2015. High velocity shear experiments with possible implications to earthquake physics
 High velocity shear experiments with possible implications to earthquake physics Thanks: Amir Sagy Andrew Madden, David Lockner, Einat Aharonov Harry Green, Jay Finberg, Jefferson Chang, Shalev Siman Tov
High velocity shear experiments with possible implications to earthquake physics Thanks: Amir Sagy Andrew Madden, David Lockner, Einat Aharonov Harry Green, Jay Finberg, Jefferson Chang, Shalev Siman Tov
Numerical simulation of seismic cycles at a subduction zone with a laboratory-derived friction law
 Numerical simulation of seismic cycles at a subduction zone with a laboratory-derived friction law Naoyuki Kato (1), Kazuro Hirahara (2) and Mikio Iizuka (3) (1) Earthquake Research Institute, University
Numerical simulation of seismic cycles at a subduction zone with a laboratory-derived friction law Naoyuki Kato (1), Kazuro Hirahara (2) and Mikio Iizuka (3) (1) Earthquake Research Institute, University
Measurements in the Creeping Section of the Central San Andreas Fault
 Measurements in the Creeping Section of the Central San Andreas Fault Introduction Duncan Agnew, Andy Michael We propose the PBO instrument, with GPS and borehole strainmeters, the creeping section of
Measurements in the Creeping Section of the Central San Andreas Fault Introduction Duncan Agnew, Andy Michael We propose the PBO instrument, with GPS and borehole strainmeters, the creeping section of
Rock and fluid thermodynamics control the dynamics of induced earthquakes
 Rock and fluid thermodynamics control the dynamics of induced earthquakes M. Acosta, F. Passelègue, A. Schubnel et M. Violay (mateo.acosta@epfl.ch) Context Induced Seismicity in Enhanced Geothermal Systems
Rock and fluid thermodynamics control the dynamics of induced earthquakes M. Acosta, F. Passelègue, A. Schubnel et M. Violay (mateo.acosta@epfl.ch) Context Induced Seismicity in Enhanced Geothermal Systems
Brittle Deformation. Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm
 Lecture 6 Brittle Deformation Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton, unless noted otherwise Brittle deformation EarthStructure (2 nd
Lecture 6 Brittle Deformation Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton, unless noted otherwise Brittle deformation EarthStructure (2 nd
Depth-dependent slip regime on the plate interface revealed from slow earthquake activities in the Nankai subduction zone
 2010/10/11-14 Earthscope Workshop Depth-dependent slip regime on the plate interface revealed from slow earthquake activities in the Nankai subduction zone Kazushige Obara, ERI, Univ. Tokyo Recurrence
2010/10/11-14 Earthscope Workshop Depth-dependent slip regime on the plate interface revealed from slow earthquake activities in the Nankai subduction zone Kazushige Obara, ERI, Univ. Tokyo Recurrence
Numerical study on multi-scaling earthquake rupture
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L266, doi:1.129/23gl1878, 24 Numerical study on multi-scaling earthquake rupture Hideo Aochi Institut de Radioprotection et de Sûreté Nucléaire, France Satoshi Ide
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L266, doi:1.129/23gl1878, 24 Numerical study on multi-scaling earthquake rupture Hideo Aochi Institut de Radioprotection et de Sûreté Nucléaire, France Satoshi Ide
Splay fault and megathrust earthquake slip in the Nankai Trough
 Earth Planets Space, 53, 243 248, 2001 Splay fault and megathrust earthquake slip in the Nankai Trough Phil R. Cummins, Takane Hori, and Yoshiyuki Kaneda Frontier Research Program for Subduction Dynamics,
Earth Planets Space, 53, 243 248, 2001 Splay fault and megathrust earthquake slip in the Nankai Trough Phil R. Cummins, Takane Hori, and Yoshiyuki Kaneda Frontier Research Program for Subduction Dynamics,
Earthquake nucleation. Pablo Ampuero Caltech Seismolab
 Earthquake nucleation Pablo Ampuero Caltech Seismolab How do earthquakes start? Do small and large earthquakes start differently? Predictive value of earthquake onset and foreshock sequences? Seismological
Earthquake nucleation Pablo Ampuero Caltech Seismolab How do earthquakes start? Do small and large earthquakes start differently? Predictive value of earthquake onset and foreshock sequences? Seismological
Development of a Predictive Simulation System for Crustal Activities in and around Japan - II
 Development of a Predictive Simulation System for Crustal Activities in and around Japan - II Project Representative Mitsuhiro Matsu'ura Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo Authors Mitsuhiro
Development of a Predictive Simulation System for Crustal Activities in and around Japan - II Project Representative Mitsuhiro Matsu'ura Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo Authors Mitsuhiro
A constitutive scaling law and a unified comprehension for frictional slip failure, shear fracture of intact rock, and earthquake rupture
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B2, 2080, doi:10.1029/2000jb000123, 2003 A constitutive scaling law and a unified comprehension for frictional slip failure, shear fracture of intact rock,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B2, 2080, doi:10.1029/2000jb000123, 2003 A constitutive scaling law and a unified comprehension for frictional slip failure, shear fracture of intact rock,
Synthetic Seismicity Models of Multiple Interacting Faults
 Synthetic Seismicity Models of Multiple Interacting Faults Russell Robinson and Rafael Benites Institute of Geological & Nuclear Sciences, Box 30368, Lower Hutt, New Zealand (email: r.robinson@gns.cri.nz).
Synthetic Seismicity Models of Multiple Interacting Faults Russell Robinson and Rafael Benites Institute of Geological & Nuclear Sciences, Box 30368, Lower Hutt, New Zealand (email: r.robinson@gns.cri.nz).
The Frictional Regime
 The Frictional Regime Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/25/2016 10:08 AM We Discuss The Frictional Regime Processes of Brittle Deformation
The Frictional Regime Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/25/2016 10:08 AM We Discuss The Frictional Regime Processes of Brittle Deformation
Creep Events Slip Less Than Ordinary Earthquakes. Emily E. Brodsky 1 and James Mori 2
 Creep Events Slip Less Than Ordinary Earthquakes Emily E. Brodsky 1 and James Mori 2 1 Dept. of Earth and Planetary Sciences, UC Santa Cruz, CA, USA 2 Disaster Prevention Research Institute, Kyoto University,
Creep Events Slip Less Than Ordinary Earthquakes Emily E. Brodsky 1 and James Mori 2 1 Dept. of Earth and Planetary Sciences, UC Santa Cruz, CA, USA 2 Disaster Prevention Research Institute, Kyoto University,
Introduction: Advancing Simulations of Sequences of Earthquakes and Aseismic Slip (SEAS)
 Introduction: Advancing Simulations of Sequences of Earthquakes and Aseismic Slip (SEAS) Brittany Erickson (Portland State University) Junle Jiang (University of California, San Diego) SCEC DR-SEAS Workshop,
Introduction: Advancing Simulations of Sequences of Earthquakes and Aseismic Slip (SEAS) Brittany Erickson (Portland State University) Junle Jiang (University of California, San Diego) SCEC DR-SEAS Workshop,
Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology (JAMSTEC), 2-15 Natsushima-cho, Yokosuka JAPAN
 Dense Ocean floor Network System for Mega Thrust Earthquakes & Tsunamis(DONET) -Towards Understanding Mega Thrust Earthquakes, the Geohazard & Disaster Mitigation- Yoshiyuki KANEDA, Katsuyoshi KAWAGUCHI,
Dense Ocean floor Network System for Mega Thrust Earthquakes & Tsunamis(DONET) -Towards Understanding Mega Thrust Earthquakes, the Geohazard & Disaster Mitigation- Yoshiyuki KANEDA, Katsuyoshi KAWAGUCHI,
Seismic and flexure constraints on lithospheric rheology and their dynamic implications
 Seismic and flexure constraints on lithospheric rheology and their dynamic implications Shijie Zhong Dept. of Physics, University of Colorado Boulder, Colorado, USA Acknowledgement: A. B. Watts Dept. of
Seismic and flexure constraints on lithospheric rheology and their dynamic implications Shijie Zhong Dept. of Physics, University of Colorado Boulder, Colorado, USA Acknowledgement: A. B. Watts Dept. of
Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size?
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, NO., PAGES 1 16, Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size? A. Ziv A. Ziv, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84105, Israel. (e-mail: zival@bgu.ac.il)
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, NO., PAGES 1 16, Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size? A. Ziv A. Ziv, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84105, Israel. (e-mail: zival@bgu.ac.il)
The San Andreas Fault Observatory at Depth: Recent Site Characterization Studies and the 2.2-Km-Deep Pilot Hole
 The San Andreas Fault Observatory at Depth: Recent Site Characterization Studies and the 2.2-Km-Deep Pilot Hole Steve Hickman and Bill Ellsworth (USGS) Mark Zoback (Stanford University) and the Pre-EarthScope
The San Andreas Fault Observatory at Depth: Recent Site Characterization Studies and the 2.2-Km-Deep Pilot Hole Steve Hickman and Bill Ellsworth (USGS) Mark Zoback (Stanford University) and the Pre-EarthScope
Expansion of aftershock areas caused by propagating post-seismic sliding
 Geophys. J. Int. (2007) 168, 797 808 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03255.x Expansion of aftershock areas caused by propagating post-seismic sliding Naoyuki Kato Earthquake Research Institute, University
Geophys. J. Int. (2007) 168, 797 808 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03255.x Expansion of aftershock areas caused by propagating post-seismic sliding Naoyuki Kato Earthquake Research Institute, University
Slip distributions of the 1944 Tonankai and 1946 Nankai earthquakes including the horizontal movement effect on tsunami generation
 Slip distributions of the 1944 Tonankai and 1946 Nankai earthquakes including the horizontal movement effect on tsunami generation Toshitaka Baba Research Program for Plate Dynamics, Institute for Frontier
Slip distributions of the 1944 Tonankai and 1946 Nankai earthquakes including the horizontal movement effect on tsunami generation Toshitaka Baba Research Program for Plate Dynamics, Institute for Frontier
Fracture surface energy of natural earthquakes from the viewpoint of seismic observations
 Bull.Earthq.Res.Inst. Univ.Tokyo Vol. 12,**- pp. /30/ Fracture surface energy of natural earthquakes from the viewpoint of seismic observations Satoshi Ide* Department of Earth and Planetary Science, University
Bull.Earthq.Res.Inst. Univ.Tokyo Vol. 12,**- pp. /30/ Fracture surface energy of natural earthquakes from the viewpoint of seismic observations Satoshi Ide* Department of Earth and Planetary Science, University
Two ways to think about the dynamics of earthquake ruptures
 Two ways to think about the dynamics of earthquake ruptures (1) In terms of friction (2) In terms of fracture mechanics Scholz describes conditions for rupture propagation (i.e. instability) via energy
Two ways to think about the dynamics of earthquake ruptures (1) In terms of friction (2) In terms of fracture mechanics Scholz describes conditions for rupture propagation (i.e. instability) via energy
Earthquakes. Forces Within Eartth. Faults form when the forces acting on rock exceed the rock s strength.
 Earthquakes Vocabulary: Stress Strain Elastic Deformation Plastic Deformation Fault Seismic Wave Primary Wave Secondary Wave Focus Epicenter Define stress and strain as they apply to rocks. Distinguish
Earthquakes Vocabulary: Stress Strain Elastic Deformation Plastic Deformation Fault Seismic Wave Primary Wave Secondary Wave Focus Epicenter Define stress and strain as they apply to rocks. Distinguish
Plate Boundary Observatory Working Group for the Central and Northern San Andreas Fault System PBO-WG-CNSA
 Plate Boundary Observatory Working Group for the Central and Northern San Andreas Fault System PBO-WG-CNSA Introduction Our proposal focuses on the San Andreas fault system in central and northern California.
Plate Boundary Observatory Working Group for the Central and Northern San Andreas Fault System PBO-WG-CNSA Introduction Our proposal focuses on the San Andreas fault system in central and northern California.
White paper for Geohazard (Submarine landslides and mass movements) at INVEST09 from Japanese research group
 White paper for Geohazard (Submarine landslides and mass movements) at INVEST09 from Japanese research group A submarine landslide team of The Japanese planning group for Geohazard science at IODP* *Kiichiro
White paper for Geohazard (Submarine landslides and mass movements) at INVEST09 from Japanese research group A submarine landslide team of The Japanese planning group for Geohazard science at IODP* *Kiichiro
(Somerville, et al., 1999) 2 (, 2001) Das and Kostrov (1986) (2002) Das and Kostrov (1986) (Fukushima and Tanaka, 1990) (, 1999) (2002) ( ) (1995
 ( ) 1995 ( ) (Somerville, et al., 1999) 2 (, 2001) (2001) Das and Kostrov (1986) (2002) Das and Kostrov (1986) GPS ) (Fukushima and Tanaka, 1990) (, 1999) (2002) ( ) (1995 1 (outer fault parameter) (inner
( ) 1995 ( ) (Somerville, et al., 1999) 2 (, 2001) (2001) Das and Kostrov (1986) (2002) Das and Kostrov (1986) GPS ) (Fukushima and Tanaka, 1990) (, 1999) (2002) ( ) (1995 1 (outer fault parameter) (inner
Creep Events Slip Less Than Ordinary Earthquakes. Emily E. Brodsky 1 and James Mori 2
 Creep Events Slip Less Than Ordinary Earthquakes Emily E. Brodsky 1 and James Mori 2 1 Dept. of Earth and Planetary Sciences, UC Santa Cruz, CA, USA 2 Disaster Prevention Research Institute, Kyoto University,
Creep Events Slip Less Than Ordinary Earthquakes Emily E. Brodsky 1 and James Mori 2 1 Dept. of Earth and Planetary Sciences, UC Santa Cruz, CA, USA 2 Disaster Prevention Research Institute, Kyoto University,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L18309, doi: /2006gl027025, 2006
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L18309, doi:10.1029/2006gl027025, 2006 Modern and ancient seismogenic out-of-sequence thrusts in the Nankai accretionary prism: Comparison
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L18309, doi:10.1029/2006gl027025, 2006 Modern and ancient seismogenic out-of-sequence thrusts in the Nankai accretionary prism: Comparison
Lecture 2: Deformation in the crust and the mantle. Read KK&V chapter 2.10
 Lecture 2: Deformation in the crust and the mantle Read KK&V chapter 2.10 Tectonic plates What are the structure and composi1on of tectonic plates? Crust, mantle, and lithosphere Crust relatively light
Lecture 2: Deformation in the crust and the mantle Read KK&V chapter 2.10 Tectonic plates What are the structure and composi1on of tectonic plates? Crust, mantle, and lithosphere Crust relatively light
Section Forces Within Earth. 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes
 Section 19.1 - Forces Within Earth 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes Stress and Strain Stress - is the total force acting on crustal rocks per unit of area (cause) Strain deformation of materials
Section 19.1 - Forces Within Earth 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes Stress and Strain Stress - is the total force acting on crustal rocks per unit of area (cause) Strain deformation of materials
Ground displacement in a fault zone in the presence of asperities
 BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 2, pp. 95-110; JUNE 2000 Ground displacement in a fault zone in the presence of asperities S. SANTINI (1),A.PIOMBO (2) and M. DRAGONI (2) (1) Istituto
BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 2, pp. 95-110; JUNE 2000 Ground displacement in a fault zone in the presence of asperities S. SANTINI (1),A.PIOMBO (2) and M. DRAGONI (2) (1) Istituto
On the nucleation of creep and the interaction between creep and seismic slip on rate- and state-dependent faults
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L15303, doi:10.1029/2007gl030337, 2007 On the nucleation of creep and the interaction between creep and seismic slip on rate- and state-dependent
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L15303, doi:10.1029/2007gl030337, 2007 On the nucleation of creep and the interaction between creep and seismic slip on rate- and state-dependent
Physics and Chemistry of the Earth and Terrestrial Planets
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.002 Physics and Chemistry of the Earth and Terrestrial Planets Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.002 Physics and Chemistry of the Earth and Terrestrial Planets Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Earthquakes. Earthquake Magnitudes 10/1/2013. Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena
 Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena Fall 2013 Northridge 1994 Kobe 1995 Mexico City 1985 China 2008 Earthquakes Earthquake Magnitudes Earthquake Magnitudes Richter Magnitude
Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena Fall 2013 Northridge 1994 Kobe 1995 Mexico City 1985 China 2008 Earthquakes Earthquake Magnitudes Earthquake Magnitudes Richter Magnitude
Supplementary Information: Data Used in Computing Porosity, Pore Pressure, and
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY ITEM 29164 Supplementary Information: Data Used in Computing Porosity, Pore Pressure, and Effective Stress, and Results for Seismic Line 284 Accompanying: Tobin, H. & Saffer, D., Elevated
GSA DATA REPOSITORY ITEM 29164 Supplementary Information: Data Used in Computing Porosity, Pore Pressure, and Effective Stress, and Results for Seismic Line 284 Accompanying: Tobin, H. & Saffer, D., Elevated
Occurrence of quasi-periodic slow-slip off the east coast of the Boso peninsula, Central Japan
 LETTER Earth Planets Space, 9, 11 1, Occurrence of quasi-periodic slow-slip off the east coast of the Boso peninsula, Central Japan Shinzaburo Ozawa, Hisashi Suito, and Mikio Tobita Geographical Survey
LETTER Earth Planets Space, 9, 11 1, Occurrence of quasi-periodic slow-slip off the east coast of the Boso peninsula, Central Japan Shinzaburo Ozawa, Hisashi Suito, and Mikio Tobita Geographical Survey
Friction Constitutive Laws and. The Mechanics of Slow Earthquakes and the Spectrum of Fault Slip Behaviors
 Friction Constitutive Laws and. The Mechanics of Slow Earthquakes and the Spectrum of Fault Slip Behaviors Chris Marone, The Pennsylvania State University John Leeman, Marco Scuderi, Elisa Tinti, Cristiano
Friction Constitutive Laws and. The Mechanics of Slow Earthquakes and the Spectrum of Fault Slip Behaviors Chris Marone, The Pennsylvania State University John Leeman, Marco Scuderi, Elisa Tinti, Cristiano
Variability of earthquake nucleation in continuum models of rate-and-state faults and implications for aftershock rates
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005154, 2008 Variability of earthquake nucleation in continuum models of rate-and-state faults and implications
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005154, 2008 Variability of earthquake nucleation in continuum models of rate-and-state faults and implications
Modeling short and long term slow slip events in the seismic cycles of large subduction earthquakes
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2010jb007566, 2010 Modeling short and long term slow slip events in the seismic cycles of large subduction earthquakes Takanori Matsuzawa, 1 Hitoshi
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2010jb007566, 2010 Modeling short and long term slow slip events in the seismic cycles of large subduction earthquakes Takanori Matsuzawa, 1 Hitoshi
Inferring fault strength from earthquake rupture properties and the tectonic implications of high pore pressure faulting
 Earth Planets Space, 54, 1173 1179, 22 Inferring fault strength from earthquake rupture properties and the tectonic implications of high pore pressure faulting Stephen A. Miller Geophysics Institute, ETH-Zurich
Earth Planets Space, 54, 1173 1179, 22 Inferring fault strength from earthquake rupture properties and the tectonic implications of high pore pressure faulting Stephen A. Miller Geophysics Institute, ETH-Zurich
Statistics of Earthquake Stress Drops on a Heterogeneous Fault in an Elastic Half-Space
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 99, No., pp. 7, June 9, doi:.7/ Statistics of Earthquake Stress Drops on a Heterogeneous Fault in an Elastic Half-Space by I. W. Bailey and Y. Ben-Zion
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 99, No., pp. 7, June 9, doi:.7/ Statistics of Earthquake Stress Drops on a Heterogeneous Fault in an Elastic Half-Space by I. W. Bailey and Y. Ben-Zion
Properties of large ruptures and the dynamical influence of fluids on earthquakes and faulting
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. B9, 2182, doi:10.1029/2000jb000032, 2002 Properties of large ruptures and the dynamical influence of fluids on earthquakes and faulting S. A. Miller 1 Geology
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. B9, 2182, doi:10.1029/2000jb000032, 2002 Properties of large ruptures and the dynamical influence of fluids on earthquakes and faulting S. A. Miller 1 Geology
Evolution of seismic signals and slip patterns along subduction zones: insights from a friction lab scale experiment.
 Evolution of seismic signals and slip patterns along subduction zones: insights from a friction lab scale experiment. Christophe Voisin, Jean-Robert Grasso, Eric Larose, François Renard * Laboratoire de
Evolution of seismic signals and slip patterns along subduction zones: insights from a friction lab scale experiment. Christophe Voisin, Jean-Robert Grasso, Eric Larose, François Renard * Laboratoire de
Permeability measurements and precipitation sealing of basalt in an ancient exhumed subduction-zone fault
 Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst. Univ. Tokyo Vol. 12,**- pp. 2-23 Permeability measurements and precipitation sealing of basalt in an ancient exhumed subduction-zone fault Aitaro Kato +),, *, Arito Sakaguchi +,Shingo
Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst. Univ. Tokyo Vol. 12,**- pp. 2-23 Permeability measurements and precipitation sealing of basalt in an ancient exhumed subduction-zone fault Aitaro Kato +),, *, Arito Sakaguchi +,Shingo
Slab pull, slab weakening, and their relation to deep intra-slab seismicity
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L14305, doi:10.1029/2005gl022922, 2005 Slab pull, slab weakening, and their relation to deep intra-slab seismicity Susan L. Bilek Earth and Environmental Science
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L14305, doi:10.1029/2005gl022922, 2005 Slab pull, slab weakening, and their relation to deep intra-slab seismicity Susan L. Bilek Earth and Environmental Science
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Overview Milestones in continuum mechanics Concepts of modulus and stiffness. Stress-strain relations Elasticity Surface and body
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Overview Milestones in continuum mechanics Concepts of modulus and stiffness. Stress-strain relations Elasticity Surface and body
Integrating Lab and Numerical Experiments to Investigate Fractured Rock
 Integrating Lab and Numerical Experiments to Investigate Fractured Rock Bradford H. Hager Director, Earth Resources Laboratory and Cecil and Ida Green Professor Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary
Integrating Lab and Numerical Experiments to Investigate Fractured Rock Bradford H. Hager Director, Earth Resources Laboratory and Cecil and Ida Green Professor Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary
Di#erences in Earthquake Source and Ground Motion Characteristics between Surface and Buried Crustal Earthquakes
 Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst. Univ. Tokyo Vol. 2+,**0 pp.,/3,00 Di#erences in Earthquake Source and Ground Motion Characteristics between Surface and Buried Crustal Earthquakes Paul Somerville* and Arben Pitarka
Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst. Univ. Tokyo Vol. 2+,**0 pp.,/3,00 Di#erences in Earthquake Source and Ground Motion Characteristics between Surface and Buried Crustal Earthquakes Paul Somerville* and Arben Pitarka
Scale Dependence in the Dynamics of Earthquake Rupture Propagation: Evidence from Geological and Seismological Observations
 Euroconference of Rock Physics and Geomechanics: Natural hazards: thermo-hydro-mechanical processes in rocks Erice, Sicily, 25-30 September, 2007 Scale Dependence in the Dynamics of Earthquake Rupture
Euroconference of Rock Physics and Geomechanics: Natural hazards: thermo-hydro-mechanical processes in rocks Erice, Sicily, 25-30 September, 2007 Scale Dependence in the Dynamics of Earthquake Rupture
An Examination of Accretionary Prisms at the Nobeoka Thrust
 Evan Tam, University of Connecticut UTRIP 2012 Participant, Kimura Labs An Examination of Accretionary Prisms at the Nobeoka Thrust Introduction Accretionary prisms form at convergent plate boundaries,
Evan Tam, University of Connecticut UTRIP 2012 Participant, Kimura Labs An Examination of Accretionary Prisms at the Nobeoka Thrust Introduction Accretionary prisms form at convergent plate boundaries,
The Tectonic Setting of New Zealand
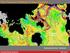 The Tectonic Setting of New Zealand we are here Subduction-driven tectonics The New Zealand continent Papua New Guinea Australia 3,000,000 sq km micro-continent back-arc basin trench volcanism faults accretionary
The Tectonic Setting of New Zealand we are here Subduction-driven tectonics The New Zealand continent Papua New Guinea Australia 3,000,000 sq km micro-continent back-arc basin trench volcanism faults accretionary
Surface Rupture in Kinematic Ruptures Models for Hayward Fault Scenario Earthquakes
 Surface Rupture in Kinematic Ruptures Models for Hayward Fault Scenario Earthquakes Brad Aagaard May 21, 2009 Surface Rupture from Kinematic Rupture Models Objective Holistic approach to calculating surface
Surface Rupture in Kinematic Ruptures Models for Hayward Fault Scenario Earthquakes Brad Aagaard May 21, 2009 Surface Rupture from Kinematic Rupture Models Objective Holistic approach to calculating surface
Source parameters II. Stress drop determination Energy balance Seismic energy and seismic efficiency The heat flow paradox Apparent stress drop
 Source parameters II Stress drop determination Energy balance Seismic energy and seismic efficiency The heat flow paradox Apparent stress drop Source parameters II: use of empirical Green function for
Source parameters II Stress drop determination Energy balance Seismic energy and seismic efficiency The heat flow paradox Apparent stress drop Source parameters II: use of empirical Green function for
Chapter 6. Conclusions. 6.1 Conclusions and perspectives
 Chapter 6 Conclusions 6.1 Conclusions and perspectives In this thesis an approach is presented for the in-situ characterization of rocks in terms of the distribution of hydraulic parameters (called SBRC
Chapter 6 Conclusions 6.1 Conclusions and perspectives In this thesis an approach is presented for the in-situ characterization of rocks in terms of the distribution of hydraulic parameters (called SBRC
Seismicity around the seaward updip limit of the Nankai Trough seismogenic zone revealed by repeated OBS observations
 FRONTIER RESEARCH ON EARTH EVOLUTION, VOL. 1 Seismicity around the seaward updip limit of the Nankai Trough seismogenic zone revealed by repeated OBS observations Koichiro Obana 1, Shuichi Kodaira 1, Yoshiyuki
FRONTIER RESEARCH ON EARTH EVOLUTION, VOL. 1 Seismicity around the seaward updip limit of the Nankai Trough seismogenic zone revealed by repeated OBS observations Koichiro Obana 1, Shuichi Kodaira 1, Yoshiyuki
friction friction a-b slow fast increases during sliding
 µ increases during sliding faster sliding --> stronger fault --> slows sliding leads to stable slip: no earthquakes can start velocity-strengthening friction slow fast µ velocity-strengthening friction
µ increases during sliding faster sliding --> stronger fault --> slows sliding leads to stable slip: no earthquakes can start velocity-strengthening friction slow fast µ velocity-strengthening friction
Fault Processes on the Anza section of the San Jacinto Fault
 Fault Processes on the nza section of the San Jacinto Fault J. Steidl (USB), M. Gladwin, R. Gwyther (SIRO ust.), F. Vernon (USD) SUMMRY We propose to instrument the nza slip gap and transition areas of
Fault Processes on the nza section of the San Jacinto Fault J. Steidl (USB), M. Gladwin, R. Gwyther (SIRO ust.), F. Vernon (USD) SUMMRY We propose to instrument the nza slip gap and transition areas of
PUBLICATIONS. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth. A friction to flow constitutive law and its application to a 2-D modeling of earthquakes
 PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: We propose a constitutive law describing transition from friction to flow The law merges a strength profile and a
PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: We propose a constitutive law describing transition from friction to flow The law merges a strength profile and a
A mechanical model of the San Andreas fault and SAFOD Pilot Hole stress measurements
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L15S13, doi:10.1029/2004gl019521, 2004 A mechanical model of the San Andreas fault and SAFOD Pilot Hole stress measurements Jean Chéry Laboratoire Dynamique de la
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L15S13, doi:10.1029/2004gl019521, 2004 A mechanical model of the San Andreas fault and SAFOD Pilot Hole stress measurements Jean Chéry Laboratoire Dynamique de la
Fault Specific, Dynamic Rupture Scenarios for Strong Ground Motion Prediction
 Fault Specific, Dynamic Rupture Scenarios for Strong Ground Motion Prediction H. Sekiguchi Disaster Prevention Research Institute, Kyoto University, Japan Blank Line 9 pt Y. Kase Active Fault and Earthquake
Fault Specific, Dynamic Rupture Scenarios for Strong Ground Motion Prediction H. Sekiguchi Disaster Prevention Research Institute, Kyoto University, Japan Blank Line 9 pt Y. Kase Active Fault and Earthquake
Earthquake and Volcano Deformation
 Earthquake and Volcano Deformation Paul Segall Stanford University Draft Copy September, 2005 Last Updated Sept, 2008 COPYRIGHT NOTICE: To be published by Princeton University Press and copyrighted, c
Earthquake and Volcano Deformation Paul Segall Stanford University Draft Copy September, 2005 Last Updated Sept, 2008 COPYRIGHT NOTICE: To be published by Princeton University Press and copyrighted, c
Scaling Laws. σ 1. σ = mean stress, which is needed to compute σ 0. η = percent strain energy released in eq. Introduction.
 Scaling Laws Introduction Scaling Laws or Relationships are the result of empirical observation. They describe how one physical parameter varies as a function of another physical parameter within a system.
Scaling Laws Introduction Scaling Laws or Relationships are the result of empirical observation. They describe how one physical parameter varies as a function of another physical parameter within a system.
Migration process of very low-frequency events based on a chain-reaction model
 Migration process of very low-frequency events based on a chain-reaction model and its application to the detection of preseismic slip for megathrust earthquakes Keisuke Ariyoshi* 1, Toru Matsuzawa, Jean-Paul
Migration process of very low-frequency events based on a chain-reaction model and its application to the detection of preseismic slip for megathrust earthquakes Keisuke Ariyoshi* 1, Toru Matsuzawa, Jean-Paul
Stress on the seismogenic and deep creep plate interface during the earthquake cycle in subduction zones
 Earth Planets Space, 53, 307 320, 2001 Stress on the seismogenic and deep creep plate interface during the earthquake cycle in subduction zones Larry J. Ruff Department of Geological Sciences, University
Earth Planets Space, 53, 307 320, 2001 Stress on the seismogenic and deep creep plate interface during the earthquake cycle in subduction zones Larry J. Ruff Department of Geological Sciences, University
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting 5 Sep. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Work of deformation, shear and volume strain Importance of volume change and diltancy rate (rate of volume strain with
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting 5 Sep. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Work of deformation, shear and volume strain Importance of volume change and diltancy rate (rate of volume strain with
Internal Layers of the Earth
 Lecture #4 notes Geology 3950, Spring 2006; CR Stern Seismic waves, earthquake magnitudes and location, and internal earth structure (pages 28-95 in the 4 th edition and 28-32 and 50-106 in the 5 th edition)
Lecture #4 notes Geology 3950, Spring 2006; CR Stern Seismic waves, earthquake magnitudes and location, and internal earth structure (pages 28-95 in the 4 th edition and 28-32 and 50-106 in the 5 th edition)
Scaling of small repeating earthquakes explained by interaction of seismic and aseismic slip in a rate and state fault model
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jb005749, 2009 Scaling of small repeating earthquakes explained by interaction of seismic and aseismic slip in a
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jb005749, 2009 Scaling of small repeating earthquakes explained by interaction of seismic and aseismic slip in a
Source modeling of hypothetical Tokai-Tonankai-Nankai, Japan, earthquake and strong ground motion simulation using the empirical Green s functions
 Source modeling of hypothetical Tokai-Tonankai-Nankai, Japan, earthquake and strong ground motion simulation using the empirical Green s functions Y. Ishii & K. Dan Ohsaki Research Institute, Inc., Tokyo
Source modeling of hypothetical Tokai-Tonankai-Nankai, Japan, earthquake and strong ground motion simulation using the empirical Green s functions Y. Ishii & K. Dan Ohsaki Research Institute, Inc., Tokyo
Rupture dynamics with energy loss outside the slip zone
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110,, doi:10.1029/2004jb003191, 2005 Rupture dynamics with energy loss outside the slip zone D. J. Andrews U.S. Geological Survey, Menlo Park, California, USA Received
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110,, doi:10.1029/2004jb003191, 2005 Rupture dynamics with energy loss outside the slip zone D. J. Andrews U.S. Geological Survey, Menlo Park, California, USA Received
Transition from stick-slip to stable sliding: the crucial effect of asperities
 Transition from stick-slip to stable sliding: the crucial effect of asperities Strasbourg, 15 Nov. 2007 François Renard LGCA, CNRS-OSUG, University of Grenoble, France PGP, University of Oslo, Norway Collaborators:
Transition from stick-slip to stable sliding: the crucial effect of asperities Strasbourg, 15 Nov. 2007 François Renard LGCA, CNRS-OSUG, University of Grenoble, France PGP, University of Oslo, Norway Collaborators:
Elastic Rebound Theory
 Earthquakes Elastic Rebound Theory Earthquakes occur when strain exceeds the strength of the rock and the rock fractures. The arrival of earthquakes waves is recorded by a seismograph. The amplitude of
Earthquakes Elastic Rebound Theory Earthquakes occur when strain exceeds the strength of the rock and the rock fractures. The arrival of earthquakes waves is recorded by a seismograph. The amplitude of
EFFECTS OF NON-LINEAR WEAKENING ON EARTHQUAKE SOURCE SCALINGS
 Extended abstract for the 11th International Conference on Fracture 2005 1 EFFECTS OF NON-LINEAR WEAKENING ON EARTHQUAKE SOURCE SCALINGS J.-P. Ampuero Geosciences Department, Princeton University, USA
Extended abstract for the 11th International Conference on Fracture 2005 1 EFFECTS OF NON-LINEAR WEAKENING ON EARTHQUAKE SOURCE SCALINGS J.-P. Ampuero Geosciences Department, Princeton University, USA
Geometrical effects of a subducted seamount on stopping megathrust ruptures
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 40, 1 6, doi:10.1002/grl.50509, 2013 Geometrical effects of a subducted seamount on stopping megathrust ruptures Hongfeng Yang, 1,2 Yajing Liu, 1,3 and Jian Lin 1 Received
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 40, 1 6, doi:10.1002/grl.50509, 2013 Geometrical effects of a subducted seamount on stopping megathrust ruptures Hongfeng Yang, 1,2 Yajing Liu, 1,3 and Jian Lin 1 Received
Estimating energy balance for hydraulic fracture stimulations: Lessons Learned from Basel
 Estimating energy balance for hydraulic fracture stimulations: Lessons Learned from Basel David W. Eaton*, Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary, Calgary, Canada eatond@ucalgary.ca and Neda Boroumand,
Estimating energy balance for hydraulic fracture stimulations: Lessons Learned from Basel David W. Eaton*, Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary, Calgary, Canada eatond@ucalgary.ca and Neda Boroumand,
The effect of water on strain localization in calcite fault gouge sheared at seismic slip rates. By Tyler Lagasse
 The effect of water on strain localization in calcite fault gouge sheared at seismic slip rates By Tyler Lagasse Co-seismic slip depth limited within sub-cm-thick gouge & cataclastic-bearing principal
The effect of water on strain localization in calcite fault gouge sheared at seismic slip rates By Tyler Lagasse Co-seismic slip depth limited within sub-cm-thick gouge & cataclastic-bearing principal
AVERAGE AND VARIATION OF FOCAL MECHANISM AROUND TOHOKU SUBDUCTION ZONE
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 414 AVERAGE AND VARIATION OF FOCAL MECHANISM AROUND TOHOKU SUBDUCTION ZONE Shunroku YAMAMOTO 1 Naohito
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 414 AVERAGE AND VARIATION OF FOCAL MECHANISM AROUND TOHOKU SUBDUCTION ZONE Shunroku YAMAMOTO 1 Naohito
Earthquakes. Pt Reyes Station 1906
 Earthquakes Pt Reyes Station 1906 Earthquakes Ground shaking caused by the sudden release of accumulated strain by an abrupt shift of rock along a fracture in the earth. You Live in Earthquake Country
Earthquakes Pt Reyes Station 1906 Earthquakes Ground shaking caused by the sudden release of accumulated strain by an abrupt shift of rock along a fracture in the earth. You Live in Earthquake Country
SOURCE MODELING OF SUBDUCTION-ZONE EARTHQUAKES AND LONG-PERIOD GROUND MOTION VALIDATION IN THE TOKYO METROPOLITAN AREA
 SOURCE MODELING OF SUBDUCTION-ZONE EARTHQUAKES AND LONG-PERIOD GROUND MOTION VALIDATION IN THE TOKYO METROPOLITAN AREA ABSTRACT : Hiroe Miyake 1, Kazuki Koketsu 2, and Takashi Furumura 3,2 1 Assistant
SOURCE MODELING OF SUBDUCTION-ZONE EARTHQUAKES AND LONG-PERIOD GROUND MOTION VALIDATION IN THE TOKYO METROPOLITAN AREA ABSTRACT : Hiroe Miyake 1, Kazuki Koketsu 2, and Takashi Furumura 3,2 1 Assistant
Seismic Efficiency, Overshoot and Enhanced Dynamic Weaking of Fractures Associated with Stimulation in Heavy Oil Reservoirs
 Seismic Efficiency, Overshoot and Enhanced Dynamic Weaking of Fractures Associated with Stimulation in Heavy Oil Reservoirs Lindsey N. Meighan, Ted Urbancic and Adam Baig ESG, Kingston, Ontario Summary
Seismic Efficiency, Overshoot and Enhanced Dynamic Weaking of Fractures Associated with Stimulation in Heavy Oil Reservoirs Lindsey N. Meighan, Ted Urbancic and Adam Baig ESG, Kingston, Ontario Summary
Finite element modelling of fault stress triggering due to hydraulic fracturing
 Finite element modelling of fault stress triggering due to hydraulic fracturing Arsalan, Sattari and David, Eaton University of Calgary, Geoscience Department Summary In this study we aim to model fault
Finite element modelling of fault stress triggering due to hydraulic fracturing Arsalan, Sattari and David, Eaton University of Calgary, Geoscience Department Summary In this study we aim to model fault
Depth (Km) + u ( ξ,t) u = v pl. η= Pa s. Distance from Nankai Trough (Km) u(ξ,τ) dξdτ. w(x,t) = G L (x,t τ;ξ,0) t + u(ξ,t) u(ξ,t) = v pl
 Slip history during one earthquake cycle at the Nankai subduction zone, inferred from the inversion analysis of levelling data with a viscoelastic slip response function Mitsuhiro Matsu'ura, Akira Nishitani
Slip history during one earthquake cycle at the Nankai subduction zone, inferred from the inversion analysis of levelling data with a viscoelastic slip response function Mitsuhiro Matsu'ura, Akira Nishitani
Aseismic slip and low-frequency earthquakes in the Bungo channel, southwestern Japan
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L769, doi:1.19/3gl19381, Aseismic slip and low-frequency earthquakes in the Bungo channel, southwestern Japan Shinzaburo Ozawa, 1 Yuki Hatanaka, 1 Masaru Kaidzu,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L769, doi:1.19/3gl19381, Aseismic slip and low-frequency earthquakes in the Bungo channel, southwestern Japan Shinzaburo Ozawa, 1 Yuki Hatanaka, 1 Masaru Kaidzu,
