Hands-on Activity Predicting Eruptions on Montserrat
|
|
|
- Quentin Arnold Benson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hands-on Activity Predicting Eruptions on Montserrat Predicting Eruptions No one can predict exactly when a volcano might explode. There are, however, common clues to look for to let people know that the danger is increasing: Land Deformation (Dome Height). Near the volcanic vent, as magma pushes up from below, the land on top of and surrounding the vent may start to deform, and grow larger. In many cases this deformation creates a dome of volcanic debris. As the dome grows in size, it becomes more unstable, and ultimately it will collapse and produce pyroclastic flows or lava flows. Increasing dome size indicates a growing danger. Ash Clouds. Large ash clouds are evidence of increasing volcanic activity. On the island of Montserrat scientists have found that during dangerous times, ash clouds occur in a cycle of 4 to 30 hours apart. What causes an ash cloud? In an active volcano, the vent may become plugged by rocky materials. This plug causes the pressure from the rising magma to build until eventually the plug is blasted apart in a flurry of explosive activity. The released pressure creates an ash cloud, shooting volcanic debris high into the air. Once an ash cloud is produced, the vent may become plugged again and the cycle may repeat. If a plugged volcano does not release its pressure, then scientists become concerned that a massive explosion is imminent. As long as the ash clouds keep appearing regularly, then there is less concern. Tremors. Flowing magma, trying to make room for itself, causes tremors on the surface. Tremors are measured both for their magnitude and the length of time between vibrations, or rate. On the island of Montserrat, scientists study two kinds of seismic data: Volcanic Tremors (VTs) and Rockfall (RF). The number of tremors or falling rocks which exceed a predetermined critical value are counted by the seismometer (see illustration). The more of these events the greater the level of the seismic activity. The rate of tremors is determined by charting the number of events per hour. An increase in the number of events can be an indication of possible eruption. Predictions Require Evidence Volcanologists use different tools and techniques to analyze and interpret data. Down below there are two different kinds of data. Table 1 shows one kind of data, which is a list of numbers. These numbers represent the amount of seismic activity in a day. Table 2 shows another kind of data, which is observations. An observation can be just as important as the numbers for predicting volcanic eruptions. For instance, if lava flows are observed as especially bubbly, then a scientist can infer that the lava contains a high level of dissolved gases and can be explosive. To be able to predict the volcanic activity during the mission on Sept. 4, you must study what has been occurring in July and August. The numerical and observational data should be considered evidence. You will want to use all the evidence to develop an explanation of the patterns you see. Using the patterns you will be able to make more scientific predictions than someone who has not studied the patterns. Others may have different explanations and predictions. To determine which prediction is most scientific, you must use your best communication skills to point out the relationship between the evidence and the prediction. Copyright Challenger Learning Center at Wheeling Jesuit University. All rights reserved. 1
2 How to Study the Evidence Table 1 gives the total seismic activity for each day from July 1 through September 2. This data has been plotted in Graph 1 below. Use the graph, and the observation data in Table 2 to follow the steps below. By answering the questions you should start to see a pattern concerning the relationship between dome height, ash production, seismic activity and the production of volcanic flows. 1) Compare Volcanic Flow to the Graph. Use the final column in Table 2, labeled, Volcanic Flows. Begin with the first week, July 1-7. Now look at the relationship between the observations and the dates on the graph. The observations say, None reported. On your graph, above 1-Jul and 8-Jul, write the words, No flows. Continue to write notes on your graph according to what the table says. For the next week, on July 11 on the graph, note the small spike reaching up to about 200 seismic events. In the table there is a report that Some small pyroclastic flows went into the Mosquito Ghaut area. On your graph, write small pyroclastic flows above the spike. Keep making notes like this for each week and big event. The big events are July 21, Aug. 6, and Aug ) Relationship between Dome Height and Volcanic Flows. In Table 2, note the column labeled, Dome Height. Read each week and compare it to the column labeled, Volcanic Flows and to your graph with the notes on it. Answer this question: How are Volcanic Flows related to changes in Dome Height? Write down two pieces of evidence which support your conclusion. 3) Relationship between Ash Production and Volcanic Flows. In Table 2, note the column labeled, Ash Production. Read each week and compare it to the column labeled, Volcanic Flows and to your graph with the notes on it. Answer this question: How are Volcanic Flows related to Ash Production? Write down two pieces of evidence which support your conclusion. 4) Relationship between Seismic Activity and Volcanic Flows. In Table 2, note the column labeled, Seismic Activity. Read each week and compare it to the column labeled, Volcanic Flows and to your graph with the notes on it. Answer this question: How are Volcanic Flows related to Seismic Activity? Write down two pieces of evidence which support your conclusion. 5) Design an Invention. Use the back of this paper to complete this step. Volcanologists try and find new ways to make the connection between evidence and predictions. Be creative for a minute. What is something an engineer could invent that would help us to make better predictions? What do you call your invention? Draw a picture if that would be helpful. Copyright Challenger Learning Center at Wheeling Jesuit University. All rights reserved. 2
3 Table 1: Total Daily Seismic Activity 1-Jul Jul Aug Jul Jul Aug Jul Jul Aug Jul Jul Aug Jul Jul Aug Jul Jul 5 19-Aug Jul Jul 0 20-Aug Jul 1 30-Jul Aug Jul Jul Aug Jul Aug Aug Jul Aug Aug Jul 34 3-Aug Aug Jul 45 4-Aug No Data Available 26-Aug Jul 49 5-Aug Aug Jul 40 6-Aug Aug Jul 44 7-Aug Aug Jul 46 8-Aug Aug Jul 45 9-Aug Aug Jul Aug Sep Jul Aug Sep Jul Aug Jul Aug 438 Graph Total Number of Seismic Events for July and August Seismic Events Jul 8-Jul 15-Jul 22-Jul 29-Jul 5-Aug 12-Aug 19-Aug 26-Aug 2-Sep Copyright Challenger Learning Center at Wheeling Jesuit University. All rights reserved. 3
4 Table2: Observations: July 1- Sep Montserrat Volcano Observatory s Dome Height Ash Production July 1-7 July m. Excellent viewing conditions confirmed that the dome was growing, mainly in the south section of the crater. Although the dome does not appear to be growing, new rocky material was seen in the center of the dome. A brief period of good visibility revealed a second peak on the dome. That day the elevation at the top of the dome was measured as 940 meters. Volcanologists say dome hieight has not changed significantly since early May. Mild to moderate levels of ash produced. One small ash cloud noted (less than 0.1 km high). A fine ashfall was reported in areas north of Plymouth and out to sea. Production less than 0.1 km high. Seismic Activity (daily VT & RF data may be found in a separate table) Seismicity remained low. Daily occurrences of intermittent tremors lasted from a few minutes to several hours. The seismic signals became longer and stronger. On July 12, helicopter inspections found that a large amount of rocky material had come down the north and south sides of Castle Peak. The fresh material was still steaming. Volcanic Flows None reported. July 11 Some small pyroclastic flows went into the Mosquito Ghaut area. July Brief glimpses of the dome revealed vigorous steaming, at times tainted with bluish vapor. Maximum height reached at 963 meters on July 20 th. Ash cloud on July 20 th reaches 2.3 km. Dome collapses on July 21. The occurrence of 681 seismic events (VT & RF) marked a sharp increase in activity. July Eight moderately-sized pyroclastic flows in areas such as the Tar River valley, Tuitt s Ghaut, White s Ghaut and the Belham River valley. One flow reached the coast in Farm Bay. July Dome measured at 929 meters. Low levels of ashfall reported around Broderick's Estate. Some moderately - sized ash clouds produced light ashfall towards the west. Observers noted that most of the rockfall activity was on the southwest side of the dome. Small pyroclastic flows from the east and northeast parts of the dome occurred daily into gulleys around White's Ghaut until they filled the entire valley area. Most of the local vegetation was set on fire by these flows. Copyright Challenger Learning Center at Wheeling Jesuit University. All rights reserved. 4
5 July 30-Aug 5 Dome measured at 935 meters. Data shows that new ash clouds are being produced every 4 to 30 hours. Height of clouds range from 0.1 to 1.5 km. As long as ash clouds occur in regular cycles like this, scientists predict that it is unlikely to develop into an explosive situation. A field party working at Farrell's Yard heard frequent rockfall activity and observed one rockfall descending the northeast side of the dome. Small pyroclastic flows reported. Aug 6-12 Dome height reached 952 meters before collapsing on Aug. 6. The new dome has almost filled the collapsed structure and some parts of it appear unstable. Aug 13. Ash cloud reported between km and was associated with thunder and lightning and significant ash fall. Periods of near-continuous rockfalls reported. Most of the rockfalls were channeled down the northeast gully. Several small-to moderately-sized pyroclastic flows reported daily. Aug. 6 many pyroclastic flows were reported. Aug Dome unstable. Aug dome collapses. Maximum dome height reached was 945 meters. Cycles of ash clouds continue every 4 to 30 hours. Cloud heights range from 5 to 10 km. Satellite imagery and aircraft reports show a band of very light ash in the atmosphere extending from Montserrat almost to Puerto Rico. The most significant events were small-to-moderate rockfalls from the growing south side of the lava dome. The largest rockfalls produced small dust storms of ash. Aug intense pyroclastic flow activity. Runny lava flow to Farm Bay shows low levels of silica and moderate levels of dissolved gases. Aug The highest point on the dome was measured from Chance's Peak and yielded an elevation of 963 meters. Cycles of ash clouds continue every 4 to 30 hours. Cloud heights range from 5 to 10 km. Seismic activity has decreased compared to the last five weeks. Pyroclastic flow and lava flow production is decreasing. Scientists are concerned it could be due to blockages in the volcanic vent. Aug 27-Sep meters. Good visibility showed that the east part of the dome was very unstable, and the observed rockfalls generally originated from this area. Ash cloud production is becoming less frequent, but stronger. Three ash clouds sighted ranging from km. Rate and strength of tremors is increasing. In April, seismic levels reached 900 just before the eruption. Seismic levels this week have reached 810. Pyroclastic flow and lava flow production continues to decrease. Scientists are concerned about increasing pressure in the volcanic vents. Copyright Challenger Learning Center at Wheeling Jesuit University. All rights reserved. 5
MVO Activity Reports 2009
 MVO Activity Reports 2009 Ash from the 3 January 2009 explosions Open File Report OFR 13-04 8 March 2013 Montserrat Volcano Observatory - P.O. Box 318 - Flemmings Montserrat Tel : +1 (664) 491-5647 Fax:
MVO Activity Reports 2009 Ash from the 3 January 2009 explosions Open File Report OFR 13-04 8 March 2013 Montserrat Volcano Observatory - P.O. Box 318 - Flemmings Montserrat Tel : +1 (664) 491-5647 Fax:
( ) USGS (United States Geological Survey) Watch Green. Normal. alert level 1 Normal
 (200610.1) USGS (United States Geological Survey) 1014 alert level 1 Normal Watch Green Normal USGS WARNING WATCH ADVISORY NORMAL SUMMARY OF VOLCANIC-ALERT LEVELS Highly hazardous eruption underway or
(200610.1) USGS (United States Geological Survey) 1014 alert level 1 Normal Watch Green Normal USGS WARNING WATCH ADVISORY NORMAL SUMMARY OF VOLCANIC-ALERT LEVELS Highly hazardous eruption underway or
Volcanoes Shake and Bake Indoor Activity
 Mount St Helens National Volcanic Monument Teacher s Corner 2011 Gifford Pinchot National Forest USDA Forest Service Volcanoes Shake and Bake Indoor Activity Time Commitment: Trail: Location: 45 minutes
Mount St Helens National Volcanic Monument Teacher s Corner 2011 Gifford Pinchot National Forest USDA Forest Service Volcanoes Shake and Bake Indoor Activity Time Commitment: Trail: Location: 45 minutes
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanic Eruptions. light in color is called a. felsic. b. oceanic. c. mantle. d. mafic. dark in color is called
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanic Eruptions 1. Lava provides an opportunity for scientists to study a. the nature of Earth s inner core. b. the nature of Earth s tectonic plates. c. temperatures
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanic Eruptions 1. Lava provides an opportunity for scientists to study a. the nature of Earth s inner core. b. the nature of Earth s tectonic plates. c. temperatures
Virtual Design Center Deliverable 4-2: Three Levels of Assessment
 Virtual Design Center Deliverable 4-2: Three Levels of Assessment Project Name Operation Montserrat Test Questions 1. Which of these is an immediate result of the movement of tectonic plates: a) Ocean
Virtual Design Center Deliverable 4-2: Three Levels of Assessment Project Name Operation Montserrat Test Questions 1. Which of these is an immediate result of the movement of tectonic plates: a) Ocean
What are two kinds of volcanic eruptions? How does the composition of magma affect eruptions? What are two ways that magma can erupt from a volcano?
 CHAPTER 9 1 Volcanic Eruptions SECTION Volcanoes BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are two kinds of volcanic eruptions? How does the composition
CHAPTER 9 1 Volcanic Eruptions SECTION Volcanoes BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are two kinds of volcanic eruptions? How does the composition
Volcanic Eruptions (pages )
 Volcanic Eruptions (pages 209 216) Magma Reaches Earth s Surface (pages 210 211) Key Concept: When a volcano erupts, the force of the expanding gases pushes magma from the magma chamber through the pipe
Volcanic Eruptions (pages 209 216) Magma Reaches Earth s Surface (pages 210 211) Key Concept: When a volcano erupts, the force of the expanding gases pushes magma from the magma chamber through the pipe
Earthquakes and Society
 CHAPTER 8 SECTION 3 Earthquakes Earthquakes and Society BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: Can scientists predict when earthquakes will happen? Why
CHAPTER 8 SECTION 3 Earthquakes Earthquakes and Society BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: Can scientists predict when earthquakes will happen? Why
Why was this eruption important?
 Mount St. Helens Mount St. Helens has a long geological history (>3,000 yrs) of explosive eruptions. The 1980 Events: Initial relatively mild steam and ash (Vulcanian) eruptions. Sustained plinian eruption
Mount St. Helens Mount St. Helens has a long geological history (>3,000 yrs) of explosive eruptions. The 1980 Events: Initial relatively mild steam and ash (Vulcanian) eruptions. Sustained plinian eruption
Introduction to volcanoes. Volcano: an opening in the earth s surface through which lava, hot gases, and rock fragments erupt
 Introduction to volcanoes Volcano: an opening in the earth s surface through which lava, hot gases, and rock fragments erupt Origin of Volcanoes 1. Magma 50-100 miles below the earth s surface slowly begins
Introduction to volcanoes Volcano: an opening in the earth s surface through which lava, hot gases, and rock fragments erupt Origin of Volcanoes 1. Magma 50-100 miles below the earth s surface slowly begins
Critical Thinking 1. Contrast How could you tell the difference between a mafic rock and a felsic rock by looking at them?
 CHAPTER 13 2 SECTION Volcanoes Volcanic Eruptions KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: How does the composition of magma affect volcanic eruptions and lava flow? What are the
CHAPTER 13 2 SECTION Volcanoes Volcanic Eruptions KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: How does the composition of magma affect volcanic eruptions and lava flow? What are the
What is Inside a Volcano?
 Volcanoes What is Inside a Volcano? A magma chamber filled with molten rock deep underground that feeds the volcano Magma is released through vents during an eruption Types of Volcanic Eruptions Non-Explosive
Volcanoes What is Inside a Volcano? A magma chamber filled with molten rock deep underground that feeds the volcano Magma is released through vents during an eruption Types of Volcanic Eruptions Non-Explosive
From Punchbowl to Panum: Long Valley Volcanism and the Mono-Inyo Crater Chain
 From Punchbowl to Panum: Leslie Schaffer E105 2002 Final Paper Long Valley Volcanism and the Mono-Inyo Crater Chain Figure 1. After a sequence of earthquakes during the late 1970 s to the early 1980 s
From Punchbowl to Panum: Leslie Schaffer E105 2002 Final Paper Long Valley Volcanism and the Mono-Inyo Crater Chain Figure 1. After a sequence of earthquakes during the late 1970 s to the early 1980 s
Module 1, Investigation 3: Predicting Eruptions
 Module 1, Investigation 3: Predicting Eruptions Introduction Welcome! Volcanoes are either "active" or "extinct". Active means that the volcano has erupted during the past 10,000 years. It can also mean
Module 1, Investigation 3: Predicting Eruptions Introduction Welcome! Volcanoes are either "active" or "extinct". Active means that the volcano has erupted during the past 10,000 years. It can also mean
3.2 Notes: Volcanoes Form as Molten Rock Erupts
 3.2 Notes: Volcanoes Form as Molten Rock Erupts Think about What happens when a volcano erupts? Volcanoes erupt many types of material Earth s thin outer layer is, but most of Earth is extremely hot rock
3.2 Notes: Volcanoes Form as Molten Rock Erupts Think about What happens when a volcano erupts? Volcanoes erupt many types of material Earth s thin outer layer is, but most of Earth is extremely hot rock
VOLCANO MONITORING PRACTICAL. Hazard alert levels established for communication at Mt. Pinatubo
 VOLCANO MONITORING PRACTICAL Predicting volcanic eruptions is a hazardous and stressful business. If an eruption has occurred and was not predicted then the volcanologists get the blame for not giving
VOLCANO MONITORING PRACTICAL Predicting volcanic eruptions is a hazardous and stressful business. If an eruption has occurred and was not predicted then the volcanologists get the blame for not giving
GEOLOGY 285: INTRO. PETROLOGY
 Dr. Helen Lang Dept. of Geology & Geography West Virginia University FALL 2005 GEOLOGY 285: INTRO. PETROLOGY Mount St. Helens 1980 Eruption Small earthquakes Small steam and ash eruptions in March and
Dr. Helen Lang Dept. of Geology & Geography West Virginia University FALL 2005 GEOLOGY 285: INTRO. PETROLOGY Mount St. Helens 1980 Eruption Small earthquakes Small steam and ash eruptions in March and
Pyroclastic Flows. Lesson 6
 Pyroclastic Flows Lesson 6 P yroclastic flows are one of the most dangerous natural events that occur on our planet. They can at hurricane speeds down the slopes of a mountain, destroying everything in
Pyroclastic Flows Lesson 6 P yroclastic flows are one of the most dangerous natural events that occur on our planet. They can at hurricane speeds down the slopes of a mountain, destroying everything in
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanic Eruptions
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanic Eruptions 1. Lava provides an opportunity for scientists to study a. the nature of Earth s inner core. b. the nature of Earth s tectonic plates. c. temperatures
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanic Eruptions 1. Lava provides an opportunity for scientists to study a. the nature of Earth s inner core. b. the nature of Earth s tectonic plates. c. temperatures
Volcanoes: Help or Hindrance?
 Volcanoes: Help or Hindrance? Volcanic eruptions can range from violent to mild. All kinds of eruptions have effects that can be both harmful and beneficial to people and the environment. Volcanoes Can
Volcanoes: Help or Hindrance? Volcanic eruptions can range from violent to mild. All kinds of eruptions have effects that can be both harmful and beneficial to people and the environment. Volcanoes Can
LECTURE #11: Volcanoes: Monitoring & Mitigation
 GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #11: Volcanoes: Monitoring & Mitigation Date: 15 February 2018 I. What is volcanic monitoring? the continuous collection of one or more data sources
GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #11: Volcanoes: Monitoring & Mitigation Date: 15 February 2018 I. What is volcanic monitoring? the continuous collection of one or more data sources
Also, when Cascade volcanoes do erupt, high-speed avalanches of pyroclastic flows
 INTRODUCTION A volcano is a vent through which molten rock escapes to the Earth s surface. Unlike other mountains, which are pushed up from below, volcanoes are built by surface accumulation of their eruptive
INTRODUCTION A volcano is a vent through which molten rock escapes to the Earth s surface. Unlike other mountains, which are pushed up from below, volcanoes are built by surface accumulation of their eruptive
Earthquakes and volcanoes in Iceland
 Jenny Jenkins Daði Harðarson Explosive Earth Earthquakes and volcanoes in Iceland The eruption of Bárðarbunga volcano in Iceland, July 2014 Key words volcano earthquake seismology prediction Bárðarbunga
Jenny Jenkins Daði Harðarson Explosive Earth Earthquakes and volcanoes in Iceland The eruption of Bárðarbunga volcano in Iceland, July 2014 Key words volcano earthquake seismology prediction Bárðarbunga
Effects of Eruptions. Most active in the world Kilauea, Hawaii.
 Inside of Old Smokey, All covered with snow, Lurk tons of hot magma, Getting ready to blow, Objectives: From deep in the chamber, Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Up a vent to the top, Describe
Inside of Old Smokey, All covered with snow, Lurk tons of hot magma, Getting ready to blow, Objectives: From deep in the chamber, Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Up a vent to the top, Describe
Volcanic Eruptions (pp )
 Name Date Class Volcanic Eruptions (pp. 221 228) This section explains how volcanoes erupt and describes types of volcanic eruptions as well as other types of volcanic activity. The section also describes
Name Date Class Volcanic Eruptions (pp. 221 228) This section explains how volcanoes erupt and describes types of volcanic eruptions as well as other types of volcanic activity. The section also describes
Chapter 7: Volcanoes 8/18/2014. Section 1 (Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics) 8 th Grade. Ring of Fire
 Section 1 (Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics) Chapter 7: Volcanoes 8 th Grade Ring of Fire a major belt of es that rims the Pacific Ocean Volcanic belts form along the boundaries of Earth s plates as they
Section 1 (Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics) Chapter 7: Volcanoes 8 th Grade Ring of Fire a major belt of es that rims the Pacific Ocean Volcanic belts form along the boundaries of Earth s plates as they
Name Hour. Environmental Science Semester 2 Study Guide. Plate Tectonics. 1. Explain sea floor spreading.
 Name Hour Environmental Science Semester 2 Study Guide Plate Tectonics 1. Explain sea floor spreading. 2. Describe Wegener s idea of continental drift. 3. List 5 pieces of evidence to support the idea
Name Hour Environmental Science Semester 2 Study Guide Plate Tectonics 1. Explain sea floor spreading. 2. Describe Wegener s idea of continental drift. 3. List 5 pieces of evidence to support the idea
Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire
 Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire On July 16, 1990, a large earthquake struck Luzon, an island in the Philippines. The earthquake devastated cities for hundreds of
Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire On July 16, 1990, a large earthquake struck Luzon, an island in the Philippines. The earthquake devastated cities for hundreds of
Objectives: Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Describe conditions that cause volcanoes. Describe the relationship between volcanoes and Earth
 Objectives: Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Describe conditions that cause volcanoes. Describe the relationship between volcanoes and Earth s moving plates. Inside of Old Smokey, All covered
Objectives: Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Describe conditions that cause volcanoes. Describe the relationship between volcanoes and Earth s moving plates. Inside of Old Smokey, All covered
Magma is a complex mixture of liquid, solid and gas
 Magma is a complex mixture of liquid, solid and gas Liquid molten silicate Solid early-formed minerals Gas Generally 0.1% to 5% of the magma by weight, but can be as much as 15% >90% of the gas in magma
Magma is a complex mixture of liquid, solid and gas Liquid molten silicate Solid early-formed minerals Gas Generally 0.1% to 5% of the magma by weight, but can be as much as 15% >90% of the gas in magma
NSF-MARGINS Expedition to Anatahan Volcano March 2005
 1 NSF-MARGINS Expedition to Anatahan Volcano March 2005 According to the Emergency Management Office (EMO) report distributed in February 2005, the third historical eruption of Anatahan began on January
1 NSF-MARGINS Expedition to Anatahan Volcano March 2005 According to the Emergency Management Office (EMO) report distributed in February 2005, the third historical eruption of Anatahan began on January
Supporting the response to the 2018 lower East Rift Zone and summit collapse at Kīlauea Volcano, Hawaiʻi
 Hawaiʻi Supersite success story Supporting the response to the 2018 lower East Rift Zone and summit collapse at Kīlauea Volcano, Hawaiʻi Since 1983, Kīlauea Volcano, on the Island of Hawaiʻi, has actively
Hawaiʻi Supersite success story Supporting the response to the 2018 lower East Rift Zone and summit collapse at Kīlauea Volcano, Hawaiʻi Since 1983, Kīlauea Volcano, on the Island of Hawaiʻi, has actively
EAS 116 Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 EAS 116 Earthquakes and Volcanoes J. Haase Forecasting Volcanic Eruptions Assessment of Volcanic Hazard Is that volcano active? Mount Lassen: 12000 BP and 1915 Santorini, IT: 180,000 BP, 70,000 BP, 21000
EAS 116 Earthquakes and Volcanoes J. Haase Forecasting Volcanic Eruptions Assessment of Volcanic Hazard Is that volcano active? Mount Lassen: 12000 BP and 1915 Santorini, IT: 180,000 BP, 70,000 BP, 21000
Volcanoes. Environmental Geology, Mr. Paul Lowrey Stacey Singleton, Cassandra Combs, Dwight Stephenson, Matt Smithyman
 Volcanoes Environmental Geology, Mr. Paul Lowrey Stacey Singleton, Cassandra Combs, Dwight Stephenson, Matt Smithyman EMPACTS Project, Spring 2017 Northwest Arkansas Community College, Bentonville, AR
Volcanoes Environmental Geology, Mr. Paul Lowrey Stacey Singleton, Cassandra Combs, Dwight Stephenson, Matt Smithyman EMPACTS Project, Spring 2017 Northwest Arkansas Community College, Bentonville, AR
3/24/2016. Geology 12 Mr. M. Gauthier 24 March 2016
 Geology 12 Mr. M. Gauthier 24 March 2016 Introduction: Mt. St. Helens Before 1980 Mt. St Helens, in Southern Washington State, had not erupted since 1857 On March 27,1980 minor ashand eruptions were due
Geology 12 Mr. M. Gauthier 24 March 2016 Introduction: Mt. St. Helens Before 1980 Mt. St Helens, in Southern Washington State, had not erupted since 1857 On March 27,1980 minor ashand eruptions were due
Eruption! Mexico's "Volcano of Fire" roars back to life. When will the next big explosion occur?
 Non-fiction: Eruption! Eruption! Mexico's "Volcano of Fire" roars back to life. When will the next big explosion occur? The Colima (koh-lee-mah) Volcano in Mexico has roared to life again. The 12,500-foot
Non-fiction: Eruption! Eruption! Mexico's "Volcano of Fire" roars back to life. When will the next big explosion occur? The Colima (koh-lee-mah) Volcano in Mexico has roared to life again. The 12,500-foot
FIRST GRADE HAZARDS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FIRST GRADE HAZARDS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIRST GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Learning the shapes of volcanoes. LAB: Experimenting with "lava." POST: Comparing
FIRST GRADE HAZARDS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIRST GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Learning the shapes of volcanoes. LAB: Experimenting with "lava." POST: Comparing
Volcano: a weak spot in the crust where molten material or magma comes to the surface
 Chapter 7 Volcano: a weak spot in the crust where molten material or magma comes to the surface Magma: a molten mixture of rock forming substances, gases and H 2 O from the mantle Volcanic Belts: Form
Chapter 7 Volcano: a weak spot in the crust where molten material or magma comes to the surface Magma: a molten mixture of rock forming substances, gases and H 2 O from the mantle Volcanic Belts: Form
Volcanoes. Introduction
 Volcanoes Introduction Display Slide V-0 Explain that a volcano is a vent through which molten rock escapes to the Earth s surface. Unlike other mountains, which are pushed up from below, volcanoes are
Volcanoes Introduction Display Slide V-0 Explain that a volcano is a vent through which molten rock escapes to the Earth s surface. Unlike other mountains, which are pushed up from below, volcanoes are
New A-Level Physical Geography
 Half Term 1 3.1 Physical Geography: 3.1.5 Hazards: Plate Tectonics This optional section of our specification focuses on the lithosphere and the atmosphere, which intermittently but regularly present natural
Half Term 1 3.1 Physical Geography: 3.1.5 Hazards: Plate Tectonics This optional section of our specification focuses on the lithosphere and the atmosphere, which intermittently but regularly present natural
About Volcanoes Volcanology IMPORTANT TERMS
 About Volcanoes IMPORTANT TERMS magma Rock that is molten (in liquid form due to heating). When magma reaches the surface, it is called lava. lava magma reservoir An underground pool that is filled with
About Volcanoes IMPORTANT TERMS magma Rock that is molten (in liquid form due to heating). When magma reaches the surface, it is called lava. lava magma reservoir An underground pool that is filled with
Bellringer: What materials are ejected from volcanoes? Quote of the Day: "Science is not belief, but the will to find out.
 Bellringer: What materials are ejected from volcanoes? Quote of the Day: "Science is not belief, but the will to find out." ~Anonymous Sep 26 10:30 AM 1 Copy Directly into your notebook... 1. Pyro Latin
Bellringer: What materials are ejected from volcanoes? Quote of the Day: "Science is not belief, but the will to find out." ~Anonymous Sep 26 10:30 AM 1 Copy Directly into your notebook... 1. Pyro Latin
Predicting and Preparing for Volcanoes
 Predicting and Preparing for Volcanoes Prediction methods for volcanic eruptions are more reliable than those for earthquakes. Some volcanoes such as Mount Etna in Italy are monitored all of the time because
Predicting and Preparing for Volcanoes Prediction methods for volcanic eruptions are more reliable than those for earthquakes. Some volcanoes such as Mount Etna in Italy are monitored all of the time because
THE EARTH S SURFACE AND BELOW
 THE EARTH S SURFACE AND BELOW Name: Class: Directions: Match the words with the big ideas by writing the letter beside the idea. Use the same words in the short article below. Use key words and phrases
THE EARTH S SURFACE AND BELOW Name: Class: Directions: Match the words with the big ideas by writing the letter beside the idea. Use the same words in the short article below. Use key words and phrases
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earthquakes Lesson 2 Volcanoes Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earthquakes Lesson 2 Volcanoes Chapter Wrap-Up What causes earthquakes and volcanic eruptions? What do you think? Before you begin, decide if you agree or disagree with each
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earthquakes Lesson 2 Volcanoes Chapter Wrap-Up What causes earthquakes and volcanic eruptions? What do you think? Before you begin, decide if you agree or disagree with each
Debris Avalanches. Debris avalanche deposits on a volcano in Chile. All of the area in the foreground is buried by a thick debris avalanche.
 Debris Avalanches Volcanoes are not very stable structures. From time to time, they collapse producing large rock and ash avalanches that travel at high speeds down valleys. Collapse maybe caused by an
Debris Avalanches Volcanoes are not very stable structures. From time to time, they collapse producing large rock and ash avalanches that travel at high speeds down valleys. Collapse maybe caused by an
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. Some volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than a(n) a. hand grenade. b. earthquake. c. geyser. d. atomic bomb. 2. The cause
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. Some volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than a(n) a. hand grenade. b. earthquake. c. geyser. d. atomic bomb. 2. The cause
Overview of Ch. 4. I. The nature of volcanic eruptions 9/19/2011. Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5
 Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
FOUNDATIONS OF GEOLOGY CHAPTER 2
 FOUNDATIONS OF GEOLOGY CHAPTER 2 2.3A- VOLCANOES Volcanoes all share common characteristics. Vent- a central channel through which gases, ash and rock are ejected. Magma- molten rock which lies several
FOUNDATIONS OF GEOLOGY CHAPTER 2 2.3A- VOLCANOES Volcanoes all share common characteristics. Vent- a central channel through which gases, ash and rock are ejected. Magma- molten rock which lies several
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 volcano sample test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Volcanic belts form along a. islands in the Pacific Ocean. b. North American
volcano sample test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Volcanic belts form along a. islands in the Pacific Ocean. b. North American
Volcanoes. What is a volcano
 What is a volcano The crust of the Earth floats on the 'liquid' mantle. At some points where the crust might be weaker there are concentrations of magma. The magma is liquid rock. These concentrations
What is a volcano The crust of the Earth floats on the 'liquid' mantle. At some points where the crust might be weaker there are concentrations of magma. The magma is liquid rock. These concentrations
Volcanology. The study of volcanoes
 Volcanology The study of volcanoes Magma forms wherever temperature and pressure are high enough to melt rock. Some magma forms at the aesthenosphere Magma also forms at plate boundaries, where intense
Volcanology The study of volcanoes Magma forms wherever temperature and pressure are high enough to melt rock. Some magma forms at the aesthenosphere Magma also forms at plate boundaries, where intense
Geography. Key facts. Volcanoes and volcanic eruptions
 Geography Volcanoes and volcanic eruptions Volcanoes form when magma reaches the Earth's surface, causing eruptions of lava and ash. They occur at destructive (compressional) and constructive (tensional)
Geography Volcanoes and volcanic eruptions Volcanoes form when magma reaches the Earth's surface, causing eruptions of lava and ash. They occur at destructive (compressional) and constructive (tensional)
A Volcano is An opening in Earth s crust through
 Volcanoes A Volcano is An opening in Earth s crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt. Also, the landform that develops around this opening. Kinds of Eruptions Geologists classify volcanic
Volcanoes A Volcano is An opening in Earth s crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt. Also, the landform that develops around this opening. Kinds of Eruptions Geologists classify volcanic
Unit 4 Lesson 4 Volcanoes. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Magma Magic What is a volcano? A volcano is any place where gas, ash, or melted rock come out of the ground. Many volcanoes are dormant, meaning an eruption has not occurred in a long period of time. What
Magma Magic What is a volcano? A volcano is any place where gas, ash, or melted rock come out of the ground. Many volcanoes are dormant, meaning an eruption has not occurred in a long period of time. What
REFERENCE: The Blue Planet An Introduction to Earth System Science. Brian J. Skinner and Barbara W. Murck (2011) Third Edition. John Wiley and Sons
 REFERENCE: The Blue Planet An Introduction to Earth System Science. Brian J. Skinner and Barbara W. Murck (2011) Third Edition. John Wiley and Sons Inc. PLATE BOUNDARIES OCEAN FLOOR SEISMIC ACTIVITY WORLD'S
REFERENCE: The Blue Planet An Introduction to Earth System Science. Brian J. Skinner and Barbara W. Murck (2011) Third Edition. John Wiley and Sons Inc. PLATE BOUNDARIES OCEAN FLOOR SEISMIC ACTIVITY WORLD'S
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12 Volcanoes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Plate tectonics explains the global pattern of volcanism. Key Figure 12.20 (page
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12 Volcanoes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Plate tectonics explains the global pattern of volcanism. Key Figure 12.20 (page
Mt St Helens was know to have entered into active periods that lasted from years once every years over the last 500 years, (Figure 5).
 Lecture #8 notes; Geology 3950, Spring 2006; CR Stern May 1980 eruption of Mt St Helens volcano (text pages 183-192 in the 4 th edition and 206-222 in the 5 th edition) Mt St Helens in southwest Washington
Lecture #8 notes; Geology 3950, Spring 2006; CR Stern May 1980 eruption of Mt St Helens volcano (text pages 183-192 in the 4 th edition and 206-222 in the 5 th edition) Mt St Helens in southwest Washington
A bowl shaped depression formed by the collapse of a volcano is called a. Magma that has left the vent of a volcano is known as. Lava.
 Magma that has left the vent of a volcano is known as Lava A bowl shaped depression formed by the collapse of a volcano is called a Caldera This can form in a caldera when magma starts to come back up
Magma that has left the vent of a volcano is known as Lava A bowl shaped depression formed by the collapse of a volcano is called a Caldera This can form in a caldera when magma starts to come back up
Year 8 Level: 5-8 GEOGRAPHY Time: 1:30min
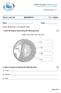 Year 8 Level: 5-8 GEOGRAPHY Time: 1:30min Name: Class: Answer all questions in the space provided. 1. Label the diagram below using the following words; (4) mantle, crust, outer core, inner core 2. Write
Year 8 Level: 5-8 GEOGRAPHY Time: 1:30min Name: Class: Answer all questions in the space provided. 1. Label the diagram below using the following words; (4) mantle, crust, outer core, inner core 2. Write
7th Grade. Science. September. Scientific Inquiry- Scientific Method
 7th Grade Science September Scientific Inquiry- Scientific Method 1. Develop a problem or question 2. Produce a hypothesis 3. Identify and organize controls and variable in an experiment 4. Perform the
7th Grade Science September Scientific Inquiry- Scientific Method 1. Develop a problem or question 2. Produce a hypothesis 3. Identify and organize controls and variable in an experiment 4. Perform the
Monitoring Volcanoes. An introduction to monitoring techniques. Name: Class: Date:
 Monitoring Volcanoes An introduction to monitoring techniques Name: Class: Date: Aims To understand how volcanoes are monitored in order to predict when they will erupt To understand the importance of
Monitoring Volcanoes An introduction to monitoring techniques Name: Class: Date: Aims To understand how volcanoes are monitored in order to predict when they will erupt To understand the importance of
The Dynamic Earth Section 1. Chapter 3 The Dynamic Earth Section 1: The Geosphere DAY 1
 Chapter 3 The Dynamic Earth Section 1: The Geosphere DAY 1 The Earth as a System The Earth is an integrated system that consists of rock, air, water, and living things that all interact with each other.
Chapter 3 The Dynamic Earth Section 1: The Geosphere DAY 1 The Earth as a System The Earth is an integrated system that consists of rock, air, water, and living things that all interact with each other.
Volcano. Magma. Lava. weak spot in crust where magma and gases come up. molten mixture of rockforming
 Volcanoes Volcano weak spot in crust where magma and gases come up Magma Lava molten mixture of rockforming substance, gases, water from the mantle Magma that flows onto earth surface forms solid rock
Volcanoes Volcano weak spot in crust where magma and gases come up Magma Lava molten mixture of rockforming substance, gases, water from the mantle Magma that flows onto earth surface forms solid rock
The Evidence of Earth s Violent Geologic Past
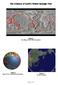 The Evidence of Earth s Violent Geologic Past Figure 1 The Ring of Fire (Flat Projection) Figure 2 Ring of Fire, (Spherical Projection) Figure 3 Ocean Trenches Page 1 of 10 Figure 4 Kamchatka Peninsula
The Evidence of Earth s Violent Geologic Past Figure 1 The Ring of Fire (Flat Projection) Figure 2 Ring of Fire, (Spherical Projection) Figure 3 Ocean Trenches Page 1 of 10 Figure 4 Kamchatka Peninsula
Montserrat Eruption = Monster rat
 Montserrat Eruption 1997 = Monster rat Small island in the Caribbean sea Montserrat is a small... Soufriere Hills volcano Key facts: Date: 25 th June 1997 (small eruptions began in July 1995) Size: 4.5
Montserrat Eruption 1997 = Monster rat Small island in the Caribbean sea Montserrat is a small... Soufriere Hills volcano Key facts: Date: 25 th June 1997 (small eruptions began in July 1995) Size: 4.5
and their risks A look at volcano risk for young students. Produced by the MED-SUV project.
 and their risks A look at volcano risk for young students. Produced by the MED-SUV project. Volcano Shapes: A volcano is a place (on Earth and OTHER PLANETS) where magma comes to the surface. This event
and their risks A look at volcano risk for young students. Produced by the MED-SUV project. Volcano Shapes: A volcano is a place (on Earth and OTHER PLANETS) where magma comes to the surface. This event
Vulcanicity. Objectives to identify the basic structure of volcanoes and understand how they form.
 Vulcanicity Objectives to identify the basic structure of volcanoes and understand how they form. Some key terms to start.. Viscosity how well a substance (lava) flows. Acid lavas have a high viscosity,
Vulcanicity Objectives to identify the basic structure of volcanoes and understand how they form. Some key terms to start.. Viscosity how well a substance (lava) flows. Acid lavas have a high viscosity,
Not all eruptions are the same. Sometimes, there is a huge explosion. The hot magma shoots
 Natural Disasters A natural disaster is an event that happens in nature. It is an event that can cause a lot of damage. Volcanoes, earthquakes, and tsunamis are all natural disasters. Volcanoes A volcano
Natural Disasters A natural disaster is an event that happens in nature. It is an event that can cause a lot of damage. Volcanoes, earthquakes, and tsunamis are all natural disasters. Volcanoes A volcano
Volcanic Processes, the Resulting Landforms, and What These Mean To the Residents Nearby
 Volcanic Processes, the Resulting Landforms, and What These Mean To the Residents Nearby INTRODUCTION Ancient Eruptions By: Erin Tarnowski Volcanoes present many hazards to the populations nearby. Famous
Volcanic Processes, the Resulting Landforms, and What These Mean To the Residents Nearby INTRODUCTION Ancient Eruptions By: Erin Tarnowski Volcanoes present many hazards to the populations nearby. Famous
Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 Name Earthquakes and Volcanoes What causes earthquakes and volcanic eruptions? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about earthquakes and volcanoes. In the first column,
Name Earthquakes and Volcanoes What causes earthquakes and volcanic eruptions? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about earthquakes and volcanoes. In the first column,
Toxic cloud caused by Hawaii volcano lava emerges over ocean 21 May 2018, by Caleb Jones And Audrey Mcavoy
 Toxic cloud caused by Hawaii volcano lava emerges over ocean 21 May 2018, by Caleb Jones And Audrey Mcavoy Joe Kekedi watches as lava enters the ocean, generating plumes of steam near Pahoa, Hawaii Sunday,
Toxic cloud caused by Hawaii volcano lava emerges over ocean 21 May 2018, by Caleb Jones And Audrey Mcavoy Joe Kekedi watches as lava enters the ocean, generating plumes of steam near Pahoa, Hawaii Sunday,
UNIT 1 - Major Land and Water Forms
 UNIT 1 - Major Land and Water Forms Chapter 1 - Landform Patterns and Processes Topography the natural and human features of the Earth s surface. ie. Surface features elevation - the height of a particular
UNIT 1 - Major Land and Water Forms Chapter 1 - Landform Patterns and Processes Topography the natural and human features of the Earth s surface. ie. Surface features elevation - the height of a particular
ST NICHOLAS COLLEGE RABAT SECONDARY. Name: Class: Register Number:
 ST NICHOLAS COLLEGE RABAT SECONDARY HALF YEARLY EXAMINATIONS Mark February 2017 Year 8 GEOGRAPHY TIME: 1 h 30 min Name: Class: Register Number: Answer all questions 1) Write True or False near each sentence.
ST NICHOLAS COLLEGE RABAT SECONDARY HALF YEARLY EXAMINATIONS Mark February 2017 Year 8 GEOGRAPHY TIME: 1 h 30 min Name: Class: Register Number: Answer all questions 1) Write True or False near each sentence.
What is the theory of plate tectonics? Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3
 Name Plate Tectonics What is the theory of plate tectonics? Date Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about plate tectonics Record your thoughts in the first column Pair
Name Plate Tectonics What is the theory of plate tectonics? Date Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about plate tectonics Record your thoughts in the first column Pair
GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca:
 Name: Date: GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca: SiO 2 silicon dioxide. This is quartz when it crystallizes.
Name: Date: GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca: SiO 2 silicon dioxide. This is quartz when it crystallizes.
GEOLOGY 285: INTRO. PETROLOGY
 Dr. Helen Lang Dept. of Geology & Geography West Virginia University SPRING 2015 GEOLOGY 285: INTRO. PETROLOGY The Cascade Volcanoes are a good example of the Circum- Pacific ring of fire of subductionrelated
Dr. Helen Lang Dept. of Geology & Geography West Virginia University SPRING 2015 GEOLOGY 285: INTRO. PETROLOGY The Cascade Volcanoes are a good example of the Circum- Pacific ring of fire of subductionrelated
When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere.
 When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere. A volcano is a mountain that forms when magma reaches the
When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere. A volcano is a mountain that forms when magma reaches the
Chapter: Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 Table of Contents Chapter: Earthquakes and Volcanoes Section 1: Earthquakes Section 2: Volcanoes Section 3: Earthquakes, Volcanoes, and Plate Tectonics 1 Earthquakes What causes earthquakes? Elastic Rebound
Table of Contents Chapter: Earthquakes and Volcanoes Section 1: Earthquakes Section 2: Volcanoes Section 3: Earthquakes, Volcanoes, and Plate Tectonics 1 Earthquakes What causes earthquakes? Elastic Rebound
Part II: Succession Stations
 Part II: Succession Stations Station 1: Mount St. Helens - Before and After Mount St. Helens is a volcano in the Cascade Mountain range in Washington state. For many years, it was dormant. Then, at 8:32
Part II: Succession Stations Station 1: Mount St. Helens - Before and After Mount St. Helens is a volcano in the Cascade Mountain range in Washington state. For many years, it was dormant. Then, at 8:32
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore VO L CANIC CO NE For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore VO L CANIC CO NE For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
1. minerals - A naturally occurring substance that takes a solid Crystal form and is made of only a single (one) type of compound
 Science Name: Mr. G/Mrs. Kelly KEY Date: Study Guide - Lessons 5 and 6 Test Define the following terms: 1. minerals - A naturally occurring substance that takes a solid Crystal form and is made of only
Science Name: Mr. G/Mrs. Kelly KEY Date: Study Guide - Lessons 5 and 6 Test Define the following terms: 1. minerals - A naturally occurring substance that takes a solid Crystal form and is made of only
Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!!
 Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!! Three Types of Volcanos Shield Cinder Cone Composite Shield Volcano Created by hot spots Gently sloping Cinder Volcano Steep Cone-shaped hill/ mountain Composite Volcano Tall,
Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!! Three Types of Volcanos Shield Cinder Cone Composite Shield Volcano Created by hot spots Gently sloping Cinder Volcano Steep Cone-shaped hill/ mountain Composite Volcano Tall,
Name: Earth Science Date:
 Name: Earth Science Date: Lab Report: Plate Tectonics Data: Submit the Mid- Atlantic Seafloor Profile Maps (from Divergent Plate Boundary Lab) on and the Convergent Plate Boundary Data Page. (6 points)
Name: Earth Science Date: Lab Report: Plate Tectonics Data: Submit the Mid- Atlantic Seafloor Profile Maps (from Divergent Plate Boundary Lab) on and the Convergent Plate Boundary Data Page. (6 points)
Take a Chance on the volcano erupting How hazardous is the volcano?
 Earthlearningidea - http://www.earthlearningidea.com/ Take a Chance on the volcano erupting How hazardous is the volcano? Earth Learning Idea has already published Party time for volcanoes! How much force
Earthlearningidea - http://www.earthlearningidea.com/ Take a Chance on the volcano erupting How hazardous is the volcano? Earth Learning Idea has already published Party time for volcanoes! How much force
Volcano Unit Pre Assessment. Match the type of volcano to the correct picture by drawing a line to connect the two.
 Volcano Unit Pre Assessment Name Matching Match the type of volcano to the correct picture by drawing a line to connect the two. Composite Volcano Shield Volcano Cinder Cone Volcano Multiple Choice Select
Volcano Unit Pre Assessment Name Matching Match the type of volcano to the correct picture by drawing a line to connect the two. Composite Volcano Shield Volcano Cinder Cone Volcano Multiple Choice Select
Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!! VOLCANOES
 Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!! VOLCANOES VOLCANOS Three Types of Volcanos Shield Cinder Cone Composite LAND FORMATIONS FROM LAVA & ASH Shield Volcano Created by hot spots Gently sloping Cinder Volcano Steep
Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!! VOLCANOES VOLCANOS Three Types of Volcanos Shield Cinder Cone Composite LAND FORMATIONS FROM LAVA & ASH Shield Volcano Created by hot spots Gently sloping Cinder Volcano Steep
TABLE OF CONTENTS. Student Letter Exploring the Strategies Unit One: Play Unit Two: Fantasy Unit Three: Mystery...
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Student Letter........................................... 2 Exploring the Strategies................................... 3 Unit One: Play........................................... 4 Unit
TABLE OF CONTENTS Student Letter........................................... 2 Exploring the Strategies................................... 3 Unit One: Play........................................... 4 Unit
Kīlauea Volcano: Be a Volcanologist. Image Credit: Julien Millet / Unsplash. Final Project
 The Kīlauea Volcano: Be a Volcanologist Image Credit: Julien Millet / Unsplash Final Project Final Project The Kīlauea Volcano: Be a Volcanologist In this two-day project, students apply their previous
The Kīlauea Volcano: Be a Volcanologist Image Credit: Julien Millet / Unsplash Final Project Final Project The Kīlauea Volcano: Be a Volcanologist In this two-day project, students apply their previous
Chapter Twelve: Earthquakes
 The Changing Earth Chapter Twelve: Earthquakes 12.1 Earthquakes 12.2 Volcanoes Investigation 12B Volcanoes How are volcanoes and plate boundaries related? 12.2 Looking inside a volcano A volcano is where
The Changing Earth Chapter Twelve: Earthquakes 12.1 Earthquakes 12.2 Volcanoes Investigation 12B Volcanoes How are volcanoes and plate boundaries related? 12.2 Looking inside a volcano A volcano is where
GLY July Ms. Nelda Breedt. Plates move slowly and eventually.
 GLY 162 Tectonic Processes: Volcanism Ms. Nelda Breedt GLY 162 Environmental Geology Plate Tectonics Plates move slowly and eventually. 2 Spread apart (divergent plates) Dive beneath one another (converging
GLY 162 Tectonic Processes: Volcanism Ms. Nelda Breedt GLY 162 Environmental Geology Plate Tectonics Plates move slowly and eventually. 2 Spread apart (divergent plates) Dive beneath one another (converging
Convergent Plate Boundary Geologic Features
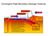 Convergent Plate Boundary Geologic Features Ocean Trench Mtn / Volcano New Ocean Crust Old Continenta l Crust Beadle, 2009 Convection cells provide the force to move the continents. The crust is carried
Convergent Plate Boundary Geologic Features Ocean Trench Mtn / Volcano New Ocean Crust Old Continenta l Crust Beadle, 2009 Convection cells provide the force to move the continents. The crust is carried
Back to the Big Question
 5.1 Understand the 5.4 Question Explore Learning Set 5 Back to the Big Question What processes within Earth cause geologic activity? You now know a lot about patterns of volcanoes in your region and around
5.1 Understand the 5.4 Question Explore Learning Set 5 Back to the Big Question What processes within Earth cause geologic activity? You now know a lot about patterns of volcanoes in your region and around
Chapter 18. Volcanism
 Chapter 18 Volcanism Ring of fire contains 66% of world s active volcanoes Convergent : Divergent: Icelandic Eruption Mount Etna Different Kinds of eruptions: Volcanic activity is controlled by plate tectonics,
Chapter 18 Volcanism Ring of fire contains 66% of world s active volcanoes Convergent : Divergent: Icelandic Eruption Mount Etna Different Kinds of eruptions: Volcanic activity is controlled by plate tectonics,
Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere. Volcanic Activity
 Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere Volcanic Activity Lesson 3 Volcanoes, Part 1 Think About It What happens when you shake a can of soda and then open it? Focus Question How does the composition of magma
Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere Volcanic Activity Lesson 3 Volcanoes, Part 1 Think About It What happens when you shake a can of soda and then open it? Focus Question How does the composition of magma
Name Midterm Review Earth Science Constructed Response
 Name Midterm Review Earth Science Constructed Response Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the world map below. Points A through H represent locations on Earth's surface. 1. Identify the tectonic
Name Midterm Review Earth Science Constructed Response Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the world map below. Points A through H represent locations on Earth's surface. 1. Identify the tectonic
Earth has more than 600 active volcanoes. An active volcano is one that has erupted within recorded history.
 Volcanoes A volcano is an opening in Earth s surface that erupts gases, ash, and lava. These materials pile up in layers around the opening, forming volcanic mountains. Earth has more than 600 active volcanoes.
Volcanoes A volcano is an opening in Earth s surface that erupts gases, ash, and lava. These materials pile up in layers around the opening, forming volcanic mountains. Earth has more than 600 active volcanoes.
Lesson 6: Predicting Eruptions. Grade Level 6-8. Volcanoes Educator Guide
 Lesson : Predicting eruptions Lesson : Predicting Eruptions Grade Level -8 Volcanoes Educator Guide Volcanoes Educator Guide Lesson : Predicting Eruptions Grade Level -8 () minute prep lesson () minute
Lesson : Predicting eruptions Lesson : Predicting Eruptions Grade Level -8 Volcanoes Educator Guide Volcanoes Educator Guide Lesson : Predicting Eruptions Grade Level -8 () minute prep lesson () minute
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands
 Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 4 22 January 2004 Turn in Homework #1 Any Questions? IMPORTANT Big Island Field Trip We need a $162 payment for airfare BEFORE January 29 th Description of logistics,
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 4 22 January 2004 Turn in Homework #1 Any Questions? IMPORTANT Big Island Field Trip We need a $162 payment for airfare BEFORE January 29 th Description of logistics,
Volcanoes. Table of Contents Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Landforms
 Volcanoes Table of Contents Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Landforms What is a volcano? cone Conduit Or Pipe vent Side vent Central vent Crater A volcano is a vent or 'chimney'
Volcanoes Table of Contents Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Landforms What is a volcano? cone Conduit Or Pipe vent Side vent Central vent Crater A volcano is a vent or 'chimney'
