IASbaba s 60 Days Plan Day 8 (Geography) 2018
|
|
|
- Clifton Doyle
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Q.1) Consider the following. 1. Himalayas 2. Peninsular Plateau 3. North Indian Plains Arrange the following in chronological order of their formations. a) b) c) d) Q.1) Solution (b) The oldest landmass, (the Peninsula part), was a part of the Gondwana land. The Gondwana land included India, Australia, South Africa, South America and Antarctica as one single land mass. The northward drift of Peninsular India resulted in the collision of the plate with the much larger Eurasian Plate. Due to this collision, the sedimentary rocks which were accumulated in the geosyncline known as the Tethys were folded to form the mountain system of western Asia and Himalayas. The Himalayan uplift out of the Tethys Sea and subsidence of the northern flank of the peninsular plateau resulted in the formation of a large basin. In due course of time this depression, gradually got filled with deposition of sediments by the rivers flowing from the mountains in the north and the peninsular plateau in the south. A flat land of extensive alluvial deposits led to the formation of the northern plains of India. Do you know? Geologically, the Peninsular Plateau constitutes one of the ancient landmasses on the earth s surface. It was supposed to be one of the most stable land blocks. THINK! Eastern and Western Ghats Q.2) Consider the following statements about Northwestern Himalayas. 1. The world-famous valley of Kashmir lies between the Karakoram Range and Ladakh Range. 2. The Kashmir Himalayas are also famous for Karewa formations. 3. Chenab in the valley of Kashmir is still in its youth stage and yet forms meanders. 1
2 Which of the above statements is/are correct? a) 1 and 2 only b) 2 only c) 1 and 3 only d) All the above. Q.2) Solution (b) Between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal range, lies the world-famous valley of Kashmir and the famous Dal Lake. The Kashmir Himalayas are also famous for Karewa formations, which are useful for the cultivation of Zafran, a local variety of saffron. Srinagar, capital city of the state of Jammu and Kashmir is located on the banks of Jhelum River. Dal Lake in Srinagar presents an interesting physical feature. Jhelum in the valley of Kashmir is still in its youth stage and yet forms meanders a typical feature associated with the mature stage in the evolution of fluvial land form. Do you know? Karewas are the thick deposits of glacial clay and other materials embedded with moraines. THINK! Molassis Basin. Q.3) Tors, block mountains, rift valleys, spurs, bare rocky structures, series of hummocky hills and wall-like quartzite dykes are some of the important physiographic features of which of the following region? a) Purvanchal Hill Complex. b) Peninsular plateau. c) North Indian Plains. d) Indian Deserts. Q.3) Solution (b) Some of the important physiographic features of peninsular plateau region are tors, block mountains, rift valleys, spurs, bare rocky structures, series of hummocky hills and wall-like quartzite dykes offering natural sites for water storage. The western and northwestern part of the plateau has an emphatic presence of black soil. 2
3 Do you know? IASbaba s 60 Days Plan Day 8 (Geography) 2018 A tor, which is also known by geomorphologists as either a castle koppie or kopje, is a large, free-standing rock outcrop that rises abruptly from the surrounding smooth and gentle slopes of a rounded hill summit or ridge crest. THINK! Ravines and gorges. Q.4) Consider the following statements 1. The western coastal plains are an example of emergent coastal plain. 2. The western coastal plains are narrow in the middle and get broader towards north and south. 3. Because of its submerged nature, eastern coast has less number of ports and harbors. 4. The lakes and the playas have brackish water which is the main source of obtaining salt in western coasts. Choose the correct answer using the codes given below. a) 1 and 4 only b) 2 and 3 only c) 2, 3 and 4 only d) 2 only 3
4 Q.4) Solution (d) The western coastal plains are an example of submerged coastal plain. It is believed that the city of Dwaraka which was once a part of the Indian mainland situated along the west coast is submerged under water. Because of this submergence it is a narrow belt and provides natural conditions for the development of ports and harbors. The western coastal plains are narrow in the middle and get broader towards north and south. As compared to the western coastal plain, the eastern coastal plain is broader and is an example of an emergent coast. Because of its emergent nature, it has less number of ports and harbours. The continental shelf extends up to 500 km into the sea, which makes it difficult for the development of good ports and harbors. The lakes and the playas have brackish water which is the main source of obtaining salt. These are feature of Indian Deserts. Do you know? The plains along the Bay of Bengal are wide and level. In the northern part, it is referred to as the Northern Circar, while the southern part is known as the Coromandel Coast. THINK! Deltas. Q.5) Consider the following pairs Passes Connects 1. Banihal Jammu and Srinagar 2. Zoji La Srinagar and Leh 3. Shipki La Himachal Pradesh and Tibet 4. Mana pass Uttarakhand and Tibet Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched? a) 1 only b) 2 only c) 1 and 3 only d) All the above 4
5 Q.5) Solution (d) Pass Connects Aghil Pass Ladakh China Burzil Pass Kashmir Giligit Karakoram Pass Ladakh China Zojila Pass Srinagar- Leh (J&K) Pensi La Ladhak -Kashmir Banihal Pass Jammu and Srinagar Baralacha Pass Ladakh Himachal Pradesh Rohtang Pass Kullu valley with Lahul and spiti. Shipki La Himachal Pradesh-Tibet border Mana Pass Uttarakhand-Tibet border (Also known as Dungri La) Niti Pass Uttarakhand-Tibet border Lipulekh Pass Uttarakhand-Tibet border Q.6) Which of the following best defines Duars? a) The tract of land lying between two converging, or confluent, rivers. b) The alluvial floodplains in northeastern India that lies south of the outer foothills of the Himalayas and north of the Brahmaputra River basin. c) The land drained by the brackish water. d) The landscape all along the foothills of Shiwaliks. Q.6) Solution (b) The Dooars or Duars are the alluvial floodplains in northeastern India that lie south of the outer foothills of the Himalayas and north of the Brahmaputra River basin. This region is about 30 km (19 mi) wide and stretches over about 350 km (220 mi) from the Teesta River in West Bengal to the Dhanshiri River in Assam. The region forms the gateway to Bhutan. It is part of the Terai-Duar savanna and grasslands ecoregion. Do you know? The Terai-Duar savanna and grasslands is a narrow lowland ecoregion at the base of the Himalayas, about 25 km (16 mi) wide, and a continuation of the Gangetic Plain. It is colloquially called Terai in the Ganges Basin east to Nepal, then Dooars in West Bengal, Bangladesh, Bhutan and Assam east to the Brahmaputra River. The world's tallest grasslands are found in this ecoregion, which are the most threatened and rare worldwide. 5
6 THINK! Bhabar Q.7) Consider the following Himalayan ranges. 1. Karakoram range 2. Phir Panjal range 3. Ladakh range 4. Zaskar range Arrange the above ranges from North to South. a) b) c) d) Q.7) Solution (a) Do you know? The longitudinal valley lying between lesser Himalaya and the Shiwaliks are known as Duns. Dehra Dun, Kotli Dun and Patli Dun are some of the well-known Duns. THINK! 6
7 Patlands. Q.8) Consider the following statements: 1. The region is swampy and marshy. 2. The underground streams re emerge in this region. 3. The region is conducive for the breeding of mosquitoes and flies. 4. The forests in this region have been cleared and intensive agriculture is being practiced. The above statements are true for which of the following regions? a) Bhabar b) Bhangar c) Khadar d) Tarai Q.8) Solution (d) The Tarai Tract: Tarai Tract Tarai lies South of Bhabar. It is 15-30km wide with its width increasing from west to east. (Note: this is opposite from the Bhabar plains). This is a zone of excessive dampness, thick forests, rich wild life and malarial climate. 7
8 This zone is formed as the rivers which got submerged in Bhabar plains reemerge in this region. In most of the northen states, from Haryana to Bihar, the Tarai forests have been cleared and plains are used for agriculture now. The Tarai belt is known for the cultivation of Sugarcane, rice, wheat, maize, oil seeds, pulses and fodder. THINK! Battle of Tarai Kankar Chuar Q.9) Dandakaranya forest has been in news because of Naxalism. Which of the following statements regarding Dandakaranya are correct? 1. It is drained by the tributaries of Mahanadi and Godavari 2. It has Abujhmar hills in the west and Eastern Ghats in the East. 3. It prominently lies in the states of Jharkhand, Bihar and Madhya Pradesh. Select the code from following: a) 1 and 2 b) 2 and 3 c) 1 and 3 d) All of the above Q.9) Solution (a) Dandakaranya Forest 8
9 Dandakaranya is a physiographic region of India which spans over the central and eastern parts of India. It covers a vast area of about 35,600 square miles and encompasses the Eastern Ghats in the east and the Abujhmar Hills in the west along with parts of the Indian states Andhra Pradesh, Odisha and Chhattisgarh. It stretches to about 200 miles from north to south and 300 miles from east to west. It has been the home to the people belonging to Gond community. Geography of Dandakaranya Major region of Dandakaranya is a sanded-over peneplain, however the land from north to southwest has a gradual slope. Hills in the eastern part of the forest rise abruptly whereas towards the west its elevation decreases gradually. Wide plateaus are covered with dense forest. Certain extensive plains in the forest are drained by the Mahanadi River along with its tributaries including Sandul, Hatti, Udanti, Jonk and Tel as well as Godavari River along with its tributaries Sabari and Indravati. A thin veneer of loamy soils can be found over the plateaus and hillsides. Valleys and plains comprise fertile alluvial soil. Dandakaranya is the home to commercially important moist forests of Sal which spans over half of the forest area. Deposits of manganese, iron ore and bauxite are also common here. THINK! Peneplain Moist deciduous forest Naxalism Q.10) Which of the following statements regarding Meghalaya plateau are NOT correct? 1. It is an extension of Himalayan range in North Easter India. 2. It is filled with fertile alluvial soil deposited by Brahmaputra. 3. It is separated from peninsular plateau by Garo Rajmahal gap. Select the code from below: a) 1 and 2 b) 3 only c) 2 and 3 d) All of the above Q.10) Solution (a) Note: Incorrect statements have been asked. 9
10 Meghalaya Plateau IASbaba s 60 Days Plan Day 8 (Geography) 2018 The peninsular plateau extends further east beyond the Rajmahal hills to from Meghalaya or the Shillong plateau. Garo-Rajmahal Gap separates this plateau from the main block. This gap was formed by down-faulting (normal fault: a block of earth slides downwards). It was later filled by sediments deposited by the Ganga and Brahmaputa. The plateau is formed by Archaean quartzites, shales and schists. The plateau slopes down to Brahmaputra valley in the north and the Surma and Meghna valleys in the south. Its western boundary more or less coincides with the Bangladesh border. The western, central and the eastern parts of the plateau are known as the Garo Hills (900 m), the Khasi-Jaintia Hills (1,500 m) and the Mikir Hills (700 m). Shillong (1,961 m) is the highest point of the plateau. Because of excessive rainfall the soil is severely leached and barren. Laterite soil is found in the region. THINK! Mawsenram Laterite soil Q.11) Which of the following Islands of India are Volcanic in character? 1. Narcondam Island 2. Barren Island 3. Minicoy 4. Majauli Select the code from following: a) 1 and 2 b) 2 and 3 c) 2 only d) 1, 2 and 3 Q.11) Solution (a) 10
11 THE BARREN AND NARCONDAM ISLANDS, north of Port Blair, are volcanic islands (Note: Barren Island is the only active volcano of India.) The Andaman and Nicobar islands archipelago consists of approximately 265 small and large islands. Andaman Islands: The Andaman islands are divided into three main islands i.e. North, Middle and South. Duncan passage separates Little Andaman from South Andaman. The Andaman group of islands in the north is separated by the Ten Degree Channel from the Nicobar group in the south. Port Blair, the capital of Andaman Nicobar Islands lies in the South Andaman. Nicobar Islands: Among the Nicobar islands, the Great Nicobar is the largest. It is the southernmost island and is very close to Sumatra island of Indonesia. The Car Nicobar is the northernmost. Most of these islands are made of tertiary sandstone, limestone and shale resting on basic and ultrabasic volcanoes [Similar to Himalayas]. Some of the islands are fringed with coral reefs. Many of them are covered with thick forests. Most of the islands are mountainous. Saddle peak (737 m) in North Andaman is the highest peak. 11
12 Note: In Andaman and Nicobar island group, the three type of Islands are found the extension of continent, the Volcanic Islands and Coral Islands. Lakshadweep Islands: Lakshadweep is an archipelago of twelve atolls, three reefs and five submerged banks, with a total of about thirty-nine islands and islets. The reefs are in fact also atolls, although mostly submerged, with only small unvegetated sand cays above the high-water mark. The submerged banks are sunken atolls. Almost all the atolls have a northeast-southwest orientation with the islands lying on the eastern rim, and a mostly submerged reef on the western rim, enclosing a lagoon. It has 10 inhabited islands, 17 uninhabited islands, attached islets, 4 newly formed islets and 5 submerged reefs. The main islands are Kavaratti, Agatti, Minicoy, and Amini. Most of the islands have low elevation and do not rise more than five metre above sea level (Extremely Vulnerable to sea level change). Their topography is flat and relief features such as hills, streams, valleys, etc. are absent. Q.12) Which of the following mountain ranges is/are folding mountain ranges? 1. Aravalis 2. Himalayas 12
13 3. Western Ghats 4. Eastern Ghats Select the code from following: a) 2 only b) 1 and 2 c) 3 and 4 d) 1,2 and 4 Q.12) Solution (b) Himalaya Himalayas are the young fold mountains. This is the highest mountain range of the world. Himalayas act as natural barrier. The extreme cold, snow and rugged topography discourage the neighbors to enter India through Himalayas. They run from west-east direction from Indus to Brahmaputra along the northern boundary of India. The Aravallis: Aravallis It runs from North East to South West for 800 km between Delhi to Gujarat. It is one of the oldest folding mountain ranges of the World. It is highly denuded. Its highest peak is Guru Shikhar. The Great Boundary fault (GBF) separates Aravallis from Vindhyan mountains. THINK! Folding mountains 13
14 Block mountains Note: Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats are examples of block mountains. Q.13) Which of the following statements regarding Thar desert are correct? 1. It lies only in India and not in Pakistan. 2. It is drained by river Luni. 3. It doesn t get rainfall because of the presence of Aravali hills parallel to the monsoon winds. Select the code from following: a) 1 and 2 b) 2 and 3 c) 1 and 3 d) All of the above Q.13) Solution (b) The Indian Desert: The Indian Desert lies towards the western margin of Aravalli Hills. It is also called Thar Desert. It is the ninth largest desert in the world. It spreads over the states of Gujarat and Rajasthan. This region has semi-arid and arid weather conditions. It receives less than 150 mm of rainfall per year. Indian Desert 14
15 The vegetation cover is low with thorny bushes. Luni is the main river in this area. All other streams appear only at the time of rainfall otherwise they disappear into the sand. Western side of Thar Desert contains large Sand dunes and Seifs. It is believed that a large part of Indian desert is formed by recession of sea. Many saline regions are found in this region as well as saline lakes. Most important saline lake of India is Sambhar lake in Rajasthan. Note: A part of desert lies in Pakistan. Q.14) Coal formation is found in which of the following type of rocks? a) Archean b) Vindhayan c) Gondwana d) Dharwad Q.14) Solution (c) The rock system of the country is divided into 4 major divisions: 15 The Archean Rock System The Purana Rock System The Dravidian Rock System The Aryan Rock System Type Sub-type location minerals Archean Archean system( Covers 2/3 part of Indian peninsula. Rich in Ferrous and non-ferrous minerals million years old) Found in Andhra, like iron ore, copper, Dharwad system ( million years old) telangana, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Rajasthan and parts of Meghalaya plateau. The system is well developed in Dharwar-Bellary- Mysore belt of manganese, mica, dolomite, lead, zinc, silver and gold. Gold, Marble, Precious and semiprecious stones.
16 Purana Rocks ( million years) Dravidian Rocks ( million years) Karnataka, Jharkhand (Ranchi-Hazaribagh), MP, Chattisgarh, Odisha and Aravalli belt between Jaipur and Palanpur in Rajasthan. Cuddapah System Cuddapah and Kurnool dist. Andhra, Chattisgarh, Rajasthan and lesser Himalayas Vindhyas Vindhayan Mountain Range Cambrian Rocks Named after Cambria, the latin name for Wales in Great Britain. They are best developed in North- West Himalayan region. Diamond, Red sandstone, Construction stone They are fossiliferous sandstones underlain by clayey salt. Carboniferous Rocks Carboniferous in -upper carboniferous geology means coal -middle bearing. Coal carboniferous -lower carboniferous formation started in carboniferous age. Upper- Mount Everest Middle- Kashmir, Spiti Valley, Shimla and Himalayas Lower- Pir Panjal trap, kumaun region Aryan Rocks Gondwana Odisha, Bihar, Jharkhand, Andhra Pradesh, Chattisgarh Deccan trap (Cretaceous) ( million years) During this period, enormous quantity of basaltic lava was poured out to the surface assuming Limestone and dolomite. Anthracite coal is found. Good Quality Coal ( Bituminous and Anthracite), iron, kaolin, fire clay, sandstone and grits. Quartz, bauxite, Magnetite, agate and semi-precious stones 16
17 great thickness. Found in Gujarat, Maharashtra, MP, Chattisgarh, Northern Andhra and North-West Karnataka. Tertiary (60-7 million years) Found in complete Himalayan formation. In peninsular region, they are found in the coast of Kutch, Kathiawar, Konkan, Malabar, Nilgiris and the eastern Ghats. Quaternary It started around years ago since the withdrawal of the last glaciations. The northern plains of India came into being during this period. It has been called the age of mammals because of the abundance of fossils in these deposits. Since most of the particles are loose and recent, some recent fossils are found. Oil and gas deposits are also found. Q.15) From the below identify the correct term which is collectively applied to all kinds of saline and alkaline soils in the plains of north India, particularly in Uttar Pradesh a) Regolith b) Talus c) Usar d) Reh Q.15) Solution (c) Usar soil is widespread in India and it is a term collectively applied to all kinds of saline and alkaline soils in the plains of north India, particularly in Uttar Pradesh. Reh is a white, grayish or ash-coloured salt that are found in low-lying plain areas in dry periods. Regolith is simply mineral remains of decomposed rocks (no organic materials). It is soil that contains organic materials such as roots of plants, fallen leaves, small animals such as worms, bacteria and so on. 17
18 Talus and scree are pile of rocks or collection of broken rock fragments at the base of crags, mountain cliffs, volcanoes or valley shoulders that has accumulated through periodic rockfall from adjacent cliff faces. Q.16) Consider the following pairs and identify the correct pair/s using the code given below: Code: Plains : : Associated region 1. Malwa Plains : : located in central India especially Madhya Pradesh 2. Marusthali : : covers sand-dune-covered eastern portion of the Great Indian (Thar) Desert in western Rajasthan state 3. Utkal plains : : coastal plains in the Odisha state a) 1 only b) 1 and 2 only c) 2 and 3 only d) 1, 2 and 3 Q.16) Solution (c) Malwa Plains are alluvial plains region in central Punjab state, northern India. It lies between the Ghaggar and Sutlej rivers south of the Bist Doab (plain). Hence, statement 1 is wrong. Malwa Plateau is a natural region in west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic upland north of the Vindhya Range. Politically and administratively, the historical Malwa region includes districts of western Madhya Pradesh and parts of south-eastern Rajasthan. Utkal plains are coastal plains in the Odisha state only. Marusthali is located in Western plains, covers sand-dune-covered eastern portion of the Great Indian (Thar) Desert in western Rajasthan state. Q.17) Consider the following statements: 1. The Pamir, popularly known as the roof of the world is the connecting link between the Himalayas and the high ranges of the Central Asia. 2. Maximum development of glaciers occurs in the Karakoram range. 18
19 3. Purvachal or the Eastern hills are part of the Himalayan mountain system having their general alignment from the north to the south direction. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? a) 1 only b) 1 and 2 only c) 2 and 3 only d) 1, 2 and 3 Q.17) Solution (d) The Pamir Mountains, or the Pamirs, are a mountain range in Central Asia at the junction of the Himalayas with the Tian Shan, Karakoram, Kunlun, Hindu Kush, Suleman and Hindu Raj ranges. They are among the world s highest mountains. The Pamir or popularly known as the roof of the world is the connecting link between the Himalayas and the high ranges of the Central Asia. To the north they join the Tian Shan mountains along the Alay Valley of Kyrgyzstan. To the south they border the Hindu Kush mountains along Afghanistan's Wakhan Corridor. Maximum development of glaciers occurs in the Karakoram range. This range accounts for about 16,000 sq km or about half of the snow bound area of the Himalayan region. Purvachal or the Eastern hills and mountains are part of the Himalayan mountain system having their general alignment from the north to the south direction. The Purvachal comprises the Patkai hills, the Naga hills, Manipur hills and the Mizo hills. Q.18) Consider the following ports. Which of the following is correct order as we traverse from south to north? a) Kochi Managlore JNPT Marmagao - Kandla b) Kochi Mangalore Marmagao JNPT Kandla c) Mangalore Kochi Marmagao JNPT Kandla d) Kochi JNPT Marmagao Managalore Kandla Q.18) Solution (b) 19
20 Q.19) Which of the statements given below is/are not true in regard to western coastal plain? a) It is a narrow belt. b) Eastern coastal plain receives comparatively low rainfall but the Western coastal plain receives heavy rainfall. c) West Coast Plain is infertile and agriculturally not prosperous except in the Malabar Coast. d) It is an example of emergent coastal plain. Q.19) Solution (d) Western coastal plain is an example of submerged coastal plain (not emergent). It provides natural conditions for development of ports. 20
21 Q.20) Which of the statements given below is/are correct about Terai region? 1. Terai is an ill-drained, damp (marshy) and thickly forested narrow tract to the south of Bhabar running parallel to it. 2. It is a swampy lowland with silty soils. 3. Terai soils are rich in phosphate and organic matter but are deficient in nitrogen. Choose the correct answer from the code given below: a) 1 only b) 1 and 2 only c) 2 and 3 only d) 1, 2 and 3 Q.20) Solution (b) Terai is an ill-drained, damp (marshy) and thickly forested narrow tract (15-30 km wide) to the south of Bhabar running parallel to it. The underground streams of the Bhabar belt re-emerge in this belt. It is a swampy lowland with silty soils. The terai soils are rich in nitrogen and organic matter but are deficient in phosphate. These soils are generally covered by tall grasses and forests but are suitable for a number of crops such as wheat, rice, sugarcane, jute etc.. This thickly forested region provides shelter to a variety of wild life. Q.21) Consider the below statements with regard to Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats: 1. The mean height of the Western Ghats is more than that of Eastern Ghats. 2. The Eastern Ghats do not form a continuous chain like the Western Ghats. 3. The Eastern Ghats average width is less than that of Western Ghats. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? a) 1 and 2 only b) 2 and 3 only c) 1, 2 and 3 d) None Q.21) Solution (a) 21
22 Statement (3) is incorrect as the Western Ghat s average width is 50 to 80 km. But Eastern Ghats width varying from 100 to 200 km. Western Ghats is continuous and can be crossed through passes only. But Eastern Ghats has been divided into several parts by large rivers. Western Ghats average elevation is 900 to 1,100 meters above sea-level. But the average elevation of Eastern Ghats is about 600 metres above sea level. Q.22) Consider the following statements about The Admiralty Act, It extends the admiralty jurisdiction to all High Courts of the coastal states 2. It has provision for transfer of cases from one High Court to other High Court by the Supreme Court 3. Inland vessels are not included under the Act Select the correct statements a) 1 and 2 b) 2 and 3 c) 1 and 3 d) All of the above Q.22) Solution (d) The Admiralty (Jurisdiction and Settlement of Maritime Claims) Act, 2017 The Act seeks to consolidate the existing laws on jurisdiction of courts on civil admiralty matters, or cases of maritime accidents or contracts related to maritime commerce, proceedings on maritime claims, and seizure of ships. It repealed obsolete British statutes on admiral jurisdiction in civil matters laws such as the Admiralty Court Act, 1861 and the Colonial Courts of Admiralty Act, It shall apply to every vessel, irrespective of the place of residence or domicile of the owner The Act shall not apply to an inland vessel or a vessel under construction that has not been launched unless it is notified by the Central Government to be a vessel for the purposes of this Act The Act shall not apply to a warship, naval auxiliary or other vessel owned or operated by the Central or a State Government and used for any non-commercial purpose, and, shall also not apply to a foreign vessel which is used for any noncommercial purpose as may be notified by the Central Government. 22
23 The Supreme Court may on an application of any party, transfer, at any stage, any admiralty proceeding from one High Court to any other High Court and the latter High Court shall proceed to try, hear and determine the matter from the stage at which it stood at the time of transfer. Initially admiralty jurisdiction applied to the Bombay, Calcutta and Madras High Courts and the Act further extends this to the Karnataka, Gujarat, Odisha, Kerala, Hyderabad High Courts and any other High Court notified by the central government. Read More - THINK! Parveen Singh Committee Source: Q.23) Consider the following statements about Wide Angle Search for Planets (WASP) 1. It is a collaboration finding exoplanets by gravitational microlensing 2. It is operated by a consortium of US based academic institutions, NASA and ESA Select the correct statements a) 1 Only b) 2 Only c) Both 1 and 2 d) Neither 1 nor 2 Q.23) Solution (d) WASP or Wide Angle Search for Planets is an international consortium of several academic organisations performing an ultra-wide angle search for exoplanets using transit photometry. WASP is the detection program composed of the Isaac Newton Group, IAC and six universities from the United Kingdom. WASP is operated by a consortium of academic institutions which include: Instituto de Astrofisica de Canarias Isaac Newton Group of Telescopes 23
24 Keele University Open University Queen's University Belfast St. Andrews University University of Leicester Warwick University. THINK! WASP-39B Source: Q.24) Which of the following statements about SOHUM are correct? 1. It is an indigenously developed low-cost hearing screening device for new-borns 2. It has been developed under the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) 3. It uses Otoacoustic Emissions (OAEs) testing Select the incorrect statements a) 1 and 2 b) 2 and 3 c) 1 and 3 d) All of the above Q.24) Solution (a) Sohum"- An innovative Newborn hearing screening Device It is developed by School of International Biodesign (SIB) startup M/s Sohum Innovation Labs India Pvt. Ltd. This innovative medical device has been developed under Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India supported (SIB). SIB is a flagship Program of the DBT aimed to develop innovative and affordable medical devices as per unmet clinical needs of India and to train the next generation of medical technology innovators in India, it is a valuable contribution to the Make in India campaign of the Government. This Program is implemented jointly at AIIMS and IIT Delhi in collaboration with International partners. Biotech Consortium India Limited manages techno-legal activities of the Program. 24
25 Sohum is a low cost and unique device which uses brainstem auditory evoked response, the gold standard in auditory testing to check for hearing response in a newborn. Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) - Brainstem-Response/ THINK! ADIP Scheme Source: Q.25) Consider the following statements about Breakthrough Starshot Project 1. The smallest spacecraft called Sprites ever launched has been developed under this project 2. It is a research and engineering project by ISRO Select the correct statements a) 1 Only b) 2 Only c) Both 1 and 2 d) Neither 1 nor 2 Q.25) Solution (a) The world s smallest spacecrafts dubbed as Sprites ever launched are successfully travelling in low Earth orbit and communicating with systems on Earth. The six prototypes of Sprites were launched in June 2017 as part of the Breakthrough Starshot project designed to test technologies that would eventually be used for interstellar missions. They are smallest spacecraft that have managed to establish contact with ground stations. Sprites have been developed by researchers at Cornell University. Each of the mini Sprite spacecrafts are built on a single 3.5*3.5 centimetre circuit board. They weigh just four grams each. Breakthrough Starshot is a comprehensive space program launched under the US $100 million Breakthrough Initiatives, announced by Yuri Milner and Stephen Hawking to develop 25
26 and launch practical interstellar space missions. The program aims to demonstrate proof of concept for light-propelled spacecraft that could fly at 20 per cent of light speed. Its main objective is to send one-gram chips to star systems beyond the solar system in search of extra-terrestrial intelligence. Q.26) Which of the following statements about International Expedited Traveller Initiative Programme is/are correct? a) It allows expedited clearance for pre-approved, low-risk travellers upon arrival in the Schengen Area b) India has joined the programme c) Both (a) and (b) d) Neither (a) nor (b) Q.26) Solution (b) India recently signed International Expedited Traveler Initiative Programme with the United States. Also called as Global Entry Programme, this scheme will allow expedited entry into the US to low-risk travellers from India. Global Entry is a US Customs and Border Protection (CBP) program that allows speedy clearance for low-risk travellers upon their arrival in US. The travellers are pre-approved for the programme after a rigorous background check. Currently, 53 US airports and 15 pre-clearance locations are available under the Global Entry programme. Source: Source: 26
2. PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA
 2. PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA Question 1: Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) A landmass bound by sea on three sides is referred to as (a) Coast (c) Peninsula (b) Island
2. PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA Question 1: Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) A landmass bound by sea on three sides is referred to as (a) Coast (c) Peninsula (b) Island
NCERT Class 9th Social Science Geography Chapter 2: Physical Features of India
 NCERT Class 9th Social Science Geography Chapter 2: Physical Features of India Question 1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) A landmass bounded by sea on three sides in
NCERT Class 9th Social Science Geography Chapter 2: Physical Features of India Question 1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) A landmass bounded by sea on three sides in
Geography: Contemporary India - For Class IX Physical Features of India
 Geography: Contemporary India - For Class IX Physical Features of India (Q.1) Which are the two broad classification of peninsular plateau? (Q.2) What is a Doab? (Q.3) What is an Alluvial Plain. (Q.4)
Geography: Contemporary India - For Class IX Physical Features of India (Q.1) Which are the two broad classification of peninsular plateau? (Q.2) What is a Doab? (Q.3) What is an Alluvial Plain. (Q.4)
India is a vast country with varied landforms. Our country has practically all major physical features of the earth i.e. mountains, plains, deserts,
 India is a vast country with varied landforms. Our country has practically all major physical features of the earth i.e. mountains, plains, deserts, plateaus and islands. India is a large landmass formed
India is a vast country with varied landforms. Our country has practically all major physical features of the earth i.e. mountains, plains, deserts, plateaus and islands. India is a large landmass formed
OUR COUNTRY INDIA LOCATIONAL SETTING
 7 India is a country of vast geographical expanse. In the north, it is bound by the lofty Himalayas. The Arabian Sea in the west, the Bay of Bengal in the east and the Indian Ocean in the south, wash the
7 India is a country of vast geographical expanse. In the north, it is bound by the lofty Himalayas. The Arabian Sea in the west, the Bay of Bengal in the east and the Indian Ocean in the south, wash the
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX : GEOGRAPHY TOPIC/CHAPTER: CHAPTER: 2 PHYSICAL FEATURES
 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX : GEOGRAPHY TOPIC/CHAPTER: CHAPTER: 2 PHYSICAL FEATURES WORKSHEET NO. 06 Summary:- Tectonic Plate Theory:- This theory is based
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX : GEOGRAPHY TOPIC/CHAPTER: CHAPTER: 2 PHYSICAL FEATURES WORKSHEET NO. 06 Summary:- Tectonic Plate Theory:- This theory is based
SMART NOTES ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 3
 ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 3 Point. Precise. Powerful. www.thesmartnotes.org ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 3 To our Hardworking and persistence aspirants. Success is going from failure to failure without losing enthusiasm.
ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 3 Point. Precise. Powerful. www.thesmartnotes.org ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 3 To our Hardworking and persistence aspirants. Success is going from failure to failure without losing enthusiasm.
SMART NOTES ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 1
 ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 1 Point. Precise. Powerful. www.thesmartnotes.org ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 1 To our Hardworking and persistence aspirants. Success is going from failure to failure without losing enthusiasm.
ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 1 Point. Precise. Powerful. www.thesmartnotes.org ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 1 To our Hardworking and persistence aspirants. Success is going from failure to failure without losing enthusiasm.
Summative Assessment I
 Class: IV Time: 3 Hrs. Summative Assessment I Social Science Marks: 88 Handwriting: 2 Total: 90 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. Use crayons for colouring. General Instruction I. Multiple choice questions:
Class: IV Time: 3 Hrs. Summative Assessment I Social Science Marks: 88 Handwriting: 2 Total: 90 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. Use crayons for colouring. General Instruction I. Multiple choice questions:
Chapter 8 [Our World Continents and Oceans]
![Chapter 8 [Our World Continents and Oceans] Chapter 8 [Our World Continents and Oceans]](/thumbs/89/101173350.jpg) 1 (iv) so. std. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) (for 2 nd Term) CLASS: IV SUBJECT: SOCIAL STUDIES Chapter 8 [Our World Continents and Oceans] 1. Earth is known as the planet. (a) red (b) blue (c) white
1 (iv) so. std. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) (for 2 nd Term) CLASS: IV SUBJECT: SOCIAL STUDIES Chapter 8 [Our World Continents and Oceans] 1. Earth is known as the planet. (a) red (b) blue (c) white
You have already learnt earlier that India
 2 PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA You have already learnt earlier that India is a vast country with varied landforms. What kind of terrain do you live in? If you live in the plains you are familiar with the
2 PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA You have already learnt earlier that India is a vast country with varied landforms. What kind of terrain do you live in? If you live in the plains you are familiar with the
Chapter 21 Southwest Asia: Harsh & Arid Lands
 Name Hour Chapter 21 Southwest Asia: Harsh & Arid Lands Essential Question: How has the physical geography of Asia influenced the development of these regions (i.e. history, population distribution, &
Name Hour Chapter 21 Southwest Asia: Harsh & Arid Lands Essential Question: How has the physical geography of Asia influenced the development of these regions (i.e. history, population distribution, &
Board Question Paper : March 2015
 Board Question Paper : March 2015 BOARD QUESTION PAPER : MARCH 2015 Time: 2 Hours Total Marks: 40 Note: i. All questions are compulsory. ii. Figure to the right indicate full marks. iii. Solve Q. No.3
Board Question Paper : March 2015 BOARD QUESTION PAPER : MARCH 2015 Time: 2 Hours Total Marks: 40 Note: i. All questions are compulsory. ii. Figure to the right indicate full marks. iii. Solve Q. No.3
[IASBABA S 60 DAYS PLAN-COMPILATION (GEOGRAPHY)
 2018 IASBABA.COM IASBABA IASBABA S 60 DAYS PLAN-COMPILATION (GEOGRAPHY) [ ] Born with the vision of Enabling a person located at the most remote destination a chance at cracking AIR 1 in IAS. Q.1) Consider
2018 IASBABA.COM IASBABA IASBABA S 60 DAYS PLAN-COMPILATION (GEOGRAPHY) [ ] Born with the vision of Enabling a person located at the most remote destination a chance at cracking AIR 1 in IAS. Q.1) Consider
UNIT 11 SOUTH ASIA SG 1 - PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY & THE ENVIRONMENT
 UNIT 11 SOUTH ASIA SG 1 - PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY & THE ENVIRONMENT I. PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY TAKE OUT YOUR PHYSICAL MAP OF SOUTH ASIA A. The Himalayan Mountains form the northern boundary of the region (color
UNIT 11 SOUTH ASIA SG 1 - PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY & THE ENVIRONMENT I. PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY TAKE OUT YOUR PHYSICAL MAP OF SOUTH ASIA A. The Himalayan Mountains form the northern boundary of the region (color
South, Southeast, and East Asia. Physical Geography
 South, Southeast, and East Asia Physical Geography Mountains v Mountains are important in Asia because they influence: A. Population patterns B. Movement of people and goods C. Climate Mountains v The
South, Southeast, and East Asia Physical Geography Mountains v Mountains are important in Asia because they influence: A. Population patterns B. Movement of people and goods C. Climate Mountains v The
India - Relief Features
 India - Relief Features CHAPTER 1 In this chapter we shall study about relief features of India. In the subsequent chapters such as Climate in India; Rivers and Water Resources; The People etc we would
India - Relief Features CHAPTER 1 In this chapter we shall study about relief features of India. In the subsequent chapters such as Climate in India; Rivers and Water Resources; The People etc we would
Figure 2.1: Constituent Area
 2 The Region 2.1 CONSTITUENT AREA The National Capital Region includes NCT-Delhi, nine districts of Haryana, six districts of Uttar Pradesh and one district of Rajasthan. Total area of the region is 34,144
2 The Region 2.1 CONSTITUENT AREA The National Capital Region includes NCT-Delhi, nine districts of Haryana, six districts of Uttar Pradesh and one district of Rajasthan. Total area of the region is 34,144
DR.M.K.K ARYA MODEL SCHOOL
 DR.M.K.K ARYA MODEL SCHOOL Sub: Social science Syllabus Class-IV Session 2018-19 Prescribed book: Candid New Trends in Social Studies Syllabus to be completed in the month of April. Chapter 1.India Our
DR.M.K.K ARYA MODEL SCHOOL Sub: Social science Syllabus Class-IV Session 2018-19 Prescribed book: Candid New Trends in Social Studies Syllabus to be completed in the month of April. Chapter 1.India Our
Chapter 6, Part Colonizers arriving in North America found extremely landscapes. It looked different to region showing great.
 Social Studies 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 6, Part 1. 1. Colonizers arriving in North America found extremely landscapes. It looked different to region showing great. 2. The Earth is years old and is composed
Social Studies 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 6, Part 1. 1. Colonizers arriving in North America found extremely landscapes. It looked different to region showing great. 2. The Earth is years old and is composed
15. THE GLOBE AND THE MAP
 15. THE GLOBE AND THE MAP 1 DEFINE THE FOLLOWING 1. AXIS : The imaginary line which passes through the centre of the earth and joins the North Pole and South Pole is called the Axis. The earth rotates
15. THE GLOBE AND THE MAP 1 DEFINE THE FOLLOWING 1. AXIS : The imaginary line which passes through the centre of the earth and joins the North Pole and South Pole is called the Axis. The earth rotates
W E E K L Y MONSOON INSIGHT
 W E E K L Y MONSOON INSIGHT 08 th July 2016 Indian Monsoon Dynamics Recent Weather Development India received 35% surplus rainfall in the week ended 6 July with all regions recording above-normal rainfall
W E E K L Y MONSOON INSIGHT 08 th July 2016 Indian Monsoon Dynamics Recent Weather Development India received 35% surplus rainfall in the week ended 6 July with all regions recording above-normal rainfall
The United States & Canada. A Regional Study of Anglo America
 A Regional Study of Anglo America Landform Regions of the United States & Canada world leaders in agricultural and industrial production because of... VAST LANDS stretch from the Atlantic Ocean on the
A Regional Study of Anglo America Landform Regions of the United States & Canada world leaders in agricultural and industrial production because of... VAST LANDS stretch from the Atlantic Ocean on the
ALL INDIA WEATHER SUMMARY AND FORECAST BULLETIN
 Saturday 21 April 2018 MORNING Time of Issue: 0800 hours IST ALL INDIA WEATHER SUMMARY AND FORECAST BULLETIN Significant Weather Features Isolated thunder squalls and hailstorms are very likely over Sub
Saturday 21 April 2018 MORNING Time of Issue: 0800 hours IST ALL INDIA WEATHER SUMMARY AND FORECAST BULLETIN Significant Weather Features Isolated thunder squalls and hailstorms are very likely over Sub
Landscape evolution. An Anthropic landscape is the landscape modified by humans for their activities and life
 Landforms Landscape evolution A Natural landscape is the original landscape that exists before it is acted upon by human culture. An Anthropic landscape is the landscape modified by humans for their activities
Landforms Landscape evolution A Natural landscape is the original landscape that exists before it is acted upon by human culture. An Anthropic landscape is the landscape modified by humans for their activities
BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (AP) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH SOCIAL MODEL PAPER PAPER - I (ENGLISH VERSION) SECTION - I
 BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (AP) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH SOCIAL MODEL PAPER PAPER - I (ENGLISH VERSION) Time: 2 hrs. 45 mins. PART - A& B Maximum Marks: 40 Time: 2 hrs. 15 mins. PART - A Marks:
BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (AP) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH SOCIAL MODEL PAPER PAPER - I (ENGLISH VERSION) Time: 2 hrs. 45 mins. PART - A& B Maximum Marks: 40 Time: 2 hrs. 15 mins. PART - A Marks:
ALL INDIA WEATHER SUMMARY AND FORECAST BULLETIN
 Sunday 22 April 2018 NIGHT Time of Issue: 2000 hours IST ALL INDIA WEATHER SUMMARY AND FORECAST BULLETIN Significant Weather Features The ongoing fairly widespread rainfall activity with isolated thunder
Sunday 22 April 2018 NIGHT Time of Issue: 2000 hours IST ALL INDIA WEATHER SUMMARY AND FORECAST BULLETIN Significant Weather Features The ongoing fairly widespread rainfall activity with isolated thunder
Geography and Economics
 Written as per the revised syllabus prescribed by the Maharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education, Pune. Social Sciences Part II Geography and Economics Std. X Salient Features
Written as per the revised syllabus prescribed by the Maharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education, Pune. Social Sciences Part II Geography and Economics Std. X Salient Features
Module 10: Resources and Virginia Geology Topic 4 Content: Virginia Geology Notes
 Virginia is composed of a very diverse landscape that extends from the beaches and barrier islands all of the way to the highly elevated Appalachian Plateau. Geologists have discovered ancient shallow
Virginia is composed of a very diverse landscape that extends from the beaches and barrier islands all of the way to the highly elevated Appalachian Plateau. Geologists have discovered ancient shallow
What landforms make up Australia?!
 What landforms make up Australia? The tectonic forces of folding, faulting and volcanic activity have created many of Australia's major landforms. Other forces that work on the surface of Australia, and
What landforms make up Australia? The tectonic forces of folding, faulting and volcanic activity have created many of Australia's major landforms. Other forces that work on the surface of Australia, and
Terrain Units PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION. Present Geology of NYS. Detailed Geologic Map of NYS
 NYS TOPOGRAPHY Why so? PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 014 Present Geology of NYS Detailed Geologic Map of NYS Generalized Geology Detailed Geology Hot links to the fold out
NYS TOPOGRAPHY Why so? PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 014 Present Geology of NYS Detailed Geologic Map of NYS Generalized Geology Detailed Geology Hot links to the fold out
Physical Geography A Living Planet
 Physical Geography A Living Planet The geography and structure of the earth are continually being changed by internal forces, like plate tectonics, and external forces, like the weather. Iguaçu Falls at
Physical Geography A Living Planet The geography and structure of the earth are continually being changed by internal forces, like plate tectonics, and external forces, like the weather. Iguaçu Falls at
Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Exercise Page 51 Question 1: Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) To which one of the following types of vegetation does rubber belong? (a)
Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Exercise Page 51 Question 1: Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) To which one of the following types of vegetation does rubber belong? (a)
ISSUED BY KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA - DOWNLOADED FROM
 UNIT II CHAPTER -2 PHYSIOGRAPHY - INDIA PHYSIOGRAPHY Structure and Relief; physiographic divisions Drainage systems: concept of water sheds the Himalayan and the Peninsular Can you map different phases
UNIT II CHAPTER -2 PHYSIOGRAPHY - INDIA PHYSIOGRAPHY Structure and Relief; physiographic divisions Drainage systems: concept of water sheds the Himalayan and the Peninsular Can you map different phases
3. HYDROMETEROLOGY. 3.1 Introduction. 3.2 Hydro-meteorological Aspect. 3.3 Rain Gauge Stations
 3. HYDROMETEROLOGY 3.1 Introduction Hydrometeorology is a branch of meteorology and hydrology that studies the transfer of water and energy between the land surface and the lower atmosphere. Detailed hydrological
3. HYDROMETEROLOGY 3.1 Introduction Hydrometeorology is a branch of meteorology and hydrology that studies the transfer of water and energy between the land surface and the lower atmosphere. Detailed hydrological
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY General Information
 PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY General Information By understanding the environment we can understand why one place is different or the same as another. See handout Geomorphology Geo --Land morph --Change ology --Study
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY General Information By understanding the environment we can understand why one place is different or the same as another. See handout Geomorphology Geo --Land morph --Change ology --Study
BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (AP) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH CLASS SOCIAL STUDIES MODEL PAPER PAPER - I (ENGLISH VERSION)
 BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (AP) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH CLASS SOCIAL STUDIES MODEL PAPER PAPER - I (ENGLISH VERSION) Time: 2 hrs. 45 mins. PART - A & B Maximum Marks: 40 INSTRUCTIONS: i) 15 minutes
BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (AP) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH CLASS SOCIAL STUDIES MODEL PAPER PAPER - I (ENGLISH VERSION) Time: 2 hrs. 45 mins. PART - A & B Maximum Marks: 40 INSTRUCTIONS: i) 15 minutes
Introduction to Oceanography. Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics Overview
 Introduction to Oceanography Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics theory. The plate tectonics model describes features and processes on Earth. Plate tectonic science
Introduction to Oceanography Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics theory. The plate tectonics model describes features and processes on Earth. Plate tectonic science
ALL INDIA WEATHER SUMMARY AND FORECAST BULLETIN
 Tuesday 08 May 2018 MID DAY Time of Issue: 1345 hours IST ALL INDIA WEATHER SUMMARY AND FORECAST BULLETIN Significant Weather Features Under the influence of the present Western Disturbance over Jammu
Tuesday 08 May 2018 MID DAY Time of Issue: 1345 hours IST ALL INDIA WEATHER SUMMARY AND FORECAST BULLETIN Significant Weather Features Under the influence of the present Western Disturbance over Jammu
Name. 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different soil horizons, A, B, C, and D, are shown.
 Name 1. In the cross section of the hill shown below, which rock units are probably most resistant to weathering? 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different
Name 1. In the cross section of the hill shown below, which rock units are probably most resistant to weathering? 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different
Continental Landscapes
 Continental Landscapes Landscape influenced by tectonics, climate & differential weathering Most landforms developed within the last 2 million years System moves toward an equilibrium Continental Landscapes
Continental Landscapes Landscape influenced by tectonics, climate & differential weathering Most landforms developed within the last 2 million years System moves toward an equilibrium Continental Landscapes
THE EARTH S RELIEF SOCIAL SCIENCES 1º ESO
 THE EARTH S RELIEF SOCIAL SCIENCES 1º ESO 1. THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH The Earth is divided into layers: The crust is the surface layer. It is a thin, solid layer made of rock. The Earth s crust has a
THE EARTH S RELIEF SOCIAL SCIENCES 1º ESO 1. THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH The Earth is divided into layers: The crust is the surface layer. It is a thin, solid layer made of rock. The Earth s crust has a
PHYSICAL FEATURES OF EUROPE. Europe Unit
 PHYSICAL FEATURES OF EUROPE Europe Unit PENINSULA OF PENINSULAS Europe is a large peninsula that consists of many smaller peninsulas Most places in Europe are no more than 300 miles from an ocean or sea
PHYSICAL FEATURES OF EUROPE Europe Unit PENINSULA OF PENINSULAS Europe is a large peninsula that consists of many smaller peninsulas Most places in Europe are no more than 300 miles from an ocean or sea
WHAT IS THE EARTH MADE OF? LITHOSPHERE AND HYDROSPHERE
 UNIT 8 WHAT IS THE EARTH MADE OF? LITHOSPHERE AND HYDROSPHERE TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH... 2 2 THE FORMATION OF THE RELIEF: INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL FORCES.... 2 2.1 Internal forces:
UNIT 8 WHAT IS THE EARTH MADE OF? LITHOSPHERE AND HYDROSPHERE TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH... 2 2 THE FORMATION OF THE RELIEF: INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL FORCES.... 2 2.1 Internal forces:
Part 1: Weather Forecast Severe Weather Warnings (Source: IMD, Date: 1 st September, 2008)
 Sphere India Unified Response Strategy Situation report (India Floods 2008) 01 st September 2008 Part 1: Weather Forecast Severe Weather Warnings (Source: IMD, Date: 1 st September, 2008) HEAVY RAINFALL
Sphere India Unified Response Strategy Situation report (India Floods 2008) 01 st September 2008 Part 1: Weather Forecast Severe Weather Warnings (Source: IMD, Date: 1 st September, 2008) HEAVY RAINFALL
Mount Everest and the Gobi Desert
 Mount Everest and the Gobi Desert 1 Mount Everest is part of the mountain chain known as the Himalaya. Adventurers from all over the world come to try to climb it. Mount Everest is the highest mountain
Mount Everest and the Gobi Desert 1 Mount Everest is part of the mountain chain known as the Himalaya. Adventurers from all over the world come to try to climb it. Mount Everest is the highest mountain
Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures
 Name: Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary rocks account for a negligibly small fraction of Earth s mass, yet they are commonly encountered because the processes that form them are ubiquitous in the
Name: Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary rocks account for a negligibly small fraction of Earth s mass, yet they are commonly encountered because the processes that form them are ubiquitous in the
Plate Tectonics CHAPTER 17
 Plate Tectonics CHAPTER 17 Layers of the Earth A. Crust- solid, 5-70 km thick Moho Two Types of Crust: Oceanic- ocean floor, more dense then because of more iron Continental-dry land (mostly silicates
Plate Tectonics CHAPTER 17 Layers of the Earth A. Crust- solid, 5-70 km thick Moho Two Types of Crust: Oceanic- ocean floor, more dense then because of more iron Continental-dry land (mostly silicates
ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF POWER STATIONS
 Region Northern Region Western Region Southern Region Eastern Region North Eastern Region Islands ALL INDIA Figures at decimal may not tally due to rounding off ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF
Region Northern Region Western Region Southern Region Eastern Region North Eastern Region Islands ALL INDIA Figures at decimal may not tally due to rounding off ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF
The Sea Floor. Chapter 2
 The Sea Floor Chapter 2 Geography of the Ocean Basins World ocean is the predominant feature on the Earth in total area Northern Hemisphere = 61% of the total area is ocean. Southern Hemisphere = about
The Sea Floor Chapter 2 Geography of the Ocean Basins World ocean is the predominant feature on the Earth in total area Northern Hemisphere = 61% of the total area is ocean. Southern Hemisphere = about
Sec$on 1: Geography and Early China. How does China s geography affect the culture?
 Sec$on 1: Geography and Early China How does China s geography affect the culture? Con$nents of the World Label the continents. Where is China located? Where is China located? In your groups, begin filling
Sec$on 1: Geography and Early China How does China s geography affect the culture? Con$nents of the World Label the continents. Where is China located? Where is China located? In your groups, begin filling
The structure of the Earth and how its motion creates the seasons. The landforms of the earth and the forces that shape the land.
 The structure of the Earth and how its motion creates the seasons. The landforms of the earth and the forces that shape the land. The role of wind and water in creating climate. The different climate and
The structure of the Earth and how its motion creates the seasons. The landforms of the earth and the forces that shape the land. The role of wind and water in creating climate. The different climate and
60% water. Big Bang: 14,000 millions years ago The Earth originated about 4,500 millions years ago its orbit allows water to exist in a liquid state!
 Ch2. The Sea Floor #1 Why geology of the oceans? Marine habitats are directly shaped by geological processes The form of the coastlines The depth of the water Type of bottom (muddy, sandy, rocky) #2 Geological
Ch2. The Sea Floor #1 Why geology of the oceans? Marine habitats are directly shaped by geological processes The form of the coastlines The depth of the water Type of bottom (muddy, sandy, rocky) #2 Geological
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output
 mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia
 The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia Gobi desert, Mongolia Essential Question: How does the geography of SE Asia impact trade and the distribution of population throughout the region? (AKS #52a)
The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia Gobi desert, Mongolia Essential Question: How does the geography of SE Asia impact trade and the distribution of population throughout the region? (AKS #52a)
Earth s Layers. Earth s Surface
 CHAPTER 1 LESSON 3 Earth s Layers Earth s Surface Key Concepts What are Earth s major landforms and how do they compare? What are the major landform regions of the United States? What do you think? Read
CHAPTER 1 LESSON 3 Earth s Layers Earth s Surface Key Concepts What are Earth s major landforms and how do they compare? What are the major landform regions of the United States? What do you think? Read
Unit 1: Geography. For additional information, refer to this website: 1 G e o g r a p h y
 Unit 1: Geography For additional information, refer to this website: http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/ 1 G e o g r a p h y Continents and Oceans SOL USI. 2a Essential Understanding: Continents are large land
Unit 1: Geography For additional information, refer to this website: http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/ 1 G e o g r a p h y Continents and Oceans SOL USI. 2a Essential Understanding: Continents are large land
(version 3) I. HumAN -Environment Interaction
 (version 3) I. HumAN -Environment Interaction A. Landforms 1. Earth s topography is made up of many different types of landforms. 2. While the planet is covered primarily with water, the four major types
(version 3) I. HumAN -Environment Interaction A. Landforms 1. Earth s topography is made up of many different types of landforms. 2. While the planet is covered primarily with water, the four major types
Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands
 Page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands Section A Overview of Lands with Dry Climates The definition of a dry climate is tied to an understanding of the hydrologic cycle
Page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands Section A Overview of Lands with Dry Climates The definition of a dry climate is tied to an understanding of the hydrologic cycle
ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF POWER STATIONS
 Region Northern Region Western Region Southern Region Eastern Region North Eastern Region Islands ALL INDIA Figures at decimal may not tally due to rounding off ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF
Region Northern Region Western Region Southern Region Eastern Region North Eastern Region Islands ALL INDIA Figures at decimal may not tally due to rounding off ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF
e Southeast Region of the United Statesg
 e Southeast of the United Statesg - relative location: the location of a place in relation to another place (i.e. south, near, bordering, next to) - barrier islands: located off the southeast coast of
e Southeast of the United Statesg - relative location: the location of a place in relation to another place (i.e. south, near, bordering, next to) - barrier islands: located off the southeast coast of
ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF POWER STATIONS
 Region Northern Region Western Region Southern Region Eastern Region North Eastern Region Islands ALL INDIA Figures at decimal may not tally due to rounding off ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF
Region Northern Region Western Region Southern Region Eastern Region North Eastern Region Islands ALL INDIA Figures at decimal may not tally due to rounding off ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF
Geography Definitions/Sentences
 Geography Definitions/Sentences 1. BEACH 1. The shore of a body of water, especially when sandy or pebbly. 2. The sand or pebbles on a shore. The zone above the water line at a shore of a body of water,
Geography Definitions/Sentences 1. BEACH 1. The shore of a body of water, especially when sandy or pebbly. 2. The sand or pebbles on a shore. The zone above the water line at a shore of a body of water,
Physical Geography of East Asia
 Physical Geography of East Asia Satellite View of China Landforms of China China s Geography China Miles 0 250 500 1,000 1,500 2,000 United States 3 rd largest country in the world. Comparable to the US
Physical Geography of East Asia Satellite View of China Landforms of China China s Geography China Miles 0 250 500 1,000 1,500 2,000 United States 3 rd largest country in the world. Comparable to the US
MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY
 MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY Bathymetry BATHYMETRY BATHYMETRY THE UNDERWATER EQUIVALENT TO TOPOGRAPHY THE STUDY OF WATER DEPTH A BATHYMETRIC MAP SHOWS FLOOR RELIEF OR TERRAIN AS CONTOUR LINES Bathymetry
MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY Bathymetry BATHYMETRY BATHYMETRY THE UNDERWATER EQUIVALENT TO TOPOGRAPHY THE STUDY OF WATER DEPTH A BATHYMETRIC MAP SHOWS FLOOR RELIEF OR TERRAIN AS CONTOUR LINES Bathymetry
Pratice Surface Processes Test
 1. The cross section below shows the movement of wind-driven sand particles that strike a partly exposed basalt cobble located at the surface of a windy desert. Which cross section best represents the
1. The cross section below shows the movement of wind-driven sand particles that strike a partly exposed basalt cobble located at the surface of a windy desert. Which cross section best represents the
Chapter 2 Planet Earth
 Chapter 2 Planet Earth Section Notes Earth and the Sun s Energy Water on Earth The Land Close-up The Water Cycle World Almanac Major Eruptions in the Ring of Fire Quick Facts Chapter 2 Visual Summary Video
Chapter 2 Planet Earth Section Notes Earth and the Sun s Energy Water on Earth The Land Close-up The Water Cycle World Almanac Major Eruptions in the Ring of Fire Quick Facts Chapter 2 Visual Summary Video
ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF POWER STATIONS
 Region Northern Region Western Region Southern Region Eastern Region North Eastern Region Islands ALL INDIA Figures at decimal may not tally due to rounding off ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF
Region Northern Region Western Region Southern Region Eastern Region North Eastern Region Islands ALL INDIA Figures at decimal may not tally due to rounding off ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF
Biodiversity-Hotspots
 GE 2211 Environmental Science and Engineering Unit II Biodiversity-Hotspots M. Subramanian Assistant Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering Kalavakkam
GE 2211 Environmental Science and Engineering Unit II Biodiversity-Hotspots M. Subramanian Assistant Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering Kalavakkam
ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF POWER STATIONS
 Region Northern Region Western Region Southern Region Eastern Region North Eastern Region Islands ALL INDIA Figures at decimal may not tally due to rounding off ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF
Region Northern Region Western Region Southern Region Eastern Region North Eastern Region Islands ALL INDIA Figures at decimal may not tally due to rounding off ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF
discussion of North America s physical features, including its landforms and bodies of
 Chapter 7 Natural Environments of North America Chapter 7 focuses on the natural environments of North America. The chapter opens with a discussion of North America s physical features, including its landforms
Chapter 7 Natural Environments of North America Chapter 7 focuses on the natural environments of North America. The chapter opens with a discussion of North America s physical features, including its landforms
The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia
 The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia Gobi desert, Mongolia Essential Question: How does the geography of SE Asia impact trade and the distribution of population throughout the region? (AKS #52a)
The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia Gobi desert, Mongolia Essential Question: How does the geography of SE Asia impact trade and the distribution of population throughout the region? (AKS #52a)
Unit 4 - Water. Earth s Interior. Earth s Interior. Continental Drift. Continental Drift. Continental Drift. Crust. Mantle. Core.
 Unit 4 - Water How did the oceans form? What special adaptations do saltwater organisms have? Where does our water come from? How do humans affect the Earth s water? Crust Rigid outer shell of Earth Oceanic
Unit 4 - Water How did the oceans form? What special adaptations do saltwater organisms have? Where does our water come from? How do humans affect the Earth s water? Crust Rigid outer shell of Earth Oceanic
UNIT 2 WARM UP. List the OCEANS. Bonus: Name the Largest LAKE on Earth
 UNIT 2 WARM UP List the OCEANS Bonus: Name the Largest LAKE on Earth Land Forms Land Mountain Hill Cliff Butte Mesa Plateau Cave Volcano Desert Plains Prairie Steppe Marsh Swamp Tundra Glacier Continent
UNIT 2 WARM UP List the OCEANS Bonus: Name the Largest LAKE on Earth Land Forms Land Mountain Hill Cliff Butte Mesa Plateau Cave Volcano Desert Plains Prairie Steppe Marsh Swamp Tundra Glacier Continent
MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY
 MARINE GEOLOGY MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY Marine Geology 4 LAYERS OF THE EARTH CRUST THICKNESS: VARIES BETWEEN OCEAN & CONTINENTS 5-40 KM STATE: SOLID ELEMENTS: SILICON, ALUMINUM, CALCIUM, SODIUM, POTASSIUM
MARINE GEOLOGY MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY Marine Geology 4 LAYERS OF THE EARTH CRUST THICKNESS: VARIES BETWEEN OCEAN & CONTINENTS 5-40 KM STATE: SOLID ELEMENTS: SILICON, ALUMINUM, CALCIUM, SODIUM, POTASSIUM
Changes in Texas Ecoregions
 Comment On Lesson Changes in Texas Ecoregions The state of Texas can be divided into 10 distinct areas based on unique combinations of vegetation, topography, landforms, wildlife, soil, rock, climate,
Comment On Lesson Changes in Texas Ecoregions The state of Texas can be divided into 10 distinct areas based on unique combinations of vegetation, topography, landforms, wildlife, soil, rock, climate,
Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor
 Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Chapter Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics theory. The plate tectonics model describes features and processes on Earth. Plate tectonic science
Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Chapter Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics theory. The plate tectonics model describes features and processes on Earth. Plate tectonic science
PALEOGEOGRAPHY of NYS. Definitions GEOLOGIC PROCESSES. Faulting. Folding 9/6/2012. TOPOGRAPHIC RELIEF MAP of NYS GRADATIONAL TECTONIC
 TOPOGRAPHIC RELIEF MAP of NYS PALEOGEOGRAPHY of NYS Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 2012 Definitions GEOLOGIC PROCESSES Geography: study of people living on the surface of the earth. Geology: the scientific study
TOPOGRAPHIC RELIEF MAP of NYS PALEOGEOGRAPHY of NYS Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 2012 Definitions GEOLOGIC PROCESSES Geography: study of people living on the surface of the earth. Geology: the scientific study
Small area of the ocean that is partially surrounded by land. The Ocean Basins. Three Major Oceans. Three Major Oceans. What is a SEA?
 The Ocean Basins How Deep is the Ocean? 1 2 Three Major Oceans Three Major Oceans Pacific Atlantic the shallowest ocean (3.3km average depth) Indian second shallowest ocean (3.8km average depth) Pacific
The Ocean Basins How Deep is the Ocean? 1 2 Three Major Oceans Three Major Oceans Pacific Atlantic the shallowest ocean (3.3km average depth) Indian second shallowest ocean (3.8km average depth) Pacific
Landforms in Canada. Canada is made up of three dis;nct types of landforms: Canadian Shield Highlands Lowlands
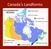 Canada s Landforms What is a Landform? A landform is any physical feature of the Earth s surface having a characteris;c, recognizable shape, produced by natural causes. Landforms include major features
Canada s Landforms What is a Landform? A landform is any physical feature of the Earth s surface having a characteris;c, recognizable shape, produced by natural causes. Landforms include major features
Social Science Class 9 th DRAINAGE Drainage System In India Himalayan River System Peninsular River System Lakes Role of Rivers in the Economy
 Social Science Class 9 th DRAINAGE Drainage System In India Himalayan River System Peninsular River System Lakes Role of Rivers in the Economy The term drainage describes the river system of an area. The
Social Science Class 9 th DRAINAGE Drainage System In India Himalayan River System Peninsular River System Lakes Role of Rivers in the Economy The term drainage describes the river system of an area. The
Chapter 1 Section 2. Land, Water, and Climate
 Chapter 1 Section 2 Land, Water, and Climate Vocabulary 1. Landforms- natural features of the Earth s land surface 2. Elevation- height above sea level 3. Relief- changes in height 4. Core- most inner
Chapter 1 Section 2 Land, Water, and Climate Vocabulary 1. Landforms- natural features of the Earth s land surface 2. Elevation- height above sea level 3. Relief- changes in height 4. Core- most inner
Alfred Wegener gave us Continental Drift. Fifty years later...
 CHAPTER 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Plate Tectonics: summary in haiku form Alfred Wegener gave us Continental Drift. Fifty years later... Words Chapter Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics
CHAPTER 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Plate Tectonics: summary in haiku form Alfred Wegener gave us Continental Drift. Fifty years later... Words Chapter Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 7 Glaciers, Desert, and Wind 7.1 Glaciers Types of Glaciers A glacier is a thick ice mass that forms above the snowline over hundreds or thousands of
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 7 Glaciers, Desert, and Wind 7.1 Glaciers Types of Glaciers A glacier is a thick ice mass that forms above the snowline over hundreds or thousands of
Fossil Clues Teacher s Notes
 Fossils are the remains of living things which have been changed into rock. The father of modern geology, James Hutton, said that we can interpret the nature of creatures from the past and the environment
Fossils are the remains of living things which have been changed into rock. The father of modern geology, James Hutton, said that we can interpret the nature of creatures from the past and the environment
N. K. Manglik Director
 N. K. Manglik Director Hydro-meteorological observations could be broadly defined as the scientific way for collection of flow data at a specific location along the river including selected meteorological
N. K. Manglik Director Hydro-meteorological observations could be broadly defined as the scientific way for collection of flow data at a specific location along the river including selected meteorological
deep within the planet. They are also shaped by conditions on the planet s surface. In
 Chapter 4 Landforms, Water, and Natural Resources Earth is home to many different types of landforms. These landforms are shaped by forces deep within the planet. They are also shaped by conditions on
Chapter 4 Landforms, Water, and Natural Resources Earth is home to many different types of landforms. These landforms are shaped by forces deep within the planet. They are also shaped by conditions on
Bell Ringer. Are soil and dirt the same material? In your explanation be sure to talk about plants.
 Bell Ringer Are soil and dirt the same material? In your explanation be sure to talk about plants. 5.3 Mass Movements Triggers of Mass Movements The transfer of rock and soil downslope due to gravity is
Bell Ringer Are soil and dirt the same material? In your explanation be sure to talk about plants. 5.3 Mass Movements Triggers of Mass Movements The transfer of rock and soil downslope due to gravity is
Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition
 Chapter Chapter 1 2 Clickers Lecture Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Alan P. Trujillo Harold V. Thurman Chapter Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics
Chapter Chapter 1 2 Clickers Lecture Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Alan P. Trujillo Harold V. Thurman Chapter Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics
1. Which of the places have been recently added to the list of Swacch Iconic Places under Swacch Bharat Mission?
 Which of the places have been recently added to the list of Swacch Iconic Places under Swacch Bharat Mission? RaghavendraSwamy Temple - Andhra Pradesh Hazardwari Palace - West Bengal 3. Pangong Lake -Leh-Ladakh,
Which of the places have been recently added to the list of Swacch Iconic Places under Swacch Bharat Mission? RaghavendraSwamy Temple - Andhra Pradesh Hazardwari Palace - West Bengal 3. Pangong Lake -Leh-Ladakh,
Chapter 02 The Sea Floor
 Chapter 02 The Sea Floor Multiple Choice Questions 1. One of the following is not one of the world's major ocean basins: A. Atlantic Ocean B. Arctic Ocean C. Indian Ocean D. Antarctic Ocean E. Pacific
Chapter 02 The Sea Floor Multiple Choice Questions 1. One of the following is not one of the world's major ocean basins: A. Atlantic Ocean B. Arctic Ocean C. Indian Ocean D. Antarctic Ocean E. Pacific
Geography Class XI Fundamentals of Physical Geography Section A Total Periods : 140 Total Marks : 70. Periods Topic Subject Matter Geographical Skills
 Geography Class XI Fundamentals of Physical Geography Section A Total Periods : 140 Total Marks : 70 Sr. No. 01 Periods Topic Subject Matter Geographical Skills Nature and Scope Definition, nature, i)
Geography Class XI Fundamentals of Physical Geography Section A Total Periods : 140 Total Marks : 70 Sr. No. 01 Periods Topic Subject Matter Geographical Skills Nature and Scope Definition, nature, i)
Geology 12 FINAL EXAM PREP. Possible Written Response Exam Questions
 Geology 12 FINAL EXAM PREP Possible Written Response Exam Questions Use this study guide to prepare for the written response portion of the final exam. Name FINAL EXAM - POSSIBLE WRITTEN RESPONSE QUESTIONS
Geology 12 FINAL EXAM PREP Possible Written Response Exam Questions Use this study guide to prepare for the written response portion of the final exam. Name FINAL EXAM - POSSIBLE WRITTEN RESPONSE QUESTIONS
ICSE Board Class X Geography Board Paper- 2014
 Time:2 hrs ICSE Board Class X Geography Board Paper- 2014 Total Marks: 80 General Instructions: 1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. 2. You will not be allowed to
Time:2 hrs ICSE Board Class X Geography Board Paper- 2014 Total Marks: 80 General Instructions: 1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. 2. You will not be allowed to
Chapter 27. Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal, & Sri Lanka
 Chapter 27 Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal, & Sri Lanka Physical Geography of Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal & Sri Lanka Landforms Their locations on the fringe of South Asia means their physical and human geography
Chapter 27 Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal, & Sri Lanka Physical Geography of Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal & Sri Lanka Landforms Their locations on the fringe of South Asia means their physical and human geography
Regional Atlas Activity C
 Political Location Activity AUSTRALIA, OCEANIA, AND ANTARCTICA Regional Atlas Activity C DIRECTIONS: Identify each country marked by a number on the map. Then write the correct name on the numbered blanks
Political Location Activity AUSTRALIA, OCEANIA, AND ANTARCTICA Regional Atlas Activity C DIRECTIONS: Identify each country marked by a number on the map. Then write the correct name on the numbered blanks
4. The map below shows a meandering stream. Points A, B, C, and D represent locations along the stream bottom.
 1. Sediment is deposited as a river enters a lake because the A) velocity of the river decreases B) force of gravity decreases C) volume of water increases D) slope of the river increases 2. Which diagram
1. Sediment is deposited as a river enters a lake because the A) velocity of the river decreases B) force of gravity decreases C) volume of water increases D) slope of the river increases 2. Which diagram
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX - GEOGRAPHY CHAPTER:3 : DRAINAGE WORKSHEET NO. 09
 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX - GEOGRAPHY CHAPTER: : DRAINAGE WORKSHEET NO. 09 Please write following question-answers in your note book: 2,4,, 8, 9, 12,18,
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX - GEOGRAPHY CHAPTER: : DRAINAGE WORKSHEET NO. 09 Please write following question-answers in your note book: 2,4,, 8, 9, 12,18,
The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia
 The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia Gobi desert, Mongolia Essential Question: How does geography impact the distribution of population throughout South and East Asia? I CAN Explain how geography
The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia Gobi desert, Mongolia Essential Question: How does geography impact the distribution of population throughout South and East Asia? I CAN Explain how geography
EQ: Discuss main geographic landforms of the U.S. & Canada and examine varied landforms in relation to their lifestyles.
 EQ: Discuss main geographic landforms of the U.S. & Canada and examine varied landforms in relation to their lifestyles. Places & Terms for Discussion Appalachian Mountains Great Plains Canadian Shield
EQ: Discuss main geographic landforms of the U.S. & Canada and examine varied landforms in relation to their lifestyles. Places & Terms for Discussion Appalachian Mountains Great Plains Canadian Shield
