LOCAL SCOUR INDUCED BY 3D FLOW AROUND ATTRACTING AND DEFLECTING GROINS
|
|
|
- Mitchell Warner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LOCAL SCOUR INDUCED BY 3D FLOW AROUND ATTRACTING AND DEFLECTING GROINS TAISUKE ISHIGAKI Disaster Prevention Research Institute, Kyoto University Fushimi, Kyoto , Japan YASUYUKI BABA Disaster Prevention Research Institute, Kyoto University Fushimi, Kyoto , Japan In recent years, groins are set perpendicular to a riverbank, which is called a deflecting groin. However, many old groins in Japan were set at angles to a bank. This type of groin is called an attracting groin of which head is shifted toward downstream. Such groin is not usually used in a submerged situation, because a flow over the groin attacks a bank and erodes it. In this paper, local scour and flow structure around these two kinds of groin are investigated experimentally in nonsubmerged and submerged situations. By comparing the results in the two groin cases, the local scour induced by a three dimensional flow is discussed. It is found that scouring position is changing on the depth of overtopping flow in both cases and that a strong downward flow produces deep scour holes near the head or root of groin. 1 Introduction Recently, groins are set not only for the protection of bank erosion but also for the environmental preservation in Japan. The main functions of groin are to deflect a flow and to reduce velocity near the riverbank. The secondary function is to form a varied bed configuration, and it is useful to preserve the river environment. There are many types of groin, however, impermeable groins are discussed in this paper. The recent groins are set perpendicular to a riverbank, which is called a deflecting groin. On the other hand, many old groins in Japan were set at angles to a bank. This is an attracting groin of which head is shifted toward downstream. Such groin is not usually used in a submerged situation, because a flow over the groin attacks a bank and erodes it. As there is an old attracting groin that was built for bank protection about 400 years ago in Kyoto Prefecture, hydraulic aspects of the groin have been investigated experimentally (Ishigaki et al 2004). In this paper, local scour and flow structure around attracting and deflecting groins are compared experimentally under same hydraulic conditions. Many researchers have studied the hydraulics of groins, and three topics have been recently investigated. These are local scour (Kuhnle et al 1999, Ohmoto and Hirakawa 2000, Elawady et al 2001, 2002), the flow structure (Tominaga et al 1997, Uittewaal and Berg 2002), and the mass exchange in the groin fields (Uittewaal et al 2001, Kurzke et al 2002). They have dealt with the groins of angle 30 to 30 degrees. The attracting groin in this paper is out of consideration, because it has large angle of 65 degrees. Thus scour 1
2 2 and flow structure around the attracting groin is investigated here, and these features are compared with results in case of a deflecting groin under the same hydraulic condition. 2 Experimental Methods Figure 1 shows two kinds of groin. Width of both groins on the y-axis and cross section shape are same as shown in the figure. The groin models were set on the right hand side bank in a straight channel with a flat bed. The channel was 10m long, 1.0m wide and 0.3m deep installed with a discharge control system. The middle part of the channel was made of movable bed filled with fine sand of which the mean diameter was 0.26mm. The movable bed section was 1.8m long and 0.2m deep. The channel width was 0.9 m in the case of attracting groin as shown in Table 1. Bed form, velocity, water level and flow were measured under clear water scour conditions in five cases of different water depths, which included four submerged and one non-submerged cases, as shown in Table 1. H/h is the relative depth, where H is the flow depth and h is the height of groin. The ratio between the friction velocity and the critical friction velocity of the bed material was kept from 0.78 to 0.91 by setting the same discharge velocity, 0.2 m/s, in all cases. Figure 1. Plan view and cross section of attracting and deflecting groin used in the experiments. Table 1. Hydraulic conditions for attracting and deflecting groin cases.
3 3 Figure 2. Bed forms around attracting and deflecting groins in the range of y=1 to 50 cm. A laser level meter, an ultra-sonic level meter and an electro-magnetic velocimeter were the equipments used for the measurements of bed form, water level and velocity, respectively. Flow patterns were observed on the water surface and in a cross section of flow by using normal and submergible video cameras. 3 Local Scour around Groins Figure 2 shows bed forms measured in the cases of attracting and deflecting groins. Bed forms were measured at each 4.25 mm in x-axis and 1 cm in y-axis by using a laser level meter. The measurements were done after one hour from the beginning of experiment in all the cases. Contour lines are shown in the difference from the original bed level in y=1 to 50 cm. Dark color shows scouring parts and bright color depositing parts. The friction velocity was almost same in all cases. The formation of scour and deposition is different according to the relative depth, H/h, in both cases. In the case of attracting groin, scouring positions in submerged
4 4 Figure 3. Longitudinal bed profiles in attracting groin cases at y=24 cm. Figure 4. Longitudinal bed profiles in deflecting groin cases at y=29 cm. Figure 5. Relations between normalize scour depth, Zs/h, and relative depth, H/h. situations are quite different from those in the non-submerged case. The position of deepest hole moves from the downstream side of groin head to the root side. The result in case of H/h=1.41 shows scour holes on both sides. The deepest points are near the root of groin in cases A3 to A5, H/h>1.4, and those are near the head in cases A1 and A2. The
5 5 Photo 1. Flow patterns on the water surface visualized by a tracer method using sawdust. position of scour holes in deflecting groin case also moves slightly to the root side, but the holes do not reach to the bank. No scour can be observed near the bank. The result in case D3 (H/h=1.41) also shows the both aspects of non-submerged and submerged cases. The longitudinal profiles of bed form near the head of groin are shown in Figure 3 and 4. Lateral distance from the bank is 24 cm and 29 cm in the case of attracting and deflecting groins respectively. The sections in both cases cross the deepest points in nonsubmerged situation, H/h=0.82. It indicates that scour hole appears apart from the head of groin. Scour hole can t be observed in the deeper cases, A4 and A5, of attracting groin, however, it can be observed in all cases of deflecting groin. Figure 5 shows the relations between the deepest scour depth and relative depth in both cases. The depth presented here is not the maximum value, because the running time of experiment was one hour. However, the result shows qualitative features. Scour depth does not vary widely in the attracting groin cases, but the depth around deflecting groin decreases in the shallow cases, D1 and D2, and becomes almost constant in the deeper cases, D3 to D5. The constant value is around Zs/h=0.5. It is found that the scour depth around an attracting groin is shallower than the depth around a deflecting groin in case of H/h< D Flow Structure around Groins 4.1. Flow Patterns on the Water Surface Photo 1 shows flow patterns on the water surface for attracting and deflecting groins. Upper photographs are in non-submerged cases, A1 and D1, and lower ones are in submerged cases, A5 and D5. The flow patterns were visualized by sawdust as a tracer.
6 6 Figure 6. Bed form, surface profile and velocity components, u and v in attracting groin case. Approach flows were deflected to the channel center by the groins in the non-submerged cases and the dead zone was produced behind the each groin. Deflection is stronger in deflecting groin case than in attracting groin case. The lower photographs of the submerged cases show different aspects respectively. In attracting groin case, the approach flow was not obviously deflected, and most part of the flow ran over the groin along the bank. It is easily anticipated that this overtopping flow causes local scour and bank erosion behind the groin. On the other hand, the approach flow was strongly deflected and the dead zone was produced on the downstream side in deflecting groin case. Velocity in the wake zones are small in both cases, however, the effect of velocity reduction is more conspicuous in deflecting groin case because reverse flow can be observed in the wake zone Local Scour and Flow Structure To investigate the relation between flow structure and bed form around the groin, profiles of water surface, velocity distributions and bed from were measured for H/h=1.92. Figure 6 and 7 are the results in the range of y=2 to 45 cm and x=-50 to 90 cm. The measurements of surface profile and velocity were conducted after fixing the bed form by using mortar. The surface profile is shown in the difference from the mean flow
7 7 Figure 7. Bed form, surface profile and velocity components, u and v in deflecting groin case. depth. The two velocity components were measured at 1 cm above the groin top by using an electro-magnetic velocimeter. Arrows in the velocity distribution are the longitudinal component of velocity u, and the contour lines show the distribution of vertical component of velocity, v. The dark color shows down-welling part and the bright color up-welling part. Notation of the bed form is identical as in Figure 2. The water level over the groin is lower than the surrounding. Lowest point is near the root of groin in attracting groin case and near the head in deflecting groin case. It means that the flow is accelerated there. From the velocity distribution, it is found that the accelerated flow goes downward and intrudes into the wake region of groin, and then scours the bed in case A5. There are rapid flow regions near the channel center and along the bank. Low speed region is between them and deposition is observed there. As shown in Photo 1, velocity in the wake zone is small in case D5. It means that a deflecting groin is effective for bank protection. As a similar and important aspect in both cases, it can be confirmed that the regions of strong downward flow are coincident with scour regions in both cases. This means that overtopping flow with high speed goes to the bed and erodes there. This flow was also observed in a cross section by using a submergible video camera in both cases. It is found that local scour around attracting and deflecting groins is closely related to the three-dimensional flow structure.
8 8 5 Conclusions Local scour and flow structure around two types of groin have been investigated experimentally. The main conclusions are as follows. 1) Scour holes are observed near the head of deflecting groin and near the root of attracting one in submerged situation with deep conditions as mentioned in the previous studies. However, the formation of scour and deposition is gradually changing with the relative depth, H/h, in both cases. 2) There is a hydraulic condition in which bed form in non-submerged and submerged situations can be observed simultaneously. 3) A deflecting groin is effective in protecting bank erosion. When an attracting groin would be used for bank protection, the magnitude of local scour along riverbank should be considered. 4) A strong downward flow overtopping the groin induces local scour and the local scour around groin is closely related to three-dimensional flow structure. It is important that hydraulic engineers have to recognize the relation between local scour and flow structure in planning the groins. References Elawady, E., M. Michiue and Hinokidani, O. (2001). Characteristics of scour around repelling spur-dikes, Proc. of 29th Con-gress of IAHR, Beijing: Theme D, II, Elawady, E., M. Michiue and Hinokidani, O. (2002). An investigation of scour around attracting spur-dikes, Advances in Fluid Modelling and Turbulence Measurements, Proc. of 8th Intr. Symp. on Flow Modelling and Turbulence Measurements, Tokyo: , World Scientific. Ishigaki, T., Ueno, Y., M.M. Rahman and Khaleduzzaman, A.T.M. (2004). Scouring of flow structure around an attracting groin, River Flow 2004, in printing. Kuhnle, R.A., C.V. Alonso and Shields Jr., F.D. (1999). Geometry of scour holes associated with 90 spur dikes, Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, ASCE: 25, (9), Kurzke, M., V. Weitbrecht and Jirka G.H. (2002). Laboratory concentration measurements for determination of mass ex-change between groin field and main stream, River Flow 2002, Bousmar & Zech (eds.): 1, Ohmoto, T and Hirakawa, R. (2000). Secondary current structure in open-channel flow with a series of submerged groyns, Proc. of 12th Congress of APD-IAHR, Bangkok: 1, Tominaga, A., M. Nagao and Nezu, I. (1997). Flow structure and mixing processes around porous and submerged dikes, Proc. of 27th Congress of IAHR, San Francisco: Theme B, 1, Uittewaal, W.S.J and Berg, M.H. (2002). Experiments on physical scale models for submerged and non-submerged groynes of various types, River Flow 2002, Bousmar & Zech (eds.): 1, Uittewaal, W.S.J., D. Lehmann and Mazijk, A. (2001). Exchange processes between a river and its groyn field: model experiments, Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, ASCE: 127, (11),
STABILITY OF OLD STONE GROINS IN THE KATSURA RIVER DURING FLOODS
 B-10 Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion 008 STABILITY OF OLD STONE GROINS IN THE KATSURA RIVER DURING FLOODS Taisuke ISHIGAKI 1, Takahiro ASANO and Ryuji KAWANAKA 3 1 Member of JSCE,
B-10 Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion 008 STABILITY OF OLD STONE GROINS IN THE KATSURA RIVER DURING FLOODS Taisuke ISHIGAKI 1, Takahiro ASANO and Ryuji KAWANAKA 3 1 Member of JSCE,
Experimental study of scour depth in attracting Groins series
 Experimental study of scour depth in attracting Groins series S. Amini 1, M.R. Kavianpour 2, M.R.M. tabatabai 3, S. Amini 4, K. Amini 5 1-MSc, Water Engineering, Shahid Beheshty University 2-Associate
Experimental study of scour depth in attracting Groins series S. Amini 1, M.R. Kavianpour 2, M.R.M. tabatabai 3, S. Amini 4, K. Amini 5 1-MSc, Water Engineering, Shahid Beheshty University 2-Associate
THE HYDRAULIC PERFORMANCE OF ORIENTED SPUR DIKE IMPLEMENTATION IN OPEN CHANNEL
 Tenth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC10 2006, Alexandria, Egypt 281 THE HYDRAULIC PERFORMANCE OF ORIENTED SPUR DIKE IMPLEMENTATION IN OPEN CHANNEL Karima Attia 1 and Gamal El Saied 2 1
Tenth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC10 2006, Alexandria, Egypt 281 THE HYDRAULIC PERFORMANCE OF ORIENTED SPUR DIKE IMPLEMENTATION IN OPEN CHANNEL Karima Attia 1 and Gamal El Saied 2 1
PRESSURE AND SCOURING AROUND A SPUR DIKE DURING THE SURGE PASS
 Annual Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, JSCE, Vol.3, 3, February PRESSURE AND SCOURING AROUND A SPUR DIKE DURING THE SURGE PASS Tomasz MIODUSZEWSKI and Shiro MAENO Student Member of JSCE, Doctoral Student,
Annual Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, JSCE, Vol.3, 3, February PRESSURE AND SCOURING AROUND A SPUR DIKE DURING THE SURGE PASS Tomasz MIODUSZEWSKI and Shiro MAENO Student Member of JSCE, Doctoral Student,
Flow Pattern in Compound Channel with Floodplain Double Groyne
 Flow Pattern in Compound Channel with Floodplain Double Groyne Ahmed, H. S., Ahmed, A. A., & Mostafa, M. M. (2015). Flow Pattern in Compound Channel with Floodplain Double Groyne. Dam Engineering, XXVI(3).
Flow Pattern in Compound Channel with Floodplain Double Groyne Ahmed, H. S., Ahmed, A. A., & Mostafa, M. M. (2015). Flow Pattern in Compound Channel with Floodplain Double Groyne. Dam Engineering, XXVI(3).
Analysis of flow around impermeable groynes on one side of symmetrical compound channel: An experimental study
 Water Science and Engineering, 2010, 3(1): 56-66 doi:10.3882/j.issn.1674-2370.2010.01.006 http://www.waterjournal.cn e-mail: wse2008@vip.163.com Analysis of flow around impermeable groynes on one side
Water Science and Engineering, 2010, 3(1): 56-66 doi:10.3882/j.issn.1674-2370.2010.01.006 http://www.waterjournal.cn e-mail: wse2008@vip.163.com Analysis of flow around impermeable groynes on one side
INFLUENCE OF THE SPUR DIKE PERMEABILITY ON FLOW AND SCOURING DURING A SURGE PASS
 INFLUENCE OF THE SPUR DIKE PERMEABILITY ON FLOW AND SCOURING DURING A SURGE PASS TOMASZ MIODUSZEWSKI Graduate School of Natural Science and Technology, Okayama 7-8, Japan, e-mail: tomasz@cc.okayama-u.ac.jp
INFLUENCE OF THE SPUR DIKE PERMEABILITY ON FLOW AND SCOURING DURING A SURGE PASS TOMASZ MIODUSZEWSKI Graduate School of Natural Science and Technology, Okayama 7-8, Japan, e-mail: tomasz@cc.okayama-u.ac.jp
Laboratory Investigation of Submerged Vane Shapes Effect on River Banks Protection
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(12): 1402-1407, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 Laboratory Investigation of Submerged Vane Shapes Effect on River Banks Protection Touraj Samimi Behbahan Department
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(12): 1402-1407, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 Laboratory Investigation of Submerged Vane Shapes Effect on River Banks Protection Touraj Samimi Behbahan Department
BED DEFORMATION AROUND GROINS IN A RIVER RESTORATION PROJECT
 Annual Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, JSCE, Vol.51, 2007, February BED DEFORMATION AROUND GROINS IN A RIVER RESTORATION PROJECT Hao ZHANG 1, Hajime NAKAGAWA 1, Yasunori MUTO 1, Yoshio MURAMOTO 2 and
Annual Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, JSCE, Vol.51, 2007, February BED DEFORMATION AROUND GROINS IN A RIVER RESTORATION PROJECT Hao ZHANG 1, Hajime NAKAGAWA 1, Yasunori MUTO 1, Yoshio MURAMOTO 2 and
Quasi-three dimensional computations for flows and bed variations in curved channel with gently sloped outer bank
 River Sedimentation Wieprecht et al. (Eds) 2017 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-02945-3 Quasi-three dimensional computations for flows and bed variations in curved channel with gently sloped
River Sedimentation Wieprecht et al. (Eds) 2017 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-02945-3 Quasi-three dimensional computations for flows and bed variations in curved channel with gently sloped
EXPLORATION OF SCOUR CHARACTERISTICS AROUND SPUR DIKE IN A STRAIGHT WIDE CHANNEL
 International Water Technology Journal, IWTJ Vol. 6 No.2, June 26 EXPLORATION OF SCOUR CHARACTERISTICS AROUND SPUR DIKE IN A STRAIGHT WIDE CHANNEL Elsaiad A.A. and Elnikhely E.A. *2 Professor of hydraulics,
International Water Technology Journal, IWTJ Vol. 6 No.2, June 26 EXPLORATION OF SCOUR CHARACTERISTICS AROUND SPUR DIKE IN A STRAIGHT WIDE CHANNEL Elsaiad A.A. and Elnikhely E.A. *2 Professor of hydraulics,
J-river engineering for Vietnam
 J-river engineering for Vietnam Workshop on erosion control in the Mekong Delta Soc Trang, June 2015 Onga river, Japan Dr. MATSUKI Trung: JICA Expert 1 Project for Building Disaster Resilient Society in
J-river engineering for Vietnam Workshop on erosion control in the Mekong Delta Soc Trang, June 2015 Onga river, Japan Dr. MATSUKI Trung: JICA Expert 1 Project for Building Disaster Resilient Society in
Sediment Transport Mechanism and Grain Size Distributions in Stony Bed Rivers. S.FUKUOKA 1 and K.OSADA 2
 Sediment Transport Mechanism and Grain Size Distributions in Stony Bed Rivers S.FUKUOKA 1 and K.OSADA 1 Professor, Research and Development Initiative, Chuo-University, 1-13-7 Kasuga Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo,
Sediment Transport Mechanism and Grain Size Distributions in Stony Bed Rivers S.FUKUOKA 1 and K.OSADA 1 Professor, Research and Development Initiative, Chuo-University, 1-13-7 Kasuga Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo,
LOCAL SCOUR AND SEDIMENT SORTING AROUND A SERIES OF GROYNES
 J. JSNDS 35 117-129 2016 LOCAL SCOUR AND SEDIMENT SORTING AROUND A SERIES OF GROYNES Hao ZHANG 1 Hajime NAKAGAWA 2 LOCAL SCOUR AND SEDIMENT SORTING AROUND A SERIES OF GROYNES Hao ZHANG 1 and Hajime NAKAGAWA
J. JSNDS 35 117-129 2016 LOCAL SCOUR AND SEDIMENT SORTING AROUND A SERIES OF GROYNES Hao ZHANG 1 Hajime NAKAGAWA 2 LOCAL SCOUR AND SEDIMENT SORTING AROUND A SERIES OF GROYNES Hao ZHANG 1 and Hajime NAKAGAWA
Countermeasure Calculations and Design
 Countermeasure Calculations and Design Summarized from Bridge Scour and Stream Instability Countermeasures, Experience, Selection, and Design Guidance, Second Edition, Publication No. FHWA NHI 01-003,
Countermeasure Calculations and Design Summarized from Bridge Scour and Stream Instability Countermeasures, Experience, Selection, and Design Guidance, Second Edition, Publication No. FHWA NHI 01-003,
COMPARISON OF SCOUR AROUND DIFFERENT SHAPES OF GROYNES IN OPEN CHANNEL
 COMPARISON OF SCOUR AROUND DIFFERENT SHAPES OF GROYNES IN OPEN CHANNEL Thangamani Vijaya Kumar 1, Devesh Tyagi 2, Lokesh Aggarwal 3, Munendra Kumar 4 1,2,3,4 Department of Civil Engineering, Delhi Technological
COMPARISON OF SCOUR AROUND DIFFERENT SHAPES OF GROYNES IN OPEN CHANNEL Thangamani Vijaya Kumar 1, Devesh Tyagi 2, Lokesh Aggarwal 3, Munendra Kumar 4 1,2,3,4 Department of Civil Engineering, Delhi Technological
CE415L Applied Fluid Mechanics Laboratory
 Applied Fluid Mechanics Laboratory Learning Objective Following completion of this experiment and the analysis of the data, you should be able to 1. generalize results of introducing changes to a natural
Applied Fluid Mechanics Laboratory Learning Objective Following completion of this experiment and the analysis of the data, you should be able to 1. generalize results of introducing changes to a natural
MORPHOLOGICAL RESPONSE OF RIVER CHANNEL DUE TO WEIR RECONSTRUCTION
 D-12 Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion 28 MORPHOLOGICAL RESPONSE OF RIVER CHANNEL DUE TO WEIR RECONSTRUCTION Hao ZHANG 1, Keiichi KANDA 2, Yasunori MUTO 3 and Hajime NAKAGAWA 4 1 Member
D-12 Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion 28 MORPHOLOGICAL RESPONSE OF RIVER CHANNEL DUE TO WEIR RECONSTRUCTION Hao ZHANG 1, Keiichi KANDA 2, Yasunori MUTO 3 and Hajime NAKAGAWA 4 1 Member
DYNAMICS OF FLOOD FLOWS AND BED VARIATIONS IN RIVER SECTIONS REPAIRED TO SHIP-BOTTOM SHAPED CHANNELS FROM COMPOUND CHANNLS
 E-proceedings of the 36 th IAHR World Congress DYNAMICS OF FLOOD FLOWS AND BED VARIATIONS IN RIVER SECTIONS REPAIRED TO SHIP-BOTTOM SHAPED CHANNELS FROM COMPOUND CHANNLS TAKUMA SASAKI (1) & SHOJI FUKUOKA
E-proceedings of the 36 th IAHR World Congress DYNAMICS OF FLOOD FLOWS AND BED VARIATIONS IN RIVER SECTIONS REPAIRED TO SHIP-BOTTOM SHAPED CHANNELS FROM COMPOUND CHANNLS TAKUMA SASAKI (1) & SHOJI FUKUOKA
EXAMPLES (SEDIMENT TRANSPORT) AUTUMN 2018
 EXAMPLES (SEDIMENT TRANSPORT) AUTUMN 2018 Q1. Using Cheng s formula estimate the settling velocity of a sand particle of diameter 1 mm in: (a) air; (b) water. Q2. Find the critical Shields parameter diameter
EXAMPLES (SEDIMENT TRANSPORT) AUTUMN 2018 Q1. Using Cheng s formula estimate the settling velocity of a sand particle of diameter 1 mm in: (a) air; (b) water. Q2. Find the critical Shields parameter diameter
2-D Particle Tracking to Determine Transport Characteristics
 2-D Particle Tracking to Determine Transport Characteristics in Rivers with Dead Zones Volker Weitbrecht, Wim Uijttewaal 2 & Gerhard H. Jirka Institute for Hydromechanics, University of Karlsruhe 2 Hydromechanics
2-D Particle Tracking to Determine Transport Characteristics in Rivers with Dead Zones Volker Weitbrecht, Wim Uijttewaal 2 & Gerhard H. Jirka Institute for Hydromechanics, University of Karlsruhe 2 Hydromechanics
Indigenous technical knowledge for bank erosion and flood management
 2017 APEC Typhoon Symposium, May 2 4, 2017, GIS NTU Convention Center, Taipei Indigenous technical knowledge for bank erosion and flood management Hao Zhang 1) and Hajime Nakagawa 2) 1) Associate Professor,
2017 APEC Typhoon Symposium, May 2 4, 2017, GIS NTU Convention Center, Taipei Indigenous technical knowledge for bank erosion and flood management Hao Zhang 1) and Hajime Nakagawa 2) 1) Associate Professor,
Evaluation of Bed Shear Stress from Velocity Measurements in Gravel-Bed River with Local Non-Uniformity
 River Flow - Dittrich, Koll, Aberle & Geisenhainer (eds) - Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978--99--7 Evaluation of Bed Shear Stress from Velocity Measurements in Gravel-Bed River with Local Non-Uniformity
River Flow - Dittrich, Koll, Aberle & Geisenhainer (eds) - Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978--99--7 Evaluation of Bed Shear Stress from Velocity Measurements in Gravel-Bed River with Local Non-Uniformity
SCOUR AND EROSION ALONGSIDE BANK PROTECTION WORK: CASE STUDIES FROM BANGLADESH
 SCOUR AND EROSION ALONGSIDE BANK PROTECTION WORK: CASE STUDIES FROM BANGLADESH KNUT OBERHAGEMANN Northwest Hydraulic Consultants Lt. 4823 99 th Street Edmonton, Alberta T6E 4Y1, Canada ABDUN NOOR Bangladesh
SCOUR AND EROSION ALONGSIDE BANK PROTECTION WORK: CASE STUDIES FROM BANGLADESH KNUT OBERHAGEMANN Northwest Hydraulic Consultants Lt. 4823 99 th Street Edmonton, Alberta T6E 4Y1, Canada ABDUN NOOR Bangladesh
Factors affecting confluence scour
 & Wang (eds) River Sedimentation 1999., Balkema, Rotterdam. ISBN 9 9 3. 17 19 Factors affecting confluence scour R. B. Rezaur & A. W. Jayawardena. Department of Civil Engineering, The University of Hong
& Wang (eds) River Sedimentation 1999., Balkema, Rotterdam. ISBN 9 9 3. 17 19 Factors affecting confluence scour R. B. Rezaur & A. W. Jayawardena. Department of Civil Engineering, The University of Hong
Hydraulics of bendway weirs
 River Basin Management IV 389 Hydraulics of bendway weirs C. Thornton 1, S. Abt 1, D. Baird 2 & R. Padilla 3 1 Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA 2 U.S. Bureau of Reclamation, Denver, CO,
River Basin Management IV 389 Hydraulics of bendway weirs C. Thornton 1, S. Abt 1, D. Baird 2 & R. Padilla 3 1 Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA 2 U.S. Bureau of Reclamation, Denver, CO,
New computation method for flood flows and bed variations in a low-lying river with complex river systems
 River Flow 2014 Schleiss et al. (Eds) 2014 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-02674-2 New computation method for flood flows and bed variations in a low-lying river with complex river systems
River Flow 2014 Schleiss et al. (Eds) 2014 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-02674-2 New computation method for flood flows and bed variations in a low-lying river with complex river systems
Hydraulics of stream deflectors used in fish-habitat restoration schemes
 River Basin Management V 305 Hydraulics of stream deflectors used in fish-habitat restoration schemes P. M. Biron 1, D. M. Carré 2 & S. J. Gaskin 2 1 Department of Geography, Planning and Environment,
River Basin Management V 305 Hydraulics of stream deflectors used in fish-habitat restoration schemes P. M. Biron 1, D. M. Carré 2 & S. J. Gaskin 2 1 Department of Geography, Planning and Environment,
Local Scouring due to Flow Jet at Downstream of Rectangular Sharp-Crested Weirs
 Local Scouring due to Flow Jet at Downstream of Rectangular Sharp-Crested Weirs DEHGHANI, AMIR. AHMAD 1, BASHIRI, HAMID and MESHKATI SHAHMIRZADI, MOHAMMAD. EBRAHIM 3 1,3 Dept. of Water Engineering, Gorgan
Local Scouring due to Flow Jet at Downstream of Rectangular Sharp-Crested Weirs DEHGHANI, AMIR. AHMAD 1, BASHIRI, HAMID and MESHKATI SHAHMIRZADI, MOHAMMAD. EBRAHIM 3 1,3 Dept. of Water Engineering, Gorgan
Flood Capacity of Shirakawa River at Tatsudajinnnai Area in Kumamoto Prefecture
 International Journal of Economy, Energy and Environment 218; 3(5): 51-57 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijeee doi: 1.11648/j.ijeee.21835.13 ISSN: 2575-513 (Print); ISSN: 2575-521 (Online) Flood
International Journal of Economy, Energy and Environment 218; 3(5): 51-57 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijeee doi: 1.11648/j.ijeee.21835.13 ISSN: 2575-513 (Print); ISSN: 2575-521 (Online) Flood
On the influence of bed permeability on flow in the leeside of coarse-grained bedforms
 On the influence of bed permeability on flow in the leeside of coarse-grained bedforms G. Blois (1), J. L. Best (1), G. H. Sambrook Smith (2), R. J. Hardy (3) 1 University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign,
On the influence of bed permeability on flow in the leeside of coarse-grained bedforms G. Blois (1), J. L. Best (1), G. H. Sambrook Smith (2), R. J. Hardy (3) 1 University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign,
Laboratory Study of Turbulence Intensity in Longitudinal, Transverse and Deep Directions and Turbulent Burst Event around Various L-Shaped Groynes
 International Journal of Science and Engineering Investigations vol. 6, issue 67, August 2017 2017 ISSN: 2251-8843 Laboratory Study of Turbulence Intensity in Longitudinal, Transverse and Deep Directions
International Journal of Science and Engineering Investigations vol. 6, issue 67, August 2017 2017 ISSN: 2251-8843 Laboratory Study of Turbulence Intensity in Longitudinal, Transverse and Deep Directions
A STUDY OF LOCAL SCOUR AT BRIDGE PIERS OF EL-MINIA
 A STUDY OF LOCAL SCOUR AT BRIDGE PIERS OF EL-MINIA Dr. Gamal A. Sallam 1 and Dr. Medhat Aziz 2 ABSTRACT Bridges are critical structures that require a substantial investment to construct and serve an important
A STUDY OF LOCAL SCOUR AT BRIDGE PIERS OF EL-MINIA Dr. Gamal A. Sallam 1 and Dr. Medhat Aziz 2 ABSTRACT Bridges are critical structures that require a substantial investment to construct and serve an important
River Processes. Learning Objective: Discover how a river erodes, transports and deposits material
 River Processes Learning Objective: Discover how a river erodes, transports and deposits material Learning Outcomes: Compare vertical and lateral erosion Describe how a river erodes, transports and deposits
River Processes Learning Objective: Discover how a river erodes, transports and deposits material Learning Outcomes: Compare vertical and lateral erosion Describe how a river erodes, transports and deposits
Earth Science Chapter 6 Section 2 Review
 Name: Class: Date: Earth Science Chapter 6 Section Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Most streams carry the largest part of their
Name: Class: Date: Earth Science Chapter 6 Section Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Most streams carry the largest part of their
EAGLES NEST AND PIASA ISLANDS
 EAGLES NEST AND PIASA ISLANDS HABITAT REHABILITATION AND ENHANCEMENT PROJECT MADISON AND JERSEY COUNTIES, ILLINOIS ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT PROGRAM ST. LOUIS DISTRICT FACT SHEET I. LOCATION The proposed
EAGLES NEST AND PIASA ISLANDS HABITAT REHABILITATION AND ENHANCEMENT PROJECT MADISON AND JERSEY COUNTIES, ILLINOIS ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT PROGRAM ST. LOUIS DISTRICT FACT SHEET I. LOCATION The proposed
GEOMORPHIC CHANGES OF A LANDSLIDE DAM BY OVERTOPPING EROSION
 DOI: 10.4408/IJEGE.2011-03.B-087 GEOMORPHIC CHANGES OF A LANDSLIDE DAM BY OVERTOPPING EROSION K. Yoshino (*), T. Uchida (*), T. shimizu (*) & K. Tamura (*) (*) Incorporated Administrative Agency, Public
DOI: 10.4408/IJEGE.2011-03.B-087 GEOMORPHIC CHANGES OF A LANDSLIDE DAM BY OVERTOPPING EROSION K. Yoshino (*), T. Uchida (*), T. shimizu (*) & K. Tamura (*) (*) Incorporated Administrative Agency, Public
Practical Use of Deflectors in River Restoration Science Digest
 Practical Use of Deflectors in River Restoration Science Digest Aim This issue of Science Digest addresses deflectors as a practical restoration method and provides an overview of how this technique can
Practical Use of Deflectors in River Restoration Science Digest Aim This issue of Science Digest addresses deflectors as a practical restoration method and provides an overview of how this technique can
A STUDY ON DEBRIS FLOW DEPOSITION BY THE ARRANGEMENT OF SABO DAM
 Annual Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, JSCE, Vol.57, 2013, February A STUDY ON DEBRIS FLOW DEPOSITION BY THE ARRANGEMENT OF SABO DAM Namgyun Kim 1, Hajime NAKAGAWA 2, Kenji KAWAIKE 3, and Hao ZHANG 4
Annual Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, JSCE, Vol.57, 2013, February A STUDY ON DEBRIS FLOW DEPOSITION BY THE ARRANGEMENT OF SABO DAM Namgyun Kim 1, Hajime NAKAGAWA 2, Kenji KAWAIKE 3, and Hao ZHANG 4
Abstract. 1 Introduction
 One-dimensional unsteady flow computation in channels with floodplains D. Bousmar, R. Scherer & Y. Zech Civil Engineering Dept., Universite Catholique de Louvain, Place du Levant, 1, B-1348 Louvain-la-Neuve,
One-dimensional unsteady flow computation in channels with floodplains D. Bousmar, R. Scherer & Y. Zech Civil Engineering Dept., Universite Catholique de Louvain, Place du Levant, 1, B-1348 Louvain-la-Neuve,
Countermeasures for Preserving Riverine Tidal Flats in a Ship-Bottom Shaped Channel of the Lower Ota River Floodway
 ICHE 214, Hamburg - Lehfeldt & Kopmann (eds) - 214 Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-939232-8 Countermeasures for Preserving Riverine Tidal Flats in a Ship-Bottom Shaped Channel of the Lower Ota River
ICHE 214, Hamburg - Lehfeldt & Kopmann (eds) - 214 Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-939232-8 Countermeasures for Preserving Riverine Tidal Flats in a Ship-Bottom Shaped Channel of the Lower Ota River
Morphodynamic effects of stone and wooden groynes in a restored river reach
 Morphodynamic effects of stone and wooden groynes in a restored river reach Bahaeldeen Zaid 1,*, Paride Nardone 1, Michael Nones 2, Christoph Gerstgraser 3 and Katinka Koll 1 1 Leichtweiß-Institute for
Morphodynamic effects of stone and wooden groynes in a restored river reach Bahaeldeen Zaid 1,*, Paride Nardone 1, Michael Nones 2, Christoph Gerstgraser 3 and Katinka Koll 1 1 Leichtweiß-Institute for
Growing and decaying processes and resistance of sand waves in the vicinity of the Tone River mouth
 Advances in River Sediment Research Fukuoka et al. (eds) 2013 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-00062-9 Growing and decaying processes and resistance of sand waves in the vicinity of the Tone
Advances in River Sediment Research Fukuoka et al. (eds) 2013 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-00062-9 Growing and decaying processes and resistance of sand waves in the vicinity of the Tone
Numerical scour modeling around parallel spur dikes in FLOW-3D
 Drink. Water Eng. Sci. Discuss., https://doi.org/.194/dwes-2017-21 Numerical scour modeling around parallel spur dikes in FLOW-3D Hanif Pourshahbaz 1, Saeed Abbasi 1, Poorya Taghvaei 2 1. Department of
Drink. Water Eng. Sci. Discuss., https://doi.org/.194/dwes-2017-21 Numerical scour modeling around parallel spur dikes in FLOW-3D Hanif Pourshahbaz 1, Saeed Abbasi 1, Poorya Taghvaei 2 1. Department of
THE EFFECT OF THICKNESS OF PILLAR IN THE CHANNEL BEND TO CHANGES THE COEFFICIENT OF SUPERELEVATION
 Journal Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 11, No. 5 (2016) 745-754 School Engineering, Taylor s University THE EFFECT OF THICKNESS OF PILLAR IN THE CHANNEL BEND TO CHANGES THE COEFFICIENT OF SUPERELEVATION
Journal Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 11, No. 5 (2016) 745-754 School Engineering, Taylor s University THE EFFECT OF THICKNESS OF PILLAR IN THE CHANNEL BEND TO CHANGES THE COEFFICIENT OF SUPERELEVATION
Possibility of Reducing Sedimentation at Lateral Diversion
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Annals of Biological Research, 212, 3 (5):2545-2554 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 976-1233 CODEN (USA): ABRNBW Possibility of
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Annals of Biological Research, 212, 3 (5):2545-2554 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 976-1233 CODEN (USA): ABRNBW Possibility of
STUDY OF THE TRANSVERSE BED TOPOGRAPHY AT BENDS OF THE ALLUVIAL RIVERS
 Seventh International Water Technology Conference Egypt 1-3 April 2003 STDY OF TE TRANSVERSE BED TOPOGRAPY AT BENDS OF TE ALLVIAL RIVERS Kassem Salah Abdel Wahab El-Alfy Associate Prof., Irrigation and
Seventh International Water Technology Conference Egypt 1-3 April 2003 STDY OF TE TRANSVERSE BED TOPOGRAPY AT BENDS OF TE ALLVIAL RIVERS Kassem Salah Abdel Wahab El-Alfy Associate Prof., Irrigation and
Flow and Bed Topography in a 180 Curved Channel
 Flow and Bed Topography in a 180 Curved Channel Jae Wook Jung 1, Sei Eui Yoon 2 Abstract The characteristics of flow and bed topography has been analyzed by changing the bed materials in a 180-degree,
Flow and Bed Topography in a 180 Curved Channel Jae Wook Jung 1, Sei Eui Yoon 2 Abstract The characteristics of flow and bed topography has been analyzed by changing the bed materials in a 180-degree,
Effect of Pipeline Orientation on Scour Mechanism in Unidirectional Steady Flow
 Proceedings of 2013 IAHR World Congress Effect of Pipeline Orientation on Scour Mechanism in Unidirectional Steady Flow Mohd. Azlan Mohd Yusoff 1*, Hazi Md. Azamathulla 1, Zorkeflee Abu Hasan 1, Nor Azazi
Proceedings of 2013 IAHR World Congress Effect of Pipeline Orientation on Scour Mechanism in Unidirectional Steady Flow Mohd. Azlan Mohd Yusoff 1*, Hazi Md. Azamathulla 1, Zorkeflee Abu Hasan 1, Nor Azazi
EFFECT OF STREAM-WISE SPACING OF BRIDGE PIERS ON SCOUR DEPTH
 EFFECT OF STREAM-WISE SPACING OF BRIDGE PIERS ON SCOUR DEPTH ASHISH KUMAR Ph. D. Student UMESH C. KOTHYARI Professor Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, (formerly: University
EFFECT OF STREAM-WISE SPACING OF BRIDGE PIERS ON SCOUR DEPTH ASHISH KUMAR Ph. D. Student UMESH C. KOTHYARI Professor Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, (formerly: University
Upper Mississippi River Basin Environmental Management Program Workshop
 Presentation to the Upper Mississippi River Basin Environmental Management Program Workshop by Michael Rodgers River Engineer US Army Corps of Engineers, St. Louis District August 17, 2007 Engineering
Presentation to the Upper Mississippi River Basin Environmental Management Program Workshop by Michael Rodgers River Engineer US Army Corps of Engineers, St. Louis District August 17, 2007 Engineering
Experimental Study on the Flow Characteristics of ㄱ -Type Groyne
 Engineering, 2011, 3, 1002-1011 doi:1236/eng.2011.310124 Published Online October 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/eng) Experimental Study on the Flow Characteristics of ㄱ -Type Groyne Abstract Joongu
Engineering, 2011, 3, 1002-1011 doi:1236/eng.2011.310124 Published Online October 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/eng) Experimental Study on the Flow Characteristics of ㄱ -Type Groyne Abstract Joongu
HAW CREEK, PIKE COUNTY, MISSOURI-TRIB TO SALT RIVER ERODING STREAM THREATHENING COUNTY ROAD #107, FOURTEEN FT TALL ERODING BANK WITHIN 4 FT OF THE
 HAW CREEK, PIKE COUNTY, MISSOURI-TRIB TO SALT RIVER ERODING STREAM THREATHENING COUNTY ROAD #107, FOURTEEN FT TALL ERODING BANK WITHIN 4 FT OF THE ROAD, PROJECT CONSTRUCTED IN 1 DAY, MARCH 10, 2009 BY
HAW CREEK, PIKE COUNTY, MISSOURI-TRIB TO SALT RIVER ERODING STREAM THREATHENING COUNTY ROAD #107, FOURTEEN FT TALL ERODING BANK WITHIN 4 FT OF THE ROAD, PROJECT CONSTRUCTED IN 1 DAY, MARCH 10, 2009 BY
Visualization of Shear Layers in Compound Channel Flows
 Visualization of Shear Layers in Compound Channel Flows Saad Mulahasan*, Professor Thorsten Stoesser and Fernando Alvarez Hydro-environmental Research Centre, School of Engineering, Cardiff University,
Visualization of Shear Layers in Compound Channel Flows Saad Mulahasan*, Professor Thorsten Stoesser and Fernando Alvarez Hydro-environmental Research Centre, School of Engineering, Cardiff University,
VARIATION OF MANNING S ROUGHNESS COEFFICIENT WITH SEEPAGE IN SAND-BED CHANNEL *Satish Patel 1 and Bimlesh Kumar 2
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 6, 2016, 3678 3685 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) VARIATION OF MANNING S ROUGHNESS COEFFICIENT WITH SEEPAGE IN SAND-BED CHANNEL
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 6, 2016, 3678 3685 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) VARIATION OF MANNING S ROUGHNESS COEFFICIENT WITH SEEPAGE IN SAND-BED CHANNEL
CHANGES IN RIVER BED AROUND THE FUKAWA CONTRACTION AREA BY FLOODS AND CHANNEL IMPROVEMENT WORKS IN THE LOWER TONE RIVER
 The 1 th Int. Conf. on Hydroscience and Engineering (ICHE-212), Nov. 4 Nov. 7, Orlando, USA 1 CHANGES IN RIVER BED AROUND THE FUKAWA CONTRACTION AREA BY FLOODS AND CHANNEL IMPROVEMENT WORKS IN THE LOWER
The 1 th Int. Conf. on Hydroscience and Engineering (ICHE-212), Nov. 4 Nov. 7, Orlando, USA 1 CHANGES IN RIVER BED AROUND THE FUKAWA CONTRACTION AREA BY FLOODS AND CHANNEL IMPROVEMENT WORKS IN THE LOWER
Transactions on Engineering Sciences vol 9, 1996 WIT Press, ISSN
 A study of turbulence characteristics in open channel transitions as a function of Froude and Reynolds numbers using Laser technique M.I.A. El-shewey, S.G. Joshi Department of Civil Engineering, Indian
A study of turbulence characteristics in open channel transitions as a function of Froude and Reynolds numbers using Laser technique M.I.A. El-shewey, S.G. Joshi Department of Civil Engineering, Indian
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF EROSION PROCESSES ON CROSSBAR BLOCK RAMPS
 E-proceedings of the 36 th IAHR World Congress NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF EROSION PROCESSES ON CROSSBAR BLOCK RAMPS MARIO OERTEL (1), JAN P. BALMES (2), DANIEL B. BUNG (3) (1) Hydraulic Engineering Section,
E-proceedings of the 36 th IAHR World Congress NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF EROSION PROCESSES ON CROSSBAR BLOCK RAMPS MARIO OERTEL (1), JAN P. BALMES (2), DANIEL B. BUNG (3) (1) Hydraulic Engineering Section,
Effect of River Levee with Geosynthetic- Reinforced Soil against Overflow Erosion and Infiltration
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU International Symposium on Hydraulic Structures Jun 28th, 4:00 PM - 6:00 PM Effect of River Levee with Geosynthetic- Reinforced Soil against Overflow Erosion and
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU International Symposium on Hydraulic Structures Jun 28th, 4:00 PM - 6:00 PM Effect of River Levee with Geosynthetic- Reinforced Soil against Overflow Erosion and
Model experiments: Influence of floods on sediment deposits in rivers equipped with groynes
 Model experiments: Influence of floods on sediment deposits in rivers equipped with groynes H. Friedrich, B.W. Melville The University of Auckland, New Zealand R. Gasset Ecole Nationale des Travaux Publics
Model experiments: Influence of floods on sediment deposits in rivers equipped with groynes H. Friedrich, B.W. Melville The University of Auckland, New Zealand R. Gasset Ecole Nationale des Travaux Publics
Rock Sizing for Multi-Pipe & Culvert Outlets
 Rock Sizing for Multi-Pipe & Culvert Outlets STORMWATER AND WATERWAY MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Rock pad outlet structure at end of a duel stormwater pipe outlet Photo 2 Rock pad outlet structure at
Rock Sizing for Multi-Pipe & Culvert Outlets STORMWATER AND WATERWAY MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Rock pad outlet structure at end of a duel stormwater pipe outlet Photo 2 Rock pad outlet structure at
Erosion Rate is a Function of Erodibility and Excess Shear Stress = k ( o - c ) From Relation between Shear Stress and Erosion We Calculate c and
 Equilibrium, Shear Stress, Stream Power and Trends of Vertical Adjustment Andrew Simon USDA-ARS, Oxford, MS asimon@msa-oxford.ars.usda.gov Non-Cohesive versus Cohesive Materials Non-cohesive: sands and
Equilibrium, Shear Stress, Stream Power and Trends of Vertical Adjustment Andrew Simon USDA-ARS, Oxford, MS asimon@msa-oxford.ars.usda.gov Non-Cohesive versus Cohesive Materials Non-cohesive: sands and
Habitat Assessment. Peggy Compton UW-Extension Water Action Volunteers Program Coordinator
 Habitat Assessment Peggy Compton UW-Extension Water Action Volunteers Program Coordinator Adapted from a presentation by Jean Unmuth, Water Quality Biologist, WI DNR dnr.wi.gov www.uwex.edu erc.cals.wisc.edu
Habitat Assessment Peggy Compton UW-Extension Water Action Volunteers Program Coordinator Adapted from a presentation by Jean Unmuth, Water Quality Biologist, WI DNR dnr.wi.gov www.uwex.edu erc.cals.wisc.edu
Pirai river (Bolivia)
 Pirai river (Bolivia) Confluent of the Amazon river which average discharge is only 6 m3/s, but with peak discharge over 5000 m3/s, a challenge for river basin management and for flood control HYDROEUROPE
Pirai river (Bolivia) Confluent of the Amazon river which average discharge is only 6 m3/s, but with peak discharge over 5000 m3/s, a challenge for river basin management and for flood control HYDROEUROPE
Project (Project No. US-CA-62-2) Maintenance Inspection and Reports (Subtask 14.1) Inspection Report No.2
 MEMORANDUM TO: FROM: Jim Well, Ducks Unlimited Mike Harvey, PhD, PG SUBJECT: M&T/ Llano Seco Fish Screen Project (Project No. US-CA-62-2) Maintenance Inspection and Reports (Subtask 14.1) Inspection Report
MEMORANDUM TO: FROM: Jim Well, Ducks Unlimited Mike Harvey, PhD, PG SUBJECT: M&T/ Llano Seco Fish Screen Project (Project No. US-CA-62-2) Maintenance Inspection and Reports (Subtask 14.1) Inspection Report
A STUDY ON DEBRIS FLOW OUTFLOW DISCHARGE AT A SERIES OF SABO DAMS
 A STUDY ON DEBRIS FLOW OUTFLOW DISCHARGE AT A SERIES OF SABO DAMS Namgyun KIM *, Hajime NAKAGAWA **, Kenji KAWAIKE *** and Hao ZHANG **** Abstract Debris flows are very dangerous phenomena in mountainous
A STUDY ON DEBRIS FLOW OUTFLOW DISCHARGE AT A SERIES OF SABO DAMS Namgyun KIM *, Hajime NAKAGAWA **, Kenji KAWAIKE *** and Hao ZHANG **** Abstract Debris flows are very dangerous phenomena in mountainous
Important Copyright Information
 Important Copyright Information The following content is provided for educational purposes by the workshop presenter. This content may or may not have been peer reviewed. Information, opinions and recommendations
Important Copyright Information The following content is provided for educational purposes by the workshop presenter. This content may or may not have been peer reviewed. Information, opinions and recommendations
Experimental Study on Effect of Houses on Debris-Flow Flooding and Deposition in Debris Flow Fan Areas
 DATA ACQUISITION AND MODELLING (MONITORING, PROCESSES, TECHNOLOGIES, MODELS) Experimental Study on Effect of Houses on Debris-Flow Flooding and Deposition in Debris Flow Fan Areas Kana Nakatani, Dr. 1
DATA ACQUISITION AND MODELLING (MONITORING, PROCESSES, TECHNOLOGIES, MODELS) Experimental Study on Effect of Houses on Debris-Flow Flooding and Deposition in Debris Flow Fan Areas Kana Nakatani, Dr. 1
Experimental Study on the Performance of Slope-crested
 J. JSNDS 37 93-105 2018 Experimental Study on the Performance of Slope-crested Groynes in Erodible Meandering Channels of Different Sinuosity Saroj KARKI 1, Hajime NAKAGAWA 2, Kenji KAWAIKE 3 and Masakazu
J. JSNDS 37 93-105 2018 Experimental Study on the Performance of Slope-crested Groynes in Erodible Meandering Channels of Different Sinuosity Saroj KARKI 1, Hajime NAKAGAWA 2, Kenji KAWAIKE 3 and Masakazu
LAB-SCALE INVESTIGATION ONBAR FORMATION COORDINATES IN RIVER BASED ON FLOW AND SEDIMENT
 LAB-SCALE INVESTIGATION ONBAR FORMATION COORDINATES IN RIVER BASED ON FLOW AND SEDIMENT Mat Salleh M. Z., Ariffin J., Mohd-Noor M. F. and Yusof N. A. U. Faculty of Civil Engineering, University Technology
LAB-SCALE INVESTIGATION ONBAR FORMATION COORDINATES IN RIVER BASED ON FLOW AND SEDIMENT Mat Salleh M. Z., Ariffin J., Mohd-Noor M. F. and Yusof N. A. U. Faculty of Civil Engineering, University Technology
Discharge. Discharge (Streamflow) is: Q = Velocity (L T -1 ) x Area (L 2 ) Units: L 3 T -1 e.g., m 3 s -1. Velocity. Area
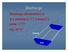 Discharge Discharge (Streamflow) is: Q = Velocity (L T -1 ) x Area (L 2 ) Units: L 3 T -1 e.g., m 3 s -1 Velocity Area Where is the average velocity?? 3 Source: Brooks et al., Hydrology and the Management
Discharge Discharge (Streamflow) is: Q = Velocity (L T -1 ) x Area (L 2 ) Units: L 3 T -1 e.g., m 3 s -1 Velocity Area Where is the average velocity?? 3 Source: Brooks et al., Hydrology and the Management
USE OF DOWNSTREAM-FACING AEROFOIL-SHAPED BRIDGE PIERS TO REDUCE LOCAL SCOUR
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (IJCIET) International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET), ISSN 0976 6308 (Print), ISSN 0976 6308 (Print) ISSN 0976 6316(Online)
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (IJCIET) International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET), ISSN 0976 6308 (Print), ISSN 0976 6308 (Print) ISSN 0976 6316(Online)
NATURAL RIVER. Karima Attia Nile Research Institute
 NATURAL RIVER CHARACTERISTICS Karima Attia Nile Research Institute NATURAL RIVER DEFINITION NATURAL RIVER DEFINITION Is natural stream of water that flows in channels with ih more or less defined banks.
NATURAL RIVER CHARACTERISTICS Karima Attia Nile Research Institute NATURAL RIVER DEFINITION NATURAL RIVER DEFINITION Is natural stream of water that flows in channels with ih more or less defined banks.
GEOMETRY EFFECT ON FLOW AND SEDIMENT DEPOSITION PATTERNS IN SHALLOW BASINS
 Annual Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, JSCE, Vol.54, 21, February GEOMETRY EFFECT ON FLOW AND SEDIMENT DEPOSITION PATTERNS IN SHALLOW BASINS Sameh A. KANTOUSH 1, Tetsuya SUMI 2 and Anton J. SCHLEISS
Annual Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, JSCE, Vol.54, 21, February GEOMETRY EFFECT ON FLOW AND SEDIMENT DEPOSITION PATTERNS IN SHALLOW BASINS Sameh A. KANTOUSH 1, Tetsuya SUMI 2 and Anton J. SCHLEISS
Evaluation of flood discharge hydrographs and bed variations in a channel network on the Ota River delta, Japan
 3 Floods: From Risk to Opportunity (IAHS Publ. 357, 3). Evaluation of flood discharge hydrographs and bed variations in a channel network on the Ota River delta, Japan T. GOTOH, S. FUKUOKA & R. TANAKA
3 Floods: From Risk to Opportunity (IAHS Publ. 357, 3). Evaluation of flood discharge hydrographs and bed variations in a channel network on the Ota River delta, Japan T. GOTOH, S. FUKUOKA & R. TANAKA
Flow Field Investigation in a Rectangular Shallow Reservoir using UVP, LSPIV and numerical model
 Flow Field Investigation in a Rectangular Shallow Reservoir using UVP, LSPIV and numerical model S AMEH KANTOUSH, ERIK BOLLAERT, GIOVANNI DE CESARE, JEAN-LOUIS BOILLAT and ANTON SCHLEISS Ecole Polytechnique
Flow Field Investigation in a Rectangular Shallow Reservoir using UVP, LSPIV and numerical model S AMEH KANTOUSH, ERIK BOLLAERT, GIOVANNI DE CESARE, JEAN-LOUIS BOILLAT and ANTON SCHLEISS Ecole Polytechnique
Erosion Surface Water. moving, transporting, and depositing sediment.
 + Erosion Surface Water moving, transporting, and depositing sediment. + Surface Water 2 Water from rainfall can hit Earth s surface and do a number of things: Slowly soak into the ground: Infiltration
+ Erosion Surface Water moving, transporting, and depositing sediment. + Surface Water 2 Water from rainfall can hit Earth s surface and do a number of things: Slowly soak into the ground: Infiltration
The impact of vegetation on the characteristics of the flow in an inclined open channel using the piv method
 Water Resources and Ocean Science 2012;1(1):1-6 Published online December 30, 2012 (http:// www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/wors) doi:.11648/j.wors.201201.11 The impact of vegetation on the characteristics
Water Resources and Ocean Science 2012;1(1):1-6 Published online December 30, 2012 (http:// www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/wors) doi:.11648/j.wors.201201.11 The impact of vegetation on the characteristics
The Upper Course of a River
 The Upper Course of a River I. Introduction A river is split along the long profile into three different sections; the upper, middle and lower course. As GCSE students you are expected to know the characteristics
The Upper Course of a River I. Introduction A river is split along the long profile into three different sections; the upper, middle and lower course. As GCSE students you are expected to know the characteristics
Waterbury Dam Disturbance Mike Fitzgerald Devin Rowland
 Waterbury Dam Disturbance Mike Fitzgerald Devin Rowland Abstract The Waterbury Dam was completed in October 1938 as a method of flood control in the Winooski Valley. The construction began in April1935
Waterbury Dam Disturbance Mike Fitzgerald Devin Rowland Abstract The Waterbury Dam was completed in October 1938 as a method of flood control in the Winooski Valley. The construction began in April1935
Beaver Creek Corridor Design and Analysis. By: Alex Previte
 Beaver Creek Corridor Design and Analysis By: Alex Previte Overview Introduction Key concepts Model Development Design Accuracy Conclusion Refresh v = Beaver Creek Site = Wittenberg Introduction Low head
Beaver Creek Corridor Design and Analysis By: Alex Previte Overview Introduction Key concepts Model Development Design Accuracy Conclusion Refresh v = Beaver Creek Site = Wittenberg Introduction Low head
2016 International Conference on Civil, Structure, Environmental Engineering (I3CSEE 2016)
 Solid model test on Daijiazhou reach of administering project for improving the channel standard of the section of Yangtze River between Yichang and Anqing Hui Zhang 1, a, Huiyun Li 1,b 1 River Research
Solid model test on Daijiazhou reach of administering project for improving the channel standard of the section of Yangtze River between Yichang and Anqing Hui Zhang 1, a, Huiyun Li 1,b 1 River Research
MEANDER MIGRATION MODEL ASSESSMENT FOR THE JANUARY 2005 STORM, WHITMAN PROPERTY, SAN ANTONIO CREEK, VENTURA COUNTY, CALIFORNIA
 MEANDER MIGRATION MODEL ASSESSMENT FOR THE JANUARY 2005 STORM, WHITMAN PROPERTY, SAN ANTONIO CREEK, VENTURA COUNTY, CALIFORNIA Prepared by Eric Larsen, Ph.D. Mark Rains, Ph.D. October 2006 INTRODUCTION
MEANDER MIGRATION MODEL ASSESSMENT FOR THE JANUARY 2005 STORM, WHITMAN PROPERTY, SAN ANTONIO CREEK, VENTURA COUNTY, CALIFORNIA Prepared by Eric Larsen, Ph.D. Mark Rains, Ph.D. October 2006 INTRODUCTION
Hydraulics Prof. Dr. Arup Kumar Sarma Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Hydraulics Prof. Dr. Arup Kumar Sarma Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module No. # 04 Gradually Varied Flow Lecture No. # 07 Rapidly Varied Flow: Hydraulic Jump
Hydraulics Prof. Dr. Arup Kumar Sarma Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module No. # 04 Gradually Varied Flow Lecture No. # 07 Rapidly Varied Flow: Hydraulic Jump
SEDIMENTATION AND ITS COUNTERMEASURE AT THE OFF-TAKE AREA OF NEW DHALESWARI RIVER
 SEDIMENTATION AND ITS COUNTERMEASURE AT THE OFF-TAKE AREA OF NEW DHALESWARI RIVER Tanjir Saif AHMED* MEE15634 Supervisors: Prof. EGASHIRA Shinji** Assoc. Prof. YOROZUYA Atsuhiro*** ABSTRACT Present study
SEDIMENTATION AND ITS COUNTERMEASURE AT THE OFF-TAKE AREA OF NEW DHALESWARI RIVER Tanjir Saif AHMED* MEE15634 Supervisors: Prof. EGASHIRA Shinji** Assoc. Prof. YOROZUYA Atsuhiro*** ABSTRACT Present study
Application of Energy Approach to Estimating Scour Depth
 Nature and Science, (), 004, Zhang, et al, Application of Energy Approach Application of Energy Approach to Estimating Scour Depth Xiaodong Zhang 1, Zhiping Liu 1, Chuan Liang, Qiang Fu 3 (1. IWHR, Beijing
Nature and Science, (), 004, Zhang, et al, Application of Energy Approach Application of Energy Approach to Estimating Scour Depth Xiaodong Zhang 1, Zhiping Liu 1, Chuan Liang, Qiang Fu 3 (1. IWHR, Beijing
Evaluation of Scour Depth around Bridge Piers with Various Geometrical Shapes
 Evaluation of Scour Depth around Bridge Piers with Various Geometrical Shapes Dr. P. D. Dahe * Department of Civil Engineering, SGGSIE&T, Vishnupuri, Nanded (Maharashtra) S. B. Kharode Department of Civil
Evaluation of Scour Depth around Bridge Piers with Various Geometrical Shapes Dr. P. D. Dahe * Department of Civil Engineering, SGGSIE&T, Vishnupuri, Nanded (Maharashtra) S. B. Kharode Department of Civil
An environmentally sensitive erosion control technique in the Mekong River Delta: 10 years on
 7 th Australian Stream Management Conference - Full Paper An environmentally sensitive erosion control technique in the Mekong River Delta: 10 years on John Tilleard 1, Tony Ladson 2 1 Moroka Pty Ltd,
7 th Australian Stream Management Conference - Full Paper An environmentally sensitive erosion control technique in the Mekong River Delta: 10 years on John Tilleard 1, Tony Ladson 2 1 Moroka Pty Ltd,
Prediction of landslide-induced debris flow hydrograph: the Atsumari debris flow disaster in Japan
 Monitoring, Simulation, Prevention and Remediation of Dense and Debris Flows 27 Prediction of landslide-induced debris flow hydrograph: the Atsumari debris flow disaster in Japan H. Takaoka 1, H. Hashimoto
Monitoring, Simulation, Prevention and Remediation of Dense and Debris Flows 27 Prediction of landslide-induced debris flow hydrograph: the Atsumari debris flow disaster in Japan H. Takaoka 1, H. Hashimoto
WORKSHOP #2 [Modeling and Sediment Transfers Review of alternative solutions] Bucharest 07 October 2015
![WORKSHOP #2 [Modeling and Sediment Transfers Review of alternative solutions] Bucharest 07 October 2015 WORKSHOP #2 [Modeling and Sediment Transfers Review of alternative solutions] Bucharest 07 October 2015](/thumbs/82/85703998.jpg) STUDIU DE FEZABILITATE PENTRU SOLUŢII TEHNICE ALTERNATIVE/COMPLEMENTARE PRIVIND LUCRĂRILE CE SE VOR EXECUTA ÎN PUNCTUL CRITIC 01 BALA DIN CADRUL PROIECTULUI ÎMBUNĂTĂŢIREA CONDIŢIILOR DE NAVIGAŢIE PE DUNĂRE
STUDIU DE FEZABILITATE PENTRU SOLUŢII TEHNICE ALTERNATIVE/COMPLEMENTARE PRIVIND LUCRĂRILE CE SE VOR EXECUTA ÎN PUNCTUL CRITIC 01 BALA DIN CADRUL PROIECTULUI ÎMBUNĂTĂŢIREA CONDIŢIILOR DE NAVIGAŢIE PE DUNĂRE
COMPARISON OF LABORATORY AND FIELD MEASUREMENTS OF BRIDGE PIER SCOUR
 COMPARISON OF LABORATORY AND FIELD MEASUREMENTS OF BRIDGE PIER SCOUR LEE, SEUNGOH, STURM, T. W., School of Civil and Environ. Engrg., Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA 30332-0512 USA GOTVALD,
COMPARISON OF LABORATORY AND FIELD MEASUREMENTS OF BRIDGE PIER SCOUR LEE, SEUNGOH, STURM, T. W., School of Civil and Environ. Engrg., Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA 30332-0512 USA GOTVALD,
GEOL 652. Poudre River Fieldtrip
 GEOL 652. Poudre River Fieldtrip One of the more difficult variables to measure and/or estimate when studying flow in natural channels is that of roughness. Roughness, usually approximated with Manning
GEOL 652. Poudre River Fieldtrip One of the more difficult variables to measure and/or estimate when studying flow in natural channels is that of roughness. Roughness, usually approximated with Manning
CliffsNotes.com. Stream Erosion. 18 Oct 2012 < ,articleId 9511.html>.
 I. Introduction What is your science question? Is there a relationship between local base plateau elevation and depth, width, and length of channels within them? Why is this question important and interesting?
I. Introduction What is your science question? Is there a relationship between local base plateau elevation and depth, width, and length of channels within them? Why is this question important and interesting?
4. The map below shows a meandering stream. Points A, B, C, and D represent locations along the stream bottom.
 1. Sediment is deposited as a river enters a lake because the A) velocity of the river decreases B) force of gravity decreases C) volume of water increases D) slope of the river increases 2. Which diagram
1. Sediment is deposited as a river enters a lake because the A) velocity of the river decreases B) force of gravity decreases C) volume of water increases D) slope of the river increases 2. Which diagram
What is weathering and how does it change Earth s surface? Answer the question using
 7 th Grade Lesson What is weathering and how does it change Earth s surface? Answer the question using the sentence frame. You have 4 minutes. Weathering is. This changes the Earth s surface because. 1
7 th Grade Lesson What is weathering and how does it change Earth s surface? Answer the question using the sentence frame. You have 4 minutes. Weathering is. This changes the Earth s surface because. 1
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) Which event is the best example of erosion? dissolving of rock particles on a limestone gravestone by acid rain breaking apart of shale as a result of water freezing in a crack rolling of a pebble
Name: 1) Which event is the best example of erosion? dissolving of rock particles on a limestone gravestone by acid rain breaking apart of shale as a result of water freezing in a crack rolling of a pebble
LATERAL MIGRATION of ALLUVIAL CHANNELS
 LATERAL MIGRATION of ALLUVIAL CHANNELS Pierre Y. Julien Colorado State University Santiago del Estero, Argentina November 2011 1 1 Objectives Discuss the lateral migration of alluvial channels and provide
LATERAL MIGRATION of ALLUVIAL CHANNELS Pierre Y. Julien Colorado State University Santiago del Estero, Argentina November 2011 1 1 Objectives Discuss the lateral migration of alluvial channels and provide
This is a refereed journal and all articles are professionally screened and reviewed
 Advances in Environmental Biology, 7(9): 2283-2292, 2013 ISSN 1995-0756 2283 This is a refereed journal and all articles are professionally screened and reviewed ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effects of submerged
Advances in Environmental Biology, 7(9): 2283-2292, 2013 ISSN 1995-0756 2283 This is a refereed journal and all articles are professionally screened and reviewed ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effects of submerged
Flood risk analysis toward floodplain risk management
 Floods, from Defence to Management Van Alphen, van Beek & Taal (eds) 2006 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 0 415 39119 9 Flood risk analysis toward floodplain risk management H. Kawaguchi, T. Suetsugi
Floods, from Defence to Management Van Alphen, van Beek & Taal (eds) 2006 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 0 415 39119 9 Flood risk analysis toward floodplain risk management H. Kawaguchi, T. Suetsugi
GEOMORPHIC CHANGES IN LOWER CACHE CREEK 2012
 GEOMORPHIC CHANGES IN LOWER CACHE CREEK 2012 Eric W. Larsen Technical Memorandum Prepared for Cache Creek Technical Advisory Committee Natural Resources Program Yolo County Board of Supervisors 2012 Prepared
GEOMORPHIC CHANGES IN LOWER CACHE CREEK 2012 Eric W. Larsen Technical Memorandum Prepared for Cache Creek Technical Advisory Committee Natural Resources Program Yolo County Board of Supervisors 2012 Prepared
