Pinellas, Manatee, and Sarasota Counties, Florida; Regional Sediment Budget
|
|
|
- August Morgan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
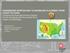
1 Pinellas, Manatee, and Sarasota Counties, Florida; Regional Sediment Budget by Kelly R. Legault and Ashley E. Frey PURPOSE: This U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) Regional Sediment Management Technical Note (RSM-TN) describes the regionalization of a sediment budget spanning three counties over 70 miles of coastline using two lidar surveys obtained by the USACE Joint Airborne Lidar Bathymetric Technical Center of Expertise. Volume change was determined between the first lidar survey during June 2006 and the second lidar survey during July The study area comprises the three counties of Pinellas, Manatee, and Sarasota, along the Gulf Coast shoreline of southwest Florida in the USACE Jacksonville District (SAJ) (Figure 1). Figure 1. Study area comprising shorelines of Pinellas, Manatee, and Sarasota Counties, along southwest Florida Gulf of Mexico. The region includes the entire shoreline from Clearwater Beach in Pinellas County to Venice Beach in Sarasota County, FL (Figure 2). Active projects in the study region include the Pinellas County Shore Protection Project (SPP) (USACE 2010), Tampa Harbor Navigation Project (deep draft), the Gulf Intracoastal Waterway (GIWW), Manatee County SPP at Anna Maria Island, the City of Sarasota SPP at Lido Key, Sarasota County SPP at Venice Beach, and a number of federally authorized navigation channels. Local projects exist as well at Longboat Key and at Siesta Key. This study was supported by the SAJ and the U.S. Army Engineer Research and Development Center through the USACE Regional Sediment Management (RSM) Program. Regional Sediment Management: Integrated Solutions for Sediment Related Challenges Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.
2 Figure 2. Sediment budget extent and active USACE Jacksonville District (SAJ) projects in Pinellas, Manatee, and Sarasota Counties, Florida. INTRODUCTION: The southwest Gulf Coast of Florida consists of a barrier island system that has been under development since the early 1900s. At present, most of the shoreline is considered to be urban. It is directly under the influence of past and present anthropogenic activities including dredging of the passes that connect the Gulf of Mexico to back bays including Boca Ciega, Tampa Bay, and Sarasota Bay, as well as dredging of the GIWW. Additionally, placement of material from the passes and from offshore sources onto the beach has been in practice for well over 50 years. As a result of the severe hurricane seasons of 2004 and 2005, most of the beaches in Pinellas, Manatee, and Sarasota Counties were nourished from 2005 to Several sediment budgets have been developed for Pinellas County (Roberts 2012) and for Manatee and Sarasota Counties (Coastal Planning & Engineering [now CBI Industries, Inc.] 2011; Coastal Technology Corporation et al. 2010). It was the objective of this study to create a sediment budget for the entire 70-mile region of shoreline from synoptic lidar measurements. Treatment of the lidar data is described by Legault (2016a). The entire extent of this new sediment budget is shown in Figure 2. The timeline for all federal project and data measurements is shown in Figure 3. 2
3 Figure 3. Timeline for federal and local shore protection projects, lidar acquisition, and beach profile measurements. ERDC/TN RSM
4 METHOD: The region of shoreline spanning Pinellas, Manatee, and Sarasota Counties includes several federal and local projects to improve navigation and to provide storm damage reduction along the shoreline beaches. The accounting and disparate analyses of such a number of projects warranted an RSM approach to determine the best sediment management practices and to examine the system holistically. The unprecedented hurricane season of 2004 and 2005, and the ensuing engineering projects spanning from 2005 to 2009, brought about a fundamental need to update the sediment budget for the entire region for the post-hurricane epoch of using synoptically acquired lidar data. Two lidar surveys acquired over the southwest Gulf Coast including Pinellas, Manatee, and Sarasota Counties were analyzed to determine volume change over the 70-mile region between the first lidar survey of June 2006 and the second lidar survey of July The treatment of the lidar data is explained by Legault (2016a). Results from the volumetric analysis were further analyzed using the Surface-water Modeling System (Aquaveo 2013) and Microsoft Excel. It was assumed that in Pinellas County a longshore sediment transport node (divergence zone) exists in the headland region of Indian Rocks and Indian Shores. This transport node has been well documented in previous studies (USACE 2010; Roberts 2012). The northern boundary was adjusted such that this divergence was reflected in the cumulative volume change calculations. Cumulative volume changes (spatially integrated changes) and changes in annual volume densities were calculated such that the former reveals spatial scales over which volume changes are balanced. The latter shows local changes in volume densities that are driven by a balance of anthropogenic activities, underlying morphology, and environmental forcing. RESULTS: A total of 5.7 million cubic yards (Mcy) of material was placed in Pinellas, Manatee, and Sarasota Counties during the reconstruction period, following the hurricane seasons of 2004 and Of the total, 3.9 Mcy were placed between the lidar surveys in June 2006 and July 2010 (Figure 3). This volume was removed from the volume change calculated and described by Legault (2016a). The divergent zone in Pinellas County, identified in previous studies and validated in resulting calculations by Legault (2016a), remains a fundamental feature in the littoral system that separates the littoral cells to the north and to the south. Resulting volume changes in cubic yards/year (cy/yr), cumulative volume changes (cy/yr), and volume density changes in cubic yards per foot of shoreline per year (cy/ft/yr) are shown in Figure 4a, 4b, and 4c, respectively. The overall sediment budget is shown in Figure 5 and displays volume density changes along the shoreline. The cumulative volume changes plot shows the alongshore location where the volume of sediment balances (Figure 4b). The first and most northerly location is that which was forced to be at the divergent zone at Indian Shores. Next, the volume is balanced at the north side of Johns Pass. The next location where volume is balanced is at the mouth of Tampa Bay. The region from Egmont Channel to mid-longboat Key is the next alongshore reach where volume is conserved. The last few reaches are from mid-longboat Key to the north side of New Pass, Lido Key, to the attachment point at Big Sarasota Pass, and from Siesta Key to the pier at Venice Beach. 4
5 Figure 4b Figure 4c Figures 4a: Volume changes (black bars) and sediment flux (white bars: - south; + north). Figure 4b: Cumulative volume changes (black bars) and sediment flux (white bars) to identify spatial extent and locations of volumetric balance (zero crossing). Figure 4c: Volume density changes to identify gradients in sediment volume rate of change. Adjusted for nourishment. Figure 4a ERDC/TN RSM
6 Figure 5. Southwest Florida Gulf Coast sediment budget volume density changes, adjusted for nourishment +/- cy/yr/ft. Contour colors denote volume changes (cool colors = erosion; warm colors = accretion). Developed using lidar. June 2006 July
7 The change in beach volume densities (Figure 4c and Figure 5) decreases from Clearwater Pass to the North Shore of Johns Pass, from the south shore of Johns Pass to Egmont Channel, from Egmont Key to the north shore of New Pass, from New Pass to Big Sarasota Pass, and from the attachment point of Big Sarasota Pass at Siesta Key to South Venice beach. DISCUSSION: Lidar data give the best regional picture of the change in beach volume densities than through the use of beach profiles alone, that are used at the project scale. Along this stretch of shoreline in southwest Florida, it is clear that the greatest increase in volume densities is at the attachment point of many of the passes. Interestingly, as the cumulative volume changes would show, the reaches of shoreline that span inlets are the very ones that do not bypass sediment efficiently. For example, at Longboat Pass, there is very little southerly sediment flux at present, and sediment needs to be mechanically bypassed by dredging the navigation channel and placing sediment on the beaches at Longboat Key (Coastal Planning & Engineering 2011; Legault 2016b). Similarly, at Blind Pass (a structured inlet), there is severe downdrift erosion at Upham Beach (Roberts 2012). At Venice Inlet (another structured inlet), the lack of bypassing creates the need for nourishment at Venice Beach. The remaining passes (Johns Pass, Egmont Channel, New Pass, and Big Sarasota Pass) all have robust attachment points that feed down-drift beaches. The lidar data give an overview of the major features of the system. Whereas project scale beach surveys remain the standard for the determination of exact volume of sediment required for a particular engineering project, lidar data contain valuable details regarding underlying morphology and sediment transport features. Here, there is an obvious pattern of transport repeated along the shoreline that is dictated by the efficiency with which sediment is bypassed at the passes, and by the volume and location of the attachment point of the ebb shoals. Overall, the shoals and passes are very important and govern the sediment transport system. On the project scale that often does not contain information about the adjacent passes, the picture of sediment transport is incomplete. However, through the use of lidar data, the important sediment transport features within the system become readily apparent. SEDIMENT BUDGET: A sediment budget based on the results shown in Figure 4 was developed in the Sediment Budget Analysis System (SBAS) (Rosati and Kraus 2001 [rev. 2003]). The latest version of SBAS is a Python toolbox, which is accessed through ArcCatalog within ArcGIS 10.1 or later. The sediment budget equation in SBAS is expressed as where Qsource and Qsink represent all sources and sinks to/from the control volume (cell), ΔV is the volume change within a cell, P is the volume of material placed within the cell, R is the volume of material removed from the cell, and Residual is the degree to which a cell is balanced (Rosati and Kraus 2001 [rev. 2003]). If the Residual is 0, the cell is balanced. 7
8 ERDC/TN RSM-17-2 The sediment budget for Pinellas, Manatee, and Sarasota counties is shown in Figures 6, 7, and 8. Green cells represent volume gain while red represents volume loss. Figure 6a spans from R56 to R127.5, and Figure 6b includes cells R127.5 to R13. Figure 7a includes cells R13 to R57.5 while Figure 7b spans R57.5 to R60. Cells R60 to R143 are shown in Figure 8. Sediment budgets are meant to show all information for each cell, so unlike Figure 4, nourishment and dredging (P and R) are included. Therefore, volume changes for each cell are different than Figure 4 because nourishment and dredging are accounted for in the sediment budget equation. The shorelines of Pinellas County experienced a volume gain of approximately 287,000 cy/yr. Ten cells in Pinellas County recorded a gain while six cells had a volume loss. Nearly 500,000 cy/yr of sand was placed on the beaches of Pinellas County, so the increase in volume is due to nourishment. Only two cells in Manatee County had a volume loss. Manatee County beaches gained approximately 88,000 cy/yr of sand from 2006 to Sarasota County experienced a volume loss of approximately 100,000 cy/yr; however, this is attributed to the two southernmost cells, which experienced a significant loss of volume. Many of the cells in Sarasota County had volume gains from beach nourishment activities. Figure 6a. Volume change in sediment budget cells representing R56 to R127.5; Figure 6b. Volume change in cells representing R127.5 to R13. P is Placement. 8
9 ERDC/TN RSM-17-2 Figure 7a. Volume change in sediment budget cells representing R13 to 57.5; Figure 7b. Volume change in cells representing R57.5 to R60. P is Placement. R is Removal. 9
10 Figure 8. Volume change in sediment budget cells representing R60 to R143. P is Placement. CONCLUSIONS: This RSM-TN documents the use of synoptic lidar data to develop a sediment budget along a 70-mile region of shoreline in southwest Florida. From this analysis, which gives an overview of the major features of the system, it is clear that the greatest increase in volume density is at the attachment point of many of the passes. Whereas project scale beach surveys remain the standard for the determination of the exact volume of sediment required for a project, far-reaching lidar data can offer a regional-scale view of the important sediment transport and morphologic features of the system at a scale that cannot be measured using beach profiles surveys alone. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION: This USACE Regional Sediment Management Technical Note (RSM-TN) was prepared by Kelly R. Legault, U.S. Army Engineer District, Jacksonville (SAJ), and Ashley E. Frey, U.S. Army Engineer Research and Development Center (ERDC), Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory (CHL). Funding for this study was provided by the USACE Regional 10
11 Sediment Management (RSM) Program, a Navigation Research, Development, and Technology (RD&T) Portfolio program administered by Headquarters USACE. Additional information pertaining to the RSM Program can be found at the RSM website Questions regarding this RSM-TN may be addressed to Kelly R. Legault (Kelly.R.Legault@usace.army.mil), SAJ Senior Coastal Engineer, Engineering Division. Additional information pertaining to the RSM Program can be obtained from the USACE RSM Program Manager, Linda S. Lillycrop (Linda.S.Lillycrop@usace.army.mil) This USACE Regional Sediment Management Technical Note (RSM-TN) should be cited as follows: Legault, Kelly R., and Ashley E. Frey Pinellas, Manatee, and Sarasota Counties, Florida; Regional Sediment Budget. ERDC/TN RSM Vicksburg, MS: U.S. Army Engineer Research and Development Center. REFERENCES Aquaveo Surface-water Modeling System (SMS). Version Coastal Planning & Engineering, Inc Inlet Management Study of Longboat Pass and Adjacent Beaches. Boca Raton, FL: Prepared for Manatee County and the Town of Longboat Key, FL. Coastal Technology Corporation, Coastal Engineering Consultants, and Department of Geology/University of South Florida Sarasota County Comprehensive Inlet Management Program; Big Pass and New Pass Management Alternatives. Prepared for Sarasota County, FL. Sarasota, FL: Coastal Technology Corporation. Records/Attachments/7219/ BigPass NewPass System.pdf. Legault, K. R. 2016a. Beach and Morphology Change Using LIDAR. ERDC/CHL CHETN-XIV-54. Vicksburg, MS: U.S. Army Engineer Research and Development Center. Legault, K. R. 2016b. Regional Sediment Management (RSM) Assessment of Longboat Pass, Manatee County, FL. ERDC/CHL CHETN-XIV-49. Vicksburg, MS: U.S. Army Engineer Research and Development Center. Roberts, T Natural and Anthropogenic Influences on the Morphodynamics of Sandy and Mixed Sand and Gravel Beaches. Graduate Thesis and Dissertation. Tampa, FL. University of South Florida. Rosati, J. D., and N. C. Kraus (rev. 2003). Sediment Budget Analysis System (SBAS): Upgrade for Regional Applications. ERDC/CHL CHETN-XIV-3. Vicksburg, MS: U.S. Army Engineer Research and Development Center. U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) Pinellas County, Florida Shore Protection Project: Long Key and Treasure Island Segments; 2006 Beach Nourishment. Third Annual Monitoring Report. Jacksonville, FL: U.S. Army Engineer District, Jacksonville. NOTE: The contents of this technical note are not to be used for advertising, publication, or promotional purposes. Citation of trade names does not constitute an official endorsement or approval of the use of such products. 11
Using GenCade to Create a Sediment Budget in SBAS
 Using GenCade to Create a Sediment Budget in SBAS by Ashley E. Frey PURPOSE: This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note (CHETN) presents a new connection between GenCade, a shoreline change
Using GenCade to Create a Sediment Budget in SBAS by Ashley E. Frey PURPOSE: This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note (CHETN) presents a new connection between GenCade, a shoreline change
INFLUENCE OF INLET / SHOAL COMPLEX ON ADJACENT SHORELINES VIA INLET SINK METHOD
 INFLUENCE OF INLET / SHOAL COMPLEX ON ADJACENT SHORELINES VIA INLET SINK METHOD Kelly R. Legault, Ph.D., P.E. 1, Tanya M. Beck 2 and Jason A. Engle, P.E. 3 The region of influence of the inlet on the adjacent
INFLUENCE OF INLET / SHOAL COMPLEX ON ADJACENT SHORELINES VIA INLET SINK METHOD Kelly R. Legault, Ph.D., P.E. 1, Tanya M. Beck 2 and Jason A. Engle, P.E. 3 The region of influence of the inlet on the adjacent
The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Philadelphia District
 The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Philadelphia District The Atlantic Coast of New Jersey Regional Sediment Budget 1986-2003 Cape May Point to Manasquan Inlet Final Report March 2006 The Atlantic Coast of
The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Philadelphia District The Atlantic Coast of New Jersey Regional Sediment Budget 1986-2003 Cape May Point to Manasquan Inlet Final Report March 2006 The Atlantic Coast of
Regional Sediment Management at East Rockaway Inlet, NY, Utilizing the USACE Coastal Modeling System
 Regional Sediment Management at East Rockaway Inlet, NY, Utilizing the USACE Coastal Modeling System by US Army Engineer District, New York PURPOSE: This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note
Regional Sediment Management at East Rockaway Inlet, NY, Utilizing the USACE Coastal Modeling System by US Army Engineer District, New York PURPOSE: This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note
Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory
 ERDC/CHL TR-12-14 Coastal Inlets Research Program Optimization of Ebb Shoal Mining and Beach Nourishment at St. Johns County, St. Augustine Inlet, Florida Report 3 Tanya M. Beck and Kelly Legault August
ERDC/CHL TR-12-14 Coastal Inlets Research Program Optimization of Ebb Shoal Mining and Beach Nourishment at St. Johns County, St. Augustine Inlet, Florida Report 3 Tanya M. Beck and Kelly Legault August
Sediment Budget Analysis System-A: SBAS-A for ArcView Application
 Sediment Budget Analysis System-A: SBAS-A for ArcView Application by Rose Dopsovic, Lynn Hardegree, and Julie Rosati PURPOSE. This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note (CHETN) describes a
Sediment Budget Analysis System-A: SBAS-A for ArcView Application by Rose Dopsovic, Lynn Hardegree, and Julie Rosati PURPOSE. This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note (CHETN) describes a
Regional Sediment Management
 Regional Sediment Management Linda S. Lillycrop Program Manager Coastal Engineer US Army Engineer Research and Development Center Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory Q AVG Coastal Resilience: The Environmental,
Regional Sediment Management Linda S. Lillycrop Program Manager Coastal Engineer US Army Engineer Research and Development Center Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory Q AVG Coastal Resilience: The Environmental,
The Sediment Budget Calculator: A Webtool to Develop a Family of Viable Inlet and Adjacent Beach Sediment Budget Solutions
 The Sediment Budget Calculator: A Webtool to Develop a Family of Viable Inlet and Adjacent Beach Sediment Budget Solutions by Julie Dean Rosati, Charles A. Sumner, and Derek A. Wilson PURPOSE: This Coastal
The Sediment Budget Calculator: A Webtool to Develop a Family of Viable Inlet and Adjacent Beach Sediment Budget Solutions by Julie Dean Rosati, Charles A. Sumner, and Derek A. Wilson PURPOSE: This Coastal
Material Workshop. Galveston District 2012 Beneficial Use of Dredged. Material Workshop. Custodians of the Coast
 Galveston District 2012 Beneficial Use of Dredged Material Workshop Galveston District 2012 Beneficial Use of Dredged Material Workshop US Army Corps of Engineers BUILDING STRONG Welcome Opening Remarks
Galveston District 2012 Beneficial Use of Dredged Material Workshop Galveston District 2012 Beneficial Use of Dredged Material Workshop US Army Corps of Engineers BUILDING STRONG Welcome Opening Remarks
An Update on Nearshore Berms in the Corps of Engineers: Recent Projects and Future Needs
 An Update on Nearshore Berms in the Corps of Engineers: Recent Projects and Future Needs by Tanya M. Beck, Julie D. Rosati, and James Rosati PURPOSE: This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note
An Update on Nearshore Berms in the Corps of Engineers: Recent Projects and Future Needs by Tanya M. Beck, Julie D. Rosati, and James Rosati PURPOSE: This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note
Coastal Inlets Research Program US Army Corps of Engineers Engineering Research and Development Center
 Coastal Inlets Research Program US Army Corps of Engineers Engineering Research and Development Center Site of Moriches Inlet Nov. 1951 Julie Dean Rosati and Nicholas C. Kraus, CIRP Program Manager Shinnecock
Coastal Inlets Research Program US Army Corps of Engineers Engineering Research and Development Center Site of Moriches Inlet Nov. 1951 Julie Dean Rosati and Nicholas C. Kraus, CIRP Program Manager Shinnecock
Sediment Budget Analysis System (SBAS)
 Coastal Engineering Technical Note IV-20 Sediment Budget Analysis System (SBAS) by Julie Dean Rosati and Nicholas C. Kraus PURPOSE: The Coastal Engineering Technical Note (CETN) herein presents the Sediment
Coastal Engineering Technical Note IV-20 Sediment Budget Analysis System (SBAS) by Julie Dean Rosati and Nicholas C. Kraus PURPOSE: The Coastal Engineering Technical Note (CETN) herein presents the Sediment
EAST PASS UP-DATE SUMMARY OF FINDINGS REPORT and INLET MANAGEMENT IMPLEMENTATION PLAN
 EAST PASS 2013 UP-DATE SUMMARY OF FINDINGS REPORT and INLET MANAGEMENT IMPLEMENTATION PLAN Introduction On June 8, 2000, the Florida Department of Environmental Protection adopted the East Pass Inlet Management
EAST PASS 2013 UP-DATE SUMMARY OF FINDINGS REPORT and INLET MANAGEMENT IMPLEMENTATION PLAN Introduction On June 8, 2000, the Florida Department of Environmental Protection adopted the East Pass Inlet Management
Hawaii Regional Sediment Management: Application of SBAS for ArcGIS 10 to Develop Regional Sediment Budgets for the Island of Maui, HI
 Hawaii Regional Sediment Management: Application of SBAS for ArcGIS 10 to Develop Regional Sediment Budgets for the Island of Maui, HI by Jessica H. Podoski PURPOSE. This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering
Hawaii Regional Sediment Management: Application of SBAS for ArcGIS 10 to Develop Regional Sediment Budgets for the Island of Maui, HI by Jessica H. Podoski PURPOSE. This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering
Mark H. Horwitz Ping Wang PhD Coastal Research Laboratory, School of Geosciences University of South Florida
 Mark H. Horwitz Ping Wang PhD Coastal Research Laboratory, School of Geosciences University of South Florida American Shore & Beach Preservation Association 2015 National Coastal Conference, New Orleans,
Mark H. Horwitz Ping Wang PhD Coastal Research Laboratory, School of Geosciences University of South Florida American Shore & Beach Preservation Association 2015 National Coastal Conference, New Orleans,
Lessons Learned in Regional Sediment Management: The Mobile District Demonstration Program; Technical Program Implementation
 Lessons Learned in Regional Sediment Management: The Mobile District Demonstration Program; Technical Program Implementation by Linda S. Lillycrop, Jennifer M. Wozencraft, Lynn C. Hardegree, Rose Dopsovic,
Lessons Learned in Regional Sediment Management: The Mobile District Demonstration Program; Technical Program Implementation by Linda S. Lillycrop, Jennifer M. Wozencraft, Lynn C. Hardegree, Rose Dopsovic,
ENGINEERING WITH NATURE: NEARSHORE BERM PLACEMENTS AT FORT MYERS BEACH AND PERDIDO KEY, FLORIDA, USA
 1 ENGINEERING WITH NATURE: NEARSHORE BERM PLACEMENTS AT FORT MYERS BEACH AND PERDIDO KEY, FLORIDA, USA KATHERINE E. BRUTSCHÉ 1, PING WANG 2, JULIE D. ROSATI 1, CHERYL E. POLLOCK 1 1. U.S. Army Engineer
1 ENGINEERING WITH NATURE: NEARSHORE BERM PLACEMENTS AT FORT MYERS BEACH AND PERDIDO KEY, FLORIDA, USA KATHERINE E. BRUTSCHÉ 1, PING WANG 2, JULIE D. ROSATI 1, CHERYL E. POLLOCK 1 1. U.S. Army Engineer
Linking Inlet Hydrodynamics and Morphologic Response at Oregon Inlet, NC
 Linking Inlet Hydrodynamics and Morphologic Response at Oregon Inlet, NC Prepared for: Sharon Ahlers Engineering Communications Program Cornell University Prepared by: Justin Vandever School of Civil and
Linking Inlet Hydrodynamics and Morphologic Response at Oregon Inlet, NC Prepared for: Sharon Ahlers Engineering Communications Program Cornell University Prepared by: Justin Vandever School of Civil and
ENGINEERING APPROACHES TO SHORELINE PLACEMENT FROM COAST TO COAST
 ENGINEERING APPROACHES TO SHORELINE PLACEMENT FROM COAST TO COAST 237 237 237 217 217 217 200 200 200 0 0 0 163 163 163 131 132 122 80 119 27 252 174.59 83 36 118 110 135 120 112 92 56 62 102 130 Comparing
ENGINEERING APPROACHES TO SHORELINE PLACEMENT FROM COAST TO COAST 237 237 237 217 217 217 200 200 200 0 0 0 163 163 163 131 132 122 80 119 27 252 174.59 83 36 118 110 135 120 112 92 56 62 102 130 Comparing
A SEDIMENT BUDGET ANALYSIS AND MANAGEMENT STRATEGY FOR FORT PIERCE INLET, FL
 A SEDIMENT BUDGET ANALYSIS AND MANAGEMENT STRATEGY FOR FORT PIERCE INLET, FL By Elba Rodriguez and Robert G. Dean Department of Civil and Coastal Engineering University of Florida Gainesville, FL 32611,
A SEDIMENT BUDGET ANALYSIS AND MANAGEMENT STRATEGY FOR FORT PIERCE INLET, FL By Elba Rodriguez and Robert G. Dean Department of Civil and Coastal Engineering University of Florida Gainesville, FL 32611,
REDUCING SHOALING IN THE TEXAS GIWW AND EROSION OF BARRIER ISLANDS ALONG WEST GALVESTON BAY
 20 Terra et Aqua Number 136 September 2014 K. TOWNSEND, C. MAGLIO, R. THOMAS, D. THORNTON, J. MILLER, T. CAMPBELL, L. LIN, S. WILLEY AND E. WOOD REDUCING SHOALING IN THE TEXAS GIWW AND EROSION OF BARRIER
20 Terra et Aqua Number 136 September 2014 K. TOWNSEND, C. MAGLIO, R. THOMAS, D. THORNTON, J. MILLER, T. CAMPBELL, L. LIN, S. WILLEY AND E. WOOD REDUCING SHOALING IN THE TEXAS GIWW AND EROSION OF BARRIER
Sediment Budget Analysis System (SBAS)
 Coastal Engineering Technical Note IV-20 US Army Corps of Engineers Sediment Budget Analysis System (SBAS) by Julie Dean Rosati and Nicholas C. Kraus PURPOSE: The Coastal Engineering Technical Note (CETN)
Coastal Engineering Technical Note IV-20 US Army Corps of Engineers Sediment Budget Analysis System (SBAS) by Julie Dean Rosati and Nicholas C. Kraus PURPOSE: The Coastal Engineering Technical Note (CETN)
GenCade. Combining and Extending the GENESIS and Cascade Models for Planning and Design in a Regional Sediment Management Framework
 GenCade Combining and Extending the GENESIS and Cascade Models for Planning and Design in a Regional Sediment Management Framework G Presented by Nicholas C. Kraus For the GenCade Development Team Ken
GenCade Combining and Extending the GENESIS and Cascade Models for Planning and Design in a Regional Sediment Management Framework G Presented by Nicholas C. Kraus For the GenCade Development Team Ken
The Impact of Hurricane Irma on the Coast of Florida
 The Impact of Hurricane Irma on the Coast of Florida Ralph Clark, Guy Weeks, Robert Wang, Mike Manausa & Peter Bacopoulos Division of Water Resource Management February 8, 2018 Overview: Hurricane Irma
The Impact of Hurricane Irma on the Coast of Florida Ralph Clark, Guy Weeks, Robert Wang, Mike Manausa & Peter Bacopoulos Division of Water Resource Management February 8, 2018 Overview: Hurricane Irma
Morphological Modeling of Inlets and Adjacent Shorelines on Engineering Timescales
 CB&I Morphological Modeling of Inlets and Adjacent Shorelines on Engineering Timescales Challenges and Model Improvements based on Recent Studies Dobrochinski, J.P.H.; Benedet, L.; Signorin, M.; Pierro,
CB&I Morphological Modeling of Inlets and Adjacent Shorelines on Engineering Timescales Challenges and Model Improvements based on Recent Studies Dobrochinski, J.P.H.; Benedet, L.; Signorin, M.; Pierro,
Regional Sediment Dynamics in Mobile Bay, Alabama; A Sediment Budget Perspective
 Regional Sediment Dynamics in Mobile Bay, Alabama; A Sediment Budget Perspective by Mark R. Byrnes, Jennifer L. Berlinghoff, and Sarah F. Griffee PURPOSE: This U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) Regional
Regional Sediment Dynamics in Mobile Bay, Alabama; A Sediment Budget Perspective by Mark R. Byrnes, Jennifer L. Berlinghoff, and Sarah F. Griffee PURPOSE: This U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) Regional
The Corps of Engineers National Regional Sediment Management Demonstration Program
 The Corps of Engineers National Regional Sediment Management Demonstration Program by Julie D. Rosati, Bruce D. Carlson, Jack E. Davis, and Thomas D. Smith PURPOSE. This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering
The Corps of Engineers National Regional Sediment Management Demonstration Program by Julie D. Rosati, Bruce D. Carlson, Jack E. Davis, and Thomas D. Smith PURPOSE. This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering
Heather Schlosser Army Corps of Engineers Coastal Studies Group August 28, 2008
 Got sand? Regional Sediment Management in Orange County Heather Schlosser Army Corps of Engineers Coastal Studies Group August 28, 2008 Regional Sediment Management Regional sediment management recognizes
Got sand? Regional Sediment Management in Orange County Heather Schlosser Army Corps of Engineers Coastal Studies Group August 28, 2008 Regional Sediment Management Regional sediment management recognizes
DESIGN ENGINEERING ANALYSIS FOR TERMINAL GROIN LENGTH
 APPENDIX F DESIGN ENGINEERING ANALYSIS FOR TERMINAL GROIN LENGTH (Prepared by Olsen Associates, Inc.) DRAFT Environmental Impact Statement Village of Bald Head Island Shoreline Protection Project Brunswick
APPENDIX F DESIGN ENGINEERING ANALYSIS FOR TERMINAL GROIN LENGTH (Prepared by Olsen Associates, Inc.) DRAFT Environmental Impact Statement Village of Bald Head Island Shoreline Protection Project Brunswick
Engineering with Nature: Nearshore Berm Placements at Fort Myers Beach and Perdido Key, Florida, USA
 Engineering with Nature: Nearshore Berm Placements at Fort Myers Beach and Perdido Key, Florida, USA Katherine E. Brutsché, Ph.D. Research Physical Scientist ERDC-Coastal & Hydraulics Laboratory May 14,
Engineering with Nature: Nearshore Berm Placements at Fort Myers Beach and Perdido Key, Florida, USA Katherine E. Brutsché, Ph.D. Research Physical Scientist ERDC-Coastal & Hydraulics Laboratory May 14,
Regional Sediment Management: The Long Island Coastal Planning Project
 Regional Sediment Management: The Long Island Coastal Planning Project Lynn M. Bocamazo Senior Coastal Engineer USACE-New York District 22 September 2009 US Army Corps of Engineers Outline Project Location
Regional Sediment Management: The Long Island Coastal Planning Project Lynn M. Bocamazo Senior Coastal Engineer USACE-New York District 22 September 2009 US Army Corps of Engineers Outline Project Location
Geology Setting Management Options Management Structure
 Geology Setting Management Options Management Structure WFF = Wallops Flight Facility LST = Longshore sediment transport SLR = Sea level rise September 29, 2015 Accomack County/Accomack Northampton County
Geology Setting Management Options Management Structure WFF = Wallops Flight Facility LST = Longshore sediment transport SLR = Sea level rise September 29, 2015 Accomack County/Accomack Northampton County
Racing against time, an unprecedented year: the US Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) response to the hurricanes of 2004
 Environmental Problems in Coastal Regions VI 205 Racing against time, an unprecedented year: the US Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) response to the hurricanes of 2004 R. I. McMillen 1, D. R. Haubner 2,
Environmental Problems in Coastal Regions VI 205 Racing against time, an unprecedented year: the US Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) response to the hurricanes of 2004 R. I. McMillen 1, D. R. Haubner 2,
A Sedimentological and Granulometric Atlas of the Beach Sediments of Florida s Southwest Coast and Keys
 A Sedimentological and Granulometric Atlas of the Beach Sediments of Florida s Southwest Coast and Keys Daniel C. Phelps, Michelle M. L. Ladle, and Adel A. Dabous The Florida Geological Survey Coastal
A Sedimentological and Granulometric Atlas of the Beach Sediments of Florida s Southwest Coast and Keys Daniel C. Phelps, Michelle M. L. Ladle, and Adel A. Dabous The Florida Geological Survey Coastal
COASTAL SEDIMENT BUDGET FOR JUPITER INLET, FLORIDA
 COASTAL SEDIMENT BUDGET FOR JUPITER INLET, FLORIDA By KRISTEN MARIE ODRONIEC A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE
COASTAL SEDIMENT BUDGET FOR JUPITER INLET, FLORIDA By KRISTEN MARIE ODRONIEC A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE
SBEACH High-Frequency Storm Erosion Model Study for Sarasota County. Final Report
 SBEACH High-Frequency Storm Erosion Model Study for Sarasota County Final Report by S. Y. Wang and M. Manausa Sponsored by Florida Department of Environmental Protection, Bureau of Beaches and Coastal
SBEACH High-Frequency Storm Erosion Model Study for Sarasota County Final Report by S. Y. Wang and M. Manausa Sponsored by Florida Department of Environmental Protection, Bureau of Beaches and Coastal
RESULTS FROM THE TEXAS COASTAL SEDIMENT SOURCES: A GENERAL EVALUATION STUDY
 RESULTS FROM THE TEXAS COASTAL SEDIMENT SOURCES: A GENERAL EVALUATION STUDY JUAN MOYA KELSEY CALVEZ CRIS WEBER ANTHONY RISKO *KEVIN FRENZEL FREESE AND NICHOLS, INC. COASTAL AND WATERWAYS GROUP OBJECTIVES
RESULTS FROM THE TEXAS COASTAL SEDIMENT SOURCES: A GENERAL EVALUATION STUDY JUAN MOYA KELSEY CALVEZ CRIS WEBER ANTHONY RISKO *KEVIN FRENZEL FREESE AND NICHOLS, INC. COASTAL AND WATERWAYS GROUP OBJECTIVES
SEDIMENT BUDGET: MISSISSIPPI SOUND BARRIER ISLANDS*
 2366 SEDIMENT BUDGET: MISSISSIPPI SOUND BARRIER ISLANDS* MARK R. BYRNES 1, JULIE D. ROSATI 2, SARAH F. GRIFFEE 1 1. Applied Coastal Research and Engineering, Inc., 766 Falmouth Road, Suite A-1, Mashpee,
2366 SEDIMENT BUDGET: MISSISSIPPI SOUND BARRIER ISLANDS* MARK R. BYRNES 1, JULIE D. ROSATI 2, SARAH F. GRIFFEE 1 1. Applied Coastal Research and Engineering, Inc., 766 Falmouth Road, Suite A-1, Mashpee,
CHAPTER 212 THE EXTENT OF INLET IMPACTS UPON ADJACENT SHORELINES. Kevin R. Bodge, Ph.D., Member ASCE 1
 CHAPTER 212 THE EXTENT OF INLET IMPACTS UPON ADJACENT SHORELINES Kevin R. Bodge, Ph.D., Member ASCE 1 Abstract The erosional impacts of improved inlets upon adjacent shorelines may be best estimated by
CHAPTER 212 THE EXTENT OF INLET IMPACTS UPON ADJACENT SHORELINES Kevin R. Bodge, Ph.D., Member ASCE 1 Abstract The erosional impacts of improved inlets upon adjacent shorelines may be best estimated by
Coastal Sediment Properties and Longshore Sediment Transport
 Coastal Sediment Properties and Longshore Sediment Transport Julie Rosati Julie.D.Rosati@erdc.usace.army.mil 601-634-3005 Coastal Planning Course Lesson #8 Tuesday 8:00-9:00 am CEM III-1, III-2 1. Coastal
Coastal Sediment Properties and Longshore Sediment Transport Julie Rosati Julie.D.Rosati@erdc.usace.army.mil 601-634-3005 Coastal Planning Course Lesson #8 Tuesday 8:00-9:00 am CEM III-1, III-2 1. Coastal
MISSISSIPPI COASTAL IMPROVEMENTS
 MISSISSIPPI COASTAL IMPROVEMENTS PROGRAM (MsCIP) Comprehensive Barrier 237 27 200 237 27 200 Island 237 Restoration 27 200 Plan 80 9 27 252 74.59 255 255 255 0 0 0 63 63 63 3 32 22 239 65 53 0 35 20 2
MISSISSIPPI COASTAL IMPROVEMENTS PROGRAM (MsCIP) Comprehensive Barrier 237 27 200 237 27 200 Island 237 Restoration 27 200 Plan 80 9 27 252 74.59 255 255 255 0 0 0 63 63 63 3 32 22 239 65 53 0 35 20 2
Beach Nourishment on the Florida East Coast. Boca Raton
 Beach Nourishment on the Florida East Coast Past Future Boca Raton Erosion is the Main Reason for Beach Past - Erosion on the east coast was mainly caused by inlets created or modified for navigation Nourishment
Beach Nourishment on the Florida East Coast Past Future Boca Raton Erosion is the Main Reason for Beach Past - Erosion on the east coast was mainly caused by inlets created or modified for navigation Nourishment
National RSM Program Bi-Monthly call 19 October 2017
 National RSM Program Bi-Monthly call 19 October 2017 1:30-1:55 FY18 Proposal Selections, Schedule, Activities, etc Linda Lillycrop 1:55-2:15 Post-Hurricane Coastal Mapping and Change Analysis NCMP (National
National RSM Program Bi-Monthly call 19 October 2017 1:30-1:55 FY18 Proposal Selections, Schedule, Activities, etc Linda Lillycrop 1:55-2:15 Post-Hurricane Coastal Mapping and Change Analysis NCMP (National
Erosion Information Paper - Barrow, Alaska Current as of September 14, 2007
 U.S. Army Corps of Engineers ALASKA BASELINE EROSION ASSESSMENT Erosion Information Paper - Barrow, Alaska Current as of September 14, 2007 Community Information Barrow (BARE-row, a.k.a. Ukpeagvik), population
U.S. Army Corps of Engineers ALASKA BASELINE EROSION ASSESSMENT Erosion Information Paper - Barrow, Alaska Current as of September 14, 2007 Community Information Barrow (BARE-row, a.k.a. Ukpeagvik), population
Morphologic Evolution of Similar Barrier Islands with Different Coastal Management
 Journal of Coastal Research SI 39 127-131 ICS 2004 (Proceedings) Brazil ISSN 0749-0208 Morphologic Evolution of Similar Barrier Islands with Different Coastal Management N.A. Elko and R.A. Davis, Jr. Coastal
Journal of Coastal Research SI 39 127-131 ICS 2004 (Proceedings) Brazil ISSN 0749-0208 Morphologic Evolution of Similar Barrier Islands with Different Coastal Management N.A. Elko and R.A. Davis, Jr. Coastal
PRESENTATION TITLE. Regional Sediment Management Application of a Coastal Model at the St. Johns River Entrance BUILDING STRONG
 PRESENTATION TITLE Regional Sediment Management Application of a Coastal Model at the St. Johns River Entrance Steven Bratos Senior Coastal Engineer U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Jacksonville District February
PRESENTATION TITLE Regional Sediment Management Application of a Coastal Model at the St. Johns River Entrance Steven Bratos Senior Coastal Engineer U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Jacksonville District February
Mapping Coastal Change Using LiDAR and Multispectral Imagery
 Mapping Coastal Change Using LiDAR and Multispectral Imagery Contributor: Patrick Collins, Technical Solutions Engineer Presented by TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 1 Coastal Change... 1 Mapping Coastal
Mapping Coastal Change Using LiDAR and Multispectral Imagery Contributor: Patrick Collins, Technical Solutions Engineer Presented by TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 1 Coastal Change... 1 Mapping Coastal
Appendix B Littoral Sediment Budget Report
 Appendix B Littoral Sediment Budget Report ERDC/CHL TR-12-9 Mississippi Coastal Improvements Program (MsCIP) Littoral Sediment Budget for the Mississippi Sound Barrier Islands Mark R. Byrnes, Julie D.
Appendix B Littoral Sediment Budget Report ERDC/CHL TR-12-9 Mississippi Coastal Improvements Program (MsCIP) Littoral Sediment Budget for the Mississippi Sound Barrier Islands Mark R. Byrnes, Julie D.
Nearshore Placement as a Regional Sediment Management Practice
 Nearshore Placement as a Regional Sediment Management Practice Katherine E. Brutsché, Ph.D. Brian C. McFall, Ph.D., P.E. Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory US Army Engineer R&D Center ASBPA National Coastal
Nearshore Placement as a Regional Sediment Management Practice Katherine E. Brutsché, Ph.D. Brian C. McFall, Ph.D., P.E. Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory US Army Engineer R&D Center ASBPA National Coastal
Alexandra Carvalho, Ph.D., GISP Kathy Fitzpatrick, P.E.
 Coastal Data Organization for Project Management and Coastal Planning Martin County, Florida Alexandra Carvalho, Ph.D., GISP Kathy Fitzpatrick, P.E. Outline County Coastal Programs Coastal Geodatabase
Coastal Data Organization for Project Management and Coastal Planning Martin County, Florida Alexandra Carvalho, Ph.D., GISP Kathy Fitzpatrick, P.E. Outline County Coastal Programs Coastal Geodatabase
ERDC Update SAD Regional Management Board
 ERDC Update SAD Regional Management Board José E. Sanchez, P.E., SES Director, Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory Engineer Research and Development Center 14FEB17 Overview of R&D Activities in AOR Cross
ERDC Update SAD Regional Management Board José E. Sanchez, P.E., SES Director, Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory Engineer Research and Development Center 14FEB17 Overview of R&D Activities in AOR Cross
West Florida Shelf and Tampa Bay Responses to Hurricane Irma: What Happened and Why
 West Florida Shelf and Tampa Bay Responses to Hurricane Irma: What Happened and Why R.H. Weisberg Y. Liu J. Chen College of Marine Science University of South Florida St. Petersburg, FL SECOORA Webinar
West Florida Shelf and Tampa Bay Responses to Hurricane Irma: What Happened and Why R.H. Weisberg Y. Liu J. Chen College of Marine Science University of South Florida St. Petersburg, FL SECOORA Webinar
Lab 12 Coastal Geology
 Lab 12 Coastal Geology I. Fluvial Systems Hydrologic Cycle Runoff that flows into rivers = precipitation (rain and snowmelt) [infiltration (loss to groundwater) + evaporation (loss to atmosphere) + transpiration
Lab 12 Coastal Geology I. Fluvial Systems Hydrologic Cycle Runoff that flows into rivers = precipitation (rain and snowmelt) [infiltration (loss to groundwater) + evaporation (loss to atmosphere) + transpiration
GSA DATA REPOSITORY
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2009206 Miner et al. Supplemental Material Bathymetric Survey Methods The bathymetric data for the area were gathered using a single-beam bathymetric survey rig mounted aboard a 21-foot
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2009206 Miner et al. Supplemental Material Bathymetric Survey Methods The bathymetric data for the area were gathered using a single-beam bathymetric survey rig mounted aboard a 21-foot
ΛTKINS. Applications of Regional Sediment Management Concepts in Texas Estuarine Restoration Projects. Riparian Workshop Fort Worth, October 17, 2012
 Juan C Moya, PhD., PG Coastal Planning and Restoration Applications of Regional Sediment Management Concepts in Texas Estuarine Restoration Projects Riparian Workshop Fort Worth, October 17, 2012 West
Juan C Moya, PhD., PG Coastal Planning and Restoration Applications of Regional Sediment Management Concepts in Texas Estuarine Restoration Projects Riparian Workshop Fort Worth, October 17, 2012 West
Monitoring Shoreline Change along Assateague Barrier Island: The First Trend Report
 Journal of Coastal Research SI 64 8-84 ICS211 (Proceedings) Poland ISSN 749-28 Monitoring Shoreline Change along Assateague Barrier Island: The First Trend Report N. P. Psuty and T. M. Silveira Marine
Journal of Coastal Research SI 64 8-84 ICS211 (Proceedings) Poland ISSN 749-28 Monitoring Shoreline Change along Assateague Barrier Island: The First Trend Report N. P. Psuty and T. M. Silveira Marine
West Galveston Bay Regional Sediment Management Plan (An Eco-geomorphologic Approach)
 West Galveston Bay Regional Sediment Management Plan (An Eco-geomorphologic Approach) Juan Moya, Matthew Mahoney and Mike Smith Restore America s Estuaries Conference Tampa, FL, October 23, 2012 Atkins
West Galveston Bay Regional Sediment Management Plan (An Eco-geomorphologic Approach) Juan Moya, Matthew Mahoney and Mike Smith Restore America s Estuaries Conference Tampa, FL, October 23, 2012 Atkins
The Great Lakes Coalition is an organization of shoreline property owners on the Great Lakes dedicated to improving the quality of life for both it s
 The Great Lakes Coalition is an organization of shoreline property owners on the Great Lakes dedicated to improving the quality of life for both it s s membership and the public at large. Facts about Section
The Great Lakes Coalition is an organization of shoreline property owners on the Great Lakes dedicated to improving the quality of life for both it s s membership and the public at large. Facts about Section
Appendix D Geotechnical
 USACE JACKSONVIE DISTRICT Appendix D Geotechnical LEE COUNTY GASPARIA SHORE PROTECTION PROJECT 934 REPORT June 216 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Background... 1 1.1 Regional Geology... 1 1.2 Local Geology... 2 2
USACE JACKSONVIE DISTRICT Appendix D Geotechnical LEE COUNTY GASPARIA SHORE PROTECTION PROJECT 934 REPORT June 216 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Background... 1 1.1 Regional Geology... 1 1.2 Local Geology... 2 2
STATE OF FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION Mimi A. Drew, Secretary. LAND AND RECREATION Robert G. Ballard, Deputy Secretary
 STATE OF FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION Mimi A. Drew, Secretary LAND AND RECREATION Robert G. Ballard, Deputy Secretary FLORIDA GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Jonathan D. Arthur, State Geologist and
STATE OF FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION Mimi A. Drew, Secretary LAND AND RECREATION Robert G. Ballard, Deputy Secretary FLORIDA GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Jonathan D. Arthur, State Geologist and
Port of Kalama, 2013 TEMCO Berth Maintenance Dredging and In-water Flow-Lane Placement Project
 2014 WEDA ENVIRONMENTAL EXCELLENCE AWARDS Category: Navigation Dredging Port of Kalama, 2013 TEMCO Berth Maintenance Dredging and In-water Flow-Lane Placement Project Port of Kalama, Washington 18 April
2014 WEDA ENVIRONMENTAL EXCELLENCE AWARDS Category: Navigation Dredging Port of Kalama, 2013 TEMCO Berth Maintenance Dredging and In-water Flow-Lane Placement Project Port of Kalama, Washington 18 April
DIVISION OF COASTAL MANAGEMENT TO STUDY CURRENT LONG-TERM EROSION RATES ADJACENT TO TERMINAL GROINS
 DIVISION OF COASTAL MANAGEMENT TO STUDY CURRENT LONG-TERM EROSION RATES ADJACENT TO TERMINAL GROINS North Carolina Department of Environmental Quality Division of Coastal Management February 22, 2018 N.
DIVISION OF COASTAL MANAGEMENT TO STUDY CURRENT LONG-TERM EROSION RATES ADJACENT TO TERMINAL GROINS North Carolina Department of Environmental Quality Division of Coastal Management February 22, 2018 N.
SEGMENTED BREAKWATERS AND THEIR USE IN COASTAL LOUISIANA
 SEGMENTED BREAKWATERS AND THEIR USE IN COASTAL LOUISIANA Prepared by: Louisiana Coastal Protection and Restoration Authority Engineering Division March 2016 The geology of Louisiana s coastal zone is intimately
SEGMENTED BREAKWATERS AND THEIR USE IN COASTAL LOUISIANA Prepared by: Louisiana Coastal Protection and Restoration Authority Engineering Division March 2016 The geology of Louisiana s coastal zone is intimately
Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory
 ERDC/CHL TR-09-6 Houston-Galveston Navigation Channels, Texas Project Navigation Channel Sedimentation Study, Phase 2 Plan Simulations Jennifer N. Tate and Cassandra G. Ross August 2009 Coastal and Hydraulics
ERDC/CHL TR-09-6 Houston-Galveston Navigation Channels, Texas Project Navigation Channel Sedimentation Study, Phase 2 Plan Simulations Jennifer N. Tate and Cassandra G. Ross August 2009 Coastal and Hydraulics
Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory
 ERDC/CHL TR-17-7 Regional Sediment Management (RSM) Program Charleston Harbor, SC, Regional Sediment Management Study; Beneficial Use of Dredged Material through Nearshore Placement Layla R. Kashlan, Sara
ERDC/CHL TR-17-7 Regional Sediment Management (RSM) Program Charleston Harbor, SC, Regional Sediment Management Study; Beneficial Use of Dredged Material through Nearshore Placement Layla R. Kashlan, Sara
Application #: TEXT
 TOWN OF FORT MYERS BEACH 2008 PROPOSED COMPREHENSIVE PLAN AMENDMENTS Application #: 2008-13-TEXT Description: Modify the Coastal Management and Future Land Use Elements to reflect the state s new definition
TOWN OF FORT MYERS BEACH 2008 PROPOSED COMPREHENSIVE PLAN AMENDMENTS Application #: 2008-13-TEXT Description: Modify the Coastal Management and Future Land Use Elements to reflect the state s new definition
Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory
 ERDC/CHL TR-05-6 Texas City Ship Channel Deepening Study, Hydrodynamic Model Lisa M. Lee, Jennifer N. Tate, and R. C. Berger August 2005 Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory Approved for public release; distribution
ERDC/CHL TR-05-6 Texas City Ship Channel Deepening Study, Hydrodynamic Model Lisa M. Lee, Jennifer N. Tate, and R. C. Berger August 2005 Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory Approved for public release; distribution
Implementation of Structures in the CMS: Part I, Rubble Mound
 ERDC/CHL CHETN-IV-93 Implementation of Structures in the CMS: Part I, Rubble Mound by Honghai Li, Alejandro Sanchez, Weiming Wu, and Christopher Reed PURPOSE: This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical
ERDC/CHL CHETN-IV-93 Implementation of Structures in the CMS: Part I, Rubble Mound by Honghai Li, Alejandro Sanchez, Weiming Wu, and Christopher Reed PURPOSE: This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical
SHORELINE AND BEACH PROCESSES: PART 2. Implications for Coastal Engineering
 SHORELINE AND BEACH PROCESSES: PART 2 Implications for Coastal Engineering Objectives of the lecture: Part 2 Show examples of coastal engineering Discuss the practical difficulties of ocean engineering
SHORELINE AND BEACH PROCESSES: PART 2 Implications for Coastal Engineering Objectives of the lecture: Part 2 Show examples of coastal engineering Discuss the practical difficulties of ocean engineering
Appendix I. Dredged Volume Estimates. Draft Contractor Document: Subject to Continuing Agency Review
 Appendix I Dredged Volume Estimates Draft Contractor Document: Subject to Continuing Agency Review Interoffice Correspondence Date: April 6, 2007 To: L. Bossi (WHI) Copy: S. Thompson (WHI), B. Fidler (NNJ)
Appendix I Dredged Volume Estimates Draft Contractor Document: Subject to Continuing Agency Review Interoffice Correspondence Date: April 6, 2007 To: L. Bossi (WHI) Copy: S. Thompson (WHI), B. Fidler (NNJ)
Identification and Selection of Representative Storm Events from a Probabilistic Storm Data Base
 Identification and Selection of Representative Storm Events from a Probabilistic Storm Data Base by Mark B. Gravens and Dylan R. Sanderson PURPOSE: This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note
Identification and Selection of Representative Storm Events from a Probabilistic Storm Data Base by Mark B. Gravens and Dylan R. Sanderson PURPOSE: This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note
Regional-scale understanding of the geologic character and sand resources of the Atlantic inner continental shelf, Maine to Virginia
 Regional-scale understanding of the geologic character and sand resources of the Atlantic inner continental shelf, Maine to Virginia Workshop on Dredging, Beach Nourishment and Bird Conservation Atlantic
Regional-scale understanding of the geologic character and sand resources of the Atlantic inner continental shelf, Maine to Virginia Workshop on Dredging, Beach Nourishment and Bird Conservation Atlantic
FILL SUITABILITY CHARACTERIZATION OF A COMPLEX COASTAL AREA: DARE COUNTY, NORTH CAROLINA
 FILL SUITABILITY CHARACTERIZATION OF A COMPLEX COASTAL AREA: DARE COUNTY, NORTH CAROLINA Donald K. Stauble 1, William Birkemeier, Michael F. Forte and William A. Dennis 3 ABSTRACT As part of the design
FILL SUITABILITY CHARACTERIZATION OF A COMPLEX COASTAL AREA: DARE COUNTY, NORTH CAROLINA Donald K. Stauble 1, William Birkemeier, Michael F. Forte and William A. Dennis 3 ABSTRACT As part of the design
ST. JOHNS COUNTY, FLORIDA South Ponte Vedra Beach, Vilano Beach, and Summer Haven Reaches
 ST. JOHNS COUNTY, FLORIDA South Ponte Vedra Beach, Vilano Beach, and Summer Haven Reaches COASTAL STORM RISK MANAGEMENT PROJECT DRAFT INTEGRATED FEASIBILITY STUDY AND ENVIRONMENTAL ASSESSMENT APPENDIX
ST. JOHNS COUNTY, FLORIDA South Ponte Vedra Beach, Vilano Beach, and Summer Haven Reaches COASTAL STORM RISK MANAGEMENT PROJECT DRAFT INTEGRATED FEASIBILITY STUDY AND ENVIRONMENTAL ASSESSMENT APPENDIX
Tropical Update. 5 AM EDT Monday, October 8, 2018 Tropical Storm Michael, Tropical Storm Leslie, Invest 92L (10%) & African Tropical Wave (50%)
 Tropical Update 5 AM EDT Monday, October 8, 2018 Tropical Storm Michael, Tropical Storm Leslie, Invest 92L (10%) & African Tropical Wave (50%) This update is intended for government and emergency response
Tropical Update 5 AM EDT Monday, October 8, 2018 Tropical Storm Michael, Tropical Storm Leslie, Invest 92L (10%) & African Tropical Wave (50%) This update is intended for government and emergency response
Environmental concerns for marina planning in the Gulf of Suez
 Journal of Coastal Conservation 6: 51-56, 2000 EUCC; Opulus Press Uppsala. Printed in Sweden - Environmental concerns for marina planning in the Gulf of Suez - 51 Environmental concerns for marina planning
Journal of Coastal Conservation 6: 51-56, 2000 EUCC; Opulus Press Uppsala. Printed in Sweden - Environmental concerns for marina planning in the Gulf of Suez - 51 Environmental concerns for marina planning
Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory
 7 ERDC/CHL TR-06-17 North Texas Sediment Budget Sabine Pass to San Luis Pass Andrew Morang September 2006 Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. ERDC/CHL
7 ERDC/CHL TR-06-17 North Texas Sediment Budget Sabine Pass to San Luis Pass Andrew Morang September 2006 Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. ERDC/CHL
EVALUATION TECHNIQUES FOR THE PROTECTIVE BENEFITS OF DUNE SYSTEMS TO COASTAL HAZARDS
 EVALUATION TECHNIQUES FOR THE PROTECTIVE BENEFITS OF DUNE SYSTEMS TO COASTAL HAZARDS 5 th Coastal Hazards Symposium Key West 2015 Matthew Janssen Thomas Herrington Jon Miller 1 Abstract Quantify and predict
EVALUATION TECHNIQUES FOR THE PROTECTIVE BENEFITS OF DUNE SYSTEMS TO COASTAL HAZARDS 5 th Coastal Hazards Symposium Key West 2015 Matthew Janssen Thomas Herrington Jon Miller 1 Abstract Quantify and predict
SBEACH High-Frequency Storm Erosion Model Study for Palm Beach County. Final Report
 SBEACH High-Frequency Storm Erosion Model Study for Palm Beach County Final Report by S. Y. Wang and M. Manausa Sponsored by Florida Department of Environmental Protection, Bureau of Beaches and Coastal
SBEACH High-Frequency Storm Erosion Model Study for Palm Beach County Final Report by S. Y. Wang and M. Manausa Sponsored by Florida Department of Environmental Protection, Bureau of Beaches and Coastal
Geol 117 Lecture 18 Beaches & Coastlines. I. Types of Coastlines A. Definition:
 I. Types of Coastlines A. Definition: 1. Shore = narrow zone where ocean meets land (e.g. beach) 2. Coast is a broad area where both ocean and land processes act a. Includes onshore marshes, dunes, sea
I. Types of Coastlines A. Definition: 1. Shore = narrow zone where ocean meets land (e.g. beach) 2. Coast is a broad area where both ocean and land processes act a. Includes onshore marshes, dunes, sea
GALVESTON BAY RSM Moving toward an Integrated, Cooperative, and Holistic Approach to Estuarine Sediments
 GALVESTON BAY RSM Moving toward an Integrated, Cooperative, and Holistic Approach to Estuarine Sediments RAE Conference 2010 Larry A. Wise Moffatt & Nichol RSM is a system-based approach for collaboratively
GALVESTON BAY RSM Moving toward an Integrated, Cooperative, and Holistic Approach to Estuarine Sediments RAE Conference 2010 Larry A. Wise Moffatt & Nichol RSM is a system-based approach for collaboratively
REGIONAL SEDIMENT MANAGEMENT IN THE CORPS OF ENGINEERS
 REGIONAL SEDIMENT MANAGEMENT IN THE CORPS OF ENGINEERS Julie D. Rosati 1, Lynn M. Bocamazo 2, Bruce D. Carlson 3, Jack E. Davis 1, Thomas D. Smith 4, Jennifer M. Wozencraft 5, Lynn Hardegree 5 ABSTRACT
REGIONAL SEDIMENT MANAGEMENT IN THE CORPS OF ENGINEERS Julie D. Rosati 1, Lynn M. Bocamazo 2, Bruce D. Carlson 3, Jack E. Davis 1, Thomas D. Smith 4, Jennifer M. Wozencraft 5, Lynn Hardegree 5 ABSTRACT
Draft for Discussion 11/11/2016
 Coastal Risk Consulting (CRC) Climate Vulnerability Assessment for Village of Key Biscayne Deliverable 1.1 in Statement of Work. Preliminary Vulnerability Assessment Identifying Flood Hotspots Introduction...
Coastal Risk Consulting (CRC) Climate Vulnerability Assessment for Village of Key Biscayne Deliverable 1.1 in Statement of Work. Preliminary Vulnerability Assessment Identifying Flood Hotspots Introduction...
Planning for the Future of Humboldt Bay: Sea Level Rise, Sediment Management, Sand Spits and Salt Marshes. Joel Gerwein
 Planning for the Future of Humboldt Bay: Sea Level Rise, Sediment Management, Sand Spits and Salt Marshes Joel Gerwein Introduction to Humboldt Bay Setting Economy, community, and environment Sediment
Planning for the Future of Humboldt Bay: Sea Level Rise, Sediment Management, Sand Spits and Salt Marshes Joel Gerwein Introduction to Humboldt Bay Setting Economy, community, and environment Sediment
Marine Analysis. LA 23 New. Louisiana. Prepared by:
 Gulf Intracoastal Waterway (GIWW) Marine Vessel Trafficc Analysis LA 23 New Orleans Gulf Coastt Railway Relocation PE/NEPA Project Jefferson and Plaquemines Parishes, Louisiana RPC Task LA23RR1 RPC/FRA
Gulf Intracoastal Waterway (GIWW) Marine Vessel Trafficc Analysis LA 23 New Orleans Gulf Coastt Railway Relocation PE/NEPA Project Jefferson and Plaquemines Parishes, Louisiana RPC Task LA23RR1 RPC/FRA
Two-Dimensional Simulation of Truckee River Hydrodynamics
 Two-Dimensional Simulation of Truckee River Hydrodynamics by Stephen H. Scott PURPOSE: The purpose of this Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note (CHETN) is to demonstrate the use of multidimensional
Two-Dimensional Simulation of Truckee River Hydrodynamics by Stephen H. Scott PURPOSE: The purpose of this Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note (CHETN) is to demonstrate the use of multidimensional
Donald K. Stauble and Bill Birkemeier Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory US Army Corps of Engineers
 Donald K. Stauble and Bill Birkemeier Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory US Army Corps of Engineers Define the Problem Navigation Shore Protection Environmental Political So what is the problem? Management
Donald K. Stauble and Bill Birkemeier Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory US Army Corps of Engineers Define the Problem Navigation Shore Protection Environmental Political So what is the problem? Management
MODELING OF EROSION CONTROL ALTERNATIVES AT STUMP PASS, CHARLOTTE COUNTY
 2014 NATIONAL CONFERENCE ON BEACH PRESERVATION TECHNOLOGY FEBRUARY 13, 2014 MODELING OF EROSION CONTROL ALTERNATIVES AT STUMP PASS, CHARLOTTE COUNTY 1 VADIM ALYMOV, PH.D. 2 CHUCK MOPPS 3 MICHAEL POFF,
2014 NATIONAL CONFERENCE ON BEACH PRESERVATION TECHNOLOGY FEBRUARY 13, 2014 MODELING OF EROSION CONTROL ALTERNATIVES AT STUMP PASS, CHARLOTTE COUNTY 1 VADIM ALYMOV, PH.D. 2 CHUCK MOPPS 3 MICHAEL POFF,
Coastal Overwash: Part 2, Upgrade to SBEACH
 Coastal Overwash: Part 2, Upgrade to SBEACH by Magnus Larson, Randall A. Wise, and Nicholas C. Kraus PURPOSE. This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note (CHETN) provides information about an
Coastal Overwash: Part 2, Upgrade to SBEACH by Magnus Larson, Randall A. Wise, and Nicholas C. Kraus PURPOSE. This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note (CHETN) provides information about an
HAWAII REGIONAL SEDIMENT MANAGEMENT
 HAWAII REGIONAL SEDIMENT MANAGEMENT KAUAI Workshop January 20, 2011 Kauai Veteran s Center Kihei, HI of Engineers, Honolulu District AGENDA 1300-1310 Welcome and Introductions Conger Conant 1310-1330 Regional
HAWAII REGIONAL SEDIMENT MANAGEMENT KAUAI Workshop January 20, 2011 Kauai Veteran s Center Kihei, HI of Engineers, Honolulu District AGENDA 1300-1310 Welcome and Introductions Conger Conant 1310-1330 Regional
Gulf of Mexico Harmful Algal Bloom Bulletin. Region: Southwest Florida. Conditions Report. Additional Resources
 Gulf of Mexico Harmful Algal Bloom Bulletin Thursday, August 30, 2018 NOAA National Ocean Service NOAA Satellite and Information Service NOAA National Weather Service Instructions for viewing this geospatial
Gulf of Mexico Harmful Algal Bloom Bulletin Thursday, August 30, 2018 NOAA National Ocean Service NOAA Satellite and Information Service NOAA National Weather Service Instructions for viewing this geospatial
Lateral Inflow into High-Velocity Channels
 Lateral Inflow into High-Velocity Channels by Richard L. Stockstill PURPOSE: This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note (CHETN) investigates lateral flow discharging into a high-velocity channel.
Lateral Inflow into High-Velocity Channels by Richard L. Stockstill PURPOSE: This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note (CHETN) investigates lateral flow discharging into a high-velocity channel.
Location: Jacksonville, FL December 11, 2012
 Technical Update Meeting Northeast Florida Surge Study Location: Jacksonville, FL December 11, 2012 Agenda 2:00 2:15 Welcome/Introductions Tucker Mahoney, FEMA Region IV Michael DelCharco, BakerAECOM 2:15
Technical Update Meeting Northeast Florida Surge Study Location: Jacksonville, FL December 11, 2012 Agenda 2:00 2:15 Welcome/Introductions Tucker Mahoney, FEMA Region IV Michael DelCharco, BakerAECOM 2:15
Earth Wind & Fire. Game Changing Restoration Options in the Texas Chenier Plain
 Earth Wind & Fire Game Changing Restoration Options in the Texas Chenier Plain EARTH: The Chenier Plain is a 5 million acre coastal region in Southwest Louisiana and Southeast Texas providing landscape
Earth Wind & Fire Game Changing Restoration Options in the Texas Chenier Plain EARTH: The Chenier Plain is a 5 million acre coastal region in Southwest Louisiana and Southeast Texas providing landscape
Supplemental Slides. Shore: Junction of Land & Water. Junction of Land & Water. Sea Level Variations. Shore vs. Coast. Sea Level Variations
 Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Shore: Junction of Land & Water. Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents
 Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Miami-Dade County Technical Update Meeting South Florida Coastal Study. May 11, 2016
 Miami-Dade County Technical Update Meeting South Florida Coastal Study May 11, 2016 Welcome and Introductions FEMA Region IV Christina Lindemer Technical Lead Production and Technical Services (PTS) Contractor
Miami-Dade County Technical Update Meeting South Florida Coastal Study May 11, 2016 Welcome and Introductions FEMA Region IV Christina Lindemer Technical Lead Production and Technical Services (PTS) Contractor
Developed in Consultation with Florida Educators
 Developed in Consultation with Florida Educators Table of Contents Next Generation Sunshine State Standards Correlation Chart... 7 Benchmarks Chapter 1 The Practice of Science...................... 11
Developed in Consultation with Florida Educators Table of Contents Next Generation Sunshine State Standards Correlation Chart... 7 Benchmarks Chapter 1 The Practice of Science...................... 11
Primer on Coastal Erosion And Habitat Creation
 2 nd Regional Conference Dredging, Beach Nourishment & Bird Conservation Primer on Coastal Erosion And Habitat Creation Timothy Kana Ph.D Source: Newsday 1962 Photo by Kelsey Aerials 1978 Source: U Mass
2 nd Regional Conference Dredging, Beach Nourishment & Bird Conservation Primer on Coastal Erosion And Habitat Creation Timothy Kana Ph.D Source: Newsday 1962 Photo by Kelsey Aerials 1978 Source: U Mass
SAVANNAH HARBOR EXPANSION BANK EROSION STUDY UPDATE
 CESAS-EN-GS SAVANNAH HARBOR EXPANSION BANK EROSION STUDY UPDATE GEOTECHNICAL AND HTRW BRANCH SOILS SECTION CITY FRONT, BIGHT SECTION, FORT PULASKI & NORTH TYBEE ISLAND GEORGIA 23 June 2011 CESAW-TS-EG
CESAS-EN-GS SAVANNAH HARBOR EXPANSION BANK EROSION STUDY UPDATE GEOTECHNICAL AND HTRW BRANCH SOILS SECTION CITY FRONT, BIGHT SECTION, FORT PULASKI & NORTH TYBEE ISLAND GEORGIA 23 June 2011 CESAW-TS-EG
