SAVANNAH HARBOR EXPANSION BANK EROSION STUDY UPDATE
|
|
|
- Felicia Lindsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CESAS-EN-GS SAVANNAH HARBOR EXPANSION BANK EROSION STUDY UPDATE GEOTECHNICAL AND HTRW BRANCH SOILS SECTION CITY FRONT, BIGHT SECTION, FORT PULASKI & NORTH TYBEE ISLAND GEORGIA 23 June 2011
2 CESAW-TS-EG i Savannah Harbor Expansion Bank Erosion Study Update Table of Contents Section Page 1.0 Introduction Overview General Fort Pulaski and North Tybee Descriptions Fort Pulaski North Tybee Fort Pulaski North Tybee City Front Confined Disposal Facility (Bight Section) Bank Stability Review Summary... 6
3 CESAW-TS-EG ii Appendices Appendix A Appendix B Appendix C 2003 Fleet Forecast 2011 Fleet Forecast General Location Map References
4 CESAW-TS-EG 1 SAVANNAH HARBOR EXPANSION BANK EROSION STUDY UPDATE 1. Introduction The Savannah District Geotechnical Section (CESAS-EN-GS) has completed review of the bank erosion studies for the shoreline at City Front, Bight Section, Fort Pulaski and North Tybee Island. This report supersedes all previous bank erosion studies for Savannah River. Study Update is based on the revised Fleet Forecast received April 2011, and includes available soils information, bathymetry, topographic surveys, aerial photographs, historical information, observation/review of channel side slopes resulting from previous harbor widening and deepening projects, and information from previous dredging regarding channel side slope performance. Direct correlations were made using the recently updated Ship Forces on the Shoreline of the Savannah Harbor Project report completed by the US Army Engineer Research and Development Center (ERDC) in May Waves generated by ships traffic begins with an initial wave of a maximum height with trailing waves of a much smaller energy level. The duration of ship wakes on the shore are compared to everyday wave events, tidal, flow, rainfall, and other influences normal to the river system without ship traffic. 2. Overview This analysis estimates the loss of shoreline due to ship wakes as a direct result of deepening the Savannah River shipping channel near the City Front, Bight Section, Fort Pulaski property and the northern beach of Tybee Island, if any. This is taken as the difference between the ship wakes of today versus the ship wakes of the future, considering the without project condition compared with after deepening (with project). The total estimated shoreline erosion (due to all causes) is based on aerial photography from 1964 through While additional data is available, it doesn t appear to change the outcome with regard to shoreline recession. Other shoreline changes are considered which include placement of dredged materials, armoring of adjacent shoreline, drainage features, and proximity of shoreline to the shipping channel. 3. General a. Original information available for the year 2003 and updated for 2010, the following without project forecast and calculations were completed for Containership + Tankers and General Cargo (GC) traffic: Information is presented for the total times (averaged) for any ship passing any given point of shoreline and thus causing waves that impact shoreline. Of the averaged event duration of 19.6 seconds for the estimated or given fleet, only three seconds maximum (approximately 15%) of the initial wave represents the highest energy level of consequence regardless of the ship size or speed. Smaller trailing waves are often less than wave activity normal to the shoreline at any given time without a ship passing event.
5 CESAW-TS-EG 2 From information available for the year 2010: 3,205 calls * 2 (inbound and outbound) equals 6,410 passing events of duration approximately 19.6 seconds for each ship corresponds to 125,636 seconds of impact during the year. Thus, the percent of time for ships passing any point is about 0.398% ( ) of the year of which only about 15% can be considered as having an effective impact on adjacent shoreline. The result is 0.060% for the year For the year 2017: 4,285 calls * 2 (inbound and outbound) equals 8,570 passing events, using same duration, corresponds to 167,972 seconds of impact during the year. Thus, the percent of time for ships passing a given point is about % of the year and after applying the 15% impact correction, the result is 0.080% for the year Predicted for the year 2030 and beyond: 7,204 calls *2 (inbound and outbound) equals 14,408 passing events of the same duration which corresponds to about 282,397 seconds of impact during the year. Thus, the percent of time for ships passing a check point is about % of the year 2030 and applying 15% for impact correction, the result is 0.134%. b. The latest Fleet Forecast from Economics, June 2011: For the year 2017: 4,285 calls were counted for the existing 42-foot channel depth and 4,133 calls are predicted if the channel is deepened to 47 or 48-feet. This indicates a notable reduction (3.5%) of calls, the result of which will reduce total energies and impacts to adjacent shorelines. For the year 2030 and beyond; 7,204 calls or 14,408 passing events are predicted for the without project (42 ) condition and 6,714 calls or 13,428 passing events predicted for the 47- foot to 48-foot depth condition. This represents about a 7 percent reduction of ship passing events which reduces erosion forces interacting with the banks of Savannah Harbor when compared to the without project condition. c. Ship length, beam, drafts, and speed were considered for the latest forecast. Evaluation of results yielded negligible adjustments to previous calculations. The results indicate that wave forces and passing events of predicted traffic within the deepened channel are reduced; therefore minor adjustments were not included. d. Field measurements are presented in the revised report Ship Forces on the Shoreline of the Savannah Harbor Project. A copy of the report is available as a separate publication. 4. Fort Pulaski and North Tybee Descriptions 4.1 Fort Pulaski The Fort Pulaski site is defined herein as the property along the shoreline from Georgia East NAD83 coordinates E , N (upstream) to E , N (downstream); a distance of about 2,480 feet. The property is located at the entrance to the Savannah River from the Atlantic Ocean, directly adjacent to and on the outside bank of a 149 degree bend in the river. The general location is shown below.
6 CESAW-TS-EG 3 FORT PULASKI / TYBEE LOCATION PLAN The Fort Pulaski shoreline is unprotected and lies immediately downstream from the protected shoreline near the Savannah Pilots Association (SPA) and immediately upstream from the protected shoreline at the lower end of Cockspur Island. A circular erosion pattern exists immediately downstream from the SPA slope protection. The erosion in this area has been observed to be caused by eddy currents from tidal flows, the extent of which far exceeds other noted erosion anomalies. In addition, three prominent drainage features formerly existed from upland areas to the shoreline spaced about 300 to 400 feet apart and located in the upstream half of the site. The drainage features appear to have been removed/filled-in. 4.2 North Tybee The North Tybee site is defined herein as the property along the shoreline from Georgia East NAD83 coordinates E , N (upstream) to E , N (downstream); a distance of approximately 2,670 feet. The property is located near the
7 CESAW-TS-EG 4 entrance to the Savannah Front River from the Atlantic Ocean and behind a jetty located between the Front River and the Savannah River shipping channel. The general location is shown on the Study Location Plan. The distance from the shoreline to shipping channel varies from less than one mile to almost one mile for North Tybee, as determined from the shoreline visible on aerial photographs and measured to the shipping channel centerline. 5. Fort Pulaski Aerial photographs from 1955 through 2006 were used to estimate the average yearly bank erosion along about 4,100 feet of shoreline. Photos indicate that about 1.8 feet minimum each year is lost toward the approach and discharge ends. The maximum erosion occurs in the bend area of this site (about 149 degrees) and measurements indicate about 3 feet of shoreline per year are lost to erosion unrelated to predicted ship traffic. Maps of the area are shown in Appendix C. Cross sections were plotted to determine channel configuration with respect to the shoreline, calculating the flow area, estimating the average velocity of flows, depths, radius, and other factors in an attempt to find the amount of scour and erosion that would take place on the bank (without ship traffic), for the existing channel depth of 46 feet, and the maximum proposed channel depth of 52 feet, including over-depth and advance maintenance. The Zeller Bend Scour method developed by David T. Williams, Ph.D. PE, and Leo R. Kreymborg, PE, with input from the Ship Wake Study, the annual erosion predicted for the Fort Pulaski bend site ranges from 1.6 feet to 3.2 feet due to all causes, present day. The model assumes that side slopes are uniform, bottom is uniform, crest contains smooth lines, and ignoring minor variations which are not easily managed by the model. Additional checks were performed using the CEDAS ACES computer based program which considers six functional areas: wave prediction, wave theory, wave transformation, structural design, wave run-up, and littoral processes. The program includes input for tides, velocities, shape and size of the entrance and discharge openings, bend angle, among other parameters. The predicted erosion from this model ranged from 3.0 to 3.3 feet and do not include ship traffic and/or ship wakes. Added was one Northeaster and associated long fetches waves on the Fort Pulaski site. This prediction was limited to a single one hour event with a maximum wind of 45 mph. The event yielded a 4.2 foot wave height and a 4.2 -second wave period. The storm duration of the scope defined above is estimated to account for about 0.1 foot of shoreline loss each year/event. Also considered is the effect of the channel shape and appurtenances constructed (Lash Facility) which influence flow, thalwag configuration and direction, and the amount of time that a ship will spend contributing energy to the shore which could in turn could contribute to erosion. The photo labeled FORT PULASKI 1977 (below) is a good example showing the ebb tide flow regime. It also shows the apparent magnitude of ship wake compared to normal ebb currents and waves. The present ship traffic has been estimated from the Fleet Forecast shown in Appendix B.
8 CESAW-TS-EG 5 FORT PULASKI From the Fleet Forecast predicted for Savannah Harbor before and after deepening, no additional erosion can be attributed to ship traffic. Study indicates about one meter of shoreline lost to erosion each year due to all causes and zero erosion due to ship traffic associated with deepening of the river. 6. North Tybee From the Fleet Forecast predicted for Savannah Harbor before and after deepening, no additional erosion can be attributed to ship traffic. 7. City Front Due to the reduced speed in the City Front area, drawdown and ship wake are predicted to remain unchanged. Deepening of the channel is predicted to reduce the effect of ship wake by approximately 10 percent. From the Fleet Forecast predicted for Savannah Harbor before and after deepening, no additional erosion can be attributed to ship traffic. 8. Confined Disposal Facility (Bight Section)
9 CESAW-TS-EG 6 This area of the bight has been predicted to experience approximately the same effect as the Fort Pulaski Site due to normal causes. However, this reach is or will be very soon armored against further erosion. After the planned dike protection has been completed, erosion from all causes is expected to be reduced to negligible. Based on the Fleet Forecast predicted for Savannah Harbor before and after deepening, no additional erosion can be attributed to ship traffic. 9. Bank Stability Review A June 2011 review of the Savannah Harbor Expansion Bank Stability Report dated April 2003 has been completed with respect to the revised Ship Wake Study, April The April 2003 report addressed the shipping channel with special attention given to areas where the deepened and/or revised channel alignment would or could impact existing shore, involve real estate taking, or directly affect real property in any way. There is nothing contained in the Ship Wake study that directly impacts the Bank Stability study in a way that would require redesign or additional takings. 10. Summary Given the current traffic predictions and forecasts, no bank erosion impact(s) can be directly attributed to the deepening project.
10 CESAW-TS-EG 7 APPENDIX A 2003 Fleet Forecast Table 6. Containership Traffic for Savannah Harbor. Numbers are for both without and with project values in 0 and % total calls. Vessel Type GEC 10% Increase 20% Increase 30% Increase Post- Panamax Panamax 3333 (82.7) Sub- 252 Panamax (6.3) Handysize 215 (5.3) Feedermax 18 (0.4) Feeder (5.2) (3.7) (14.0) (12.7) (22.8) (21.7) (31.6) (30.7) 6718 (86.1) 458 (5.9) 315 (4.0) 18 (0.2) (73.9) 252 (6.3) 215 (5.3) 18 (0.4) (77.1) 458 (5.9) 315 (4.0) 18 (0.2) (65.1) 252 (6.3) 215 (5.3) 18 (0.4) (68.1) 458 (5.9) 315 (4.0) 18 (0.2) (56.3) 252 (6.3) 215 (5.3) 18 (0.4) (59.2) 458 (5.9) 315 (4.0) 18 (0.2) 1 Total Calls
11 CESAW-TS-EG 8 APPENDIX B REVISED FLEET FORECAST
12 CESAW-TS-EG 9 Forecast Vessel Calls by Vessel Size Class, Channel Depth, and Year June 23, Foot Depth SPX PX 1,124 1, ,122 1,196 1,196 PPX ,006 1,421 1,421 PPX Gen + LNG 1,528 1,993 2,204 2,619 3,113 3,113 All Vessel Calls Total 3,205 4,285 4,712 5,887 7,204 7, Foot Depth SPX PX 1,096 1, ,067 1,067 PPX PPX ,035 1,035 Gen + LNG 1,528 1,993 2,204 2,619 3,113 3,113 All Vessel Calls Total 3,177 4,176 4,508 5,601 6,834 6, Foot Depth SPX PX 1,085 1, ,007 1,007 PPX PPX ,027 1,027 Gen + LNG 1,528 1,993 2,204 2,619 3,113 3,113 All Vessel Calls Total 3,166 4,150 4,469 5,549 6,760 6, Foot Depth SPX PX 1,084 1, PPX PPX ,021 1,021 Gen + LNG 1,528 1,993 2,204 2,619 3,113 3,113 All Vessel Calls Total 3,165 4,137 4,450 5,523 6,725 6, Foot Depth SPX PX 1,084 1, PPX PPX ,018 1,018 Gen + LNG 1,528 1,993 2,204 2,619 3,113 3,113 All Vessel Calls Total 3,165 4,133 4,441 5,512 6,714 6, Foot Depth SPX PX 1,084 1, PPX PPX ,018 1,018 Gen + LNG 1,528 1,993 2,204 2,619 3,113 3,113 All Vessel Calls Total 3,165 4,133 4,441 5,512 6,714 6,714
13 CESAW-TS-EG 10 APPENDIX C GENERAL LOCATION MAP
14 CESAW-TS-EG 11
15 CESAW-TS-EG 12 References ERDC, (2006, r-2011). Ship Forces on the Shoreline of the Savannah Harbor Project, Technical Report, US Army Engineer Research and Development Center, Vicksburg, MS. CECW-EH-D Engineer Manual (1991). Engineering and Design Tidal Hydraulics. Department of the Army, Corps of Engineers, Washington, DC. CECW-EW, Engineer Manual (2002, Updated 2003). Engineering and Design Coastal Engineering Manual. Department of the Army, Corps of Engineers, Washington, DC. CESAS-EN, (2003). Savannah Harbor Expansion Bank Stability Report. Department of the Army, Corps of Engineers, Savannah District, Savannah, Georgia.
3.0 ROBERTS BANK TIDAL FLAT MORPHOLOGY
 Vancouver Port Authority Northwest Hydraulic Consultants Ltd. /Triton Consultants Ltd. Roberts Bank Container Expansion File: 33863 Coastal Geomorphology Study - 19 - November 2004 3.0 ROBERTS BANK TIDAL
Vancouver Port Authority Northwest Hydraulic Consultants Ltd. /Triton Consultants Ltd. Roberts Bank Container Expansion File: 33863 Coastal Geomorphology Study - 19 - November 2004 3.0 ROBERTS BANK TIDAL
ENGINEERING APPROACHES TO SHORELINE PLACEMENT FROM COAST TO COAST
 ENGINEERING APPROACHES TO SHORELINE PLACEMENT FROM COAST TO COAST 237 237 237 217 217 217 200 200 200 0 0 0 163 163 163 131 132 122 80 119 27 252 174.59 83 36 118 110 135 120 112 92 56 62 102 130 Comparing
ENGINEERING APPROACHES TO SHORELINE PLACEMENT FROM COAST TO COAST 237 237 237 217 217 217 200 200 200 0 0 0 163 163 163 131 132 122 80 119 27 252 174.59 83 36 118 110 135 120 112 92 56 62 102 130 Comparing
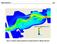
Annual transport rates at two locations on the fore-slope.
 Sediment Transport by Currents Fore-slope Sediment transport rates and sediment concentrations were computed from the hydrodynamic model runs as well as from direct measurements of current velocities at
Sediment Transport by Currents Fore-slope Sediment transport rates and sediment concentrations were computed from the hydrodynamic model runs as well as from direct measurements of current velocities at
DIVISION OF COASTAL MANAGEMENT TO STUDY CURRENT LONG-TERM EROSION RATES ADJACENT TO TERMINAL GROINS
 DIVISION OF COASTAL MANAGEMENT TO STUDY CURRENT LONG-TERM EROSION RATES ADJACENT TO TERMINAL GROINS North Carolina Department of Environmental Quality Division of Coastal Management February 22, 2018 N.
DIVISION OF COASTAL MANAGEMENT TO STUDY CURRENT LONG-TERM EROSION RATES ADJACENT TO TERMINAL GROINS North Carolina Department of Environmental Quality Division of Coastal Management February 22, 2018 N.
Donald K. Stauble and Bill Birkemeier Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory US Army Corps of Engineers
 Donald K. Stauble and Bill Birkemeier Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory US Army Corps of Engineers Define the Problem Navigation Shore Protection Environmental Political So what is the problem? Management
Donald K. Stauble and Bill Birkemeier Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory US Army Corps of Engineers Define the Problem Navigation Shore Protection Environmental Political So what is the problem? Management
Erosion Information Paper - Barrow, Alaska Current as of September 14, 2007
 U.S. Army Corps of Engineers ALASKA BASELINE EROSION ASSESSMENT Erosion Information Paper - Barrow, Alaska Current as of September 14, 2007 Community Information Barrow (BARE-row, a.k.a. Ukpeagvik), population
U.S. Army Corps of Engineers ALASKA BASELINE EROSION ASSESSMENT Erosion Information Paper - Barrow, Alaska Current as of September 14, 2007 Community Information Barrow (BARE-row, a.k.a. Ukpeagvik), population
Appendix G.19 Hatch Report Pacific NorthWest LNG Lelu Island LNG Maintenance Dredging at the Materials Offloading Facility
 Appendix G.19 Hatch Report Pacific NorthWest LNG Lelu Island LNG Maintenance Dredging at the Materials Offloading Facility Project Memo H345670 To: Capt. David Kyle From: O. Sayao/L. Absalonsen December
Appendix G.19 Hatch Report Pacific NorthWest LNG Lelu Island LNG Maintenance Dredging at the Materials Offloading Facility Project Memo H345670 To: Capt. David Kyle From: O. Sayao/L. Absalonsen December
SEGMENTED BREAKWATERS AND THEIR USE IN COASTAL LOUISIANA
 SEGMENTED BREAKWATERS AND THEIR USE IN COASTAL LOUISIANA Prepared by: Louisiana Coastal Protection and Restoration Authority Engineering Division March 2016 The geology of Louisiana s coastal zone is intimately
SEGMENTED BREAKWATERS AND THEIR USE IN COASTAL LOUISIANA Prepared by: Louisiana Coastal Protection and Restoration Authority Engineering Division March 2016 The geology of Louisiana s coastal zone is intimately
UPPER COSUMNES RIVER FLOOD MAPPING
 UPPER COSUMNES RIVER FLOOD MAPPING DRAFT BASIC DATA NARRATIVE FLOOD INSURANCE STUDY SACRAMENTO COUTY, CALIFORNIA Community No. 060262 November 2008 Prepared By: CIVIL ENGINEERING SOLUTIONS, INC. 1325 Howe
UPPER COSUMNES RIVER FLOOD MAPPING DRAFT BASIC DATA NARRATIVE FLOOD INSURANCE STUDY SACRAMENTO COUTY, CALIFORNIA Community No. 060262 November 2008 Prepared By: CIVIL ENGINEERING SOLUTIONS, INC. 1325 Howe
VICTORIA BEND HYDRAULIC SEDIMENT RESPONSE MODEL INVESTIGATION LOWER MISSISSIPPI RIVER MILES
 Technical Report M48 VICTORIA BEND HYDRAULIC SEDIMENT RESPONSE MODEL INVESTIGATION LOWER MISSISSIPPI RIVER MILES 600-590 By Peter M. Russell, P.E. Jasen L. Brown, P.E Edward J. Brauer, P.E. Robert D. Davinroy,
Technical Report M48 VICTORIA BEND HYDRAULIC SEDIMENT RESPONSE MODEL INVESTIGATION LOWER MISSISSIPPI RIVER MILES 600-590 By Peter M. Russell, P.E. Jasen L. Brown, P.E Edward J. Brauer, P.E. Robert D. Davinroy,
Redwood City Harbor, California, Navigation Improvement Feasibility Study. Appendix D. Geotechnical Engineering. DRAFT April 2015
 1 Redwood City Harbor, California, Navigation Improvement Feasibility Study Appendix D Geotechnical Engineering DRAFT April 2015 2 Contents 1 Purposes of Report... 3 2 Background... 3 3 References and
1 Redwood City Harbor, California, Navigation Improvement Feasibility Study Appendix D Geotechnical Engineering DRAFT April 2015 2 Contents 1 Purposes of Report... 3 2 Background... 3 3 References and
ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 100. Figure 7-3 Maximum velocity magnitudes for existing conditions for 100-year flood event
 ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 100 Figure 7-3 Maximum velocity magnitudes for existing conditions for 100-year flood event ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 101 Figure 7-4 Model schematization of Option 1 Figure 7-5 Bed displacement
ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 100 Figure 7-3 Maximum velocity magnitudes for existing conditions for 100-year flood event ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 101 Figure 7-4 Model schematization of Option 1 Figure 7-5 Bed displacement
Project (Project No. US-CA-62-2) Maintenance Inspection and Reports (Subtask 14.1) Inspection Report No.2
 MEMORANDUM TO: FROM: Jim Well, Ducks Unlimited Mike Harvey, PhD, PG SUBJECT: M&T/ Llano Seco Fish Screen Project (Project No. US-CA-62-2) Maintenance Inspection and Reports (Subtask 14.1) Inspection Report
MEMORANDUM TO: FROM: Jim Well, Ducks Unlimited Mike Harvey, PhD, PG SUBJECT: M&T/ Llano Seco Fish Screen Project (Project No. US-CA-62-2) Maintenance Inspection and Reports (Subtask 14.1) Inspection Report
Coastal Inlets Research Program US Army Corps of Engineers Engineering Research and Development Center
 Coastal Inlets Research Program US Army Corps of Engineers Engineering Research and Development Center Site of Moriches Inlet Nov. 1951 Julie Dean Rosati and Nicholas C. Kraus, CIRP Program Manager Shinnecock
Coastal Inlets Research Program US Army Corps of Engineers Engineering Research and Development Center Site of Moriches Inlet Nov. 1951 Julie Dean Rosati and Nicholas C. Kraus, CIRP Program Manager Shinnecock
PRESENTATION TITLE. Regional Sediment Management Application of a Coastal Model at the St. Johns River Entrance BUILDING STRONG
 PRESENTATION TITLE Regional Sediment Management Application of a Coastal Model at the St. Johns River Entrance Steven Bratos Senior Coastal Engineer U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Jacksonville District February
PRESENTATION TITLE Regional Sediment Management Application of a Coastal Model at the St. Johns River Entrance Steven Bratos Senior Coastal Engineer U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Jacksonville District February
The use of MIKE21 to study the. barrier beach system of Inner Dingle Bay, Co. Kerry, Ireland. Dr. Michael O Shea Malachy Walsh and Partners
 The use of MIKE21 to study the morphodynamic evolution of the mid-bay barrier beach system of Inner Dingle Bay, Co. Kerry, Ireland Dr. Michael O Shea Malachy Walsh and Partners Contents Why Study Morphodynamics
The use of MIKE21 to study the morphodynamic evolution of the mid-bay barrier beach system of Inner Dingle Bay, Co. Kerry, Ireland Dr. Michael O Shea Malachy Walsh and Partners Contents Why Study Morphodynamics
Port of Kalama, 2013 TEMCO Berth Maintenance Dredging and In-water Flow-Lane Placement Project
 2014 WEDA ENVIRONMENTAL EXCELLENCE AWARDS Category: Navigation Dredging Port of Kalama, 2013 TEMCO Berth Maintenance Dredging and In-water Flow-Lane Placement Project Port of Kalama, Washington 18 April
2014 WEDA ENVIRONMENTAL EXCELLENCE AWARDS Category: Navigation Dredging Port of Kalama, 2013 TEMCO Berth Maintenance Dredging and In-water Flow-Lane Placement Project Port of Kalama, Washington 18 April
Regional Sediment Management
 Regional Sediment Management Linda S. Lillycrop Program Manager Coastal Engineer US Army Engineer Research and Development Center Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory Q AVG Coastal Resilience: The Environmental,
Regional Sediment Management Linda S. Lillycrop Program Manager Coastal Engineer US Army Engineer Research and Development Center Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory Q AVG Coastal Resilience: The Environmental,
Decline of Lake Michigan-Huron Levels Caused by Erosion of the St. Clair River
 Decline of Lake Michigan-Huron Levels Caused by Erosion of the St. Clair River W.F. & Associates Coastal Engineers (in association with Frank Quinn) April 13, 2005 Outline Problem Definition Understanding
Decline of Lake Michigan-Huron Levels Caused by Erosion of the St. Clair River W.F. & Associates Coastal Engineers (in association with Frank Quinn) April 13, 2005 Outline Problem Definition Understanding
INFLOW DESIGN FLOOD CONTROL SYSTEM PLAN 40 C.F.R. PART PLANT YATES ASH POND 2 (AP-2) GEORGIA POWER COMPANY
 INFLOW DESIGN FLOOD CONTROL SYSTEM PLAN 40 C.F.R. PART 257.82 PLANT YATES ASH POND 2 (AP-2) GEORGIA POWER COMPANY EPA s Disposal of Coal Combustion Residuals from Electric Utilities Final Rule (40 C.F.R.
INFLOW DESIGN FLOOD CONTROL SYSTEM PLAN 40 C.F.R. PART 257.82 PLANT YATES ASH POND 2 (AP-2) GEORGIA POWER COMPANY EPA s Disposal of Coal Combustion Residuals from Electric Utilities Final Rule (40 C.F.R.
The Impact of Hurricane Irma on the Coast of Florida
 The Impact of Hurricane Irma on the Coast of Florida Ralph Clark, Guy Weeks, Robert Wang, Mike Manausa & Peter Bacopoulos Division of Water Resource Management February 8, 2018 Overview: Hurricane Irma
The Impact of Hurricane Irma on the Coast of Florida Ralph Clark, Guy Weeks, Robert Wang, Mike Manausa & Peter Bacopoulos Division of Water Resource Management February 8, 2018 Overview: Hurricane Irma
The last three sections of the main body of this report consist of:
 Threatened and Endangered Species Geological Hazards Floodplains Cultural Resources Hazardous Materials A Cost Analysis section that provides comparative conceptual-level costs follows the Environmental
Threatened and Endangered Species Geological Hazards Floodplains Cultural Resources Hazardous Materials A Cost Analysis section that provides comparative conceptual-level costs follows the Environmental
Material Workshop. Galveston District 2012 Beneficial Use of Dredged. Material Workshop. Custodians of the Coast
 Galveston District 2012 Beneficial Use of Dredged Material Workshop Galveston District 2012 Beneficial Use of Dredged Material Workshop US Army Corps of Engineers BUILDING STRONG Welcome Opening Remarks
Galveston District 2012 Beneficial Use of Dredged Material Workshop Galveston District 2012 Beneficial Use of Dredged Material Workshop US Army Corps of Engineers BUILDING STRONG Welcome Opening Remarks
MEANDER MIGRATION MODEL ASSESSMENT FOR THE JANUARY 2005 STORM, WHITMAN PROPERTY, SAN ANTONIO CREEK, VENTURA COUNTY, CALIFORNIA
 MEANDER MIGRATION MODEL ASSESSMENT FOR THE JANUARY 2005 STORM, WHITMAN PROPERTY, SAN ANTONIO CREEK, VENTURA COUNTY, CALIFORNIA Prepared by Eric Larsen, Ph.D. Mark Rains, Ph.D. October 2006 INTRODUCTION
MEANDER MIGRATION MODEL ASSESSMENT FOR THE JANUARY 2005 STORM, WHITMAN PROPERTY, SAN ANTONIO CREEK, VENTURA COUNTY, CALIFORNIA Prepared by Eric Larsen, Ph.D. Mark Rains, Ph.D. October 2006 INTRODUCTION
Appendix I. Dredged Volume Estimates. Draft Contractor Document: Subject to Continuing Agency Review
 Appendix I Dredged Volume Estimates Draft Contractor Document: Subject to Continuing Agency Review Interoffice Correspondence Date: April 6, 2007 To: L. Bossi (WHI) Copy: S. Thompson (WHI), B. Fidler (NNJ)
Appendix I Dredged Volume Estimates Draft Contractor Document: Subject to Continuing Agency Review Interoffice Correspondence Date: April 6, 2007 To: L. Bossi (WHI) Copy: S. Thompson (WHI), B. Fidler (NNJ)
SEDIMENTATION STUDY OF THE MIDDLE MISSISSIPPI RIVER AT BUFFALO ISLAND RIVER MILES 28.0 TO 22.0 HYDRAULIC MICRO MODEL INVESTIGATION
 Technical Report M29 SEDIMENTATION STUDY OF THE MIDDLE MISSISSIPPI RIVER AT BUFFALO ISLAND RIVER MILES 28.0 TO 22.0 HYDRAULIC MICRO MODEL INVESTIGATION By Jasen L. Brown Michael T. Rodgers Dawn M.Lamm
Technical Report M29 SEDIMENTATION STUDY OF THE MIDDLE MISSISSIPPI RIVER AT BUFFALO ISLAND RIVER MILES 28.0 TO 22.0 HYDRAULIC MICRO MODEL INVESTIGATION By Jasen L. Brown Michael T. Rodgers Dawn M.Lamm
Draft exercise for share fair at Bozeman workshop only. This exercise is not ready for distribution. Please send helpful suggestions to
 Draft exercise for share fair at Bozeman workshop only. This exercise is not ready for distribution. Please send helpful suggestions to foleyd@plu.edu Figure list 1. Trailer photograph 2. Location map
Draft exercise for share fair at Bozeman workshop only. This exercise is not ready for distribution. Please send helpful suggestions to foleyd@plu.edu Figure list 1. Trailer photograph 2. Location map
Probabilistic Evaluation of a Meandering Low-Flow Channel. February 24 th, UMSRS
 Probabilistic Evaluation of a Meandering Low-Flow Channel February 24 th, 2014 2014 UMSRS 1 2 acknowledgments Low- Flow Channel (LFC) overview Proposed Diversion Channel collects runoff from: The Rush
Probabilistic Evaluation of a Meandering Low-Flow Channel February 24 th, 2014 2014 UMSRS 1 2 acknowledgments Low- Flow Channel (LFC) overview Proposed Diversion Channel collects runoff from: The Rush
YELLOWSTONE RIVER FLOOD STUDY REPORT TEXT
 YELLOWSTONE RIVER FLOOD STUDY REPORT TEXT TECHNICAL REPORT Prepared for: City of Livingston 411 East Callender Livingston, MT 59047 Prepared by: Clear Creek Hydrology, Inc. 1627 West Main Street, #294
YELLOWSTONE RIVER FLOOD STUDY REPORT TEXT TECHNICAL REPORT Prepared for: City of Livingston 411 East Callender Livingston, MT 59047 Prepared by: Clear Creek Hydrology, Inc. 1627 West Main Street, #294
PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING DISTRICT 3-0
 PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING DISTRICT 3-0 LYCOMING COUNTY S.R.15, SECTION C41 FINAL HYDROLOGIC AND HYDRAULIC REPORT STEAM VALLEY RUN STREAM RELOCATION DATE: June, 2006 REVISED:
PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING DISTRICT 3-0 LYCOMING COUNTY S.R.15, SECTION C41 FINAL HYDROLOGIC AND HYDRAULIC REPORT STEAM VALLEY RUN STREAM RELOCATION DATE: June, 2006 REVISED:
CHAPTER 28. PHYSIOGRAPHY Cook Inlet Drainages
 PEBBLE PROJECT ENVIRONMENTAL BASELINE DOCUMENT 2004 through 2008 CHAPTER 28. PHYSIOGRAPHY Cook Inlet Drainages PREPARED BY: Knight Piésold Ltd. PHYSIOGRAPHY COOK INLET DRAINAGES TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE
PEBBLE PROJECT ENVIRONMENTAL BASELINE DOCUMENT 2004 through 2008 CHAPTER 28. PHYSIOGRAPHY Cook Inlet Drainages PREPARED BY: Knight Piésold Ltd. PHYSIOGRAPHY COOK INLET DRAINAGES TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE
APPENDIX A M&T/Llano Seco Long-Term Water Reliability Study These photos are examples of rock spurs in use throughout the United States
 APPENDIX A M&T/Llano Seco Long-Term Water Reliability Study These photos are examples of rock spurs in use throughout the United States Glenn Colusa Irrigation District completed a Sacramento River project
APPENDIX A M&T/Llano Seco Long-Term Water Reliability Study These photos are examples of rock spurs in use throughout the United States Glenn Colusa Irrigation District completed a Sacramento River project
EROSION HAZARD OF MINNESOTA'S LAKE SUPERIOR SHORELINE. Carol A. Johnston Principal Investigator
 EROSION HAZARD OF MINNESOTA'S LAKE SUPERIOR SHORELINE Carol A. Johnston Principal Investigator Maps prepared by: James Salés, John Bonde, Tim Aunan, and Richard Raby Minnesota Sea Grant Research Bulletin
EROSION HAZARD OF MINNESOTA'S LAKE SUPERIOR SHORELINE Carol A. Johnston Principal Investigator Maps prepared by: James Salés, John Bonde, Tim Aunan, and Richard Raby Minnesota Sea Grant Research Bulletin
Erosion Information Paper Eagle City and Eagle Village, Alaska Current as of January 21, 2008
 U.S. Army Corps of Engineers ALASKA BASELINE EROSION ASSESSMENT Erosion Information Paper Eagle City and Eagle Village, Alaska Current as of January 21, 2008 Community Information The City of Eagle, population
U.S. Army Corps of Engineers ALASKA BASELINE EROSION ASSESSMENT Erosion Information Paper Eagle City and Eagle Village, Alaska Current as of January 21, 2008 Community Information The City of Eagle, population
Sediment Budget Analysis System (SBAS)
 Coastal Engineering Technical Note IV-20 Sediment Budget Analysis System (SBAS) by Julie Dean Rosati and Nicholas C. Kraus PURPOSE: The Coastal Engineering Technical Note (CETN) herein presents the Sediment
Coastal Engineering Technical Note IV-20 Sediment Budget Analysis System (SBAS) by Julie Dean Rosati and Nicholas C. Kraus PURPOSE: The Coastal Engineering Technical Note (CETN) herein presents the Sediment
Phase II Storm Surge Analysis
 Phase II Storm Surge Analysis Post 45 Project, Charleston, SC Prepared for: USACE Charleston District Charleston, SC Prepared by: Water Environment Consultants Mount Pleasant, SC October 21, 2016 Table
Phase II Storm Surge Analysis Post 45 Project, Charleston, SC Prepared for: USACE Charleston District Charleston, SC Prepared by: Water Environment Consultants Mount Pleasant, SC October 21, 2016 Table
Controlling Processes That Change Land
 1 Name Date Controlling Processes That Change Land People try to control some of the processes that change land. To do this, people apply technology- the use of science to solve problems in everyday life.
1 Name Date Controlling Processes That Change Land People try to control some of the processes that change land. To do this, people apply technology- the use of science to solve problems in everyday life.
Analysis of the Effects of Bendway Weir Construction on Channel Cross Sectional Geometry
 Mississippi River Miles 275.2 1.7 Analysis of the Effects of Bendway Weir Construction on Channel Cross Sectional Geometry By Timothy Lauth David Gordon, P.E. Katherine Clancey Adam Rockwell Brad Krischel
Mississippi River Miles 275.2 1.7 Analysis of the Effects of Bendway Weir Construction on Channel Cross Sectional Geometry By Timothy Lauth David Gordon, P.E. Katherine Clancey Adam Rockwell Brad Krischel
HURRICANE SANDY LIMITED REEVALUATION REPORT UNION BEACH, NEW JERSEY DRAFT ENGINEERING APPENDIX SUB APPENDIX A PRELIMINARY FLOODWALL DESIGN
 HURRICANE SANDY LIMITED REEVALUATION REPORT UNION BEACH, NEW JERSEY DRAFT ENGINEERING APPENDIX SUB APPENDIX A PRELIMINARY FLOODWALL DESIGN March 2014Revised March 2015 UNITED STATES ARMY CORPS OF ENGINEERS
HURRICANE SANDY LIMITED REEVALUATION REPORT UNION BEACH, NEW JERSEY DRAFT ENGINEERING APPENDIX SUB APPENDIX A PRELIMINARY FLOODWALL DESIGN March 2014Revised March 2015 UNITED STATES ARMY CORPS OF ENGINEERS
Sessom Creek Sand Bar Removal HCP Task 5.4.6
 Sessom Creek Sand Bar Removal HCP Task 5.4.6 Prepared by: Dr. Thomas Hardy Texas State University Dr. Nolan Raphelt Texas Water Development Board January 6, 2013 DRAFT 1 Introduction The confluence of
Sessom Creek Sand Bar Removal HCP Task 5.4.6 Prepared by: Dr. Thomas Hardy Texas State University Dr. Nolan Raphelt Texas Water Development Board January 6, 2013 DRAFT 1 Introduction The confluence of
COASTAL SEDIMENT BUDGET FOR JUPITER INLET, FLORIDA
 COASTAL SEDIMENT BUDGET FOR JUPITER INLET, FLORIDA By KRISTEN MARIE ODRONIEC A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE
COASTAL SEDIMENT BUDGET FOR JUPITER INLET, FLORIDA By KRISTEN MARIE ODRONIEC A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE
Ship Effects Before and After Deepening of Sabine-Neches Waterway, Port Arthur, Texas
 us Army Corps of Engineers Engineer Research and Development Center Ship Effects Before and After Deepening of Sabine-Neches Waterway, Port Arthur, Texas Stephen T. Maynord September 2003 200304 032 Approved
us Army Corps of Engineers Engineer Research and Development Center Ship Effects Before and After Deepening of Sabine-Neches Waterway, Port Arthur, Texas Stephen T. Maynord September 2003 200304 032 Approved
Regional Sediment Management at East Rockaway Inlet, NY, Utilizing the USACE Coastal Modeling System
 Regional Sediment Management at East Rockaway Inlet, NY, Utilizing the USACE Coastal Modeling System by US Army Engineer District, New York PURPOSE: This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note
Regional Sediment Management at East Rockaway Inlet, NY, Utilizing the USACE Coastal Modeling System by US Army Engineer District, New York PURPOSE: This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note
Mapping of Future Coastal Hazards. for Southern California. January 7th, David Revell, Ph.D. E.
 Mapping of Future Coastal Hazards for Southern California January 7th, 2014 David Revell, Ph.D. drevell@esassoc.com E. Vandebroek, 2012 Outline Coastal erosion hazard zones Flood hazard zones: Coastal
Mapping of Future Coastal Hazards for Southern California January 7th, 2014 David Revell, Ph.D. drevell@esassoc.com E. Vandebroek, 2012 Outline Coastal erosion hazard zones Flood hazard zones: Coastal
Materials. Use materials meeting the following.
 208.01 Section 208. SOIL EROSION AND SEDIMENTATION CONTROL 208.01 Description. Install and maintain erosion and sedimentation controls to minimize soil erosion and to control sedimentation from affecting
208.01 Section 208. SOIL EROSION AND SEDIMENTATION CONTROL 208.01 Description. Install and maintain erosion and sedimentation controls to minimize soil erosion and to control sedimentation from affecting
Design of Levee Breaches in Sheltered Water for Flood Risk Reduction & Marsh Restoration ASFMP; June 5, 2014 Presented By:
 Design of Levee Breaches in Sheltered Water for Flood Risk Reduction & Marsh Restoration ASFMP; June 5, 2014 Presented By: Rohin Saleh Alameda County Flood Control District Matt Powers, P.E. GEI Consultants
Design of Levee Breaches in Sheltered Water for Flood Risk Reduction & Marsh Restoration ASFMP; June 5, 2014 Presented By: Rohin Saleh Alameda County Flood Control District Matt Powers, P.E. GEI Consultants
Estimated Sediment Volume: Bridge Street Dam Impoundment, Royal River, Yarmouth, Maine
 University of Southern Maine USM Digital Commons Publications Casco Bay Estuary Partnership (CBEP) 2015 Estimated Sediment Volume: Bridge Street Dam Impoundment, Royal River, Yarmouth, Maine Stantec Follow
University of Southern Maine USM Digital Commons Publications Casco Bay Estuary Partnership (CBEP) 2015 Estimated Sediment Volume: Bridge Street Dam Impoundment, Royal River, Yarmouth, Maine Stantec Follow
GIS 2010: Coastal Erosion in Mississippi Delta
 1) Introduction Problem overview To what extent do large storm events play in coastal erosion rates, and what is the rate at which coastal erosion is occurring in sediment starved portions of the Mississippi
1) Introduction Problem overview To what extent do large storm events play in coastal erosion rates, and what is the rate at which coastal erosion is occurring in sediment starved portions of the Mississippi
Hydraulics of bendway weirs
 River Basin Management IV 389 Hydraulics of bendway weirs C. Thornton 1, S. Abt 1, D. Baird 2 & R. Padilla 3 1 Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA 2 U.S. Bureau of Reclamation, Denver, CO,
River Basin Management IV 389 Hydraulics of bendway weirs C. Thornton 1, S. Abt 1, D. Baird 2 & R. Padilla 3 1 Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA 2 U.S. Bureau of Reclamation, Denver, CO,
A SEDIMENT BUDGET ANALYSIS AND MANAGEMENT STRATEGY FOR FORT PIERCE INLET, FL
 A SEDIMENT BUDGET ANALYSIS AND MANAGEMENT STRATEGY FOR FORT PIERCE INLET, FL By Elba Rodriguez and Robert G. Dean Department of Civil and Coastal Engineering University of Florida Gainesville, FL 32611,
A SEDIMENT BUDGET ANALYSIS AND MANAGEMENT STRATEGY FOR FORT PIERCE INLET, FL By Elba Rodriguez and Robert G. Dean Department of Civil and Coastal Engineering University of Florida Gainesville, FL 32611,
MEMORANDUM FOR SWG
 MEMORANDUM FOR SWG-2007-1623 Subject: Jurisdictional Determination (JD) for SWG-2007-1623 on Interdunal Wetlands Adjacent to Traditional Navigable Waters (TNWs) Summary The U.S. Environmental Protection
MEMORANDUM FOR SWG-2007-1623 Subject: Jurisdictional Determination (JD) for SWG-2007-1623 on Interdunal Wetlands Adjacent to Traditional Navigable Waters (TNWs) Summary The U.S. Environmental Protection
EAST PASS UP-DATE SUMMARY OF FINDINGS REPORT and INLET MANAGEMENT IMPLEMENTATION PLAN
 EAST PASS 2013 UP-DATE SUMMARY OF FINDINGS REPORT and INLET MANAGEMENT IMPLEMENTATION PLAN Introduction On June 8, 2000, the Florida Department of Environmental Protection adopted the East Pass Inlet Management
EAST PASS 2013 UP-DATE SUMMARY OF FINDINGS REPORT and INLET MANAGEMENT IMPLEMENTATION PLAN Introduction On June 8, 2000, the Florida Department of Environmental Protection adopted the East Pass Inlet Management
Appendix E Guidance for Shallow Flooding Analyses and Mapping
 Appendix E Guidance for Shallow Flooding Analyses and Mapping E.1 Introduction Different types of shallow flooding commonly occur throughout the United States. Types of flows that result in shallow flooding
Appendix E Guidance for Shallow Flooding Analyses and Mapping E.1 Introduction Different types of shallow flooding commonly occur throughout the United States. Types of flows that result in shallow flooding
IMPORTANCE OF GEOLOGIC CHARACTERIZATION FOR LEVEE FOUNDATION AND BORROW MATERIALS AS STUDIED AT THE INDIAN GRAVES LEVEE DISTRICT, ADAMS COUNTY, IL
 IMPORTANCE OF GEOLOGIC CHARACTERIZATION FOR LEVEE FOUNDATION AND BORROW MATERIALS AS STUDIED AT THE INDIAN GRAVES LEVEE DISTRICT, ADAMS COUNTY, IL Conor Watkins Missouri University of Science and Technology
IMPORTANCE OF GEOLOGIC CHARACTERIZATION FOR LEVEE FOUNDATION AND BORROW MATERIALS AS STUDIED AT THE INDIAN GRAVES LEVEE DISTRICT, ADAMS COUNTY, IL Conor Watkins Missouri University of Science and Technology
Lateral Inflow into High-Velocity Channels
 Lateral Inflow into High-Velocity Channels by Richard L. Stockstill PURPOSE: This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note (CHETN) investigates lateral flow discharging into a high-velocity channel.
Lateral Inflow into High-Velocity Channels by Richard L. Stockstill PURPOSE: This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note (CHETN) investigates lateral flow discharging into a high-velocity channel.
SEDIMENTATION STUDY OF THE MIDDLE MISSISSIPPI RIVER AT SALT LAKE CHUTE, RIVER MILES 141 TO 133 HYDRAULIC MICRO MODEL INVESTIGATION
 Technical Report M16 SEDIMENTATION STUDY OF THE MIDDLE MISSISSIPPI RIVER AT SALT LAKE CHUTE, RIVER MILES 141 TO 133 HYDRAULIC MICRO MODEL INVESTIGATION By David C. Gordon Robert D. Davinroy Peter M. Russell
Technical Report M16 SEDIMENTATION STUDY OF THE MIDDLE MISSISSIPPI RIVER AT SALT LAKE CHUTE, RIVER MILES 141 TO 133 HYDRAULIC MICRO MODEL INVESTIGATION By David C. Gordon Robert D. Davinroy Peter M. Russell
The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Philadelphia District
 The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Philadelphia District The Atlantic Coast of New Jersey Regional Sediment Budget 1986-2003 Cape May Point to Manasquan Inlet Final Report March 2006 The Atlantic Coast of
The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Philadelphia District The Atlantic Coast of New Jersey Regional Sediment Budget 1986-2003 Cape May Point to Manasquan Inlet Final Report March 2006 The Atlantic Coast of
MEANDER MIGRATION MODEL ASSESSMENT FOR THE 50- AND 100-YEAR STORMS, WHITMAN PROPERTY, SAN ANTONIO CREEK, VENTURA COUNTY, CALIFORNIA
 MEANDER MIGRATION MODEL ASSESSMENT FOR THE 50- AND 100-YEAR STORMS, WHITMAN PROPERTY, SAN ANTONIO CREEK, VENTURA COUNTY, CALIFORNIA Prepared by Eric Larsen, Ph.D. Mark Rains, Ph.D. October 2006 TABLE OF
MEANDER MIGRATION MODEL ASSESSMENT FOR THE 50- AND 100-YEAR STORMS, WHITMAN PROPERTY, SAN ANTONIO CREEK, VENTURA COUNTY, CALIFORNIA Prepared by Eric Larsen, Ph.D. Mark Rains, Ph.D. October 2006 TABLE OF
Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory
 ERDC/CHL TR-09-6 Houston-Galveston Navigation Channels, Texas Project Navigation Channel Sedimentation Study, Phase 2 Plan Simulations Jennifer N. Tate and Cassandra G. Ross August 2009 Coastal and Hydraulics
ERDC/CHL TR-09-6 Houston-Galveston Navigation Channels, Texas Project Navigation Channel Sedimentation Study, Phase 2 Plan Simulations Jennifer N. Tate and Cassandra G. Ross August 2009 Coastal and Hydraulics
FUTURE MEANDER BEND MIGRATION AND FLOODPLAIN DEVELOPMENT PATTERNS NEAR RIVER MILES 200 TO 191 OF THE SACRAMENTO RIVER PHASE III REPORT
 FUTURE MEANDER BEND MIGRATION AND FLOODPLAIN DEVELOPMENT PATTERNS NEAR RIVER MILES 200 TO 191 OF THE SACRAMENTO RIVER PHASE III REPORT Eric W. Larsen REPORT FOR DUCKS UNLIMITED March 31, 2006-1 - Contents
FUTURE MEANDER BEND MIGRATION AND FLOODPLAIN DEVELOPMENT PATTERNS NEAR RIVER MILES 200 TO 191 OF THE SACRAMENTO RIVER PHASE III REPORT Eric W. Larsen REPORT FOR DUCKS UNLIMITED March 31, 2006-1 - Contents
Sediment Budget Analysis System (SBAS)
 Coastal Engineering Technical Note IV-20 US Army Corps of Engineers Sediment Budget Analysis System (SBAS) by Julie Dean Rosati and Nicholas C. Kraus PURPOSE: The Coastal Engineering Technical Note (CETN)
Coastal Engineering Technical Note IV-20 US Army Corps of Engineers Sediment Budget Analysis System (SBAS) by Julie Dean Rosati and Nicholas C. Kraus PURPOSE: The Coastal Engineering Technical Note (CETN)
Four Mile Run Levee Corridor Stream Restoration
 Four Mile Run Levee Corridor Stream Restoration 30% Design Summary U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Baltimore District Presentation Outline Four Mile Run 1.) Historic Perspective 2.) Existing Conditions 3.)
Four Mile Run Levee Corridor Stream Restoration 30% Design Summary U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Baltimore District Presentation Outline Four Mile Run 1.) Historic Perspective 2.) Existing Conditions 3.)
Analysis of Environmental Impacts from the Port of Miami Expansion. Julienne Beblo
 Analysis of Environmental Impacts from the Port of Miami Expansion Julienne Beblo 6.28.16 The Port of Miami One of the most prominent ports for global tourism and commerce Contributes $28 billion/yr to
Analysis of Environmental Impacts from the Port of Miami Expansion Julienne Beblo 6.28.16 The Port of Miami One of the most prominent ports for global tourism and commerce Contributes $28 billion/yr to
Mississippi River West Bay Diversion Geomorphic Assessment and 1-D Modeling Plan
 Mississippi River West Bay Diversion Geomorphic Assessment and 1-D Modeling Plan Freddie Pinkard and Charlie Little Research Hydraulic Engineers ERDC-CHL-River Engineering Branch 27 February 2009 Lane
Mississippi River West Bay Diversion Geomorphic Assessment and 1-D Modeling Plan Freddie Pinkard and Charlie Little Research Hydraulic Engineers ERDC-CHL-River Engineering Branch 27 February 2009 Lane
Alexandra Carvalho, Ph.D., GISP Kathy Fitzpatrick, P.E.
 Coastal Data Organization for Project Management and Coastal Planning Martin County, Florida Alexandra Carvalho, Ph.D., GISP Kathy Fitzpatrick, P.E. Outline County Coastal Programs Coastal Geodatabase
Coastal Data Organization for Project Management and Coastal Planning Martin County, Florida Alexandra Carvalho, Ph.D., GISP Kathy Fitzpatrick, P.E. Outline County Coastal Programs Coastal Geodatabase
Linking Inlet Hydrodynamics and Morphologic Response at Oregon Inlet, NC
 Linking Inlet Hydrodynamics and Morphologic Response at Oregon Inlet, NC Prepared for: Sharon Ahlers Engineering Communications Program Cornell University Prepared by: Justin Vandever School of Civil and
Linking Inlet Hydrodynamics and Morphologic Response at Oregon Inlet, NC Prepared for: Sharon Ahlers Engineering Communications Program Cornell University Prepared by: Justin Vandever School of Civil and
What are the issues?
 Water Quality along Lake Huron What are the issues? Lake Huron Water Quality Algal fouling Irregular, less frequent, less widespread, but some significant local events Influences Tributaries contribute;
Water Quality along Lake Huron What are the issues? Lake Huron Water Quality Algal fouling Irregular, less frequent, less widespread, but some significant local events Influences Tributaries contribute;
ENGINEERING WITH NATURE: NEARSHORE BERM PLACEMENTS AT FORT MYERS BEACH AND PERDIDO KEY, FLORIDA, USA
 1 ENGINEERING WITH NATURE: NEARSHORE BERM PLACEMENTS AT FORT MYERS BEACH AND PERDIDO KEY, FLORIDA, USA KATHERINE E. BRUTSCHÉ 1, PING WANG 2, JULIE D. ROSATI 1, CHERYL E. POLLOCK 1 1. U.S. Army Engineer
1 ENGINEERING WITH NATURE: NEARSHORE BERM PLACEMENTS AT FORT MYERS BEACH AND PERDIDO KEY, FLORIDA, USA KATHERINE E. BRUTSCHÉ 1, PING WANG 2, JULIE D. ROSATI 1, CHERYL E. POLLOCK 1 1. U.S. Army Engineer
Bank Erosion and Morphology of the Kaskaskia River
 Bank Erosion and Morphology of the Kaskaskia River US Army Corps Of Engineers St. Louis District Fayette County Soil and Water Conservation District Team Partners : Carlyle Lake Ecosystem Partnership Vicinity
Bank Erosion and Morphology of the Kaskaskia River US Army Corps Of Engineers St. Louis District Fayette County Soil and Water Conservation District Team Partners : Carlyle Lake Ecosystem Partnership Vicinity
Morphological Modeling of Inlets and Adjacent Shorelines on Engineering Timescales
 CB&I Morphological Modeling of Inlets and Adjacent Shorelines on Engineering Timescales Challenges and Model Improvements based on Recent Studies Dobrochinski, J.P.H.; Benedet, L.; Signorin, M.; Pierro,
CB&I Morphological Modeling of Inlets and Adjacent Shorelines on Engineering Timescales Challenges and Model Improvements based on Recent Studies Dobrochinski, J.P.H.; Benedet, L.; Signorin, M.; Pierro,
Relatively little hard substrate occurs naturally in the
 CHAPTER FIVE Rock Habitats Relatively little hard substrate occurs naturally in the estuary, owing mainly to the vast quantities of fine sediment that have been deposited by the rivers. Rock habitat is
CHAPTER FIVE Rock Habitats Relatively little hard substrate occurs naturally in the estuary, owing mainly to the vast quantities of fine sediment that have been deposited by the rivers. Rock habitat is
THC-T-2013 Conference & Exhibition
 Modeling of Shutter Coastal Protection against Storm Surge for Galveston Bay C. Vipulanandan, Ph.D., P.E., Y. Jeannot Ahossin Guezo and and B. Basirat Texas Hurricane Center for Innovative Technology (THC-IT)
Modeling of Shutter Coastal Protection against Storm Surge for Galveston Bay C. Vipulanandan, Ph.D., P.E., Y. Jeannot Ahossin Guezo and and B. Basirat Texas Hurricane Center for Innovative Technology (THC-IT)
Appendix O. Sediment Transport Modelling Technical Memorandum
 Appendix O Sediment Transport Modelling Technical Memorandum w w w. b a i r d. c o m Baird o c e a n s engineering l a k e s design r i v e r s science w a t e r s h e d s construction Final Report Don
Appendix O Sediment Transport Modelling Technical Memorandum w w w. b a i r d. c o m Baird o c e a n s engineering l a k e s design r i v e r s science w a t e r s h e d s construction Final Report Don
MISSISSIPPI COASTAL IMPROVEMENTS
 MISSISSIPPI COASTAL IMPROVEMENTS PROGRAM (MsCIP) Comprehensive Barrier 237 27 200 237 27 200 Island 237 Restoration 27 200 Plan 80 9 27 252 74.59 255 255 255 0 0 0 63 63 63 3 32 22 239 65 53 0 35 20 2
MISSISSIPPI COASTAL IMPROVEMENTS PROGRAM (MsCIP) Comprehensive Barrier 237 27 200 237 27 200 Island 237 Restoration 27 200 Plan 80 9 27 252 74.59 255 255 255 0 0 0 63 63 63 3 32 22 239 65 53 0 35 20 2
ENGINEER S CERTIFICATION OF FAULT AREA DEMONSTRATION (40 CFR )
 PLATTE RIVER POWER AUTHORITY RAWHIDE ENERGY STATION BOTTOM ASH TRANSFER (BAT) IMPOUNDMENTS LARIMER COUNTY, CO ENGINEER S CERTIFICATION OF FAULT AREA DEMONSTRATION (40 CFR 257.62) FOR COAL COMBUSTION RESIDUALS
PLATTE RIVER POWER AUTHORITY RAWHIDE ENERGY STATION BOTTOM ASH TRANSFER (BAT) IMPOUNDMENTS LARIMER COUNTY, CO ENGINEER S CERTIFICATION OF FAULT AREA DEMONSTRATION (40 CFR 257.62) FOR COAL COMBUSTION RESIDUALS
Savannah Harbor Expansion Project
 Savannah Harbor Expansion Project Evaluation of Hurricane Surge Impacts with Proposed Mitigation Plan December 2007 Introduction This report summarizes the results of hurricane surge impacts with implementation
Savannah Harbor Expansion Project Evaluation of Hurricane Surge Impacts with Proposed Mitigation Plan December 2007 Introduction This report summarizes the results of hurricane surge impacts with implementation
DRAFT DETAILED PROJECT REPORT TANGIER ISLAND JETTY ACCOMACK COUNTY, VIRGINIA SECTION 107 NAVIGATION STUDY
 DRAFT DETAILED PROJECT REPORT TANGIER ISLAND JETTY ACCOMACK COUNTY, VIRGINIA SECTION 107 NAVIGATION STUDY APPENDIX A ENGINEERING, DESIGN AND COST ESTIMATES U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Norfolk District
DRAFT DETAILED PROJECT REPORT TANGIER ISLAND JETTY ACCOMACK COUNTY, VIRGINIA SECTION 107 NAVIGATION STUDY APPENDIX A ENGINEERING, DESIGN AND COST ESTIMATES U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Norfolk District
Appendix G.18 Hatch Report Pacific NorthWest LNG Lelu Island LNG Potential Impacts of the Marine Structures on the Hydrodynamics and Sedimentation
 Appendix G.18 Hatch Report Pacific NorthWest LNG Lelu Island LNG Potential Impacts of the Marine Structures on the Hydrodynamics and Sedimentation Patterns Project Memo H345670 To: Capt. David Kyle From:
Appendix G.18 Hatch Report Pacific NorthWest LNG Lelu Island LNG Potential Impacts of the Marine Structures on the Hydrodynamics and Sedimentation Patterns Project Memo H345670 To: Capt. David Kyle From:
DESIGN ENGINEERING ANALYSIS FOR TERMINAL GROIN LENGTH
 APPENDIX F DESIGN ENGINEERING ANALYSIS FOR TERMINAL GROIN LENGTH (Prepared by Olsen Associates, Inc.) DRAFT Environmental Impact Statement Village of Bald Head Island Shoreline Protection Project Brunswick
APPENDIX F DESIGN ENGINEERING ANALYSIS FOR TERMINAL GROIN LENGTH (Prepared by Olsen Associates, Inc.) DRAFT Environmental Impact Statement Village of Bald Head Island Shoreline Protection Project Brunswick
The Sediment Budget Calculator: A Webtool to Develop a Family of Viable Inlet and Adjacent Beach Sediment Budget Solutions
 The Sediment Budget Calculator: A Webtool to Develop a Family of Viable Inlet and Adjacent Beach Sediment Budget Solutions by Julie Dean Rosati, Charles A. Sumner, and Derek A. Wilson PURPOSE: This Coastal
The Sediment Budget Calculator: A Webtool to Develop a Family of Viable Inlet and Adjacent Beach Sediment Budget Solutions by Julie Dean Rosati, Charles A. Sumner, and Derek A. Wilson PURPOSE: This Coastal
SAN FRANCISCO DISTRICT INFORMATION REQUESTED FOR VERIFICATION OF CORPS JURISDICTION
 DEPARTMENT OF THE ARMY SAN FRANCISCO DISTRICT, U.S. ARMY CORPS OF ENGINEERS 1455 MARKET STREET SAN FRANCISCO, CALIFORNIA 94103-1398 SAN FRANCISCO DISTRICT INFORMATION REQUESTED FOR VERIFICATION OF CORPS
DEPARTMENT OF THE ARMY SAN FRANCISCO DISTRICT, U.S. ARMY CORPS OF ENGINEERS 1455 MARKET STREET SAN FRANCISCO, CALIFORNIA 94103-1398 SAN FRANCISCO DISTRICT INFORMATION REQUESTED FOR VERIFICATION OF CORPS
WORKSHOP #2 [Modeling and Sediment Transfers Review of alternative solutions] Bucharest 07 October 2015
![WORKSHOP #2 [Modeling and Sediment Transfers Review of alternative solutions] Bucharest 07 October 2015 WORKSHOP #2 [Modeling and Sediment Transfers Review of alternative solutions] Bucharest 07 October 2015](/thumbs/82/85703998.jpg) STUDIU DE FEZABILITATE PENTRU SOLUŢII TEHNICE ALTERNATIVE/COMPLEMENTARE PRIVIND LUCRĂRILE CE SE VOR EXECUTA ÎN PUNCTUL CRITIC 01 BALA DIN CADRUL PROIECTULUI ÎMBUNĂTĂŢIREA CONDIŢIILOR DE NAVIGAŢIE PE DUNĂRE
STUDIU DE FEZABILITATE PENTRU SOLUŢII TEHNICE ALTERNATIVE/COMPLEMENTARE PRIVIND LUCRĂRILE CE SE VOR EXECUTA ÎN PUNCTUL CRITIC 01 BALA DIN CADRUL PROIECTULUI ÎMBUNĂTĂŢIREA CONDIŢIILOR DE NAVIGAŢIE PE DUNĂRE
Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory
 ERDC/CHL TR-05-6 Texas City Ship Channel Deepening Study, Hydrodynamic Model Lisa M. Lee, Jennifer N. Tate, and R. C. Berger August 2005 Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory Approved for public release; distribution
ERDC/CHL TR-05-6 Texas City Ship Channel Deepening Study, Hydrodynamic Model Lisa M. Lee, Jennifer N. Tate, and R. C. Berger August 2005 Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory Approved for public release; distribution
Great Lakes Update. Volume 194: 2015 Annual Summary
 Great Lakes Update Volume 194: 2015 Annual Summary Background The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) tracks and forecasts the water levels of each of the Great Lakes. This report summarizes the hydrologic
Great Lakes Update Volume 194: 2015 Annual Summary Background The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) tracks and forecasts the water levels of each of the Great Lakes. This report summarizes the hydrologic
Certification Process for North Indio East Side Dike in the Coachella Valley
 Certification Process for North Indio East Side Dike in the Coachella Valley September 7, 2016 Brady McDaniel (Northwest Hydraulic Consultants) Contributors Andrey Shvidchenko, Brent Wolfe and Jimmy Pan
Certification Process for North Indio East Side Dike in the Coachella Valley September 7, 2016 Brady McDaniel (Northwest Hydraulic Consultants) Contributors Andrey Shvidchenko, Brent Wolfe and Jimmy Pan
Historical Bathymetric Data for the Lower Passaic River
 Historical Bathymetric Data for the Lower Passaic River 4th Passaic River Symposium June 22nd, 2010 Dr. William Hansen Jeffrey Cranson Worcester State College Project Supported by The Hudson River Foundation
Historical Bathymetric Data for the Lower Passaic River 4th Passaic River Symposium June 22nd, 2010 Dr. William Hansen Jeffrey Cranson Worcester State College Project Supported by The Hudson River Foundation
Advancing Real Time Observations and Coastal Modeling Forecasts-
 Advancing Real Time Observations and Coastal Modeling Forecasts- Moving Forward in a Changing Coastal Landscape Next Generation Navigation-Coastal Operations- Coastal and Nearshore Coastal Operational
Advancing Real Time Observations and Coastal Modeling Forecasts- Moving Forward in a Changing Coastal Landscape Next Generation Navigation-Coastal Operations- Coastal and Nearshore Coastal Operational
CE415L Applied Fluid Mechanics Laboratory
 Applied Fluid Mechanics Laboratory Learning Objective Following completion of this experiment and the analysis of the data, you should be able to 1. generalize results of introducing changes to a natural
Applied Fluid Mechanics Laboratory Learning Objective Following completion of this experiment and the analysis of the data, you should be able to 1. generalize results of introducing changes to a natural
NOAA s National Weather Service Philadelphia/Mt. Holly NJ
 Next Briefing Package: Friday, October 2, 2015 no later than 300 PM Hazards and Impacts: Overview: A dangerous weather pattern still threatens our region. Threats include very heavy rainfall, inland river
Next Briefing Package: Friday, October 2, 2015 no later than 300 PM Hazards and Impacts: Overview: A dangerous weather pattern still threatens our region. Threats include very heavy rainfall, inland river
Primer on Coastal Erosion And Habitat Creation
 2 nd Regional Conference Dredging, Beach Nourishment & Bird Conservation Primer on Coastal Erosion And Habitat Creation Timothy Kana Ph.D Source: Newsday 1962 Photo by Kelsey Aerials 1978 Source: U Mass
2 nd Regional Conference Dredging, Beach Nourishment & Bird Conservation Primer on Coastal Erosion And Habitat Creation Timothy Kana Ph.D Source: Newsday 1962 Photo by Kelsey Aerials 1978 Source: U Mass
COASTAL FLOODING IMPACT REPORT (100-YEAR RETURN PERIOD EVENT) CORDECO DISCOVERY BAY RESORT & MARINA BO. ESPINAL, AGUADA, P.R.
 COASTAL FLOODING IMPACT REPORT (100-YEAR RETURN PERIOD EVENT) CORDECO DISCOVERY BAY RESORT & MARINA BO. ESPINAL, AGUADA, P.R. submitted to CORDECO NORTHWEST CORP. 2305 LAUREL ST. SAN JUAN, P.R. 00913 by
COASTAL FLOODING IMPACT REPORT (100-YEAR RETURN PERIOD EVENT) CORDECO DISCOVERY BAY RESORT & MARINA BO. ESPINAL, AGUADA, P.R. submitted to CORDECO NORTHWEST CORP. 2305 LAUREL ST. SAN JUAN, P.R. 00913 by
B-1. Attachment B-1. Evaluation of AdH Model Simplifications in Conowingo Reservoir Sediment Transport Modeling
 Attachment B-1 Evaluation of AdH Model Simplifications in Conowingo Reservoir Sediment Transport Modeling 1 October 2012 Lower Susquehanna River Watershed Assessment Evaluation of AdH Model Simplifications
Attachment B-1 Evaluation of AdH Model Simplifications in Conowingo Reservoir Sediment Transport Modeling 1 October 2012 Lower Susquehanna River Watershed Assessment Evaluation of AdH Model Simplifications
A STUDY OF LOCAL SCOUR AT BRIDGE PIERS OF EL-MINIA
 A STUDY OF LOCAL SCOUR AT BRIDGE PIERS OF EL-MINIA Dr. Gamal A. Sallam 1 and Dr. Medhat Aziz 2 ABSTRACT Bridges are critical structures that require a substantial investment to construct and serve an important
A STUDY OF LOCAL SCOUR AT BRIDGE PIERS OF EL-MINIA Dr. Gamal A. Sallam 1 and Dr. Medhat Aziz 2 ABSTRACT Bridges are critical structures that require a substantial investment to construct and serve an important
Community Erosion Assessment Napakiak, Alaska 15 January 2008
 1. Community: Napakiak, Alaska Community Erosion Assessment Napakiak, Alaska 15 January 2008 Figure 1: Napakiak Location & Vicinity Map 2. Community Profile Summary: Napakiak is a 2 nd class city of 378
1. Community: Napakiak, Alaska Community Erosion Assessment Napakiak, Alaska 15 January 2008 Figure 1: Napakiak Location & Vicinity Map 2. Community Profile Summary: Napakiak is a 2 nd class city of 378
Island Design. UMRS EMP Regional Workshop. Presentation for the
 Island Design Presentation for the UMRS EMP Regional Workshop by Jon Hendrickson Hydraulic Engineer Regional Technical Specialist, Water Quality and Habitat Restoration August 17 19, 2005 Project Delivery
Island Design Presentation for the UMRS EMP Regional Workshop by Jon Hendrickson Hydraulic Engineer Regional Technical Specialist, Water Quality and Habitat Restoration August 17 19, 2005 Project Delivery
STRUCTURAL STABILITY ASSESSMENT
 STRUCTURAL STABILITY ASSESSMENT CFR 257.73(d) Bottom Ash Pond Complex Cardinal Plant Brilliant, Ohio October, 2016 Prepared for: Cardinal Operating Company Cardinal Plant Brilliant, Ohio Prepared by: Geotechnical
STRUCTURAL STABILITY ASSESSMENT CFR 257.73(d) Bottom Ash Pond Complex Cardinal Plant Brilliant, Ohio October, 2016 Prepared for: Cardinal Operating Company Cardinal Plant Brilliant, Ohio Prepared by: Geotechnical
Major Hurricane Matthew Briefing Situation Overview
 Major Hurricane Matthew Briefing Situation Overview At 5 p.m. Tuesday, Category 4 Hurricane Matthew was about 860 miles South-Southeast of Mayport, Florida, moving north around 10 mph. Maximum sustained
Major Hurricane Matthew Briefing Situation Overview At 5 p.m. Tuesday, Category 4 Hurricane Matthew was about 860 miles South-Southeast of Mayport, Florida, moving north around 10 mph. Maximum sustained
COASTAL DYNAMICS VIRTUAL FIELD TRIP, NORTHEAST FLORIDA. Joann Mossa Department of Geography University of Florida
 COASTAL DYNAMICS VIRTUAL FIELD TRIP, NORTHEAST FLORIDA Joann Mossa Department of Geography University of Florida WHERE ARE WE GOING? In NE Florida (Flagler and St. Johns County, south of St. Augustine),
COASTAL DYNAMICS VIRTUAL FIELD TRIP, NORTHEAST FLORIDA Joann Mossa Department of Geography University of Florida WHERE ARE WE GOING? In NE Florida (Flagler and St. Johns County, south of St. Augustine),
CLIMATE READY BOSTON. Climate Projections Consensus ADAPTED FROM THE BOSTON RESEARCH ADVISORY GROUP REPORT MAY 2016
 CLIMATE READY BOSTON Sasaki Steering Committee Meeting, March 28 nd, 2016 Climate Projections Consensus ADAPTED FROM THE BOSTON RESEARCH ADVISORY GROUP REPORT MAY 2016 WHAT S IN STORE FOR BOSTON S CLIMATE?
CLIMATE READY BOSTON Sasaki Steering Committee Meeting, March 28 nd, 2016 Climate Projections Consensus ADAPTED FROM THE BOSTON RESEARCH ADVISORY GROUP REPORT MAY 2016 WHAT S IN STORE FOR BOSTON S CLIMATE?
Vegetation effects on river hydraulics. Johannes J. (Joe) DeVries David Ford Consulting Engineers, Inc. Sacramento, CA
 Vegetation effects on river hydraulics Johannes J. (Joe) DeVries David Ford Consulting Engineers, Inc. Sacramento, CA jjdevries@ford-consulting.com SAC05 D2P31 RM 99.0L VIEW UPSTREAM AT UPSTREAM END DWR
Vegetation effects on river hydraulics Johannes J. (Joe) DeVries David Ford Consulting Engineers, Inc. Sacramento, CA jjdevries@ford-consulting.com SAC05 D2P31 RM 99.0L VIEW UPSTREAM AT UPSTREAM END DWR
