CHAPTER 28. PHYSIOGRAPHY Cook Inlet Drainages
|
|
|
- August King
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PEBBLE PROJECT ENVIRONMENTAL BASELINE DOCUMENT 2004 through 2008 CHAPTER 28. PHYSIOGRAPHY Cook Inlet Drainages PREPARED BY: Knight Piésold Ltd.
2 PHYSIOGRAPHY COOK INLET DRAINAGES TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS i LIST OF FIGURES ii PHOTOGRAPHS ii 28. PHYSIOGRAPHY Introduction Study Objectives Study Area Scope of Work Methods Results and Discussion Summary References Glossary i 05/10/2011
3 PEBBLE PROJECT, ENVIRONMENTAL BASELINE DOCUMENT, 2004 THROUGH 2008 LIST OF FIGURES Figure 28-1, Physiography Study Area, Cook Inlet Drainages Figure 28-2, Photograph Locations, Cook Inlet Drainages PHOTOGRAPHS 28-ii 05/10/2011
4 PHYSIOGRAPHY COOK INLET DRAINAGES 28. PHYSIOGRAPHY 28.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter discusses the physiography of the Cook Inlet drainages study area including topography, landforms, stream drainage patterns, and coastal features. This discussion is based on review of published information and oblique aerial photographs taken during reconnaissance and mapping exercises. More detailed investigations of coastal physiography and marine habitat are presented in Chapter STUDY OBJECTIVES The objective of the physiography study is to describe the physiographic characteristics of the study area in the Cook Inlet drainages STUDY AREA The physiography study area is located within the southern part of the Alaska Range physiographic division, as defined by Detterman and Reed (1973), within a subordinate mountain range called the Chigmit Mountains. The study area is defined by the drainage boundaries of Iliamna and Iniskin Bays, two fjords with a common mouth on the west side of Cook Inlet. An unnamed drainage basin comprising much of the peninsula between the two bays is referred to as Y Valley in this document. The physiography study area for the Cook Inlet drainages is shown on Figure SCOPE OF WORK The information in this chapter is based on a review of published information and reconnaissance photographs. Work was conducted by Knight Piésold Ltd METHODS The information presented in this chapter is based on a review of the following published information and reconnaissance photographs: Bathymetric and Geophysical Survey Iniskin Bay, Alaska (Golder Associates Inc., 2005). Dredge Slopes in Iliamna Bay near Williamsport, Alaska (Golder Associates Inc., 1995). Navigation Channel Feasibility Report and Environmental Assessment, (U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE), 1995). Surficial Geology of the Iliamna Quadrangle, Alaska (Detterman and Reed, 1973). Regional topographic information obtained from the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) /10/2011
5 PEBBLE PROJECT, ENVIRONMENTAL BASELINE DOCUMENT, 2004 THROUGH 2008 Oblique aerial photographs taken by Eagle Mapping Ltd. during mapping work in 2004, and by Knight Piésold Ltd. during site reconnaissance in The approximate location of the camera and the direction of the photo views for each photograph are shown on Figure RESULTS AND DISCUSSION The physiography study area falls within the southern part of the Alaska Range physiographic division in the Chigmit Mountains. This is an area of rugged mountains, glacially carved valleys, and fjord inlets created by glacial valley scour to depths below present sea level. The mountains rise abruptly along the coast and form a climatic barrier between the coast and the interior. The general landscape of the two main fjords in the study area, Iliamna Bay and Iniskin Bay, and the glacially carved valley on the peninsula between them ( Y Valley ), are shown in Photos 28-1 to 28-3, respectively. Shoreline terrain along the sides of the fjords is generally steep and rocky. In contrast, broad tidal mud flats are located at the heads of the fjords due to sediment deposition from tributary watercourses. The largest watercourses in the study area are the Iniskin River, which flows into the head of Iniskin Bay; Cottonwood Creek, which flows into the head of Cottonwood Bay, an arm of Iliamna Bay; and the unnamed stream that drains the Y Valley. A stream called Williams Creek flows parallel to the existing road from the pass between the Bristol Bay and Cook Inlet drainages down to Iliamna Bay at Williamsport. Numerous small glaciers and alpine lakes occupying glacial cirque basins are present in the Iliamna Bay and Iniskin Bay drainages. The Cook Inlet/Bristol Bay drainage divide lies to the west of Iliamna Bay and is shown on Photos 28-4 and Williamsport is located on the western shore of Iliamna Bay as seen on Photo Mountains east of Iliamna Bay rise to 2,735 feet above sea level (Detterman and Reed, 1973). Tidal flats occupy the upper portion of Iliamna Bay as shown on Photos 28-7 and Mountains in the Y Valley, shown in Photo 28-9, rise to 2,805 feet above sea level (Detterman and Reed, 1973). The rocky headlands to the west and east of the Y Valley mouth are called North Head and Knoll Head, respectively. The western coastline of Iniskin Bay is shown in Photo The tidal mud flats near the head of Iniskin Bay are seen in Photo The tidal flats and floodplain near the mouth of the Iniskin River, and the glacially carved valley of the Iniskin River, are shown in Photos and Several rocky islands and reefs are located near the mouths of Iliamna Bay and Iniskin Bay. The physical characteristics of the islands, reefs, and coastal shorelines are described in more detail in Chapter 36. A preliminary evaluation of the physiography of the Iniskin Bay channel offshore of Knoll Head can be based on a geophysical investigation report by Golder Associates Inc. (2005), which included a bathymetric investigation of Iniskin Bay offshore of Knoll Head. Water depth measurements were acquired at a rate of ten measurements per second as the survey vessel followed a series of parallel transects. The bathymetric survey indicates that the bay floor offshore of Knoll Head drops off at approximately a 10 percent grade from the western shoreline to a maximum depth of 80 feet near midchannel, then gradually slopes up to the eastern shoreline from mid-channel. More details of the bathymetric and geophysical survey of Iniskin Bay can be found in Golder Associates Inc. (2005). Another site investigation program completed by Golder Associates Inc. (1995) assessed the geotechnical conditions of the sediments in Iliamna Bay to support the dredging of a channel to the Williamsport dock. The water depth in the vicinity of Williamsport is very shallow, and vessels having a draft of 5 feet or /10/2011
6 PHYSIOGRAPHY COOK INLET DRAINAGES greater will likely be beached between high tides. Seismic refraction survey data indicates that there are approximately 100 to 130 feet of unconsolidated sediments in Iliamna Bay within approximately 3,000 feet of the existing dock at Williamsport. Colluvial boulders originating from the cliffs are present on the tidelands in Iliamna Bay and also should be expected to occur in the estuarine deposits. More details of the site investigation completed in Iliamna Bay can be found in Golder Associates Inc.(1995) SUMMARY The information in this chapter is based on a review of published information by others and primarily focuses on the area surrounding Iliamna Bay and Iniskin Bay on the west coast of Cook Inlet. The study area falls into the southern part of the Alaska Range physiographic division, an area consisting of rugged mountains and glacially carved valleys with numerous bays along the shoreline. Tidal flats are found in Iliamna Bay and Iniskin Bay, especially near the heads of the inlets. The water depth in the vicinity of Williamsport, located at the head of an arm of Iliamna Bay, is very shallow. Several rocky islands and reefs are found near the mouths of Iliamna Bay and Iniskin Bay. The floor of Iniskin Bay descends to 80 feet below water level at approximately mid-channel offshore of Knoll Head REFERENCES Detterman, R.L., and B.L. Reed Surficial Geology of the Iliamna Quadrangle, Alaska. U.S. Department of the Interior. Geological Survey Bulletin # 1368-A. Golder Associates Inc Bathymetric and Geophysical Survey Iniskin Bay, Alaska. Ref. No August. Golder Associates Inc Dredge Slopes in Iliamna Bay near Williamsport, Alaska. August. U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) Navigation Channel Feasibility Report and Environmental Assessment. December GLOSSARY Bathymetry the measurement of the depth of the ocean floor from the water surface, the oceanic equivalent of topography. Colluvial deposits material transported by gravity, typically deposited and accumulated on lower slopes and/or at the base of slopes. Draft (nautical) the depth of a vessel's keel below the water line, especially when loaded. Estuarine relating to a semi-enclosed coastal body of water which has a free connection with the open sea and where fresh water, derived from land drainage, is mixed with sea water due to tidal action. Physiography the study of the physical features of the earth s surface /10/2011
7 PEBBLE PROJECT, ENVIRONMENTAL BASELINE DOCUMENT, 2004 THROUGH 2008 Quadrangle a USGS 7.5-minute quadrangle map. Seismic refraction a type of seismic survey that measures the refraction of seismic waves from a surface source back to a geophone array. Tidal flat a sand flat, mud flat, or marshy area that is alternately covered and uncovered by the tide /10/2011
8 FIGURES PHYSIOGRAPHY COOK INLET DRAINAGES
9 Port Alsworth! 1,640,000 1,700,000 1,760,000 1,820,000 2,250,000 1,580,000 Lake Clark National Park and Preserve k Lake Clark National Park and Preserve Figure 28-1 Physiography Study Area Cook Inlet Drainages 2,200,000 Mt. Iliamna Legend Study Area Boundary National Park and Preserve Boundary BB / CI Drainages Boundary Existing Roads Population Centers 2,150,000! Notes! Pile Bay 1. BB/CI refers to Bristol Bay/Cook Inlet drainages. Iniskin Peninsula 2,050,000 Ili am na Ba BERING SEA y let In ok 1,700,000 1,760,000 F OF AL AS KA Map Location Co 1,640,000 GU L Oil Ba y 0 1,580,000 N Canada Inis k! TIC O CEA in B ay Williamsport Ili amn a La ke ARC Russia 1,820, Miles Scale 1:300, Kilometers 20 Alaska State Plane Zone 5 (units feet) 1983 North American Datum File: B01_r0.mxd Date: June 10, 2010 Version: Author: Knight Piesold Ltd. ³ SAVED: M:\1\01\00176\28\A\GIS\ArcView\figures\PLP_CEBD\Chapter_28\B01_r0_new.mxd; Jun 28, :40:03 AM adinca 2,100,000 Pedro Bay
10 1,660,000 1,680,000 1,700,000 1,720,000 1,740,000 1,760,000 1,780,000 1,800,000 2,040,000 2,060,000 2,080,000 2,100,000 2,120,000 2,140,000 C o t t o n w o o d C r e e k 28-4 W i l l i a m s C r e e k Williamsport Diamond Point 28-7 C o t t o n w o o d B a y 28-8 I l i a m n a B a y AC Point White Gull Island "Y" Valley North Head South Head Knoll Head I n i s k i n R i v e r Entrance Rock I n i s k i n B a y Mushroom Islets Scott Island Iniskin Island Mount Pomeroy O i l B a y C o o k I n l e t Legend Russia BERING SEA Version: Figure 28-2 Physiography Study Area Photograph Locations Cook Inlet Drainages Camera Location Photo Direction Study Area Boundary BB / CI Drainages Boundary Existing Roads! Population Centers Notes 1. BB/CI refers to Bristol Bay/Cook Inlet drainages. ARCTIC OCEAN GULF OF AL ASK A Key Map Location Canada Miles Kilometers ³ Scale 1:150,000 Alaska State Plane Zone 5 (units feet) 1983 North American Datum File: B42_r0.mxd Date: June 10, 2010 Author: Knight Piesold Ltd. SAVED: M:\1\01\00176\28\A\GIS\ArcView\figures\PLP_CEBD\Chapter_28\B42_r0_new.mxd; Jun 28, :15:53 PM adinca 1,660,000 1,680,000 1,700,000 1,720,000 1,740,000 1,760,000 1,780,000 1,800,000
11 PHOTOGRAPHS PHYSIOGRAPHY COOK INLET DRAINAGES
12 PHOTO 28-1: View to the northwest into lliamna Bay, July PHYSIOGRAPHY COOK INLET REGION
13 PHOTO 28-2: View to the northeast toward the entrance to Iniskin Bay, July PHYSIOGRAPHY COOK INLET REGION
14 PHYSIOGRAPHY COOK INLET REGION PHOTO 28-3: View to the north toward North Head (on left) and the mouth of Y Valley on the peninsula between Iniskin Bay and Iliamna Bay, July 2004.
15 PHYSIOGRAPHY COOK INLET REGION Cook Inlet Drainage Bristol Bay Drainage Summit Lake PHOTO 28-4: Summit Lake and the Bristol Bay / Cook Inlet drainage divide, July 2008.
16 PHYSIOGRAPHY COOK INLET REGION Cook Inlet Drainage Bristol Bay Drainage PHOTO 28-5: Bristol Bay / Cook Inlet drainage divide near Summit Lake (Bristol Bay drainage) and the headwaters of Williams Creek (Cook Inlet drainage), July 2008.
17 PHYSIOGRAPHY COOK INLET REGION Iliamna Bay Williamsport PHOTO 28-6: View to the east along existing road and Williams Creek to Williamsport and Iliamna Bay, July 2008.
18 PHYSIOGRAPHY COOK INLET REGION Tidal Flats PHOTO 28-7: View to the northeast toward the head of Iliamna Bay, July 2008.
19 PHYSIOGRAPHY COOK INLET REGION Tidal Flats PHOTO 28-8: View to the southeast along the eastern coast of Iliamna Bay, July 2008.
20 PHYSIOGRAPHY COOK INLET REGION PHOTO 28-9: View to the northeast across the mouth of the Y Valley on the peninsula between Iliamna Bay and Iniskin Bay, July 2008.
21 PHOTO 28-10: Coastline of Iniskin Bay, July PHYSIOGRAPHY COOK INLET REGION
22 PHYSIOGRAPHY COOK INLET REGION Tidal Flats PHOTO 28-11: Tidal Flats in Iniskin Bay, July 2008.
23 PHOTO 28-12: View to the north up the Iniskin River valley from Iniskin Bay, July PHYSIOGRAPHY COOK INLET REGION
24 PHYSIOGRAPHY COOK INLET REGION PHOTO 28-13: View to the south down the Iniskin River valley toward Iniskin Bay, July 2008.
 Page 1 of 9 Name: Base your answer to the question on the diagram below. The arrows show the direction in which sediment is being transported along the shoreline. A barrier beach has formed, creating a
Page 1 of 9 Name: Base your answer to the question on the diagram below. The arrows show the direction in which sediment is being transported along the shoreline. A barrier beach has formed, creating a
4. The map below shows a meandering stream. Points A, B, C, and D represent locations along the stream bottom.
 1. Sediment is deposited as a river enters a lake because the A) velocity of the river decreases B) force of gravity decreases C) volume of water increases D) slope of the river increases 2. Which diagram
1. Sediment is deposited as a river enters a lake because the A) velocity of the river decreases B) force of gravity decreases C) volume of water increases D) slope of the river increases 2. Which diagram
3. GEOLOGY. 3.1 Introduction. 3.2 Results and Discussion Regional Geology Surficial Geology Mine Study Area
 3. GEOLOGY 3.1 Introduction This chapter discusses the baseline study of the geology and mineralization characteristics of the mine study area. The study consolidates existing geological data and exploration
3. GEOLOGY 3.1 Introduction This chapter discusses the baseline study of the geology and mineralization characteristics of the mine study area. The study consolidates existing geological data and exploration
Earth s Layers. Earth s Surface
 CHAPTER 1 LESSON 3 Earth s Layers Earth s Surface Key Concepts What are Earth s major landforms and how do they compare? What are the major landform regions of the United States? What do you think? Read
CHAPTER 1 LESSON 3 Earth s Layers Earth s Surface Key Concepts What are Earth s major landforms and how do they compare? What are the major landform regions of the United States? What do you think? Read
Developed in Consultation with Florida Educators
 Developed in Consultation with Florida Educators Table of Contents Next Generation Sunshine State Standards Correlation Chart... 7 Benchmarks Chapter 1 The Practice of Science...................... 11
Developed in Consultation with Florida Educators Table of Contents Next Generation Sunshine State Standards Correlation Chart... 7 Benchmarks Chapter 1 The Practice of Science...................... 11
The Geology of Sebago Lake State Park
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities September, 2002 43 55 17.46 N, 70 34 13.07 W Text by Robert Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by Robert Johnston Introduction Sebago
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities September, 2002 43 55 17.46 N, 70 34 13.07 W Text by Robert Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by Robert Johnston Introduction Sebago
WHAT IS THE EARTH MADE OF? LITHOSPHERE AND HYDROSPHERE
 UNIT 8 WHAT IS THE EARTH MADE OF? LITHOSPHERE AND HYDROSPHERE TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH... 2 2 THE FORMATION OF THE RELIEF: INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL FORCES.... 2 2.1 Internal forces:
UNIT 8 WHAT IS THE EARTH MADE OF? LITHOSPHERE AND HYDROSPHERE TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH... 2 2 THE FORMATION OF THE RELIEF: INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL FORCES.... 2 2.1 Internal forces:
Draft exercise for share fair at Bozeman workshop only. This exercise is not ready for distribution. Please send helpful suggestions to
 Draft exercise for share fair at Bozeman workshop only. This exercise is not ready for distribution. Please send helpful suggestions to foleyd@plu.edu Figure list 1. Trailer photograph 2. Location map
Draft exercise for share fair at Bozeman workshop only. This exercise is not ready for distribution. Please send helpful suggestions to foleyd@plu.edu Figure list 1. Trailer photograph 2. Location map
6. GEOTECHNICAL STUDIES, SEISMICITY AND VOLCANISM
 Geotechnical Studies, Seismicity, and Volcanism Bristol Bay Drainages 6. GEOTECHNICAL STUDIES, SEISMICITY AND VOLCANISM 6.1 Introduction This chapter describes the baseline geotechnical characteristics
Geotechnical Studies, Seismicity, and Volcanism Bristol Bay Drainages 6. GEOTECHNICAL STUDIES, SEISMICITY AND VOLCANISM 6.1 Introduction This chapter describes the baseline geotechnical characteristics
The Marine Environment
 The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write true or
The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write true or
discussion of North America s physical features, including its landforms and bodies of
 Chapter 7 Natural Environments of North America Chapter 7 focuses on the natural environments of North America. The chapter opens with a discussion of North America s physical features, including its landforms
Chapter 7 Natural Environments of North America Chapter 7 focuses on the natural environments of North America. The chapter opens with a discussion of North America s physical features, including its landforms
Supplemental Slides. Shore: Junction of Land & Water. Junction of Land & Water. Sea Level Variations. Shore vs. Coast. Sea Level Variations
 Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Shore: Junction of Land & Water. Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents
 Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Chapter 17. Ocean and Coastal Processes
 Chapter 17 Ocean and Coastal Processes Ocean Basins and Plates Ocean Basins Ocean Basins are profoundly different from the continents. Ocean crust is thin and dense and young. New ocean crust is generated
Chapter 17 Ocean and Coastal Processes Ocean Basins and Plates Ocean Basins Ocean Basins are profoundly different from the continents. Ocean crust is thin and dense and young. New ocean crust is generated
Small area of the ocean that is partially surrounded by land. The Ocean Basins. Three Major Oceans. Three Major Oceans. What is a SEA?
 The Ocean Basins How Deep is the Ocean? 1 2 Three Major Oceans Three Major Oceans Pacific Atlantic the shallowest ocean (3.3km average depth) Indian second shallowest ocean (3.8km average depth) Pacific
The Ocean Basins How Deep is the Ocean? 1 2 Three Major Oceans Three Major Oceans Pacific Atlantic the shallowest ocean (3.3km average depth) Indian second shallowest ocean (3.8km average depth) Pacific
3.0 ROBERTS BANK TIDAL FLAT MORPHOLOGY
 Vancouver Port Authority Northwest Hydraulic Consultants Ltd. /Triton Consultants Ltd. Roberts Bank Container Expansion File: 33863 Coastal Geomorphology Study - 19 - November 2004 3.0 ROBERTS BANK TIDAL
Vancouver Port Authority Northwest Hydraulic Consultants Ltd. /Triton Consultants Ltd. Roberts Bank Container Expansion File: 33863 Coastal Geomorphology Study - 19 - November 2004 3.0 ROBERTS BANK TIDAL
Ocean and Coastal Processes. Ocean Basins. Chapter 20. Ocean Basins and Plates. Ocean Terms. Sea Arch Bay-mouth Bar Spit Tombolo Coast.
 Chapter 20 Ocean Basins and Plates Ocean and Coastal Processes Tide Wave Height Length Period Base Refraction Tsunami Beach Sea stack Ocean Terms Sea Arch Bay-mouth Bar Spit Tombolo Coast Emergent Submergent
Chapter 20 Ocean Basins and Plates Ocean and Coastal Processes Tide Wave Height Length Period Base Refraction Tsunami Beach Sea stack Ocean Terms Sea Arch Bay-mouth Bar Spit Tombolo Coast Emergent Submergent
The United States & Canada. A Regional Study of Anglo America
 A Regional Study of Anglo America Landform Regions of the United States & Canada world leaders in agricultural and industrial production because of... VAST LANDS stretch from the Atlantic Ocean on the
A Regional Study of Anglo America Landform Regions of the United States & Canada world leaders in agricultural and industrial production because of... VAST LANDS stretch from the Atlantic Ocean on the
In 1990, 50% of the U.S. population lived within 75 km of a coast. By 2010, 75% of the U.S. population will live within 75 km of a coast.
 In 1990, 50% of the U.S. population lived within 75 km of a coast. By 2010, 75% of the U.S. population will live within 75 km of a coast. High Tech Methods for Surveying the Deep Sea Floor Fig. 20.18 1
In 1990, 50% of the U.S. population lived within 75 km of a coast. By 2010, 75% of the U.S. population will live within 75 km of a coast. High Tech Methods for Surveying the Deep Sea Floor Fig. 20.18 1
3.1 GEOLOGY AND SOILS Introduction Definition of Resource
 3.1 GEOLOGY AND SOILS 3.1.1 Introduction 3.1.1.1 Definition of Resource The geologic resources of an area consist of all soil and bedrock materials. This includes sediments and rock outcroppings in the
3.1 GEOLOGY AND SOILS 3.1.1 Introduction 3.1.1.1 Definition of Resource The geologic resources of an area consist of all soil and bedrock materials. This includes sediments and rock outcroppings in the
GY 301: Geomorphology Lab 3: Introduction to Topographic Maps; Coastal Geomorphology
 Name: Raw score: /65 Percentage: /100% GY 301: Geomorphology Your Task: Today s lab is your first opportunity to closely examine topographic maps. You will be asked to answer various questions about map
Name: Raw score: /65 Percentage: /100% GY 301: Geomorphology Your Task: Today s lab is your first opportunity to closely examine topographic maps. You will be asked to answer various questions about map
CHAPTER 1. Geo Challenges 1A to 1D. & World Map Activity
 CHAPTER 1 Geo Challenges 1A to 1D & World Map Activity SELECT YOUR CHALLENGE World Map Activity Challenge 1A Challenge 1B Challenge 1C Challenge 1D Challenge 1A WS PG. 2 STEP #1 Label the largest continent
CHAPTER 1 Geo Challenges 1A to 1D & World Map Activity SELECT YOUR CHALLENGE World Map Activity Challenge 1A Challenge 1B Challenge 1C Challenge 1D Challenge 1A WS PG. 2 STEP #1 Label the largest continent
Ch 10 Deposition Practice Questions
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the data table below. Six identical cylinders, A through F, were filled with equal volumes of sorted spherical particles. The data table shows the particle
1. Base your answer to the following question on the data table below. Six identical cylinders, A through F, were filled with equal volumes of sorted spherical particles. The data table shows the particle
MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY
 MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY Bathymetry BATHYMETRY BATHYMETRY THE UNDERWATER EQUIVALENT TO TOPOGRAPHY THE STUDY OF WATER DEPTH A BATHYMETRIC MAP SHOWS FLOOR RELIEF OR TERRAIN AS CONTOUR LINES Bathymetry
MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY Bathymetry BATHYMETRY BATHYMETRY THE UNDERWATER EQUIVALENT TO TOPOGRAPHY THE STUDY OF WATER DEPTH A BATHYMETRIC MAP SHOWS FLOOR RELIEF OR TERRAIN AS CONTOUR LINES Bathymetry
The Marine Environment
 The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write or. 1.
The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write or. 1.
Lab 12 Coastal Geology
 Lab 12 Coastal Geology I. Fluvial Systems Hydrologic Cycle Runoff that flows into rivers = precipitation (rain and snowmelt) [infiltration (loss to groundwater) + evaporation (loss to atmosphere) + transpiration
Lab 12 Coastal Geology I. Fluvial Systems Hydrologic Cycle Runoff that flows into rivers = precipitation (rain and snowmelt) [infiltration (loss to groundwater) + evaporation (loss to atmosphere) + transpiration
Physiographic Provinces (West, Ch. 13)
 Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 13 Physiographic Provinces (West, Ch. 13) The definition of the term Physiography Physiography (n.) The science which treats of the earth's exterior physical features,
Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 13 Physiographic Provinces (West, Ch. 13) The definition of the term Physiography Physiography (n.) The science which treats of the earth's exterior physical features,
Topographic Maps and Landforms Geology Lab
 Topographic Maps and Landforms Geology Lab Ray Rector: Instructor Today s Lab Activities 1) Discussion of Last Week s Lab 2) Lecture on Topo Maps and Elevation Contours 3) Construct Topographic Maps and
Topographic Maps and Landforms Geology Lab Ray Rector: Instructor Today s Lab Activities 1) Discussion of Last Week s Lab 2) Lecture on Topo Maps and Elevation Contours 3) Construct Topographic Maps and
Why is Sebago Lake so deep?
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities February, 1999 Why is Sebago Lake so deep? 43 51 13.36 N, 70 33 43.98 W Text by Robert A. Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Introduction
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities February, 1999 Why is Sebago Lake so deep? 43 51 13.36 N, 70 33 43.98 W Text by Robert A. Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Introduction
THE QUATERNARY GEOLOGY OF NEWARK BAY AND KILL VAN KULL CHANNEL, NEW YORK AND NEW JERSEY. and
 THE QUATERNARY GEOLOGY OF NEWARK BAY AND KILL VAN KULL CHANNEL, NEW YORK AND NEW JERSEY Stephanie Beda, W. Bruce Ward, William Murphy, Robert Fleming, Gary Fleming, Beckett Boyd Earthworks LLC 27 Glen
THE QUATERNARY GEOLOGY OF NEWARK BAY AND KILL VAN KULL CHANNEL, NEW YORK AND NEW JERSEY Stephanie Beda, W. Bruce Ward, William Murphy, Robert Fleming, Gary Fleming, Beckett Boyd Earthworks LLC 27 Glen
Sea-level Rise on Cape Cod: How Vulnerable Are We? Rob Thieler U.S. Geological Survey Woods Hole, MA
 Sea-level Rise on Cape Cod: How Vulnerable Are We? Rob Thieler U.S. Geological Survey Woods Hole, MA Outline Sea-level and coastal processes Past sea-level change Predictions for the future Coastal responses
Sea-level Rise on Cape Cod: How Vulnerable Are We? Rob Thieler U.S. Geological Survey Woods Hole, MA Outline Sea-level and coastal processes Past sea-level change Predictions for the future Coastal responses
Unit 1: Geography. For additional information, refer to this website: 1 G e o g r a p h y
 Unit 1: Geography For additional information, refer to this website: http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/ 1 G e o g r a p h y Continents and Oceans SOL USI. 2a Essential Understanding: Continents are large land
Unit 1: Geography For additional information, refer to this website: http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/ 1 G e o g r a p h y Continents and Oceans SOL USI. 2a Essential Understanding: Continents are large land
The Coast: Beaches and Shoreline Processes
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Coast: es and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10 Oceanography 101 Chapter Objectives Recognize the various landforms characteristic of beaches and coastal regions.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Coast: es and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10 Oceanography 101 Chapter Objectives Recognize the various landforms characteristic of beaches and coastal regions.
1 Shoreline Landforms 2. 2 Emergent v. Submergent 2. 3 Wavecutting 3. 4 Planview 4. 5 Marine Terraces 5. 6 California 7. 7 Tombolos, Sea Stacks 8
 Shorelines November 9, 2008 Contents 1 Shoreline Landforms 2 2 Emergent v. Submergent 2 3 Wavecutting 3 4 Planview 4 5 Marine Terraces 5 6 California 7 7 Tombolos, Sea Stacks 8 8 Active Processes 9 9 Emergence
Shorelines November 9, 2008 Contents 1 Shoreline Landforms 2 2 Emergent v. Submergent 2 3 Wavecutting 3 4 Planview 4 5 Marine Terraces 5 6 California 7 7 Tombolos, Sea Stacks 8 8 Active Processes 9 9 Emergence
The Coast: Beaches and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10
 The Coast: es and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10 Oceanography 101 Chapter Objectives Recognize the various landforms characteristic of beaches and coastal regions. Identify seasonal
The Coast: es and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10 Oceanography 101 Chapter Objectives Recognize the various landforms characteristic of beaches and coastal regions. Identify seasonal
Terrain Units PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION. Present Geology of NYS. Detailed Geologic Map of NYS
 NYS TOPOGRAPHY Why so? PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 014 Present Geology of NYS Detailed Geologic Map of NYS Generalized Geology Detailed Geology Hot links to the fold out
NYS TOPOGRAPHY Why so? PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 014 Present Geology of NYS Detailed Geologic Map of NYS Generalized Geology Detailed Geology Hot links to the fold out
3.12 Geology and Topography Affected Environment
 3 Affected Environment and Environmental Consequences 3.12 Geology and Topography 3.12.1 Affected Environment 3.12.1.1 Earthquakes Sterling Highway MP 45 60 Project Draft SEIS The Kenai Peninsula is predisposed
3 Affected Environment and Environmental Consequences 3.12 Geology and Topography 3.12.1 Affected Environment 3.12.1.1 Earthquakes Sterling Highway MP 45 60 Project Draft SEIS The Kenai Peninsula is predisposed
Science EOG Review: Landforms
 Mathematician Science EOG Review: Landforms Vocabulary Definition Term canyon deep, large, V- shaped valley formed by a river over millions of years of erosion; sometimes called gorges (example: Linville
Mathematician Science EOG Review: Landforms Vocabulary Definition Term canyon deep, large, V- shaped valley formed by a river over millions of years of erosion; sometimes called gorges (example: Linville
The Ocean Floor Earth Science, 13e Chapter 13
 The Ocean Floor Earth Science, 13e Chapter 13 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The vast world ocean Earth is often referred to as the blue planet Seventy-one percent of Earth s surface
The Ocean Floor Earth Science, 13e Chapter 13 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The vast world ocean Earth is often referred to as the blue planet Seventy-one percent of Earth s surface
Cattaraugus Creek: A Story of Flowing Water and the Geology of the Channel It Flows Through Presentation to West Valley Citizen Task Force 4/27/16
 Cattaraugus Creek: A Story of Flowing Water and the Geology of the Channel It Flows Through Presentation to West Valley Citizen Task Force 4/27/16 Raymond C. Vaughan, Ph.D. What happens if you drop a
Cattaraugus Creek: A Story of Flowing Water and the Geology of the Channel It Flows Through Presentation to West Valley Citizen Task Force 4/27/16 Raymond C. Vaughan, Ph.D. What happens if you drop a
What is a landform? These shapes (except for bodies of water) on the earth s surface are all examples of landforms.
 Landforms What is a landform? These shapes (except for bodies of water) on the earth s surface are all examples of landforms. archipelago a large group of many islands. The Hawaiian Islands Lighthouse
Landforms What is a landform? These shapes (except for bodies of water) on the earth s surface are all examples of landforms. archipelago a large group of many islands. The Hawaiian Islands Lighthouse
Lab Topographic Maps. Name: Partner: Purpose. Background Information
 Lab Topographic Maps Name: Partner: Purpose The purpose of this lab is to familiarize you with graphic representations of the Earth s surface primarily maps. Simple line maps show the spatial relationship
Lab Topographic Maps Name: Partner: Purpose The purpose of this lab is to familiarize you with graphic representations of the Earth s surface primarily maps. Simple line maps show the spatial relationship
COSMORPHOLOGY - May 2009
 Name COSMORPHOLOGY - May 2009 Geologic landforms Purpose: By studying aerial photographs you will learn to identify different kinds of geologic features based on their different morphologies and learn
Name COSMORPHOLOGY - May 2009 Geologic landforms Purpose: By studying aerial photographs you will learn to identify different kinds of geologic features based on their different morphologies and learn
What is a landform? These shapes (except for bodies of water) on the earth s surface are all examples of landforms.
 Landforms What is a landform? These shapes (except for bodies of water) on the earth s surface are all examples of landforms. archipelago a large group of many islands. The Hawaiian Islands Lighthouse
Landforms What is a landform? These shapes (except for bodies of water) on the earth s surface are all examples of landforms. archipelago a large group of many islands. The Hawaiian Islands Lighthouse
Regional-scale understanding of the geologic character and sand resources of the Atlantic inner continental shelf, Maine to Virginia
 Regional-scale understanding of the geologic character and sand resources of the Atlantic inner continental shelf, Maine to Virginia Workshop on Dredging, Beach Nourishment and Bird Conservation Atlantic
Regional-scale understanding of the geologic character and sand resources of the Atlantic inner continental shelf, Maine to Virginia Workshop on Dredging, Beach Nourishment and Bird Conservation Atlantic
CANADA S LANDFORM REGIONS
 CANADA S LANDFORM REGIONS Canada s Regions Canada is divided into Eight major regions. A Region is an area that is defined on the basis of the presence or absence of certain characteristics: Age of rock
CANADA S LANDFORM REGIONS Canada s Regions Canada is divided into Eight major regions. A Region is an area that is defined on the basis of the presence or absence of certain characteristics: Age of rock
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) Which property would best distinguish sediment deposited by a river from sediment deposited by a glacier? thickness of sediment layers age of fossils found in the sediment mineral composition
Name: 1) Which property would best distinguish sediment deposited by a river from sediment deposited by a glacier? thickness of sediment layers age of fossils found in the sediment mineral composition
GLY Coastal Geomorphology Notes
 GLY 4734 - Coastal Geomorphology Notes Dr. Peter N. Adams Spring 2011 2 Coastal Classification In this lecture, we discuss some successful classification schemes of the coastal landscape, and pay particular
GLY 4734 - Coastal Geomorphology Notes Dr. Peter N. Adams Spring 2011 2 Coastal Classification In this lecture, we discuss some successful classification schemes of the coastal landscape, and pay particular
Landforms in Canada. Canada is made up of three dis;nct types of landforms: Canadian Shield Highlands Lowlands
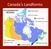 Canada s Landforms What is a Landform? A landform is any physical feature of the Earth s surface having a characteris;c, recognizable shape, produced by natural causes. Landforms include major features
Canada s Landforms What is a Landform? A landform is any physical feature of the Earth s surface having a characteris;c, recognizable shape, produced by natural causes. Landforms include major features
Chapter 3 Erosion and Deposition. The Big Question:
 Chapter 3 Erosion and Deposition The Big Question: 1 Design a way to represent and describe the 4 types of mass movement. You may use pictures, diagrams, list, web, chart, etc 2 Chapter 3: Erosion and
Chapter 3 Erosion and Deposition The Big Question: 1 Design a way to represent and describe the 4 types of mass movement. You may use pictures, diagrams, list, web, chart, etc 2 Chapter 3: Erosion and
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output
 mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
EXTERNAL LAND FORMING PROCESSES
 NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE EXTERNAL LAND FORMING PROCESSES WEATHERING 1 1998 Q 7 (a) (i) What is the difference between weathering and mass wasting (ii) List five processes involved in chemical weathering
NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE EXTERNAL LAND FORMING PROCESSES WEATHERING 1 1998 Q 7 (a) (i) What is the difference between weathering and mass wasting (ii) List five processes involved in chemical weathering
SHORELINE AND BEACH PROCESSES: PART 2. Implications for Coastal Engineering
 SHORELINE AND BEACH PROCESSES: PART 2 Implications for Coastal Engineering Objectives of the lecture: Part 2 Show examples of coastal engineering Discuss the practical difficulties of ocean engineering
SHORELINE AND BEACH PROCESSES: PART 2 Implications for Coastal Engineering Objectives of the lecture: Part 2 Show examples of coastal engineering Discuss the practical difficulties of ocean engineering
Erosion and Deposition along Rivers and Seashores - Part 1: Modeling in the Classroom
 Erosion and Deposition along Rivers and Seashores - Part 1: Modeling in the Classroom Lesson Focus: Erosion and Deposition Learning Objectives: Students will learn to recognize landforms found on Earth.
Erosion and Deposition along Rivers and Seashores - Part 1: Modeling in the Classroom Lesson Focus: Erosion and Deposition Learning Objectives: Students will learn to recognize landforms found on Earth.
The Systems Approach. Alun Williams, ABPmer
 The Systems Approach Alun Williams, ABPmer Overview What is A Systems Approach? Behavioural / Qualitative Modelling? System Definition / Mapping (Behavioural Statements Objective) What is a Systems Approach?
The Systems Approach Alun Williams, ABPmer Overview What is A Systems Approach? Behavioural / Qualitative Modelling? System Definition / Mapping (Behavioural Statements Objective) What is a Systems Approach?
MABEL LAKE RECONNAISSANCE TERRAIN STABILITY REPORT (T.S.I. LEVEL '0') to accompany
 MABEL LAKE RECONNAISSANCE TERRAIN STABILITY REPORT (T.S.I. LEVEL '0') to accompany Terrain Stability Maps 82L.046; 047; 056;057;058;067; 068;077; 078; 088 Prepared for Riverside Forest Products Limited
MABEL LAKE RECONNAISSANCE TERRAIN STABILITY REPORT (T.S.I. LEVEL '0') to accompany Terrain Stability Maps 82L.046; 047; 056;057;058;067; 068;077; 078; 088 Prepared for Riverside Forest Products Limited
Elevations are in meters above mean sea level. Scale 1:2000
 12.001 LAB 7: TOPOGRAPHIC MAPS Due: Monday, April 11 PART I: CONTOURING AND PROFILES (20 PTS) 1. Contour this area map using a 5 meter contour interval. Remember some fundamental rules of contour lines,
12.001 LAB 7: TOPOGRAPHIC MAPS Due: Monday, April 11 PART I: CONTOURING AND PROFILES (20 PTS) 1. Contour this area map using a 5 meter contour interval. Remember some fundamental rules of contour lines,
MEMORANDUM FOR SWG
 MEMORANDUM FOR SWG-2007-1623 Subject: Jurisdictional Determination (JD) for SWG-2007-1623 on Interdunal Wetlands Adjacent to Traditional Navigable Waters (TNWs) Summary The U.S. Environmental Protection
MEMORANDUM FOR SWG-2007-1623 Subject: Jurisdictional Determination (JD) for SWG-2007-1623 on Interdunal Wetlands Adjacent to Traditional Navigable Waters (TNWs) Summary The U.S. Environmental Protection
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa
 Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Oceans: The Last Frontier Foundations, 6e - Chapter 9 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The vast world ocean Earth is often referred
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Oceans: The Last Frontier Foundations, 6e - Chapter 9 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The vast world ocean Earth is often referred
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore CO NTINENTAL SHEL F For the complete encyclopedic entry with media
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore CO NTINENTAL SHEL F For the complete encyclopedic entry with media
2. What type of rocks would you expect in this area, based on the topography? What is your reasoning?
 Geology 101 Bonus Lab Name Topographic maps are useful in helping us interpret the history of the landscape of an area. The questions below are designed to help you learn to interpret topographic maps.
Geology 101 Bonus Lab Name Topographic maps are useful in helping us interpret the history of the landscape of an area. The questions below are designed to help you learn to interpret topographic maps.
Depositional Environment
 Depositional Environment Sedimentary depositional environment describes the combination of physical, chemical and biological processes associated with the deposition of a particular type of sediment. Types
Depositional Environment Sedimentary depositional environment describes the combination of physical, chemical and biological processes associated with the deposition of a particular type of sediment. Types
Name Roy G Biv Page 1
 Name Roy G Biv Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the diagram below. The arrows show the direction in which sediment is being transported along the shoreline. A barrier beach has formed, creating
Name Roy G Biv Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the diagram below. The arrows show the direction in which sediment is being transported along the shoreline. A barrier beach has formed, creating
FINMARINET: Inventories and Planning for the Marine Natura 2000 Network in Finland. A.2 Geological inventories of the seafloor Final Report
 LIFE07 NAT/FIN/000151 FINMARINET: Inventories and Planning for the Marine Natura 2000 Network in Finland A.2 Geological inventories of the seafloor Final Report Geological Survey of Finland, GTK 1. Introduction
LIFE07 NAT/FIN/000151 FINMARINET: Inventories and Planning for the Marine Natura 2000 Network in Finland A.2 Geological inventories of the seafloor Final Report Geological Survey of Finland, GTK 1. Introduction
5. The topographic map below shows a lake and two rivers.
 Mapping A B1 1. The diagram below shows latitude measurements every 10 degrees and longitude measurements every 15 degrees. What is the latitude and longitude of point X? 5. The topographic map below shows
Mapping A B1 1. The diagram below shows latitude measurements every 10 degrees and longitude measurements every 15 degrees. What is the latitude and longitude of point X? 5. The topographic map below shows
ALASKA GEOLOGICAL SOCIETY PUBLICATIONS Stratigraphic And Structure Sections
 ALASKA GEOLOGICAL SOCIETY PUBLICATIONS 2007-2008 Stratigraphic And Structure Sections Price Western Alaska Bristol Bay Region Stratigraphic Correlation Sections (CD)... $12.00 AGS Member Price... $10.00
ALASKA GEOLOGICAL SOCIETY PUBLICATIONS 2007-2008 Stratigraphic And Structure Sections Price Western Alaska Bristol Bay Region Stratigraphic Correlation Sections (CD)... $12.00 AGS Member Price... $10.00
Redwood City Harbor, California, Navigation Improvement Feasibility Study. Appendix D. Geotechnical Engineering. DRAFT April 2015
 1 Redwood City Harbor, California, Navigation Improvement Feasibility Study Appendix D Geotechnical Engineering DRAFT April 2015 2 Contents 1 Purposes of Report... 3 2 Background... 3 3 References and
1 Redwood City Harbor, California, Navigation Improvement Feasibility Study Appendix D Geotechnical Engineering DRAFT April 2015 2 Contents 1 Purposes of Report... 3 2 Background... 3 3 References and
Section 2.1 Ocean Basins. - Has helped determine where ocean basins are located. - Tectonic plates move changing the position of the continents.
 Science 8 Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Chapter 2: Oceans Control the Water Cycle Section 2.1 Ocean Basins Oceans are important because: 1. Primary water source for the water cycle 2. Control weather
Science 8 Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Chapter 2: Oceans Control the Water Cycle Section 2.1 Ocean Basins Oceans are important because: 1. Primary water source for the water cycle 2. Control weather
Name: Which rock layers appear to be most resistant to weathering? A) A, C, and E B) B and D
 Name: 1) The formation of soil is primarily the result of A) stream deposition and runoff B) precipitation and wind erosion C) stream erosion and mass movement D) weathering and biological activity 2)
Name: 1) The formation of soil is primarily the result of A) stream deposition and runoff B) precipitation and wind erosion C) stream erosion and mass movement D) weathering and biological activity 2)
Midterm Review. Nata/Lee
 Name: 1. Which statement best supports the theory that all the continents were once a single landmass? (1) Rocks of the ocean ridges are older than those of the adjacent sea floor. (2) Rock and fossil
Name: 1. Which statement best supports the theory that all the continents were once a single landmass? (1) Rocks of the ocean ridges are older than those of the adjacent sea floor. (2) Rock and fossil
Hiking the Bold Coast, Cutler, Maine
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities June, 2010 Hiking the Bold Coast, Cutler, Maine 44 o 39 36.34 N, 67 o 12 46.99 W Text by Robert A. Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities June, 2010 Hiking the Bold Coast, Cutler, Maine 44 o 39 36.34 N, 67 o 12 46.99 W Text by Robert A. Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map
Landscape. Review Note Cards
 Landscape Review Note Cards Last Ice Age Pleistocene Epoch that occurred about 22,000 Years ago Glacier A large, long lasting mass of ice which forms on land and moves downhill because of gravity. Continental
Landscape Review Note Cards Last Ice Age Pleistocene Epoch that occurred about 22,000 Years ago Glacier A large, long lasting mass of ice which forms on land and moves downhill because of gravity. Continental
Day 3 Weathering and Erosion.notebook. October 02, Section 7.2. Erosion and Deposition. Objectives
 Objectives Describe the relationship of gravity to all agents of erosion. Contrast the features left from different types of erosion. Analyze the impact of living and nonliving things on the processes
Objectives Describe the relationship of gravity to all agents of erosion. Contrast the features left from different types of erosion. Analyze the impact of living and nonliving things on the processes
Donald K. Stauble and Bill Birkemeier Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory US Army Corps of Engineers
 Donald K. Stauble and Bill Birkemeier Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory US Army Corps of Engineers Define the Problem Navigation Shore Protection Environmental Political So what is the problem? Management
Donald K. Stauble and Bill Birkemeier Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory US Army Corps of Engineers Define the Problem Navigation Shore Protection Environmental Political So what is the problem? Management
Module 10: Resources and Virginia Geology Topic 4 Content: Virginia Geology Notes
 Virginia is composed of a very diverse landscape that extends from the beaches and barrier islands all of the way to the highly elevated Appalachian Plateau. Geologists have discovered ancient shallow
Virginia is composed of a very diverse landscape that extends from the beaches and barrier islands all of the way to the highly elevated Appalachian Plateau. Geologists have discovered ancient shallow
Chapter 2. Wearing Down Landforms: Rivers and Ice. Physical Weathering
 Chapter 2 Wearing Down Landforms: Rivers and Ice Physical Weathering Weathering vs. Erosion Weathering is the breakdown of rock and minerals. Erosion is a two fold process that starts with 1) breakdown
Chapter 2 Wearing Down Landforms: Rivers and Ice Physical Weathering Weathering vs. Erosion Weathering is the breakdown of rock and minerals. Erosion is a two fold process that starts with 1) breakdown
Highland Lake Bathymetric Survey
 Highland Lake Bathymetric Survey Final Report, Prepared For: The Town of Highland Lake 612 Lakeshore Drive Oneonta, AL 35121 Prepared By: Tetra Tech 2110 Powers Ferry Road SE Suite 202 Atlanta, GA 30339
Highland Lake Bathymetric Survey Final Report, Prepared For: The Town of Highland Lake 612 Lakeshore Drive Oneonta, AL 35121 Prepared By: Tetra Tech 2110 Powers Ferry Road SE Suite 202 Atlanta, GA 30339
Glacial Geology of Moose Point State Park, ME
 Geologic Site of the Month May, 2013 Glacial Geology of Moose Point State Park, Maine 44 o 25 59.18"N, 68 o 56 37.11"W Text and photos by Woodrow B. Thompson, Department of Agriculture, Conservation &
Geologic Site of the Month May, 2013 Glacial Geology of Moose Point State Park, Maine 44 o 25 59.18"N, 68 o 56 37.11"W Text and photos by Woodrow B. Thompson, Department of Agriculture, Conservation &
Geol 117 Lecture 18 Beaches & Coastlines. I. Types of Coastlines A. Definition:
 I. Types of Coastlines A. Definition: 1. Shore = narrow zone where ocean meets land (e.g. beach) 2. Coast is a broad area where both ocean and land processes act a. Includes onshore marshes, dunes, sea
I. Types of Coastlines A. Definition: 1. Shore = narrow zone where ocean meets land (e.g. beach) 2. Coast is a broad area where both ocean and land processes act a. Includes onshore marshes, dunes, sea
Moosehead Lake and the Tale of Two Rivers
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities June, 2005 45 o 53 5.09 N, 69 o 42 14.54 W Text by Kelley, A.R.; Kelley, J.T.; Belknap, D.F.; and Gontz, A.M. Department of Earth Sciences, University of Maine, Orono,
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities June, 2005 45 o 53 5.09 N, 69 o 42 14.54 W Text by Kelley, A.R.; Kelley, J.T.; Belknap, D.F.; and Gontz, A.M. Department of Earth Sciences, University of Maine, Orono,
Earth Science Chapter 9. Day 6 - Finish Capillary Action Lab - Quiz over Notes - Review Worksheets over Sections 9.2 and 9.3
 Earth Science Chapter 9 Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Read Section 9.1 Surface Water Chapter 9 Term Sheet Notes over Section 9.1 Surface Water Section 9.1 Review Worksheets Quiz over Section 9.1 Notes Virtual Lab
Earth Science Chapter 9 Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Read Section 9.1 Surface Water Chapter 9 Term Sheet Notes over Section 9.1 Surface Water Section 9.1 Review Worksheets Quiz over Section 9.1 Notes Virtual Lab
Erosion Information Paper - South Naknek, Alaska Current as of November 14, 2007
 U.S. Army Corps of Engineers ALASKA BASELINE EROSION ASSESSMENT Erosion Information Paper - South Naknek, Alaska Current as of November 14, 2007 Community Information South Naknek (NACK-neck), originally
U.S. Army Corps of Engineers ALASKA BASELINE EROSION ASSESSMENT Erosion Information Paper - South Naknek, Alaska Current as of November 14, 2007 Community Information South Naknek (NACK-neck), originally
What are the different ways rocks can be weathered?
 Romano - 223 What are the different ways rocks can be weathered? Weathering - the breakdown of rocks and minerals at the Earth s surface 1. 2. PHYSICAL WEATHERING Rock is broken into smaller pieces with
Romano - 223 What are the different ways rocks can be weathered? Weathering - the breakdown of rocks and minerals at the Earth s surface 1. 2. PHYSICAL WEATHERING Rock is broken into smaller pieces with
Which landscape best represents the shape of the valleys occupied by glaciers? A) B) C) D)
 1. Glaciers often form parallel scratches and grooves in bedrock because glaciers A) deposit sediment in unsorted piles B) deposit rounded sand in V-shaped valleys C) continually melt and refreeze D) drag
1. Glaciers often form parallel scratches and grooves in bedrock because glaciers A) deposit sediment in unsorted piles B) deposit rounded sand in V-shaped valleys C) continually melt and refreeze D) drag
Importance of Understanding Coastal Landforms
 Importance of Understanding Coastal Landforms Costa Concordia Shipwreck, Isola del Giglio, Italy Depositional Coastal Landforms Can interpret landforms in light of geomorphic processes, both terrestrial
Importance of Understanding Coastal Landforms Costa Concordia Shipwreck, Isola del Giglio, Italy Depositional Coastal Landforms Can interpret landforms in light of geomorphic processes, both terrestrial
The subject paper is being submitted for approval for publication in the annual volume entitled Geological Survey Research.
 Water Resources Division 345 Middlefield Road Menlo Park, California January 12, 1965 Memorandum To: Mr. Frank E. Clark, Chief, General Hydrology Branch Thru: Area Hydrologist PCA From: Valmore C. LaMarche
Water Resources Division 345 Middlefield Road Menlo Park, California January 12, 1965 Memorandum To: Mr. Frank E. Clark, Chief, General Hydrology Branch Thru: Area Hydrologist PCA From: Valmore C. LaMarche
ARE YOU READY TO THINK? Look at the first slide THINK PAIR SHARE!
 ARE YOU READY TO THINK? Look at the first slide THINK PAIR SHARE! WHAT PROMINENT FEATURE CAN YOU IDENTIFY IN THIS PICTURE? What do you think the different colors represent? Who might find such a picture
ARE YOU READY TO THINK? Look at the first slide THINK PAIR SHARE! WHAT PROMINENT FEATURE CAN YOU IDENTIFY IN THIS PICTURE? What do you think the different colors represent? Who might find such a picture
The Niagara Escarpment extends from western New York, through the GTA all the way up to Manitoulin Island and into Michigan and Wisconsin.
 is southern Ontario s most prominent topographic feature, extending more than 500 kilometres from western New York, through Niagara Falls and the western part of the Greater Toronto Area (GTA), and north
is southern Ontario s most prominent topographic feature, extending more than 500 kilometres from western New York, through Niagara Falls and the western part of the Greater Toronto Area (GTA), and north
UNIT 1: WATER SYSTEMS ON EARTH CHAPTER 2: OCEANS CONTROL THE WATER CYCLE
 UNIT 1: WATER SYSTEMS ON EARTH CHAPTER 2: OCEANS CONTROL THE WATER CYCLE ORIGINS OF OCEAN WATER OCEANS HAVE FILLED OVER HUNDREDS OF MILLIONS OF YEARS SCIENTISTS BELIEVE THE OCEANS ARE MORE THAN 3 BILLION
UNIT 1: WATER SYSTEMS ON EARTH CHAPTER 2: OCEANS CONTROL THE WATER CYCLE ORIGINS OF OCEAN WATER OCEANS HAVE FILLED OVER HUNDREDS OF MILLIONS OF YEARS SCIENTISTS BELIEVE THE OCEANS ARE MORE THAN 3 BILLION
Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Chapter 2
 Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Chapter 2 Create a mind map with the driving question, Why are Oceans Important? Remember: Why are oceans so important? Why are oceans so important? Primary water source
Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Chapter 2 Create a mind map with the driving question, Why are Oceans Important? Remember: Why are oceans so important? Why are oceans so important? Primary water source
Map shows 3 main features of ocean floor
 Map shows 3 main features of ocean floor 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 3 Marine Provinces 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Chapter 3 Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean
Map shows 3 main features of ocean floor 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 3 Marine Provinces 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Chapter 3 Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean
The Geology of Cobscook Bay State Park
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities August, 2000 44 50 24.67 N, 67 9 3.01 W Text by Robert A. Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by USGS Introduction Cobscook Bay State
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities August, 2000 44 50 24.67 N, 67 9 3.01 W Text by Robert A. Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by USGS Introduction Cobscook Bay State
Earth / Environmental Science. Ch. 14 THE OCEAN FLOOR
 Earth / Environmental Science Ch. 14 THE OCEAN FLOOR The Blue Planet Nearly 70% of the Earth s surface is covered by the global ocean It was not until the 1800s that the ocean became an important focus
Earth / Environmental Science Ch. 14 THE OCEAN FLOOR The Blue Planet Nearly 70% of the Earth s surface is covered by the global ocean It was not until the 1800s that the ocean became an important focus
Australian Coastal Councils Conference
 Australian Coastal Councils Conference 11 March 2015 Estimating Future Coastal Inundation and Erosion Hazards Dr Andrew McCowan Dr Christine Lauchlan-Arrowsmith Warwick Bishop Background Victorian Future
Australian Coastal Councils Conference 11 March 2015 Estimating Future Coastal Inundation and Erosion Hazards Dr Andrew McCowan Dr Christine Lauchlan-Arrowsmith Warwick Bishop Background Victorian Future
Essential Questions. What is erosion? What is mass wasting?
 Erosion Essential Questions What is erosion? What is mass wasting? What is Erosion? Erosion The transportation of sediment from one area to another Caused mainly by running water but also caused by glaciers,
Erosion Essential Questions What is erosion? What is mass wasting? What is Erosion? Erosion The transportation of sediment from one area to another Caused mainly by running water but also caused by glaciers,
Landscape evolution. An Anthropic landscape is the landscape modified by humans for their activities and life
 Landforms Landscape evolution A Natural landscape is the original landscape that exists before it is acted upon by human culture. An Anthropic landscape is the landscape modified by humans for their activities
Landforms Landscape evolution A Natural landscape is the original landscape that exists before it is acted upon by human culture. An Anthropic landscape is the landscape modified by humans for their activities
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 13 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 13 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 13 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Notes and Summary pages:
 Topographic Mapping 8.9C Interpret topographical maps and satellite views to identify land and erosional features and predict how these shapes may be reshaped by weathering ATL Skills: Communication taking
Topographic Mapping 8.9C Interpret topographical maps and satellite views to identify land and erosional features and predict how these shapes may be reshaped by weathering ATL Skills: Communication taking
What is weathering and how does it change Earth s surface? Answer the question using
 7 th Grade Lesson What is weathering and how does it change Earth s surface? Answer the question using the sentence frame. You have 4 minutes. Weathering is. This changes the Earth s surface because. 1
7 th Grade Lesson What is weathering and how does it change Earth s surface? Answer the question using the sentence frame. You have 4 minutes. Weathering is. This changes the Earth s surface because. 1
PEBBLE PROJECT ENVIRONMENTAL BASELINE DOCUMENT 2004 through CHAPTER 29. SOILS Cook Inlet Drainages
 PEBBLE PROJECT ENVIRONMENTAL BASELINE DOCUMENT 2004 through 2008 CHAPTER 29. SOILS Cook Inlet Drainages PREPARED BY: THREE PARAMETERS PLUS, INC. SOILS COOK INLET DRAINAGES TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS...
PEBBLE PROJECT ENVIRONMENTAL BASELINE DOCUMENT 2004 through 2008 CHAPTER 29. SOILS Cook Inlet Drainages PREPARED BY: THREE PARAMETERS PLUS, INC. SOILS COOK INLET DRAINAGES TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS...
