Polyploid Induction by Colchicine Treatments and Plant Regeneration of Dendrobium chrysotoxum
|
|
|
- Myles Tate
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Thai Journal of Agricultural Science 2013, 46(1): Polyploid Induction by Colchicine Treatments and Plant Regeneration of Dendrobium chrysotoxum P. Atichart Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Mahasarakham University Kantarawichai District, Mahasarakham 44150, Thailand Corresponding author. Abstract The purpose of this research was to investigate the effect of colchicines concentration and duration time to polyploid induction and plant regeneration of Dendrobium chrysotoxum L. The method was conducted by inclusion of colchicine into semi-solid VW medium. Protocorm like bodies (PLBs) of diploid D. chrysotoxum were treated with 0, 0.01, 0.02, 0.03, 0.04, and 0.05% colchicines (w/v) for 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 days. The most effective treatment was 0.04% colchicine for 1 day which resulted in about 84% surviving PLBs and with 47 % of tetraploid orchids, as measured by flow cytometry. The treated PLBs were cultured on the same medium supplemented with 0, 0.5 and 1 mg L -1 NAA and 0, 0.5 and 1 mg L -1 BA for plant regeneration. Treated PLBs with 0.01% and 0.02% colchicines, the highest number of proliferated shoot (2.36 per explants and 2.44 per explant respectively) was obtained from 1 mg L -1 NAA and 0.5 mg L -1 BA. In the treatment with 0.03% and 0.04% colchicines, the highest number of proliferated shoot (3.40 per explants and 4.35 per explants respectively) was obtained from the culture media supplemented only with 0.5 mg L -1 BA and 1 mg L -1 BA. Keywords: colchicine, protocorm, flow cytometry, orchid Introduction Dendrobium is one of the most important types of commercial orchids used for cut flowers and potted plants, flower sizes of some varieties are small such as D. chrysotoxum. It is a cluster of bright yellow, fifty cent size and honey scented. Chromosome doubling has been used in breeding program for improved new characteristics of orchid flower. Colchicine treatment has become a common tool use for polyploid induction in many plants. Economic crops such as wheat, oats, cotton, coffee, apples, roses, and bananas are polyploid (Luckett, 1989; Thao et al., 2003; Sundov et al., 2005). The process can occur naturally or through human manipulation. In general, polyploid plants exhibit superior phenotypes to those of diploids such as stronger stems, and thicker and larger leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds. Polyploid induction can be used as a means to create and select new and better breeds for further use. In order to produce polyploidy plants, the chemical colchicine is widely used because of its effectiveness and availability but it is toxic to cells. Polyploids were induced successfully from in vitro plants of diploid by treating with cochicine in different concentrations in Miscanthus sinensis (Petersen et al., 2003), oil palm (Madon et al., 2005), sesame (Mensah et al., 2007), Ginger (Sakhanokho et al., 2009), Basil (Omidbaigi et al., 2010) and cocoyam (Oumar et al., 2011), different explant materials were treated with colchicine to induce chromosome doubling. Ploidy levels could be easily determined by flow cytometry (Costich et al., 1993; Allum et al., 2007; Sarathum et al., 2011; Oumar et al., The objectives for this experiment were to determine the effective concentrations of colchicine, the appropriate duration time in the polyploid induction
2 60 P. Atichart Thai Journal of Agricultural Science and plant regeneration from treated PLBs of D. chrysotoxum. Materials and Methods Plant Material PLBs of D. chrysotoxum were used as explant sources derived from cultured of D. chrysotoxum seed on Vacin and Went (1949) medium (VW) containing 100 mg L -1 myo-inositol, 1 mg L -1 thiamine, 1 mg L -1 nicotinic acid, 1 mg L -1 pyridoxine and 4 mg mg L -1 glycine, 20 g l mg L -1 sucrose, 15% coconut water and 0.8% agar at ph 5.4. The explants were cultured under 16 h photoperiod (light intensity 40 µmole m -2 s -1 ) at 25±2 o C for 4 weeks. After 4 weeks of cultured seeds were formed Protocorm like bodies (PLBs). Colchicine Treatment PLBs were treated with 0, 0.01, 0.02, 0.03, 0.04, and 0.05% colchicine for 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 days. After the treatment, they were washed with steriled distilled water and then cultured on VW medium containing 100 mg L -1 myo-inositol, 1 mg L -1 thiamine, 1 mg L -1 nicotinic acid, 1 mg L -1 pyridoxine, 4 mg mg L -1 glycine, 15% coconut water, 20 g L -1 sucrose 8 g L -1 agar, ph 5.4. Each treatment was replicated 5 times and 50 protocorms were cultured per each replication. After culturing for 12 weeks, the survival plantlets was examined. Plant Regeneration Treated PLBs of D. chrysotoxum with colchicines were cultured on VW medium for 3 month they could not regenerated therefore treated PLBs would transfer to VW medium supplemented with 0, 0.5 and 1 mg L -1 -naphthalene acetic acid (NAA) and 0, 0.5 and 1 mg L -1 Benzyl adenine (BA) for plant regeneration. The explants were cultured under 16 h photoperiod (light intensity 40 µmole m -2 s -1 ) at 25±2 o C. The observation was taken at regular intervals of one week up to the 20 weeks and the obtained result was recorded. Ploidy Level Determination After 20 weeks, the proliferated shoots were subjected to test their ploidy levels by flow cytometry. Young leaves of colchicine treated plants were used for flow cytometric measurement. Approximately 1 g of each leaf was chopped with a sharp razor blade in a 55-mm plastic Petri dish containing hypotonic buffer Cy stain R UV ploidy (one step DAPI staining solution) and then filtered through a 30 µm celltrics disposable filter. The samples were analyzed with Partec PAII. Statistical Analysis Mean values for each duration and concentration of colchicine treatment and plant regeneration were tested in five replications and subjected to factorial in Completely Randomized Design (CRD) analysis of variance and compared by Duncan s new multiple range test (DMRT) at P<0.05. Results Survival Rate There are statistically significant differences (p<0.05) between the average survival rates over all duration and concentration of colchicines treatment, declining from 100% in the colchicines free control to 44% at the highest concentration of 0.05% treated for 3 days. The interaction between concentration and the duration of the colchicine treatments found that higher concentration and longer duration reduced survival of explants (Figure 1). Plant Regeneration Regeneration of treated PLBs after treated with colchicines on modified VW medium supplemented with 0, 0.5 and 1 mg L -1 NAA and 0, 0.5 and 1 mg L -1 BA. The mean number of proliferated shoot were evaluated after 20 weeks of cultures. The result showed significantly (p<0.05), treated PLBs with 0.01% and 0.02% colchicines, the highest number of proliferated shoot (2.36±0.4 per explants and 2.44±1.3 per explant respectively) was obtained from 1 mg L -1 NAA and 0.5 mg L -1 BA. But the treated PLBs with 0.03% and 0.04% colchicines, the highest number of proliferated shoot (3.40±1.26 per explants and 4.35±1.45 per explant respectively) was obtained from the culture media supplement only with 0.5 mg L -1 BA and 1 mg L -1 BA, respectively (Table 1).
3 Vol. 46, No. 1, 2013 Polyploid induction of D. chrysotoxum 61 Figure 1 The effect of in vitro colchicine treatment on the survival rate of D. chrysotoxum PLBs. Table 1 Effect of different concentration of - naphthalene acetic acid (NAA) and Benzyl adenine (BA) on plant regeneration of D. chrysotoxum treated protocorm with colchicines. Treatment concentration (%) Growth regulator (mg L -1 ) NAA BA Mean number of regenerated shoots (mean±s.e) ± 0.2bc ± 0.4abc ± 0.5 a ± 0.3 a ± 0.1ab ± 0.3 ab ± ± 0.4 c ± 0.2 a ± 1.35bc ± 0.4ab ± 1.267c ± 0.4a ± 0.6ab ± 0.3ab ± 1.23 abc ± 1.35bc ± 0.23 ab ± 1.23bc ± 1.26 ab ± 0.4a ± 0.6ab ± 0.6 ab ± 1.34 bc ± 0.5 ab ± 0.4 ab ± 1.15 ab ± 0.5 a ± 1.52b ± 1.45 b ± 1.23a ± 0.5 a ± 0.5a ± 1.25a ± 0.9 a ± 0.3 a Determination of Ploidy Level by Flow Cytometric Analysis In diploid control plants, used as an external standard, 100% of the nuclei were in G1 phase of the cell cycle, peaking at a relative nuclear DNA content of 200 (chanel number) indicated that the diploid (Figure 3A), whereas the tetraploid remaining nuclei appeared at a relative nuclear DNA content of 400 (chanel number), in late S or G2 phase of the cell cycle (Figure 3B), and mixoploid remaining nuclei appeared at a relative nuclear DNA content of 200 and 400 (chanel number) (Figure 3C)The ploidy level of the treated plantlets was affected by the concentration of colchicine and the duration of treatment. When plantlets were treated with 0.04% colchicine, plantlets exhibit increases in ploidy level. At the same concentration of colchicines (0.04%) but when the time of exposure was increased to 2 days, 30% tetraploids and 46% mixoploids (2x+4x) were found among tested plantlets (Table 2). Discussion In vitro induction of polyploid in D. chrysotoxum proved successful when treated PLBs with colchicines concentration at 0.04% for 1 and 2 days, Tetraploid and mixoploid were found. Several reports used colchicine as antimitotic substances. It binds to cell protein tubulin and arrests mitosis in metaphase due to failure of spindle formation. It causes depolymerisation and disappearance of the fibrillar microtubules in granulocytes and other motile cells, inhibiting their migration as well as metabolic and phagocytic activity (Sundov et al., 2005) In many plant species colchicine causes side effects such as sterility, abnormal growth and morphology, chromosome losses or rearrangements and gene mutation (Luckett, 1989). Using high colchicines concentration at 0.1, 0.15 and 0.2% for longer than 24 h, chrolophyll contents were decreased and plantets were died after treated. The survival of the explants after colchicine treatments depend on the concentration and duration of the treatment. In general, higher coccentration and longer duration reduced survival of plants (Thao et al., 2003; Atichart and Bunnag, 2007).
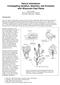
4 62 P. Atichart Thai Journal of Agricultural Science C A Figure 2 Plant regeneration of D. chrysotoxum treated protocorm with co% cultured on 0.03% cultured on VW lchicines (A), 0.01% cultured on VW supplement with 1 mg L -1 NAA and 0.5 mg L -1 BA (B), VW supplement with 1 mg L -1 NAA and 0.5 mg L -1 BA (C), and 0.02 supplement with 0.5 mg L -1 BA 0.04% cultured on VW supplement with 1 mg L -1 BA (D). Number of nuclei Number of nuclei Number of nuclei 2n 2n 4n 4n A Relative nuclear DNA content Figure 3 Histograms showing different ploidy levels for the standard diploid (A) the induced tetraploid and (C) mixoploid. B C B D Treated PLBs of D. chrysotoxum with colchicines in various concentration and duration could not regenerated to plantlet. Used of growth regulators may help them to shoot proliferated. The type and concentration of growth regulators are an initial consideration for micropropagation of orchid species (Genkov and Ivanova, 1995). Addition of cytokinin to the medium increase the number of shoots which demonstrates the significance of exogenous cytokinin to enhance the multiple shoots. BA influences shoot proliferation by stimulating quick cell divisions to induce large number of multiple shoots (Yakimova et al., 2000; Roy and Banerjee, 2002; Ronzhina, 2003; Hameed et al., 2006). Results are also according to Asghar et al. (20011) who reported that axillary buds of orchid Dendrobium nobile var. Emma white were proliferated by using phytotechnology medium (O753) supplemented with benzylaminopurine (BAP) and kinetin (Kin) as well as coconut water (CW) and Roy and Banerjee (2002) who reported that BAP enhances the shoot multiplication more actively than Kin. BAP provided smaller lengths of proliferated shoots in contrast to shoots number. Being a strong cytokinin, it depresses shoot length by an increase in number of axillary buds (Hameed et al., 2006). The following conclusions regarding the efficiency of polyploidy induction, base on the in vitro application of colchicines to D. chrysotoxum, plantlets of this study will multiply and observation about plant growth, plant morphology such as the number of leaves and flower per plant, plant size and flower size and determine chlorophyll content for the next experiment. Acknowledgments This research was supported by Mahasarakham University and 2553 research fund form National Research Council of Thailand. References Allum, J.F, D.H. Bringloe and A.V. Robert Chromosome doubling in a Rosa rugosa Thunb. Hybrid by exposure of in vitro nodes to oryzalin: the effects of node length, oryzalin concentration and exposure time. Plant Cell Rep. 26:
5 Vol. 46, No. 1, 2013 Polyploid induction of D. chrysotoxum 63 Table 2 Ploidy level was analyzed two months after colchicines treatment. Treatment concentration Duration Ploidy level (%) (%) (days) 2X 4X 2x + 4X Control 0.04 colchicine Asghar, S., T. Ahmad, I. Ahmad Hafiz and M. Yaseen In vitro propagation of orchid (Dendrobium nobile) var. Emma white. African Journal of Biotechnology 10: Atichart, P. and S. Bunnag Polyploid Induction in Dendrobium secundum (Bl.) Lindl. by in vitro Techniques. Thai Journal of Agricultural Science 40: Costich, D.E., R. Ortiz, T.R. Meagher, L.P. Bruederle and N. Vorsa Determination of ploidy level and nuclear DNA content in blueberry by flow cytometry. Theor. Appl. Genet. 86: Genkov, T. and I. Ivanova Effect of cytokinin active phenylurea derivatives on shoot multiplication, peroxidase and superoxide dismutase activities of in vitro cultured carnation. Bulg. J. Plant Physiol. 21: Hameed, N., A. Shabbir, A. Ali and R. Bajwa In vitro micropropagation of disease free rose (Rosa indica L.). Mycopath 4: Luckett, D Colchicine mutagenesis is associated with substantial heritable variation in cotton. Euphytica 42: Madon, M., Clyde, M.M., Hashim, H., Mohd yusuf, Y. and Mat, H., Saratha, S., Polyploidy induction of oil palm through Colchicine and oryzalin treatments. Journal of Oil Palm Research, 17: Mensah, J.K., B.O. Obadoni, P.A. Akomeah, B. Ikhajiagbe and J. Ajibolu The effects of sodium azide and colchicine treatments on morphological and yield traits of sesame seed (Sesame indicum L.). African Journal of Biotechnology 6: Omidbaigi, R., M. Mirzaee, M.E. Hassani and M.S. Moghadam Induction and identification of polyploidy in basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) medicinal plant by colchicine treatment. International Journal of Plant Production 4: Petersen, K.K., P. Hagberg and K. Kristiansen Colchicine and oryzalin Mediated chromosome doubling in different genotypes of Miscanthus sinensis. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 73: Roy, J. and N. Banerjee Rhizome and shoot development during in vitro propagation of Geodorum densiflorum (Lam.) Schltr. Sci. Hortic. 94: Ronzhina, E.S Effect of 6-benzylaminopurine on the structure of photosynthetic apparatus of Faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 39: Sundov, Z., Z. Nincevicb, M. Definis-Gojanovicc, M. Glavina-Durdovc, I. Jukica, N. Hulinad and A. Tonkica Fatal colchicine poisoning by accidental ingestion of meadow saffron-case report. Forensic Science International 149: Sakhanokho, H.F., V.K. Rowena and N. Islam-Faridi Induced polyploidy in diploid ornamental ginger (Hedychium muluense R. M. Smith) using colchicine and oryzalin. Journal of Hortscience 44: Sarathum, S., M. Hegele, S. Tantiviwat and M. Nanakorn Effect of concentration and duration of colchicine treatment on polyploidy induction in Dendrobium scabrilingue L. Europ. J. Hort. Sci. 75: Thao, N.T.P., K. Ureshino, I. Miyajima, Y. Ozaki and H. Okubo Induction of tetraploids in ornamental Alocasia through colchicine and oryzalin treatments. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 72: Vacin, E. and F. Went Some ph changes in nutrient solution. Bot. Gaz. 110: Yakimova, E., V.K. Toteva, I. Groshkoff and G. Ivanova Effect of BA and CPPU on protease and α-amylase activity of in vitro cultured explants of Rosa hybrida L. Bulg. J. Plant Physiol. 26: Manuscript received 3 March 2013, accepted 22 May 2013 Now online at
Alteration of Spathoglottis eburnea Gagnep. Ploidy Level after Colchicine Treatments
 Agricultural Technology and Biological Sciences Alteration of Spathoglottis eburnea Gagnep. Ploidy Level after Colchicine Treatments Witayaporn PORNCHUTI 1, Kanchit THAMMASIRI 2,*, Ngarmnij CHUENBOONNGARM
Agricultural Technology and Biological Sciences Alteration of Spathoglottis eburnea Gagnep. Ploidy Level after Colchicine Treatments Witayaporn PORNCHUTI 1, Kanchit THAMMASIRI 2,*, Ngarmnij CHUENBOONNGARM
Alteration of Spathoglottis eburnea Gagnep. Ploidy Level after. Colchicine Treatments
 Article Alteration of Spathoglottis eburnea Gagnep. Ploidy Level after Witayaporn PORNCHUTI a, Kanchit THAMMASIRI b*, Ngarmnij CHUENBOONNGARM b and Nathinee PANVISAVAS b a Department of Biotechnology,
Article Alteration of Spathoglottis eburnea Gagnep. Ploidy Level after Witayaporn PORNCHUTI a, Kanchit THAMMASIRI b*, Ngarmnij CHUENBOONNGARM b and Nathinee PANVISAVAS b a Department of Biotechnology,
In Vitro Polyploid Induction of Ophiopogon planiscapus. Dominic A. Gillooly, Darren H. Touchell and Thomas G. Ranney
 In Vitro Polyploid Induction of Ophiopogon planiscapus Dominic A. Gillooly, Darren H. Touchell and Thomas G. Ranney North Carolina State University, Departement of Horticultural Science Mountain Crop Improvement
In Vitro Polyploid Induction of Ophiopogon planiscapus Dominic A. Gillooly, Darren H. Touchell and Thomas G. Ranney North Carolina State University, Departement of Horticultural Science Mountain Crop Improvement
Production of Haploid and Doubled Haploid Plants from Anther-derived Callus of Lilium formosanum
 Production of Haploid and Doubled Haploid Plants from Anther-derived Callus of Lilium formosanum D.-S. Han and Y. Niimi Faculty of Agriculture, Niigata University 2-8050 Ikarashi, Niigata 950-2181 Japan
Production of Haploid and Doubled Haploid Plants from Anther-derived Callus of Lilium formosanum D.-S. Han and Y. Niimi Faculty of Agriculture, Niigata University 2-8050 Ikarashi, Niigata 950-2181 Japan
POLYPLOIDY AND AN IN VITRO-MEDIATED PROPAGATION PROTOCOL FOR POTENTIALLY INDUCING CHROMOSOME DOUBLING IN MACADAMIA
 POLYPLOIDY AND AN IN VITRO-MEDIATED PROPAGATION PROTOCOL FOR POTENTIALLY INDUCING CHROMOSOME DOUBLING IN MACADAMIA Karin Hannweg and Mark Penter Plant Improvement Division Agricultural Research Council
POLYPLOIDY AND AN IN VITRO-MEDIATED PROPAGATION PROTOCOL FOR POTENTIALLY INDUCING CHROMOSOME DOUBLING IN MACADAMIA Karin Hannweg and Mark Penter Plant Improvement Division Agricultural Research Council
State Forest Research Institute, Post Box No. 159, Itanagar , India 1 Department of Botany, Rajiv Gandhi University, Itanagar , India
 Indian Journal of Biotechnology Vol 6, April 2007, pp. 256-261 Effects of different culture media on seed germination and subsequent in vitro development of protocorms of Hygrochilus parishii (Veith &
Indian Journal of Biotechnology Vol 6, April 2007, pp. 256-261 Effects of different culture media on seed germination and subsequent in vitro development of protocorms of Hygrochilus parishii (Veith &
VQ403 The development of tetraploid ginger varieties. M K Smith and S D Hamill Queensland Horticulture Institute, Nambour
 VQ403 The development of tetraploid ginger varieties M K Smith and S D Hamill Queensland Horticulture Institute, Nambour VG403 This report is published by the Horticultural Research and Development Corporation
VQ403 The development of tetraploid ginger varieties M K Smith and S D Hamill Queensland Horticulture Institute, Nambour VG403 This report is published by the Horticultural Research and Development Corporation
Improvement of Orchid Vanda Hybrid (Vanda limbata Blume X Vanda tricolor Lindl. var. suavis) By Colchicines Treatment In Vitro
 Modern Applied Science; Vol. 10, No. 11; 2016 ISSN 1913-1844 E-ISSN 1913-1852 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Improvement of Orchid Vanda Hybrid (Vanda limbata Blume X Vanda tricolor
Modern Applied Science; Vol. 10, No. 11; 2016 ISSN 1913-1844 E-ISSN 1913-1852 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Improvement of Orchid Vanda Hybrid (Vanda limbata Blume X Vanda tricolor
POLYPLOID PRODUCTION IN LILIUM LEICHTLINII VAR. MAXIMOWICZII USING COLCHICINE ABSTRACT
 Heo et al., The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences, 26(4): 2016, The Page: J. Anim. 1111-1116 Plant Sci. 26(4):2016 ISSN: 1018-7081 POLYPLOID PRODUCTION IN LILIUM LEICHTLINII VAR. MAXIMOWICZII USING COLCHICINE
Heo et al., The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences, 26(4): 2016, The Page: J. Anim. 1111-1116 Plant Sci. 26(4):2016 ISSN: 1018-7081 POLYPLOID PRODUCTION IN LILIUM LEICHTLINII VAR. MAXIMOWICZII USING COLCHICINE
In vitro induction of tetraploids from immature embryos through colchicine treatments in Clivia miniata Regel
 African Journal of Agricultural Research Vol. 7(25), pp. 3712-3718, 3 July, 2012 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajar DOI: 10.5897/AJAR11.2343 ISSN 1991-637X 2012 Academic Journals
African Journal of Agricultural Research Vol. 7(25), pp. 3712-3718, 3 July, 2012 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajar DOI: 10.5897/AJAR11.2343 ISSN 1991-637X 2012 Academic Journals
Genetic variability/stability of micropropagated and standard propagated raspberry and blackberry plants
 THE SUSTAINABLE IMPROVEMENT OF EUROPEAN BERRY PRODUCTION, QUALITY AND NUTRITIONAL VALUE IN CHANGING ENVIRONMENT: STRAWBERRIES, CURRANTS, BLACKBERRIES, BLUEBERRIES AND RASPBERRIES (EUBERRY) SUBCONTARCT:
THE SUSTAINABLE IMPROVEMENT OF EUROPEAN BERRY PRODUCTION, QUALITY AND NUTRITIONAL VALUE IN CHANGING ENVIRONMENT: STRAWBERRIES, CURRANTS, BLACKBERRIES, BLUEBERRIES AND RASPBERRIES (EUBERRY) SUBCONTARCT:
Induction of Haploid Callus from Isolated Microspores of Peony in vitro
 Plant & Cell Physiol. 22(2): 337-34 (98) Short communication Induction of Haploid Callus from Isolated Microspores of Peony in vitro Kanji Ono and Shuichi Harashima Department of Biology, Faculty of Science,
Plant & Cell Physiol. 22(2): 337-34 (98) Short communication Induction of Haploid Callus from Isolated Microspores of Peony in vitro Kanji Ono and Shuichi Harashima Department of Biology, Faculty of Science,
Plant Regeneration and Chromosome Doubling of Wild Gladiolus Species
 Plant Regeneration and Chromosome Doubling of Wild Gladiolus Species K. Suzuki, Y. Takatsu, T. Gonai and M. Kasumi Plant Biotechnology Institute Ibaraki Agricultural Center, Ibaraki Japan Keywords: gladiolus,
Plant Regeneration and Chromosome Doubling of Wild Gladiolus Species K. Suzuki, Y. Takatsu, T. Gonai and M. Kasumi Plant Biotechnology Institute Ibaraki Agricultural Center, Ibaraki Japan Keywords: gladiolus,
Somaclonal Variation
 Tissue-culture cycle involves: dedifferentiation in culture proliferation of cells (implies sev. cell generations removed from original differentiated cell) subsequent regeneration to plants no selection
Tissue-culture cycle involves: dedifferentiation in culture proliferation of cells (implies sev. cell generations removed from original differentiated cell) subsequent regeneration to plants no selection
The Effect of Pollination Time and Gibberellic Acid (GA3) on the Production and Seed Germination of Phalaenopsis Orchids
 The Effect of Pollination Time and Gibberellic Acid (GA3) on the Production and Seed Germination of Phalaenopsis Orchids Hassan Kia Heirati 1*, Rasoul Onsinejad 2 and Fattaneh Yari 3 1 M.S. Student, Department
The Effect of Pollination Time and Gibberellic Acid (GA3) on the Production and Seed Germination of Phalaenopsis Orchids Hassan Kia Heirati 1*, Rasoul Onsinejad 2 and Fattaneh Yari 3 1 M.S. Student, Department
X-Sheet 3 Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis
 X-Sheet 3 Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis 13 Key Concepts In this session we will focus on summarising what you need to know about: Revise Mitosis (Grade 11), the process of meiosis, First Meiotic division,
X-Sheet 3 Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis 13 Key Concepts In this session we will focus on summarising what you need to know about: Revise Mitosis (Grade 11), the process of meiosis, First Meiotic division,
Essential Questions. Meiosis. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education
 Essential Questions How does the reduction in chromosome number occur during meiosis? What are the stages of meiosis? What is the importance of meiosis in providing genetic variation? Meiosis Vocabulary
Essential Questions How does the reduction in chromosome number occur during meiosis? What are the stages of meiosis? What is the importance of meiosis in providing genetic variation? Meiosis Vocabulary
EFFECT OF PURINE AND PHENYLUREA CYTOKININS ON PEROXIDASE ACTIVITY IN RELATION TO APICAL DOMINANCE OF IN VITRO CULTIVATED ROSA HYBRIDA L.
 40 BULG. J. PLANT PHYSIOL., 1997, 23(1 2), 40 48 EFFECT OF PURINE AND PHENYLUREA CYTOKININS ON PEROXIDASE ACTIVITY IN RELATION TO APICAL DOMINANCE OF IN VITRO CULTIVATED ROSA HYBRIDA L. Veneta Kapchina-Toteva*
40 BULG. J. PLANT PHYSIOL., 1997, 23(1 2), 40 48 EFFECT OF PURINE AND PHENYLUREA CYTOKININS ON PEROXIDASE ACTIVITY IN RELATION TO APICAL DOMINANCE OF IN VITRO CULTIVATED ROSA HYBRIDA L. Veneta Kapchina-Toteva*
Efficient plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis from anthers of Datura stramonium L.
 Available online http://www.ijat-rmutto.com Journal of Agricultural Technology 2010 Vol. ISSN 6(4): 1686-9141 741-745 Efficient plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis from anthers of Datura stramonium
Available online http://www.ijat-rmutto.com Journal of Agricultural Technology 2010 Vol. ISSN 6(4): 1686-9141 741-745 Efficient plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis from anthers of Datura stramonium
Useful Propagation Terms. Propagation The application of specific biological principles and concepts in the multiplication of plants.
 Useful Propagation Terms Propagation The application of specific biological principles and concepts in the multiplication of plants. Adventitious Typically describes new organs such as roots that develop
Useful Propagation Terms Propagation The application of specific biological principles and concepts in the multiplication of plants. Adventitious Typically describes new organs such as roots that develop
The Effect of Different levels and kinds of Cytokinins on Buds proliferation of Iraqian Date Palm Cultiver (Barhi) In vitro
 The Effect of Different levels and kinds of Cytokinins on Buds proliferation of Iraqian Date Palm Cultiver (Barhi) In vitro A. A. H. Al-Khalisi Department of Biology, College of Education Ibn Al-Haitham,
The Effect of Different levels and kinds of Cytokinins on Buds proliferation of Iraqian Date Palm Cultiver (Barhi) In vitro A. A. H. Al-Khalisi Department of Biology, College of Education Ibn Al-Haitham,
INTRODUCING PLANT TISSUE CULTURE IN THE CLASSROOM CONCEPTS & HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE
 INTRODUCING PLANT TISSUE CULTURE IN THE CLASSROOM CONCEPTS & HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE Dr. Mike Kane University of Florida Applications of Plant Tissue Culture Concepts & Terminology Micropropagation: A Historical
INTRODUCING PLANT TISSUE CULTURE IN THE CLASSROOM CONCEPTS & HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE Dr. Mike Kane University of Florida Applications of Plant Tissue Culture Concepts & Terminology Micropropagation: A Historical
Doubled haploid ramets via embryogenesis of haploid tissue cultures
 Doubled haploid ramets via embryogenesis of haploid tissue cultures Harry E. Iswandar 1, J. M. Dunwell 2, Brian P. Forster 3, Stephen P. C. Nelson 1,4 and Peter D. S. Caligari,3,4,5 ABSTRACT Tissue culture
Doubled haploid ramets via embryogenesis of haploid tissue cultures Harry E. Iswandar 1, J. M. Dunwell 2, Brian P. Forster 3, Stephen P. C. Nelson 1,4 and Peter D. S. Caligari,3,4,5 ABSTRACT Tissue culture
Plant Tissue Cult. & Biotech. 15(2): , 2005 (December) Colchicine Induced Morphological Variants in Pineapple
 Plant Tissue Cult. & Biotech. 15(2): 127-133, 2005 (December) PTC&B Colchicine Induced Morphological Variants in Pineapple A. Mujib Department of Botany, Hamdard University, New Delhi-110 062, India Key
Plant Tissue Cult. & Biotech. 15(2): 127-133, 2005 (December) PTC&B Colchicine Induced Morphological Variants in Pineapple A. Mujib Department of Botany, Hamdard University, New Delhi-110 062, India Key
Induced Mutation of Chrysanthemum by Colchicine
 International Journal of Agricultural Technology 2017 Vol. 13(7.3): 2325-2332 Available online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com ISSN 1686-9141 Induced Mutation of Chrysanthemum by Colchicine Anan Lertsutthichawan
International Journal of Agricultural Technology 2017 Vol. 13(7.3): 2325-2332 Available online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com ISSN 1686-9141 Induced Mutation of Chrysanthemum by Colchicine Anan Lertsutthichawan
Flow cytometric analysis of Ploidy level
 Flow cytometric analysis of Ploidy level Centre of Plant Structural and Functional Genomics of the Institute of Experimental Botany AS CR, Olomouc, Czech Republic Riccardo Pasculli Roman Hudec Field application
Flow cytometric analysis of Ploidy level Centre of Plant Structural and Functional Genomics of the Institute of Experimental Botany AS CR, Olomouc, Czech Republic Riccardo Pasculli Roman Hudec Field application
HYBRID DENDROBIUM ORCHID ON VARIOUS TYPES AND CONCENTRATION OF CYTOKININ AND AUXIN ON MURASHIGE AND SKOOG (MS) MEDIUM
 Responses of Protocorm Like Bodies Hybrid. Anne Nuraini RESPONSES OF Protocorm Like Bodies HYBRID DENDROBIUM ORCHID ON VARIOUS TYPES AND CONCENTRATION OF CYTOKININ AND AUXIN ON MURASHIGE AND SKOOG (MS)
Responses of Protocorm Like Bodies Hybrid. Anne Nuraini RESPONSES OF Protocorm Like Bodies HYBRID DENDROBIUM ORCHID ON VARIOUS TYPES AND CONCENTRATION OF CYTOKININ AND AUXIN ON MURASHIGE AND SKOOG (MS)
Plant Growth Regulators(NCERT)
 Plant Growth Regulators(NCERT) Promoters: 1. Auxins: -first isolated from urine, contains Zinc. -Natural: Indole Acetic Acid (IAA) Indole Butyric Acid (IBA) -Synthetic: Naphthalene Acetic Acid (NAA) 2-4
Plant Growth Regulators(NCERT) Promoters: 1. Auxins: -first isolated from urine, contains Zinc. -Natural: Indole Acetic Acid (IAA) Indole Butyric Acid (IBA) -Synthetic: Naphthalene Acetic Acid (NAA) 2-4
Callus induction and plant regeneration on optimization of the culture conditions in Jow Haw rice (Oryza sativa L.)
 Journal of Agricultural Technology 2016 Vol. 12(2):241-248 Available online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com ISSN 1686-9141 Callus induction and plant regeneration on optimization of the culture conditions in
Journal of Agricultural Technology 2016 Vol. 12(2):241-248 Available online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com ISSN 1686-9141 Callus induction and plant regeneration on optimization of the culture conditions in
Identification of tetraploid mutants of Platycodon grandiflorus by colchicine induction
 CARYOLOGIA Vol. 64, no. 3: 343-349, 2011 Identification of tetraploid mutants of Platycodon grandiflorus by colchicine induction YUXIANG WU +, FUHONG YANG +, XIAOMING ZHAO and WUDE YANG* College of Agriculture,
CARYOLOGIA Vol. 64, no. 3: 343-349, 2011 Identification of tetraploid mutants of Platycodon grandiflorus by colchicine induction YUXIANG WU +, FUHONG YANG +, XIAOMING ZHAO and WUDE YANG* College of Agriculture,
The Science of Plants in Agriculture Pl.Sci 102. Getting to Know Plants
 The Science of Plants in Agriculture Pl.Sci 102 Getting to Know Plants Growth and Development of Plants Growth and Development of Plants Why it s important to have knowledge about plant development. What
The Science of Plants in Agriculture Pl.Sci 102 Getting to Know Plants Growth and Development of Plants Growth and Development of Plants Why it s important to have knowledge about plant development. What
Sporic life cycles involve 2 types of multicellular bodies:
 Chapter 3- Human Manipulation of Plants Sporic life cycles involve 2 types of multicellular bodies: -a diploid, spore-producing sporophyte -a haploid, gamete-producing gametophyte Sexual Reproduction in
Chapter 3- Human Manipulation of Plants Sporic life cycles involve 2 types of multicellular bodies: -a diploid, spore-producing sporophyte -a haploid, gamete-producing gametophyte Sexual Reproduction in
GENETIC ANALYSES OF ROOT SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT IN THE TOMATO CROP MODEL
 GENETIC ANALYSES OF ROOT SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT IN THE TOMATO CROP MODEL Kelsey Hoth 1 Dr. Maria Ivanchenko 2 Bioresourse Research 1, Department of Botany and Plant Physiology 2, Oregon State University, Corvallis,
GENETIC ANALYSES OF ROOT SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT IN THE TOMATO CROP MODEL Kelsey Hoth 1 Dr. Maria Ivanchenko 2 Bioresourse Research 1, Department of Botany and Plant Physiology 2, Oregon State University, Corvallis,
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-15 PLANT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT
 CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-15 PLANT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT Root, stem leaves, flower, fruits and seeds arise in orderly manner in plants. The sequence of growth is as follows-
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-15 PLANT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT Root, stem leaves, flower, fruits and seeds arise in orderly manner in plants. The sequence of growth is as follows-
Application of flow cytometry in plant sciences Elwira Sliwinska
 Application of flow cytometry in plant sciences Elwira Sliwinska Head, Laboratory of Molecular Biology and Cytometry Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding University of Technology and Life Sciences,,
Application of flow cytometry in plant sciences Elwira Sliwinska Head, Laboratory of Molecular Biology and Cytometry Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding University of Technology and Life Sciences,,
Induction of Polyploid Phalaenopsis amabilis by N_2O Treatment
 九州大学学術情報リポジトリ Kyushu University Institutional Repository Induction of Polyploid Phalaenopsis amabilis by N_2O Treatment Wongprichachan, Prapassorn Huang, Kuang-Liang Hsu, Shan-Te Chou, Yi-Mei 他 http://hdl.handle.net/2324/26158
九州大学学術情報リポジトリ Kyushu University Institutional Repository Induction of Polyploid Phalaenopsis amabilis by N_2O Treatment Wongprichachan, Prapassorn Huang, Kuang-Liang Hsu, Shan-Te Chou, Yi-Mei 他 http://hdl.handle.net/2324/26158
Plant Propagation PLS 3221/5222
 Plant Propagation PLS 3221/5222 Dr. Sandra Wilson Dr. Mack Thetford Chapter 2 Introduction to the Biology of Plant Propagation -A review- 1 5. Plant Hormones and Plant development Phytohormones Nt Naturally
Plant Propagation PLS 3221/5222 Dr. Sandra Wilson Dr. Mack Thetford Chapter 2 Introduction to the Biology of Plant Propagation -A review- 1 5. Plant Hormones and Plant development Phytohormones Nt Naturally
INVITRO MICROPROPAGATION OF EULOPHIA NUDA LIND AN ENDANGERED TERRESTRIAL ORCHID THROUGH PLB (PROTOCORM LIKE BODIES)
 Received: 21 st Dec-2013 Revised: 29 th Dec-2013 Accepted: 30 th Dec-2013 Research article INVITRO MICROPROPAGATION OF EULOPHIA NUDA LIND AN ENDANGERED TERRESTRIAL ORCHID THROUGH PLB (PROTOCORM LIKE BODIES)
Received: 21 st Dec-2013 Revised: 29 th Dec-2013 Accepted: 30 th Dec-2013 Research article INVITRO MICROPROPAGATION OF EULOPHIA NUDA LIND AN ENDANGERED TERRESTRIAL ORCHID THROUGH PLB (PROTOCORM LIKE BODIES)
In vitro flowering and in vitro pollination: methods that will benefit the orchid industry
 In vitro flowering and in vitro pollination: methods that will benefit the orchid industry Kim Hor HEE, Hock Hin YEOH, Chiang Shiong LOH Department of Biological Sciences, National University of Singapore
In vitro flowering and in vitro pollination: methods that will benefit the orchid industry Kim Hor HEE, Hock Hin YEOH, Chiang Shiong LOH Department of Biological Sciences, National University of Singapore
Micropropagation of Lisianthus (Eustoma grandiflorum L.) from different explants to flowering onset
 583 Micropropagation of Lisianthus (Eustoma grandiflorum L.) from different explants to flowering onset Fatemeh Rezaee, Faezeh Ghanati* and Laleh Yusefzadeh Boroujeni Department of Plant Biology, Faculty
583 Micropropagation of Lisianthus (Eustoma grandiflorum L.) from different explants to flowering onset Fatemeh Rezaee, Faezeh Ghanati* and Laleh Yusefzadeh Boroujeni Department of Plant Biology, Faculty
THE DEVELOPMENT OF PLANT REGENERATION SYSTEMS FOR THE GENETIC IMPROVEMENT OF WALNUT. Walt Tu1ecke and Gale McGranahan
 THE DEVELOPMENT OF PLANT REGENERATION SYSTEMS FOR THE GENETIC IMPROVEMENT OF WALNUT Walt Tu1ecke and Gale McGranahan ABSTRACT The techniques and capability to regenerate asexual embryos from walnut cotyledon
THE DEVELOPMENT OF PLANT REGENERATION SYSTEMS FOR THE GENETIC IMPROVEMENT OF WALNUT Walt Tu1ecke and Gale McGranahan ABSTRACT The techniques and capability to regenerate asexual embryos from walnut cotyledon
Doubled haploid plant production from unpollinated ovules of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.)
 Plant Cell Reports (2000) 19:1155 1159 Q Springer-Verlag 2000 CELL BIOLOGY AND MORPHOGENESIS S. Gürel 7 E. Gürel 7 Z. Kaya Doubled haploid plant production from unpollinated ovules of sugar beet (Beta
Plant Cell Reports (2000) 19:1155 1159 Q Springer-Verlag 2000 CELL BIOLOGY AND MORPHOGENESIS S. Gürel 7 E. Gürel 7 Z. Kaya Doubled haploid plant production from unpollinated ovules of sugar beet (Beta
Effect of Colchicine Tablets on Morphology of Torenia fournieri
 2013 International Transaction Journal of Engineering, Management, & Applied Sciences & Technologies. International Transaction Journal of Engineering, Management, & Applied Sciences & Technologies http://tuengr.com
2013 International Transaction Journal of Engineering, Management, & Applied Sciences & Technologies. International Transaction Journal of Engineering, Management, & Applied Sciences & Technologies http://tuengr.com
Reproduction, Seeds and Propagation
 Reproduction, Seeds and Propagation Diploid (2n) somatic cell Two diploid (2n) somatic cells Telophase Anaphase Metaphase Prophase I One pair of homologous chromosomes (homologues) II Homologues condense
Reproduction, Seeds and Propagation Diploid (2n) somatic cell Two diploid (2n) somatic cells Telophase Anaphase Metaphase Prophase I One pair of homologous chromosomes (homologues) II Homologues condense
Melon Meiosis.
 Objective Students will read about the discovery of colchicine, which made seedless watermelon possible. Students will use modelling clay and beans to model meiosis and mitosis. Students will design imaginary
Objective Students will read about the discovery of colchicine, which made seedless watermelon possible. Students will use modelling clay and beans to model meiosis and mitosis. Students will design imaginary
Cytological Analysis of Embryogenic Callus and Regenerated Plants of Urginea Indica Kunth., Indian Squill
 Caryologia International Journal of Cytology, Cytosystematics and Cytogenetics ISSN: 0008-7114 (Print) 2165-5391 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tcar20 Cytological Analysis of
Caryologia International Journal of Cytology, Cytosystematics and Cytogenetics ISSN: 0008-7114 (Print) 2165-5391 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tcar20 Cytological Analysis of
Essential idea: Plants adapt their growth to environmental conditions.
 9.3 Growth in plants AHL https://c1.staticflickr.com/3/2347/2573372542_a959ecfd4f_b.jpg Essential idea: Plants adapt their growth to environmental conditions. Boxwood, Pivet and Yew are plants commonly
9.3 Growth in plants AHL https://c1.staticflickr.com/3/2347/2573372542_a959ecfd4f_b.jpg Essential idea: Plants adapt their growth to environmental conditions. Boxwood, Pivet and Yew are plants commonly
Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain. (A) Phenotype of the HI and wild type plant after flowering (~1month). Wild type plant is tall with well elongated inflorescence. All four HI plants
Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain. (A) Phenotype of the HI and wild type plant after flowering (~1month). Wild type plant is tall with well elongated inflorescence. All four HI plants
Cryopreservation of Ornamental Plants
 Cryopreservation of Ornamental Plants Adela Halmagyi Institute of Biological Research, branch of NIRDBS, Republicii str. 48, 400015 Cluj-Napoca, Romania Cryopreservation benefits for ornamental plants
Cryopreservation of Ornamental Plants Adela Halmagyi Institute of Biological Research, branch of NIRDBS, Republicii str. 48, 400015 Cluj-Napoca, Romania Cryopreservation benefits for ornamental plants
Cytokinin treatment and flower quality in Phalaenopsis orchids: Comparing N-6-benzyladenine, kinetin and 2- isopentenyl adenine
 African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 11(7), pp. 1592-1596, 24 January, 2012 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb DOI: 10.5897/AJB11.2472 ISSN 1684 5315 2012 Academic Journals Full Length
African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 11(7), pp. 1592-1596, 24 January, 2012 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb DOI: 10.5897/AJB11.2472 ISSN 1684 5315 2012 Academic Journals Full Length
Ch. 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics. p
 Ch. 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics p. 270 - 10.1 Meiosis p. 270-276 Essential Question Main Idea! Meiosis produces haploid gametes Where are the instructions for each trait located in a cell?! On
Ch. 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics p. 270 - 10.1 Meiosis p. 270-276 Essential Question Main Idea! Meiosis produces haploid gametes Where are the instructions for each trait located in a cell?! On
CONTROL OF GROWTH BY HORMONES
 CONTROL OF GROWTH BY HORMONES Growth and organogenesis are controlled......by genes (independent of environment): e.g., number of primary vascular bundles, general shape of a leaf or flower...by genes
CONTROL OF GROWTH BY HORMONES Growth and organogenesis are controlled......by genes (independent of environment): e.g., number of primary vascular bundles, general shape of a leaf or flower...by genes
IN VITRO FLOWERING AND FRUITING IN CULTURE OF DENDROBIUM OFFICINATE KIMURA ET MIGO. (ORCHIDACEAE)
 Pak. J. Bot., 46(5): 1877-1882, 2014. IN VITRO FLOWERING AND FRUITING IN CULTURE OF DENDROBIUM OFFICINATE KIMURA ET MIGO. (ORCHIDACEAE) XIN QIAN, CAIXIA WANG, TONG OUYANG AND MIN TIAN * Key Laboratory
Pak. J. Bot., 46(5): 1877-1882, 2014. IN VITRO FLOWERING AND FRUITING IN CULTURE OF DENDROBIUM OFFICINATE KIMURA ET MIGO. (ORCHIDACEAE) XIN QIAN, CAIXIA WANG, TONG OUYANG AND MIN TIAN * Key Laboratory
Microevolutionary changes show us how populations change over time. When do we know that distinctly new species have evolved?
 Microevolutionary changes show us how populations change over time. When do we know that distinctly new species have evolved? Critical to determining the limits of a species is understanding if two populations
Microevolutionary changes show us how populations change over time. When do we know that distinctly new species have evolved? Critical to determining the limits of a species is understanding if two populations
Horticulture 201H Spring, 2002 Exam 2 Name:
 Horticulture 201H Spring, 2002 Exam 2 Name: Section 1. In the space to the left of the statements below, write the word(s) that best fit the definition or description. (20 pts) Vegetative reproduction
Horticulture 201H Spring, 2002 Exam 2 Name: Section 1. In the space to the left of the statements below, write the word(s) that best fit the definition or description. (20 pts) Vegetative reproduction
TOPIC 9.3 GROWTH IN PLANTS
 TOPIC 9.3 GROWTH IN PLANTS 9.3 A Growth INTRO http://cdn2.hubspot.net/hubfs/18130/social-suggested-images/plant_growing.jpeg IB BIO 9.3 3 In general, plants are able to grow indeterminately. This means
TOPIC 9.3 GROWTH IN PLANTS 9.3 A Growth INTRO http://cdn2.hubspot.net/hubfs/18130/social-suggested-images/plant_growing.jpeg IB BIO 9.3 3 In general, plants are able to grow indeterminately. This means
AP Biology Unit 6 Practice Test 1. A group of cells is assayed for DNA content immediately following mitosis and is found to have an average of 8
 AP Biology Unit 6 Practice Test Name: 1. A group of cells is assayed for DNA content immediately following mitosis and is found to have an average of 8 picograms of DNA per nucleus. How many picograms
AP Biology Unit 6 Practice Test Name: 1. A group of cells is assayed for DNA content immediately following mitosis and is found to have an average of 8 picograms of DNA per nucleus. How many picograms
Plant transformation
 Plant transformation Objectives: 1. What is plant transformation? 2. What is Agrobacterium? How and why does it transform plant cells? 3. How is Agrobacterium used as a tool in molecular genetics? References:
Plant transformation Objectives: 1. What is plant transformation? 2. What is Agrobacterium? How and why does it transform plant cells? 3. How is Agrobacterium used as a tool in molecular genetics? References:
Pitahayas: introduction, agrotechniques and breeding
 Pitahayas: introduction, agrotechniques and breeding The French Associates Institute for Agriculture and Biotechnology of Drylands May 8 Noemi Tel-Zur The J. Blaustein Institutes for Desert Research Ben-Gurion
Pitahayas: introduction, agrotechniques and breeding The French Associates Institute for Agriculture and Biotechnology of Drylands May 8 Noemi Tel-Zur The J. Blaustein Institutes for Desert Research Ben-Gurion
IN VITRO COLCHICINE TREATMENT OF ANTHER-DERIVED PEPPER HAPLOIDS
 806 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 21 (No 4) 2015, 806-810 Agricultural Academy IN VITRO COLCHICINE TREATMENT OF ANTHER-DERIVED PEPPER HAPLOIDS D. OLSZEWSKA, I. JEDRZEJCZYK *, P. NOWACZYK,
806 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 21 (No 4) 2015, 806-810 Agricultural Academy IN VITRO COLCHICINE TREATMENT OF ANTHER-DERIVED PEPPER HAPLOIDS D. OLSZEWSKA, I. JEDRZEJCZYK *, P. NOWACZYK,
Name Class Date. In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase.
 Assessment Chapter Test B Plant Responses In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. 1. thigmonasty 2. auxin 3. ethylene 4. phytochrome 5. abscisic
Assessment Chapter Test B Plant Responses In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. 1. thigmonasty 2. auxin 3. ethylene 4. phytochrome 5. abscisic
Chromosomal Analysis of Cultured Cells of Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.): Chromosome Number Variation
 _??_ 1990 by Cytologia, Tokyo Cytologia 55: 399-404, 1990 Chromosomal Analysis of Cultured Cells of Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.): Chromosome Number Variation B. D. Mohanty1 Department of Botany, University
_??_ 1990 by Cytologia, Tokyo Cytologia 55: 399-404, 1990 Chromosomal Analysis of Cultured Cells of Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.): Chromosome Number Variation B. D. Mohanty1 Department of Botany, University
Mitosis and Genetics Study Guide Answer Key
 Mitosis and Genetics Study Guide Answer Key 1. Which of the following is true of Interphase? a. It is part of Meiosis b. It occurs before Meiosis c. The cell does normal cell activities during interphase
Mitosis and Genetics Study Guide Answer Key 1. Which of the following is true of Interphase? a. It is part of Meiosis b. It occurs before Meiosis c. The cell does normal cell activities during interphase
HORTSCIENCE 44(3):
 HORTSCIENCE 44(3):646 650. 2009. In Vitro Induction of Tetraploids in Dieffenbachia Star Bright M-1 by Richard J. Henny 1,5, James R. Holm 2, Jianjun Chen 3, and Michelle Scheiber 4 University of Florida,
HORTSCIENCE 44(3):646 650. 2009. In Vitro Induction of Tetraploids in Dieffenbachia Star Bright M-1 by Richard J. Henny 1,5, James R. Holm 2, Jianjun Chen 3, and Michelle Scheiber 4 University of Florida,
Induction of Autotetraploids in Pummelo (Citrus grandis L. Osbeck) through Colchicine Treatment of Meristematically Active Seeds In Vitro
 Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 123:44 48. 2010. Student Best Presentation Award 1st place Induction of Autotetraploids in Pummelo (Citrus grandis L. Osbeck) through Colchicine Treatment of Meristematically
Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 123:44 48. 2010. Student Best Presentation Award 1st place Induction of Autotetraploids in Pummelo (Citrus grandis L. Osbeck) through Colchicine Treatment of Meristematically
Evaluation of chemical and physical parameters for callus induction from anther cultures of tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze)
 Evaluation of chemical and physical parameters for callus induction from anther cultures of tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) Mishra Vijay Kumar a and Chaturvedi Rakhi *a a Department of Biotechnology
Evaluation of chemical and physical parameters for callus induction from anther cultures of tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) Mishra Vijay Kumar a and Chaturvedi Rakhi *a a Department of Biotechnology
Last time: Obtaining information from a cloned gene
 Last time: Obtaining information from a cloned gene Objectives: 1. What is the biochemical role of the gene? 2. Where and when is the gene expressed (transcribed)? 3. Where and when is the protein made?
Last time: Obtaining information from a cloned gene Objectives: 1. What is the biochemical role of the gene? 2. Where and when is the gene expressed (transcribed)? 3. Where and when is the protein made?
By P. M. GRESSHOFF* and C. H. Doy* [Manuscript received 21 October 1971] AbBtract
![By P. M. GRESSHOFF* and C. H. Doy* [Manuscript received 21 October 1971] AbBtract By P. M. GRESSHOFF* and C. H. Doy* [Manuscript received 21 October 1971] AbBtract](/thumbs/86/93483237.jpg) HAPLOID ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA CALLUS AND PLANTS FROM ANTHER CULTURE By P. M. GRESSHOFF* and C. H. Doy* [Manuscript received 21 October 1971] AbBtract Haploid callus and plants were cultured from the anthers
HAPLOID ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA CALLUS AND PLANTS FROM ANTHER CULTURE By P. M. GRESSHOFF* and C. H. Doy* [Manuscript received 21 October 1971] AbBtract Haploid callus and plants were cultured from the anthers
Effect of colchicine on mitotic polyploidization and morphological characteristics of Phlox drummondi
 African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 11(39), pp. 9336-9342, 15 May, 2012 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb DOI: 10.5897/AJB11.2196 ISSN 1684 5315 2012 Academic Journals Full Length
African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 11(39), pp. 9336-9342, 15 May, 2012 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb DOI: 10.5897/AJB11.2196 ISSN 1684 5315 2012 Academic Journals Full Length
Biology Unit 3 Exam DO NOT WRITE ON THIS EXAM. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Biology Unit 3 Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Water moves into a cell placed in a(n) solution. a. osmotic c. hypotonic b. hypertonic
Biology Unit 3 Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Water moves into a cell placed in a(n) solution. a. osmotic c. hypotonic b. hypertonic
A. Correct! Genetically a female is XX, and has 22 pairs of autosomes.
 MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 08: Meiosis and Genetic Variability Question No. 1 of 10 1. A human female has pairs of autosomes and her sex chromosomes are. Question #01 (A) 22, XX. (B) 23, X. (C) 23, XX.
MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 08: Meiosis and Genetic Variability Question No. 1 of 10 1. A human female has pairs of autosomes and her sex chromosomes are. Question #01 (A) 22, XX. (B) 23, X. (C) 23, XX.
Figure 1. Identification of UGT74E2 as an IBA glycosyltransferase. (A) Relative conversion rates of different plant hormones to their glucosylated
 Figure 1. Identification of UGT74E2 as an IBA glycosyltransferase. (A) Relative conversion rates of different plant hormones to their glucosylated form by recombinant UGT74E2. The naturally occurring auxin
Figure 1. Identification of UGT74E2 as an IBA glycosyltransferase. (A) Relative conversion rates of different plant hormones to their glucosylated form by recombinant UGT74E2. The naturally occurring auxin
Reproduction & Development. 1 parent cell divides to form 2 daughter cells All offspring have exact same DNA as parent
 Living Environment Dr. Golub Reproduction & Development Asexual reproduction 1 parent cell divides to form 2 daughter cells All offspring have exact same DNA as parent Sexual Reproduction Requires 2 parents
Living Environment Dr. Golub Reproduction & Development Asexual reproduction 1 parent cell divides to form 2 daughter cells All offspring have exact same DNA as parent Sexual Reproduction Requires 2 parents
16 The Cell Cycle. Chapter Outline The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression The Events of M Phase Meiosis and Fertilization
 The Cell Cycle 16 The Cell Cycle Chapter Outline The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression The Events of M Phase Meiosis and Fertilization Introduction Self-reproduction is perhaps
The Cell Cycle 16 The Cell Cycle Chapter Outline The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression The Events of M Phase Meiosis and Fertilization Introduction Self-reproduction is perhaps
Raphanus sativus L. Raphaiol. Thin Layer Chromatography R f
 Raphaiol Thin Layer Chromatography R f Tissue Cultivation of Plant and Identification of Raphaiol Alkaloid of Extraction of The Seeds, Explants, Callus and produced Plants from tissue Cultivation Asst.
Raphaiol Thin Layer Chromatography R f Tissue Cultivation of Plant and Identification of Raphaiol Alkaloid of Extraction of The Seeds, Explants, Callus and produced Plants from tissue Cultivation Asst.
Class XI Chapter 15 Plant Growth and Development Biology
 Question 1: Define growth, differentiation, development, dedifferentiation, redifferentiation, determinate growth, meristem and growth rate. (a) Growth It is an irreversible and permanent process, accomplished
Question 1: Define growth, differentiation, development, dedifferentiation, redifferentiation, determinate growth, meristem and growth rate. (a) Growth It is an irreversible and permanent process, accomplished
Class XI Chapter 15 Plant Growth and Development Biology
 Question 1: Define growth, differentiation, development, dedifferentiation, redifferentiation, determinate growth, meristem and growth rate. (a) Growth It is an irreversible and permanent process, accomplished
Question 1: Define growth, differentiation, development, dedifferentiation, redifferentiation, determinate growth, meristem and growth rate. (a) Growth It is an irreversible and permanent process, accomplished
The Origin of Species
 The Origin of Species Introduction A species can be defined as a group of organisms whose members can breed and produce fertile offspring, but who do not produce fertile offspring with members of other
The Origin of Species Introduction A species can be defined as a group of organisms whose members can breed and produce fertile offspring, but who do not produce fertile offspring with members of other
Development of High Yielding Saffron Mutant
 Development of High Yielding Saffron Mutant I.A. Khan G.B. Pant University of Agriculture & Technology Saffron Cultivation and Marketing Project Chaubatia-263651 Almora India Keywords: 5-Branched stigma,
Development of High Yielding Saffron Mutant I.A. Khan G.B. Pant University of Agriculture & Technology Saffron Cultivation and Marketing Project Chaubatia-263651 Almora India Keywords: 5-Branched stigma,
March 14, Roll and Bell Work: Explain the difference between point mutation and frame shift mutation.
 March 14, 2014 1. Roll and Bell Work: Explain the difference between point mutation and frame shift mutation. 2. Announcements 3. Vocab and Notes- Selective Breeding 4. Articles and Political Cartoons
March 14, 2014 1. Roll and Bell Work: Explain the difference between point mutation and frame shift mutation. 2. Announcements 3. Vocab and Notes- Selective Breeding 4. Articles and Political Cartoons
Ginkgo leaf. Ginkgo is dioecious, separate sexes: male and female plants are separate. Monoecious plants have both male and female parts.
 Ginkgo leaf Figure 22-30 Ginkgo tree. Ginkgo is dioecious, separate sexes: male and female plants are separate. Monoecious plants have both male and female parts. The vein pattern is dichotomous: Divided
Ginkgo leaf Figure 22-30 Ginkgo tree. Ginkgo is dioecious, separate sexes: male and female plants are separate. Monoecious plants have both male and female parts. The vein pattern is dichotomous: Divided
CALLUS INDUCTION AND SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS FROM MAIZE MATURE EMBRYOS (ZEA MAYS L.)
 Journal of Cell and Tissue Research Vol. 13(1) 3565-3569 (2013) (Available online at www.tcrjournals.com) ISSN: 0973-0028; E-ISSN: 0974-0910 Original Article CALLUS INDUCTION AND SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS
Journal of Cell and Tissue Research Vol. 13(1) 3565-3569 (2013) (Available online at www.tcrjournals.com) ISSN: 0973-0028; E-ISSN: 0974-0910 Original Article CALLUS INDUCTION AND SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS
Plant Growth and Development
 Plant Growth and Development Growth : An irreversible permanent increase in size of an organ or its parts or even of an individual cell. Growth is accompanied by metabolic process that occurs at the expense
Plant Growth and Development Growth : An irreversible permanent increase in size of an organ or its parts or even of an individual cell. Growth is accompanied by metabolic process that occurs at the expense
Plant Propagation PLS 3221/5222
 Plant Propagation PLS 3221/5222 Dr. Sandra Wilson Dr. Mack Thetford Chapter 2 Introduction to the Biology of Plant Propagation -A review- 1 The Plant Breeder and the Plant Propagator Plant Breeder, The
Plant Propagation PLS 3221/5222 Dr. Sandra Wilson Dr. Mack Thetford Chapter 2 Introduction to the Biology of Plant Propagation -A review- 1 The Plant Breeder and the Plant Propagator Plant Breeder, The
Chapter 4. Biology of Flowering Plants. Regulation of Plant Growth by Plant Hormones
 BOT 3015L (Sherdan/Outlaw/Aghoram); Page 1 of 8 Chapter 4 Biology of Flowering Plants Regulation of Plant Growth by Plant Hormones Objectives Plant Growth Regulators. Know the names of the plant growth
BOT 3015L (Sherdan/Outlaw/Aghoram); Page 1 of 8 Chapter 4 Biology of Flowering Plants Regulation of Plant Growth by Plant Hormones Objectives Plant Growth Regulators. Know the names of the plant growth
Comparative Studies on Diploid and Tetraploid Levels of Nicotiana alata
 Academic Journal of Plant Sciences 2 (3): 182-188, 2009 ISSN 1995-8986 IDOSI Publications, 2009 Comparative Studies on Diploid and Tetraploid Levels of Nicotiana alata 1 2 3 El-Morsy Sh. I., M.D.M.Dorra,
Academic Journal of Plant Sciences 2 (3): 182-188, 2009 ISSN 1995-8986 IDOSI Publications, 2009 Comparative Studies on Diploid and Tetraploid Levels of Nicotiana alata 1 2 3 El-Morsy Sh. I., M.D.M.Dorra,
Exam 1 PBG430/
 1 Exam 1 PBG430/530 2014 1. You read that the genome size of maize is 2,300 Mb and that in this species 2n = 20. This means that there are 2,300 Mb of DNA in a cell that is a. n (e.g. gamete) b. 2n (e.g.
1 Exam 1 PBG430/530 2014 1. You read that the genome size of maize is 2,300 Mb and that in this species 2n = 20. This means that there are 2,300 Mb of DNA in a cell that is a. n (e.g. gamete) b. 2n (e.g.
Biology 211 (1) Exam 4! Chapter 12!
 Biology 211 (1) Exam 4 Chapter 12 1. Why does replication occurs in an uncondensed state? 1. 2. A is a single strand of DNA. When DNA is added to associated protein molecules, it is referred to as. 3.
Biology 211 (1) Exam 4 Chapter 12 1. Why does replication occurs in an uncondensed state? 1. 2. A is a single strand of DNA. When DNA is added to associated protein molecules, it is referred to as. 3.
The involvement of photosynthesis in inducing bud formation on excised leaf segments of Heloniopsis orientalis (Liliaceae)
 Plant & Cell Physiol. 19(5): 791-799 (1978) The involvement of photosynthesis in inducing bud formation on excised leaf of Heloniopsis orientalis (Liliaceae) Yukio Kato Biological Laboratory, Fukui University,
Plant & Cell Physiol. 19(5): 791-799 (1978) The involvement of photosynthesis in inducing bud formation on excised leaf of Heloniopsis orientalis (Liliaceae) Yukio Kato Biological Laboratory, Fukui University,
Hairy s Inheritance: Investigating Variation, Selection, and Evolution with Wisconsin Fast Plants
 Introduction Hairy s Inheritance: Investigating Variation, Selection, and Evolution with Wisconsin Fast Plants Daniel Lauffer Wisconsin Fast Plants Program University of Wisconsin - Madison Since the dawn
Introduction Hairy s Inheritance: Investigating Variation, Selection, and Evolution with Wisconsin Fast Plants Daniel Lauffer Wisconsin Fast Plants Program University of Wisconsin - Madison Since the dawn
CONTROL SYSTEMS IN PLANTS
 AP BIOLOGY PLANTS FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROL SYSTEMS IN PLANTS HORMONES MECHANISM FOR HORMONE ACTION Plant Form and Function Activity #5 page 1 CONTROL OF CELL ELONGATION Plant
AP BIOLOGY PLANTS FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROL SYSTEMS IN PLANTS HORMONES MECHANISM FOR HORMONE ACTION Plant Form and Function Activity #5 page 1 CONTROL OF CELL ELONGATION Plant
15. PHOTOPERIODISM. 1. Short day plants
 15. PHOTOPERIODISM Photoperiodism is the phenomenon of physiological changes that occur in plants in response to relative length of day and night (i.e. photoperiod). The response of the plants to the photoperiod,
15. PHOTOPERIODISM Photoperiodism is the phenomenon of physiological changes that occur in plants in response to relative length of day and night (i.e. photoperiod). The response of the plants to the photoperiod,
Chromosome variations in protoplast-derived calli and in plants regenerated from the calli of
 Jpn. J. Genet. (1989) 64, pp. 355-361 Chromosome variations in protoplast-derived calli and in plants regenerated from the calli of cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) Soryu NISHIBAYASHI*, Yasuyuki HAYASHI,
Jpn. J. Genet. (1989) 64, pp. 355-361 Chromosome variations in protoplast-derived calli and in plants regenerated from the calli of cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) Soryu NISHIBAYASHI*, Yasuyuki HAYASHI,
Name Chapter 10: Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis Mrs. Laux Take home test #7 DUE: MONDAY, NOVEMBER 16, 2009 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A bacterial chromosome consists of: A. a linear DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. B. a circular DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. C. a circular DNA
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A bacterial chromosome consists of: A. a linear DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. B. a circular DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. C. a circular DNA
EFFICIENT PRODUCTION OF TETRAPLOID BARLEY (Hordeum vulgare L.) BY COLCHICINE TREATMENT OF DIPLOID BARLEY
 , March - 2014; Volume 2(1S) ISSN No. 2320 8694 EFFICIENT PRODUCTION OF TETRAPLOID BARLEY (Hordeum vulgare L.) BY COLCHICINE TREATMENT OF DIPLOID BARLEY Ayed Sourour 1*, Bouharb Ameni 2 and Cherif Mejda
, March - 2014; Volume 2(1S) ISSN No. 2320 8694 EFFICIENT PRODUCTION OF TETRAPLOID BARLEY (Hordeum vulgare L.) BY COLCHICINE TREATMENT OF DIPLOID BARLEY Ayed Sourour 1*, Bouharb Ameni 2 and Cherif Mejda
Nucleic acid hybridization assays, detecting genotypes C12Q 1/68. Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
 A01H NEW PLANTS OR PROCESSES FOR OBTAINING THEM; PLANT REPRODUCTION BY TISSUE CULTURE TECHNIQUES New non-transgenic plants (including multicellular algae, multicellular fungi and lichens), plant varieties,
A01H NEW PLANTS OR PROCESSES FOR OBTAINING THEM; PLANT REPRODUCTION BY TISSUE CULTURE TECHNIQUES New non-transgenic plants (including multicellular algae, multicellular fungi and lichens), plant varieties,
INDUCTION OF IN VITRO FLOWERING OF INDONESIAN WILD ORCHID, Phalaenopsis amabilis (L.) Blume
 ISSN 2413-0877 Volume 2 (2015) 398-404 The 3rd International Conference on Biological Science 2013 (The 3rd ICBS-2013) INDUCTION OF IN VITRO FLOWERING OF INDONESIAN WILD ORCHID, Phalaenopsis amabilis (L.)
ISSN 2413-0877 Volume 2 (2015) 398-404 The 3rd International Conference on Biological Science 2013 (The 3rd ICBS-2013) INDUCTION OF IN VITRO FLOWERING OF INDONESIAN WILD ORCHID, Phalaenopsis amabilis (L.)
Polyploidy induced by colchicine in Taraxacum kok-saghyz
 Polyploidy induced by colchicine in Taraxacum kok-saghyz and its effects on morphological and biochemical traits Zinan Luo, Brian J. Iaffaldano, Katrina Cornish* Contact Information Zinan Luo, luo.356@osu.edu,
Polyploidy induced by colchicine in Taraxacum kok-saghyz and its effects on morphological and biochemical traits Zinan Luo, Brian J. Iaffaldano, Katrina Cornish* Contact Information Zinan Luo, luo.356@osu.edu,
VCE BIOLOGY Relationship between the key knowledge and key skills of the Study Design and the Study Design
 VCE BIOLOGY 2006 2014 Relationship between the key knowledge and key skills of the 2000 2005 Study Design and the 2006 2014 Study Design The following table provides a comparison of the key knowledge (and
VCE BIOLOGY 2006 2014 Relationship between the key knowledge and key skills of the 2000 2005 Study Design and the 2006 2014 Study Design The following table provides a comparison of the key knowledge (and
E. Incorrect! At telophase II, cells are nearly completed with meiosis, with no cross-over.
 OAT Biology - Problem Drill 06: Mitosis and Meiosis Question No. 1 of 10 1. During meiosis, cross-over between homologous chromosomes occurs at the end of. Question #01 (A) Anaphase II (B) Metaphase I
OAT Biology - Problem Drill 06: Mitosis and Meiosis Question No. 1 of 10 1. During meiosis, cross-over between homologous chromosomes occurs at the end of. Question #01 (A) Anaphase II (B) Metaphase I
