Improvement of Orchid Vanda Hybrid (Vanda limbata Blume X Vanda tricolor Lindl. var. suavis) By Colchicines Treatment In Vitro
|
|
|
- Diane Summers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Modern Applied Science; Vol. 10, No. 11; 2016 ISSN E-ISSN Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Improvement of Orchid Vanda Hybrid (Vanda limbata Blume X Vanda tricolor Lindl. var. suavis) By Colchicines Treatment In Vitro Mustika Tuwo 1 & Ari Indrianto 2 1 Master Program of Biology Faculty, Gadjah Mada University, Yogyakarta, Indonesia 2 Department of Biology, Faculty of Biology, Gadjah Mada University, Yogyakarta, Indonesia Correspondence: Mustika Tuwo, Master Program of Biology Faculty, Gadjah Mada University, Yogyakarta, Indonesia. Tel: mustikamukti@yahoo.co.id Received: May 27, 2016 Accepted: June 24, 2016 Online Published: July 29, 2016 doi: /mas.v10n11p83 URL: Abstract The purpose of this research was to evaluate the growth phase of orchid Vanda hybrid (Vanda limbata Blume X Vanda tricolor Lindl. var. suavis) response with colchicines treatment, to determine precise effective concentration of colchicines and duration of treatment to induce polyploidy. This research used variation of colchicines concentration which were 0.01%; 0.05%; 0.1%; 0.5%; 1% and 0% and incubation for 6 hours; 12 hours; 18 hours; 24 hours; and 4 days. Treatment was done in aseptic condition using protocorm aged 7 week after sowing. After treatments, plants were planted on Vacint and Went (VW) medium supplemented with of 150 ml/l coconut water. After four months, plants were subcultured in medium VW ml/l + 150g/l banana extract. The results showed that the orchid Vanda hybrid was intolerant to colchicine concentration of 0.1; 0.5 and 1% by death protocorm was more than 50%. Concentration of 0,5% with 6 hours soaking time is the most effective to induced tetraploid in orchid Vanda hybrid. Morphological characters of tetraploid plantlets had lower average number and length of roots, number, length, and width of leaves than those of control. Anatomical characters of tetraploid plantlets revealed the highest stomatal size and had smaller of stomatal index than controls. This evident indicated a negative correlation between stomatal index and ploidy level. Cytological analysis with flow cytometry revealed that tetraploid plantlets (2n=4x=76) stained with DAPI showed the chromosome number more than those of control (2n=2x=38). Keywords: polyploidization, colchicine, vanda orchid, chromosome number 1. Introduction Indonesia is a country that is very rich in diversity of species and varieties of various horticultural crops, one of them is orchid. Of the 20,000 species of orchids in the world, Indonesia has about 5000 species of wild orchids (Irawati, 2002; Schuiteman, 2010). The types of orchids that have been received in the international market, among others Dendrobium, Arachis, Cymbidium, Phalaeonopsis, Vanda, and Oncidium (Nurmalinda et al., 1999). Vanda limbata Blume and Vanda tricolor Lindl. var. suavis is a local orchid of Indonesia which has a superior characters as the parent crosses, so expect through crossbreeding both local Indonesian orchid species will be produced orchid hybrids that have diverse properties because it comes from a different species. Quality improvement of orchid can be achieved by genetic improvement through crossing, while quantity improvement can be done by propagation through in vitro culture, number of seedlings obtained more in a relatively short time. Development of orchids can be done through mutation and transgenic. Genetic mutations are increasingly being used to produce new varieties with physical characteristics and particular phenotypes, such as changes in growth, flower color, increase in size and adaptability. One of mutation techniques can be applied to plants is a chemical mutation using colchicine compound. Treatment with colchicine mutation would cause a duplication of chromosomes (polyploidization) followed by an increase in the size of the cells and tissues of plants. Polyploid orchids generally showed more characteristics compared to its diploid type. Some of the characters are related with polyploidy is an increase in vigor and plant resistance to pests and diseases, the size of the larger flowers and flower colors are more vivid, and the vitality of flowers longer than the type diploid (Zainuddin, 2006; Silalahi, 2011). The method used in this research is explant immersion technique is protocorm in a solution of 83
2 colchicine that has been dissolved in a liquid medium. Various of concentration and length of immersion was conducted to determine the optimum concentration and soaking time that can produce the highest percentage of cells undergoing changes become polyploid. 2. Materials and Methods Materials used in this research were protocorm aged 7 Weeks After Sowing derived from F1 seed germination from crossing of Vanda limbata Blume X Vanda tricolor Lindl. var. suavis on medium Vacint and Went (VW) containing 150 ml / L of coconut water. 2.1 Colchicine Treatment Protocorm were treated at a concentration of 0.01; 0.05; 0.1; 0.5; 1% with long time 6, 12, 18, 24 hours and 4 days. Control plants soaked in a VW liquid medium without colchicines. Soaking stopped when compliance with the time variation of each treatment and washed with distilled water three times and placed in a petri dish which was covered with filter paper, waiting for it to dry before planting again to VW solid medium. The cultures were maintained under continuous white light at of 25 0 C. 2.2 Plant Regeneration After the colchicine treatment, explants were grown on VW solid medium enriched 150 ml / L of coconut water. After two months, protocorms were subcultured on medium protokorm VW + coconut water 150 ml / l + banana extract 150 g / l for 4 months. 2.3 Evaluation of Stomata Size, Stomata Index and Morphology Anatomical analysis done by making preparations in the lower epidermis of leaves using glue ALTECO. Orchid plant leaves are cut with a scalpel as much as a leaf blade and then made pieces rectangles with a size of ± 1 x 1 cm. Samples were placed on a glass object that has been given glue ALTECO, wait for 30 minutes. Samples removed with tweezers (Andini, 2011). Mixture was observed with a microscope with a magnification of 40X, images taken using opti lab. 2.4 Determination of Ploidy Level Staining with DAPI (4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride) Chromosome preparation is done by cutting root tip ± 3-4 mm then inserted into the tube containing carnoys solution and incubated at 4 0 C for 15 minutes. Samples were washed with 50% ethanol solution to remove carnoys. Solution of DAPI included 100 ml and incubated for 15 minutes. The sample is placed on a glass object and then drops of glycerin and covered with a deck glass. Squashing process conducted with the tip of the brush to form a single layer cells. Mixture was observed with inverted microscope and documented through optilab. Slide preparation are stored in boxes and placed at 4 0 C Analysis of Flow Cytometry Samples were analyzed is the leaf of orchid Vanda hybrid plantlets ± 6 months old. Leaves chopped in a petri dish which has been given 1 ml of buffer solution OTTO I (0, 1 M citric acid monohydrate 4,2 gr, 0,5% (v/v) Tween 20 1 ml ). Sample is filtered using 30 μm nylon mesh filter into the eppendorf tube. The filtered solution was incubated ± 1 minute and centrifuged 5000 rpm for 5 min, the supernatant was discarded and then added solution of OTTO II buffer (0.4 M Na2HPO4.12H2O g) to 500 ml. The solution was homogenized and poured into the cuvet. The solution added propidium iodide 100 ml and 100 ml RNase. Samples were analyzed by Flow Cy space. 2.5 Statistical Analysis Data were analyzed using analysis of variance (ANOVA). Significant differences among treatments were detected using Duncan's Multiple Range Test (DMRT) at the 0, 01 or 0, 05 level of probability (Gomez & Gomez, 1995). 3. Results 3.1 Survival Level Protocorm tolerance 0.01 to 0.05% colchicine in the treatment of 6, 12, 24 hours, and 4 days with a survival rate above 50%, but treatment 18 hours increased to 0.1% (Fig. 1). 84
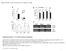
3 Survival rate (%) hours 12 hours 24 hours 96 hours (4 days) Colchicine concentration (%) Figure 1. Survival rate of protocorms at various colchicine concentration 3.2 Morphological Analysis Interaction between concentration of colchicines with soaking time significantly affected on morphological characters. Colchicine treatment decreases the amount of root, root length, number of leaves, leaf length and width of leaves. This is shown at the treatment of colchicine concentration of 1% for 24 hours and 4 days resulted average number of roots as much as 1 less than the controls had a average number of roots 3 (Fig. 2A and 2B). A B C D Figure 2. Orchid Vanda hybrid ± 6 months old, A) Control; B) and C) Colchicine 1% for 4 days Note. The red arrow show character root changes. Bar: 0, 5 cm. Root length on all variety of concentration and duration of colchicine treatment is smaller than control with a mean length of the roots were 1 cm. The smallest root length was obtained at the concentration of 0.1% for 4 days, 0.5% for 12 hours and 4 days and 1% for 24 hours and 4 days. Root observation in the control and different colchicines treatment, the colchicine treatment have roots that swell and appear thicker and shorter than the size of the control (Fig. 2C). Number of leaves decreased at concentrations of 0.5 and 1% with 4 day long treatment compared to control as much as one piece with the average number of leaves 4 strands (Fig. 2D). 3.3 Anatomical Analysis The length and width of the highest stomata obtained at a concentration 1% with long colchicine treatment 24 hours compared with controls. Average length of stomata at 1% colchicine treatment for 24 hours was μm and width stomata μm. Stomata length obtained in the control plants was 92.6 μm and increased after treated with colchicine 1% for 24 hours to μm (Fig. 3A). The width of stomata also increased from 95.8 μm becomes μm (Fig. 3B). 85
4 A B Figure 3. Effect of colchicines on length and width stomata orchid Vanda hybrid Note. A. Control; B. Colchicine 1% for 24 hours 3.4 Cytological Analysis The calculation result of chromosomes by staining with DAPI (4, 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride) after treatment colchicine concentration of 0.5% for 18 was 58. This evident that colchicine successfully induce polyploidisation by folding number of chromosomes (Fig. 4). The number of chromosomes that undergo folding followed by increasing the diameter of the cell nucleus. It looks after colchicine treatment, diameter of the cell nucleus in control plants was μm increased μm after treatment colchicine concentration of 0.5% for 6 hours (Figure 5). A B Figure 4. Number chromosomes of orchid Vanda hybrid at colchicines 0.5% for 18 hours Note. A. Before reconstruction; B. After reconstruction. 86
5 A B Figure 5. Diameter of nucleus orchid vanda hybrid Note. A. Control; B. Colchicine 0.5% for 6 hours Cytological analysis followed by flow cytometry also showed that colchicine evidently induce polyploidization on orchid Vanda hybrid. Control plants for ploidy analysis by flow cytometry derived from plantlets ± 4 months old. Results analysis of control plants presented in the form of DNA G1 peak at channel 200, which is set as standard 2C for diploid cells with a small peak at channel 400 as a characteristic of the peak G2 (Fig. 6A). Treatment colchicine concentration of 0.5% to 6 hours soaking time produce tetraploid cells with G1 DNA peak at channel 400 and peak G2 at channel 800 (Fig. 6B). Content of DNA Content of DNA Figure 6. Flow cytometry analysis of orchid vanda hybrid Note. A. Diploid; B. Colchicine 0.5% for 6 hours 4. Discussion Protocorm resistance level after colchicine treatment depends on the concentration and duration of treatment given. According Atichart & Bunnag (2007) high concentrations and longer treatment time will decrease the survival rates of explants. Growth phase were treated with colchicine average does not show tolerance at a concentration of 0.1 to 1%. The same is stated by Sarathum et al. (2010), that colchicine concentration of 0.1% is very toxic for protokorm with the death rate more than 60%. According Atichart (2013), the use of high concentrations colchicine 0.1; 0.15 and 0.2% with longer treatment more than 24 hours will cause to reduced chlorophyll content and plantlets death after treated with colchicine. Colchicine treatment at various concentrations showed browning occurs more rapidly than the control that occurs on average in the third week. The possibility as a result of colchicines treatment perceived threats that cause changes in plant physiological and biochemical. Plant reaction to this threat will induce defense 87
6 mechanisms, one of which is to produce phenolic compounds. According to Ebrahim et al. (2011), higher plants have mechanisms to protect themselves from various threats of physical, chemical and biological. This threat will cause to physiological changes in the plants are like strengthening the cell walls through lignifikasi, suberisation, and production of phenolic compounds. As Abdelwahd et al. (2008) states that the phenolic are secondary metabolites regulate plant growth and protect plants from abiotic and biotic stresses. An increase of phenolic compounds in response to the threat of colchicine would cause the accumulation of phenolic causing delays protocorm growth orchid Vanda hybrids. Colchicine treatment significantly affected number of roots, root length and leaf length, that is high concentration and long treatment decreases the number of roots, root length and leaf length smaller than control. As Chen et al. (2009) stated that plantlets at a lower ploidy levels grew faster and bigger than plantlets which have higher ploidy levels in the same culture period. Oktoploid plant growth is very slow and very small in size compared to plants with low ploidy level. According Omezzine et al. (2012) identification of polyploid plants can be known through the parameters of morphological, cytological, chemical and physiological. The same is stated by Wongpiyasatid et al. (2005), that length of stomata is an accurate indicator to determine the ploidy levels in some plant species. Size and number of stomata change significantly with the increasing number of chromosomes. Colchicine has been proven as a chemical compound used to induce polyploid on orchids. According to Alberts et al. (2008) colchicine cause depolymerization of microtubules thus inhibiting formation of threads of the spindle and chromosomes do not separate into cell poles at stage of anaphase resulting doubling of chromosome. 5. Conclusion The results showed that the orchid Vanda hybrid was intolerant to colchicine concentration of 0.1, 0.5 and 1% by death protocorm was more than 50%. Colchicines concentration 0,5% for 6 hours is the most effective to induced tetraploidization in orchid Vanda hybrid (Vanda limbata Blume x Vanda tricolor Lindl. var. suavis). Tetraploid plantlets had lower average number and length of roots, number, length, and width of the leaves than those of control. Anatomical characters of tetraploid plantlets revealed the highest stomatal size and had smaller of stomatal index than controls. Cytological analysis with flow cytometry revealed that tetraploid plantlets (2n=4x=76) stained with DAPI showed the chromosome number more than those of control (2n=2x=38). Acknowledgement The authors are grateful to Dr.rer.nat Ari Indrianto, Head of Biotechnology Laboratory, Department of Biology, Faculty of Biology, Gadjah Mada University for providing laboratory facilities and Suka Pertiwi for his kind assistance during the research. References Abdelwahd, R., Hakam, N., Labhilili, M., & Udupa, S. M. (2008). Use of an Adsobent and Antioxidants to Reduce the Effects of Leached Phenolics In Vitro Plantlet Regeneration of Faba Bean L. African Journal of Biotechnology, 7(8), Alberts, B., Johnson, A., Lewis, J., Raff, M., Roberts, K., & Walter, P. (2008). Molecular Biology of the Cell (5th Eds.). New York: Garland Science. Andini, A. N. (2011). Anatomi Jaringan Daun dan Pertumbuhan Tanaman Celosia cristata, Catharanthus roseus, dan Gomphrena globosa pada Lingkungan Udara Tercemar. Bogor. Departemen Biologi FMIPA IPB, Indonesia. Atichart, P., & Bunnag, S. (2007). Polyploid Induction in Dendrobium secundum (BI.) Lindl. By in vitro Techniques. Thai Journal of Agricultural Science, 40(1-2), Atichart, P. (2013). Polyploid Induction by Colchicine Treatments and Plant Regeneration of Dendrobium chrysotoxum. Thai Journal of Agricultural Science, 46(1), Chen, W. H., Tang, C. Y., & Kao, Y. L. (2009). Ploidy Doubling by In Vitro Culture of Excised Protocorms or Protocorm-Like-Bodies in Phalaenopsis Species. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture, 98, Ebrahim, S., Usha, K., & Singh, B. (2011). Pathogenitas Related (PR) Protein in Plant Defense Mechanism. Science Againts Microbial Pathogens, Gomez, K. A., & Gomez, A. A. (1984). Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research. Irawati (2002). The Conservation of Orchid Species in Indonesia. Indonesian Orchid Seminar, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, October, 20,
7 Nurmalinda, D., Widyastoeti, L., Marpaung, & Dan, D. M. (1999). Preferensi Konsumen terhadap Bunga Anggrek Potong di Jakarta. Jurnal Hortikultura, 9(2), (In Indonesia). Omezzine, F., Ladhari, A., Nefzi, F., Harrath, R., Aouni, M., & Haoula, R. (2012). Induction and Flow Cytometry Identification of Mixoploidy through Colchicine Treatment of Trigonella foenum-graecum L. African Journal of Biotechnology, 11, Sarathum, S., Hegele, M., Tantiviwat, S., & Nanakorm, M. (2010). Effect of concentration and duration of Colchicine treatment on polyploidy induction in Dendrobium scabrilingue L. Europ. J. Hort. Sci., 75(3), Schuiteman, A. (2010). Orchid in Indonesia and Their Conservation. Prosiding the 2010 International Seminar on Orchid Coservation and Agribusiness, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, October, 27, Silalahi, R. L. W. (2011). Induksi Poliploid pada Anggrek Dendrobium strebloceras dengan Kolkisin. Fakultas Pertanian. Universitas Brawijaya, Malang, Indonesia. Wongpiyasatid, A., Hormchan, P., Chusreeaeom, K., & Ratanadilok, N. (2005). Stomatal Size, Stomatal Frequency and Pollen Grain Diameter as Indirect Method for Identification of Ploidy Levels in Cotton. Natural Science, 39, Zainuddin, A. (2006). Optimasi Proses PCR-RAPD Anggrek Phalaeonopsis sp. yang telah diperlakukan dengan Colchicine. Jurusan Agronomi. Fakultas Pertanian. Universitas Muhammadiyah Malang, Indonesia. Copyrights Copyright for this article is retained by the author(s), with first publication rights granted to the journal. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( 89
Flow cytometric analysis of Ploidy level
 Flow cytometric analysis of Ploidy level Centre of Plant Structural and Functional Genomics of the Institute of Experimental Botany AS CR, Olomouc, Czech Republic Riccardo Pasculli Roman Hudec Field application
Flow cytometric analysis of Ploidy level Centre of Plant Structural and Functional Genomics of the Institute of Experimental Botany AS CR, Olomouc, Czech Republic Riccardo Pasculli Roman Hudec Field application
Alteration of Spathoglottis eburnea Gagnep. Ploidy Level after Colchicine Treatments
 Agricultural Technology and Biological Sciences Alteration of Spathoglottis eburnea Gagnep. Ploidy Level after Colchicine Treatments Witayaporn PORNCHUTI 1, Kanchit THAMMASIRI 2,*, Ngarmnij CHUENBOONNGARM
Agricultural Technology and Biological Sciences Alteration of Spathoglottis eburnea Gagnep. Ploidy Level after Colchicine Treatments Witayaporn PORNCHUTI 1, Kanchit THAMMASIRI 2,*, Ngarmnij CHUENBOONNGARM
POLYPLOIDY AND AN IN VITRO-MEDIATED PROPAGATION PROTOCOL FOR POTENTIALLY INDUCING CHROMOSOME DOUBLING IN MACADAMIA
 POLYPLOIDY AND AN IN VITRO-MEDIATED PROPAGATION PROTOCOL FOR POTENTIALLY INDUCING CHROMOSOME DOUBLING IN MACADAMIA Karin Hannweg and Mark Penter Plant Improvement Division Agricultural Research Council
POLYPLOIDY AND AN IN VITRO-MEDIATED PROPAGATION PROTOCOL FOR POTENTIALLY INDUCING CHROMOSOME DOUBLING IN MACADAMIA Karin Hannweg and Mark Penter Plant Improvement Division Agricultural Research Council
Alteration of Spathoglottis eburnea Gagnep. Ploidy Level after. Colchicine Treatments
 Article Alteration of Spathoglottis eburnea Gagnep. Ploidy Level after Witayaporn PORNCHUTI a, Kanchit THAMMASIRI b*, Ngarmnij CHUENBOONNGARM b and Nathinee PANVISAVAS b a Department of Biotechnology,
Article Alteration of Spathoglottis eburnea Gagnep. Ploidy Level after Witayaporn PORNCHUTI a, Kanchit THAMMASIRI b*, Ngarmnij CHUENBOONNGARM b and Nathinee PANVISAVAS b a Department of Biotechnology,
Abiotic Stress in Crop Plants
 1 Abiotic Stress in Crop Plants Mirza Hasanuzzaman, PhD Professor Department of Agronomy Sher-e-Bangla Agricultural University E-mail: mhzsauag@yahoo.com Stress Stress is usually defined as an external
1 Abiotic Stress in Crop Plants Mirza Hasanuzzaman, PhD Professor Department of Agronomy Sher-e-Bangla Agricultural University E-mail: mhzsauag@yahoo.com Stress Stress is usually defined as an external
Sporic life cycles involve 2 types of multicellular bodies:
 Chapter 3- Human Manipulation of Plants Sporic life cycles involve 2 types of multicellular bodies: -a diploid, spore-producing sporophyte -a haploid, gamete-producing gametophyte Sexual Reproduction in
Chapter 3- Human Manipulation of Plants Sporic life cycles involve 2 types of multicellular bodies: -a diploid, spore-producing sporophyte -a haploid, gamete-producing gametophyte Sexual Reproduction in
Figure 1. Identification of UGT74E2 as an IBA glycosyltransferase. (A) Relative conversion rates of different plant hormones to their glucosylated
 Figure 1. Identification of UGT74E2 as an IBA glycosyltransferase. (A) Relative conversion rates of different plant hormones to their glucosylated form by recombinant UGT74E2. The naturally occurring auxin
Figure 1. Identification of UGT74E2 as an IBA glycosyltransferase. (A) Relative conversion rates of different plant hormones to their glucosylated form by recombinant UGT74E2. The naturally occurring auxin
VQ403 The development of tetraploid ginger varieties. M K Smith and S D Hamill Queensland Horticulture Institute, Nambour
 VQ403 The development of tetraploid ginger varieties M K Smith and S D Hamill Queensland Horticulture Institute, Nambour VG403 This report is published by the Horticultural Research and Development Corporation
VQ403 The development of tetraploid ginger varieties M K Smith and S D Hamill Queensland Horticulture Institute, Nambour VG403 This report is published by the Horticultural Research and Development Corporation
Production of Haploid and Doubled Haploid Plants from Anther-derived Callus of Lilium formosanum
 Production of Haploid and Doubled Haploid Plants from Anther-derived Callus of Lilium formosanum D.-S. Han and Y. Niimi Faculty of Agriculture, Niigata University 2-8050 Ikarashi, Niigata 950-2181 Japan
Production of Haploid and Doubled Haploid Plants from Anther-derived Callus of Lilium formosanum D.-S. Han and Y. Niimi Faculty of Agriculture, Niigata University 2-8050 Ikarashi, Niigata 950-2181 Japan
Polyploid Induction by Colchicine Treatments and Plant Regeneration of Dendrobium chrysotoxum
 www.thaiagj.org Thai Journal of Agricultural Science 2013, 46(1): 59-63 Polyploid Induction by Colchicine Treatments and Plant Regeneration of Dendrobium chrysotoxum P. Atichart Department of Biology,
www.thaiagj.org Thai Journal of Agricultural Science 2013, 46(1): 59-63 Polyploid Induction by Colchicine Treatments and Plant Regeneration of Dendrobium chrysotoxum P. Atichart Department of Biology,
Unit D: Controlling Pests and Diseases in the Orchard. Lesson 5: Identify and Control Diseases in the Orchard
 Unit D: Controlling Pests and Diseases in the Orchard Lesson 5: Identify and Control Diseases in the Orchard 1 Terms Abiotic disease Bacteria Biotic diseases Cultural disease control Disease avoidance
Unit D: Controlling Pests and Diseases in the Orchard Lesson 5: Identify and Control Diseases in the Orchard 1 Terms Abiotic disease Bacteria Biotic diseases Cultural disease control Disease avoidance
In Vitro Polyploid Induction of Ophiopogon planiscapus. Dominic A. Gillooly, Darren H. Touchell and Thomas G. Ranney
 In Vitro Polyploid Induction of Ophiopogon planiscapus Dominic A. Gillooly, Darren H. Touchell and Thomas G. Ranney North Carolina State University, Departement of Horticultural Science Mountain Crop Improvement
In Vitro Polyploid Induction of Ophiopogon planiscapus Dominic A. Gillooly, Darren H. Touchell and Thomas G. Ranney North Carolina State University, Departement of Horticultural Science Mountain Crop Improvement
Doubled haploid ramets via embryogenesis of haploid tissue cultures
 Doubled haploid ramets via embryogenesis of haploid tissue cultures Harry E. Iswandar 1, J. M. Dunwell 2, Brian P. Forster 3, Stephen P. C. Nelson 1,4 and Peter D. S. Caligari,3,4,5 ABSTRACT Tissue culture
Doubled haploid ramets via embryogenesis of haploid tissue cultures Harry E. Iswandar 1, J. M. Dunwell 2, Brian P. Forster 3, Stephen P. C. Nelson 1,4 and Peter D. S. Caligari,3,4,5 ABSTRACT Tissue culture
The Effect of Pollination Time and Gibberellic Acid (GA3) on the Production and Seed Germination of Phalaenopsis Orchids
 The Effect of Pollination Time and Gibberellic Acid (GA3) on the Production and Seed Germination of Phalaenopsis Orchids Hassan Kia Heirati 1*, Rasoul Onsinejad 2 and Fattaneh Yari 3 1 M.S. Student, Department
The Effect of Pollination Time and Gibberellic Acid (GA3) on the Production and Seed Germination of Phalaenopsis Orchids Hassan Kia Heirati 1*, Rasoul Onsinejad 2 and Fattaneh Yari 3 1 M.S. Student, Department
HYBRID DENDROBIUM ORCHID ON VARIOUS TYPES AND CONCENTRATION OF CYTOKININ AND AUXIN ON MURASHIGE AND SKOOG (MS) MEDIUM
 Responses of Protocorm Like Bodies Hybrid. Anne Nuraini RESPONSES OF Protocorm Like Bodies HYBRID DENDROBIUM ORCHID ON VARIOUS TYPES AND CONCENTRATION OF CYTOKININ AND AUXIN ON MURASHIGE AND SKOOG (MS)
Responses of Protocorm Like Bodies Hybrid. Anne Nuraini RESPONSES OF Protocorm Like Bodies HYBRID DENDROBIUM ORCHID ON VARIOUS TYPES AND CONCENTRATION OF CYTOKININ AND AUXIN ON MURASHIGE AND SKOOG (MS)
Reduction of Exudates (Browning) in Sugarcane Micro Propagation
 Nig J. Biotech. Vol. 23 (2011) 40-44 ISSN: 0189 17131 Available online at www.biotechsocietynigeria.org. Reduction of Exudates (Browning) in Sugarcane Micro Propagation Ishaq M.N. and Ehirim Bernard O.
Nig J. Biotech. Vol. 23 (2011) 40-44 ISSN: 0189 17131 Available online at www.biotechsocietynigeria.org. Reduction of Exudates (Browning) in Sugarcane Micro Propagation Ishaq M.N. and Ehirim Bernard O.
INDUCTION OF IN VITRO FLOWERING OF INDONESIAN WILD ORCHID, Phalaenopsis amabilis (L.) Blume
 ISSN 2413-0877 Volume 2 (2015) 398-404 The 3rd International Conference on Biological Science 2013 (The 3rd ICBS-2013) INDUCTION OF IN VITRO FLOWERING OF INDONESIAN WILD ORCHID, Phalaenopsis amabilis (L.)
ISSN 2413-0877 Volume 2 (2015) 398-404 The 3rd International Conference on Biological Science 2013 (The 3rd ICBS-2013) INDUCTION OF IN VITRO FLOWERING OF INDONESIAN WILD ORCHID, Phalaenopsis amabilis (L.)
State Forest Research Institute, Post Box No. 159, Itanagar , India 1 Department of Botany, Rajiv Gandhi University, Itanagar , India
 Indian Journal of Biotechnology Vol 6, April 2007, pp. 256-261 Effects of different culture media on seed germination and subsequent in vitro development of protocorms of Hygrochilus parishii (Veith &
Indian Journal of Biotechnology Vol 6, April 2007, pp. 256-261 Effects of different culture media on seed germination and subsequent in vitro development of protocorms of Hygrochilus parishii (Veith &
Genetic Transformation of the Indonesian Black Orchid (Coelogyne pandurata Lindley) through Agrobacterium tumefaciens for Micropropagation
 Genetic Transformation of the Indonesian Black Orchid (Coelogyne pandurata Lindley) through Agrobacterium tumefaciens for Micropropagation Endang Semiarti 1,2, Ari Indrianto 1, Eko A. Suyono 1, Rizqie
Genetic Transformation of the Indonesian Black Orchid (Coelogyne pandurata Lindley) through Agrobacterium tumefaciens for Micropropagation Endang Semiarti 1,2, Ari Indrianto 1, Eko A. Suyono 1, Rizqie
The Science of Plants in Agriculture Pl.Sci 102. Getting to Know Plants
 The Science of Plants in Agriculture Pl.Sci 102 Getting to Know Plants Growth and Development of Plants Growth and Development of Plants Why it s important to have knowledge about plant development. What
The Science of Plants in Agriculture Pl.Sci 102 Getting to Know Plants Growth and Development of Plants Growth and Development of Plants Why it s important to have knowledge about plant development. What
Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain. (A) Phenotype of the HI and wild type plant after flowering (~1month). Wild type plant is tall with well elongated inflorescence. All four HI plants
Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain. (A) Phenotype of the HI and wild type plant after flowering (~1month). Wild type plant is tall with well elongated inflorescence. All four HI plants
In vitro induction of tetraploids from immature embryos through colchicine treatments in Clivia miniata Regel
 African Journal of Agricultural Research Vol. 7(25), pp. 3712-3718, 3 July, 2012 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajar DOI: 10.5897/AJAR11.2343 ISSN 1991-637X 2012 Academic Journals
African Journal of Agricultural Research Vol. 7(25), pp. 3712-3718, 3 July, 2012 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajar DOI: 10.5897/AJAR11.2343 ISSN 1991-637X 2012 Academic Journals
Induction of Haploid Callus from Isolated Microspores of Peony in vitro
 Plant & Cell Physiol. 22(2): 337-34 (98) Short communication Induction of Haploid Callus from Isolated Microspores of Peony in vitro Kanji Ono and Shuichi Harashima Department of Biology, Faculty of Science,
Plant & Cell Physiol. 22(2): 337-34 (98) Short communication Induction of Haploid Callus from Isolated Microspores of Peony in vitro Kanji Ono and Shuichi Harashima Department of Biology, Faculty of Science,
ROLE OF THE ALLELOPATHY IN MIXED VEGETABLE CROPS IN THE ORGANIC FARMING
 Abstract Scientific Papers. Series A. Agronomy, Vol. LVI, 2013 ISSN 2285-5785; ISSN CD-ROM 2285-5793; ISSN Online 2285-5807; ISSN-L 2285-5785 ROLE OF THE ALLELOPATHY IN MIXED VEGETABLE CROPS IN THE ORGANIC
Abstract Scientific Papers. Series A. Agronomy, Vol. LVI, 2013 ISSN 2285-5785; ISSN CD-ROM 2285-5793; ISSN Online 2285-5807; ISSN-L 2285-5785 ROLE OF THE ALLELOPATHY IN MIXED VEGETABLE CROPS IN THE ORGANIC
Effect of colchicine on mitotic polyploidization and morphological characteristics of Phlox drummondi
 African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 11(39), pp. 9336-9342, 15 May, 2012 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb DOI: 10.5897/AJB11.2196 ISSN 1684 5315 2012 Academic Journals Full Length
African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 11(39), pp. 9336-9342, 15 May, 2012 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb DOI: 10.5897/AJB11.2196 ISSN 1684 5315 2012 Academic Journals Full Length
Unit G: Pest Management. Lesson 2: Managing Crop Diseases
 Unit G: Pest Management Lesson 2: Managing Crop Diseases 1 Terms Abiotic disease Bacteria Biotic disease Cultural disease control Disease avoidance Disease resistance Disease tolerance Fungi Infectious
Unit G: Pest Management Lesson 2: Managing Crop Diseases 1 Terms Abiotic disease Bacteria Biotic disease Cultural disease control Disease avoidance Disease resistance Disease tolerance Fungi Infectious
Melon Meiosis.
 Objective Students will read about the discovery of colchicine, which made seedless watermelon possible. Students will use modelling clay and beans to model meiosis and mitosis. Students will design imaginary
Objective Students will read about the discovery of colchicine, which made seedless watermelon possible. Students will use modelling clay and beans to model meiosis and mitosis. Students will design imaginary
Artificial Triploids in Luffa echinato Roxb. P. K. Agarwal,1 R. P. Roy and D. P. Mishra Department of Botany, University of Patna, Patna-5, India
 Cytologia 44: 739-743, 1979 Received April 10, 1975 Artificial Triploids in Luffa echinato Roxb. P. K. Agarwal,1 R. P. Roy and D. P. Mishra Department of Botany, University of Patna, Patna-5, India Luffa
Cytologia 44: 739-743, 1979 Received April 10, 1975 Artificial Triploids in Luffa echinato Roxb. P. K. Agarwal,1 R. P. Roy and D. P. Mishra Department of Botany, University of Patna, Patna-5, India Luffa
X-Sheet 3 Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis
 X-Sheet 3 Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis 13 Key Concepts In this session we will focus on summarising what you need to know about: Revise Mitosis (Grade 11), the process of meiosis, First Meiotic division,
X-Sheet 3 Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis 13 Key Concepts In this session we will focus on summarising what you need to know about: Revise Mitosis (Grade 11), the process of meiosis, First Meiotic division,
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN DIPLOID AND INDUCED TETRAPLOID LOTUS GLABER MILL. (LOTUS TENUIS WALDST. & KIT.) PLANTS. CC: 47 Azul, Argentina, 7300.
 DIFFERENCES BETWEEN DIPLOID AND INDUCED TETRAPLOID LOTUS GLABER MILL. (LOTUS TENUIS WALDST. & KIT.) PLANTS ID # 12-05 M. S. Barufaldi 1, H. N. Crosta 1, M. F. Eseiza 1, R. H. Rodríguez 1,2 and E. Sánchez
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN DIPLOID AND INDUCED TETRAPLOID LOTUS GLABER MILL. (LOTUS TENUIS WALDST. & KIT.) PLANTS ID # 12-05 M. S. Barufaldi 1, H. N. Crosta 1, M. F. Eseiza 1, R. H. Rodríguez 1,2 and E. Sánchez
Observing Root and Stem Structures
 Name Class Date Chapter 23 Structure and Function of Seed Plants Observing Root and Stem Structures Introduction The first structures to appear on a germinating seed are the roots. The initial root to
Name Class Date Chapter 23 Structure and Function of Seed Plants Observing Root and Stem Structures Introduction The first structures to appear on a germinating seed are the roots. The initial root to
POTASSIUM IN PLANT GROWTH AND YIELD. by Ismail Cakmak Sabanci University Istanbul, Turkey
 POTASSIUM IN PLANT GROWTH AND YIELD by Ismail Cakmak Sabanci University Istanbul, Turkey Low K High K High K Low K Low K High K Low K High K Control K Deficiency Cakmak et al., 1994, J. Experimental Bot.
POTASSIUM IN PLANT GROWTH AND YIELD by Ismail Cakmak Sabanci University Istanbul, Turkey Low K High K High K Low K Low K High K Low K High K Control K Deficiency Cakmak et al., 1994, J. Experimental Bot.
GFP GAL bp 3964 bp
 Supplemental Data. Møller et al. (2009) Shoot Na + exclusion and increased salinity tolerance engineered by cell type-specific alteration of Na + transport in Arabidopsis Supplemental Figure 1. Salt-sensitive
Supplemental Data. Møller et al. (2009) Shoot Na + exclusion and increased salinity tolerance engineered by cell type-specific alteration of Na + transport in Arabidopsis Supplemental Figure 1. Salt-sensitive
Effect of Colchicine Tablets on Morphology of Torenia fournieri
 2013 International Transaction Journal of Engineering, Management, & Applied Sciences & Technologies. International Transaction Journal of Engineering, Management, & Applied Sciences & Technologies http://tuengr.com
2013 International Transaction Journal of Engineering, Management, & Applied Sciences & Technologies. International Transaction Journal of Engineering, Management, & Applied Sciences & Technologies http://tuengr.com
Pitahayas: introduction, agrotechniques and breeding
 Pitahayas: introduction, agrotechniques and breeding The French Associates Institute for Agriculture and Biotechnology of Drylands May 8 Noemi Tel-Zur The J. Blaustein Institutes for Desert Research Ben-Gurion
Pitahayas: introduction, agrotechniques and breeding The French Associates Institute for Agriculture and Biotechnology of Drylands May 8 Noemi Tel-Zur The J. Blaustein Institutes for Desert Research Ben-Gurion
Bacterial Gram Staining
 PR021 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Bacterial Gram Staining Teacher s Guidebook (Cat. # BE 202) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
PR021 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Bacterial Gram Staining Teacher s Guidebook (Cat. # BE 202) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
Useful Propagation Terms. Propagation The application of specific biological principles and concepts in the multiplication of plants.
 Useful Propagation Terms Propagation The application of specific biological principles and concepts in the multiplication of plants. Adventitious Typically describes new organs such as roots that develop
Useful Propagation Terms Propagation The application of specific biological principles and concepts in the multiplication of plants. Adventitious Typically describes new organs such as roots that develop
In vitro flowering and in vitro pollination: methods that will benefit the orchid industry
 In vitro flowering and in vitro pollination: methods that will benefit the orchid industry Kim Hor HEE, Hock Hin YEOH, Chiang Shiong LOH Department of Biological Sciences, National University of Singapore
In vitro flowering and in vitro pollination: methods that will benefit the orchid industry Kim Hor HEE, Hock Hin YEOH, Chiang Shiong LOH Department of Biological Sciences, National University of Singapore
Cells: 3 Star. Which row in the chart below best explains the movement of some molecules between the model cell and the solution in the beaker?
 ells: 3 Star 1. ase your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents a model cell setup. The locations of three different substances
ells: 3 Star 1. ase your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents a model cell setup. The locations of three different substances
GENETIC ANALYSES OF ROOT SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT IN THE TOMATO CROP MODEL
 GENETIC ANALYSES OF ROOT SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT IN THE TOMATO CROP MODEL Kelsey Hoth 1 Dr. Maria Ivanchenko 2 Bioresourse Research 1, Department of Botany and Plant Physiology 2, Oregon State University, Corvallis,
GENETIC ANALYSES OF ROOT SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT IN THE TOMATO CROP MODEL Kelsey Hoth 1 Dr. Maria Ivanchenko 2 Bioresourse Research 1, Department of Botany and Plant Physiology 2, Oregon State University, Corvallis,
Genetic variability/stability of micropropagated and standard propagated raspberry and blackberry plants
 THE SUSTAINABLE IMPROVEMENT OF EUROPEAN BERRY PRODUCTION, QUALITY AND NUTRITIONAL VALUE IN CHANGING ENVIRONMENT: STRAWBERRIES, CURRANTS, BLACKBERRIES, BLUEBERRIES AND RASPBERRIES (EUBERRY) SUBCONTARCT:
THE SUSTAINABLE IMPROVEMENT OF EUROPEAN BERRY PRODUCTION, QUALITY AND NUTRITIONAL VALUE IN CHANGING ENVIRONMENT: STRAWBERRIES, CURRANTS, BLACKBERRIES, BLUEBERRIES AND RASPBERRIES (EUBERRY) SUBCONTARCT:
NOVABEADS FOOD 1 DNA KIT
 NOVABEADS FOOD 1 DNA KIT NOVABEADS FOOD DNA KIT is the new generation tool in molecular biology techniques and allows DNA isolations from highly processed food products. The method is based on the use
NOVABEADS FOOD 1 DNA KIT NOVABEADS FOOD DNA KIT is the new generation tool in molecular biology techniques and allows DNA isolations from highly processed food products. The method is based on the use
Practical course 1. Microscopy
 Cellular and Molecular Biology Practicum 1 Practical course 1. Microscopy Name and surname Exercise 1. Prepare a part of plant tissue, for example a part of the leaf of Elodea canadensis by putting it
Cellular and Molecular Biology Practicum 1 Practical course 1. Microscopy Name and surname Exercise 1. Prepare a part of plant tissue, for example a part of the leaf of Elodea canadensis by putting it
Somaclonal Variation
 Tissue-culture cycle involves: dedifferentiation in culture proliferation of cells (implies sev. cell generations removed from original differentiated cell) subsequent regeneration to plants no selection
Tissue-culture cycle involves: dedifferentiation in culture proliferation of cells (implies sev. cell generations removed from original differentiated cell) subsequent regeneration to plants no selection
The grade 5 English science unit, Plants, meets the academic content standards set in the Korean curriculum, which state students should:
 This unit deals with the structures and functions of plant organs including roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. Students learn that a plant is sustained by the systematic functioning of all its organs.
This unit deals with the structures and functions of plant organs including roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. Students learn that a plant is sustained by the systematic functioning of all its organs.
Cryotherapy: A New Method to Eliminate Pathogens from Sweetpotato Propagation Materials
 Cryotherapy: A New Method to Eliminate Pathogens from Sweetpotato Propagation Materials Margaret Worthington Graduate Group in Horticulture and Agronomy University of California, Davis April 14, 2009 http://www.judithbarathart.com
Cryotherapy: A New Method to Eliminate Pathogens from Sweetpotato Propagation Materials Margaret Worthington Graduate Group in Horticulture and Agronomy University of California, Davis April 14, 2009 http://www.judithbarathart.com
INTRODUCING PLANT TISSUE CULTURE IN THE CLASSROOM CONCEPTS & HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE
 INTRODUCING PLANT TISSUE CULTURE IN THE CLASSROOM CONCEPTS & HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE Dr. Mike Kane University of Florida Applications of Plant Tissue Culture Concepts & Terminology Micropropagation: A Historical
INTRODUCING PLANT TISSUE CULTURE IN THE CLASSROOM CONCEPTS & HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE Dr. Mike Kane University of Florida Applications of Plant Tissue Culture Concepts & Terminology Micropropagation: A Historical
Cell Division THE MAJOR STEPS OF CELL DIVISION: 10/28/2013. When does DNA replicate? The first step of cell division is DNA replication:
 Cell Division Biology 105 Laboratory 8 THE MAJOR STEPS OF CELL DIVISION: When does DNA replicate? The first step of cell division is DNA replication: This occurs just prior to cell division. Cells need
Cell Division Biology 105 Laboratory 8 THE MAJOR STEPS OF CELL DIVISION: When does DNA replicate? The first step of cell division is DNA replication: This occurs just prior to cell division. Cells need
Ginkgo leaf. Ginkgo is dioecious, separate sexes: male and female plants are separate. Monoecious plants have both male and female parts.
 Ginkgo leaf Figure 22-30 Ginkgo tree. Ginkgo is dioecious, separate sexes: male and female plants are separate. Monoecious plants have both male and female parts. The vein pattern is dichotomous: Divided
Ginkgo leaf Figure 22-30 Ginkgo tree. Ginkgo is dioecious, separate sexes: male and female plants are separate. Monoecious plants have both male and female parts. The vein pattern is dichotomous: Divided
Propagating Plants Sexually
 Lesson C5 1 Propagating Plants Sexually Unit C. Plant and Soil Science Problem Area 5. Plant Propagation Lesson 1. Propagating Plants Sexually New Mexico Content Standard: Pathway Strand: Plant Systems
Lesson C5 1 Propagating Plants Sexually Unit C. Plant and Soil Science Problem Area 5. Plant Propagation Lesson 1. Propagating Plants Sexually New Mexico Content Standard: Pathway Strand: Plant Systems
mrna Isolation Kit for Blood/Bone Marrow For isolation mrna from blood or bone marrow lysates Cat. No
 For isolation mrna from blood or bone marrow lysates Cat. No. 1 934 333 Principle Starting material Application Time required Results Key advantages The purification of mrna requires two steps: 1. Cells
For isolation mrna from blood or bone marrow lysates Cat. No. 1 934 333 Principle Starting material Application Time required Results Key advantages The purification of mrna requires two steps: 1. Cells
Detection limit: grain, feed 500 ppb; milk 50 ppb; cream, cheese 5 ppb
 Product information Background Deoxynivalenol (DON) Deoxynivalenol, called vomitoxin, is a toxic metabolite mainly produced by Fusarium graminearum. It is mainly found in wheat, barley, corn and feed.
Product information Background Deoxynivalenol (DON) Deoxynivalenol, called vomitoxin, is a toxic metabolite mainly produced by Fusarium graminearum. It is mainly found in wheat, barley, corn and feed.
CONTROL OF GROWTH BY HORMONES
 CONTROL OF GROWTH BY HORMONES Growth and organogenesis are controlled......by genes (independent of environment): e.g., number of primary vascular bundles, general shape of a leaf or flower...by genes
CONTROL OF GROWTH BY HORMONES Growth and organogenesis are controlled......by genes (independent of environment): e.g., number of primary vascular bundles, general shape of a leaf or flower...by genes
POLYPLOID PRODUCTION IN LILIUM LEICHTLINII VAR. MAXIMOWICZII USING COLCHICINE ABSTRACT
 Heo et al., The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences, 26(4): 2016, The Page: J. Anim. 1111-1116 Plant Sci. 26(4):2016 ISSN: 1018-7081 POLYPLOID PRODUCTION IN LILIUM LEICHTLINII VAR. MAXIMOWICZII USING COLCHICINE
Heo et al., The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences, 26(4): 2016, The Page: J. Anim. 1111-1116 Plant Sci. 26(4):2016 ISSN: 1018-7081 POLYPLOID PRODUCTION IN LILIUM LEICHTLINII VAR. MAXIMOWICZII USING COLCHICINE
Development of High Yielding Saffron Mutant
 Development of High Yielding Saffron Mutant I.A. Khan G.B. Pant University of Agriculture & Technology Saffron Cultivation and Marketing Project Chaubatia-263651 Almora India Keywords: 5-Branched stigma,
Development of High Yielding Saffron Mutant I.A. Khan G.B. Pant University of Agriculture & Technology Saffron Cultivation and Marketing Project Chaubatia-263651 Almora India Keywords: 5-Branched stigma,
Chromosome numbers and karyotype in three species of the genus Vernonia Schreber in Southern Nigerian
 Vol. 7(11), pp. 538-542, November 2013 DOI: 10.5897/AJPS2013.1048 ISSN 1996-0824 2013 Academic Journals http://www.academicjournals.org/ajps African Journal of Plant Science Full Length Research Paper
Vol. 7(11), pp. 538-542, November 2013 DOI: 10.5897/AJPS2013.1048 ISSN 1996-0824 2013 Academic Journals http://www.academicjournals.org/ajps African Journal of Plant Science Full Length Research Paper
IMPROVEMENT OF SUGAR BEET BY MEANS OF INDUCED TRIPLOIDY 1) SEIJI MATSUMURA National Institute of Genetics, Misima
 IMPROVEMENT OF SUGAR BEET BY MEANS OF INDUCED TRIPLOIDY 1) SEIJI MATSUMURA National Institute of Genetics, Misima and AKIRA MOCHIZUKI Laboratory of Genetics, Ky8'o University Received November 10, 1952
IMPROVEMENT OF SUGAR BEET BY MEANS OF INDUCED TRIPLOIDY 1) SEIJI MATSUMURA National Institute of Genetics, Misima and AKIRA MOCHIZUKI Laboratory of Genetics, Ky8'o University Received November 10, 1952
Contents. Foreword. ORCHID BIOTECHNOLOGY II World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd.
 Foreword Preface v vii 1. Molecular Phylogeny and Biogeography of Phalaenopsis Species 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Biogeographical Pattern of Genus Phalaenopsis.. 6 1.3 Molecular Phylogeny and Biogeography
Foreword Preface v vii 1. Molecular Phylogeny and Biogeography of Phalaenopsis Species 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Biogeographical Pattern of Genus Phalaenopsis.. 6 1.3 Molecular Phylogeny and Biogeography
LAB #6 Chromatography Techniques
 LAB #6 Chromatography Techniques Objectives: To learn how to story board a procedure Explain how a chromatograph of pigments is formed from both paper and thin layer chromatography. Isolate and identify
LAB #6 Chromatography Techniques Objectives: To learn how to story board a procedure Explain how a chromatograph of pigments is formed from both paper and thin layer chromatography. Isolate and identify
Exam 1 PBG430/
 1 Exam 1 PBG430/530 2014 1. You read that the genome size of maize is 2,300 Mb and that in this species 2n = 20. This means that there are 2,300 Mb of DNA in a cell that is a. n (e.g. gamete) b. 2n (e.g.
1 Exam 1 PBG430/530 2014 1. You read that the genome size of maize is 2,300 Mb and that in this species 2n = 20. This means that there are 2,300 Mb of DNA in a cell that is a. n (e.g. gamete) b. 2n (e.g.
TrioMol Isolation Reagent
 TrioMol Isolation Reagent Technical Manual No. 0242 Version 06142007 I Description... 1 II Key Features... 1 III Storage..... 1 IV General Protocol Using Triomol Isolation Reagent 1 V Troubleshooting.
TrioMol Isolation Reagent Technical Manual No. 0242 Version 06142007 I Description... 1 II Key Features... 1 III Storage..... 1 IV General Protocol Using Triomol Isolation Reagent 1 V Troubleshooting.
FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS OF Phalaenopsis aphrodite Flowering locus T1 FLOWERING GENE ON TOBACCO PLANT (Nicotiana tabacum L.) ABSTRACT
 FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS OF Phalaenopsis aphrodite Flowering locus T1 FLOWERING GENE ON TOBACCO PLANT (Nicotiana tabacum L.) ABSTRACT Flowering gene Phalaenopsis aphrodite Flowering locus T1 (PaFT1) is an FT
FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS OF Phalaenopsis aphrodite Flowering locus T1 FLOWERING GENE ON TOBACCO PLANT (Nicotiana tabacum L.) ABSTRACT Flowering gene Phalaenopsis aphrodite Flowering locus T1 (PaFT1) is an FT
TrioMol Isolation Reagent
 TrioMol Isolation Reagent Technical Manual No. 0242 Version 06142007 I Description... 1 II Key Features... 1 III Storage..... 1 IV General Protocol Using Triomol Isolation Reagent 1 V Troubleshooting.
TrioMol Isolation Reagent Technical Manual No. 0242 Version 06142007 I Description... 1 II Key Features... 1 III Storage..... 1 IV General Protocol Using Triomol Isolation Reagent 1 V Troubleshooting.
ALLELOPATHY: NATURAL AND AN ENVIRONMENT-FRIENDLY UNIQUE TOOL FOR WEED CONTROL
 ALLELOPATHY: NATURAL AND AN ENVIRONMENT-FRIENDLY UNIQUE TOOL Arpana Mishra* FOR WEED CONTROL Abstract: Allelopathy term refers to all biochemical interactions ( stimulatory and inhibitory) among plants,
ALLELOPATHY: NATURAL AND AN ENVIRONMENT-FRIENDLY UNIQUE TOOL Arpana Mishra* FOR WEED CONTROL Abstract: Allelopathy term refers to all biochemical interactions ( stimulatory and inhibitory) among plants,
Chapter 3 Materials and methods
 Chapter 3 3. MATERIALS AND METHODS 3.1 M aterials The experimental plant species of the present investigation belong to the family Asclepiadaceae and are available in the North Eastern regions of India.
Chapter 3 3. MATERIALS AND METHODS 3.1 M aterials The experimental plant species of the present investigation belong to the family Asclepiadaceae and are available in the North Eastern regions of India.
Characterisation of abiotic stress inducible plant promoters and bacterial genes for osmotolerance using transgenic approach
 Characterisation of abiotic stress inducible plant promoters and bacterial genes for osmotolerance using transgenic approach ABSTRACT SUBMITTED TO JAMIA MILLIA ISLAMIA NEW DELHI IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT OF
Characterisation of abiotic stress inducible plant promoters and bacterial genes for osmotolerance using transgenic approach ABSTRACT SUBMITTED TO JAMIA MILLIA ISLAMIA NEW DELHI IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT OF
Horticulture Science
 Horticulture Science 012000 6045 Course Description This course includes the study of structure and functions of plants, including requirements for growth, methods of propagation, and the management of
Horticulture Science 012000 6045 Course Description This course includes the study of structure and functions of plants, including requirements for growth, methods of propagation, and the management of
Model plants and their Role in genetic manipulation. Mitesh Shrestha
 Model plants and their Role in genetic manipulation Mitesh Shrestha Definition of Model Organism Specific species or organism Extensively studied in research laboratories Advance our understanding of Cellular
Model plants and their Role in genetic manipulation Mitesh Shrestha Definition of Model Organism Specific species or organism Extensively studied in research laboratories Advance our understanding of Cellular
THE UNIVERSITY OF NEWCASTLE- DISCIPLINE OF MEDICAL BIOCHEMISTRY. STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE PROCEDURE NO: GLP 021 MOD: 1st Issue Page: 1 of 6
 Page: 1 of 6 1. Risk Assessment: This Risk Assessment is to be used as a general guide and as such, cannot accommodate all the varying factors that may be encountered when using this equipment. Therefore,
Page: 1 of 6 1. Risk Assessment: This Risk Assessment is to be used as a general guide and as such, cannot accommodate all the varying factors that may be encountered when using this equipment. Therefore,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature09414 Supplementary Figure 1 FACS-isolated 8c hepatocytes are highly pure. a, Gating strategy for identifying hepatocyte populations based on DNA content. b, Detection of mchry and mchr9
doi:10.1038/nature09414 Supplementary Figure 1 FACS-isolated 8c hepatocytes are highly pure. a, Gating strategy for identifying hepatocyte populations based on DNA content. b, Detection of mchry and mchr9
Biology First Nine Weeks Review
 Name Date Test Date: November 12, 2009 Biology First Nine Weeks Review Modified True/False Directions: Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or fals If false, change the identified word to
Name Date Test Date: November 12, 2009 Biology First Nine Weeks Review Modified True/False Directions: Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or fals If false, change the identified word to
Plant Responses. NOTE: plant responses involve growth and changes in growth. Their movement is much slower than that of animals.
 Plant Responses A stimulus is anything that causes a reaction in an organism. Examples: light, gravity and temperature A response is the activity of an organism as a result of a stimulus. Examples: Growth,
Plant Responses A stimulus is anything that causes a reaction in an organism. Examples: light, gravity and temperature A response is the activity of an organism as a result of a stimulus. Examples: Growth,
Cytokinin. Fig Cytokinin needed for growth of shoot apical meristem. F Cytokinin stimulates chloroplast development in the dark
 Cytokinin Abundant in young, dividing cells Shoot apical meristem Root apical meristem Synthesized in root tip, developing embryos, young leaves, fruits Transported passively via xylem into shoots from
Cytokinin Abundant in young, dividing cells Shoot apical meristem Root apical meristem Synthesized in root tip, developing embryos, young leaves, fruits Transported passively via xylem into shoots from
Asexual & Plant Reproduction
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ sexual & Plant Reproduction Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ sexual & Plant Reproduction Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
MyBioSource.com. This package insert must be read in its entirety before using this product.
 Tetracyclines ELISA Kit Catalog Number. MBS940077 This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro quantitative determination of Tetracyclines concentrations in honey, tissue(chicken, pork). This package insert
Tetracyclines ELISA Kit Catalog Number. MBS940077 This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro quantitative determination of Tetracyclines concentrations in honey, tissue(chicken, pork). This package insert
The table lists some functions of parts of a plant. Match the part of the plant (A, B, C or D) to its function by writing the letters in the table.
 Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows a flowering plant. A Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D. (c) (d) B C D A... B C... D [4] The table lists some functions of parts of a plant. Match
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows a flowering plant. A Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D. (c) (d) B C D A... B C... D [4] The table lists some functions of parts of a plant. Match
Irrigation water salinity limits faba bean (Vicia faba L.) photosynthesis
 5 th CASEE Conference Healthy Food Production and Environmental Preservation The Role of Agriculture, Forestry and Applied Biology Irrigation water salinity limits faba bean (Vicia faba L.) photosynthesis
5 th CASEE Conference Healthy Food Production and Environmental Preservation The Role of Agriculture, Forestry and Applied Biology Irrigation water salinity limits faba bean (Vicia faba L.) photosynthesis
Chromosome variations in protoplast-derived calli and in plants regenerated from the calli of
 Jpn. J. Genet. (1989) 64, pp. 355-361 Chromosome variations in protoplast-derived calli and in plants regenerated from the calli of cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) Soryu NISHIBAYASHI*, Yasuyuki HAYASHI,
Jpn. J. Genet. (1989) 64, pp. 355-361 Chromosome variations in protoplast-derived calli and in plants regenerated from the calli of cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) Soryu NISHIBAYASHI*, Yasuyuki HAYASHI,
Topic 14. The Root System. II. Anatomy of an Actively Growing Root Tip
 Topic 14. The Root System Introduction. This is the first of two lab topics that focus on the three plant organs (root, stem, leaf). In these labs we want you to recognize how tissues are organized in
Topic 14. The Root System Introduction. This is the first of two lab topics that focus on the three plant organs (root, stem, leaf). In these labs we want you to recognize how tissues are organized in
CONSIDERATION OF PROPOSALS FOR AMENDMENT OF APPENDICES I AND II
 A. Proposal CONSIDERATION OF PROPOSALS FOR AMENDMENT OF APPENDICES I AND II Annotation of Orchidaceae in Appendix II to read as follows: B. Proponent CoP13 Prop. 40 Artificially propagated specimens of
A. Proposal CONSIDERATION OF PROPOSALS FOR AMENDMENT OF APPENDICES I AND II Annotation of Orchidaceae in Appendix II to read as follows: B. Proponent CoP13 Prop. 40 Artificially propagated specimens of
Working with Mycorrhizas in Forestry and Agriculture
 Working with Mycorrhizas in Forestry and Agriculture SUB Gdttingen 206 384661 Mark Brundrett, Neale Bougher, Bernie Dell, Tim Grove and Nick Malajczuk CONTENTS Chapter I. INTRODUCTION 1.1. MYCORRHIZAL
Working with Mycorrhizas in Forestry and Agriculture SUB Gdttingen 206 384661 Mark Brundrett, Neale Bougher, Bernie Dell, Tim Grove and Nick Malajczuk CONTENTS Chapter I. INTRODUCTION 1.1. MYCORRHIZAL
Bio 105: Cell Division
 Cell Division Bio 105: Cell Division Starts with DNA Replication Laboratory 8 DNA Replication When does DNA replicate? Just prior to cell division Multicellular Organisms Grow Replace old cells Unicellular
Cell Division Bio 105: Cell Division Starts with DNA Replication Laboratory 8 DNA Replication When does DNA replicate? Just prior to cell division Multicellular Organisms Grow Replace old cells Unicellular
Mag-Bind Soil DNA Kit. M preps M preps M preps
 Mag-Bind Soil DNA Kit M5635-00 5 preps M5635-01 50 preps M5635-02 200 preps January 2013 Mag-Bind Soil DNA Kit Table of Contents Introduction and Overview...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Preparing
Mag-Bind Soil DNA Kit M5635-00 5 preps M5635-01 50 preps M5635-02 200 preps January 2013 Mag-Bind Soil DNA Kit Table of Contents Introduction and Overview...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Preparing
Name Chapter 10: Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis Mrs. Laux Take home test #7 DUE: MONDAY, NOVEMBER 16, 2009 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A bacterial chromosome consists of: A. a linear DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. B. a circular DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. C. a circular DNA
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A bacterial chromosome consists of: A. a linear DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. B. a circular DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. C. a circular DNA
INSTITUT FÜR ANGEWANDTE LABORANALYSEN GMBH. First-Beer Magnetic DNA Kit. Extraktion von Hefe- und Bakterien-DNA aus Bier und anderen Getränken
 First-Beer INSTITUT FÜR ANGEWANDTE LABORANALYSEN GMBH First-Beer Magnetic DNA Kit Extraktion von Hefe- und Bakterien-DNA aus Bier und anderen Getränken Extraction of bacteria and yeast DNA from beer and
First-Beer INSTITUT FÜR ANGEWANDTE LABORANALYSEN GMBH First-Beer Magnetic DNA Kit Extraktion von Hefe- und Bakterien-DNA aus Bier und anderen Getränken Extraction of bacteria and yeast DNA from beer and
Bring Your Text to Lab!!!
 Bring Your Text to Lab!!! Vascular Plant Anatomy: Flowering Plants Objectives: 1. To observe what the basic structure of vascular plants is, and how and where this form originates. 2. To begin to understand
Bring Your Text to Lab!!! Vascular Plant Anatomy: Flowering Plants Objectives: 1. To observe what the basic structure of vascular plants is, and how and where this form originates. 2. To begin to understand
PART I: BOTANY. Proceeding ICGRC 2013
 PART I: BOTANY Brawijaya University, February 7-8 th, 2013 1 Sanseviera trifasciata Potential to Reduce Noise Viewed from the Anatomy Structure L. Indah Murwani Yulianti Biotechnology Faculty, Atma Jaya
PART I: BOTANY Brawijaya University, February 7-8 th, 2013 1 Sanseviera trifasciata Potential to Reduce Noise Viewed from the Anatomy Structure L. Indah Murwani Yulianti Biotechnology Faculty, Atma Jaya
Application of flow cytometry in plant sciences Elwira Sliwinska
 Application of flow cytometry in plant sciences Elwira Sliwinska Head, Laboratory of Molecular Biology and Cytometry Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding University of Technology and Life Sciences,,
Application of flow cytometry in plant sciences Elwira Sliwinska Head, Laboratory of Molecular Biology and Cytometry Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding University of Technology and Life Sciences,,
Methods of isolation of Cucumis sativus and C. melo pollen grains and their utilization in in vitro pollination 1
 Methods of isolation of Cucumis sativus and C. melo pollen grains and their utilization in in vitro pollination 1 D. Skálová *, B. Navrátilová, and A. Lebeda * Palacký University, Faculty of Science, Department
Methods of isolation of Cucumis sativus and C. melo pollen grains and their utilization in in vitro pollination 1 D. Skálová *, B. Navrátilová, and A. Lebeda * Palacký University, Faculty of Science, Department
Stomatal length and frequency as a measure of ploidy level in black wattle, Acacia mearnsii (de Wild)
 Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKBOJBotanical Journal of the Linnean Society0024-4074The Linnean Society of London, 2003 141 Original Article S. L. BECK ET AL. STOMATAL INDICATORS OF PLOIDY LEVEL IN BLACK
Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKBOJBotanical Journal of the Linnean Society0024-4074The Linnean Society of London, 2003 141 Original Article S. L. BECK ET AL. STOMATAL INDICATORS OF PLOIDY LEVEL IN BLACK
TRANSPIRATION With LabQuest INTRODUCTION
 TRANSPIRATION With LabQuest LAB 10 From Biology with Vernier Westminster College INTRODUCTION Water is transported in plants from the roots to the leaves, following a decreasing water potential gradient.
TRANSPIRATION With LabQuest LAB 10 From Biology with Vernier Westminster College INTRODUCTION Water is transported in plants from the roots to the leaves, following a decreasing water potential gradient.
Efficient plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis from anthers of Datura stramonium L.
 Available online http://www.ijat-rmutto.com Journal of Agricultural Technology 2010 Vol. ISSN 6(4): 1686-9141 741-745 Efficient plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis from anthers of Datura stramonium
Available online http://www.ijat-rmutto.com Journal of Agricultural Technology 2010 Vol. ISSN 6(4): 1686-9141 741-745 Efficient plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis from anthers of Datura stramonium
Transport in Plants Question Paper 3
 Transport in Plants Question Paper 3 Level IGCSE Subject Biology Exam Board CIE Topic Transport in Plants Paper Type (Extended) Theory Paper Booklet Question Paper 3 Time Allowed: 57 minutes Score: /47
Transport in Plants Question Paper 3 Level IGCSE Subject Biology Exam Board CIE Topic Transport in Plants Paper Type (Extended) Theory Paper Booklet Question Paper 3 Time Allowed: 57 minutes Score: /47
** * * * Col-0 cau1 CAU1. Actin2 CAS. Actin2. Supplemental Figure 1. CAU1 affects calcium accumulation.
 Ca 2+ ug g -1 DW Ca 2+ ug g -1 DW Ca 2+ ug g -1 DW Supplemental Data. Fu et al. Plant Cell. (213). 1.115/tpc.113.113886 A 5 4 3 * Col- cau1 B 4 3 2 Col- cau1 ** * * ** C 2 1 25 2 15 1 5 Shoots Roots *
Ca 2+ ug g -1 DW Ca 2+ ug g -1 DW Ca 2+ ug g -1 DW Supplemental Data. Fu et al. Plant Cell. (213). 1.115/tpc.113.113886 A 5 4 3 * Col- cau1 B 4 3 2 Col- cau1 ** * * ** C 2 1 25 2 15 1 5 Shoots Roots *
Effect of Allelopathic weeds on Characteristics seed Growth in maize (Zea mays L. cv. KSC 704)
 Advances in Environmental Biology, 6(1): 297-301, 2012 ISSN 1995-0756 297 This is a refereed journal and all articles are professionally screened and reviewed ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Allelopathic weeds
Advances in Environmental Biology, 6(1): 297-301, 2012 ISSN 1995-0756 297 This is a refereed journal and all articles are professionally screened and reviewed ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Allelopathic weeds
Standards Map Basic Comprehensive Program Science Grade Seven Focus on Life Sciences SE/TE: , SE/TE: ,
 Publisher: Pearson Program Title: Biology: Exploring Life 2006 Components: 0-13-250-925-3 (SE), 0-13-250-883-4 (TE) Grade Level(s): 7-12 s Map Basic Comprehensive Program Science Grade Seven Focus on Life
Publisher: Pearson Program Title: Biology: Exploring Life 2006 Components: 0-13-250-925-3 (SE), 0-13-250-883-4 (TE) Grade Level(s): 7-12 s Map Basic Comprehensive Program Science Grade Seven Focus on Life
THE UNIVERSITY OF NEWCASTLE- DISCIPLINE OF MEDICAL BIOCHEMISTRY. STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE PROCEDURE NO: GLP 019 MOD: 1st Issue Page: 1 of 6
 Page: 1 of 6 1. Risk Assessment:. This Risk Assessment is to be used as a general guide and as such, cannot accommodate all the varying factors that may be encountered when using this equipment. Therefore,
Page: 1 of 6 1. Risk Assessment:. This Risk Assessment is to be used as a general guide and as such, cannot accommodate all the varying factors that may be encountered when using this equipment. Therefore,
This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro quantitative determination of Aflatoxin M1 concentrations in milk, milk power.
 Aflatoxin M1 (AFM1) ELISA Kit This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro quantitative determination of Aflatoxin M1 concentrations in milk, milk power. This package insert must be read in its entirety
Aflatoxin M1 (AFM1) ELISA Kit This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro quantitative determination of Aflatoxin M1 concentrations in milk, milk power. This package insert must be read in its entirety
2. The development of revolutionized the of life.
 Science 10 Unit 7 Worksheet Chapter 15, Part 1. 1. Briefly describe the three main parts of cell theory: 2. The development of revolutionized the of life. 3. Individual cells need to take in to build and
Science 10 Unit 7 Worksheet Chapter 15, Part 1. 1. Briefly describe the three main parts of cell theory: 2. The development of revolutionized the of life. 3. Individual cells need to take in to build and
Transgenic plants over-expressing HbCuZnSOD cytosolic isoform are more tolerant to a water deficit
 Transgenic plants over-expressing HbCuZnSOD cytosolic isoform are more tolerant to a water deficit J. Leclercq, F. Martin, C. Sanier, A. Clément-Vidal, D. Fabre, G. Oliver, L. Lardet, A. Ayar, M. Peyramard
Transgenic plants over-expressing HbCuZnSOD cytosolic isoform are more tolerant to a water deficit J. Leclercq, F. Martin, C. Sanier, A. Clément-Vidal, D. Fabre, G. Oliver, L. Lardet, A. Ayar, M. Peyramard
