Adaptations to the Environment
|
|
|
- Lisa Warner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Adaptations to the Environment MODULE 07: ADAPTATIONS TO THE ENVIRONMENT UNIT 1: ENVIRONMENT Objectives At the end of this series of lectures you should be able to: Define terms. Discuss the concept of scale. Describe the different ways that heat is transferred Discuss the different ways that organisms can regulate their temperatures. Explain water potential and how water moves through plants. Discuss the different challenges faced by saltwater and freshwater organisms and their different strategies and adaptations for overcoming those challenges. Discuss the challenges faced by terrestrial organisms in regards to water regulation and adaptations that they can use to overcome those challenges. Distinguish between energy and nutrients. Describe and distinguish between different photosynthetic pathways. 1
2 Defining Scale Scale spatial or temporal dimension of an object or process Example (I am going to measure. Do I bring ocular micrometer, calipers, ruler, meter stick, chain, wheel Differs from the level of organization in the ecological hierarchy Scale is not used consistently Ecological vs. Cartographic/Geographic scale (Small vs. Large) Fine vs. broad Scale The answer to a question depends on the scale it is investigated at. Changing the size of the quadrat or study area yields different results. The spatial and temporal scales important to humans are not necessarily the scale that are relevant to other organisms or ecological processes. 2
3 Defining Scale Scale is characterized by: Grain finest spatial resolution within a given data set. Extent The overall size of the study area. Grain and extent are practically correlated as the area of interest increases the grain size increases, but if the area interest is small we need to use a small grain. 3
4 Response to Environmental Variation The physical environment influences organisms in two ways: Availability of energy and resources impacts growth and reproduction. Extreme conditions can exceed tolerance limits and impact survival. 4
5 Heat Heat moves from regions of warmth to regions to cooler regions: Conduction Convection Radiation 5
6 Organism Performance Environment influences the physiology and behavior of organisms. Environment Light Temperature Water Performance How fast they grow How many offspring they produce How fast they run, fly, or swim How well they avoid predation Organism Performance Most organisms performance best over a narrow range of environmental conditions. Physiological processes have optimal conditions for functioning. Stress: Decreased rates of physiological processes because of suboptimal environmental conditions. Decreases survival, growth, or reproduction. 6
7 Response to Environmental Variation Acclimation: Adjusting to stress through behavior or physiology. It is usually a short-term, reversible process. Adaptation: The result of natural selection to environmental stress. Increased fitness of individuals with traits that enable them to cope with stress. Alleles for coping with stress become more common in the population. 7
8 Regulating Body Temperature Poikilotherms (cold-blooded) Do not regulate body temperature. Ectotherms Regulate body temperature using external sources of energy. Endotherms Regulate body temperature using internal metabolic heat. Homeotherms (warm-blooded) Endotherms that maintain a relatively constant body temperature. Variation in Temperature An organismʼs temperature is determined: Heat gained from the environment. Heat lost to the environment. An organism can modify its temperature (change the heat it gains or losses) by changing its: Physiology Morphology Behavior 8
9 Regulating Temperature Organisms regulate body temperature by manipulating heat gain and loss. Hs Heat stored in body Hm Heat from metabolism Hcd Heat gained or lost through conduction Hcv Heat gained or lost through convection Hr Heat gained or lost through radiation He Heat lost through evaporation Temperature Regulation in Plants Desert Plants Challenge: Reduce heat storage Adaptations for altering heat exchange: Leaves relatively high above ground decreases conductive heating. Small leaves and open growth form increases surface to area ratio which increases convective cooling. Reflective surfaces hairy white surfaces which decreases radiative heating. Change the orientation of leaves and stems -- decreases radiative heating. 9
10 Temperature Regulation in Plants Arctic or Alpine Plants Challenge: Increase heat storage Adaptations for altering heat exchange Leaves close to ground minimize convective loss and maximize conductive heating. Cushion growth form decreases surface area to volume ratio which decreases convective cooling. Dark surfaces increases radiative heating. Change the orientation of leaves and stems -- increases radiative heating. 10
11 Temperature Regulation in Plants Other ways plants can influence temperature: Transpiration evaporation Stomate control Deciduous leaves Pubescence Hairs on leaves and stems Air flow conduction/convection Color differences radiation Metabolic heat What does a plant gain from thermoregulating? Ectothermic Animals Use external sources of energy to regulate body temperature. Variation of body size, shape, and pigmentation Greater ability to use behavior to thermoregulate 11
12 Ectothermic Animals Reptile under cool conditions Challenge: Increase heat storage Adaptations for altering heat exchange: Laying flat against ground Reduces convective heat loss Basks on a mat of plant material Reduces heat loss to conduction. Dark pigmentation Increases radiative heat gain. What does a lizard gain from thermoregulating? Ectothermic Animals Mechanisms of altering heat exchange: Morphology and behavior. Laying flat against ground Reduces convective heat loss Basks on a mat of plant material Reduces heat loss to conduction. Dark pigmentation Increases radiative heat gain. What does a lizard gain from thermoregulating? 12
13 Endothermic Animals Use internal sources of energy to regulate body temperature. Increased Hm Variation of body size, shape, and pigmentation Greater ability to use behavior to thermoregulate Greater importance of metabolic heat. Endothermic Animals Thermal neutral zone Low temperatures Increase metabolic rate Increase metabolic heat Shiver Increase metabolic heat High temperatures Move blood to near skin Increase radiative heat loss Sweat Increase evaporative heat loss Salivate or lick Increase evaporative heat loss 13
14 Endothermic Animals Aquatic Endotherms Special challenge High specific heat of water Aquatic endotherms will lose heat to water readily. Conductive and Convective heat loss is much greater in water than in air. Gill-breathing species are exposed directly to cold water. Aquatic birds and mammals Air-breathing no exposure of large respiratory surface to water. Insulating fat layer Countercurrent heat exchange 14
15 Surviving Extremes Inactivity Avoid environmental extremes during the day. Find a microclimate that is suitable and stay there. Reducing metabolic activity Dormancy Torpor Low metabolic rate and lowered body temperature Hibernation During winter, extended lengths of times Estivation During summer, extended lengths of times 15
16 Water and Life Water is closely associated with life. Water content of organisms ranges from 50% -90%. Life is built around a biochemistry which requires water as a solvent. To maintain life an organism must maintain a balance between its internal concentrations of water and solutes. Balance water intake and water losses to the environment. Variation in Water Availability Aquatic environments may be: Hyperosmotic more solutes than an organismʼs cells. Isoosmotic same solutes as an organism s cells. Hypoosmotic less solutes than an organism s cells. Remember these terms are in reference to the environment. Organisms in hypoosomotic and hyperosmotic environments must expend energy to maintain their internal water balance. 16
17 Water and Salt Regulation in Aquatic Organisms Marine Invertebrates Isomotic Energy conservation Sharks, rays, and skates Hyperosmotic Gain water through osmosis Excrete excess salt (sodium) through a specialized gland Salt diffuses into body Teleosts (bony fish) Hyperosomotic Lose water through gills Drink seawater to increase body water Drinking salt water increases salt diffusion through gills Specialized glands and kidneys secrete excess salt Produce concentrated urine "Osmoseragulation Carangoides bartholomaei bw en2" by Kare Kare modified by Biezl translation improved by smartse - Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 via Wikipedia - g 17
18 Water in Aquatic Organisms Freshwater Invertebrates Expend energy pump out water Expend energy gathering salt Reduced internal salt concentration decreases gradient Teleosts Hypoosmotic Tend to gain water and lose salts through their gills Gain salt by specialized structures from water and from food Produce large quantities of dilute urine "Bachforelle osmoregulatoin bw en2" by Raver, Duane; modified by Biezl translation improved by User:smartse - NOAA. Transferred from en.wikipedia to Commons by User:Quadell using CommonsHelper.. Licensed under Public Domain via Wikimedia Commons
19 Water in Terrestrial Animals Animals Acquire water Absorb from air Drink Metabolic water Waterproofing Cuticles of terrestrials insects Dry skin of reptiles, birds, and mammals relative to moist skin of amphibians. Concentrated urine or feces Reclaiming water from breath Restricted activity Variation in Water Availability Marine organisms live in an isoosmotic environment, so water balance is not a problem. Freshwater organisms lose solutes to and gain water from their hypoosmotic environment. Terrestrial organisms lose water to the dry atmosphere. 19
20 Water Potential Pressure potential: Water moves from an area of higher pressure, to lower pressure. Osmotic potential: Water flows from a region of high concentration (low solute concentration) to a region of low concentration (high solute concentration). Matric potential: Water is attracted to surfaces. Adhesion. Water Potential Water potential is the sum of all these potentials: Water always moves from a higher Ψ to lower Ψ. 20
21 Water in Plants Osmotic pressure will depend on the solutes in the soil and the in cells of the plant. Matric pressure will depend on the size of spaces and the composition of the materials (soil and vessel elements). Adhesion Capillary action Evaporation from the stomates of the leaf cause negative pressure (tension) on the water column. Cohesion Hydrogen bonds Water in Plants Water moves from the soil into the roots of the plant. (From high water potential to lower water potential) In the roots, the water joins a column of water extending from the roots to the leaves of the plant. (Cohesion hydrogen bonds) Water molecules that evaporate the from the leaves exert a negative pressure (tension) on the water column moving up lowering the water potential of the roots. As soils dry, their water potential drops and the ability of the plant to gather water also decreases. 21
22 Water in Plants Water Acquisition -- Plants Absorb from air Roots Root systems more elaborate in drier areas Root systems go deeper in drier areas Roots can make up a significant portion of the plants biomass Biomass? Water in Plants Water Conservation Plants Deciduous leaves Thick leaves Reduced number of stomates Modified stomates Stomatal crypts Trichomes Dormancy Alternative pathways for photosynthesis 22
23 Energy and Matter Energy The ability to do work. Work is the moving of matter. Matter Anything that takes up space and has mass. Energy and Nutrients Energy Ability to move matter. Move material in and out of the organism as well as in an organism. Chemical bonds. Nutrients Matter Raw materials that make up the organism 23
24 Energy and Nutrients People frequently use energy and nutrients interchangeably an animal bias we obtain both in the same way. The plant difference Energy Sources Autotrophs Photosynthetic Chemosynthetic Heterotroph 24
25 Photosynthesis Basic photosynthesis Light reaction (photochemical reactions) Requires light, water Produces ATP and NADPH Carbon reaction (biochemical/dark reactions) Does not require light can occur in light or in dark Requires ATP, NADPH, and CO2 Captures the CO2 as carbohydrate Photosynthesis Variation in photosynthetic pathways primarily variation in how the CO2 is processed. C3 C4 CAM 25
26 C3 Photosynthesis Problem with C3 photosynthesis. Opening stomates for CO2 allows water to be lost. The water potential of the air is less that the water potential of the leaf. More water is lost than CO2 is gained steeper water than CO2 gradient in the leaf. This is not a real issue in wet places. RuBP caboxylase has a low affinity for CO2 Other Photosynthetic Pathways In arid environments, other pathways allow for greater water conservation. Separating in time or space the light and dark reactions. Fix CO2 with 4-carbon compounds 26
27 C4 Photosynthesis Separates the light and dark reactions into different types of cells. Concentrates CO2 in bundle sheath cells decreasing concentration in the mesophyll cells (increasing the CO2 gradient from the air to the mesophyll cells CO2 moves more quickly from air to the mesophyll cells. Less stomates have to be open to obtain the same amount of CO2. CAM Photosynthesis In CAM (crassulacean acid metabolism) photosynthesis, carbon is fixed (dark reaction) at night and the light reaction occurs during the day. Temperature is lower and humidity is higher during night decreasing water loss from the stomates. CAM all occurs in the same cell. 27
Whittaker s Biomes. Regulating T b : Heat Loss & Heat Gain. Gain. Loss. Fertilizer: basis of Leibig s Law of the Minimum Shelford s Law of Tolerance
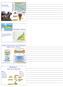 Skunk Cabbage An exothermic plant Whittaker s Biomes Whittaker's diagram showing how the type of plant community found in an area varies with temperature and precipitation. Text Fertilizer: basis of Leibig
Skunk Cabbage An exothermic plant Whittaker s Biomes Whittaker's diagram showing how the type of plant community found in an area varies with temperature and precipitation. Text Fertilizer: basis of Leibig
Endocrine Physiology. Introduction to Endocrine Principles
 Endocrine Physiology Introduction to Endocrine Principles There are TWO major groups of hormones Peptide and protein hormones Amine hormones Peptide and protein hormones act through cell membrane receptors
Endocrine Physiology Introduction to Endocrine Principles There are TWO major groups of hormones Peptide and protein hormones Amine hormones Peptide and protein hormones act through cell membrane receptors
Unit code: R/503/1742 QCF level: 5 Credit value: 15
 Unit 23: Animal Adaptations Unit code: R/503/1742 QCF level: 5 Credit value: 15 Aim The aim of this unit is to give learners an overview of the trends in the evolution of the animal kingdom. It develops
Unit 23: Animal Adaptations Unit code: R/503/1742 QCF level: 5 Credit value: 15 Aim The aim of this unit is to give learners an overview of the trends in the evolution of the animal kingdom. It develops
AP Biology Transpiration and Stomata
 AP Biology Transpiration and Stomata Living things must exchange matter with the environment to survive, Example: Gas Exchange in Plants photosynthesis cellular respiration 1. During which hours does a
AP Biology Transpiration and Stomata Living things must exchange matter with the environment to survive, Example: Gas Exchange in Plants photosynthesis cellular respiration 1. During which hours does a
Biology 2 Chapter 21 Review
 Biology 2 Chapter 21 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is not a tissue system of vascular plants? a. vascular
Biology 2 Chapter 21 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is not a tissue system of vascular plants? a. vascular
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 20 of 34
 Page 20 of 34 (i) The role of haemoglobin in transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide To include the reversible binding of oxygen molecules, carbonic anhydrase, haemoglobinic acid, HCO3- and the chloride
Page 20 of 34 (i) The role of haemoglobin in transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide To include the reversible binding of oxygen molecules, carbonic anhydrase, haemoglobinic acid, HCO3- and the chloride
PLANT SCIENCE. 9.2 Transport in Angiospermophytes
 PLANT SCIENCE 9.2 Transport in Angiospermophytes Support of terrestrial plants Support of terrestrial plants comes through: Thickened cellulose in cell walls Turgor pressure of cells Lignified xylem Xylem
PLANT SCIENCE 9.2 Transport in Angiospermophytes Support of terrestrial plants Support of terrestrial plants comes through: Thickened cellulose in cell walls Turgor pressure of cells Lignified xylem Xylem
C4 and CAM Photosynthesis Variations on the Theme
 C4 and CAM Photosynthesis Variations on the Theme AP 2007-2008 Biology Remember what plants need Photosynthesis light reactions light H 2 O Calvin cycle sun ground air O C O What structures have plants
C4 and CAM Photosynthesis Variations on the Theme AP 2007-2008 Biology Remember what plants need Photosynthesis light reactions light H 2 O Calvin cycle sun ground air O C O What structures have plants
Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function
 Chapter 40 Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Big Ideas Physical laws and environment constrain
Chapter 40 Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Big Ideas Physical laws and environment constrain
Energy Conversions. Photosynthesis. Plants. Chloroplasts. Plant Pigments 10/13/2014. Chapter 10 Pg
 Energy Conversions Photosynthesis Chapter 10 Pg. 184 205 Life on Earth is solar-powered by autotrophs Autotrophs make their own food and have no need to consume other organisms. They are the ultimate source
Energy Conversions Photosynthesis Chapter 10 Pg. 184 205 Life on Earth is solar-powered by autotrophs Autotrophs make their own food and have no need to consume other organisms. They are the ultimate source
The three principal organs of seed plants are roots, stems, and leaves.
 23 1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure The three principal organs of seed plants are roots, stems, and leaves. 1 of 34 23 1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure Roots: absorb
23 1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure The three principal organs of seed plants are roots, stems, and leaves. 1 of 34 23 1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure Roots: absorb
Chapter 8: Plant Organs: Leaves
 Leaf Form & Function Chapter 8: Plant Organs: Leaves Leaves are the most variable Composed of a and a May have (pair of leaf like outgrowths at petiole) : having a single blade : having a blade divided
Leaf Form & Function Chapter 8: Plant Organs: Leaves Leaves are the most variable Composed of a and a May have (pair of leaf like outgrowths at petiole) : having a single blade : having a blade divided
Temperature and light as ecological factors for plants
 PLB/EVE 117 Plant Ecology Fall 2005 1 Temperature and light as ecological factors for plants I. Temperature as an environmental factor A. The influence of temperature as an environmental factor is pervasive
PLB/EVE 117 Plant Ecology Fall 2005 1 Temperature and light as ecological factors for plants I. Temperature as an environmental factor A. The influence of temperature as an environmental factor is pervasive
Think about it Water, water, everywhere
 Think about it Water, water, everywhere It s just about everywhere! It covers almost 3/4 of the Earth s surface. It makes up about 2/3 of your body s weight! Every living thing needs it to survive. It
Think about it Water, water, everywhere It s just about everywhere! It covers almost 3/4 of the Earth s surface. It makes up about 2/3 of your body s weight! Every living thing needs it to survive. It
Physiological Ecology. Physiological Ecology. Physiological Ecology. Nutrient and Energy Transfer. Introduction to Ecology
 Physiological Ecology Outline Introduction to Ecology Evolution and Natural Selection Physiological Ecology Behavioural Ecology Physiological Ecology study of species needs and tolerances that determine
Physiological Ecology Outline Introduction to Ecology Evolution and Natural Selection Physiological Ecology Behavioural Ecology Physiological Ecology study of species needs and tolerances that determine
OCR (A) Biology A-level
 OCR (A) Biology A-level Topic 3.3: Transport in plants Notes Plants require a transport system to ensure that all the cells of a plant receive a sufficient amount of nutrients. This is achieved through
OCR (A) Biology A-level Topic 3.3: Transport in plants Notes Plants require a transport system to ensure that all the cells of a plant receive a sufficient amount of nutrients. This is achieved through
Remember what plants need! Photosynthesis. Photosynthesis: Variations on the Theme " Leaf Structure. Controlling water loss from leaves
 Remember what plants need! Photosynthesis O light reactions C O! light! sun! H2O! ground Photosynthesis: Variations on the Theme Calvin cycle!! air 2007-2008 vascular bundle Leaf Structure phloem (transports
Remember what plants need! Photosynthesis O light reactions C O! light! sun! H2O! ground Photosynthesis: Variations on the Theme Calvin cycle!! air 2007-2008 vascular bundle Leaf Structure phloem (transports
Introduction to Plant Transport
 Introduction to Plant Transport The algal ancestors of plants were completely immersed in water and dissolved minerals. The adaptation to land involved the differentiation of the plant body into roots,
Introduction to Plant Transport The algal ancestors of plants were completely immersed in water and dissolved minerals. The adaptation to land involved the differentiation of the plant body into roots,
Organs and leaf structure
 Organs and leaf structure Different types of tissues are arranged together to form organs. Structure: 2 parts (Petiole and Leaf Blade) Thin flat blade, large surface area Leaves contain all 3 types of
Organs and leaf structure Different types of tissues are arranged together to form organs. Structure: 2 parts (Petiole and Leaf Blade) Thin flat blade, large surface area Leaves contain all 3 types of
Gas Exchange 3/26/12. Biology: life study of. What is Life? Ch. 44 pg Properties of Life Cellular Structure: the unit of life, one or many
 Biology: life study of What is Life? Properties of Life Cellular Structure: the unit of life, one or many Metabolism: photosynthesis, respiration, fermentation, digestion, gas exchange, secretion, excretion,
Biology: life study of What is Life? Properties of Life Cellular Structure: the unit of life, one or many Metabolism: photosynthesis, respiration, fermentation, digestion, gas exchange, secretion, excretion,
Bio Factsheet. Transport in Plants. Number 342
 Number 342 Transport in Plants This Factsheet: Explains why plants need a transport system Describes what plants transport Describes the tissues which carry out transport Outlines the position of the xylem
Number 342 Transport in Plants This Factsheet: Explains why plants need a transport system Describes what plants transport Describes the tissues which carry out transport Outlines the position of the xylem
Biology. Slide 1 of 32. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 32 23 4 Leaves 2 of 32 Leaf Structure Leaf Structure How does the structure of a leaf enable it to carry out photosynthesis? 3 of 32 Leaf Structure The structure of a leaf is optimized for
Biology 1 of 32 23 4 Leaves 2 of 32 Leaf Structure Leaf Structure How does the structure of a leaf enable it to carry out photosynthesis? 3 of 32 Leaf Structure The structure of a leaf is optimized for
Chapter 5: Photosynthesis: The Energy of Life pg : Alternative Mechanisms of Carbon Fixation pg
 UNIT 2: Metabolic Processes Chapter 5: Photosynthesis: The Energy of Life pg. 210-240 5.4: Alternative Mechanisms of Carbon Fixation pg. 231 234 Photosynthesis requires reactants; CO 2 and H 2 O, to produce
UNIT 2: Metabolic Processes Chapter 5: Photosynthesis: The Energy of Life pg. 210-240 5.4: Alternative Mechanisms of Carbon Fixation pg. 231 234 Photosynthesis requires reactants; CO 2 and H 2 O, to produce
Describe plant meristems. Where are they located? perpetually embryonic cells found at tips of roots and shoots (apical vs.
 Which conditions have the higher rate of transpiration? Light or dark: Humid or dry: Breezy or still air: Hot or warm: light (need CO 2 for photosyn.) dry (lower H 2 O potential out) breezy (greater evaporation)
Which conditions have the higher rate of transpiration? Light or dark: Humid or dry: Breezy or still air: Hot or warm: light (need CO 2 for photosyn.) dry (lower H 2 O potential out) breezy (greater evaporation)
2018 Version. Photosynthesis Junior Science
 2018 Version Photosynthesis Junior Science 1 Plants fill the role of Producers in a community Plants are special because they have leaves and are able to produce their own food by the process of photosynthesis
2018 Version Photosynthesis Junior Science 1 Plants fill the role of Producers in a community Plants are special because they have leaves and are able to produce their own food by the process of photosynthesis
The summary equation of photosynthesis including the source and fate of the reactants and products. How leaf and chloroplast anatomy relates to
 1 The summary equation of photosynthesis including the source and fate of the reactants and products. How leaf and chloroplast anatomy relates to photosynthesis. How photosystems convert solar energy to
1 The summary equation of photosynthesis including the source and fate of the reactants and products. How leaf and chloroplast anatomy relates to photosynthesis. How photosystems convert solar energy to
Chapter 10 Photosynthesis
 Chapter 10 Photosynthesis Photosynthesis Process by which plants use light energy to make food. A reduction process that makes complex organic molecules from simple molecules. Ps General Equation 6 CO
Chapter 10 Photosynthesis Photosynthesis Process by which plants use light energy to make food. A reduction process that makes complex organic molecules from simple molecules. Ps General Equation 6 CO
Photosynthesis: Variations on the Theme. AP Biology
 Photosynthesis: Variations on the Theme 2007-2008 Remember what plants need Photosynthesis u light reactions light H 2 O sun ground u Calvin cycle CO 2 air O C O What structures have plants evolved to
Photosynthesis: Variations on the Theme 2007-2008 Remember what plants need Photosynthesis u light reactions light H 2 O sun ground u Calvin cycle CO 2 air O C O What structures have plants evolved to
23 4 Leaves Slide 1 of 32
 23 4 Leaves 1 of 32 Leaf Structure The structure of a leaf is optimized for absorbing light and carrying out photosynthesis. 2 of 32 Leaf Structure To collect sunlight, most leaves have thin, flattened
23 4 Leaves 1 of 32 Leaf Structure The structure of a leaf is optimized for absorbing light and carrying out photosynthesis. 2 of 32 Leaf Structure To collect sunlight, most leaves have thin, flattened
CHAPTER 8 PHOTOSYNTHESIS
 CHAPTER 8 PHOTOSYNTHESIS Con. 8.1 Photosynthesis process by which plants use light to make food molecules from carbon dioxide and water (chlorophyll) 6CO 2 + 12H 2 O + Light C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 + 6H 2
CHAPTER 8 PHOTOSYNTHESIS Con. 8.1 Photosynthesis process by which plants use light to make food molecules from carbon dioxide and water (chlorophyll) 6CO 2 + 12H 2 O + Light C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 + 6H 2
Biological Science Stage 2 Work Samples
 Biological Science Stage 2 Work Samples Question 1 Complete the following by typing in your answers. a) Autotroph means self feeding. Why are plants also known as autotrophs? b) Why are plants also known
Biological Science Stage 2 Work Samples Question 1 Complete the following by typing in your answers. a) Autotroph means self feeding. Why are plants also known as autotrophs? b) Why are plants also known
Transpiration. Interesting Fact:
 Transpiration Transpiration is a process that involves loss of water vapour through the stomata of plants. Transpiration is thought to be a 'necessary cost or evil' to allow the plant to absorb water from
Transpiration Transpiration is a process that involves loss of water vapour through the stomata of plants. Transpiration is thought to be a 'necessary cost or evil' to allow the plant to absorb water from
Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function. Chapter 40
 Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function Chapter 40 Form and Function Anatomy- biological form of an organism. Physiology- biological function. Size and Shape Development of body plan and shape is
Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function Chapter 40 Form and Function Anatomy- biological form of an organism. Physiology- biological function. Size and Shape Development of body plan and shape is
Form and Function. Physical Laws and Form. Chapter 40: Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function. AP Biology Fig Figs & 40.
 Chapter 40: Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function AP Biology 2013 1 Form and Function Comparative studies show that form and function are closely related Natural selection can fit the form (anatomy)
Chapter 40: Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function AP Biology 2013 1 Form and Function Comparative studies show that form and function are closely related Natural selection can fit the form (anatomy)
13. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 Name 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and
Name 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and
Ch. 10- Photosynthesis: Life from Light and Air
 Ch. 10- Photosynthesis: Life from Light and Air 2007-2008 Ch. 10 Photosynthesis: Life from Light and Air 2007-2008 Energy needs of life All life needs a constant input of energy consumers Heterotrophs
Ch. 10- Photosynthesis: Life from Light and Air 2007-2008 Ch. 10 Photosynthesis: Life from Light and Air 2007-2008 Energy needs of life All life needs a constant input of energy consumers Heterotrophs
Water and Food Transportation
 Water and Food Transportation Sugars in a Plant Sugar Form Location in Plant Organ Function of Sugar form Glucose Leaf Energy (made in photosynthesis summer, used in cellular respiration for growth-spring)
Water and Food Transportation Sugars in a Plant Sugar Form Location in Plant Organ Function of Sugar form Glucose Leaf Energy (made in photosynthesis summer, used in cellular respiration for growth-spring)
AP Biology. Chloroplasts: sites of photosynthesis in plants
 The summary equation of photosynthesis including the source and fate of the reactants and products. How leaf and chloroplast anatomy relates to photosynthesis. How photosystems convert solar energy to
The summary equation of photosynthesis including the source and fate of the reactants and products. How leaf and chloroplast anatomy relates to photosynthesis. How photosystems convert solar energy to
Chapter 10 Photosynthesis. Photosynthesis
 Chapter 10 Photosynthesis Photosynthesis The process which feeds the Biosphere! Recall that all forms of life require energy Some forms of life have the ability to sustain themselves without eating anything
Chapter 10 Photosynthesis Photosynthesis The process which feeds the Biosphere! Recall that all forms of life require energy Some forms of life have the ability to sustain themselves without eating anything
How Does Temperature Affect Daphnia Heart Rate? Student Study Guide
 TM How Does Temperature Affect Daphnia Heart Rate? Student Study Guide The body temperature of the Arctic squirrel drops from 98.6 F to 26.4 F, which is below the freezing point of water and is the lowest
TM How Does Temperature Affect Daphnia Heart Rate? Student Study Guide The body temperature of the Arctic squirrel drops from 98.6 F to 26.4 F, which is below the freezing point of water and is the lowest
Chapter 35 Regulation and Transport in Plants
 Chapter 35 Regulation and Remember what plants need Photosynthesis light reactions Calvin cycle light sun H 2 O ground CO 2 air What structures have plants evolved to supply these needs? Interdependent
Chapter 35 Regulation and Remember what plants need Photosynthesis light reactions Calvin cycle light sun H 2 O ground CO 2 air What structures have plants evolved to supply these needs? Interdependent
of water unless it is moving via the symplast Water moves into the xylem for transport up the plant Water that does not cross the
 Uptake of water The through Casparian Strip blocks root epidermis by passage osmosis of water unless it is moving via the symplast Water moves into the xylem for transport up the plant Water that does
Uptake of water The through Casparian Strip blocks root epidermis by passage osmosis of water unless it is moving via the symplast Water moves into the xylem for transport up the plant Water that does
Physiological ecology - concerned with the dynamic relationship of individuals to their physical environments and resources.
 Physiological Ecology I. Ecology of Individuals Behavior Physiology Physiological ecology - concerned with the dynamic relationship of individuals to their physical environments and resources. A. What
Physiological Ecology I. Ecology of Individuals Behavior Physiology Physiological ecology - concerned with the dynamic relationship of individuals to their physical environments and resources. A. What
First & Second Term Booklet
 Science Department 2 nd Primary First & Second Term Booklet 1 Unit 1 Plants Kindly watch this video before reading the lesson: http://youtube.com/watch?v=18amlz9vfg8 Plants are living organisms. Plants
Science Department 2 nd Primary First & Second Term Booklet 1 Unit 1 Plants Kindly watch this video before reading the lesson: http://youtube.com/watch?v=18amlz9vfg8 Plants are living organisms. Plants
Desert Patterns. Plants Growth and reproduction Water loss prevention Defenses. Animals Growth and reproduction Water loss prevention Defenses
 Desert Patterns Plants Growth and reproduction Water loss prevention Defenses Animals Growth and reproduction Water loss prevention Defenses Abiotic Features Introduction A major emphasis in ecology is
Desert Patterns Plants Growth and reproduction Water loss prevention Defenses Animals Growth and reproduction Water loss prevention Defenses Abiotic Features Introduction A major emphasis in ecology is
1 Plant Characteristics!
 www.ck12.org Chapter 1. Plant Characteristics! CHAPTER 1 Plant Characteristics! Identify common traits of plants. What are Plants? Plants are multicellular eukaryotic organisms with cell wallscellulosechloroplasts
www.ck12.org Chapter 1. Plant Characteristics! CHAPTER 1 Plant Characteristics! Identify common traits of plants. What are Plants? Plants are multicellular eukaryotic organisms with cell wallscellulosechloroplasts
Behavioral and Structural Adaptations PPT Guided Notes
 A Essential Standard 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms accomplish the following life functions through adaptations with particular environments and that these adaptations have evolved to ensure survival
A Essential Standard 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms accomplish the following life functions through adaptations with particular environments and that these adaptations have evolved to ensure survival
AP Biology Chapter 36
 Chapter 36 Chapter 36 Transport in Plants 2006-2007 Transport in plants - Overview H2O & minerals transport in xylem transpiration evaporation, adhesion & cohesion negative pressure Sugars transport in
Chapter 36 Chapter 36 Transport in Plants 2006-2007 Transport in plants - Overview H2O & minerals transport in xylem transpiration evaporation, adhesion & cohesion negative pressure Sugars transport in
Biology. Chapter 2 Notes
 Biology Chapter 2 Notes Section 1: Nature of Matter Objectives: 1) Differentiate between atoms and elements 2) Analyze how compounds are formed 3) Distinguish between covalent bonds, hydrogen bonds and
Biology Chapter 2 Notes Section 1: Nature of Matter Objectives: 1) Differentiate between atoms and elements 2) Analyze how compounds are formed 3) Distinguish between covalent bonds, hydrogen bonds and
in angiosperms 10/29/08 Roots take up water via roots Large surface area is needed Roots branch and have root hairs Cortex structure also helps uptake
 in angiosperms A. Root System Roots take up water via roots Large surface area is needed Roots branch and have root hairs Cortex structure also helps uptake 1 B. Minerals Nitrogen (NO 3-,NH 4+ ) Potassium
in angiosperms A. Root System Roots take up water via roots Large surface area is needed Roots branch and have root hairs Cortex structure also helps uptake 1 B. Minerals Nitrogen (NO 3-,NH 4+ ) Potassium
THE BASICS OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS
 THE BASICS OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS Almost all plants are photosynthetic autotrophs, as are some bacteria and protists Autotrophs generate their own organic matter through photosynthesis Sunlight energy is transformed
THE BASICS OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS Almost all plants are photosynthetic autotrophs, as are some bacteria and protists Autotrophs generate their own organic matter through photosynthesis Sunlight energy is transformed
PHOTOSYNTHESIS. Joseph Priestly 1772 experiment. SFSU Geography 316 Fall 2006 Dr. Barbara A. Holzman
 Nutrient Cycling I. A.Photosynthesis B. Respiration C. Production Primary productivity Gross Production Net Production II. Types of photosynthesis A. C3, B. C4, C. CAM D. Comparisons III. General Carbon
Nutrient Cycling I. A.Photosynthesis B. Respiration C. Production Primary productivity Gross Production Net Production II. Types of photosynthesis A. C3, B. C4, C. CAM D. Comparisons III. General Carbon
Chapter 30: Plant Nutrition & Transport
 Chapter 30: Plant Nutrition & Transport Carnivorous Plants Capture animals to supplement their nutrient intake Venus flytrap lures insects with sugary bait; closes on victim Cobra lily lures insects down
Chapter 30: Plant Nutrition & Transport Carnivorous Plants Capture animals to supplement their nutrient intake Venus flytrap lures insects with sugary bait; closes on victim Cobra lily lures insects down
The Chemistry of Seawater. Unit 3
 The Chemistry of Seawater Unit 3 Water occurs naturally on earth in 3 phases: solid, liquid, or gas (liquid is most abundant) Water Phases Basic Chemistry Review What is an atom? Smallest particles of
The Chemistry of Seawater Unit 3 Water occurs naturally on earth in 3 phases: solid, liquid, or gas (liquid is most abundant) Water Phases Basic Chemistry Review What is an atom? Smallest particles of
Chapter 10. Photosynthesis: Variations on the Theme. AP Biology
 Chapter 10. Photosynthesis: Variations on the Theme Remember what plants need Photosynthesis light reactions Calvin cycle light sun H 2 O ground CO 2 air What structures have plants evolved to supply these
Chapter 10. Photosynthesis: Variations on the Theme Remember what plants need Photosynthesis light reactions Calvin cycle light sun H 2 O ground CO 2 air What structures have plants evolved to supply these
6 Plant Nutrition. Question Paper. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Plant Nutrition Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Unit ooklet IGSE iology ambridge International Examinations 6 Plant Nutrition
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Plant Nutrition Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Unit ooklet IGSE iology ambridge International Examinations 6 Plant Nutrition
Water Properties Foldable
 Water Properties Foldable Definition: Polarity Polarity Definition: Unequal charge distribution on a molecule. Elaboration (Polarity) Elaboration (Polarity) Bond polarities arise from bonds between atoms
Water Properties Foldable Definition: Polarity Polarity Definition: Unequal charge distribution on a molecule. Elaboration (Polarity) Elaboration (Polarity) Bond polarities arise from bonds between atoms
build stuff!! Stomates Warm-up Remember what it means to be a Photosynthesis: The Calvin Cycle Life from Air Autotrophs Light reactions
 Warm-up Objective: Describe how the chemical products of the light-trapping reactions couple to the synthesis of carbohydrates. Warm-up: What is the advantage of the light reaction producing H and ATP
Warm-up Objective: Describe how the chemical products of the light-trapping reactions couple to the synthesis of carbohydrates. Warm-up: What is the advantage of the light reaction producing H and ATP
BIO 2 GO! Abiotic Factors 3.2.2
 BIO 2 GO! Abiotic Factors 3.2.2 Abiotic factors are non-living, but are extremely important to all cells as well as the entire organism. Cells live within a narrow range of abiotic factors. Beyond that
BIO 2 GO! Abiotic Factors 3.2.2 Abiotic factors are non-living, but are extremely important to all cells as well as the entire organism. Cells live within a narrow range of abiotic factors. Beyond that
Copy into Note Packet and Return to Teacher
 Copy into Note Packet and Return to Teacher Section 1: Nature of Matter Objectives: Differentiate between atoms and elements. Analyze how compounds are formed. Distinguish between covalent bonds, hydrogen
Copy into Note Packet and Return to Teacher Section 1: Nature of Matter Objectives: Differentiate between atoms and elements. Analyze how compounds are formed. Distinguish between covalent bonds, hydrogen
2/6/2011. Essentials of Biology. 6.1 Overview of Photosynthesis. Investigating Photosynthesis
 Investigating Photosynthesis Essentials of Biology Sylvia S. Mader One of the first questions. When a tiny seedling grows into a tall tree with a mass of several tons, where does all that mass come from?
Investigating Photosynthesis Essentials of Biology Sylvia S. Mader One of the first questions. When a tiny seedling grows into a tall tree with a mass of several tons, where does all that mass come from?
1 (a) carbon dioxide / CO 2 ; (aerobic) respiration ; (simple) diffusion ; [3] A excretion I gas exchange
![1 (a) carbon dioxide / CO 2 ; (aerobic) respiration ; (simple) diffusion ; [3] A excretion I gas exchange 1 (a) carbon dioxide / CO 2 ; (aerobic) respiration ; (simple) diffusion ; [3] A excretion I gas exchange](/thumbs/84/90652061.jpg) 1 (a) carbon dioxide / CO 2 ; (aerobic) respiration ; (simple) diffusion ; [] A excretion I gas exchange (b) water enters by osmosis ; down a water potential gradient / high(er) to low(er) water potential
1 (a) carbon dioxide / CO 2 ; (aerobic) respiration ; (simple) diffusion ; [] A excretion I gas exchange (b) water enters by osmosis ; down a water potential gradient / high(er) to low(er) water potential
TREES. Functions, structure, physiology
 TREES Functions, structure, physiology Trees in Agroecosystems - 1 Microclimate effects lower soil temperature alter soil moisture reduce temperature fluctuations Maintain or increase soil fertility biological
TREES Functions, structure, physiology Trees in Agroecosystems - 1 Microclimate effects lower soil temperature alter soil moisture reduce temperature fluctuations Maintain or increase soil fertility biological
Carbon Input to Ecosystems
 Objectives Carbon Input Leaves Photosynthetic pathways Canopies (i.e., ecosystems) Controls over carbon input Leaves Canopies (i.e., ecosystems) Terminology Photosynthesis vs. net photosynthesis vs. gross
Objectives Carbon Input Leaves Photosynthetic pathways Canopies (i.e., ecosystems) Controls over carbon input Leaves Canopies (i.e., ecosystems) Terminology Photosynthesis vs. net photosynthesis vs. gross
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 3: Water and Life: The Molecule that supports all Live
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 3: Water and Life: The Molecule that supports all Live The Molecule that Supports all Life CONCEPTS: 3.1 Polar covalent bonds in water molecules result in hydrogen bonding 3.2 Four
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 3: Water and Life: The Molecule that supports all Live The Molecule that Supports all Life CONCEPTS: 3.1 Polar covalent bonds in water molecules result in hydrogen bonding 3.2 Four
Ch20_Ecology, community & ecosystems
 Community Ecology Populations of different species living in the same place NICHE The sum of all the different use of abiotic resources in the habitat by s given species what the organism does what is
Community Ecology Populations of different species living in the same place NICHE The sum of all the different use of abiotic resources in the habitat by s given species what the organism does what is
Abiotic Structural Components
 1 Module # 10 Component # 2 Abiotic Structural Components Introduction The abiotic aspects of the ecosystem are often neglected in ecological studies. Therefore, this entire component will be devoted to
1 Module # 10 Component # 2 Abiotic Structural Components Introduction The abiotic aspects of the ecosystem are often neglected in ecological studies. Therefore, this entire component will be devoted to
Chapter 21: Plant Structure & Function
 Chapter 21: Plant Structure & Function Chapter 21: Plant Structure & Function All organisms must: Take in certain materials, e.g. O 2, food, drink Eliminate other materials, e.g. CO 2, waste products Chapter
Chapter 21: Plant Structure & Function Chapter 21: Plant Structure & Function All organisms must: Take in certain materials, e.g. O 2, food, drink Eliminate other materials, e.g. CO 2, waste products Chapter
Ecology - the study of how living things interact with each other and their environment
 Ecology Ecology - the study of how living things interact with each other and their environment Biotic Factors - the living parts of a habitat Abiotic Factors - the non-living parts of a habitat examples:
Ecology Ecology - the study of how living things interact with each other and their environment Biotic Factors - the living parts of a habitat Abiotic Factors - the non-living parts of a habitat examples:
Recap. Waxy layer which protects the plant & conserves water. Contains chloroplasts: Specialized for light absorption.
 Recap Contains chloroplasts: Specialized for light absorption Waxy layer which protects the plant & conserves water mesophyll Layer contains air spaces: Specialized for gas exchange Vascular Tissue Exchange
Recap Contains chloroplasts: Specialized for light absorption Waxy layer which protects the plant & conserves water mesophyll Layer contains air spaces: Specialized for gas exchange Vascular Tissue Exchange
Photosynthesis: Using Light to Make Food
 Chapter 7 Photosynthesis: Using Light to Make Food Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fourth Edition Eric Simon, Jane Reece, and
Chapter 7 Photosynthesis: Using Light to Make Food Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fourth Edition Eric Simon, Jane Reece, and
Transport, Storage and Gas Exchange in Flowering Plants
 Sixth Year Biology Transport, Storage and Gas Exchange in Flowering Plants Miss Rochford In this topic: Uptake and transport of: Water and minerals Carbon dioxide Gas exchange Transport of photosynthesis
Sixth Year Biology Transport, Storage and Gas Exchange in Flowering Plants Miss Rochford In this topic: Uptake and transport of: Water and minerals Carbon dioxide Gas exchange Transport of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis: Life from Light and Air. Regents Biology
 Photosynthesis: Life from Light and Air Plants are energy producers Like animals, plants need energy to live unlike animals, plants don t need to eat food to make that energy Plants make both FOOD & ENERGY
Photosynthesis: Life from Light and Air Plants are energy producers Like animals, plants need energy to live unlike animals, plants don t need to eat food to make that energy Plants make both FOOD & ENERGY
Animal Form & Function Lecture 10 Winter 2014
 Animal Form & Function Lecture 10 Winter 2014 Physical Constraints on Form & Function 1 Anatomy & physiology (define) Environmental constraints on form Convergent evolution Larger organisms Need thicker
Animal Form & Function Lecture 10 Winter 2014 Physical Constraints on Form & Function 1 Anatomy & physiology (define) Environmental constraints on form Convergent evolution Larger organisms Need thicker
Introduction to Plant Transport
 Introduction to Plant Transport The algal ancestors of plants were completely immersed in water and dissolved minerals. What would be the advantages to living on the land? What would be the problems? This
Introduction to Plant Transport The algal ancestors of plants were completely immersed in water and dissolved minerals. What would be the advantages to living on the land? What would be the problems? This
Name AP Biology - Lab 06
 LAB 06 Transpiration Objectives: To understand how water moves from roots to leaves in terms of the physical/chemical properties of water and the forces provided by differences in water potential. To test
LAB 06 Transpiration Objectives: To understand how water moves from roots to leaves in terms of the physical/chemical properties of water and the forces provided by differences in water potential. To test
Section A2: The Pathways of Photosynthesis
 CHAPTER 10 PHOTOSYNTHESIS Section A2: The Pathways of Photosynthesis 4. The Calvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH to convert CO2 to sugar: a closer look 5. Alternative mechanisms of carbon fixation have evolved
CHAPTER 10 PHOTOSYNTHESIS Section A2: The Pathways of Photosynthesis 4. The Calvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH to convert CO2 to sugar: a closer look 5. Alternative mechanisms of carbon fixation have evolved
Photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants make food using carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll.
 Name: 2.2 Cell Metabolism Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 2.2.4 Photosynthesis 1. Define the term: photosynthesis. 2. Express photosynthesis as a balanced reaction..
Name: 2.2 Cell Metabolism Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 2.2.4 Photosynthesis 1. Define the term: photosynthesis. 2. Express photosynthesis as a balanced reaction..
Plant form and function. Photosynthesis Phloem Plant Nutrition
 Plant form and function Photosynthesis Phloem Plant Nutrition Photosynthetic Water Use Efficiency Fundamental plant problem: Stomata: pathway for diffusion of CO 2 into leaves is the same as the pathway
Plant form and function Photosynthesis Phloem Plant Nutrition Photosynthetic Water Use Efficiency Fundamental plant problem: Stomata: pathway for diffusion of CO 2 into leaves is the same as the pathway
Photosynthesis (Chapter 7 Outline) A. For life based on organic compounds, two questions can be raised:
 Photosynthesis (Chapter 7 Outline) Sun, Rain, and Survival A. For life based on organic compounds, two questions can be raised: 1. Where does the carbon come from? 2. Where does the energy come from to
Photosynthesis (Chapter 7 Outline) Sun, Rain, and Survival A. For life based on organic compounds, two questions can be raised: 1. Where does the carbon come from? 2. Where does the energy come from to
Class XII Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Biology
 Question 1: How is diapause different from hibernation? Diapause is a stage of suspended development to cope with unfavourable conditions. Many species of Zooplankton and insects exhibit diapause to tide
Question 1: How is diapause different from hibernation? Diapause is a stage of suspended development to cope with unfavourable conditions. Many species of Zooplankton and insects exhibit diapause to tide
Photosynthesis: Life from Light and Air
 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wi60tqa8jfe Photosynthesis: Life from Light and Air 2011-2012 Energy needs of life All life needs a constant input of energy consumers producers Heterotrophs (Animals) obtain
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wi60tqa8jfe Photosynthesis: Life from Light and Air 2011-2012 Energy needs of life All life needs a constant input of energy consumers producers Heterotrophs (Animals) obtain
Transport of substances in plants
 Transport of substances in plants We have already looked at why many organisms need transport systems with special reference to surface area and volume. The larger the volume : surface area ratio, the
Transport of substances in plants We have already looked at why many organisms need transport systems with special reference to surface area and volume. The larger the volume : surface area ratio, the
2/22/ Photosynthesis & The Greenhouse Effect. 4.1 The Greenhouse Effect. 4.2 The Flow of Carbon
 4.1 Photosynthesis & The Greenhouse Effect Solar radiation warms the Earth. Most radiates back into space. Only 2% is captured for use by plants Nearly all life depends on that 2%! Earth Sun rays 2% captured
4.1 Photosynthesis & The Greenhouse Effect Solar radiation warms the Earth. Most radiates back into space. Only 2% is captured for use by plants Nearly all life depends on that 2%! Earth Sun rays 2% captured
BIOL 221 Concepts of Botany Spring Water Relations, Osmosis and Transpiration
 BIOL 221 Concepts of Botany Spring 2008 Topic 07: Water Relations, Osmosis and Transpiration A. Water Relations Water plays a critical role in plants. Water is the universal solvent that allows biochemical
BIOL 221 Concepts of Botany Spring 2008 Topic 07: Water Relations, Osmosis and Transpiration A. Water Relations Water plays a critical role in plants. Water is the universal solvent that allows biochemical
Bio 10 Lecture Notes 7: Plant Diversity, Structure and Function SRJC
 Physiology study of the adaptations by which organisms function in their environ. 1.) Plants, Tissues and Function Plant types and their evolution Terrestrial plants evolved from aquatic green algae There
Physiology study of the adaptations by which organisms function in their environ. 1.) Plants, Tissues and Function Plant types and their evolution Terrestrial plants evolved from aquatic green algae There
Overview - the process that feeds the biosphere. Photosynthesis: transformation of solar energy into chemical energy.
 Chapter 7 Capturing Solar Energy: Photosynthesis Overview - the process that feeds the biosphere Photosynthesis: transformation of solar energy into chemical energy. Responsible for O 2 in our atmosphere
Chapter 7 Capturing Solar Energy: Photosynthesis Overview - the process that feeds the biosphere Photosynthesis: transformation of solar energy into chemical energy. Responsible for O 2 in our atmosphere
TRANSPIRATION. An important regulator of transpiration is the stomatal complex composed of the opening or
 BIOL 1134 1 TRANSPIRATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES After completing this exercise, students should be able to: Describe the process of and principles behind transpiration. Describe how stomata, guard cells,
BIOL 1134 1 TRANSPIRATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES After completing this exercise, students should be able to: Describe the process of and principles behind transpiration. Describe how stomata, guard cells,
What makes water so special?
 What makes water so special? Water A water molecule (H 2 O), is made up of three atoms --- one oxygen and two hydrogen. H O H Atom review Bonding review Animations on atomic bonding So what makes water
What makes water so special? Water A water molecule (H 2 O), is made up of three atoms --- one oxygen and two hydrogen. H O H Atom review Bonding review Animations on atomic bonding So what makes water
Section 1 The Light Reactions. Section 2 The Calvin Cycle. Resources
 How to Use This Presentation To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects select View on the menu bar and click on Slide Show. To advance through the presentation, click the right-arrow key or
How to Use This Presentation To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects select View on the menu bar and click on Slide Show. To advance through the presentation, click the right-arrow key or
Water and the Fitness of the Environment
 Water and the Fitness of the Environment A water molecule can form hydrogen bond with 4 neighbor molecules of water: -polar molecule -cohesive molecule -high surface tension -good solvent -high specific
Water and the Fitness of the Environment A water molecule can form hydrogen bond with 4 neighbor molecules of water: -polar molecule -cohesive molecule -high surface tension -good solvent -high specific
Biology: Life on Earth
 Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 1 An Introduction to Life on Earth Section 1.3 Outline 1.3 What Are the Characteristics of Living Things? Living Things Are Both Complex, Organized,
Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 1 An Introduction to Life on Earth Section 1.3 Outline 1.3 What Are the Characteristics of Living Things? Living Things Are Both Complex, Organized,
Physiology and Behaviour I. Dr Mike Wride School of Natural Sciences Zoology Department
 Physiology and Behaviour I Dr Mike Wride School of Natural Sciences Zoology Department email: wridem@tcd.ie Two Lectures Physiology and Behaviour I: Physiological mechanisms - hormones and behaviour, the
Physiology and Behaviour I Dr Mike Wride School of Natural Sciences Zoology Department email: wridem@tcd.ie Two Lectures Physiology and Behaviour I: Physiological mechanisms - hormones and behaviour, the
Chapter 10 Photosynthesis
 Chapter 10 Photosynthesis Overview: The Process That Feeds the Biosphere Photosynthesis is the process that converts solar energy into chemical energy Photosynthesis occurs in plants, algae, certain other
Chapter 10 Photosynthesis Overview: The Process That Feeds the Biosphere Photosynthesis is the process that converts solar energy into chemical energy Photosynthesis occurs in plants, algae, certain other
Why Water Is Your Friend
 Why Water Is Your Friend Water has several properties which make life possible. Transparency Cohesion Capillary action Surface tension: watch this Fluid nature Temperature buffer Solvent ability 2.A.3.a.3.
Why Water Is Your Friend Water has several properties which make life possible. Transparency Cohesion Capillary action Surface tension: watch this Fluid nature Temperature buffer Solvent ability 2.A.3.a.3.
From smallest to largest plants
 Plant anatomy From smallest to largest plants What is plant anatomy? ANATOMY: study of the structure of organisms looking at cells, tissues How can water move from the ground all the way to the top of
Plant anatomy From smallest to largest plants What is plant anatomy? ANATOMY: study of the structure of organisms looking at cells, tissues How can water move from the ground all the way to the top of
Welcome to the Iowa Certified Nursery Professional Training program Module 2: How Plants Work: Plant Growth and Development.
 Welcome to the Iowa Certified Nursery Professional Training program Module 2: How Plants Work: Plant Growth and Development. 1 Upon completion of this module, you will be able to fulfill each of the objectives
Welcome to the Iowa Certified Nursery Professional Training program Module 2: How Plants Work: Plant Growth and Development. 1 Upon completion of this module, you will be able to fulfill each of the objectives
CHAPTER TRANSPORT
 CHAPTER 2 2.4 TRANSPORT Uptake of CO2 FOCUS: Uptake and transport of water and mineral salts Transport of organic substances Physical forces drive the transport of materials in plants over a range of distances
CHAPTER 2 2.4 TRANSPORT Uptake of CO2 FOCUS: Uptake and transport of water and mineral salts Transport of organic substances Physical forces drive the transport of materials in plants over a range of distances
Ecosystem: Ecology Abiotic Biotic Micro-organism Producers Consumers Photosynthesis Decomposers herbivores
 Ecosystem Ecosystem: Ecology Abiotic Biotic Micro-organism Producers Consumers Photosynthesis Decomposers herbivores Carnivores Omnivores Ectodermic Endothermic Transpiration Terrestrial Aquatic Xerophytes
Ecosystem Ecosystem: Ecology Abiotic Biotic Micro-organism Producers Consumers Photosynthesis Decomposers herbivores Carnivores Omnivores Ectodermic Endothermic Transpiration Terrestrial Aquatic Xerophytes
Semester 1 Study Guide Name Period
 2017-2018 Semester 1 Study Guide Name Period Chapter 1: Scientific Method and Microscopes (p. 2-31 and A-1 through A-17) Vocab: experiment, hypothesis, scientific theory, scientific law, controlled experiment,
2017-2018 Semester 1 Study Guide Name Period Chapter 1: Scientific Method and Microscopes (p. 2-31 and A-1 through A-17) Vocab: experiment, hypothesis, scientific theory, scientific law, controlled experiment,
