Table of plasmids and yeast strains and their relation to the laboratory database
|
|
|
- Albert Floyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 209 Appendix Table of plasmids and yeast strains and their relation to the laboratory database All plasmids (maintained in bacteria) and yeast strains described in this thesis are listed in the following table. They appear with their respective plasmid stock and yeast strain numbers in the Smolke laboratory database. Unless indicated in the database, all plasmid stocks are maintained in the E. coli DH10B strain and/or the S. cerevisiae W303 strain. Different nomenclatures were utilized in the initial creation of the plasmids/strains (as they appear in the database) and in the text of this thesis. The name as they appear in the thesis is found in the column and the name as they appear in the database can be found in the column. The column contains the s in which the indicated plasmids/strains appear in the thesis.
2 Plasmid modified prs316 II prs316 (low-copy, URA3 selection) with GAL1 promoter 8 prs316 II low-copy, URA3 selection pkw430 V high-copy, ADH1 promoter, URA3 selection, contains NLS-NES-GFP 37 psva13 II, V yegfp3 source 55 prsetb/ mrfp1 59 pcs59 V prfp V yegfp3-mrfp1 V 101 pcs101, mrfp1-yegfp3 V V mrfp1 source modified ADH1 promoter of pcs13 (modified to have one transcript start site), created by Maung Win pcs59/mrfp1: monocistronic mrfp1, high-copy, ADH1 pcs59/gfp/rfp: dicistronic yegfp3-mrfp1, high-copy, ADH1 pcs59/rfp/gfp: dicistronic mrfp1-yegfp3, high-copy, ADH1, incorrect IR sequence 141 pmela V MEL1 source pcs165 V pcs59/mrfp1/mel1: dicistronic mrfp1-mel1, high-copy, ADH1, incorrect IR sequence pcs182 II pcs4/yegfp3: monocistronic yegfp3, low-copy, GAL1 promoter, no terminator, URA3 selection 270 pug6 II integration cassette with kanamycin resistance selection marker pmel1, pm V pcs59/mel1: monocistronic MEL1 vector, high-copy, ADH pcs321, no insert II, III, pcs182 with ADH1 terminator IV included downstream of yegfp pr-yap1-m, YAP1 V pcs165/yap1: YAP1 IRES placed in IR (correct IR sequence) prm V pcs59/mrfp1/mel1: dicistronic mrfp1-mel1, high-copy, ADH1 (corrected IR sequence) pr-ires47x5-m, x5 V pcs471/ires47x5: 5 modules of IRES47 in IR 256 pr-ires47x6-m, x6 V pcs471/ires47x6: 6 modules of IRES47 in IR 257 pr-ires47x7-m, x7 V pcs471/ires47x7: 7 modules of IRES47 in IR RS IV pcs321/tr2_12: working theophyline Rnt1p switch
3 Plasmid RSN IV pcs321/tr2_12_neg: mutated tetraloop (CAUC) 206 RSnt IV pcs321/tr2_12_no_theo: inactive theophylline aptamer pcs59/rfp/ypet: dicistronic 1192 pcs1192 V mrfp1-ypet, high-copy, ADH pcypet V pcs59/cypet: monocistronic CyPET, high-copy, ADH pypet V pcs59/ypet: monocistronic YPET, high-copy, ADH1 promoter, URA3 selection RSx2 IV pcs321/tr2_12x2: two modules of TR2_12 in tandem pcyy V pcs59/cypet/ypet: dicistronic CyPET-YPET, high-copy, ADH RSx3 IV pcs321/tr2_12x3: three modules of TR2_12 in tandem 1333 pbad33/ypet V YPET source 1334 pbad33/cypet V CyPET source 1418 prnt1 II, III, pproex/rnt1p: Rnt1p expression IV plasmid 1682 pcs321-erg9 II pcs321/erg9: yegfp3 replaced by ERG modified pug6 II pug6 XhoI mutant (XhoI site changed to CTGGAG) 1813 pcs1813 II pcs1717/erg9: ERG9 cloned upstream of first loxp site RS-B05 IV pcs321/tr2-bind RS-B06 IV pcs321/tr2-bind RS-B07 IV pcs321/tr2-bind RS-B17 IV pcs321/tr2-bind RS-B07x2 IV pcs321/tr2-bind7x RS-B17x2 IV pcs321/tr2-bind17x2 3 wild-type strain, W303 II, III, IV, V 329 A01 (GFP) II pcs321/r2 330 A02, A02-B00 (GFP) II, III, IV pcs321/r3 791 C01 (GFP) II pcs321/a1 792 C02 (GFP) II pcs321/a8 793 C03 (GFP) II pcs321/b1 794 C04 (GFP) II pcs321/b4 795 C05 (GFP) II pcs321/b7 796 C06 (GFP) II pcs321/b10 W303 (MATa, his3-11,15 trp1-1 leu2-3 ura3-1 ade2-1)
4 212 Plasmid 797 C07 (GFP) II pcs321/b C08 (GFP) II pcs321/c2 799 C09 (GFP) II pcs321/c6 800 C10 (GFP) II pcs321/c C11 (GFP) II pcs321/c C12 (GFP) II pcs321/d3 331 C13, C13-B00 (GFP) II, III pcs321/d6 803 C14 (GFP) II pcs321/d A01 (GFP) (CAUC) II pcs321/r2_neg 468 A02, A02-B00 (GFP) (CAUC) II, III pcs321/r3_neg 469 C01 (GFP) (CAUC) II pcs321/d6_neg 753 C02 (GFP) (CAUC) II pcs321/a1_neg 754 C03 (GFP) (CAUC) II pcs321/a8_neg 755 C04 (GFP) (CAUC) II pcs321/b1_neg 756 C05 (GFP) (CAUC) II pcs321/b4_neg 474 C06 (GFP) (CAUC) II pcs321/b7_neg 757 C07 (GFP) (CAUC) II pcs321/b10_neg 475 C08 (GFP) (CAUC) II pcs321/b11_neg 758 C09 (GFP) (CAUC) II pcs321/c2_neg 759 C10 (GFP) (CAUC) II pcs321/c6_neg 760 C11 (GFP) (CAUC) II pcs321/c10_neg 479 C12 (GFP) (CAUC) II pcs321/c11_neg 761 C13, C13-B00 (GFP) (CAUC) II, III pcs321/d3_neg 762 C14 (GFP) (CAUC) II pcs321/d10_neg 605 no insert (ERG9) II ERG9::ERG9-AvrII-XhoI-ADH1tkanMX (ERG9 3' UTR replacement) 606 C13-B01 III pcs321/d6_p C13-B02 III pcs321/d6_p C13-B03 III pcs321/d6_p A02-B01 III pcs321/r3_p A02-B02 III pcs321/r3_p A02-B03 III, IV pcs321/r3_p RS-B03 IV pcs321/tr2_p A02-B04 III pcs321/r3-bind2 649 A02-B05 III, IV pcs321/r3-bind4 650 A02-B06 III, IV pcs321/r3-bind5 651 A02-B07 III, IV pcs321/r3-bind6
5 213 Plasmid 652 A02-B08 III pcs321/r3-bind7 653 A02-B09 III pcs321/r3-bind8 654 A02-B10 III pcs321/r3-bind A02-B11 III pcs321/r3-bind A02-B12 III, IV pcs321/r3-bind A02-B13 III pcs321/r3-bind A02-B14 III pcs321/r3-bind A02-B15 III pcs321/r3-bind A02-B04 (CAUC) III pcs321/r3-bind2n 661 A02-B05 (CAUC) III pcs321/r3-bind4n 662 A02-B06 (CAUC) III pcs321/r3-bind5n 667 A01 (ERG9) II ERG9::ERG9-R2-ADH1t-kanMX 668 C13-GA3 (ERG9) II ERG9::ERG9-GA3-ADH1t-kanMX 669 C06 (ERG9) II ERG9::ERG9-B10-ADH1t-kanMX 670 C07 (ERG9) II ERG9::ERG9-B11-ADH1t-kanMX 671 C13-B04 III pcs321/d6-bind2 672 C13-B05 III pcs321/d6-bind4 673 C13-B06 III pcs321/d6-bind5 674 C13-B07 III pcs321/d6-bind6 675 C13-B08 III pcs321/d6-bind7 676 C13-B09 III pcs321/d6-bind8 677 C13-B10 III pcs321/d6-bind C13-B11 III pcs321/d6-bind C13-B12 III pcs321/d6-bind C13-B13 III pcs321/d6-bind C13-B14 III pcs321/d6-bind C13-B15 III pcs321/d6-bind A02 (ERG9) II ERG9::ERG9-R3-ADH1t-kanMX 692 C10 (ERG9) II ERG9::ERG9-C10-ADH1t-kanMX 693 C08 (ERG9) II ERG9::ERG9-C2-ADH1t-kanMX 694 C13-B00 (GAAA) III pcs321/d6 (GA3) 695 A02-B00 (GAAA) III pcs321/r3 (GA3) 702 RS-theo2 IV pcs321/tr2_theo2 704 RS-theo3 IV pcs321/tr2_theo4 763 A01 (mcherry) II pcs1749/r2 764 A02 (mcherry) II pcs1749/r3 765 C01 (mcherry) II pcs1749/a1 766 C02 (mcherry) II pcs1749/a8
6 Plasmid C03 (mcherry) II pcs1749/b1 768 C04 (mcherry) II pcs1749/b4 769 C05 (mcherry) II pcs1749/b7 770 C06 (mcherry) II pcs1749/b C07 (mcherry) II pcs1749/b C08 (mcherry) II pcs1749/c2 773 C09 (mcherry) II pcs1749/c6 774 C10 (mcherry) II pcs1749/c C11 (mcherry) II pcs1749/c C12 (mcherry) II pcs1749/d3 777 C13 (mcherry) II pcs1749/d6 778 C14 (mcherry) II pcs1749/d pcs1749 II monocistronic ymcherry, TEF1 promoter, CYC1 terminator, lowcopy, URA3 selection, created by Joe Liang 1585 pcs1585 III monocistronic yegfp3, TEF1 promoter, ADH1 terminator, lowcopy, URA3 selection, created by Joe Liang 1748 pcs1748 III contains the ymcherry and yegfp3 ORFs of pcs1749 and yegfp3, low-copy, URA3 selection, created by Joe Liang
cote cote-yfp spc This work cote cote-yfp spc This work cote cote-yfp spc This work cote cote-yfp spc This work cote cote-yfp spc This work
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Table S1. List of strains Strains Genotype Source B. subtilis PY79 Prototrophic derivative of B. subtilis 168 (60) RL1070 spovid::kan (12) HS176 cotz phs2 (cotz-gfp spc) (22)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Table S1. List of strains Strains Genotype Source B. subtilis PY79 Prototrophic derivative of B. subtilis 168 (60) RL1070 spovid::kan (12) HS176 cotz phs2 (cotz-gfp spc) (22)
Stochastic simulations
 Stochastic simulations Application to molecular networks Literature overview Noise in genetic networks Origins How to measure and distinguish between the two types of noise (intrinsic vs extrinsic)? What
Stochastic simulations Application to molecular networks Literature overview Noise in genetic networks Origins How to measure and distinguish between the two types of noise (intrinsic vs extrinsic)? What
Eukaryotic Gene Expression
 Eukaryotic Gene Expression Lectures 22-23 Several Features Distinguish Eukaryotic Processes From Mechanisms in Bacteria 123 Eukaryotic Gene Expression Several Features Distinguish Eukaryotic Processes
Eukaryotic Gene Expression Lectures 22-23 Several Features Distinguish Eukaryotic Processes From Mechanisms in Bacteria 123 Eukaryotic Gene Expression Several Features Distinguish Eukaryotic Processes
Analysis and modelling of protein interaction networks
 Analysis and modelling of protein interaction networks - A study of the two-hybrid experiment Karin Stibius Jensen Analysis and modelling of protein interaction networks - A study of the two-hybrid experiment
Analysis and modelling of protein interaction networks - A study of the two-hybrid experiment Karin Stibius Jensen Analysis and modelling of protein interaction networks - A study of the two-hybrid experiment
Mini-Tn7 Derivative Construction and Characterization. Mini-Tn7 derivatives for
 Supplemental Methods Mini-Tn7 Derivative Construction and Characterization. Mini-Tn7 derivatives for constitutive expression of fluorescent proteins in S. oneidensis were constructed as follows. The EcoRI-XbaI
Supplemental Methods Mini-Tn7 Derivative Construction and Characterization. Mini-Tn7 derivatives for constitutive expression of fluorescent proteins in S. oneidensis were constructed as follows. The EcoRI-XbaI
AP Bio Module 16: Bacterial Genetics and Operons, Student Learning Guide
 Name: Period: Date: AP Bio Module 6: Bacterial Genetics and Operons, Student Learning Guide Getting started. Work in pairs (share a computer). Make sure that you log in for the first quiz so that you get
Name: Period: Date: AP Bio Module 6: Bacterial Genetics and Operons, Student Learning Guide Getting started. Work in pairs (share a computer). Make sure that you log in for the first quiz so that you get
Post-termination ribosome interactions with the 5 UTR modulate yeast mrna stability
 The EMBO Journal Vol.18 No.11 pp.3139 3152, 1999 Post-termination ribosome interactions with the 5 UTR modulate yeast mrna stability Cristina Vilela 1,2, Carmen Velasco Ramirez 1, Bodo Linz 1, Claudina
The EMBO Journal Vol.18 No.11 pp.3139 3152, 1999 Post-termination ribosome interactions with the 5 UTR modulate yeast mrna stability Cristina Vilela 1,2, Carmen Velasco Ramirez 1, Bodo Linz 1, Claudina
A complementation test would be done by crossing the haploid strains and scoring the phenotype in the diploids.
 Problem set H answers 1. To study DNA repair mechanisms, geneticists isolated yeast mutants that were sensitive to various types of radiation; for example, mutants that were more sensitive to UV light.
Problem set H answers 1. To study DNA repair mechanisms, geneticists isolated yeast mutants that were sensitive to various types of radiation; for example, mutants that were more sensitive to UV light.
2. Yeast two-hybrid system
 2. Yeast two-hybrid system I. Process workflow a. Mating of haploid two-hybrid strains on YPD plates b. Replica-plating of diploids on selective plates c. Two-hydrid experiment plating on selective plates
2. Yeast two-hybrid system I. Process workflow a. Mating of haploid two-hybrid strains on YPD plates b. Replica-plating of diploids on selective plates c. Two-hydrid experiment plating on selective plates
Supplementary information Supplementary figures
 Supplementary information Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1. Quantitation by FCS of GFP-tagged proteasomes in supernatant of cell extract (a) In vitro assay for evaluation of the hydrodynamic
Supplementary information Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1. Quantitation by FCS of GFP-tagged proteasomes in supernatant of cell extract (a) In vitro assay for evaluation of the hydrodynamic
the noisy gene Biology of the Universidad Autónoma de Madrid Jan 2008 Juan F. Poyatos Spanish National Biotechnology Centre (CNB)
 Biology of the the noisy gene Universidad Autónoma de Madrid Jan 2008 Juan F. Poyatos Spanish National Biotechnology Centre (CNB) day III: noisy bacteria - Regulation of noise (B. subtilis) - Intrinsic/Extrinsic
Biology of the the noisy gene Universidad Autónoma de Madrid Jan 2008 Juan F. Poyatos Spanish National Biotechnology Centre (CNB) day III: noisy bacteria - Regulation of noise (B. subtilis) - Intrinsic/Extrinsic
Promoter Sequence Determines the Relationship between Expression Level and Noise
 Promoter Sequence Determines the Relationship between Expression Level and Noise Lucas. Carey 1., David van Dijk 1,3., Peter M. A. Sloot 2,3, Jaap A. Kaandorp 3, Eran Segal 1 * 1 Department of Computer
Promoter Sequence Determines the Relationship between Expression Level and Noise Lucas. Carey 1., David van Dijk 1,3., Peter M. A. Sloot 2,3, Jaap A. Kaandorp 3, Eran Segal 1 * 1 Department of Computer
EST1 Homology Domain. 100 aa. hest1a / SMG6 PIN TPR TPR. Est1-like DBD? hest1b / SMG5. TPR-like TPR. a helical. hest1c / SMG7.
 hest1a / SMG6 EST1 Homology Domain 100 aa 853 695 761 780 1206 hest1 / SMG5 -like? -like 109 145 214 237 497 165 239 1016 114 207 212 381 583 hest1c / SMG7 a helical 1091 Sc 57 185 267 284 699 Figure S1:
hest1a / SMG6 EST1 Homology Domain 100 aa 853 695 761 780 1206 hest1 / SMG5 -like? -like 109 145 214 237 497 165 239 1016 114 207 212 381 583 hest1c / SMG7 a helical 1091 Sc 57 185 267 284 699 Figure S1:
Introduction. Gene expression is the combined process of :
 1 To know and explain: Regulation of Bacterial Gene Expression Constitutive ( house keeping) vs. Controllable genes OPERON structure and its role in gene regulation Regulation of Eukaryotic Gene Expression
1 To know and explain: Regulation of Bacterial Gene Expression Constitutive ( house keeping) vs. Controllable genes OPERON structure and its role in gene regulation Regulation of Eukaryotic Gene Expression
Genetically Engineering Yeast to Understand Molecular Modes of Speciation
 Genetically Engineering Yeast to Understand Molecular Modes of Speciation Mark Umbarger Biophysics 242 May 6, 2004 Abstract: An understanding of the molecular mechanisms of speciation (reproductive isolation)
Genetically Engineering Yeast to Understand Molecular Modes of Speciation Mark Umbarger Biophysics 242 May 6, 2004 Abstract: An understanding of the molecular mechanisms of speciation (reproductive isolation)
Stochastic simulations!
 Stochastic simulations! Application to biomolecular networks! Literature overview Noise in genetic networks! Origins! How to measure the noise and distinguish between the two sources of noise (intrinsic
Stochastic simulations! Application to biomolecular networks! Literature overview Noise in genetic networks! Origins! How to measure the noise and distinguish between the two sources of noise (intrinsic
P. syringae and E. coli
 CHAPTER 6 A comparison of the recd mutant phenotypes of P. syringae and E. coli 6.1 INTRODUCTION The RecBCD complex is essential for recombination mediated repair of double strand breaks (DSBs) of DNA
CHAPTER 6 A comparison of the recd mutant phenotypes of P. syringae and E. coli 6.1 INTRODUCTION The RecBCD complex is essential for recombination mediated repair of double strand breaks (DSBs) of DNA
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.12 GENE REGULATION IN PROKARYOTES.
 GEETICS - CLUTCH CH.12 GEE REGULATIO I PROKARYOTES!! www.clutchprep.com GEETICS - CLUTCH CH.12 GEE REGULATIO I PROKARYOTES COCEPT: LAC OPERO An operon is a group of genes with similar functions that are
GEETICS - CLUTCH CH.12 GEE REGULATIO I PROKARYOTES!! www.clutchprep.com GEETICS - CLUTCH CH.12 GEE REGULATIO I PROKARYOTES COCEPT: LAC OPERO An operon is a group of genes with similar functions that are
Supporting Information
 1 Supporting Information 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1 1 1 15 16 17 Sequences: E. coli lysine riboswitch (ECRS): GTACTACCTGCGCTAGCGCAGGCCAGAAGAGGCGCGTTGCCCAAGTAACGGTGTTGGAGGAGCCAG TCCTGTGATAACACCTGAGGGGGTGCATCGCCGAGGTGATTGAACGGCTGGCCACGTTCATCATCGG
1 Supporting Information 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1 1 1 15 16 17 Sequences: E. coli lysine riboswitch (ECRS): GTACTACCTGCGCTAGCGCAGGCCAGAAGAGGCGCGTTGCCCAAGTAACGGTGTTGGAGGAGCCAG TCCTGTGATAACACCTGAGGGGGTGCATCGCCGAGGTGATTGAACGGCTGGCCACGTTCATCATCGG
Bypass and interaction suppressors; pathway analysis
 Bypass and interaction suppressors; pathway analysis The isolation of extragenic suppressors is a powerful tool for identifying genes that encode proteins that function in the same process as a gene of
Bypass and interaction suppressors; pathway analysis The isolation of extragenic suppressors is a powerful tool for identifying genes that encode proteins that function in the same process as a gene of
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Purification of yeast CKM. (a) Silver-stained SDS-PAGE analysis of CKM purified through a TAP-tag engineered into the Cdk8 C-terminus. (b) Kinase activity
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Purification of yeast CKM. (a) Silver-stained SDS-PAGE analysis of CKM purified through a TAP-tag engineered into the Cdk8 C-terminus. (b) Kinase activity
Gene expression in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, Plasmids: types, maintenance and functions. Mitesh Shrestha
 Gene expression in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, Plasmids: types, maintenance and functions. Mitesh Shrestha Plasmids 1. Extrachromosomal DNA, usually circular-parasite 2. Usually encode ancillary
Gene expression in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, Plasmids: types, maintenance and functions. Mitesh Shrestha Plasmids 1. Extrachromosomal DNA, usually circular-parasite 2. Usually encode ancillary
1. YEAST STRAINS AND PLASMIDS SINGLE CELL MICROSCOPY CALCULATION OF TOTAL FLUORESCENCE...6
 Supplementary Materials to Colman-Lerner et al. 1 1. YEAST STRAINS AND PLASMIDS...3 1.1 Strains...3 1.2 Plasmids...4 2 SINGLE CELL MICROSCOPY...5 3 CALCULATION OF TOTAL FLUORESCENCE...6 4 DEFINING PATHWAY
Supplementary Materials to Colman-Lerner et al. 1 1. YEAST STRAINS AND PLASMIDS...3 1.1 Strains...3 1.2 Plasmids...4 2 SINGLE CELL MICROSCOPY...5 3 CALCULATION OF TOTAL FLUORESCENCE...6 4 DEFINING PATHWAY
Supplemental Table 1: Strains used in this study
 Supplemental Table : Strains used in this study Name Parent Genotype Reference GA-8 MATa, ade-; can-; his3-,5; trp-; ura3-; leu-3, W33-A GA-3 GA-8 his3-,5::gfp-laci-his3, NUP49::GFP-NUP49-URA3 [] GA-46
Supplemental Table : Strains used in this study Name Parent Genotype Reference GA-8 MATa, ade-; can-; his3-,5; trp-; ura3-; leu-3, W33-A GA-3 GA-8 his3-,5::gfp-laci-his3, NUP49::GFP-NUP49-URA3 [] GA-46
Ti plasmid derived plant vector systems: binary and co - integrative vectors transformation process; regeneration of the transformed lines
 Ti plasmid derived plant vector systems: binary and co - integrative vectors transformation process; regeneration of the transformed lines Mitesh Shrestha Constraints of Wild type Ti/Ri-plasmid Very large
Ti plasmid derived plant vector systems: binary and co - integrative vectors transformation process; regeneration of the transformed lines Mitesh Shrestha Constraints of Wild type Ti/Ri-plasmid Very large
Sequential and Distinct Roles of the Cadherin Domain-containing Protein Axl2p in
 Sequential and Distinct Roles of the Cadherin Domain-containing Protein Axl2p in Cell Polarization in Yeast Cell Cycle Xiang-Dong Gao *, Lauren M. Sperber *, Steven A. Kane *, Zongtian Tong *, Amy Hin
Sequential and Distinct Roles of the Cadherin Domain-containing Protein Axl2p in Cell Polarization in Yeast Cell Cycle Xiang-Dong Gao *, Lauren M. Sperber *, Steven A. Kane *, Zongtian Tong *, Amy Hin
Regulation of Gene Expression in Bacteria and Their Viruses
 11 Regulation of Gene Expression in Bacteria and Their Viruses WORKING WITH THE FIGURES 1. Compare the structure of IPTG shown in Figure 11-7 with the structure of galactose shown in Figure 11-5. Why is
11 Regulation of Gene Expression in Bacteria and Their Viruses WORKING WITH THE FIGURES 1. Compare the structure of IPTG shown in Figure 11-7 with the structure of galactose shown in Figure 11-5. Why is
Control of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes
 Why? Control of Expression in Prokaryotes How do prokaryotes use operons to control gene expression? Houses usually have a light source in every room, but it would be a waste of energy to leave every light
Why? Control of Expression in Prokaryotes How do prokaryotes use operons to control gene expression? Houses usually have a light source in every room, but it would be a waste of energy to leave every light
Optimization of the heme biosynthesis pathway for the production of. 5-aminolevulinic acid in Escherichia coli
 Supplementary Information Optimization of the heme biosynthesis pathway for the production of 5-aminolevulinic acid in Escherichia coli Junli Zhang 1,2,3, Zhen Kang 1,2,3, Jian Chen 2,3 & Guocheng Du 2,4
Supplementary Information Optimization of the heme biosynthesis pathway for the production of 5-aminolevulinic acid in Escherichia coli Junli Zhang 1,2,3, Zhen Kang 1,2,3, Jian Chen 2,3 & Guocheng Du 2,4
Lecture 4: Transcription networks basic concepts
 Lecture 4: Transcription networks basic concepts - Activators and repressors - Input functions; Logic input functions; Multidimensional input functions - Dynamics and response time 2.1 Introduction The
Lecture 4: Transcription networks basic concepts - Activators and repressors - Input functions; Logic input functions; Multidimensional input functions - Dynamics and response time 2.1 Introduction The
Penghui Li, Beibei Chen, Gaoyang Zhang, Longxiang Chen, Qiang Dong, Jiangqi Wen, Kirankumar S. Mysore and Jian Zhao
 New Phytologist Supporting Information Regulation of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis by Medicago truncatula bhlh transcription factor MtTT8 Penghui Li, Beibei Chen, Gaoyang Zhang, Longxiang
New Phytologist Supporting Information Regulation of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis by Medicago truncatula bhlh transcription factor MtTT8 Penghui Li, Beibei Chen, Gaoyang Zhang, Longxiang
Supplemental Data. Gao et al. (2012). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Plant EMP Proteins. (A) The Accession numbers of the 12 EMP members from Arabidopsis. (B) Phylogenetic analysis of EMP proteins from Arabidopsis, human and yeast using the Mac Vector
Supplemental Figure 1. Plant EMP Proteins. (A) The Accession numbers of the 12 EMP members from Arabidopsis. (B) Phylogenetic analysis of EMP proteins from Arabidopsis, human and yeast using the Mac Vector
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Erlemann et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201111123/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Test for functionality of yegfp-tagged -TuSC proteins
Supplemental material Erlemann et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201111123/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Test for functionality of yegfp-tagged -TuSC proteins
Bacterial Genetics & Operons
 Bacterial Genetics & Operons The Bacterial Genome Because bacteria have simple genomes, they are used most often in molecular genetics studies Most of what we know about bacterial genetics comes from the
Bacterial Genetics & Operons The Bacterial Genome Because bacteria have simple genomes, they are used most often in molecular genetics studies Most of what we know about bacterial genetics comes from the
Welcome to Class 21!
 Welcome to Class 21! Introductory Biochemistry! Lecture 21: Outline and Objectives l Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes! l transcriptional regulation! l principles! l lac operon! l trp attenuation!
Welcome to Class 21! Introductory Biochemistry! Lecture 21: Outline and Objectives l Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes! l transcriptional regulation! l principles! l lac operon! l trp attenuation!
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/41480 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Tleis, Mohamed Title: Image analysis for gene expression based phenotype characterization
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/41480 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Tleis, Mohamed Title: Image analysis for gene expression based phenotype characterization
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005
 7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
15.2 Prokaryotic Transcription *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m52697 1 15.2 Prokaryotic Transcription * Shannon McDermott Based on Prokaryotic Transcription by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m52697 1 15.2 Prokaryotic Transcription * Shannon McDermott Based on Prokaryotic Transcription by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
Fitness constraints on horizontal gene transfer
 Fitness constraints on horizontal gene transfer Dan I Andersson University of Uppsala, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology, Uppsala, Sweden GMM 3, 30 Aug--2 Sep, Oslo, Norway Acknowledgements:
Fitness constraints on horizontal gene transfer Dan I Andersson University of Uppsala, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology, Uppsala, Sweden GMM 3, 30 Aug--2 Sep, Oslo, Norway Acknowledgements:
Protein-Protein Interactions of the Cytoplasmic Loops of the Yeast Multidrug Resistance Protein,PDR 5: A Two -Hybrid Based Analysis.
 Researcher : Rao Subba G (2001) SUMMARY Guide :Gupta,C.M.(Dr.) Protein-Protein Interactions of the Cytoplasmic Loops of the Yeast Multidrug Resistance Protein,PDR 5: A Two -Hybrid Based Analysis. Mukidrug
Researcher : Rao Subba G (2001) SUMMARY Guide :Gupta,C.M.(Dr.) Protein-Protein Interactions of the Cytoplasmic Loops of the Yeast Multidrug Resistance Protein,PDR 5: A Two -Hybrid Based Analysis. Mukidrug
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/5/eaar2740/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The fission yeast Stn1-Ten1 complex limits telomerase activity via its SUMO-interacting motif and promotes telomeres
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/5/eaar2740/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The fission yeast Stn1-Ten1 complex limits telomerase activity via its SUMO-interacting motif and promotes telomeres
4. Why not make all enzymes all the time (even if not needed)? Enzyme synthesis uses a lot of energy.
 1 C2005/F2401 '10-- Lecture 15 -- Last Edited: 11/02/10 01:58 PM Copyright 2010 Deborah Mowshowitz and Lawrence Chasin Department of Biological Sciences Columbia University New York, NY. Handouts: 15A
1 C2005/F2401 '10-- Lecture 15 -- Last Edited: 11/02/10 01:58 PM Copyright 2010 Deborah Mowshowitz and Lawrence Chasin Department of Biological Sciences Columbia University New York, NY. Handouts: 15A
Altered dosage of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae spindle pole body duplication gene, NDC1, leads to aneuploidy and polyploidy
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 96, pp. 10200 10205, August 1999 Cell Biology Altered dosage of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae spindle pole body duplication gene, NDC1, leads to aneuploidy and polyploidy
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 96, pp. 10200 10205, August 1999 Cell Biology Altered dosage of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae spindle pole body duplication gene, NDC1, leads to aneuploidy and polyploidy
Three Myosins Contribute Uniquely to the Assembly and Constriction of the Fission Yeast Cytokinetic Contractile Ring
 Current Biology Supplemental Information Three Myosins Contribute Uniquely to the Assembly and Constriction of the Fission Yeast Cytokinetic Contractile Ring Caroline Laplante, Julien Berro, Erdem Karatekin,
Current Biology Supplemental Information Three Myosins Contribute Uniquely to the Assembly and Constriction of the Fission Yeast Cytokinetic Contractile Ring Caroline Laplante, Julien Berro, Erdem Karatekin,
ACCGGTTTCGAATTGACAATTAATCATCGGCTCGTATAATGGTACC TGAAATGAGCTGTTGACAATTAATCATCCGGCTCGTATAATGTGTGG AATTGTGAGCGGATAACAATTTCACAGGTACC
 SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE S1. Promoter and riboswitch sequences used in this study. Predicted transcriptional start sites are bolded and underlined. Riboswitch sequences were obtained from Topp et al., Appl Environ
SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE S1. Promoter and riboswitch sequences used in this study. Predicted transcriptional start sites are bolded and underlined. Riboswitch sequences were obtained from Topp et al., Appl Environ
A transcription activator-like effector induction system mediated by proteolysis
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION A transcription activator-like effector induction system mediated by proteolysis Matthew F. Copeland 1,2, Mark C. Politz 1, Charles B. Johnson 1,3, Andrew L. Markley 1, Brian
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION A transcription activator-like effector induction system mediated by proteolysis Matthew F. Copeland 1,2, Mark C. Politz 1, Charles B. Johnson 1,3, Andrew L. Markley 1, Brian
CHAPTER : Prokaryotic Genetics
 CHAPTER 13.3 13.5: Prokaryotic Genetics 1. Most bacteria are not pathogenic. Identify several important roles they play in the ecosystem and human culture. 2. How do variations arise in bacteria considering
CHAPTER 13.3 13.5: Prokaryotic Genetics 1. Most bacteria are not pathogenic. Identify several important roles they play in the ecosystem and human culture. 2. How do variations arise in bacteria considering
The geneticist s questions
 The geneticist s questions a) What is consequence of reduced gene function? 1) gene knockout (deletion, RNAi) b) What is the consequence of increased gene function? 2) gene overexpression c) What does
The geneticist s questions a) What is consequence of reduced gene function? 1) gene knockout (deletion, RNAi) b) What is the consequence of increased gene function? 2) gene overexpression c) What does
EXPRESSION OF THE FIS2 PROMOTER IN ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA
 EXPRESSION OF THE FIS2 PROMOTER IN ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA Item Type text; Electronic Thesis Authors Bergstrand, Lauren Janel Publisher The University of Arizona. Rights Copyright is held by the author. Digital
EXPRESSION OF THE FIS2 PROMOTER IN ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA Item Type text; Electronic Thesis Authors Bergstrand, Lauren Janel Publisher The University of Arizona. Rights Copyright is held by the author. Digital
pvivo2-gfp/seap An innovative multigenic plasmid for high levels of expression of the GFP and SEAP reporter genes Catalog # pvivo2-gfpsp
 pvivo2-gfp/seap An innovative multigenic plasmid for high levels of expression of the GFP and SEAP reporter genes Catalog # pvivo2-gfpsp For research use only Version # 12J30-MM PRoduCT information Content:
pvivo2-gfp/seap An innovative multigenic plasmid for high levels of expression of the GFP and SEAP reporter genes Catalog # pvivo2-gfpsp For research use only Version # 12J30-MM PRoduCT information Content:
Matrix and Steiner-triple-system smart pooling assays for high-performance transcription regulatory network mapping
 Matrix and Steiner-triple-system smart pooling assays for high-performance transcription regulatory network mapping Vanessa Vermeirssen, Bart Deplancke, M Inmaculada Barrasa, John S Reece-Hoyes, H Efsun
Matrix and Steiner-triple-system smart pooling assays for high-performance transcription regulatory network mapping Vanessa Vermeirssen, Bart Deplancke, M Inmaculada Barrasa, John S Reece-Hoyes, H Efsun
Ptc1, a Type 2C Ser/Thr Phosphatase, Inactivates the HOG Pathway by Dephosphorylating the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Hog1
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Jan. 2001, p. 51 60 Vol. 21, No. 1 0270-7306/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.1.51 60.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Ptc1, a
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Jan. 2001, p. 51 60 Vol. 21, No. 1 0270-7306/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.1.51 60.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Ptc1, a
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 Activity [RLU] Activity [RLU] RAB:TALA TALA:RAB TALB:RAB RAB:TALB RAB:TALB TALB:RAB TALA:RAB RAB:TALA Activity [nrlu] Activity [nrlu] SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL a b 100 100 50 50 0 0 5 25 50 5 25 50 0 50 50
Activity [RLU] Activity [RLU] RAB:TALA TALA:RAB TALB:RAB RAB:TALB RAB:TALB TALB:RAB TALA:RAB RAB:TALA Activity [nrlu] Activity [nrlu] SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL a b 100 100 50 50 0 0 5 25 50 5 25 50 0 50 50
Puf3p binds preferentially to messenger RNAs
 Published Online: 8 January, 2007 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200606054 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on July 3, 2018 JCB: ARTICLE Puf3p, a Pumilio family RNA binding protein, localizes to
Published Online: 8 January, 2007 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200606054 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on July 3, 2018 JCB: ARTICLE Puf3p, a Pumilio family RNA binding protein, localizes to
The order and the amount of the samples: marker 10μL, 1-12M 10μL, T7 promoter 10μL, 1-12O 10μL.
 Cloning of T7 promoter + rbs + GFP + terminator 2009/6/24 10:50 Miniprep the plasmids containing T7 promoter, standard parts 1-12M and 1-12O. 1-12M: medium rbs + GFP coding gene + terminator 1-12O: strong
Cloning of T7 promoter + rbs + GFP + terminator 2009/6/24 10:50 Miniprep the plasmids containing T7 promoter, standard parts 1-12M and 1-12O. 1-12M: medium rbs + GFP coding gene + terminator 1-12O: strong
Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2014). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure1: Mock and NPA-treated tomato plants. (A) NPA treated tomato (cv. Moneymaker) developed a pin-like inflorescence (arrowhead). (B) Comparison of first and second leaves from mock and
Supplemental Figure1: Mock and NPA-treated tomato plants. (A) NPA treated tomato (cv. Moneymaker) developed a pin-like inflorescence (arrowhead). (B) Comparison of first and second leaves from mock and
Development Team. Regulation of gene expression in Prokaryotes: Lac Operon. Molecular Cell Biology. Department of Zoology, University of Delhi
 Paper Module : 15 : 23 Development Team Principal Investigator : Prof. Neeta Sehgal Department of Zoology, University of Delhi Co-Principal Investigator : Prof. D.K. Singh Department of Zoology, University
Paper Module : 15 : 23 Development Team Principal Investigator : Prof. Neeta Sehgal Department of Zoology, University of Delhi Co-Principal Investigator : Prof. D.K. Singh Department of Zoology, University
The novel fission yeast (1,3)β-D-glucan synthase catalytic subunit Bgs4p is essential during both cytokinesis and polarized growth
 Research Article 157 The novel fission yeast (1,3)β-D-glucan synthase catalytic subunit Bgs4p is essential during both cytokinesis and polarized growth Juan Carlos G. Cortés 1, Elena Carnero 1, Junpei
Research Article 157 The novel fission yeast (1,3)β-D-glucan synthase catalytic subunit Bgs4p is essential during both cytokinesis and polarized growth Juan Carlos G. Cortés 1, Elena Carnero 1, Junpei
Supplementary Information Genome architecture is a selectable trait that can be maintained by antagonistic pleiotropy
 Supplementary Information Genome architecture is a selectable trait that can be maintained by antagonistic pleiotropy Ana Teresa Avelar, Lília Perfeito, Isabel Gordo and Miguel Godinho Ferreira 1 Supplementary
Supplementary Information Genome architecture is a selectable trait that can be maintained by antagonistic pleiotropy Ana Teresa Avelar, Lília Perfeito, Isabel Gordo and Miguel Godinho Ferreira 1 Supplementary
Supporting Online Material
 Supporting Online Material 1 Materials and Methods 1.1 Strains and Plasmids All plasmids used in this study were derived from a set of yeast single integration vectors which were gifts from N. Helman and
Supporting Online Material 1 Materials and Methods 1.1 Strains and Plasmids All plasmids used in this study were derived from a set of yeast single integration vectors which were gifts from N. Helman and
Supplementary Materials for
 www.advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/5/e1500358/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Transplantability of a circadian clock to a noncircadian organism Anna H. Chen, David Lubkowicz, Vivian Yeong,
www.advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/5/e1500358/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Transplantability of a circadian clock to a noncircadian organism Anna H. Chen, David Lubkowicz, Vivian Yeong,
Lecture 18 June 2 nd, Gene Expression Regulation Mutations
 Lecture 18 June 2 nd, 2016 Gene Expression Regulation Mutations From Gene to Protein Central Dogma Replication DNA RNA PROTEIN Transcription Translation RNA Viruses: genome is RNA Reverse Transcriptase
Lecture 18 June 2 nd, 2016 Gene Expression Regulation Mutations From Gene to Protein Central Dogma Replication DNA RNA PROTEIN Transcription Translation RNA Viruses: genome is RNA Reverse Transcriptase
Organization of Genes Differs in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA Chapter 10 p
 Organization of Genes Differs in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA Chapter 10 p.110-114 Arrangement of information in DNA----- requirements for RNA Common arrangement of protein-coding genes in prokaryotes=
Organization of Genes Differs in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA Chapter 10 p.110-114 Arrangement of information in DNA----- requirements for RNA Common arrangement of protein-coding genes in prokaryotes=
Relationship between the function and the location of G1 cyclins in S. cerevisiae
 RESEARCH ARTICLE 4599 Relationship between the function and the location of G1 cyclins in S. cerevisiae Nicholas P. Edgington and Bruce Futcher* Department of Molecular Genetics and Microbiology, Life
RESEARCH ARTICLE 4599 Relationship between the function and the location of G1 cyclins in S. cerevisiae Nicholas P. Edgington and Bruce Futcher* Department of Molecular Genetics and Microbiology, Life
Leaky termination at premature stop codons antagonizes nonsense-mediated mrna decay in S. cerevisiae
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Faculty Publications in the Biological Sciences Papers in the Biological Sciences 2014 Leaky termination at premature stop
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Faculty Publications in the Biological Sciences Papers in the Biological Sciences 2014 Leaky termination at premature stop
Bacterial strains, plasmids, and growth conditions. Bacterial strains and
 I Text I Materials and Methods acterial strains, plasmids, and growth conditions. acterial strains and plasmids used in this study are listed in I Table. almonella enterica serovar Typhimurium strains
I Text I Materials and Methods acterial strains, plasmids, and growth conditions. acterial strains and plasmids used in this study are listed in I Table. almonella enterica serovar Typhimurium strains
Enhanced zinc-finger-nuclease activity with improved obligate heterodimeric architectures
 Nature Methods Enhanced zinc-finger-nuclease activity with improved obligate heterodimeric architectures Yannick Doyon, Thuy D Vo, Matthew C Mendel, Shon G Greenberg, Jianbin Wang, Danny F Xia, Jeffrey
Nature Methods Enhanced zinc-finger-nuclease activity with improved obligate heterodimeric architectures Yannick Doyon, Thuy D Vo, Matthew C Mendel, Shon G Greenberg, Jianbin Wang, Danny F Xia, Jeffrey
Origins of extrinsic variability in eukaryotic gene expression Supplementary Information
 Origins of extrinsic variability in eukaryotic gene expression Supplementary Information Dmitri Volfson 1,2,, Jennifer Y. Marciniak 1,, William J. Blake 3, Natalie Ostroff 1, Lev S. Tsimring 2 & Jeff Hasty
Origins of extrinsic variability in eukaryotic gene expression Supplementary Information Dmitri Volfson 1,2,, Jennifer Y. Marciniak 1,, William J. Blake 3, Natalie Ostroff 1, Lev S. Tsimring 2 & Jeff Hasty
Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 3 (eif3) and eif2 Can Promote mrna Binding to 40S Subunits Independently of eif4g in Yeast
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Feb. 2006, p. 1355 1372 Vol. 26, No. 4 0270-7306/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/mcb.26.4.1355 1372.2006 Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 3 (eif3) and eif2 Can Promote mrna
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Feb. 2006, p. 1355 1372 Vol. 26, No. 4 0270-7306/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/mcb.26.4.1355 1372.2006 Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 3 (eif3) and eif2 Can Promote mrna
Regulation of Gene Expression at the level of Transcription
 Regulation of Gene Expression at the level of Transcription (examples are mostly bacterial) Diarmaid Hughes ICM/Microbiology VT2009 Regulation of Gene Expression at the level of Transcription (examples
Regulation of Gene Expression at the level of Transcription (examples are mostly bacterial) Diarmaid Hughes ICM/Microbiology VT2009 Regulation of Gene Expression at the level of Transcription (examples
Introduction of Biotechnology
 Handai Cyber University Introduction of Biotechnology No.5:Genome biotechnology and yeast Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University Graduate School of Information Science, Osaka University 1 International
Handai Cyber University Introduction of Biotechnology No.5:Genome biotechnology and yeast Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University Graduate School of Information Science, Osaka University 1 International
Wan-Ju Liu 1,2, John S Reece-Hoyes 3, Albertha JM Walhout 3 and David M Eisenmann 1*
 Liu et al. BMC Developmental Biology 2014, 14:17 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Multiple transcription factors directly regulate Hox gene lin-39 expression in ventral hypodermal cells of the C. elegans embryo
Liu et al. BMC Developmental Biology 2014, 14:17 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Multiple transcription factors directly regulate Hox gene lin-39 expression in ventral hypodermal cells of the C. elegans embryo
3.B.1 Gene Regulation. Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization.
 3.B.1 Gene Regulation Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization. We will focus on gene regulation in prokaryotes first. Gene regulation accounts for some of
3.B.1 Gene Regulation Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization. We will focus on gene regulation in prokaryotes first. Gene regulation accounts for some of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
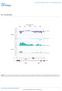 DOI:.8/ncb65 Chromosom XII cdc5- - - RDN7 4585 459 4595 46 465 IGS RDN5- RDN7 Figur S Cdc4 is rquird for rdna silncing. Yast tiling array intnsitis along 5kb of chromosom XII containing IGS rgions ( and
DOI:.8/ncb65 Chromosom XII cdc5- - - RDN7 4585 459 4595 46 465 IGS RDN5- RDN7 Figur S Cdc4 is rquird for rdna silncing. Yast tiling array intnsitis along 5kb of chromosom XII containing IGS rgions ( and
Supplemental Information. Expanded Coverage of the 26S Proteasome. Conformational Landscape Reveals. Mechanisms of Peptidase Gating
 Cell Reports, Volume 24 Supplemental Information Expanded Coverage of the 26S Proteasome Conformational Landscape Reveals Mechanisms of Peptidase Gating Markus R. Eisele, Randi G. Reed, Till Rudack, Andreas
Cell Reports, Volume 24 Supplemental Information Expanded Coverage of the 26S Proteasome Conformational Landscape Reveals Mechanisms of Peptidase Gating Markus R. Eisele, Randi G. Reed, Till Rudack, Andreas
An expression plasmid encoding the GFP and SEAP reporter genes. For research use only
 pvitro2-blasti-gfp/seap An expression plasmid encoding the GFP and SEAP reporter genes Catalog # pvitro2-bgfpsp For research use only Version # 15I09-MM PRODUCT INFORMATION Contents: - 20 µg of pvitro2-blasti-gfp/seap
pvitro2-blasti-gfp/seap An expression plasmid encoding the GFP and SEAP reporter genes Catalog # pvitro2-bgfpsp For research use only Version # 15I09-MM PRODUCT INFORMATION Contents: - 20 µg of pvitro2-blasti-gfp/seap
Supporting Information. Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2007
 Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2007 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2008 Supporting Information for Authentic Heterologous
Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2007 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2008 Supporting Information for Authentic Heterologous
Lipid transfer proteins confer resistance to trichothecenes
 Lipid transfer proteins confer resistance to trichothecenes John McLaughlin and Anwar Bin-Umer Tumer Laboratory National Fusarium Head Blight Forum December 6th, 2012 FY09-11: Identify trichothecene resistance
Lipid transfer proteins confer resistance to trichothecenes John McLaughlin and Anwar Bin-Umer Tumer Laboratory National Fusarium Head Blight Forum December 6th, 2012 FY09-11: Identify trichothecene resistance
Supplementary Information for. Single-cell dynamics of the chromosome replication and cell division cycles in mycobacteria
 Supplementary Information for Single-cell dynamics of the chromosome replication and cell division cycles in mycobacteria Isabella Santi 1 *, Neeraj Dhar 1, Djenet Bousbaine 1, Yuichi Wakamoto, John D.
Supplementary Information for Single-cell dynamics of the chromosome replication and cell division cycles in mycobacteria Isabella Santi 1 *, Neeraj Dhar 1, Djenet Bousbaine 1, Yuichi Wakamoto, John D.
Translation. A ribosome, mrna, and trna.
 Translation The basic processes of translation are conserved among prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotic Translation A ribosome, mrna, and trna. In the initiation of translation in prokaryotes, the Shine-Dalgarno
Translation The basic processes of translation are conserved among prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotic Translation A ribosome, mrna, and trna. In the initiation of translation in prokaryotes, the Shine-Dalgarno
Functional Characterization of the N Terminus of Sir3p
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Oct. 1998, p. 6110 6120 Vol. 18, No. 10 0270-7306/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Functional Characterization of the
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Oct. 1998, p. 6110 6120 Vol. 18, No. 10 0270-7306/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Functional Characterization of the
Molecular Biology (9)
 Molecular Biology (9) Translation Mamoun Ahram, PhD Second semester, 2017-2018 1 Resources This lecture Cooper, Ch. 8 (297-319) 2 General information Protein synthesis involves interactions between three
Molecular Biology (9) Translation Mamoun Ahram, PhD Second semester, 2017-2018 1 Resources This lecture Cooper, Ch. 8 (297-319) 2 General information Protein synthesis involves interactions between three
An Internal Domain of Exo70p Is Required for Actin-independent Localization and Mediates Assembly of Specific Exocyst Components
 Molecular Biology of the Cell Vol. 20, 153 163, January 1, 2009 An Internal Domain of Exo70p Is Required for Actin-independent Localization and Mediates Assembly of Specific Exocyst Components Alex H.
Molecular Biology of the Cell Vol. 20, 153 163, January 1, 2009 An Internal Domain of Exo70p Is Required for Actin-independent Localization and Mediates Assembly of Specific Exocyst Components Alex H.
CHAPTER 13 PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON
 PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON CHAPTER 13 CHAPTER 13 PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON Figure 1. Electron micrograph of growing E. coli. Some show the constriction at the location where daughter
PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON CHAPTER 13 CHAPTER 13 PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON Figure 1. Electron micrograph of growing E. coli. Some show the constriction at the location where daughter
The Gene The gene; Genes Genes Allele;
 Gene, genetic code and regulation of the gene expression, Regulating the Metabolism, The Lac- Operon system,catabolic repression, The Trp Operon system: regulating the biosynthesis of the tryptophan. Mitesh
Gene, genetic code and regulation of the gene expression, Regulating the Metabolism, The Lac- Operon system,catabolic repression, The Trp Operon system: regulating the biosynthesis of the tryptophan. Mitesh
Biology 105/Summer Bacterial Genetics 8/12/ Bacterial Genomes p Gene Transfer Mechanisms in Bacteria p.
 READING: 14.2 Bacterial Genomes p. 481 14.3 Gene Transfer Mechanisms in Bacteria p. 486 Suggested Problems: 1, 7, 13, 14, 15, 20, 22 BACTERIAL GENETICS AND GENOMICS We still consider the E. coli genome
READING: 14.2 Bacterial Genomes p. 481 14.3 Gene Transfer Mechanisms in Bacteria p. 486 Suggested Problems: 1, 7, 13, 14, 15, 20, 22 BACTERIAL GENETICS AND GENOMICS We still consider the E. coli genome
downstream (0.8 kb) homologous sequences to the genomic locus of DIC. A DIC mutant strain (ro- 6
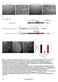 A B C D ts Figure S1 Generation of DIC- mcherry expressing N.crassa strain. A. N. crassa colony morphology. When a cot1 (top, left panel) strain is grown at permissive temperature (25 C), it exhibits straight
A B C D ts Figure S1 Generation of DIC- mcherry expressing N.crassa strain. A. N. crassa colony morphology. When a cot1 (top, left panel) strain is grown at permissive temperature (25 C), it exhibits straight
An Orthogonal Permease-Inducer-Repressor. Supporting Information
 An Orthogonal Permease-Inducer-Repressor Feedback Loop Shows Bistability Supporting Information Robert Gnügge,,, Lekshmi Dharmarajan, Moritz Lang,, and Jörg Stelling, Life Science Zurich Ph.D. Program
An Orthogonal Permease-Inducer-Repressor Feedback Loop Shows Bistability Supporting Information Robert Gnügge,,, Lekshmi Dharmarajan, Moritz Lang,, and Jörg Stelling, Life Science Zurich Ph.D. Program
Effects of Polylinker uatgs on the Function of Grass HKT1 Transporters Expressed in Yeast Cells
 Effects of Polylinker uatgs on the Function of Grass HKT1 Transporters Expressed in Yeast Cells Maria A. Banuelos, Rosario Haro, Ana Fraile-Escanciano and Alonso Rodriguez-Navarro Departamento de Biotecnologia,
Effects of Polylinker uatgs on the Function of Grass HKT1 Transporters Expressed in Yeast Cells Maria A. Banuelos, Rosario Haro, Ana Fraile-Escanciano and Alonso Rodriguez-Navarro Departamento de Biotecnologia,
Genetics 304 Lecture 6
 Genetics 304 Lecture 6 00/01/27 Assigned Readings Busby, S. and R.H. Ebright (1994). Promoter structure, promoter recognition, and transcription activation in prokaryotes. Cell 79:743-746. Reed, W.L. and
Genetics 304 Lecture 6 00/01/27 Assigned Readings Busby, S. and R.H. Ebright (1994). Promoter structure, promoter recognition, and transcription activation in prokaryotes. Cell 79:743-746. Reed, W.L. and
Whole-genome analysis of GCN4 binding in S.cerevisiae
 Whole-genome analysis of GCN4 binding in S.cerevisiae Lillian Dai Alex Mallet Gcn4/DNA diagram (CREB symmetric site and AP-1 asymmetric site: Song Tan, 1999) removed for copyright reasons. What is GCN4?
Whole-genome analysis of GCN4 binding in S.cerevisiae Lillian Dai Alex Mallet Gcn4/DNA diagram (CREB symmetric site and AP-1 asymmetric site: Song Tan, 1999) removed for copyright reasons. What is GCN4?
Gene Expression: Translation. transmission of information from mrna to proteins Chapter 5 slide 1
 Gene Expression: Translation transmission of information from mrna to proteins 601 20000 Chapter 5 slide 1 Fig. 6.1 General structural formula for an amino acid Peter J. Russell, igenetics: Copyright Pearson
Gene Expression: Translation transmission of information from mrna to proteins 601 20000 Chapter 5 slide 1 Fig. 6.1 General structural formula for an amino acid Peter J. Russell, igenetics: Copyright Pearson
Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants that tolerate centromere plasmids
 Proc. NatI. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 84, pp. 7203-7207, October 1987 Genetics Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants that tolerate centromere plasmids at high copy number (yeast centromeres/yeast transposons/g418
Proc. NatI. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 84, pp. 7203-7207, October 1987 Genetics Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants that tolerate centromere plasmids at high copy number (yeast centromeres/yeast transposons/g418
Analysis of Escherichia coli amino acid transporters
 Ph.D thesis Analysis of Escherichia coli amino acid transporters Presented by Attila Szvetnik Supervisor: Dr. Miklós Kálmán Biology Ph.D School University of Szeged Bay Zoltán Foundation for Applied Research
Ph.D thesis Analysis of Escherichia coli amino acid transporters Presented by Attila Szvetnik Supervisor: Dr. Miklós Kálmán Biology Ph.D School University of Szeged Bay Zoltán Foundation for Applied Research
Cannibalism by Sporulating Bacteria
 Cannibalism by Sporulating Bacteria José E. González-Pastor, Erret C. Hobbs, Richard Losick 2003. Science 301:510-513 Introduction Some bacteria form spores. Scientist are intrigued by them. Bacillus subtilis
Cannibalism by Sporulating Bacteria José E. González-Pastor, Erret C. Hobbs, Richard Losick 2003. Science 301:510-513 Introduction Some bacteria form spores. Scientist are intrigued by them. Bacillus subtilis
Introduction to Bioinformatics
 CSCI8980: Applied Machine Learning in Computational Biology Introduction to Bioinformatics Rui Kuang Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Minnesota kuang@cs.umn.edu History of Bioinformatics
CSCI8980: Applied Machine Learning in Computational Biology Introduction to Bioinformatics Rui Kuang Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Minnesota kuang@cs.umn.edu History of Bioinformatics
Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. Tuesday, December 27, 16
 Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. Enduring understanding 3.B: Expression of genetic information involves cellular and molecular
Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. Enduring understanding 3.B: Expression of genetic information involves cellular and molecular
Epigenetics of the yeast galactose genetic switch
 Yeast galactose genetic switch 513 Epigenetics of the yeast galactose genetic switch PAIKE JAYADEVA BHAT and REVATHI S IYER Laboratory of Molecular Genetics, School of Biosciences and Bioengineering, Indian
Yeast galactose genetic switch 513 Epigenetics of the yeast galactose genetic switch PAIKE JAYADEVA BHAT and REVATHI S IYER Laboratory of Molecular Genetics, School of Biosciences and Bioengineering, Indian
Chapter 15 Active Reading Guide Regulation of Gene Expression
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 15 Active Reading Guide Regulation of Gene Expression The overview for Chapter 15 introduces the idea that while all cells of an organism have all genes in the genome,
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 15 Active Reading Guide Regulation of Gene Expression The overview for Chapter 15 introduces the idea that while all cells of an organism have all genes in the genome,
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Spindle pole body-anchored Kar3 drives the nucleus along microtubules from
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Spindle pole body-anchored Kar3 drives the nucleus along microtubules from another nucleus in preparation for nuclear fusion during yeast karyogamy Romain Gibeaux 1, Antonio Z. Politi
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Spindle pole body-anchored Kar3 drives the nucleus along microtubules from another nucleus in preparation for nuclear fusion during yeast karyogamy Romain Gibeaux 1, Antonio Z. Politi
