Compe&&on. Why is compe,,on important to consider?
|
|
|
- Allen Roland James
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Compe&&on Why is compe,,on important to consider? Defini,on: An interac(on among individuals for a common, limi&ng resource that results in reduced individual fitness How do we measure reduced fitness? correlates of fitness what can be more easily measured): Growth, Survival, Fecundity What is compe,,ve exclusion? When one species eliminates another from a habitat by monopolizing resources and driving fitness of out competed species to zero.
2 Typical resources? Food Space (access to food) Mates If you add more of a limi(ng resource to a habitat, what happens to growth, survival of individuals that rely on that resource? When are resources most likely to be limi,ng? When popula(on density is high. K N &me
3 2 TYPES of compe,,on: 1) Intraspecific among individuals within a species ( conspecifics ) 2) Interspecific among different species ( heterospecifics ) 2 MECHANISMS of compe,,on: 1) Exploita,ve deple&on of resource to disadvantage of some other individuals 2) Interference behavioral interac&on that deprives another individual resource [e.g., territoriality]
4 Niche concept The condi,ons and resources required for an individual or species to exist and reproduce. The full range of condi&ons and resources in which species can survive and reproduce = Fundamental Niche. The more narrow range of condi&ons and resources in which species actually survives and reproduces, in the presence of compe&tors and predators = Realized Niche. Are these fundamental or realized niches?
5 Evidence for compe,,on in streams: Evidence Type #1: Niche Overlap Studies Do species overlap in resource use? Example: Fish use different microhabitat niches in a Mississippi stream [Baker & Ross 1981] Is the strong or weak evidence for compe&&on? How could you test for compe@@on? Niche shi`s if superior compe&tor removed.
6 Evidence Type #2: Niche ShiS Studies Does resource use change in presence of other species Examples A) 2 species of crayfish (Bovbjerg 1970) Where species do not co occur, both species in riffles Where they do co occur, one species displaced to pools B) Fish: Sculpins and speckled dace (Baltz et al. 1982) Prefer similar water velocity and substrate size In cooler, upstream reaches sculpins dominate riffles In warmer, downstream reaches few sculpins, dace occupy riffles If sculpins experimentally excluded from cooler riffles, what should dace do? Move to occupy riffles
7 C) Na&ve Cughroat Trout and Brook Trout in Rocky Mtns. (Kurt Fausch lab) Brook trout introduced and Cughroats now restricted to coldest headwaters where brookies are excluded. Main mechanism for brook trout exclusion of cughroat trout is compe&&on ( compe&&ve exclusion ) Brook trout are fall spawners while cughroat trout spawn in spring, so in first summer, brook YOY are larger than cuts and appear to outcompete them for dri` resources (interference for feeding sta&ons and exploita&ve depression of resource). In field experiments, cughroat young grow faster in first summer in absence of brook trout, offering evidence for compe&&on. Cughroats have a refuge in coldest headwater streams, but this a subop&mal thermal regime, so growth rate is low.
8 What if species do not shi` niches in absence of poten&al compe&tors? Niche par((oning: The ghost of compe((on past?
9 Evidence Type #3: Experimental studies Some studies experimentally demonstrate mechanism (or cause) of compe&&on on fitness. How do we measure fitness effect? Growth, survival, fecundity Recall, 2 types of compe&&on: Intraspecific and interspecific 2 causes or mechanisms: Exploita&ve and Interference Ques&on: Is compe&&on common in streams? That is, does it occur at ambient popula&on densi&es?
10 1) Intraspecific (one species) compe&&on in caddifly grazer Helicopsyche (Fig. 3) Experimental density increases from 0.25x to 2x ambient Helicopsyche Normal food levels ( ) Nega&ve slope (p < 0.01) and strong effect of increasing larval density on larval size Addi&onal food provided ( ) S&ll nega&ve slope (p < 0.05) but effect much smaller. Implies compe&&on IS occurrying at normal streambed densi&es of grazer Note increased growth rate at at ambient (1x) density ( ) ambient 1x 2x Fitness cost of increased density? (body mass) Mechanism? (exploita&on)
11 Interspecific exploita,on (several examples) (#1) Snail and caddisfly in southeast US Hill (1992) In Streams natural experiment 6 streams with snail + caddisfly, 6 with caddisfly only Fitness correlate: fat reserves and body mass of caddisfly [Fig. 9.5a] Effect on stream food resources [Fig. 9.5b] In Lab Dietary overlap, both species food limited CONCLUSION: Elimia reduces fitness of Neophylax via exploita&on Elimia Streams with snails Neophylax
12 (#2) Small scale experiments in lab and field (Kohler 1992) Laboratory Glossosoma (G) and Bae(s (B) at field (= ambient) densi&es [Fig. 4] Glossosoma Bae(s Algal biomass reduced by B and G ( ) Add G and reduce B growth ( ) Add B reduces G growth ( ) Both compete, i.e., each species affects growth rate of other species! (Not shown): Glossosoma survives beger at low resource levels. [Why do you think?]
13 How could we test for effects of compe&&on at appropriate whole stream scale with maximum realism and minimal cage effects? (#3) Large scale natural experiment with Glossosoma Kohler and Wiley (1997) Large scale, i.e., whole stream manipulated Glossosoma popula&ons crashed and virtually eliminated from 6 streams in Michigan by parasite (Cougourdella sp.) over period of few years
14 Findings: Func&onal Groups Algae? (compare before v. aqer) Grazers respond posi&vely (e.g., Fig b, c) ( ), probably due to release from exploita&ve compe&&on since more algae present Some filter feeders also increased (Fig d, e, f) ( ), probably due to lack of interference with Glossosoma (able to occupy space on rock surfaces)? Note that not all streams responded with similar magnitude or direc&on (e.g., Fig c, f) Outcomes of experiment at this whole stream scale may not be reproduced in small scale lab experiments. Some responses consistent with small scale results e.g., algae, Bae(s increase BUT, some responses not detected in smallscale experiments (e.g., rare grazers Goera, Neophylax increase) [Kohler & Wiley, Fig text] before a`er Glossosoma is an ecologically important grazer and a dominant species in these streams!
15 Interspecific interference compe,,on More o`en observed for space limited, sedentary species 1) The territorial Leucotrichia microcaddisfly build silk cases agached to rocks, graze algae uniform spacing of defended territories Territory size increases with larval mass.
16 Lecotrichia weed unpalatable bluegreen algae with scissors like mandibles (Hart 1985) If Leucotrichia removed, patches free of bluegreen algae decrease ( ) (Table 2). Edible algae (diatoms) >4x more abundant in Leucotrichia territory than outside Leucotrichia defend territory and Bae(s avoids! weeding effect
17 Removing Leucotrichia opens space for other consumers Increase midges [Fig. 9.6] Increases Glossosoma and blackflies [McAuliffe Fig. 6] Figures show how other insects avoid Leucotrichia s snipping mouthparts!
18 2) Territorial blackflies (simuliids) and interference compe&&on a) Dudley et al. (1990) Sta&onary blackflies snip at mobile blepharicerids In field, fewer blephs where more simuliids (Fig. 1) Manipula&ng simuliid abundance causes shi`s in bleph behavior (Fig. 2) What is fitness cost of modified behavior?? smaller body size at maturity
19 3) Hydropsychids (caddisfly) Hemphill and Cooper (1983) aggressively displace blackflies More when we learn about disturbance 4) Trout species aggressively compete for preferred feeding sta&ons (Fausch work on cughroat and brook trout)
Multiple choice 2 pts each): x 2 = 18) Essay (pre-prepared) / 15 points. 19) Short Answer: / 2 points. 20) Short Answer / 5 points
 P 1 Biology 217: Ecology Second Exam Fall 2004 There should be 7 ps in this exam - take a moment and count them now. Put your name on the first p of the exam, and on each of the ps with short answer questions.
P 1 Biology 217: Ecology Second Exam Fall 2004 There should be 7 ps in this exam - take a moment and count them now. Put your name on the first p of the exam, and on each of the ps with short answer questions.
D. Correct! Allelopathy is a form of interference competition in plants. Therefore this answer is correct.
 Ecology Problem Drill 18: Competition in Ecology Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. The concept of allelopathy focuses on which of the following: (A) Carrying capacity (B) Limiting resource (C) Law of the
Ecology Problem Drill 18: Competition in Ecology Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. The concept of allelopathy focuses on which of the following: (A) Carrying capacity (B) Limiting resource (C) Law of the
Modeling Fish Assemblages in Stream Networks Representation of Stream Network Introduction habitat attributes Criteria for Success
 Modeling Fish Assemblages in Stream Networks Joan P. Baker and Denis White Western Ecology Division National Health & Environmental Effects Research Laboratory U.S. Environmental Protection Agency baker.joan@epa.gov
Modeling Fish Assemblages in Stream Networks Joan P. Baker and Denis White Western Ecology Division National Health & Environmental Effects Research Laboratory U.S. Environmental Protection Agency baker.joan@epa.gov
Maintenance of species diversity
 1. Ecological succession A) Definition: the sequential, predictable change in species composition over time foling a disturbance - Primary succession succession starts from a completely empty community
1. Ecological succession A) Definition: the sequential, predictable change in species composition over time foling a disturbance - Primary succession succession starts from a completely empty community
Lesson Overview. Niches and Community Interactions. Lesson Overview. 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions
 Lesson Overview 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions The Niche What is a niche? A niche is the range of physical and biological conditions in which a species lives and the way the species obtains what
Lesson Overview 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions The Niche What is a niche? A niche is the range of physical and biological conditions in which a species lives and the way the species obtains what
Aggregations on larger scales. Metapopulation. Definition: A group of interconnected subpopulations Sources and Sinks
 Aggregations on larger scales. Metapopulation Definition: A group of interconnected subpopulations Sources and Sinks Metapopulation - interconnected group of subpopulations sink source McKillup and McKillup
Aggregations on larger scales. Metapopulation Definition: A group of interconnected subpopulations Sources and Sinks Metapopulation - interconnected group of subpopulations sink source McKillup and McKillup
Ch. 54 Community Ecology
 Ch. 54 Community Ecology BIOL 221 Overview: A Sense of Community biological community an assemblage of popula9ons of various species living close enough for poten9al interac9on Community Interac
Ch. 54 Community Ecology BIOL 221 Overview: A Sense of Community biological community an assemblage of popula9ons of various species living close enough for poten9al interac9on Community Interac
Half Hollow Hills High School AP Biology
 Chapter 53 Community Ecology Essential questions What factors structure a community? What species & how many are present in a community? In what way do the populations interact? What roles do species play
Chapter 53 Community Ecology Essential questions What factors structure a community? What species & how many are present in a community? In what way do the populations interact? What roles do species play
Ecology 2. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: Ecology 2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following statements is consistent with the principle of competitive
Name: Class: Date: Ecology 2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following statements is consistent with the principle of competitive
Lecture 2: Individual-based Modelling
 Lecture 2: Individual-based Modelling Part I Steve Railsback Humboldt State University Department of Mathematics & Lang, Railsback & Associates Arcata, California USA www.langrailsback.com 1 Outline 1.
Lecture 2: Individual-based Modelling Part I Steve Railsback Humboldt State University Department of Mathematics & Lang, Railsback & Associates Arcata, California USA www.langrailsback.com 1 Outline 1.
Effect of Species 2 on Species 1 Competition - - Predator-Prey + - Parasite-Host + -
 Community Ecology Community - a group of organisms, of different species, living in the same area Community ecology is the study of the interactions between species The presence of one species may affect
Community Ecology Community - a group of organisms, of different species, living in the same area Community ecology is the study of the interactions between species The presence of one species may affect
Community Ecology. Classification of types of interspecific interactions: Effect of Species 1 on Species 2
 Community Ecology Community - a group of organisms, of different species, living in the same area Community ecology is the study of the interactions between species The presence of one species may affect
Community Ecology Community - a group of organisms, of different species, living in the same area Community ecology is the study of the interactions between species The presence of one species may affect
Community Structure. Community An assemblage of all the populations interacting in an area
 Community Structure Community An assemblage of all the populations interacting in an area Community Ecology The ecological community is the set of plant and animal species that occupy an area Questions
Community Structure Community An assemblage of all the populations interacting in an area Community Ecology The ecological community is the set of plant and animal species that occupy an area Questions
Chapter Niches and Community Interactions
 Chapter 4 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions Key Questions: 1) What is a niche? 2) How does competition shape communities? 3) How do predation and herbivory shape communites? 4) What are three primary
Chapter 4 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions Key Questions: 1) What is a niche? 2) How does competition shape communities? 3) How do predation and herbivory shape communites? 4) What are three primary
V) Maintenance of species diversity
 V) Maintenance of species diversity 1. Ecological succession A) Definition: the sequential, predictable change in species composition over time following a disturbance - Primary succession succession starts
V) Maintenance of species diversity 1. Ecological succession A) Definition: the sequential, predictable change in species composition over time following a disturbance - Primary succession succession starts
Lesson Overview 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions
 THINK ABOUT IT If you ask someone where an organism lives, that person might answer on a coral reef or in the desert. Lesson Overview 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions These answers give the environment
THINK ABOUT IT If you ask someone where an organism lives, that person might answer on a coral reef or in the desert. Lesson Overview 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions These answers give the environment
-The study of the interactions between the different species in an area
 Community Ecology -The study of the interactions between the different species in an area Interspecific Interactions -Interaction between different species -May be positive, negative, or neutral and include
Community Ecology -The study of the interactions between the different species in an area Interspecific Interactions -Interaction between different species -May be positive, negative, or neutral and include
History and meaning of the word Ecology A. Definition 1. Oikos, ology - the study of the house - the place we live
 History and meaning of the word Ecology. Definition 1. Oikos, ology - the study of the house - the place we live. Etymology - origin and development of the the word 1. Earliest - Haeckel (1869) - comprehensive
History and meaning of the word Ecology. Definition 1. Oikos, ology - the study of the house - the place we live. Etymology - origin and development of the the word 1. Earliest - Haeckel (1869) - comprehensive
Evidence for Competition
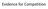 Evidence for Competition Population growth in laboratory experiments carried out by the Russian scientist Gause on growth rates in two different yeast species Each of the species has the same food e.g.,
Evidence for Competition Population growth in laboratory experiments carried out by the Russian scientist Gause on growth rates in two different yeast species Each of the species has the same food e.g.,
BIOS 5970: Plant-Herbivore Interactions Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences
 BIOS 5970: Plant-Herbivore Interactions Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences D. POPULATION & COMMUNITY DYNAMICS Week 10. Population models 1: Lecture summary: Distribution and abundance
BIOS 5970: Plant-Herbivore Interactions Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences D. POPULATION & COMMUNITY DYNAMICS Week 10. Population models 1: Lecture summary: Distribution and abundance
Stream Autotrophs. Energy Pathways in Streams. 1) diatoms 2) green algae 3) blue-green algae. Benthic algae -- composition. Benthic Algae Macrophytes
 Energy Pathways in Streams Secondary consumers carnivory Primary consumers herbivory detritivory coagulation and precipitation senescence Autochthonous primary production Photosynthesis Allochthonous primary
Energy Pathways in Streams Secondary consumers carnivory Primary consumers herbivory detritivory coagulation and precipitation senescence Autochthonous primary production Photosynthesis Allochthonous primary
Factors Affecting Rate of Food Consumption
 Factors Affecting Rate of Food Consumption Factors Affecting Rate of Food Consumption Prey density (availabilty) Attack rate Handling time Learning, switching, microhabitat selection Functional Response:
Factors Affecting Rate of Food Consumption Factors Affecting Rate of Food Consumption Prey density (availabilty) Attack rate Handling time Learning, switching, microhabitat selection Functional Response:
How Does Competition Affect Population Growth?
 Name: Period: How Does Competition Affect Population Growth? Background Information The genus Paramecium spp. consists of unicellular species of protists that live in freshwater environments. Under ideal
Name: Period: How Does Competition Affect Population Growth? Background Information The genus Paramecium spp. consists of unicellular species of protists that live in freshwater environments. Under ideal
Tolerance. Tolerance. Tolerance 10/22/2010
 Section 4.2 Mrs. Michaelsen Tolerance Every species has its own range of tolerance: The ability to survive and reproduce under a range of environmental circumstances. Tolerance Stress can result when an
Section 4.2 Mrs. Michaelsen Tolerance Every species has its own range of tolerance: The ability to survive and reproduce under a range of environmental circumstances. Tolerance Stress can result when an
organism population community ecosystem biosphere Community Ecology AP Biology
 organism Community Ecology population community ecosystem biosphere Community Ecology Community all the organisms that live together in a place interactions Community Ecology study of interactions among
organism Community Ecology population community ecosystem biosphere Community Ecology Community all the organisms that live together in a place interactions Community Ecology study of interactions among
organism population community ecosystem biosphere Community Ecology AP Biology
 organism Community Ecology population community ecosystem biosphere Community Ecology Community all the organisms that live together in a place = interactions Community Ecology To answer: study of interactions
organism Community Ecology population community ecosystem biosphere Community Ecology Community all the organisms that live together in a place = interactions Community Ecology To answer: study of interactions
V) Maintenance of species diversity
 1. Ecological succession A) Definition: the sequential, predictable change in species composition over time foling a disturbance - Primary succession succession starts from a completely empty community
1. Ecological succession A) Definition: the sequential, predictable change in species composition over time foling a disturbance - Primary succession succession starts from a completely empty community
Chapter 6 Reading Questions
 Chapter 6 Reading Questions 1. Fill in 5 key events in the re-establishment of the New England forest in the Opening Story: 1. Farmers begin leaving 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Broadleaf forest reestablished 2.
Chapter 6 Reading Questions 1. Fill in 5 key events in the re-establishment of the New England forest in the Opening Story: 1. Farmers begin leaving 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Broadleaf forest reestablished 2.
Understanding Populations Section 1. Chapter 8 Understanding Populations Section1, How Populations Change in Size DAY ONE
 Chapter 8 Understanding Populations Section1, How Populations Change in Size DAY ONE What Is a Population? A population is a group of organisms of the same species that live in a specific geographical
Chapter 8 Understanding Populations Section1, How Populations Change in Size DAY ONE What Is a Population? A population is a group of organisms of the same species that live in a specific geographical
A population is a group of individuals of the same species occupying a particular area at the same time
 A population is a group of individuals of the same species occupying a particular area at the same time Population Growth As long as the birth rate exceeds the death rate a population will grow Immigration
A population is a group of individuals of the same species occupying a particular area at the same time Population Growth As long as the birth rate exceeds the death rate a population will grow Immigration
Current controversies in Marine Ecology with an emphasis on Coral reef systems. Niche Diversification Hypothesis Assumptions:
 Current controversies in Marine Ecology with an emphasis on Coral reef systems Open vs closed populations (already Discussed) The extent and importance of larval dispersal Maintenance of Diversity Equilibrial
Current controversies in Marine Ecology with an emphasis on Coral reef systems Open vs closed populations (already Discussed) The extent and importance of larval dispersal Maintenance of Diversity Equilibrial
Weather is the day-to-day condition of Earth s atmosphere.
 4.1 Climate Weather and Climate Weather is the day-to-day condition of Earth s atmosphere. Climate refers to average conditions over long periods and is defined by year-after-year patterns of temperature
4.1 Climate Weather and Climate Weather is the day-to-day condition of Earth s atmosphere. Climate refers to average conditions over long periods and is defined by year-after-year patterns of temperature
Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: London City. Assessment: 07 Science Science Test 4. Description: Life Science Final 1.
 Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: London City Assessment: 07 Science Science Test 4 Description: Life Science Final 1 Form: 301 1. A food chain is shown. Sunlight Grass Rabbit Snake What is the abiotic
Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: London City Assessment: 07 Science Science Test 4 Description: Life Science Final 1 Form: 301 1. A food chain is shown. Sunlight Grass Rabbit Snake What is the abiotic
Competition. Different kinds of competition Modeling competition Examples of competition-case studies Understanding the role of competition
 Competition Different kinds of competition Modeling competition Examples of competition-case studies Understanding the role of competition Competition The outcome of competition is that an individual suffers
Competition Different kinds of competition Modeling competition Examples of competition-case studies Understanding the role of competition Competition The outcome of competition is that an individual suffers
REVISION: POPULATION ECOLOGY 18 SEPTEMBER 2013
 REVISION: POPULATION ECOLOGY 18 SEPTEMBER 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Revise population ecology by working through some exam questions. Key Concepts Definition of Population A population
REVISION: POPULATION ECOLOGY 18 SEPTEMBER 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Revise population ecology by working through some exam questions. Key Concepts Definition of Population A population
Chapter 54: Community Ecology
 Name Period Concept 54.1 Community interactions are classified by whether they help, harm, or have no effect on the species involved. 1. What is a community? List six organisms that would be found in your
Name Period Concept 54.1 Community interactions are classified by whether they help, harm, or have no effect on the species involved. 1. What is a community? List six organisms that would be found in your
Current controversies in Marine Ecology with an emphasis on Coral reef systems
 Current controversies in Marine Ecology with an emphasis on Coral reef systems Open vs closed populations (already discussed) The extent and importance of larval dispersal Maintenance of Diversity Equilibrial
Current controversies in Marine Ecology with an emphasis on Coral reef systems Open vs closed populations (already discussed) The extent and importance of larval dispersal Maintenance of Diversity Equilibrial
Population Ecology. Text Readings. Questions to Answer in the Chapter. Chapter Reading:
 Population Ecology Text Readings Chapter Reading: Chapter # 26 in Audesirk, Audesirk and Byers: Population Growth and Regulation Pg. # 513-534. Questions to Answer in the Chapter How Does Population Size
Population Ecology Text Readings Chapter Reading: Chapter # 26 in Audesirk, Audesirk and Byers: Population Growth and Regulation Pg. # 513-534. Questions to Answer in the Chapter How Does Population Size
BIOS 6150: Ecology Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences
 BIOS 6150: Ecology Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences Week 5: Interspecific Competition: Lecture summary: Definition. Examples. Outcomes. Lotka-Volterra model. Semibalanus balanoides
BIOS 6150: Ecology Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences Week 5: Interspecific Competition: Lecture summary: Definition. Examples. Outcomes. Lotka-Volterra model. Semibalanus balanoides
Ecology. How the World Works
 Ecology How the World Works Ecology is the study of interactions between living organisms and other living organisms and non living resources that they interact with. Levels of Organization Organism- a
Ecology How the World Works Ecology is the study of interactions between living organisms and other living organisms and non living resources that they interact with. Levels of Organization Organism- a
organism Community Ecology population community ecosystem biosphere
 organism Community Ecology population community ecosystem biosphere Community Ecology Community all the organisms that live together in a place interactions Community Ecology study of interactions among
organism Community Ecology population community ecosystem biosphere Community Ecology Community all the organisms that live together in a place interactions Community Ecology study of interactions among
Exponen'al growth Limi'ng factors Environmental resistance Carrying capacity logis'c growth curve
 Exponen'al growth Popula)on increases by a fixed percent Fixed percent of a large number produces a large increase Graphed as a J- shaped curve Cannot be sustained indefinitely It occurs in nature With
Exponen'al growth Popula)on increases by a fixed percent Fixed percent of a large number produces a large increase Graphed as a J- shaped curve Cannot be sustained indefinitely It occurs in nature With
Organism Interactions in Ecosystems
 Organism Interactions in Ecosystems Have you ever grown a plant or taken care of a pet? If so, you know they have certain needs such as water or warmth. Plants need sunlight to grow. Animals need food
Organism Interactions in Ecosystems Have you ever grown a plant or taken care of a pet? If so, you know they have certain needs such as water or warmth. Plants need sunlight to grow. Animals need food
4/17/17. Community Ecology populations interact? Community Ecology. Niche. Community all the organisms that live together in a place interactions
 Community Ecology organism populatio n community ecosystem biosphere Community Ecology Community all the organisms that live together in a place interactions To answer: In what way do the Community Ecology
Community Ecology organism populatio n community ecosystem biosphere Community Ecology Community all the organisms that live together in a place interactions To answer: In what way do the Community Ecology
Human Carrying Capacity. Dangers of overshooting
 How to calculate carrying capacity 1. Sum estimates of regional K. 2. Curve Fitting 3. Assume Single Resource Constraint 4. Reduce Multiple Requirements to one factor 5. Assume Multiple Independent Constraints
How to calculate carrying capacity 1. Sum estimates of regional K. 2. Curve Fitting 3. Assume Single Resource Constraint 4. Reduce Multiple Requirements to one factor 5. Assume Multiple Independent Constraints
3/24/10. Amphibian community ecology. Lecture goal. Lecture concepts to know
 Amphibian community ecology Lecture goal To familiarize students with the abiotic and biotic factors that structure amphibian communities, patterns in species richness, and encourage discussion about community
Amphibian community ecology Lecture goal To familiarize students with the abiotic and biotic factors that structure amphibian communities, patterns in species richness, and encourage discussion about community
Field experiments on competition. Field experiments on competition. Field experiments on competition
 INTERACTIONS BETWEEN SPECIES Type of interaction species 1 species 2 competition consumer-resource (pred, herb, para) mutualism detritivore-detritus (food is dead) Field experiments on competition Example
INTERACTIONS BETWEEN SPECIES Type of interaction species 1 species 2 competition consumer-resource (pred, herb, para) mutualism detritivore-detritus (food is dead) Field experiments on competition Example
Chapter 4 Ecosystems and Living Organisms
 Chapter 4 Ecosystems and Living Organisms I. Evolution A. The cumulative genetic changes that occur in a population of organisms over time 1. Current theories proposed by Charles Darwin, a 19 th century
Chapter 4 Ecosystems and Living Organisms I. Evolution A. The cumulative genetic changes that occur in a population of organisms over time 1. Current theories proposed by Charles Darwin, a 19 th century
Rocky Intertidal Ecology -- part II The development of experimental ecology. Connell and the experimental revolution
 Rocky Intertidal Ecology -- part II The development of experimental ecology I. Intertidal Zonation, part II 1. Follow ups on Connell 2. Predation 3. Exceptions II. Horizontal Distribution 1. Variation
Rocky Intertidal Ecology -- part II The development of experimental ecology I. Intertidal Zonation, part II 1. Follow ups on Connell 2. Predation 3. Exceptions II. Horizontal Distribution 1. Variation
Evolution and Community Ecology Chapter 5 HOMEWORK. Name. Period TEACHER
 Evolution and Community Ecology Chapter 5 HOMEWORK Name Period TEACHER Chapter 5: Evolution and Community Ecology Page 124-155 What is evolution? What is biological evolution? What is a gene pool? What
Evolution and Community Ecology Chapter 5 HOMEWORK Name Period TEACHER Chapter 5: Evolution and Community Ecology Page 124-155 What is evolution? What is biological evolution? What is a gene pool? What
Ch.5 Evolution and Community Ecology How do organisms become so well suited to their environment? Evolution and Natural Selection
 Ch.5 Evolution and Community Ecology How do organisms become so well suited to their environment? Evolution and Natural Selection Gene: A sequence of DNA that codes for a particular trait Gene pool: All
Ch.5 Evolution and Community Ecology How do organisms become so well suited to their environment? Evolution and Natural Selection Gene: A sequence of DNA that codes for a particular trait Gene pool: All
4-3: Species Interactions
 4-3: Species Interactions After this lecture you should be able to Differentiate between the various types of symbiotic relationships Examine the dynamics of predator-prey relationships. Predict population
4-3: Species Interactions After this lecture you should be able to Differentiate between the various types of symbiotic relationships Examine the dynamics of predator-prey relationships. Predict population
Competitive exclusion & Niche concept
 Competitive exclusion & Niche concept [Academic Script] Subject: Course: Paper No. & Title: Zoology B.Sc. 3 rd Year Z-301B Ecology Topic Title: Topic - 5 Competition in nature intraspecific and interspecific.
Competitive exclusion & Niche concept [Academic Script] Subject: Course: Paper No. & Title: Zoology B.Sc. 3 rd Year Z-301B Ecology Topic Title: Topic - 5 Competition in nature intraspecific and interspecific.
Ecology Symbiotic Relationships
 Ecology Symbiotic Relationships Overview of the Co-evolution and Relationships Exhibited Among Community Members What does Symbiosis mean? How do we define Symbiosis? Symbiosis in the broadest sense is
Ecology Symbiotic Relationships Overview of the Co-evolution and Relationships Exhibited Among Community Members What does Symbiosis mean? How do we define Symbiosis? Symbiosis in the broadest sense is
Interspecific Patterns. Interference vs. exploitative
 Types of Competition Interference vs. exploitative Intraspecific vs. Interspeific Asymmetric vs. Symmetric Interspecific Patterns When two similar species coexist, there are three outcomes: Competitive
Types of Competition Interference vs. exploitative Intraspecific vs. Interspeific Asymmetric vs. Symmetric Interspecific Patterns When two similar species coexist, there are three outcomes: Competitive
Groups of organisms living close enough together for interactions to occur.
 Community ecology: First, let's define a community: Groups of organisms living close enough together for interactions to occur. First we probably want to describe the community a bit, so we look at: Biodiversity
Community ecology: First, let's define a community: Groups of organisms living close enough together for interactions to occur. First we probably want to describe the community a bit, so we look at: Biodiversity
14.1. KEY CONCEPT Every organism has a habitat and a niche. 38 Reinforcement Unit 5 Resource Book
 14.1 HABITAT AND NICHE KEY CONCEPT Every organism has a habitat and a niche. A habitat is all of the living and nonliving factors in the area where an organism lives. For example, the habitat of a frog
14.1 HABITAT AND NICHE KEY CONCEPT Every organism has a habitat and a niche. A habitat is all of the living and nonliving factors in the area where an organism lives. For example, the habitat of a frog
Age (x) nx lx. Population dynamics Population size through time should be predictable N t+1 = N t + B + I - D - E
 Population dynamics Population size through time should be predictable N t+1 = N t + B + I - D - E Time 1 N = 100 20 births 25 deaths 10 immigrants 15 emmigrants Time 2 100 + 20 +10 25 15 = 90 Life History
Population dynamics Population size through time should be predictable N t+1 = N t + B + I - D - E Time 1 N = 100 20 births 25 deaths 10 immigrants 15 emmigrants Time 2 100 + 20 +10 25 15 = 90 Life History
Ecosystems. 2. Ecosystem
 1. Studying our living Planet The biosphere consist of all life on Earth and all parts of the Earth in which life exists, including land, water, and the atmosphere. Ecology is the scientific study of interactions
1. Studying our living Planet The biosphere consist of all life on Earth and all parts of the Earth in which life exists, including land, water, and the atmosphere. Ecology is the scientific study of interactions
NCEA Level 3 Biology (90716) 2005 page 1 of 5. Q Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with Excellence
 NCEA Level 3 Biology (90716) 2005 page 1 of 5 Assessment Schedule 2005 Biology: Describe animal behaviour and plant responses (90716) Evidence Statement 1(a) Describes TWO methods of navigation. (orientation
NCEA Level 3 Biology (90716) 2005 page 1 of 5 Assessment Schedule 2005 Biology: Describe animal behaviour and plant responses (90716) Evidence Statement 1(a) Describes TWO methods of navigation. (orientation
HW/CW #5 CHAPTER 3 PRACTICE
 HW/CW #5 CHAPTER 3 PRACTICE 1. The portion of Earth in which all life exists is known as A) the climax stage B) the biosphere C) a population D) a biotic community 2. The study of the interactions between
HW/CW #5 CHAPTER 3 PRACTICE 1. The portion of Earth in which all life exists is known as A) the climax stage B) the biosphere C) a population D) a biotic community 2. The study of the interactions between
Interspecific Competition
 Interspecific Competition Intraspecific competition Classic logistic model Interspecific extension of densitydependence Individuals of other species may also have an effect on per capita birth & death
Interspecific Competition Intraspecific competition Classic logistic model Interspecific extension of densitydependence Individuals of other species may also have an effect on per capita birth & death
Section 2: How Species Interact with Each Other
 Section 2: How Species Interact with Each Other Preview Bellringer Objectives An Organism s Niche Ways in Which Species Interact Competition Indirect Competition Adaptations to Competition Section 2: How
Section 2: How Species Interact with Each Other Preview Bellringer Objectives An Organism s Niche Ways in Which Species Interact Competition Indirect Competition Adaptations to Competition Section 2: How
Niche The sum of all interactions a species has with biotic/abiotic components of the environment N-dimensional hypervolume
 Niche The sum of all interactions a species has with biotic/abiotic components of the environment N-dimensional hypervolume Each dimension is a biotic or abiotic resource Ecomorphology Ecology (niche)
Niche The sum of all interactions a species has with biotic/abiotic components of the environment N-dimensional hypervolume Each dimension is a biotic or abiotic resource Ecomorphology Ecology (niche)
Chapter 04 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 04 Lecture Outline William P. Cunningham University of Minnesota Mary Ann Cunningham Vassar College Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1
Chapter 04 Lecture Outline William P. Cunningham University of Minnesota Mary Ann Cunningham Vassar College Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1
Interspecific Competition
 Use Interspecific Competition 0.8 0.6 0.4 0. 0 0 0.5.5.5 3 Resource The niche and interspecific competition Species A Use Use 0.8 0.6 0.4 0. Species B 0 0 0.5.5.5 3 0.8 0.6 0.4 0. 0 0 0.5.5.5 3 Resource
Use Interspecific Competition 0.8 0.6 0.4 0. 0 0 0.5.5.5 3 Resource The niche and interspecific competition Species A Use Use 0.8 0.6 0.4 0. Species B 0 0 0.5.5.5 3 0.8 0.6 0.4 0. 0 0 0.5.5.5 3 Resource
Case Studies in Ecology and Evolution
 7 Competition (this chapter is still unfinished) Species compete in many ways. Sometimes there are dramatic contests, such as when male bighorns compete for access to mates. Territoriality. That kind of
7 Competition (this chapter is still unfinished) Species compete in many ways. Sometimes there are dramatic contests, such as when male bighorns compete for access to mates. Territoriality. That kind of
Ch20_Ecology, community & ecosystems
 Community Ecology Populations of different species living in the same place NICHE The sum of all the different use of abiotic resources in the habitat by s given species what the organism does what is
Community Ecology Populations of different species living in the same place NICHE The sum of all the different use of abiotic resources in the habitat by s given species what the organism does what is
FW662 Lecture 11 Competition 1
 FW662 Lecture 11 Competition 1 Lecture 11. Competition. Reading: Gotelli, 2001, A Primer of Ecology, Chapter 5, pages 99-124. Renshaw (1991) Chapter 5 Competition processes, Pages 128-165. Optional: Schoener,
FW662 Lecture 11 Competition 1 Lecture 11. Competition. Reading: Gotelli, 2001, A Primer of Ecology, Chapter 5, pages 99-124. Renshaw (1991) Chapter 5 Competition processes, Pages 128-165. Optional: Schoener,
Community Ecology Feral cat populations can be damaging to ecosystems.
 Community Ecology Feral cat populations can be damaging to ecosystems. Why? Photo Credit: http://www.flickr.com/photos/daveograve/4562537127/ Concept of the Community Community = assemblage of populations
Community Ecology Feral cat populations can be damaging to ecosystems. Why? Photo Credit: http://www.flickr.com/photos/daveograve/4562537127/ Concept of the Community Community = assemblage of populations
Stream Autotrophs. Benthic 10/3/13
 Stream Autotrophs Benthic -, often colonial (e.g., filamentous algae) - Each cell has nucleus, chloroplast, reproduction by cell division - Some cells specialized, but no tissues, vascular system, etc.
Stream Autotrophs Benthic -, often colonial (e.g., filamentous algae) - Each cell has nucleus, chloroplast, reproduction by cell division - Some cells specialized, but no tissues, vascular system, etc.
Overview of Chapter 5
 Chapter 5 Ecosystems and Living Organisms Overview of Chapter 5 Evolution Natural Selection Biological Communities Symbiosis Predation & Competition Community Development Succession Evolution The cumulative
Chapter 5 Ecosystems and Living Organisms Overview of Chapter 5 Evolution Natural Selection Biological Communities Symbiosis Predation & Competition Community Development Succession Evolution The cumulative
BIOS 6150: Ecology Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences
 BIOS 6150: Ecology Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences Week 14: Roles of competition, predation & disturbance in community structure. Lecture summary: (A) Competition: Pattern vs process.
BIOS 6150: Ecology Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences Week 14: Roles of competition, predation & disturbance in community structure. Lecture summary: (A) Competition: Pattern vs process.
(3) Sediment Movement Classes of sediment transported
 9/17/15 (3) Sediment Movement Classes of sediment transported Dissolved load Suspended load Important for scouring algae Bedload (5-10% total load) Moves along bed during floods Source of crushing for
9/17/15 (3) Sediment Movement Classes of sediment transported Dissolved load Suspended load Important for scouring algae Bedload (5-10% total load) Moves along bed during floods Source of crushing for
Honors Biology Ecology Concept List
 1. For each pair of terms, explain how the meanings of the terms differ. a. mutualism and commensalism b. parasitism and predation c. species richness and species diversity d. primary succession and secondary
1. For each pair of terms, explain how the meanings of the terms differ. a. mutualism and commensalism b. parasitism and predation c. species richness and species diversity d. primary succession and secondary
The Living World Continued: Populations and Communities
 The Living World Continued: Populations and Communities Ecosystem Communities Populations Review: Parts of an Ecosystem 1) An individual in a species: One organism of a species. a species must be genetically
The Living World Continued: Populations and Communities Ecosystem Communities Populations Review: Parts of an Ecosystem 1) An individual in a species: One organism of a species. a species must be genetically
WORKSHEET F.I.B.S: Complete the chart: ( + ) organism is beneficial. ( - ) Organism is harmed. ( 0 ) organism is neither harmed or beneficial.
 Name: F.I.B.S: WORKSHEET 1. The effects that the organism in a community have on one another is called. 2. Inflicting harm to other organism without any costs or benefits is knows as. 3. Interaction between
Name: F.I.B.S: WORKSHEET 1. The effects that the organism in a community have on one another is called. 2. Inflicting harm to other organism without any costs or benefits is knows as. 3. Interaction between
HOMEWORK PACKET UNIT 2A. Part I: Introduction to Ecology
 CP Biology Name Date Period HOMEWORK PACKET UNIT 2A Part I: Introduction to Ecology Name Class Date 3.1 What Is Ecology? Studying Our Living Planet 1. What is ecology? 2. What does the biosphere contain?
CP Biology Name Date Period HOMEWORK PACKET UNIT 2A Part I: Introduction to Ecology Name Class Date 3.1 What Is Ecology? Studying Our Living Planet 1. What is ecology? 2. What does the biosphere contain?
What standard are we focusing on today?
 What standard are we focusing on today? Standard H.B.6 The student will demonstrate an understanding that ecosystems are complex, interactive systems that include both biological communities and physical
What standard are we focusing on today? Standard H.B.6 The student will demonstrate an understanding that ecosystems are complex, interactive systems that include both biological communities and physical
The Problem of Where to Live
 April 5: Habitat Selection: Intro The Problem of Where to Live Physical and biotic environment critically affects fitness An animal's needs may be met only in certain habitats, which should select for
April 5: Habitat Selection: Intro The Problem of Where to Live Physical and biotic environment critically affects fitness An animal's needs may be met only in certain habitats, which should select for
Summary. A Bird s- Eye View of Community and Population Effects of Ontogenetic Development
 Chapter one Summary A Bird s- Eye View of Community and Population Effects of Ontogenetic Development Why start with summarizing the contents of a book? In the present case we see at least two good reasons.
Chapter one Summary A Bird s- Eye View of Community and Population Effects of Ontogenetic Development Why start with summarizing the contents of a book? In the present case we see at least two good reasons.
Distribution patterns of stream grazers and relationships between grazers and periphyton at multiple spatial scales
 J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc., 2008, 27(2):295 303 Ó 2008 by The North American Benthological Society DOI: 10.1899/07-067.1 Published online: 25 March 2008 Distribution patterns of stream grazers and relationships
J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc., 2008, 27(2):295 303 Ó 2008 by The North American Benthological Society DOI: 10.1899/07-067.1 Published online: 25 March 2008 Distribution patterns of stream grazers and relationships
Interactions of Living Things
 CHAPTER 14 LESSON 2 Interactions of Living Things Populations and Communities Key Concepts How do individuals and groups of organisms interact? What are some examples of symbiotic relationships? What do
CHAPTER 14 LESSON 2 Interactions of Living Things Populations and Communities Key Concepts How do individuals and groups of organisms interact? What are some examples of symbiotic relationships? What do
Populations and Ecosystems. 1. Two different species with the same ecological niche are placed in the same habitat. These two species will most likely
 Name: ate: 1. Two different species with the same ecological niche are placed in the same habitat. These two species will most likely. have different food requirements. compete for the same environmental
Name: ate: 1. Two different species with the same ecological niche are placed in the same habitat. These two species will most likely. have different food requirements. compete for the same environmental
A population is a group of individuals of the same species, living in a shared space at a specific point in time.
 A population is a group of individuals of the same species, living in a shared space at a specific point in time. A population size refers to the number of individuals in a population. Increase Decrease
A population is a group of individuals of the same species, living in a shared space at a specific point in time. A population size refers to the number of individuals in a population. Increase Decrease
GENERAL ECOLOGY STUDY NOTES
 1.0 INTRODUCTION GENERAL ECOLOGY STUDY NOTES A community is made up of populations of different organisms living together in a unit environment. The manner in which these organisms relate together for
1.0 INTRODUCTION GENERAL ECOLOGY STUDY NOTES A community is made up of populations of different organisms living together in a unit environment. The manner in which these organisms relate together for
CHAPTER. Evolution and Community Ecology
 CHAPTER 5 Evolution and Community Ecology Lesson 5.2 Species Interactions The zebra mussel has completely displaced 20 native mussel species in Lake St. Clair. Lesson 5.2 Species Interactions The Niche
CHAPTER 5 Evolution and Community Ecology Lesson 5.2 Species Interactions The zebra mussel has completely displaced 20 native mussel species in Lake St. Clair. Lesson 5.2 Species Interactions The Niche
What to take home. Resource Compe,,on Removing things Compe,,on: One plant depletes a resource; that deple,on has a deleterious effect on another.
 Plant- Plant Interac,ons What to take home Plants interact passively Plants remove things from the environment (generally resource compe,,on) Plants add things to the environment (organic chemicals [allelochemics],
Plant- Plant Interac,ons What to take home Plants interact passively Plants remove things from the environment (generally resource compe,,on) Plants add things to the environment (organic chemicals [allelochemics],
biotic factors camouflage carnivore chloroplast
 non-living parts of an organism's environment Eg air currents, temperature, moisture, light, and soil type special features about an organism that help it survive and reproduce living things that is different
non-living parts of an organism's environment Eg air currents, temperature, moisture, light, and soil type special features about an organism that help it survive and reproduce living things that is different
Chapter 6 Population and Community Ecology
 Chapter 6 Population and Community Ecology Friedland and Relyea Environmental Science for AP, second edition 2015 W.H. Freeman and Company/BFW AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board,
Chapter 6 Population and Community Ecology Friedland and Relyea Environmental Science for AP, second edition 2015 W.H. Freeman and Company/BFW AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board,
Ecology. Science Matters Chapter 16
 Ecology Science Matters Chapter 16 Learning outcomes Understand what the term ecology means. Be able to name different habitats. Be able to give examples of producers, consumers and decomposers in the
Ecology Science Matters Chapter 16 Learning outcomes Understand what the term ecology means. Be able to name different habitats. Be able to give examples of producers, consumers and decomposers in the
14.1. Every organism has a habitat and a niche. A habitat differs from a niche. Interactions in Ecosystems CHAPTER 14.
 SECTION 14.1 HABITAT AND NICHE Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Every organism has a habitat and a niche. VOCABULARY habitat ecological niche competitive exclusion ecological equivalent A habitat differs from a
SECTION 14.1 HABITAT AND NICHE Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Every organism has a habitat and a niche. VOCABULARY habitat ecological niche competitive exclusion ecological equivalent A habitat differs from a
Yakın Doğu Üniversitesi Mimarlık Fakültesi Peyzaj Mimarlığı Bölümü. PM 317 Human and Environment Assoc. Prof. Dr. Salih GÜCEL
 Yakın Doğu Üniversitesi Mimarlık Fakültesi Peyzaj Mimarlığı Bölümü PM 317 Human and Environment Assoc. Prof. Dr. Salih GÜCEL Ecology & Ecosystems Principles of Ecology Ecology is the study of the interactions
Yakın Doğu Üniversitesi Mimarlık Fakültesi Peyzaj Mimarlığı Bölümü PM 317 Human and Environment Assoc. Prof. Dr. Salih GÜCEL Ecology & Ecosystems Principles of Ecology Ecology is the study of the interactions
2 Components of Species Diversity:
 2 Components of Species Diversity: Species Richness: of species Species richness seems to increase productivity and because many species are better able to withstand environmental disturbances Species
2 Components of Species Diversity: Species Richness: of species Species richness seems to increase productivity and because many species are better able to withstand environmental disturbances Species
Name: Date: ID: 3. What are some limitations to scientific models? - Most models include simplifications, approximations, and/or lack details
 Name: Date: ID: 2 ND 9-WEEKS STUDY GUIDE Shared Answers Communication Skills 1. Define the term Scientific Model in your own terms. - A description of a system, theory, or phenomenon 2. List 5 things we
Name: Date: ID: 2 ND 9-WEEKS STUDY GUIDE Shared Answers Communication Skills 1. Define the term Scientific Model in your own terms. - A description of a system, theory, or phenomenon 2. List 5 things we
Chapter 6 Population and Community Ecology. Thursday, October 19, 17
 Chapter 6 Population and Community Ecology Module 18 The Abundance and Distribution of After reading this module you should be able to explain how nature exists at several levels of complexity. discuss
Chapter 6 Population and Community Ecology Module 18 The Abundance and Distribution of After reading this module you should be able to explain how nature exists at several levels of complexity. discuss
CHAPTER 14. Interactions in Ecosystems: Day One
 CHAPTER 14 Interactions in Ecosystems: Day One Habitat versus Niche Review! What is a habitat? All of the biotic and abiotic factors in the area where an organism lives. Examples: grass, trees, and watering
CHAPTER 14 Interactions in Ecosystems: Day One Habitat versus Niche Review! What is a habitat? All of the biotic and abiotic factors in the area where an organism lives. Examples: grass, trees, and watering
Chapter 22: Descent with Modification
 NAME DATE Chapter 22: Descent with Modification 1. What was the significance of the publishing of Charles Darwin s book, On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection? 2. Explain the two major
NAME DATE Chapter 22: Descent with Modification 1. What was the significance of the publishing of Charles Darwin s book, On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection? 2. Explain the two major
Additional Case Study: Calculating the Size of a Small Mammal Population
 Student Worksheet LSM 14.1-2 Additional Case Study: Calculating the Size of a Small Mammal Population Objective To use field study data on shrew populations to examine the characteristics of a natural
Student Worksheet LSM 14.1-2 Additional Case Study: Calculating the Size of a Small Mammal Population Objective To use field study data on shrew populations to examine the characteristics of a natural
Community ecology. Abdulhafez A Selim, MD, PhD
 Community ecology Abdulhafez A Selim, MD, PhD Community ecology is very complex Niches The term 'Niche' was coined by the naturalist Joseph Grinnell in 1917, in his paper "The niche relationships of the
Community ecology Abdulhafez A Selim, MD, PhD Community ecology is very complex Niches The term 'Niche' was coined by the naturalist Joseph Grinnell in 1917, in his paper "The niche relationships of the
