BIOS 6150: Ecology Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences
|
|
|
- Sabina McGee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BIOS 6150: Ecology Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences Week 14: Roles of competition, predation & disturbance in community structure. Lecture summary: (A) Competition: Pattern vs process. Simberloff & Strong criticism. Neutral models & null hypotheses. (B) Predation, herbivory, parasitism & disease: (C) Disturbance: Chapters 16, 19, 21 (4 th ed.) BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 1
2 2. (A) Role of competition in community structure: Prevalent view among ecologists in 1970s: Competition was of overriding importance in, (1) shaping community structure and (2) how many species can coexist. Especially competitive exclusion: Existence of a single species when two or more compete for the same limiting resource = limit to similarity of competing species. More recently this view has given way to: More prominence for non-equilibrial & stochastic factors, such as physical disturbance and condition variability. But under certain circumstances competition can be important, so: to what extent and in which cases in practice is interspecific competition an active force? BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 2
3 3. Evidence for competition: Intraspecific competition was only detectable in 20% of published studies on phytophagous insects and interspecific competition was found in 41% of them. Possibly because many available niches on plants remain unoccupied (Fig. 19.2, 4 th ed.). Herbivores also show less competition than plants, carnivores or detritivores: Perhaps because their food resources are abundant and less likely to be limiting. (a) England (b) Papua New Guinea (c) New Mexico & Arizona BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 3
4 4. Evidence for competition: Evidence of current competition in action includes: Experimental removal of species to determine: Whether remaining species fill the available niche space, or, Resource patchiness may lead to coexistence (Fig. 20.2, 3 rd ed.). Connell s ghost of competition past may also have been important in niche differentiation. Heterogeneous environment (closed symbols) generates coexistence and not niche differentiation. Homogeneous environment (open symbols) leads to competitive exclusion. Species 1 Species 2 BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 4
5 5. Evidence from community patterns: 2 basic steps: (1) Predict community structure given the existence of interspecific competition: (i) Coexisting competitors should show niche differentiation. (ii) Niche differentiation often appears as morphological differentiation. (iii) Negative spatial associations expected among similar species with little niche differentiation. (2) Examine real communities to see if they conform to this structure (Fig. 20.3). Most likely to detect current competition within feeding guilds: groups of species that exploit the same class of environmental resource in a similar way (after Root, 1967). BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 5
6 6. Niche differentiation in bumblebees: Fig rd ed. BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 6
7 7. Niche differentiation in weasels (Fig. 20.4, 3 rd ): Morphological niche differentiation by upper canine size and resource partitioning in weasels (Fig. 20.4). BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 7
8 8. Temporal niche differentiation in flowering periods: Fig (3 rd ed.) shows temporal separation of nectar resources in 10 Costa Rican rainforest plants to reduce competition for hummingbird pollinators. BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 8
9 9. Spatial niche differentiation in birds of the Bismarck Archipelago near New Guinea: Fig : Checkerboard distribution of 2 cuckoo dove species (4 th ed.). Fig : Incidence functions (J) against number of species (S) on islands for: (a) supertramps, (b) good colonizer/competitor, (c) good competitors on larger islands (4 th ed.). BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 9
10 10. The criticisms of Simberloff and Strong: Dan Simberloff and Don Strong criticized the tendency to interpret mere differences as evidence for interspecific competition. They also pointed out the weaknesses inherent in observing patterns rather than experimenting to detect processes such as competition. BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 10
11 11. Simberloff and Strong s solution: Competition theory predicts that niches will be arranged regularly in niche space rather than randomly and similar niches should differ more than would be expected by chance alone. Thus they established the criterion of: testing experimentally, whether community patterns differ significantly from random assembly, in the absence of any interactions among the species, before competition can be invoked as a structuring mechanism. BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 11
12 12. Neutral models and null hypotheses: These are randomly reassembled mixes of species based on real communities, excluding the consequences of biological interactions. Constructed in order to establish a null hypothesis of what a community would look like in the absence of biological interactions. If the community under investigation differs significantly (statistically) from this neutral model then the null hypothesis can be rejected, and an alternative hypothesis that invokes a mechanism (such as competition) can be inferred. This is the Popperian method of science in which statistical power is reinforced by hypothesis rejection or falsification as deductive rather than inductive. We cannot test statistically whether things are significantly similar - only whether they are significantly different (hypothesis falsification). BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 12
13 13. Randomly reassembled lizard communities compared to actual community resource use overlaps (Fig. 19.7, 4 th ): BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 13
14 14. The role of competition - Conclusions: After highly acrimonious argument in the early 1980s about the role of competition and the development of neutral models and null hypotheses, most people now agree that the neutral model approach is appropriate. Both critics and supporters of the approach have developed the method and applied it to interactions within guilds where competition is suspected. BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 14
15 15. Problems still remain: But neutral models can fail to detect competition even when it is included deliberately because current communities are the product of both current competition and the ghost of competition past which may have eliminated species most vulnerable to competitive exclusion: e.g. Colwell & Winkler, A null model for null models in biogeography - God and Wallace models. But this approach still only compares patterns and cannot and should not replace manipulative experiments and detailed understanding of field ecology. BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 15
16 16. (B) Role of predation in community structure Effects of grazing herbivores: Herbivory, predation, disease and parasitism, competition, earthquakes, fire, rain, wind, temperature etc. can all disturb communities. Disturbance is: any relatively discrete event in time that removes organisms or otherwise disrupts the community by influencing the availability of space or food resources, or by changing the physical environment. A general consequence is likely to be the opening up of space, or freeing up of resources, that can be taken over by new individuals. For example, a predator, or herbivore, or lawn mower, or a strong wave, or a strong wind can all open gaps in communities. BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 16
17 17. Effects of grazing disturbance on community richness: Grazing by rabbits can strongly influence the structure of plant communities, especially at intermediate grazing intensities (Fig. 21.1, 3 rd ). BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 17
18 18. Intermediate grazing promotes most diversity through its influence on competition - exploiter-mediated coexistence (Fig. 21.2, 3 rd ed.): BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 18
19 19. The effects of predators: Removal of predatory starfish by Paine (1966) led to reduction in community species number from 15 to 8 because space made available by the predator helped competitively subordinate species and increased species diversity Fig. 7.8 (Begon, Mortimer & Thompson, 1996). Exploiter-mediated coexistence. BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 19
20 20. Effect of switching predatory behavior: Frequency-dependent effects can also influence community structure: For example switching in roach according to density of planktonic or benthic waterflea prey (Fig. 21.3, 3 rd ed.). BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 20
21 21. The effects of parasites and disease: These exploiters can also affect other interactions and facilitate coexistence of species as in Fig (3 rd ed.). BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 21
22 22. Impact of invasion into susceptible communities: Strongly negative effects on communities can also occur for highly pathogenic invading diseases such as malaria and bird pox in Hawaii which may have exterminated 50% of the endemic bird species. Also the destruction of chestnut and elm forests in North America by introduced pathogens. These effects are also likely to be frequency dependent: Influenced by the frequency of encounter in high density populations. BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 22
23 23. (C) Role of disturbance in community structure Community structure and temporal variation in conditions: Conditions constantly change in space and time and they have a marked impact on ecological processes and hence on species composition of communities (Fig. 21.5, 3 rd ed.). BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 23
24 24. Effects of density-independent factors: Periodic, density independent reductions in population size may be expected to promote coexistence of competing species (Fig. 21.6, 3 rd ed.). Huston (1979). BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 24
25 25. Effects of density-independent factors: Frequency of disturbance also impacts diversity, as does growth rate (rate of increase) of species: Fig. 21.7, 3 rd ed. (Huston, 1979). BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 25
26 26. Effects of both disturbance frequency and species growth rate on community diversity (Fig. 21.8, 3 rd ). BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 26
27 27. Disturbances and patch dynamics: Includes the effects of movement among patches of resource available for colonization: Dynamics within patches are like Lotka- Volterra interactions, but extinctions can be reversed or created by immigration and emigration: Like metapopulations. BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 27
28 28. Dominance-controlled communities: Some species are competitively superior: Gaps lead to succession-like changes in species composition and disturbance knocks the community back to an earlier stage (Fig & Table 21.1) from pioneer species (p) to midsuccession species (m) to climax competitor species (c). Diversity is also greatest at intermediate levels of disturbance (Figs & 16.18) = Connell s intermediate disturbance hypothesis. Fig. 7.9 (Begon, Mortimer & Thompson, 1996). BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 28
29 Figure (4 th ed.): BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 29
30 BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 30
31 Figure (4 th ed.): BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 31
32 Figure 16.18: 4 th ed. BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 32
33 Figure 7.9: Connell s intermediate disturbance hypothesis A - opportunistic spp. B - secondarily colonizing spp. C - climax spp. Begon, Mortimer & Thompson (1996) Heron Island, Queensland, coral reef - damaged o - undamaged BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 33
34 34. Founder-controlled communities: All species are competitively similar: Succession is not expected. There is no competitive exclusion. Presence in the community becomes a lottery (Fig ): Some tropical reef fish communities may be like this and diversity may remain high. Species may be competing for living space in which larvae are the tickets, and the first arrival at the vacant space wins the site, matures quickly and holds the space for its lifetime. BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 34
35 Figure (4 th ed.): BIOS 6150: Ecology - Dr. S. Malcolm. Week 14: Roles of competition. Predation & disturbance in community structure Slide - 35
BIOS 3010: Ecology Lecture 20: Community Structure & Predation: 2. The effect of grazing herbivores: 3. The effect of grazing herbivores:
 BIOS 3010: Ecology Lecture 20: Community Structure & Predation: Lecture summary: Effects of grazing herbivores. Effects of predators. Effects of parasites & disease. Variation in time. Disturbance & community
BIOS 3010: Ecology Lecture 20: Community Structure & Predation: Lecture summary: Effects of grazing herbivores. Effects of predators. Effects of parasites & disease. Variation in time. Disturbance & community
BIOS 5970: Plant-Herbivore Interactions Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences
 BIOS 5970: Plant-Herbivore Interactions Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences D. POPULATION & COMMUNITY DYNAMICS Week 13. Herbivory, predation & parasitism: Lecture summary: Predation:
BIOS 5970: Plant-Herbivore Interactions Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences D. POPULATION & COMMUNITY DYNAMICS Week 13. Herbivory, predation & parasitism: Lecture summary: Predation:
BIOS 5970: Plant-Herbivore Interactions Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences
 BIOS 5970: Plant-Herbivore Interactions Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences D. POPULATION & COMMUNITY DYNAMICS Week 10. Population models 1: Lecture summary: Distribution and abundance
BIOS 5970: Plant-Herbivore Interactions Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences D. POPULATION & COMMUNITY DYNAMICS Week 10. Population models 1: Lecture summary: Distribution and abundance
Chapter 54: Community Ecology
 AP Biology Guided Reading Name Chapter 54: Community Ecology Overview 1. What does community ecology explore? Concept 54.1 Community interactions are classified by whether they help, harm, or have no effect
AP Biology Guided Reading Name Chapter 54: Community Ecology Overview 1. What does community ecology explore? Concept 54.1 Community interactions are classified by whether they help, harm, or have no effect
Current controversies in Marine Ecology with an emphasis on Coral reef systems
 Current controversies in Marine Ecology with an emphasis on Coral reef systems Open vs closed populations (already discussed) The extent and importance of larval dispersal Maintenance of Diversity Equilibrial
Current controversies in Marine Ecology with an emphasis on Coral reef systems Open vs closed populations (already discussed) The extent and importance of larval dispersal Maintenance of Diversity Equilibrial
Current controversies in Marine Ecology with an emphasis on Coral reef systems. Niche Diversification Hypothesis Assumptions:
 Current controversies in Marine Ecology with an emphasis on Coral reef systems Open vs closed populations (already Discussed) The extent and importance of larval dispersal Maintenance of Diversity Equilibrial
Current controversies in Marine Ecology with an emphasis on Coral reef systems Open vs closed populations (already Discussed) The extent and importance of larval dispersal Maintenance of Diversity Equilibrial
Community Interactions. Community An assemblage of all the populations interacting in an area
 Community Interactions Community An assemblage of all the populations interacting in an area Populations are affected by: Available living space habitat Resource Availability niche Species interactions
Community Interactions Community An assemblage of all the populations interacting in an area Populations are affected by: Available living space habitat Resource Availability niche Species interactions
Community and Population Ecology Populations & Communities Species Diversity Sustainability and Environmental Change Richness and Sustainability
 1 2 3 4 Community and Population Ecology Chapter 6 Populations & Communities Biosphere> ecosystems> communities> populations> individuals A population is all of the individuals of the same species in a
1 2 3 4 Community and Population Ecology Chapter 6 Populations & Communities Biosphere> ecosystems> communities> populations> individuals A population is all of the individuals of the same species in a
-The study of the interactions between the different species in an area
 Community Ecology -The study of the interactions between the different species in an area Interspecific Interactions -Interaction between different species -May be positive, negative, or neutral and include
Community Ecology -The study of the interactions between the different species in an area Interspecific Interactions -Interaction between different species -May be positive, negative, or neutral and include
Aggregations on larger scales. Metapopulation. Definition: A group of interconnected subpopulations Sources and Sinks
 Aggregations on larger scales. Metapopulation Definition: A group of interconnected subpopulations Sources and Sinks Metapopulation - interconnected group of subpopulations sink source McKillup and McKillup
Aggregations on larger scales. Metapopulation Definition: A group of interconnected subpopulations Sources and Sinks Metapopulation - interconnected group of subpopulations sink source McKillup and McKillup
Effect of Species 2 on Species 1 Competition - - Predator-Prey + - Parasite-Host + -
 Community Ecology Community - a group of organisms, of different species, living in the same area Community ecology is the study of the interactions between species The presence of one species may affect
Community Ecology Community - a group of organisms, of different species, living in the same area Community ecology is the study of the interactions between species The presence of one species may affect
Community Ecology. Classification of types of interspecific interactions: Effect of Species 1 on Species 2
 Community Ecology Community - a group of organisms, of different species, living in the same area Community ecology is the study of the interactions between species The presence of one species may affect
Community Ecology Community - a group of organisms, of different species, living in the same area Community ecology is the study of the interactions between species The presence of one species may affect
BIOS 6150: Ecology Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences
 BIOS 6150: Ecology Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences Week 7: Dynamics of Predation. Lecture summary: Categories of predation. Linked prey-predator cycles. Lotka-Volterra model. Density-dependence.
BIOS 6150: Ecology Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences Week 7: Dynamics of Predation. Lecture summary: Categories of predation. Linked prey-predator cycles. Lotka-Volterra model. Density-dependence.
Resource Partitioning and Why It Matters
 Resource Partitioning and Why It Matters By: John N. Griffin (Department of Zoology, University of Florida) & Brian R. Silliman (Department of Zoology, University of Florida) 2011 Nature Education Citation:
Resource Partitioning and Why It Matters By: John N. Griffin (Department of Zoology, University of Florida) & Brian R. Silliman (Department of Zoology, University of Florida) 2011 Nature Education Citation:
Community Structure Temporal Patterns
 Community Structure Temporal Patterns Temporal Patterns Seasonality Phenology study of repeated patterns in time and their relationship to physical aspects of the environment Seasonal changes that are
Community Structure Temporal Patterns Temporal Patterns Seasonality Phenology study of repeated patterns in time and their relationship to physical aspects of the environment Seasonal changes that are
Questions from reading and discussion section (1-3 will be on exam)- 5 or 10 points each
 2017 Mock Exam - Marine Ecology 108; page 1 The concepts and questions on the exam will come from the terms and questions listed below except there may be new questions from lecture and readings from remaining
2017 Mock Exam - Marine Ecology 108; page 1 The concepts and questions on the exam will come from the terms and questions listed below except there may be new questions from lecture and readings from remaining
Field experiments on competition. Field experiments on competition. Field experiments on competition
 INTERACTIONS BETWEEN SPECIES Type of interaction species 1 species 2 competition consumer-resource (pred, herb, para) mutualism detritivore-detritus (food is dead) Field experiments on competition Example
INTERACTIONS BETWEEN SPECIES Type of interaction species 1 species 2 competition consumer-resource (pred, herb, para) mutualism detritivore-detritus (food is dead) Field experiments on competition Example
Chapter 54: Community Ecology
 Name Period Concept 54.1 Community interactions are classified by whether they help, harm, or have no effect on the species involved. 1. What is a community? List six organisms that would be found in your
Name Period Concept 54.1 Community interactions are classified by whether they help, harm, or have no effect on the species involved. 1. What is a community? List six organisms that would be found in your
Honors Biology Ecology Concept List
 1. For each pair of terms, explain how the meanings of the terms differ. a. mutualism and commensalism b. parasitism and predation c. species richness and species diversity d. primary succession and secondary
1. For each pair of terms, explain how the meanings of the terms differ. a. mutualism and commensalism b. parasitism and predation c. species richness and species diversity d. primary succession and secondary
Interspecific Competition
 Interspecific Competition Intraspecific competition Classic logistic model Interspecific extension of densitydependence Individuals of other species may also have an effect on per capita birth & death
Interspecific Competition Intraspecific competition Classic logistic model Interspecific extension of densitydependence Individuals of other species may also have an effect on per capita birth & death
BIOS 6150: Ecology Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences
 BIOS 6150: Ecology Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences Week 5: Interspecific Competition: Lecture summary: Definition. Examples. Outcomes. Lotka-Volterra model. Semibalanus balanoides
BIOS 6150: Ecology Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences Week 5: Interspecific Competition: Lecture summary: Definition. Examples. Outcomes. Lotka-Volterra model. Semibalanus balanoides
Gary G. Mittelbach Michigan State University
 Community Ecology Gary G. Mittelbach Michigan State University Sinauer Associates, Inc. Publishers Sunderland, Massachusetts U.S.A. Brief Table of Contents 1 Community Ecology s Roots 1 PART I The Big
Community Ecology Gary G. Mittelbach Michigan State University Sinauer Associates, Inc. Publishers Sunderland, Massachusetts U.S.A. Brief Table of Contents 1 Community Ecology s Roots 1 PART I The Big
Chapter 6 Reading Questions
 Chapter 6 Reading Questions 1. Fill in 5 key events in the re-establishment of the New England forest in the Opening Story: 1. Farmers begin leaving 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Broadleaf forest reestablished 2.
Chapter 6 Reading Questions 1. Fill in 5 key events in the re-establishment of the New England forest in the Opening Story: 1. Farmers begin leaving 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Broadleaf forest reestablished 2.
Chapter 6 Population and Community Ecology. Thursday, October 19, 17
 Chapter 6 Population and Community Ecology Module 18 The Abundance and Distribution of After reading this module you should be able to explain how nature exists at several levels of complexity. discuss
Chapter 6 Population and Community Ecology Module 18 The Abundance and Distribution of After reading this module you should be able to explain how nature exists at several levels of complexity. discuss
Community Ecology. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 54 Community Ecology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 54 Community Ecology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Biology 11 Unit 1: Fundamentals. Lesson 1: Ecology
 Biology 11 Unit 1: Fundamentals Lesson 1: Ecology Objectives In this section you will be learning about: ecosystem structure energy flow through an ecosystem photosynthesis and cellular respiration factors
Biology 11 Unit 1: Fundamentals Lesson 1: Ecology Objectives In this section you will be learning about: ecosystem structure energy flow through an ecosystem photosynthesis and cellular respiration factors
Chapter 6 Population and Community Ecology
 Chapter 6 Population and Community Ecology Friedland and Relyea Environmental Science for AP, second edition 2015 W.H. Freeman and Company/BFW AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board,
Chapter 6 Population and Community Ecology Friedland and Relyea Environmental Science for AP, second edition 2015 W.H. Freeman and Company/BFW AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board,
Maintenance of species diversity
 1. Ecological succession A) Definition: the sequential, predictable change in species composition over time foling a disturbance - Primary succession succession starts from a completely empty community
1. Ecological succession A) Definition: the sequential, predictable change in species composition over time foling a disturbance - Primary succession succession starts from a completely empty community
Ch20_Ecology, community & ecosystems
 Community Ecology Populations of different species living in the same place NICHE The sum of all the different use of abiotic resources in the habitat by s given species what the organism does what is
Community Ecology Populations of different species living in the same place NICHE The sum of all the different use of abiotic resources in the habitat by s given species what the organism does what is
Unit 6 Populations Dynamics
 Unit 6 Populations Dynamics Define these 26 terms: Commensalism Habitat Herbivory Mutualism Niche Parasitism Predator Prey Resource Partitioning Symbiosis Age structure Population density Population distribution
Unit 6 Populations Dynamics Define these 26 terms: Commensalism Habitat Herbivory Mutualism Niche Parasitism Predator Prey Resource Partitioning Symbiosis Age structure Population density Population distribution
Community phylogenetics review/quiz
 Community phylogenetics review/quiz A. This pattern represents and is a consequent of. Most likely to observe this at phylogenetic scales. B. This pattern represents and is a consequent of. Most likely
Community phylogenetics review/quiz A. This pattern represents and is a consequent of. Most likely to observe this at phylogenetic scales. B. This pattern represents and is a consequent of. Most likely
History and meaning of the word Ecology A. Definition 1. Oikos, ology - the study of the house - the place we live
 History and meaning of the word Ecology. Definition 1. Oikos, ology - the study of the house - the place we live. Etymology - origin and development of the the word 1. Earliest - Haeckel (1869) - comprehensive
History and meaning of the word Ecology. Definition 1. Oikos, ology - the study of the house - the place we live. Etymology - origin and development of the the word 1. Earliest - Haeckel (1869) - comprehensive
Ch.5 Evolution and Community Ecology How do organisms become so well suited to their environment? Evolution and Natural Selection
 Ch.5 Evolution and Community Ecology How do organisms become so well suited to their environment? Evolution and Natural Selection Gene: A sequence of DNA that codes for a particular trait Gene pool: All
Ch.5 Evolution and Community Ecology How do organisms become so well suited to their environment? Evolution and Natural Selection Gene: A sequence of DNA that codes for a particular trait Gene pool: All
BIOS 3010: Ecology Lecture 11: Processes: Herbivory. 2. Basic feeding guilds of herbivores: 3. Effects of herbivores on plants:
 BIOS 3010: Ecology Lecture 11: Processes: Herbivory Lecture summary: Feeding guilds. Effects of herbivores on plants: Distribution and abundance. Compensation. Recruitment. Fecundity. Plant defense. Diversity.
BIOS 3010: Ecology Lecture 11: Processes: Herbivory Lecture summary: Feeding guilds. Effects of herbivores on plants: Distribution and abundance. Compensation. Recruitment. Fecundity. Plant defense. Diversity.
1. competitive exclusion => local elimination of one => competitive exclusion principle (Gause and Paramecia)
 Chapter 54: Community Ecology A community is defined as an assemblage of species living close enough together for potential interaction. Each member of same community has a particular habitat and niche.
Chapter 54: Community Ecology A community is defined as an assemblage of species living close enough together for potential interaction. Each member of same community has a particular habitat and niche.
Chapter 6 Test: Species Interactions and Community Ecology
 ! Chapter 6 Test: Species Interactions and Community Ecology Graph and Figure Interpretation Questions Use the accompanying figure to answer the following questions. 1) What does the diagram illustrate?
! Chapter 6 Test: Species Interactions and Community Ecology Graph and Figure Interpretation Questions Use the accompanying figure to answer the following questions. 1) What does the diagram illustrate?
Ecosystem change: an example Ecosystem change: an example
 5/13/13 Community = An assemblage of populations (species) in a particular area or habitat. Here is part of a community in the grassland of the Serengetti. Trophic downgrading of planet Earth: What escapes
5/13/13 Community = An assemblage of populations (species) in a particular area or habitat. Here is part of a community in the grassland of the Serengetti. Trophic downgrading of planet Earth: What escapes
Evidence for Competition
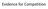 Evidence for Competition Population growth in laboratory experiments carried out by the Russian scientist Gause on growth rates in two different yeast species Each of the species has the same food e.g.,
Evidence for Competition Population growth in laboratory experiments carried out by the Russian scientist Gause on growth rates in two different yeast species Each of the species has the same food e.g.,
2 Components of Species Diversity:
 2 Components of Species Diversity: Species Richness: of species Species richness seems to increase productivity and because many species are better able to withstand environmental disturbances Species
2 Components of Species Diversity: Species Richness: of species Species richness seems to increase productivity and because many species are better able to withstand environmental disturbances Species
Metacommunities Spatial Ecology of Communities
 Spatial Ecology of Communities Four perspectives for multiple species Patch dynamics principles of metapopulation models (patchy pops, Levins) Mass effects principles of source-sink and rescue effects
Spatial Ecology of Communities Four perspectives for multiple species Patch dynamics principles of metapopulation models (patchy pops, Levins) Mass effects principles of source-sink and rescue effects
14.1 Habitat And Niche
 14.1 Habitat And Niche A habitat differs from a niche. Habitat physical area in which an organism lives Niche each species plays a specific role in an ecosystem niche includes the species habitat, feeding
14.1 Habitat And Niche A habitat differs from a niche. Habitat physical area in which an organism lives Niche each species plays a specific role in an ecosystem niche includes the species habitat, feeding
SUCCESSION Community & Ecosystem Change over time
 Schueller NRE 509: Lecture 23 SUCCESSION Community & Ecosystem Change over time 1. Forest study revisited 2. Patterns in community change over time: 3 cases 3. What is changing? 4. What determines the
Schueller NRE 509: Lecture 23 SUCCESSION Community & Ecosystem Change over time 1. Forest study revisited 2. Patterns in community change over time: 3 cases 3. What is changing? 4. What determines the
Ch. 14 Interactions in Ecosystems
 Ch. 14 Interactions in Ecosystems 1 14.1 Habitat vs. Niche Habitat all biotic and abiotic factors where an organism lives WHERE a species lives 2 Ecological Niche All physical, chemical, and biological
Ch. 14 Interactions in Ecosystems 1 14.1 Habitat vs. Niche Habitat all biotic and abiotic factors where an organism lives WHERE a species lives 2 Ecological Niche All physical, chemical, and biological
What determines: 1) Species distributions? 2) Species diversity? Patterns and processes
 Species diversity What determines: 1) Species distributions? 2) Species diversity? Patterns and processes At least 120 different (overlapping) hypotheses explaining species richness... We are going to
Species diversity What determines: 1) Species distributions? 2) Species diversity? Patterns and processes At least 120 different (overlapping) hypotheses explaining species richness... We are going to
Groups of organisms living close enough together for interactions to occur.
 Community ecology: First, let's define a community: Groups of organisms living close enough together for interactions to occur. First we probably want to describe the community a bit, so we look at: Biodiversity
Community ecology: First, let's define a community: Groups of organisms living close enough together for interactions to occur. First we probably want to describe the community a bit, so we look at: Biodiversity
V) Maintenance of species diversity
 1. Ecological succession A) Definition: the sequential, predictable change in species composition over time foling a disturbance - Primary succession succession starts from a completely empty community
1. Ecological succession A) Definition: the sequential, predictable change in species composition over time foling a disturbance - Primary succession succession starts from a completely empty community
Ecology. Bio Sphere. Feeding Relationships
 Ecology Bio Sphere Feeding Relationships with a whole lot of other creatures Ecology Putting it all together study of interactions between creatures & their environment, because Everything is connected
Ecology Bio Sphere Feeding Relationships with a whole lot of other creatures Ecology Putting it all together study of interactions between creatures & their environment, because Everything is connected
ENVE203 Environmental Engineering Ecology (Nov 19, 2012)
 ENVE203 Environmental Engineering Ecology (Nov 19, 2012) Elif Soyer Biological Communities COMPETITION Occurs when 2 or more individuals attempt to use an essential common resource such as food, water,
ENVE203 Environmental Engineering Ecology (Nov 19, 2012) Elif Soyer Biological Communities COMPETITION Occurs when 2 or more individuals attempt to use an essential common resource such as food, water,
Metabolic trade-offs promote diversity in a model ecosystem
 Metabolic trade-offs promote diversity in a model ecosystem Anna Posfai, Thibaud Taillefumier, Ben Weiner, Ned Wingreen Princeton University q-bio Rutgers University, July 25 2017 How can we explain species
Metabolic trade-offs promote diversity in a model ecosystem Anna Posfai, Thibaud Taillefumier, Ben Weiner, Ned Wingreen Princeton University q-bio Rutgers University, July 25 2017 How can we explain species
What Shapes an Ecosystem? Section 4-2 pgs 90-97
 What Shapes an Ecosystem? Section 4-2 pgs 90-97 What Shapes an Ecosystem? If you ask an ecologist where a particular organism lives, that person might say the organism lives on a Caribbean coral reef,
What Shapes an Ecosystem? Section 4-2 pgs 90-97 What Shapes an Ecosystem? If you ask an ecologist where a particular organism lives, that person might say the organism lives on a Caribbean coral reef,
V) Maintenance of species diversity
 V) Maintenance of species diversity 1. Ecological succession A) Definition: the sequential, predictable change in species composition over time following a disturbance - Primary succession succession starts
V) Maintenance of species diversity 1. Ecological succession A) Definition: the sequential, predictable change in species composition over time following a disturbance - Primary succession succession starts
Non-native Invasive Species
 Non-native Invasive Species Quiz: Mack et al. 2000 2. List and describe two examples of hypotheses about why a community might be vulnerable to invasion. Vocab: Mack et al. 2000 Allelopathy chemical defense
Non-native Invasive Species Quiz: Mack et al. 2000 2. List and describe two examples of hypotheses about why a community might be vulnerable to invasion. Vocab: Mack et al. 2000 Allelopathy chemical defense
Chapter 04 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 04 Lecture Outline William P. Cunningham University of Minnesota Mary Ann Cunningham Vassar College Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1
Chapter 04 Lecture Outline William P. Cunningham University of Minnesota Mary Ann Cunningham Vassar College Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1
What Shapes an Ecosystem Section 4-2
 What Shapes an Ecosystem Section 4-2 Biotic and Abiotic Factors Ecosystems are influenced by a combination of biological and physical factors. Biotic factors are the biological influences on an organism.
What Shapes an Ecosystem Section 4-2 Biotic and Abiotic Factors Ecosystems are influenced by a combination of biological and physical factors. Biotic factors are the biological influences on an organism.
BIOS 230 Landscape Ecology. Lecture #32
 BIOS 230 Landscape Ecology Lecture #32 What is a Landscape? One definition: A large area, based on intuitive human scales and traditional geographical studies 10s of hectares to 100s of kilometers 2 (1
BIOS 230 Landscape Ecology Lecture #32 What is a Landscape? One definition: A large area, based on intuitive human scales and traditional geographical studies 10s of hectares to 100s of kilometers 2 (1
A population is a group of individuals of the same species, living in a shared space at a specific point in time.
 A population is a group of individuals of the same species, living in a shared space at a specific point in time. A population size refers to the number of individuals in a population. Increase Decrease
A population is a group of individuals of the same species, living in a shared space at a specific point in time. A population size refers to the number of individuals in a population. Increase Decrease
EnSt 110 Exam II (Sp06) Multiple Choice. Select the best answer. One only. 2 points each
 Name: 1 EnSt 110 Exam II (Sp06) This test is worth 100 points; you have approximately 90 minutes. Multiple Choice. Select the best answer. One only. 2 points each 1) An ecosystem consists of A) a physical
Name: 1 EnSt 110 Exam II (Sp06) This test is worth 100 points; you have approximately 90 minutes. Multiple Choice. Select the best answer. One only. 2 points each 1) An ecosystem consists of A) a physical
Chapters 4-5, 4-6, 5-1, 5-2, & 5-4 Biodiversity, Species Interactions & Succession
 Chapters 4-5, 4-6, 5-1, 5-2, & 5-4 Biodiversity, Species Interactions & Succession 2 Components of Species Diversity: Species Richness: of species Species richness seems to increase productivity and because
Chapters 4-5, 4-6, 5-1, 5-2, & 5-4 Biodiversity, Species Interactions & Succession 2 Components of Species Diversity: Species Richness: of species Species richness seems to increase productivity and because
Community Ecology Feral cat populations can be damaging to ecosystems.
 Community Ecology Feral cat populations can be damaging to ecosystems. Why? Photo Credit: http://www.flickr.com/photos/daveograve/4562537127/ Concept of the Community Community = assemblage of populations
Community Ecology Feral cat populations can be damaging to ecosystems. Why? Photo Credit: http://www.flickr.com/photos/daveograve/4562537127/ Concept of the Community Community = assemblage of populations
Ecology 2. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: Ecology 2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following statements is consistent with the principle of competitive
Name: Class: Date: Ecology 2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following statements is consistent with the principle of competitive
Weather is the day-to-day condition of Earth s atmosphere.
 4.1 Climate Weather and Climate Weather is the day-to-day condition of Earth s atmosphere. Climate refers to average conditions over long periods and is defined by year-after-year patterns of temperature
4.1 Climate Weather and Climate Weather is the day-to-day condition of Earth s atmosphere. Climate refers to average conditions over long periods and is defined by year-after-year patterns of temperature
Ecology 203, Exam III. November 16, Print name:
 Ecology 203, Exam III. November 16, 2005. Print name: Read carefully. Work accurately and efficiently. The exam is worth 100 points (plus 6 extra credit points). Choose four of ten concept-exploring questions
Ecology 203, Exam III. November 16, 2005. Print name: Read carefully. Work accurately and efficiently. The exam is worth 100 points (plus 6 extra credit points). Choose four of ten concept-exploring questions
Chapter 4 Ecosystems and Living Organisms
 Chapter 4 Ecosystems and Living Organisms I. Evolution A. The cumulative genetic changes that occur in a population of organisms over time 1. Current theories proposed by Charles Darwin, a 19 th century
Chapter 4 Ecosystems and Living Organisms I. Evolution A. The cumulative genetic changes that occur in a population of organisms over time 1. Current theories proposed by Charles Darwin, a 19 th century
D. Correct! Allelopathy is a form of interference competition in plants. Therefore this answer is correct.
 Ecology Problem Drill 18: Competition in Ecology Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. The concept of allelopathy focuses on which of the following: (A) Carrying capacity (B) Limiting resource (C) Law of the
Ecology Problem Drill 18: Competition in Ecology Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. The concept of allelopathy focuses on which of the following: (A) Carrying capacity (B) Limiting resource (C) Law of the
AP Environmental Science I. Unit 1-2: Biodiversity & Evolution
 NOTE/STUDY GUIDE: Unit 1-2, Biodiversity & Evolution AP Environmental Science I, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: ID#: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE AP Environmental
NOTE/STUDY GUIDE: Unit 1-2, Biodiversity & Evolution AP Environmental Science I, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: ID#: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE AP Environmental
Community Structure. Community An assemblage of all the populations interacting in an area
 Community Structure Community An assemblage of all the populations interacting in an area Community Ecology The ecological community is the set of plant and animal species that occupy an area Questions
Community Structure Community An assemblage of all the populations interacting in an area Community Ecology The ecological community is the set of plant and animal species that occupy an area Questions
Community Ecology Bio 147/247 Species Richness 3: Diversity& Abundance Deeper Meanings of Biodiversity Speci es and Functional Groups
 Community Ecology Bio 147/247 Species Richness 3: Diversity& Abundance Deeper Meanings of Biodiversity Speci es and Functional Groups The main Qs for today are: 1. How many species are there in a community?
Community Ecology Bio 147/247 Species Richness 3: Diversity& Abundance Deeper Meanings of Biodiversity Speci es and Functional Groups The main Qs for today are: 1. How many species are there in a community?
Ecology. How the World Works
 Ecology How the World Works Ecology is the study of interactions between living organisms and other living organisms and non living resources that they interact with. Levels of Organization Organism- a
Ecology How the World Works Ecology is the study of interactions between living organisms and other living organisms and non living resources that they interact with. Levels of Organization Organism- a
Lesson Overview. Niches and Community Interactions. Lesson Overview. 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions
 Lesson Overview 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions The Niche What is a niche? A niche is the range of physical and biological conditions in which a species lives and the way the species obtains what
Lesson Overview 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions The Niche What is a niche? A niche is the range of physical and biological conditions in which a species lives and the way the species obtains what
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Overview: Communities in Motion Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece Pearson Education, Inc.
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Overview: Communities in Motion Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 41 A biological community = ex: carrier crab : Species Interactions Lecture Presentations by Kathleen
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Overview: Communities in Motion Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 41 A biological community = ex: carrier crab : Species Interactions Lecture Presentations by Kathleen
HOMEWORK PACKET UNIT 2A. Part I: Introduction to Ecology
 CP Biology Name Date Period HOMEWORK PACKET UNIT 2A Part I: Introduction to Ecology Name Class Date 3.1 What Is Ecology? Studying Our Living Planet 1. What is ecology? 2. What does the biosphere contain?
CP Biology Name Date Period HOMEWORK PACKET UNIT 2A Part I: Introduction to Ecology Name Class Date 3.1 What Is Ecology? Studying Our Living Planet 1. What is ecology? 2. What does the biosphere contain?
ECOLOGY: the scientific study of interactions of organisms with each other and with their environment
 1 Biology Unit 9 Ecology 9:1 Populations SPECIES: organisms of the same kind which are able to interbreed and reproduce Example: Horse + Donkey Mule (64 + 62 63 chromosomes and cannot produce offspring)
1 Biology Unit 9 Ecology 9:1 Populations SPECIES: organisms of the same kind which are able to interbreed and reproduce Example: Horse + Donkey Mule (64 + 62 63 chromosomes and cannot produce offspring)
Community ecology. Abdulhafez A Selim, MD, PhD
 Community ecology Abdulhafez A Selim, MD, PhD Community ecology is very complex Niches The term 'Niche' was coined by the naturalist Joseph Grinnell in 1917, in his paper "The niche relationships of the
Community ecology Abdulhafez A Selim, MD, PhD Community ecology is very complex Niches The term 'Niche' was coined by the naturalist Joseph Grinnell in 1917, in his paper "The niche relationships of the
The Living World Continued: Populations and Communities
 The Living World Continued: Populations and Communities Ecosystem Communities Populations Review: Parts of an Ecosystem 1) An individual in a species: One organism of a species. a species must be genetically
The Living World Continued: Populations and Communities Ecosystem Communities Populations Review: Parts of an Ecosystem 1) An individual in a species: One organism of a species. a species must be genetically
REVISION: POPULATION ECOLOGY 18 SEPTEMBER 2013
 REVISION: POPULATION ECOLOGY 18 SEPTEMBER 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Revise population ecology by working through some exam questions. Key Concepts Definition of Population A population
REVISION: POPULATION ECOLOGY 18 SEPTEMBER 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Revise population ecology by working through some exam questions. Key Concepts Definition of Population A population
FW662 Lecture 11 Competition 1
 FW662 Lecture 11 Competition 1 Lecture 11. Competition. Reading: Gotelli, 2001, A Primer of Ecology, Chapter 5, pages 99-124. Renshaw (1991) Chapter 5 Competition processes, Pages 128-165. Optional: Schoener,
FW662 Lecture 11 Competition 1 Lecture 11. Competition. Reading: Gotelli, 2001, A Primer of Ecology, Chapter 5, pages 99-124. Renshaw (1991) Chapter 5 Competition processes, Pages 128-165. Optional: Schoener,
Age (x) nx lx. Population dynamics Population size through time should be predictable N t+1 = N t + B + I - D - E
 Population dynamics Population size through time should be predictable N t+1 = N t + B + I - D - E Time 1 N = 100 20 births 25 deaths 10 immigrants 15 emmigrants Time 2 100 + 20 +10 25 15 = 90 Life History
Population dynamics Population size through time should be predictable N t+1 = N t + B + I - D - E Time 1 N = 100 20 births 25 deaths 10 immigrants 15 emmigrants Time 2 100 + 20 +10 25 15 = 90 Life History
14.1. KEY CONCEPT Every organism has a habitat and a niche. 38 Reinforcement Unit 5 Resource Book
 14.1 HABITAT AND NICHE KEY CONCEPT Every organism has a habitat and a niche. A habitat is all of the living and nonliving factors in the area where an organism lives. For example, the habitat of a frog
14.1 HABITAT AND NICHE KEY CONCEPT Every organism has a habitat and a niche. A habitat is all of the living and nonliving factors in the area where an organism lives. For example, the habitat of a frog
Describe how ecosystems recover from a disturbance. Compare succession after a natural disturbance with succession after a human-caused disturbance.
 1 2 Objectives Describe how ecosystems recover from a disturbance. Compare succession after a natural disturbance with succession after a human-caused disturbance. 3 Succesion Cartoon Guide to the Environment
1 2 Objectives Describe how ecosystems recover from a disturbance. Compare succession after a natural disturbance with succession after a human-caused disturbance. 3 Succesion Cartoon Guide to the Environment
BIO S380T Page 1 Summer 2005: Exam 2
 BIO S380T Page 1 Part I: Definitions. [5 points for each term] For each term, provide a brief definition that also indicates why the term is important in ecology or evolutionary biology. Where I ve provided
BIO S380T Page 1 Part I: Definitions. [5 points for each term] For each term, provide a brief definition that also indicates why the term is important in ecology or evolutionary biology. Where I ve provided
Chapter Niches and Community Interactions
 Chapter 4 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions Key Questions: 1) What is a niche? 2) How does competition shape communities? 3) How do predation and herbivory shape communites? 4) What are three primary
Chapter 4 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions Key Questions: 1) What is a niche? 2) How does competition shape communities? 3) How do predation and herbivory shape communites? 4) What are three primary
An ecological community 7/12/2012. Consists of all the interacting populations within an ecosystem
 Strategies for Success Community Interactions Prepared by Diana Wheat For General Biology 101 Linn-Benton Community College When alarmed, the Least Bittern freezes in place with its bill pointing up, turns
Strategies for Success Community Interactions Prepared by Diana Wheat For General Biology 101 Linn-Benton Community College When alarmed, the Least Bittern freezes in place with its bill pointing up, turns
BIOS 6150: Ecology Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences
 BIOS 6150: Ecology Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences Week 6: Predation and predatory behavior: Lecture summary: Nature of predation. Diet breadth & choice. Optimal foraging. Functional
BIOS 6150: Ecology Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences Week 6: Predation and predatory behavior: Lecture summary: Nature of predation. Diet breadth & choice. Optimal foraging. Functional
Multiple choice 2 pts each): x 2 = 18) Essay (pre-prepared) / 15 points. 19) Short Answer: / 2 points. 20) Short Answer / 5 points
 P 1 Biology 217: Ecology Second Exam Fall 2004 There should be 7 ps in this exam - take a moment and count them now. Put your name on the first p of the exam, and on each of the ps with short answer questions.
P 1 Biology 217: Ecology Second Exam Fall 2004 There should be 7 ps in this exam - take a moment and count them now. Put your name on the first p of the exam, and on each of the ps with short answer questions.
Lesson Overview 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions
 THINK ABOUT IT If you ask someone where an organism lives, that person might answer on a coral reef or in the desert. Lesson Overview 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions These answers give the environment
THINK ABOUT IT If you ask someone where an organism lives, that person might answer on a coral reef or in the desert. Lesson Overview 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions These answers give the environment
CHAPTER. Evolution and Community Ecology
 CHAPTER 5 Evolution and Community Ecology Lesson 5.1 Evolution Scientists have identified and described over 1.5 million species. Millions more have yet to be discovered. Lesson 5.1 Evolution Evolution
CHAPTER 5 Evolution and Community Ecology Lesson 5.1 Evolution Scientists have identified and described over 1.5 million species. Millions more have yet to be discovered. Lesson 5.1 Evolution Evolution
Ch 4 Ecosystems and Communities. 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions
 Ch 4 Ecosystems and Communities 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions The Niche The conditions in which an organisms lives, and how it interacts with its environment (in the trees, on the ground, inside
Ch 4 Ecosystems and Communities 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions The Niche The conditions in which an organisms lives, and how it interacts with its environment (in the trees, on the ground, inside
organism population community ecosystem biosphere Community Ecology AP Biology
 organism Community Ecology population community ecosystem biosphere Community Ecology Community all the organisms that live together in a place = interactions Community Ecology To answer: study of interactions
organism Community Ecology population community ecosystem biosphere Community Ecology Community all the organisms that live together in a place = interactions Community Ecology To answer: study of interactions
Competition: Observations and Experiments. Cedar Creek MN, copyright David Tilman
 Competition: Observations and Experiments Cedar Creek MN, copyright David Tilman Resource-Ratio (R*) Theory Species differ in critical limiting concentration for resources (R* values) R* values differ
Competition: Observations and Experiments Cedar Creek MN, copyright David Tilman Resource-Ratio (R*) Theory Species differ in critical limiting concentration for resources (R* values) R* values differ
Dynamic and Succession of Ecosystems
 Dynamic and Succession of Ecosystems Kristin Heinz, Anja Nitzsche 10.05.06 Basics of Ecosystem Analysis Structure Ecosystem dynamics Basics Rhythms Fundamental model Ecosystem succession Basics Energy
Dynamic and Succession of Ecosystems Kristin Heinz, Anja Nitzsche 10.05.06 Basics of Ecosystem Analysis Structure Ecosystem dynamics Basics Rhythms Fundamental model Ecosystem succession Basics Energy
Section 4 Professor Donald McFarlane
 Craniates Section 4 Professor Donald McFarlane Lecture 20 Ecology 3: Species Interactions. 2 defining characteristics compared to invertebrate chordates 1. Cranium - protective bony or cartilaginous housing
Craniates Section 4 Professor Donald McFarlane Lecture 20 Ecology 3: Species Interactions. 2 defining characteristics compared to invertebrate chordates 1. Cranium - protective bony or cartilaginous housing
Name Student ID. Good luck and impress us with your toolkit of ecological knowledge and concepts!
 Page 1 BIOLOGY 150 Final Exam Winter Quarter 2000 Before starting be sure to put your name and student number on the top of each page. MINUS 3 POINTS IF YOU DO NOT WRITE YOUR NAME ON EACH PAGE! You have
Page 1 BIOLOGY 150 Final Exam Winter Quarter 2000 Before starting be sure to put your name and student number on the top of each page. MINUS 3 POINTS IF YOU DO NOT WRITE YOUR NAME ON EACH PAGE! You have
Introduction interspecific interactions
 Introduction There are different interspecific interactions, relationships between the species of a community (what s the definition of a community again?). While you re at it, what s the definition of
Introduction There are different interspecific interactions, relationships between the species of a community (what s the definition of a community again?). While you re at it, what s the definition of
Weeds, Exotics or Invasives?
 Invasive Species Geography 444 Adopted from Dr. Deborah Kennard Weeds, Exotics or Invasives? What is a weed? Invasive species? 1 Weeds, Exotics or Invasives? Exotic or non-native: Non-native invasive pest
Invasive Species Geography 444 Adopted from Dr. Deborah Kennard Weeds, Exotics or Invasives? What is a weed? Invasive species? 1 Weeds, Exotics or Invasives? Exotic or non-native: Non-native invasive pest
CHAPTER. Population Ecology
 CHAPTER 4 Population Ecology Chapter 4 TOPIC POPULATION ECOLOGY Indicator Species Serve as Biological Smoke Alarms Indicator species Provide early warning of damage to a community Can monitor environmental
CHAPTER 4 Population Ecology Chapter 4 TOPIC POPULATION ECOLOGY Indicator Species Serve as Biological Smoke Alarms Indicator species Provide early warning of damage to a community Can monitor environmental
Ecology Regulation, Fluctuations and Metapopulations
 Ecology Regulation, Fluctuations and Metapopulations The Influence of Density on Population Growth and Consideration of Geographic Structure in Populations Predictions of Logistic Growth The reality of
Ecology Regulation, Fluctuations and Metapopulations The Influence of Density on Population Growth and Consideration of Geographic Structure in Populations Predictions of Logistic Growth The reality of
organism Community Ecology population community ecosystem biosphere
 organism Community Ecology population community ecosystem biosphere Community Ecology Community all the organisms that live together in a place interactions Community Ecology study of interactions among
organism Community Ecology population community ecosystem biosphere Community Ecology Community all the organisms that live together in a place interactions Community Ecology study of interactions among
What is competition? Competition among individuals. Competition: Neutral Theory vs. the Niche
 Competition: Neutral Theory vs. the Niche Reading assignment: Ch. 10, GSF (especially p. 237-249) Optional: Clark 2009 9/21/09 1 What is competition? A reduction in fitness due to shared use of a limited
Competition: Neutral Theory vs. the Niche Reading assignment: Ch. 10, GSF (especially p. 237-249) Optional: Clark 2009 9/21/09 1 What is competition? A reduction in fitness due to shared use of a limited
2008 ECOLOGY (B&C) Training Handout by Karen Lancour Ecology Event: Ecology Content Principles of Ecology (about 50%) Forests and Deserts (about 50%)
 2008 ECOLOGY (B&C) Training Handout by Karen Lancour Ecology Event: Ecology Content Principles of Ecology (about 50%) Forests and Deserts (about 50%) Process skills - in data, graph and diagram analysis
2008 ECOLOGY (B&C) Training Handout by Karen Lancour Ecology Event: Ecology Content Principles of Ecology (about 50%) Forests and Deserts (about 50%) Process skills - in data, graph and diagram analysis
Competition. Not until we reach the extreme confines of life, in the arctic regions or on the borders of an utter desert, will competition cease
 Competition Not until we reach the extreme confines of life, in the arctic regions or on the borders of an utter desert, will competition cease Darwin 1859 Origin of Species Competition A mutually negative
Competition Not until we reach the extreme confines of life, in the arctic regions or on the borders of an utter desert, will competition cease Darwin 1859 Origin of Species Competition A mutually negative
