BIFs. BIFs. Last time we covered. Oxygen. Oxygen
|
|
|
- Benjamin Kennedy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA Last time we covered Archean Oceans Discussion (Robbie) MAS 603: Geological Oceanography Banded Iron Formations (Evolution of the Earth s atmosphere and hydrosphere) Lecture 10: Ediacarins 1) The Early Atmosphere 2) The Oceans and Hydrosphere 3) The Change Oxygen The how is easy: Cyanobacteria (e.g., the microorganisms comprising stromatolites) and photosynthesis Oxygen Of particular interest are banded iron formations (BIFs) that are composed of alternating layers of hematite (Fe2O3) and silica. Photosynthesis 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 ( sugar ) + 6O2 BIFs The first BIFs formed around 3.1 GA and peaked in abundance at GA BIFs BIFs are thought to have been formed through oxygenation of sea water containing Fe2+ (reduced iron). Fe2+ Soluble Fe3+ Insoluble 1
2 Oxygen in the Atmosphere Oxygen in the Atmosphere What about the atmosphere? Around the world, we see a shift in color of river floodplain shale Green to Red Fe 2+ Fe 3+ At 1.8 GA Today s s Agenda Proterozoic Beasties 1) Eukaryotes (Acritarchs) 2) Metazoans (Ediacarin Fauna) During the Archean, we saw the rise of the prokaryotes: Small No nucleus DNA spread throughout the cell Asexual reproduction Could only be single-celled During the Proterozoic, something wonderful happens: the rise of the eukaryotes: Larger (>0.06 mm) A nucleus and organelles DNA contained within the nucleus Sexual reproduction Could be multi-celled (metazoans) The first eukaryotes appeared around 2 GA. Archritarchs were small, single celled silica beasties that floated in the oceans (pelagic). They peaked in abundance at 750 MA and then went away 0.1mm 2
3 or did they? They might in fact be ancestors to equally small single celled organisms that are around today called dinoflaggelates Another big change in the Proterozoic was the appearance of the first Metazoans 0.1mm 5 cm They are known as the Ediacarin Fauna And they are found around the world What were the Ediacarins? Three major forms What happened to them? What happened to them? 1) a now extinct line of beasties 3
4 What happened to them? 1) a now extinct line of beasties 2) ancestors to living phyla Kimberella sp. What were the Ediacarins? 1) a now extinct line of beasties 2) ancestors to living phyla Dickinsonia sp. Whatever they were, they exploded onto the scene immediately after the last Snowball Earth. Coincidence? More likely, severe environmental changes drives evolutionary adaptation. We need bad things to happen in order to evolve. The Cambrian Explosion Not so much an explosion The Cambrian Explosion more of a shift to hard body parts 4
5 The Cambrian Explosion The Cambrian Explosion Burgess Shale Fauna Chengjiang Fauna What we know about the early development of all of the current phyla is limited to sites where we have lots of beasties preserved Burgess Shale Site Burgess Shale Site 5
6 Pikaia gracilens (phylum: Chordata) Limb Anomalocaris canadensis Hallucigenia sparsa (phylum: Arthropoda?) (Proto-Arthropod; Problematica) (phylum: Arthropoda) 6
7 Jaws Anomalocaris canadensis (phylum: Arthropoda?) (Proto-Arthropod; Problematica) s.jpg Next Time 1. Monday: Proterozoic Evolution Discussion (Isabella) 2. Wednesday: Sedimentary Facies Warning: Take home exam issued next Monday (No reading next week) 7
GY 112 Lecture Notes Proterozoic Life forms
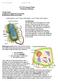 GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 Lecture Goals: A) Eukaryote Life forms (Acritarchs) B) Metazoans (Ediacaran Fauna) GY 112 Lecture Notes Proterozoic Life forms Textbook reference: Levin 7 th edition
GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 Lecture Goals: A) Eukaryote Life forms (Acritarchs) B) Metazoans (Ediacaran Fauna) GY 112 Lecture Notes Proterozoic Life forms Textbook reference: Levin 7 th edition
EVOLUTION OF COMPLEX LIFE FORMS
 0.002 0.6 1.0 1.9 2.8 Ancestral humans Diversification of mammals Invasion of the land Diversification of animals Origin of the major eukaryotic groups Eukaryotic cells abundant Atmospheric oxygen plentiful
0.002 0.6 1.0 1.9 2.8 Ancestral humans Diversification of mammals Invasion of the land Diversification of animals Origin of the major eukaryotic groups Eukaryotic cells abundant Atmospheric oxygen plentiful
PTYS 214 Spring Announcements Midterm #4: two weeks from today!
 PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm #4: two weeks from today! 1 Previously Radiometric Dating Compare parent / daughter to determine # of half lives 14C, 40K, 238U, 232Th, 87Ru Evidence for Early
PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm #4: two weeks from today! 1 Previously Radiometric Dating Compare parent / daughter to determine # of half lives 14C, 40K, 238U, 232Th, 87Ru Evidence for Early
Lecture 24: Paleozoic 1:
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lecture 24: Paleozoic 1: Laurentia Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time (before the exam) The Cambrian Explosion A) Why a Cambrian explosion B)
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lecture 24: Paleozoic 1: Laurentia Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time (before the exam) The Cambrian Explosion A) Why a Cambrian explosion B)
Radiation and Evolution of Metazoans: The Cambrian Explosion and the Burgess Shale Fossils. Geology 331, Paleontology
 Radiation and Evolution of Metazoans: The Cambrian Explosion and the Burgess Shale Fossils Geology 331, Paleontology Marshall, 2006 Halkierids, which produced some of the small, shelly fossils of the Early
Radiation and Evolution of Metazoans: The Cambrian Explosion and the Burgess Shale Fossils Geology 331, Paleontology Marshall, 2006 Halkierids, which produced some of the small, shelly fossils of the Early
Calculating extra credit from clicker points. Total points through last week: Participation: 6 x 2 = 12 Performance: = 26
 Clicker Questions, Test 2 February 10, 2016, Outline 7 1. Darwin coined the term Natural Selection to contrast with what other term? A. Evolutionary Selection B. Competition C. Artificial Selection D.
Clicker Questions, Test 2 February 10, 2016, Outline 7 1. Darwin coined the term Natural Selection to contrast with what other term? A. Evolutionary Selection B. Competition C. Artificial Selection D.
Development of Life. Stephen Eikenberry 06 September 2012 AST 2037
 Development of Life Stephen Eikenberry 06 September 2012 AST 2037 1 Evolution This time with a capital E Reproduction occurs via DNA Any change in the DNA from one generation to the next creates mutation
Development of Life Stephen Eikenberry 06 September 2012 AST 2037 1 Evolution This time with a capital E Reproduction occurs via DNA Any change in the DNA from one generation to the next creates mutation
3. Evolutionary change is random because gene mutations are random. A. True B. False
 Clicker Questions, Test 2 February 9, 2015, Outline 7 1. Darwin coined the term Natural Selection to contrast with what other term? A. Evolutionary Selection B. Competition C. Artificial Selection D. Survival
Clicker Questions, Test 2 February 9, 2015, Outline 7 1. Darwin coined the term Natural Selection to contrast with what other term? A. Evolutionary Selection B. Competition C. Artificial Selection D. Survival
Outline 11: Fossil Record of Early Life Life in the Precambrian
 Outline 11: Fossil Record of Early Life Life in the Precambrian Time Line 0.545 BY animals with hard parts, start of the Phanerozoic Eon 0.600 BY first animals, no hard parts 2.0 BY first definite eukaryotes
Outline 11: Fossil Record of Early Life Life in the Precambrian Time Line 0.545 BY animals with hard parts, start of the Phanerozoic Eon 0.600 BY first animals, no hard parts 2.0 BY first definite eukaryotes
Effect of Life on the Atmosphere: The Rise of Oxygen and Ozone
 Some preliminary chemistry Chapter 11 Effect of Life on the Atmosphere: The Rise of Oxygen and Ozone Chemical reactions involve the giving and taking of electrons between atoms. the nucleus is not affected
Some preliminary chemistry Chapter 11 Effect of Life on the Atmosphere: The Rise of Oxygen and Ozone Chemical reactions involve the giving and taking of electrons between atoms. the nucleus is not affected
Earth History & Geobiology. O. Jagoutz
 Earth History & Geobiology O. Jagoutz 12.001 Intro: Earth differs from other rocky planets by the presence of the hydrosphere, free oxygen and the presence of complex life. It is a major scientific challenge
Earth History & Geobiology O. Jagoutz 12.001 Intro: Earth differs from other rocky planets by the presence of the hydrosphere, free oxygen and the presence of complex life. It is a major scientific challenge
Visualizing Earth Science. Chapter Overview. The Ever-Changing Earth. Early Life. Evolution and the Fossil Record. Life in the Phanerozoic Eon
 Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 11 A Brief History of Life on Earth Chapter Overview The Ever-Changing Earth Early Life Evolution and the Fossil Record Life in the Phanerozoic
Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 11 A Brief History of Life on Earth Chapter Overview The Ever-Changing Earth Early Life Evolution and the Fossil Record Life in the Phanerozoic
Geology Summer Independent Learning: Introduction to Evolution and Mass Extinction Events
 Geology Summer Independent Learning: Introduction to Evolution and Mass Extinction Events First Life Episode 1 Arrival (David Attenborough) Watch the video in the link https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o7-sqwqlg8i
Geology Summer Independent Learning: Introduction to Evolution and Mass Extinction Events First Life Episode 1 Arrival (David Attenborough) Watch the video in the link https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o7-sqwqlg8i
Biol 415 Cambrian Explosion. Billie J. Swalla 238 Kincaid Hall 9-11 Tuesday
 Biol 415 Cambrian Explosion Billie J. Swalla 238 Kincaid Hall 9-11 Tuesday bjswalla@u.washington.edu Milestones in Life s Evolution 1.Formation first life 2. Diversification of life - lateral gene transfer
Biol 415 Cambrian Explosion Billie J. Swalla 238 Kincaid Hall 9-11 Tuesday bjswalla@u.washington.edu Milestones in Life s Evolution 1.Formation first life 2. Diversification of life - lateral gene transfer
Chapter 19. History of Life on Earth
 Chapter 19 History of Life on Earth Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Chapter 19 Section 3: Evolution of Life Key Vocabulary Terms Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Cyanobacteria Photosynthetic prokaryotes Adapted
Chapter 19 History of Life on Earth Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Chapter 19 Section 3: Evolution of Life Key Vocabulary Terms Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Cyanobacteria Photosynthetic prokaryotes Adapted
GY 112 Lecture Notes Cambrian Explosion
 GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 GY 112 Lecture Notes Cambrian Explosion Lecture Goals: A) Phanerozoic time frame (Paleozoic Era) B) Why a Cambrian explosion C) Introducing our ancestors Textbook
GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 GY 112 Lecture Notes Cambrian Explosion Lecture Goals: A) Phanerozoic time frame (Paleozoic Era) B) Why a Cambrian explosion C) Introducing our ancestors Textbook
The Hadean Earth Gya Impacts melt the surface. Volatiles escape to space
 Life on Earth. II 4.5-3.9 Gya Impacts melt the surface. Volatiles escape to space The Hadean Earth Source of atmosphere, oceans: outgassing and impacts Early atmosphere: CO 2, H 2 O, N 2, H 2 S, SO 2,
Life on Earth. II 4.5-3.9 Gya Impacts melt the surface. Volatiles escape to space The Hadean Earth Source of atmosphere, oceans: outgassing and impacts Early atmosphere: CO 2, H 2 O, N 2, H 2 S, SO 2,
The Proterozoic: Ga. Archean-early Proterozoic Continents:
 The Proterozoic: 2.5-0.542 Ga Early Proterozoic Orogenesis ~ modern Growth of continents and Supercontinents Life and Environments of Proterozoic Archean-early Proterozoic Continents: First large continent
The Proterozoic: 2.5-0.542 Ga Early Proterozoic Orogenesis ~ modern Growth of continents and Supercontinents Life and Environments of Proterozoic Archean-early Proterozoic Continents: First large continent
Earth Science. Name Block. Unit 3 Review Worksheet. Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer
 Earth Science Unit 3 Review Worksheet Name Block Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1. Which geologic principle is used when a geologist observes an outcrop or rocks and determines
Earth Science Unit 3 Review Worksheet Name Block Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1. Which geologic principle is used when a geologist observes an outcrop or rocks and determines
Phys 214. Planets and Life
 Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 22. Origin and evolution of life. Part II March
Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 22. Origin and evolution of life. Part II March
Chapter 12. Life of the Paleozoic
 Chapter 12 Life of the Paleozoic Paleozoic Invertebrates Representatives of most major invertebrate phyla were present during Paleozoic, including sponges, corals, bryozoans, brachiopods, mollusks, arthropods,
Chapter 12 Life of the Paleozoic Paleozoic Invertebrates Representatives of most major invertebrate phyla were present during Paleozoic, including sponges, corals, bryozoans, brachiopods, mollusks, arthropods,
Ch. 12 Proterozoic Eon
 Ch. 12 Proterozoic Eon Proterozoic Eon is ~ 1.95 billion years in duration, from 2.5 Ga to 0.543 Ga 2.5 Ga 1.6 Ga 1.0 Ga 0.54 Ga Paleoproterozoic Era Mesoproterozoic Era Neoproterozoic Era PROTEROZOIC
Ch. 12 Proterozoic Eon Proterozoic Eon is ~ 1.95 billion years in duration, from 2.5 Ga to 0.543 Ga 2.5 Ga 1.6 Ga 1.0 Ga 0.54 Ga Paleoproterozoic Era Mesoproterozoic Era Neoproterozoic Era PROTEROZOIC
Biological Evolution. Darwinian Evolution and Natural Selection
 Biological Evolution Darwinian Evolution and Natural Selection 1. Linnaean Classification Major Concepts 2. Fossils 3. Radioactive Dating 4. Fossil Record and Genetic Analysis 5. Theory of Evolution Random,
Biological Evolution Darwinian Evolution and Natural Selection 1. Linnaean Classification Major Concepts 2. Fossils 3. Radioactive Dating 4. Fossil Record and Genetic Analysis 5. Theory of Evolution Random,
9.1- Earth Forms and Life Begins
 9.1- Earth Forms and Life Begins About Earth: Earth was formed about 4.6 billion years ago! The first life on earth appeared about 4 billion years ago Life started out as small, single-celled organisms
9.1- Earth Forms and Life Begins About Earth: Earth was formed about 4.6 billion years ago! The first life on earth appeared about 4 billion years ago Life started out as small, single-celled organisms
The Proterozoic Eon (2500 ma to 540 ma)
 The Proterozoic Eon (2500 ma to 540 ma) December November October September August July June May April March February January 0 Ma Phanerozoic C M P 540 Ma oldest shelly fossils Proterozoic 2500 Ma first
The Proterozoic Eon (2500 ma to 540 ma) December November October September August July June May April March February January 0 Ma Phanerozoic C M P 540 Ma oldest shelly fossils Proterozoic 2500 Ma first
SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR GEOLOGY 103, TEST 2
 SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR GEOLOGY 103, TEST 2 The correct answers are listed at the bottom (no peeking!). These questions are to give you an idea of the type of questions that will be asked. They are not a
SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR GEOLOGY 103, TEST 2 The correct answers are listed at the bottom (no peeking!). These questions are to give you an idea of the type of questions that will be asked. They are not a
Geologic Time on a Strip of Paper
 Geologic Time on a Strip of Paper Introduction The Earth is 4,600,000,000 years old. That s 4.6 billion years! But what does this mean? This activity is designed to help you get a feel for the age of the
Geologic Time on a Strip of Paper Introduction The Earth is 4,600,000,000 years old. That s 4.6 billion years! But what does this mean? This activity is designed to help you get a feel for the age of the
Origin of Life. What is Life? The evolutionary tree of life can be documented with evidence. The Origin of Life on Earth is another
 sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Origin of Life 500 Paleozoic 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 ARCHEAN Millions of years ago 1000 PROTEROZOIC Cenozoic Mesozoic 4000
sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Origin of Life 500 Paleozoic 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 ARCHEAN Millions of years ago 1000 PROTEROZOIC Cenozoic Mesozoic 4000
Chapter 25: The Origin and Evolutionary History of Life on Earth
 Chapter 25: The Origin and Evolutionary History of Life on Earth Chemical conditions of the early Earth A model for the first cells First life Life changes the planet: oxygenating Earth s oceans and atmosphere
Chapter 25: The Origin and Evolutionary History of Life on Earth Chemical conditions of the early Earth A model for the first cells First life Life changes the planet: oxygenating Earth s oceans and atmosphere
Name Class Date. 2. What first appeared on Earth during Precambrian time? a. dinosaurs b. mammals c. life d. humans
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: Eras of the Geologic Time Scale 1. What are the four biggest eras in geologic history? a. Precambrian, Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic b. Precambrian, Prehistoric,
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: Eras of the Geologic Time Scale 1. What are the four biggest eras in geologic history? a. Precambrian, Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic b. Precambrian, Prehistoric,
Planets & Life. Planets & Life PHYS 214. Please start all class related s with 214: 214: Dept of Physics (308A)
 Planets & Life Planets & Life PHYS 214 Dr Rob Thacker Dept of Physics (308A) thacker@astro.queensu.ca Please start all class related emails with 214: 214: Today s s Lecture Evolution of the cell Possibility
Planets & Life Planets & Life PHYS 214 Dr Rob Thacker Dept of Physics (308A) thacker@astro.queensu.ca Please start all class related emails with 214: 214: Today s s Lecture Evolution of the cell Possibility
X The evolution of life on Earth.
 X The evolution of life on Earth http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 10.0 Introduction A combination of the fossil record, biology and genetics allows us to examine the evolution of life on Earth.
X The evolution of life on Earth http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 10.0 Introduction A combination of the fossil record, biology and genetics allows us to examine the evolution of life on Earth.
Lecture V Eukaryotes and the Cambrian Explosion.
 Lecture V Eukaryotes and the Cambrian Explosion. I. Early Metabolisms. 1. Heterotrophs: Anaerobic; aerobic; 2. Autotrophs: Anoxic; oxygenic. Some Metabolic Pathways Heterotrophy Pathway Energy Source Initial
Lecture V Eukaryotes and the Cambrian Explosion. I. Early Metabolisms. 1. Heterotrophs: Anaerobic; aerobic; 2. Autotrophs: Anoxic; oxygenic. Some Metabolic Pathways Heterotrophy Pathway Energy Source Initial
UNIT 4: EVOLUTION Chapter 12: The History of Life. I. The Fossil Record (12.1) A. Fossils can form in several ways
 UNIT IV Chapter 12 The History Of Life UNIT 4: EVOLUTION Chapter 12: The History of Life I. The Fossil Record (12.1) A. Fossils can form in several ways 1. Permineralization- minerals carried by water
UNIT IV Chapter 12 The History Of Life UNIT 4: EVOLUTION Chapter 12: The History of Life I. The Fossil Record (12.1) A. Fossils can form in several ways 1. Permineralization- minerals carried by water
IV. Major events in biological development on Earth
 IV. Major events in biological development on Earth Cambrian explosion We are trying to fill in some of the biological details in the timelines shown here. Meiosis UV shield Snowball Earth XX Horizontal
IV. Major events in biological development on Earth Cambrian explosion We are trying to fill in some of the biological details in the timelines shown here. Meiosis UV shield Snowball Earth XX Horizontal
Chapter 12 - Long term climate regulation. Chapter 10-11* -Brief History of the Atmosphere. What is p really about? New and improved!
 What is p16164 really about? New and improved! 1) When CO 2 dissolves in water, some reacts with water to produce acid and ions, making gas exchange NOT just CO 2 (g in atm) CO 2 (aq in ocn) 2) If
What is p16164 really about? New and improved! 1) When CO 2 dissolves in water, some reacts with water to produce acid and ions, making gas exchange NOT just CO 2 (g in atm) CO 2 (aq in ocn) 2) If
History of Life on Earth
 History of Life on Earth Deep Time 4550 mya to present era eon era era Precambrian Eon Hadean Era Geology Birth of solar system - 4.55 bya Escaping gasses create early atmosphere Earth s core forms - 4.4
History of Life on Earth Deep Time 4550 mya to present era eon era era Precambrian Eon Hadean Era Geology Birth of solar system - 4.55 bya Escaping gasses create early atmosphere Earth s core forms - 4.4
Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages )
 Name Class Date Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages 417-422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils?
Name Class Date Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages 417-422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils?
Biogeography. Lecture 5
 Biogeography. Lecture 5 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University January 25, 2016 Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 5 January 25, 2016 1 / 34 Outline Palaeogeography Plate tectonics Cryogenian period
Biogeography. Lecture 5 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University January 25, 2016 Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 5 January 25, 2016 1 / 34 Outline Palaeogeography Plate tectonics Cryogenian period
I. Early Theory! A. Spontaneous Generation - The hypothesis that life arises regularly from non-living things
 ORIGIN OF LIFE! I. Early Theory! A. Spontaneous Generation - The hypothesis that life arises regularly from non-living things II. Experiments That Helped to Disprove Spontaneous Generation! A. Italian
ORIGIN OF LIFE! I. Early Theory! A. Spontaneous Generation - The hypothesis that life arises regularly from non-living things II. Experiments That Helped to Disprove Spontaneous Generation! A. Italian
The Proterozoic Part 1
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History The Proterozoic Part 1 Lectures 18/19: Tectonics Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) The Early Atmosphere 2) The Oceans and Hydrosphere 3)
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History The Proterozoic Part 1 Lectures 18/19: Tectonics Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) The Early Atmosphere 2) The Oceans and Hydrosphere 3)
Evolution of Life and the Atmosphere
 Evolution of Life and the Atmosphere White board used for Evolution of the Atmosphere and Early Evolution of Life The Pitfalls of Preservation It is obvious that a major change occurred in the Earth s
Evolution of Life and the Atmosphere White board used for Evolution of the Atmosphere and Early Evolution of Life The Pitfalls of Preservation It is obvious that a major change occurred in the Earth s
The Geological Time Scale. Geological time scaled to a cross-country tour of Canada.
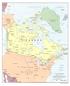 Dryden The Geological Time Scale Geological time scaled to a cross-country tour of anada. The universe came into existence about 14 billion years ago, through an explosion known as the "big bang". ur galaxy
Dryden The Geological Time Scale Geological time scaled to a cross-country tour of anada. The universe came into existence about 14 billion years ago, through an explosion known as the "big bang". ur galaxy
Evolution and diversity of organisms
 Evolution and diversity of organisms Competency Levels - 7 3.1.1 Uses the theories of origin of life and natural selection to analyze the process of evolution of life 3.2.1 Constructs hierarchy of taxa
Evolution and diversity of organisms Competency Levels - 7 3.1.1 Uses the theories of origin of life and natural selection to analyze the process of evolution of life 3.2.1 Constructs hierarchy of taxa
Proterozoic Life and Environments
 Proterozoic Life and Environments (or: 3 billion years in 70 minutes) Cambrian Explosion Origin of Life Great Oxygenation Event Origin of Life Early Life Localities >2.5 Ga Named localities: >3.2 Ga Isua
Proterozoic Life and Environments (or: 3 billion years in 70 minutes) Cambrian Explosion Origin of Life Great Oxygenation Event Origin of Life Early Life Localities >2.5 Ga Named localities: >3.2 Ga Isua
The Microbial World. Microorganisms of the Sea
 The Microbial World Microorganisms of the Sea Microorganisms Smallest, simplest marine organisms. Very important in evolutionary history of life on Earth. Important primary producers. Include prokaryotes
The Microbial World Microorganisms of the Sea Microorganisms Smallest, simplest marine organisms. Very important in evolutionary history of life on Earth. Important primary producers. Include prokaryotes
REFERENCE: The Blue Planet An Introduction to Earth System Science. Brian J. Skinner and Barbara W. Murck (2011) Third Edition. John Wiley and Sons
 REFERENCE: The Blue Planet An Introduction to Earth System Science. Brian J. Skinner and Barbara W. Murck (2011) Third Edition. John Wiley and Sons Inc. Most life on Earth lives within a zone no wider
REFERENCE: The Blue Planet An Introduction to Earth System Science. Brian J. Skinner and Barbara W. Murck (2011) Third Edition. John Wiley and Sons Inc. Most life on Earth lives within a zone no wider
Origins of Life & the Cambrian Explosion
 Origins of Life & the Cambrian Explosion Impact Frustration period forces origins of life into a narrow time period to have gotten started! Hydrothermal vents may have served as zones of refuge. Origin
Origins of Life & the Cambrian Explosion Impact Frustration period forces origins of life into a narrow time period to have gotten started! Hydrothermal vents may have served as zones of refuge. Origin
Origins of Life & the Cambrian Explosion
 Origins of Life & the Cambrian Explosion Impact Frustration period forces origins of life into a narrow time period to have gotten started! Hydrothermal vents may have served as zones of refuge. 1 Origin
Origins of Life & the Cambrian Explosion Impact Frustration period forces origins of life into a narrow time period to have gotten started! Hydrothermal vents may have served as zones of refuge. 1 Origin
Origin & History of Life
 Origin & History of Life SIX Kingdoms! New one = Archea Thanks C. Woese Prokaryotes = no discrete nucleus containing genetic material This bush of life accurately shows Archea, Eubacteria and Eukaryotes
Origin & History of Life SIX Kingdoms! New one = Archea Thanks C. Woese Prokaryotes = no discrete nucleus containing genetic material This bush of life accurately shows Archea, Eubacteria and Eukaryotes
Unit 6: Interpreting Earth s History
 Unit 6: Interpreting Earth s History How do we know that the Earth has changed over time? Regent s Earth Science Name: Topics Relative Dating Uniformitarianism Superposition Original Horizontality Igneous
Unit 6: Interpreting Earth s History How do we know that the Earth has changed over time? Regent s Earth Science Name: Topics Relative Dating Uniformitarianism Superposition Original Horizontality Igneous
Biological Evolution. Darwinian Evolution and Natural Selection
 Biological Evolution Darwinian Evolution and Natural Selection 1. Linnaean Classification Major Concepts 2. Fossils 3. Radioactive Dating 4. Fossil Record and Genetic Analysis 5. Theory of Evolution Random,
Biological Evolution Darwinian Evolution and Natural Selection 1. Linnaean Classification Major Concepts 2. Fossils 3. Radioactive Dating 4. Fossil Record and Genetic Analysis 5. Theory of Evolution Random,
The History of the Earth
 The History of the Earth Origin of the Universe The universe began about 13.9 billion years ago According to Big Bang theory almost all matter was in the form of energy E = MC 2 E = energy, M = mass and
The History of the Earth Origin of the Universe The universe began about 13.9 billion years ago According to Big Bang theory almost all matter was in the form of energy E = MC 2 E = energy, M = mass and
1. Be able to explain how the development of a magnetosphere affected the evolution of Earth s atmosphere (3) Atmosphere 1. Be able to describe the
 I. Evolution 1. be able to define biologic evolution. 2. be able to define and apply the principles of Natural Selection. 3. be able to describe Gregor Mendel s experiment with pea plants. a) be able to
I. Evolution 1. be able to define biologic evolution. 2. be able to define and apply the principles of Natural Selection. 3. be able to describe Gregor Mendel s experiment with pea plants. a) be able to
Use evidence of characteristics of life to differentiate between living and nonliving things.
 Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards All living things have a common set characteristic needs and functions that separate them from nonliving things such as:
Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards All living things have a common set characteristic needs and functions that separate them from nonliving things such as:
Life on Earth Topic Test
 Life on Earth Topic Test Multiple Choice Questions Select the best alternative and indicate your response on the answer sheet. (1 mark each) 1. The list below contains common substances that exist in Earth
Life on Earth Topic Test Multiple Choice Questions Select the best alternative and indicate your response on the answer sheet. (1 mark each) 1. The list below contains common substances that exist in Earth
GY 112 Lecture Notes Evolution of the Earth's Atmosphere and Hydrosphere
 GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 GY 112 Lecture Notes Evolution of the Earth's Atmosphere and Hydrosphere Lecture Goals: A) The Early Atmosphere B) The Oceans and Hydrosphere C) The Change Textbook
GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 GY 112 Lecture Notes Evolution of the Earth's Atmosphere and Hydrosphere Lecture Goals: A) The Early Atmosphere B) The Oceans and Hydrosphere C) The Change Textbook
ET Life #17. Today: Reminders: Energy of Life. Paper Proposal Due Friday First Mid-term Next Monday
 ET Life #17 Today: Energy of Life Reminders: Paper Proposal Due Friday First Mid-term Next Monday Origin of Life: Summary 1. Early Organic Molecules 2. Complex organics developed (mineral templates?).
ET Life #17 Today: Energy of Life Reminders: Paper Proposal Due Friday First Mid-term Next Monday Origin of Life: Summary 1. Early Organic Molecules 2. Complex organics developed (mineral templates?).
A brief history of the Earth!
 A brief history of the Earth! The Geologic Time Scale Age of the Earth Hadean Eon Hadean Eon (4.57-3.85 Gyrs) Hell on Earth: 4.527 Gyrs formation of Moon 4.5 Gyrs - magma ocean, differentiation of core,
A brief history of the Earth! The Geologic Time Scale Age of the Earth Hadean Eon Hadean Eon (4.57-3.85 Gyrs) Hell on Earth: 4.527 Gyrs formation of Moon 4.5 Gyrs - magma ocean, differentiation of core,
History of Life on Earth
 Macroevolution Broad pattern of evolution at and above the species level (in contrast to microevolution) History of Life on Earth Chapter 25 Early earth Miller and Urey Experiments ~4.5 billion years old
Macroevolution Broad pattern of evolution at and above the species level (in contrast to microevolution) History of Life on Earth Chapter 25 Early earth Miller and Urey Experiments ~4.5 billion years old
Laboratory 7 Geologic Time
 (Name) Laboratory 7 Geologic Time We will be exploring ideas behind the development of the geological column. The geological column is a general term that is used to describe the template behind which
(Name) Laboratory 7 Geologic Time We will be exploring ideas behind the development of the geological column. The geological column is a general term that is used to describe the template behind which
The Origins and evolution of life
 The Origins and evolution of life The Origins and evolution of life Geologic time scale The geologic time scale provides a system of chronologic measurement used by geologists, paleontologists and other
The Origins and evolution of life The Origins and evolution of life Geologic time scale The geologic time scale provides a system of chronologic measurement used by geologists, paleontologists and other
4Gya Gya. Bombardment over: Oceans had formed and stabilized Atmosphere had stabilized. The Archean Era
 Life on Earth. II 4Gya - 2.5 Gya Bombardment over: Oceans had formed and stabilized Atmosphere had stabilized The Archean Era First Life What was the first life on Earth? The first living things must have
Life on Earth. II 4Gya - 2.5 Gya Bombardment over: Oceans had formed and stabilized Atmosphere had stabilized The Archean Era First Life What was the first life on Earth? The first living things must have
Study Guide. Biology 2101B. Science. Biodiversity. Adult Basic Education. Biology 2101A. Prerequisite: Credit Value: 1
 Adult Basic Education Science Biodiversity Prerequisite: Biology 2101A Credit Value: 1 Text: Biology. Bullard, Chetty, et al; McGraw-Hill Ryerson, 2003. Biology Concentration Biology 1101 Biology 2101A
Adult Basic Education Science Biodiversity Prerequisite: Biology 2101A Credit Value: 1 Text: Biology. Bullard, Chetty, et al; McGraw-Hill Ryerson, 2003. Biology Concentration Biology 1101 Biology 2101A
Outline. Origin and History of Life
 Origin and History of Life Chapter 19 Primitive Earth Origin of First Cells Fossils The Precambrian The Paleozoic The Mesozoic The Cenozoic Continental Drift Mass Extinctions Outline 1 2 The Primitive
Origin and History of Life Chapter 19 Primitive Earth Origin of First Cells Fossils The Precambrian The Paleozoic The Mesozoic The Cenozoic Continental Drift Mass Extinctions Outline 1 2 The Primitive
Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages )
 Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils? What
Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils? What
Chapter 11. The Archean Era of Precambrian Time
 Chapter 11 The Archean Era of Precambrian Time 1 Guiding Questions When and how did Earth and its moon come into being? How did the core, mantle, crust form? Where did Archean rocks form, and what is their
Chapter 11 The Archean Era of Precambrian Time 1 Guiding Questions When and how did Earth and its moon come into being? How did the core, mantle, crust form? Where did Archean rocks form, and what is their
Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math
 Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours 1/37 *AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which does not
Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours 1/37 *AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which does not
Study of Biology. copyright cmassengale
 Study of Biology 1 What is Biology? Biology is the study of all living things Living things are called organisms Organisms include bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, & animals 2 All Living Things Share
Study of Biology 1 What is Biology? Biology is the study of all living things Living things are called organisms Organisms include bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, & animals 2 All Living Things Share
The History of Life. Fossils and Ancient Life (page 417) How Fossils Form (page 418) Interpreting Fossil Evidence (pages ) Chapter 17
 Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time scale that is used
Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time scale that is used
Bio10 Practice Lab Exam 1
 Bio10 Practice Lab Exam 1 Instructions: Answer the following questions using the concepts pertaining to laboratory exercises. This information is in your textbook, lab manual, or instructor provided handouts.
Bio10 Practice Lab Exam 1 Instructions: Answer the following questions using the concepts pertaining to laboratory exercises. This information is in your textbook, lab manual, or instructor provided handouts.
THEORY OF EVOLUTION BY; MICHAEL AND PAIGE
 THEORY OF EVOLUTION BY; MICHAEL AND PAIGE FIRST THINGS FIRST THERE ARE MANY THEORIES AND IDEAS OF EVOLUTION THAT MANY SCIENTIST STILL HAVE NOT PROVEN YET. EVOLUTION IS A MYSTERY ITSELF. KEY MA=1,000,00
THEORY OF EVOLUTION BY; MICHAEL AND PAIGE FIRST THINGS FIRST THERE ARE MANY THEORIES AND IDEAS OF EVOLUTION THAT MANY SCIENTIST STILL HAVE NOT PROVEN YET. EVOLUTION IS A MYSTERY ITSELF. KEY MA=1,000,00
Biology. Slide 1 of 40. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 40 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life The fossil record provides evidence about the history of life on Earth. It also shows how different
Biology 1 of 40 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life The fossil record provides evidence about the history of life on Earth. It also shows how different
sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Origin of Life
 sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Origin of Life 2010-2011 ARCHEAN Millions of years ago PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC 0 500 1000 Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Colonization
sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Origin of Life 2010-2011 ARCHEAN Millions of years ago PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC 0 500 1000 Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Colonization
Monday-Tuesday (1/7-1/8)
 Monday-Tuesday (1/7-1/8) You have 4 minutes to write the following about your winter break: 3 things you did 2 places you went 1 favorite memory Geologic Time Line Contest 1. Start of the age of the dinosaurs
Monday-Tuesday (1/7-1/8) You have 4 minutes to write the following about your winter break: 3 things you did 2 places you went 1 favorite memory Geologic Time Line Contest 1. Start of the age of the dinosaurs
Evolution and Diversification of Life
 Evolution and Diversification of Life Frogfish OCN 201 Science of the Sea Biology Lecture 2 Grieg Steward (Oceanography) Office: CMORE Hale 121 Phone: x6-6775 Evolution Nothing in biology makes sense except
Evolution and Diversification of Life Frogfish OCN 201 Science of the Sea Biology Lecture 2 Grieg Steward (Oceanography) Office: CMORE Hale 121 Phone: x6-6775 Evolution Nothing in biology makes sense except
Earth s history can be broken up into 4 time periods: Precambrian Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era
 Earth s History Video Clip Earth s History Earth s history can be broken up into 4 time periods: Precambrian Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era Scientists have put together a timeline of Earth s history
Earth s History Video Clip Earth s History Earth s history can be broken up into 4 time periods: Precambrian Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era Scientists have put together a timeline of Earth s history
Rare Earth? See Rare Earth, by Ward and Brownlee
 Rare Earth? See Rare Earth, by Ward and Brownlee N to date N = N * f s f p n H f l f i f c L/T N * = 4 x 10 11 f s = 0.2 f p = 1.0 n H = 2 f l = 1.0 N = 1.6 x 10 11 The Goldilocks Effect Earth is Just
Rare Earth? See Rare Earth, by Ward and Brownlee N to date N = N * f s f p n H f l f i f c L/T N * = 4 x 10 11 f s = 0.2 f p = 1.0 n H = 2 f l = 1.0 N = 1.6 x 10 11 The Goldilocks Effect Earth is Just
How do we learn about ancient life? Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological processes.
 Unit 1B Lesson 4 History of Life on Earth How do we learn about ancient life? Paleontologists scientists that studies fossils Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological
Unit 1B Lesson 4 History of Life on Earth How do we learn about ancient life? Paleontologists scientists that studies fossils Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological
sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Life s Origin & Early Evolution (Ch. 20)
 sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Life s Origin & Early Evolution (Ch. 20) 2007-2008 ARCHEAN Millions of years ago PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC 0 500 1000 Cenozoic
sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Life s Origin & Early Evolution (Ch. 20) 2007-2008 ARCHEAN Millions of years ago PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC 0 500 1000 Cenozoic
UNIT 4: EVOLUTION Chapter 12: The History of Life
 CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be stamped after each assigned
CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be stamped after each assigned
Plate Tectonics. Alfred Lothar Wegener. Relatively new theory - introduced about 30 years ago Unifies several branches of the Earth Sciences
 Plate Tectonics Relatively new theory - introduced about 30 years ago Unifies several branches of the Earth Sciences http://pubs.usgs.gov/publications/text/dynamic.html Alfred Lothar Wegener In 1858, geographer
Plate Tectonics Relatively new theory - introduced about 30 years ago Unifies several branches of the Earth Sciences http://pubs.usgs.gov/publications/text/dynamic.html Alfred Lothar Wegener In 1858, geographer
Identify stages of plant life cycle Botany Oral/written pres, exams
 DPI Standards Biology Education (for students) 1. Characteristics of organisms Know Properties of living organisms, including: Acquire and use energy and materials Sense and respond to stimuli Reproduce
DPI Standards Biology Education (for students) 1. Characteristics of organisms Know Properties of living organisms, including: Acquire and use energy and materials Sense and respond to stimuli Reproduce
12.1. KEY CONCEPT Fossils are a record of life that existed in the past. 68 Reinforcement Unit 4 Resource Book
 12.1 THE FOSSIL RECORD KEY CONCEPT Fossils are a record of life that existed in the past. Fossils can form in several different ways: Permineralization occurs when water surrounds a hard structure such
12.1 THE FOSSIL RECORD KEY CONCEPT Fossils are a record of life that existed in the past. Fossils can form in several different ways: Permineralization occurs when water surrounds a hard structure such
17-1 The Fossil Record Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about past life is called the fossil record. The fossil record includes
1 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about past life is called the fossil record. The fossil record includes
A. Incorrect! Sponges are mostly marine animals. This is a feature of sponges.
 College Biology - Problem Drill 15: The Evolution of Animal Diversity Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which is not a feature of the phyla porifera- sponges? Question #01 (A) Most are marine animals. (B) They have
College Biology - Problem Drill 15: The Evolution of Animal Diversity Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which is not a feature of the phyla porifera- sponges? Question #01 (A) Most are marine animals. (B) They have
Banded Iron Formations (BIF) - Reading
 Banded Iron Formations (BIF) (University of Oregon) Banded Iron Formation (also known as BIF) is a term that is applied to a very unique sedimentary rock of biochemical origin. Unique in their make-up,
Banded Iron Formations (BIF) (University of Oregon) Banded Iron Formation (also known as BIF) is a term that is applied to a very unique sedimentary rock of biochemical origin. Unique in their make-up,
Name Class Date. Crossword Puzzle Use the clues below to complete the puzzle.
 Chapter 17 The History of Life Chapter Vocabulary Review Crossword Puzzle Use the clues below to complete the puzzle. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Across 2. time span shorter than an era, such as Quaternary
Chapter 17 The History of Life Chapter Vocabulary Review Crossword Puzzle Use the clues below to complete the puzzle. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Across 2. time span shorter than an era, such as Quaternary
Biology. Slide 1 / 44. Slide 2 / 44. Slide 3 / 44. Origins of Life Multiple Choice
 Slide 1 / 44 Slide 2 / 44 iology Origins of Life Multiple hoice 2015-10-14 www.njctl.org 1 Where did the heavier elements, present in our solar system, come from? Slide 3 / 44 collisions between the earth
Slide 1 / 44 Slide 2 / 44 iology Origins of Life Multiple hoice 2015-10-14 www.njctl.org 1 Where did the heavier elements, present in our solar system, come from? Slide 3 / 44 collisions between the earth
Requirements for Life. What is Life? Definition of Life. One of the biggest questions in astronomy is whether life exists elsewhere in the universe
 Requirements for Life One of the biggest questions in astronomy is whether life exists elsewhere in the universe Before we discuss the possibility of life elsewhere, we must have a better understanding
Requirements for Life One of the biggest questions in astronomy is whether life exists elsewhere in the universe Before we discuss the possibility of life elsewhere, we must have a better understanding
Animal Origins and Evolution
 Animal Origins and Evolution Common Features of Animals multicellular heterotrophic motile Sexual reproduction, embryo Evolution of Animals All animals are multicellular and heterotrophic, which means
Animal Origins and Evolution Common Features of Animals multicellular heterotrophic motile Sexual reproduction, embryo Evolution of Animals All animals are multicellular and heterotrophic, which means
Biology. Slide 1 / 44. Slide 2 / 44. Slide 3 / 44. Origins of Life Multiple Choice
 Slide 1 / 44 Slide 2 / 44 iology Origins of Life Multiple hoice 2015-10-14 www.njctl.org 1 Where did the heavier elements, present in our solar system, come from? Slide 3 / 44 collisions between the earth
Slide 1 / 44 Slide 2 / 44 iology Origins of Life Multiple hoice 2015-10-14 www.njctl.org 1 Where did the heavier elements, present in our solar system, come from? Slide 3 / 44 collisions between the earth
b. By Proterozoic, - protected from solar radiation if about 10 M below surface of water - dominated by
 I. Diversification of Life A. Review 1. Hadean Eon a. b. 2. Archaean Eon a. Earliest fossils of b. Establishment of three major domains B. Proterozoic Eon (2.5 bya - 543 mya) 1. Emergence of the a. Rock
I. Diversification of Life A. Review 1. Hadean Eon a. b. 2. Archaean Eon a. Earliest fossils of b. Establishment of three major domains B. Proterozoic Eon (2.5 bya - 543 mya) 1. Emergence of the a. Rock
Evolution of Earth Environments Bio-Geo-Chemical Cycling
 Evolution of Earth Environments Bio-Geo-Chemical Cycling Evolution of the Earliest Atmospheres of Mars and Earth Volcanic Outgassing Evolving to Equilibrium Atmosphere To Atmosphere Lost to space (Abundant)
Evolution of Earth Environments Bio-Geo-Chemical Cycling Evolution of the Earliest Atmospheres of Mars and Earth Volcanic Outgassing Evolving to Equilibrium Atmosphere To Atmosphere Lost to space (Abundant)
Earth History
 Earth History 89.331 Course information Prof. Lori Weeden Office: Olney 402b Office phone: 978-934-3344 Lori_weeden@uml.edu Course web page: http://faculty.uml.edu/lweeden/earthlife.htm Earth System History
Earth History 89.331 Course information Prof. Lori Weeden Office: Olney 402b Office phone: 978-934-3344 Lori_weeden@uml.edu Course web page: http://faculty.uml.edu/lweeden/earthlife.htm Earth System History
First, an supershort History of the Earth by Eon
 HISTORY OF LIFE WRITTEN IN THE ROCKS (geological record): notice how at first no life, very simple if for billions of years, complex life only recently 600 mya In these chapters, two primary themes: History
HISTORY OF LIFE WRITTEN IN THE ROCKS (geological record): notice how at first no life, very simple if for billions of years, complex life only recently 600 mya In these chapters, two primary themes: History
4) Outline the major developments that allowed life to exist on Earth.
 Objectives 4) Outline the major developments that allowed life to exist on Earth. 5) Describe the types of organisms that arose during the four major divisions of the geologic time scale. Each layer of
Objectives 4) Outline the major developments that allowed life to exist on Earth. 5) Describe the types of organisms that arose during the four major divisions of the geologic time scale. Each layer of
 All Living Things Share Common Characteristics 1. Living Things are Composed of Cells: Single-cell organisms have everything they need to be self-sufficient. In multicellular organisms, some cells do only
All Living Things Share Common Characteristics 1. Living Things are Composed of Cells: Single-cell organisms have everything they need to be self-sufficient. In multicellular organisms, some cells do only
Origins of Life and Extinction
 Origins of Life and Extinction What is evolution? What is evolution? The change in the genetic makeup of a population over time Evolution accounts for the diversity of life on Earth Natural selection is
Origins of Life and Extinction What is evolution? What is evolution? The change in the genetic makeup of a population over time Evolution accounts for the diversity of life on Earth Natural selection is
4.0 Billion Years of Earth Environmental Change
 4.0 Billion Years of Earth Environmental Change We have already explored the various ways the Earth has evolved over the past 4 billion years. 1. Volcanic arcs, to proto-continents, to microcontinents,
4.0 Billion Years of Earth Environmental Change We have already explored the various ways the Earth has evolved over the past 4 billion years. 1. Volcanic arcs, to proto-continents, to microcontinents,
