Contents. 1 Introduction to Meiobenthology Meiobenthos and Meiofauna: Definitions A History of Meiobenthology...
|
|
|
- Eunice Gilmore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Contents 1 Introduction to Meiobenthology Meiobenthos and Meiofauna: Definitions A History of Meiobenthology The Biotope: Factors and Study Methods Abiotic Factors (Sediment Physiography) Sediment Pores and Particles Granulometric Characteristics The Sediment Water Regime Physicochemical Characteristics Biotic Habitat Factors: A Connected Complex Detritus and Particulate Organic Matter (POM) Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) Mucus, Exopolymers, and Biofilms Bacteria Microphytobenthos Higher Plants Animals Structuring the Ecosystem Conclusion: The Microtexture of Natural Sediments Sampling and Processing Meiofauna Sampling Number of Replicates and Size of Sampling Units Sampling Devices Processing of Meiofaunal Samples Preserving Meiofauna in Their Natural Void System Extraction of Meiofauna Fixation and Preservation Processing and Identifying Meiofaunal Organisms Extraction of Pore Water xiii
2 xiv Contents 4 Biological Characteristics of Meiofauna Adaptations to the Biotope Adaptations to Narrow Spaces: Miniaturization, Elongation, Flexibility Adaptations to the Mobile Environment: Adhesion, Special Locomotion, Reinforcing Structures Adaptations to the Three-Dimensional Dark Environment: Static Organs, Reduction of Pigment and Eyes Adaptations Related to Reproduction and Development Meiofauna Taxa: A Systematic Account Protista (Protoctista) Foraminifera (Rhizaria: Granuloreticulosa) Heliozoa (Actinopodia) Amoebozoa ( Rhizopoda ): Gymnamoebea, Testacea Ciliophora (Ciliata) Cnidaria Hydroida (Medusae) Hydroida (Polyps) Scyphozoa Anthozoa Free-Living Platyhelminthes: Turbellarians Major Turbellarian Groups Distributional and Ecological Aspects Gnathifera Gnathostomulida Rotifera, Rotatoria Micrognathozoa Nemertinea Nemathelminthes: A Valid Taxon? Nematoda (Free-Living) Kinorhyncha Priapulida Loricifera Gastrotricha Tardigrada Crustacea Cephalocarida Anostraca: Anomopoda ( Cladocera ; Branchiopoda ) Ostracoda
3 Contents xv Mystacocarida Copepoda: Harpacticoida Copepoda: Cyclopoida and Siphonostomatoida Malacostraca Chelicerata: Acari Halacaroidea: Halacaridae Freshwater Mites: Hydrachnidia, Stygothrombiidae, and Others Palpigradi (Arachnida) Pycnogonida, Pantopoda Terrigenous Arthropoda (Thalassobionts) Annelida Polychaeta Oligochaeta Annelida Incertae sedis Sipuncula Mollusca Monoplacophora and Aplacophora Gastropoda Tentaculata Brachiopoda Bryozoa, Ectoprocta Kamptozoa, Entoprocta Echinodermata Holothuroidea Chaetognatha Tunicata (Chordata) Ascidiacea Sorberacea Meiofaunal Taxa: Concluding Remarks Evolutionary and Phylogenetic Effects in Meiobenthology Body Structures of Evolutionary Relevance Meiofauna in the Fossil Record Patterns of Meiofauna Distribution Evolutionary Aspects Zoogeographic Aspects Mechanisms of Dispersal Geological Structures and Processes Ecological Aspects of Distributional Importance: Horizontal Patterns Vertical Zonation of Meio benthos
4 xvi Contents 8 Meiofauna from Selected Biotopes and Regions Polar Regions Sea Ice Marine Subtropical and Tropical Regions Tropical Sands Mangroves The Deep-Sea The Habitat The Meiofauna Dysoxic, Anoxic, and Sulfidic Environments: Discussing the Thiobios Reducing Habitats of the Thiobios Thiobiotic Meio benthos Survival of Thiobios Under Anoxia and Sulphide Mechanisms and Adaptations Food Spectrum of the Thiobios Distribution and Succession of the Thiobios Diversity and Evolution of the Thiobios Chemoautotrophy-Based Ecosystems: Vents, Seeps, and Other Exotic Habitats Phytal Habitats and Hard Substrates Brackish Water Sites Freshwater Biotopes Running Waters: Stream and River Beds The Groundwater System Standing Waters, Lakes Polluted Habitats General Aspects and Method Survey Selected Cases of Pollution and Meiofauna Synecological Perspectives in Meiobenthology Community Structure and Diversity Processes of Recolonization Community Structure and Size Spectra The Meio benthos in the Benthic Energy Flow General Considerations Assessing Production: Abundance, Biomass, P/B Ratio, Respiration The Energetic Divergence Between Meiofauna and Macrofauna The Position of Meiofauna in the Benthic Ecosystem: A Compilation of Energy Fluxes The Meiofauna as Members of the Small Food Web Links Between the Meiofauna and the Macrofauna Meiofauna as an Integrative Benthic Complex
5 Contents xvii 10 Retrospect on Meiobenthology and Outlook on New Approaches and Future Research References Glossary Index
6
The Ecology of Meiofauna and the Adaption to its Habitat. Marinbiologische Seminar Raimund Schnegg
 The Ecology of Meiofauna and the Adaption to its Habitat Marinbiologische Seminar 17.06.2014 Raimund Schnegg What is the meiofauna? Members of the zoobenthos defined by mesh size of sieves: >1 mm = macrofauna
The Ecology of Meiofauna and the Adaption to its Habitat Marinbiologische Seminar 17.06.2014 Raimund Schnegg What is the meiofauna? Members of the zoobenthos defined by mesh size of sieves: >1 mm = macrofauna
Invertebrate Zoology Tuesdays and Thursdays (8:30 am - 5:30 pm) Earlier than 8:30 am on many morning field trips
 Invertebrate Zoology Tuesdays and Thursdays (8:30 am - 5:30 pm) Earlier than 8:30 am on many morning field trips Spring Quarter 2014 Instructors: Cynthia Trowbridge (cdt@uoregon.edu) Maya Watts (mwolf1@uoregon.edu)
Invertebrate Zoology Tuesdays and Thursdays (8:30 am - 5:30 pm) Earlier than 8:30 am on many morning field trips Spring Quarter 2014 Instructors: Cynthia Trowbridge (cdt@uoregon.edu) Maya Watts (mwolf1@uoregon.edu)
Invertebrate Zoology (BI451/551, 8 credits) Tuesdays and Thursdays (8:30 am - 5:30 pm) Earlier than 8:30 am on many morning field trips
 Invertebrate Zoology (BI451/551, 8 credits) Tuesdays and Thursdays (8:30 am - 5:30 pm) Earlier than 8:30 am on many morning field trips Spring Quarter 2016 (ver 2-18-2016) Instructors: Richard Emlet (remlet@uoregon.edu)
Invertebrate Zoology (BI451/551, 8 credits) Tuesdays and Thursdays (8:30 am - 5:30 pm) Earlier than 8:30 am on many morning field trips Spring Quarter 2016 (ver 2-18-2016) Instructors: Richard Emlet (remlet@uoregon.edu)
Class Webpage. Forms of Diversity. biol170/biol170syl.htm
 Class Webpage http://userwww.sfsu.edu/~efc/classes/ biol170/biol170syl.htm What is an animal? While there are exceptions, five criteria distinguish animals from other life forms. (1)Animals are multicellular,
Class Webpage http://userwww.sfsu.edu/~efc/classes/ biol170/biol170syl.htm What is an animal? While there are exceptions, five criteria distinguish animals from other life forms. (1)Animals are multicellular,
Number of Species. Taxonomic Hierarchy. Representing the Groups. Binomial Nomenclature. Taxonomy and Animal Phylogeny. Carolus Linnaeus ( )
 Taxonomy and Animal Phylogeny Number of Species Approx. 1.5 million species known Miller and Harley Chap. 7 Taxonomy = Systematics = Phylogeny Taxonomic Hierarchy Carolus Linnaeus (1707-1778) Kingdom Phylum
Taxonomy and Animal Phylogeny Number of Species Approx. 1.5 million species known Miller and Harley Chap. 7 Taxonomy = Systematics = Phylogeny Taxonomic Hierarchy Carolus Linnaeus (1707-1778) Kingdom Phylum
Chapter 12: Aquatic Mandibulates
 Chapter 12: Aquatic Mandibulates Phylum Arthropoda Subphylum: Crustacea (Latin crusta = shell) Class: Malacostraca Order: Decapoda Order: Euphausiacea Order: Amphipoda Order: Isopoda Class: Maxillopoda
Chapter 12: Aquatic Mandibulates Phylum Arthropoda Subphylum: Crustacea (Latin crusta = shell) Class: Malacostraca Order: Decapoda Order: Euphausiacea Order: Amphipoda Order: Isopoda Class: Maxillopoda
Number of Species. Taxonomy and Animal Phylogeny. Approx. 1.5 million species known. Taxonomy = Systematics = Phylogeny. Miller and Harley Chap.
 Taxonomy and Animal Phylogeny Miller and Harley Chap. 7 Number of Species Approx. 1.5 million species known Taxonomy = Systematics = Phylogeny 1 Taxonomic Hierarchy Carolus Linnaeus (1707-1778) Kingdom
Taxonomy and Animal Phylogeny Miller and Harley Chap. 7 Number of Species Approx. 1.5 million species known Taxonomy = Systematics = Phylogeny 1 Taxonomic Hierarchy Carolus Linnaeus (1707-1778) Kingdom
CHAPTER 2: PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC CELLS THE PROKARYOTIC CELL...86 THE EUKARYOTE CELL...92
 TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION... 1 THE STORY OF LIFE ON EARTH... 2 LIVING AND NON-LIVING... 7 THE DOMAINS... 9 SIX KINGDOMS: PRESENTATION...14 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SIX KINGDOMS...23 SIX KINGDOMS
TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION... 1 THE STORY OF LIFE ON EARTH... 2 LIVING AND NON-LIVING... 7 THE DOMAINS... 9 SIX KINGDOMS: PRESENTATION...14 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SIX KINGDOMS...23 SIX KINGDOMS
Porifera. BIO2135 Animal Form & Function ACD. Page 1. Kingdom Animalia. Cladistics Useful terms. Cladistics - Useful terms
 Kingdom Animalia 1 Cladistics - Useful terms Apomorphies Derived characters within a group Plesiomorphies Primitive characters within a group Synapomorphies Derived characters shared between groups Symplesiomorphies
Kingdom Animalia 1 Cladistics - Useful terms Apomorphies Derived characters within a group Plesiomorphies Primitive characters within a group Synapomorphies Derived characters shared between groups Symplesiomorphies
Number of Species. Taxonomy and Animal Phylogeny. Approx. 1.5 million species known. Taxonomy = Systematics = Phylogeny. Miller and Harley Chap.
 Taxonomy and Animal Phylogeny Miller and Harley Chap. 7 Number of Species Approx. 1.5 million species known Taxonomy = Systematics = Phylogeny 1 Taxonomic Hierarchy Carolus Linnaeus (1707-1778) Kingdom
Taxonomy and Animal Phylogeny Miller and Harley Chap. 7 Number of Species Approx. 1.5 million species known Taxonomy = Systematics = Phylogeny 1 Taxonomic Hierarchy Carolus Linnaeus (1707-1778) Kingdom
BIOLOGICAL OCEANOGRAPHY
 BIOLOGICAL OCEANOGRAPHY AN INTRODUCTION 0 ^ J ty - y\ 2 S CAROL M. LALLI and TIMOTHY R. PARSONS University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada PERGAMON PRESS OXFORD NEW YORK SEOUL TOKYO ABOUT THIS VOLUME
BIOLOGICAL OCEANOGRAPHY AN INTRODUCTION 0 ^ J ty - y\ 2 S CAROL M. LALLI and TIMOTHY R. PARSONS University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada PERGAMON PRESS OXFORD NEW YORK SEOUL TOKYO ABOUT THIS VOLUME
BIO2135 Animal Form & Function 2 9:10 AM 1 9:10 AM. A= Symplesiomorphy C= Synapomorphy. (Autoapomorphy) 3 9:10 AM
 Kingdom nimalia Cladistics - Useful terms pomorphies Derived characters within a group Plesiomorphies Primitive characters within a group Synapomorphies Derived characters shared between groups Symplesiomorphies
Kingdom nimalia Cladistics - Useful terms pomorphies Derived characters within a group Plesiomorphies Primitive characters within a group Synapomorphies Derived characters shared between groups Symplesiomorphies
Due Friday, January 11, 2008
 Due Friday, January 11, 2008 Name AP Biology Winter Assignment Parade Through the Kingdoms A Brief Survey of Life s Diversity Complete the questions using Chapters 26 34 of your textbook: Biology (7th
Due Friday, January 11, 2008 Name AP Biology Winter Assignment Parade Through the Kingdoms A Brief Survey of Life s Diversity Complete the questions using Chapters 26 34 of your textbook: Biology (7th
DNA barcoding of North Atlantic zooplankton
 DNA barcoding of North Atlantic zooplankton Ann Bucklin University of Connecticut, Groton, CT USA Brian D. Ortman (Univ. British Columbia) Robert M. Jennings (Univ. Massachusetts Boston) and Lisa M. Nigro
DNA barcoding of North Atlantic zooplankton Ann Bucklin University of Connecticut, Groton, CT USA Brian D. Ortman (Univ. British Columbia) Robert M. Jennings (Univ. Massachusetts Boston) and Lisa M. Nigro
CHAPTER 6 & 7 VOCABULARY
 CHAPTER 6 & 7 VOCABULARY 1. Biome 2. Climate 3. Latitude 4. Altitude 5. Emergent layer 6. Epiphyte 7. Understory 8. Permafrost 9. Wetland 10.Plankton 11.Nekton 12.Benthos 13.Littoral zone 14.Benthic zone
CHAPTER 6 & 7 VOCABULARY 1. Biome 2. Climate 3. Latitude 4. Altitude 5. Emergent layer 6. Epiphyte 7. Understory 8. Permafrost 9. Wetland 10.Plankton 11.Nekton 12.Benthos 13.Littoral zone 14.Benthic zone
Invertebrate Survey Lab
 Answer these questions before lab. 1. What kingdom do all animals fall into? a. Protist b. Animalia c. Eukarya 2. How many phyla of invertebrates are in appendix E on pages 1074-1076? a. 9 b. 7 c. 8 3.
Answer these questions before lab. 1. What kingdom do all animals fall into? a. Protist b. Animalia c. Eukarya 2. How many phyla of invertebrates are in appendix E on pages 1074-1076? a. 9 b. 7 c. 8 3.
Georgia Performance Standards for Urban Watch Restoration Field Trips
 Georgia Performance Standards for Field Trips 6 th grade S6E3. Students will recognize the significant role of water in earth processes. a. Explain that a large portion of the Earth s surface is water,
Georgia Performance Standards for Field Trips 6 th grade S6E3. Students will recognize the significant role of water in earth processes. a. Explain that a large portion of the Earth s surface is water,
The Ecology of Soil Decomposition
 115? The Ecology of Soil Decomposition Sina M. Adi Department of Biology Dalhousie University Halifax, Nova Scotia Canada CABI Publishing Preface Acknowledgements 1 The Saprotrophs 1 Eukaryotic Cells 2
115? The Ecology of Soil Decomposition Sina M. Adi Department of Biology Dalhousie University Halifax, Nova Scotia Canada CABI Publishing Preface Acknowledgements 1 The Saprotrophs 1 Eukaryotic Cells 2
1 1:29 PM 2 1:29 PM. Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida Cycliophora Rotifera Annelida
 Phylum Mollusca 1 Extant Animalia ~1,300,000 species Parazoa (1.2%) Radiata (0.9%) Protostomia (3.9%) Platyzoa (2.2%) Platyhelminthes (1.9%) Others (0.3%) Lophotrochozoa (9.8%) Mollusca (8.5%) Annelida
Phylum Mollusca 1 Extant Animalia ~1,300,000 species Parazoa (1.2%) Radiata (0.9%) Protostomia (3.9%) Platyzoa (2.2%) Platyhelminthes (1.9%) Others (0.3%) Lophotrochozoa (9.8%) Mollusca (8.5%) Annelida
Benthic communities of Russian Arctic Seas under radioactive pollution condition
 Radioprotection, vol.44, n 5 (2009) 713 718 C EDP Sciences, 2009 DOI: 10.1051/radiopro/20095130 Benthic communities of Russian Arctic Seas under radioactive pollution condition V. Galtsova and D. Alexeev
Radioprotection, vol.44, n 5 (2009) 713 718 C EDP Sciences, 2009 DOI: 10.1051/radiopro/20095130 Benthic communities of Russian Arctic Seas under radioactive pollution condition V. Galtsova and D. Alexeev
A Brief Survey of Life s Diversity 1
 Name A Brief Survey of Life s Diversity 1 AP WINTER BREAK ASSIGNMENT (CH 25-34). Complete the questions using the chapters of your textbook Campbell s Biology (8 th edition). CHAPTER 25: The History of
Name A Brief Survey of Life s Diversity 1 AP WINTER BREAK ASSIGNMENT (CH 25-34). Complete the questions using the chapters of your textbook Campbell s Biology (8 th edition). CHAPTER 25: The History of
Animal Diversity I: Porifera, Cnidaria, Ctenophora, Platyhelminthes, Rotifera, Annelida
 1 Animal Diversity I: Porifera, Cnidaria, Ctenophora, Platyhelminthes, Rotifera, Annelida Objectives: Be able to distinguish radial symmetry from bilateral symmetry. Be able to identify which of the phyla
1 Animal Diversity I: Porifera, Cnidaria, Ctenophora, Platyhelminthes, Rotifera, Annelida Objectives: Be able to distinguish radial symmetry from bilateral symmetry. Be able to identify which of the phyla
PLANET EARTH CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS. Cesare Emiliani. Cosmology, Geology, and the Evolution off Life and Environment
 PLANET EARTH Cosmology, Geology, and the Evolution off Life and Environment Cesare Emiliani Department of Geological Sciences, The University of Miami CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface page xi PART I
PLANET EARTH Cosmology, Geology, and the Evolution off Life and Environment Cesare Emiliani Department of Geological Sciences, The University of Miami CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface page xi PART I
An Introduction to the Invertebrates
 An Introduction to the Invertebrates Janet Moore New Hall, Cambridge niustrations by Raith Overhill Second Edition. :::.. CAMBRIDGE :: UNIVERSITY PRESS ~nts ao Paulo, Delhi rcss, New York._ MOO 586 List
An Introduction to the Invertebrates Janet Moore New Hall, Cambridge niustrations by Raith Overhill Second Edition. :::.. CAMBRIDGE :: UNIVERSITY PRESS ~nts ao Paulo, Delhi rcss, New York._ MOO 586 List
Status of Macrofaunal Studies Carried Out by the Interoceanmetal Joint Organization (IOM)
 WORKSHOP ON TAXONOMIC METHODS AND STANDARDIZATION OF MACROFAUNA IN THE CLARION CLIPPERTON FRACTURE ZONE 23 30 November 2014 Uljin gun, Gyeongsangbuk do, South Korea Status of Macrofaunal Studies Carried
WORKSHOP ON TAXONOMIC METHODS AND STANDARDIZATION OF MACROFAUNA IN THE CLARION CLIPPERTON FRACTURE ZONE 23 30 November 2014 Uljin gun, Gyeongsangbuk do, South Korea Status of Macrofaunal Studies Carried
Pee Dee Explorer. Science Standards
 Science Standards About Pee Dee Explorer What does it mean when someone says they are from the "Pee Dee" of South Carolina? A place is bigger than its physical geography. A "sense of place" weaves together
Science Standards About Pee Dee Explorer What does it mean when someone says they are from the "Pee Dee" of South Carolina? A place is bigger than its physical geography. A "sense of place" weaves together
Unit 2: Ecology. Big Idea...
 Name: Block: Unit 2: Ecology Big Idea... The natural world is defined by organisms and life processes which conform to principles regarding conservation and transformation of matter and energy. Knowledge
Name: Block: Unit 2: Ecology Big Idea... The natural world is defined by organisms and life processes which conform to principles regarding conservation and transformation of matter and energy. Knowledge
UNIT 5: ECOLOGY Chapter 15: The Biosphere
 CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be stamped after each assigned
CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be stamped after each assigned
M.Sc. (Previous) DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY First Year ZOOLOGY. Paper I : Systematics and Anatomy of Invertebrates
 (DZOO 01) M.Sc. (Previous) DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY 2015 First Year ZOOLOGY Paper I : Systematics and Anatomy of Invertebrates Time : 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 80 Answer all questions All questions carry equal
(DZOO 01) M.Sc. (Previous) DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY 2015 First Year ZOOLOGY Paper I : Systematics and Anatomy of Invertebrates Time : 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 80 Answer all questions All questions carry equal
The Abundance and Spatial Distribution of Soft Sediment Communities in Tanjung Bungah, Malaysia: A Preliminary Study
 Tropical Life Sciences Research, 27(Supp. 1), 71 77, 2016 The Abundance and Spatial Distribution of Soft Sediment Communities in Tanjung Bungah, Malaysia: A Preliminary Study 1 Nur Aqilah Muhamad Darif,
Tropical Life Sciences Research, 27(Supp. 1), 71 77, 2016 The Abundance and Spatial Distribution of Soft Sediment Communities in Tanjung Bungah, Malaysia: A Preliminary Study 1 Nur Aqilah Muhamad Darif,
Animal Phyla: A Summary. Danilo V. Rogayan Jr. Faculty, College of Education, Arts and Sciences Ramon Magsaysay Technological University
 Animal Phyla: A Summary Danilo V. Rogayan Jr. Faculty, College of Education, Arts and Sciences Ramon Magsaysay Technological University Phylum Platyhelminthes The phylum consists of four classes Turbellaria
Animal Phyla: A Summary Danilo V. Rogayan Jr. Faculty, College of Education, Arts and Sciences Ramon Magsaysay Technological University Phylum Platyhelminthes The phylum consists of four classes Turbellaria
Revista Chilena de Historia Natural ISSN: X Sociedad de Biología de Chile Chile
 Revista Chilena de Historia Natural ISSN: 0716-078X editorial@revchilhistnat.com Sociedad de Biología de Chile Chile LEE, MATTHEW R.; CASTILLA, JUAN CARLOS; FERNÁNDEZ, MIRIAM; CLARKE, MARCELA; GONZÁLEZ,
Revista Chilena de Historia Natural ISSN: 0716-078X editorial@revchilhistnat.com Sociedad de Biología de Chile Chile LEE, MATTHEW R.; CASTILLA, JUAN CARLOS; FERNÁNDEZ, MIRIAM; CLARKE, MARCELA; GONZÁLEZ,
Marine Biodiversity: Global Ocean to the Salish Sea Design Your Own Salish Sea Creature
 Science Unit: Lesson #2 Marine Biodiversity: Global Ocean to the Salish Sea Design Your Own Salish Sea Creature Summary: Lesson type: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Developed by: Developed for: Based
Science Unit: Lesson #2 Marine Biodiversity: Global Ocean to the Salish Sea Design Your Own Salish Sea Creature Summary: Lesson type: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Developed by: Developed for: Based
EXPECTED OUTCOMES TIME FRAME (TOPICS/TASKS)
 Republic of the Philippines RAMON MAGSAYSAY TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SAN MARCELINO CAMPUS San Marcelino, Zambales COLLEGE OF TEACHER EDUCATION, ARTS AND SCIENCES COURSE SYLLABUS in ZOOLOGY Second Semester,
Republic of the Philippines RAMON MAGSAYSAY TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SAN MARCELINO CAMPUS San Marcelino, Zambales COLLEGE OF TEACHER EDUCATION, ARTS AND SCIENCES COURSE SYLLABUS in ZOOLOGY Second Semester,
Biology 3-4 Essential Questions:
 Biology 3-4 Essential Questions: 1. How does the process of evolution drive the unity and diversity of life? 2. How do biological systems utilize free energy and molecular building blocks to grow, reproduce
Biology 3-4 Essential Questions: 1. How does the process of evolution drive the unity and diversity of life? 2. How do biological systems utilize free energy and molecular building blocks to grow, reproduce
IMO HARMFUL AQUATIC ORGANISMS IN BALLAST WATER. Description of the proposed model groups defined under Tier 1. Submitted by Norway
 INTERNATIONAL MARITIME ORGANIZATION E IMO MARINE ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION COMMITTEE 47th session Agenda item 2 MEPC 47/INF.11 28 December 2001 ENGLISH ONLY HARMFUL AQUATIC ORGANISMS IN BALLAST WATER Description
INTERNATIONAL MARITIME ORGANIZATION E IMO MARINE ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION COMMITTEE 47th session Agenda item 2 MEPC 47/INF.11 28 December 2001 ENGLISH ONLY HARMFUL AQUATIC ORGANISMS IN BALLAST WATER Description
Treasure Coast Science Scope and Sequence
 Course: Marine Science I Honors Course Code: 2002510 Quarter: 3 Topic(s) of Study: Marine Organisms and Ecosystems Bodies of Knowledge: Nature of Science and Life Science Standard(s): 1: The Practice of
Course: Marine Science I Honors Course Code: 2002510 Quarter: 3 Topic(s) of Study: Marine Organisms and Ecosystems Bodies of Knowledge: Nature of Science and Life Science Standard(s): 1: The Practice of
Brunel, Pierre Département de Sciences Biologiques, Université de Montréal, Canada
 MARINE BIODIVERSITY Brunel, Pierre Département de Sciences Biologiques, Université de Montréal, Canada Keywords: marine, biodiversity, ecological, species, oceans, genetic, taxonomic Contents 1. Four Kinds
MARINE BIODIVERSITY Brunel, Pierre Département de Sciences Biologiques, Université de Montréal, Canada Keywords: marine, biodiversity, ecological, species, oceans, genetic, taxonomic Contents 1. Four Kinds
BIOLOGY. An Introduction to Invertebrates CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 33 An Introduction to Invertebrates Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Figure 33.UN08 Metazoa Eumetazoa
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 33 An Introduction to Invertebrates Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Figure 33.UN08 Metazoa Eumetazoa
The BIOTIC Component
 The BIOTIC Component Ecology = the study of organisms and their interaction with their environment Environment includes abiotic components and processes: light rainfall temperature humidity topography
The BIOTIC Component Ecology = the study of organisms and their interaction with their environment Environment includes abiotic components and processes: light rainfall temperature humidity topography
Phanerozic - Paleozoic
 Phanerozoic Paleozoic era Carboniferous and Permian 1 2 3 4 Carboniferous terrestrial environment 5 6 Page 1 Carboniferous coal forests Club mosses Giant horse tails Tree ferns Plant phylogeny Figure 24.9
Phanerozoic Paleozoic era Carboniferous and Permian 1 2 3 4 Carboniferous terrestrial environment 5 6 Page 1 Carboniferous coal forests Club mosses Giant horse tails Tree ferns Plant phylogeny Figure 24.9
Phanerozic - Paleozoic
 Phanerozoic Paleozoic era 1 Carboniferous and Permian 2 3 Page 1 4 5 Carboniferous terrestrial environment 6 Page 2 Carboniferous coal forests Club mosses Giant horse tails Tree ferns 7 Plant phylogeny
Phanerozoic Paleozoic era 1 Carboniferous and Permian 2 3 Page 1 4 5 Carboniferous terrestrial environment 6 Page 2 Carboniferous coal forests Club mosses Giant horse tails Tree ferns 7 Plant phylogeny
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 206 GENERAL ZOOLOGY. 5 Credit Hours. Prepared by: Dora Mitchell. Revised Date: September 2013
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 206 GENERAL ZOOLOGY 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Dora Mitchell Revised Date: September 2013 Ms. Linda Abernathy, Division Chair, Math, Science & Business Ms. Shirley
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 206 GENERAL ZOOLOGY 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Dora Mitchell Revised Date: September 2013 Ms. Linda Abernathy, Division Chair, Math, Science & Business Ms. Shirley
Learning Objectives. The Animal Kingdom: An Introduction to Animal Diversity. Sexual Reproduction
 Learning Objectives The Animal Kingdom: An Introduction to Animal Diversity Chapter 29 What characters are common to most animals? Advantages and disadvantages of different environments Searching for relationships
Learning Objectives The Animal Kingdom: An Introduction to Animal Diversity Chapter 29 What characters are common to most animals? Advantages and disadvantages of different environments Searching for relationships
Classification: Evolution:
 Review for Final Exam Suggestions All material covered in the course is testable. The following are suggested topics to cover, but is not meant to be an exhaustive list. Topics that are not listed but
Review for Final Exam Suggestions All material covered in the course is testable. The following are suggested topics to cover, but is not meant to be an exhaustive list. Topics that are not listed but
Antarctic Undersea Foodweb
 Details Completion Time: 2-3 hours Permission: Download, Share, and Remix Antarctic Undersea Foodweb Overview Using photos from a variety of websites, including the PolarTREC and SCINI websites, students
Details Completion Time: 2-3 hours Permission: Download, Share, and Remix Antarctic Undersea Foodweb Overview Using photos from a variety of websites, including the PolarTREC and SCINI websites, students
Marine biodiversity - PBBT102
 Marine biodiversity - PBBT102 UNIT 1 (2 marks) 1. Define marine biodiversity? 2. How biodiversity is measured? 3. Why many species go extinct every day? 4. What is biodiversity hotspot? 5. What are endemic
Marine biodiversity - PBBT102 UNIT 1 (2 marks) 1. Define marine biodiversity? 2. How biodiversity is measured? 3. Why many species go extinct every day? 4. What is biodiversity hotspot? 5. What are endemic
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 206 GENERAL ZOOLOGY. 5 Credit Hours. Prepared by: Dora Mitchell. Revised Date: September 2013
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 206 GENERAL ZOOLOGY 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Dora Mitchell Revised Date: September 2013 Ms. Linda Abernathy, Division Chair, Math, Science & Business Ms. Shirley
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 206 GENERAL ZOOLOGY 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Dora Mitchell Revised Date: September 2013 Ms. Linda Abernathy, Division Chair, Math, Science & Business Ms. Shirley
Organic Inputs. system (in lakes, this is usually leaves, needles, wood, and twigs from terrestrial vegetation)
 Aquatic Ecosystems Organic Inputs! Allochthonous organic matter! Organic matter that is derived from outside the system (in lakes, this is usually leaves, needles, wood, and twigs from terrestrial vegetation)!
Aquatic Ecosystems Organic Inputs! Allochthonous organic matter! Organic matter that is derived from outside the system (in lakes, this is usually leaves, needles, wood, and twigs from terrestrial vegetation)!
FAUNA OF SANDY BEACHES CALVI-EXCURSION VIANA WILLE
 FAUNA OF SANDY BEACHES CALVI-EXCURSION VIANA WILLE 12.07.2018 LIST OF CONTENT Beach formation Zonation of sandy beaches Vertical Horizontal Meiofauna Macrofauna Summary BEACH FORMATION Product of kinetic
FAUNA OF SANDY BEACHES CALVI-EXCURSION VIANA WILLE 12.07.2018 LIST OF CONTENT Beach formation Zonation of sandy beaches Vertical Horizontal Meiofauna Macrofauna Summary BEACH FORMATION Product of kinetic
Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Common Name or Group / Hint 1) 2) Infection
 MULTIPLE CHOICE / MATCHING 1. Fill In the following table of classification for this organism Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Common Name or Group / Hint 1) 2) Infection Page 1 of 16 BIO 110 QZM 6 Q
MULTIPLE CHOICE / MATCHING 1. Fill In the following table of classification for this organism Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Common Name or Group / Hint 1) 2) Infection Page 1 of 16 BIO 110 QZM 6 Q
Marine Ecology Pacing Guide
 Marine Ecology Pacing Guide Course Description: The focus of the course is the interrelationships among marine organisms and the physical, chemical, geological and biological factors. North Carolina coastal
Marine Ecology Pacing Guide Course Description: The focus of the course is the interrelationships among marine organisms and the physical, chemical, geological and biological factors. North Carolina coastal
Skeletal grains. Pores. Matrix <20 m) Cement. Non-skeletal grains. 1 cm
 Components of a Carbonate rock Skeletal grains Pores Matrix
Components of a Carbonate rock Skeletal grains Pores Matrix
Chapter 8. Sponges Phylum Porifera Basic characteristics: simple asymmetric sessile
 Chapter 8 Key Concepts Sponges are asymmetric, sessile animals that filter food from the water circulating through their bodies. Sponges provide habitats for other animals. Cnidarians and ctenophores exhibit
Chapter 8 Key Concepts Sponges are asymmetric, sessile animals that filter food from the water circulating through their bodies. Sponges provide habitats for other animals. Cnidarians and ctenophores exhibit
Few long-term and large-scale studies of
 Gulf of Mexico Science, 2012(1 2), pp. 20 29 A Multi-Year Survey of Meiofaunal Abundance From the Northern Gulf of Mexico Continental Shelf and Slope STEPHEN C. LANDERS, FRANK A. ROMANO III, PAUL M. STEWART,
Gulf of Mexico Science, 2012(1 2), pp. 20 29 A Multi-Year Survey of Meiofaunal Abundance From the Northern Gulf of Mexico Continental Shelf and Slope STEPHEN C. LANDERS, FRANK A. ROMANO III, PAUL M. STEWART,
Marine Life. and Ecology. 2. From phytoplanktons to invertebates
 Marine Life and Ecology 2. From phytoplanktons to invertebates Virtually all primary productivity on land comes from large seaweeds such as these do exist, but they need shallow water where Sunlight is
Marine Life and Ecology 2. From phytoplanktons to invertebates Virtually all primary productivity on land comes from large seaweeds such as these do exist, but they need shallow water where Sunlight is
INVERTEBRATE DIVERSITY
 INVERTEBRATE DIVERSITY 1 INVERTEBRATES Animals that lack a backbone Invertebrates 2 1 ANIMAL DEVELOPMENT Meiosis Egg Sperm Zygote Adult Blastula hollow ball of cells in a developing animal Gastrula Stage
INVERTEBRATE DIVERSITY 1 INVERTEBRATES Animals that lack a backbone Invertebrates 2 1 ANIMAL DEVELOPMENT Meiosis Egg Sperm Zygote Adult Blastula hollow ball of cells in a developing animal Gastrula Stage
1) Give detailed notes on classification of the Phylum Porifera up to orders.
 (DZOO 01 (NR)) ASSIGNMENT - 1, MAY - 2015. PAPER-I : SYSTEMATICS AND ANATODECEMBER OF INVERTEBRATES 1) Give detailed notes on classification of the Phylum Porifera up to orders. 2) Write short notes on:
(DZOO 01 (NR)) ASSIGNMENT - 1, MAY - 2015. PAPER-I : SYSTEMATICS AND ANATODECEMBER OF INVERTEBRATES 1) Give detailed notes on classification of the Phylum Porifera up to orders. 2) Write short notes on:
Invertebrate Zoology Midterm Exam 1- Fall 2015
 Invertebrate Zoology Midterm Exam 1- Fall 2015 Name Read through the exam before you begin. This exam consists of four (4) Parts. You must provide answers for each Part. However, you are required to answer
Invertebrate Zoology Midterm Exam 1- Fall 2015 Name Read through the exam before you begin. This exam consists of four (4) Parts. You must provide answers for each Part. However, you are required to answer
Animals. Chapters Exam November 22, 2011
 Animals Chapters 32-35 Exam November 22, 2011 Overview of Animals Chapter 32 General Features of Animals and Evolution of the Body Plan General Features of Animals Heterotrophs Multicellular No Cell Walls
Animals Chapters 32-35 Exam November 22, 2011 Overview of Animals Chapter 32 General Features of Animals and Evolution of the Body Plan General Features of Animals Heterotrophs Multicellular No Cell Walls
Lab 4 Identifying metazoan phyla and plant groups
 Geol G308 Paleontology and Geology of Indiana Name: Lab 4 Identifying metazoan phyla and plant groups The objective of this lab is to classify all of the fossils from your site to phylum (or to plant group)
Geol G308 Paleontology and Geology of Indiana Name: Lab 4 Identifying metazoan phyla and plant groups The objective of this lab is to classify all of the fossils from your site to phylum (or to plant group)
Quantitative distribution of meiobenthos in the Gulf of Martaban, Myanmar Coast, north-east Andaman Sea
 Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences Vol. 43(2), Febuary 2014, pp. 189-197 Quantitative distribution of meiobenthos in the Gulf of Martaban, Myanmar Coast, north-east Andaman Sea Z. A. Ansari 1*, Pratik
Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences Vol. 43(2), Febuary 2014, pp. 189-197 Quantitative distribution of meiobenthos in the Gulf of Martaban, Myanmar Coast, north-east Andaman Sea Z. A. Ansari 1*, Pratik
Physiography Ocean Provinces p. 1 Dimensions p. 1 Physiographic Provinces p. 2 Continental Margin Province p. 2 Deep-Ocean Basin Province p.
 Physiography Ocean Provinces p. 1 Dimensions p. 1 Physiographic Provinces p. 2 Continental Margin Province p. 2 Deep-Ocean Basin Province p. 2 Mid-Ocean Ridge Province p. 3 Benthic and Pelagic Provinces
Physiography Ocean Provinces p. 1 Dimensions p. 1 Physiographic Provinces p. 2 Continental Margin Province p. 2 Deep-Ocean Basin Province p. 2 Mid-Ocean Ridge Province p. 3 Benthic and Pelagic Provinces
Prentice Hall. Biology: Concepts and Connections, 6th edition 2009, (Campbell, et. al) High School
 Prentice Hall Biology: Concepts and Connections, 6th edition 2009, (Campbell, et. al) High School C O R R E L A T E D T O Correlation to the Mississippi Curriculum Frameworks - Biology II (High School)
Prentice Hall Biology: Concepts and Connections, 6th edition 2009, (Campbell, et. al) High School C O R R E L A T E D T O Correlation to the Mississippi Curriculum Frameworks - Biology II (High School)
Subtidal permanently flooded with tidal water. Irregularly exposed surface exposed by tides less often than daily
 Types of Wetlands Tidal Systems COASTAL WETLAND ECOSYSTEMS Tidal Salt Marshes Tidal Freshwater Marshes Mangrove Wetlands Tidal Estuarine Wetland 1 Definition and Formation of Estuaries u Estuary : partially
Types of Wetlands Tidal Systems COASTAL WETLAND ECOSYSTEMS Tidal Salt Marshes Tidal Freshwater Marshes Mangrove Wetlands Tidal Estuarine Wetland 1 Definition and Formation of Estuaries u Estuary : partially
Types of Wetlands. Tidal Systems
 Types of Wetlands Tidal Systems 1 COASTAL WETLAND ECOSYSTEMS Tidal Salt Marshes Tidal Freshwater Marshes Mangrove Wetlands 2 Tidal Estuarine Wetland 3 Definition and Formation of Estuaries Estuary: : partially
Types of Wetlands Tidal Systems 1 COASTAL WETLAND ECOSYSTEMS Tidal Salt Marshes Tidal Freshwater Marshes Mangrove Wetlands 2 Tidal Estuarine Wetland 3 Definition and Formation of Estuaries Estuary: : partially
Evolution and Life in the Ocean
 Characteristics of All Living Things Contain matter in a highly organized state Capture, store and transmit energy; all organisms require energy Capable of reproduction Change through time and adapt to
Characteristics of All Living Things Contain matter in a highly organized state Capture, store and transmit energy; all organisms require energy Capable of reproduction Change through time and adapt to
Chapter 10. Marine Ecology
 Chapter 10 Marine Ecology Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. Marine Ecology Ecology is
Chapter 10 Marine Ecology Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. Marine Ecology Ecology is
Successful completion of Algebra 1 provides the mathematical skills you ll need for Biology B.
 Syllabus Biology B Course Overview Biology is a science dedicated to studying all forms of life on Earth. You are probably familiar with a number of plants and animals, but do you know what makes them
Syllabus Biology B Course Overview Biology is a science dedicated to studying all forms of life on Earth. You are probably familiar with a number of plants and animals, but do you know what makes them
STATION 4. STATION refer to specimen in box see page 3 for pictures for online version. Can you name this fossil? Class
 STATION 1 Can you name this fossil? Phylum Class STATION 2 --- refer to specimen in box see page 3 for pictures for online version Identify the Phylum of each specimen Genus When did he live? Cambrian,
STATION 1 Can you name this fossil? Phylum Class STATION 2 --- refer to specimen in box see page 3 for pictures for online version Identify the Phylum of each specimen Genus When did he live? Cambrian,
Announcements. Third problem site due November 30 Review calculations
 Announcements Geology Primary Fields of Oceanography Chemistry Third problem site due November 30 Review calculations Next Thursday quiz on Kirchman reading (microbes) Moving from physical to biological
Announcements Geology Primary Fields of Oceanography Chemistry Third problem site due November 30 Review calculations Next Thursday quiz on Kirchman reading (microbes) Moving from physical to biological
GENERAL ECOLOGY STUDY NOTES
 1.0 INTRODUCTION GENERAL ECOLOGY STUDY NOTES A community is made up of populations of different organisms living together in a unit environment. The manner in which these organisms relate together for
1.0 INTRODUCTION GENERAL ECOLOGY STUDY NOTES A community is made up of populations of different organisms living together in a unit environment. The manner in which these organisms relate together for
Photosynthetic Habitats
 6. Kelps, Mangroves & Photosynthetic Habitats Photosynthetic Habitats Kelps Anatomy Community Ecosystem Mangroves Anatomy Community Ecosystem Other photosynthetic habitats Seagrasses Dr Rhian G. Waller
6. Kelps, Mangroves & Photosynthetic Habitats Photosynthetic Habitats Kelps Anatomy Community Ecosystem Mangroves Anatomy Community Ecosystem Other photosynthetic habitats Seagrasses Dr Rhian G. Waller
ANIMAL ECOLOGY (A ECL)
 Animal Ecology (A ECL) 1 ANIMAL ECOLOGY (A ECL) Courses primarily for undergraduates: A ECL 312: Ecology (Cross-listed with BIOL, ENSCI). (3-3) Cr. 4. SS. Prereq: BIOL 211, BIOL 211L, BIOL 212, and BIOL
Animal Ecology (A ECL) 1 ANIMAL ECOLOGY (A ECL) Courses primarily for undergraduates: A ECL 312: Ecology (Cross-listed with BIOL, ENSCI). (3-3) Cr. 4. SS. Prereq: BIOL 211, BIOL 211L, BIOL 212, and BIOL
Introduction to. Kinorhyncha and Gnathostomulida
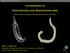 Introduction to Kinorhyncha and Gnathostomulida Block course on Zoology and Evolution, Biozentrum, Uni. Basel Martin V. Sørensen Associate Professor and curator of microscopic invertebrates Dias 1 Natural
Introduction to Kinorhyncha and Gnathostomulida Block course on Zoology and Evolution, Biozentrum, Uni. Basel Martin V. Sørensen Associate Professor and curator of microscopic invertebrates Dias 1 Natural
Benthic fauna of macrotidal sandy beaches along a small-scale morphodynamic gradient on the Amazon coast (Algodoal Island, Brazil).
 Journal of Coastal Research SI 64 435-439 ICS2011 (Proceedings) Poland ISSN 0749-0208 Benthic fauna of macrotidal sandy beaches along a small-scale morphodynamic gradient on the Amazon coast (Algodoal
Journal of Coastal Research SI 64 435-439 ICS2011 (Proceedings) Poland ISSN 0749-0208 Benthic fauna of macrotidal sandy beaches along a small-scale morphodynamic gradient on the Amazon coast (Algodoal
Major Factors influencing Seamount Niches
 2018 May 27-30, Quindao, China International Workshop of the REMP for the Cobalt-Rich Ferromanganese Crust in the Triangle Area in the northwest Pacific Ocean Major Factors influencing Seamount Niches
2018 May 27-30, Quindao, China International Workshop of the REMP for the Cobalt-Rich Ferromanganese Crust in the Triangle Area in the northwest Pacific Ocean Major Factors influencing Seamount Niches
Ecosystems Chapter 4. What is an Ecosystem? Section 4-1
 Ecosystems Chapter 4 What is an Ecosystem? Section 4-1 Ecosystems Key Idea: An ecosystem includes a community of organisms and their physical environment. A community is a group of various species that
Ecosystems Chapter 4 What is an Ecosystem? Section 4-1 Ecosystems Key Idea: An ecosystem includes a community of organisms and their physical environment. A community is a group of various species that
APPENDIX DR1: METHODOLOGICAL DETAILS AND INFORMATION
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2018261 Klompmaker and Finnegan APPENDIX DR1: METHODOLOGICAL DETAILS AND INFORMATION METHODS Fossil datasets (Appendix DR2) were downloaded from the Paleobiology Database (PBDB: https://paleobiodb.org)
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2018261 Klompmaker and Finnegan APPENDIX DR1: METHODOLOGICAL DETAILS AND INFORMATION METHODS Fossil datasets (Appendix DR2) were downloaded from the Paleobiology Database (PBDB: https://paleobiodb.org)
Name: Characteristics of Life and Ecology Guided Notes (PAP)
 Name: Characteristics of Life and Ecology Guided Notes (PAP) I. What is Biology? a. Biology is the study of II. The Eight Characteristics of Life a. Organization & the presence of or more cells b. Response
Name: Characteristics of Life and Ecology Guided Notes (PAP) I. What is Biology? a. Biology is the study of II. The Eight Characteristics of Life a. Organization & the presence of or more cells b. Response
Life on Earth
 Life on Earth By feeding, i.e. source of energy a) Autotrophs, self-feeding, e.g. plants (phyto-) b) Heterotrophs, eat others, e.g. animals (zoo-) By feeding, i.e. source of energy a) Autotrophs b)
Life on Earth By feeding, i.e. source of energy a) Autotrophs, self-feeding, e.g. plants (phyto-) b) Heterotrophs, eat others, e.g. animals (zoo-) By feeding, i.e. source of energy a) Autotrophs b)
Blastocoelomates. General Features. General Features. Phylogenetic Relationships. Phylogenetic Relationships
 General Features Blastocoelomates 1. A large and heterogeneous group. a. also known as "Aschelminthes" - cavity worms. General Features b. Nearly any source you consult will have a different arrangement
General Features Blastocoelomates 1. A large and heterogeneous group. a. also known as "Aschelminthes" - cavity worms. General Features b. Nearly any source you consult will have a different arrangement
UNIT 8A MARINE SCIENCE: Lower Invertebrates
 UNIT 8A MARINE SCIENCE: Lower Invertebrates Essential Questions: What are the characteristics of the simple body structured organisms? Unit Objectives/I Can Statements: General Invertebrates 1. List taxa
UNIT 8A MARINE SCIENCE: Lower Invertebrates Essential Questions: What are the characteristics of the simple body structured organisms? Unit Objectives/I Can Statements: General Invertebrates 1. List taxa
Taxon: generally refers to any named group of organisms, such as species, genus, family, order, etc.. Node: represents the hypothetical ancestor
 A quick review Taxon: generally refers to any named group of organisms, such as species, genus, family, order, etc.. Node: represents the hypothetical ancestor Branches: lines diverging from a node Root:
A quick review Taxon: generally refers to any named group of organisms, such as species, genus, family, order, etc.. Node: represents the hypothetical ancestor Branches: lines diverging from a node Root:
Knowledge and data gaps on the Rio Grande Rise, South Atlantic Ocean benthic and pelagic ecosystems
 Workshop Towards the development of a strategic Environmental Management Plan for deep seabed mineral exploration and exploitation in the Atlantic basin (SEMPIA) 1-3 June 2015, Horta, Azores, Portugal
Workshop Towards the development of a strategic Environmental Management Plan for deep seabed mineral exploration and exploitation in the Atlantic basin (SEMPIA) 1-3 June 2015, Horta, Azores, Portugal
Sci.tanta.edu.eg PALEOECOLOGY, GE 2218
 Sci.tanta.edu.eg PALEOECOLOGY, GE 2218 Lec. 4 1 Biosphere Lithosphere Community Hydrosphere Atmosphere 2 1 Temperature Temperature range in the ocean is approximately 2 to 40 º C. Coldest waters are found
Sci.tanta.edu.eg PALEOECOLOGY, GE 2218 Lec. 4 1 Biosphere Lithosphere Community Hydrosphere Atmosphere 2 1 Temperature Temperature range in the ocean is approximately 2 to 40 º C. Coldest waters are found
Month Content Skills Next Generation and Louisville Standards
 August Living Things - Develops an understanding of the organism. Classification Distinguishes between unicellular and multicellular organisms. Recognizes organisms are organized into tissues, organs,
August Living Things - Develops an understanding of the organism. Classification Distinguishes between unicellular and multicellular organisms. Recognizes organisms are organized into tissues, organs,
Characteristics of Animals
 Characteristics of Animals Multicellular Cellular Organization What is this? Heterotrophic Adaptations CHAPTER 9 Cellular Organization 4 Major Functions of Animals Obtain food and water Sustain metabolism
Characteristics of Animals Multicellular Cellular Organization What is this? Heterotrophic Adaptations CHAPTER 9 Cellular Organization 4 Major Functions of Animals Obtain food and water Sustain metabolism
Communities Structure and Dynamics
 Communities Structure and Dynamics (Outline) 1. Community & niche. 2. Inter-specific interactions with examples. 3. The trophic structure of a community 4. Food chain: primary, secondary, tertiary, and
Communities Structure and Dynamics (Outline) 1. Community & niche. 2. Inter-specific interactions with examples. 3. The trophic structure of a community 4. Food chain: primary, secondary, tertiary, and
Unit 4 - Water. Earth s Interior. Earth s Interior. Continental Drift. Continental Drift. Continental Drift. Crust. Mantle. Core.
 Unit 4 - Water How did the oceans form? What special adaptations do saltwater organisms have? Where does our water come from? How do humans affect the Earth s water? Crust Rigid outer shell of Earth Oceanic
Unit 4 - Water How did the oceans form? What special adaptations do saltwater organisms have? Where does our water come from? How do humans affect the Earth s water? Crust Rigid outer shell of Earth Oceanic
1. General Features of Animals
 Chapter 32: An Overview of Animal Diversity 1. General Features of Animals 2. The History of Animals 1. General Features of Animals General Characteristics of Animals animals are multicellular eukaryotic
Chapter 32: An Overview of Animal Diversity 1. General Features of Animals 2. The History of Animals 1. General Features of Animals General Characteristics of Animals animals are multicellular eukaryotic
Macrozoobenthos monitoring
 Macrozoobenthos monitoring Macrozoobenthos is considered as a biological element to assess the ecological quality status in transitional ecosystems Since 2008 a monitoring program was established for the
Macrozoobenthos monitoring Macrozoobenthos is considered as a biological element to assess the ecological quality status in transitional ecosystems Since 2008 a monitoring program was established for the
4-2 What Shapes an Ecosystem? Slide 1 of 39
 4-2 What Shapes an Ecosystem? 1 of 39 Biotic and Abiotic Factors Biotic and Abiotic Factors Ecosystems are influenced by a combination of biological and physical factors. The biological influences on organisms
4-2 What Shapes an Ecosystem? 1 of 39 Biotic and Abiotic Factors Biotic and Abiotic Factors Ecosystems are influenced by a combination of biological and physical factors. The biological influences on organisms
PENNSYLVANIA. How living things interact with each other and the non-living components of the environment. Page 1 of 6. S11.A.1.3.
 Know: Understand: Do: 4.1.12.A.a -- Essential Analyze the significance of biological diversity in an ecosystem. How living things interact with each other and the non-living components of the environment.
Know: Understand: Do: 4.1.12.A.a -- Essential Analyze the significance of biological diversity in an ecosystem. How living things interact with each other and the non-living components of the environment.
AP Biology. Read college-level text for understanding and be able to summarize main concepts
 St. Mary's College AP Biology Continuity and Change Consider how specific changes to an ecosystem (geological, climatic, introduction of new organisms, etc.) can affect the organisms that live within it.
St. Mary's College AP Biology Continuity and Change Consider how specific changes to an ecosystem (geological, climatic, introduction of new organisms, etc.) can affect the organisms that live within it.
I. Protostomia - Pseudocoelom
 Z202-Unit3 Chapter 15 Pseudocoelomate Animals I. Protostomia - Pseudocoelom A. Structure - Embryonic blastocoel persist as a space or cavity - Pseudocoel internal cavity surrounding the gut, lacks mesoderm
Z202-Unit3 Chapter 15 Pseudocoelomate Animals I. Protostomia - Pseudocoelom A. Structure - Embryonic blastocoel persist as a space or cavity - Pseudocoel internal cavity surrounding the gut, lacks mesoderm
4-2 What Shapes an Ecosystem?
 Biology 1 of 39 4-2 What Shapes an Ecosystem? 2 of 39 Biotic and Abiotic Factors Biotic and Abiotic Factors Ecosystems are influenced by a combination of biological and physical factors. 3 of 39 1 Biotic
Biology 1 of 39 4-2 What Shapes an Ecosystem? 2 of 39 Biotic and Abiotic Factors Biotic and Abiotic Factors Ecosystems are influenced by a combination of biological and physical factors. 3 of 39 1 Biotic
Workshop: The Evolution of Animalia body symmetry embryonic germ layers ontogenetic origins I. What is an Animal?
 Workshop: The Evolution of Animalia by Dana Krempels Perhaps even more than the other Eukarya, Animalia is characterized by a distinct progression of complexity in form and function as one moves from the
Workshop: The Evolution of Animalia by Dana Krempels Perhaps even more than the other Eukarya, Animalia is characterized by a distinct progression of complexity in form and function as one moves from the
Classification & History of Life
 Classification & History of Life Today & next time Taxonomy Modes of Life Origin of Life Traditional new History of life Taxonomy: Organize life into related groups Traditional Taxonomy Grouped by shared
Classification & History of Life Today & next time Taxonomy Modes of Life Origin of Life Traditional new History of life Taxonomy: Organize life into related groups Traditional Taxonomy Grouped by shared
Porifera. Thomas M. Frost Trout Lake Station Center for Limnology University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin '"'. , ' I.
 , ' Porifera Thomas M. Frost Trout Lake Station Center for Limnology University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin 53706 4 '"'. Chapter Outline I. INTRODUCTION II. ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY A. External Morphology
, ' Porifera Thomas M. Frost Trout Lake Station Center for Limnology University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin 53706 4 '"'. Chapter Outline I. INTRODUCTION II. ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY A. External Morphology
