Semiconductor Devices. C. Hu: Modern Semiconductor Devices for Integrated Circuits Chapter 6
|
|
|
- Alexander Hall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Semiconducor Devices C. Hu: Modern Semiconducor Devices for Inegraed Circuis Chaper 6
2 For hose of you who are sudying a bachelor level and need he old course S Mikro- ja nanoelekroniikan perusee o finish your degree, we organize an exra exam in May (Thursday 12h of May 13 -> in Micronova). Mandaory regisraion for he exam via o ville.vahanissi@aalo.fi a he laes on 1s of May. The exam language is finnish. The exam will be abou he book of Hu (Modern Semiconducor Devices for Inegraed Circuis), chapers 1-6. If you like, you can sill of course replace he old course S wih his on-going course. Excursion: Sill room for 2 sudens
3 3 differen operaion regimes & 2 ineresing ransiion poins accumulaion, fla band, depleion, hreshold, inversion FLAT-BAND THRESHOLD MOS capacior C-V characerisics Oxide capaciance Depleion region capaciance
4 Inroducion MOSFET on i s on sae Surface mobiliy, V, body effec, Q inv I-V model & characerisics
5 The mos imporan semiconducor device Building block of Gb memory chips GHz microprosessors Analog circuis RF circuis Mach he following MOSFET characerisics wih heir applicaions: small size high speed low power high gain
6 The mos imporan semiconducor device Building block of Gb memory chips GHz microprosessors Analog circuis RF circuis Mach he following MOSFET characerisics wih heir applicaions: small size Gb memory chips high speed GHz microprosessors, RF circuis low power GHz microprosessors, RF circuis high gain analog circuis
7 Basic MOSFET srucure and IV characerisics Wha is desirable? Large I on, small I off
8 Two ways of represening a MOSFET
9 The superioriy of he MOSFET-srucure is based on he abiliy o fabricae very high-qualiy oxide-silicon inerfaces and very high qualiy oxides, even in he case of exremely hin layers 1.2 nm size of four SiO 2 molecules
10
11 Boh NMOSFET and PMOSFET needed PMOSFET pull-up device NMOSFET pull-down device V ou =? if V in = 0 V Small power consumpion
12 NMOSFET and PMOSFET can be fabricaed on he same chip
13 I is highly desirable o have a large ransisor curren (high circui speed) Elecron or hole mobiliy in he surface inversion layer is an imporan facor deermining he MOSFET curren How o measure he surface mobiliy I ds = W Q v = WQ m inv inv nse = WC ( V -V ) m V / oxe gs ns ds = WQ L inv m ns V ds / L
14 Mobiliy is a funcion of he average of he fields a he boom and he op of he inversion charge layer, E b and E From Gauss s Law, E b = Q dep /e s V = V -Q / C E b fb C = e s Therefore, - dep - ) oxe ( V V fb s s oxe E = -( Q = E b C = e oxe s dep - Q ( V Q inv gs inv s -V ) / e / e = fb E s b - ) C e s oxe s ( V gs -V ) 1 2 ( E b E ) = = Coxe 2e V gs s Coxe 2e s ( V ( V V gs gs 6T V oxe V 0.2 V - 2V fb 0.2 V) - 2 ) s
15 Surface mobiliy is clearly lower (1/3) han bulk mobiliy Surface roughness scaering Surface roughness scaering is sronger a higher V g, higher V and smaller T oxe
16 EXAMPLE: Wha is he surface mobiliy a V gs =1 V in an N-channel MOSFET wih V =0.3 V and T oxe =2 nm? ( V V 0.2) / 6T gs oxe
17 EXAMPLE: Wha is he surface mobiliy a V gs =1 V in an N-channel MOSFET wih V =0.3 V and T oxe =2 nm? Soluion: ( V gs V 0.2) / 6T = 1.5 V / oxe cm = 1.25 MV/cm 1 MV is a megavol. From he mobiliy figure, m ns =190 cm2/vs, which is several imes smaller han he bulk mobiliy.
18 The mos obvious way o improve is o use a semiconducor having higher mobiliy han Si MESFET = Meal-Semiconducor-Field-Effec-Transisor Operaion is based on he volage dependency of he depleion region of a reverse biased Schoky-diode Depending on he gae volage, he depleion region under he gae expands or conracs The hickness of he conducive channel is modulaed The channel curren is modulaed
19 Componen is based on GaAlAs/GaAs-heerojuncions A large Eg semiconducor, GaAlAs, serves as he gae dielecric Elecrons in he channel (GaAs) are far away from he donors (AlGaAs) Impuriy scaering decreases and mobiliy increases Smooh surface, small surface scaering
20 The gae is a PN-juncion By conrolling he deph of he depleion region, also he channel deph can be conrolled Deeper depleion region, smaller conducion channel
21 Mehod A V is deermined by exrapolaing he I ds vs. V gs curve o I ds = 0 I dsa V W = Coxe( Vgs -V ) mnsv L -V gs ds Mehod B The Vg a which Ids = 0.1 µa W/L
22 MOSFET is a 4-erminal componen, also he subsrae bias has an effec on he channel Inversion layer forms a capacior boh wih he gae (oxide) and also wih he subsrae (depleion layer) Two capaciors, wo charge componens oxe e Sio 2 C = T oxe C dep e s = W d max Q inv = -C ( V -V ) C = -C oxe oxe gs dep V Cdep ( Vgs - ( V Vsb)) C oxe sb Redefine V as V ( V sb ) C dep = V 0 Vsb = V 0 Coxe V sb
23 Body effec V is a funcion of V sb. When he source-body juncion is reverse-biased, V increases. Body effec coefficien V = V 0 V sb = C dep /C oxe = 3T oxe / W dep Body effec raises V and herefore slows down circuis. How can i be reduced?
24 Rerograde doping is popular because i reduces offsae leakage and allows higher surface mobiliy
25 Channel volage V c =V s a x = 0 and V c =V d a x = L Applied source-drain-volage causes an addiional poenial (in addiion o gae-volage) This has o be aken ino accoun when calculaing he charge in he channel Q inv = C oxe (V gs V cs V 0 (V sb +V cs ) = C oxe (V gs V cs (V 0 + V sb ) V cs ) = C oxe (V gs mv cs V ) m 1 + = 1 + 3T oxe /W dmax m is called he body-effec facor or bulk-charge facor
26 Curren in he channel I ds = WQ inv v= WQ inv m ns E = WC oxe (V gs mv cs V )m ns dv cs /dx Inegraion allong he channel L V ds Idsdx = WCoxem ns ( Vgs - mvcs V ) dv cs I ds L = WC oxe m ns (V gs V mv ds /2)V ds Model for he linear region (applies before curren sauraion) I ds W = C m oxe s( Vgs -V - L m V 2 ds ) V ds
27 Wih high enough source-drain-volages he curren in he channel sauraes dids W = 0 = C m V - V - V a V = V dv L ds V dsa V = gs oxe ns gs ds ds dsa -V m In his case he inversion charge a he drain end is 0 (channel pinch-off) Area wih high resisance is formed (large volage loss) A he channel area he poenial disribuion is no significanly changed evenhough volage is increased Curren sauraes
28 V cs (x), Q inv (x) and herefore Ids are he same I ds does no change wih V ds beyond V dsa A V ds > V dsa here exiss a shor high-field pinch-off region where Q inv = 0 and across which he volage V ds -V dsa is dropped In he pinch-off region elecrons are swep down he seep poenial drop Elecron flow raes equal (same drif field and Q inv in he channel
29 Sauraion curren W Idsa = Coxemns( Vgs -V 2mL Transconducance W gmsa = Coxem - ml 2 ) ns( Vgs V Applicable in he case of long channel (L > 10mm) )
30
31
32 MOSFET coninues
Chapter 6 MOSFET in the On-state
 Chaper 6 MOSFET in he On-sae The MOSFET (MOS Field-Effec Transisor) is he building block of Gb memory chips, GHz microprocessors, analog, and RF circuis. Mach he following MOSFET characerisics wih heir
Chaper 6 MOSFET in he On-sae The MOSFET (MOS Field-Effec Transisor) is he building block of Gb memory chips, GHz microprocessors, analog, and RF circuis. Mach he following MOSFET characerisics wih heir
Introduction to Digital Circuits
 The NMOS nerer The NMOS Depleion oad 50 [ D ] µ A GS.0 + 40 30 0 0 Resisance characerisic of Q 3 4 5 6 GS 0.5 GS 0 GS 0.5 GS.0 GS.5 [ ] DS GS i 0 Q Q Depleion load Enhancemen drier Drain characerisic of
The NMOS nerer The NMOS Depleion oad 50 [ D ] µ A GS.0 + 40 30 0 0 Resisance characerisic of Q 3 4 5 6 GS 0.5 GS 0 GS 0.5 GS.0 GS.5 [ ] DS GS i 0 Q Q Depleion load Enhancemen drier Drain characerisic of
Chapter 4. Circuit Characterization and Performance Estimation
 VLSI Design Chaper 4 Circui Characerizaion and Performance Esimaion Jin-Fu Li Chaper 4 Circui Characerizaion and Performance Esimaion Resisance & Capaciance Esimaion Swiching Characerisics Transisor Sizing
VLSI Design Chaper 4 Circui Characerizaion and Performance Esimaion Jin-Fu Li Chaper 4 Circui Characerizaion and Performance Esimaion Resisance & Capaciance Esimaion Swiching Characerisics Transisor Sizing
Silicon Controlled Rectifiers UNIT-1
 Silicon Conrolled Recifiers UNIT-1 Silicon Conrolled Recifier A Silicon Conrolled Recifier (or Semiconducor Conrolled Recifier) is a four layer solid sae device ha conrols curren flow The name silicon
Silicon Conrolled Recifiers UNIT-1 Silicon Conrolled Recifier A Silicon Conrolled Recifier (or Semiconducor Conrolled Recifier) is a four layer solid sae device ha conrols curren flow The name silicon
L1, L2, N1 N2. + Vout. C out. Figure 2.1.1: Flyback converter
 page 11 Flyback converer The Flyback converer belongs o he primary swiched converer family, which means here is isolaion beween in and oupu. Flyback converers are used in nearly all mains supplied elecronic
page 11 Flyback converer The Flyback converer belongs o he primary swiched converer family, which means here is isolaion beween in and oupu. Flyback converers are used in nearly all mains supplied elecronic
Mobile Ion Effects on SiC MOS Bias- Temperature Instability Measurements
 14-15 Aug 2014 1 U.S. Army Research, Developmen and Engineering Command Mobile Ion Effecs on SiC MOS Bias- Temperaure Insabiliy Measuremens Daniel B. Habersa Neil Goldsman (UMD), and Aivars Lelis 14-15
14-15 Aug 2014 1 U.S. Army Research, Developmen and Engineering Command Mobile Ion Effecs on SiC MOS Bias- Temperaure Insabiliy Measuremens Daniel B. Habersa Neil Goldsman (UMD), and Aivars Lelis 14-15
Chapter 7 Response of First-order RL and RC Circuits
 Chaper 7 Response of Firs-order RL and RC Circuis 7.- The Naural Response of RL and RC Circuis 7.3 The Sep Response of RL and RC Circuis 7.4 A General Soluion for Sep and Naural Responses 7.5 Sequenial
Chaper 7 Response of Firs-order RL and RC Circuis 7.- The Naural Response of RL and RC Circuis 7.3 The Sep Response of RL and RC Circuis 7.4 A General Soluion for Sep and Naural Responses 7.5 Sequenial
EE 560 MOS INVERTERS: DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS. Kenneth R. Laker, University of Pennsylvania
 1 EE 560 MOS INVERTERS: DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS C gsp V DD C sbp C gd, C gs, C gb -> Oxide Caps C db, C sb -> Juncion Caps 2 S C in -> Ineconnec Cap G B D C dbp V in C gdp V ou C gdn D C dbn G B S C in
1 EE 560 MOS INVERTERS: DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS C gsp V DD C sbp C gd, C gs, C gb -> Oxide Caps C db, C sb -> Juncion Caps 2 S C in -> Ineconnec Cap G B D C dbp V in C gdp V ou C gdn D C dbn G B S C in
R.#W.#Erickson# Department#of#Electrical,#Computer,#and#Energy#Engineering# University#of#Colorado,#Boulder#
 .#W.#Erickson# Deparmen#of#Elecrical,#Compuer,#and#Energy#Engineering# Universiy#of#Colorado,#Boulder# Chaper 2 Principles of Seady-Sae Converer Analysis 2.1. Inroducion 2.2. Inducor vol-second balance,
.#W.#Erickson# Deparmen#of#Elecrical,#Compuer,#and#Energy#Engineering# Universiy#of#Colorado,#Boulder# Chaper 2 Principles of Seady-Sae Converer Analysis 2.1. Inroducion 2.2. Inducor vol-second balance,
NDP4050L / NDB4050L N-Channel Logic Level Enhancement Mode Field Effect Transistor
 April 996 NP45L / NB45L N-Channel Logic Level Enhancemen Mode Field Effec Transisor General escripion Feaures These logic level N-Channel enhancemen mode power field effec ransisors are produced using
April 996 NP45L / NB45L N-Channel Logic Level Enhancemen Mode Field Effec Transisor General escripion Feaures These logic level N-Channel enhancemen mode power field effec ransisors are produced using
EE100 Lab 3 Experiment Guide: RC Circuits
 I. Inroducion EE100 Lab 3 Experimen Guide: A. apaciors A capacior is a passive elecronic componen ha sores energy in he form of an elecrosaic field. The uni of capaciance is he farad (coulomb/vol). Pracical
I. Inroducion EE100 Lab 3 Experimen Guide: A. apaciors A capacior is a passive elecronic componen ha sores energy in he form of an elecrosaic field. The uni of capaciance is he farad (coulomb/vol). Pracical
V L. DT s D T s t. Figure 1: Buck-boost converter: inductor current i(t) in the continuous conduction mode.
 ECE 445 Analysis and Design of Power Elecronic Circuis Problem Se 7 Soluions Problem PS7.1 Erickson, Problem 5.1 Soluion (a) Firs, recall he operaion of he buck-boos converer in he coninuous conducion
ECE 445 Analysis and Design of Power Elecronic Circuis Problem Se 7 Soluions Problem PS7.1 Erickson, Problem 5.1 Soluion (a) Firs, recall he operaion of he buck-boos converer in he coninuous conducion
ECE 2100 Circuit Analysis
 ECE 1 Circui Analysis Lesson 35 Chaper 8: Second Order Circuis Daniel M. Liynski, Ph.D. ECE 1 Circui Analysis Lesson 3-34 Chaper 7: Firs Order Circuis (Naural response RC & RL circuis, Singulariy funcions,
ECE 1 Circui Analysis Lesson 35 Chaper 8: Second Order Circuis Daniel M. Liynski, Ph.D. ECE 1 Circui Analysis Lesson 3-34 Chaper 7: Firs Order Circuis (Naural response RC & RL circuis, Singulariy funcions,
ECE 2100 Circuit Analysis
 ECE 1 Circui Analysis Lesson 37 Chaper 8: Second Order Circuis Discuss Exam Daniel M. Liynski, Ph.D. Exam CH 1-4: On Exam 1; Basis for work CH 5: Operaional Amplifiers CH 6: Capaciors and Inducor CH 7-8:
ECE 1 Circui Analysis Lesson 37 Chaper 8: Second Order Circuis Discuss Exam Daniel M. Liynski, Ph.D. Exam CH 1-4: On Exam 1; Basis for work CH 5: Operaional Amplifiers CH 6: Capaciors and Inducor CH 7-8:
NDH834P P-Channel Enhancement Mode Field Effect Transistor
 May 997 NH834P P-Channel Enhancemen Mode Field Effec Transisor General escripion Feaures SuperSOT TM -8 P-Channel enhancemen mode power field effec ransisors are produced using Fairchild's proprieary,
May 997 NH834P P-Channel Enhancemen Mode Field Effec Transisor General escripion Feaures SuperSOT TM -8 P-Channel enhancemen mode power field effec ransisors are produced using Fairchild's proprieary,
dv 7. Voltage-current relationship can be obtained by integrating both sides of i = C :
 EECE202 NETWORK ANALYSIS I Dr. Charles J. Kim Class Noe 22: Capaciors, Inducors, and Op Amp Circuis A. Capaciors. A capacior is a passive elemen designed o sored energy in is elecric field. 2. A capacior
EECE202 NETWORK ANALYSIS I Dr. Charles J. Kim Class Noe 22: Capaciors, Inducors, and Op Amp Circuis A. Capaciors. A capacior is a passive elemen designed o sored energy in is elecric field. 2. A capacior
NDS332P P-Channel Logic Level Enhancement Mode Field Effect Transistor
 June 997 NS33P P-Channel Logic Level Enhancemen Mode Field Effec Transisor General escripion Feaures These P-Channel logic level enhancemen mode power field effec ransisors are produced using Fairchild's
June 997 NS33P P-Channel Logic Level Enhancemen Mode Field Effec Transisor General escripion Feaures These P-Channel logic level enhancemen mode power field effec ransisors are produced using Fairchild's
CHAP.4 Circuit Characteristics and Performance Estimation
 HAP.4 ircui haracerisics and Performance Esimaion 4. Resisance esimaion R ρ l w (ohms) where ρ Resisiviy Thickness l onducor lengh w onducor widh l R Rs w where Rs Shee resisance (Ω/square) in 0.5µm o
HAP.4 ircui haracerisics and Performance Esimaion 4. Resisance esimaion R ρ l w (ohms) where ρ Resisiviy Thickness l onducor lengh w onducor widh l R Rs w where Rs Shee resisance (Ω/square) in 0.5µm o
Reading from Young & Freedman: For this topic, read sections 25.4 & 25.5, the introduction to chapter 26 and sections 26.1 to 26.2 & 26.4.
 PHY1 Elecriciy Topic 7 (Lecures 1 & 11) Elecric Circuis n his opic, we will cover: 1) Elecromoive Force (EMF) ) Series and parallel resisor combinaions 3) Kirchhoff s rules for circuis 4) Time dependence
PHY1 Elecriciy Topic 7 (Lecures 1 & 11) Elecric Circuis n his opic, we will cover: 1) Elecromoive Force (EMF) ) Series and parallel resisor combinaions 3) Kirchhoff s rules for circuis 4) Time dependence
University of Cyprus Biomedical Imaging and Applied Optics. Appendix. DC Circuits Capacitors and Inductors AC Circuits Operational Amplifiers
 Universiy of Cyprus Biomedical Imaging and Applied Opics Appendix DC Circuis Capaciors and Inducors AC Circuis Operaional Amplifiers Circui Elemens An elecrical circui consiss of circui elemens such as
Universiy of Cyprus Biomedical Imaging and Applied Opics Appendix DC Circuis Capaciors and Inducors AC Circuis Operaional Amplifiers Circui Elemens An elecrical circui consiss of circui elemens such as
Chapter 2: Principles of steady-state converter analysis
 Chaper 2 Principles of Seady-Sae Converer Analysis 2.1. Inroducion 2.2. Inducor vol-second balance, capacior charge balance, and he small ripple approximaion 2.3. Boos converer example 2.4. Cuk converer
Chaper 2 Principles of Seady-Sae Converer Analysis 2.1. Inroducion 2.2. Inducor vol-second balance, capacior charge balance, and he small ripple approximaion 2.3. Boos converer example 2.4. Cuk converer
NDS356P P-Channel Logic Level Enhancement Mode Field Effect Transistor
 March 996 NS356P P-Channel Logic Level Enhancemen Mode Field Effec Transisor General escripion These P-Channel logic level enhancemen mode power field effec ransisors are produced using Fairchild's proprieary,
March 996 NS356P P-Channel Logic Level Enhancemen Mode Field Effec Transisor General escripion These P-Channel logic level enhancemen mode power field effec ransisors are produced using Fairchild's proprieary,
2.4 Cuk converter example
 2.4 Cuk converer example C 1 Cuk converer, wih ideal swich i 1 i v 1 2 1 2 C 2 v 2 Cuk converer: pracical realizaion using MOSFET and diode C 1 i 1 i v 1 2 Q 1 D 1 C 2 v 2 28 Analysis sraegy This converer
2.4 Cuk converer example C 1 Cuk converer, wih ideal swich i 1 i v 1 2 1 2 C 2 v 2 Cuk converer: pracical realizaion using MOSFET and diode C 1 i 1 i v 1 2 Q 1 D 1 C 2 v 2 28 Analysis sraegy This converer
Electrical and current self-induction
 Elecrical and curren self-inducion F. F. Mende hp://fmnauka.narod.ru/works.hml mende_fedor@mail.ru Absrac The aricle considers he self-inducance of reacive elemens. Elecrical self-inducion To he laws of
Elecrical and curren self-inducion F. F. Mende hp://fmnauka.narod.ru/works.hml mende_fedor@mail.ru Absrac The aricle considers he self-inducance of reacive elemens. Elecrical self-inducion To he laws of
EECS 141: FALL 00 MIDTERM 2
 Universiy of California College of Engineering Deparmen of Elecrical Engineering and Compuer Science J. M. Rabaey TuTh9:30-11am ee141@eecs EECS 141: FALL 00 MIDTERM 2 For all problems, you can assume he
Universiy of California College of Engineering Deparmen of Elecrical Engineering and Compuer Science J. M. Rabaey TuTh9:30-11am ee141@eecs EECS 141: FALL 00 MIDTERM 2 For all problems, you can assume he
Chapter 16: Summary. Instructor: Jean-François MILLITHALER.
 Chaper 16: Summary Insrucor: Jean-François MILLITHALER hp://faculy.uml.edu/jeanfrancois_millihaler/funelec/spring2017 Slide 1 Curren & Charge Elecric curren is he ime rae of change of charge, measured
Chaper 16: Summary Insrucor: Jean-François MILLITHALER hp://faculy.uml.edu/jeanfrancois_millihaler/funelec/spring2017 Slide 1 Curren & Charge Elecric curren is he ime rae of change of charge, measured
Designing Information Devices and Systems I Spring 2019 Lecture Notes Note 17
 EES 16A Designing Informaion Devices and Sysems I Spring 019 Lecure Noes Noe 17 17.1 apaciive ouchscreen In he las noe, we saw ha a capacior consiss of wo pieces on conducive maerial separaed by a nonconducive
EES 16A Designing Informaion Devices and Sysems I Spring 019 Lecure Noes Noe 17 17.1 apaciive ouchscreen In he las noe, we saw ha a capacior consiss of wo pieces on conducive maerial separaed by a nonconducive
Outline. Chapter 2: DC & Transient Response. Introduction to CMOS VLSI. DC Response. Transient Response Delay Estimation
 Inroducion o CMOS VLSI Design Chaper : DC & Transien Response David Harris, 004 Updaed by Li Chen, 010 Ouline DC Response Logic Levels and Noise Margins Transien Response Delay Esimaion Slide 1 Aciviy
Inroducion o CMOS VLSI Design Chaper : DC & Transien Response David Harris, 004 Updaed by Li Chen, 010 Ouline DC Response Logic Levels and Noise Margins Transien Response Delay Esimaion Slide 1 Aciviy
Chapter 28 - Circuits
 Physics 4B Lecure Noes Chaper 28 - Circuis Problem Se #7 - due: Ch 28 -, 9, 4, 7, 23, 38, 47, 53, 57, 66, 70, 75 Lecure Ouline. Kirchoff's ules 2. esisors in Series 3. esisors in Parallel 4. More Complex
Physics 4B Lecure Noes Chaper 28 - Circuis Problem Se #7 - due: Ch 28 -, 9, 4, 7, 23, 38, 47, 53, 57, 66, 70, 75 Lecure Ouline. Kirchoff's ules 2. esisors in Series 3. esisors in Parallel 4. More Complex
EE650R: Reliability Physics of Nanoelectronic Devices Lecture 9:
 EE65R: Reliabiliy Physics of anoelecronic Devices Lecure 9: Feaures of Time-Dependen BTI Degradaion Dae: Sep. 9, 6 Classnoe Lufe Siddique Review Animesh Daa 9. Background/Review: BTI is observed when he
EE65R: Reliabiliy Physics of anoelecronic Devices Lecure 9: Feaures of Time-Dependen BTI Degradaion Dae: Sep. 9, 6 Classnoe Lufe Siddique Review Animesh Daa 9. Background/Review: BTI is observed when he
Semiconductor Devices. C. Hu: Modern Semiconductor Devices for Integrated Circuits Chapter 5
 Semiconductor Devices C. Hu: Modern Semiconductor Devices for Integrated Circuits Chapter 5 Global leader in environmental and industrial measurement Wednesday 3.2. afternoon Tour around facilities & lecture
Semiconductor Devices C. Hu: Modern Semiconductor Devices for Integrated Circuits Chapter 5 Global leader in environmental and industrial measurement Wednesday 3.2. afternoon Tour around facilities & lecture
EECE251. Circuit Analysis I. Set 4: Capacitors, Inductors, and First-Order Linear Circuits
 EEE25 ircui Analysis I Se 4: apaciors, Inducors, and Firs-Order inear ircuis Shahriar Mirabbasi Deparmen of Elecrical and ompuer Engineering Universiy of Briish olumbia shahriar@ece.ubc.ca Overview Passive
EEE25 ircui Analysis I Se 4: apaciors, Inducors, and Firs-Order inear ircuis Shahriar Mirabbasi Deparmen of Elecrical and ompuer Engineering Universiy of Briish olumbia shahriar@ece.ubc.ca Overview Passive
KEYWORDS: FD SOI MOSFET, charge pumping, geometric component, rise and fall time method, DC reverse bias, pulse reverse bias
 Jpn. J. ppl. Phys. Vol. 38 (1999) pp. 2496 25 Par 1, No. 4B, pril 1999 c 1999 Publicaion Board, Japanese Journal of pplied Physics Measuremen of Energeic and Laeral Disribuion of Inerface Sae Densiy in
Jpn. J. ppl. Phys. Vol. 38 (1999) pp. 2496 25 Par 1, No. 4B, pril 1999 c 1999 Publicaion Board, Japanese Journal of pplied Physics Measuremen of Energeic and Laeral Disribuion of Inerface Sae Densiy in
Physical Limitations of Logic Gates Week 10a
 Physical Limiaions of Logic Gaes Week 10a In a compuer we ll have circuis of logic gaes o perform specific funcions Compuer Daapah: Boolean algebraic funcions using binary variables Symbolic represenaion
Physical Limiaions of Logic Gaes Week 10a In a compuer we ll have circuis of logic gaes o perform specific funcions Compuer Daapah: Boolean algebraic funcions using binary variables Symbolic represenaion
MOSFET. Id-Vd curve. I DS Transfer curve V G. Lec. 8. Vd=1V. Saturation region. V Th
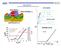 MOSFET Id-Vd curve Saturation region I DS Transfer curve Vd=1V V Th V G 1 0 < V GS < V T V GS > V T V Gs >V T & Small V D > 0 I DS WQ inv WC v WC i V V VDS V V G i T G n T L n I D g V D (g conductance
MOSFET Id-Vd curve Saturation region I DS Transfer curve Vd=1V V Th V G 1 0 < V GS < V T V GS > V T V Gs >V T & Small V D > 0 I DS WQ inv WC v WC i V V VDS V V G i T G n T L n I D g V D (g conductance
NDS355AN N-Channel Logic Level Enhancement Mode Field Effect Transistor
 January 997 NS3AN N-Channel Logic Level Enhancemen Mode Field Effec Transisor General escripion Feaures SuperSOT TM -3 N-Channel logic level enhancemen mode power field effec ransisors are produced using
January 997 NS3AN N-Channel Logic Level Enhancemen Mode Field Effec Transisor General escripion Feaures SuperSOT TM -3 N-Channel logic level enhancemen mode power field effec ransisors are produced using
Direct Current Circuits. February 19, 2014 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 26 1
 Direc Curren Circuis February 19, 2014 Physics for Scieniss & Engineers 2, Chaper 26 1 Ammeers and Volmeers! A device used o measure curren is called an ammeer! A device used o measure poenial difference
Direc Curren Circuis February 19, 2014 Physics for Scieniss & Engineers 2, Chaper 26 1 Ammeers and Volmeers! A device used o measure curren is called an ammeer! A device used o measure poenial difference
V AK (t) I T (t) I TRM. V AK( full area) (t) t t 1 Axial turn-on. Switching losses for Phase Control and Bi- Directionally Controlled Thyristors
 Applicaion Noe Swiching losses for Phase Conrol and Bi- Direcionally Conrolled Thyrisors V AK () I T () Causing W on I TRM V AK( full area) () 1 Axial urn-on Plasma spread 2 Swiching losses for Phase Conrol
Applicaion Noe Swiching losses for Phase Conrol and Bi- Direcionally Conrolled Thyrisors V AK () I T () Causing W on I TRM V AK( full area) () 1 Axial urn-on Plasma spread 2 Swiching losses for Phase Conrol
Chapter 5-4 Operational amplifier Department of Mechanical Engineering
 MEMS08 Chaper 5-4 Operaional amplifier Deparmen of Mechanical Engineering Insrumenaion amplifier Very high inpu impedance Large common mode rejecion raio (CMRR) Capabiliy o amplify low leel signals Consisen
MEMS08 Chaper 5-4 Operaional amplifier Deparmen of Mechanical Engineering Insrumenaion amplifier Very high inpu impedance Large common mode rejecion raio (CMRR) Capabiliy o amplify low leel signals Consisen
Lecture -14: Chopper fed DC Drives
 Lecure -14: Chopper fed DC Drives Chopper fed DC drives o A chopper is a saic device ha convers fixed DC inpu volage o a variable dc oupu volage direcly o A chopper is a high speed on/off semiconducor
Lecure -14: Chopper fed DC Drives Chopper fed DC drives o A chopper is a saic device ha convers fixed DC inpu volage o a variable dc oupu volage direcly o A chopper is a high speed on/off semiconducor
Module 10 SCR. 2. To understand two Transistor Static and Transient Models. 3. To learn the SCR Turn-on and Turn-off methods
 1 Module 1 SR 1. Inroducion 2. SR characerisics 3. Two ransisor saic and ransien models 4. SR urnon mehods 5. SR urnoff mehods 6. SR proecion and Triggering circuis 7. ae proecion circuis 8. Summary Learning
1 Module 1 SR 1. Inroducion 2. SR characerisics 3. Two ransisor saic and ransien models 4. SR urnon mehods 5. SR urnoff mehods 6. SR proecion and Triggering circuis 7. ae proecion circuis 8. Summary Learning
The problem with linear regulators
 he problem wih linear regulaors i in P in = i in V REF R a i ref i q i C v CE P o = i o i B ie P = v i o o in R 1 R 2 i o i f η = P o P in iref is small ( 0). iq (quiescen curren) is small (probably).
he problem wih linear regulaors i in P in = i in V REF R a i ref i q i C v CE P o = i o i B ie P = v i o o in R 1 R 2 i o i f η = P o P in iref is small ( 0). iq (quiescen curren) is small (probably).
Reliability of Technical Systems
 eliabiliy of Technical Sysems Main Topics Inroducion, Key erms, framing he problem eliabiliy parameers: Failure ae, Failure Probabiliy, Availabiliy, ec. Some imporan reliabiliy disribuions Componen reliabiliy
eliabiliy of Technical Sysems Main Topics Inroducion, Key erms, framing he problem eliabiliy parameers: Failure ae, Failure Probabiliy, Availabiliy, ec. Some imporan reliabiliy disribuions Componen reliabiliy
Sub Module 2.6. Measurement of transient temperature
 Mechanical Measuremens Prof. S.P.Venkaeshan Sub Module 2.6 Measuremen of ransien emperaure Many processes of engineering relevance involve variaions wih respec o ime. The sysem properies like emperaure,
Mechanical Measuremens Prof. S.P.Venkaeshan Sub Module 2.6 Measuremen of ransien emperaure Many processes of engineering relevance involve variaions wih respec o ime. The sysem properies like emperaure,
Cosmic Feb 06, 2007 by Raja Reddy P
 osmic ircuis@iisc, Feb 6, 7 by aja eddy P. ou() i() alculae ou(s)/(s). plo o(). calculae ime consan and pole frequency. ou ( e τ ) ou (s) ( s) Time consan (/) Pole frequency : ω p. i() n he above circui
osmic ircuis@iisc, Feb 6, 7 by aja eddy P. ou() i() alculae ou(s)/(s). plo o(). calculae ime consan and pole frequency. ou ( e τ ) ou (s) ( s) Time consan (/) Pole frequency : ω p. i() n he above circui
Università degli Studi di Roma Tor Vergata Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettronica. Analogue Electronics. Paolo Colantonio A.A.
 Universià degli Sudi di Roma Tor Vergaa Diparimeno di Ingegneria Eleronica Analogue Elecronics Paolo Colanonio A.A. 2015-16 Diode circui analysis The non linearbehaviorofdiodesmakesanalysisdifficul consider
Universià degli Sudi di Roma Tor Vergaa Diparimeno di Ingegneria Eleronica Analogue Elecronics Paolo Colanonio A.A. 2015-16 Diode circui analysis The non linearbehaviorofdiodesmakesanalysisdifficul consider
CHAPTER 6: FIRST-ORDER CIRCUITS
 EEE5: CI CUI T THEOY CHAPTE 6: FIST-ODE CICUITS 6. Inroducion This chaper considers L and C circuis. Applying he Kirshoff s law o C and L circuis produces differenial equaions. The differenial equaions
EEE5: CI CUI T THEOY CHAPTE 6: FIST-ODE CICUITS 6. Inroducion This chaper considers L and C circuis. Applying he Kirshoff s law o C and L circuis produces differenial equaions. The differenial equaions
AO V Complementary Enhancement Mode Field Effect Transistor
 AO46 6V Complemenary Enhancemen Mode Field Effec Transisor General Descripion The AO46 uses advanced rench echnology MOSFETs o provide excellen and low gae charge. The complemenary MOSFETs may be used
AO46 6V Complemenary Enhancemen Mode Field Effec Transisor General Descripion The AO46 uses advanced rench echnology MOSFETs o provide excellen and low gae charge. The complemenary MOSFETs may be used
A FAMILY OF THREE-LEVEL DC-DC CONVERTERS
 A FAMIY OF THREE-EVE DC-DC CONVERTERS Anonio José Beno Boion, Ivo Barbi Federal Universiy of Sana Caarina - UFSC, Power Elecronics Insiue - INEP PO box 5119, ZIP code 88040-970, Florianópolis, SC, BRAZI
A FAMIY OF THREE-EVE DC-DC CONVERTERS Anonio José Beno Boion, Ivo Barbi Federal Universiy of Sana Caarina - UFSC, Power Elecronics Insiue - INEP PO box 5119, ZIP code 88040-970, Florianópolis, SC, BRAZI
EE 330 Lecture 23. Small Signal Analysis Small Signal Modelling
 EE 330 Lecure 23 Small Signal Analysis Small Signal Modelling Exam 2 Friday March 9 Exam 3 Friday April 13 Review Session for Exam 2: 6:00 p.m. on Thursday March 8 in Room Sweeney 1116 Review from Las
EE 330 Lecure 23 Small Signal Analysis Small Signal Modelling Exam 2 Friday March 9 Exam 3 Friday April 13 Review Session for Exam 2: 6:00 p.m. on Thursday March 8 in Room Sweeney 1116 Review from Las
Section 2.2 Charge and Current 2.6 b) The current direction is designated as the direction of the movement of positive charges.
 Chaper Soluions Secion. Inroducion. Curren source. Volage source. esisor.4 Capacior.5 Inducor Secion. Charge and Curren.6 b) The curren direcion is designaed as he direcion of he movemen of posiive charges..7
Chaper Soluions Secion. Inroducion. Curren source. Volage source. esisor.4 Capacior.5 Inducor Secion. Charge and Curren.6 b) The curren direcion is designaed as he direcion of he movemen of posiive charges..7
Topic Astable Circuits. Recall that an astable circuit has two unstable states;
 Topic 2.2. Asable Circuis. Learning Objecives: A he end o his opic you will be able o; Recall ha an asable circui has wo unsable saes; Explain he operaion o a circui based on a Schmi inverer, and esimae
Topic 2.2. Asable Circuis. Learning Objecives: A he end o his opic you will be able o; Recall ha an asable circui has wo unsable saes; Explain he operaion o a circui based on a Schmi inverer, and esimae
MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics
 ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY
 Homework #10 Soluions EECS 40, Fall 2006 Prof. Chang-Hasnain Due a 6 pm in 240 Cory on Wednesday, 04/18/07 oal Poins: 100 Pu (1) your name and (2) discussion secion number on your homework. You need o
Homework #10 Soluions EECS 40, Fall 2006 Prof. Chang-Hasnain Due a 6 pm in 240 Cory on Wednesday, 04/18/07 oal Poins: 100 Pu (1) your name and (2) discussion secion number on your homework. You need o
EEEB113 CIRCUIT ANALYSIS I
 9/14/29 1 EEEB113 CICUIT ANALYSIS I Chaper 7 Firs-Order Circuis Maerials from Fundamenals of Elecric Circuis 4e, Alexander Sadiku, McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 2 Firs-Order Circuis -Chaper 7 7.2 The Source-Free
9/14/29 1 EEEB113 CICUIT ANALYSIS I Chaper 7 Firs-Order Circuis Maerials from Fundamenals of Elecric Circuis 4e, Alexander Sadiku, McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 2 Firs-Order Circuis -Chaper 7 7.2 The Source-Free
Fundamentals of Power Electronics Second edition. Robert W. Erickson Dragan Maksimovic University of Colorado, Boulder
 Fundamenals of Power Elecronics Second ediion Rober W. Erickson Dragan Maksimovic Universiy of Colorado, Boulder Chaper 1: Inroducion 1.1. Inroducion o power processing 1.2. Some applicaions of power elecronics
Fundamenals of Power Elecronics Second ediion Rober W. Erickson Dragan Maksimovic Universiy of Colorado, Boulder Chaper 1: Inroducion 1.1. Inroducion o power processing 1.2. Some applicaions of power elecronics
Chapter 5: Discontinuous conduction mode. Introduction to Discontinuous Conduction Mode (DCM)
 haper 5. The isconinuous onducion Mode 5.. Origin of he disconinuous conducion mode, and mode boundary 5.. Analysis of he conversion raio M(,K) 5.3. Boos converer example 5.4. Summary of resuls and key
haper 5. The isconinuous onducion Mode 5.. Origin of he disconinuous conducion mode, and mode boundary 5.. Analysis of he conversion raio M(,K) 5.3. Boos converer example 5.4. Summary of resuls and key
Application Note AN Software release of SemiSel version 3.1. New semiconductor available. Temperature ripple at low inverter output frequencies
 Applicaion Noe AN-8004 Revision: Issue Dae: Prepared by: 00 2008-05-21 Dr. Arend Winrich Ke y Words: SemiSel, Semiconducor Selecion, Loss Calculaion Sofware release of SemiSel version 3.1 New semiconducor
Applicaion Noe AN-8004 Revision: Issue Dae: Prepared by: 00 2008-05-21 Dr. Arend Winrich Ke y Words: SemiSel, Semiconducor Selecion, Loss Calculaion Sofware release of SemiSel version 3.1 New semiconducor
Chapter 15: Phenomena. Chapter 15 Chemical Kinetics. Reaction Rates. Reaction Rates R P. Reaction Rates. Rate Laws
 Chaper 5: Phenomena Phenomena: The reacion (aq) + B(aq) C(aq) was sudied a wo differen emperaures (98 K and 35 K). For each emperaure he reacion was sared by puing differen concenraions of he 3 species
Chaper 5: Phenomena Phenomena: The reacion (aq) + B(aq) C(aq) was sudied a wo differen emperaures (98 K and 35 K). For each emperaure he reacion was sared by puing differen concenraions of he 3 species
Semiconductor Devices and Models
 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan - 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Semiconducor Devices and Models Resisor apacior Diode Bipolar Transisor MOSFET SPIE Model ppendix Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan
Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan - 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Semiconducor Devices and Models Resisor apacior Diode Bipolar Transisor MOSFET SPIE Model ppendix Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan
Reading. Lecture 28: Single Stage Frequency response. Lecture Outline. Context
 Reading Lecure 28: Single Sage Frequency response Prof J. S. Sih Reading: We are discussing he frequency response of single sage aplifiers, which isn reaed in he ex unil afer uli-sae aplifiers (beginning
Reading Lecure 28: Single Sage Frequency response Prof J. S. Sih Reading: We are discussing he frequency response of single sage aplifiers, which isn reaed in he ex unil afer uli-sae aplifiers (beginning
INDEX. Transient analysis 1 Initial Conditions 1
 INDEX Secion Page Transien analysis 1 Iniial Condiions 1 Please inform me of your opinion of he relaive emphasis of he review maerial by simply making commens on his page and sending i o me a: Frank Mera
INDEX Secion Page Transien analysis 1 Iniial Condiions 1 Please inform me of your opinion of he relaive emphasis of he review maerial by simply making commens on his page and sending i o me a: Frank Mera
8. Basic RL and RC Circuits
 8. Basic L and C Circuis This chaper deals wih he soluions of he responses of L and C circuis The analysis of C and L circuis leads o a linear differenial equaion This chaper covers he following opics
8. Basic L and C Circuis This chaper deals wih he soluions of he responses of L and C circuis The analysis of C and L circuis leads o a linear differenial equaion This chaper covers he following opics
Lab 10: RC, RL, and RLC Circuits
 Lab 10: RC, RL, and RLC Circuis In his experimen, we will invesigae he behavior of circuis conaining combinaions of resisors, capaciors, and inducors. We will sudy he way volages and currens change in
Lab 10: RC, RL, and RLC Circuis In his experimen, we will invesigae he behavior of circuis conaining combinaions of resisors, capaciors, and inducors. We will sudy he way volages and currens change in
Multi-Frequency Sheath Dynamics
 Muli-Frequency Sheah Dynamics Seven Shannon, Alex Paerson, Theodoros Panagopoulos, Daniel Hoffman, John Holland, Dennis Grimard (Universiy of Michigan) Purpose of research RF plasmas wih muliple frequency
Muli-Frequency Sheah Dynamics Seven Shannon, Alex Paerson, Theodoros Panagopoulos, Daniel Hoffman, John Holland, Dennis Grimard (Universiy of Michigan) Purpose of research RF plasmas wih muliple frequency
The Devices: MOS Transistors
 The Devices: MOS Transistors References: Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, R. F. Pierret, Addison-Wesley Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey et.al. Prentice Hall NMOS Transistor
The Devices: MOS Transistors References: Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, R. F. Pierret, Addison-Wesley Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey et.al. Prentice Hall NMOS Transistor
Capacitors & Inductors
 apaciors & Inducors EEE5 Elecric ircuis Anawach Sangswang Dep. of Elecrical Engineering KMUTT Elecric Field Elecric flux densiy Elecric field srengh E Elecric flux lines always exend from a posiively charged
apaciors & Inducors EEE5 Elecric ircuis Anawach Sangswang Dep. of Elecrical Engineering KMUTT Elecric Field Elecric flux densiy Elecric field srengh E Elecric flux lines always exend from a posiively charged
3. Alternating Current
 3. Alernaing Curren TOPCS Definiion and nroducion AC Generaor Componens of AC Circuis Series LRC Circuis Power in AC Circuis Transformers & AC Transmission nroducion o AC The elecric power ou of a home
3. Alernaing Curren TOPCS Definiion and nroducion AC Generaor Componens of AC Circuis Series LRC Circuis Power in AC Circuis Transformers & AC Transmission nroducion o AC The elecric power ou of a home
Lecture 28: Single Stage Frequency response. Context
 Lecure 28: Single Sage Frequency response Prof J. S. Sih Conex In oday s lecure, we will coninue o look a he frequency response of single sage aplifiers, saring wih a ore coplee discussion of he CS aplifier,
Lecure 28: Single Sage Frequency response Prof J. S. Sih Conex In oday s lecure, we will coninue o look a he frequency response of single sage aplifiers, saring wih a ore coplee discussion of he CS aplifier,
CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS 257 12.1 RESISTORS IN SERIES AND IN PARALLEL When wo resisors are conneced ogeher as shown in Figure 12.1 we said ha hey are conneced in series. As
CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS 257 12.1 RESISTORS IN SERIES AND IN PARALLEL When wo resisors are conneced ogeher as shown in Figure 12.1 we said ha hey are conneced in series. As
Diodes. Midterm exam. Ideal diode. Semiconductors and doping. Notes. Eugeniy E. Mikhailov. Lecture 05. Notes
 Diodes. Eugeniy E. Mikhailov The College of William & Mary Lecure 5 Eugeniy Mikhailov (W&M) Elecronics 1 Lecure 5 1 / 13 Miderm exam Where: n he lab When: During he firs hour of he lab Maerial: everyhing
Diodes. Eugeniy E. Mikhailov The College of William & Mary Lecure 5 Eugeniy Mikhailov (W&M) Elecronics 1 Lecure 5 1 / 13 Miderm exam Where: n he lab When: During he firs hour of he lab Maerial: everyhing
6.2 Transforms of Derivatives and Integrals.
 SEC. 6.2 Transforms of Derivaives and Inegrals. ODEs 2 3 33 39 23. Change of scale. If l( f ()) F(s) and c is any 33 45 APPLICATION OF s-shifting posiive consan, show ha l( f (c)) F(s>c)>c (Hin: In Probs.
SEC. 6.2 Transforms of Derivaives and Inegrals. ODEs 2 3 33 39 23. Change of scale. If l( f ()) F(s) and c is any 33 45 APPLICATION OF s-shifting posiive consan, show ha l( f (c)) F(s>c)>c (Hin: In Probs.
Lecture 11: MOS Transistor
 Lecture 11: MOS Transistor Prof. Niknejad Lecture Outline Review: MOS Capacitors Regions MOS Capacitors (3.8 3.9) CV Curve Threshold Voltage MOS Transistors (4.1 4.3): Overview Cross-section and layout
Lecture 11: MOS Transistor Prof. Niknejad Lecture Outline Review: MOS Capacitors Regions MOS Capacitors (3.8 3.9) CV Curve Threshold Voltage MOS Transistors (4.1 4.3): Overview Cross-section and layout
MC74HC138A. 1 of 8 Decoder/ Demultiplexer. High Performance Silicon Gate CMOS
 of 8 Decoder/ Demuliplexer High Performance Silicon Gae CMOS The is idenical in pinou o he LS8. The device inpus are compaible wih sandard CMOS oupus; wih pullup resisors, hey are compaible wih LSTTL oupus.
of 8 Decoder/ Demuliplexer High Performance Silicon Gae CMOS The is idenical in pinou o he LS8. The device inpus are compaible wih sandard CMOS oupus; wih pullup resisors, hey are compaible wih LSTTL oupus.
Smart Highside Power Switch
 Smar ighside Power Swich Feaures Overload proecion Curren limiaion Shor circui proecion Thermal shudown Overvolage proecion (including load dump) Fas demagneizaion of inducive loads Reverse baery proecion
Smar ighside Power Swich Feaures Overload proecion Curren limiaion Shor circui proecion Thermal shudown Overvolage proecion (including load dump) Fas demagneizaion of inducive loads Reverse baery proecion
Top View. Top View. V DS Gate-Source Voltage ±8 ±8 Continuous Drain Current Pulsed Drain Current C V GS I D -2.5 I DM P D 0.
 V Complemenary MOSFET General Descripion The AO664 combines advanced rench MOSFET echnology wih a low resisance package o provide exremely low R DS(ON). This device is ideal for load swich and baery proecion
V Complemenary MOSFET General Descripion The AO664 combines advanced rench MOSFET echnology wih a low resisance package o provide exremely low R DS(ON). This device is ideal for load swich and baery proecion
S G V DS V GS Pulsed Drain Current B -15 Schottky reverse voltage Continuous Forward Current A F I DM V KA
 ON473 2V PChannel MOSFET wih Schoky Diode General Descripion The ON473 uses advanced rench echnology o provide excellen R DS(ON) and low gae charge. Schoky diode is provided o faciliae he implemenaion
ON473 2V PChannel MOSFET wih Schoky Diode General Descripion The ON473 uses advanced rench echnology o provide excellen R DS(ON) and low gae charge. Schoky diode is provided o faciliae he implemenaion
Pattern Classification and NNet applications with memristive crossbar circuits. Fabien ALIBART D. Strukov s group, ECE-UCSB Now at IEMN-CNRS, France
 Paern Classificaion and NNe applicaions wih memrisive crossbar circuis Fabien ALIBART D. Srukov s group, ECE-UCSB Now a IEMN-CNRS, France Ouline Inroducion: Neural Nework wih memrisive devices Engineering
Paern Classificaion and NNe applicaions wih memrisive crossbar circuis Fabien ALIBART D. Srukov s group, ECE-UCSB Now a IEMN-CNRS, France Ouline Inroducion: Neural Nework wih memrisive devices Engineering
U(t) (t) -U T 1. (t) (t)
 Prof. Dr.-ng. F. Schuber Digial ircuis Exercise. () () A () - T T The highpass is driven by he square pulse (). alculae and skech A (). = µf, = KΩ, = 5 V, T = T = ms. Exercise. () () A () T T The highpass
Prof. Dr.-ng. F. Schuber Digial ircuis Exercise. () () A () - T T The highpass is driven by he square pulse (). alculae and skech A (). = µf, = KΩ, = 5 V, T = T = ms. Exercise. () () A () T T The highpass
Electromagnetic Induction: The creation of an electric current by a changing magnetic field.
 Inducion 1. Inducion 1. Observaions 2. Flux 1. Inducion Elecromagneic Inducion: The creaion of an elecric curren by a changing magneic field. M. Faraday was he firs o really invesigae his phenomenon o
Inducion 1. Inducion 1. Observaions 2. Flux 1. Inducion Elecromagneic Inducion: The creaion of an elecric curren by a changing magneic field. M. Faraday was he firs o really invesigae his phenomenon o
Advanced Power Electronics For Automotive and Utility Applications
 Advanced Power Elecronics For Auomoive and Uiliy Applicaions Fang Z. Peng Dep. of Elecrical and Compuer Engineering Michigan Sae Universiy Phone: 517-336-4687, Fax: 517-353-1980 Email: fzpeng@egr.msu.edu
Advanced Power Elecronics For Auomoive and Uiliy Applicaions Fang Z. Peng Dep. of Elecrical and Compuer Engineering Michigan Sae Universiy Phone: 517-336-4687, Fax: 517-353-1980 Email: fzpeng@egr.msu.edu
( ) = Q 0. ( ) R = R dq. ( t) = I t
 ircuis onceps The addiion of a simple capacior o a circui of resisors allows wo relaed phenomena o occur The observaion ha he ime-dependence of a complex waveform is alered by he circui is referred o as
ircuis onceps The addiion of a simple capacior o a circui of resisors allows wo relaed phenomena o occur The observaion ha he ime-dependence of a complex waveform is alered by he circui is referred o as
Top View. Top View S2 G2 S1 G1
 AO49 3V Complemenary MOSFET General Descripion AO49 uses advanced rench echnology o provide excellen R DS(ON) and low gae charge. This complemenary N and P channel MOSFET configuraion is ideal for low
AO49 3V Complemenary MOSFET General Descripion AO49 uses advanced rench echnology o provide excellen R DS(ON) and low gae charge. This complemenary N and P channel MOSFET configuraion is ideal for low
h[n] is the impulse response of the discrete-time system:
![h[n] is the impulse response of the discrete-time system: h[n] is the impulse response of the discrete-time system:](/thumbs/89/99208034.jpg) Definiion Examples Properies Memory Inveribiliy Causaliy Sabiliy Time Invariance Lineariy Sysems Fundamenals Overview Definiion of a Sysem x() h() y() x[n] h[n] Sysem: a process in which inpu signals are
Definiion Examples Properies Memory Inveribiliy Causaliy Sabiliy Time Invariance Lineariy Sysems Fundamenals Overview Definiion of a Sysem x() h() y() x[n] h[n] Sysem: a process in which inpu signals are
Phys1112: DC and RC circuits
 Name: Group Members: Dae: TA s Name: Phys1112: DC and RC circuis Objecives: 1. To undersand curren and volage characerisics of a DC RC discharging circui. 2. To undersand he effec of he RC ime consan.
Name: Group Members: Dae: TA s Name: Phys1112: DC and RC circuis Objecives: 1. To undersand curren and volage characerisics of a DC RC discharging circui. 2. To undersand he effec of he RC ime consan.
Technology Scaling. 9nm. Advanced Digital IC-Design. Content. What happens when technology is scaled? Progress: Described by Gordon Moore
 Advanced Digial IC-Design Conen 0.μm Wha happens when echnology is scaled? Technology caling 9nm ource Gae Drain ource Gae Drain ubsrae ubsrae IC Design pace Progress: Described by Gordon Moore peed Tradiional
Advanced Digial IC-Design Conen 0.μm Wha happens when echnology is scaled? Technology caling 9nm ource Gae Drain ource Gae Drain ubsrae ubsrae IC Design pace Progress: Described by Gordon Moore peed Tradiional
Chapter 4 DC converter and DC switch
 haper 4 D converer and D swich 4.1 Applicaion - Assumpion Applicaion: D swich: Replace mechanic swiches D converer: in racion drives Assumions: Ideal D sources Ideal Power emiconducor Devices 4.2 D swich
haper 4 D converer and D swich 4.1 Applicaion - Assumpion Applicaion: D swich: Replace mechanic swiches D converer: in racion drives Assumions: Ideal D sources Ideal Power emiconducor Devices 4.2 D swich
4. Electric field lines with respect to equipotential surfaces are
 Pre-es Quasi-saic elecromagneism. The field produced by primary charge Q and by an uncharged conducing plane disanced from Q by disance d is equal o he field produced wihou conducing plane by wo following
Pre-es Quasi-saic elecromagneism. The field produced by primary charge Q and by an uncharged conducing plane disanced from Q by disance d is equal o he field produced wihou conducing plane by wo following
EE105 - Fall 2005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 EE105 - Fall 005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits ecture 7 MOS Transistor Announcements Homework 3, due today Homework 4 due next week ab this week Reading: Chapter 4 1 ecture Material ast lecture
EE105 - Fall 005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits ecture 7 MOS Transistor Announcements Homework 3, due today Homework 4 due next week ab this week Reading: Chapter 4 1 ecture Material ast lecture
Slides: CMOS Basics.
 MO Basics ysem-on-hi oluions & Archiecures Technische Universiä München www.lis.ei.um.de Module ouline Inroducion o MO Where is MO? Wha is MO? Why is MO so aracive? How does MO work? Basics MO evice Basics
MO Basics ysem-on-hi oluions & Archiecures Technische Universiä München www.lis.ei.um.de Module ouline Inroducion o MO Where is MO? Wha is MO? Why is MO so aracive? How does MO work? Basics MO evice Basics
Homework-8(1) P8.3-1, 3, 8, 10, 17, 21, 24, 28,29 P8.4-1, 2, 5
 Homework-8() P8.3-, 3, 8, 0, 7, 2, 24, 28,29 P8.4-, 2, 5 Secion 8.3: The Response of a Firs Order Circui o a Consan Inpu P 8.3- The circui shown in Figure P 8.3- is a seady sae before he swich closes a
Homework-8() P8.3-, 3, 8, 0, 7, 2, 24, 28,29 P8.4-, 2, 5 Secion 8.3: The Response of a Firs Order Circui o a Consan Inpu P 8.3- The circui shown in Figure P 8.3- is a seady sae before he swich closes a
Non Linear Op Amp Circuits.
 Non Linear Op Amp ircuis. omparaors wih 0 and non zero reference volage. omparaors wih hyseresis. The Schmid Trigger. Window comparaors. The inegraor. Waveform conversion. Sine o ecangular. ecangular o
Non Linear Op Amp ircuis. omparaors wih 0 and non zero reference volage. omparaors wih hyseresis. The Schmid Trigger. Window comparaors. The inegraor. Waveform conversion. Sine o ecangular. ecangular o
ELG 2135 ELECTRONICS I SIXTH CHAPTER: DIGITAL CIRCUITS
 ELG 35 ELECTRONICS I SIXTH CHAPTER: DIGITAL CIRCUITS Session WINTER 003 Dr. M. YAGOUB Sixh Chaper: Digial Circuis VI - _ This las chaper is devoed o digial circuis and paricularly o MOS digial inegraed
ELG 35 ELECTRONICS I SIXTH CHAPTER: DIGITAL CIRCUITS Session WINTER 003 Dr. M. YAGOUB Sixh Chaper: Digial Circuis VI - _ This las chaper is devoed o digial circuis and paricularly o MOS digial inegraed
ES 250 Practice Final Exam
 ES 50 Pracice Final Exam. Given ha v 8 V, a Deermine he values of v o : 0 Ω, v o. V 0 Firs, v o 8. V 0 + 0 Nex, 8 40 40 0 40 0 400 400 ib i 0 40 + 40 + 40 40 40 + + ( ) 480 + 5 + 40 + 8 400 400( 0) 000
ES 50 Pracice Final Exam. Given ha v 8 V, a Deermine he values of v o : 0 Ω, v o. V 0 Firs, v o 8. V 0 + 0 Nex, 8 40 40 0 40 0 400 400 ib i 0 40 + 40 + 40 40 40 + + ( ) 480 + 5 + 40 + 8 400 400( 0) 000
V DS. 100% UIS Tested 100% R g Tested. Top View. Top View S2 G2
 3V Dual PChannel MOSFET General Descripion The AO483 uses advanced rench echnology o provide excellen R DS(ON) wih low gae charge. This device is suiable for use as a load swich or in PWM applicaions.
3V Dual PChannel MOSFET General Descripion The AO483 uses advanced rench echnology o provide excellen R DS(ON) wih low gae charge. This device is suiable for use as a load swich or in PWM applicaions.
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23. The MOSFET Square Law Model
 ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23 The MOSFET Square Law Model Lecture Outline As with the diode and bipolar, have looked at basic structure of the MOSFET and now turn to derivation of a current
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23 The MOSFET Square Law Model Lecture Outline As with the diode and bipolar, have looked at basic structure of the MOSFET and now turn to derivation of a current
6.01: Introduction to EECS I Lecture 8 March 29, 2011
 6.01: Inroducion o EES I Lecure 8 March 29, 2011 6.01: Inroducion o EES I Op-Amps Las Time: The ircui Absracion ircuis represen sysems as connecions of elemens hrough which currens (hrough variables) flow
6.01: Inroducion o EES I Lecure 8 March 29, 2011 6.01: Inroducion o EES I Op-Amps Las Time: The ircui Absracion ircuis represen sysems as connecions of elemens hrough which currens (hrough variables) flow
Switching Characteristics of Power Devices
 Swiching Characeriic of Power Device Device uilizaion can be grealy improved by underanding he device wiching charcaeriic. he main performance wiching characeriic of power device: he ave operaing area
Swiching Characeriic of Power Device Device uilizaion can be grealy improved by underanding he device wiching charcaeriic. he main performance wiching characeriic of power device: he ave operaing area
1. VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION
 1. VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION 1.1 Kinemaics Equaions s = u + 1 a and s = v 1 a s = 1 (u + v) v = u + as 1. Displacemen-Time Graph Gradien = speed 1.3 Velociy-Time Graph Gradien = acceleraion Area under
1. VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION 1.1 Kinemaics Equaions s = u + 1 a and s = v 1 a s = 1 (u + v) v = u + as 1. Displacemen-Time Graph Gradien = speed 1.3 Velociy-Time Graph Gradien = acceleraion Area under
555 Timer. Digital Electronics
 555 Timer Digial Elecronics This presenaion will Inroduce he 555 Timer. 555 Timer Derive he characerisic equaions for he charging and discharging of a capacior. Presen he equaions for period, frequency,
555 Timer Digial Elecronics This presenaion will Inroduce he 555 Timer. 555 Timer Derive he characerisic equaions for he charging and discharging of a capacior. Presen he equaions for period, frequency,
