P1.12 MESOSCALE VARIATIONAL ASSIMILATION OF PROFILING RADIOMETER DATA. Thomas Nehrkorn and Christopher Grassotti *
|
|
|
- Arthur Williamson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 P1.12 MESOSCALE VARIATIONAL ASSIMILATION OF PROFILING RADIOMETER DATA Thomas Nehrkorn and Christopher Grassotti * Atmospheric and Environmental Research, Inc. Lexington, Massachusetts Randolph Ware Radiometrics Corporation Boulder, Colorado 1. INTRODUCTION The variational assimilation of measurements from a vertically pointing, ground-based 12-channel microwave profiling radiometer is tested with the MM5 3dvar and 4dvar data assimilation systems. The Radiometrics TP/WVP-3000 radiometer measures brightness temperature in 7 microwave frequencies from 51 to 59 GHz on the flank of the 60 GHz oxygen resonance line and 5 frequencies from 22 to 30 GHz associated with the water vapor resonance peak at 22.2 GHz (see Ware et al. 2003, and references contained therein). Retrieved profiles of temperature, water vapor, and cloud liquid water are obtained through neural net inversions of the brightness temperatures, where the neural net is trained using radiosonde soundings and corresponding forward modeled brightness temperatures. An observation operator has also been developed for the direct assimilation of the measured brightness temperatures, using the forward model and its adjoint. The impact of assimilation of the retrieved profiles, and direct assimilation of the brightness temperatures, on analyses and subsequent forecasts have been tested using the MM5 mesoscale model and its associated 4dvar assimilation system. Results are presented here from two separate case studies: one using data from a profiler located at the ARM CART site in Oklahoma, another from a profiler on the NCAR Foothills campus in Boulder, Colorado. The results demonstrate the proper implementation of the 4dvar assimilation of both retrieved profiles and brightness temperature data from the profiler. Forecast impacts are generally small in the cases studied here, since only a single observation site was available. Current efforts are concentrated on implementation of the observation operator into the MM5 3dvar system, and extensions of the observation operator to include slant-range profiler measurements. Results from these studies will be presented at the conference. 2. ARM CASE STUDY Real-data experiments have been performed for a case over the Atmospheric Radiation Measurement (ARM) program Cloud and Radiation Testbed (CART) site in Oklahoma. The case studied here is March 19, Data assimilation runs were performed by assimilating data over a six-hour window, from 06 to 12 UTC. The initial state for the experiments was generated from a single-domain (15 km grid spacing) six-hour forecast, using the 00 UTC Eta analysis and forecast for initial and lateral boundary conditions. A control run forecast was performed with the version of the MM5 forecast model that is part of the MM5 4dvar. The temperature and wind fields of the control run are shown in Figure 1 for level σ=0.854 (near 850 hpa). The synoptic situation is characterized by a lower level closed low associated with an upper level short-wave, which progresses east during the 6- hour assimilation time period. A series of data assimilation runs have been performed to test the proper functioning of the 4dvar system in this configuration, and the to test and analyze the performance of the microwave profiler brightness temperature observation operator. For each experiment, a 4dvar assimilation between 06 and 12 UTC 19 March was used to arrive at an optimized set of initial conditions at 06 UTC. A forecast was then run out to 18 hours (00 UTC 20 March 2000) from these initial conditions. * Corresponding author address: Thomas Nehrkorn, AER, Inc., 131 Hartwell Ave, Lexington MA 02421; tnehrkor@aer.coml
2 The following table gives an overview of the data assimilation experiments. ARM sonde data was available every three hours. The raw microwave profiler data are available every 9 minutes, but in the experiments here, those data were median filtered and used at hourly intervals. Data flagged as raincontaminated were excluded, resulting in the loss of data for the first three hours. Table 1: Data used in the data assimilation experiments for UTC 19 March Sonde data are the ARM sondes at the central and surrounding sites, and the microwave profiler data is from the profiler at the ARM central site. Experiment Sondes Microwave Profiler Retrievals Brightness Control Sonde 6, 9, 12 MPRet 9, 10, 11, 12 MPTb 9, 10, 11, 12 The results from these runs all show relatively small analysis increments. As is to be expected, assimilation of the sonde data resulted in the largest analysis increments. An example of the sonde run temperature increments at the end of the assimilation window is shown in Figure 2, which shows generally colder temperatures in the western half of the domain, and warmer temperatures in the eastern half. The corresponding temperature increments for the MPret and MPTb runs (not shown) are generally less than half as large as those for the sonde run, and cover a smaller area of the model domain. An example of the control and sonde and MPRet wind fields is shown Figure 3 for level σ=0.261 at hour 6. Changes in the wind fields due to assimilation of sonde data are primarily speed differences, except near the trough axis, which has a slightly sharper definition in the sonde control run. The corresponding increments in the MPRet are much smaller, with no visibly discernible differences from the control run wind. The effects of assimilating the microwave profiler retrievals are more easily demonstrated by a comparison of measured and simulated profiler retrieval data. Figure 4 shows the microwave profiler retrievals of temperature for hours 3-18 (09 UTC 19 Mar - 00 UTC 20 Mar). Model values from the control run (interpolated to the location of the profiler) are also shown. Comparison of the control difference field shown in Figure 4 with that for the MPRet run shown in Figure 5 shows the improved fit of the model values during times within the assimilation window (09-12 UTC). During the free forecast (after 12 UTC), values at the profiler site are largely determined from grid points upstream, and differences between the two runs are much smaller. The corresponding fits of simulated and measured brightness temperatures is summarized in Figure 6. In this case, simulated brightness temperatures for channels 9-12 are within 1-2 K of observed values during the assimilation window for all experiments, and assimilation of the brightness temperatures has a negligible impact on the fit to the observations. However, the fit to channels 1-8 is noticeably improved by assimilation of these data. As was the case in the MPRet run, however, the effects of assimilating these data are negligible at the profiler site during the free forecast. The results from this set of assimilation experiments demonstrate the proper functioning of the 4dvar assimilation system, both for assimilation of profile data from sonde and micrwave profiler retrievals, and of profiler brightness temperatures. In this case, assimilation of 3-hourly profiles of temperature, moisture, and wind at the 5 sonde locations in the center of the domain introduced a small, but consistent change in the model fields that resulted in a slight sharpening of the short wave trough, both during the assimilation period and in the free forecast. Assimilation of hourly microwave profiler data of temperature and moisture at a single location in the model domain resulted in a better fit to the assimilated data, but had a much smaller impact at at other locations and forecast times. 3. BOULDER CASE A second real-data case study was performed with data from a microwave profiler located in Boulder, Colorado. This case was characterized by low-level cold air advection associated with a freezing drizzle event in Boulder and Denver, where it had a significant impact on operations of the airport. This case has been the subject of studies by Herzegh et al. (2003) Ikeda and Rasmussen (2003). For this case, a 12 km resolution grid was used for forecasts from 00 UTC 4 March 2003 (see Figure 7). The control forecast was run with initial and lateral boundary conditions derived from the 00 UTC Eta forecast. Microwave profiler temperature retrievals in Boulder, and corresponding simulated control run values, are shown in Figure 8 for this case. Boundary layer temperatures in the control are slightly colder than then the retrieved values during the first 9 hours of the forecast. The rapid cooling of the boundary layer between UTC seen in the profiler data (as was shown in Herzegh et al., these observations are consistent with the 12 UTC Denver radiosonde sounding), are accompanied by an increase in boundary layer moisture, with maximum values at 11 UTC (see Figure 9). In the control run, these temperature changes are more gradual, and occur later. The moistening of the boundary layer is shifted almost 10 hours in time in the control run. An initial set of assimilation experiments was performed with an assimilation time window of UTC, before the onset of the PBL cooling and moistening in Denver and Boulder.
3 The effects of assimilating retrieved profiles on forecast values at the profiler site is shown in Figure 10. Comparison with the corresponding plots for the control run shows an improved fit to the temperature and moisture (the latter more so at the initial time) during the assimilation time period, but little effect during the free forecast. Differences from the control run are larger at other grid locations, but there is no consistent improvement in the forecast evolution of the intrusion of the cold, moist boundary layer air form the Northeast. The evolution of observed and simulated brightness temperatures at the Boulder profiler location is shown in Figure 11. The brightness temperatures for channels 1-8 clearly show the signature of cloud liquid water in the observed (at 12 UTC) and simulated (at 18 UTC) brightness temperatures. During the assimilation time window, observed and simulated brightness temperatures of these channels agree to within 1-2 K for all experiments, and assimilation of the brightness temperatures has little effect. In contrast, the brightness temperatures in channels 9-12 reflect the observed and simulated cooling of the boundary layer throughout the forecast. During the assimilation window, simulated values in the control run are too low, and the fit is improved by assimilation of the brightness temperatures, and, to a lesser extent, by assimilation of the retrieved profiles. During the free forecast, the situation is reversed, and there is no discernible difference in simulated values at the profiler site. 3. SUMMARY AND FUTURE WORK The results demonstrate the proper implementation of the 4dvar assimilation of both retrieved profiles and brightness temperature data from the profiler. Forecast impacts are generally small in the cases studied here, since only a single observation site was available in the model domain, and errors in the control run forecasts were related to errors in the mesoscale or larger scale forcing. and extensions of the observation operator to include slant-range profiler measurements. 4. REFERENCES P. H. Herzegh, S. Landolt, and T. Schneider, 2003: The structure, evolution and cloud processes of a Colorado upslope storm as shown by profiling radiometer, radar and tower data. In 31st Conference on Radar Meteorology, Seattle, WA, American Meteorological Society, Boston, MA Available from am/paper_64469.htm. K. Ikeda and R. M. Rasmussen, 2003: Radar observations of a freezing drizzle case in Colorado. In 31st Conference on Radar Meteorology, Seattle, WA, American Meteorological Society, Boston, MA. Available from am/paper_64788.htm. Ware, R., R. Carpenter, J. Güldner, J. Liljegren, T. Nehrkorn, F. Solheim and F. Vandenberghe, 2003: A multichannel radiometric profiler of temperature, humidity, and cloud liquid, Radio Science, 38, 8079, doi: /2002rs ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work was supported by Army Research Laboratory contract DAAD17-01-C The authors thank Francois Vandenberghe of NCAR for the software for the computation of the simulated retrieval profiles. 6. FIGURES Current efforts are concentrated on implementation of the observation operator into the MM5 3dvar system,
4 Figure 1: Control wind field (m/s) and temperature (K) at σ=0.854, at hour 0 (06 UTC, top panel) and 6 (12 UTC, bottom panel). The profiler location is indicated by the red circle. Figure 2: Sonde run temperature analysis increments (sonde-control) at hour 6 (12 UTC), at σ= The model domain corresponds to the geographic area shown in Figure 1. The axes are labeled by gridpoint index, and the sonde data locations are shown as red crosses.
5 Figure 4: Time-height section of observed (top panel), simulated (center panel), and differences between simulated and observed (bottom panel) temperatures (K) at the microwave profiler location for the ARM control run. Figure 3: Wind fields at σ= The control run wind field is shown in black (a full barb corresponds to 10 m/s), and sonde run (top panel) or MPRet run (bottom panel) wind fields are overplotted in blue. The respective data locations for each run are marked by red crosses. The color shading indicates the analysis increment vector magnitude (note the change in scale between the panels). Figure 5: Differences between simulated and observed temperatures (K) at the microwave profiler location for the ARM MPRet run.
6 Figure 6: Observed and simulated brightness temperatures for channels 1-12, for the ARM case. Observed values are shown in black (black labels indicate the frequency in GHz), control run simulated values in blue, MPRet run values in green, and MPTb run values in red. Figure 7: The model terrain (m) for the domain used for the Boulder case. The axes are label by grid point index, and lines of constant latitude and longitude are overlaid. The grid spacing is 12 km. The location of the Denver radiosonde and the Boulder microwave profiler are shown as red crosses.
7 Figure 8: Observed (top panel), simulated (center panel), and differences between simulated and observed (bottom panel) temperatures (K) for the Boulder control run. Figure 9: Observed (top panel), simulated (center panel), and differences between simulated and observed (bottom panel) water vapor density (g/m 3 ) for the Boulder control run. Figure 10: Differences between simulated and observed profiler temperature (left panel) and moisture (right panel) profiles in Boulder for the retrieval assimilation run.
8 Figure 11: Observed and simulated brightness temperatures for channels 1-12, for the Boulder case. Observed values are shown in black (black labels indicate the frequency in GHz), control run simulated values in blue, MPRet run values in green, and MPTb run values in red.
Ground-Based Radiometric Profiling during Dynamic Weather Conditions
 Ground-Based Radiometric Profiling during Dynamic Weather Conditions R. Ware 1,2, P. Herzegh 3, F. Vandenberghe 3, J. Vivekanandan 3, and E. Westwater 4 1 Corresponding Author: Radiometrics Corporation,
Ground-Based Radiometric Profiling during Dynamic Weather Conditions R. Ware 1,2, P. Herzegh 3, F. Vandenberghe 3, J. Vivekanandan 3, and E. Westwater 4 1 Corresponding Author: Radiometrics Corporation,
Observations of Integrated Water Vapor and Cloud Liquid Water at SHEBA. James Liljegren
 Observations of Integrated Water Vapor and Cloud Liquid Water at SHEBA James Liljegren Ames Laboratory Ames, IA 515.294.8428 liljegren@ameslab.gov Introduction In the Arctic water vapor and clouds influence
Observations of Integrated Water Vapor and Cloud Liquid Water at SHEBA James Liljegren Ames Laboratory Ames, IA 515.294.8428 liljegren@ameslab.gov Introduction In the Arctic water vapor and clouds influence
Improvements in the Upper-Air Observation Systems in Japan
 Improvements in the Upper-Air Observation Systems in Japan Masahito Ishihara, Masanori Chiba, Yasushi Izumikawa, Nobuyuki Kinoshita, and Naoki Tsukamoto Japan Meteorological Agency, 1-3-4 Otemachi, Chiyoda-ku,
Improvements in the Upper-Air Observation Systems in Japan Masahito Ishihara, Masanori Chiba, Yasushi Izumikawa, Nobuyuki Kinoshita, and Naoki Tsukamoto Japan Meteorological Agency, 1-3-4 Otemachi, Chiyoda-ku,
Rapid Environmental Changes observed by Remote Sensing Systems in the local vicinity of an unusual Colorado Tornado
 Rapid Environmental Changes observed by Remote Sensing Systems in the local vicinity of an unusual Colorado Tornado 27th Conference on Severe Local Storms 3 7 November 2014, Madison, Wisconsin Steven E.
Rapid Environmental Changes observed by Remote Sensing Systems in the local vicinity of an unusual Colorado Tornado 27th Conference on Severe Local Storms 3 7 November 2014, Madison, Wisconsin Steven E.
IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS PRECIPITABLE WATER VAPOR AND COSMIC GPS REFRACTIVITY PROFILE ON HURRICANE DEAN FORECAST. (a) (b) (c)
 9B.3 IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS PRECIPITABLE WATER VAPOR AND COSMIC GPS REFRACTIVITY PROFILE ON HURRICANE DEAN FORECAST Tetsuya Iwabuchi *, J. J. Braun, and T. Van Hove UCAR, Boulder, Colorado 1. INTRODUCTION
9B.3 IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS PRECIPITABLE WATER VAPOR AND COSMIC GPS REFRACTIVITY PROFILE ON HURRICANE DEAN FORECAST Tetsuya Iwabuchi *, J. J. Braun, and T. Van Hove UCAR, Boulder, Colorado 1. INTRODUCTION
P3.5 A COMPARISON OF ATMOSPHERIC PROFILES USING A TWELVE CHANNEL MICROWAVE PROFILING RADIOMETER AND RADIOSONDES DURING LOW CEILING EVENTS
 P3.5 A COMPARISON OF ATMOSPHERIC PROFILES USING A TWELVE CHANNEL MICROWAVE PROFILING RADIOMETER AND RADIOSONDES DURING LOW CEILING EVENTS Scott D. Landolt*, Robert Tardif and Paul H. Herzegh National Center
P3.5 A COMPARISON OF ATMOSPHERIC PROFILES USING A TWELVE CHANNEL MICROWAVE PROFILING RADIOMETER AND RADIOSONDES DURING LOW CEILING EVENTS Scott D. Landolt*, Robert Tardif and Paul H. Herzegh National Center
1/10/ Radiometrics (Boulder, CO), 2 U. Oklahoma (Norman, OK), 3 NCAR (Boulder, CO), 4 Kennedy Space Center (Merritt Island, FL), 5
 T. Wilfong 1, R. Ware 1, K. Brewster 2, F. Carr 2, K. Reed 1,3, T. Brauer 4, D. Berchoff 5,6, J. Brotzge 7, W. Conway 8, W. Emery 9, G. Guillot 10, L. Huddleston 4, R. Kursinski 11, C. McCormick 11, N.
T. Wilfong 1, R. Ware 1, K. Brewster 2, F. Carr 2, K. Reed 1,3, T. Brauer 4, D. Berchoff 5,6, J. Brotzge 7, W. Conway 8, W. Emery 9, G. Guillot 10, L. Huddleston 4, R. Kursinski 11, C. McCormick 11, N.
STATION If relative humidity is 60% and saturation vapor pressure is 35 mb, what is the actual vapor pressure?
 STATION 1 Vapor pressure is a measure of relative humidity and saturation vapor pressure. Using this information and the information given in the problem, answer the following question. 1. If relative
STATION 1 Vapor pressure is a measure of relative humidity and saturation vapor pressure. Using this information and the information given in the problem, answer the following question. 1. If relative
Impact of GPS and TMI Precipitable Water Data on Mesoscale Numerical Weather Prediction Model Forecasts
 Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, Vol. 82, No. 1B, pp. 453--457, 2004 453 Impact of GPS and TMI Precipitable Water Data on Mesoscale Numerical Weather Prediction Model Forecasts Ko KOIZUMI
Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, Vol. 82, No. 1B, pp. 453--457, 2004 453 Impact of GPS and TMI Precipitable Water Data on Mesoscale Numerical Weather Prediction Model Forecasts Ko KOIZUMI
Northeastern United States Snowstorm of 9 February 2017
 Northeastern United States Snowstorm of 9 February 2017 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A strong shortwave produced a stripe of precipitation
Northeastern United States Snowstorm of 9 February 2017 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A strong shortwave produced a stripe of precipitation
Ground-based temperature and humidity profiling using microwave radiometer retrievals at Sydney Airport.
 Ground-based temperature and humidity profiling using microwave radiometer retrievals at Sydney Airport. Peter Ryan Bureau of Meteorology, Melbourne, Australia Peter.J.Ryan@bom.gov.au ABSTRACT The aim
Ground-based temperature and humidity profiling using microwave radiometer retrievals at Sydney Airport. Peter Ryan Bureau of Meteorology, Melbourne, Australia Peter.J.Ryan@bom.gov.au ABSTRACT The aim
THE IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS SLANT-PATH WET DELAY MEASUREMENTS ON SHORT-RANGE PREDICTION OF A PREFRONTAL SQUALL LINE
 JP1.17 THE IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS SLANT-PATH WET DELAY MEASUREMENTS ON SHORT-RANGE PREDICTION OF A PREFRONTAL SQUALL LINE So-Young Ha *1,, Ying-Hwa Kuo 1, Gyu-Ho Lim 1 National Center for Atmospheric
JP1.17 THE IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS SLANT-PATH WET DELAY MEASUREMENTS ON SHORT-RANGE PREDICTION OF A PREFRONTAL SQUALL LINE So-Young Ha *1,, Ying-Hwa Kuo 1, Gyu-Ho Lim 1 National Center for Atmospheric
Christian Sutton. Microwave Water Radiometer measurements of tropospheric moisture. ATOC 5235 Remote Sensing Spring 2003
 Christian Sutton Microwave Water Radiometer measurements of tropospheric moisture ATOC 5235 Remote Sensing Spring 23 ABSTRACT The Microwave Water Radiometer (MWR) is a two channel microwave receiver used
Christian Sutton Microwave Water Radiometer measurements of tropospheric moisture ATOC 5235 Remote Sensing Spring 23 ABSTRACT The Microwave Water Radiometer (MWR) is a two channel microwave receiver used
TWO CASES OF HEAVY RAIN ON THE MEDITERRANEAN SIDE OF THE ALPS IN MAP. Robert Houze 1 and Socorro Medina University of Washington
 1.1 TWO CASES OF HEAVY RAIN ON THE MEDITERRANEAN SIDE OF THE ALPS IN MAP Robert Houze 1 and Socorro Medina University of Washington Matthias Steiner Princeton University 1. INTRODUCTION The Mesoscale Alpine
1.1 TWO CASES OF HEAVY RAIN ON THE MEDITERRANEAN SIDE OF THE ALPS IN MAP Robert Houze 1 and Socorro Medina University of Washington Matthias Steiner Princeton University 1. INTRODUCTION The Mesoscale Alpine
A Comparison of Clear-Sky Emission Models with Data Taken During the 1999 Millimeter-Wave Radiometric Arctic Winter Water Vapor Experiment
 A Comparison of Clear-Sky Emission Models with Data Taken During the 1999 Millimeter-Wave Radiometric Arctic Winter Water Vapor Experiment E. R. Westwater, Y. Han, A. Gasiewski, and M. Klein Cooperative
A Comparison of Clear-Sky Emission Models with Data Taken During the 1999 Millimeter-Wave Radiometric Arctic Winter Water Vapor Experiment E. R. Westwater, Y. Han, A. Gasiewski, and M. Klein Cooperative
ANSWER KEY. Part I: Synoptic Scale Composite Map. Lab 12 Answer Key. Explorations in Meteorology 54
 ANSWER KEY Part I: Synoptic Scale Composite Map 1. Using Figure 2, locate and highlight, with a black dashed line, the 500-mb trough axis. Also, locate and highlight, with a black zigzag line, the 500-mb
ANSWER KEY Part I: Synoptic Scale Composite Map 1. Using Figure 2, locate and highlight, with a black dashed line, the 500-mb trough axis. Also, locate and highlight, with a black zigzag line, the 500-mb
Use and impact of satellite data in the NZLAM mesoscale model for the New Zealand region
 Use and impact of satellite data in the NZLAM mesoscale model for the New Zealand region V. Sherlock, P. Andrews, H. Oliver, A. Korpela and M. Uddstrom National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research,
Use and impact of satellite data in the NZLAM mesoscale model for the New Zealand region V. Sherlock, P. Andrews, H. Oliver, A. Korpela and M. Uddstrom National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research,
Variational assimilation of slant-path wet delay. measurements from a hypothetical ground-based. GPS network. Part I: Comparison with
 Variational assimilation of slant-path wet delay measurements from a hypothetical ground-based GPS network. Part I: Comparison with precipitable water assimilation So-Young Ha 1,2, Ying-Hwa Kuo 1, Yong-Run
Variational assimilation of slant-path wet delay measurements from a hypothetical ground-based GPS network. Part I: Comparison with precipitable water assimilation So-Young Ha 1,2, Ying-Hwa Kuo 1, Yong-Run
Clear-Air Forward Microwave and Millimeterwave Radiative Transfer Models for Arctic Conditions
 Clear-Air Forward Microwave and Millimeterwave Radiative Transfer Models for Arctic Conditions E. R. Westwater 1, D. Cimini 2, V. Mattioli 3, M. Klein 1, V. Leuski 1, A. J. Gasiewski 1 1 Center for Environmental
Clear-Air Forward Microwave and Millimeterwave Radiative Transfer Models for Arctic Conditions E. R. Westwater 1, D. Cimini 2, V. Mattioli 3, M. Klein 1, V. Leuski 1, A. J. Gasiewski 1 1 Center for Environmental
The impact of assimilation of microwave radiance in HWRF on the forecast over the western Pacific Ocean
 The impact of assimilation of microwave radiance in HWRF on the forecast over the western Pacific Ocean Chun-Chieh Chao, 1 Chien-Ben Chou 2 and Huei-Ping Huang 3 1Meteorological Informatics Business Division,
The impact of assimilation of microwave radiance in HWRF on the forecast over the western Pacific Ocean Chun-Chieh Chao, 1 Chien-Ben Chou 2 and Huei-Ping Huang 3 1Meteorological Informatics Business Division,
P11R.3. David J. Serke 1*, G. Zhang 2, J. Vivekanandan 1, T. Schneider 3, P. Minnis 4 and M. Poellot 5 1. INTRODUCTION
 P11R.3 VERIFICATION OF S-POLKA KA BAND RADAR/RADIOMETER LWC AND RES RETRIEVALS WITH GRIDS RETRIEVALS AND AIRCRAFT MEASUREMENTS AND COMPARISON TO GOES ICING PRODUCTS FOR THE WISP04 10-11MARCH EVENT David
P11R.3 VERIFICATION OF S-POLKA KA BAND RADAR/RADIOMETER LWC AND RES RETRIEVALS WITH GRIDS RETRIEVALS AND AIRCRAFT MEASUREMENTS AND COMPARISON TO GOES ICING PRODUCTS FOR THE WISP04 10-11MARCH EVENT David
291. IMPACT OF AIRS THERMODYNAMIC PROFILES ON PRECIPITATION FORECASTS FOR ATMOSPHERIC RIVER CASES AFFECTING THE WESTERN UNITED STATES
 291. IMPACT OF AIRS THERMODYNAMIC PROFILES ON PRECIPITATION FORECASTS FOR ATMOSPHERIC RIVER CASES AFFECTING THE WESTERN UNITED STATES Clay B. Blankenship, USRA, Huntsville, Alabama Bradley T. Zavodsky
291. IMPACT OF AIRS THERMODYNAMIC PROFILES ON PRECIPITATION FORECASTS FOR ATMOSPHERIC RIVER CASES AFFECTING THE WESTERN UNITED STATES Clay B. Blankenship, USRA, Huntsville, Alabama Bradley T. Zavodsky
AROME Nowcasting - tool based on a convective scale operational system
 AROME Nowcasting - tool based on a convective scale operational system RC - LACE stay report Supervisors (ZAMG): Yong Wang Florian Meier Christoph Wittmann Author: Mirela Pietrisi (NMA) 1. Introduction
AROME Nowcasting - tool based on a convective scale operational system RC - LACE stay report Supervisors (ZAMG): Yong Wang Florian Meier Christoph Wittmann Author: Mirela Pietrisi (NMA) 1. Introduction
F O U N D A T I O N A L C O U R S E
 F O U N D A T I O N A L C O U R S E December 6, 2018 Satellite Foundational Course for JPSS (SatFC-J) F O U N D A T I O N A L C O U R S E Introduction to Microwave Remote Sensing (with a focus on passive
F O U N D A T I O N A L C O U R S E December 6, 2018 Satellite Foundational Course for JPSS (SatFC-J) F O U N D A T I O N A L C O U R S E Introduction to Microwave Remote Sensing (with a focus on passive
The Nowcasting Demonstration Project for London 2012
 The Nowcasting Demonstration Project for London 2012 Susan Ballard, Zhihong Li, David Simonin, Jean-Francois Caron, Brian Golding, Met Office, UK Introduction The success of convective-scale NWP is largely
The Nowcasting Demonstration Project for London 2012 Susan Ballard, Zhihong Li, David Simonin, Jean-Francois Caron, Brian Golding, Met Office, UK Introduction The success of convective-scale NWP is largely
3.23 IMPROVING VERY-SHORT-TERM STORM PREDICTIONS BY ASSIMILATING RADAR AND SATELLITE DATA INTO A MESOSCALE NWP MODEL
 3.23 IMPROVING VERY-SHORT-TERM STORM PREDICTIONS BY ASSIMILATING RADAR AND SATELLITE DATA INTO A MESOSCALE NWP MODEL Q. Zhao 1*, J. Cook 1, Q. Xu 2, and P. Harasti 3 1 Naval Research Laboratory, Monterey,
3.23 IMPROVING VERY-SHORT-TERM STORM PREDICTIONS BY ASSIMILATING RADAR AND SATELLITE DATA INTO A MESOSCALE NWP MODEL Q. Zhao 1*, J. Cook 1, Q. Xu 2, and P. Harasti 3 1 Naval Research Laboratory, Monterey,
PARCWAPT Passive Radiometry Cloud Water Profiling Technique
 PARCWAPT Passive Radiometry Cloud Water Profiling Technique By: H. Czekala, T. Rose, Radiometer Physics GmbH, Germany A new cloud liquid water profiling technique by Radiometer Physics GmbH (patent pending)
PARCWAPT Passive Radiometry Cloud Water Profiling Technique By: H. Czekala, T. Rose, Radiometer Physics GmbH, Germany A new cloud liquid water profiling technique by Radiometer Physics GmbH (patent pending)
ASIA-PACIFIC JOURNAL OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, 45, 1, 2009, p
 ASIA-PACIFIC JOURNAL OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, 45, 1, 2009, p. 55-69 Ground-based microwave radiometers (MWR) provide continuous thermodynamic (temperature, water vapor, and cloud liquid) soundings in the
ASIA-PACIFIC JOURNAL OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, 45, 1, 2009, p. 55-69 Ground-based microwave radiometers (MWR) provide continuous thermodynamic (temperature, water vapor, and cloud liquid) soundings in the
Radiometric profiling of temperature, water vapor and cloud liquid water using various inversion methods
 Radiometric profiling of temperature, water vapor and cloud liquid water using various inversion methods Fredrick Solheim and John R. Godwin Radiometrics Corporation, Boulder, Colorado E. R. Westwater
Radiometric profiling of temperature, water vapor and cloud liquid water using various inversion methods Fredrick Solheim and John R. Godwin Radiometrics Corporation, Boulder, Colorado E. R. Westwater
NUMERICAL weather prediction (NWP) and nowcasting
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 45, NO. 7, JULY 2007 2163 1D-VAR Retrieval of Temperature and Humidity Profiles From a Ground-Based Microwave Radiometer Tim J. Hewison, Member,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 45, NO. 7, JULY 2007 2163 1D-VAR Retrieval of Temperature and Humidity Profiles From a Ground-Based Microwave Radiometer Tim J. Hewison, Member,
Atmospheric Research
 Atmospheric Research 140 141 (2014) 85 94 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Atmospheric Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/atmos Effect of off-zenith observations on reducing the
Atmospheric Research 140 141 (2014) 85 94 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Atmospheric Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/atmos Effect of off-zenith observations on reducing the
The project that I originally selected to research for the OC 3570 course was based on
 Introduction The project that I originally selected to research for the OC 3570 course was based on remote sensing applications of the marine boundary layer and their verification with actual observed
Introduction The project that I originally selected to research for the OC 3570 course was based on remote sensing applications of the marine boundary layer and their verification with actual observed
Radar data assimilation using a modular programming approach with the Ensemble Kalman Filter: preliminary results
 Radar data assimilation using a modular programming approach with the Ensemble Kalman Filter: preliminary results I. Maiello 1, L. Delle Monache 2, G. Romine 2, E. Picciotti 3, F.S. Marzano 4, R. Ferretti
Radar data assimilation using a modular programming approach with the Ensemble Kalman Filter: preliminary results I. Maiello 1, L. Delle Monache 2, G. Romine 2, E. Picciotti 3, F.S. Marzano 4, R. Ferretti
Development of 3D Variational Assimilation System for ATOVS Data in China
 Development of 3D Variational Assimilation System for ATOVS Data in China Xue Jishan, Zhang Hua, Zhu Guofu, Zhuang Shiyu 1) Zhang Wenjian, Liu Zhiquan, Wu Xuebao, Zhang Fenyin. 2) 1) Chinese Academy of
Development of 3D Variational Assimilation System for ATOVS Data in China Xue Jishan, Zhang Hua, Zhu Guofu, Zhuang Shiyu 1) Zhang Wenjian, Liu Zhiquan, Wu Xuebao, Zhang Fenyin. 2) 1) Chinese Academy of
Calibration and Temperature Retrieval of Improved Ground-based Atmospheric Microwave Sounder
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 6, NO. 1, 2010 6 Calibration and Temperature Retrieval of Improved Ground-based Atmospheric Microwave Sounder Jie Ying He 1, 2, Yu Zhang 1, 2, and Sheng Wei Zhang 1 1 Center for Space
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 6, NO. 1, 2010 6 Calibration and Temperature Retrieval of Improved Ground-based Atmospheric Microwave Sounder Jie Ying He 1, 2, Yu Zhang 1, 2, and Sheng Wei Zhang 1 1 Center for Space
Francis O. 1, David H. Bromwich 1,2
 Impact of assimilating COSMIC GPS RO moisture and temperature profiles on Polar WRF simulations of West Antarctic cyclones Francis O. O@eno 1, David H. Bromwich 1,2 1 Polar Meteorology Group BPRC 2 Atmospheric
Impact of assimilating COSMIC GPS RO moisture and temperature profiles on Polar WRF simulations of West Antarctic cyclones Francis O. O@eno 1, David H. Bromwich 1,2 1 Polar Meteorology Group BPRC 2 Atmospheric
P6.13 GLOBAL AND MONTHLY DIURNAL PRECIPITATION STATISTICS BASED ON PASSIVE MICROWAVE OBSERVATIONS FROM AMSU
 P6.13 GLOBAL AND MONTHLY DIURNAL PRECIPITATION STATISTICS BASED ON PASSIVE MICROWAVE OBSERVATIONS FROM AMSU Frederick W. Chen*, David H. Staelin, and Chinnawat Surussavadee Massachusetts Institute of Technology,
P6.13 GLOBAL AND MONTHLY DIURNAL PRECIPITATION STATISTICS BASED ON PASSIVE MICROWAVE OBSERVATIONS FROM AMSU Frederick W. Chen*, David H. Staelin, and Chinnawat Surussavadee Massachusetts Institute of Technology,
Introduction to Ensemble Kalman Filters and the Data Assimilation Research Testbed
 Introduction to Ensemble Kalman Filters and the Data Assimilation Research Testbed Jeffrey Anderson, Tim Hoar, Nancy Collins NCAR Institute for Math Applied to Geophysics pg 1 What is Data Assimilation?
Introduction to Ensemble Kalman Filters and the Data Assimilation Research Testbed Jeffrey Anderson, Tim Hoar, Nancy Collins NCAR Institute for Math Applied to Geophysics pg 1 What is Data Assimilation?
Atmospheric Profiles Over Land and Ocean from AMSU
 P1.18 Atmospheric Profiles Over Land and Ocean from AMSU John M. Forsythe, Kevin M. Donofrio, Ron W. Kessler, Andrew S. Jones, Cynthia L. Combs, Phil Shott and Thomas H. Vonder Haar DoD Center for Geosciences
P1.18 Atmospheric Profiles Over Land and Ocean from AMSU John M. Forsythe, Kevin M. Donofrio, Ron W. Kessler, Andrew S. Jones, Cynthia L. Combs, Phil Shott and Thomas H. Vonder Haar DoD Center for Geosciences
Temporal Variation of Close-Proximity Soundings within a Tornadic Supercell Environment
 SOLA, 2014, Vol. 10, 57 61, doi:10.2151/sola.2014-012 57 Temporal Variation of Close-Proximity Soundings within a Tornadic Supercell Environment Kentaro Araki, Hiroshi Ishimoto, Masataka Murakami, and
SOLA, 2014, Vol. 10, 57 61, doi:10.2151/sola.2014-012 57 Temporal Variation of Close-Proximity Soundings within a Tornadic Supercell Environment Kentaro Araki, Hiroshi Ishimoto, Masataka Murakami, and
Clear-Air Forward Microwave and Millimeterwave Radiative Transfer Models for Arctic Conditions
 Clear-Air Forward Microwave and Millimeterwave Radiative Transfer Models for Arctic Conditions E. R. Westwater 1, D. Cimini 2, V. Mattioli 3, M. Klein 1, V. Leuski 1, A. J. Gasiewski 1 1 Center for Environmental
Clear-Air Forward Microwave and Millimeterwave Radiative Transfer Models for Arctic Conditions E. R. Westwater 1, D. Cimini 2, V. Mattioli 3, M. Klein 1, V. Leuski 1, A. J. Gasiewski 1 1 Center for Environmental
For the operational forecaster one important precondition for the diagnosis and prediction of
 Initiation of Deep Moist Convection at WV-Boundaries Vienna, Austria For the operational forecaster one important precondition for the diagnosis and prediction of convective activity is the availability
Initiation of Deep Moist Convection at WV-Boundaries Vienna, Austria For the operational forecaster one important precondition for the diagnosis and prediction of convective activity is the availability
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America
 Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
Rosemary Munro*, Graeme Kelly, Michael Rohn* and Roger Saunders
 ASSIMILATION OF METEOSAT RADIANCE DATA WITHIN THE 4DVAR SYSTEM AT ECMWF Rosemary Munro*, Graeme Kelly, Michael Rohn* and Roger Saunders European Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasts Shinfield Park,
ASSIMILATION OF METEOSAT RADIANCE DATA WITHIN THE 4DVAR SYSTEM AT ECMWF Rosemary Munro*, Graeme Kelly, Michael Rohn* and Roger Saunders European Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasts Shinfield Park,
Modelling and measurement of rainfall by ground-based multispectral microwave radiometry
 Modelling and measurement of rainfall by ground-based multispectral microwave radiometry Frank S. Marzano 1, Domenico Cimini 1, Randolph Ware 2, Ermanno Fionda 3 and Piero Ciotti 1 1. Center of Excellence
Modelling and measurement of rainfall by ground-based multispectral microwave radiometry Frank S. Marzano 1, Domenico Cimini 1, Randolph Ware 2, Ermanno Fionda 3 and Piero Ciotti 1 1. Center of Excellence
Lecture 19: Operational Remote Sensing in Visible, IR, and Microwave Channels
 MET 4994 Remote Sensing: Radar and Satellite Meteorology MET 5994 Remote Sensing in Meteorology Lecture 19: Operational Remote Sensing in Visible, IR, and Microwave Channels Before you use data from any
MET 4994 Remote Sensing: Radar and Satellite Meteorology MET 5994 Remote Sensing in Meteorology Lecture 19: Operational Remote Sensing in Visible, IR, and Microwave Channels Before you use data from any
Some Applications of WRF/DART
 Some Applications of WRF/DART Chris Snyder, National Center for Atmospheric Research Mesoscale and Microscale Meteorology Division (MMM), and Institue for Mathematics Applied to Geoscience (IMAGe) WRF/DART
Some Applications of WRF/DART Chris Snyder, National Center for Atmospheric Research Mesoscale and Microscale Meteorology Division (MMM), and Institue for Mathematics Applied to Geoscience (IMAGe) WRF/DART
VERIFICATION OF MERIS LEVEL 2 PRODUCTS: CLOUD TOP PRESSURE AND CLOUD OPTICAL THICKNESS
 VERIFICATION OF MERIS LEVEL 2 PRODUCTS: CLOUD TOP PRESSURE AND CLOUD OPTICAL THICKNESS Rene Preusker, Peter Albert and Juergen Fischer 17th December 2002 Freie Universitaet Berlin Institut fuer Weltraumwissenschaften
VERIFICATION OF MERIS LEVEL 2 PRODUCTS: CLOUD TOP PRESSURE AND CLOUD OPTICAL THICKNESS Rene Preusker, Peter Albert and Juergen Fischer 17th December 2002 Freie Universitaet Berlin Institut fuer Weltraumwissenschaften
A COMPARISON OF VERY SHORT-TERM QPF S FOR SUMMER CONVECTION OVER COMPLEX TERRAIN AREAS, WITH THE NCAR/ATEC WRF AND MM5-BASED RTFDDA SYSTEMS
 A COMPARISON OF VERY SHORT-TERM QPF S FOR SUMMER CONVECTION OVER COMPLEX TERRAIN AREAS, WITH THE NCAR/ATEC WRF AND MM5-BASED RTFDDA SYSTEMS Wei Yu, Yubao Liu, Tom Warner, Randy Bullock, Barbara Brown and
A COMPARISON OF VERY SHORT-TERM QPF S FOR SUMMER CONVECTION OVER COMPLEX TERRAIN AREAS, WITH THE NCAR/ATEC WRF AND MM5-BASED RTFDDA SYSTEMS Wei Yu, Yubao Liu, Tom Warner, Randy Bullock, Barbara Brown and
New Technique for Retrieving Liquid Water Path over Land using Satellite Microwave Observations
 New Technique for Retrieving Liquid Water Path over Land using Satellite Microwave Observations M.N. Deeter and J. Vivekanandan Research Applications Library National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder,
New Technique for Retrieving Liquid Water Path over Land using Satellite Microwave Observations M.N. Deeter and J. Vivekanandan Research Applications Library National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder,
USE OF SURFACE MESONET DATA IN THE NCEP REGIONAL GSI SYSTEM
 6A.7 USE OF SURFACE MESONET DATA IN THE NCEP REGIONAL GSI SYSTEM Seung-Jae Lee *, David F. Parrish, Wan-Shu Wu, Manuel Pondeca, Dennis Keyser, and Geoffery J. DiMego NCEP/Environmental Meteorological Center,
6A.7 USE OF SURFACE MESONET DATA IN THE NCEP REGIONAL GSI SYSTEM Seung-Jae Lee *, David F. Parrish, Wan-Shu Wu, Manuel Pondeca, Dennis Keyser, and Geoffery J. DiMego NCEP/Environmental Meteorological Center,
Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004
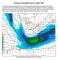 Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004 This event was characterized by a very strong jet streak that developed over North Carolina by 00 UTC 8 March, as seen in the Eta model analysis at 300 mb, with
Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004 This event was characterized by a very strong jet streak that developed over North Carolina by 00 UTC 8 March, as seen in the Eta model analysis at 300 mb, with
P2.57 PRECIPITATION STRUCTURE IN MIDLATITUDE CYCLONES
 P2.57 PRECIPITATION STRUCTURE IN MIDLATITUDE CYCLONES Paul R. Field 1, Robert Wood 2 1. National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado. 2. University of Washington, Seattle, Washington. 1.
P2.57 PRECIPITATION STRUCTURE IN MIDLATITUDE CYCLONES Paul R. Field 1, Robert Wood 2 1. National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado. 2. University of Washington, Seattle, Washington. 1.
A Microwave Snow Emissivity Model
 A Microwave Snow Emissivity Model Fuzhong Weng Joint Center for Satellite Data Assimilation NOAA/NESDIS/Office of Research and Applications, Camp Springs, Maryland and Banghua Yan Decision Systems Technologies
A Microwave Snow Emissivity Model Fuzhong Weng Joint Center for Satellite Data Assimilation NOAA/NESDIS/Office of Research and Applications, Camp Springs, Maryland and Banghua Yan Decision Systems Technologies
Thermodynamic Profiling during the Winter Olympics
 Thermodynamic Profiling during the Winter Olympics CMOS 2010 Congress Scientific Session: Vancouver 2010 Olympic and Paralympic Winter Games 4 June 2010 R. Ware 1, N. Cimini 2, G. Giuliani 2, E. Westwater
Thermodynamic Profiling during the Winter Olympics CMOS 2010 Congress Scientific Session: Vancouver 2010 Olympic and Paralympic Winter Games 4 June 2010 R. Ware 1, N. Cimini 2, G. Giuliani 2, E. Westwater
AN OBSERVING SYSTEM EXPERIMENT OF MTSAT RAPID SCAN AMV USING JMA MESO-SCALE OPERATIONAL NWP SYSTEM
 AN OBSERVING SYSTEM EXPERIMENT OF MTSAT RAPID SCAN AMV USING JMA MESO-SCALE OPERATIONAL NWP SYSTEM Koji Yamashita Japan Meteorological Agency / Numerical Prediction Division 1-3-4, Otemachi, Chiyoda-ku,
AN OBSERVING SYSTEM EXPERIMENT OF MTSAT RAPID SCAN AMV USING JMA MESO-SCALE OPERATIONAL NWP SYSTEM Koji Yamashita Japan Meteorological Agency / Numerical Prediction Division 1-3-4, Otemachi, Chiyoda-ku,
MOISTURE PROFILE RETRIEVALS FROM SATELLITE MICROWAVE SOUNDERS FOR WEATHER ANALYSIS OVER LAND AND OCEAN
 MOISTURE PROFILE RETRIEVALS FROM SATELLITE MICROWAVE SOUNDERS FOR WEATHER ANALYSIS OVER LAND AND OCEAN John M. Forsythe, Stanley Q. Kidder, Andrew S. Jones and Thomas H. Vonder Haar Cooperative Institute
MOISTURE PROFILE RETRIEVALS FROM SATELLITE MICROWAVE SOUNDERS FOR WEATHER ANALYSIS OVER LAND AND OCEAN John M. Forsythe, Stanley Q. Kidder, Andrew S. Jones and Thomas H. Vonder Haar Cooperative Institute
Nerushev A.F., Barkhatov A.E. Research and Production Association "Typhoon" 4 Pobedy Street, , Obninsk, Kaluga Region, Russia.
 DETERMINATION OF ATMOSPHERIC CHARACTERISTICS IN THE ZONE OF ACTION OF EXTRA-TROPICAL CYCLONE XYNTHIA (FEBRUARY 2010) INFERRED FROM SATELLITE MEASUREMENT DATA Nerushev A.F., Barkhatov A.E. Research and
DETERMINATION OF ATMOSPHERIC CHARACTERISTICS IN THE ZONE OF ACTION OF EXTRA-TROPICAL CYCLONE XYNTHIA (FEBRUARY 2010) INFERRED FROM SATELLITE MEASUREMENT DATA Nerushev A.F., Barkhatov A.E. Research and
Performance of Radar Wind Profilers, Radiosondes, and Surface Flux Stations at the Southern Great Plains (SGP) Cloud and Radiation Testbed (CART) Site
 Performance of Radar Wind Profilers, Radiosondes, and Surface Flux Stations at the Southern Great Plains (SGP) Cloud and Radiation Testbed (CART) Site R. L. Coulter, B. M. Lesht, M. L. Wesely, D. R. Cook,
Performance of Radar Wind Profilers, Radiosondes, and Surface Flux Stations at the Southern Great Plains (SGP) Cloud and Radiation Testbed (CART) Site R. L. Coulter, B. M. Lesht, M. L. Wesely, D. R. Cook,
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer. The Surface Energy Balance (9.2)
 The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) What processes control
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) What processes control
Arctic Atmospheric Rivers: Linking Atmospheric Synoptic Transport, Cloud Phase, Surface Energy Fluxes and Sea-Ice Growth
 Arctic Atmospheric Rivers: Linking Atmospheric Synoptic Transport, Cloud Phase, Surface Energy Fluxes and Sea-Ice Growth Ola Persson Cooperative Institute for the Research in the Environmental Sciences,
Arctic Atmospheric Rivers: Linking Atmospheric Synoptic Transport, Cloud Phase, Surface Energy Fluxes and Sea-Ice Growth Ola Persson Cooperative Institute for the Research in the Environmental Sciences,
Meteorological Satellite Image Interpretations, Part III. Acknowledgement: Dr. S. Kidder at Colorado State Univ.
 Meteorological Satellite Image Interpretations, Part III Acknowledgement: Dr. S. Kidder at Colorado State Univ. Dates EAS417 Topics Jan 30 Introduction & Matlab tutorial Feb 1 Satellite orbits & navigation
Meteorological Satellite Image Interpretations, Part III Acknowledgement: Dr. S. Kidder at Colorado State Univ. Dates EAS417 Topics Jan 30 Introduction & Matlab tutorial Feb 1 Satellite orbits & navigation
THE FEASIBILITY OF EXTRACTING LOWLEVEL WIND BY TRACING LOW LEVEL MOISTURE OBSERVED IN IR IMAGERY OVER CLOUD FREE OCEAN AREA IN THE TROPICS
 THE FEASIBILITY OF EXTRACTING LOWLEVEL WIND BY TRACING LOW LEVEL MOISTURE OBSERVED IN IR IMAGERY OVER CLOUD FREE OCEAN AREA IN THE TROPICS Toshiro Ihoue and Tetsuo Nakazawa Meteorological Research Institute
THE FEASIBILITY OF EXTRACTING LOWLEVEL WIND BY TRACING LOW LEVEL MOISTURE OBSERVED IN IR IMAGERY OVER CLOUD FREE OCEAN AREA IN THE TROPICS Toshiro Ihoue and Tetsuo Nakazawa Meteorological Research Institute
Czech Hydrometeorological Institute, Na Šabatce 17, CZ Praha 4, Czech Republic. 3
 MOISTURE DETECTION ABOVE CONVECTIVE STORMS UTILIZING THE METHOD OF BRIGHTNESS TEMPERATURE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN WATER VAPOR AND IR WINDOW BANDS, BASED ON 2008 MSG RAPID SCAN SERVICE DATA Jindřich Šťástka1,2,
MOISTURE DETECTION ABOVE CONVECTIVE STORMS UTILIZING THE METHOD OF BRIGHTNESS TEMPERATURE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN WATER VAPOR AND IR WINDOW BANDS, BASED ON 2008 MSG RAPID SCAN SERVICE DATA Jindřich Šťástka1,2,
INTERPRETATION GUIDE TO MSG WATER VAPOUR CHANNELS
 INTERPRETATION GUIDE TO MSG WATER VAPOUR CHANNELS C.G. Georgiev1 and P. Santurette2 1 National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology, Tsarigradsko chaussee 66, 1784 Sofia, Bulgaria 2 Météo-France, 42,
INTERPRETATION GUIDE TO MSG WATER VAPOUR CHANNELS C.G. Georgiev1 and P. Santurette2 1 National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology, Tsarigradsko chaussee 66, 1784 Sofia, Bulgaria 2 Météo-France, 42,
We have processed RO data for climate research and for validation of weather data since 1995 as illustrated in Figure 1.
 Real-time Analysis of COSMIC Data Christian Rocken, Doug Hunt, Bill Schreiner University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR) COSMIC Project Office Boulder, CO Abstract UCAR has analyzed GPS radio
Real-time Analysis of COSMIC Data Christian Rocken, Doug Hunt, Bill Schreiner University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR) COSMIC Project Office Boulder, CO Abstract UCAR has analyzed GPS radio
Prospects for radar and lidar cloud assimilation
 Prospects for radar and lidar cloud assimilation Marta Janisková, ECMWF Thanks to: S. Di Michele, E. Martins, A. Beljaars, S. English, P. Lopez, P. Bauer ECMWF Seminar on the Use of Satellite Observations
Prospects for radar and lidar cloud assimilation Marta Janisková, ECMWF Thanks to: S. Di Michele, E. Martins, A. Beljaars, S. English, P. Lopez, P. Bauer ECMWF Seminar on the Use of Satellite Observations
Answers to Clicker Questions
 Answers to Clicker Questions Chapter 1 What component of the atmosphere is most important to weather? A. Nitrogen B. Oxygen C. Carbon dioxide D. Ozone E. Water What location would have the lowest surface
Answers to Clicker Questions Chapter 1 What component of the atmosphere is most important to weather? A. Nitrogen B. Oxygen C. Carbon dioxide D. Ozone E. Water What location would have the lowest surface
A Longwave Broadband QME Based on ARM Pyrgeometer and AERI Measurements
 A Longwave Broadband QME Based on ARM Pyrgeometer and AERI Measurements Introduction S. A. Clough, A. D. Brown, C. Andronache, and E. J. Mlawer Atmospheric and Environmental Research, Inc. Cambridge, Massachusetts
A Longwave Broadband QME Based on ARM Pyrgeometer and AERI Measurements Introduction S. A. Clough, A. D. Brown, C. Andronache, and E. J. Mlawer Atmospheric and Environmental Research, Inc. Cambridge, Massachusetts
Aviation Hazards: Thunderstorms and Deep Convection
 Aviation Hazards: Thunderstorms and Deep Convection TREND Diagnosis of thunderstorm hazards using imagery Contents Satellite imagery Visible, infrared, water vapour Basic cloud identification Identifying
Aviation Hazards: Thunderstorms and Deep Convection TREND Diagnosis of thunderstorm hazards using imagery Contents Satellite imagery Visible, infrared, water vapour Basic cloud identification Identifying
Effect of the off-zenith observation on reducing the impact of precipitation on ground-based microwave radiometer measurement accuracy in Wuhan
 1 2 3 Effect of the off-zenith observation on reducing the impact of precipitation on ground-based microwave radiometer measurement accuracy in Wuhan 4 5 6 7 8 Guirong Xu 1, Randolph (Stick) Ware 2, Wengang
1 2 3 Effect of the off-zenith observation on reducing the impact of precipitation on ground-based microwave radiometer measurement accuracy in Wuhan 4 5 6 7 8 Guirong Xu 1, Randolph (Stick) Ware 2, Wengang
Weather vs. Climate. Tucson NWS homepage:
 Weather vs. Climate Tucson NWS homepage: www.nws.noaa.gov/twc/ A Weather Forecaster? Betty claims to know exactly when it s going to rain because her knee starts to hurt. Ms. Betty Martin of Newburgh,
Weather vs. Climate Tucson NWS homepage: www.nws.noaa.gov/twc/ A Weather Forecaster? Betty claims to know exactly when it s going to rain because her knee starts to hurt. Ms. Betty Martin of Newburgh,
Real-time PBL analysis system using profilers observations from The New York State Mesonet
 Real-time PBL analysis system using profilers observations from The New York State Mesonet Sarah Lu University at Albany State University of New York Outline Background System description and progress
Real-time PBL analysis system using profilers observations from The New York State Mesonet Sarah Lu University at Albany State University of New York Outline Background System description and progress
CHAPTER 8 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE ITCZ OVER THE INDIAN OCEAN AND INDONESIA DURING A NORMAL YEAR AND DURING AN ENSO YEAR
 CHAPTER 8 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE ITCZ OVER THE INDIAN OCEAN AND INDONESIA DURING A NORMAL YEAR AND DURING AN ENSO YEAR In this chapter, comparisons between the model-produced and analyzed streamlines,
CHAPTER 8 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE ITCZ OVER THE INDIAN OCEAN AND INDONESIA DURING A NORMAL YEAR AND DURING AN ENSO YEAR In this chapter, comparisons between the model-produced and analyzed streamlines,
Dynamic Inference of Background Error Correlation between Surface Skin and Air Temperature
 Dynamic Inference of Background Error Correlation between Surface Skin and Air Temperature Louis Garand, Mark Buehner, and Nicolas Wagneur Meteorological Service of Canada, Dorval, P. Quebec, Canada Abstract
Dynamic Inference of Background Error Correlation between Surface Skin and Air Temperature Louis Garand, Mark Buehner, and Nicolas Wagneur Meteorological Service of Canada, Dorval, P. Quebec, Canada Abstract
Masahiro Kazumori, Takashi Kadowaki Numerical Prediction Division Japan Meteorological Agency
 Development of an all-sky assimilation of microwave imager and sounder radiances for the Japan Meteorological Agency global numerical weather prediction system Masahiro Kazumori, Takashi Kadowaki Numerical
Development of an all-sky assimilation of microwave imager and sounder radiances for the Japan Meteorological Agency global numerical weather prediction system Masahiro Kazumori, Takashi Kadowaki Numerical
P3.1 Development of MOS Thunderstorm and Severe Thunderstorm Forecast Equations with Multiple Data Sources
 P3.1 Development of MOS Thunderstorm and Severe Thunderstorm Forecast Equations with Multiple Data Sources Kathryn K. Hughes * Meteorological Development Laboratory Office of Science and Technology National
P3.1 Development of MOS Thunderstorm and Severe Thunderstorm Forecast Equations with Multiple Data Sources Kathryn K. Hughes * Meteorological Development Laboratory Office of Science and Technology National
Weather report 28 November 2017 Campinas/SP
 Weather report 28 November 2017 Campinas/SP Summary: 1) Synoptic analysis and pre-convective environment 2) Verification 1) Synoptic analysis and pre-convective environment: At 1200 UTC 28 November 2017
Weather report 28 November 2017 Campinas/SP Summary: 1) Synoptic analysis and pre-convective environment 2) Verification 1) Synoptic analysis and pre-convective environment: At 1200 UTC 28 November 2017
Use of AMSU data in the Met Office UK Mesoscale Model
 Use of AMSU data in the Met Office UK Mesoscale Model 1. Introduction Brett Candy, Stephen English, Richard Renshaw & Bruce Macpherson The Met Office, Exeter, United Kingdom In common with other global
Use of AMSU data in the Met Office UK Mesoscale Model 1. Introduction Brett Candy, Stephen English, Richard Renshaw & Bruce Macpherson The Met Office, Exeter, United Kingdom In common with other global
WEATHER. rain. thunder. The explosive sound of air as it is heated by lightning.
 WEATHER rain thunder The explosive sound of air as it is heated by lightning. rainbow lightning hurricane They are intense storms with swirling winds up to 150 miles per hour. tornado cold front warm front
WEATHER rain thunder The explosive sound of air as it is heated by lightning. rainbow lightning hurricane They are intense storms with swirling winds up to 150 miles per hour. tornado cold front warm front
Combining Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods to Produce Gridded Climatologies
 Combining Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods to Produce Gridded Climatologies Michael Squires Alan McNab National Climatic Data Center (NCDC - NOAA) Asheville, NC Abstract There are nearly 8,000 sites
Combining Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods to Produce Gridded Climatologies Michael Squires Alan McNab National Climatic Data Center (NCDC - NOAA) Asheville, NC Abstract There are nearly 8,000 sites
Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox
 Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox Flash floods account for the greatest number of fatalities among convective storm-related events but it still remains difficult to forecast
Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox Flash floods account for the greatest number of fatalities among convective storm-related events but it still remains difficult to forecast
5.3 TESTING AND EVALUATION OF THE GSI DATA ASSIMILATION SYSTEM
 5.3 TESTING AND EVALUATION OF THE GSI DATA ASSIMILATION SYSTEM Kathryn M Newman*, C. Zhou, H. Shao, X.Y. Huang, M. Hu National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO Developmental Testbed Center
5.3 TESTING AND EVALUATION OF THE GSI DATA ASSIMILATION SYSTEM Kathryn M Newman*, C. Zhou, H. Shao, X.Y. Huang, M. Hu National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO Developmental Testbed Center
WRF Model Simulated Proxy Datasets Used for GOES-R Research Activities
 WRF Model Simulated Proxy Datasets Used for GOES-R Research Activities Jason Otkin Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies Space Science and Engineering Center University of Wisconsin
WRF Model Simulated Proxy Datasets Used for GOES-R Research Activities Jason Otkin Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies Space Science and Engineering Center University of Wisconsin
Multiscale Analyses of Inland Tropical Cyclone Midlatitude Jet Interactions: Camille (1969) and Danny (1997)
 Multiscale Analyses of Inland Tropical Cyclone Midlatitude Jet Interactions: Camille (1969) and Danny (1997) Matthew Potter, Lance Bosart, and Daniel Keyser Department of Atmospheric and Environmental
Multiscale Analyses of Inland Tropical Cyclone Midlatitude Jet Interactions: Camille (1969) and Danny (1997) Matthew Potter, Lance Bosart, and Daniel Keyser Department of Atmospheric and Environmental
Joshua M. Boustead *1, and Barbara E. Mayes NOAA/NWS WFO Omaha/Valley, NE. William Gargan, George Phillips, and Jared Leighton NOAA/NWS WFO Topeka, KS
 7B.3 Composite Analysis of Environmental Conditions Favorable for Significant Tornadoes across Eastern Kansas Joshua M. Boustead *1, and Barbara E. Mayes NOAA/NWS WFO Omaha/Valley, NE William Gargan, George
7B.3 Composite Analysis of Environmental Conditions Favorable for Significant Tornadoes across Eastern Kansas Joshua M. Boustead *1, and Barbara E. Mayes NOAA/NWS WFO Omaha/Valley, NE William Gargan, George
P3.17 THE DEVELOPMENT OF MULTIPLE LOW-LEVEL MESOCYCLONES WITHIN A SUPERCELL. Joshua M. Boustead *1 NOAA/NWS Weather Forecast Office, Topeka, KS
 P3.17 THE DEVELOPMENT OF MULTIPLE LOW-LEVEL MESOCYCLONES WITHIN A SUPERCELL Joshua M. Boustead *1 NOAA/NWS Weather Forecast Office, Topeka, KS Philip N. Schumacher NOAA/NWS Weather Forecaster Office, Sioux
P3.17 THE DEVELOPMENT OF MULTIPLE LOW-LEVEL MESOCYCLONES WITHIN A SUPERCELL Joshua M. Boustead *1 NOAA/NWS Weather Forecast Office, Topeka, KS Philip N. Schumacher NOAA/NWS Weather Forecaster Office, Sioux
Forecast for 6/28-7/31. Forecaster: Matthew Brewer Forecast made at: 12z 6/27/2017
 Forecast for 6/28-7/31 Forecaster: Matthew Brewer Forecast made at: 12z 6/27/2017 Whiteface lodge Mesonet Meteogram for the past 24 hours http://www.nysmesonet.org/data/meteogram#?stid=wfmb Whiteface Summit
Forecast for 6/28-7/31 Forecaster: Matthew Brewer Forecast made at: 12z 6/27/2017 Whiteface lodge Mesonet Meteogram for the past 24 hours http://www.nysmesonet.org/data/meteogram#?stid=wfmb Whiteface Summit
Evaluating Parametrizations using CEOP
 Evaluating Parametrizations using CEOP Paul Earnshaw and Sean Milton Met Office, UK Crown copyright 2005 Page 1 Overview Production and use of CEOP data Results SGP Seasonal & Diurnal cycles Other extratopical
Evaluating Parametrizations using CEOP Paul Earnshaw and Sean Milton Met Office, UK Crown copyright 2005 Page 1 Overview Production and use of CEOP data Results SGP Seasonal & Diurnal cycles Other extratopical
1.5 HIGH-RESOLUTION LAND DATA ASSIMILATION IN THE NCAR/ATEC 1.5 REAL-TIME FDDA AND FORECASTING SYSTEM
 1.5 HIGH-RESOLUTION LAND DATA ASSIMILATION IN THE NCAR/ATEC 1.5 REAL-TIME FDDA AND FORECASTING SYSTEM Andrea N. Hahmann, Yubao Liu, Fei Chen, Kevin W. Manning, Thomas T. Warner, and Laurie Carlson Research
1.5 HIGH-RESOLUTION LAND DATA ASSIMILATION IN THE NCAR/ATEC 1.5 REAL-TIME FDDA AND FORECASTING SYSTEM Andrea N. Hahmann, Yubao Liu, Fei Chen, Kevin W. Manning, Thomas T. Warner, and Laurie Carlson Research
Direct assimilation of all-sky microwave radiances at ECMWF
 Direct assimilation of all-sky microwave radiances at ECMWF Peter Bauer, Alan Geer, Philippe Lopez, Deborah Salmond European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Reading, Berkshire, UK Slide 1 17
Direct assimilation of all-sky microwave radiances at ECMWF Peter Bauer, Alan Geer, Philippe Lopez, Deborah Salmond European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Reading, Berkshire, UK Slide 1 17
Representation of the stratosphere in ECMWF operations and ERA-40
 Representation of the stratosphere in ECMWF operations and ERA-40 History Time series of forecast verification statistics Wind increments, PV and parametrized gravity-wave drag Forecast accuracy: The Antarctic
Representation of the stratosphere in ECMWF operations and ERA-40 History Time series of forecast verification statistics Wind increments, PV and parametrized gravity-wave drag Forecast accuracy: The Antarctic
Convection-Resolving NWP with WRF. Section coordinator Ming Xue University of Oklahoma
 Convection-Resolving NWP with WRF Section coordinator Ming Xue University of Oklahoma Convection-resolving NWP Is NWP that explicitly treats moist convective systems ranging from organized MCSs to individual
Convection-Resolving NWP with WRF Section coordinator Ming Xue University of Oklahoma Convection-resolving NWP Is NWP that explicitly treats moist convective systems ranging from organized MCSs to individual
Aviation Weather Hazards Nowcasting Based on Remote Temperature Sensing Data
 Aviation Weather Hazards Nowcasting Based on Remote Temperature Sensing Data Mikhail Kanevsky*, Evgeny Miller**, Nikolay Baranov*** *International Aeronavigation Systems, kanevsky@ians.aero, **RPO ATTEX,
Aviation Weather Hazards Nowcasting Based on Remote Temperature Sensing Data Mikhail Kanevsky*, Evgeny Miller**, Nikolay Baranov*** *International Aeronavigation Systems, kanevsky@ians.aero, **RPO ATTEX,
J8.2 INITIAL CONDITION SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF A MESOSCALE FORECAST USING VERY LARGE ENSEMBLES. University of Oklahoma Norman, Oklahoma 73019
 J8.2 INITIAL CONDITION SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF A MESOSCALE FORECAST USING VERY LARGE ENSEMBLES William J. Martin 1, * and Ming Xue 1,2 1 Center for Analysis and Prediction of Storms and 2 School of Meteorology
J8.2 INITIAL CONDITION SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF A MESOSCALE FORECAST USING VERY LARGE ENSEMBLES William J. Martin 1, * and Ming Xue 1,2 1 Center for Analysis and Prediction of Storms and 2 School of Meteorology
Operational Forecasting With Very-High-Resolution Models. Tom Warner
 Operational Forecasting With Very-High-Resolution Models Tom Warner Background Since 1997 NCAR Has Been Developing Operational Mesoscale Forecasting Systems for General Meteorological Support at Army Test
Operational Forecasting With Very-High-Resolution Models Tom Warner Background Since 1997 NCAR Has Been Developing Operational Mesoscale Forecasting Systems for General Meteorological Support at Army Test
AOSC201: Weather and Climate Lab
 AOSC201: Weather and Climate Lab Week 8: Forecasting - Analysis Section 107/108 Instructor: Agniv Sengupta q Lab #7 of Lab Manual (pages 41-49) q 50 points in total q INDIVIDUAL Work for the entire lab
AOSC201: Weather and Climate Lab Week 8: Forecasting - Analysis Section 107/108 Instructor: Agniv Sengupta q Lab #7 of Lab Manual (pages 41-49) q 50 points in total q INDIVIDUAL Work for the entire lab
ASSESMENT OF THE SEVERE WEATHER ENVIROMENT IN NORTH AMERICA SIMULATED BY A GLOBAL CLIMATE MODEL
 JP2.9 ASSESMENT OF THE SEVERE WEATHER ENVIROMENT IN NORTH AMERICA SIMULATED BY A GLOBAL CLIMATE MODEL Patrick T. Marsh* and David J. Karoly School of Meteorology, University of Oklahoma, Norman OK and
JP2.9 ASSESMENT OF THE SEVERE WEATHER ENVIROMENT IN NORTH AMERICA SIMULATED BY A GLOBAL CLIMATE MODEL Patrick T. Marsh* and David J. Karoly School of Meteorology, University of Oklahoma, Norman OK and
 This article was originally published in a journal published by Elsevier, and the attached copy is provided by Elsevier for the author s benefit and for the benefit of the author s institution, for non-commercial
This article was originally published in a journal published by Elsevier, and the attached copy is provided by Elsevier for the author s benefit and for the benefit of the author s institution, for non-commercial
Thanksgiving Snow and Arctic Front 25 November 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 16801
 Thanksgiving Snow and Arctic Front 25 November 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 16801 1. INTRODUCTION An approaching arctic front brought light snow to most of western
Thanksgiving Snow and Arctic Front 25 November 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 16801 1. INTRODUCTION An approaching arctic front brought light snow to most of western
