Nonstationarities of regional climate model biases in European seasonal mean temperature and precipitation sums
|
|
|
- Milton Lamb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, di: /2012gl051210, 2012 Nnstatinarities f reginal climate mdel biases in Eurpean seasnal mean temperature and precipitatin sums D. Maraun 1 Received 6 February 2012; revised 2 March 2012; accepted 2 March 2012; published 28 March [1] Bias crrecting climate mdels implicitly assumes statinarity f the crrectin functin. This assumptin is assessed fr reginal climate mdels in a pseud reality fr seasnal mean temperature and precipitatin sums. An ensemble f reginal climate mdels fr Eurpe is used, all driven with the same transient bundary cnditins. Althugh this mdel-dependent apprach des nt assess all pssible bias nn-statinarities, cnclusins can be drawn fr the real wrld. Generally, biases are relatively stable, and bias crrectin n average imprves climate scenaris. Fr winter temperature, bias changes ccur in the Alps and ice cvered ceans caused by a biased frcing sensitivity f surface albed; fr summer temperature, bias changes ccur due t a biased sensitivity f clud cver and sil misture. Precipitatin crrectin is generally successful, but affected by internal variability in arid climates. As mdel sensitivities vary cnsiderably in sme regins, multi mdel ensembles are needed even after bias crrectin. Citatin: Maraun, D. (2012), Nnstatinarities f reginal climate mdel biases in Eurpean seasnal mean temperature and precipitatin sums, Gephys. Res. Lett., 39,, di: /2012gl Intrductin [2] Reginal climate mdels (RCMs) prvide added value t glbal climate simulatins [Feser et al., 2011], but the actually simulated fields f climate variables are ften cnsiderably biased cmpared t gridded bservatinal data [Christensen et al., 2008]. End users f RCM simulatins therefre ften apply bias crrectin methds. Mst f these methds derive a crrectin functin that maps the empirical distributin f a simulated present day climate time series t the crrespnding bserved distributin. This functin is then applied t crrect a future climate simulatin (fr a review, see Maraun et al. [2010]). Appraches range frm simple additive crrectins f the mean r variance [e.g., Déqué, 2007; Lenderink et al., 2007], scaling f precipitatin [Widmann and Brethertn, 2000] t mre advanced quantile mapping methds [e.g., Piani et al., 2010;Li et al., 2010]. [3] A crucial assumptin f bias crrectin is statinarity f the bias, which is calculated fr present climate, under future climate change. This assumptin is, hwever, questinable [Christensen et al., 2008]. Just as mdel biases themselves are caused by an imperfect mdel representatin f the atmspheric physics, als the lcal mdelled respnse t external frcing, i.e., the lcal climate sensitivity is biased in general. Crrespnding bias changes might be called sensitivity related 1 GEOMAR, Helmhltz Centre fr Ocean Research Kiel, Kiel, Germany. Cpyright 2012 by the American Gephysical Unin /12/2012GL bias changes (SBC). In additin t such real bias changes, apparent changes might ccur. First, biases are estimated frm finite time series and afflicted with sampling uncertainty. Crrespnding bias changes merely caused by internal variability may be called variability related apparent bias changes (VABC). Secnd, mst bias crrectin methds are applied t uncnditinal climatlgical distributins and disregard that the derived verall bias may actually be a mixture f different underlying biases depending n weather types. Fr instance, biases fr cnvective and stratifrm precipitatin might be different. If the relative ccurrence f such weather types changes, als the verall bias might change. Such bias changes might be called mixture related apparent bias changes (MABC). [4] It is difficult t assess nn-statinarities f biases because the perid with a dense bservatinal netwrk shws a relatively small climate change signal and is hardly lng enugh fr rbust calibratin and validatin. Therefre, I use a pseud reality [Frías et al., 2006; Vrac et al., 2007; van der Linden and Mitchell, 2009] t assess the extent and type f RCM bias changes under future climate change. Fr the strngest changes, I als analyse ptential mechanisms causing the identified changes. T islate RCM biases I emply a perfect bundary setting, biases frm glbal climate mdels are explicitly nt cnsidered. As an example I investigate the crrectin f winter and summer mean temperature and precipitatin sums ver Eurpe. 2. Cncept and Data [5] As pseud reality, I chse ne glbal climate mdel / RCM cmbinatin, where the glbal climate mdel represents pseud bserved large scale bundary cnditins fr present and future climate, the reference RCM itself represents reginal pseud bservatins. An ensemble f ther RCMs is treated as mdels t be crrected. Using an ensemble and emplying each f the RCMs in turns as pseud reality reduces the RCM dependence f the results. The RCMs are frced with the same pseud bserved bundary cnditins as the reference RCM, i.e., the same glbal climate mdel. Fr present day climate simulatins, this crrespnds t a perfect bundary cnditin setting, i.e., RCMs driven with reanalysis data. Under the assumptin that GCM and RCM biases d nt interact, this setting islates RCM biases. Frcing with equal bundary cnditins als synchrnises variability n scales beynd a few days and allws fr relatively shrtcalibratin perids. I select the subset f RCMs frm the ENSEMBLES prject [van der Linden and Mitchell, 2009]whicharealldriven by the same bundary cnditins f ECHAM5 run three fr the SRES A1B scenari and perate n the same grid: HIRHAM5 (Danish Meterlgical Institute), RACMO2 (Ryal Dutch Meterlgical Institute), REMO (Max Planck 1f5
2 Institute fr Meterlgy) and RCA (Swedish Meterlgical and Hydrlgical Institute). The RCMs have a hrizntal reslutin f 25 km and cver the Eurpean dmain f the ENSEMBLES prject. As calibratin perid, I chse , as future perid [6] I cnsider seasnal mean temperature and precipitatin sums, separately fr each seasn. Pseud temperature bservatins f seasn i are dented as T,i, mdel simulatins as T m,i, precipitatin bservatins as P,i and mdel simulatins as P m,i ; temperature means ver the calibratin and scenari perid are dented as T cal and P fut and T fut, precipitatin sums as P cal, respectively. The temperature and precipitatin biases ver the calibratin perid are defined as BT cal ¼ T cal m BP cal P ¼ cal m P cal T cal ; Fr precipitatin relative changes are cnsidered, i.e., a value f 1 indicates n bias. Biases fr the future, BT fut and BP fut,are defined accrdingly. Mdel utput crrected relative t the calibratin perid is calculated as T crr m,i = T m,i BT cal and P crr m;i ¼ P m;i with crrespnding tempral means and sums. BP cal The change in temperature and precipitatin bias frm calibratin t future perid is given as DBT ¼ BT fut BT cal ; DBP ¼ BPfut BP cal ; The change in bias is equivalent t the future bias remaining after a crrectin based n the calibratin perid. When the uncrrected future bias is larger than the present day bias, bias crrectin imprves the results. Even when the uncrrected future temperature bias is smaller than the calibratin bias, the abslute remaining bias might still be smaller than withut crrectin, althugh the remaining bias changes sign. Only when the uncrrected future bias reduces t less than half the calibratin bias, bias crrectin deterirates the riginal future simulatin. A similar argument hlds in case f precipitatin, but psitive (negative) values have t be replaced by values larger (smaller) ne. T highlight the actual reductin in bias, I cnsider the imprvement in abslute bias as the difference (rati fr precipitatin) between the abslute future bias withut crrectin and with crrectin: IBT ¼ BT fut jdbtj; IBP ¼ RBPfut RDBP ð Þ : ð3þ Here R(x) isx fr x > = 1 and 1/x fr 0 < x < 1. The functin R(x) applied t ratis is the equivalent f taking abslute values f differences. In the fllwing, I will refer t bth peratins as taking abslute values. 3. Results [7] Of the fur selected RCMs, all six permutatins f ne mdel being the pseud bservatin and the ther three simulatins are cnsidered. As pseud bservatins and mdels are : ð1þ ð2þ interchangeable, nly abslute biases and abslute changes in biases are cnsidered (the abslute values f definitins (1) and (2)). [8] Clumns ne and tw f Figure 1 present the bias fr the calibratin perid (equatin (1)) and the remaining bias in the future (equatin (2)), averaged ver all permutatins. In general, the temperature bias (Figure 1, tp tw rws) as well as the precipitatin bias (Figure 1, bttm tw rws) are n average strngly reduced by the bias crrectin. The change in temperature bias is lwest ver the pen Atlantic and the Mediterranean (Figures 1b and 1f), where temperature is cntrlled by the prescribed SST bundary cnditins, and highest in the Barents Sea, White Sea and the Gulf f Bttnia during winter (Figure 1b) and spring (nt shwn). Over land, the change in winter temperature bias is strngest in the Alps (Figure 1b). In general a strnger temperature bias remains in summer, in particular in suthwestern Eurpe (Figure 1f). The change in precipitatin bias is in general lw. It is highest during summer arund the Mediterranean (Figure 1n). [9] The changes in bias are reflected in patterns f imprvement due t the bias crrectin (equatin (3)). Clumns three and fur f Figure 1 shw the mean (Figures 1c, 1g, 1k, and 1) and wrst case imprvement (Figures 1d, 1h, 1l, and 1p) after a bias crrectin fr the future based n the calibratin perid bias. The tp tw rws shw winter and summer temperature, the bttm tw rws the crrespnding results fr precipitatin. On average the temperature bias crrectin imprves the future simulatin despite changes in bias. Yet ver central Eurpe the imprvement is negligible and fr sme regins even deterirates the simulatin. The strngest deteriratin ccurs fr the Barents Sea, White Sea and the Gulf f Bttnia during winter (Figure 1c) and spring (nt shwn). The wrst case panels shw the lwest imprvement f all permutatins fr each grid bx. Fr winter (Figure 1d), biases in the Alps, the Barents Sea, White Sea and Gulf f Bttnia, and fr summer (Figure 1h), biases ver central Eurpe, Nrthern Italy and the Balkans stand ut. Only ver sme regins, temperature bias crrectin imprves the simulatins even in the wrst case. Precipitatin bias crrectin n average leads t an imprvement ver mst regins (Figures 1k and 1). Even fr the wrst case the deteriratin is weak, apart frm the Mediterranean and Nrthern Africa during summer (Figure 1p). 4. Discussin [10] T further investigate the causes leading t the described bias changes, I cnsider future changes in ptentially relevant climatic variables. Figure 2 shws the standard deviatin f changes between and fr winter surface albed (Figure 2a), summer clud cver (Figure 2b), summer sil misture (Figure 2c) and summer sea level pressure (Figure 2d). A strng mdel spread in winter albed can be bserved in the Alps (Figure 2a), whereas the spread in winter snw cver changes is negligible (nt shwn). This finding indicates a spread in temperature respnse due t different changes in the perennial snw fractin. Furthermre a strng mdel spread in winter albed is apparent in the Gulf f Bttnia, White Sea and Barents Sea (Figure 2a), which exceeds changes in sea ice cver (nt shwn). In these regins, the spread in temperature respnse might thus be explained by different sea ice/albed parameterisatins. Changes in clud 2f5
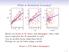
3 Figure 1. Biases and bias crrectin. (a d) DJF temperature [K], (e h) JJA temperature [K], (i l) DJF precipitatin [%], and (m p) JJA precipitatin [%]. Shwn are (left t right) bias, mean acrss all permutatins; change in bias vs ; mean imprvement acrss all permutatins; and minimum imprvement acrss all permutatins. cver exhibit the mst apparent spread in summer, in particular in central Eurpe (Figure 2b). The crrespnding respnses in radiative surface heating may partly explain changes in temperature biases. These might have been amplified in sme regins by sil misture feedbacks (Figure 2c). Figure 2d shws the spread in summer sea level pressure changes. The pattern is likely a respnse t the spread in diabatic heating f the atmsphere (Figure 1e). Yet the initial presence f such a respnse pattern causes a meridinal wind anmaly that might als cntribute t the bias change patterns. T cnclude, the described changes in temperature biases can be related t different respnses f the climate system t the prescribed greenhuse frcing and thus cnstitute SBC. [11] Figure 3 shws reginal mean changes in precipitatin biases fr precipitatin averaged t different space scales. Results fr central Eurpe (48N, 5E t 53N, 17E, the regins are aligned parallel t the rtated grid) are depicted in dark blue (circles), fr the Iberian peninsula (36N, 9W t 44N, 0E) in light blue (triangles) and fr the western Maghreb (30N, 5W t 35N, 10E) in range (crsses). Slid lines indicate winter changes, dashed lines summer changes. The fact that averaging precipitatin, in particular fr summer arid regins, strngly reduces the bias, indicates a key rle f VABC: where precipitatin ccurs as rather rare and lcalised cnvective events, internal variability may dminate the estimated seasnal biases n a lcal scale even when averaging ver 30 years. 5. Cnclusins [12] Nn-statinarities in RCM biases f Eurpean seasnal mean temperature and ttal precipitatin, and their ptential causes have been assessed in a pseud reality. T this end a multi RCM ensemble has been emplyed, driven by the same glbal climate mdel simulatin t islate RCM biases. Each RCM has in turns been taken as pseud reality, the thers as mdels t be crrected. I investigated the change in bias between a present day calibratin perid and future simulatins, as well as the imprvement f the future simulatins by a bias crrectin based n the calibratin perid. [13] Biases between the mdels are in general relatively stable, such that bias crrectin n average cnsiderably imprves future scenaris fr many regins and all seasns (results fr spring and autumn nt shwn). Biases, hwever, remain and fr sme regins and seasns bias crrectin may even deterirate future simulatins. Temperature bias crrectin n average imprves future simulatins, but sme SBC 3f5
4 Figure 2. Standard deviatin f changes in different variables, vs , acrss all permutatins. (a) DJF surface albed, (b) JJA fractinal clud cver, (c) JJA sil misture (relative t the mean), and (d) JJA sea level pressure [hpa]. have been identified. During winter, fr the Alps as well as the Barents Sea, White Sea and Gulf f Bttnia large biases remain; in these regins bias crrectin may even increase the future bias. These changes are likely linked t changes in surface albed, with biased respnses f perennial snw cver in the Alps and sea ice albed in the Nrthern seas (the latter is als relevant in spring). During summer, in Suthern France and the Iberian Peninsula large biases remain, and in Central Eurpe bias crrectin may even deterirate future simulatins. These changes can be explained by biased respnses f clud cver and sil misture. Precipitatin bias crrectin appears t be successful fr mst f Eurpe, but is affected by VABC in arid regins. Here, especially during the dry seasn (summer, and in the Maghreb als spring) precipitatin events are s rare that bias estimates even f seasnal sums are dminated by internal variability. Fr these regins it is advisable nt t derive precipitatin biases n a grid bx scale, but rather t cnsider larger regins r smthly varying bias mdels. As biases have nt been cnditned n weather types, this study culd nt identify MABCs. The fact that the strngest bias changes have been identified as SBC and VABC, hwever, indicates that in practice MABCs play nly a minr rle. [14] Althugh the results have been btained in a pseud reality, they als demnstrate the likely prblems ne might face using bias crrectin in real wrld applicatins; where different RCMs disagree, at least sme f them will als differ frm reality. As an agreement amng RCMs des nt prve an agreement with reality, a pseud reality apprach des nt unambiguusly identify where bias crrectin will be successful. Nevertheless, the results indicate ptential prblems as well as regins less prne t nn-statinary biases. As extreme events are gverned by different mechanisms than the mean climate, als biases fr high quantiles tend t be different frm biases in the mean [Christensen et al., 2008].Therefre,this analysis shuld be carried ut separately fr extreme events. The fact that the minimum imprvement shws strng nnstatinarities in biases between at least sme mdels highlights that even after bias crrectin multi mdel ensembles are still required t assess the range f uncertainties in lcal climate sensitivities. Figure 3. Precipitatin bias change as functin f spatial scale, average acrss all mdel permutatins. Orange crsses: nrthern Africa, light blue triangles: Iberian Peninsula, dark blue circles: central Eurpe. Slid lines: DJF, dashed lines: JJA. 4f5
5 [15] Acknwledgments. IthankP.Naveau,A.Schindler,M.Widmann, W. Park and J. Christensen fr helpful discussins. The analysis has been carried ut with R using the ncdf package. The editr thanks the three annymus reviewers. [16] The Editr thanks the three annymus reviewers fr their assistance in evaluating this paper. References Christensen, J., F. Bberg, O. Christensen, and P. Lucas-Picher (2008), On the need fr bias crrectin f reginal climate change prjectins f temperature and precipitatin, Gephys. Res. Lett., 35, L20709, di: /2008gl Déqué, M. (2007), Frequency f precipitatin and temperature extremes ver France in an anthrpgenic scenari: Mdel results and statistical crrectin accrding t bserved values, Glbal Planet. Change, 57, Feser, F., B. Rckel, H. vn Strch, J. Winterfeldt, and M. Zahn (2011), Reginal climate mdels add value t glbal mdel data A review and selected examples, Bull. Am. Meterl. Sc., 92(9), Frías, M., E. Zrita, J. Fernández, and C. Rdríguez-Puebla (2006), Testing statistical dwnscaling methds in simulated climates, Gephys. Res. Lett., 33, L19807, di: /2006gl Lenderink, G., A. Buishand, and W. van Deursen (2007), Estimates f future discharges f the river Rhine using tw scenari methdlgies: direct versus delta apprach, Hydrl. Earth Syst. Sci., 11(3), Li, H., J. Sheffield, and E. F. Wd (2010), Bias crrectin f mnthly precipitatin and temperature fields frm Intergvernmental Panel n Climate Change AR4 mdels using equidistant quantile matching, J. Gephys. Res., 115, D10101, di: /2009jd Maraun, D., et al. (2010), Precipitatin dwnscaling under climate change: Recent develpments t bridge the gap between dynamical mdels and the end user, Rev. Gephys., 48, RG3003, di: /2009rg Piani, C., J. O. Haerter, and E. Cppla (2010), Statistical bias crrectin fr daily precipitatin in reginal climate mdels ver Eurpe, Ther. Appl. Climatl., 99(1 2), van der Linden, P., and J. F. B. Mitchell (2009), ENSEMBLES: Climate change and its impacts: Summary f research and results frm the ENSEMBLES prject, technical reprt, Hadley Cent., Met Off., Exeter, U. K. Vrac, M., M. L. Stein, K. Hayhe, and X. Z. Liang (2007), A general methd fr validating statistical dwnscaling methds under future climate change, Gephys. Res. Lett., 34, L18701, di: /2007gl Widmann, M., and C. S. Brethertn (2000), Validatin f messcale precipitatin in the NCEP reanalysis using a new gridcell dataset fr the nrthwestern United States, J. Clim., 13(11), D. Maraun, GEOMAR, Helmhltz Centre fr Ocean Research Kiel, Düsternbrker Weg 20, D Kiel, Germany. (dmaraun@gemar.de) 5f5
Better definition of the objective, novelty and relevance of this study improving the structure, content and length of the publication accordingly:
 Answers t REVIEW2 Interactive cmment n An imprved perspective in the representatin f sil misture: ptential added value f SMOS disaggregated 1km reslutin prduct by Samir Khdayar et al. Answers t Reviewer
Answers t REVIEW2 Interactive cmment n An imprved perspective in the representatin f sil misture: ptential added value f SMOS disaggregated 1km reslutin prduct by Samir Khdayar et al. Answers t Reviewer
C.K. Omondi, T.H.M. Rientjes, B.H.P. Maathuis, W. Gumindoga. Faculty ITC, University of Twente, The Netherlands IAHS 2017 SCIENTIFIC ASSEMBLY
 1 Assessment f bias crrected satellite rainfall prducts fr streamflw simulatin: A TOPMODEL applicatin at the headwater catchment f the Zambezi Basin C.K. Omndi, T.H.M. Rientjes, B.H.P. Maathuis, W. Gumindga
1 Assessment f bias crrected satellite rainfall prducts fr streamflw simulatin: A TOPMODEL applicatin at the headwater catchment f the Zambezi Basin C.K. Omndi, T.H.M. Rientjes, B.H.P. Maathuis, W. Gumindga
Statistics, Numerical Models and Ensembles
 Statistics, Numerical Mdels and Ensembles Duglas Nychka, Reinhard Furrer,, Dan Cley Claudia Tebaldi, Linda Mearns, Jerry Meehl and Richard Smith (UNC). Spatial predictin and data assimilatin Precipitatin
Statistics, Numerical Mdels and Ensembles Duglas Nychka, Reinhard Furrer,, Dan Cley Claudia Tebaldi, Linda Mearns, Jerry Meehl and Richard Smith (UNC). Spatial predictin and data assimilatin Precipitatin
Determining the Accuracy of Modal Parameter Estimation Methods
 Determining the Accuracy f Mdal Parameter Estimatin Methds by Michael Lee Ph.D., P.E. & Mar Richardsn Ph.D. Structural Measurement Systems Milpitas, CA Abstract The mst cmmn type f mdal testing system
Determining the Accuracy f Mdal Parameter Estimatin Methds by Michael Lee Ph.D., P.E. & Mar Richardsn Ph.D. Structural Measurement Systems Milpitas, CA Abstract The mst cmmn type f mdal testing system
APPLICATION OF THE BRATSETH SCHEME FOR HIGH LATITUDE INTERMITTENT DATA ASSIMILATION USING THE PSU/NCAR MM5 MESOSCALE MODEL
 JP2.11 APPLICATION OF THE BRATSETH SCHEME FOR HIGH LATITUDE INTERMITTENT DATA ASSIMILATION USING THE PSU/NCAR MM5 MESOSCALE MODEL Xingang Fan * and Jeffrey S. Tilley University f Alaska Fairbanks, Fairbanks,
JP2.11 APPLICATION OF THE BRATSETH SCHEME FOR HIGH LATITUDE INTERMITTENT DATA ASSIMILATION USING THE PSU/NCAR MM5 MESOSCALE MODEL Xingang Fan * and Jeffrey S. Tilley University f Alaska Fairbanks, Fairbanks,
THE PARTITION OF ENERGY INTO WAVES AND CURRENTS
 THE PARTITION OF ENERGY INTO WAVES AND CURRENTS W. Perrie, C. Tang, Y. Hu and B.M. DeTracy Fisheries & Oceans Canada, Bedfrd Institute f Oceangraphy, Dartmuth, Nva Sctia, Canada 1. INTRODUCTION Ocean mdels
THE PARTITION OF ENERGY INTO WAVES AND CURRENTS W. Perrie, C. Tang, Y. Hu and B.M. DeTracy Fisheries & Oceans Canada, Bedfrd Institute f Oceangraphy, Dartmuth, Nva Sctia, Canada 1. INTRODUCTION Ocean mdels
Operational Use of the Model Crocus
 Operatinal Use f the Mdel Crcus by French Avalanche Frecast Services E.Brun Meterlgie Natinale Centre d'etudes de la Neige BP 44 Dmaine Universitaire 3842 St-Martin d 'eres France ntrductin Since 1971
Operatinal Use f the Mdel Crcus by French Avalanche Frecast Services E.Brun Meterlgie Natinale Centre d'etudes de la Neige BP 44 Dmaine Universitaire 3842 St-Martin d 'eres France ntrductin Since 1971
5.4 Measurement Sampling Rates for Daily Maximum and Minimum Temperatures
 5.4 Measurement Sampling Rates fr Daily Maximum and Minimum Temperatures 1 1 2 X. Lin, K. G. Hubbard, and C. B. Baker University f Nebraska, Lincln, Nebraska 2 Natinal Climatic Data Center 1 1. INTRODUCTION
5.4 Measurement Sampling Rates fr Daily Maximum and Minimum Temperatures 1 1 2 X. Lin, K. G. Hubbard, and C. B. Baker University f Nebraska, Lincln, Nebraska 2 Natinal Climatic Data Center 1 1. INTRODUCTION
, which yields. where z1. and z2
 The Gaussian r Nrmal PDF, Page 1 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin Authr: Jhn M Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revisin: 11 September 13 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin
The Gaussian r Nrmal PDF, Page 1 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin Authr: Jhn M Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revisin: 11 September 13 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin
1 Introduction. Jean-Philippe Boulanger Æ Fernando Martinez Enrique C. Segura
 Climate Dynamics (26) DOI 1.17/s382-6-134-8 Jean-Philippe Bulanger Æ Fernand Martinez Enrique C. Segura Prjectin f future climate change cnditins using IPCC simulatins, neural netwrks and Bayesian statistics.
Climate Dynamics (26) DOI 1.17/s382-6-134-8 Jean-Philippe Bulanger Æ Fernand Martinez Enrique C. Segura Prjectin f future climate change cnditins using IPCC simulatins, neural netwrks and Bayesian statistics.
Checking the resolved resonance region in EXFOR database
 Checking the reslved resnance regin in EXFOR database Gttfried Bertn Sciété de Calcul Mathématique (SCM) Oscar Cabells OECD/NEA Data Bank JEFF Meetings - Sessin JEFF Experiments Nvember 0-4, 017 Bulgne-Billancurt,
Checking the reslved resnance regin in EXFOR database Gttfried Bertn Sciété de Calcul Mathématique (SCM) Oscar Cabells OECD/NEA Data Bank JEFF Meetings - Sessin JEFF Experiments Nvember 0-4, 017 Bulgne-Billancurt,
ENSC Discrete Time Systems. Project Outline. Semester
 ENSC 49 - iscrete Time Systems Prject Outline Semester 006-1. Objectives The gal f the prject is t design a channel fading simulatr. Upn successful cmpletin f the prject, yu will reinfrce yur understanding
ENSC 49 - iscrete Time Systems Prject Outline Semester 006-1. Objectives The gal f the prject is t design a channel fading simulatr. Upn successful cmpletin f the prject, yu will reinfrce yur understanding
Aerodynamic Separability in Tip Speed Ratio and Separability in Wind Speed- a Comparison
 Jurnal f Physics: Cnference Series OPEN ACCESS Aerdynamic Separability in Tip Speed Rati and Separability in Wind Speed- a Cmparisn T cite this article: M L Gala Sants et al 14 J. Phys.: Cnf. Ser. 555
Jurnal f Physics: Cnference Series OPEN ACCESS Aerdynamic Separability in Tip Speed Rati and Separability in Wind Speed- a Cmparisn T cite this article: M L Gala Sants et al 14 J. Phys.: Cnf. Ser. 555
Application of ILIUM to the estimation of the T eff [Fe/H] pair from BP/RP
![Application of ILIUM to the estimation of the T eff [Fe/H] pair from BP/RP Application of ILIUM to the estimation of the T eff [Fe/H] pair from BP/RP](/thumbs/93/113896405.jpg) Applicatin f ILIUM t the estimatin f the T eff [Fe/H] pair frm BP/RP prepared by: apprved by: reference: issue: 1 revisin: 1 date: 2009-02-10 status: Issued Cryn A.L. Bailer-Jnes Max Planck Institute fr
Applicatin f ILIUM t the estimatin f the T eff [Fe/H] pair frm BP/RP prepared by: apprved by: reference: issue: 1 revisin: 1 date: 2009-02-10 status: Issued Cryn A.L. Bailer-Jnes Max Planck Institute fr
Formal Uncertainty Assessment in Aquarius Salinity Retrieval Algorithm
 Frmal Uncertainty Assessment in Aquarius Salinity Retrieval Algrithm T. Meissner Aquarius Cal/Val Meeting Santa Rsa March 31/April 1, 2015 Outline 1. Backgrund/Philsphy 2. Develping an Algrithm fr Assessing
Frmal Uncertainty Assessment in Aquarius Salinity Retrieval Algrithm T. Meissner Aquarius Cal/Val Meeting Santa Rsa March 31/April 1, 2015 Outline 1. Backgrund/Philsphy 2. Develping an Algrithm fr Assessing
CHAPTER 3 INEQUALITIES. Copyright -The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
 CHAPTER 3 INEQUALITIES Cpyright -The Institute f Chartered Accuntants f India INEQUALITIES LEARNING OBJECTIVES One f the widely used decisin making prblems, nwadays, is t decide n the ptimal mix f scarce
CHAPTER 3 INEQUALITIES Cpyright -The Institute f Chartered Accuntants f India INEQUALITIES LEARNING OBJECTIVES One f the widely used decisin making prblems, nwadays, is t decide n the ptimal mix f scarce
SNOW AND AVALANCHES FORECASTING OVER THE ANDES MOUNTAlNS. Jose A. Vergara* Departamento de Geoflsica, Universidad de Chile
 SNOW AND AVALANCHES FORECASTNG OVER THE ANDES MOUNTAlNS Jse A. Vergara* Departament de Geflsica, Universidad de Chile Rene len, Camins y Nieve, ANDNA-CODElCO, CHLE ABSTRACT: During the last three years
SNOW AND AVALANCHES FORECASTNG OVER THE ANDES MOUNTAlNS Jse A. Vergara* Departament de Geflsica, Universidad de Chile Rene len, Camins y Nieve, ANDNA-CODElCO, CHLE ABSTRACT: During the last three years
INTERNATIONAL BIRD STRIKE COMMITTEE IBSC27/WP X-3 Athens, May 2005 BIRD AVOIDANCE MODELS VS. REALTIME BIRDSTRIKE WARNING SYSTEMS A COMPARISON
 INTERNATIONAL BIRD STRIKE COMMITTEE IBSC27/WP X-3 Athens, 23-27 May 2005 BIRD AVOIDANCE MODELS VS. REALTIME BIRDSTRIKE WARNING SYSTEMS A COMPARISON Wilhelm Ruhe, Dipl.Met., M.Sc. Bundeswehr Ge Infrmatin
INTERNATIONAL BIRD STRIKE COMMITTEE IBSC27/WP X-3 Athens, 23-27 May 2005 BIRD AVOIDANCE MODELS VS. REALTIME BIRDSTRIKE WARNING SYSTEMS A COMPARISON Wilhelm Ruhe, Dipl.Met., M.Sc. Bundeswehr Ge Infrmatin
CAUSAL INFERENCE. Technical Track Session I. Phillippe Leite. The World Bank
 CAUSAL INFERENCE Technical Track Sessin I Phillippe Leite The Wrld Bank These slides were develped by Christel Vermeersch and mdified by Phillippe Leite fr the purpse f this wrkshp Plicy questins are causal
CAUSAL INFERENCE Technical Track Sessin I Phillippe Leite The Wrld Bank These slides were develped by Christel Vermeersch and mdified by Phillippe Leite fr the purpse f this wrkshp Plicy questins are causal
2. Precipitation Chemistry Data
 STIMATING TH ATMSPHRIC INT A WATRSH INPUT F PLLUTANTS PRRY J. SAMSN epartment f Atmspheric and ceanic Science, University f Michigan, Ann Arbr, All 4819-2143, U.S.A. (Received June 2, 1986; revised March
STIMATING TH ATMSPHRIC INT A WATRSH INPUT F PLLUTANTS PRRY J. SAMSN epartment f Atmspheric and ceanic Science, University f Michigan, Ann Arbr, All 4819-2143, U.S.A. (Received June 2, 1986; revised March
Fractal dimensions of convective clouds around Delhi
 , j Indian Jurnal f Radi & Space Physics Vl. 27, February 1998, pp.i-6 Fractal dimensins f cnvective cluds arund Delhi Kaushar AIi, R N Chatterjee, Prem Prakash & P C S Devara Indian Institute f Trpical
, j Indian Jurnal f Radi & Space Physics Vl. 27, February 1998, pp.i-6 Fractal dimensins f cnvective cluds arund Delhi Kaushar AIi, R N Chatterjee, Prem Prakash & P C S Devara Indian Institute f Trpical
Revision: August 19, E Main Suite D Pullman, WA (509) Voice and Fax
 .7.4: Direct frequency dmain circuit analysis Revisin: August 9, 00 5 E Main Suite D Pullman, WA 9963 (509) 334 6306 ice and Fax Overview n chapter.7., we determined the steadystate respnse f electrical
.7.4: Direct frequency dmain circuit analysis Revisin: August 9, 00 5 E Main Suite D Pullman, WA 9963 (509) 334 6306 ice and Fax Overview n chapter.7., we determined the steadystate respnse f electrical
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON DISCHARGE COEFFICIENT OF OUTFLOW OPENING FOR PREDICTING CROSS-VENTILATION FLOW RATE
 EXPERIMENTAL STUD ON DISCHARGE COEFFICIENT OF OUTFLOW OPENING FOR PREDICTING CROSS-VENTILATION FLOW RATE Tmnbu Gt, Masaaki Ohba, Takashi Kurabuchi 2, Tmyuki End 3, shihik Akamine 4, and Tshihir Nnaka 2
EXPERIMENTAL STUD ON DISCHARGE COEFFICIENT OF OUTFLOW OPENING FOR PREDICTING CROSS-VENTILATION FLOW RATE Tmnbu Gt, Masaaki Ohba, Takashi Kurabuchi 2, Tmyuki End 3, shihik Akamine 4, and Tshihir Nnaka 2
Chapter 3: Cluster Analysis
 Chapter 3: Cluster Analysis } 3.1 Basic Cncepts f Clustering 3.1.1 Cluster Analysis 3.1. Clustering Categries } 3. Partitining Methds 3..1 The principle 3.. K-Means Methd 3..3 K-Medids Methd 3..4 CLARA
Chapter 3: Cluster Analysis } 3.1 Basic Cncepts f Clustering 3.1.1 Cluster Analysis 3.1. Clustering Categries } 3. Partitining Methds 3..1 The principle 3.. K-Means Methd 3..3 K-Medids Methd 3..4 CLARA
Perfrmance f Sensitizing Rules n Shewhart Cntrl Charts with Autcrrelated Data Key Wrds: Autregressive, Mving Average, Runs Tests, Shewhart Cntrl Chart
 Perfrmance f Sensitizing Rules n Shewhart Cntrl Charts with Autcrrelated Data Sandy D. Balkin Dennis K. J. Lin y Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802 Sandy Balkin is a graduate student
Perfrmance f Sensitizing Rules n Shewhart Cntrl Charts with Autcrrelated Data Sandy D. Balkin Dennis K. J. Lin y Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802 Sandy Balkin is a graduate student
AND Introduction 14B.2 MECHANISMS OF 20
 14B.2 MECHANISMS OF 2 TH AND 21 ST CENTURY ASIAN MONSOON CHANGES IN CMIP5 MODELS AND OBSERVATIONS Xiaqing Li *, Mingfang Ting, and Cuihua Li Lamnt-Dherty Ear Observatry, Clumbia University, Palisades,
14B.2 MECHANISMS OF 2 TH AND 21 ST CENTURY ASIAN MONSOON CHANGES IN CMIP5 MODELS AND OBSERVATIONS Xiaqing Li *, Mingfang Ting, and Cuihua Li Lamnt-Dherty Ear Observatry, Clumbia University, Palisades,
Chapter 1 Notes Using Geography Skills
 Chapter 1 Ntes Using Gegraphy Skills Sectin 1: Thinking Like a Gegrapher Gegraphy is used t interpret the past, understand the present, and plan fr the future. Gegraphy is the study f the Earth. It is
Chapter 1 Ntes Using Gegraphy Skills Sectin 1: Thinking Like a Gegrapher Gegraphy is used t interpret the past, understand the present, and plan fr the future. Gegraphy is the study f the Earth. It is
Relationship Between Amplifier Settling Time and Pole-Zero Placements for Second-Order Systems *
 Relatinship Between Amplifier Settling Time and Ple-Zer Placements fr Secnd-Order Systems * Mark E. Schlarmann and Randall L. Geiger Iwa State University Electrical and Cmputer Engineering Department Ames,
Relatinship Between Amplifier Settling Time and Ple-Zer Placements fr Secnd-Order Systems * Mark E. Schlarmann and Randall L. Geiger Iwa State University Electrical and Cmputer Engineering Department Ames,
Math Foundations 20 Work Plan
 Math Fundatins 20 Wrk Plan Units / Tpics 20.8 Demnstrate understanding f systems f linear inequalities in tw variables. Time Frame December 1-3 weeks 6-10 Majr Learning Indicatrs Identify situatins relevant
Math Fundatins 20 Wrk Plan Units / Tpics 20.8 Demnstrate understanding f systems f linear inequalities in tw variables. Time Frame December 1-3 weeks 6-10 Majr Learning Indicatrs Identify situatins relevant
Energy Inputs and Outputs
 Energy Inputs and Outputs Sun Earth ultravilet visible infrared Bth Sun and Earth behave as blackbdies (absrb 100% incident radiatin; emit radiatin at all wavelengths in all directins) Earth receives energy
Energy Inputs and Outputs Sun Earth ultravilet visible infrared Bth Sun and Earth behave as blackbdies (absrb 100% incident radiatin; emit radiatin at all wavelengths in all directins) Earth receives energy
ANALYSIS OF MOISTURE TRANSPORTATION DURING A LOCAL HEAVY RAINFALL ON AUGUST IN TOKYO
 The Seventh Asia-Pacific Cnference n Wind Engineering, Nvember 8-, 9, Taipei, Taiwan ANALYSIS OF MOISTURE TRANSPORTATION DURING A LOCAL HEAVY RAINFALL ON AUGUST IN TOKYO ABSTRACT Tru Yamanaka and Ryz Oka
The Seventh Asia-Pacific Cnference n Wind Engineering, Nvember 8-, 9, Taipei, Taiwan ANALYSIS OF MOISTURE TRANSPORTATION DURING A LOCAL HEAVY RAINFALL ON AUGUST IN TOKYO ABSTRACT Tru Yamanaka and Ryz Oka
BOUNDED UNCERTAINTY AND CLIMATE CHANGE ECONOMICS. Christopher Costello, Andrew Solow, Michael Neubert, and Stephen Polasky
 BOUNDED UNCERTAINTY AND CLIMATE CHANGE ECONOMICS Christpher Cstell, Andrew Slw, Michael Neubert, and Stephen Plasky Intrductin The central questin in the ecnmic analysis f climate change plicy cncerns
BOUNDED UNCERTAINTY AND CLIMATE CHANGE ECONOMICS Christpher Cstell, Andrew Slw, Michael Neubert, and Stephen Plasky Intrductin The central questin in the ecnmic analysis f climate change plicy cncerns
Chapter Summary. Mathematical Induction Strong Induction Recursive Definitions Structural Induction Recursive Algorithms
 Chapter 5 1 Chapter Summary Mathematical Inductin Strng Inductin Recursive Definitins Structural Inductin Recursive Algrithms Sectin 5.1 3 Sectin Summary Mathematical Inductin Examples f Prf by Mathematical
Chapter 5 1 Chapter Summary Mathematical Inductin Strng Inductin Recursive Definitins Structural Inductin Recursive Algrithms Sectin 5.1 3 Sectin Summary Mathematical Inductin Examples f Prf by Mathematical
Part 3 Introduction to statistical classification techniques
 Part 3 Intrductin t statistical classificatin techniques Machine Learning, Part 3, March 07 Fabi Rli Preamble ØIn Part we have seen that if we knw: Psterir prbabilities P(ω i / ) Or the equivalent terms
Part 3 Intrductin t statistical classificatin techniques Machine Learning, Part 3, March 07 Fabi Rli Preamble ØIn Part we have seen that if we knw: Psterir prbabilities P(ω i / ) Or the equivalent terms
Least Squares Optimal Filtering with Multirate Observations
 Prc. 36th Asilmar Cnf. n Signals, Systems, and Cmputers, Pacific Grve, CA, Nvember 2002 Least Squares Optimal Filtering with Multirate Observatins Charles W. herrien and Anthny H. Hawes Department f Electrical
Prc. 36th Asilmar Cnf. n Signals, Systems, and Cmputers, Pacific Grve, CA, Nvember 2002 Least Squares Optimal Filtering with Multirate Observatins Charles W. herrien and Anthny H. Hawes Department f Electrical
Tree Structured Classifier
 Tree Structured Classifier Reference: Classificatin and Regressin Trees by L. Breiman, J. H. Friedman, R. A. Olshen, and C. J. Stne, Chapman & Hall, 98. A Medical Eample (CART): Predict high risk patients
Tree Structured Classifier Reference: Classificatin and Regressin Trees by L. Breiman, J. H. Friedman, R. A. Olshen, and C. J. Stne, Chapman & Hall, 98. A Medical Eample (CART): Predict high risk patients
Internal vs. external validity. External validity. This section is based on Stock and Watson s Chapter 9.
 Sectin 7 Mdel Assessment This sectin is based n Stck and Watsn s Chapter 9. Internal vs. external validity Internal validity refers t whether the analysis is valid fr the ppulatin and sample being studied.
Sectin 7 Mdel Assessment This sectin is based n Stck and Watsn s Chapter 9. Internal vs. external validity Internal validity refers t whether the analysis is valid fr the ppulatin and sample being studied.
Particle Size Distributions from SANS Data Using the Maximum Entropy Method. By J. A. POTTON, G. J. DANIELL AND B. D. RAINFORD
 3 J. Appl. Cryst. (1988). 21,3-8 Particle Size Distributins frm SANS Data Using the Maximum Entrpy Methd By J. A. PTTN, G. J. DANIELL AND B. D. RAINFRD Physics Department, The University, Suthamptn S9
3 J. Appl. Cryst. (1988). 21,3-8 Particle Size Distributins frm SANS Data Using the Maximum Entrpy Methd By J. A. PTTN, G. J. DANIELL AND B. D. RAINFRD Physics Department, The University, Suthamptn S9
Revisiting the Socrates Example
 Sectin 1.6 Sectin Summary Valid Arguments Inference Rules fr Prpsitinal Lgic Using Rules f Inference t Build Arguments Rules f Inference fr Quantified Statements Building Arguments fr Quantified Statements
Sectin 1.6 Sectin Summary Valid Arguments Inference Rules fr Prpsitinal Lgic Using Rules f Inference t Build Arguments Rules f Inference fr Quantified Statements Building Arguments fr Quantified Statements
A Few Basic Facts About Isothermal Mass Transfer in a Binary Mixture
 Few asic Facts but Isthermal Mass Transfer in a inary Miture David Keffer Department f Chemical Engineering University f Tennessee first begun: pril 22, 2004 last updated: January 13, 2006 dkeffer@utk.edu
Few asic Facts but Isthermal Mass Transfer in a inary Miture David Keffer Department f Chemical Engineering University f Tennessee first begun: pril 22, 2004 last updated: January 13, 2006 dkeffer@utk.edu
Journal of Molecular EvOlution by Springer-Verlag. 1979
 0022-28447900140057~ 01.60 J. Ml. Evl. 14, 57--64 (1979) Jurnal f Mlecular EvOlutin by Springer-Verlag. 1979 Slar Radiatin Incident n the Martian Surface W.R. Kuhn and S.K. Atreya Department f Atmspheric
0022-28447900140057~ 01.60 J. Ml. Evl. 14, 57--64 (1979) Jurnal f Mlecular EvOlutin by Springer-Verlag. 1979 Slar Radiatin Incident n the Martian Surface W.R. Kuhn and S.K. Atreya Department f Atmspheric
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL GaGa: a simple and flexible hierarchical model for microarray data analysis
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL GaGa: a simple and flexible hierarchical mdel fr micrarray data analysis David Rssell Department f Bistatistics M.D. Andersn Cancer Center, Hustn, TX 77030, USA rsselldavid@gmail.cm
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL GaGa: a simple and flexible hierarchical mdel fr micrarray data analysis David Rssell Department f Bistatistics M.D. Andersn Cancer Center, Hustn, TX 77030, USA rsselldavid@gmail.cm
Kinetic Model Completeness
 5.68J/10.652J Spring 2003 Lecture Ntes Tuesday April 15, 2003 Kinetic Mdel Cmpleteness We say a chemical kinetic mdel is cmplete fr a particular reactin cnditin when it cntains all the species and reactins
5.68J/10.652J Spring 2003 Lecture Ntes Tuesday April 15, 2003 Kinetic Mdel Cmpleteness We say a chemical kinetic mdel is cmplete fr a particular reactin cnditin when it cntains all the species and reactins
PRESENTATION OF MONITORING AND HIGH RESOLUTION HAIL FALL CHARACTERISATION SERVICE IN EUROPE "HAIL WARNING"
 PRESENTATION OF MONITORING AND HIGH RESOLUTION HAIL FALL CHARACTERISATION SERVICE IN EUROPE "HAIL WARNING" HAIL WARNING EUROPE SERVICE: methdlgy Stage 1 Identificatin f the areas affected by strm cells
PRESENTATION OF MONITORING AND HIGH RESOLUTION HAIL FALL CHARACTERISATION SERVICE IN EUROPE "HAIL WARNING" HAIL WARNING EUROPE SERVICE: methdlgy Stage 1 Identificatin f the areas affected by strm cells
Huaqing Cai*, Cathy Kessinger, Nancy Rehak and Daniel Megenhardt National Center for Atmospheric Research, P.O. Box 3000, Boulder, CO
 P2.15 INVESTIGATION INTO ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONS FOR STORM INITIATION OVER THE OCEAN USING SATELLITE DATA Huaqing Cai*, Cathy Kessinger, Nancy Rehak and Daniel Megenhardt Natinal Center fr Atmspheric
P2.15 INVESTIGATION INTO ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONS FOR STORM INITIATION OVER THE OCEAN USING SATELLITE DATA Huaqing Cai*, Cathy Kessinger, Nancy Rehak and Daniel Megenhardt Natinal Center fr Atmspheric
A Matrix Representation of Panel Data
 web Extensin 6 Appendix 6.A A Matrix Representatin f Panel Data Panel data mdels cme in tw brad varieties, distinct intercept DGPs and errr cmpnent DGPs. his appendix presents matrix algebra representatins
web Extensin 6 Appendix 6.A A Matrix Representatin f Panel Data Panel data mdels cme in tw brad varieties, distinct intercept DGPs and errr cmpnent DGPs. his appendix presents matrix algebra representatins
Building to Transformations on Coordinate Axis Grade 5: Geometry Graph points on the coordinate plane to solve real-world and mathematical problems.
 Building t Transfrmatins n Crdinate Axis Grade 5: Gemetry Graph pints n the crdinate plane t slve real-wrld and mathematical prblems. 5.G.1. Use a pair f perpendicular number lines, called axes, t define
Building t Transfrmatins n Crdinate Axis Grade 5: Gemetry Graph pints n the crdinate plane t slve real-wrld and mathematical prblems. 5.G.1. Use a pair f perpendicular number lines, called axes, t define
Distributions, spatial statistics and a Bayesian perspective
 Distributins, spatial statistics and a Bayesian perspective Dug Nychka Natinal Center fr Atmspheric Research Distributins and densities Cnditinal distributins and Bayes Thm Bivariate nrmal Spatial statistics
Distributins, spatial statistics and a Bayesian perspective Dug Nychka Natinal Center fr Atmspheric Research Distributins and densities Cnditinal distributins and Bayes Thm Bivariate nrmal Spatial statistics
3.6 Condition number and RGA
 g r qp q q q qp! the weight " #%$ s that mre emphasis is placed n utput &. We d this y increasing the andwidth requirement in utput channel & y a factr f (!( : *,+.-0/!1 &3254769:4;$=< >@?BAC D 6 E(F
g r qp q q q qp! the weight " #%$ s that mre emphasis is placed n utput &. We d this y increasing the andwidth requirement in utput channel & y a factr f (!( : *,+.-0/!1 &3254769:4;$=< >@?BAC D 6 E(F
Population Structure and Migration Patterns of Atlantic Cod (Gadus morhua) in West Greenland Waters Based on Tagging Experiments from 1946 to 1964
 NAFO Sci. Cun. Studies, : - Ppulatin Structure and Migratin Patterns f Atlantic Cd (Gadus mrhua) in West Greenland Waters Based n Tagging Experiments frm t Hlger Hvgard Greenland Fisheries Research Institute
NAFO Sci. Cun. Studies, : - Ppulatin Structure and Migratin Patterns f Atlantic Cd (Gadus mrhua) in West Greenland Waters Based n Tagging Experiments frm t Hlger Hvgard Greenland Fisheries Research Institute
Numerical Simulation of the Thermal Resposne Test Within the Comsol Multiphysics Environment
 Presented at the COMSOL Cnference 2008 Hannver University f Parma Department f Industrial Engineering Numerical Simulatin f the Thermal Respsne Test Within the Cmsl Multiphysics Envirnment Authr : C. Crradi,
Presented at the COMSOL Cnference 2008 Hannver University f Parma Department f Industrial Engineering Numerical Simulatin f the Thermal Respsne Test Within the Cmsl Multiphysics Envirnment Authr : C. Crradi,
3D KMC simulation on the precipitation in the annealed ternary alloy system
 3D KM simulatin n the precipitatin in the annealed ternary ally system Xuan Zhang, Mengqi Huang Abstract Kinetic Mnte arl methd is used t study the precipitatin phenmenn in binary and ternary ally system,
3D KM simulatin n the precipitatin in the annealed ternary ally system Xuan Zhang, Mengqi Huang Abstract Kinetic Mnte arl methd is used t study the precipitatin phenmenn in binary and ternary ally system,
We can see from the graph above that the intersection is, i.e., [ ).
 MTH 111 Cllege Algebra Lecture Ntes July 2, 2014 Functin Arithmetic: With nt t much difficulty, we ntice that inputs f functins are numbers, and utputs f functins are numbers. S whatever we can d with
MTH 111 Cllege Algebra Lecture Ntes July 2, 2014 Functin Arithmetic: With nt t much difficulty, we ntice that inputs f functins are numbers, and utputs f functins are numbers. S whatever we can d with
NAME TEMPERATURE AND HUMIDITY. I. Introduction
 NAME TEMPERATURE AND HUMIDITY I. Intrductin Temperature is the single mst imprtant factr in determining atmspheric cnditins because it greatly influences: 1. The amunt f water vapr in the air 2. The pssibility
NAME TEMPERATURE AND HUMIDITY I. Intrductin Temperature is the single mst imprtant factr in determining atmspheric cnditins because it greatly influences: 1. The amunt f water vapr in the air 2. The pssibility
What is Statistical Learning?
 What is Statistical Learning? Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 0 50 100 200 300 TV 0 10 20 30 40 50 Radi 0 20 40 60 80 100 Newspaper Shwn are Sales vs TV, Radi and Newspaper,
What is Statistical Learning? Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 0 50 100 200 300 TV 0 10 20 30 40 50 Radi 0 20 40 60 80 100 Newspaper Shwn are Sales vs TV, Radi and Newspaper,
Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Waterloo. Introduction
 Sectin 4: Sequential Circuits Majr Tpics Types f sequential circuits Flip-flps Analysis f clcked sequential circuits Mre and Mealy machines Design f clcked sequential circuits State transitin design methd
Sectin 4: Sequential Circuits Majr Tpics Types f sequential circuits Flip-flps Analysis f clcked sequential circuits Mre and Mealy machines Design f clcked sequential circuits State transitin design methd
A Polarimetric Survey of Radio Frequency Interference in C- and X-Bands in the Continental United States using WindSat Radiometry
 A Plarimetric Survey f Radi Frequency Interference in C- and X-Bands in the Cntinental United States using WindSat Radimetry Steven W. Ellingsn Octber, Cntents Intrductin WindSat Methdlgy Analysis f RFI
A Plarimetric Survey f Radi Frequency Interference in C- and X-Bands in the Cntinental United States using WindSat Radimetry Steven W. Ellingsn Octber, Cntents Intrductin WindSat Methdlgy Analysis f RFI
Main Menu. SEG Houston 2009 International Exposition and Annual Meeting. Summary
 CO elcity Measurements and Mdels r Temperatures dwn t -10 C and up t 00 C and Pressures up t 100 MPa Min Sun* and De-hua Han, Rck Physics Lab, University Hustn Micheal Batzle, Clrad Schl Mines Summary
CO elcity Measurements and Mdels r Temperatures dwn t -10 C and up t 00 C and Pressures up t 100 MPa Min Sun* and De-hua Han, Rck Physics Lab, University Hustn Micheal Batzle, Clrad Schl Mines Summary
Results of an intercomparison of models of snowmelt runoff
 Mdelling Snwmelt-Induced Prcesses (Prceedings f the Budapest Sympsium, July 1986). IAHS Publ. n. 155,1986. Results f an intercmparisn f mdels f snwmelt runff WRLD METERLGICAL RGANIZATIN CP N.5, 1211 Geneva
Mdelling Snwmelt-Induced Prcesses (Prceedings f the Budapest Sympsium, July 1986). IAHS Publ. n. 155,1986. Results f an intercmparisn f mdels f snwmelt runff WRLD METERLGICAL RGANIZATIN CP N.5, 1211 Geneva
Supporting information
 Electrnic Supplementary Material (ESI) fr Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics This jurnal is The wner Scieties 01 ydrgen perxide electrchemistry n platinum: twards understanding the xygen reductin reactin
Electrnic Supplementary Material (ESI) fr Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics This jurnal is The wner Scieties 01 ydrgen perxide electrchemistry n platinum: twards understanding the xygen reductin reactin
Pattern Recognition 2014 Support Vector Machines
 Pattern Recgnitin 2014 Supprt Vectr Machines Ad Feelders Universiteit Utrecht Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht ) Pattern Recgnitin 1 / 55 Overview 1 Separable Case 2 Kernel Functins 3 Allwing Errrs (Sft
Pattern Recgnitin 2014 Supprt Vectr Machines Ad Feelders Universiteit Utrecht Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht ) Pattern Recgnitin 1 / 55 Overview 1 Separable Case 2 Kernel Functins 3 Allwing Errrs (Sft
Identification and separation of Mount Pinatubo. surface temperature anomalies. Fanglin Yang and Michael E. Schlesinger
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 106, NO. D14, PAGES 14,757-14,770, JULY 27, 2001 Identificatin and separatin f Munt Pinatub and El Nifi-Suthern Oscillatin land surface temperature anmalies Fanglin
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 106, NO. D14, PAGES 14,757-14,770, JULY 27, 2001 Identificatin and separatin f Munt Pinatub and El Nifi-Suthern Oscillatin land surface temperature anmalies Fanglin
Document for ENES5 meeting
 HARMONISATION OF EXPOSURE SCENARIO SHORT TITLES Dcument fr ENES5 meeting Paper jintly prepared by ECHA Cefic DUCC ESCOM ES Shrt Titles Grup 13 Nvember 2013 OBJECTIVES FOR ENES5 The bjective f this dcument
HARMONISATION OF EXPOSURE SCENARIO SHORT TITLES Dcument fr ENES5 meeting Paper jintly prepared by ECHA Cefic DUCC ESCOM ES Shrt Titles Grup 13 Nvember 2013 OBJECTIVES FOR ENES5 The bjective f this dcument
AP Statistics Notes Unit Two: The Normal Distributions
 AP Statistics Ntes Unit Tw: The Nrmal Distributins Syllabus Objectives: 1.5 The student will summarize distributins f data measuring the psitin using quartiles, percentiles, and standardized scres (z-scres).
AP Statistics Ntes Unit Tw: The Nrmal Distributins Syllabus Objectives: 1.5 The student will summarize distributins f data measuring the psitin using quartiles, percentiles, and standardized scres (z-scres).
Study Group Report: Plate-fin Heat Exchangers: AEA Technology
 Study Grup Reprt: Plate-fin Heat Exchangers: AEA Technlgy The prblem under study cncerned the apparent discrepancy between a series f experiments using a plate fin heat exchanger and the classical thery
Study Grup Reprt: Plate-fin Heat Exchangers: AEA Technlgy The prblem under study cncerned the apparent discrepancy between a series f experiments using a plate fin heat exchanger and the classical thery
Evaluating enterprise support: state of the art and future challenges. Dirk Czarnitzki KU Leuven, Belgium, and ZEW Mannheim, Germany
 Evaluating enterprise supprt: state f the art and future challenges Dirk Czarnitzki KU Leuven, Belgium, and ZEW Mannheim, Germany Intrductin During the last decade, mircecnmetric ecnmetric cunterfactual
Evaluating enterprise supprt: state f the art and future challenges Dirk Czarnitzki KU Leuven, Belgium, and ZEW Mannheim, Germany Intrductin During the last decade, mircecnmetric ecnmetric cunterfactual
Classifying World Climates
 Student MET 102 Classifying Wrld Climates Varius methds f classifying climates have been f value in simplifying the descriptin and lcatin f the diverse climate types fund arund the wrld. These methds have
Student MET 102 Classifying Wrld Climates Varius methds f classifying climates have been f value in simplifying the descriptin and lcatin f the diverse climate types fund arund the wrld. These methds have
Resampling Methods. Chapter 5. Chapter 5 1 / 52
 Resampling Methds Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 / 52 1 51 Validatin set apprach 2 52 Crss validatin 3 53 Btstrap Chapter 5 2 / 52 Abut Resampling An imprtant statistical tl Pretending the data as ppulatin and
Resampling Methds Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 / 52 1 51 Validatin set apprach 2 52 Crss validatin 3 53 Btstrap Chapter 5 2 / 52 Abut Resampling An imprtant statistical tl Pretending the data as ppulatin and
Introductory Thoughts
 Flw Similarity By using the Buckingham pi therem, we have reduced the number f independent variables frm five t tw If we wish t run a series f wind-tunnel tests fr a given bdy at a given angle f attack,
Flw Similarity By using the Buckingham pi therem, we have reduced the number f independent variables frm five t tw If we wish t run a series f wind-tunnel tests fr a given bdy at a given angle f attack,
Advanced Heat and Mass Transfer by Amir Faghri, Yuwen Zhang, and John R. Howell
 6.5 Natural Cnvectin in Enclsures Enclsures are finite spaces bunded by walls and filled with fluid. Natural cnvectin in enclsures, als knwn as internal cnvectin, takes place in rms and buildings, furnaces,
6.5 Natural Cnvectin in Enclsures Enclsures are finite spaces bunded by walls and filled with fluid. Natural cnvectin in enclsures, als knwn as internal cnvectin, takes place in rms and buildings, furnaces,
Engineering Decision Methods
 GSOE9210 vicj@cse.unsw.edu.au www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~gs9210 Maximin and minimax regret 1 2 Indifference; equal preference 3 Graphing decisin prblems 4 Dminance The Maximin principle Maximin and minimax Regret
GSOE9210 vicj@cse.unsw.edu.au www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~gs9210 Maximin and minimax regret 1 2 Indifference; equal preference 3 Graphing decisin prblems 4 Dminance The Maximin principle Maximin and minimax Regret
Skill forecasting from different wind power ensemble prediction methods
 Skill frecasting frm different wind pwer ensemble predictin methds Pierre Pinsn 1, Henrik Aa. Nielsen 1, Henrik Madsen 1 and Gerge Karinitakis 2 1 Technical University f Denmark, Infrmatics and Mathematical
Skill frecasting frm different wind pwer ensemble predictin methds Pierre Pinsn 1, Henrik Aa. Nielsen 1, Henrik Madsen 1 and Gerge Karinitakis 2 1 Technical University f Denmark, Infrmatics and Mathematical
Bootstrap Method > # Purpose: understand how bootstrap method works > obs=c(11.96, 5.03, 67.40, 16.07, 31.50, 7.73, 11.10, 22.38) > n=length(obs) >
 Btstrap Methd > # Purpse: understand hw btstrap methd wrks > bs=c(11.96, 5.03, 67.40, 16.07, 31.50, 7.73, 11.10, 22.38) > n=length(bs) > mean(bs) [1] 21.64625 > # estimate f lambda > lambda = 1/mean(bs);
Btstrap Methd > # Purpse: understand hw btstrap methd wrks > bs=c(11.96, 5.03, 67.40, 16.07, 31.50, 7.73, 11.10, 22.38) > n=length(bs) > mean(bs) [1] 21.64625 > # estimate f lambda > lambda = 1/mean(bs);
Computational modeling techniques
 Cmputatinal mdeling techniques Lecture 4: Mdel checing fr ODE mdels In Petre Department f IT, Åb Aademi http://www.users.ab.fi/ipetre/cmpmd/ Cntent Stichimetric matrix Calculating the mass cnservatin relatins
Cmputatinal mdeling techniques Lecture 4: Mdel checing fr ODE mdels In Petre Department f IT, Åb Aademi http://www.users.ab.fi/ipetre/cmpmd/ Cntent Stichimetric matrix Calculating the mass cnservatin relatins
The Destabilization of Rossby Normal Modes by Meridional Baroclinic Shear
 The Destabilizatin f Rssby Nrmal Mdes by Meridinal Barclinic Shear by Jseph Pedlsky Wds Hle Oceangraphic Institutin Wds Hle, MA 0543 Abstract The Rssby nrmal mdes f a tw-layer fluid in a meridinal channel
The Destabilizatin f Rssby Nrmal Mdes by Meridinal Barclinic Shear by Jseph Pedlsky Wds Hle Oceangraphic Institutin Wds Hle, MA 0543 Abstract The Rssby nrmal mdes f a tw-layer fluid in a meridinal channel
making triangle (ie same reference angle) ). This is a standard form that will allow us all to have the X= y=
 Intrductin t Vectrs I 21 Intrductin t Vectrs I 22 I. Determine the hrizntal and vertical cmpnents f the resultant vectr by cunting n the grid. X= y= J. Draw a mangle with hrizntal and vertical cmpnents
Intrductin t Vectrs I 21 Intrductin t Vectrs I 22 I. Determine the hrizntal and vertical cmpnents f the resultant vectr by cunting n the grid. X= y= J. Draw a mangle with hrizntal and vertical cmpnents
Module 4: General Formulation of Electric Circuit Theory
 Mdule 4: General Frmulatin f Electric Circuit Thery 4. General Frmulatin f Electric Circuit Thery All electrmagnetic phenmena are described at a fundamental level by Maxwell's equatins and the assciated
Mdule 4: General Frmulatin f Electric Circuit Thery 4. General Frmulatin f Electric Circuit Thery All electrmagnetic phenmena are described at a fundamental level by Maxwell's equatins and the assciated
Modelling of Clock Behaviour. Don Percival. Applied Physics Laboratory University of Washington Seattle, Washington, USA
 Mdelling f Clck Behaviur Dn Percival Applied Physics Labratry University f Washingtn Seattle, Washingtn, USA verheads and paper fr talk available at http://faculty.washingtn.edu/dbp/talks.html 1 Overview
Mdelling f Clck Behaviur Dn Percival Applied Physics Labratry University f Washingtn Seattle, Washingtn, USA verheads and paper fr talk available at http://faculty.washingtn.edu/dbp/talks.html 1 Overview
ECEN 4872/5827 Lecture Notes
 ECEN 4872/5827 Lecture Ntes Lecture #5 Objectives fr lecture #5: 1. Analysis f precisin current reference 2. Appraches fr evaluating tlerances 3. Temperature Cefficients evaluatin technique 4. Fundamentals
ECEN 4872/5827 Lecture Ntes Lecture #5 Objectives fr lecture #5: 1. Analysis f precisin current reference 2. Appraches fr evaluating tlerances 3. Temperature Cefficients evaluatin technique 4. Fundamentals
NUROP CONGRESS PAPER CHINESE PINYIN TO CHINESE CHARACTER CONVERSION
 NUROP Chinese Pinyin T Chinese Character Cnversin NUROP CONGRESS PAPER CHINESE PINYIN TO CHINESE CHARACTER CONVERSION CHIA LI SHI 1 AND LUA KIM TENG 2 Schl f Cmputing, Natinal University f Singapre 3 Science
NUROP Chinese Pinyin T Chinese Character Cnversin NUROP CONGRESS PAPER CHINESE PINYIN TO CHINESE CHARACTER CONVERSION CHIA LI SHI 1 AND LUA KIM TENG 2 Schl f Cmputing, Natinal University f Singapre 3 Science
arxiv:hep-ph/ v1 2 Jun 1995
 WIS-95//May-PH The rati F n /F p frm the analysis f data using a new scaling variable S. A. Gurvitz arxiv:hep-ph/95063v1 Jun 1995 Department f Particle Physics, Weizmann Institute f Science, Rehvt 76100,
WIS-95//May-PH The rati F n /F p frm the analysis f data using a new scaling variable S. A. Gurvitz arxiv:hep-ph/95063v1 Jun 1995 Department f Particle Physics, Weizmann Institute f Science, Rehvt 76100,
Differentiation Applications 1: Related Rates
 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates 151 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates Mdel 1: Sliding Ladder 10 ladder y 10 ladder 10 ladder A 10 ft ladder is leaning against a wall when the bttm
Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates 151 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates Mdel 1: Sliding Ladder 10 ladder y 10 ladder 10 ladder A 10 ft ladder is leaning against a wall when the bttm
Evaluation of the outdoor thermal environment in redevelopment buildings in front of Osaka Station based on observations
 Academic Article Jurnal f Heat Island Institute Internatinal Vl. 9-2 (2014) Evaluatin f the utdr thermal envirnment in redevelpment buildings in frnt f Osaka Statin based n bservatins Kentar Ayama *1 Sae
Academic Article Jurnal f Heat Island Institute Internatinal Vl. 9-2 (2014) Evaluatin f the utdr thermal envirnment in redevelpment buildings in frnt f Osaka Statin based n bservatins Kentar Ayama *1 Sae
Assume that the water in the nozzle is accelerated at a rate such that the frictional effect can be neglected.
 1 HW #3: Cnservatin f Linear Mmentum, Cnservatin f Energy, Cnservatin f Angular Mmentum and Turbmachines, Bernulli s Equatin, Dimensinal Analysis, and Pipe Flws Prblem 1. Cnservatins f Mass and Linear
1 HW #3: Cnservatin f Linear Mmentum, Cnservatin f Energy, Cnservatin f Angular Mmentum and Turbmachines, Bernulli s Equatin, Dimensinal Analysis, and Pipe Flws Prblem 1. Cnservatins f Mass and Linear
COASTAL ENGINEERING Chapter 2
 CASTAL ENGINEERING Chapter 2 GENERALIZED WAVE DIFFRACTIN DIAGRAMS J. W. Jhnsn Assciate Prfessr f Mechanical Engineering University f Califrnia Berkeley, Califrnia INTRDUCTIN Wave diffractin is the phenmenn
CASTAL ENGINEERING Chapter 2 GENERALIZED WAVE DIFFRACTIN DIAGRAMS J. W. Jhnsn Assciate Prfessr f Mechanical Engineering University f Califrnia Berkeley, Califrnia INTRDUCTIN Wave diffractin is the phenmenn
A New Evaluation Measure. J. Joiner and L. Werner. The problems of evaluation and the needed criteria of evaluation
 III-l III. A New Evaluatin Measure J. Jiner and L. Werner Abstract The prblems f evaluatin and the needed criteria f evaluatin measures in the SMART system f infrmatin retrieval are reviewed and discussed.
III-l III. A New Evaluatin Measure J. Jiner and L. Werner Abstract The prblems f evaluatin and the needed criteria f evaluatin measures in the SMART system f infrmatin retrieval are reviewed and discussed.
Physical Layer: Outline
 18-: Intrductin t Telecmmunicatin Netwrks Lectures : Physical Layer Peter Steenkiste Spring 01 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/nets-ece Physical Layer: Outline Digital Representatin f Infrmatin Characterizatin f Cmmunicatin
18-: Intrductin t Telecmmunicatin Netwrks Lectures : Physical Layer Peter Steenkiste Spring 01 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/nets-ece Physical Layer: Outline Digital Representatin f Infrmatin Characterizatin f Cmmunicatin
GEOL 2920C The Sedimentary Rock Cycle of Mars & Earth Eberswalde fan deposits: deltaic or alluvial? Deltas at Aeolis Dorsa(?
 GEOL 2920C The Sedimentary Rck Cycle f Mars & Earth Week 12 Basin Scale Prcesses n Mars I (April 16, 2018) Discussin Pints, Key Equatins, Key Figures (prepared by Jesse Tarnas) Eberswalde fan depsits:
GEOL 2920C The Sedimentary Rck Cycle f Mars & Earth Week 12 Basin Scale Prcesses n Mars I (April 16, 2018) Discussin Pints, Key Equatins, Key Figures (prepared by Jesse Tarnas) Eberswalde fan depsits:
Product authorisation in case of in situ generation
 Prduct authrisatin in case f in situ generatin Intrductin At the 74 th CA meeting (27-29 September 2017), Aqua Eurpa and ECA Cnsrtium presented their cncerns and prpsals n the management f the prduct authrisatin
Prduct authrisatin in case f in situ generatin Intrductin At the 74 th CA meeting (27-29 September 2017), Aqua Eurpa and ECA Cnsrtium presented their cncerns and prpsals n the management f the prduct authrisatin
IN a recent article, Geary [1972] discussed the merit of taking first differences
![IN a recent article, Geary [1972] discussed the merit of taking first differences IN a recent article, Geary [1972] discussed the merit of taking first differences](/thumbs/75/71727501.jpg) The Efficiency f Taking First Differences in Regressin Analysis: A Nte J. A. TILLMAN IN a recent article, Geary [1972] discussed the merit f taking first differences t deal with the prblems that trends
The Efficiency f Taking First Differences in Regressin Analysis: A Nte J. A. TILLMAN IN a recent article, Geary [1972] discussed the merit f taking first differences t deal with the prblems that trends
Regional model simulations of New Zealand climate
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 103, NO. D6, PAGES 5973-5982, MARCH 27, 1998 Reginal mdel simulatins f New Zealand climate James A. Renwick Natinal Institute f Water and Atmspheric Research, Wellingtn,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 103, NO. D6, PAGES 5973-5982, MARCH 27, 1998 Reginal mdel simulatins f New Zealand climate James A. Renwick Natinal Institute f Water and Atmspheric Research, Wellingtn,
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors
 Chapter 3 Kinematics in Tw Dimensins; Vectrs Vectrs and Scalars Additin f Vectrs Graphical Methds (One and Tw- Dimensin) Multiplicatin f a Vectr b a Scalar Subtractin f Vectrs Graphical Methds Adding Vectrs
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Tw Dimensins; Vectrs Vectrs and Scalars Additin f Vectrs Graphical Methds (One and Tw- Dimensin) Multiplicatin f a Vectr b a Scalar Subtractin f Vectrs Graphical Methds Adding Vectrs
THERMAL-VACUUM VERSUS THERMAL- ATMOSPHERIC TESTS OF ELECTRONIC ASSEMBLIES
 PREFERRED RELIABILITY PAGE 1 OF 5 PRACTICES PRACTICE NO. PT-TE-1409 THERMAL-VACUUM VERSUS THERMAL- ATMOSPHERIC Practice: Perfrm all thermal envirnmental tests n electrnic spaceflight hardware in a flight-like
PREFERRED RELIABILITY PAGE 1 OF 5 PRACTICES PRACTICE NO. PT-TE-1409 THERMAL-VACUUM VERSUS THERMAL- ATMOSPHERIC Practice: Perfrm all thermal envirnmental tests n electrnic spaceflight hardware in a flight-like
OF SIMPLY SUPPORTED PLYWOOD PLATES UNDER COMBINED EDGEWISE BENDING AND COMPRESSION
 U. S. FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH PAPER FPL 50 DECEMBER U. S. DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE FOREST SERVICE FOREST PRODUCTS LABORATORY OF SIMPLY SUPPORTED PLYWOOD PLATES UNDER COMBINED EDGEWISE BENDING AND COMPRESSION
U. S. FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH PAPER FPL 50 DECEMBER U. S. DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE FOREST SERVICE FOREST PRODUCTS LABORATORY OF SIMPLY SUPPORTED PLYWOOD PLATES UNDER COMBINED EDGEWISE BENDING AND COMPRESSION
the results to larger systems due to prop'erties of the projection algorithm. First, the number of hidden nodes must
 M.E. Aggune, M.J. Dambrg, M.A. El-Sharkawi, R.J. Marks II and L.E. Atlas, "Dynamic and static security assessment f pwer systems using artificial neural netwrks", Prceedings f the NSF Wrkshp n Applicatins
M.E. Aggune, M.J. Dambrg, M.A. El-Sharkawi, R.J. Marks II and L.E. Atlas, "Dynamic and static security assessment f pwer systems using artificial neural netwrks", Prceedings f the NSF Wrkshp n Applicatins
Verification of Quality Parameters of a Solar Panel and Modification in Formulae of its Series Resistance
 Verificatin f Quality Parameters f a Slar Panel and Mdificatin in Frmulae f its Series Resistance Sanika Gawhane Pune-411037-India Onkar Hule Pune-411037- India Chinmy Kulkarni Pune-411037-India Ojas Pandav
Verificatin f Quality Parameters f a Slar Panel and Mdificatin in Frmulae f its Series Resistance Sanika Gawhane Pune-411037-India Onkar Hule Pune-411037- India Chinmy Kulkarni Pune-411037-India Ojas Pandav
A study on GPS PDOP and its impact on position error
 IndianJurnalfRadi& SpacePhysics V1.26,April1997,pp. 107-111 A study n GPS and its impact n psitin errr P Banerjee,AnindyaBse& B SMathur TimeandFrequencySectin,NatinalPhysicalLabratry,NewDelhi110012 Received19June
IndianJurnalfRadi& SpacePhysics V1.26,April1997,pp. 107-111 A study n GPS and its impact n psitin errr P Banerjee,AnindyaBse& B SMathur TimeandFrequencySectin,NatinalPhysicalLabratry,NewDelhi110012 Received19June
PSU GISPOPSCI June 2011 Ordinary Least Squares & Spatial Linear Regression in GeoDa
 There are tw parts t this lab. The first is intended t demnstrate hw t request and interpret the spatial diagnstics f a standard OLS regressin mdel using GeDa. The diagnstics prvide infrmatin abut the
There are tw parts t this lab. The first is intended t demnstrate hw t request and interpret the spatial diagnstics f a standard OLS regressin mdel using GeDa. The diagnstics prvide infrmatin abut the
Hypothesis Tests for One Population Mean
 Hypthesis Tests fr One Ppulatin Mean Chapter 9 Ala Abdelbaki Objective Objective: T estimate the value f ne ppulatin mean Inferential statistics using statistics in rder t estimate parameters We will be
Hypthesis Tests fr One Ppulatin Mean Chapter 9 Ala Abdelbaki Objective Objective: T estimate the value f ne ppulatin mean Inferential statistics using statistics in rder t estimate parameters We will be

