EasyChair Preprint. Sotirios Tsiougkos and Dimitrios Brikas. November 9, 2018
|
|
|
- Milton Homer Preston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EasyChair Preprint 616 Calculation of dynamic and thermodynamic parameters from spatial data of high spatial resolution of a weather event s specific case study event that occurred on the 16th and 17th of July 2017 Sotirios Tsiougkos and Dimitrios Brikas EasyChair preprints are intended for rapid dissemination of research results and are integrated with the rest of EasyChair. November 9, 2018
2 Calculation of dynamic and thermodynamic parameters from spatial data of high spatial resolution of a weather event s specific case study event that occurred on the 16th and 17th of July Tsiougkos S. 1*, A Brikas D. 2 1 Tsiougkos S. Meteorologist, Weather forecaster at Regional Meteorological Center of Larissa 2 Brikas D. Meteorologist, Weather forecaster at Regional Meteorological Center of Macedonia *corresponding author sottsiougkos@gmail.com Abstract The intense weather conditions that occurred on July 16 and 17, 2017 were the reason for further analysis and study of this event. For the results to have a higher confidence level, ERA interim data on a normal X grid, which are available from the European Center Meteorological Weather Forecasting (ECMWF), available at the Hellenic National Meteorological Service (HNMS) were used. Thermodynamic parameters such as potential vorticity, potential temperature, sensible and latent heat fluxes and static stability were calculated. Finally, all of the above were compared with the more objective of the weather and Eumetsat s satellite imagery. 1 Introduction First of all, it is considered necessary to have a look of the synoptic environment of this specific case study. In the upper troposphere and the level of 500hPa 1706UTC, we observe that the circulation in Europe is a meridian one and the anticyclone has almost covered West Europe. Also, colder air masses are in the eastern zone along with a runoff disturbance and a wind stress curl. The distribution of the wind level at 500hPa depicted the specific type of disturbance in a characteristic way, where the wind force values on its west side were above 50kt. It is well known that diffluent troughs on a NW flow have the tendency to deepen and relocate the colder air masses into lower geographical levels and relate to the frontogenesis in the upper atmosphere (Schultz and Sanders 2002). Fig. 1. Geographical distribution at 170/6UTC (a) geodynamic heights, relative vorticity and temperatures at 500hPa (b) geodynamic heights and temperature at 850hPa (c) Mean sea level pressure Also, in the level of 850hPa, it is obvious that between the geodynamic heights and temperatures there is a phase difference of approximately 90 o. The above indicates the existence of a well-structured baroclinic structure in the lower layers, where the cold convection is within and the thermal convection in front of the disturbance. According to Lupo et al. 1992, such a
3 2 structure in the lower layers favors the updrafts. Meanwhile, the surface analysis has depicted the center of the low in Russia, while the anticyclone has been transferred to the western parts of East Europe compressing even more the isobars towards the Balkans and the front has acquired a S-SE direction 2 Data and Methodology In this study, high spatial gridded data from ECMWF / ERA-INTERIM to a regular grid of X latitude-longitude was used and the maps were plotted using Metview, a meteorological workstation application designed to be a complete working environment for both the operational and research meteorologist. To make our study more objective, dynamic and thermodynamic parameters such as potential vorticity, potential temperature, relative humidity, sensible and latent heat fluxes and static stability were calculated and studied separately for the upper and lower layers of the atmosphere. 3 Results 3.1 Upper layers. The dynamic temperature distribution in the 2PVU surface (Fig.1a), the corresponding potential vorticity in the isentropical surface 315K for the 17/06UTC (Fig.1b) and the relative humidity at 300hPa indicate the high values of cold air in the isentropic potential vorticity, which are higher than the 2PVU that lay above the areas of the phenomena. The above show that air from the stratosphere has come down to the upper troposphere (stratospheric intrusion) and has set a tropopause folding, according to the study of Hoskins et al. (1985). According to the study of Uccellini et al., 1986, the tropopause folding and the stratospheric intrusion of cold and dry air in the upper troposphere favor updrafts. Fig. 1. (a) Dynamic temperature geographic distribution in the iso-pv surface of 2PVU. The isopleths are per 5K for 1618UTC (b) Potential vorticity geographical distribution in the isentropic surface of 315K. The isopleths are per 1 PVU (for the 17/06UTC. When these characteristics are combined with the existence of a strong upper frontal surface of the surface low and partially with the polar jet stream, which relates to the upper disturbance, then the updrafts get even more intensified. Due to the stratospheric intrusion into the upper troposphere, the impact that the downdrafts carry is depicted by the distribution of pressure onto the isentropic surface of 315K, for the
4 17/06UTC. Taking into consideration that this specific isentropic surface corresponds to 450hPa, we observe that pressures above the area of the most intense phenomena are almost at 300hPa. The corresponding isobaric surfaces have come down and are located at 450hPa, indicating a vertical shrinking of the upper troposphere, a fact that implies the layer lowering of the upper troposphere and, as a result, the creation of upper movements in the lower troposphere, according to the function of the geodynamic tension (Holton, 1992). 3 Fig. 2. (a) Vertical section of the atmosphere alongside the dotted line for the period of July 17/06Z. (1) Blue lines: potential temperature (isentropics) per 3K. Red arrows: Circulation parallel to the section. (2) Red dotted line: dynamic tropopause (PV= 2 PVU). Areas where the vertical component of the wind upon the section surpasses the 5m/s are gradually colored in grey color. Dotted (continual) lines enclose areas with NNE (SSW) winds. The cores of the jet streams are written: polar jet (PJ), subtropical (SJ).). Finally, the areas where the relative humidity surpasses 85 and 95% are shadowed with lines (b) Distribution of the potential vorticity for the 17/06UTC. The isopleths are per 1 PVU. The tropopause folding, that takes place within the mechanism of stratospheric air transfer towards the median troposphere along the axis of the jet stream (Reed, 1955), is characterized by high values of the potential vorticity in the upper troposphere (Fig. 2b). It is characteristic that, while on the west and east side of the area of intense rainfall there are strong jet streams, above the center of this area the wind speed is almost zero. Similarly, for the tropopause, the jet streams blow at 480 and 420 hpa, respectively, on the west and east side of the area with intense rainfall. The above fact does not favor the high cloud levels, since above the center of the area of intense rainfall jet streams extend up to 250 hpa. Fig. 3. (a) WV satellite picture for 17/03 UTC (b) Relative humidity at 300hPa for 16/16UTC. The WV picture of the satellite depicts a snapshot of the gradient of humidity in Central East Mediterranean (an important element of the upper layers dynamic), (Fig. 3a), which indicates the partial existence of the jet stream in the particular area (upper level jet streak). It is in accordance with the recorded intensified winds zone, as it results from the analysis of the geodynamic heights at 300hPa and 500hPa. In these cases, the dry zone is in the cold section of the jet axis (Bader et al. 1995) and is related to the existence of a disturbance in the upper
5 troposphere. This disturbance indicates the existence of a positive transfer of vorticity and a cold transfer to the upper layers, respectively, to the cold section of the jet stream, above the area of the enhanced baroclinicity of the lower layers (Barry and Carleton 2001) and it favors the appearance of convection. The distributions of the static stability at the level of 500hPa and 300hPa, had a more stable structure in comparison to the level of 700 hpa and 500hPa, where the unstable structure of the atmosphere is obvious. As a matter of fact, for the period of 17/15UTC until 17/18UTC the area of NW Aegean Sea did not present any important changes at the level of 700hPa, while, on the contrary, the thermodynamic structure of the atmosphere in NE Aegean Sea became more unstable Lower layers. The structure and the layout of this specific system, where the warmer masses are in Turkey and East Aegean Sea and the colder masses above the country, were also depicted by the dynamic temperature at the lower layers. However, the distributions of the potential temperature at 925hPa did not present any specific fluctuation in comparison to the fluctuation of the equivalent potential temperature for the 17/12 UTC or at any point of its development in general. It should be noted that the diabatic processes are favored by the higher values of the equivalent potential temperature in comparison to those of the dynamic one. However, if we study the structure of the lower layers through the scope of the alteration of the potential temperature in relation to height, we will notice that the layer 925/850hPa did not present any specific alteration as far as its static stability is concerned in North Aegean Sea. The area of Central Aegean Sea was the only one that appeared to have the most important alteration in this specific parameter, as well as the area at the eastern side of Sporades, which is related to the surface convergences. Fig. 4. Geographical distribution (a) of sensible heat fluxes for the 17/06UTC in W/m 2 (b) latent heat fluxes for the 17/06UTC in W/m 2 (c) cross section of divergence for the 17/12UTC. Danard (1964) showed that the effect of latent heat is such that it can reinforce and broaden the upward motions in areas of high precipitation values and it can also contribute to the creation of weak downward vertical motions in the surrounding area, while, at the same time, it can reinforce the convergence in lower layers and deviate in the upper layers. The geographical distribution of the latent heat fluxes for the 17/06UTC (Fig 4a) depicts negative flows in North Aegean Sea, where the most intense phenomena were recorded. However, what is more characteristic is the deviance of the sensible heat fluxes (Fig 4b), where the negative values are recorded in Northwest Aegean Sea, while the positive values were recorded in East Aegean. This shows that the thermal mass from the area of Turkey was horizontally transferred in
6 accordance with the wind direction at the lower layers and met the colder mass at the western areas. Even though the heat air in the lower layers did not favor the diabatic processes, the sea surface reinforced the air with water vapors favoring the emission of latent heat. Moreover, the depiction of the wind zone convergence at the lower layers for the 17/12UTC in Northwest Aegean Sea is very characteristic as well as its deviation towards the upper layers (Fig 4c), where the most intense upward motions were recorded, as it was mentioned in the previous paragraph. What reassures the above-mentioned elements is the depiction of the heat difference between the sea level and the adjacent colder air. Even though we are in the middle of a warm period, both in the area Ionian Sea and North Aegean Sea, we observed negative differences during the outburst of the intense phenomena. Such values correspond to cold invasions at low layers, during the cold periods, along with the blow of mainland wind into the thermal sea of the Mediterranean. Finally, according to the study of Fita et al. (2007), the appearance of increased values in the potential vorticity in the lower troposphere, which depict a localized maximum of it, are a strong proof of the existence of diabatic heating source. This specific characteristic, however, is not a sufficient condition on its own. In this specific case the depiction of the vertical distribution of potential vorticity in North Aegean Sea between Sporades Lemnos for the 17/06UTC and 17/18UTC, depict the high values of potential vorticity (>1.5PVU) for the area of Northwest Aegean Sea both in low and upper layers. On the contrary, in Lemnos for the 17/18UTC the highest values of the potential vorticity were detected mainly in the upper layers, a fact that reinforces the influence of the diabatic processes in the areas of convergence. 5 4 Conclusions 1. Jetstream s position in the upper troposphere in response to the 500hPa level established a meridian circulation at eastern European traffic, favoring the fall of cold air masses in Southeastern Europe. 2. The enhanced temperature gradient in the lower layers combined with the corresponding arrangement of the winds was a particularly stimulating factor for upward motions in the region mainly of the north-western Aegean, since the hottest air from the Turkish region was swept into the colder air that was in the Central- Northern Greece Potential vorticity s values > 2PVU combined with a tropopause folding and dry stratospheric intrusion, have been particularly effective in enhancing phenomena. 4. The upper layers showed a decrease in static stability as expected and appeared to have the most catalytic role in the development of the case under consideration. 5. The lower layers did not exhibit a corresponding change in their static stability except the north-western Aegean, where the other thermodynamic factors were like those of a winter system.
7 References 6 Bader MJ, Forbes GS, Grant JR, Liley RB, Waters AJ (1995) Images in weather forecasting. A practical guide for interpreting satellite and radar imagery Cambridge University Press Barry RG, Carleton AM (2001) Synoptic and Dynamic Climatology. Routledge, 620pp Danard M.B. and G.E. Ellenton, 1980: Physical influences on east coast cyclogenesis. Atm. Ocean., 18, Fita, L., R. Romero, A. Luque, K. Emanuel, and C. Ramis (2007), Analysis of the environments of seven Mediterranean tropical-like storms using an axisymmetric, nonhydrostatic, cloudresolvingmodel, Nat.HazardsEarth Syst. Sci., 7,1 Hoskins BJ, McIntyre ME, Robertson AW (1985) On the use and significance of isentropic potential vorticity maps. Q J R Meteorol Soc 111: doi: /qj Holton J.R., (1992) An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology, Third Edition, Academic Press, San Diego. Hoskins BJ, McIntyre ME, Robertson AW (1985) On the use and significance of isentropic potential vorticity maps. Q J R Meteorol Soc 111: doi: /qj Reed R. J., 1955: A study of a characteristic type of upper level frontogenesis. J. Meteor., 12, Uccellini L.W, D. Keyser, K.F. Brill and C.H. Wash, 1985: The Presidents Day Cyclone of Feb. 1979: Influence of upstream trough amplification and associated tropopause folding in rapid cyclogenesis. Mon. Wea. Rev., 113, Schultz DM, Sanders F (2002) Upper Level Frontogenesis Associated with the Birth of Mobile Troughs in Northwesterly Flow. Mon Wea Rev 130:
A SEVERE WEATHER EVENT IN ROMANIA DUE TO MEDITERRANEAN CYCLONIC ACTIVITY
 A SEVERE WEATHER EVENT IN ROMANIA DUE TO MEDITERRANEAN CYCLONIC ACTIVITY Florinela Georgescu, Gabriela Bancila, Viorica Dima National Meteorological Administration, Bucharest, Romania Abstract Mediterranean
A SEVERE WEATHER EVENT IN ROMANIA DUE TO MEDITERRANEAN CYCLONIC ACTIVITY Florinela Georgescu, Gabriela Bancila, Viorica Dima National Meteorological Administration, Bucharest, Romania Abstract Mediterranean
3. Midlatitude Storm Tracks and the North Atlantic Oscillation
 3. Midlatitude Storm Tracks and the North Atlantic Oscillation Copyright 2006 Emily Shuckburgh, University of Cambridge. Not to be quoted or reproduced without permission. EFS 3/1 Review of key results
3. Midlatitude Storm Tracks and the North Atlantic Oscillation Copyright 2006 Emily Shuckburgh, University of Cambridge. Not to be quoted or reproduced without permission. EFS 3/1 Review of key results
1. INTRODUCTION: 2. DATA AND METHODOLOGY:
 27th Conference on Hurricanes and Tropical Meteorology, 24-28 April 2006, Monterey, CA 3A.4 SUPERTYPHOON DALE (1996): A REMARKABLE STORM FROM BIRTH THROUGH EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITION TO EXPLOSIVE REINTENSIFICATION
27th Conference on Hurricanes and Tropical Meteorology, 24-28 April 2006, Monterey, CA 3A.4 SUPERTYPHOON DALE (1996): A REMARKABLE STORM FROM BIRTH THROUGH EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITION TO EXPLOSIVE REINTENSIFICATION
10B.2 THE ROLE OF THE OCCLUSION PROCESS IN THE EXTRATROPICAL-TO-TROPICAL TRANSITION OF ATLANTIC HURRICANE KAREN
 10B.2 THE ROLE OF THE OCCLUSION PROCESS IN THE EXTRATROPICAL-TO-TROPICAL TRANSITION OF ATLANTIC HURRICANE KAREN Andrew L. Hulme* and Jonathan E. Martin University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, Wisconsin
10B.2 THE ROLE OF THE OCCLUSION PROCESS IN THE EXTRATROPICAL-TO-TROPICAL TRANSITION OF ATLANTIC HURRICANE KAREN Andrew L. Hulme* and Jonathan E. Martin University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, Wisconsin
Synoptic-Dynamic Meteorology in Midlatitudes
 Synoptic-Dynamic Meteorology in Midlatitudes VOLUME II Observations and Theory of Weather Systems HOWARD B. BLUESTEIN New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1993 Contents 1. THE BEHAVIOR OF SYNOPTIC-SCALE,
Synoptic-Dynamic Meteorology in Midlatitudes VOLUME II Observations and Theory of Weather Systems HOWARD B. BLUESTEIN New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1993 Contents 1. THE BEHAVIOR OF SYNOPTIC-SCALE,
Occlusion Cyclogenesis
 Occlusion Cyclogenesis Part I: Occlusion cloud bands in comparison to CF and WFs Concepts for cyclogenesis Different types of cyclogenesis and examples Numerical parameters on isobaric and isentropic surfaces
Occlusion Cyclogenesis Part I: Occlusion cloud bands in comparison to CF and WFs Concepts for cyclogenesis Different types of cyclogenesis and examples Numerical parameters on isobaric and isentropic surfaces
Isentropic Analysis. Much of this presentation is due to Jim Moore, SLU
 Isentropic Analysis Much of this presentation is due to Jim Moore, SLU Utility of Isentropic Analysis Diagnose and visualize vertical motion - through advection of pressure and system-relative flow Depict
Isentropic Analysis Much of this presentation is due to Jim Moore, SLU Utility of Isentropic Analysis Diagnose and visualize vertical motion - through advection of pressure and system-relative flow Depict
Multiscale Analyses of Inland Tropical Cyclone Midlatitude Jet Interactions: Camille (1969) and Danny (1997)
 Multiscale Analyses of Inland Tropical Cyclone Midlatitude Jet Interactions: Camille (1969) and Danny (1997) Matthew Potter, Lance Bosart, and Daniel Keyser Department of Atmospheric and Environmental
Multiscale Analyses of Inland Tropical Cyclone Midlatitude Jet Interactions: Camille (1969) and Danny (1997) Matthew Potter, Lance Bosart, and Daniel Keyser Department of Atmospheric and Environmental
INTERPRETATION GUIDE TO MSG WATER VAPOUR CHANNELS
 INTERPRETATION GUIDE TO MSG WATER VAPOUR CHANNELS C.G. Georgiev1 and P. Santurette2 1 National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology, Tsarigradsko chaussee 66, 1784 Sofia, Bulgaria 2 Météo-France, 42,
INTERPRETATION GUIDE TO MSG WATER VAPOUR CHANNELS C.G. Georgiev1 and P. Santurette2 1 National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology, Tsarigradsko chaussee 66, 1784 Sofia, Bulgaria 2 Météo-France, 42,
Rapid cyclogenesis over Poland on 28 March 1997
 Meteorol. Appl. 6, 363 370 (1999) Rapid cyclogenesis over Poland on 28 March 1997 Jan Waclaw Parfiniewicz, Institute of Meteorology and Water Management, ul. Podleœna 61, 01 673 Warszawa, Poland A small
Meteorol. Appl. 6, 363 370 (1999) Rapid cyclogenesis over Poland on 28 March 1997 Jan Waclaw Parfiniewicz, Institute of Meteorology and Water Management, ul. Podleœna 61, 01 673 Warszawa, Poland A small
Upper-tropospheric downstream development leading to surface cyclogenesis in the central Mediterranean
 Meteorol. Appl. 6, 33 3 (999) Upper-tropospheric downstream development leading to surface cyclogenesis in the central Mediterranean Nicholas G Prezerakos, Helena A Flocas and Silas C Michaelides 3 General
Meteorol. Appl. 6, 33 3 (999) Upper-tropospheric downstream development leading to surface cyclogenesis in the central Mediterranean Nicholas G Prezerakos, Helena A Flocas and Silas C Michaelides 3 General
INVESTIGATION FOR A POSSIBLE INFLUENCE OF IOANNINA AND METSOVO LAKES (EPIRUS, NW GREECE), ON PRECIPITATION, DURING THE WARM PERIOD OF THE YEAR
 Proceedings of the 13 th International Conference of Environmental Science and Technology Athens, Greece, 5-7 September 2013 INVESTIGATION FOR A POSSIBLE INFLUENCE OF IOANNINA AND METSOVO LAKES (EPIRUS,
Proceedings of the 13 th International Conference of Environmental Science and Technology Athens, Greece, 5-7 September 2013 INVESTIGATION FOR A POSSIBLE INFLUENCE OF IOANNINA AND METSOVO LAKES (EPIRUS,
 http://www.ssec.wisc.edu/data/composites.html Red curve: Incoming solar radiation Blue curve: Outgoing infrared radiation. Three-cell model of general circulation Mid-latitudes: 30 to 60 latitude MID-LATITUDES
http://www.ssec.wisc.edu/data/composites.html Red curve: Incoming solar radiation Blue curve: Outgoing infrared radiation. Three-cell model of general circulation Mid-latitudes: 30 to 60 latitude MID-LATITUDES
A case of Rapid Cyclogenesis over Ionian Sea on February 6 th, 2012
 Author: Kyriaki Metheniti, HNMS Showcase Title: A case of Rapid Cyclogenesis Time frame: February 6 to February 7, 2012 Study region: Eastern Mediterranean, Ionian Sea A case of Rapid Cyclogenesis over
Author: Kyriaki Metheniti, HNMS Showcase Title: A case of Rapid Cyclogenesis Time frame: February 6 to February 7, 2012 Study region: Eastern Mediterranean, Ionian Sea A case of Rapid Cyclogenesis over
Occlusion cyclogenesis II
 Occlusion cyclogenesis II Upper level influences on cyclogenesis Vorticity Advection (CVA) and the 4-quadrant jet streak model (Uccellini) Potential Vorticity (PV) (Hoskins Theory) Rapid cyclogenesis 14
Occlusion cyclogenesis II Upper level influences on cyclogenesis Vorticity Advection (CVA) and the 4-quadrant jet streak model (Uccellini) Potential Vorticity (PV) (Hoskins Theory) Rapid cyclogenesis 14
and 24 mm, hPa lapse rates between 3 and 4 K km 1, lifted index values
 3.2 Composite analysis 3.2.1 Pure gradient composites The composite initial NE report in the pure gradient northwest composite (N = 32) occurs where the mean sea level pressure (MSLP) gradient is strongest
3.2 Composite analysis 3.2.1 Pure gradient composites The composite initial NE report in the pure gradient northwest composite (N = 32) occurs where the mean sea level pressure (MSLP) gradient is strongest
Victor Homar * and David J. Stensrud NOAA/NSSL, Norman, Oklahoma
 3.5 SENSITIVITIES OF AN INTENSE CYCLONE OVER THE WESTERN MEDITERRANEAN Victor Homar * and David J. Stensrud NOAA/NSSL, Norman, Oklahoma 1. INTRODUCTION The Mediterranean region is a very active cyclogenetic
3.5 SENSITIVITIES OF AN INTENSE CYCLONE OVER THE WESTERN MEDITERRANEAN Victor Homar * and David J. Stensrud NOAA/NSSL, Norman, Oklahoma 1. INTRODUCTION The Mediterranean region is a very active cyclogenetic
Chapter 12 Fronts & Air Masses
 Chapter overview: Anticyclones or highs Air Masses o Classification o Source regions o Air masses of North America Fronts o Stationary fronts o Cold fronts o Warm fronts o Fronts and the jet stream o Frontogenesis
Chapter overview: Anticyclones or highs Air Masses o Classification o Source regions o Air masses of North America Fronts o Stationary fronts o Cold fronts o Warm fronts o Fronts and the jet stream o Frontogenesis
Diabatic processes and the structure of the warm conveyor belt
 2 nd European Windstorm Workshop Leeds, 3-4 September 2012 Diabatic processes and the structure of the warm conveyor belt Oscar Martínez-Alvarado J. Chagnon, S. Gray, R. Plant, J. Methven Department of
2 nd European Windstorm Workshop Leeds, 3-4 September 2012 Diabatic processes and the structure of the warm conveyor belt Oscar Martínez-Alvarado J. Chagnon, S. Gray, R. Plant, J. Methven Department of
Lower-Tropospheric Height Tendencies Associated with the Shearwise and Transverse Components of Quasigeostrophic Vertical Motion
 JULY 2007 N O T E S A N D C O R R E S P O N D E N C E 2803 Lower-Tropospheric Height Tendencies Associated with the Shearwise and Transverse Components of Quasigeostrophic Vertical Motion JONATHAN E. MARTIN
JULY 2007 N O T E S A N D C O R R E S P O N D E N C E 2803 Lower-Tropospheric Height Tendencies Associated with the Shearwise and Transverse Components of Quasigeostrophic Vertical Motion JONATHAN E. MARTIN
WATER VAPOUR IMAGERY ANALYSIS IN 7.3µ/6.2µ FOR DIAGNOSING THERMO-DYNAMIC CONTEXT OF INTENSE CONVECTION
 WATER VAPOUR IMAGERY ANALYSIS IN 7.3µ/6.2µ FOR DIAGNOSING THERMO-DYNAMIC CONTEXT OF INTENSE CONVECTION P. Santurette 1 and C.G. Georgiev 2 1 Météo-France, 42, Avenue G. Coriolis, 31057 Toulouse Cedex 01,
WATER VAPOUR IMAGERY ANALYSIS IN 7.3µ/6.2µ FOR DIAGNOSING THERMO-DYNAMIC CONTEXT OF INTENSE CONVECTION P. Santurette 1 and C.G. Georgiev 2 1 Météo-France, 42, Avenue G. Coriolis, 31057 Toulouse Cedex 01,
Mesoscale Atmospheric Systems. Surface fronts and frontogenesis. 06 March 2018 Heini Wernli. 06 March 2018 H. Wernli 1
 Mesoscale Atmospheric Systems Surface fronts and frontogenesis 06 March 2018 Heini Wernli 06 March 2018 H. Wernli 1 Temperature (degc) Frontal passage in Mainz on 26 March 2010 06 March 2018 H. Wernli
Mesoscale Atmospheric Systems Surface fronts and frontogenesis 06 March 2018 Heini Wernli 06 March 2018 H. Wernli 1 Temperature (degc) Frontal passage in Mainz on 26 March 2010 06 March 2018 H. Wernli
1. COLD FRONT - CLOUD STRUCTURE IN SATELLITE IMAGES
 1. COLD FRONT - CLOUD STRUCTURE IN SATELLITE IMAGES The satellite image shows a cyclonically curved synoptic scale cloud band usually a few hundred kilometres wide; in the VIS image the cloud band mostly
1. COLD FRONT - CLOUD STRUCTURE IN SATELLITE IMAGES The satellite image shows a cyclonically curved synoptic scale cloud band usually a few hundred kilometres wide; in the VIS image the cloud band mostly
Final Examination, MEA 443 Fall 2008, Lackmann
 Place an X here to count it double! Name: Final Examination, MEA 443 Fall 2008, Lackmann If you wish to have the final exam count double and replace your midterm score, place an X in the box above. As
Place an X here to count it double! Name: Final Examination, MEA 443 Fall 2008, Lackmann If you wish to have the final exam count double and replace your midterm score, place an X in the box above. As
Synoptic Meteorology II: Self-Development in the IPV Framework. 5-7 May 2015
 Synoptic Meteorology II: Self-Development in the IPV Framework 5-7 May 2015 Readings: Section 5.3.6 of Midlatitude Synoptic Meteorology. Introduction In this and other recent lectures, we have developed
Synoptic Meteorology II: Self-Development in the IPV Framework 5-7 May 2015 Readings: Section 5.3.6 of Midlatitude Synoptic Meteorology. Introduction In this and other recent lectures, we have developed
THE LOW-LEVEL JET FOR BUCHAREST S AIRPORTS - A STUDY OF ITS CHARACTERISTICS IN WINTER SEASON BETWEEN 1959 AND 1982
 Romanian Reports in Physics, Vol. 67. No. 2, P. 638 652, 2015 THE LOW-LEVEL JET FOR BUCHAREST S AIRPORTS - A STUDY OF ITS CHARACTERISTICS IN WINTER SEASON BETWEEN 1959 AND 1982 M. BALMEZ 1,2, F. GEORGESCU
Romanian Reports in Physics, Vol. 67. No. 2, P. 638 652, 2015 THE LOW-LEVEL JET FOR BUCHAREST S AIRPORTS - A STUDY OF ITS CHARACTERISTICS IN WINTER SEASON BETWEEN 1959 AND 1982 M. BALMEZ 1,2, F. GEORGESCU
Vertical structure. To conclude, we will review the critical factors invloved in the development of extratropical storms.
 Vertical structure Now we will examine the vertical structure of the intense baroclinic wave using three visualization tools: Upper level charts at selected pressure levels Vertical soundings for selected
Vertical structure Now we will examine the vertical structure of the intense baroclinic wave using three visualization tools: Upper level charts at selected pressure levels Vertical soundings for selected
Tropical Cyclone Formation/Structure/Motion Studies
 Tropical Cyclone Formation/Structure/Motion Studies Patrick A. Harr Department of Meteorology Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943-5114 phone: (831) 656-3787 fax: (831) 656-3061 email: paharr@nps.edu
Tropical Cyclone Formation/Structure/Motion Studies Patrick A. Harr Department of Meteorology Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943-5114 phone: (831) 656-3787 fax: (831) 656-3061 email: paharr@nps.edu
Project 2 Fronts
 12.307 Project 2 Fronts Lodovica Illari and John Marshall March 2010 Abstract We inspect fronts crossing the country associated with day-to-day variations in the weather using real-time atmospheric observations.
12.307 Project 2 Fronts Lodovica Illari and John Marshall March 2010 Abstract We inspect fronts crossing the country associated with day-to-day variations in the weather using real-time atmospheric observations.
An extreme thunderstorm event over Athens on February 22 nd, 2013
 An extreme thunderstorm event over Athens on February 22 nd, 2013 A. Marinaki*, G. Alexandropoulou, K. Metheniti, C. Petrou, E. Tsiniari, I. Nikolaou, A. Lalos Hellenic National Meteorological Service
An extreme thunderstorm event over Athens on February 22 nd, 2013 A. Marinaki*, G. Alexandropoulou, K. Metheniti, C. Petrou, E. Tsiniari, I. Nikolaou, A. Lalos Hellenic National Meteorological Service
Numerical Simulation of a Severe Cold and Rainy Event over the East Mediterranean
 JKAU: Met., Env. & Arid Land Agric. Sci., Vol. 20, No. 2, pp: 95-109 (2009 A.D. / 1430 A.H.) Numerical Simulation of a Severe Cold and Rainy Event over the East Mediterranean Department of Meteorology,
JKAU: Met., Env. & Arid Land Agric. Sci., Vol. 20, No. 2, pp: 95-109 (2009 A.D. / 1430 A.H.) Numerical Simulation of a Severe Cold and Rainy Event over the East Mediterranean Department of Meteorology,
QUALITY OF MPEF DIVERGENCE PRODUCT AS A TOOL FOR VERY SHORT RANGE FORECASTING OF CONVECTION
 QUALITY OF MPEF DIVERGENCE PRODUCT AS A TOOL FOR VERY SHORT RANGE FORECASTING OF CONVECTION C.G. Georgiev 1, P. Santurette 2 1 National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences
QUALITY OF MPEF DIVERGENCE PRODUCT AS A TOOL FOR VERY SHORT RANGE FORECASTING OF CONVECTION C.G. Georgiev 1, P. Santurette 2 1 National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences
The water vapour channels of SEVIRI (Meteosat). An introduction
 The water vapour channels of SEVIRI (Meteosat). An introduction jose.prieto@eumetsat.int Cachoeira P. July 2006 Formats 1.5 1 Objectives 2 Describe the characteristics of WV channels on board of SEVIRI
The water vapour channels of SEVIRI (Meteosat). An introduction jose.prieto@eumetsat.int Cachoeira P. July 2006 Formats 1.5 1 Objectives 2 Describe the characteristics of WV channels on board of SEVIRI
The Impact of air-sea interaction on the extratropical transition of tropical cyclones
 The Impact of air-sea interaction on the extratropical transition of tropical cyclones Sarah Jones Institut für Meteorologie und Klimaforschung Universität Karlsruhe / Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe 1. Introduction
The Impact of air-sea interaction on the extratropical transition of tropical cyclones Sarah Jones Institut für Meteorologie und Klimaforschung Universität Karlsruhe / Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe 1. Introduction
THE EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITION OF TYPHOON WINNIE (1997): SELF-AMPLIFICATION AFTER LANDFALL
 THE EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITION OF TYPHOON WINNIE (1997): SELF-AMPLIFICATION AFTER LANDFALL Chih-Shin Liu *1,2 and George Tai-Jen Chen 2 1 Weather Forecast Center, Central Weather Bureau, 2 Department of
THE EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITION OF TYPHOON WINNIE (1997): SELF-AMPLIFICATION AFTER LANDFALL Chih-Shin Liu *1,2 and George Tai-Jen Chen 2 1 Weather Forecast Center, Central Weather Bureau, 2 Department of
AN EXTRATROPICAL CYCLONE ATLAS
 AN EXTRATROPICAL CYCLONE ATLAS A tool for illustrating cyclone structure and evolution characteristics BY H. F. DACRE, M. K. HAWCROFT, M. A. STRINGER AND K. I. HODGES Authors Affiliations H.F.Dacre, Department
AN EXTRATROPICAL CYCLONE ATLAS A tool for illustrating cyclone structure and evolution characteristics BY H. F. DACRE, M. K. HAWCROFT, M. A. STRINGER AND K. I. HODGES Authors Affiliations H.F.Dacre, Department
Divergence, Spin, and Tilt. Convergence and Divergence. Midlatitude Cyclones. Large-Scale Setting
 Midlatitude Cyclones Equator-to-pole temperature gradient tilts pressure surfaces and produces westerly jets in midlatitudes Waves in the jet induce divergence and convergence aloft, leading to surface
Midlatitude Cyclones Equator-to-pole temperature gradient tilts pressure surfaces and produces westerly jets in midlatitudes Waves in the jet induce divergence and convergence aloft, leading to surface
Diagnostic Study of a Severe Thunderstorm over Jeddah
 Atmospheric and Climate Sciences, 2013, 3, 150-164 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/acs.2013.31017 Published Online January 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/acs) Diagnostic Study of a Severe Thunderstorm over
Atmospheric and Climate Sciences, 2013, 3, 150-164 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/acs.2013.31017 Published Online January 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/acs) Diagnostic Study of a Severe Thunderstorm over
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1. Summary of the climatic responses to the Gulf Stream. On the offshore flank of the SST front (black dashed curve) of the Gulf Stream (green long arrow), surface wind convergence associated with
Figure S1. Summary of the climatic responses to the Gulf Stream. On the offshore flank of the SST front (black dashed curve) of the Gulf Stream (green long arrow), surface wind convergence associated with
The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007
 The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007 Hiroshi Hasegawa 1, Yayoi Harada 1, Hiroshi Nakamigawa 1, Atsushi Goto 1 1 Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological
The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007 Hiroshi Hasegawa 1, Yayoi Harada 1, Hiroshi Nakamigawa 1, Atsushi Goto 1 1 Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological
Interaction of Potential Vorticity Anomalies in Extratropical Cyclogenesis. Part I: Static Piecewise Inversion
 2546 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW VOLUME 127 Interaction of Potential Vorticity Anomalies in Extratropical Cyclogenesis. Part I: Static Piecewise Inversion ZONGHUI HUO CMRP, School of Meteorology, University
2546 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW VOLUME 127 Interaction of Potential Vorticity Anomalies in Extratropical Cyclogenesis. Part I: Static Piecewise Inversion ZONGHUI HUO CMRP, School of Meteorology, University
Chapter 1 Anatomy of a Cyclone
 Chapter 1 Anatomy of a Cyclone The Beast in the East 15-17 February 2003 Extra-tropical cyclone an area of low pressure outside of the tropics Other names for extra-tropical cyclones: Cyclone Mid-latitude
Chapter 1 Anatomy of a Cyclone The Beast in the East 15-17 February 2003 Extra-tropical cyclone an area of low pressure outside of the tropics Other names for extra-tropical cyclones: Cyclone Mid-latitude
Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004
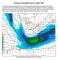 Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004 This event was characterized by a very strong jet streak that developed over North Carolina by 00 UTC 8 March, as seen in the Eta model analysis at 300 mb, with
Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004 This event was characterized by a very strong jet streak that developed over North Carolina by 00 UTC 8 March, as seen in the Eta model analysis at 300 mb, with
Air Masses of North America cp and ca air masses Air mass characterized by very cold and dry conditions
 Chapter 8: Air Masses, Fronts, and Middle-Latitude Cyclones Air masses Fronts Middle-latitude cyclones Air Masses Air mass an extremely large body of air whose properties of temperature and humidity are
Chapter 8: Air Masses, Fronts, and Middle-Latitude Cyclones Air masses Fronts Middle-latitude cyclones Air Masses Air mass an extremely large body of air whose properties of temperature and humidity are
SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION OF SOME DYNAMIC PARAMETERS DURING THE EVOLUTION OF SELECTED DEPRESSIONS OVER THE AREA OF CYPRUS
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. 24: 1829 1844 (04) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/joc.1105 SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION OF SOME DYNAMIC
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. 24: 1829 1844 (04) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/joc.1105 SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION OF SOME DYNAMIC
1.4 CONNECTIONS BETWEEN PV INTRUSIONS AND TROPICAL CONVECTION. Beatriz M. Funatsu* and Darryn Waugh The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD
 1.4 CONNECTIONS BETWEEN PV INTRUSIONS AND TROPICAL CONVECTION Beatriz M. Funatsu* and Darryn Waugh The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD 1. INTRODUCTION Stratospheric intrusions into the tropical
1.4 CONNECTIONS BETWEEN PV INTRUSIONS AND TROPICAL CONVECTION Beatriz M. Funatsu* and Darryn Waugh The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD 1. INTRODUCTION Stratospheric intrusions into the tropical
P1.16 WARM-SECLUSION EXTRATROPICAL CYCLONE DEVELOPMENT: SENSITIVITY TO THE NATURE OF THE INCIPIENT VORTEX
 P1.16 WARM-SECLUSION EXTRATROPICAL CYCLONE DEVELOPMENT: SENSITIVITY TO THE NATURE OF THE INCIPIENT VORTEX Ryan N. Maue* 1 and Robert E. Hart 1 1 Department of Meteorology, Florida State University 1. INTRODUCTION
P1.16 WARM-SECLUSION EXTRATROPICAL CYCLONE DEVELOPMENT: SENSITIVITY TO THE NATURE OF THE INCIPIENT VORTEX Ryan N. Maue* 1 and Robert E. Hart 1 1 Department of Meteorology, Florida State University 1. INTRODUCTION
This is a refereed journal and all articles are professionally screened and reviewed
 Advances in Environmental Biology, 5(10): 3425-3433, 2011 ISSN 1995-0756 3425 This is a refereed journal and all articles are professionally screened and reviewed ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Divergence Field
Advances in Environmental Biology, 5(10): 3425-3433, 2011 ISSN 1995-0756 3425 This is a refereed journal and all articles are professionally screened and reviewed ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Divergence Field
Quasi-Geostrophic Implications
 Chapter 10 Quasi-Geostrophic Implications When you look at a weather chart with all its isolines and plotted data, you need a framework upon which to interpret what you see. Quasi-geostrophic theory provides
Chapter 10 Quasi-Geostrophic Implications When you look at a weather chart with all its isolines and plotted data, you need a framework upon which to interpret what you see. Quasi-geostrophic theory provides
Examples of Pressure Gradient. Pressure Gradient Force. Chapter 7: Forces and Force Balances. Forces that Affect Atmospheric Motion 2/2/2015
 Chapter 7: Forces and Force Balances Forces that Affect Atmospheric Motion Fundamental force - Apparent force - Pressure gradient force Gravitational force Frictional force Centrifugal force Forces that
Chapter 7: Forces and Force Balances Forces that Affect Atmospheric Motion Fundamental force - Apparent force - Pressure gradient force Gravitational force Frictional force Centrifugal force Forces that
The Potential Role of a Stratospheric Intrusion in the March 7, 2004, High Wind Event
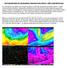 The Potential Role of a Stratospheric Intrusion in the March 7, 2004, High Wind Event Dry downbursts are rather rare in North Carolina, so the high wind event of Sunday, March 7, 2004, merits particular
The Potential Role of a Stratospheric Intrusion in the March 7, 2004, High Wind Event Dry downbursts are rather rare in North Carolina, so the high wind event of Sunday, March 7, 2004, merits particular
McGraw Hill Yearbook of Science & Technology Extratropical cyclone occlusion. McGraw Hill 2008 Yearbook of Science & Technology.
 McGraw Hill Yearbook of Science & Technology 0 Extratropical cyclone occlusion Journal: McGraw Hill 0 Yearbook of Science & Technology Manuscript ID: draft Manuscript Type: Date Submitted by the Author:
McGraw Hill Yearbook of Science & Technology 0 Extratropical cyclone occlusion Journal: McGraw Hill 0 Yearbook of Science & Technology Manuscript ID: draft Manuscript Type: Date Submitted by the Author:
Middle Latitude Cyclones a storm that forms at middle and high latitudes, outside of the tropics.
 Middle Latitude Cyclones a storm that forms at middle and high latitudes, outside of the tropics. Polar Front Theory a theory that explains the life cycle of mid latitude cyclones and their associated
Middle Latitude Cyclones a storm that forms at middle and high latitudes, outside of the tropics. Polar Front Theory a theory that explains the life cycle of mid latitude cyclones and their associated
Mesoscale analysis of a comma cloud observed during FASTEX
 Meteorol. Appl. 7, 129 134 (2000) Mesoscale analysis of a comma cloud observed during FASTEX K D Williams, Joint Centre for Mesoscale Meteorology, Department of Meteorology, University of Reading, PO Box
Meteorol. Appl. 7, 129 134 (2000) Mesoscale analysis of a comma cloud observed during FASTEX K D Williams, Joint Centre for Mesoscale Meteorology, Department of Meteorology, University of Reading, PO Box
Weather report 28 November 2017 Campinas/SP
 Weather report 28 November 2017 Campinas/SP Summary: 1) Synoptic analysis and pre-convective environment 2) Verification 1) Synoptic analysis and pre-convective environment: At 1200 UTC 28 November 2017
Weather report 28 November 2017 Campinas/SP Summary: 1) Synoptic analysis and pre-convective environment 2) Verification 1) Synoptic analysis and pre-convective environment: At 1200 UTC 28 November 2017
ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 11 Tropical Cyclones: Formation, Maintenance, and Intensification
 ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 11 Tropical Cyclones: Formation, Maintenance, and Intensification References: A Global View of Tropical Cyclones, Elsberry (ed.) Global Perspectives on Tropical Cylones:
ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 11 Tropical Cyclones: Formation, Maintenance, and Intensification References: A Global View of Tropical Cyclones, Elsberry (ed.) Global Perspectives on Tropical Cylones:
Synoptic Meteorology
 M.Sc. in Meteorology Synoptic Meteorology [MAPH P312] Prof Peter Lynch Second Semester, 2004 2005 Seminar Room Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield. Part 9 Extratropical Weather Systems These lectures
M.Sc. in Meteorology Synoptic Meteorology [MAPH P312] Prof Peter Lynch Second Semester, 2004 2005 Seminar Room Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield. Part 9 Extratropical Weather Systems These lectures
Diabatic processes and the structure of extratropical cyclones
 Geophysical and Nonlinear Fluid Dynamics Seminar AOPP, Oxford, 23 October 2012 Diabatic processes and the structure of extratropical cyclones Oscar Martínez-Alvarado R. Plant, J. Chagnon, S. Gray, J. Methven
Geophysical and Nonlinear Fluid Dynamics Seminar AOPP, Oxford, 23 October 2012 Diabatic processes and the structure of extratropical cyclones Oscar Martínez-Alvarado R. Plant, J. Chagnon, S. Gray, J. Methven
Transient and Eddy. Transient/Eddy Flux. Flux Components. Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance. Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean
 Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies Transient and Eddy Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean Eddy: deviations
Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies Transient and Eddy Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean Eddy: deviations
Lec 10: Interpreting Weather Maps
 Lec 10: Interpreting Weather Maps Case Study: October 2011 Nor easter FIU MET 3502 Synoptic Hurricane Forecasts Genesis: on large scale weather maps or satellite images, look for tropical waves (Africa
Lec 10: Interpreting Weather Maps Case Study: October 2011 Nor easter FIU MET 3502 Synoptic Hurricane Forecasts Genesis: on large scale weather maps or satellite images, look for tropical waves (Africa
ENSO, AO, and climate in Japan. 15 November 2016 Yoshinori Oikawa, Tokyo Climate Center, Japan Meteorological Agency
 ENSO, AO, and climate in Japan 15 November 2016 Yoshinori Oikawa, Tokyo Climate Center, Japan Meteorological Agency Aims of this lecture At the end of the yesterday s lecture, Hare-run said, - In the exercise
ENSO, AO, and climate in Japan 15 November 2016 Yoshinori Oikawa, Tokyo Climate Center, Japan Meteorological Agency Aims of this lecture At the end of the yesterday s lecture, Hare-run said, - In the exercise
AOSC201: Weather and Climate Lab
 AOSC201: Weather and Climate Lab Week 8: Forecasting - Analysis Section 107/108 Instructor: Agniv Sengupta q Lab #7 of Lab Manual (pages 41-49) q 50 points in total q INDIVIDUAL Work for the entire lab
AOSC201: Weather and Climate Lab Week 8: Forecasting - Analysis Section 107/108 Instructor: Agniv Sengupta q Lab #7 of Lab Manual (pages 41-49) q 50 points in total q INDIVIDUAL Work for the entire lab
11B.1 INFLUENCE OF DIABATIC POTENTIAL VORTICITY ANOMALIES UPON WARM CONVEYOR BELT FLOW. PART I: FEBRUARY 2003
 INFLUENCE OF DIABATIC POTENTIAL VORTICITY ANOMALIES UPON WARM CONVEYOR BELT FLOW. PART I: 14-15 FEBRUARY 2003 Philip N. Schumacher, NOAA/NWS, Sioux Falls, SD Joshua M. Boustead, NOAA/NWS, Valley, NE Martin
INFLUENCE OF DIABATIC POTENTIAL VORTICITY ANOMALIES UPON WARM CONVEYOR BELT FLOW. PART I: 14-15 FEBRUARY 2003 Philip N. Schumacher, NOAA/NWS, Sioux Falls, SD Joshua M. Boustead, NOAA/NWS, Valley, NE Martin
ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 7 Temperature, Clouds, and Rain
 ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 7 Temperature, Clouds, and Rain References: Forecaster s Guide to Tropical Meteorology (updated), Ramage Tropical Climatology, McGregor and Nieuwolt Climate and Weather
ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 7 Temperature, Clouds, and Rain References: Forecaster s Guide to Tropical Meteorology (updated), Ramage Tropical Climatology, McGregor and Nieuwolt Climate and Weather
The Planetary Circulation System
 12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
THE SYNOPTIC ENVIRONMENT OF THE 11 APRIL 2001 CENTRAL PLAINS TORNADO OUTBREAK VIEWED IN THREE DIMENSIONS
 P1.1 THE SYNOPTIC ENVIRONMENT OF THE 11 APRIL 2001 CENTRAL PLAINS TORNADO OUTBREAK VIEWED IN THREE DIMENSIONS Daniel D. Nietfeld * NOAA/NWS/WFO Omaha/Valley, NE 1. INTRODUCTION A powerful low pressure
P1.1 THE SYNOPTIC ENVIRONMENT OF THE 11 APRIL 2001 CENTRAL PLAINS TORNADO OUTBREAK VIEWED IN THREE DIMENSIONS Daniel D. Nietfeld * NOAA/NWS/WFO Omaha/Valley, NE 1. INTRODUCTION A powerful low pressure
5D.6 EASTERLY WAVE STRUCTURAL EVOLUTION OVER WEST AFRICA AND THE EAST ATLANTIC 1. INTRODUCTION 2. COMPOSITE GENERATION
 5D.6 EASTERLY WAVE STRUCTURAL EVOLUTION OVER WEST AFRICA AND THE EAST ATLANTIC Matthew A. Janiga* University at Albany, Albany, NY 1. INTRODUCTION African easterly waves (AEWs) are synoptic-scale disturbances
5D.6 EASTERLY WAVE STRUCTURAL EVOLUTION OVER WEST AFRICA AND THE EAST ATLANTIC Matthew A. Janiga* University at Albany, Albany, NY 1. INTRODUCTION African easterly waves (AEWs) are synoptic-scale disturbances
1. Rossby and Ertel 2. Conservation and invertibility - a useful combination 2.1 Action at a distance
 Met Office College - Course Notes Potential vorticity Contents 1. Rossby and Ertel 2. Conservation and invertibility - a useful combination 2.1 Action at a distance 3. Conceptual models of development
Met Office College - Course Notes Potential vorticity Contents 1. Rossby and Ertel 2. Conservation and invertibility - a useful combination 2.1 Action at a distance 3. Conceptual models of development
Mid-Latitude Dynamics and Atmospheric Rivers
 Mid-Latitude Dynamics and Atmospheric Rivers Session: Theory, Structure, Processes 1 Wednesday, 10 August 2016 Contribution from: Heini Werni Peter Knippertz Harold Sodemann Andreas Stohl Francina Dominguez
Mid-Latitude Dynamics and Atmospheric Rivers Session: Theory, Structure, Processes 1 Wednesday, 10 August 2016 Contribution from: Heini Werni Peter Knippertz Harold Sodemann Andreas Stohl Francina Dominguez
Mesoscale Frontal Waves Associated with Landfalling Atmospheric Rivers
 Mesoscale Frontal Waves Associated with Landfalling Atmospheric Rivers FIRO Science Task Group Workshop May 30, 2017 Andrew Martin, Brian Kawzenuk, Julie Kalansky, Anna Wilson, F. Martin Ralph Contacts:
Mesoscale Frontal Waves Associated with Landfalling Atmospheric Rivers FIRO Science Task Group Workshop May 30, 2017 Andrew Martin, Brian Kawzenuk, Julie Kalansky, Anna Wilson, F. Martin Ralph Contacts:
A polar low named Vera: the use of potential vorticity diagnostics to assess its development
 Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 137: 179 183, October 11 A A polar low named Vera: the use of potential vorticity diagnostics to assess its development Thor
Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 137: 179 183, October 11 A A polar low named Vera: the use of potential vorticity diagnostics to assess its development Thor
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) As the difference between the dewpoint temperature and the air temperature decreases, the probability of precipitation increases remains the same decreases 2) Which statement best explains why
Name: 1) As the difference between the dewpoint temperature and the air temperature decreases, the probability of precipitation increases remains the same decreases 2) Which statement best explains why
Low-level Jet(LLJ) and western Iran heavy rain: case study Dec 1991
 2011 2nd International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology IPCBEE vol.6 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Low-level Jet(LLJ) and western Iran heavy rain: case study Dec 1991 Elham Mobarak
2011 2nd International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology IPCBEE vol.6 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Low-level Jet(LLJ) and western Iran heavy rain: case study Dec 1991 Elham Mobarak
Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term may be used only once.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Air Masses Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term may be used only once. high pressure poles low pressure equator wind
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Air Masses Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term may be used only once. high pressure poles low pressure equator wind
Satellites, Weather and Climate Module??: Polar Vortex
 Satellites, Weather and Climate Module??: Polar Vortex SWAC Jan 2014 AKA Circumpolar Vortex Science or Hype? Will there be one this year? Today s objectives Pre and Post exams What is the Polar Vortex
Satellites, Weather and Climate Module??: Polar Vortex SWAC Jan 2014 AKA Circumpolar Vortex Science or Hype? Will there be one this year? Today s objectives Pre and Post exams What is the Polar Vortex
p = ρrt p = ρr d = T( q v ) dp dz = ρg
 Chapter 1: Properties of the Atmosphere What are the major chemical components of the atmosphere? Atmospheric Layers and their major characteristics: Troposphere, Stratosphere Mesosphere, Thermosphere
Chapter 1: Properties of the Atmosphere What are the major chemical components of the atmosphere? Atmospheric Layers and their major characteristics: Troposphere, Stratosphere Mesosphere, Thermosphere
14A.3 POTENTIAL VORTICITY AS A TOOL FOR ASSESSING DYNAMICAL IMPACTS OF LATENT HEAT RELEASE IN MODEL FORECASTS
 14A.3 POTENTIAL VORTICITY AS A TOOL FOR ASSESSING DYNAMICAL IMPACTS OF LATENT HEAT RELEASE IN MODEL FORECASTS Michael J.Brennan*, Gary M. Lackmann, and Kelly M. Mahoney North Carolina State University,
14A.3 POTENTIAL VORTICITY AS A TOOL FOR ASSESSING DYNAMICAL IMPACTS OF LATENT HEAT RELEASE IN MODEL FORECASTS Michael J.Brennan*, Gary M. Lackmann, and Kelly M. Mahoney North Carolina State University,
The Impact of the Extratropical Transition of Typhoon Dale (1996) on the Early Wintertime Stratospheric Circulation
 The Impact of the Extratropical Transition of Typhoon Dale (1996) on the Early 1996-97 Wintertime Stratospheric Circulation Andrea L. Lang 1, Jason M. Cordeira 2, Lance F. Bosart 1 and Daniel Keyser 1
The Impact of the Extratropical Transition of Typhoon Dale (1996) on the Early 1996-97 Wintertime Stratospheric Circulation Andrea L. Lang 1, Jason M. Cordeira 2, Lance F. Bosart 1 and Daniel Keyser 1
Energy Budget of a Mediterranean system affecting the weather of Saudi Arabia. A. K AL-Khalaf
 1 Energy Budget of a Mediterranean system affecting the weather of Saudi Arabia A. K AL-Khalaf Department of Meteorology, Faculty of Meteorology, Environment, and Arid Land Agriculture, King Abdulaziz
1 Energy Budget of a Mediterranean system affecting the weather of Saudi Arabia A. K AL-Khalaf Department of Meteorology, Faculty of Meteorology, Environment, and Arid Land Agriculture, King Abdulaziz
ATM OCN 452. The Frontal Cyclone. Fall 2013
 ATM OCN 452 The Frontal Cyclone Fall 2013 Instructor: Dr. Jonathan E. Martin 1425A Meteorology and Space Science jemarti1@wisc.edu 262-9845 Office Hours: Wed. 12:30 2:25 (or by appointment) T. A.: Andrew
ATM OCN 452 The Frontal Cyclone Fall 2013 Instructor: Dr. Jonathan E. Martin 1425A Meteorology and Space Science jemarti1@wisc.edu 262-9845 Office Hours: Wed. 12:30 2:25 (or by appointment) T. A.: Andrew
Scale Interactions during the Formation of Typhoon Irving 边建谱 ELIZABETH A. RITCHIE GREG J. HOLLAND
 Scale Interactions during the Formation of Typhoon Irving 边建谱 ELIZABETH A. RITCHIE GREG J. HOLLAND Pre-research Fujiwhara: laboratory experiments in water (1921, 1923, 1931). Cloud clusters are a well-known
Scale Interactions during the Formation of Typhoon Irving 边建谱 ELIZABETH A. RITCHIE GREG J. HOLLAND Pre-research Fujiwhara: laboratory experiments in water (1921, 1923, 1931). Cloud clusters are a well-known
Synoptic Meteorology II: Frontogenesis Examples Figure 1
 Synoptic Meteorology II: Frontogenesis Examples The below images, taken from the 1200 UTC 17 January 2019 GFS forecast run, provide examples of the contributions of deformation and divergence to frontogenesis.
Synoptic Meteorology II: Frontogenesis Examples The below images, taken from the 1200 UTC 17 January 2019 GFS forecast run, provide examples of the contributions of deformation and divergence to frontogenesis.
Fixed Rossby Waves: Quasigeostrophic Explanations and Conservation of Potential Vorticity
 Fixed Rossby Waves: Quasigeostrophic Explanations and Conservation of Potential Vorticity 1. Observed Planetary Wave Patterns After upper air observations became routine, it became easy to produce contour
Fixed Rossby Waves: Quasigeostrophic Explanations and Conservation of Potential Vorticity 1. Observed Planetary Wave Patterns After upper air observations became routine, it became easy to produce contour
4/29/2011. Mid-latitude cyclones form along a
 Chapter 10: Cyclones: East of the Rocky Mountain Extratropical Cyclones Environment prior to the development of the Cyclone Initial Development of the Extratropical Cyclone Early Weather Along the Fronts
Chapter 10: Cyclones: East of the Rocky Mountain Extratropical Cyclones Environment prior to the development of the Cyclone Initial Development of the Extratropical Cyclone Early Weather Along the Fronts
Isentropic Thinking & Airstreams Analysis
 Isentropic Thinking & Airstreams Analysis Drs. James T. Moore & Sam Ng Saint Louis University & Metropolitan State College of Denver Utility of Isentropic Analysis Diagnose and visualize vertical motion
Isentropic Thinking & Airstreams Analysis Drs. James T. Moore & Sam Ng Saint Louis University & Metropolitan State College of Denver Utility of Isentropic Analysis Diagnose and visualize vertical motion
Numerical Prediction of the Heavy Rainfall Vortex Over Eastern Asia Monsoon Region
 730 Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan Vol. 62, No. 5 Numerical Prediction of the Heavy Rainfall Vortex Over Eastern Asia Monsoon Region By Shou-Jun Chen* and Lorenzo Dell'Osso European Centre
730 Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan Vol. 62, No. 5 Numerical Prediction of the Heavy Rainfall Vortex Over Eastern Asia Monsoon Region By Shou-Jun Chen* and Lorenzo Dell'Osso European Centre
A Cyclogenesis south of the Alps. Manfred Kurz Neustadt/Weinstraße
 A Cyclogenesis south of the Alps Manfred Kurz Neustadt/Weinstraße A cyclogenesis south of the Alps Surface maps 06-11-99, 00 UTC The occluded frontal system of a quasi-stationary low above the North Sea
A Cyclogenesis south of the Alps Manfred Kurz Neustadt/Weinstraße A cyclogenesis south of the Alps Surface maps 06-11-99, 00 UTC The occluded frontal system of a quasi-stationary low above the North Sea
ATMOSPHERIC MODELLING. GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 9 Ahrens: Chapter 13; A&B: Chapters 12 and 13
 ATMOSPHERIC MODELLING GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 9 Ahrens: Chapter 13; A&B: Chapters 12 and 13 Agenda for February 3 Assignment 3: Due on Friday Lecture Outline Numerical modelling Long-range forecasts Oscillations
ATMOSPHERIC MODELLING GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 9 Ahrens: Chapter 13; A&B: Chapters 12 and 13 Agenda for February 3 Assignment 3: Due on Friday Lecture Outline Numerical modelling Long-range forecasts Oscillations
Boundary layer controls on extratropical cyclone development
 Boundary layer controls on extratropical cyclone development R. S. Plant (With thanks to: I. A. Boutle and S. E. Belcher) 28th May 2010 University of East Anglia Outline Introduction and background Baroclinic
Boundary layer controls on extratropical cyclone development R. S. Plant (With thanks to: I. A. Boutle and S. E. Belcher) 28th May 2010 University of East Anglia Outline Introduction and background Baroclinic
POTENTIAL VORTICITY DYNAMICS AND TROPOPAUSE FOLD
 POTENTIAL VORTICITY DYNAMICS AND TROPOPAUSE FOLD M.D. ANDREI 1,2, M. PIETRISI 1,2, S. STEFAN 1 1 University of Bucharest, Faculty of Physics, P.O.BOX MG 11, Magurele, Bucharest, Romania Emails: meda.georgescu@gmail.com;
POTENTIAL VORTICITY DYNAMICS AND TROPOPAUSE FOLD M.D. ANDREI 1,2, M. PIETRISI 1,2, S. STEFAN 1 1 University of Bucharest, Faculty of Physics, P.O.BOX MG 11, Magurele, Bucharest, Romania Emails: meda.georgescu@gmail.com;
Lecture 14. Extratropical Cyclones extratropical cyclone
 Lecture 14. Extratropical Cyclones In mid-latitudes, much of our weather is associated with a particular kind of storm, the extratropical cyclone Cyclone: circulation around low pressure center Some midwesterners
Lecture 14. Extratropical Cyclones In mid-latitudes, much of our weather is associated with a particular kind of storm, the extratropical cyclone Cyclone: circulation around low pressure center Some midwesterners
Measurement of Rotation. Circulation. Example. Lecture 4: Circulation and Vorticity 1/31/2017
 Lecture 4: Circulation and Vorticity Measurement of Rotation Circulation Bjerknes Circulation Theorem Vorticity Potential Vorticity Conservation of Potential Vorticity Circulation and vorticity are the
Lecture 4: Circulation and Vorticity Measurement of Rotation Circulation Bjerknes Circulation Theorem Vorticity Potential Vorticity Conservation of Potential Vorticity Circulation and vorticity are the
Characteristic blocking events over Ural-Siberia in Boreal Winter under Present and Future Climate Conditions
 Characteristic blocking events over Ural-Siberia in Boreal Winter under Present and Future Climate Conditions Wen Zhou & Hoffman Cheung Guy Carpenter Asia-Pacific Climate Impact Center School of Energy
Characteristic blocking events over Ural-Siberia in Boreal Winter under Present and Future Climate Conditions Wen Zhou & Hoffman Cheung Guy Carpenter Asia-Pacific Climate Impact Center School of Energy
Observation Homework Due 11/24. Previous Lecture. Midlatitude Cyclones
 Lecture 21 Midlatitude Cyclones Observation Homework Due 11/24 1 2 Midlatitude Cyclones Midlatitude Cyclone or Winter Storm Cyclogenesis Energy Source Life Cycle Air Streams Vertical Structure Storm Hazards
Lecture 21 Midlatitude Cyclones Observation Homework Due 11/24 1 2 Midlatitude Cyclones Midlatitude Cyclone or Winter Storm Cyclogenesis Energy Source Life Cycle Air Streams Vertical Structure Storm Hazards
Science Olympiad Meteorology Quiz #1 Page 1 of 7
 1) What is generally true about the stratosphere: a) Has turbulent updrafts and downdrafts. b) Has either a stable or increasing temperature profile with altitude. c) Where the auroras occur. d) Both a)
1) What is generally true about the stratosphere: a) Has turbulent updrafts and downdrafts. b) Has either a stable or increasing temperature profile with altitude. c) Where the auroras occur. d) Both a)
Polar Front Theory. Cyclogenesis. Day 1. Days 2-5. What Happens Aloft. Up Above
 Cyclogenesis Tor Bergeron lecturing Mid latitude cyclones are born on the Polar Front as a developing wave Theory of cyclogenesis (formation of cyclones) first developed by the Norwegian meteorologists
Cyclogenesis Tor Bergeron lecturing Mid latitude cyclones are born on the Polar Front as a developing wave Theory of cyclogenesis (formation of cyclones) first developed by the Norwegian meteorologists
Dynamics and Kinematics
 Geophysics Fluid Dynamics () Syllabus Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3,
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics () Syllabus Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3,
Why rainfall may reduce when the ocean warms
 Why rainfall may reduce when the ocean warms Tim Hewson*, Ian Boutle** and Benedetta Dini** *ECMWF, Reading, UK **Met Office, Exeter, UK Work mainly undertaken at the Met Office Slide 1 Contents Introduction
Why rainfall may reduce when the ocean warms Tim Hewson*, Ian Boutle** and Benedetta Dini** *ECMWF, Reading, UK **Met Office, Exeter, UK Work mainly undertaken at the Met Office Slide 1 Contents Introduction
Global Wind Patterns
 Name: Earth Science: Date: Period: Global Wind Patterns 1. Which factor causes global wind patterns? a. changes in the distance between Earth and the Moon b. unequal heating of Earth s surface by the Sun
Name: Earth Science: Date: Period: Global Wind Patterns 1. Which factor causes global wind patterns? a. changes in the distance between Earth and the Moon b. unequal heating of Earth s surface by the Sun
The Morphology of Northern Hemisphere Blocking
 MAY 2008 T Y R L I S A N D H O S K I N S 1653 The Morphology of Northern Hemisphere Blocking E. TYRLIS AND B. J. HOSKINS Department of Meteorology, University of Reading, Reading, United Kingdom (Manuscript
MAY 2008 T Y R L I S A N D H O S K I N S 1653 The Morphology of Northern Hemisphere Blocking E. TYRLIS AND B. J. HOSKINS Department of Meteorology, University of Reading, Reading, United Kingdom (Manuscript
