WARM SECTOR TORNADOES WITHOUT DISCERNIBLE SURFACE BOUNDARIES AND WITH MINIMAL DEEP LAYER SHEA
|
|
|
- August Willis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2.1 WARM SECTOR TORNADOES WITHOUT DISCERNIBLE SURFACE BOUNDARIES AND WITH MINIMAL DEEP LAYER SHEA * Joshua M. Boustead and Philip N. Schumacher National Weaer Service Sioux Falls, SD 1. INTRODUCTION On 24 June 2003 an outbreak of tornadoes affected e states of Nebraska, Iowa, Minnesota and Sou Dakota. Of e 100 tornadoes at occurred, 91 of e tornadoes were weak (F1 or less; Fujita 1971), e strongest tornado, rated F4, destroyed e town of Manchester, Sou Dakota. The state of Sou Dakota recorded a record 67 tornadoes, of which 64 occurred in e county warning area (CWA) of e National Weaer Service (NWS) in Sioux Falls, SD (FSD) (Fig. 1). This outbreak is an example of an extreme local tornado outbreak. All of e tornadoes occurred wiin a 6 hour period from near 2200 UTC 24 June rough 0400 UTC 25 June. This significant of a tornado outbreak not only presents a danger to life and property in e local area, but also presents workload and resources problem to e NWS bo staffing during e event and during post-event survey and documentation. In addition to e number of tornadoes in a short period of time, e environment in which e parent supercells developed varied across e FSD CWA. A significant number of e tornadoes reported on 24 June occurred wi four cyclonic supercells at occurred in e warm sector. These supercells produced tornadoes in an environment at only weakly supported supercell potential. The NWS FSD CWA can be divided into 3 distinct environments during e 24 June outbreak (Fig. 2). Area #1 favored e more classic and persistent supercells, while area #2 supported multi-celled understorms and high precipitation supercells, and was e source region of an intense squall line which became dominate later in e event. The environment in area #3 produced a number of cyclonic and anticyclone warm-sector supercells wi numerous tornadoes. This note will compare e mode of convection and resultant severe weaer in areas of #1 and #3. spreading large-scale adiabatic vertical motion across eastern Sou Dakota and Nebraska during e afternoon hours of 24 June. Figure 1. County warning area of e National Weaer Service in Sioux Falls, SD. The atmosphere across eastern Sou Dakota and Nebraska became extremely unstable during e afternoon wi good insolation and steep 700 to 500 hpa lapse rates of 7.5 C km. Observed upper air soundings from bo Omaha, Nebraska (OAX) and Aberdeen, Sou Dakota (ABR) indicated ese steep lapse rates at bo 1800 UTC 24 June and 0000 UTC 25 June (Fig. 5). ABR is located on e cool side of e synoptic surface boundary and is stable when lifting a 100 hpa mixed-layer (ML) parcel. However, wi steep mid tropospheric lapse rates, ere is 2000 J kg of convective available potential energy (CAPE) wi parcels 2. Synoptic Environment The large-scale environment at 1200 UTC 24 June indicated a long-wave trough over e western United States (Fig. 3). A number of short-wave troughs were embedded in e broad souwest flow across e central and western United States. The short-wave located from Wyoming to noreast Colorado at 1200 UTC lifted into souern Sou Dakota by 0000 UTC 25 June (Fig. 4). This short-wave was responsible for Figure 2. Environmental areas of e FSD CWA during e 24 June tornado outbreak. * Corresponding auor address:26 Weaer Lane, Sioux Falls, SD 57104; ; joshboustead@noaa.gov
2 lifted from 800 hpa at 0000 UTC. The OAX sounding is located wiin e warm sector of e surface cyclone. The amount of boundary layer deepening and lift from 1800 to 0000 UTC is visible when e soundings are compared. A parcel would lift wiout restraint to e level of free convection (LFC) wi a surface temperature and dewpoint of 33 C and 21 C respectively. These surface conditions would yield a MLCAPE of 4300 J kg wi near 0 J kg of convective inhibition (CIN). Thus e warm sector ahead of e surface cyclone and upper-level disturbance was unstable and only weakly capped as e temperatures across Nebraska and eastern Sou Dakota climbed into e 30 to 33 C range wi surface dewpoint temperatures around 24 C. Figure UTC 24 June subjective 500 hpa analysis. Thick dark contours are heights ever 30 meters and labeled ever 60 meters. Short-dashed light lines are temperatures in C ever 2 C and labeled ever 4 C. Dotted line indicates position of short-wave trough. Also visible in e observed soundings is e increased gradient in deep-layer shear from ABR to OAX. At OAX e boundary-layer (500 m) to 6 km (hereafter BL-6km) shear increased from 16 ms at 1800 UTC 24 June to 18 ms at 0000 UTC 25 June. The shear at ABR increased from 30 ms at 1800 UTC to 37 ms at 0000 UTC. This increased gradient was a response to a short-wave ridge at moved over eastern Nebraska during e afternoon, while e Wyoming shortwave moved into Sou Dakota. Using e Neligh, Nebraska (NLG) wind profiler, e velocity azimual display (VAD) wind profilers from Nor Platte, Nebraska (LBF) and FSD weaer surveillance radar (WSR) 1988-Doppler (WSR-88D), as well as e 0000 UTC 25 June RUC analysis (not shown), e eastward extent of e 15 ms BL-6km isoshear can be plotted. The 15 ms isoshear extended from noreast Nebraska into souwest Minnesota (Fig. 6), which created a significant gradient in expected storm type and longevity across e FSD CWA. This gradient was responsible for e 3 modes of convection observed across e FSD CWA on 24 June. Figure 4. Same as figure 3 for 0000 UTC 25 June. 3. Mesoscale Environment Figure 5. Observed upper air soundings from Omaha, NE (A) and Aberdeen, SD (B). Short-dashed line is e 1800 UTC 24 June sounding and e ick dark line is e 0000 UTC 25 June soudning. Wind position one is 1800 UTC and wind position two is 0000 UTC. A true mesoscale (Orlanski 1975) analysis cannot be conducted e on 24 June tornado outbreak due to an average of 95 km space between observation points across e FSD CWA. Nevereless, wi e help of satellite and radar data (not shown), a near mesoscale analysis can be performed. In addition, wi e use of observed upper air soundings, e wind profiler network, VAD wind profilers, and model analysis
3 Figure UTC 25 June subjective BL-6km isoshear analysis. Contours are in ms ever 5 ms and labeled ever 10 ms. Figure 8. Same as figure 7 for 2100 UTC 24 June. fields, hodographs can be constructed to represent e 3 different sectors across e FSD CWA. The 1800 UTC 24 June subjective surface analysis is presented in figure 7. The synoptic warm front extended from a surface low in Nebraska across soueast Sou Dakota into souwest Minnesota. A secondary warm front induced from Figure 9. Same as figure 7 for 0000 UTC 25 June. indicated at as e Wyoming short-wave approached, WAA allowed for quick recovery of e warm sector. By 2100 UTC ere appears to be a lack of discernible surface boundaries across e warm-sector, and is is also supported by radar and satellite imagery (not shown). Figure UTC subjective surface analysis. Thick contour are isobars measured ever 1 hpa and labeled ever 2 hpa. Station plots temperature and dewpoint are in C. Wind barbs are in ms wi a short-barb being 5 ms and a long barb being 10 ms. nocturnal convection extended across eastern Nebraska and western Iowa. By 2100 UTC (Fig. 8) e surface low had lifted into soueast Sou Dakota in response to e advance of e Wyoming short-wave. The warm sector had quickly recovered from e nocturnal convection wi e souern warm front losing definition in e deep warm air advection (WAA) regime. At 0000 UTC 25 June e surface low was located over soueast Sou Dakota wi e synoptic warm front extending from e low into central Minnesota (Fig. 9). The majority of e FSD CWA was now in e warm sector of e surface cyclone. The evolution of e surface analyses Figure 10 is a hodograph constructed in area #1 at 0000 UTC 24 June. This hodograph indicated a number of characteristics at have been identified as favorable for potential supercell and tornadogenesis. Rasmussen and Blanchard (1998) published a baseline climatology of severe weaer parameters which can help forecasters anticipate e mode of convection and potential for tornadoes. The BL-6km shear in figure 10 indicates a strong potential for supercell understorms. Later research by Rasmussen (2003) indicated at storm-relative helicity (SRH; Davies-Jones et al. 1990) integrated in e lowest 1 km is a good indicator of tornadic supercells. The SRH 2-2 computed for e 0 to 1 km layer in area #1 was 140 m s, which is above e 50 percentile found in e Rasmussen study. The combination of strong deep-layer shear, strong low-level SRH and sufficient instability led to e development of classic supercells and associated strong tornadoes in is area.
4 Figure 11 is e hodograph from area #2 of e FSD CWA. In is area, four cyclonic supercells were responsible for 31 of e total tornadoes wi two of ese tornadoes reaching F2 streng. BL-6km shear for is sounding is 16 ms, wi a significant portion of is shear associated wi mid-level directional shear. Thunderstorms at developed in is region were able to develop a mid-level mesocyclone but were relatively short-lived wi no supercell lasting longer an 1 hour. Alough e BL-6km shear indicates some supercell potential, ere is a lack of directional shear in e lowest 1 km of e hodograph. SRH integrated in e lowest 1 km 2-2 computed wi storm motion is only 9 m s. This is well below e 25 percentile at Rasmussen indicated in As indicated in e subjective surface analysis, ere also appeared to be a lack of discernable surface boundaries wi which understorms could interact to increase e low-level SRH. This has been shown to be helpful in situations ere is Figure 11. Same as figure 10 for area #3 of e FSD CWA. Figure UTC hodograph from area #1 of e FSD CWA. Wind is in ms. a lack of very strong ambient shear (Markowski et al. 1998). It appears ese short-lived supercells were able to produce a significant number of tornadoes, wi two being in e strong category (F2), by a combination of significant speed shear in e lowest 2 km and a significant amount of instability in e lowest 3 km. The amount of speed shear in e lowest 2 km of e hodograph in area #3 is 13 ms. The quantity of speed shear significantly increases after 0000 UTC 25 June as e nocturnal plains low-level jet developed. A RUC analysis sounding at 0000 UTC from area #2 indicates near 135 J kg of CAPE, which is above e 75 percentile found in e Rasmussen (1998) study to be supportive of tornadic supercells. The combination of e understorms remaining surface-based as e low-level jet increased and e degree of lower level instability led to e ability of e supercells in is area to produce tornadoes, even wi a lack of discernable low-level boundaries. 4. Conclusion The tornado outbreak on 24 June 2004 is important for a number of reasons. First, is is a case of an extreme local outbreak wi a significant number of tornadoes. This amount of severe weaer in a local WFO CWA can be difficult to handle during and after e event. Second, ere appears to be a large number of tornadoes at occurred in e warm sector wi a lack of strong BL-6km shear and no discernable surface boundaries. Finally, is presents a significant forecast challenge to local and national forecasters to anticipate such an event. On 24 June 2004 supercells developed in an environment at was not supportive of long-lived supercells wi strong tornadoes. These supercells produced a significant amount of e tornadoes on 24 June, wi two of e tornadoes reaching F2 streng. The anticipation of environments at can produce is type of supercell is not well understood. There appeared to be sufficient lower level instability and speed shear in e lowest 3 and 2 km respectively to overcome e lack of significant SRH in e 0 to 1 km layer. Thus e short-lived supercells also were able to produce tornadoes wiout discernable surface boundaries. Thus in e warm season, when extreme instability is expected, it is important to also anticipate if warm sector understorms will be able to ingest surface parcels once insolation decreases and e nocturnal low-level jet increases and e low-level speed shear increases significantly. During e 24 June event ere were 3 distinct environments in which understorms were developing in e FSD CWA. Each individual warning forecaster needed to be award of how e environment in eir area is evolving, and how is affects e mode of convection and resultant severe weaer at could expected. This
5 emphasizes e need for detailed mesoscale analysis during convective events. 5. References Davies-Jones, R.P., D. Burgess, and M. Foster, 1990: Test of helicity as a tornado forecast parameter. Preprints, 16 Conf. On Severe Local Storms, Kananaskis Park, AB, Canada, Amer. Meteor. Soc., Fujita, T. T., 1971: Proposed characterization of tornadoes and hurricanes by area and intensity. Satellite and Meteor. Res. Project. Department of Geophy. Sci., The University of Chicago., 42. Orlanski, I., 1975: A rational subdivision of scale for atmospheric processes. Bull. Amer.Meteor. Soc., 56, Rasmussen, E. A., Blanchard, D. O., 1998: A baseline climatology of sounding-derived supercell and tornado forecast parameters. Wea. Forecasting, 13, , 2003: Refined supercell and tornado forecast parameters. Wea.Forecasting, 5,
P3.17 THE DEVELOPMENT OF MULTIPLE LOW-LEVEL MESOCYCLONES WITHIN A SUPERCELL. Joshua M. Boustead *1 NOAA/NWS Weather Forecast Office, Topeka, KS
 P3.17 THE DEVELOPMENT OF MULTIPLE LOW-LEVEL MESOCYCLONES WITHIN A SUPERCELL Joshua M. Boustead *1 NOAA/NWS Weather Forecast Office, Topeka, KS Philip N. Schumacher NOAA/NWS Weather Forecaster Office, Sioux
P3.17 THE DEVELOPMENT OF MULTIPLE LOW-LEVEL MESOCYCLONES WITHIN A SUPERCELL Joshua M. Boustead *1 NOAA/NWS Weather Forecast Office, Topeka, KS Philip N. Schumacher NOAA/NWS Weather Forecaster Office, Sioux
Joshua M. Boustead *1, and Barbara E. Mayes NOAA/NWS WFO Omaha/Valley, NE. William Gargan, George Phillips, and Jared Leighton NOAA/NWS WFO Topeka, KS
 7B.3 Composite Analysis of Environmental Conditions Favorable for Significant Tornadoes across Eastern Kansas Joshua M. Boustead *1, and Barbara E. Mayes NOAA/NWS WFO Omaha/Valley, NE William Gargan, George
7B.3 Composite Analysis of Environmental Conditions Favorable for Significant Tornadoes across Eastern Kansas Joshua M. Boustead *1, and Barbara E. Mayes NOAA/NWS WFO Omaha/Valley, NE William Gargan, George
Identification of Inhibiting Factors of a Null Significant Tornado Event
 Identification of Inhibiting Factors of a Null Significant Tornado Event Joshua M. Boustead National Weather Service Forecast Office Omaha, Nebraska Philip N. Schumacher National Weather Service Forecast
Identification of Inhibiting Factors of a Null Significant Tornado Event Joshua M. Boustead National Weather Service Forecast Office Omaha, Nebraska Philip N. Schumacher National Weather Service Forecast
Jonathan M. Davies* Private Meteorologist, Wichita, Kansas
 4.3 RUC Soundings with Cool Season Tornadoes in Small CAPE Settings and the 6 November 2005 Evansville, Indiana Tornado Jonathan M. Davies* Private Meteorologist, Wichita, Kansas 1. Introduction Several
4.3 RUC Soundings with Cool Season Tornadoes in Small CAPE Settings and the 6 November 2005 Evansville, Indiana Tornado Jonathan M. Davies* Private Meteorologist, Wichita, Kansas 1. Introduction Several
Boundary-layer Decoupling Affects on Tornadoes
 Boundary-layer Decoupling Affects on Tornadoes Chris Karstens ABSTRACT The North American low-level jet is known to have substantial impacts on the climatology of central and eastern regions of the United
Boundary-layer Decoupling Affects on Tornadoes Chris Karstens ABSTRACT The North American low-level jet is known to have substantial impacts on the climatology of central and eastern regions of the United
Environmental Characteristics Associated with Nighttime Tornadoes
 National Weather Association, Electronic Journal of Operational Meteorology, 2009-EJ3 Environmental Characteristics Associated with Nighttime Tornadoes Jonathan M. Davies Private Meteorologist, Trimble/Kansas
National Weather Association, Electronic Journal of Operational Meteorology, 2009-EJ3 Environmental Characteristics Associated with Nighttime Tornadoes Jonathan M. Davies Private Meteorologist, Trimble/Kansas
P1.3 Tornadoes in a Deceptively Small CAPE Environment: The 4/20/04 Outbreak in Illinois and Indiana
 P1.3 Tornadoes in a Deceptively Small CAPE Environment: The 4/20/04 Outbreak in Illinois and Indiana Albert E. Pietrycha* Jonathan M. Davies #, Mark Ratzer*, and Paul Merzlock* *National Weather Service,
P1.3 Tornadoes in a Deceptively Small CAPE Environment: The 4/20/04 Outbreak in Illinois and Indiana Albert E. Pietrycha* Jonathan M. Davies #, Mark Ratzer*, and Paul Merzlock* *National Weather Service,
Hurricane and Tropical Cyclone Tornado Environments from RUC Proximity Soundings
 P8.1 Hurricane and Tropical Cyclone Tornado Environments from RUC Proximity Soundings Jonathan M. Davies* Private Meteorologist, Wichita, Kansas 1. Introduction Studies such as those by McCaul (1991, 1996)
P8.1 Hurricane and Tropical Cyclone Tornado Environments from RUC Proximity Soundings Jonathan M. Davies* Private Meteorologist, Wichita, Kansas 1. Introduction Studies such as those by McCaul (1991, 1996)
David O. Blanchard* and Brian A. Klimowski National Weather Service, Flagstaff, Arizona
 P12.1 SUPERCE EVOUTION IN ENVIRONMENTS WITH UNUSUA HODOGRAPHS David O. Blanchard* and Brian A. Klimowski National Weather Service, Flagstaff, Arizona 1. INTRODUCTION The events that transpired across northern
P12.1 SUPERCE EVOUTION IN ENVIRONMENTS WITH UNUSUA HODOGRAPHS David O. Blanchard* and Brian A. Klimowski National Weather Service, Flagstaff, Arizona 1. INTRODUCTION The events that transpired across northern
A DETAILED ANALYSIS OF THE NOCTURNAL QLCS TORNADOES THAT MOVED THROUGH OMAHA, NEBRASKA, ON 8 JUNE 2008
 JP1.10 A DETAILED ANALYSIS OF THE NOCTURNAL QLCS TORNADOES THAT MOVED THROUGH OMAHA, NEBRASKA, ON 8 JUNE 2008 Barbara E. Mayes *1, Jason T. Martinelli #, and Daniel Nietfeld * * National Weather Service
JP1.10 A DETAILED ANALYSIS OF THE NOCTURNAL QLCS TORNADOES THAT MOVED THROUGH OMAHA, NEBRASKA, ON 8 JUNE 2008 Barbara E. Mayes *1, Jason T. Martinelli #, and Daniel Nietfeld * * National Weather Service
Tornadogenesis in Supercells: The Three Main Ingredients. Ted Funk
 Tornadogenesis in Supercells: The Three Main Ingredients Ted Funk NWS Louisville, KY Spring 2002 Environmental Parameters Supercells occur within environments exhibiting several wellknown characteristics
Tornadogenesis in Supercells: The Three Main Ingredients Ted Funk NWS Louisville, KY Spring 2002 Environmental Parameters Supercells occur within environments exhibiting several wellknown characteristics
P12.14 A SOUNDING-DERIVED CLIMATOLOGY OF SIGNIFICANT TORNADO EVENTS IN THE GREENVILLE-SPARTANBURG, SOUTH CAROLINA COUNTY WARNING AREA ( )
 P12.14 A SOUNDING-DERIVED CIMATOOGY OF SIGNIFICANT TORNADO EVENTS IN THE GREENVIE-SPARTANBURG, SOUTH CAROINA COUNTY WARNING AREA (1948-26) Justin D. ane* NOAA/National Weather Service Greer, South Carolina
P12.14 A SOUNDING-DERIVED CIMATOOGY OF SIGNIFICANT TORNADO EVENTS IN THE GREENVIE-SPARTANBURG, SOUTH CAROINA COUNTY WARNING AREA (1948-26) Justin D. ane* NOAA/National Weather Service Greer, South Carolina
Evolution and Maintenance of the June 2003 Nocturnal Convection
 Evolution and Maintenance of the 22-23 June 2003 Nocturnal Convection Jerilyn Billings NOAA/NWS Wichita, KS August 6 th, 2011 Work Completed at North Carolina State University for MS Thesis During the
Evolution and Maintenance of the 22-23 June 2003 Nocturnal Convection Jerilyn Billings NOAA/NWS Wichita, KS August 6 th, 2011 Work Completed at North Carolina State University for MS Thesis During the
The Father s Day 2002 Severe Weather Outbreak across New York and Western New England
 P 1.5 22nd Conference on Severe Local Storms Hyannis, MA, 4-8 October 2004 The Father s Day 2002 Severe Weather Outbreak across New York and Western New England Thomas A. Wasula NOAA/National Weather Service,
P 1.5 22nd Conference on Severe Local Storms Hyannis, MA, 4-8 October 2004 The Father s Day 2002 Severe Weather Outbreak across New York and Western New England Thomas A. Wasula NOAA/National Weather Service,
Joshua M. Boustead *1 NOAA/NWS WFO Omaha/Valley, NE. Philip N. Schumacher NOAA/NWS WFO Sioux Falls, SD
 11B.2 Influence of Diabatic Potential Vorticity Anomalies upon Warm Conveyor Belt Flow. Part II: 3-5 January 2005 Joshua M. Boustead *1 NOAA/NWS WFO Omaha/Valley, NE Philip N. Schumacher NOAA/NWS WFO Sioux
11B.2 Influence of Diabatic Potential Vorticity Anomalies upon Warm Conveyor Belt Flow. Part II: 3-5 January 2005 Joshua M. Boustead *1 NOAA/NWS WFO Omaha/Valley, NE Philip N. Schumacher NOAA/NWS WFO Sioux
P4.9 THE SEVERE THUNDERSTORM OUTBREAK IN FINLAND ON 5 JULY 2002
 P4.9 THE SEVERE THUNDERSTORM OUTBREAK IN FINLAND ON 5 JULY 2002 Ari-Juhani Punkka* and Jenni Teittinen Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki, Finland 1. INTRODUCTION On 5 July 2002 a fast propagating
P4.9 THE SEVERE THUNDERSTORM OUTBREAK IN FINLAND ON 5 JULY 2002 Ari-Juhani Punkka* and Jenni Teittinen Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki, Finland 1. INTRODUCTION On 5 July 2002 a fast propagating
Summary of November Central U.S. Winter Storm By Christopher Hedge
 Summary of November 12-13 2010 Central U.S. Winter Storm By Christopher Hedge Event Overview The first significant snowfall of the 2010-2011 season affected portions of the plains and upper Mississippi
Summary of November 12-13 2010 Central U.S. Winter Storm By Christopher Hedge Event Overview The first significant snowfall of the 2010-2011 season affected portions of the plains and upper Mississippi
A Detailed Analysis of a Long-Tracked Supercell. Jason T. Martinelli and Andrew Elliott. Fred Glass
 A Detailed Analysis of a Long-Tracked Supercell Jason T. Martinelli and Andrew Elliott Department of Atmospheric Sciences, Creighton University, Omaha, Nebraska Fred Glass National Weather Service Forecast
A Detailed Analysis of a Long-Tracked Supercell Jason T. Martinelli and Andrew Elliott Department of Atmospheric Sciences, Creighton University, Omaha, Nebraska Fred Glass National Weather Service Forecast
Storm-Relative Flow and its Relationship to Low-Level Vorticity in Simulated Storms
 TH CONF. ON SEVERE LOCAL STORMS, 15. 1 Storm-Relative Flow and its Relationship to Low-Level Vorticity in Simulated Storms Cody Kirkpatrick University of Alabama in Huntsville Eugene W. McCaul, Jr. Universities
TH CONF. ON SEVERE LOCAL STORMS, 15. 1 Storm-Relative Flow and its Relationship to Low-Level Vorticity in Simulated Storms Cody Kirkpatrick University of Alabama in Huntsville Eugene W. McCaul, Jr. Universities
David G. Biggar. National Weather Service Forecast Office, Jackson, Mississippi
 A CASE STUDY OF A POSITIVE STRIKE DOMINATED SUPERCELL THUNDERSTORM THAT PRODUCED AN F2 TORNADO AFTER UNDERGOING A SIGNIFICANT CLOUD-TO-GROUND LIGHTNING POLARITY SHIFT Abstract David G. Biggar National
A CASE STUDY OF A POSITIVE STRIKE DOMINATED SUPERCELL THUNDERSTORM THAT PRODUCED AN F2 TORNADO AFTER UNDERGOING A SIGNIFICANT CLOUD-TO-GROUND LIGHTNING POLARITY SHIFT Abstract David G. Biggar National
Comparison of November 15, 2008 Killer Tornado Outbreak with the December 2, 2009 Non Tornado Event
 Comparison of November 15, 2008 Killer Tornado Outbreak with the December 2, 2009 Non Tornado Event The two events featured similar patterns but with much different results in central NC. The slides on
Comparison of November 15, 2008 Killer Tornado Outbreak with the December 2, 2009 Non Tornado Event The two events featured similar patterns but with much different results in central NC. The slides on
WISCONSIN TORNADO OUTBREAK OF 18 AUGUST 2005: AN EXAMINATION OF THE VIOLA, WISCONSIN TORNADO
 WISCONSIN TORNADO OUTBREAK OF 18 AUGUST 2005: AN EXAMINATION OF THE VIOLA, WISCONSIN TORNADO Charles D. Koch University of Wisconsin Madison AOS 453: Mesoscale Meteorology Professor Greg Tripoli 13 May
WISCONSIN TORNADO OUTBREAK OF 18 AUGUST 2005: AN EXAMINATION OF THE VIOLA, WISCONSIN TORNADO Charles D. Koch University of Wisconsin Madison AOS 453: Mesoscale Meteorology Professor Greg Tripoli 13 May
Multi-day severe event of May 2013
 Abstract: Multi-day severe event of 18-22 May 2013 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA A relatively slow moving Trough over the western United States and a ridge
Abstract: Multi-day severe event of 18-22 May 2013 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA A relatively slow moving Trough over the western United States and a ridge
Storm-Relative Flow and its Relationship to Low-Level Vorticity in Simulated Storms
 TH CONF. ON SEVERE LOCAL STORMS, 15. 1 Storm-Relative Flow and its Relationship to Low-Level Vorticity in Simulated Storms Cody Kirkpatrick University of Alabama in Huntsville Eugene W. McCaul, Jr. Universities
TH CONF. ON SEVERE LOCAL STORMS, 15. 1 Storm-Relative Flow and its Relationship to Low-Level Vorticity in Simulated Storms Cody Kirkpatrick University of Alabama in Huntsville Eugene W. McCaul, Jr. Universities
Boundary layer Decoupling Affects on Tornadoes. Chris Karstens Meteorology 507 May 6, 2008
 Boundary layer Decoupling Affects on Tornadoes Chris Karstens Meteorology 507 May 6, 2008 Outline Background Motivation Methodology Results Conclusions References Questions Blackadar (1957). Background
Boundary layer Decoupling Affects on Tornadoes Chris Karstens Meteorology 507 May 6, 2008 Outline Background Motivation Methodology Results Conclusions References Questions Blackadar (1957). Background
P12.7 THE ROLE OF A SURFACE BOUNDARY AND MULTIPLE CELL-MERGERS IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE 21 APRIL 2003 TORNADO IN UPSTATE SOUTH CAROLINA
 P12.7 THE ROLE OF A SURFACE BOUNDARY AND MULTIPLE CELL-MERGERS IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE 21 APRIL 2003 TORNADO IN UPSTATE SOUTH CAROLINA 1. INTRODUCTION Bryan McAvoy NOAA/National Weather Service Greer,
P12.7 THE ROLE OF A SURFACE BOUNDARY AND MULTIPLE CELL-MERGERS IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE 21 APRIL 2003 TORNADO IN UPSTATE SOUTH CAROLINA 1. INTRODUCTION Bryan McAvoy NOAA/National Weather Service Greer,
Chapter 14 Thunderstorm Fundamentals
 Chapter overview: Thunderstorm appearance Thunderstorm cells and evolution Thunderstorm types and organization o Single cell thunderstorms o Multicell thunderstorms o Orographic thunderstorms o Severe
Chapter overview: Thunderstorm appearance Thunderstorm cells and evolution Thunderstorm types and organization o Single cell thunderstorms o Multicell thunderstorms o Orographic thunderstorms o Severe
On the usage of composite parameters in High-Shear, Low-CAPE environments
 P72 On the usage of composite parameters in High-Shear, Low-CAPE environments Keith D. Sherburn* and Matthew D. Parker Department of Marine, Earth, and Atmospheric Sciences, North Carolina State University,
P72 On the usage of composite parameters in High-Shear, Low-CAPE environments Keith D. Sherburn* and Matthew D. Parker Department of Marine, Earth, and Atmospheric Sciences, North Carolina State University,
Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox
 Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox Flash floods account for the greatest number of fatalities among convective storm-related events but it still remains difficult to forecast
Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox Flash floods account for the greatest number of fatalities among convective storm-related events but it still remains difficult to forecast
P1.14 DAMAGE ASSESSMENT AND RADAR ANALYSIS OF THE JULY 2011 DERECHO IN IOWA
 P1.14 DAMAGE ASSESSMENT AND RADAR ANALYSIS OF THE 10-11 JULY 2011 DERECHO IN IOWA Ray Wolf* and Donna Dubberke NOAA/National Weather Service, Davenport, Iowa Jeff Johnson, Kevin Deitsch and Kevin Skow
P1.14 DAMAGE ASSESSMENT AND RADAR ANALYSIS OF THE 10-11 JULY 2011 DERECHO IN IOWA Ray Wolf* and Donna Dubberke NOAA/National Weather Service, Davenport, Iowa Jeff Johnson, Kevin Deitsch and Kevin Skow
1. INTRODUCTION GSP Dr, Greer, SC tropical cyclones. 1 This study did not include tornadoes associated with
 4.5 OBSERVATIONS OF A NON-SUPERCELL TORNADIC THUNDERSTORM FROM A TERMINAL DOPPLER WEATHER RADAR Justin D. Lane * and Patrick D. Moore NOAA/National Weather Service Greer, SC 1. INTRODUCTION Despite numerous
4.5 OBSERVATIONS OF A NON-SUPERCELL TORNADIC THUNDERSTORM FROM A TERMINAL DOPPLER WEATHER RADAR Justin D. Lane * and Patrick D. Moore NOAA/National Weather Service Greer, SC 1. INTRODUCTION Despite numerous
Boundary Influences on the 7 July 2008 Tornado Event
 National Weather Association, Electronic Journal of Operational Meteorology, 2009-EJ8 Boundary Influences on the 7 July 2008 Tornado Event CHAUNCY J. SCHULTZ National Weather Service, North Platte, Nebraska
National Weather Association, Electronic Journal of Operational Meteorology, 2009-EJ8 Boundary Influences on the 7 July 2008 Tornado Event CHAUNCY J. SCHULTZ National Weather Service, North Platte, Nebraska
An Examination of how Manitoba Lake Breezes may Influence. Convective Storms
 An Examination of how Manitoba Lake Breezes may Influence Convective Storms by Scott Kehler A report submitted to the Department of Environment and Geography, University of Manitoba, In partial fulfillment
An Examination of how Manitoba Lake Breezes may Influence Convective Storms by Scott Kehler A report submitted to the Department of Environment and Geography, University of Manitoba, In partial fulfillment
11A.2 Forecasting Short Term Convective Mode And Evolution For Severe Storms Initiated Along Synoptic Boundaries
 11A.2 Forecasting Short Term Convective Mode And Evolution For Severe Storms Initiated Along Synoptic Boundaries Greg L. Dial and Jonathan P. Racy Storm Prediction Center, Norman, Oklahoma 1. Introduction
11A.2 Forecasting Short Term Convective Mode And Evolution For Severe Storms Initiated Along Synoptic Boundaries Greg L. Dial and Jonathan P. Racy Storm Prediction Center, Norman, Oklahoma 1. Introduction
1. INTRODUCTION * Figure 1. National Weather Service Storm Prediction Center (SPC) storm reports for December 1, 2006.
 P1.14 FORECAST ISSUES RELATED TO THE UNPRECEDENTED SEVERE AND HIGH WIND EVENT OF DECEMBER 2006 by Greg A. DeVoir* and Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION
P1.14 FORECAST ISSUES RELATED TO THE UNPRECEDENTED SEVERE AND HIGH WIND EVENT OF DECEMBER 2006 by Greg A. DeVoir* and Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION
P12.7 MESOCYCLONE AND RFD INDUCED DAMAGING WINDS OBSERVED IN THE 27 MAY 2004 SOUTHWEST OHIO SUPERCELL
 P12.7 MESOCYCLONE AND RFD INDUCED DAMAGING WINDS OBSERVED IN THE 27 MAY 2004 SOUTHWEST OHIO SUPERCELL John T. DiStefano* National Weather Service Office, Wilmington, Ohio 1. INTRODUCTION During the early
P12.7 MESOCYCLONE AND RFD INDUCED DAMAGING WINDS OBSERVED IN THE 27 MAY 2004 SOUTHWEST OHIO SUPERCELL John T. DiStefano* National Weather Service Office, Wilmington, Ohio 1. INTRODUCTION During the early
THE WISCONSIN TORNADO OUTBREAK OF 23 JUNE 2004
 THE WISCONSIN TORNADO OUTBREAK OF 23 JUNE 2004 Mark G. Gehring NOAA/National Weather Service Weather Forecast Office Milwaukee/Sullivan, Wisconsin Abstract Wisconsin recorded its fifth largest tornado
THE WISCONSIN TORNADO OUTBREAK OF 23 JUNE 2004 Mark G. Gehring NOAA/National Weather Service Weather Forecast Office Milwaukee/Sullivan, Wisconsin Abstract Wisconsin recorded its fifth largest tornado
1 of 7 Thunderstorm Notes by Paul Sirvatka College of DuPage Meteorology. Thunderstorms
 1 of 7 Thunderstorm Notes by Paul Sirvatka College of DuPage Meteorology Thunderstorms There are three types of thunderstorms: single-cell (or air mass) multicell (cluster or squall line) supercell Although
1 of 7 Thunderstorm Notes by Paul Sirvatka College of DuPage Meteorology Thunderstorms There are three types of thunderstorms: single-cell (or air mass) multicell (cluster or squall line) supercell Although
12.1 PRELIMINARY EVALUATION OF A PARAMETER TO FORECAST ENVIRONMENTS CONDUCIVE TO NON-MESOCYCLONE TORNADOGENESIS
 12.1 PRELIMINARY EVALUATION OF A PARAMETER TO FORECAST ENVIRONMENTS CONDUCIVE TO NON-MESOCYCLONE TORNADOGENESIS Dan A. Baumgardt* NOAA/National Weather Service La Crosse, Wisconsin Kenneth Cook NOAA/National
12.1 PRELIMINARY EVALUATION OF A PARAMETER TO FORECAST ENVIRONMENTS CONDUCIVE TO NON-MESOCYCLONE TORNADOGENESIS Dan A. Baumgardt* NOAA/National Weather Service La Crosse, Wisconsin Kenneth Cook NOAA/National
Severe Weather with a strong cold front: 2-3 April 2006 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803
 Severe Weather with a strong cold front: 2-3 April 2006 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION A strong cold front brought severe weather to much of
Severe Weather with a strong cold front: 2-3 April 2006 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION A strong cold front brought severe weather to much of
A COMPREHENSIVE 5-YEAR SEVERE STORM ENVIRONMENT CLIMATOLOGY FOR THE CONTINENTAL UNITED STATES 3. RESULTS
 16A.4 A COMPREHENSIVE 5-YEAR SEVERE STORM ENVIRONMENT CLIMATOLOGY FOR THE CONTINENTAL UNITED STATES Russell S. Schneider 1 and Andrew R. Dean 1,2 1 DOC/NOAA/NWS/NCEP Storm Prediction Center 2 OU-NOAA Cooperative
16A.4 A COMPREHENSIVE 5-YEAR SEVERE STORM ENVIRONMENT CLIMATOLOGY FOR THE CONTINENTAL UNITED STATES Russell S. Schneider 1 and Andrew R. Dean 1,2 1 DOC/NOAA/NWS/NCEP Storm Prediction Center 2 OU-NOAA Cooperative
AN INVESTIGATION OF THE SIGNIFICANT TORNADO OUTBREAK IN SOUTHERN SOUTH CAROLINA AND NORTH COASTAL GEORGIA ON MARCH 15, 2008
 P3.6 AN INVESTIGATION OF THE SIGNIFICANT TORNADO OUTBREAK IN SOUTHERN SOUTH CAROLINA AND NORTH COASTAL GEORGIA ON MARCH 15, 2008 Frank W. Alsheimer*, Robert Bright, Jonathon Jelsema, Wendy Moen, John Quagliariello,
P3.6 AN INVESTIGATION OF THE SIGNIFICANT TORNADO OUTBREAK IN SOUTHERN SOUTH CAROLINA AND NORTH COASTAL GEORGIA ON MARCH 15, 2008 Frank W. Alsheimer*, Robert Bright, Jonathon Jelsema, Wendy Moen, John Quagliariello,
11B.1 INFLUENCE OF DIABATIC POTENTIAL VORTICITY ANOMALIES UPON WARM CONVEYOR BELT FLOW. PART I: FEBRUARY 2003
 INFLUENCE OF DIABATIC POTENTIAL VORTICITY ANOMALIES UPON WARM CONVEYOR BELT FLOW. PART I: 14-15 FEBRUARY 2003 Philip N. Schumacher, NOAA/NWS, Sioux Falls, SD Joshua M. Boustead, NOAA/NWS, Valley, NE Martin
INFLUENCE OF DIABATIC POTENTIAL VORTICITY ANOMALIES UPON WARM CONVEYOR BELT FLOW. PART I: 14-15 FEBRUARY 2003 Philip N. Schumacher, NOAA/NWS, Sioux Falls, SD Joshua M. Boustead, NOAA/NWS, Valley, NE Martin
13.5 DOPPLER RADAR ANALYSIS OF THE 28 APRIL 2002 LA PLATA, MD TORNADIC SUPERCELL
 13.5 DOPPLER RADAR ANALYSIS OF THE 28 APRIL 2002 LA PLATA, MD TORNADIC SUPERCELL David R. Manning* and Steven M. Zubrick NOAA/National Weather Service, Sterling, Virginia 1. Introduction A severe weather
13.5 DOPPLER RADAR ANALYSIS OF THE 28 APRIL 2002 LA PLATA, MD TORNADIC SUPERCELL David R. Manning* and Steven M. Zubrick NOAA/National Weather Service, Sterling, Virginia 1. Introduction A severe weather
Synoptic Environments Associated with Significant Tornadoes in the Contiguous United States
 Synoptic Environments Associated with Significant Tornadoes in the Contiguous United States JAYSON A. PRENTICE Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences, Iowa State University, Ames, IA Mentor:
Synoptic Environments Associated with Significant Tornadoes in the Contiguous United States JAYSON A. PRENTICE Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences, Iowa State University, Ames, IA Mentor:
Steve Keighton * and Steve Nogueira NOAA/NWS Blacksburg, VA. Nicole Belk NOAA/NWS Charleston, WV
 P5.17 SYNOPTIC AND MESOSCALE ANALYSIS OF THE 9 AUGUST 2000 APPALACHIAN-CROSSING DERECHOS Steve Keighton * and Steve Nogueira NOAA/NWS Blacksburg, VA Nicole Belk NOAA/NWS Charleston, WV 1. INTRODUCTION
P5.17 SYNOPTIC AND MESOSCALE ANALYSIS OF THE 9 AUGUST 2000 APPALACHIAN-CROSSING DERECHOS Steve Keighton * and Steve Nogueira NOAA/NWS Blacksburg, VA Nicole Belk NOAA/NWS Charleston, WV 1. INTRODUCTION
Investigating the Environment of the Indiana and Ohio Tornado Outbreak of 24 August 2016 Using a WRF Model Simulation 1.
 Investigating the Environment of the Indiana and Ohio Tornado Outbreak of 24 August 2016 Using a WRF Model Simulation Kevin Gray and Jeffrey Frame Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Illinois
Investigating the Environment of the Indiana and Ohio Tornado Outbreak of 24 August 2016 Using a WRF Model Simulation Kevin Gray and Jeffrey Frame Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Illinois
A Preliminary Climatology of Tornado Events with Closed Cold Core 500 mb Lows in the Central and Eastern United States
 7B.4 A Preliminary Climatology of Tornado Events with Closed Cold Core 500 mb Lows in the Central and Eastern United States Jonathan M. Davies* Private Meteorologist, Wichita, Kansas Jared L. Guyer Storm
7B.4 A Preliminary Climatology of Tornado Events with Closed Cold Core 500 mb Lows in the Central and Eastern United States Jonathan M. Davies* Private Meteorologist, Wichita, Kansas Jared L. Guyer Storm
Proximity sounding analysis for derechos and supercells: an assessment of similarities and differences
 Atmospheric Research 67 68 (2003) 117 133 www.elsevier.com/locate/atmos Proximity sounding analysis for derechos and supercells: an assessment of similarities and differences Charles A. Doswell III a,
Atmospheric Research 67 68 (2003) 117 133 www.elsevier.com/locate/atmos Proximity sounding analysis for derechos and supercells: an assessment of similarities and differences Charles A. Doswell III a,
P1.13 GROUND BASED REMOTELY SENSED HIGH TEMPORAL RESOLUTION STABILITY INDICES ASSOCIATED WITH SOUTHERN GREAT PLAINS TORNADO OUTBREAKS
 P1.13 GROUND BASED REMOTELY SENSED HIGH TEMPORAL RESOLUTION STABILITY INDICES ASSOCIATED WITH SOUTHERN GREAT PLAINS TORNADO OUTBREAKS Timothy J. Wagner*, Wayne F. Feltz, Ralph Petersen, Steven A. Ackerman
P1.13 GROUND BASED REMOTELY SENSED HIGH TEMPORAL RESOLUTION STABILITY INDICES ASSOCIATED WITH SOUTHERN GREAT PLAINS TORNADO OUTBREAKS Timothy J. Wagner*, Wayne F. Feltz, Ralph Petersen, Steven A. Ackerman
Deep Cyclone and rapid moving severe weather event of 5-6 June 2010 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803
 Deep Cyclone and rapid moving severe weather event of 5-6 June 2010 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION A rapidly deepening surface cyclone raced
Deep Cyclone and rapid moving severe weather event of 5-6 June 2010 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION A rapidly deepening surface cyclone raced
Weather report 28 November 2017 Campinas/SP
 Weather report 28 November 2017 Campinas/SP Summary: 1) Synoptic analysis and pre-convective environment 2) Verification 1) Synoptic analysis and pre-convective environment: At 1200 UTC 28 November 2017
Weather report 28 November 2017 Campinas/SP Summary: 1) Synoptic analysis and pre-convective environment 2) Verification 1) Synoptic analysis and pre-convective environment: At 1200 UTC 28 November 2017
Tornado Probabilities Derived from Rapid Update Cycle Forecast Soundings
 Tornado Probabilities Derived from Rapid Update Cycle Forecast Soundings Zachary M. Byko National Weather Center Research Experiences for Undergraduates, and The Pennsylvania State University, University
Tornado Probabilities Derived from Rapid Update Cycle Forecast Soundings Zachary M. Byko National Weather Center Research Experiences for Undergraduates, and The Pennsylvania State University, University
Paul Yura*, Frank Alsheimer, and Joseph Calderone NOAA, National Weather Service Forecast Office, Charleston South Carolina 1.
 7B.8 AN EXAMINATION OF THE SYNOPTIC AND MESOSCALE ENVIRONMENTS INVOLVED IN TORNADO OUTBREAKS FROM HURRICANES FRANCES (2004) AND JEANNE (2004) OVER NORTHEAST COASTAL GEORGIA AND SOUTHERN SOUTH CAROLINA
7B.8 AN EXAMINATION OF THE SYNOPTIC AND MESOSCALE ENVIRONMENTS INVOLVED IN TORNADO OUTBREAKS FROM HURRICANES FRANCES (2004) AND JEANNE (2004) OVER NORTHEAST COASTAL GEORGIA AND SOUTHERN SOUTH CAROLINA
2.2 APPLICATIONS OF AIRCRAFT SOUNDING DATA IN SHORT-TERM CONVECTIVE FORECASTING
 2.2 APPLICATIONS OF AIRCRAFT SOUNDING DATA IN SHORT-TERM CONVECTIVE FORECASTING Phillip G. Kurimski* and Eugene S. Brusky Jr. NOAA/National Weather Service, Green Bay, WI 1. INTRODUCTION Automated real-time
2.2 APPLICATIONS OF AIRCRAFT SOUNDING DATA IN SHORT-TERM CONVECTIVE FORECASTING Phillip G. Kurimski* and Eugene S. Brusky Jr. NOAA/National Weather Service, Green Bay, WI 1. INTRODUCTION Automated real-time
Analysis of Severe Storm Initiation Along Drylines in the Southern Plains
 Analysis of Severe Storm Initiation Along Drylines in the Southern Plains NICOLE L. BARBEE Meteorology Program, Iowa State University, Ames Mentor: Dr. William Gallus 1 1 Department of Geological and Atmospheric
Analysis of Severe Storm Initiation Along Drylines in the Southern Plains NICOLE L. BARBEE Meteorology Program, Iowa State University, Ames Mentor: Dr. William Gallus 1 1 Department of Geological and Atmospheric
An Evaluation of CAPE Tendency in Tornado Outbreaks
 An Evaluation of CAPE Tendency in Tornado Outbreaks Undergraduate Research, ATM 499 Fall 2011-Spring 2012 Date: 15 May 2011 Timothy W. Humphrey and Lance F. Bosart Department of Atmospheric and Environmental
An Evaluation of CAPE Tendency in Tornado Outbreaks Undergraduate Research, ATM 499 Fall 2011-Spring 2012 Date: 15 May 2011 Timothy W. Humphrey and Lance F. Bosart Department of Atmospheric and Environmental
The Thanksgiving 2004 Severe Weather Event across Upstate New York and New England
 P 12.9 23rd Conference on Severe Local Storms Saint Louis, MO, 6-10 November 2006 The Thanksgiving 2004 Severe Weather Event across Upstate New York and New England *Thomas A. Wasula and Kenneth D. LaPenta
P 12.9 23rd Conference on Severe Local Storms Saint Louis, MO, 6-10 November 2006 The Thanksgiving 2004 Severe Weather Event across Upstate New York and New England *Thomas A. Wasula and Kenneth D. LaPenta
Case Study 3: Dryline in TX and OK 3 May 1999
 Case Study 3: Dryline in TX and OK 3 May 1999 Brandy Lumpkins Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison 8 May 2006 ABSTRACT A massive tornadic outbreak swept across
Case Study 3: Dryline in TX and OK 3 May 1999 Brandy Lumpkins Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison 8 May 2006 ABSTRACT A massive tornadic outbreak swept across
THE SUMMER STUDENT VOLUNTEER PROGRAM AT NWS WFO BALTIMORE/WASHINGTON
 THE SUMMER STUDENT VOLUNTEER PROGRAM AT NWS WFO BALTIMORE/WASHINGTON Matthew R. Kramar, Andrew B. Woodcock, Jared R. Klein and Steven M. Zubrick NOAA/National Weather Service Weather Forecast Office Baltimore/Washington
THE SUMMER STUDENT VOLUNTEER PROGRAM AT NWS WFO BALTIMORE/WASHINGTON Matthew R. Kramar, Andrew B. Woodcock, Jared R. Klein and Steven M. Zubrick NOAA/National Weather Service Weather Forecast Office Baltimore/Washington
THE SYNOPTIC ENVIRONMENT OF THE 11 APRIL 2001 CENTRAL PLAINS TORNADO OUTBREAK VIEWED IN THREE DIMENSIONS
 P1.1 THE SYNOPTIC ENVIRONMENT OF THE 11 APRIL 2001 CENTRAL PLAINS TORNADO OUTBREAK VIEWED IN THREE DIMENSIONS Daniel D. Nietfeld * NOAA/NWS/WFO Omaha/Valley, NE 1. INTRODUCTION A powerful low pressure
P1.1 THE SYNOPTIC ENVIRONMENT OF THE 11 APRIL 2001 CENTRAL PLAINS TORNADO OUTBREAK VIEWED IN THREE DIMENSIONS Daniel D. Nietfeld * NOAA/NWS/WFO Omaha/Valley, NE 1. INTRODUCTION A powerful low pressure
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America
 Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
What is Storm Anticipation (SA)? Using the SPC mesoanalysis fields to anticipate what is likely to occur.
 Fisher 2018 What is Storm Anticipation (SA)? Using the SPC mesoanalysis fields to anticipate what is likely to occur. Why do I need it? I have read the SPC outlooks and discussions (part of SA) I have
Fisher 2018 What is Storm Anticipation (SA)? Using the SPC mesoanalysis fields to anticipate what is likely to occur. Why do I need it? I have read the SPC outlooks and discussions (part of SA) I have
April 13, 2006: Analysis of the Severe Thunderstorms that produced Hail in Southern Wisconsin
 April 13, 2006: Analysis of the Severe Thunderstorms that produced Hail in Southern Wisconsin Danielle Triolo UW Madison Undergraduate 453 Case Study May 5, 2009 ABSTRACT On April 13, 2006 the states of
April 13, 2006: Analysis of the Severe Thunderstorms that produced Hail in Southern Wisconsin Danielle Triolo UW Madison Undergraduate 453 Case Study May 5, 2009 ABSTRACT On April 13, 2006 the states of
P1.1 EXAMINING PRECONVECTIVE HEAVY RAINFALL ENVIRONMENTS UTILIZING OBSERVATIONAL AND MODEL ANALYSIS PROXIMITY SOUNDINGS
 P1.1 EXAMINING PRECONVECTIVE HEAVY RAINFALL ENVIRONMENTS UTILIZING OBSERVATIONAL AND MODEL ANALYSIS PROXIMITY SOUNDINGS Michael J. Paddock and Charles E. Graves Saint Louis University, St. Louis, Missouri
P1.1 EXAMINING PRECONVECTIVE HEAVY RAINFALL ENVIRONMENTS UTILIZING OBSERVATIONAL AND MODEL ANALYSIS PROXIMITY SOUNDINGS Michael J. Paddock and Charles E. Graves Saint Louis University, St. Louis, Missouri
Supercells. Base lecture and Graphics created by The COMET Program May University Corporation for Atmospheric Research
 Supercells Base lecture and Graphics created by The COMET Program May 2002 University Corporation for Atmospheric Research Objective To be able to forecast and better recognize supercell storms in all
Supercells Base lecture and Graphics created by The COMET Program May 2002 University Corporation for Atmospheric Research Objective To be able to forecast and better recognize supercell storms in all
Practical Use of the Skew-T, log-p diagram for weather forecasting. Primer on organized convection
 Practical Use of the Skew-T, log-p diagram for weather forecasting Primer on organized convection Outline Rationale and format of the skew-t, log-p diagram Some basic derived diagnostic measures Characterizing
Practical Use of the Skew-T, log-p diagram for weather forecasting Primer on organized convection Outline Rationale and format of the skew-t, log-p diagram Some basic derived diagnostic measures Characterizing
Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004
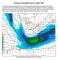 Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004 This event was characterized by a very strong jet streak that developed over North Carolina by 00 UTC 8 March, as seen in the Eta model analysis at 300 mb, with
Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004 This event was characterized by a very strong jet streak that developed over North Carolina by 00 UTC 8 March, as seen in the Eta model analysis at 300 mb, with
NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE. Aspects of a Tornadic Left-Moving Thunderstorm of 25 May 1999
 614 WEATHER AND FORECASTING NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE Aspects of a Tornadic Left-Moving Thunderstorm of 25 May 1999 JOHN F. DOSTALEK Cooperative Institute for Research in the Atmosphere, Colorado State
614 WEATHER AND FORECASTING NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE Aspects of a Tornadic Left-Moving Thunderstorm of 25 May 1999 JOHN F. DOSTALEK Cooperative Institute for Research in the Atmosphere, Colorado State
J. Brad McGavock*, Robert B. Darby, Steven F. Piltz
 P1.9 Interactive Mesoscale Analysis Utilized in Assisting Local Decision Makers: A Review of the 24 March 2005 Supercell 1. INTRODUCTION J. Brad McGavock*, Robert B. Darby, Steven F. Piltz Severe weather
P1.9 Interactive Mesoscale Analysis Utilized in Assisting Local Decision Makers: A Review of the 24 March 2005 Supercell 1. INTRODUCTION J. Brad McGavock*, Robert B. Darby, Steven F. Piltz Severe weather
THE MAP ROOM. BAND ON THE RUN Chasing the Physical Processes Associated with Heavy Snowfall
 THE MAP ROOM BAND ON THE RUN Chasing the Physical Processes Associated with Heavy Snowfall BY CHARLES E. GRAVES, JAMES T. MOORE, MARC J. SINGER, AND SAM NG AFFILIATIONS: GRAVES, MOORE, AND NG Department
THE MAP ROOM BAND ON THE RUN Chasing the Physical Processes Associated with Heavy Snowfall BY CHARLES E. GRAVES, JAMES T. MOORE, MARC J. SINGER, AND SAM NG AFFILIATIONS: GRAVES, MOORE, AND NG Department
contact with ground for 1 hour plus, starting 1500 MDT moved N., covered about 37 km width varied m
 Goal for today: Finish Ch. 11 Lightning, Thunder & Tornadoes 16 Nov., 2011 Edmonton tornado 31 July 1987 contact with ground for 1 hour plus, starting 1500 MDT moved N., covered about 37 km width varied
Goal for today: Finish Ch. 11 Lightning, Thunder & Tornadoes 16 Nov., 2011 Edmonton tornado 31 July 1987 contact with ground for 1 hour plus, starting 1500 MDT moved N., covered about 37 km width varied
P10.4 EXAMINATION OF TORNADIC AND NON-TORNADIC SUPERCELLS IN SOUTHWEST VIRGINIA ON 28 APRIL 2002
 P10.4 EXAMINATION OF TORNADIC AND NON-TORNADIC SUPERCELLS IN SOUTHWEST VIRGINIA ON 28 APRIL 2002 Steve Keighton*, Kenneth Kostura, and Chris Liscinsky NOAA/National Weather Service Blacksburg, VA 1. INTRODUCTION
P10.4 EXAMINATION OF TORNADIC AND NON-TORNADIC SUPERCELLS IN SOUTHWEST VIRGINIA ON 28 APRIL 2002 Steve Keighton*, Kenneth Kostura, and Chris Liscinsky NOAA/National Weather Service Blacksburg, VA 1. INTRODUCTION
Predecessor Rain Events: A Literature Review. By: Tony Viramontez
 Predecessor Rain Events: A Literature Review By: Tony Viramontez Introduction Predecessor Rain Event (PRE): meso- and subsynopticscale regions of high-impact heavy rainfall that occur well in advance of
Predecessor Rain Events: A Literature Review By: Tony Viramontez Introduction Predecessor Rain Event (PRE): meso- and subsynopticscale regions of high-impact heavy rainfall that occur well in advance of
4/18/2010. National Weather Service. Severe Weather Forecasting: A Western North Carolina Case Study
 National Weather Service Severe Weather Forecasting: A Western North Carolina Case Study Laurence G. Lee Science and Operations Officer National Weather Service Greer, SC Plus 13 River Forecast Centers
National Weather Service Severe Weather Forecasting: A Western North Carolina Case Study Laurence G. Lee Science and Operations Officer National Weather Service Greer, SC Plus 13 River Forecast Centers
Reprinted from: November 1993 Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 74,
 Reprinted from: November 1993 Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 74, 2213 2218 Comments on Anomalous Cloud-to- Ground Lighting in an F5 Tornadoproducing Supercell Thunderstorm on 28 August 1990 In his very interesting
Reprinted from: November 1993 Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 74, 2213 2218 Comments on Anomalous Cloud-to- Ground Lighting in an F5 Tornadoproducing Supercell Thunderstorm on 28 August 1990 In his very interesting
An Unprecedented Wisconsin Tornado Outbreak on 18 August 2005
 An Unprecedented Wisconsin Tornado Outbreak on 18 August 2005 Zachary P. Uttech Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences University of Wisconsin-Madison May 5, 2009 ABSTRACT On 18 August 2005, a
An Unprecedented Wisconsin Tornado Outbreak on 18 August 2005 Zachary P. Uttech Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences University of Wisconsin-Madison May 5, 2009 ABSTRACT On 18 August 2005, a
P8.10 AN EXAMINATION OF VARYING SUPERCELL ENVIRONMENTS OVER THE COMPLEX TERRAIN OF THE EASTERN TENNESSEE RIVER VALLEY
 P8.10 AN EXAMINATION OF VARYING SUPERCELL ENVIRONMENTS OVER THE COMPLEX TERRAIN OF THE EASTERN TENNESSEE RIVER VALLEY by David M. Gaffin* and David G. Hotz National Weather Service, Morristown TN 1. INTRODUCTION
P8.10 AN EXAMINATION OF VARYING SUPERCELL ENVIRONMENTS OVER THE COMPLEX TERRAIN OF THE EASTERN TENNESSEE RIVER VALLEY by David M. Gaffin* and David G. Hotz National Weather Service, Morristown TN 1. INTRODUCTION
Anthony A. Rockwood Robert A. Maddox
 Anthony A. Rockwood Robert A. Maddox An unusually intense MCS produced large hail and wind damage in northeast Kansas and northern Missouri during the predawn hours of June 7 th, 1982. Takes a look at
Anthony A. Rockwood Robert A. Maddox An unusually intense MCS produced large hail and wind damage in northeast Kansas and northern Missouri during the predawn hours of June 7 th, 1982. Takes a look at
Thunderstorm Dynamics. Helicity and Hodographs and their effect on thunderstorm longevity. Bluestein Vol II. Page
 Thunderstorm Dynamics Helicity and Hodographs and their effect on thunderstorm longevity Bluestein Vol II. Page471-476. Dowsell, 1991: A REVIEW FOR FORECASTERS ON THE APPLICATION OF HODOGRAPHS TO FORECASTING
Thunderstorm Dynamics Helicity and Hodographs and their effect on thunderstorm longevity Bluestein Vol II. Page471-476. Dowsell, 1991: A REVIEW FOR FORECASTERS ON THE APPLICATION OF HODOGRAPHS TO FORECASTING
A LOOK AT TROPICAL STORM GASTON FLOODING IN VIRGINIA
 J12B.4 A LOOK AT TROPICAL STORM GASTON FLOODING IN VIRGINIA John Billet* and Keith Lynch NOAA/NWS Wakefield, VA 1. INTRODUCTION Hurricane Gaston made landfall north of Charleston, SC on Sunday morning
J12B.4 A LOOK AT TROPICAL STORM GASTON FLOODING IN VIRGINIA John Billet* and Keith Lynch NOAA/NWS Wakefield, VA 1. INTRODUCTION Hurricane Gaston made landfall north of Charleston, SC on Sunday morning
AN INVESTIGATION OF THE JUNE 1984 BARNEVELD, WI TORNADO
 AN INVESTIGATION OF THE JUNE 1984 BARNEVELD, WI TORNADO BRANDON SWEDLUND Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Wisconsin, Madison, Wisconsin 13 May 2007 I. Introduction On the morning
AN INVESTIGATION OF THE JUNE 1984 BARNEVELD, WI TORNADO BRANDON SWEDLUND Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Wisconsin, Madison, Wisconsin 13 May 2007 I. Introduction On the morning
Determining Environmental Parameters Most Important for Significant Cool Season Tornadoes across the Gulf Coastal States
 Determining Environmental Parameters Most Important for Significant Cool Season Tornadoes across the Gulf Coastal States Kar retta Venable Jackson State University, Jackson, MS Mentors David Imy NOAA/NWS/NCEP/Storm
Determining Environmental Parameters Most Important for Significant Cool Season Tornadoes across the Gulf Coastal States Kar retta Venable Jackson State University, Jackson, MS Mentors David Imy NOAA/NWS/NCEP/Storm
Case Study of the Record Hail Event and Severe Thunderstorm Outbreak in East-Central Nebraska on June 2003
 Case Study of the Record Hail Event and Severe Thunderstorm Outbreak in East-Central Nebraska on 22-23 June 2003 DANIEL C. HARTUNG Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Wisconsin-Madison,
Case Study of the Record Hail Event and Severe Thunderstorm Outbreak in East-Central Nebraska on 22-23 June 2003 DANIEL C. HARTUNG Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Wisconsin-Madison,
National Weather Service-Pennsylvania State University Weather Events
 National Weather Service-Pennsylvania State University Weather Events Eastern United States Winter Storm and Severe Event of 28-29 February 2012 by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College
National Weather Service-Pennsylvania State University Weather Events Eastern United States Winter Storm and Severe Event of 28-29 February 2012 by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College
End of heat-event severe event of 7 July 2012
 End of heat-event severe event of 7 July 2012 Richard H. Grumm And Elyse Colbert National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. Overview A widespread severe weather event affected Pennsylvania
End of heat-event severe event of 7 July 2012 Richard H. Grumm And Elyse Colbert National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. Overview A widespread severe weather event affected Pennsylvania
DOPPLER RADAR AND STORM ENVIRONMENT OBSERVATIONS OF A MARITIME TORNADIC SUPERCELL IN SYDNEY, AUSTRALIA
 155 DOPPLER RADAR AND STORM ENVIRONMENT OBSERVATIONS OF A MARITIME TORNADIC SUPERCELL IN SYDNEY, AUSTRALIA Harald Richter *, Alain Protat Research and Development Branch, Bureau of Meteorology, Melbourne,
155 DOPPLER RADAR AND STORM ENVIRONMENT OBSERVATIONS OF A MARITIME TORNADIC SUPERCELL IN SYDNEY, AUSTRALIA Harald Richter *, Alain Protat Research and Development Branch, Bureau of Meteorology, Melbourne,
SEVERE LOCAL STORM WARNINGS: CHALLENGES FROM THE 04 MARCH 2004 EVENT. Gregory R. Patrick * and Gary R. Woodall, NOAA/NWS, Fort Worth, TX
 P2.5 SEVERE LOCAL STORM WARNINGS: CHALLENGES FROM THE 04 MARCH 2004 EVENT Gregory R. Patrick * and Gary R. Woodall, NOAA/NWS, Fort Worth, TX 1. INTRODUCTION A powerful low pressure center at 500 hpa moved
P2.5 SEVERE LOCAL STORM WARNINGS: CHALLENGES FROM THE 04 MARCH 2004 EVENT Gregory R. Patrick * and Gary R. Woodall, NOAA/NWS, Fort Worth, TX 1. INTRODUCTION A powerful low pressure center at 500 hpa moved
POLARIMETRIC RADAR OBSERVATION OF A TORNADO AT C-BAND
 P2.21 POLARIMETRIC RADAR OBSERVATION OF A TORNADO AT C-BAND Raquel Evaristo, Teresa Bals-Elsholz, Adam Stepanek, Bart Wolf, Kevin Goebbert, Anthony Lyza, Travis Elless Valparaiso University, Valparaiso,
P2.21 POLARIMETRIC RADAR OBSERVATION OF A TORNADO AT C-BAND Raquel Evaristo, Teresa Bals-Elsholz, Adam Stepanek, Bart Wolf, Kevin Goebbert, Anthony Lyza, Travis Elless Valparaiso University, Valparaiso,
Severe Weather Event of 13 July 2014
 Severe Weather Event of 13 July 2014 By Richard H. Grumm and Elyse M. Colbert National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview Severe weather affected the eastern United States (Fig. 1) from northwestern
Severe Weather Event of 13 July 2014 By Richard H. Grumm and Elyse M. Colbert National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview Severe weather affected the eastern United States (Fig. 1) from northwestern
Oakfield, WI Tornado of July 18 th, 1996: "Everything in its Right Place"
 Oakfield, WI Tornado of July 18 th, 1996: "Everything in its Right Place" Arian Sarsalari Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Wisconsin Madison ABSTRACT This paper will serve
Oakfield, WI Tornado of July 18 th, 1996: "Everything in its Right Place" Arian Sarsalari Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Wisconsin Madison ABSTRACT This paper will serve
Investigation of Supercells in China : Environmental and Storm Characteristics
 11A.6 Investigation of Supercells in China : Environmental and Storm Characteristics Xiaoding Yu Xiuming Wang Juan Zhao Haiyan Fei ( China Meteorological Administration Training Center) Abstract Based
11A.6 Investigation of Supercells in China : Environmental and Storm Characteristics Xiaoding Yu Xiuming Wang Juan Zhao Haiyan Fei ( China Meteorological Administration Training Center) Abstract Based
P PRELIMINARY ANALYSIS OF THE 10 JUNE 2010 SUPERCELLS INTERCEPTED BY VORTEX2 NEAR LAST CHANCE, COLORADO
 P12.164 PRELIMINARY ANALYSIS OF THE 10 JUNE 2010 SUPERCELLS INTERCEPTED BY VORTEX2 NEAR LAST CHANCE, COLORADO 1. INTRODUCTION An outstanding question in the field of severe storms research is why some
P12.164 PRELIMINARY ANALYSIS OF THE 10 JUNE 2010 SUPERCELLS INTERCEPTED BY VORTEX2 NEAR LAST CHANCE, COLORADO 1. INTRODUCTION An outstanding question in the field of severe storms research is why some
and 24 mm, hPa lapse rates between 3 and 4 K km 1, lifted index values
 3.2 Composite analysis 3.2.1 Pure gradient composites The composite initial NE report in the pure gradient northwest composite (N = 32) occurs where the mean sea level pressure (MSLP) gradient is strongest
3.2 Composite analysis 3.2.1 Pure gradient composites The composite initial NE report in the pure gradient northwest composite (N = 32) occurs where the mean sea level pressure (MSLP) gradient is strongest
P10.1 TORNADOGENESIS IN A SIMULATED HP SUPERCELL
 Preprints, 21 st Conference on Severe Local Storms 12-16 August 2002, San Antonio, Texas P10.1 TORNADOGENESIS IN A SIMULATED HP SUPERCELL 1. INTRODUCTION Catherine A. Finley * Department of Earth Sciences
Preprints, 21 st Conference on Severe Local Storms 12-16 August 2002, San Antonio, Texas P10.1 TORNADOGENESIS IN A SIMULATED HP SUPERCELL 1. INTRODUCTION Catherine A. Finley * Department of Earth Sciences
Severe Thunderstorms. MET 200 Lecture 24 Flooding in Hawaii and Intro to Severe Thunderstorms. MET 200 Lecture 24 Severe Thunderstorms.
 MET 200 Lecture 24 Severe Thunderstorms Damage Swath 1 2 MET 200 Lecture 24 Flooding in Hawaii and Intro to Severe Thunderstorms Severe Thunderstorms Kona Lows Cause more flash floods in Hawaii than any
MET 200 Lecture 24 Severe Thunderstorms Damage Swath 1 2 MET 200 Lecture 24 Flooding in Hawaii and Intro to Severe Thunderstorms Severe Thunderstorms Kona Lows Cause more flash floods in Hawaii than any
Cold frontal Rainband and Mid-Atlantic Severe Weather Event 28 September 2006 by Richard H. Grumm And Ron Holmes
 Cold frontal Rainband and Mid-Atlantic Severe Weather Event 28 September 2006 by Richard H. Grumm And Ron Holmes 1. INTRODUCTION A strong cold front moved across central Pennsylvania and the Mid-Atlantic
Cold frontal Rainband and Mid-Atlantic Severe Weather Event 28 September 2006 by Richard H. Grumm And Ron Holmes 1. INTRODUCTION A strong cold front moved across central Pennsylvania and the Mid-Atlantic
Mid-Atlantic Severe Event of 1 June 2012
 Mid-Atlantic Severe Event of 1 June 2012 1. Introduction An unseasonably deep midtropospheric ridge (Fig. 1) brought a strong cold front into the Mid-Atlantic region on 1 June 2012. A surge of warm moist
Mid-Atlantic Severe Event of 1 June 2012 1. Introduction An unseasonably deep midtropospheric ridge (Fig. 1) brought a strong cold front into the Mid-Atlantic region on 1 June 2012. A surge of warm moist
P12.6 Multiple Modes of Convection in Moderate to High Wind Shear Environments
 P12.6 Multiple Modes of Convection in Moderate to High Wind Shear Environments Adam J. French and Matthew D. Parker North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North Carolina 1. INTRODUCTION A principle
P12.6 Multiple Modes of Convection in Moderate to High Wind Shear Environments Adam J. French and Matthew D. Parker North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North Carolina 1. INTRODUCTION A principle
Isolated severe weather and cold air damming 9 November 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16801
 Isolated severe weather and cold air damming 9 November 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16801 1. INTRODUCTION Two lines of convection moved over the State of
Isolated severe weather and cold air damming 9 November 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16801 1. INTRODUCTION Two lines of convection moved over the State of
