The Father s Day 2002 Severe Weather Outbreak across New York and Western New England
|
|
|
- Moris Jennings
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 P nd Conference on Severe Local Storms Hyannis, MA, 4-8 October 2004 The Father s Day 2002 Severe Weather Outbreak across New York and Western New England Thomas A. Wasula NOAA/National Weather Service, Weather Forecast Office, Albany, New York 1. Introduction On 16 June 2002, a substantial severe weather outbreak occurred across the northeast, United States (US). This was the third major outbreak in three weeks across eastern New York and western New England during the 2002 severe weather season. Severe thunderstorms developed that produced large hail, strong winds and tornadoes. The two tornadoes that developed in the Mohawk and Hudson River Valleys were F0's and F1's. A 500 hpa closed low that moved across the northern Great Lakes region on 15 June helped initiate the severe weather on Father s Day (16 June). The midlevel cold pool associated with the 500 hpa low sparked a second day of severe weather for eastern New York and western New England. Several large hail (greater than 1.9 cm) producing thunderstorms on Monday, 17 June 2002 developed, as the trough continued moving east across the Northeast. Convective initiation occurred early in the afternoon on 16 June with thunderstorms developing over central New York. Steep midlevel lapse rates, moderately high surface dewpoints and Convective Available Potential Energy (CAPE) values coupled with a vigorous 500 hpa short wave trough helped trigger the convection. A 500 hpa southwesterly jet streak greater than 25 ms -1 (50 knots) was moving across upstate New York and New England during this outbreak. Wind profiles from soundings across eastern New York and New England indicated the possibility of supercell thunderstorm development conducive for potential tornadoes. The tornado that developed in the mid-hudson River Valley was associated with a well-defined supercell that formed in Dutchess County, New York and moved into Litchfield County, Connecticut. This poster will focus on an investigation of the evolution of the large-scale synoptic pattern associated with the severe weather outbreak, and the mesoscale environment that generated the convection. The role of jet streaks at various levels Corresponding author address: Thomas A. Wasula, NOAA/NWS Weather Forecast Office, 251 Fuller Rd, Albany NY, tom.wasula@noaa.gov will also be examined. The purpose of this case study analysis is to understand why severe weather occurred. Severe weather was not anticipated on these days. This case study is very intriguing that it produced so much severe weather across New York and western New England. The operational forecast challenges of 500 hpa closed lows across the Northeast will also be addressed in the poster. 2. Data Data analyzed include 80-km Eta model grids, surface observations (will be shown in poster), upper air data, satellite imagery (will be shown in poster), and Weather Surveillance Radar 1988 Doppler (WSR-88D) radar data. The WSR-88D data is high resolution archive IV data from KENX (Albany). The sounding analysis was done with the Skew-T Hodograph Analysis and Research Program (SHARP) software (Hart and Korotky 1991). 3. Synoptic Overview A closed 500 hpa low was moving through the northern Great Lakes and southern Ontario on 15 June 2002 continued its slow eastward progression to the border of Ontario and Quebec, just north of Lake Ontario by 1200 UTC 16 June (Fig. 1). This vertically stacked system had a very intense midlevel cold pool with 500 hpa temperatures of -20 C upstream of Albany over Buffalo and Maniwaki (southern Quebec), as shown in Fig. 1 and 2a. This is a typical closed low track moving through the Great Lakes region, established in a 21-year subjective climatology in the months of May to September (Novak et al. 2002; Najuch et al. 2004). A very strong 500 hpa jet streak of 25 to 30 ms -1 (50 to 60 knots) was moving through eastern Ohio, Pennsylvania, New York, New Jersey and New England at 1200 UTC 16 June. Much of eastern New York and western New England was located on the left front quadrant of the midlevel jet streak. This area is usually conducive for cyclone development or severe weather development with the right moisture 1
2 and instability parameters in place. A strong 500 hpa absolute vorticity maxima was pivoting around the closed low into central and eastern New York on 1200 UTC 16 June (Fig. 2b). The 850 hpa flow was westerly at 12.5 ms -1 to 15 ms -1 (25 to 30 knots) over New York and Pennsylvania with dewpoints of approximately 8 to 10 C (not shown). A 250 hpa jet streak of 40 to 50 ms -1 (80 to 100 knots) was moving through the Ohio Valley and Pennsylvania with good upper-level divergence on the morning of 16 June (Fig. 3). Again, eastern New York and New England was located left front quadrant of the upper-level jet streak (Uccellini and Kocin 1987; Nemeth Jr. and Farina 1994). By 1800 UTC the Eta model forecast showed, this upper-level jet streak strengthened to greater than 50 m s -1 (>100 knots) over New Jersey, Pennsylvania and Maryland with a large area of upper-level divergence just off the New England Coast (not shown). At the surface, a trough began to generate scattered showers and thunderstorms over central NY in the late morning. However, most of eastern NY and western New England had substantial surface based heating by 1600 UTC. Surface temperatures in the Hudson River Valley rose into the 17 C to 20 C range (60 s) with surface dewpoints in the 12 C to 15 C range (mid to upper 50 s F; not shown). The diurnal heating ahead of the cloud cover upstream helped destabilize the atmosphere to spark the severe convection that began over the central Mohawk Valley and spread into the Greater Capital Region between 1600 and 1700 UTC. Also, the Eta model continued to forecast strong upward vertical motion (large values of omega) at 700 hpa coupled with cyclonic vorticity advection ahead of the surface trough and the 500 hpa vorticity maxima associated with the closed low (shown on poster). 4. Sounding and Radar Analysis Upper air analysis showed good support for convective activity 16 June. Eastern New York and western New England were in an area of instability as shown by the SHARP modified Albany, NY sounding at 1200 UTC 16 June. The sounding was modified to a high temperature of 20.9 C and a peak surface dewpoint temperature of 15.0 C, which produced a surface based CAPE value of 1581 J kg -1 (range across the forecast area was J kg -1 The lifted index calculated was very unstable at -5. The freezing level and wet bulb zero level were very low at 8.4 kft and 6.8 kft respectively, which is a good indicator of potential large hail, if severe thunderstorms develop. Also the hpa lapse rate was 6.5 C km -1 and the 850 hpa-500 hpa lapse rates were also approaching C km -1. The midlevel lapse rates were very steep. Shallow lowlevel veering was evident in the sounding between the surface and 900 hpa. The low-level veering in the Hudson River Valley with strong southwesterly flow aloft (500 hpa to 250 hpa) is a favorable shear profile for supercell development potentially spawning tornadoes. Although the Energy Helicity Index (EHI) was reasonably low at 0.6 and the 0-3 km storm relative helicity was a mere -57 (m/s) 2. These parameters are usually much higher for potential tornado development. The precipitable water value off the Albany sounding was 2.06 cm (0.81 inches), which indicated that heavy rainfall would not be a problem. The Vertically Integrated Liquid (VIL) of the Day (VOD) was calculated to be around 35 kg m 2. The forecast thinking was for small hail and not a significant severe weather event on Father s Day. Despite, these conducive sounding parameters, NOAA's Storm Prediction Center (SPC) did not issue severe thunderstorm or tornado watch boxes, since the severe weather occurred in a small area. Also, the significant surface heating and destabilization of the atmosphere was not anticipated by forecasters. The convection rapidly developed over the southern Adirondacks, central Mohawk Valley and northern Catskills (Fig. 5a) shortly before noon. By 1650 UTC, a line of thunderstorms developed and was moving over the KENX radar (Fig. 5b). However, multi-cellular convection was developing in the cooler air north/northwest of the line. At 1650 UTC, a hook signature (Fig. 6a) had developed over northeastern Montgomery County near the city of Amsterdam. This hook was approximately 25 nautical miles (nm) from the radar with a measured gate to gate 0.5 nm rotational velocity of 21.0 knots and a shear value of s -1 (Fig. 6b). This falls below the local warning threshold criteria, but an F0 tornado was reported at 1650 UTC. This tornadic cell was evident in the two previous radar scans with similar weak rotational and shear values. The forecaster focus was on 1) the line of thunderstorms emerging from the KENX radar data acquisition (RDA) site that were producing damaging winds and large hail and 2) multi-cellular convection in the warmer, more unstable air to the south of this line. The shallow low-level veering in the lower 2-3 kft was the primary mechanism for the tornadic development. The Albany sounding and VAD wind profile from the KENX radar (not shown) were very representative of this shallow veering signature. By 1749 UTC, a line of thunderstorms had moved into western New England with a history of producing damaging winds and large hail (Fig. 7). A supercell began to develop well south of the line east 2
3 of the Catskills. This supercell moved into the mid- Hudson Valley and produced an F1 tornado near Pawling in Dutchess County at around 1848 UTC (Fig. 8). It continued to produce F0/F1 damage into Litchfield County, Connecticut near Salisbury. 5. Summary A potent 500 hpa closed low moving through the Great Lakes region helped initiate a convective outbreak on Fathers Day 2002 across New York and western New England. A surface trough coupled with steep midlevel lapse rates (cold pool aloft), low wet bulb zero heights, moderately high surface based CAPE values and dewpoints in the 10 to 15 C (50-59 F) helped fuel organized low-topped multicellular convection that coalesced into a line with a supercell to the south of it. The area hit by the severe convection was on the cyclonic exit region/left front quadrant of the 500 and 250 hpa jet streaks. Tornadic development was aided by large instability (CAPE) and shallow low-level veering from the surface to about 850 hpa. The predominant flow in the mid and upper-levels was southwesterly. Much can be learned from this case study. Forecasters should not underestimate the strength of the midlevel cold pool with closed lows, especially if significant surface heating occurs, which aids in destabilizing the air mass. This case shows the wide variety of severe weather generated by warm season closed lows in the Northeast and how challenging they can be to forecast. 6. Acknowledgements Thanks to Eastern Region Scientific Services Division, and Alicia C. Wasula for reviewing and assisting with this preprint. Thanks also to Kenneth LaPenta, WFO at Albany Senior Forecaster, for helping with some of the figure formatting. This research was also initiated out of the CSTARsupported research at the University at Albany/SUNY, NOAA Grant NAO7WAO References Hart, J.A. and W. Korotky, 1991: The SHARP workstation v1.5 users guide. National Weather Service, NOAA, U.S. Department of Commerce, 30 pp. [Available from NWS Eastern Region Headquarters Scientific Services Division, 630 Johnson Ave., Bohemia, NY 11716]. Najuch, J. S., L. F. Bosart, D. Keyser, T. A. Wasula, K. D. LaPenta, 2004: Case Studies of Warm Season Cutoff Cyclone Precipitation Distribution. Preprints of the 20 th AMS Conference on Weather Analysis and Forecasting, Seattle, WA, Amer. Meteo. Soc., CD-ROM, P Nemeth Jr., J. S., K. J. Farina, 1994: The Role of Jet Streaks in the Tornadic Development of November 16, 1989 over the Northeast United States. Eastern Region Technical Attachment, NO. 94-6A 16 pp. [Available from NWS Eastern Region Headquarters Scientific Services Division, 630 Johnson Ave., Bohemia, NY 11716]. Novak, M. J., A. Aiyyer, L. F. Bosart, D. Keyser, T. A. Wasula, K. D. LaPenta, 2002: Warm Season 500 hpa Closed Lows. Preprints of the 19 th AMS Conference on Weather Analysis and Forecasting, San Antonio, TX, Amer. Meteo. Soc., Uccellini, L. W., Kocin, P. J. 1987: The interaction of jet streak circulations during heavy snow events along the East Coast of the United States. Wea. Forecasting, 2,
4 Fig. 1: 500 hpa Radiosonde Observational (RAOB) analysis of height (dam), temperature ( C) and winds (knots) at 1200 UTC 16 June Fig. 2: a) Mean sea level pressure (hpa, solid), hpa thickness (dam, dashed), b) 500 hpa height (dam, solid) and absolute vorticity (x 10-5 s -1 ; shaded above 10 x 10-5 s -1 ), valid 1200 UTC 16 June. 4
5 Fig. 3: 250 hpa Divergence (x10-5 s -1 ) solid contours and Isotachs (m s -1 ) shaded every 10 m s -1 valid 1200 UTC 16 June. Fig. 4: Albany modified 1200 UTC 16 June sounding in SHARP for peak temperature (20.9 C) and dewpoint (15 C) before the severe weather. Winds are in knots on the sounding. 5
6 ENX RDA ALY a Fig. 5 KENX 0.5 Base Reflectivity (dbz) at a) 1557 UTC 16 June and b) 1650 UTC 16 June where convection is moving over ENX (Albany) RDA. Montgomery County Montgomery County aa b Fig. 6: a) 1650 UTC 16 June KENX 0.5 Base Reflectivity (dbz) for F0 tornado over Amsterdam, Montgomery County b) 1650 UTC 16 June KENX 0.5 Storm Relative Motion (SRM; knots) for F0 tornado over Amsterdam, Montgomery County. The hook signature was about 25 nm from the radar with a 0.5 nm gate-to-gate rotational velocity of 21.0 knots and a shear value of s-1. 6
7 2 1 Fig. 7: 1749 UTC 16 June KENX Composite Reflectivity (dbz). Number 1 shows a supercell moving into southwestern Dutchess County. Number 2 shows a line of convection moving into western New England. Dutchess County Fig. 8: 1848 UTC 16 June KENX 0.5 Base Reflectivity (dbz) with hook signature of F1 tornado near Pawling, Dutchess County. 7
The Thanksgiving 2004 Severe Weather Event across Upstate New York and New England
 P 12.9 23rd Conference on Severe Local Storms Saint Louis, MO, 6-10 November 2006 The Thanksgiving 2004 Severe Weather Event across Upstate New York and New England *Thomas A. Wasula and Kenneth D. LaPenta
P 12.9 23rd Conference on Severe Local Storms Saint Louis, MO, 6-10 November 2006 The Thanksgiving 2004 Severe Weather Event across Upstate New York and New England *Thomas A. Wasula and Kenneth D. LaPenta
P9.5 An Application of a Cutoff Low Forecaster Pattern Recognition Model to the 30 June - 2 July 2009 Significant Event for the Northeast
 P9.5 An Application of a Cutoff Low Forecaster Pattern Recognition Model to the 30 June - 2 July 2009 Significant Event for the Northeast Thomas A. Wasula* and Neil A. Stuart NOAA/National Weather Service,
P9.5 An Application of a Cutoff Low Forecaster Pattern Recognition Model to the 30 June - 2 July 2009 Significant Event for the Northeast Thomas A. Wasula* and Neil A. Stuart NOAA/National Weather Service,
P3.17 THE DEVELOPMENT OF MULTIPLE LOW-LEVEL MESOCYCLONES WITHIN A SUPERCELL. Joshua M. Boustead *1 NOAA/NWS Weather Forecast Office, Topeka, KS
 P3.17 THE DEVELOPMENT OF MULTIPLE LOW-LEVEL MESOCYCLONES WITHIN A SUPERCELL Joshua M. Boustead *1 NOAA/NWS Weather Forecast Office, Topeka, KS Philip N. Schumacher NOAA/NWS Weather Forecaster Office, Sioux
P3.17 THE DEVELOPMENT OF MULTIPLE LOW-LEVEL MESOCYCLONES WITHIN A SUPERCELL Joshua M. Boustead *1 NOAA/NWS Weather Forecast Office, Topeka, KS Philip N. Schumacher NOAA/NWS Weather Forecaster Office, Sioux
Severe Weather with a strong cold front: 2-3 April 2006 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803
 Severe Weather with a strong cold front: 2-3 April 2006 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION A strong cold front brought severe weather to much of
Severe Weather with a strong cold front: 2-3 April 2006 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION A strong cold front brought severe weather to much of
P1.15 The May 26-27, 2010 Eastern New York and Western New England Backdoor Cold Front Severe Weather Event
 P1.15 The May 26-27, 2010 Eastern New York and Western New England Backdoor Cold Front Severe Weather Event Thomas A. Wasula*, Brian J. Frugis, and Neil A. Stuart NOAA/National Weather Service, Weather
P1.15 The May 26-27, 2010 Eastern New York and Western New England Backdoor Cold Front Severe Weather Event Thomas A. Wasula*, Brian J. Frugis, and Neil A. Stuart NOAA/National Weather Service, Weather
Isolated severe weather and cold air damming 9 November 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16801
 Isolated severe weather and cold air damming 9 November 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16801 1. INTRODUCTION Two lines of convection moved over the State of
Isolated severe weather and cold air damming 9 November 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16801 1. INTRODUCTION Two lines of convection moved over the State of
P9.112 A STORM-SCALE ANALYSIS OF THE 29 MAY 2013 TORNADO EVENT ACROSS EAST- CENTRAL NEW YORK
 P9.112 A STORM-SCALE ANALYSIS OF THE 29 MAY 2013 TORNADO EVENT ACROSS EAST- CENTRAL NEW YORK Thomas A. Wasula*, Brian J. Frugis, Ian R. Lee and Luigi F. Meccariello NOAA/National Weather Service, Weather
P9.112 A STORM-SCALE ANALYSIS OF THE 29 MAY 2013 TORNADO EVENT ACROSS EAST- CENTRAL NEW YORK Thomas A. Wasula*, Brian J. Frugis, Ian R. Lee and Luigi F. Meccariello NOAA/National Weather Service, Weather
1. INTRODUCTION * Figure 1. National Weather Service Storm Prediction Center (SPC) storm reports for December 1, 2006.
 P1.14 FORECAST ISSUES RELATED TO THE UNPRECEDENTED SEVERE AND HIGH WIND EVENT OF DECEMBER 2006 by Greg A. DeVoir* and Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION
P1.14 FORECAST ISSUES RELATED TO THE UNPRECEDENTED SEVERE AND HIGH WIND EVENT OF DECEMBER 2006 by Greg A. DeVoir* and Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION
Comparison of November 15, 2008 Killer Tornado Outbreak with the December 2, 2009 Non Tornado Event
 Comparison of November 15, 2008 Killer Tornado Outbreak with the December 2, 2009 Non Tornado Event The two events featured similar patterns but with much different results in central NC. The slides on
Comparison of November 15, 2008 Killer Tornado Outbreak with the December 2, 2009 Non Tornado Event The two events featured similar patterns but with much different results in central NC. The slides on
David O. Blanchard* and Brian A. Klimowski National Weather Service, Flagstaff, Arizona
 P12.1 SUPERCE EVOUTION IN ENVIRONMENTS WITH UNUSUA HODOGRAPHS David O. Blanchard* and Brian A. Klimowski National Weather Service, Flagstaff, Arizona 1. INTRODUCTION The events that transpired across northern
P12.1 SUPERCE EVOUTION IN ENVIRONMENTS WITH UNUSUA HODOGRAPHS David O. Blanchard* and Brian A. Klimowski National Weather Service, Flagstaff, Arizona 1. INTRODUCTION The events that transpired across northern
Cold frontal Rainband and Mid-Atlantic Severe Weather Event 28 September 2006 by Richard H. Grumm And Ron Holmes
 Cold frontal Rainband and Mid-Atlantic Severe Weather Event 28 September 2006 by Richard H. Grumm And Ron Holmes 1. INTRODUCTION A strong cold front moved across central Pennsylvania and the Mid-Atlantic
Cold frontal Rainband and Mid-Atlantic Severe Weather Event 28 September 2006 by Richard H. Grumm And Ron Holmes 1. INTRODUCTION A strong cold front moved across central Pennsylvania and the Mid-Atlantic
Appalachian Lee Troughs and their Association with Severe Thunderstorms
 Appalachian Lee Troughs and their Association with Severe Thunderstorms Daniel B. Thompson, Lance F. Bosart and Daniel Keyser Department of Atmospheric and Environmental Sciences University at Albany/SUNY,
Appalachian Lee Troughs and their Association with Severe Thunderstorms Daniel B. Thompson, Lance F. Bosart and Daniel Keyser Department of Atmospheric and Environmental Sciences University at Albany/SUNY,
Low-end derecho of 19 August 2017
 Low-end derecho of 19 August 2017 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A cluster of thunderstorms developed in eastern Ohio around 1800 UTC on 19
Low-end derecho of 19 August 2017 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A cluster of thunderstorms developed in eastern Ohio around 1800 UTC on 19
Heavy Rainfall Event of June 2013
 Heavy Rainfall Event of 10-11 June 2013 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A 500 hpa short-wave moved over the eastern United States (Fig. 1) brought a surge of
Heavy Rainfall Event of 10-11 June 2013 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A 500 hpa short-wave moved over the eastern United States (Fig. 1) brought a surge of
13.5 DOPPLER RADAR ANALYSIS OF THE 28 APRIL 2002 LA PLATA, MD TORNADIC SUPERCELL
 13.5 DOPPLER RADAR ANALYSIS OF THE 28 APRIL 2002 LA PLATA, MD TORNADIC SUPERCELL David R. Manning* and Steven M. Zubrick NOAA/National Weather Service, Sterling, Virginia 1. Introduction A severe weather
13.5 DOPPLER RADAR ANALYSIS OF THE 28 APRIL 2002 LA PLATA, MD TORNADIC SUPERCELL David R. Manning* and Steven M. Zubrick NOAA/National Weather Service, Sterling, Virginia 1. Introduction A severe weather
WARM SECTOR TORNADOES WITHOUT DISCERNIBLE SURFACE BOUNDARIES AND WITH MINIMAL DEEP LAYER SHEA
 2.1 WARM SECTOR TORNADOES WITHOUT DISCERNIBLE SURFACE BOUNDARIES AND WITH MINIMAL DEEP LAYER SHEA * Joshua M. Boustead and Philip N. Schumacher National Weaer Service Sioux Falls, SD 1. INTRODUCTION On
2.1 WARM SECTOR TORNADOES WITHOUT DISCERNIBLE SURFACE BOUNDARIES AND WITH MINIMAL DEEP LAYER SHEA * Joshua M. Boustead and Philip N. Schumacher National Weaer Service Sioux Falls, SD 1. INTRODUCTION On
Multi-day severe event of May 2013
 Abstract: Multi-day severe event of 18-22 May 2013 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA A relatively slow moving Trough over the western United States and a ridge
Abstract: Multi-day severe event of 18-22 May 2013 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA A relatively slow moving Trough over the western United States and a ridge
Deep Cyclone and rapid moving severe weather event of 5-6 June 2010 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803
 Deep Cyclone and rapid moving severe weather event of 5-6 June 2010 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION A rapidly deepening surface cyclone raced
Deep Cyclone and rapid moving severe weather event of 5-6 June 2010 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION A rapidly deepening surface cyclone raced
National Weather Service-Pennsylvania State University Weather Events
 National Weather Service-Pennsylvania State University Weather Events Historic Ohio Valley January Severe weather and Tornado Event by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College PA 16803 and
National Weather Service-Pennsylvania State University Weather Events Historic Ohio Valley January Severe weather and Tornado Event by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College PA 16803 and
Summary of November Central U.S. Winter Storm By Christopher Hedge
 Summary of November 12-13 2010 Central U.S. Winter Storm By Christopher Hedge Event Overview The first significant snowfall of the 2010-2011 season affected portions of the plains and upper Mississippi
Summary of November 12-13 2010 Central U.S. Winter Storm By Christopher Hedge Event Overview The first significant snowfall of the 2010-2011 season affected portions of the plains and upper Mississippi
Tornadogenesis in Supercells: The Three Main Ingredients. Ted Funk
 Tornadogenesis in Supercells: The Three Main Ingredients Ted Funk NWS Louisville, KY Spring 2002 Environmental Parameters Supercells occur within environments exhibiting several wellknown characteristics
Tornadogenesis in Supercells: The Three Main Ingredients Ted Funk NWS Louisville, KY Spring 2002 Environmental Parameters Supercells occur within environments exhibiting several wellknown characteristics
Weather report 28 November 2017 Campinas/SP
 Weather report 28 November 2017 Campinas/SP Summary: 1) Synoptic analysis and pre-convective environment 2) Verification 1) Synoptic analysis and pre-convective environment: At 1200 UTC 28 November 2017
Weather report 28 November 2017 Campinas/SP Summary: 1) Synoptic analysis and pre-convective environment 2) Verification 1) Synoptic analysis and pre-convective environment: At 1200 UTC 28 November 2017
1. INTRODUCTION GSP Dr, Greer, SC tropical cyclones. 1 This study did not include tornadoes associated with
 4.5 OBSERVATIONS OF A NON-SUPERCELL TORNADIC THUNDERSTORM FROM A TERMINAL DOPPLER WEATHER RADAR Justin D. Lane * and Patrick D. Moore NOAA/National Weather Service Greer, SC 1. INTRODUCTION Despite numerous
4.5 OBSERVATIONS OF A NON-SUPERCELL TORNADIC THUNDERSTORM FROM A TERMINAL DOPPLER WEATHER RADAR Justin D. Lane * and Patrick D. Moore NOAA/National Weather Service Greer, SC 1. INTRODUCTION Despite numerous
April 13, 2006: Analysis of the Severe Thunderstorms that produced Hail in Southern Wisconsin
 April 13, 2006: Analysis of the Severe Thunderstorms that produced Hail in Southern Wisconsin Danielle Triolo UW Madison Undergraduate 453 Case Study May 5, 2009 ABSTRACT On April 13, 2006 the states of
April 13, 2006: Analysis of the Severe Thunderstorms that produced Hail in Southern Wisconsin Danielle Triolo UW Madison Undergraduate 453 Case Study May 5, 2009 ABSTRACT On April 13, 2006 the states of
A COMPREHENSIVE 5-YEAR SEVERE STORM ENVIRONMENT CLIMATOLOGY FOR THE CONTINENTAL UNITED STATES 3. RESULTS
 16A.4 A COMPREHENSIVE 5-YEAR SEVERE STORM ENVIRONMENT CLIMATOLOGY FOR THE CONTINENTAL UNITED STATES Russell S. Schneider 1 and Andrew R. Dean 1,2 1 DOC/NOAA/NWS/NCEP Storm Prediction Center 2 OU-NOAA Cooperative
16A.4 A COMPREHENSIVE 5-YEAR SEVERE STORM ENVIRONMENT CLIMATOLOGY FOR THE CONTINENTAL UNITED STATES Russell S. Schneider 1 and Andrew R. Dean 1,2 1 DOC/NOAA/NWS/NCEP Storm Prediction Center 2 OU-NOAA Cooperative
P1.4 AN EARLY MORNING MID-ATLANTIC SEVERE WEATHER EPISODE: SHORT-LIVED TORNADOS IN A HIGH-SHEAR LOW-INSTABILITY ENVIRONMENT
 P1.4 AN EARLY MORNING MID-ATLANTIC SEVERE WEATHER EPISODE: SHORT-LIVED TORNADOS IN A HIGH-SHEAR LOW-INSTABILITY ENVIRONMENT Alan M. Cope * NOAA/National Weather Service Forecast Office, Mount Holly, New
P1.4 AN EARLY MORNING MID-ATLANTIC SEVERE WEATHER EPISODE: SHORT-LIVED TORNADOS IN A HIGH-SHEAR LOW-INSTABILITY ENVIRONMENT Alan M. Cope * NOAA/National Weather Service Forecast Office, Mount Holly, New
P0.98 Composite Analysis of Heavy-Rain-Producing Elevated Thunderstorms in the MO-KS-OK region of the United States
 P0.98 Composite Analysis of Heavy-Rain-Producing Elevated Thunderstorms in the MO-KS-OK region of the United States Laurel P. McCoy and Patrick S. Market Department of Soil, Environmental, and Atmospheric
P0.98 Composite Analysis of Heavy-Rain-Producing Elevated Thunderstorms in the MO-KS-OK region of the United States Laurel P. McCoy and Patrick S. Market Department of Soil, Environmental, and Atmospheric
A LOOK AT TROPICAL STORM GASTON FLOODING IN VIRGINIA
 J12B.4 A LOOK AT TROPICAL STORM GASTON FLOODING IN VIRGINIA John Billet* and Keith Lynch NOAA/NWS Wakefield, VA 1. INTRODUCTION Hurricane Gaston made landfall north of Charleston, SC on Sunday morning
J12B.4 A LOOK AT TROPICAL STORM GASTON FLOODING IN VIRGINIA John Billet* and Keith Lynch NOAA/NWS Wakefield, VA 1. INTRODUCTION Hurricane Gaston made landfall north of Charleston, SC on Sunday morning
P10.2 SUBTLE RADAR SIGNATURES IN THE WEST BROOKFIELD, MA TORNADO OF 23 JULY 2002
 P10.2 SUBTLE RADAR SIGNATURES IN THE WEST BROOKFIELD, MA TORNADO OF 23 JULY 2002 Glenn A. Field and David R. Vallee NOAA/National Weather Service Forecast Office, Taunton, MA 1. INTRODUCTION Tornadic storms
P10.2 SUBTLE RADAR SIGNATURES IN THE WEST BROOKFIELD, MA TORNADO OF 23 JULY 2002 Glenn A. Field and David R. Vallee NOAA/National Weather Service Forecast Office, Taunton, MA 1. INTRODUCTION Tornadic storms
The Severe Weather Event of 7 August 2013 By Richard H. Grumm and Bruce Budd National Weather Service State College, PA 1. INTRODUCTION and Overview
 The Severe Weather Event of 7 August 2013 By Richard H. Grumm and Bruce Budd National Weather Service State College, PA 1. INTRODUCTION and Overview A fast moving short-wave (Fig. 1) with -1σ 500 hpa height
The Severe Weather Event of 7 August 2013 By Richard H. Grumm and Bruce Budd National Weather Service State College, PA 1. INTRODUCTION and Overview A fast moving short-wave (Fig. 1) with -1σ 500 hpa height
National Weather Service-Pennsylvania State University Weather Events
 National Weather Service-Pennsylvania State University Weather Events Eastern United States Winter Storm and Severe Event of 28-29 February 2012 by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College
National Weather Service-Pennsylvania State University Weather Events Eastern United States Winter Storm and Severe Event of 28-29 February 2012 by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College
On the usage of composite parameters in High-Shear, Low-CAPE environments
 P72 On the usage of composite parameters in High-Shear, Low-CAPE environments Keith D. Sherburn* and Matthew D. Parker Department of Marine, Earth, and Atmospheric Sciences, North Carolina State University,
P72 On the usage of composite parameters in High-Shear, Low-CAPE environments Keith D. Sherburn* and Matthew D. Parker Department of Marine, Earth, and Atmospheric Sciences, North Carolina State University,
Early May Cut-off low and Mid-Atlantic rains
 Abstract: Early May Cut-off low and Mid-Atlantic rains By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA A deep 500 hpa cutoff developed in the southern Plains on 3 May 2013. It produced a
Abstract: Early May Cut-off low and Mid-Atlantic rains By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA A deep 500 hpa cutoff developed in the southern Plains on 3 May 2013. It produced a
Paul Yura*, Frank Alsheimer, and Joseph Calderone NOAA, National Weather Service Forecast Office, Charleston South Carolina 1.
 7B.8 AN EXAMINATION OF THE SYNOPTIC AND MESOSCALE ENVIRONMENTS INVOLVED IN TORNADO OUTBREAKS FROM HURRICANES FRANCES (2004) AND JEANNE (2004) OVER NORTHEAST COASTAL GEORGIA AND SOUTHERN SOUTH CAROLINA
7B.8 AN EXAMINATION OF THE SYNOPTIC AND MESOSCALE ENVIRONMENTS INVOLVED IN TORNADO OUTBREAKS FROM HURRICANES FRANCES (2004) AND JEANNE (2004) OVER NORTHEAST COASTAL GEORGIA AND SOUTHERN SOUTH CAROLINA
Anthony A. Rockwood Robert A. Maddox
 Anthony A. Rockwood Robert A. Maddox An unusually intense MCS produced large hail and wind damage in northeast Kansas and northern Missouri during the predawn hours of June 7 th, 1982. Takes a look at
Anthony A. Rockwood Robert A. Maddox An unusually intense MCS produced large hail and wind damage in northeast Kansas and northern Missouri during the predawn hours of June 7 th, 1982. Takes a look at
16 September 2005 Northern Pennsylvania Supercell Thunderstorm by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803
 16 September 2005 Northern Pennsylvania Supercell Thunderstorm by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION During the afternoon hours of 16 September 2005,
16 September 2005 Northern Pennsylvania Supercell Thunderstorm by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION During the afternoon hours of 16 September 2005,
Mid Atlantic Severe Event of 1 May 2017 Central Pennsylvania QLCS event By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service, State College, PA 16803
 1. Overview Mid Atlantic Severe Event of 1 May 2017 Central Pennsylvania QLCS event By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service, State College, PA 16803 A strong upper-level wave (Fig.1) moving into a
1. Overview Mid Atlantic Severe Event of 1 May 2017 Central Pennsylvania QLCS event By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service, State College, PA 16803 A strong upper-level wave (Fig.1) moving into a
Forecasting Precipitation Distributions Associated with Cool-Season 500-hPa Cutoff Cyclones in the Northeastern United States
 Forecasting Precipitation Distributions Associated with Cool-Season 500-hPa Cutoff Cyclones in the Northeastern United States Melissa Payer, Lance F. Bosart, Daniel Keyser Department of Atmospheric and
Forecasting Precipitation Distributions Associated with Cool-Season 500-hPa Cutoff Cyclones in the Northeastern United States Melissa Payer, Lance F. Bosart, Daniel Keyser Department of Atmospheric and
Severe Weather Event of 13 July 2014
 Severe Weather Event of 13 July 2014 By Richard H. Grumm and Elyse M. Colbert National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview Severe weather affected the eastern United States (Fig. 1) from northwestern
Severe Weather Event of 13 July 2014 By Richard H. Grumm and Elyse M. Colbert National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview Severe weather affected the eastern United States (Fig. 1) from northwestern
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America
 Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
Joshua M. Boustead *1, and Barbara E. Mayes NOAA/NWS WFO Omaha/Valley, NE. William Gargan, George Phillips, and Jared Leighton NOAA/NWS WFO Topeka, KS
 7B.3 Composite Analysis of Environmental Conditions Favorable for Significant Tornadoes across Eastern Kansas Joshua M. Boustead *1, and Barbara E. Mayes NOAA/NWS WFO Omaha/Valley, NE William Gargan, George
7B.3 Composite Analysis of Environmental Conditions Favorable for Significant Tornadoes across Eastern Kansas Joshua M. Boustead *1, and Barbara E. Mayes NOAA/NWS WFO Omaha/Valley, NE William Gargan, George
Northeastern United States Snowstorm of 9 February 2017
 Northeastern United States Snowstorm of 9 February 2017 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A strong shortwave produced a stripe of precipitation
Northeastern United States Snowstorm of 9 February 2017 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A strong shortwave produced a stripe of precipitation
Practical Use of the Skew-T, log-p diagram for weather forecasting. Primer on organized convection
 Practical Use of the Skew-T, log-p diagram for weather forecasting Primer on organized convection Outline Rationale and format of the skew-t, log-p diagram Some basic derived diagnostic measures Characterizing
Practical Use of the Skew-T, log-p diagram for weather forecasting Primer on organized convection Outline Rationale and format of the skew-t, log-p diagram Some basic derived diagnostic measures Characterizing
The Oakfield, Wisconsin, Tornado from July Brett Berenz Student at the University of Wisconsin
 The Oakfield, Wisconsin, Tornado from 18-19 July 1996 Brett Berenz Student at the University of Wisconsin Abstract On July 18 th, 1996 an F5 tornado affected the region of Oakfield, Wisconsin. Leading
The Oakfield, Wisconsin, Tornado from 18-19 July 1996 Brett Berenz Student at the University of Wisconsin Abstract On July 18 th, 1996 an F5 tornado affected the region of Oakfield, Wisconsin. Leading
Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004
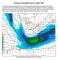 Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004 This event was characterized by a very strong jet streak that developed over North Carolina by 00 UTC 8 March, as seen in the Eta model analysis at 300 mb, with
Summary of High Wind Event of 7 March 2004 This event was characterized by a very strong jet streak that developed over North Carolina by 00 UTC 8 March, as seen in the Eta model analysis at 300 mb, with
DEVELOPMENT OF FORECAST EQUATIONS TO PREDICT THE SEVERITY OF HAIL EVENTS IN NEW YORK STATE
 DEVELOPMENT OF FORECAST EQUATIONS TO PREDICT THE SEVERITY OF HAIL EVENTS IN NEW YORK STATE Kenneth D. LaPenta and George J. Maglaras NOAA/National Weather Service Albany, New York Robert R. Mundschenk
DEVELOPMENT OF FORECAST EQUATIONS TO PREDICT THE SEVERITY OF HAIL EVENTS IN NEW YORK STATE Kenneth D. LaPenta and George J. Maglaras NOAA/National Weather Service Albany, New York Robert R. Mundschenk
Winter Storm of 15 December 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803
 Winter Storm of 15 December 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION A complex winter storm brought snow, sleet, and freezing rain to central Pennsylvania.
Winter Storm of 15 December 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION A complex winter storm brought snow, sleet, and freezing rain to central Pennsylvania.
P9.6 SEVERE THUNDERSTORMS OF 3 APRIL 2004: AN EXAMINATION OF A DRY-SEASON SEVERE WEATHER EVENT IN THE BORDERLAND
 P9.6 SEVERE THUNDERSTORMS OF 3 APRIL 2004: AN EXAMINATION OF A DRY-SEASON SEVERE WEATHER EVENT IN THE BORDERLAND 1. INTRODUCTION Michael P. Hardiman Joseph A. Rogash National Weather Service, Santa Teresa,
P9.6 SEVERE THUNDERSTORMS OF 3 APRIL 2004: AN EXAMINATION OF A DRY-SEASON SEVERE WEATHER EVENT IN THE BORDERLAND 1. INTRODUCTION Michael P. Hardiman Joseph A. Rogash National Weather Service, Santa Teresa,
Justin Arnott and Michael Evans NOAA National Weather Service, Binghamton, NY. Richard Grumm NOAA National Weather Service, State College, PA
 3A.5 REGIONAL SCALE ENSEMBLE FORECAST OF THE LAKE EFFECT SNOW EVENT OF 7 FEBRUARY 2007 Justin Arnott and Michael Evans NOAA National Weather Service, Binghamton, NY Richard Grumm NOAA National Weather
3A.5 REGIONAL SCALE ENSEMBLE FORECAST OF THE LAKE EFFECT SNOW EVENT OF 7 FEBRUARY 2007 Justin Arnott and Michael Evans NOAA National Weather Service, Binghamton, NY Richard Grumm NOAA National Weather
IWT Scenario 2 Integrated Warning Team Workshop National Weather Service Albany, NY October 31, 2014
 IWT Scenario 2 Integrated Warning Team Workshop National Weather Service Albany, NY October 31, 2014 09 10 11 12 13 Scenario 2 Timeline December 9-13 Tue Wed Thu Fri Sat Tue, Dec. 9 @ 5 am 2014 2014 2014
IWT Scenario 2 Integrated Warning Team Workshop National Weather Service Albany, NY October 31, 2014 09 10 11 12 13 Scenario 2 Timeline December 9-13 Tue Wed Thu Fri Sat Tue, Dec. 9 @ 5 am 2014 2014 2014
Final Report. We will discuss the project accomplishments in two sub sections, reflecting the two major efforts given in Section 1.
 Final Report to Cooperative Program for Operational Meteorology, Education and Training (COMET) University: University of Illinois in Urbana Champaign Name of University Researcher Preparing Report: David
Final Report to Cooperative Program for Operational Meteorology, Education and Training (COMET) University: University of Illinois in Urbana Champaign Name of University Researcher Preparing Report: David
Science Olympiad Meteorology Quiz #2 Page 1 of 8
 1) The prevailing general direction of the jet stream is from west to east in the northern hemisphere: 2) Advection is the vertical movement of an air mass from one location to another: 3) Thunderstorms
1) The prevailing general direction of the jet stream is from west to east in the northern hemisphere: 2) Advection is the vertical movement of an air mass from one location to another: 3) Thunderstorms
4/18/2010. National Weather Service. Severe Weather Forecasting: A Western North Carolina Case Study
 National Weather Service Severe Weather Forecasting: A Western North Carolina Case Study Laurence G. Lee Science and Operations Officer National Weather Service Greer, SC Plus 13 River Forecast Centers
National Weather Service Severe Weather Forecasting: A Western North Carolina Case Study Laurence G. Lee Science and Operations Officer National Weather Service Greer, SC Plus 13 River Forecast Centers
Influence of Topography on Convective. Patterns across the Greater Capital Region of. New York
 Influence of Topography on Convective Patterns across the Greater Capital Region of New York Honors College Undergraduate Research Thesis (8 May 2016) Rachel O Donnell and Professor Brian Tang Department
Influence of Topography on Convective Patterns across the Greater Capital Region of New York Honors College Undergraduate Research Thesis (8 May 2016) Rachel O Donnell and Professor Brian Tang Department
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa
 Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Weather Patterns and Severe Weather Foundations, 6e - Chapter 14 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Air masses Characteristics Large body
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Weather Patterns and Severe Weather Foundations, 6e - Chapter 14 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Air masses Characteristics Large body
NWS-PSU Case Study Site 2010 Severe Weather Case
 NWS-PSU Case Study Site 2010 Severe Weather Case New Years Eve Severe Weather Event of 31 December 2010 by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College PA 16083 Abstract: A surge of warm humid
NWS-PSU Case Study Site 2010 Severe Weather Case New Years Eve Severe Weather Event of 31 December 2010 by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College PA 16083 Abstract: A surge of warm humid
AN INVESTIGATION OF THE SIGNIFICANT TORNADO OUTBREAK IN SOUTHERN SOUTH CAROLINA AND NORTH COASTAL GEORGIA ON MARCH 15, 2008
 P3.6 AN INVESTIGATION OF THE SIGNIFICANT TORNADO OUTBREAK IN SOUTHERN SOUTH CAROLINA AND NORTH COASTAL GEORGIA ON MARCH 15, 2008 Frank W. Alsheimer*, Robert Bright, Jonathon Jelsema, Wendy Moen, John Quagliariello,
P3.6 AN INVESTIGATION OF THE SIGNIFICANT TORNADO OUTBREAK IN SOUTHERN SOUTH CAROLINA AND NORTH COASTAL GEORGIA ON MARCH 15, 2008 Frank W. Alsheimer*, Robert Bright, Jonathon Jelsema, Wendy Moen, John Quagliariello,
Case Study 3: Dryline in TX and OK 3 May 1999
 Case Study 3: Dryline in TX and OK 3 May 1999 Brandy Lumpkins Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison 8 May 2006 ABSTRACT A massive tornadic outbreak swept across
Case Study 3: Dryline in TX and OK 3 May 1999 Brandy Lumpkins Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison 8 May 2006 ABSTRACT A massive tornadic outbreak swept across
THE SUMMER STUDENT VOLUNTEER PROGRAM AT NWS WFO BALTIMORE/WASHINGTON
 THE SUMMER STUDENT VOLUNTEER PROGRAM AT NWS WFO BALTIMORE/WASHINGTON Matthew R. Kramar, Andrew B. Woodcock, Jared R. Klein and Steven M. Zubrick NOAA/National Weather Service Weather Forecast Office Baltimore/Washington
THE SUMMER STUDENT VOLUNTEER PROGRAM AT NWS WFO BALTIMORE/WASHINGTON Matthew R. Kramar, Andrew B. Woodcock, Jared R. Klein and Steven M. Zubrick NOAA/National Weather Service Weather Forecast Office Baltimore/Washington
THE SYNOPTIC ENVIRONMENT OF THE 11 APRIL 2001 CENTRAL PLAINS TORNADO OUTBREAK VIEWED IN THREE DIMENSIONS
 P1.1 THE SYNOPTIC ENVIRONMENT OF THE 11 APRIL 2001 CENTRAL PLAINS TORNADO OUTBREAK VIEWED IN THREE DIMENSIONS Daniel D. Nietfeld * NOAA/NWS/WFO Omaha/Valley, NE 1. INTRODUCTION A powerful low pressure
P1.1 THE SYNOPTIC ENVIRONMENT OF THE 11 APRIL 2001 CENTRAL PLAINS TORNADO OUTBREAK VIEWED IN THREE DIMENSIONS Daniel D. Nietfeld * NOAA/NWS/WFO Omaha/Valley, NE 1. INTRODUCTION A powerful low pressure
Jonathan M. Davies* Private Meteorologist, Wichita, Kansas
 4.3 RUC Soundings with Cool Season Tornadoes in Small CAPE Settings and the 6 November 2005 Evansville, Indiana Tornado Jonathan M. Davies* Private Meteorologist, Wichita, Kansas 1. Introduction Several
4.3 RUC Soundings with Cool Season Tornadoes in Small CAPE Settings and the 6 November 2005 Evansville, Indiana Tornado Jonathan M. Davies* Private Meteorologist, Wichita, Kansas 1. Introduction Several
P12.7 MESOCYCLONE AND RFD INDUCED DAMAGING WINDS OBSERVED IN THE 27 MAY 2004 SOUTHWEST OHIO SUPERCELL
 P12.7 MESOCYCLONE AND RFD INDUCED DAMAGING WINDS OBSERVED IN THE 27 MAY 2004 SOUTHWEST OHIO SUPERCELL John T. DiStefano* National Weather Service Office, Wilmington, Ohio 1. INTRODUCTION During the early
P12.7 MESOCYCLONE AND RFD INDUCED DAMAGING WINDS OBSERVED IN THE 27 MAY 2004 SOUTHWEST OHIO SUPERCELL John T. DiStefano* National Weather Service Office, Wilmington, Ohio 1. INTRODUCTION During the early
Thanksgiving Snow and Arctic Front 25 November 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 16801
 Thanksgiving Snow and Arctic Front 25 November 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 16801 1. INTRODUCTION An approaching arctic front brought light snow to most of western
Thanksgiving Snow and Arctic Front 25 November 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 16801 1. INTRODUCTION An approaching arctic front brought light snow to most of western
July24th, 2008 New Hampshire tornado. Hunter Straus. University of Wisconsin department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Madison, WI ABSTRACT
 July24th, 2008 New Hampshire tornado Hunter Straus University of Wisconsin department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Madison, WI 53715 ABSTRACT On July 24 th, 2008 at approximately 1530Z, an EF-2
July24th, 2008 New Hampshire tornado Hunter Straus University of Wisconsin department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Madison, WI 53715 ABSTRACT On July 24 th, 2008 at approximately 1530Z, an EF-2
P12.7 THE ROLE OF A SURFACE BOUNDARY AND MULTIPLE CELL-MERGERS IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE 21 APRIL 2003 TORNADO IN UPSTATE SOUTH CAROLINA
 P12.7 THE ROLE OF A SURFACE BOUNDARY AND MULTIPLE CELL-MERGERS IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE 21 APRIL 2003 TORNADO IN UPSTATE SOUTH CAROLINA 1. INTRODUCTION Bryan McAvoy NOAA/National Weather Service Greer,
P12.7 THE ROLE OF A SURFACE BOUNDARY AND MULTIPLE CELL-MERGERS IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE 21 APRIL 2003 TORNADO IN UPSTATE SOUTH CAROLINA 1. INTRODUCTION Bryan McAvoy NOAA/National Weather Service Greer,
Mid Atlantic Heavy rainfall event 1. Overview 2. Methods and Data 3. Pattern
 1. Overview Mid Atlantic Heavy rainfall event With an inertial gravity wave? By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service, State College, PA 16803 Contributions from the Albany MAP An unseasonably strong
1. Overview Mid Atlantic Heavy rainfall event With an inertial gravity wave? By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service, State College, PA 16803 Contributions from the Albany MAP An unseasonably strong
P8.14 CLASSIC AND HP MINI-SUPERCELLS IN SOUTHEAST OREGON AND SOUTHWEST IDAHO ON 3 MAY
 P8.14 CLASSIC AND HP MINI-SUPERCELLS IN SOUTHEAST OREGON AND SOUTHWEST IDAHO ON 3 MAY 2009 Stephen S. Parker* National Weather Service, Boise, ID 1. INTRODUCTION During the early afternoon hours of 3 May
P8.14 CLASSIC AND HP MINI-SUPERCELLS IN SOUTHEAST OREGON AND SOUTHWEST IDAHO ON 3 MAY 2009 Stephen S. Parker* National Weather Service, Boise, ID 1. INTRODUCTION During the early afternoon hours of 3 May
Boundary-layer Decoupling Affects on Tornadoes
 Boundary-layer Decoupling Affects on Tornadoes Chris Karstens ABSTRACT The North American low-level jet is known to have substantial impacts on the climatology of central and eastern regions of the United
Boundary-layer Decoupling Affects on Tornadoes Chris Karstens ABSTRACT The North American low-level jet is known to have substantial impacts on the climatology of central and eastern regions of the United
5A.3 THE USE OF ENSEMBLE AND ANOMALY DATA TO ANTICIPATE EXTREME FLOOD EVENTS IN THE NORTHEASTERN U.S.
 5A.3 THE USE OF ENSEMBLE AND ANOMALY DATA TO ANTICIPATE EXTREME FLOOD EVENTS IN THE NORTHEASTERN U.S. Neil A. Stuart(1), Richard H. Grumm(2), John Cannon(3), and Walt Drag(4) (1)NOAA/National Weather Service,
5A.3 THE USE OF ENSEMBLE AND ANOMALY DATA TO ANTICIPATE EXTREME FLOOD EVENTS IN THE NORTHEASTERN U.S. Neil A. Stuart(1), Richard H. Grumm(2), John Cannon(3), and Walt Drag(4) (1)NOAA/National Weather Service,
Mid-Atlantic Severe Weather Event of 23 June 2015
 Mid-Atlantic Severe Weather Event of 23 June 2015 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A widespread severe weather event occurred in the eastern United States on 23
Mid-Atlantic Severe Weather Event of 23 June 2015 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A widespread severe weather event occurred in the eastern United States on 23
Determining Environmental Parameters Most Important for Significant Cool Season Tornadoes across the Gulf Coastal States
 Determining Environmental Parameters Most Important for Significant Cool Season Tornadoes across the Gulf Coastal States Kar retta Venable Jackson State University, Jackson, MS Mentors David Imy NOAA/NWS/NCEP/Storm
Determining Environmental Parameters Most Important for Significant Cool Season Tornadoes across the Gulf Coastal States Kar retta Venable Jackson State University, Jackson, MS Mentors David Imy NOAA/NWS/NCEP/Storm
A Review of the 1 June 2011 Hampden and Worcester County Massachusetts EF-3 Tornado
 A Review of the 1 June 2011 Hampden and Worcester County Massachusetts EF-3 Tornado Ryan Hanrahan NBC Connecticut / WVIT DRAFT - May 9, 2012 Introduction Strong and violent tornadoes are rare in southern
A Review of the 1 June 2011 Hampden and Worcester County Massachusetts EF-3 Tornado Ryan Hanrahan NBC Connecticut / WVIT DRAFT - May 9, 2012 Introduction Strong and violent tornadoes are rare in southern
Case Study: Severe Thunderstorm Over Fairbanks, AK on 8 th of June, 1997
 Case Study: Severe Thunderstorm Over Fairbanks, AK on 8 th of June, 1997 Michael Richmond NWS - WFO Fairbanks 23 August, 2007 Introduction: Thunderstorms are a prominent feature of the Alaska Interior
Case Study: Severe Thunderstorm Over Fairbanks, AK on 8 th of June, 1997 Michael Richmond NWS - WFO Fairbanks 23 August, 2007 Introduction: Thunderstorms are a prominent feature of the Alaska Interior
Convective Storm Structures and Ambient Conditions Associated with Severe Weather over the Northeast United States
 940 W E A T H E R A N D F O R E C A S T I N G VOLUME 26 Convective Storm Structures and Ambient Conditions Associated with Severe Weather over the Northeast United States KELLY A. LOMBARDO AND BRIAN A.
940 W E A T H E R A N D F O R E C A S T I N G VOLUME 26 Convective Storm Structures and Ambient Conditions Associated with Severe Weather over the Northeast United States KELLY A. LOMBARDO AND BRIAN A.
Multiscale Analyses of Inland Tropical Cyclone Midlatitude Jet Interactions: Camille (1969) and Danny (1997)
 Multiscale Analyses of Inland Tropical Cyclone Midlatitude Jet Interactions: Camille (1969) and Danny (1997) Matthew Potter, Lance Bosart, and Daniel Keyser Department of Atmospheric and Environmental
Multiscale Analyses of Inland Tropical Cyclone Midlatitude Jet Interactions: Camille (1969) and Danny (1997) Matthew Potter, Lance Bosart, and Daniel Keyser Department of Atmospheric and Environmental
Investigation of the Arizona Severe Weather Event of August 8 th, 1997
 Investigation of the Arizona Severe Weather Event of August 8 th, 1997 Tim Hollfelder May 10 th, 2006 Abstract Synoptic scale forcings were very weak for these thunderstorms on August 7-8, 1997 over the
Investigation of the Arizona Severe Weather Event of August 8 th, 1997 Tim Hollfelder May 10 th, 2006 Abstract Synoptic scale forcings were very weak for these thunderstorms on August 7-8, 1997 over the
P4.9 THE SEVERE THUNDERSTORM OUTBREAK IN FINLAND ON 5 JULY 2002
 P4.9 THE SEVERE THUNDERSTORM OUTBREAK IN FINLAND ON 5 JULY 2002 Ari-Juhani Punkka* and Jenni Teittinen Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki, Finland 1. INTRODUCTION On 5 July 2002 a fast propagating
P4.9 THE SEVERE THUNDERSTORM OUTBREAK IN FINLAND ON 5 JULY 2002 Ari-Juhani Punkka* and Jenni Teittinen Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki, Finland 1. INTRODUCTION On 5 July 2002 a fast propagating
WISCONSIN TORNADO OUTBREAK OF 18 AUGUST 2005: AN EXAMINATION OF THE VIOLA, WISCONSIN TORNADO
 WISCONSIN TORNADO OUTBREAK OF 18 AUGUST 2005: AN EXAMINATION OF THE VIOLA, WISCONSIN TORNADO Charles D. Koch University of Wisconsin Madison AOS 453: Mesoscale Meteorology Professor Greg Tripoli 13 May
WISCONSIN TORNADO OUTBREAK OF 18 AUGUST 2005: AN EXAMINATION OF THE VIOLA, WISCONSIN TORNADO Charles D. Koch University of Wisconsin Madison AOS 453: Mesoscale Meteorology Professor Greg Tripoli 13 May
Type of storm viewed by Spotter A Ordinary, multi-cell thunderstorm. Type of storm viewed by Spotter B Supecell thunderstorm
 ANSWER KEY Part I: Locating Geographical Features 1. The National Weather Service s Storm Prediction Center (www.spc.noaa.gov) has issued a tornado watch on a warm spring day. The watch covers a large
ANSWER KEY Part I: Locating Geographical Features 1. The National Weather Service s Storm Prediction Center (www.spc.noaa.gov) has issued a tornado watch on a warm spring day. The watch covers a large
Steve Keighton * and Steve Nogueira NOAA/NWS Blacksburg, VA. Nicole Belk NOAA/NWS Charleston, WV
 P5.17 SYNOPTIC AND MESOSCALE ANALYSIS OF THE 9 AUGUST 2000 APPALACHIAN-CROSSING DERECHOS Steve Keighton * and Steve Nogueira NOAA/NWS Blacksburg, VA Nicole Belk NOAA/NWS Charleston, WV 1. INTRODUCTION
P5.17 SYNOPTIC AND MESOSCALE ANALYSIS OF THE 9 AUGUST 2000 APPALACHIAN-CROSSING DERECHOS Steve Keighton * and Steve Nogueira NOAA/NWS Blacksburg, VA Nicole Belk NOAA/NWS Charleston, WV 1. INTRODUCTION
IWT Scenario 1 Integrated Warning Team Workshop National Weather Service Albany, NY October 31, 2014
 Integrated Warning Team Workshop National Weather Service Albany, NY October 31, 2014 23 24 25 26 27 Scenario 1 Timeline November 23-27 Sun Mon Tue Wed Thu Thanksgiving Day Sunday, Nov. 23 @ 430 pm NWS
Integrated Warning Team Workshop National Weather Service Albany, NY October 31, 2014 23 24 25 26 27 Scenario 1 Timeline November 23-27 Sun Mon Tue Wed Thu Thanksgiving Day Sunday, Nov. 23 @ 430 pm NWS
Winter Storm of February 2008 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College PA 16803
 1. INTRODUCTION Winter Storm of 11-13 February 2008 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College PA 16803 A potent winter storm brought snow, sleet, freezing rain, and rain to the
1. INTRODUCTION Winter Storm of 11-13 February 2008 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College PA 16803 A potent winter storm brought snow, sleet, freezing rain, and rain to the
The 13 April 2006 Severe Thunderstorm and Large Hail Event in Iowa & Wisconsin:A Case Study
 The 13 April 2006 Severe Thunderstorm and Large Hail Event in Iowa & Wisconsin:A Case Study David M. DeMeuse Undergraduate University of Wisconsin Department of Atmospheric & Oceanic Science Mesoscale
The 13 April 2006 Severe Thunderstorm and Large Hail Event in Iowa & Wisconsin:A Case Study David M. DeMeuse Undergraduate University of Wisconsin Department of Atmospheric & Oceanic Science Mesoscale
1. INTRODUCTION. The super storm of March 1993 produced severe weather and tornadoes as it s trailing cold front pushed through Florida (Kocin eta 1l
 1. INTRODUCTION Super Tuesday and awful Wednesday: the 5-6 February 2008 Severe Weather Outbreak By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA And Seth Binau National Weather Service,
1. INTRODUCTION Super Tuesday and awful Wednesday: the 5-6 February 2008 Severe Weather Outbreak By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA And Seth Binau National Weather Service,
Pre-Christmas Warm-up December 2013-Draft
 Pre-Christmas Warm-up 21-23 December 2013-Draft By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A large ridge over the west-central Atlantic (Fig.1) and trough moving into eastern
Pre-Christmas Warm-up 21-23 December 2013-Draft By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A large ridge over the west-central Atlantic (Fig.1) and trough moving into eastern
P12.6 Multiple Modes of Convection in Moderate to High Wind Shear Environments
 P12.6 Multiple Modes of Convection in Moderate to High Wind Shear Environments Adam J. French and Matthew D. Parker North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North Carolina 1. INTRODUCTION A principle
P12.6 Multiple Modes of Convection in Moderate to High Wind Shear Environments Adam J. French and Matthew D. Parker North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North Carolina 1. INTRODUCTION A principle
David G. Biggar. National Weather Service Forecast Office, Jackson, Mississippi
 A CASE STUDY OF A POSITIVE STRIKE DOMINATED SUPERCELL THUNDERSTORM THAT PRODUCED AN F2 TORNADO AFTER UNDERGOING A SIGNIFICANT CLOUD-TO-GROUND LIGHTNING POLARITY SHIFT Abstract David G. Biggar National
A CASE STUDY OF A POSITIVE STRIKE DOMINATED SUPERCELL THUNDERSTORM THAT PRODUCED AN F2 TORNADO AFTER UNDERGOING A SIGNIFICANT CLOUD-TO-GROUND LIGHTNING POLARITY SHIFT Abstract David G. Biggar National
P8.10 AN EXAMINATION OF VARYING SUPERCELL ENVIRONMENTS OVER THE COMPLEX TERRAIN OF THE EASTERN TENNESSEE RIVER VALLEY
 P8.10 AN EXAMINATION OF VARYING SUPERCELL ENVIRONMENTS OVER THE COMPLEX TERRAIN OF THE EASTERN TENNESSEE RIVER VALLEY by David M. Gaffin* and David G. Hotz National Weather Service, Morristown TN 1. INTRODUCTION
P8.10 AN EXAMINATION OF VARYING SUPERCELL ENVIRONMENTS OVER THE COMPLEX TERRAIN OF THE EASTERN TENNESSEE RIVER VALLEY by David M. Gaffin* and David G. Hotz National Weather Service, Morristown TN 1. INTRODUCTION
Hurricane and Tropical Cyclone Tornado Environments from RUC Proximity Soundings
 P8.1 Hurricane and Tropical Cyclone Tornado Environments from RUC Proximity Soundings Jonathan M. Davies* Private Meteorologist, Wichita, Kansas 1. Introduction Studies such as those by McCaul (1991, 1996)
P8.1 Hurricane and Tropical Cyclone Tornado Environments from RUC Proximity Soundings Jonathan M. Davies* Private Meteorologist, Wichita, Kansas 1. Introduction Studies such as those by McCaul (1991, 1996)
Oakfield, WI Tornado of July 18 th, 1996: "Everything in its Right Place"
 Oakfield, WI Tornado of July 18 th, 1996: "Everything in its Right Place" Arian Sarsalari Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Wisconsin Madison ABSTRACT This paper will serve
Oakfield, WI Tornado of July 18 th, 1996: "Everything in its Right Place" Arian Sarsalari Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Wisconsin Madison ABSTRACT This paper will serve
2 July 2013 Flash Flood Event
 2 July 2013 Flash Flood Event By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A retrograding 500 hpa cyclone and anticyclone (Fig. 1) set up deep southerly flow
2 July 2013 Flash Flood Event By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A retrograding 500 hpa cyclone and anticyclone (Fig. 1) set up deep southerly flow
COMPOSITE MEANS AND ANOMALIES OF METEOROLOGICAL PARAMETERS FOR SUMMERTIME FLASH FLOODING IN THE NATIONAL WEATHER SERVICE EASTERN REGION
 COMPOSITE MEANS AND ANOLIES OF METEOROLOGICAL PARAMETERS FOR SUMMERTIME FLASH FLOODING IN THE NATIONAL WEATHER SERVICE EASTERN REGION Alan M. Cope and Lee Robertson NOAA/National Weather Service Mount
COMPOSITE MEANS AND ANOLIES OF METEOROLOGICAL PARAMETERS FOR SUMMERTIME FLASH FLOODING IN THE NATIONAL WEATHER SERVICE EASTERN REGION Alan M. Cope and Lee Robertson NOAA/National Weather Service Mount
The Jarrell Tornado of May 27, 1997
 The Jarrell Tornado of May 27, 1997 ANDREW MANKOWSKI University of Wisconsin Madison Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences ABSTRACT A tornado outbreak occurred over Central Texas on May 27, 1997. This outbreak
The Jarrell Tornado of May 27, 1997 ANDREW MANKOWSKI University of Wisconsin Madison Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences ABSTRACT A tornado outbreak occurred over Central Texas on May 27, 1997. This outbreak
End of heat-event severe event of 7 July 2012
 End of heat-event severe event of 7 July 2012 Richard H. Grumm And Elyse Colbert National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. Overview A widespread severe weather event affected Pennsylvania
End of heat-event severe event of 7 July 2012 Richard H. Grumm And Elyse Colbert National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. Overview A widespread severe weather event affected Pennsylvania
11B.1 INFLUENCE OF DIABATIC POTENTIAL VORTICITY ANOMALIES UPON WARM CONVEYOR BELT FLOW. PART I: FEBRUARY 2003
 INFLUENCE OF DIABATIC POTENTIAL VORTICITY ANOMALIES UPON WARM CONVEYOR BELT FLOW. PART I: 14-15 FEBRUARY 2003 Philip N. Schumacher, NOAA/NWS, Sioux Falls, SD Joshua M. Boustead, NOAA/NWS, Valley, NE Martin
INFLUENCE OF DIABATIC POTENTIAL VORTICITY ANOMALIES UPON WARM CONVEYOR BELT FLOW. PART I: 14-15 FEBRUARY 2003 Philip N. Schumacher, NOAA/NWS, Sioux Falls, SD Joshua M. Boustead, NOAA/NWS, Valley, NE Martin
1. INTRODUCTION. For brevity times are referred to in the format of 20/1800 for 20 August UTC. 3. RESULTS
 Heavy rains and precipitable water anomalies 20-23 August 2010-Draft By Jason Krekeler And Richard Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION Heavy rain fell across the central
Heavy rains and precipitable water anomalies 20-23 August 2010-Draft By Jason Krekeler And Richard Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION Heavy rain fell across the central
Investigating the Environment of the Indiana and Ohio Tornado Outbreak of 24 August 2016 Using a WRF Model Simulation 1.
 Investigating the Environment of the Indiana and Ohio Tornado Outbreak of 24 August 2016 Using a WRF Model Simulation Kevin Gray and Jeffrey Frame Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Illinois
Investigating the Environment of the Indiana and Ohio Tornado Outbreak of 24 August 2016 Using a WRF Model Simulation Kevin Gray and Jeffrey Frame Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Illinois
1. COLD FRONT - CLOUD STRUCTURE IN SATELLITE IMAGES
 1. COLD FRONT - CLOUD STRUCTURE IN SATELLITE IMAGES The satellite image shows a cyclonically curved synoptic scale cloud band usually a few hundred kilometres wide; in the VIS image the cloud band mostly
1. COLD FRONT - CLOUD STRUCTURE IN SATELLITE IMAGES The satellite image shows a cyclonically curved synoptic scale cloud band usually a few hundred kilometres wide; in the VIS image the cloud band mostly
Synoptic Environments Associated with Significant Tornadoes in the Contiguous United States
 Synoptic Environments Associated with Significant Tornadoes in the Contiguous United States JAYSON A. PRENTICE Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences, Iowa State University, Ames, IA Mentor:
Synoptic Environments Associated with Significant Tornadoes in the Contiguous United States JAYSON A. PRENTICE Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences, Iowa State University, Ames, IA Mentor:
24: Monthly Report September Seeding Operations & Atmospheric Research (SOAR) Snapshot of Seeding Operations
 0.3.05 Monthly Report September 05 Project Puerto Rico Cloud Seeding Program Project Manager Gary L. Walker Snapshot of Seeding Operations Date Flight Time (hours) Number of Flares (total) September 0:04
0.3.05 Monthly Report September 05 Project Puerto Rico Cloud Seeding Program Project Manager Gary L. Walker Snapshot of Seeding Operations Date Flight Time (hours) Number of Flares (total) September 0:04
