Cosmic Vision ESA s new long term plan for space science
|
|
|
- Leona Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cosmic Vision ESA s new long term plan for space science
2 IRSI DARWIN XEUS Aurora SOLAR ORBITER F 3 LISA GAIA BEPI COLOMBO LPF JWST ROSETTA ILWS VENUS * PLANCK EXPRESS HERSCHEL SMART 1 MARS EXPRESS CASSINI/ HUYGENS ULYSSES SOHO CLUSTER CLUSTER II XMM NEWTON ISO INTEGRAL HST Time
3 Missions in preparation Corot Herschel-Planck (CNES-ESA) JWST (NASA-ESA) Astro-F 2011 (Japan-ESA) 2006 Venus Express Microscope (CNES-ESA) 2008 Lisa- Pathfinder 2009 Bepi-Colombo 2012 Gaia Lisa 2014 Solar Orbiter
4 Cosmic Vision process Cosmic Vision process launched on 2 April 04 with call for Science themes 1June 04: deadline for proposal submission July 04: Analysis of responses by the ESA Science advisory bodies (AWG, SSWG, FPAG, SSAC) September 04: Workshop in Paris (~400 participants) Nov 04: progress report to SPC Spring 05: presentation of Cosmic Vision to community May 05: Final Presentation of Cosmic Vision to SPC
5 Response to Cosmic Vision call In excess of 150 responses received! Horizon consultation received less than 100 responses Reveals today s strong expectations of the community from the ESA Science Programme
6 Cosmic Vision proposal evaluation Proposals evaluated for prime scientific objectives by ESA s working groups Astronomy/Astrophysics (AWG) Fundamental Physics (FPAG) Solar System Science (SSWG) Space Science Advisory Committee (SSAC) merged working group objectives into 4 grand themes Building on scientific heritage from H2000 missions Capitalizing on synergies across disciplines Propose implementation strategy
7 Grand themes 1. What are the conditions for life and planetary formation? 2. How does the Solar System work. 3. What are the fundamental laws of the Universe? 4. How did the Universe originate and what is it made of?
8 1. What are the conditions for life and planetary formation? Place the Solar System into the overall context of planetary formation, aiming at comparative planetology 1.1 From gas and dust to stars and planets. 1.2 From exo-planets to bio-markers. 1.3 Life and habitability in the Solar System.
9 1.1 From gas and dust to stars and planets Map the birth of stars and planets by peering into the highly obscured cocoons where they form. Investigate star formation areas, protostars and protoplanetary disks Investigate the conditions for star and planet formation and evolution Investigate which properties of the host stars and which location in the Galaxy are more favourable to the formation of planets Tool: Far Infrared observatory with high spatial and low to high spectral resolution.
10 1.2 From exo-planets to bio-markers Search for and image planets around stars other than the Sun, looking for biomarkers in their atmospheres Direct detection of Earth-like planets. Physical and chemical characterization of their atmospheres for the identification of unique biomarkers. Systematic census of terrestrial planets Ultimate goal: image terrestrial planets Tool: Space nulling interferometer with near to mid-infrared low resolution spectroscopy capability. Later: terrestrial astrometric surveyor Much later: large optical interferometer
11 1.3 Life and habitability in the Solar System Explore in situ the surface and subsurface of the solid bodies in the Solar System more likely to host or have hosted- life. Appearance and evolution of life depends on environmental conditions (geological processes, water presence, climatic and atmospheric conditions, Solar magnetic and radiation environment) Mars is ideally suited to address key scientific questions of habitability. Europa is the other priority for study of internal structure, composition of ocean and icy crust and radiation environment around Jupiter.
12 1.3 Life and habitability in the Solar System Tools: Mars exploration with in-situ measurements(rovers) and sample return. 3D solar magnetic field explorer (Solar Polar Orbiter) Dedicated Europa orbiter (lander) on Jupiter Explorer Probe (JEP).
13 Strategies for Theme 1 First: In-depth analysis of terrestrial planets -Exoplanets: a space nulling interferometer with near to mid-infrared low resolution spectroscopy capability. -Mars exploration: in-situ measurements (rovers) and sample return. Later: Understand the conditions for star, planet and life formation -Stars and exoplanets: Far Infrared observatory with high spatial and low to high spectral resolution. -Solar system: 3-D solar magnetic field explorer (Solar Polar Orbiter)
14 Strategies for Theme 1 Still later: -Make a census of terrestrial planets orbiting stars < 100 pc: Terrestrial astrometric surveyor -Explore in-situ the surface of other solid bodies in the Solar System: Dedicated Europa orbiter (lander) on Jupiter Explorer Probe (JEP) Much later: -Image a terrestrial exo-planet: Large optical interferometer
15 2. How does the Solar System work? 2.1 From the Sun to the edge of the Solar System 2.2 Gaseous Giants and their Moons 2.3 The Building Blocks of the Solar System: Asteroids and Small Bodies
16 2.1 From the Sun to the edge of the Solar System Study the plasma and magnetic field environment around the Earth, the Jovian system as a mini Solar System-, the Solar poles and the heliopause where the Solar influence area meets the interstellar medium. The structure of the magnetic field at the solar surface requires observations from above the poles to understand the field s origin. The Solar System pervaded by the solar plasma and magnetic field provides a range of laboratories to study the interactions of planets (Jupiter) with the solar wind In-situ observation of the heliopause would provide ground truth measurements of the interstellar medium. Tools: Solar Polar Orbiter, Earth magnetospheric swarm, Jupiter Probe, Interstellar Helio-Pause Probe.
17 2.2 Gaseous Giants and their Moons Study Jupiter In-situ, its atmosphere and internal structure. Giant planets with their rings,diverse satellites and complex environments, constitute systems which play a key role in the evolution of planetary systems. Tools: Jupiter Explorer Probe/JEP
18 2.3 The Building Blocks of the Solar System Obtain direct laboratory information of the building blocks of the Solar System by analysing samples from a Near-Earth Object (NEO). As primitive building blocks in the solar system, small bodies give clues to the chemical mixture and initial conditions from which the planets formed in the early solar nebula Tools: NEO sample return, Mars sample return
19 Strategies for Theme 2 From the Sun to the edge of the solar system measure : First., the hierarchy of scales in the magnetosphere (e.g. M 3, Magnetospheric SWARM) Next, the 3-D solar magnetic field: (e.g. Solar Polar Orbiter) Finally, the outer reaches of the heliosphere (e.g. Heliopause probe) The Giant Planets and their environments explore : First, the Jovian environment, including Europa, using a series of multiple micro-spacecraft Then the Jovian atmosphere and Europan surface with in-situ probes Asteroids and small bodies return samples from : First, primitive Near-Earth objects (e.g. NEO sample return) Then Mars (e.g. Mars Sample return)
20 3. What are the fundamental laws of the Universe? 3.1 Explore the limits of contemporary physics 3.2 The gravitational wave Universe 3.3 Matter under extreme conditions
21 3.1 Explore the limits of contemporary physics Probe the limits of GR, symmetry violations, fundamental constants, Short Range Forces, Quantum Physics of Bose-Einstein Condensates, Cosmic rays, to look for clues to Unified Theories. Use the stable and gravity-free environment of space to implement high precision experiments to search for tiny deviations from the standard model of fundamental interactions. Tool: Fundamental Physics Exlorer programme
22 3.2 The gravitational wave Universe Detect and study the gravitational radiation background generated at the Big Bang. Probe the universe at high red shift and explore the dark universe. Primordial gravitational waves, unaffected by matter, are ideal probes of the laws of physics at the primordial energies and temperatures. They open an ideal window to probe the very early Universe and dark energy at very early times. Tool: Gravitational Wave Cosmic Surveyor
23 3.3 Matter under extreme conditions Probe General Relativity in the environment of Black Holes and compact objects, as well as the equation of state of matter in Neutron Stars. The study of the spectrum and time variability of radiation from matter near BHs carry the imprint of the curvature of space-time as predicted by general relativity. This has strong implications for astrophysics and cosmology in general. Tools: Large aperture X-ray observatory, gamma-ray observatory.
24 To probe the limits of our current understanding: Fundamental Physics Explorer Series ( ) Sequence of inexpensive small missions using the same platform, designed for ultra-high-precision experiments, impossible on ground. An opportunity for Europe to take leadership in a new field of science Going into space with completely new technologies, developed on the ground in Nobel-Prize winning experiments: cold atoms, Bose-Einstein condensates. Big increases in precision measurement, tracking, pointing. e Strategies for Theme 3 g k L g Laser Many experiments already proposed by community: Test foundations of theoretical physics (nature of space and time) Explore limits of quantum theory (entanglement, decoherence) Look for signs of quantum gravity in high-precision experiments
25 To explore the Gravitational Universe Strategies for Theme 3 Probing black holes and high-energy physics (2015) Large-area X-ray telescope mission (XEUS) Mission to detect anomalous ultra-high-energy cosmic rays Explore solar-system gravity for hints of quantum effects ( ) Large-scale violations of Einstein gravity Resolve anomalies in tracking of Pioneer, other spacecraft Speed of light tests, quantum measurements over large distances, Gravitational Wave Explorer (2025) Build on LISA experience, but open up a new frequency window for gravitational waves: Hz. In this window it should be possible to see the Big Bang in gravitational waves, along with the earliest neutron stars and the first generation of black holes. Technology development should start now: lasers, mirrors, controls Partnerships with NASA ( Big Bang Observer ), other agencies desirable
26 4. How did the Universe originate and what is it made of? 4.1 The early Universe 4.2 The Universe taking shape 4.3 The evolving violent Universe
27 4.1 The early Universe Investigate the physical processes that lead to the inflationary phase in the early Universe during which a drastic expansion took place. Investigate the nature and origin of the Dark Energy that currently drives our Universe apart. Imprints of inflation are related to the polarization parameters of anisotropies of the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) due to primordial gravitational waves from Big Bang. Dark energy can be studied in the gravitational lensing from cosmic large scale structures and the measurement of the luminosity-redshift relation of distant Supernovae (SN) Ia. Tools: All-sky CMB polarisation mapper,, Wide-field optical- near IR imager. Later: Gravitational Wave Cosmic Surveyor
28 4.2 The Universe taking shape Find the very first gravitationally bound structures assembled in the Universe (precursors to today s galaxies and clusters of galaxies) and trace their evolution to today. The very first clusters of galaxies back to their formation epoch are keys to study their relation to AGN activity and the chemical enrichment of the Inter Galactic Medium. Also important are the studies of the joint galaxy and supermassive BH evolution, the resolution of the far IR background into discrete sources and the star-formation activity hidden by dust absorption. Tools: Large aperture X-ray observatory, far-infrared imaging observatory
29 4.3 The evolving violent Universe Formation and evolution of the super-massive black holes at galaxy centres in relation to galaxy and star formation. Life cycles of matter in the Universe along its cosmic history. Observing Black Holes in the centre of most galaxies allows the study of the interplay between their formation and evolution and that of their host galaxies. Matter falling onto Black Holes produces X and γ rays. Their spectral and time variability trace the accretion process, and are clues to understand the processes at work in SN and Hypernova explosions connected to Gamma Ray Bursts Tools: Large aperture X-ray observatory, gamma-ray observatory.
30 Strategies for Theme 4 First Trace the evolution of galaxies back to their formation epoch and the life cycle of matter in the Universe. Investigate the inflationary phases in the evolution of the Universe. -Observatory-type mission: Large aperture X-ray observatory -Focused missions: All-sky CMB polarisation mapper, Wide-field optical-near IR imager.
31 Strategies for Theme 4 Later Resolve the sky background into discrete sources and the star formation activity hidden by dust absorption -Far-infrared imaging observatory Understand in detail the supernova history in our Galaxy and in the Local Group: -Gamma-ray observatory Directly detect the primordial gravitational waves issued from the Big Bang: -Gravitational Wave Cosmic Surveyor
32 From themes to proto-missions How How does does the the Solar Solar System work work? What What are are the the conditions for for life life & planetary formation? Solar-Polar Orbiter (Solar Sailor) Helio-pause Probe (Solar Sailor) From From the the sun sun to to the the edge edge of of the the solar solar system system Far Infrared Interferometer From From dust dust and and gas gas to to stars stars and and planets planets Earth Magnetospheric Swarm Jovian In-situ Planetary Observer (JEP) The The Giant Giant Planets Planets and and their their environment environment Jupiter Magnetospheric Explorer (JEP) Near Infrared Terrestrial Planet Interferometer Europa Orbiting Surveyor (JEP) From From exo-planets exo-planets to to biomarkers biomarkers Kuiper belt Explorer Near Earth Asteroid sample & return Asteroids Asteroids and and small small bodies bodies Mars In-situ Programme (Rovers & sub-surface) Mars sample and return Life Life & & habitability habitability in in the the solar solar system system Terrestrial Planet Astrometric Surveyor Terrestrial-Planet Spectroscopic Observer Terrestrial Planet Imaging Observer Looking Looking for for life life beyond beyond the the solar solar system system
33 From themes to proto-missions What What are are the the fundamental laws laws of of the the Universe? How How did did the the Universe originate and and what what is is the the Universe made made of? of? Fundamental Physics Explorer Programme General Relativity Probes Exploring Exploring the the limits limits of of contemporary contemporary physics physics Wide Field NIR Dark Energy Observer CMB Polarization Surveyor The early Universe The early Universe Binary source Gravitational Surveyor The The gravitational gravitational wave wave Universe Universe Far Infrared Observatory The The Universe Universe taking taking shape shape Big Bang Cosmic Gravitational Surveyor Next Generation X-ray Observatory Matter Matter under under extreme extreme conditions conditions Gamma-ray Observatory The The evolving evolving violent violent Universe Universe
34 COSMIC VISION Potential implementation
35 Proposal for increased Level of Resources (LoR) In preparation of next ESA Council meeting at Ministerial level in December 2005 and after concurrence by ESA DG, it is proposed to: Maintain the present Science Programme LoR with inflation correction to 2006 From 2007, seek a 5 year annual increase of 2.4% over the current LoR
36 General assumptions Loan reimbursement extended to 2009 Continuation of current charging policy Present envelopes for BC, GAIA, LISA and SO Launcher for JWST
37 Uncertainties The income level and the loan reimbursement. The envelopes of GAIA, BepiColombo and LISA and their impact on the future programme. The launcher for JWST.
38 Programme Slices To implement the major objectives of Cosmic Vision while keeping flexibility of planning, slices of 1 to 1.5 B each can be identified for missions to be launched in Flexibility within each slice will depend on size, number and order of missions and inclusion of international cooperation. Flexibility within each slice allows to maintain a good balance of scientific disciplines The first Call for Mission Proposals to cover first slice ( ). Next slices to be implemented through subsequent Calls.
39 500,000 COSMIC VISION ESA Corridor Planning Three programme slices 450,000 LOAN REIMBURSEMENT 400, ,000 GAIA 11 SO 15 Keuro (2005 EC) 300, , ,000 LISA-PF 08 H-P BC 12 LISA 200M 14 PROGRAMME SLICE PROGRAMME SLICE PROGRAMME SLICE ,000 JWST 11 UNTIL VEX 100,000 D/SCI contingency 50,000 0 Basic activities
40 Importance of proposed LoR increase Enables early support of Aurora programme by Science Directorate in areas of scientific payloads and science operations. Opens a programme wedge in 2010 to start industrial development for timely implementation (2015 launch) of initial mission of first Cosmic Vision slice.
41 Conclusions let s start soon dishing out the first slice! a launch in 2015 requires a phase B start at the beginning of 08 Phase A in 07 Call for mission proposals early 06
Cosmic Vision : The scientific priorities for astrophysics and fundamental physics
 Cosmic Vision 2015-2025: The scientific priorities for astrophysics and fundamental physics Fabio Favata ESA, Astronomy & Fundamental Physics Mission Coordinator Grand themes 1. What are the conditions
Cosmic Vision 2015-2025: The scientific priorities for astrophysics and fundamental physics Fabio Favata ESA, Astronomy & Fundamental Physics Mission Coordinator Grand themes 1. What are the conditions
Astronomy. Catherine Turon. for the Astronomy Working Group
 Astronomy Catherine Turon for the Astronomy Working Group Answers to the call for ideas Illustration of the strong expectation of the community from the ESA Science Programme: In astronomy 1983: Horizon
Astronomy Catherine Turon for the Astronomy Working Group Answers to the call for ideas Illustration of the strong expectation of the community from the ESA Science Programme: In astronomy 1983: Horizon
Herschel and Planck: ESA s New Astronomy Missions an introduction. Martin Kessler Schloss Braunshardt 19/03/2009
 Herschel and Planck: ESA s New Astronomy Missions an introduction Martin Kessler Schloss Braunshardt 19/03/2009 Missions in Operations Rosetta Hubble Integral Newton Mars Express SOHO Ulysses Cluster Venus
Herschel and Planck: ESA s New Astronomy Missions an introduction Martin Kessler Schloss Braunshardt 19/03/2009 Missions in Operations Rosetta Hubble Integral Newton Mars Express SOHO Ulysses Cluster Venus
Cosmology The Road Map
 Cosmology The Road Map Peter Schneider Institut für Astrophysik, Bonn University on behalf of the Astronomy Working Group Cosmology s Themes Fundamental Cosmology Probing inflation Investigating Dark Energy
Cosmology The Road Map Peter Schneider Institut für Astrophysik, Bonn University on behalf of the Astronomy Working Group Cosmology s Themes Fundamental Cosmology Probing inflation Investigating Dark Energy
Exploring the Universe: Synergies in the ESA Science Programme
 Exploring the Universe: Synergies in the ESA Science Programme Günther Hasinger, ESA Director of Science (D/SCI) 14 th Appleton Space Conference, RAL, 6.12.2018 Towards ESA UNCLASSIFIED - For Official
Exploring the Universe: Synergies in the ESA Science Programme Günther Hasinger, ESA Director of Science (D/SCI) 14 th Appleton Space Conference, RAL, 6.12.2018 Towards ESA UNCLASSIFIED - For Official
ESA Science Programme and the Ice Giants study
 Outer Planets Assessment Group meeting 11-12 September 2018 ESA Science Programme and the Ice Giants study Luigi Colangeli Head Science coordination Office Directorate of Science ESA UNCLASSIFIED - For
Outer Planets Assessment Group meeting 11-12 September 2018 ESA Science Programme and the Ice Giants study Luigi Colangeli Head Science coordination Office Directorate of Science ESA UNCLASSIFIED - For
Astronomy Today. Eighth edition. Eric Chaisson Steve McMillan
 Global edition Astronomy Today Eighth edition Eric Chaisson Steve McMillan The Distance Scale ~1 Gpc Velocity L Distance Hubble s law Supernovae ~200 Mpc Time Tully-Fisher ~25 Mpc ~10,000 pc Time Variable
Global edition Astronomy Today Eighth edition Eric Chaisson Steve McMillan The Distance Scale ~1 Gpc Velocity L Distance Hubble s law Supernovae ~200 Mpc Time Tully-Fisher ~25 Mpc ~10,000 pc Time Variable
Planetary probes: ESA Perspective Jean-Pierre Lebreton
 Planetary probes: ESA Perspective Jean-Pierre Lebreton ESA s Huygens Project Scientist/Mission Manager ESA s EJSM & TSSM Cosmic Vision Study Scientist Solar System Missions Division Research and Scientific
Planetary probes: ESA Perspective Jean-Pierre Lebreton ESA s Huygens Project Scientist/Mission Manager ESA s EJSM & TSSM Cosmic Vision Study Scientist Solar System Missions Division Research and Scientific
Exo-planet research from Space The ESA Picture
 Exo-planet research from Space The ESA Picture Cosmic Vision is centered around four Grand Themes: 1. What are the conditions for planet formation and the emergence of life? From gas and dust to stars
Exo-planet research from Space The ESA Picture Cosmic Vision is centered around four Grand Themes: 1. What are the conditions for planet formation and the emergence of life? From gas and dust to stars
Europe-Japan Space Science Collaboration. Saku Tsuneta Institute of Space and Astronautical Science Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency
 Europe-Japan Space Science Collaboration Saku Tsuneta Institute of Space and Astronautical Science Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency March 7, 2018 JAXA recent science missions HAYABUSA 2003-2010 Asteroid
Europe-Japan Space Science Collaboration Saku Tsuneta Institute of Space and Astronautical Science Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency March 7, 2018 JAXA recent science missions HAYABUSA 2003-2010 Asteroid
ILWS Update April 2005
 CLUSTER Space Plasma Missions in the Science Programme of ESA ILWS Update April 2005 Hermann J. Opgenoorth ESA ESTEC Solar and Solar Terrestrial Missions Division (SCI-SH) Research and Scientific Support
CLUSTER Space Plasma Missions in the Science Programme of ESA ILWS Update April 2005 Hermann J. Opgenoorth ESA ESTEC Solar and Solar Terrestrial Missions Division (SCI-SH) Research and Scientific Support
Solar System Advisory Panel Roadmap for Solar System Research Recommendations to STFC
 Solar System Advisory Panel Roadmap for Solar System Research Recommendations to STFC UK-ELIPS Workshop on Astrobiology and Dust Open University April 2013 Sunrise over Lindos Bay, Rhodes (MMG, Sept. 2012)
Solar System Advisory Panel Roadmap for Solar System Research Recommendations to STFC UK-ELIPS Workshop on Astrobiology and Dust Open University April 2013 Sunrise over Lindos Bay, Rhodes (MMG, Sept. 2012)
Resource Allocation Planning and Scheduling Office. Deep Space Station-15 Out-of-Service Assessment Report. April 11, 2003
 Resource Allocation Planning and Scheduling Office Deep Space Station-15 Out-of-Service Assessment Report April 11, 2003 Roger Bartoo Study Description This study describes a Deep Space Network (DSN) loading
Resource Allocation Planning and Scheduling Office Deep Space Station-15 Out-of-Service Assessment Report April 11, 2003 Roger Bartoo Study Description This study describes a Deep Space Network (DSN) loading
LISA: Probing the Universe with Gravitational Waves. Tom Prince Caltech/JPL. Laser Interferometer Space Antenna LISA
 : Probing the Universe with Gravitational Waves Tom Caltech/JPL Laser Interferometer Space Antenna http://lisa.nasa.gov Gravitational Wave Astronomy is Being Born LIGO, VIRGO, GEO, TAMA 4000m, 3000m, 2000m,
: Probing the Universe with Gravitational Waves Tom Caltech/JPL Laser Interferometer Space Antenna http://lisa.nasa.gov Gravitational Wave Astronomy is Being Born LIGO, VIRGO, GEO, TAMA 4000m, 3000m, 2000m,
International Olympiad on Astronomy and Astrophysics (IOAA)
 Syllabus of International Olympiad on Astronomy and Astrophysics (IOAA) General Notes 1. Extensive contents in basic astronomical concepts are required in theoretical and practical problems. 2. Basic concepts
Syllabus of International Olympiad on Astronomy and Astrophysics (IOAA) General Notes 1. Extensive contents in basic astronomical concepts are required in theoretical and practical problems. 2. Basic concepts
The Solar System in the ESA scientific program
 The Solar System in the ESA scientific program 1 ESA-ESTEC/SRE-SM, Postbus 299 2200 AG Noordwijk (The Netherlands) Tel: +31-71 565 3573 Fax: +31-71 565 4697 luigi.colangeli@esa.int Luigi Colangeli Head,
The Solar System in the ESA scientific program 1 ESA-ESTEC/SRE-SM, Postbus 299 2200 AG Noordwijk (The Netherlands) Tel: +31-71 565 3573 Fax: +31-71 565 4697 luigi.colangeli@esa.int Luigi Colangeli Head,
ATHENA in the Context of the Next Decade. R. Kennicutt, IoA Cambridge
 ATHENA in the Context of the Next Decade R. Kennicutt, IoA Cambridge 1 Cosmic Dawn Searching for the first stars, galaxies, and black holes New Worlds Seeking nearby, habitable planets Physics of the Universe
ATHENA in the Context of the Next Decade R. Kennicutt, IoA Cambridge 1 Cosmic Dawn Searching for the first stars, galaxies, and black holes New Worlds Seeking nearby, habitable planets Physics of the Universe
From the VLT to ALMA and to the E-ELT
 From the VLT to ALMA and to the E-ELT Mission Develop and operate world-class observing facilities for astronomical research Organize collaborations in astronomy Intergovernmental treaty-level organization
From the VLT to ALMA and to the E-ELT Mission Develop and operate world-class observing facilities for astronomical research Organize collaborations in astronomy Intergovernmental treaty-level organization
Astro 1: Introductory Astronomy
 Astro 1: Introductory Astronomy David Cohen Class 16: Thursday, March 20 Spring 2014 large cloud of interstellar gas and dust - giving birth to millions of stars Hubble Space Telescope: Carina Nebula
Astro 1: Introductory Astronomy David Cohen Class 16: Thursday, March 20 Spring 2014 large cloud of interstellar gas and dust - giving birth to millions of stars Hubble Space Telescope: Carina Nebula
Learning Objectives: Chapter 13, Part 1: Lower Main Sequence Stars. AST 2010: Chapter 13. AST 2010 Descriptive Astronomy
 Chapter 13, Part 1: Lower Main Sequence Stars Define red dwarf, and describe the internal dynamics and later evolution of these low-mass stars. Appreciate the time scale of late-stage stellar evolution
Chapter 13, Part 1: Lower Main Sequence Stars Define red dwarf, and describe the internal dynamics and later evolution of these low-mass stars. Appreciate the time scale of late-stage stellar evolution
Theme 2: Outer Solar System Tracing the origin of the Solar System
 Theme 2: Outer Solar System Tracing the origin of the Solar System Essential for our understanding of the formation and evolution of our own Solar System Exploration of the outer solar system has traditionally
Theme 2: Outer Solar System Tracing the origin of the Solar System Essential for our understanding of the formation and evolution of our own Solar System Exploration of the outer solar system has traditionally
Foundations of Astrophysics
 Foundations of Astrophysics Barbara Ryden The Ohio State University Bradley M. Peterson The Ohio State University Preface xi 1 Early Astronomy 1 1.1 The Celestial Sphere 1 1.2 Coordinate Systems on a Sphere
Foundations of Astrophysics Barbara Ryden The Ohio State University Bradley M. Peterson The Ohio State University Preface xi 1 Early Astronomy 1 1.1 The Celestial Sphere 1 1.2 Coordinate Systems on a Sphere
Earth Space Systems. Semester 1 Exam. Astronomy Vocabulary
 Earth Space Systems Semester 1 Exam Astronomy Vocabulary Astronomical Unit- Aurora- Big Bang- Black Hole- 1AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun (93 million miles). This unit of measurement
Earth Space Systems Semester 1 Exam Astronomy Vocabulary Astronomical Unit- Aurora- Big Bang- Black Hole- 1AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun (93 million miles). This unit of measurement
(Astronomy for Dummies) remark : apparently I spent more than 1 hr giving this lecture
 (Astronomy for Dummies) remark : apparently I spent more than 1 hr giving this lecture A.D. 125? Ptolemy s geocentric model Planets ( ) wander among stars ( ) For more info: http://aeea.nmns.edu.tw/aeea/contents_list/universe_concepts.html
(Astronomy for Dummies) remark : apparently I spent more than 1 hr giving this lecture A.D. 125? Ptolemy s geocentric model Planets ( ) wander among stars ( ) For more info: http://aeea.nmns.edu.tw/aeea/contents_list/universe_concepts.html
ESA s Juice: Mission Summary and Fact Sheet
 ESA s Juice: Mission Summary and Fact Sheet JUICE - JUpiter ICy moons Explorer - is the first large-class mission in ESA's Cosmic Vision 2015-2025 programme. Planned for launch in 2022 and arrival at Jupiter
ESA s Juice: Mission Summary and Fact Sheet JUICE - JUpiter ICy moons Explorer - is the first large-class mission in ESA's Cosmic Vision 2015-2025 programme. Planned for launch in 2022 and arrival at Jupiter
CHAPTER 6. The Solar System
 CHAPTER 6 The Solar System 6.1 An Inventory of the Solar System The Greeks knew about 5 planets other than Earth They also knew about two other objects that were not planets or stars: meteors and comets
CHAPTER 6 The Solar System 6.1 An Inventory of the Solar System The Greeks knew about 5 planets other than Earth They also knew about two other objects that were not planets or stars: meteors and comets
The ESA scientific program
 The ESA scientific program Luigi Colangeli Science and Robotic Exploration Directorate Head, ESA Solar System Missions Division and Coordinator, ESA Solar System Missions ESA-ESTEC 1 The ESA fleet in Astronomy
The ESA scientific program Luigi Colangeli Science and Robotic Exploration Directorate Head, ESA Solar System Missions Division and Coordinator, ESA Solar System Missions ESA-ESTEC 1 The ESA fleet in Astronomy
Universe Now. 12. Revision and highlights
 Universe Now 12. Revision and highlights Practical issues about the exam The exam is on Monday 6.5. (12.00-16.00), lecture hall B121 (Exactum). Paper will be provided. You have 4 hours to finish the exam,
Universe Now 12. Revision and highlights Practical issues about the exam The exam is on Monday 6.5. (12.00-16.00), lecture hall B121 (Exactum). Paper will be provided. You have 4 hours to finish the exam,
Astro 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 3
 Astro 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 3 Chapter 6 1. Which of the following statements is false? a) Refraction is the bending of light when it passes from one medium to another. b) Mirrors
Astro 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 3 Chapter 6 1. Which of the following statements is false? a) Refraction is the bending of light when it passes from one medium to another. b) Mirrors
Astronomy Ch. 6 The Solar System: Comparative Planetology
 Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 6 The Solar System: Comparative Planetology MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The largest asteroid,
Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 6 The Solar System: Comparative Planetology MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The largest asteroid,
Astronomy Ch. 6 The Solar System. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 6 The Solar System MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The largest asteroid, and probably the only
Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 6 The Solar System MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The largest asteroid, and probably the only
Solar System Sch. Space Instrumentation
 o Space Instrumentation Space Instrumentation - Outline Introduction I (S.K. Sanki & J. Woch) Why we go to Space Space Exploration: then and now Realization of Space Projects Introduction II (S.K. Sanki
o Space Instrumentation Space Instrumentation - Outline Introduction I (S.K. Sanki & J. Woch) Why we go to Space Space Exploration: then and now Realization of Space Projects Introduction II (S.K. Sanki
Braneworld Cosmological Perturbations
 2005 2005 2005 Spectropolarimetric Studies on Circumstellar Structure of Low-Mass Pre-Main-Sequence Stars ELT Statistical Properties of Lyman a Emitters at Redshift 5.7 Neutrino Probes of Galactic and
2005 2005 2005 Spectropolarimetric Studies on Circumstellar Structure of Low-Mass Pre-Main-Sequence Stars ELT Statistical Properties of Lyman a Emitters at Redshift 5.7 Neutrino Probes of Galactic and
Formation of the Universe & What is in Space? The Big Bang Theory and components of the Universe
 Formation of the Universe & What is in Space? The Big Bang Theory and components of the Universe The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory is the most widely accepted scientific explanation
Formation of the Universe & What is in Space? The Big Bang Theory and components of the Universe The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory is the most widely accepted scientific explanation
AN INTRODUCTIONTO MODERN ASTROPHYSICS
 AN INTRODUCTIONTO MODERN ASTROPHYSICS Second Edition Bradley W. Carroll Weber State University DaleA. Ostlie Weber State University PEARSON Addison Wesley San Francisco Boston New York Cape Town Hong Kong
AN INTRODUCTIONTO MODERN ASTROPHYSICS Second Edition Bradley W. Carroll Weber State University DaleA. Ostlie Weber State University PEARSON Addison Wesley San Francisco Boston New York Cape Town Hong Kong
The Universe. What is it? What is in it? How did it form? How will it end? How do we know?
 The Universe What is it? What is in it? How did it form? How will it end? How do we know? What is your place in the Universe? What is the universe? a. The study of the universe its nature, origins, and
The Universe What is it? What is in it? How did it form? How will it end? How do we know? What is your place in the Universe? What is the universe? a. The study of the universe its nature, origins, and
ASTRONOMY. Eric Chaisson. Steve McMillan. A Beginner's Guide to the Universe FOURTH EDITION. Tufts University. Drexel University
 ASTRONOMY A Beginner's Guide to the Universe FOURTH EDITION Eric Chaisson Tufts University Steve McMillan Drexel University PEARSON Prentice Hall Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey
ASTRONOMY A Beginner's Guide to the Universe FOURTH EDITION Eric Chaisson Tufts University Steve McMillan Drexel University PEARSON Prentice Hall Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey
The ESA Science Programme
 The ESA Science Programme Günther Hasinger D/SCI ESSC Plenary Meeting, Geneva Observatory, 23. May 2018 ESA UNCLASSIFIED - For Official Use Four generations of ESA Science Directors Günther Hasinger 2018-
The ESA Science Programme Günther Hasinger D/SCI ESSC Plenary Meeting, Geneva Observatory, 23. May 2018 ESA UNCLASSIFIED - For Official Use Four generations of ESA Science Directors Günther Hasinger 2018-
What is Earth Science?
 What is Earth Science? A.EARTH SCIENCE: the study of Earth and its history B. Earth science is divided into 4 main branches: 1. Geology: study of the lithosphere 2. Oceanography: study of oceans 3. Meteorology:
What is Earth Science? A.EARTH SCIENCE: the study of Earth and its history B. Earth science is divided into 4 main branches: 1. Geology: study of the lithosphere 2. Oceanography: study of oceans 3. Meteorology:
ESASky, ESA s new open-science portal for ESA space astronomy missions
 ESASky, ESA s new open-science portal for ESA space astronomy missions Bruno Merín ESAC Science Data Centre European Space Agency bruno.merin@esa.int Visit to NAOC, Beijing, 19/05/2017 ESA UNCLASSIFIED
ESASky, ESA s new open-science portal for ESA space astronomy missions Bruno Merín ESAC Science Data Centre European Space Agency bruno.merin@esa.int Visit to NAOC, Beijing, 19/05/2017 ESA UNCLASSIFIED
Lunar Eclipse. Solar Eclipse
 Lunar Eclipse SUN Moon Solar Eclipse SUN SUN Moon Total solar eclipse Partial solar eclipse Moon Phases What does the moon look like from at each position? G H F A E B D C SUNLIGHT Refracting Telescopes
Lunar Eclipse SUN Moon Solar Eclipse SUN SUN Moon Total solar eclipse Partial solar eclipse Moon Phases What does the moon look like from at each position? G H F A E B D C SUNLIGHT Refracting Telescopes
THE KAVLI UNIVERSE. Kavli Building Dedication March 17, 2006
 THE KAVLI UNIVERSE Kavli Building Dedication March 17, 2006 From the Fred Kavli Building on the SLAC campus and the physics buildings on Stanford s main university campus, KIPAC researchers seek solutions
THE KAVLI UNIVERSE Kavli Building Dedication March 17, 2006 From the Fred Kavli Building on the SLAC campus and the physics buildings on Stanford s main university campus, KIPAC researchers seek solutions
THE STRATEGIC VISION OF INAF
 THE STRATEGIC VISION OF INAF 2015-2024 Scientific Council Enzo Brocato Stefano Covino Silvia Masi Francesca Matteucci Stefano Orsini Bianca Poggianti Pietro Schipani Scientific challenges in the 21th century
THE STRATEGIC VISION OF INAF 2015-2024 Scientific Council Enzo Brocato Stefano Covino Silvia Masi Francesca Matteucci Stefano Orsini Bianca Poggianti Pietro Schipani Scientific challenges in the 21th century
Black Holes Thursday, 14 March 2013
 Black Holes General Relativity Intro We try to explain the black hole phenomenon by using the concept of escape velocity, the speed to clear the gravitational field of an object. According to Newtonian
Black Holes General Relativity Intro We try to explain the black hole phenomenon by using the concept of escape velocity, the speed to clear the gravitational field of an object. According to Newtonian
Class 15 Formation of the Solar System
 Class 16 Extra-solar planets The radial-velocity technique for finding extrasolar planets Other techniques for finding extrasolar planets Class 15 Formation of the Solar System What does a successful model
Class 16 Extra-solar planets The radial-velocity technique for finding extrasolar planets Other techniques for finding extrasolar planets Class 15 Formation of the Solar System What does a successful model
Introduction The Role of Astronomy p. 3 Astronomical Objects of Research p. 4 The Scale of the Universe p. 7 Spherical Astronomy Spherical
 Introduction The Role of Astronomy p. 3 Astronomical Objects of Research p. 4 The Scale of the Universe p. 7 Spherical Astronomy Spherical Trigonometry p. 9 The Earth p. 12 The Celestial Sphere p. 14 The
Introduction The Role of Astronomy p. 3 Astronomical Objects of Research p. 4 The Scale of the Universe p. 7 Spherical Astronomy Spherical Trigonometry p. 9 The Earth p. 12 The Celestial Sphere p. 14 The
8. Solar System Origins
 8. Solar System Origins Chemical composition of the galaxy The solar nebula Planetary accretion Extrasolar planets Our Galaxy s Chemical Composition es Big Bang produced hydrogen & helium Stellar processes
8. Solar System Origins Chemical composition of the galaxy The solar nebula Planetary accretion Extrasolar planets Our Galaxy s Chemical Composition es Big Bang produced hydrogen & helium Stellar processes
NASA Planetary Science Programs
 NASA Planetary Science Programs James L. Green NASA, Planetary Science Division February 19, 2015 Presentation at OPAG 1 Outline Mission events Passed FY15 Budget elements President s FY16 Budget Discovery
NASA Planetary Science Programs James L. Green NASA, Planetary Science Division February 19, 2015 Presentation at OPAG 1 Outline Mission events Passed FY15 Budget elements President s FY16 Budget Discovery
Astrophysics & Gravitational Physics with the LISA Mission
 Astrophysics & Gravitational Physics with the LISA Mission Peter L. Bender JILA, University of Colorado, and NIST Workshop on Robotic Science from the Moon Boulder, CO 5-6 October, 2010 LISA Overview The
Astrophysics & Gravitational Physics with the LISA Mission Peter L. Bender JILA, University of Colorado, and NIST Workshop on Robotic Science from the Moon Boulder, CO 5-6 October, 2010 LISA Overview The
Directed Reading. Section: Viewing the Universe THE VALUE OF ASTRONOMY. Skills Worksheet. 1. How did observations of the sky help farmers in the past?
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe 1. How did observations of the sky help farmers in the past? 2. How did observations of the sky help sailors in the past? 3. What is the
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe 1. How did observations of the sky help farmers in the past? 2. How did observations of the sky help sailors in the past? 3. What is the
Tracing the origin of the Solar System. Michel Blanc OAMP, Marseille
 Tracing the origin of the Solar System Michel Blanc OAMP, Marseille This talk was prepared with highly appreciated contributions from : Yann Alibert, Antonella Barucci, Willy Benz, Dominique Bockelée-Morvan,Scott
Tracing the origin of the Solar System Michel Blanc OAMP, Marseille This talk was prepared with highly appreciated contributions from : Yann Alibert, Antonella Barucci, Willy Benz, Dominique Bockelée-Morvan,Scott
A brief history of cosmological ideas
 A brief history of cosmological ideas Cosmology: Science concerned with the origin and evolution of the universe, using the laws of physics. Cosmological principle: Our place in the universe is not special
A brief history of cosmological ideas Cosmology: Science concerned with the origin and evolution of the universe, using the laws of physics. Cosmological principle: Our place in the universe is not special
Cosmic Vision : ESA's long term programme in space sciences
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 81, 467 c SAIt 2010 Memorie della Cosmic Vision 2015-2025: ESA's long term programme in space sciences J. Clavel ESTEC/SRE-SA Postbus 299, 2200 AG - Noordwijk, The Netherlands e-mail:
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 81, 467 c SAIt 2010 Memorie della Cosmic Vision 2015-2025: ESA's long term programme in space sciences J. Clavel ESTEC/SRE-SA Postbus 299, 2200 AG - Noordwijk, The Netherlands e-mail:
Major Option C1 Astrophysics. C1 Astrophysics
 C1 Astrophysics Course co-ordinator: Julien Devriendt jeg@astro.ox.ac.uk C1 offers a total of ~40 lectures on five themes covering a broad range of topics in contemporary astrophysics. Each theme takes
C1 Astrophysics Course co-ordinator: Julien Devriendt jeg@astro.ox.ac.uk C1 offers a total of ~40 lectures on five themes covering a broad range of topics in contemporary astrophysics. Each theme takes
ASTR 200 : Lecture 6 Introduction to the Solar System Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison-Wesley
 ASTR 200 : Lecture 6 Introduction to the Solar System 1 2004 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison-Wesley Comparative Planetology Studying the similarities among and differences between the planets
ASTR 200 : Lecture 6 Introduction to the Solar System 1 2004 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison-Wesley Comparative Planetology Studying the similarities among and differences between the planets
ASTRONOMY CURRICULUM Unit 1: Introduction to Astronomy
 Chariho Regional School District - Science Curriculum September, 2016 ASTRONOMY CURRICULUM Unit 1: Introduction to Astronomy OVERVIEW Summary Students will be introduced to the overarching concept of astronomy.
Chariho Regional School District - Science Curriculum September, 2016 ASTRONOMY CURRICULUM Unit 1: Introduction to Astronomy OVERVIEW Summary Students will be introduced to the overarching concept of astronomy.
Comparative Planetology I: Our Solar System
 Comparative Planetology I: Our Solar System Guiding Questions 1. Are all the other planets similar to Earth, or are they very different? 2. Do other planets have moons like Earth s Moon? 3. How do astronomers
Comparative Planetology I: Our Solar System Guiding Questions 1. Are all the other planets similar to Earth, or are they very different? 2. Do other planets have moons like Earth s Moon? 3. How do astronomers
Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999
 Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999 Reminder: When I write these questions, I believe that there is one one correct answer. The questions consist of all parts a e. Read the entire
Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999 Reminder: When I write these questions, I believe that there is one one correct answer. The questions consist of all parts a e. Read the entire
GraspIT Questions AQA GCSE Physics Space physics
 A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
Astronomy. physics.wm.edu/~hancock/171/ A. Dayle Hancock. Small 239. Office hours: MTWR 10-11am
 Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Planetology II Key characteristics Chemical elements and planet size Radioactive dating Solar system formation Solar nebula
Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Planetology II Key characteristics Chemical elements and planet size Radioactive dating Solar system formation Solar nebula
Name Date Period. 10. convection zone 11. radiation zone 12. core
 240 points CHAPTER 29 STARS SECTION 29.1 The Sun (40 points this page) In your textbook, read about the properties of the Sun and the Sun s atmosphere. Use each of the terms below just once to complete
240 points CHAPTER 29 STARS SECTION 29.1 The Sun (40 points this page) In your textbook, read about the properties of the Sun and the Sun s atmosphere. Use each of the terms below just once to complete
Active Galaxies and Galactic Structure Lecture 22 April 18th
 Active Galaxies and Galactic Structure Lecture 22 April 18th FINAL Wednesday 5/9/2018 6-8 pm 100 questions, with ~20-30% based on material covered since test 3. Do not miss the final! Extra Credit: Thursday
Active Galaxies and Galactic Structure Lecture 22 April 18th FINAL Wednesday 5/9/2018 6-8 pm 100 questions, with ~20-30% based on material covered since test 3. Do not miss the final! Extra Credit: Thursday
A star is a massive sphere of gases with a core like a thermonuclear reactor. They are the most common celestial bodies in the universe are stars.
 A star is a massive sphere of gases with a core like a thermonuclear reactor. They are the most common celestial bodies in the universe are stars. They radiate energy (electromagnetic radiation) from a
A star is a massive sphere of gases with a core like a thermonuclear reactor. They are the most common celestial bodies in the universe are stars. They radiate energy (electromagnetic radiation) from a
AST 301, Introduction to Astronomy Course Description and Syllabus Fall 2012
 AST 301, Introduction to Astronomy Course Description and Syllabus Fall 2012 Instructor: Dr. Edward L. Robinson Dept. of Astronomy, UT Unique Number: 47705 Lecture Time MWF 10 11 AM Lecture Location: WEL
AST 301, Introduction to Astronomy Course Description and Syllabus Fall 2012 Instructor: Dr. Edward L. Robinson Dept. of Astronomy, UT Unique Number: 47705 Lecture Time MWF 10 11 AM Lecture Location: WEL
Formation of the Solar System and Other Planetary Systems
 Formation of the Solar System and Other Planetary Systems 1 Questions to Ponder 1. Are all the other planets similar to Earth, or are they very different? 2. Do other planets have moons like Earth s Moon?
Formation of the Solar System and Other Planetary Systems 1 Questions to Ponder 1. Are all the other planets similar to Earth, or are they very different? 2. Do other planets have moons like Earth s Moon?
m V Density Formation of the Solar System and Other Planetary Systems Questions to Ponder
 Formation of the Solar System and Other Planetary Systems Questions to Ponder 1. Are all the other planets similar to Earth, or are they very different? 2. Do other planets have moons like Earth s Moon?
Formation of the Solar System and Other Planetary Systems Questions to Ponder 1. Are all the other planets similar to Earth, or are they very different? 2. Do other planets have moons like Earth s Moon?
Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE
 Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the universe; its nature, origin and evolution. General Relativity is the mathematical basis of cosmology from which
Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the universe; its nature, origin and evolution. General Relativity is the mathematical basis of cosmology from which
Hypertelescope Optical Observatory
 Hypertelescope Optical Observatory Antoine Labeyrie Collège de France & Observatoire de la Côte d Azur Laboratoire d Interféromètrie Stellaire et Exoplanétaire simulated direct image of Earth at 3 pc 30mn
Hypertelescope Optical Observatory Antoine Labeyrie Collège de France & Observatoire de la Côte d Azur Laboratoire d Interféromètrie Stellaire et Exoplanétaire simulated direct image of Earth at 3 pc 30mn
m V Formation of the Solar System and Other Planetary Systems Questions to Ponder about Solar System
 Formation of the Solar System and Other Planetary Systems Questions to Ponder about Solar System 1 1. Are all the other planets similar to Earth, or are they very different? 2. Do other planets have moons
Formation of the Solar System and Other Planetary Systems Questions to Ponder about Solar System 1 1. Are all the other planets similar to Earth, or are they very different? 2. Do other planets have moons
7. Our Solar System. Planetary Orbits to Scale. The Eight Planetary Orbits
 7. Our Solar System Terrestrial & Jovian planets Seven large satellites [moons] Chemical composition of the planets Asteroids & comets The Terrestrial & Jovian Planets Four small terrestrial planets Like
7. Our Solar System Terrestrial & Jovian planets Seven large satellites [moons] Chemical composition of the planets Asteroids & comets The Terrestrial & Jovian Planets Four small terrestrial planets Like
Space Physics: Recent Advances and Near-term Challenge. Chi Wang. National Space Science Center, CAS
 Space Physics: Recent Advances and Near-term Challenge Chi Wang National Space Science Center, CAS Feb.25, 2014 Contents Significant advances from the past decade Key scientific challenges Future missions
Space Physics: Recent Advances and Near-term Challenge Chi Wang National Space Science Center, CAS Feb.25, 2014 Contents Significant advances from the past decade Key scientific challenges Future missions
Potential ESA Contributions to International Living With a Star (ILWS)
 Potential ESA Contributions to International Living With a Star (ILWS) NASA ESA International Japan Russia Canada... LWS Cover Page ILWS should contain more than the NASA LWS Line and international add-ons......
Potential ESA Contributions to International Living With a Star (ILWS) NASA ESA International Japan Russia Canada... LWS Cover Page ILWS should contain more than the NASA LWS Line and international add-ons......
Astrobiology: The Semester in Review
 A Universe of Life Astrobiology: The Semester in Review Honors 228 with Dr. Harold Geller Searching for life everywhere Planets, stars, galaxies, Big Bang Conception of size and distance Stars and the
A Universe of Life Astrobiology: The Semester in Review Honors 228 with Dr. Harold Geller Searching for life everywhere Planets, stars, galaxies, Big Bang Conception of size and distance Stars and the
Astr 170B1 Sec 3 SOLUTIONS April 11, 2016
 Correct responses in BOLDFACE. Brightness 1. Look at the graph at the left. What is the period for this star? a. 9 days b. 1 day c. 5.5 days d. 4.5 days e. need more information 2. Comets are comprised
Correct responses in BOLDFACE. Brightness 1. Look at the graph at the left. What is the period for this star? a. 9 days b. 1 day c. 5.5 days d. 4.5 days e. need more information 2. Comets are comprised
Science advances by a combination of normal science and discovery of anomalies.
 Science advances by a combination of normal science and discovery of anomalies. Many revolutions come from long periods of normal science reinforced by exceptional science. example: accelerating universe
Science advances by a combination of normal science and discovery of anomalies. Many revolutions come from long periods of normal science reinforced by exceptional science. example: accelerating universe
Helmut Lammer Austrian Academy of Sciences, Space Research Institute Schmiedlstr. 6, A-8042 Graz, Austria (
 The search of habitable Earth-like exoplanets Helmut Lammer Austrian Academy of Sciences, Space Research Institute Schmiedlstr. 6, A-8042 Graz, Austria (email: helmut.lammer@oeaw.ac.at) Graz in Space 2008
The search of habitable Earth-like exoplanets Helmut Lammer Austrian Academy of Sciences, Space Research Institute Schmiedlstr. 6, A-8042 Graz, Austria (email: helmut.lammer@oeaw.ac.at) Graz in Space 2008
ESA UNCLASSIFIED For Official Use. BepiColombo à Exploring Mercury
 BepiColombo à Exploring Mercury ESA / JAXA BepiColombo Mercury Mercury has always been something of a puzzle for planetary scientists. Its close position to the Sun means it is very difficult to observe.
BepiColombo à Exploring Mercury ESA / JAXA BepiColombo Mercury Mercury has always been something of a puzzle for planetary scientists. Its close position to the Sun means it is very difficult to observe.
Astr 170B1 Sec 3 SOLUTIONS April 11, 2016
 Correct responses in BOLDFACE. 1. The metallic hydrogen in Jupiter's interior contributes to a. its rapid rotation b. its extreme temperature c. its extreme weather patterns d. its strong magnetic field
Correct responses in BOLDFACE. 1. The metallic hydrogen in Jupiter's interior contributes to a. its rapid rotation b. its extreme temperature c. its extreme weather patterns d. its strong magnetic field
Astr 170B1 Sec 3 SOLUTIONS April 11, 2016
 Correct responses in BOLDFACE. 1. Galaxy collisions can a. trigger high rates of star formation b. perturb the planets orbiting stars in the colliding galaxies c. drag most of the interstellar gas out
Correct responses in BOLDFACE. 1. Galaxy collisions can a. trigger high rates of star formation b. perturb the planets orbiting stars in the colliding galaxies c. drag most of the interstellar gas out
Properties of the Solar System
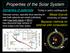 Properties of the Solar System Dynamics of asteroids Telescopic surveys, especially those searching for near-earth asteroids and comets (collectively called near-earth objects or NEOs) have discovered
Properties of the Solar System Dynamics of asteroids Telescopic surveys, especially those searching for near-earth asteroids and comets (collectively called near-earth objects or NEOs) have discovered
Announcements. Homework. Set 8now open. due late at night Friday, Dec 10 (3AM Saturday Nov. 11) Set 7 answers on course web site.
 Homework. Set 8now. due late at night Friday, Dec 10 (3AM Saturday Nov. 11) Set 7 answers on course web site. Review for Final. In class on Thursday. Course Evaluation. https://rateyourclass.msu.edu /
Homework. Set 8now. due late at night Friday, Dec 10 (3AM Saturday Nov. 11) Set 7 answers on course web site. Review for Final. In class on Thursday. Course Evaluation. https://rateyourclass.msu.edu /
Life and habitability in the Solar System and beyond: the Roadmap
 "There are more things in heaven and earth, Horatio, than are dreamt of in your philosophy." Hamlet (I, v, 166-167) Life and habitability in the Solar System and beyond: the Roadmap Lucia Marinangeli and
"There are more things in heaven and earth, Horatio, than are dreamt of in your philosophy." Hamlet (I, v, 166-167) Life and habitability in the Solar System and beyond: the Roadmap Lucia Marinangeli and
Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS)
![Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS) Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS)](/thumbs/77/76655554.jpg) Page1 Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS) HS-ESSI-1; HS-ESS1-2; HS-ESS1-3; HS-ESSI-4 NGSS Civic Memorial High School - Earth Science A Concept # What we will be learning Mandatory
Page1 Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS) HS-ESSI-1; HS-ESS1-2; HS-ESS1-3; HS-ESSI-4 NGSS Civic Memorial High School - Earth Science A Concept # What we will be learning Mandatory
Habitability Outside the Solar System. A discussion of Bennett & Shostak Chapter 11 HNRS 228 Dr. H. Geller
 Habitability Outside the Solar System A discussion of Bennett & Shostak Chapter 11 HNRS 228 Dr. H. Geller 1 Chapter Overview Distant Suns (11.1) Life cycle of stars and their habitability zones Extrasolar
Habitability Outside the Solar System A discussion of Bennett & Shostak Chapter 11 HNRS 228 Dr. H. Geller 1 Chapter Overview Distant Suns (11.1) Life cycle of stars and their habitability zones Extrasolar
The exploration of the solar system and the search for water. Thérèse Encrenaz LESIA, Observatoire de Paris
 The exploration of the solar system and the search for water Thérèse Encrenaz LESIA, Observatoire de Paris The exploration of the solar system and the search for water The exploration of solar system:
The exploration of the solar system and the search for water Thérèse Encrenaz LESIA, Observatoire de Paris The exploration of the solar system and the search for water The exploration of solar system:
New Ideas from Astronomy and Cosmology. Martin Buoncristiani Session 5 4/21/2011
 New Ideas from Astronomy and Cosmology Martin Buoncristiani Session 5 Agenda Introduction Space, Time and Matter Early views of the cosmos Important Ideas from Classical Physics Two 20 th Century revolutions
New Ideas from Astronomy and Cosmology Martin Buoncristiani Session 5 Agenda Introduction Space, Time and Matter Early views of the cosmos Important Ideas from Classical Physics Two 20 th Century revolutions
Exoplanet Detection and Characterization with Mid-Infrared Interferometry
 Exoplanet Detection and Characterization with Mid-Infrared Interferometry Rachel Akeson NASA Exoplanet Science Institute With thanks to Peter Lawson for providing material Sagan Workshop July 21, 2009
Exoplanet Detection and Characterization with Mid-Infrared Interferometry Rachel Akeson NASA Exoplanet Science Institute With thanks to Peter Lawson for providing material Sagan Workshop July 21, 2009
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 6. Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 6 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 6 The Solar System Units of Chapter 6 6.1 An Inventory of the Solar System 6.2 Measuring the Planets 6.3 The Overall Layout
Lecture Outlines Chapter 6 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 6 The Solar System Units of Chapter 6 6.1 An Inventory of the Solar System 6.2 Measuring the Planets 6.3 The Overall Layout
Light and Telescopes
 Light and Telescopes Astronomy 1 Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Spring F2015 Quotes & Cartoon of the Day We find them smaller and fainter, in constantly increasing numbers, and we know that we
Light and Telescopes Astronomy 1 Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Spring F2015 Quotes & Cartoon of the Day We find them smaller and fainter, in constantly increasing numbers, and we know that we
ASTR2050: Introductory Astronomy and Astrophysics Syllabus for Spring 1999 January 4, 1999
 ASTR2050: Introductory Astronomy and Astrophysics Syllabus for Spring 1999 January 4, 1999 This is a working document and will change periodically. It outlines the topics that will be covered during the
ASTR2050: Introductory Astronomy and Astrophysics Syllabus for Spring 1999 January 4, 1999 This is a working document and will change periodically. It outlines the topics that will be covered during the
Science with a Wide-Field Telescope in Space. NASA HQ Perspective. Richard Griffiths. Astrophysics Division Science Mission Directorate
 Science with a Wide-Field Telescope in Space NASA HQ Perspective Richard Griffiths Astrophysics Division Science Mission Directorate February 13, 2012 1 Mission Timeline Last updated: January 4, 2012 ORION
Science with a Wide-Field Telescope in Space NASA HQ Perspective Richard Griffiths Astrophysics Division Science Mission Directorate February 13, 2012 1 Mission Timeline Last updated: January 4, 2012 ORION
The SocioEconomic Opportunity of Satellites
 The SocioEconomic Opportunity of Satellites UCL Space Week 9 th Apr 2018 Dr Nick Appleyard Head of Downstream Business Applications ESA UNCLASSIFIED - For Official Use UCL Space Week 09/04/2018 Slide 1
The SocioEconomic Opportunity of Satellites UCL Space Week 9 th Apr 2018 Dr Nick Appleyard Head of Downstream Business Applications ESA UNCLASSIFIED - For Official Use UCL Space Week 09/04/2018 Slide 1
Sun Earth Connection Missions
 Sun Earth Connection Missions ACE Advanced Composition Explorer The Earth is constantly bombarded with a stream of accelerated particles arriving not only from the Sun, but also from interstellar and galactic
Sun Earth Connection Missions ACE Advanced Composition Explorer The Earth is constantly bombarded with a stream of accelerated particles arriving not only from the Sun, but also from interstellar and galactic
Survey of Astronomy ASTRO 110-5
 Survey of Astronomy ASTRO 110-5 Prof. Istvan Szapudi Institute for Astronomy IfA B204/WAT 401 Phone: 956 6196 Email: szapudi@ifa.hawaii.edu Class meets TTh 12:00 to 13:15 WAT 112 Office Hours after class
Survey of Astronomy ASTRO 110-5 Prof. Istvan Szapudi Institute for Astronomy IfA B204/WAT 401 Phone: 956 6196 Email: szapudi@ifa.hawaii.edu Class meets TTh 12:00 to 13:15 WAT 112 Office Hours after class
The formation & evolution of solar systems
 The formation & evolution of solar systems Content expectations Birth of the Solar System What did the material that eventually became the Sun and planets look like originally? Interstellar clouds like
The formation & evolution of solar systems Content expectations Birth of the Solar System What did the material that eventually became the Sun and planets look like originally? Interstellar clouds like
SOLAR SYSTEM B Division
 SOLAR SYSTEM B Division Team Name: Team #: Student Names: IMAGE SHEET A E B C D F G H Spectrum I Spectrum II SS2014 Spectrum III Spectrum IV Spectrum V Spectrum VI 1. A. What satellite is pictured in Image
SOLAR SYSTEM B Division Team Name: Team #: Student Names: IMAGE SHEET A E B C D F G H Spectrum I Spectrum II SS2014 Spectrum III Spectrum IV Spectrum V Spectrum VI 1. A. What satellite is pictured in Image
Planetary Science. Actually. Looking down. 7.1 Studying the Solar System. Chapter 7 Our Planetary System. What does the solar system look like?
 Chapter 7 Our Planetary System 7.1 Studying the Solar System Our goals for learning What does the solar system look like? How has it evolved over time? What are the major features of the Sun and planets?
Chapter 7 Our Planetary System 7.1 Studying the Solar System Our goals for learning What does the solar system look like? How has it evolved over time? What are the major features of the Sun and planets?
Uranus & Neptune: The Ice Giants. Discovery of Uranus. Bode s Law. Discovery of Neptune
 Uranus & Neptune: The Ice Giants Discovery of Uranus Discovery of Uranus & Neptune Properties Density & Composition Internal Heat Source Magnetic fields Rings Uranus Rotational Axis by William Herschel
Uranus & Neptune: The Ice Giants Discovery of Uranus Discovery of Uranus & Neptune Properties Density & Composition Internal Heat Source Magnetic fields Rings Uranus Rotational Axis by William Herschel
Last Class. Today s Class 11/28/2017
 Today s Class: The Jovian Planets & Their Water Worlds 1. Exam #3 on Thursday, Nov. 30 th! a) Covers all the reading Nov. 2-28. b) Covers Homework #6 and #7. c) Review Space in the News articles/discussions.
Today s Class: The Jovian Planets & Their Water Worlds 1. Exam #3 on Thursday, Nov. 30 th! a) Covers all the reading Nov. 2-28. b) Covers Homework #6 and #7. c) Review Space in the News articles/discussions.
Synergy with Gravitational Waves
 Synergy with Gravitational Waves Alexandre Le Tiec and Jérôme Novak Laboratoire Univers et Théories Observatoire de Paris / CNRS LIGO, Virgo, ( elisa, ET,... ( What is a gravitational wave? A gravitational
Synergy with Gravitational Waves Alexandre Le Tiec and Jérôme Novak Laboratoire Univers et Théories Observatoire de Paris / CNRS LIGO, Virgo, ( elisa, ET,... ( What is a gravitational wave? A gravitational
