University of Asia Pacific School of Engineering Admission Test Spring 2017 (Set 1) Section A: Mathematics [Full Marks = 8 5 = 40]
|
|
|
- Whitney Horn
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University of Asia Pacific School of Engineering Admission Test Spring 2017 (Set 1) Date: Time: 90 minutes Full Marks: 100 Name: Serial No.: (Answer all the questions. Assume reasonable value for missing data, if necessary) Section A: Mathematics [Full Marks = 8 5 = 40] 1. Roots of the quadratic equation x 2 + px + q = 0 are 2 and 15. Determine its roots if the value of q is doubled. 2. If log 10 (x) + 3 = 2 ln(y), express x in terms of y seats at an examination hall at UAP are to be filled by 10 candidates of CE and 8 of EEE. In how many ways can they be seated so that no two EEE candidates will sit next to each other? Page 1 of 16
2 4. Plot (freehand) graphs for x 2 y = 2x and 5x + 7 = 12y in the gridlines provided below. y y x x 5. Determine the (a) length, (b) co-ordinates of midpoint, (c) perpendicular distance from origin of the portion of line 5x + y = 10 intercepted between the x- and y-axes. 6. Determine the equation of the circle that touches the x- and y-axes at distance 2 and 4 respectively from origin. Page 2 of 16
3 7. Perform the integration of (tan x) 0.5 /(sin x cos x) between x = 0 and x = /4. 8. Determine C 1 and C 2 for f(x) = e ax [C 1 Cos(bx) + C 2 Sin(bx)], if f(0) = 0 and f (0) = v 0. Page 3 of 16
4 9. (a) What are the four fundamental forces of nature? (b) What is absolute zero temperature in C and F? Section B: Physics [Full Marks = 6 5 = 30] (2) (3) 10. Calculate the (a) stress, (b) longitudinal strain, (c) transverse strain in a wire of diameter 0.25 in, if it is subjected to a tensile force of 1000 lb [Given: Modulus of elasticity = lb/in 2, Poisson s ratio = 0.25]. 11. For a stone of mass 2 kg allowed to fall freely from a height of 50 m above ground, calculate the (a) Initial Potential energy, (b) Time required to reach ground, (c) Kinetic energy when it reaches ground. Page 4 of 16
5 12. Show the necessary calculations to convert (a) 1000 kg/m 3 to lb/ft 3 (b) 1 Light-year to kilometer. 13. Two equal forces act perpendicular to each other to move a mass of 1000 kg a distance 10 m in 10 seconds. Determine the (a) Magnitude of the forces, (b) Distance the mass would move if the forces acted parallel to each other. 14. Two ends of a cell are connected in a parallel connection with two wires of 5 Ω and 10 Ω resistance. If the current flow through the cell is 2 Amperes, calculate the current flow if the two wires are connected in series. Page 5 of 16
6 Section C: English [Full Marks = 20] 15. Write an essay on Ekushey Boi Mela (within 100 words). (10) 16. Translate the following passage into English (5) তথ ও য গ য গ য র উৎকষত র প শ প শ ভ র জন ত ত মবধম ন অ ন য়ত র ফ ল আধ নক ব বষম ও বক র ব ড় র ঝ ক আ ছ ত প রবত নর এই য গ কমস নর ত য গত ম লক ব জ রর জন ত র হ ত ত ণ দর জন ম নস শ ন ত কর জ র একই স থ ন ভ ক অথন তর বক শ প রক ন ন ত হ ব, যখ ন ব ক প রবত নর স থ খ প খ ই য় ন ত স জনশ লত ক ব শষ দ ত হ ব Page 6 of 16
7 17. Read the following passage carefully and tick mark corresponding circle to choose the correct or the best one from the four answers following each question: (5) Supernovas are the most powerful and spectacular outbursts known on nature. What is called a Type II supernova is due to the collapse of a massive star, at least eight times as massive as the sun that has used up its main nuclear fuel and produced a nickel-iron core. When this core can no longer support the pressure of the star s outer layers, it collapses to form a neutron star of immense density. Multitudes of neutrons are produced in the collapsed star, which pass directly through the star into space, and this release of neutrons causes the core to respond with a shock wave that moves outward. When it meets the material that is falling inward, the result is a catastrophic explosion. Sometimes most of the star s material is blown away, leaving only a small, incredibly dense remnant that may be a neutron star or, in extreme cases, a black hole. A supernova remnant (SNR) may be detectable as a pulsar. The 1987 supernova in the Large Cloud of Magellan had low peak luminosity by supernova standards. Only about 250 million times that of the sun at its brightest, the supernova shone as a star between magnitudes 2 and 3, even though it was 170,000 light-years away. (a) The word remnant in the passage is closest in meaning to relic characteristic specter remainder (b) The word detectable in the passage is closest in meaning to assumed know perceptible audible (c) According to the paragraph, what marks the beginning of a supernova? A star has grown too big A star is born The neutrons of a star become very dense A massive star uses up its main nuclear fuel (d) According to the paragraph, which of the following is NOT true about the 1987 supernova? It was located in the Large Cloud of Magellan It was 170,000 light-years away It shone as a star between magnitudes 3 and 4 It had a low peak luminosity (e) What can be inferred from the paragraph about supernovas? They only happen to pulsars The sun is a remnant of a supernova They occur when two stars collide They sometimes result in a black hole Page 7 of 16
8 Section D: Aptitude [Full Marks = 10 1 = 10] 18. Complete the following series?,?, 10, 8, 15, 12, 20, 16, 25, How many days are there in x weeks x days? (a) 14x (b) 8x (c) 7x 2 (d) The angles of depression and elevation of the top of a 10-ft high wall from the top and bottom of a tree are both 45. What is the height of the tree, if the bottom of the tree and the wall are at the same level? (a) 10 ft (b) 20 ft (c) 30 ft (d) None of these 21. How many times will the hands of a clock coincide in a day? (a) 24 (b) 22 (c) 20 (d) A rectangular field has to be fenced on three sides leaving a side of 25 feet uncovered. If the area of the field is 1000 sq. feet, how many feet of fencing will be required? (a) 130 (b) 105 (c) 40 (d) What is the probability of getting an even product from two throws of a dice? (a) (b) (c) (d) 24. Product of two 2-digit numbers is 2028 and their Highest Common Factor (HCF) is 13. What are the numbers? (a) 26, 78 (b) 39, 52 (c) 13, 156 (d) 31, Which of the following are in descending order of their value? (a) (b) (c) (d) None of these 26. A student must obtain 40% of the total marks to pass. He got 270 marks and failed by 50 marks. The total mark is 27. If log log 10 (x + 2) = 1, then x is equal to (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4 Page 8 of 16
9 University of Asia Pacific School of Engineering Admission Test Spring 2017 (Set 2) Date: Time: 90 minutes Full Marks: 100 Name: Serial No.: (Answer all the questions. Assume reasonable value for missing data, if necessary) 1. Complete the following series?,?, 10, 8, 15, 12, 20, 16, 25, How many days are there in x weeks x days? (a) 14x (b) 8x (c) 7x 2 (d) 7 Section A: Aptitude [Full Marks = 10 1 = 10] 3. The angles of depression and elevation of the top of a 10-ft high wall from the top and bottom of a tree are both 45. What is the height of the tree, if the bottom of the tree and the wall are at the same level? (a) 10 ft (b) 20 ft (c) 30 ft (d) None of these 4. How many times will the hands of a clock coincide in a day? (a) 24 (b) 22 (c) 20 (d) A rectangular field has to be fenced on three sides leaving a side of 25 feet uncovered. If the area of the field is 1000 sq. feet, how many feet of fencing will be required? (a) 130 (b) 105 (c) 40 (d) What is the probability of getting an even product from two throws of a dice? (a) (b) (c) (d) 7. Product of two 2-digit numbers is 2028 and their Highest Common Factor (HCF) is 13. What are the numbers? (a) 26, 78 (b) 39, 52 (c) 13, 156 (d) 31, Which of the following are in descending order of their value? (a) (b) (c) (d) None of these 9. A student must obtain 40% of the total marks to pass. He got 270 marks and failed by 50 marks. The total mark is 10. If log log 10 (x + 2) = 1, then x is equal to (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4 Page 9 of 16
10 Section B: English [Full Marks = 20] 11. Write an essay on Ekushey Boi Mela (within 100 words). (10) 12. Translate the following passage into English (5) তথ ও য গ য গ য র উৎকষত র প শ প শ ভ র জন ত ত মবধম ন অ ন য়ত র ফ ল আধ নক ব বষম ও বক র ব ড় র ঝ ক আ ছ ত প রবত নর এই য গ কমস নর ত য গত ম লক ব জ রর জন ত র হ ত ত ণ দর জন ম নস শ ন ত কর জ র একই স থ ন ভ ক অথন তর বক শ প রক ন ন ত হ ব, যখ ন ব ক প রবত নর স থ খ প খ ই য় ন ত স জনশ লত ক ব শষ দ ত হ ব Page 10 of 16
11 13. Read the following passage carefully and tick mark corresponding circle to choose the correct or the best one from the four answers following each question: (5) Supernovas are the most powerful and spectacular outbursts known on nature. What is called a Type II supernova is due to the collapse of a massive star, at least eight times as massive as the sun that has used up its main nuclear fuel and produced a nickel-iron core. When this core can no longer support the pressure of the star s outer layers, it collapses to form a neutron star of immense density. Multitudes of neutrons are produced in the collapsed star, which pass directly through the star into space, and this release of neutrons causes the core to respond with a shock wave that moves outward. When it meets the material that is falling inward, the result is a catastrophic explosion. Sometimes most of the star s material is blown away, leaving only a small, incredibly dense remnant that may be a neutron star or, in extreme cases, a black hole. A supernova remnant (SNR) may be detectable as a pulsar. The 1987 supernova in the Large Cloud of Magellan had low peak luminosity by supernova standards. Only about 250 million times that of the sun at its brightest, the supernova shone as a star between magnitudes 2 and 3, even though it was 170,000 light-years away. (a) The word remnant in the passage is closest in meaning to relic characteristic specter remainder (b) The word detectable in the passage is closest in meaning to assumed know perceptible audible (c) According to the paragraph, what marks the beginning of a supernova? A star has grown too big A star is born The neutrons of a star become very dense A massive star uses up its main nuclear fuel (d) According to the paragraph, which of the following is NOT true about the 1987 supernova? It was located in the Large Cloud of Magellan It was 170,000 light-years away It shone as a star between magnitudes 3 and 4 It had a low peak luminosity (e) What can be inferred from the paragraph about supernovas? They only happen to pulsars The sun is a remnant of a supernova They occur when two stars collide They sometimes result in a black hole Page 11 of 16
12 14. (a) What are the four fundamental forces of nature? (b) What is absolute zero temperature in C and F? Section C: Physics [Full Marks = 6 5 = 30] (2) (3) 15. Calculate the (a) stress, (b) longitudinal strain, (c) transverse strain in a wire of diameter 0.25 in, if it is subjected to a tensile force of 1000 lb [Given: Modulus of elasticity = lb/in 2, Poisson s ratio = 0.25]. 16. For a stone of mass 2 kg allowed to fall freely from a height of 50 m above ground, calculate the (a) Initial Potential energy, (b) Time required to reach ground, (c) Kinetic energy when it reaches ground. Page 12 of 16
13 17. Show the necessary calculations to convert (a) 1000 kg/m 3 to lb/ft 3 (b) 1 Light-year to kilometer. 18. Two equal forces act perpendicular to each other to move a mass of 1000 kg a distance 10 m in 10 seconds. Determine the (a) Magnitude of the forces, (b) Distance the mass would move if the forces acted parallel to each other. 19. Two ends of a cell are connected in a parallel connection with two wires of 5 Ω and 10 Ω resistance. If the current flow through the cell is 2 Amperes, calculate the current flow if the two wires are connected in series. Page 13 of 16
14 Section D: Mathematics [Full Marks = 8 5 = 40] 20. Roots of the quadratic equation x 2 + px + q = 0 are 2 and 15. Determine its roots if the value of q is doubled. 21. If log 10 (x) + 3 = 2 ln(y), express x in terms of y seats at an examination hall at UAP are to be filled by 10 candidates of CE and 8 of EEE. In how many ways can they be seated so that no two EEE candidates will sit next to each other? Page 14 of 16
15 23. Plot (freehand) graphs for x 2 y = 2x and 5x + 7 = 12y in the gridlines provided below. y y x x 24. Determine the (a) length, (b) co-ordinates of midpoint, (c) perpendicular distance from origin of the portion of line 5x + y = 10 intercepted between the x- and y-axes. 25. Determine the equation of the circle that touches the x- and y-axes at distance 2 and 4 respectively from origin. Page 15 of 16
16 26. Perform the integration of (tan x) 0.5 /(sin x cos x) between x = 0 and x = / Determine C 1 and C 2 for f(x) = e ax [C 1 Cos(bx) + C 2 Sin(bx)], if f(0) = 0 and f (0) = v 0. Page 16 of 16
17 University of Asia Pacific Admission Test Fall 2016 (Set 1) Date: Time: 90 minutes Full Marks: 100 Name: Serial No.: (Answer all the questions. Assume reasonable value for missing data, if necessary) Section A: Mathematics [Full Marks = 42] 1. Calculate x and y if 4x + 4y = 20, and x 2 5 = y 2. (3) 2. Calculate x and y if z 3 = 36 5, x = log 6 (z) 2/3, and y = x 5. (3) /3 + 5/9 + 5/27 + =? (3) 4. If n C 2 = n C 3, calculate the value of 6 C n-1. (3) Page 1 of 8
18 5. Evaluate: (4) 6. Determine if. (5) 7. Integrate: (5) 8. Plot (freehand) graphs for y 2 = 5 (x 1) and x/3 1 = y in the gridlines provided below. (4) y y x x Page 2 of 8
19 9. Determine the equation of the chord of the circle x 2 + y 2 6x + 10y 21 = 0 which bisects at (1, 2). (3) 10. Determine the equation of a straight line passing through the point of intersection of the straight lines x + 2y = 1 and 2x + 3y = 2, whose slope if 45. (3) 11. Calculate the area of triangle ABC if the coordinates of its three vertices are A(1,2), B(3, 4) and C(5,8). (3) 12. Determine the coordinates of a point on the parabola y 2 = 8x whose distance from the origin is 8. (3) Page 3 of 8
20 Section B: Physics [Full Marks = 28] 13. What is the difference between a permanent magnet and a temporary magnet? (3) 14. Shakib Al Hasan hit a cricket ball with a velocity of 30 m/s at an inclination of 30 with horizontal. The boundary distance was 75 m. If the ball followed parabolic path, could he be able to score a six? (5) 15. Fielder F threw a cricket ball at a constant speed of 15 m/s and hit the stumps from a distance 30 m. The batsman B was 15 m from the stumps and had an initial speed of 6 m/s when F threw the ball. If B ran with an acceleration of 1.0 m/s 2, determine if B would be run out. (5) Page 4 of 8
21 16. If a 25 kg load is applied on Spring A, it elongates 0.25 m, but it elongates 0.30 m after being attached to another Spring B in series. Determine the spring constant of both springs. (5) 17. A series of loads are shown in below. Determine the magnitude and location of the resultant force. (5) 50 kg 40 kg 30 kg 75 kg A 1m B 3m C 2m D 18. Messi (weighing 67 kg) runs with the ball at 8.0 m/s when a 60 kg defender runs in the same direction at 10.0 m/s to jump on his back. Determine the speed of the two players immediately after the collision. (5) Page 5 of 8
22 Section C: English [Full Marks = 20] 19. Write an essay on Nobel Prize (within 100 words). (10) 20. Translate the following passage into English (5) ই- মইল তথ ই ল নক মইল হল ড জট ল ব ত য ক উট র নটওয় কর ম ধ ম রণ কর হয় ১৯৭২ সব থম ই ল নক মইল রণ কর হয় ই- মইল প ত থম দ কর ই- মইল ব ব য় রক এব পক জন কই অনল ই ন থ ক ত হত এখনক র ই- মইল ল ত এই সমস নই ই- মইল স ভ র ল মইল হণ ক র এব স র ন ক র প র প ঠ য় ব বহ রক র ব পক ক অথব ক উট র ক অনল ই ন থ ক র য় জন হয় ন Page 6 of 8
23 21. Read the following passage carefully and tick mark corresponding circle to choose the correct or the best one from the four answers following each question: (5) A supernova is a brief stellar explosion so luminous that it can briefly outshine an entire galaxy. While the explosion itself takes less than fifteen seconds, supernovae take weeks or months to fade from view; during that time, a supernova can emit an amount of energy equivalent to the energy the sun is expected to radiate over its entire lifespan. Supernovae generate enough heat to create heavy elements, such as mercury, gold and silver. Although supernovae explode frequently, few of them are visible (from Earth) to the naked eye. In 1604 in Padua, Italy, a supernova became visible, appearing as a star so bright that it was visible in daylight for more than a year. Galileo, who lectured at the university, gave several lectures widely attended by the public. The lectures not only sought to explain the origin of the star (some posited that perhaps it was merely vapor near the earth ), but seriously undermined the views of many philosophers that the heavens were unchangeable. This idea was foundational to a worldview underpinned by a central and all-important Earth, with heavenly bodies merely rotating around it. a) The primary purpose of the passage is to give the history of supernovae describe a shift in thought as a result of a natural event compare two opposing views about supernovae explain how science and philosophy interrelate b) Which of the following can be inferred by the passage? Supernovae can take over a year to fade from view. Prior to 1604, no one had ever seen a supernova. Galileo convinced philosophers of the incorrectness of their views. Supernovae emits insufficient energy c) What is the synonym of the word heavenly? Nearly Divine Earthly Mortal d) The author mentions which of the following as a result of the supernova of 1604? Galileo explained the origin of the supernova. The public was interested in hearing lectures about the phenomenon. Galileo s lectures were opposed by philosophers. Those who thought the supernova was vapor were proved wrong. e) The heat generated from Supernovae helps in creating. Galaxy Vapor Liquids Dense metals Page 7 of 8
24 22. The sum of ten consecutive odd numbers is always divisible by (i) 20 (ii) 30 (iii) 40 (iv) In how many ways can a team 18 be chosen out of a batch of 20 players? (i) 2 (ii) 190 (iii) 360 (iv) What will be the 10 th term in the series 5, 10, 20..? (i) 2034 (ii) 2560 (iii) 3020 (iv) If 26 th March 2006 was a Friday, which day was 1 st May 2008? Section D: Aptitude [Full Marks = 1 10 = 10] 26. A 575 meter long train crosses a tunnel of 325 meter in 90 sec. What is the speed of the train in kmph? 27. Two buses A and B leave the same bus depot, A towards the North and B towards the East. After four hours the distance between the two buses is 100 km. Determine the speed of the bus A if it travels at a speed of 5 km/hr more than that of bus B. 28. A monkey starts climbing up a 20 ft tall tree. Each minute it hops 3 ft and slips back 2 ft. How much time would it take the monkey to reach the top? 29. Some months have 30 days, some have 31 days, but how many months have 28 days? (i) 2 (ii) 3 (iii) 11 (iv) A man travelled 6 miles towards east and then turned right to travel 3 miles. Again he turned right to travel 4 miles. How far is he now from starting point? (i) 3 miles (ii) 3.2 miles (iii) 3.4 miles ( iv) 3.6 miles 31. Everybody has to shake hand with others at a party. If the total number of handshake is 15, what is the number of persons at the party? Page 8 of 8
Poems Poems By Abhiuday Singha (Sunny - 7 years)
 Poems Poems By Abhiuday Singha (Sunny - 7 years) I am sunny My mom thinks I m funny She s right because my name is Sunny I like to go outside and play, when it s sunny So I can do a lot of running I want
Poems Poems By Abhiuday Singha (Sunny - 7 years) I am sunny My mom thinks I m funny She s right because my name is Sunny I like to go outside and play, when it s sunny So I can do a lot of running I want
CLASS V. Format of the question paper: Reading and Conversations 10 marks. ENGLISH LITERATURE Book- New Mulberry English Course (Bk 5)
 CLASS V ENGLISH LANGUAGE Book- Essentials of English Grammar and Composition I Nouns Collective and Abstract Noun Case Adjective Degrees of Comparison Articles Pronouns Tenses Simple Present, Simple Past,
CLASS V ENGLISH LANGUAGE Book- Essentials of English Grammar and Composition I Nouns Collective and Abstract Noun Case Adjective Degrees of Comparison Articles Pronouns Tenses Simple Present, Simple Past,
GEMS AKADEMIAGLOBAL SCHOOL HOLIDAY- HOMEWORK Grade-IX. What is the diameter of one sphere? A 1.0 cm B 2.0 cm C 3.0 cm D 4.0 cm
 Summer Holiday Homework Session 2017 2018 Grade IX BIOLOGY Project Stem cell and Carbon trading # Students will make model of brain with stem cell and charts on it. # Students will make chart and poster
Summer Holiday Homework Session 2017 2018 Grade IX BIOLOGY Project Stem cell and Carbon trading # Students will make model of brain with stem cell and charts on it. # Students will make chart and poster
Bangladesh Bank Exam Aid (BBEA)
 Senior Officer Exam 2017 Date 24/11/2017 Prepared By Md. Abdullah Al Mamun (BBA, MBA; IIUC) S M Khalid Hossen (BBS, MBS; NU) Mohammad Mintu (BBS; NU) Dedicated to all members of Bangladesh Bank Exam Aid
Senior Officer Exam 2017 Date 24/11/2017 Prepared By Md. Abdullah Al Mamun (BBA, MBA; IIUC) S M Khalid Hossen (BBS, MBS; NU) Mohammad Mintu (BBS; NU) Dedicated to all members of Bangladesh Bank Exam Aid
NAME: CLASS : SECTION: ROLL NO:
 NAME: CLASS : SECTION: ROLL NO: GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS 1.ALL THE ASSIGNMENTS SHOULD BE DONE IN GOOD QUALITY A-4 PAPER. 2. DON T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME, CLASS, SEC, ROLL NO., SUB. & TOPIC ON THE COVER
NAME: CLASS : SECTION: ROLL NO: GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS 1.ALL THE ASSIGNMENTS SHOULD BE DONE IN GOOD QUALITY A-4 PAPER. 2. DON T FORGET TO WRITE YOUR NAME, CLASS, SEC, ROLL NO., SUB. & TOPIC ON THE COVER
VOL Living the Lotus Vol. 128 (May 2016)
 5 2016 VOL. 128 Living the Lotus Vol. 128 (May 2016) Published by Rissho Kosei-kai International, Fumonkan, 2-6-1 Wada, Suginami-ku, Tokyo, 166-8537 Japan TEL: +81-3-5341-1124 FAX: +81-3-5341-1224 Email:living.the.lotus.rk-international@
5 2016 VOL. 128 Living the Lotus Vol. 128 (May 2016) Published by Rissho Kosei-kai International, Fumonkan, 2-6-1 Wada, Suginami-ku, Tokyo, 166-8537 Japan TEL: +81-3-5341-1124 FAX: +81-3-5341-1224 Email:living.the.lotus.rk-international@
MAY News Letter May 2017
 News Letter May 2017 P a t r o n s D r. A s h i m M a j u m d a r O A M M r. S u n i l M u k h e r j e e M r. M a n a b K a r D r. A s h i s h D a s P r e s i d e n t M r R a n a j i t D a s V i c e P
News Letter May 2017 P a t r o n s D r. A s h i m M a j u m d a r O A M M r. S u n i l M u k h e r j e e M r. M a n a b K a r D r. A s h i s h D a s P r e s i d e n t M r R a n a j i t D a s V i c e P
Supernovae, Neutron Stars, Pulsars, and Black Holes
 Supernovae, Neutron Stars, Pulsars, and Black Holes Massive stars and Type II supernovae Massive stars (greater than 8 solar masses) can create core temperatures high enough to burn carbon and heavier
Supernovae, Neutron Stars, Pulsars, and Black Holes Massive stars and Type II supernovae Massive stars (greater than 8 solar masses) can create core temperatures high enough to burn carbon and heavier
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES
 SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
A supernova is the explosion of a star. It is the largest explosion that takes place in space.
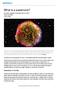 What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
Introduction to exploding stars and pulsars
 Introduction to exploding stars and pulsars Harsha Blumer Department of Physics & Astronomy West Virginia University Winnipeg, Canada About me WV, USA Kerala, India Carl Sagan (1934-1996) Neil degrasse
Introduction to exploding stars and pulsars Harsha Blumer Department of Physics & Astronomy West Virginia University Winnipeg, Canada About me WV, USA Kerala, India Carl Sagan (1934-1996) Neil degrasse
Beyond Our Solar System Chapter 24
 Beyond Our Solar System Chapter 24 PROPERTIES OF STARS Distance Measuring a star's distance can be very difficult Stellar parallax Used for measuring distance to a star Apparent shift in a star's position
Beyond Our Solar System Chapter 24 PROPERTIES OF STARS Distance Measuring a star's distance can be very difficult Stellar parallax Used for measuring distance to a star Apparent shift in a star's position
Khannar Vachan - 1 Of
 Khannar Vachan - 1 Of Varamihira s Daughter-In-Law By Abhishekha & Amrita, USA Bengali Typing: Amrita D, USA A Mission Saptarishis Initiative Publisher: I t is a tough job to write an introduction to a
Khannar Vachan - 1 Of Varamihira s Daughter-In-Law By Abhishekha & Amrita, USA Bengali Typing: Amrita D, USA A Mission Saptarishis Initiative Publisher: I t is a tough job to write an introduction to a
Neutron Stars. But what happens to the super-dense core? It faces two possible fates:
 Neutron Stars When a massive star runs out of fuel, its core collapses from the size of the Earth to a compact ball of neutrons just ten miles or so across. Material just outside the core falls onto this
Neutron Stars When a massive star runs out of fuel, its core collapses from the size of the Earth to a compact ball of neutrons just ten miles or so across. Material just outside the core falls onto this
Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens
 Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens Beyond Our Solar System Earth Science, 13e Chapter 24 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Properties of stars Distance Distances to the stars are very
Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens Beyond Our Solar System Earth Science, 13e Chapter 24 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Properties of stars Distance Distances to the stars are very
Late stages of stellar evolution for high-mass stars
 Late stages of stellar evolution for high-mass stars Low-mass stars lead a relatively peaceful life in their old age: although some may gently blow off their outer envelopes to form beautiful planetary
Late stages of stellar evolution for high-mass stars Low-mass stars lead a relatively peaceful life in their old age: although some may gently blow off their outer envelopes to form beautiful planetary
 Remedies Fr Planet Mercury - Budhan Mercury (Budhan) When yu are running weak Mercury Maha Dasa r antardasa (bukthi) r when yu are facing prblems related t Mercury Graha Wear 10 faces Rudraksha Pray Lrd
Remedies Fr Planet Mercury - Budhan Mercury (Budhan) When yu are running weak Mercury Maha Dasa r antardasa (bukthi) r when yu are facing prblems related t Mercury Graha Wear 10 faces Rudraksha Pray Lrd
Stellar Evolution Notes
 Name: Block: Stellar Evolution Notes Stars mature, grow old and die. The more massive a star is, the shorter its life will be. Our Sun will live about 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old,
Name: Block: Stellar Evolution Notes Stars mature, grow old and die. The more massive a star is, the shorter its life will be. Our Sun will live about 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old,
Physics HW Set 3 Spring 2015
 1) If the Sun were replaced by a one solar mass black hole 1) A) life here would be unchanged. B) we would still orbit it in a period of one year. C) all terrestrial planets would fall in immediately.
1) If the Sun were replaced by a one solar mass black hole 1) A) life here would be unchanged. B) we would still orbit it in a period of one year. C) all terrestrial planets would fall in immediately.
Session: SYLLABUS GRADE: VII (ICSE)
 Session: 2018 2019 SYLLABUS GRADE: VII (ICSE) ENGLISH LANGUAGE Topics Aims and Objectives: Develop and integrate the use of the four fold language skills of listening, speaking, reading and writing, build
Session: 2018 2019 SYLLABUS GRADE: VII (ICSE) ENGLISH LANGUAGE Topics Aims and Objectives: Develop and integrate the use of the four fold language skills of listening, speaking, reading and writing, build
Physics. Exam Choice. Student Number PRELIMINARY COURSE EXAMINATION. Total marks 75. General Instructions
 Student Number Exam Choice 008 PRELIMINARY COURSE EXAMINATION Physics Total marks 75 General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time hours Write using black or blue pen Draw diagrams using pencil
Student Number Exam Choice 008 PRELIMINARY COURSE EXAMINATION Physics Total marks 75 General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time hours Write using black or blue pen Draw diagrams using pencil
Ishika. Anika. Eeshita
 Ishika Anika Eeshita Writings/Poems/Stories Writers/Poets Page Association and Puja Committee 2 Message from the Board 3 Performers of the Cultural Shows 4 Editorial: Anjali in Three Lyrics Biru Paksha
Ishika Anika Eeshita Writings/Poems/Stories Writers/Poets Page Association and Puja Committee 2 Message from the Board 3 Performers of the Cultural Shows 4 Editorial: Anjali in Three Lyrics Biru Paksha
The Death of Stars. Today s Lecture: Post main-sequence (Chapter 13, pages ) How stars explode: supernovae! White dwarfs Neutron stars
 The Death of Stars Today s Lecture: Post main-sequence (Chapter 13, pages 296-323) How stars explode: supernovae! White dwarfs Neutron stars White dwarfs Roughly the size of the Earth with the mass of
The Death of Stars Today s Lecture: Post main-sequence (Chapter 13, pages 296-323) How stars explode: supernovae! White dwarfs Neutron stars White dwarfs Roughly the size of the Earth with the mass of
Unit 7 Review Guide: The Universe
 Unit 7 Review Guide: The Universe Light Year: Unit of distance used to measure the great vastness of space. Galaxy: Large group of stars, gas, and dust held together by gravity. Spiral Galaxy: Galaxy in
Unit 7 Review Guide: The Universe Light Year: Unit of distance used to measure the great vastness of space. Galaxy: Large group of stars, gas, and dust held together by gravity. Spiral Galaxy: Galaxy in
Chapter Units and Measurement
 2 Chapter Units and Measurement 1. Identify the pair whose dimensions are equal [2002] torque and work stress and energy force and stress force and work 2. [2003] [L -1 T] ] [L -2 T 2 ] [L 2 T -2 ] [LT
2 Chapter Units and Measurement 1. Identify the pair whose dimensions are equal [2002] torque and work stress and energy force and stress force and work 2. [2003] [L -1 T] ] [L -2 T 2 ] [L 2 T -2 ] [LT
The Universe. is space and everything in it.
 The Universe is space and everything in it. Galaxies A galaxy is a supercluster of stars, gas, and dust that are held together by gravity. There are three main types of galaxies: Irregular Elliptical Spiral
The Universe is space and everything in it. Galaxies A galaxy is a supercluster of stars, gas, and dust that are held together by gravity. There are three main types of galaxies: Irregular Elliptical Spiral
Astronomy Ch. 21 Stellar Explosions. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 21 Stellar Explosions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A surface explosion on a white dwarf, caused
Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 21 Stellar Explosions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A surface explosion on a white dwarf, caused
SUPERNOVA LIGHT CURVES What type of supernova?
 SUPERNOVA LIGHT CURVES What type of supernova? ImageJ In the spring of 1994 several high school students were studying M51, the spiral galaxy also known as the Whirlpool Galaxy. Various images had been
SUPERNOVA LIGHT CURVES What type of supernova? ImageJ In the spring of 1994 several high school students were studying M51, the spiral galaxy also known as the Whirlpool Galaxy. Various images had been
Cassiopeia A: Supernova Remnant
 Crab Nebula: Pulsar During a supernova, the core of a massive star can be compressed to form a rapidly rotating ball composed mostly of neutrons that is only twelve miles in diameter. A teaspoon of such
Crab Nebula: Pulsar During a supernova, the core of a massive star can be compressed to form a rapidly rotating ball composed mostly of neutrons that is only twelve miles in diameter. A teaspoon of such
Session: SYLLABUS GRADE: VIII (ICSE)
 Session: 2018 2019 ENGLISH LANGUAGE SYLLABUS GRADE: VIII (ICSE) A. Aims and Objectives: Develop and integrate the use of the four fold language skills of listening, speaking, reading and writing, build
Session: 2018 2019 ENGLISH LANGUAGE SYLLABUS GRADE: VIII (ICSE) A. Aims and Objectives: Develop and integrate the use of the four fold language skills of listening, speaking, reading and writing, build
1 The Life Cycle of a Star
 CHAPTER 1 The Life Cycle of a Star Describe the life cycle of various size stars. Rings of glowing gas encircling Supernova 1987A, about 179,000 light-years away in the Large Magellanic Cloud, one of the
CHAPTER 1 The Life Cycle of a Star Describe the life cycle of various size stars. Rings of glowing gas encircling Supernova 1987A, about 179,000 light-years away in the Large Magellanic Cloud, one of the
Mass: 1.99 x 1030 kg. Diameter: about km = 100 x the Earth diameter. Density: about kg/m3
 Mass: 1.99 x 1030 kg Diameter: about 1 400 00 km = 100 x the Earth diameter Produces a strong gravitational forces: about 28 times greater than the gravitational force produces by the Earth Temperature:
Mass: 1.99 x 1030 kg Diameter: about 1 400 00 km = 100 x the Earth diameter Produces a strong gravitational forces: about 28 times greater than the gravitational force produces by the Earth Temperature:
Chapter 21 Stellar Explosions
 Chapter 21 Stellar Explosions Units of Chapter 21 21.1 XXLife after Death for White Dwarfs (not on exam) 21.2 The End of a High-Mass Star 21.3 Supernovae Supernova 1987A The Crab Nebula in Motion 21.4
Chapter 21 Stellar Explosions Units of Chapter 21 21.1 XXLife after Death for White Dwarfs (not on exam) 21.2 The End of a High-Mass Star 21.3 Supernovae Supernova 1987A The Crab Nebula in Motion 21.4
Death of stars is based on. one thing mass.
 Death of stars is based on one thing mass. Not the mass they have when born, but the mass they have when they die. Star Death for mass 1.4 solar masses and less. These stars started big 7.5-10 solar masses.
Death of stars is based on one thing mass. Not the mass they have when born, but the mass they have when they die. Star Death for mass 1.4 solar masses and less. These stars started big 7.5-10 solar masses.
What is a star? A body of gases that gives off tremendous amounts of energy in the form of light & heat. What star is closest to the earth?
 Stars What is a star? A body of gases that gives off tremendous amounts of energy in the form of light & heat. What star is closest to the earth? Answer: The SUN It s about 150,000,000 km from earth =
Stars What is a star? A body of gases that gives off tremendous amounts of energy in the form of light & heat. What star is closest to the earth? Answer: The SUN It s about 150,000,000 km from earth =
Protostars on the HR Diagram. Lifetimes of Stars. Lifetimes of Stars: Example. Pressure-Temperature Thermostat. Hydrostatic Equilibrium
 Protostars on the HR Diagram Once a protostar is hot enough to start, it can blow away the surrounding gas Then it is visible: crosses the on the HR diagram The more the cloud, the it will form stars Lifetimes
Protostars on the HR Diagram Once a protostar is hot enough to start, it can blow away the surrounding gas Then it is visible: crosses the on the HR diagram The more the cloud, the it will form stars Lifetimes
Ch. 16 & 17: Stellar Evolution and Death
 Ch. 16 & 17: Stellar Evolution and Death Stars have lives: born, evolve, die Mass determines stellar evolution: Really Low Mass (0.08 to 0.4 M sun ) Low Mass: (0.4 to 4 M sun ) Long lives High Mass (4
Ch. 16 & 17: Stellar Evolution and Death Stars have lives: born, evolve, die Mass determines stellar evolution: Really Low Mass (0.08 to 0.4 M sun ) Low Mass: (0.4 to 4 M sun ) Long lives High Mass (4
SUPERNOVA LIGHT CURVES
 HANDS-ON UNIVERSE DISCUSSION SHEET SUPERNOVA LIGHT CURVES In the spring of 1994 several high school students were studying M51, the spiral galaxy also known as the Whirlpool Galaxy. Various images had
HANDS-ON UNIVERSE DISCUSSION SHEET SUPERNOVA LIGHT CURVES In the spring of 1994 several high school students were studying M51, the spiral galaxy also known as the Whirlpool Galaxy. Various images had
Gravity simplest. fusion
 Gravity simplest fusion The life of a star has a complex relationship with gravity: 1. Gravity is what brings the original dust together to make a star 2. Gravity wants to crush the star Gravity pulls
Gravity simplest fusion The life of a star has a complex relationship with gravity: 1. Gravity is what brings the original dust together to make a star 2. Gravity wants to crush the star Gravity pulls
Evolution of High Mass Stars
 Luminosity (L sun ) Evolution of High Mass Stars High Mass Stars O & B Stars (M > 4 M sun ): Burn Hot Live Fast Die Young Main Sequence Phase: Burn H to He in core Build up a He core, like low-mass stars
Luminosity (L sun ) Evolution of High Mass Stars High Mass Stars O & B Stars (M > 4 M sun ): Burn Hot Live Fast Die Young Main Sequence Phase: Burn H to He in core Build up a He core, like low-mass stars
ASTRONOMY 1 FINAL EXAM 1 Name
 ASTRONOMY 1 FINAL EXAM 1 Name Multiple Choice (2 pts each) 1. Sullivan Star is an F spectral class star that is part of a binary star system. It has a MS lifetime of 5 billion years. Its life will eventually
ASTRONOMY 1 FINAL EXAM 1 Name Multiple Choice (2 pts each) 1. Sullivan Star is an F spectral class star that is part of a binary star system. It has a MS lifetime of 5 billion years. Its life will eventually
They developed a graph, called the H-R diagram, that relates the temperature of a star to its absolute magnitude.
 Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Russell noticed that stars with higher temperatures and large sizes also have brighter absolute magnitudes the actual amount of light given off by a star. (also referred to
Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Russell noticed that stars with higher temperatures and large sizes also have brighter absolute magnitudes the actual amount of light given off by a star. (also referred to
Chapter 5 Newton s Universe
 Chapter 5 Newton s Universe Lecture notes about gravitation Dr. Armen Kocharian Units of Chapter 5 The Idea of Gravity: The Apple and the Moon The Law of Gravity: Moving the Farthest Star Gravitational
Chapter 5 Newton s Universe Lecture notes about gravitation Dr. Armen Kocharian Units of Chapter 5 The Idea of Gravity: The Apple and the Moon The Law of Gravity: Moving the Farthest Star Gravitational
What is Astronomy? 1. The study of. A. EM spectrum includes waves of all different that travel through space, NOT just visible light
 Name Period NOTE OUTLINE: Ch 30-31 Stars & Universe Objectives 1. Describe electromagnetic radiation (EM). This means I can: A. Describe how the EM is organized and which forms of EM waves are the most
Name Period NOTE OUTLINE: Ch 30-31 Stars & Universe Objectives 1. Describe electromagnetic radiation (EM). This means I can: A. Describe how the EM is organized and which forms of EM waves are the most
Neutron Stars. Chapter 14: Neutron Stars and Black Holes. Neutron Stars. What s holding it up? The Lighthouse Model of Pulsars
 Neutron Stars Form from a 8-20 M Sun star Chapter 14: Neutron Stars and Black Holes Leftover 1.4-3 M Sun core after supernova Neutron Stars consist entirely of neutrons (no protons) Neutron Star (tennis
Neutron Stars Form from a 8-20 M Sun star Chapter 14: Neutron Stars and Black Holes Leftover 1.4-3 M Sun core after supernova Neutron Stars consist entirely of neutrons (no protons) Neutron Star (tennis
Rolling, Torque & Angular Momentum
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 11 Rolling, Torque & Angular Momentum Rolling motion Torque Angular momentum Conservation of angular momentum 1. A uniform hoop (ring) is rolling smoothly from the
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 11 Rolling, Torque & Angular Momentum Rolling motion Torque Angular momentum Conservation of angular momentum 1. A uniform hoop (ring) is rolling smoothly from the
Physics Midterm Review KEY
 Name: Date: 1. Which quantities are scalar? A. speed and work B. velocity and force C. distance and acceleration D. momentum and power 2. A 160.-kilogram space vehicle is traveling along a straight line
Name: Date: 1. Which quantities are scalar? A. speed and work B. velocity and force C. distance and acceleration D. momentum and power 2. A 160.-kilogram space vehicle is traveling along a straight line
STARS AND GALAXIES STARS
 STARS AND GALAXIES STARS enormous spheres of plasma formed from strong gravitational forces PLASMA the most energetic state of matter; responsible for the characteristic glow emitted by these heavenly
STARS AND GALAXIES STARS enormous spheres of plasma formed from strong gravitational forces PLASMA the most energetic state of matter; responsible for the characteristic glow emitted by these heavenly
Abundance of Elements. Relative abundance of elements in the Solar System
 Abundance of Elements Relative abundance of elements in the Solar System What is the origin of elements in the universe? Three elements formed in the first minutes after the big bang (hydrogen, helium
Abundance of Elements Relative abundance of elements in the Solar System What is the origin of elements in the universe? Three elements formed in the first minutes after the big bang (hydrogen, helium
Stars. The composition of the star It s temperature It s lifespan
 Stars Stars A star is a ball of different elements in the form of gases The elements and gases give off electromagnetic radiation (from nuclear fusion) in the form of light Scientists study the light coming
Stars Stars A star is a ball of different elements in the form of gases The elements and gases give off electromagnetic radiation (from nuclear fusion) in the form of light Scientists study the light coming
TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify This star is in the last stage of its life cycle. What is that stage?
 CHAPTER 15 2 SECTION Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe The Life Cycle of Stars BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do stars change over time?
CHAPTER 15 2 SECTION Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe The Life Cycle of Stars BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do stars change over time?
SAMPLE. paper provided. Each question carries 2 marks. Marks will not be. from any one option. Write your answers on the answer paper provided.
 UNIVERSITY ENTRANCE EXAMINATION 2017 MATHEMATICS ( A LEVEL EQUIVALENT) Duration: 2 hours INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES 1. This examination paper has TWO (2) sections A and B, and comprises SIXTEEN (16) printed
UNIVERSITY ENTRANCE EXAMINATION 2017 MATHEMATICS ( A LEVEL EQUIVALENT) Duration: 2 hours INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES 1. This examination paper has TWO (2) sections A and B, and comprises SIXTEEN (16) printed
1. The diagram below shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object.
 1. The diagram below shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object. The area between the line of the graph and the time-axis represents A. the average velocity of the object. B. the displacement
1. The diagram below shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object. The area between the line of the graph and the time-axis represents A. the average velocity of the object. B. the displacement
Lecture 33: The Lives of Stars
 Lecture 33 The Lives of Stars Astronomy 141 Winter 2012 This lecture concerns the life cycle of normal stars. Stars shine because they are hot, and need a source of energy to keep shining. Main Sequence
Lecture 33 The Lives of Stars Astronomy 141 Winter 2012 This lecture concerns the life cycle of normal stars. Stars shine because they are hot, and need a source of energy to keep shining. Main Sequence
Stellar Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4
 Stellar Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4 Chapter 15 1. Emission nebulas emit light because a) they absorb high energy radiation (mostly UV) from nearby bright hot stars and re-emit it in visible wavelengths.
Stellar Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4 Chapter 15 1. Emission nebulas emit light because a) they absorb high energy radiation (mostly UV) from nearby bright hot stars and re-emit it in visible wavelengths.
Ch. 29 The Stars Stellar Evolution
 Ch. 29 The Stars 29.3 Stellar Evolution Basic Structure of Stars Mass effects The more massive a star is, the greater the gravity pressing inward, and the hotter and more dense the star must be inside
Ch. 29 The Stars 29.3 Stellar Evolution Basic Structure of Stars Mass effects The more massive a star is, the greater the gravity pressing inward, and the hotter and more dense the star must be inside
This class: Life cycle of high mass stars Supernovae Neutron stars, pulsars, pulsar wind nebulae, magnetars Quark-nova stars Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs)
 This class: Life cycle of high mass stars Supernovae Neutron stars, pulsars, pulsar wind nebulae, magnetars Quark-nova stars Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs)!1 Cas$A$ All$Image$&$video$credits:$Chandra$X7ray$ Observatory$
This class: Life cycle of high mass stars Supernovae Neutron stars, pulsars, pulsar wind nebulae, magnetars Quark-nova stars Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs)!1 Cas$A$ All$Image$&$video$credits:$Chandra$X7ray$ Observatory$
The light curves for a nova look like the following.
 End of high mass stars Nova Supernova Type I Type II Stellar nucleo-synthesis Stellar Recycling Nova (means new): is a star that suddenly increases greatly in brightness, then slowly fades back to its
End of high mass stars Nova Supernova Type I Type II Stellar nucleo-synthesis Stellar Recycling Nova (means new): is a star that suddenly increases greatly in brightness, then slowly fades back to its
PHYSICS. 2. A force of 6 kgf and another force of 8 kg f can be applied to produce the effect of a single force equal to
 PHYSICS 1. A body falls from rest, in the last second of its fall, it covers half of the total distance. Then the total time of its fall is (A) 2 + 2 sec (B) 2-2 sec (C) 2 2 (D) 4 sec 2. A force of 6 kgf
PHYSICS 1. A body falls from rest, in the last second of its fall, it covers half of the total distance. Then the total time of its fall is (A) 2 + 2 sec (B) 2-2 sec (C) 2 2 (D) 4 sec 2. A force of 6 kgf
Stars & Galaxies. Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science
 Stars & Galaxies Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Chapter 27, Section 1 27.1 Characteristics of Stars How do astronomers determine the composition and surface temperature of a star? Composition & Temperature
Stars & Galaxies Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Chapter 27, Section 1 27.1 Characteristics of Stars How do astronomers determine the composition and surface temperature of a star? Composition & Temperature
Review Sheet for Math 5a Final Exam. The Math 5a final exam will be Tuesday, May 1 from 9:15 am 12:15 p.m.
 Review Sheet for Math 5a Final Exam The Math 5a final exam will be Tuesday, May from 9:5 am :5 p.m. Location: Gerstenzang The final exam is cumulative (i.e., it will cover all the material we covered in
Review Sheet for Math 5a Final Exam The Math 5a final exam will be Tuesday, May from 9:5 am :5 p.m. Location: Gerstenzang The final exam is cumulative (i.e., it will cover all the material we covered in
Chapter 4 Force and Motion
 Chapter 4 Force and Motion Units of Chapter 4 The Concepts of Force and Net Force Inertia and Newton s First Law of Motion Newton s Second Law of Motion Newton s Third Law of Motion More on Newton s Laws:
Chapter 4 Force and Motion Units of Chapter 4 The Concepts of Force and Net Force Inertia and Newton s First Law of Motion Newton s Second Law of Motion Newton s Third Law of Motion More on Newton s Laws:
CDS-I 2019 Elementary Mathematics (Set-C)
 1 CDS-I 019 Elementary Mathematics (Set-C) Direction: Consider the following for the next three (03) items : A cube is inscribed in a sphere. A right circular cylinder is within the cube touching all the
1 CDS-I 019 Elementary Mathematics (Set-C) Direction: Consider the following for the next three (03) items : A cube is inscribed in a sphere. A right circular cylinder is within the cube touching all the
Comparing a Supergiant to the Sun
 The Lifetime of Stars Once a star has reached the main sequence stage of it life, it derives its energy from the fusion of hydrogen to helium Stars remain on the main sequence for a long time and most
The Lifetime of Stars Once a star has reached the main sequence stage of it life, it derives its energy from the fusion of hydrogen to helium Stars remain on the main sequence for a long time and most
2016 ENGINEERING MECHANICS
 Set No 1 I B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Dec 2016 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Com. to AE, AME, BOT, CHEM, CE, EEE, ME, MTE, MM, PCE, PE) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Question Paper Consists of Part-A
Set No 1 I B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Dec 2016 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Com. to AE, AME, BOT, CHEM, CE, EEE, ME, MTE, MM, PCE, PE) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Question Paper Consists of Part-A
Regents Physics Most Missed Questions of 2014 Review
 Regents Physics Most Missed Questions of 2014 Review Answers And Explanations Here: http://youtu.be/meoporthklo 1. A sound wave traveling eastward through air causes the air molecules to 1) vibrate east
Regents Physics Most Missed Questions of 2014 Review Answers And Explanations Here: http://youtu.be/meoporthklo 1. A sound wave traveling eastward through air causes the air molecules to 1) vibrate east
To infinity, and beyond!
 stars The night sky is filled with stars that shine at different levels of brightness. The brightness of the stars we observe can be related to the size of the star or its distance from Earth. In order
stars The night sky is filled with stars that shine at different levels of brightness. The brightness of the stars we observe can be related to the size of the star or its distance from Earth. In order
Chapters 12 and 13 Review: The Life Cycle and Death of Stars. How are stars born, and how do they die? 4/1/2009 Habbal Astro Lecture 27 1
 Chapters 12 and 13 Review: The Life Cycle and Death of Stars How are stars born, and how do they die? 4/1/2009 Habbal Astro 110-01 Lecture 27 1 Stars are born in molecular clouds Clouds are very cold:
Chapters 12 and 13 Review: The Life Cycle and Death of Stars How are stars born, and how do they die? 4/1/2009 Habbal Astro 110-01 Lecture 27 1 Stars are born in molecular clouds Clouds are very cold:
Properties of Stars. Characteristics of Stars
 Properties of Stars Characteristics of Stars A constellation is an apparent group of stars originally named for mythical characters. The sky contains 88 constellations. Star Color and Temperature Color
Properties of Stars Characteristics of Stars A constellation is an apparent group of stars originally named for mythical characters. The sky contains 88 constellations. Star Color and Temperature Color
Page 386 SUMMARY. d TABLE 14.2 EVOLUTION OF LOW MASS AND HIGH MASS STARS Low Mass Star (Mass Less Than 8 M ) High Mass Star (Mass More Than 8 M )
 Page 386 SUMMARY A star forms from interstellar gas drawn together by gravity, which compresses and heats the gas to form a protostar. Further heating causes the core of the protostar to fuse hydrogen
Page 386 SUMMARY A star forms from interstellar gas drawn together by gravity, which compresses and heats the gas to form a protostar. Further heating causes the core of the protostar to fuse hydrogen
Stars & Galaxies. Chapter 27, Section 1. Composition & Temperature. Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Characteristics of Stars
 Stars & Galaxies Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Chapter 27, Section 1 27.1 Characteristics of Stars Composition & Temperature Scientists use the following tools to study stars Telescope Observation Spectral
Stars & Galaxies Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Chapter 27, Section 1 27.1 Characteristics of Stars Composition & Temperature Scientists use the following tools to study stars Telescope Observation Spectral
Kinematics II Mathematical Analysis of Motion
 AP Physics Kinematics II Mathematical Analysis of Motion Introduction: Everything in the universe is in a state of motion. It might seem impossible to find a simple way to describe and understand the motion
AP Physics Kinematics II Mathematical Analysis of Motion Introduction: Everything in the universe is in a state of motion. It might seem impossible to find a simple way to describe and understand the motion
CHAPTER 14 II Stellar Evolution
 14-5. Supernova CHAPTER 14 II Stellar Evolution Exactly which stars become supernovae is not yet clear, but more than likely they are massive stars that become highly evolved. A star that develops an iron
14-5. Supernova CHAPTER 14 II Stellar Evolution Exactly which stars become supernovae is not yet clear, but more than likely they are massive stars that become highly evolved. A star that develops an iron
PHYS-1050 Measuring Cosmic Distances Spring 2013
 Name: 1 Introduction This lab will introduce the concepts of distance modulus and using supernovae as a measuring tool to determine the distances to galaxies beyond our own. Read through this information
Name: 1 Introduction This lab will introduce the concepts of distance modulus and using supernovae as a measuring tool to determine the distances to galaxies beyond our own. Read through this information
Kinematics II Mathematical Analysis of Motion
 AP Physics-B Kinematics II Mathematical Analysis of Motion Introduction: Everything in the universe is in a state of motion. It might seem impossible to find a simple way to describe and understand the
AP Physics-B Kinematics II Mathematical Analysis of Motion Introduction: Everything in the universe is in a state of motion. It might seem impossible to find a simple way to describe and understand the
Stellar Explosions (ch. 21)
 Stellar Explosions (ch. 21) First, a review of low-mass stellar evolution by means of an illustration I showed in class. You should be able to talk your way through this diagram and it should take at least
Stellar Explosions (ch. 21) First, a review of low-mass stellar evolution by means of an illustration I showed in class. You should be able to talk your way through this diagram and it should take at least
CHAPTER 9 FORCE AND LAWS OF MOTION
 CHAPTER 9 FORCE AND LAWS OF MOTION Q 1. What is a force? Ans: Force is a push or pull which tries to bring the change in the state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line. Unit of force: force
CHAPTER 9 FORCE AND LAWS OF MOTION Q 1. What is a force? Ans: Force is a push or pull which tries to bring the change in the state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line. Unit of force: force
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions
 PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions (In summer 2014 we have not covered questions 30-35,40,41) 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions (In summer 2014 we have not covered questions 30-35,40,41) 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor
PHYS 154 Practice Test 3 Spring 2018
 The actual test contains 1 multiple choice questions and 2 problems. However, for extra exercise, this practice test includes 4 problems. Questions: N.B. Make sure that you justify your answers explicitly
The actual test contains 1 multiple choice questions and 2 problems. However, for extra exercise, this practice test includes 4 problems. Questions: N.B. Make sure that you justify your answers explicitly
FIITJEE PET I (EXTENDED-2)
 FIITJEE PET I (EXTENDED-) MAINS DATE: 9.07.017 Time: hours Maximum Marks: 60 INSTRUCTIONS: Instructions to the Candidates 1. This Test Booklet consists of 90 questions. Use Blue/Black ball Point Pen only
FIITJEE PET I (EXTENDED-) MAINS DATE: 9.07.017 Time: hours Maximum Marks: 60 INSTRUCTIONS: Instructions to the Candidates 1. This Test Booklet consists of 90 questions. Use Blue/Black ball Point Pen only
For the intersections: cos x = 0 or sin x = 1 2
 Chapter 6 Set-up examples The purpose of this document is to demonstrate the work that will be required if you are asked to set-up integrals on an exam and/or quiz.. Areas () Set up, do not evaluate, any
Chapter 6 Set-up examples The purpose of this document is to demonstrate the work that will be required if you are asked to set-up integrals on an exam and/or quiz.. Areas () Set up, do not evaluate, any
Analyzing X-Ray Pulses from Stellar Cores Pencil & Paper Version
 Analyzing X-Ray Pulses from Stellar Cores Pencil & Paper Version Purpose: To determine if two end products of stellar evolution GK Per and Cen X-3 could be white dwarfs or neutron stars by calculating
Analyzing X-Ray Pulses from Stellar Cores Pencil & Paper Version Purpose: To determine if two end products of stellar evolution GK Per and Cen X-3 could be white dwarfs or neutron stars by calculating
Sample Physics Placement Exam
 Sample Physics 130-1 Placement Exam A. Multiple Choice Questions: 1. A cable is used to take construction equipment from the ground to the top of a tall building. During the trip up, when (if ever) is
Sample Physics 130-1 Placement Exam A. Multiple Choice Questions: 1. A cable is used to take construction equipment from the ground to the top of a tall building. During the trip up, when (if ever) is
Astronomy Notes Chapter 13.notebook. April 11, 2014
 All stars begin life in a similar way the only difference is in the rate at which they move through the various stages (depends on the star's mass). A star's fate also depends on its mass: 1) Low Mass
All stars begin life in a similar way the only difference is in the rate at which they move through the various stages (depends on the star's mass). A star's fate also depends on its mass: 1) Low Mass
CHAPTER ONE FUNCTIONS AND GRAPHS. In everyday life, many quantities depend on one or more changing variables eg:
 CHAPTER ONE FUNCTIONS AND GRAPHS 1.0 Introduction to Functions In everyday life, many quantities depend on one or more changing variables eg: (a) plant growth depends on sunlight and rainfall (b) speed
CHAPTER ONE FUNCTIONS AND GRAPHS 1.0 Introduction to Functions In everyday life, many quantities depend on one or more changing variables eg: (a) plant growth depends on sunlight and rainfall (b) speed
What do the Roman numerals mean and how do stars die
 What do the Roman numerals mean and how do stars die What is luminosity? Luminosity is the energy emitted from a star, or basically how bright it is compared to our Sun The higher the luminosity, the higher
What do the Roman numerals mean and how do stars die What is luminosity? Luminosity is the energy emitted from a star, or basically how bright it is compared to our Sun The higher the luminosity, the higher
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) You are standing in a moving bus, facing forward, and you suddenly fall forward as the
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) You are standing in a moving bus, facing forward, and you suddenly fall forward as the
Chapter 28 Stars and Their Characteristics
 Chapter 28 Stars and Their Characteristics Origin of the Universe Big Bang Theory about 10-20 bya all matter in the universe existed in a hot dense state about the size of an atom (tiny). That matter sort
Chapter 28 Stars and Their Characteristics Origin of the Universe Big Bang Theory about 10-20 bya all matter in the universe existed in a hot dense state about the size of an atom (tiny). That matter sort
Stars Star birth and kinds Elemental furnaces Star death and heavy elements
 Stars Star birth and kinds Elemental furnaces Star death and heavy elements Matter was not uniformly distributed as the universe expanded after the Big Bang. This lumpy universe coalesced under the force
Stars Star birth and kinds Elemental furnaces Star death and heavy elements Matter was not uniformly distributed as the universe expanded after the Big Bang. This lumpy universe coalesced under the force
ASTR Midterm 2 Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson
 ASTR 1120-001 Midterm 2 Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson SECOND MID-TERM EXAM MARCH 21 st 2006: Closed books and notes, 1 hour. Please PRINT your name and student ID on the places provided on the scan sheet.
ASTR 1120-001 Midterm 2 Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson SECOND MID-TERM EXAM MARCH 21 st 2006: Closed books and notes, 1 hour. Please PRINT your name and student ID on the places provided on the scan sheet.
Stellar Evolution - Chapter 12 and 13. The Lives and Deaths of Stars White dwarfs, neutron stars and black holes
 Stellar Evolution - Chapter 12 and 13 The Lives and Deaths of Stars White dwarfs, neutron stars and black holes During the early stages of a star formation the objects are called a protostars. The internal
Stellar Evolution - Chapter 12 and 13 The Lives and Deaths of Stars White dwarfs, neutron stars and black holes During the early stages of a star formation the objects are called a protostars. The internal
Lecture 26. High Mass Post Main Sequence Stages
 Lecture 26 Fate of Massive Stars Heavy Element Fusion Core Collapse Supernova Neutrinoes Gaseous Remnants Neutron Stars Mar 27, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 26 1 High Mass Post Main Sequence Stages For M(main
Lecture 26 Fate of Massive Stars Heavy Element Fusion Core Collapse Supernova Neutrinoes Gaseous Remnants Neutron Stars Mar 27, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 26 1 High Mass Post Main Sequence Stages For M(main
the nature of the universe, galaxies, and stars can be determined by observations over time by using telescopes
 the nature of the universe, galaxies, and stars can be determined by observations over time by using telescopes The spectral lines of stars tell us their approximate composition Remember last year in Physics?
the nature of the universe, galaxies, and stars can be determined by observations over time by using telescopes The spectral lines of stars tell us their approximate composition Remember last year in Physics?
PHYA2. General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June Mechanics, Materials and Waves
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Physics A Unit 2 For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator a Data and Formulae Booklet.
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Physics A Unit 2 For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator a Data and Formulae Booklet.
Astronomy 104: Second Exam
 Astronomy 104: Second Exam Stephen Lepp October 29, 2014 Each question is worth 2 points. Write your name on this exam and on the scantron. Short Answer A The Sun is powered by converting hydrogen to what?
Astronomy 104: Second Exam Stephen Lepp October 29, 2014 Each question is worth 2 points. Write your name on this exam and on the scantron. Short Answer A The Sun is powered by converting hydrogen to what?
Physics Standard level Paper 1
 Physics Standard level Paper 1 Tuesday 8 November 2016 (morning) 45 minutes Instructions to candidates Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. Answer all the questions. For each question,
Physics Standard level Paper 1 Tuesday 8 November 2016 (morning) 45 minutes Instructions to candidates Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. Answer all the questions. For each question,
Supernovae Through the Ages
 Supernovae Through the Ages We ourselves are stardust. -Carl Sagan Jason Kezwer September 11, 2013 Outline - What are supernovae? Why are they important? - An observational history - How supernovae affect
Supernovae Through the Ages We ourselves are stardust. -Carl Sagan Jason Kezwer September 11, 2013 Outline - What are supernovae? Why are they important? - An observational history - How supernovae affect
Beyond the Solar System 2006 Oct 17 Page 1 of 5
 I. Stars have color, brightness, mass, temperature and size. II. Distances to stars are measured using stellar parallax a. The further away, the less offset b. Parallax angles are extremely small c. Measured
I. Stars have color, brightness, mass, temperature and size. II. Distances to stars are measured using stellar parallax a. The further away, the less offset b. Parallax angles are extremely small c. Measured
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 25 Beyond Our Solar System 25.1 Properties of Stars Characteristics of Stars A constellation is an apparent group of stars originally named for mythical
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 25 Beyond Our Solar System 25.1 Properties of Stars Characteristics of Stars A constellation is an apparent group of stars originally named for mythical
PHYS-1050 Measuring Cosmic Distances Solutions Spring 2013
 Name: 1 Introduction This lab will introduce the concepts of distance modulus and using supernovae as a measuring tool to determine the distances to galaxies beyond our own. Read through this information
Name: 1 Introduction This lab will introduce the concepts of distance modulus and using supernovae as a measuring tool to determine the distances to galaxies beyond our own. Read through this information
