10 THE HISTORY OF EVERYTHING
|
|
|
- Dulcie Cunningham
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 10 THE HISTORY OF EVERYTHING 0:16 1:35 SCRAMBLED EGGS First, a video. Yes, it is a scrambled egg. But as you look at it, I hope you ll begin to feel just slightly uneasy. Because you may notice that what s actually happening is that the egg is unscrambling itself. And you ll now see the yolk and the white have separated, and now they re going to be poured back into the egg. And we all know in our heart of hearts that this is not the way the Universe works. A scrambled egg is mush, tasty mush, but it s mush. An egg is a beautiful, sophisticated thing that can create even more sophisticated things, such as chickens. And we know in our heart of hearts that the Universe does not travel from mush to complexity. In fact, this gut instinct is reflected in one of the most fundamental laws of physics, the second law of thermodynamics, or the law of entropy. What that says basically is that the general tendency of the Universe is to move from order and structure to lack of order, lack of structure in fact, to mush. And that s why that video feels a bit strange. And yet, look around us. What we see around us is staggering complexity. Eric Beinhocker estimates that in New York City alone, there are some ten billion SKUs or distinct commodities being traded. That s hundreds of times as many species as there are on Earth. And they re being traded by a species of almost seven billion individuals who are linked by trade, travel and the Internet into a global system of stupendous complexity. So here s a great puzzle. In a Universe ruled by the second law of thermodynamics, how is it possible to generate the sort of complexity I ve described, the sort of complexity represented by you and me and the convention center? Well, the answer seems to be the Universe can create complexity, but with great difficulty. In pockets, there appear what my colleague Fred Spier calls Goldilocks Conditions. Not too hot, not too cold, just right for the creation of complexity and slightly more complex things appear. And where you have slightly more complex things, you can get slightly more complex things. 1:35 2:29 VAST COMPLEXITY 2:29 3:24 GOLDILOCKS CONDITIONS BIG HISTORY PROJECT 2
2 3:24 4:26 IMAGINE NOTHING 4:26 4:57 BIG BANG And in this way, complexity builds stage by stage. Each stage is magical because it creates the impression of something utterly new appearing almost out of nowhere in the Universe. We refer in Big History to these moments as threshold moments. And at each threshold, the going gets tougher. The complex things get more fragile, more vulnerable. The Goldilocks Conditions get more stringent and it s more difficult to create complexity. Now, we as extremely complex creatures desperately need to know the story of how the Universe creates complexity despite the second law and why complexity means vulnerability and fragility. And that s the story that we tell in Big History. But to do it, you have to do something that may at first sight seem completely impossible. You have to survey the whole history of the Universe. So let s do it. Let s begin by winding the timeline back 13.7 billion years to the beginning of time. Around us, there s nothing. There s not even time or space. Imagine the darkest, emptiest thing you can and cube it a gazillion times, and that s where we are. And then suddenly, BAM, a Universe appears, an entire Universe and we ve crossed our first threshold. The Universe is tiny, it s smaller than an atom, it s incredibly hot, it contains everything that s in today s Universe. So you can imagine, it s busting and it s expanding at incredible speed. And at first, it s just a blur, but very quickly distinct things begin to appear in that blur. Within the first second, energy itself shatters into distinct forces, including electromagnetism and gravity. And energy does something else quite magical. It congeals to form matter, quarks that will create protons and leptons that include electrons. And all of that happens in the first second. Now, we move forward 380,000 years. That s twice as long as humans have been on this planet. And now, simple atoms appear of hydrogen and helium. Now, I want to pause for a moment, 380,000 years after the origins of the Universe, because we actually know quite a lot about the Universe at this stage. We know above all that it was extremely simple. It consisted of huge clouds of hydrogen and helium atoms and they have no structure. They re really a sort of cosmic mush. But that s not completely true. Recent studies by satellites such as the WMAP satellite have shown that in fact there are just tiny differences in that background. What you see here, the blue areas are about a thousandth of a degree cooler than the red areas. These are tiny differences, but it was enough for the Universe to move on to the next stage of building complexity. 4:57 5:46 THE FIRST SECOND 5:46 6:22 GRAVITY 3 BIG HISTORY PROJECT 4
3 6:22 7:26 STARS AND ELEMENTS And this is how it works. Gravity is more powerful where there s more stuff. So where you get slightly denser areas, gravity starts compacting clouds of hydrogen and helium atoms. So we can imagine the early Universe breaking up into a billion clouds. And each cloud is compacted, gravity gets more powerful as density increases, the temperature begins to rise at the center of each cloud, and then at the center of each cloud, the temperature crosses the threshold temperature of 10 million degrees, protons start to fuse, there s a huge release of energy, and, BAM, we have our first stars. From about 200 million years after the Big Bang, stars begin to appear all through the Universe, billions of them. So now the Universe is chemically more complex. And in a chemically more complex Universe, it s possible to make more things. And what starts happening is that around young suns, young stars, all these elements combine. They swirl around, the energy of the star stirs them around, they form particles, they form snowflakes, they form little dust motes, they form rocks, they form asteroids and eventually, they form planets and moons. And that is how our Solar System was formed four-and-a-half billion years ago. Rocky planets like our Earth are significantly more complex than stars because they contain a much greater diversity of materials. So we ve crossed a fourth threshold of complexity. 7:26 8:32 EARTH & OUR SOLAR SYSTEM And the Universe is now significantly more interesting and more complex. Stars will create the Goldilocks Conditions for crossing two new thresholds. When very large stars die, they create temperatures so high that protons begin to fuse in all sorts of exotic combinations to form all the elements of the periodic table. If, like me, you re wearing a gold ring, it was forged in a supernova explosion. Now, the going gets tougher. The next stage introduces entities that are significantly more fragile, significantly more vulnerable, but they re also much more creative and much more capable of generating further complexity. I m talking, of course, about living organisms. Living organisms are created by chemistry. We are huge packages of chemicals. So, chemistry is dominated by the electromagnetic force that operates over smaller scales in gravity which explains why you and I are smaller than stars or planets. Now what are the ideal conditions for chemistry? What are the Goldilocks Conditions? 8:32 9:10 LIFE 5 BIG HISTORY PROJECT 6
4 9:10 10:12 MORE GOLDILOCKS CONDITIONS Well, first, you need energy, but not too much. In the center of a star, there s so much energy that any atoms that combine, will just get busted apart again. But not too little. In intergalactic space, there s so little energy the atoms can t combine. What you want is just the right amount. And planets, it turns out are just right because they re close to stars, but not too close. You also need a great diversity of chemical elements and you need liquids, such as water. Why? Well, in gases, atoms move past each other so fast that they can t hitch up. In solids, atoms stuck together. They can t move. In liquids, they can cruise and cuddle and link up to form molecules. Now, where do you find such Goldilocks Conditions? Well, planets are great and our early Earth was almost perfect. It was just the right distance from its star to contain huge oceans of liquid water. And deep beneath those oceans at cracks in the Earth s crust, you got heat seeping up from inside the earth and you got a great diversity of elements. So at those deep oceanic vents, fantastic chemistry began to happen. And atoms combined in all sorts of exotic combinations. But, of course, life is more than just exotic chemistry. How do you stabilize those huge molecules that seem to be viable? Well, it s here that life introduces an entirely new trick. You don t stabilize the individual, you stabilize the template the thing that carries information and you allow the template to copy itself. And DNA, of course, is the beautiful molecule that contains that information. You ll be familiar with the double helix of DNA. Each rung contains information. So DNA contains information about how to make living organisms. And DNA also copies itself, so it copies itself and scatters the templates through the oceans. So the information spreads. Notice that information has become part of our story. The real beauty of DNA though, is in its imperfections. As it copies itself, once in every billion rungs, there tends to be an error. And what that means is that DNA is in effect learning. It s accumulating new ways of making living organisms because some of those errors work. So DNA is learning and it s building greater diversity and greater complexity. 10:12 11:01 DNA IS INFORMATION 11:40 12:23 THE DINOSAURS DISAPPEAR 7 BIG HISTORY PROJECT 8
5 12:23 13:13 HOMO SAPIENS APPEAR 13:13 13:48 HUMAN LANGUAGE And we can see this happening over the last four billion years. For most of that time of life on Earth, living organisms are being relatively simple single cells, but they had great diversity and inside great complexity. Then from about 600 to 800 million years ago, multi-celled organisms appear. You get fungi, you get fish, you get plants, you get amphibia, you get reptiles, and then, of course, you get the dinosaurs. And occasionally, there are disasters. 65 million years ago, an asteroid landed on Earth near the Yucatan Peninsula creating conditions equivalent to those of a nuclear war, and the dinosaurs were wiped out. Terrible news for the dinosaurs, but great news for our mammalian ancestors who flourished in the niches left empty by the dinosaurs. And we human beings are part of that creative evolutionary pulse that began 65 million years ago with the landing of an asteroid. Humans appeared about 200,000 years ago. And I believe we count as a threshold in this great story. Let me explain why. We ve seen that DNA learns in a sense. It accumulates information, but it is so slow. DNA accumulates information through random errors that just some of which just happened to work. But DNA had actually generated a faster way of learning. It had reproduced organisms with brains, and those organisms can learn in real time. They accumulate information, they learn. The sad thing is, when they die, the information dies with them. Now what makes humans different is human language. We are blessed with a language, a system of communication so powerful and so precise that we can share what we ve learned with such precision that it can accumulate in the collective memory. And that means it can outlast the individuals who learnt that information and it can accumulate from generation to generation. And that s why as a species we re so creative and so powerful and that s why we have a history. We seem to be the only species in four billion years to have this gift. I call this ability collective learning. It s what makes us different. We can see it at work in the earliest stages of human history. We evolved as a species in the savanna lands of Africa. But then you see humans migrating into new environments, into desert lands, into jungles, into the ice aged tundra of Siberia. Tough, tough environment. Into the Americas, into Australasia. Each migration involved learning, learning new ways of exploiting the environment, new ways of dealing with the surroundings. Then 10,000 years ago, exploiting a sudden change in global climates, with the end of the last ice age, humans learned to farm. Farming was an energy bonanza. And exploiting that energy, human populations multiplied, human societies got larger, denser, more interconnected. And then, from about 500 years ago, humans began to link up globally, through shipping, through trains, through telegraph, through the Internet, until now we ve seem to form a single global brain of almost seven billion individuals and that brain is learning at warp speed. 13:48 14:20 COLLECTIVE LEARNING 14:20 15:22 AGRICULTURE AND THE MODERN REVOUTION 9 BIG HISTORY PROJECT 10
6 15:22 16:08 A NOTE OF CAUTION And in the last 200 years, something else has happened. We ve stumbled on another energy bonanza in fossil fuels. So fossil fuels and collective learning together explain the staggering complexity we see around us. So, here we are back at the convention center. We ve been on a journey a return journey of 13.7 billion years. I hope you ll agree this is a powerful story. And it s a story in which humans play an astonishing and creative role, but it also contains warnings. Collective learning is a very, very powerful force and it s not clear that we humans are in charge of it. I remember very vividly as a child growing up in England, living through the Cuban missile crisis. For a few days, the entire biosphere seemed to be on the verge of destruction. And the same weapons are still here and they re still armed. If we avoid that trap, others are waiting for us. And now, finally, this is what I want. I want my grandson, Daniel, and his friends and his generation throughout the world to know the story of Big History. And to know it so well, that they understand both the challenges that face us and the opportunities that face us. And that s why a group of us are building a free online syllabus in Big History for high school students throughout the world. We believe that Big History will be a vital intellectual tool for them, as Daniel and his generation face the huge challenges and also the huge opportunities ahead of them at this threshold moment in the history of our beautiful planet. I thank you for your attention. 16:58 17:29 FREE ONLINE COURSE 16:08 16:58 FUTURE THREATS We re burning fossil fuels at such a rate that we seem to be undermining the Goldilocks Conditions that made it possible for human civilizations to flourish over the last 10,000 years. So what Big History can do is show us the nature of our complexity and fragility and the dangers that face us. But it can also show us our power with collective learning. 11 BIG HISTORY PROJECT 12
4 HOW DID THE EARTH FORM?
 4 HOW DID THE EARTH FORM? New stars and space debris spinning like pizza dough are a couple of the things that explain the formation of solar systems like ours. In this three-part lecture, David Christian
4 HOW DID THE EARTH FORM? New stars and space debris spinning like pizza dough are a couple of the things that explain the formation of solar systems like ours. In this three-part lecture, David Christian
1 MODERN SCIENTIFIC ORIGIN STORY 1070L
 1 MODERN SCIENTIFIC ORIGIN STORY 1070L MODERN SCIENTIFIC THE BIG BANG By Cynthia Stokes Brown From vast nothingness to a Universe of stars and galaxies and our own Earth. 2 3 This version of modern science
1 MODERN SCIENTIFIC ORIGIN STORY 1070L MODERN SCIENTIFIC THE BIG BANG By Cynthia Stokes Brown From vast nothingness to a Universe of stars and galaxies and our own Earth. 2 3 This version of modern science
CHARLES DARWIN 1 COMPLEXITY & XX THRESHOLDS 820L. 5 billion years ago 1 billion years ago 1million years ago billion.
 1 COMPLEXITY & XX THRESHOLDS CHARLES DARWIN 13.7 billion years ago Stars die and create heavier elements SERIES TITLE Photosynthesis / ARTICLE TYPE The first stars and galaxies Hydrogen and helium form
1 COMPLEXITY & XX THRESHOLDS CHARLES DARWIN 13.7 billion years ago Stars die and create heavier elements SERIES TITLE Photosynthesis / ARTICLE TYPE The first stars and galaxies Hydrogen and helium form
5 LIFE HOW ARE WE STILL EVOLVING?
 5 LIFE HOW ARE WE STILL EVOLVING? UNIT 5 LIFE CONTENTS UNIT 5 BASICS 3 Unit 5 Overview 4 Unit 5 Learning Outcomes 5 Unit 5 Lessons 6 Unit 5 Key Concepts LOOKING BACK 8 What Happened in Unit 4? KEY CONTENT
5 LIFE HOW ARE WE STILL EVOLVING? UNIT 5 LIFE CONTENTS UNIT 5 BASICS 3 Unit 5 Overview 4 Unit 5 Learning Outcomes 5 Unit 5 Lessons 6 Unit 5 Key Concepts LOOKING BACK 8 What Happened in Unit 4? KEY CONTENT
5 HOW DO EARTH & LIFE INTERACT?
 5 HOW DO EARTH & LIFE INTERACT? In this four-part lecture, David Christian will explain what the biosphere is and discuss the interplay between life and the Earth. David will explain how astronomy, geology,
5 HOW DO EARTH & LIFE INTERACT? In this four-part lecture, David Christian will explain what the biosphere is and discuss the interplay between life and the Earth. David will explain how astronomy, geology,
The Formation of the Solar System
 Earth and the Solar System The Formation of the Solar System Write a number beside each picture to rank each from the oldest (1) to the youngest (4). The universe includes everything that exists: all matter,
Earth and the Solar System The Formation of the Solar System Write a number beside each picture to rank each from the oldest (1) to the youngest (4). The universe includes everything that exists: all matter,
1 WHAT IS BIG HISTORY? WHY DO WE LOOK AT THINGS FROM FAR AWAY AND CLOSE UP?
 1 WHAT IS BIG HISTORY? WHY DO WE LOOK AT THINGS FROM FAR AWAY AND CLOSE UP? UNIT 1 WHAT IS BIG HISTORY? CONTENTS UNIT 1 BASICS 3 Unit 1 Overview 4 Unit 1 Learning Outcomes 5 Unit 1 Lessons 7 Unit 1 Key
1 WHAT IS BIG HISTORY? WHY DO WE LOOK AT THINGS FROM FAR AWAY AND CLOSE UP? UNIT 1 WHAT IS BIG HISTORY? CONTENTS UNIT 1 BASICS 3 Unit 1 Overview 4 Unit 1 Learning Outcomes 5 Unit 1 Lessons 7 Unit 1 Key
Review: HR Diagram. Label A, B, C respectively
 Stellar Evolution Review: HR Diagram Label A, B, C respectively A C B a) A: White dwarfs, B: Giants, C: Main sequence b) A: Main sequence, B: Giants, C: White dwarfs c) A: Main sequence, B: White Dwarfs,
Stellar Evolution Review: HR Diagram Label A, B, C respectively A C B a) A: White dwarfs, B: Giants, C: Main sequence b) A: Main sequence, B: Giants, C: White dwarfs c) A: Main sequence, B: White Dwarfs,
Questions Sometimes Asked About the Theory of Evolution
 Chapter 9: Evidence for Plant and Animal Evolution Questions Sometimes Asked About the Theory of Evolution Many questions about evolution arise in Christian circles. We ll discuss just a few that we frequently
Chapter 9: Evidence for Plant and Animal Evolution Questions Sometimes Asked About the Theory of Evolution Many questions about evolution arise in Christian circles. We ll discuss just a few that we frequently
GraspIT Questions AQA GCSE Physics Space physics
 A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
What does Dark Matter have to do with the Big Bang Theory?
 Gents of Texas A&M What does Dark Matter have to do with the Big Bang Theory? Prof. David Toback Texas A&M University Mitchell Institute for Fundamental Physics and Astronomy March 2018 Prologue We live
Gents of Texas A&M What does Dark Matter have to do with the Big Bang Theory? Prof. David Toback Texas A&M University Mitchell Institute for Fundamental Physics and Astronomy March 2018 Prologue We live
Our Place in the Universe (Chapter 1) The Structure and Size of the Universe
 Our Place in the Universe (Chapter 1) The Structure and Size of the Universe Based on Chapter 1 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 2, 3, and 13 on Years, Seasons, and Months, The Orbits
Our Place in the Universe (Chapter 1) The Structure and Size of the Universe Based on Chapter 1 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 2, 3, and 13 on Years, Seasons, and Months, The Orbits
Last time: looked at proton-proton chain to convert Hydrogen into Helium, releases energy.
 Last time: looked at proton-proton chain to convert Hydrogen into Helium, releases energy. Last time: looked at proton-proton chain to convert Hydrogen into Helium, releases energy. Fusion rate ~ Temperature
Last time: looked at proton-proton chain to convert Hydrogen into Helium, releases energy. Last time: looked at proton-proton chain to convert Hydrogen into Helium, releases energy. Fusion rate ~ Temperature
What does Dark Matter have to do with the Big Bang Theory?
 Lunar Society What does Dark Matter have to do with the Big Bang Theory? Prof. David Toback Texas A&M University Mitchell Institute for Fundamental Physics and Astronomy Prologue We live in a time of remarkable
Lunar Society What does Dark Matter have to do with the Big Bang Theory? Prof. David Toback Texas A&M University Mitchell Institute for Fundamental Physics and Astronomy Prologue We live in a time of remarkable
Earth s Formation: 4.6 Billion Years ago
 Earth s Formation: 4.6 Billion Years ago Formed from interstellar gas & dust into molten planet Earth s early atmosphere was hostile, made of carbon monoxide, methane, ammonia, nitrogen, nitrogen, sulfur,
Earth s Formation: 4.6 Billion Years ago Formed from interstellar gas & dust into molten planet Earth s early atmosphere was hostile, made of carbon monoxide, methane, ammonia, nitrogen, nitrogen, sulfur,
ASTRO 114 Lecture Okay. We re now gonna continue discussing and conclude discussing the entire
 ASTRO 114 Lecture 55 1 Okay. We re now gonna continue discussing and conclude discussing the entire universe. So today we re gonna learn about everything, everything that we know of. There s still a lot
ASTRO 114 Lecture 55 1 Okay. We re now gonna continue discussing and conclude discussing the entire universe. So today we re gonna learn about everything, everything that we know of. There s still a lot
What does Dark Matter have to do with the Big Bang Theory?
 MSC Bethancourt Lecture What does Dark Matter have to do with the Big Bang Theory? Prof. David Toback Texas A&M University Mitchell Institute for Fundamental Physics and Astronomy Prologue We live in a
MSC Bethancourt Lecture What does Dark Matter have to do with the Big Bang Theory? Prof. David Toback Texas A&M University Mitchell Institute for Fundamental Physics and Astronomy Prologue We live in a
5 LIFE HOW DO WE DEFINE LIFE AND WHAT DO WE KNOW ABOUT IT?
 5 LIFE HOW DO WE DEFINE LIFE AND WHAT DO WE KNOW ABOUT IT? UNIT 5 OVERVIEW Key Disciplines: Biology Timespan: The first life forms appeared about 3.8 billion years ago Key Question: How do we define life
5 LIFE HOW DO WE DEFINE LIFE AND WHAT DO WE KNOW ABOUT IT? UNIT 5 OVERVIEW Key Disciplines: Biology Timespan: The first life forms appeared about 3.8 billion years ago Key Question: How do we define life
21/11/ /11/2017 Space Physics AQA Physics topic 8
 Space Physics AQA Physics topic 8 8.1 Solar System, Orbits and Satellites The eight planets of our Solar System Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune As well as the eight planets, the
Space Physics AQA Physics topic 8 8.1 Solar System, Orbits and Satellites The eight planets of our Solar System Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune As well as the eight planets, the
Study Guide Chapter 2
 Section: Stars Pages 32-38 Study Guide Chapter 2 Circle the letter of the best answer for each question. 1. What do scientists study to learn about stars? a. gravity c. space b. starlight d. colors COLOR
Section: Stars Pages 32-38 Study Guide Chapter 2 Circle the letter of the best answer for each question. 1. What do scientists study to learn about stars? a. gravity c. space b. starlight d. colors COLOR
The Universe. Unit 3 covers the following framework standards: ES 8 and 12. Content was adapted the following:
 Unit 3 The Universe Chapter 4 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 1 ~ The Scale of the Universe o Section 2 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 3 ~ The Future of the Universe Chapter 5 ~ Galaxies
Unit 3 The Universe Chapter 4 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 1 ~ The Scale of the Universe o Section 2 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 3 ~ The Future of the Universe Chapter 5 ~ Galaxies
Learning Outcomes 2. Key Concepts 2. Misconceptions and Teaching Challenges 3. Vocabulary 4. Lesson and Content Overview 5
 UNIT 3 GUIDE Table of Contents Learning Outcomes 2 Key Concepts 2 Misconceptions and Teaching Challenges 3 Vocabulary 4 Lesson and Content Overview 5 BIG HISTORY PROJECT / UNIT 3 GUIDE 1 Unit 3 Stars and
UNIT 3 GUIDE Table of Contents Learning Outcomes 2 Key Concepts 2 Misconceptions and Teaching Challenges 3 Vocabulary 4 Lesson and Content Overview 5 BIG HISTORY PROJECT / UNIT 3 GUIDE 1 Unit 3 Stars and
The expansion of the Universe, and the big bang
 The expansion of the Universe, and the big bang Q: What is Hubble s law? A. The larger the galaxy, the faster it is moving way from us. B. The farther away the galaxy, the faster it is moving away from
The expansion of the Universe, and the big bang Q: What is Hubble s law? A. The larger the galaxy, the faster it is moving way from us. B. The farther away the galaxy, the faster it is moving away from
Parenting Tip of the Month. April. Lower Elementary Teachers
 Parenting Tip of the Month April Lower Elementary Teachers Why Use Higher Order Thinking Skills Everyday? Research tells us that Higher Order Thinking Skills help to build life long interaction and communication
Parenting Tip of the Month April Lower Elementary Teachers Why Use Higher Order Thinking Skills Everyday? Research tells us that Higher Order Thinking Skills help to build life long interaction and communication
Formation of the Universe The organization of Space
 February 21, 2014 Formation of the Universe The organization of Space Theory: A theory is An example is cell Cell Theory Cell Theory states 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells 2.
February 21, 2014 Formation of the Universe The organization of Space Theory: A theory is An example is cell Cell Theory Cell Theory states 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells 2.
A supernova is the explosion of a star. It is the largest explosion that takes place in space.
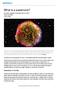 What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
Outline: Cosmological Origins. The true basics of life The age of Earth and the Universe The origin of the heavy elements Molecules in space
 Outline: Cosmological Origins The true basics of life The age of Earth and the Universe The origin of the heavy elements Molecules in space Reminder: HW #1 due in one week Homework is on class webpage
Outline: Cosmological Origins The true basics of life The age of Earth and the Universe The origin of the heavy elements Molecules in space Reminder: HW #1 due in one week Homework is on class webpage
Figure 19.19: HST photo called Hubble Deep Field.
 19.3 Galaxies and the Universe Early civilizations thought that Earth was the center of the universe. In the sixteenth century, we became aware that Earth is a small planet orbiting a medium-sized star.
19.3 Galaxies and the Universe Early civilizations thought that Earth was the center of the universe. In the sixteenth century, we became aware that Earth is a small planet orbiting a medium-sized star.
SCIENCE SAMPLER ~ Geology ~ Unit 4 of 5
 College Guild PO Box 6448, Brunswick ME 04011 SCIENCE SAMPLER ~ Geology ~ Unit 4 of 5 1 Over the past three units we have learned about the birth of the universe, the laws of nature, and the structure
College Guild PO Box 6448, Brunswick ME 04011 SCIENCE SAMPLER ~ Geology ~ Unit 4 of 5 1 Over the past three units we have learned about the birth of the universe, the laws of nature, and the structure
4 WHAT WAS THE YOUNG EARTH LIKE?
 4 WHAT WAS THE YOUNG EARTH LIKE? This two-part lecture describes the early Earth and the forces that have shaped the planet as we know it now. Jump in a time machine to visit the early Earth, a hot and
4 WHAT WAS THE YOUNG EARTH LIKE? This two-part lecture describes the early Earth and the forces that have shaped the planet as we know it now. Jump in a time machine to visit the early Earth, a hot and
6 HOW DID OUR ANCESTORS EVOLVE?
 6 HOW DID OUR ANCESTORS EVOLVE? David Christian introduces the science of taxonomy and explains some of the important methods used to identify and classify different species and several key human ancestors.
6 HOW DID OUR ANCESTORS EVOLVE? David Christian introduces the science of taxonomy and explains some of the important methods used to identify and classify different species and several key human ancestors.
The Big Bang Theory, General Timeline. The Planck Era. (Big Bang To 10^-35 Seconds) Inflationary Model Added. (10^-35 to 10^-33 Of A Second)
 The Big Bang Theory, General Timeline The Planck Era. (Big Bang To 10^-35 Seconds) The time from the exact moment of the Big Bang until 10^-35 of a second later is referred to as the Planck Era. While
The Big Bang Theory, General Timeline The Planck Era. (Big Bang To 10^-35 Seconds) The time from the exact moment of the Big Bang until 10^-35 of a second later is referred to as the Planck Era. While
Requirements for Life. What is Life? Definition of Life. One of the biggest questions in astronomy is whether life exists elsewhere in the universe
 Requirements for Life One of the biggest questions in astronomy is whether life exists elsewhere in the universe Before we discuss the possibility of life elsewhere, we must have a better understanding
Requirements for Life One of the biggest questions in astronomy is whether life exists elsewhere in the universe Before we discuss the possibility of life elsewhere, we must have a better understanding
SU230R Grades 4-8. Hayes FAST FACTS & DAZZLING DATA OUR SOLAR SYSTEM
 Hayes SU230R Grades 4-8 FAST FACTS & DAZZLING DATA OUR SOLAR SYSTEM Fast Facts & Dazzling Data Our Solar System This book was developed for Hayes School Publishing Co., Inc. by Good Neighbor Press, Inc.,
Hayes SU230R Grades 4-8 FAST FACTS & DAZZLING DATA OUR SOLAR SYSTEM Fast Facts & Dazzling Data Our Solar System This book was developed for Hayes School Publishing Co., Inc. by Good Neighbor Press, Inc.,
A Brief Guide to Our Cosmic Context
 A Brief Guide to Our Cosmic Context Todd Duncan (duncant@pdx.edu) PSU Center for Science Education last modified 11/21/08 There is a theory which states that if ever anyone discovers exactly what the Universe
A Brief Guide to Our Cosmic Context Todd Duncan (duncant@pdx.edu) PSU Center for Science Education last modified 11/21/08 There is a theory which states that if ever anyone discovers exactly what the Universe
Introduction to Astronomy
 Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
THE UNIVERSE CHAPTER 20
 THE UNIVERSE CHAPTER 20 THE UNIVERSE UNIVERSE everything physical in and Includes all space, matter, and energy that has existed, now exists, and will exist in the future. How did our universe form, how
THE UNIVERSE CHAPTER 20 THE UNIVERSE UNIVERSE everything physical in and Includes all space, matter, and energy that has existed, now exists, and will exist in the future. How did our universe form, how
Relative Sizes of Stars. Today Exam#3 Review. Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram. Blackbody Radiation
 Today Exam#3 Review Exam #3 is Thursday April 4th in this room, BPS 40; Extra credit is due 8:00 am Tuesday April 9 Final Exam is 3:00pm Monday April 8 in BPS 40 The exam is 40 multiple choice questions.
Today Exam#3 Review Exam #3 is Thursday April 4th in this room, BPS 40; Extra credit is due 8:00 am Tuesday April 9 Final Exam is 3:00pm Monday April 8 in BPS 40 The exam is 40 multiple choice questions.
Test Name: 09.LCW.0352.SCIENCE.GR Q1.S.THEUNIVERSE-SOLARSYSTEMHONORS Test ID: Date: 09/21/2017
 Test Name: 09.LCW.0352.SCIENCE.GR7.2017.Q1.S.THEUNIVERSE-SOLARSYSTEMHONORS Test ID: 243920 Date: 09/21/2017 Section 1.1 - According to the Doppler Effect, what happens to the wavelength of light as galaxies
Test Name: 09.LCW.0352.SCIENCE.GR7.2017.Q1.S.THEUNIVERSE-SOLARSYSTEMHONORS Test ID: 243920 Date: 09/21/2017 Section 1.1 - According to the Doppler Effect, what happens to the wavelength of light as galaxies
Exam #3. Final Exam. Exam 3 review. How do we measure properties of a star? A detailed outline of study topics is here:
 Exam #3 Exam #3 is Thursday 4/9 in this room You can bring page of notes (front and back) Bring your calculator and a # pencil Exam 3 covers material from 4/1 onward (only 8 lectures) Consequently, no
Exam #3 Exam #3 is Thursday 4/9 in this room You can bring page of notes (front and back) Bring your calculator and a # pencil Exam 3 covers material from 4/1 onward (only 8 lectures) Consequently, no
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4 Lesson 3. Sun
 Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4 Lesson 3 Suggested time: 1.25 Hours What s important in this lesson: Sun demonstrate an understanding of the structure, and nature of our solar system investigate the
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4 Lesson 3 Suggested time: 1.25 Hours What s important in this lesson: Sun demonstrate an understanding of the structure, and nature of our solar system investigate the
Formation of the Universe. What evidence supports current scientific theory?
 Formation of the Universe What evidence supports current scientific theory? Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the Nature, Structure, Origin, And fate of the universe. How did it all begin? Astronomers
Formation of the Universe What evidence supports current scientific theory? Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the Nature, Structure, Origin, And fate of the universe. How did it all begin? Astronomers
Answers. The Universe. Year 10 Science Chapter 6
 Answers The Universe Year 10 Science Chapter 6 p133 1 The universe is considered to be the whole of all matter, energy, planets, solar systems, galaxies, and space. Many definitions of the universe also
Answers The Universe Year 10 Science Chapter 6 p133 1 The universe is considered to be the whole of all matter, energy, planets, solar systems, galaxies, and space. Many definitions of the universe also
Star. Planet. Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe. 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe?
 Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the
Chapter 5 Newton s Universe
 Chapter 5 Newton s Universe Lecture notes about gravitation Dr. Armen Kocharian Units of Chapter 5 The Idea of Gravity: The Apple and the Moon The Law of Gravity: Moving the Farthest Star Gravitational
Chapter 5 Newton s Universe Lecture notes about gravitation Dr. Armen Kocharian Units of Chapter 5 The Idea of Gravity: The Apple and the Moon The Law of Gravity: Moving the Farthest Star Gravitational
Lesson 3 THE SOLAR SYSTEM
 Lesson 3 THE SOLAR SYSTEM THE NATURE OF THE SUN At the center of our solar system is the Sun which is a typical medium sized star. Composed mainly of Hydrogen (73% by mass), 23% helium and the rest is
Lesson 3 THE SOLAR SYSTEM THE NATURE OF THE SUN At the center of our solar system is the Sun which is a typical medium sized star. Composed mainly of Hydrogen (73% by mass), 23% helium and the rest is
Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE
 Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the universe; its nature, origin and evolution. General Relativity is the mathematical basis of cosmology from which
Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the universe; its nature, origin and evolution. General Relativity is the mathematical basis of cosmology from which
The Big Bang and The Formation of the Universe. Earth Science- Where It All Began
 The Big Bang and The Formation of the Universe Earth Science- Where It All Began Welcome to the beginning Before understanding where we are now and what impacts humans have on the Earth, we need to learn
The Big Bang and The Formation of the Universe Earth Science- Where It All Began Welcome to the beginning Before understanding where we are now and what impacts humans have on the Earth, we need to learn
Chapter 33 The History of a Star. Introduction. Radio telescopes allow us to look into the center of the galaxy. The milky way
 Chapter 33 The History of a Star Introduction Did you read chapter 33 before coming to class? A. Yes B. No You can see about 10,000 stars with the naked eye. The milky way Radio telescopes allow us to
Chapter 33 The History of a Star Introduction Did you read chapter 33 before coming to class? A. Yes B. No You can see about 10,000 stars with the naked eye. The milky way Radio telescopes allow us to
Our Sun. The centre of our solar system
 Our Sun The centre of our solar system Nicolaus Copernicus Our Sun The sun represents 99.86% of the mass in our solar system. It is ¾ hydrogen and ¼ helium. More than 1 million Earths can fit inside the
Our Sun The centre of our solar system Nicolaus Copernicus Our Sun The sun represents 99.86% of the mass in our solar system. It is ¾ hydrogen and ¼ helium. More than 1 million Earths can fit inside the
High Mass Stars and then Stellar Graveyard 7/16/09. Astronomy 101
 High Mass Stars and then Stellar Graveyard 7/16/09 Astronomy 101 Astronomy Picture of the Day Astronomy 101 Something Cool Betelgeuse Astronomy 101 Outline for Today Astronomy Picture of the Day Something
High Mass Stars and then Stellar Graveyard 7/16/09 Astronomy 101 Astronomy Picture of the Day Astronomy 101 Something Cool Betelgeuse Astronomy 101 Outline for Today Astronomy Picture of the Day Something
The Earth in the Universe
 The Earth in the Universe (OCR) Evidence for the age of the Earth Scientists once thought that the Earth was only 6000 years old. Rocks have provided lots of evidence for the world being older. 1) Erosion
The Earth in the Universe (OCR) Evidence for the age of the Earth Scientists once thought that the Earth was only 6000 years old. Rocks have provided lots of evidence for the world being older. 1) Erosion
How do we measure properties of a star? Today. Some Clicker Questions - #1. Some Clicker Questions - #1
 Today Announcements: HW#8 due Friday 4/9 at 8:00 am. The size of the Universe (It s expanding!) The Big Bang Video on the Big Bang NOTE: I will take several questions on exam 3 and the final from the videos
Today Announcements: HW#8 due Friday 4/9 at 8:00 am. The size of the Universe (It s expanding!) The Big Bang Video on the Big Bang NOTE: I will take several questions on exam 3 and the final from the videos
Lec 9: Stellar Evolution and DeathBirth and. Why do stars leave main sequence? What conditions are required for elements. Text
 1 Astr 102 Lec 9: Stellar Evolution and DeathBirth and Evolution Why do stars leave main sequence? What conditions are required for elements Text besides Hydrogen to fuse, and why? How do stars die: white
1 Astr 102 Lec 9: Stellar Evolution and DeathBirth and Evolution Why do stars leave main sequence? What conditions are required for elements Text besides Hydrogen to fuse, and why? How do stars die: white
EARTH TAKES SHAPE 1. Define all vocabulary words. Crust: The thin and solid outermost layer of the Earth above the mantle. Mantle: The layer of rock
 EARTH TAKES SHAPE 1. Define all vocabulary words. Crust: The thin and solid outermost layer of the Earth above the mantle. Mantle: The layer of rock between the Earth s crust and core Core: The central
EARTH TAKES SHAPE 1. Define all vocabulary words. Crust: The thin and solid outermost layer of the Earth above the mantle. Mantle: The layer of rock between the Earth s crust and core Core: The central
and two neutrons. It is so improbable that four protons all happen to hit at once and two convert that this never happens. Instead, there is a
 Last time we left off at hydrogen and helium, because that s all that formed for the first hundred million years of the universe except for dribbly little bits of lithium and beryllium. As this isn t enough
Last time we left off at hydrogen and helium, because that s all that formed for the first hundred million years of the universe except for dribbly little bits of lithium and beryllium. As this isn t enough
Investigating Planets Name: Block: E1:R6
 FYI: Planetary Temperatures and Atmospheres Read FYI: A Planet s Temperature, The Importance of an Atmosphere, and The Greenhouse Effect As you read answer the following questions about the readings: Word/Term
FYI: Planetary Temperatures and Atmospheres Read FYI: A Planet s Temperature, The Importance of an Atmosphere, and The Greenhouse Effect As you read answer the following questions about the readings: Word/Term
Unit 1: Space. Section 2- Stars
 Unit 1: Space Section 2- Stars Stars Recall: stars are celestial bodies of hot gas that give off heat and light Stars The milky way contains hundreds of billions of stars and is only one of hundreds of
Unit 1: Space Section 2- Stars Stars Recall: stars are celestial bodies of hot gas that give off heat and light Stars The milky way contains hundreds of billions of stars and is only one of hundreds of
Accretion Disks. Review: Stellar Remnats. Lecture 12: Black Holes & the Milky Way A2020 Prof. Tom Megeath 2/25/10. Review: Creating Stellar Remnants
 Lecture 12: Black Holes & the Milky Way A2020 Prof. Tom Megeath Review: Creating Stellar Remnants Binaries may be destroyed in white dwarf supernova Binaries be converted into black holes Review: Stellar
Lecture 12: Black Holes & the Milky Way A2020 Prof. Tom Megeath Review: Creating Stellar Remnants Binaries may be destroyed in white dwarf supernova Binaries be converted into black holes Review: Stellar
The Outer Planets. Video Script: The Outer Planets. Visual Learning Company
 11 Video Script: 1. For thousands of years people have looked up at the night sky pondering the limits of our solar system. 2. Perhaps you too, have looked up at the evening stars and planets, and wondered
11 Video Script: 1. For thousands of years people have looked up at the night sky pondering the limits of our solar system. 2. Perhaps you too, have looked up at the evening stars and planets, and wondered
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES
 SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
Introduction to Cosmology Big Bang-Big Crunch-Dark Matter-Dark Energy The Story of Our Universe. Dr. Ugur GUVEN Aerospace Engineer / Space Scientist
 Introduction to Cosmology Big Bang-Big Crunch-Dark Matter-Dark Energy The Story of Our Universe Dr. Ugur GUVEN Aerospace Engineer / Space Scientist The Age of the Universe Through various measurements
Introduction to Cosmology Big Bang-Big Crunch-Dark Matter-Dark Energy The Story of Our Universe Dr. Ugur GUVEN Aerospace Engineer / Space Scientist The Age of the Universe Through various measurements
Atoms and molecules are in motion and have energy
 Atoms and molecules are in motion and have energy By now you know that substances are made of atoms and molecules. These atoms and molecules are always in motion and have attractions to each other. When
Atoms and molecules are in motion and have energy By now you know that substances are made of atoms and molecules. These atoms and molecules are always in motion and have attractions to each other. When
Life Cycle of a Star Worksheet
 Life Cycle of a Star Worksheet A STAR IS BORN STAGES COMMON TO ALL STARS All stars start as a nebula. A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas and dust in a nebula together.
Life Cycle of a Star Worksheet A STAR IS BORN STAGES COMMON TO ALL STARS All stars start as a nebula. A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas and dust in a nebula together.
According to the currents models of stellar life cycle, our sun will eventually become a. Chapter 34: Cosmology. Cosmology: How the Universe Works
 Chapter 34: Cosmology According to the currents models of stellar life cycle, our sun will eventually become a a) Cloud of hydrogen gas b) Protostar c) Neutron star d) Black hole e) White dwarf id you
Chapter 34: Cosmology According to the currents models of stellar life cycle, our sun will eventually become a a) Cloud of hydrogen gas b) Protostar c) Neutron star d) Black hole e) White dwarf id you
The Raw Power of the Sun: How Was the Sun Formed?
 The Raw Power of the Sun: How Was the Sun Formed? Did you know that the sun is approximately 4.5 billion years old? In addition to it being an essential component of life on Earth, we ve always used it
The Raw Power of the Sun: How Was the Sun Formed? Did you know that the sun is approximately 4.5 billion years old? In addition to it being an essential component of life on Earth, we ve always used it
Science for Everyone. Kevin Cahill
 Science for Everyone Kevin Cahill March 11, 2017 ii Contents 1 Back to the beginning 1 1.1 Cosmic inflation and the Big Bang................... 1 1.1.1 A second look.......................... 3 1.2 The
Science for Everyone Kevin Cahill March 11, 2017 ii Contents 1 Back to the beginning 1 1.1 Cosmic inflation and the Big Bang................... 1 1.1.1 A second look.......................... 3 1.2 The
Big Bang, Black Holes, No Math
 ASTR/PHYS 109 Dr. David Toback Lecture 19 1 Was due Today L19 Reading: (Unit 4) Unit 5: Assigned today Pre-Lecture Reading Questions (PLRQ) Unit 3 (Original or Revision) and Unit 4 Let us know if you think
ASTR/PHYS 109 Dr. David Toback Lecture 19 1 Was due Today L19 Reading: (Unit 4) Unit 5: Assigned today Pre-Lecture Reading Questions (PLRQ) Unit 3 (Original or Revision) and Unit 4 Let us know if you think
Topic 02B: The Nature of Science and Oceanography, Part II. Online Lecture: Origins
 2B_2 Slide 1 Topic 02B: The Nature of Science and Oceanography, Part II Online Lecture: Origins The Formation of Atoms, Molecules, the Earth, and the Oceans. Being Scientific I If no matter what the evidence
2B_2 Slide 1 Topic 02B: The Nature of Science and Oceanography, Part II Online Lecture: Origins The Formation of Atoms, Molecules, the Earth, and the Oceans. Being Scientific I If no matter what the evidence
A Star is born: The Sun. SNC1D7-Space
 A Star is born: The Sun SNC1D7-Space Exploring the Sun Our Sun, a star, is the most important celestial object for life on Earth. The solar nebula theory is the current theory used to explain the formation
A Star is born: The Sun SNC1D7-Space Exploring the Sun Our Sun, a star, is the most important celestial object for life on Earth. The solar nebula theory is the current theory used to explain the formation
1PRELUDE: THE MYSTERY OF
 1PRELUDE: THE MYSTERY OF THE MISSING ANTIMATTER In the beginning what was the beginning? Every culture asks this question. Traditionally each finds some answer, a creation myth, a cosmology. These stories
1PRELUDE: THE MYSTERY OF THE MISSING ANTIMATTER In the beginning what was the beginning? Every culture asks this question. Traditionally each finds some answer, a creation myth, a cosmology. These stories
Recall what you know about the Big Bang.
 What is this? Recall what you know about the Big Bang. Most of the normal matter in the universe is made of what elements? Where do we find most of this normal matter? Interstellar medium (ISM) The universe
What is this? Recall what you know about the Big Bang. Most of the normal matter in the universe is made of what elements? Where do we find most of this normal matter? Interstellar medium (ISM) The universe
THE STORY OF EARTH S FORMATION
 0 Vocabulary tendencies differentiation rotating supernova cloud of gas/dust asteroid cloud of gas/dust gravity dense solar nebula planets accretion planetessimal protoplanets meteors moon rotation wobble
0 Vocabulary tendencies differentiation rotating supernova cloud of gas/dust asteroid cloud of gas/dust gravity dense solar nebula planets accretion planetessimal protoplanets meteors moon rotation wobble
Modern Physics notes Spring 2005 Paul Fendley Lecture 38
 Modern Physics notes Spring 2005 Paul Fendley fendley@virginia.edu Lecture 38 Dark matter and energy Cosmic Microwave Background Weinberg, chapters II and III cosmological parameters: Tegmark et al, http://arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0310723
Modern Physics notes Spring 2005 Paul Fendley fendley@virginia.edu Lecture 38 Dark matter and energy Cosmic Microwave Background Weinberg, chapters II and III cosmological parameters: Tegmark et al, http://arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0310723
Our Created Solar System Video
 Our Created Solar System Video After the first segment of the video (0:00 8:54 min.) is played, the video will be stopped. Then, answer the following questions: 1) In short, what is the solar system? 2)
Our Created Solar System Video After the first segment of the video (0:00 8:54 min.) is played, the video will be stopped. Then, answer the following questions: 1) In short, what is the solar system? 2)
1/13/16. The Big Bang Theory
 1/13/16 The Big Bang Theory 1 The universe begins ~13.7 Billion years ago The universe begins as the size of a single atom The universe began as a violent expansion All maaer and space were created from
1/13/16 The Big Bang Theory 1 The universe begins ~13.7 Billion years ago The universe begins as the size of a single atom The universe began as a violent expansion All maaer and space were created from
A star is a massive sphere of gases with a core like a thermonuclear reactor. They are the most common celestial bodies in the universe are stars.
 A star is a massive sphere of gases with a core like a thermonuclear reactor. They are the most common celestial bodies in the universe are stars. They radiate energy (electromagnetic radiation) from a
A star is a massive sphere of gases with a core like a thermonuclear reactor. They are the most common celestial bodies in the universe are stars. They radiate energy (electromagnetic radiation) from a
Coriolis Effect - the apparent curved paths of projectiles, winds, and ocean currents
 Regents Earth Science Unit 5: Astronomy Models of the Universe Earliest models of the universe were based on the idea that the Sun, Moon, and planets all orbit the Earth models needed to explain how the
Regents Earth Science Unit 5: Astronomy Models of the Universe Earliest models of the universe were based on the idea that the Sun, Moon, and planets all orbit the Earth models needed to explain how the
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION
 TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION (The Universe) A. THE UNIVERSE: The universe encompasses all matter in existence. According to the Big Bang Theory, the universe was formed 10-20 billion years ago from a
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION (The Universe) A. THE UNIVERSE: The universe encompasses all matter in existence. According to the Big Bang Theory, the universe was formed 10-20 billion years ago from a
ET: Astronomy 230 Section 1 MWF Astronomy Building. Outline. The Early Universe? HW1 due today!
 This Class (Lecture 5): From Atoms to Molecules to Clouds Next Class: Star Formation ET: Astronomy 230 Section 1 MWF 1400-1450 134 Astronomy Building HW1 due today! Outline What is life made of? We are
This Class (Lecture 5): From Atoms to Molecules to Clouds Next Class: Star Formation ET: Astronomy 230 Section 1 MWF 1400-1450 134 Astronomy Building HW1 due today! Outline What is life made of? We are
Comparative Planetology II: The Origin of Our Solar System. Chapter Eight
 Comparative Planetology II: The Origin of Our Solar System Chapter Eight ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 07 Oct. 15, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6)
Comparative Planetology II: The Origin of Our Solar System Chapter Eight ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 07 Oct. 15, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6)
CHAPTER 11. We continue to Learn a lot about the Solar System by using Space Exploration
 CHAPTER 11 We continue to Learn a lot about the Solar System by using Space Exploration Section 11.1 The Sun page 390 -Average sized star -Millions of km away -300,000 more massive then Earth, 99% of all
CHAPTER 11 We continue to Learn a lot about the Solar System by using Space Exploration Section 11.1 The Sun page 390 -Average sized star -Millions of km away -300,000 more massive then Earth, 99% of all
Stars. 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe. What Objects Do We Find in The Universe? 8/12/2010. Our goals for learning:
 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the past? Can we see the entire universe?
1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the past? Can we see the entire universe?
Learning About Our Solar System
 Learning About Our Solar System By debbie Routh COPYRIGHT 2004 Mark Twain Media, Inc. ISBN 978-1-58037-876-5 Printing No. 404007-EB Mark Twain Media, Inc., Publishers Distributed by Carson-Dellosa Publishing
Learning About Our Solar System By debbie Routh COPYRIGHT 2004 Mark Twain Media, Inc. ISBN 978-1-58037-876-5 Printing No. 404007-EB Mark Twain Media, Inc., Publishers Distributed by Carson-Dellosa Publishing
Comparative Planetology II: The Origin of Our Solar System. Chapter Eight
 Comparative Planetology II: The Origin of Our Solar System Chapter Eight ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 06 Oct. 09, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6)
Comparative Planetology II: The Origin of Our Solar System Chapter Eight ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 06 Oct. 09, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6)
Page 2. Q1. The diagram shows part of the life cycle of a star which is much bigger than the Sun.
 Q1. The diagram shows part of the life cycle of a star which is much bigger than the Sun. (a) (i) What is the relationship between the masses of the dust and gas in the cloud in Stage 2 and the force of
Q1. The diagram shows part of the life cycle of a star which is much bigger than the Sun. (a) (i) What is the relationship between the masses of the dust and gas in the cloud in Stage 2 and the force of
THE ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE AND BLACK HOLES
 THE ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE AND BLACK HOLES WHAT IS COSMOGONY? Cosmogony (or cosmogeny) is any model explaining the origin of the universe. Cosmogony = Coming into existence WHAT IS COSMOLOGY Cosmology
THE ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE AND BLACK HOLES WHAT IS COSMOGONY? Cosmogony (or cosmogeny) is any model explaining the origin of the universe. Cosmogony = Coming into existence WHAT IS COSMOLOGY Cosmology
4 Changes in Climate. TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why is more land exposed during glacial periods than at other times?
 Name Class CHAPTER 3 Date Climate 4 Changes in Climate SECTION National Science Education Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: ES 1k, 2a
Name Class CHAPTER 3 Date Climate 4 Changes in Climate SECTION National Science Education Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: ES 1k, 2a
Universe Celestial Object Galaxy Solar System
 ASTRONOMY Universe- Includes all known matter (everything). Celestial Object Any object outside or above Earth s atmosphere. Galaxy- A large group (billions) of stars (held together by gravity). Our galaxy
ASTRONOMY Universe- Includes all known matter (everything). Celestial Object Any object outside or above Earth s atmosphere. Galaxy- A large group (billions) of stars (held together by gravity). Our galaxy
Chapter 27: The Early Universe
 Chapter 27: The Early Universe The plan: 1. A brief survey of the entire history of the big bang universe. 2. A more detailed discussion of each phase, or epoch, from the Planck era through particle production,
Chapter 27: The Early Universe The plan: 1. A brief survey of the entire history of the big bang universe. 2. A more detailed discussion of each phase, or epoch, from the Planck era through particle production,
The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?)
 The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?) Unseen Influences Dark Matter: An undetected form of mass that emits little or no light but whose existence we infer from
The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?) Unseen Influences Dark Matter: An undetected form of mass that emits little or no light but whose existence we infer from
Stars and Galaxies. The Big History of our Planet The 2nd threshold
 Stars and Galaxies The Big History of our Planet The 2nd threshold Big Bang Our universe starts from a Big Bang The early universe was simple, with little structure A thin mist of H & He atoms + photons
Stars and Galaxies The Big History of our Planet The 2nd threshold Big Bang Our universe starts from a Big Bang The early universe was simple, with little structure A thin mist of H & He atoms + photons
From VOA Learning English, this is SCIENCE IN THE NEWS, in Special English. I m Kelly Jean Kelly.
 From VOA Learning English, this is SCIENCE IN THE NEWS, in Special English. I m Kelly Jean Kelly. And I m Christopher Cruise. Scientists who study the Earth tell us the continents and ocean floors are
From VOA Learning English, this is SCIENCE IN THE NEWS, in Special English. I m Kelly Jean Kelly. And I m Christopher Cruise. Scientists who study the Earth tell us the continents and ocean floors are
The sun, yellow dwarf star at the heart of the solar system NASA.gov, adapted by Newsela staff
 Name: Period: Date: Article of the Week Directions: Read the following article carefully and annotate. You need to include at least 1 annotation per paragraph. Be sure to include all of the following in
Name: Period: Date: Article of the Week Directions: Read the following article carefully and annotate. You need to include at least 1 annotation per paragraph. Be sure to include all of the following in
TABLE OF CONTENTS. click one to go to that page, or just go on. What is the Solar System? Neptune (Pluto) The Sun. Asteroids. Mercury.
 The Solar System TABLE OF CONTENTS click one to go to that page, or just go on. What is the Solar System? The Sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune (Pluto) Asteroids Meteors and Meteorites
The Solar System TABLE OF CONTENTS click one to go to that page, or just go on. What is the Solar System? The Sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune (Pluto) Asteroids Meteors and Meteorites
WHAT WE KNOW. Scientists observe that every object in the universe is moving away from each other. Objects furthest away are moving the fastest. So..
 ASTRONOMY THE BIG BANG THEORY WHAT WE KNOW Scientists observe that every object in the universe is moving away from each other. Objects furthest away are moving the fastest. So.. WHAT DOES THIS MEAN? If
ASTRONOMY THE BIG BANG THEORY WHAT WE KNOW Scientists observe that every object in the universe is moving away from each other. Objects furthest away are moving the fastest. So.. WHAT DOES THIS MEAN? If
GEOS 2900 Sample Instructor Notes
 3.3.1 THE HISTORY OF THE EARTH GEOS 2900 Sample Instructor Notes Things to do before class begins: 1. Place the following daily agenda on the board: a. Announcements b. Go over Activity 3.2.2 (Absolute
3.3.1 THE HISTORY OF THE EARTH GEOS 2900 Sample Instructor Notes Things to do before class begins: 1. Place the following daily agenda on the board: a. Announcements b. Go over Activity 3.2.2 (Absolute
The History of the Earth
 The History of the Earth We have talked about how the universe and sun formed, but what about the planets and moons? Review: Origin of the Universe The universe began about 13.7 billion years ago The Big
The History of the Earth We have talked about how the universe and sun formed, but what about the planets and moons? Review: Origin of the Universe The universe began about 13.7 billion years ago The Big
The Formation of Stars
 The Formation of Stars A World of Dust The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful objects in the sky. We are interested
The Formation of Stars A World of Dust The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful objects in the sky. We are interested
Chapter 12- The Law of Increasing Disorder
 Second Law of Thermodynamics Changes occurring in natural systems always proceed in such a way that the total amount of entropy in the universe is either unchanged or increased. If total disorder is increased,
Second Law of Thermodynamics Changes occurring in natural systems always proceed in such a way that the total amount of entropy in the universe is either unchanged or increased. If total disorder is increased,
