Magnetic Field in Galaxies and clusters
|
|
|
- Alexia Edwards
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Magnetic Field in Galaxies and clusters Kandaswamy Subramanian Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune , India. The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.0/27
2 Plan Observing galactic and cluster B: Radio crucial The fluctuation dynamo, Young galaxies/old clusters The large scale galactic dynamo K. Subramanian, Magnetizing the Universe, PoS proceedings, arxiv: The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.1/27
3 Measuring B fields:synchrotorn Radiation B Electron trajectory Electron acceleration Electron's instantaneous velocity k H E Faraday Rotation gives B φ = λ 2 RM = λ 2 K n e B dl K = 0.81 rad m 2 (µg) 1 (pc) 1 cm 3 Synchrotron polarization gives B E ˆn [(ˆn β) d β/dt] d β/dt The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.2/27
4 Galactic Magnetic Fields: Observations Synchrotron polarization and Faraday rotation probe B fields. M51 at 6 cm (Fletcher and Beck) Few µg mean Fields coherent on 10 kpc scales Correlated with optical spiral The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.3/27
5 Magnetic Spirals: NGC6946 NGC6946 6cm Polarized Intensity + B-Vectors (VLA+Effelsberg) + H-Alpha DECLINATION (J2000) RIGHT ASCENSION (J2000) Why are optical and magnetic spirals correlated? The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.4/27
6 Edge on Galaxies: NGC4631 Halo magnetic fields The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.5/27
7 B in high z galaxies? The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.6/27
8 Cluster Radio halos Chandra (X-Ray)-GMRT (235 Mhz): Giant radio halo in RXC J Giacintucci et al. A & A, 505, 45, 2009 The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.7/27
9 Cluster Magnetism: Observations Radio halos and Faraday Rotation probe cluster B fields Vogt & Ensslin, A&A, 434, 67, e 11 k E B(k) 3 [erg/cm ] 1e 12 Magnetic Power Spectrum of Hydra A Cluster Kolmogoroff spectrum 1e 13 B = ( ) µ G l = ( ) kpc B 1e k [kpc ] Hydra Cluster B 7µG coherent on 3 kpc scale The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.8/27
10 Cluster Magnetism: Observations Clarke et al., ApJ, 547, L111, 2001 Statistical RM study B 5(l/10kpc) 1/2 µg embedded sources background sources How are cluster fields generated/maintained against turbulent decay? The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.9/27
11 Fluctation/Small scale turbulent dynamo Turbulence common: Stars, galaxies, galaxy clusters: leads to Random Stretching + Flux freezing Growth of B Cancellation (Eyink, 2011) and Resistance limits growth. Random B grows if R M = vl/η > R crit (Kazantsev 1967) Eigenmode solutions of form: Ψ(r)exp(2Γt) = r 2 ηt M L ΓΨ = η T d 2 Ψ dr 2 +U 0(r)Ψ Growing modes if there are bound states in potential U 0 (r). Growth rate fast ǫ v/l (10 7 yr: Galaxies; 10 8 yr clusters). Field intermittent: Eddy scale L, to resistive scale L/R 1/2 m L How does it saturate? Important for young galaxy/cluster/igm Faraday RM and mean field dynamos? The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.10/27
12 The fluctuation dynamo Simulations Simulations by Pallavi Bhat, 2012, P m = ν/η = k -5/ M(k) K(k) k 3/ k The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.11/27
13 The fluctuation dynamo Generated B intermittent (Pallavi Bhat, 2012) The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.12/27
14 Faraday RM from Fluctuation dynamo (Pallavi Bhat, KS, MNRAS, 429, 6429, 2013) RMS Faraday RM σ RM by shooting lines of sight through the simulation box. Normalize by σ 0 = Kn e (B rms / 3) Ll σ RM σ 0 for various R m and P m explored. Rare structures contribute < 20% to σ RM 0.6 Rotation Measure : σ RM nocutoff 2B rms cutoff 1B rms cutoff 512 3, Pm= Eddy turn over time The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.13/27
15 Kazantsev with Helicity: Tunneling? Fluctuation dynamo bound state problem (Kazantsev, 1967) Helicity of turbulence allows tunneling to larger scales than L (Subramanian, PRL, 1999; Brandenburg, Subramanian, A&A Lett, 2000) For M L 0, Ḣ 0 η T (d 2 Ψ/dr 2 )+Ψ [ U 0 (α 2 (r)/η T (r)) ] = 0, r L, M L (r) = M L (r) r 3/2 J ±3/2 (µr), U(r) 2 η / r 2 0 Γ = E = 0 r 2η T / r 2 α2 0 / η T L r > L The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.14/27
16 Helically forced turbulent dynamos Axel Brandenburg, ; k f = 15 Rapid growth in kinematic stage conserving magnetic helicity. Further Slow Growth on resistive timescale (dissipating small-scale helicity) Can be understood in terms of magnetic helicity conservation; (Field and Blackman, 2002). The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.15/27
17 Supernovae Drive Helical turbulence The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.16/27
18 Galactic Shear and α effect Kinematic Limit? Helicity (links) conservation? Competing Fluctuation dynamo? The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.17/27
19 Turbulent Mean-Field Dynamo Consider flow with large-scale velocity V and a turbulent stochastic velocity v V = V+v, B = B+b: Mean + Stochastic fields Average can be volume average over intermediate scales or ensemble average Averages satisfy Reynolds rules V 1 +V 2 = V 1 +V 2, V = V, V v = 0, V 1 V 2 = V 1 V 2, V / t = V / t, V / x i = V / x i. Average now the induction equation The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.18/27
20 Turbulent Mean-Field Dynamo V = V+v, B = B+b: Mean + Stochastic fields Mean satisfies DYNAMO equation, with E = v b: B t = ( V B+E η( B) ) ; The stochastic small-scale field satisfies: b t = (V b+v B η b)+g Here G is the pain in neck nonlinear term in v and b. G = (v b) = [v b v b] Finding E = v b is a closure problem: E = αb η turb ( B) The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.19/27
21 The kinematic limit of E For short correlation times (τ cor ), neglect G, also assume statistical isotropy of the random v : E = v t dt ( b/ τ) = v(t) t dt [ v(t ) B +B v(t )] E i = t 0 [ ] ǫ ijk v j (t)v k,p (t )B p (t )+ǫ ijp v j (t)v l (t )B p,l (t ) dt, So: E = αb η t B, where α = 1 3 t 0 v(t) ω(t ) dt 1 3 τ corv ω, η t = 1 3 t 0 v(t) v(t ) dt 1 3 τ corv 2, B/ t = ( V B+αB (η t +η)( B) ) ; The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.20/27
22 Mean-Field Dynamo: Galactic Galactic Shear generates B φ from B r Supernovae drive HELICAL turbulence (Due to Rotation + Stratification) Helical motions generate B r from B φ α-effect (Parker, 55) Mean field satisfies dynamo equation B t = ( U B+E η( B) ) ; E = u b = αb η turb ( B) α = τ corr 3 u ω η turb = τ corr 3 u2 RSS, 1988 Exponential growth of B, t growth 10 9 yr The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.21/27
23 A revised picture for α-effect Anvar and Natasha Shukurov 2009 E transfers helicity: Oppositely signed WRITHE AND TWIST Helicities Lorentz force of small-scale twist Helicity grows to cancel kinetic α The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.22/27
24 Nonlinear saturation of helical dynamos E transfers helicity between small-large scales Small scale current helicity grows to cancel kinetic α Nonlinear α = (τ/3) v ω +(τ/3ρ)(4π/c) j b 0? CATASTROPHIC QUENCHING OF DYNAMO? Need to get rid of small scale helicity, by Helicity fluxes? (Blackman & Field; Kleeorin et al). But what is gauge invariant helicity density and flux? Small scale helicity density h is density of correlated b field links (Subramanian & Brandenburg, ApJ Lett., 2006) h/ t+ F = 2E B 2η(4π/c)j b Large scale dynamos need helicity fluxes The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.23/27
25 Effect of α-quenching in galaxy Luke Chamandy, Subramanian, Shukurov, MNRAS, 428, 3569 (2013) The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.24/27
26 Effect of advective flux in galaxy Luke Chamandy, Subramanian, Shukurov, MNRAS, 428, 3569 (2013) The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.25/27
27 Galactic outflows and magnetic spiral Winding up Spiral with enhanced outflow along spiral (Chamandy, Shukurov, KS, 2014) The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.26/27
28 Questions When do the first fields arise? How do they evolve with redshift in galaxies and the IGM? Dynamos required to amplify/maintain fields. Fluctuation dynamo saturation? Galaxy cluster plasma nearly collisionless...how to treat? For mean field dynamos: α, η t at large R m? How do MFD s saturate; helicity fluxes? Is an Early universe field needed? Is it inevitable? SKA will be crucial to probe the Magnetic Universe. The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.27/27
Basics of MHD. Kandaswamy Subramanian a. Pune , India. a Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics,
 Basics of MHD Kandaswamy Subramanian a a Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. The magnetic Universe, Feb 16, 2015 p.0/27 Plan Magnetic fields in Astrophysics MHD
Basics of MHD Kandaswamy Subramanian a a Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. The magnetic Universe, Feb 16, 2015 p.0/27 Plan Magnetic fields in Astrophysics MHD
MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE UNIVERSE
 ARTICLE MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE UNIVERSE KANDASWAMY SUBRAMANIAN* The origin and maintenance of large scale magnetic fields in the Universe is discussed. A popular idea is that cosmic batteries generate
ARTICLE MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE UNIVERSE KANDASWAMY SUBRAMANIAN* The origin and maintenance of large scale magnetic fields in the Universe is discussed. A popular idea is that cosmic batteries generate
Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies
 Lecture 4: Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies Rainer Beck, MPIfR Bonn Generation and amplification of cosmic magnetic fields Stage 1: Field seeding Stage 2: Field amplification Stage 3: Coherent field
Lecture 4: Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies Rainer Beck, MPIfR Bonn Generation and amplification of cosmic magnetic fields Stage 1: Field seeding Stage 2: Field amplification Stage 3: Coherent field
Dynamic simulations of the Galactic Dynamo based on supernova-driven ISM turbulence
 Dynamic simulations of the Galactic Dynamo based on supernova-driven ISM turbulence Oliver Gressel, Axel Brandenburg Astrophysics group, NORDITA, Stockholm Abhijit Bendre, Detlef Elstner, Udo Ziegler &
Dynamic simulations of the Galactic Dynamo based on supernova-driven ISM turbulence Oliver Gressel, Axel Brandenburg Astrophysics group, NORDITA, Stockholm Abhijit Bendre, Detlef Elstner, Udo Ziegler &
Turbulent Magnetic Helicity Transport and the Rapid Growth of Large Scale Magnetic Fields
 Turbulent Magnetic Helicity Transport and the Rapid Growth of Large Scale Magnetic Fields Jungyeon Cho Dmitry Shapovalov MWMF Madison, Wisconsin April 2012 The Large Scale Dynamo The accumulation of magnetic
Turbulent Magnetic Helicity Transport and the Rapid Growth of Large Scale Magnetic Fields Jungyeon Cho Dmitry Shapovalov MWMF Madison, Wisconsin April 2012 The Large Scale Dynamo The accumulation of magnetic
University, Bld. 1, GSP-2, Leninskie Gory, Moscow, Russia;
 Baltic Astronomy, vol. 24, 194 200, 2015 STAR FORMATION AND GALAXY DYNAMO EQUATIONS WITH RANDOM COEFFICIENTS E. A. Mikhailov 1 and I. I. Modyaev 2 1 Faculty of Physics, M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University,
Baltic Astronomy, vol. 24, 194 200, 2015 STAR FORMATION AND GALAXY DYNAMO EQUATIONS WITH RANDOM COEFFICIENTS E. A. Mikhailov 1 and I. I. Modyaev 2 1 Faculty of Physics, M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University,
Radio Continuum: Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields. Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn
 Radio Continuum: Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn Synchrotron emission Beam angle: Ψ/2=1/γ=E o /E Radio continuum tools to study GeV Cosmic ray electrons (CRE) Synchrotron spectrum:
Radio Continuum: Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn Synchrotron emission Beam angle: Ψ/2=1/γ=E o /E Radio continuum tools to study GeV Cosmic ray electrons (CRE) Synchrotron spectrum:
Fluctuating governing parameters in galaxy dynamo
 Fluctuating governing parameters in galaxy dynamo E.A.Mikhailov, V.V.Pushkarev M.V.Lomonosov Moscow State University Russian Federation X Serbian-Bulgarian Astronomical Conference Belgrade, Serbia Introduction
Fluctuating governing parameters in galaxy dynamo E.A.Mikhailov, V.V.Pushkarev M.V.Lomonosov Moscow State University Russian Federation X Serbian-Bulgarian Astronomical Conference Belgrade, Serbia Introduction
Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA
 Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn & SKA Science Working Group Fundamental magnetic questions When and how were the first fields generated?
Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn & SKA Science Working Group Fundamental magnetic questions When and how were the first fields generated?
Creation and destruction of magnetic fields
 HAO/NCAR July 30 2007 Magnetic fields in the Universe Earth Magnetic field present for 3.5 10 9 years, much longer than Ohmic decay time ( 10 4 years) Strong variability on shorter time scales (10 3 years)
HAO/NCAR July 30 2007 Magnetic fields in the Universe Earth Magnetic field present for 3.5 10 9 years, much longer than Ohmic decay time ( 10 4 years) Strong variability on shorter time scales (10 3 years)
Large scale magnetic fields and Dynamo theory. Roman Shcherbakov, Turbulence Discussion Group 14 Apr 2008
 Large scale magnetic fields and Dynamo theory Roman Shcherbakov, Turbulence Discussion Group 14 Apr 2008 The Earth Mainly dipolar magnetic field Would decay in 20kyr if not regenerated Declination of the
Large scale magnetic fields and Dynamo theory Roman Shcherbakov, Turbulence Discussion Group 14 Apr 2008 The Earth Mainly dipolar magnetic field Would decay in 20kyr if not regenerated Declination of the
Amplification of magnetic fields from turbulence in the early Universe
 Amplification of magnetic fields from turbulence in the early Universe Jacques M. Wagstaff 1 arxiv:1304.4723 Robi Banerjee 1, Dominik Schleicher 2, Günter Sigl 3 1 Hamburg University 2 Institut für Astrophysik,
Amplification of magnetic fields from turbulence in the early Universe Jacques M. Wagstaff 1 arxiv:1304.4723 Robi Banerjee 1, Dominik Schleicher 2, Günter Sigl 3 1 Hamburg University 2 Institut für Astrophysik,
Small-Scale Dynamo and the Magnetic Prandtl Number
 MRI Turbulence Workshop, IAS, Princeton, 17.06.08 Small-Scale Dynamo and the Magnetic Prandtl Number Alexander Schekochihin (Imperial College) with Steve Cowley (Culham & Imperial) Greg Hammett (Princeton)
MRI Turbulence Workshop, IAS, Princeton, 17.06.08 Small-Scale Dynamo and the Magnetic Prandtl Number Alexander Schekochihin (Imperial College) with Steve Cowley (Culham & Imperial) Greg Hammett (Princeton)
Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters
 Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) with Hyesung Kang (Pusan Nat. U, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (Chungnam Nat. U.),
Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) with Hyesung Kang (Pusan Nat. U, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (Chungnam Nat. U.),
The amplification of magnetic fields by the turbulent dynamo in the early Universe
 The amplification of magnetic fields by the turbulent dynamo in the early Universe Jacques M. Wagstaff Phys. Rev. D89:103001 arxiv:1304.4723 Hamburger Sternwarte, Hamburg University Robi Banerjee 1, Dominik
The amplification of magnetic fields by the turbulent dynamo in the early Universe Jacques M. Wagstaff Phys. Rev. D89:103001 arxiv:1304.4723 Hamburger Sternwarte, Hamburg University Robi Banerjee 1, Dominik
COSMIC-RAY DRIVEN MAGNETIC FIELD DYNAMO IN GALAXIES
 COSMIC-RAY DRIVEN MAGNETIC FIELD DYNAMO IN GALAXIES Michał Hanasz, Centre for Astronomy Nicolaus Copernicus University, Toruń MAGNETIC FIELDS IN SPIRAL GALAXIES - RADIO OBSERVATIONS M51 NGC891 A. Fletcher
COSMIC-RAY DRIVEN MAGNETIC FIELD DYNAMO IN GALAXIES Michał Hanasz, Centre for Astronomy Nicolaus Copernicus University, Toruń MAGNETIC FIELDS IN SPIRAL GALAXIES - RADIO OBSERVATIONS M51 NGC891 A. Fletcher
Dynamos on galactic scales, or Dynamos around us.
 Dynamos on galactic scales, or Dynamos around us. Part IV. Cluster dynamos Anvar Shukurov School of Mathematics and Statistics, Newcastle University, U.K. Outline 1. Evidence for intracluster magnetic
Dynamos on galactic scales, or Dynamos around us. Part IV. Cluster dynamos Anvar Shukurov School of Mathematics and Statistics, Newcastle University, U.K. Outline 1. Evidence for intracluster magnetic
Reduced MHD. Nick Murphy. Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics. February 19, 2014
 Reduced MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 19, 2014 These lecture notes are largely based on Lectures in Magnetohydrodynamics by Dalton
Reduced MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 19, 2014 These lecture notes are largely based on Lectures in Magnetohydrodynamics by Dalton
The Madison Dynamo Experiment: magnetic instabilities driven by sheared flow in a sphere. Cary Forest Department of Physics University of Wisconsin
 The Madison Dynamo Experiment: magnetic instabilities driven by sheared flow in a sphere Cary Forest Department of Physics University of Wisconsin February 28, 2001 Planets, stars and perhaps the galaxy
The Madison Dynamo Experiment: magnetic instabilities driven by sheared flow in a sphere Cary Forest Department of Physics University of Wisconsin February 28, 2001 Planets, stars and perhaps the galaxy
Fluctuation dynamo amplified by intermittent shear bursts
 by intermittent Thanks to my collaborators: A. Busse (U. Glasgow), W.-C. Müller (TU Berlin) Dynamics Days Europe 8-12 September 2014 Mini-symposium on Nonlinear Problems in Plasma Astrophysics Introduction
by intermittent Thanks to my collaborators: A. Busse (U. Glasgow), W.-C. Müller (TU Berlin) Dynamics Days Europe 8-12 September 2014 Mini-symposium on Nonlinear Problems in Plasma Astrophysics Introduction
Helicity and Large Scale Dynamos; Lessons From Mean Field Theory and Astrophysical Implications
 Helicity and Large Scale Dynamos; Lessons From Mean Field Theory and Astrophysical Implications Eric Blackman (U. Rochester) 21st century theory based on incorporating mag. hel conservation has predictive
Helicity and Large Scale Dynamos; Lessons From Mean Field Theory and Astrophysical Implications Eric Blackman (U. Rochester) 21st century theory based on incorporating mag. hel conservation has predictive
Magnetic fields in the early universe
 Magnetic fields in the early universe KandaswamySubramanian a a Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. Heidelberg Joint Astronomical Colloquium, 1st December, 2009
Magnetic fields in the early universe KandaswamySubramanian a a Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. Heidelberg Joint Astronomical Colloquium, 1st December, 2009
Inter University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Post Bag 4, Ganeshkhind, Pune , India.
 Inter University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Post Bag 4, Ganeshkhind, Pune-411007, India. E-mail: kandu@iucaa.ernet.in The origin of cosmic magnetism is an issue of fundamental importance in
Inter University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Post Bag 4, Ganeshkhind, Pune-411007, India. E-mail: kandu@iucaa.ernet.in The origin of cosmic magnetism is an issue of fundamental importance in
Creation and destruction of magnetic fields
 HAO/NCAR July 20 2011 Magnetic fields in the Universe Earth Magnetic field present for 3.5 10 9 years, much longer than Ohmic decay time ( 10 4 years) Strong variability on shorter time scales (10 3 years)
HAO/NCAR July 20 2011 Magnetic fields in the Universe Earth Magnetic field present for 3.5 10 9 years, much longer than Ohmic decay time ( 10 4 years) Strong variability on shorter time scales (10 3 years)
Magnetic fields in galaxies
 Magnetic fields in galaxies Selected items (high-speed version) Rainer Beck, MPIfR Bonn Fundamental questions on galactic magnetic fields When and how were the first magnetic fields generated? How and
Magnetic fields in galaxies Selected items (high-speed version) Rainer Beck, MPIfR Bonn Fundamental questions on galactic magnetic fields When and how were the first magnetic fields generated? How and
Mean field dynamos and magnetic helicity
 Mean field dynamos and magnetic helicity KandaswamySubramanian a Axel Brandenburg(Nordita), Anvar Shukurov(Newcastle Univ.), Sharanya Sur(Heidelberg), Dimitry Sokoloff(Moscow), Sanved Kolekar(IUCAA), S.
Mean field dynamos and magnetic helicity KandaswamySubramanian a Axel Brandenburg(Nordita), Anvar Shukurov(Newcastle Univ.), Sharanya Sur(Heidelberg), Dimitry Sokoloff(Moscow), Sanved Kolekar(IUCAA), S.
Lecture 13 Interstellar Magnetic Fields
 Lecture 13 Interstellar Magnetic Fields 1. Introduction. Synchrotron radiation 3. Faraday rotation 4. Zeeman effect 5. Polarization of starlight 6. Summary of results References Zweibel & Heiles, Nature
Lecture 13 Interstellar Magnetic Fields 1. Introduction. Synchrotron radiation 3. Faraday rotation 4. Zeeman effect 5. Polarization of starlight 6. Summary of results References Zweibel & Heiles, Nature
SKA AND THE COSMOLOGICAL EVOLUTION OF CLUSTER MAGNETIC FIELDS
 SKA AND THE COSMOLOGICAL EVOLUTION OF CLUSTER MAGNETIC FIELDS MARTIN KRAUSE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE, UNIVERSITÄTSSTERNWARTE MÜNCHEN & MAX-PLANCK-INSTITUT FÜR EXTRATERRESTRISCHE PHYSIK COLLABORATORS: PAUL
SKA AND THE COSMOLOGICAL EVOLUTION OF CLUSTER MAGNETIC FIELDS MARTIN KRAUSE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE, UNIVERSITÄTSSTERNWARTE MÜNCHEN & MAX-PLANCK-INSTITUT FÜR EXTRATERRESTRISCHE PHYSIK COLLABORATORS: PAUL
PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS. ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP. NOTES: (references therein)
 PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP NOTES:http://www.astro.iag.usp.br/~dalpino (references therein) ICTP-SAIFR, October 7-18, 2013 Contents What is plasma? Why plasmas in astrophysics?
PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP NOTES:http://www.astro.iag.usp.br/~dalpino (references therein) ICTP-SAIFR, October 7-18, 2013 Contents What is plasma? Why plasmas in astrophysics?
The FIR-Radio Correlation & Implications for GLAST Observations of Starburst Galaxies Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley)
 The FIR-Radio Correlation & Implications for GLAST Observations of Starburst Galaxies Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) w/ Todd Thompson & Eli Waxman Thompson, Quataert, & Waxman 2007, ApJ, 654, 219 Thompson,
The FIR-Radio Correlation & Implications for GLAST Observations of Starburst Galaxies Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) w/ Todd Thompson & Eli Waxman Thompson, Quataert, & Waxman 2007, ApJ, 654, 219 Thompson,
Using Pulsars to study the Magnetic Field in The Milky way
 Using Pulsars to study the Magnetic Field in The Milky way Dipanjan Mitra ( MPIFR Bonn) R. Wielebinski ( MPIFR Bonn) M. Kramer ( Jodrell Bank) A. Jessner ( MPIFR Bonn) MPIFR, Bonn (24 th April 2003) To
Using Pulsars to study the Magnetic Field in The Milky way Dipanjan Mitra ( MPIFR Bonn) R. Wielebinski ( MPIFR Bonn) M. Kramer ( Jodrell Bank) A. Jessner ( MPIFR Bonn) MPIFR, Bonn (24 th April 2003) To
Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs
 Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs Klaus Dolag ( ) Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik ( ) Introduction Evolution of the structures in the Universe t =
Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs Klaus Dolag ( ) Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik ( ) Introduction Evolution of the structures in the Universe t =
Astrophysical Dynamos
 Astrophysical Dynamos Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics April 19, 2016 These lecture notes are based off of Kulsrud, Cowling (1981), Beck et al.
Astrophysical Dynamos Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics April 19, 2016 These lecture notes are based off of Kulsrud, Cowling (1981), Beck et al.
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 12 Jun 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 12 Jun 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 12 Jun 2008](/thumbs/93/112965100.jpg) To appear in Magnetic Fields in the Universe II (2008) RevMexAA(SC) MAGNETIC FIELDS AND STAR FORMATION IN SPIRAL GALAXIES Marita Krause, 1 RESUMEN arxiv:0806.2060v1 [astro-ph] 12 Jun 2008 ABSTRACT The
To appear in Magnetic Fields in the Universe II (2008) RevMexAA(SC) MAGNETIC FIELDS AND STAR FORMATION IN SPIRAL GALAXIES Marita Krause, 1 RESUMEN arxiv:0806.2060v1 [astro-ph] 12 Jun 2008 ABSTRACT The
Nonlinear galactic dynamo models with magnetic-supported interstellar gas-density stratification
 Astron. Astrophys. 319, 781 787 1997) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Nonlinear galactic dynamo models magnetic-supported interstellar gas-density stratification G. Rüdiger and M. Schultz Astrophysikalisches
Astron. Astrophys. 319, 781 787 1997) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Nonlinear galactic dynamo models magnetic-supported interstellar gas-density stratification G. Rüdiger and M. Schultz Astrophysikalisches
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 6 Aug 2015
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 6 Aug 2015 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 6 Aug 2015](/thumbs/82/86411124.jpg) Generation of large-scale magnetic fields by small-scale dynamo in shear flows J. Squire and A. Bhattacharjee Max Planck/Princeton Center for Plasma Physics, Department of Astrophysical Sciences and Princeton
Generation of large-scale magnetic fields by small-scale dynamo in shear flows J. Squire and A. Bhattacharjee Max Planck/Princeton Center for Plasma Physics, Department of Astrophysical Sciences and Princeton
Plasma Physics for Astrophysics
 - ' ' * ' Plasma Physics for Astrophysics RUSSELL M. KULSRUD PRINCETON UNIVERSITY E;RESS '. ' PRINCETON AND OXFORD,, ', V. List of Figures Foreword by John N. Bahcall Preface Chapter 1. Introduction 1
- ' ' * ' Plasma Physics for Astrophysics RUSSELL M. KULSRUD PRINCETON UNIVERSITY E;RESS '. ' PRINCETON AND OXFORD,, ', V. List of Figures Foreword by John N. Bahcall Preface Chapter 1. Introduction 1
arxiv:physics/ v1 8 Sep 2005
 On the inverse cascade of magnetic helicity Alexandros Alexakis, Pablo Mininni, and Annick Pouquet National Center for Atmospheric Research (Dated: September 12, 2005) arxiv:physics/0509069 v1 8 Sep 2005
On the inverse cascade of magnetic helicity Alexandros Alexakis, Pablo Mininni, and Annick Pouquet National Center for Atmospheric Research (Dated: September 12, 2005) arxiv:physics/0509069 v1 8 Sep 2005
Simulating magnetic fields in structure formation
 Simulating magnetic fields in structure formation USM / MPE / MPA Harald Lesch & Klaus Dolag Annette Geng, Federico Stasyszyn & Marcus Beck July, 2012 (Mainz) Alexander Beck Magnetic fields in galaxies
Simulating magnetic fields in structure formation USM / MPE / MPA Harald Lesch & Klaus Dolag Annette Geng, Federico Stasyszyn & Marcus Beck July, 2012 (Mainz) Alexander Beck Magnetic fields in galaxies
Cold gas at high redshifts. R. Srianand Inter-University Center for Astronomy & Astrophysics, Pune - India
 Cold gas at high redshifts R. Srianand Inter-University Center for Astronomy & Astrophysics, Pune - India Why cold gas? Stars are formed from the cold gas. IAS, Bangalore,Nov, 2009 1 Why cold gas? Physical
Cold gas at high redshifts R. Srianand Inter-University Center for Astronomy & Astrophysics, Pune - India Why cold gas? Stars are formed from the cold gas. IAS, Bangalore,Nov, 2009 1 Why cold gas? Physical
Amplification of magnetic fields in core collapse
 Amplification of magnetic fields in core collapse Miguel Àngel Aloy Torás, Pablo Cerdá-Durán, Thomas Janka, Ewald Müller, Martin Obergaulinger, Tomasz Rembiasz Universitat de València; Max-Planck-Institut
Amplification of magnetic fields in core collapse Miguel Àngel Aloy Torás, Pablo Cerdá-Durán, Thomas Janka, Ewald Müller, Martin Obergaulinger, Tomasz Rembiasz Universitat de València; Max-Planck-Institut
Galactic radio loops. Philipp Mertsch with Subir Sarkar. The Radio Synchrotron Background Workshop, University of Richmond 21 July 2017
 Galactic radio loops Philipp Mertsch with Subir Sarkar The Radio Synchrotron Background Workshop, University of Richmond 21 July 2017 Foregrounds in B-modes Adam et al., arxiv:1502.01588 1409.5738 (Planck
Galactic radio loops Philipp Mertsch with Subir Sarkar The Radio Synchrotron Background Workshop, University of Richmond 21 July 2017 Foregrounds in B-modes Adam et al., arxiv:1502.01588 1409.5738 (Planck
IS THE SMALL-SCALE MAGNETIC FIELD CORRELATED WITH THE DYNAMO CYCLE? ApJ press (arxiv: ) Bidya Binay Karak & Axel Brandenburg (Nordita)
 IS THE SMALL-SCALE MAGNETIC FIELD CORRELATED WITH THE DYNAMO CYCLE? ApJ press (arxiv:1505.06632) Bidya Binay Karak & Axel Brandenburg (Nordita) Solar Seminar at MPS Oct 25, 2015 Large-scale magnetic field
IS THE SMALL-SCALE MAGNETIC FIELD CORRELATED WITH THE DYNAMO CYCLE? ApJ press (arxiv:1505.06632) Bidya Binay Karak & Axel Brandenburg (Nordita) Solar Seminar at MPS Oct 25, 2015 Large-scale magnetic field
Beyond Ideal MHD. Nick Murphy. Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics. February 8, 2016
 Beyond Ideal MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 8, 2016 These lecture notes are largely based on Plasma Physics for Astrophysics by
Beyond Ideal MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 8, 2016 These lecture notes are largely based on Plasma Physics for Astrophysics by
Vortex Dynamos. Steve Tobias (University of Leeds) Stefan Llewellyn Smith (UCSD)
 Vortex Dynamos Steve Tobias (University of Leeds) Stefan Llewellyn Smith (UCSD) An introduction to vortices Vortices are ubiquitous in geophysical and astrophysical fluid mechanics (stratification & rotation).
Vortex Dynamos Steve Tobias (University of Leeds) Stefan Llewellyn Smith (UCSD) An introduction to vortices Vortices are ubiquitous in geophysical and astrophysical fluid mechanics (stratification & rotation).
A Lagrangian approach to the study of the kinematic dynamo
 1 A Lagrangian approach to the study of the kinematic dynamo Jean-Luc Thiffeault Department of Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics Columbia University http://plasma.ap.columbia.edu/~jeanluc/ October
1 A Lagrangian approach to the study of the kinematic dynamo Jean-Luc Thiffeault Department of Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics Columbia University http://plasma.ap.columbia.edu/~jeanluc/ October
FARADAY ROTATION OBSERVATIONS OF MAGNETIC FIELDS IN GALAXY CLUSTERS
 Journal of The Korean Astronomical Society 37: 337 342, 2004 FARADAY ROTATION OBSERVATIONS OF MAGNETIC FIELDS IN GALAXY CLUSTERS Tracy E. Clarke Department of Astronomy, University of Virginia, P. O. Box
Journal of The Korean Astronomical Society 37: 337 342, 2004 FARADAY ROTATION OBSERVATIONS OF MAGNETIC FIELDS IN GALAXY CLUSTERS Tracy E. Clarke Department of Astronomy, University of Virginia, P. O. Box
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 15 Dec 2004
 Importance of magnetic helicity in dynamos Axel Brandenburg Nordita, Blegdamsvej 17, DK-2100 Copenhagen Ø, Denmark brandenb@nordita.dk arxiv:astro-ph/0412366v1 15 Dec 2004 Magnetic helicity is nearly conserved
Importance of magnetic helicity in dynamos Axel Brandenburg Nordita, Blegdamsvej 17, DK-2100 Copenhagen Ø, Denmark brandenb@nordita.dk arxiv:astro-ph/0412366v1 15 Dec 2004 Magnetic helicity is nearly conserved
Radio emission from galaxies in the Bootes Voids
 Radio emission from galaxies in the Bootes Voids Mousumi Das, Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Bangalore Large Scale Structure and galaxy flows, Quy Nhon, July 3-9, 2016 Collaborators K.S. Dwarkanath
Radio emission from galaxies in the Bootes Voids Mousumi Das, Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Bangalore Large Scale Structure and galaxy flows, Quy Nhon, July 3-9, 2016 Collaborators K.S. Dwarkanath
Testing the magnetic field models of disk galaxies with the SKA
 Testing the magnetic field models of disk galaxies with the SKA, a R. Stepanov b, R. Beck a, P. Frick b and M. Krause a a Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie, Auf dem Hügel 69, 3121 Bonn, Germany b
Testing the magnetic field models of disk galaxies with the SKA, a R. Stepanov b, R. Beck a, P. Frick b and M. Krause a a Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie, Auf dem Hügel 69, 3121 Bonn, Germany b
Constraining primordial magnetic fields with observations
 Constraining primordial magnetic fields with observations Kerstin Kunze (University of Salamanca and IUFFyM) KK PRD 83 (2011) 023006; PRD 85 (2012) 083004; PRD 87 (2013) 103005; PRD 89 (2014) 103016, arxiv:1703.03650
Constraining primordial magnetic fields with observations Kerstin Kunze (University of Salamanca and IUFFyM) KK PRD 83 (2011) 023006; PRD 85 (2012) 083004; PRD 87 (2013) 103005; PRD 89 (2014) 103016, arxiv:1703.03650
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations. simulations of galaxy and structure formation
 Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 11 26 / Colloquium University of Victoria Outline 1 Cosmic
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 11 26 / Colloquium University of Victoria Outline 1 Cosmic
Soma De Post-doctoral Fellow, Arizona State University presentation at 27th Texas Symposium, Dec 11,2013
 Linear Polarization of CMB and 21cm & Circular Polarization of CMB Soma De Post-doctoral Fellow, Arizona State University presentation at 27th Texas Symposium, Dec 11,2013 Collaboration: Levon Pogosian
Linear Polarization of CMB and 21cm & Circular Polarization of CMB Soma De Post-doctoral Fellow, Arizona State University presentation at 27th Texas Symposium, Dec 11,2013 Collaboration: Levon Pogosian
Q: Why do the Sun and planets have magnetic fields?
 Q: Why do the Sun and planets have magnetic fields? Dana Longcope Montana State University w/ liberal borrowing from Bagenal, Stanley, Christensen, Schrijver, Charbonneau, Q: Why do the Sun and planets
Q: Why do the Sun and planets have magnetic fields? Dana Longcope Montana State University w/ liberal borrowing from Bagenal, Stanley, Christensen, Schrijver, Charbonneau, Q: Why do the Sun and planets
Radio infrared correlation for galaxies: from today's instruments to SKA
 Radio infrared correlation for galaxies: from today's instruments to SKA Agata P piak 1 T.T. Takeuchi 2, A. Pollo 1,3, A. Solarz 2, and AKARI team 1 Astronomical Observatory of the Jagiellonian University,
Radio infrared correlation for galaxies: from today's instruments to SKA Agata P piak 1 T.T. Takeuchi 2, A. Pollo 1,3, A. Solarz 2, and AKARI team 1 Astronomical Observatory of the Jagiellonian University,
Galaxy Ecosystems Adam Leroy (OSU), Eric Murphy (NRAO/IPAC) on behalf of ngvla Working Group 2
 Next Generation Very Large Array Working Group 2 HI in M74: Walter+ 08 CO in M51: Schinnerer+ 13 Continuum in M82: Marvil & Owen Galaxy Ecosystems Adam Leroy (OSU), Eric Murphy (NRAO/IPAC) on behalf of
Next Generation Very Large Array Working Group 2 HI in M74: Walter+ 08 CO in M51: Schinnerer+ 13 Continuum in M82: Marvil & Owen Galaxy Ecosystems Adam Leroy (OSU), Eric Murphy (NRAO/IPAC) on behalf of
Fundamentals of Turbulence
 Fundamentals of Turbulence Stanislav Boldyrev (University of Wisconsin - Madison) Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical Plasmas What is turbulence? No exact definition.
Fundamentals of Turbulence Stanislav Boldyrev (University of Wisconsin - Madison) Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical Plasmas What is turbulence? No exact definition.
Current Status of Turbulent Dynamo Theory
 Space Sci Rev DOI 10.1007/s11214-012-9909-x Current Status of Turbulent Dynamo Theory From Large-Scale to Small-Scale Dynamos Axel Brandenburg Dmitry Sokoloff Kandaswamy Subramanian Received: 28 March
Space Sci Rev DOI 10.1007/s11214-012-9909-x Current Status of Turbulent Dynamo Theory From Large-Scale to Small-Scale Dynamos Axel Brandenburg Dmitry Sokoloff Kandaswamy Subramanian Received: 28 March
Small-scale magnetic helicity losses from a mean-field dynamo
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 398, 1414 1422 (2009) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.15188.x Small-scale magnetic helicity losses from a mean-field dynamo Axel Brandenburg, 1,2 Simon Candelaresi 1,2 and Piyali
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 398, 1414 1422 (2009) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.15188.x Small-scale magnetic helicity losses from a mean-field dynamo Axel Brandenburg, 1,2 Simon Candelaresi 1,2 and Piyali
NUMERICAL STUDIES OF DYNAMO ACTION IN A TURBULENT SHEAR FLOW. I.
 The Astrophysical Journal, 806:8 (0pp), 05 June 0 05. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. doi:0.088/0004-637x/806//8 NUMERICAL STUDIES OF DYNAMO ACTION IN A TURBULENT SHEAR FLOW. I.
The Astrophysical Journal, 806:8 (0pp), 05 June 0 05. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. doi:0.088/0004-637x/806//8 NUMERICAL STUDIES OF DYNAMO ACTION IN A TURBULENT SHEAR FLOW. I.
Orianne ROOS CEA-Saclay Collaborators : F. Bournaud, J. Gabor, S. Juneau
 Orianne ROOS CEA-Saclay Collaborators : F. Bournaud, J. Gabor, S. Juneau Bachelor of Physics, Master of Astrophysics Université de Strasbourg PhD, Université Paris-Diderot Observatoire de Strasbourg Les
Orianne ROOS CEA-Saclay Collaborators : F. Bournaud, J. Gabor, S. Juneau Bachelor of Physics, Master of Astrophysics Université de Strasbourg PhD, Université Paris-Diderot Observatoire de Strasbourg Les
A New Mechanism of Nonlinearity in the Disc Dynamo
 A New Mechanism of Nonlinearity in the Disc Dynamo W. Dobler Astrophysics Institute, Göttingen University, Germany A.D. Poezd Physics Department, Moscow University, Moscow 119899, Russia and A. Shukurov
A New Mechanism of Nonlinearity in the Disc Dynamo W. Dobler Astrophysics Institute, Göttingen University, Germany A.D. Poezd Physics Department, Moscow University, Moscow 119899, Russia and A. Shukurov
Chapter 17. Active Galaxies and Supermassive Black Holes
 Chapter 17 Active Galaxies and Supermassive Black Holes Guidepost In the last few chapters, you have explored our own and other galaxies, and you are ready to stretch your scientific imagination and study
Chapter 17 Active Galaxies and Supermassive Black Holes Guidepost In the last few chapters, you have explored our own and other galaxies, and you are ready to stretch your scientific imagination and study
Growth of Magnetic Fields by Turbulent Motions and Characteristic Scales of MHD Turbulence
 Growth of Magnetic Fields by Turbulent Motions and Characteristic Scales of MHD Turbulence Jungyeon Cho Chungnam National University, Korea Cho, Vishniac, Beresnyak, Lazarian & Ryu 2009, ApJ Cho & Ryu,
Growth of Magnetic Fields by Turbulent Motions and Characteristic Scales of MHD Turbulence Jungyeon Cho Chungnam National University, Korea Cho, Vishniac, Beresnyak, Lazarian & Ryu 2009, ApJ Cho & Ryu,
Probing Primordial Magnetic Fields with Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
 Probing Primordial Magnetic Fields with Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation Department of Physics and Astrophysics University of Delhi IIT Madras, May 17, 2012 Collaborators: K. Subramanian, Pranjal
Probing Primordial Magnetic Fields with Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation Department of Physics and Astrophysics University of Delhi IIT Madras, May 17, 2012 Collaborators: K. Subramanian, Pranjal
The Mystery of Fast Radio Bursts and its possible resolution. Pawan Kumar
 The Mystery of Fast Radio Bursts and its possible resolution Outline Pawan Kumar FRBs: summary of relevant observations Radiation mechanism and polarization FRB cosmology Wenbin Lu Niels Bohr Institute,
The Mystery of Fast Radio Bursts and its possible resolution Outline Pawan Kumar FRBs: summary of relevant observations Radiation mechanism and polarization FRB cosmology Wenbin Lu Niels Bohr Institute,
Astronomy 422! Lecture 7: The Milky Way Galaxy III!
 Astronomy 422 Lecture 7: The Milky Way Galaxy III Key concepts: The supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way Radio and X-ray sources Announcements: Test next Tuesday, February 16 Chapters
Astronomy 422 Lecture 7: The Milky Way Galaxy III Key concepts: The supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way Radio and X-ray sources Announcements: Test next Tuesday, February 16 Chapters
Turbulence and Magnetic Field in High-β Plasma of Intracluster Medium
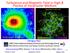 Turbulence and Magnetic Field in High-β Plasma of Intracluster Medium Coma cluster of galaxies Dongsu Ryu UNIST (Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) KASI (Korea Astronomy and Space
Turbulence and Magnetic Field in High-β Plasma of Intracluster Medium Coma cluster of galaxies Dongsu Ryu UNIST (Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) KASI (Korea Astronomy and Space
Radio relics and magnetic field amplification in the Intra-cluster Medium
 Radio relics and magnetic field amplification in the Intra-cluster Medium Annalisa Annalisa Bonafede Bonafede Hamburger Hamburg Sternwarte University Hamburg University Jacobs University Bremen Collaborators:
Radio relics and magnetic field amplification in the Intra-cluster Medium Annalisa Annalisa Bonafede Bonafede Hamburger Hamburg Sternwarte University Hamburg University Jacobs University Bremen Collaborators:
SKA & The Plasma Universe
 SKA & The Plasma Universe Martin Krause Excellence Cluster Universe with: Martin Huarte-Espinosa, Paul Alexander, Rosie Bolton, Jörn Geisbüsch, Julia Riley & Dave Green The Plasma Universe The vast majority
SKA & The Plasma Universe Martin Krause Excellence Cluster Universe with: Martin Huarte-Espinosa, Paul Alexander, Rosie Bolton, Jörn Geisbüsch, Julia Riley & Dave Green The Plasma Universe The vast majority
Broadband X-ray emission from radio-quiet Active Galactic Nuclei
 29 th ASI Meeting ASI Conference Series, 2011, Vol. 3, pp 19 23 Edited by Pushpa Khare & C. H. Ishwara-Chandra Broadband X-ray emission from radio-quiet Active Galactic Nuclei G. C. Dewangan Inter-University
29 th ASI Meeting ASI Conference Series, 2011, Vol. 3, pp 19 23 Edited by Pushpa Khare & C. H. Ishwara-Chandra Broadband X-ray emission from radio-quiet Active Galactic Nuclei G. C. Dewangan Inter-University
Explosive reconnection of the double tearing mode in relativistic plasmas
 Explosive reconnection of the double tearing mode in relativistic plasmas Application to the Crab Jérôme Pétri 1 Hubert Baty 1 Makoto Takamoto 2, Seiji Zenitani 3 1 Observatoire astronomique de Strasbourg,
Explosive reconnection of the double tearing mode in relativistic plasmas Application to the Crab Jérôme Pétri 1 Hubert Baty 1 Makoto Takamoto 2, Seiji Zenitani 3 1 Observatoire astronomique de Strasbourg,
Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays. UHECRs from Mildly Relativistic Supernovae
 Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays from Mildly Relativistic Supernovae Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai, India March 13, 2012 Outline UHECRS Chakraborti, Ray, Soderberg, Loeb, Chandra 2011 Nature
Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays from Mildly Relativistic Supernovae Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai, India March 13, 2012 Outline UHECRS Chakraborti, Ray, Soderberg, Loeb, Chandra 2011 Nature
Inferring source polarisation properties from SKA observations. Joern Geisbuesch
 Inferring source polarisation properties from SKA observations In collaboration with Paul Alexander, Rosie Bolton, Martin Krause April 2008 University of Cambridge Department of Physics Motivation and
Inferring source polarisation properties from SKA observations In collaboration with Paul Alexander, Rosie Bolton, Martin Krause April 2008 University of Cambridge Department of Physics Motivation and
A Lagrangian approach to the kinematic dynamo
 1 A Lagrangian approach to the kinematic dynamo Jean-Luc Thiffeault Department of Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics Columbia University http://plasma.ap.columbia.edu/~jeanluc/ 5 March 2001 with Allen
1 A Lagrangian approach to the kinematic dynamo Jean-Luc Thiffeault Department of Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics Columbia University http://plasma.ap.columbia.edu/~jeanluc/ 5 March 2001 with Allen
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 13 Jul 2012
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 13 Jul 2012 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 13 Jul 2012](/thumbs/74/70127793.jpg) Magnetic field transport from disk to halo via the galactic chimney process in NGC 6946 George H. Heald 1 ASTRON, Postbus 2, 7990 AA Dwingeloo, The Netherlands arxiv:1206.6569v2 [astro-ph.co] 13 Jul 2012
Magnetic field transport from disk to halo via the galactic chimney process in NGC 6946 George H. Heald 1 ASTRON, Postbus 2, 7990 AA Dwingeloo, The Netherlands arxiv:1206.6569v2 [astro-ph.co] 13 Jul 2012
Part 1 : solar dynamo models [Paul] Part 2 : Fluctuations and intermittency [Dario] Part 3 : From dynamo to interplanetary magnetic field [Paul]
![Part 1 : solar dynamo models [Paul] Part 2 : Fluctuations and intermittency [Dario] Part 3 : From dynamo to interplanetary magnetic field [Paul] Part 1 : solar dynamo models [Paul] Part 2 : Fluctuations and intermittency [Dario] Part 3 : From dynamo to interplanetary magnetic field [Paul]](/thumbs/82/84973983.jpg) Dynamo tutorial Part 1 : solar dynamo models [Paul] Part 2 : Fluctuations and intermittency [Dario] Part 3 : From dynamo to interplanetary magnetic field [Paul] ISSI Dynamo tutorial 1 1 Dynamo tutorial
Dynamo tutorial Part 1 : solar dynamo models [Paul] Part 2 : Fluctuations and intermittency [Dario] Part 3 : From dynamo to interplanetary magnetic field [Paul] ISSI Dynamo tutorial 1 1 Dynamo tutorial
Circulation-dominated solar shell dynamo models with positive alpha-effect
 A&A 374, 301 308 (2001) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20010686 c ESO 2001 Astronomy & Astrophysics Circulation-dominated solar shell dynamo models with positive alpha-effect M. Küker,G.Rüdiger, and M. Schultz
A&A 374, 301 308 (2001) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20010686 c ESO 2001 Astronomy & Astrophysics Circulation-dominated solar shell dynamo models with positive alpha-effect M. Küker,G.Rüdiger, and M. Schultz
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations. simulations of galaxy and structure formation
 Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 13 26 / Workshop Dark halos, UBC Vancouver Outline 1
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 13 26 / Workshop Dark halos, UBC Vancouver Outline 1
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 16 Jun 2005
 Astrophysical magnetic fields and nonlinear dynamo theory Axel Brandenburg a and Kandaswamy Subramanian b arxiv:astro-ph/0405052v2 16 Jun 2005 a NORDITA, Blegdamsvej 17, DK-2100 Copenhagen Ø, Denmark.
Astrophysical magnetic fields and nonlinear dynamo theory Axel Brandenburg a and Kandaswamy Subramanian b arxiv:astro-ph/0405052v2 16 Jun 2005 a NORDITA, Blegdamsvej 17, DK-2100 Copenhagen Ø, Denmark.
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 18 Dec 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 18 Dec 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 18 Dec 2008](/thumbs/90/103052846.jpg) Proceedings Title IAU Symposium Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 259, 09 K.G. Strassmeier, A.G. Kosovichev, & J. Beckmann c 09 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X The magnetic
Proceedings Title IAU Symposium Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 259, 09 K.G. Strassmeier, A.G. Kosovichev, & J. Beckmann c 09 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X The magnetic
Occurrence of Radio Halos in galaxy clusters Insight from a mass-selected sample Virginia Cuciti
 Occurrence of Radio Halos in galaxy clusters Insight from a mass-selected sample Virginia Cuciti In collaboration with: Gianfranco Brunetti, Rossella Cassano, Daniele Dallacasa Coma WSRT radio contours
Occurrence of Radio Halos in galaxy clusters Insight from a mass-selected sample Virginia Cuciti In collaboration with: Gianfranco Brunetti, Rossella Cassano, Daniele Dallacasa Coma WSRT radio contours
Lower bound on the extragalactic magnetic field
 Lower bound on the extragalactic magnetic field Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Dolag, MK, Ostapchenko, Tomàs 10 Neronov, Semikoz, MK, Ostapchenko, Elyiv 10 Introduction Mean free path of photons
Lower bound on the extragalactic magnetic field Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Dolag, MK, Ostapchenko, Tomàs 10 Neronov, Semikoz, MK, Ostapchenko, Elyiv 10 Introduction Mean free path of photons
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 26 Jul 2005
 A High Resolution HI Study of Selected Virgo Galaxies - Preliminary Results on Gas Morphology & Extra-Planar Gas arxiv:astro-ph/0507592v1 26 Jul 2005 Aeree Chung and J. H. van Gorkom Department of Astronomy,
A High Resolution HI Study of Selected Virgo Galaxies - Preliminary Results on Gas Morphology & Extra-Planar Gas arxiv:astro-ph/0507592v1 26 Jul 2005 Aeree Chung and J. H. van Gorkom Department of Astronomy,
DYNAMO THEORY: THE PROBLEM OF THE GEODYNAMO PRESENTED BY: RAMANDEEP GILL
 DYNAMO THEORY: THE PROBLEM OF THE GEODYNAMO PRESENTED BY: RAMANDEEP GILL MAGNETIC FIELD OF THE EARTH DIPOLE Field Structure Permanent magnetization of Core? 80% of field is dipole 20 % is non dipole 2)
DYNAMO THEORY: THE PROBLEM OF THE GEODYNAMO PRESENTED BY: RAMANDEEP GILL MAGNETIC FIELD OF THE EARTH DIPOLE Field Structure Permanent magnetization of Core? 80% of field is dipole 20 % is non dipole 2)
Importance of Magnetic Helicity in Dynamos
 Importance of Magnetic Helicity in Dynamos Axel Brandenburg Nordita, Blegdamsvej 17, 2100 Copenhagen Ø, Denmark brandenb@nordita.dk Magnetic helicity is nearly conserved and its evolution equation provides
Importance of Magnetic Helicity in Dynamos Axel Brandenburg Nordita, Blegdamsvej 17, 2100 Copenhagen Ø, Denmark brandenb@nordita.dk Magnetic helicity is nearly conserved and its evolution equation provides
Theoretical Geomagnetism. Lecture 2: Self- Exciting Dynamos: Kinematic Theory
 Theoretical Geomagnetism Lecture 2: Self- Exciting Dynamos: Kinematic Theory 1 2.0 What is a self-exciting dynamo? Dynamo = A device that converts kinetic energy into electromagnetic energy. Dynamos use
Theoretical Geomagnetism Lecture 2: Self- Exciting Dynamos: Kinematic Theory 1 2.0 What is a self-exciting dynamo? Dynamo = A device that converts kinetic energy into electromagnetic energy. Dynamos use
Why does the magnetic field of the Earth reverse?
 IMPRS Solar System Seminar June 2002 Why does the magnetic field of the Earth reverse? Dieter Schmitt (Katlenburg-Lindau) 1. Geomagnetic field >99% of matter in universe is plasma: gas of electrons, ions
IMPRS Solar System Seminar June 2002 Why does the magnetic field of the Earth reverse? Dieter Schmitt (Katlenburg-Lindau) 1. Geomagnetic field >99% of matter in universe is plasma: gas of electrons, ions
Accretion Disks I. High Energy Astrophysics: Accretion Disks I 1/60
 Accretion Disks I References: Accretion Power in Astrophysics, J. Frank, A. King and D. Raine. High Energy Astrophysics, Vol. 2, M.S. Longair, Cambridge University Press Active Galactic Nuclei, J.H. Krolik,
Accretion Disks I References: Accretion Power in Astrophysics, J. Frank, A. King and D. Raine. High Energy Astrophysics, Vol. 2, M.S. Longair, Cambridge University Press Active Galactic Nuclei, J.H. Krolik,
The Black Hole in the Galactic Center. Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley)
 The Black Hole in the Galactic Center Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Why focus on the Galactic Center? The Best Evidence for a BH: M 3.6 10 6 M (M = mass of sun) It s s close! only ~ 10 55 Planck Lengths
The Black Hole in the Galactic Center Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Why focus on the Galactic Center? The Best Evidence for a BH: M 3.6 10 6 M (M = mass of sun) It s s close! only ~ 10 55 Planck Lengths
Plasma Effects. Massimo Ricotti. University of Maryland. Plasma Effects p.1/17
 Plasma Effects p.1/17 Plasma Effects Massimo Ricotti ricotti@astro.umd.edu University of Maryland Plasma Effects p.2/17 Wave propagation in plasma E = 4πρ e E = 1 c B t B = 0 B = 4πJ e c (Faraday law of
Plasma Effects p.1/17 Plasma Effects Massimo Ricotti ricotti@astro.umd.edu University of Maryland Plasma Effects p.2/17 Wave propagation in plasma E = 4πρ e E = 1 c B t B = 0 B = 4πJ e c (Faraday law of
Simulations and understanding large-scale dynamos
 Simulations and understanding large-scale dynamos Issues with global models Possibility of smaller scales Consequences of this Magnetic flux concentrations Unusual dynamo effects Axel randenburg (Nordita,
Simulations and understanding large-scale dynamos Issues with global models Possibility of smaller scales Consequences of this Magnetic flux concentrations Unusual dynamo effects Axel randenburg (Nordita,
Anisotropic turbulence in rotating magnetoconvection
 Anisotropic turbulence in rotating magnetoconvection André Giesecke Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam An der Sternwarte 16 14482 Potsdam MHD-Group seminar, 2006 André Giesecke (AIP) Anisotropic turbulence
Anisotropic turbulence in rotating magnetoconvection André Giesecke Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam An der Sternwarte 16 14482 Potsdam MHD-Group seminar, 2006 André Giesecke (AIP) Anisotropic turbulence
PROPERTIES OF MAGNETIC HELICITY FLUX IN TURBULENT DYNAMOS
 The Astrophysical Journal, 780:144 (10pp), 014 January 10 C 014. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in the U.S.A. doi:10.1088/0004-637x/780//144 PROPERTIES OF MAGNETIC HELICITY
The Astrophysical Journal, 780:144 (10pp), 014 January 10 C 014. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in the U.S.A. doi:10.1088/0004-637x/780//144 PROPERTIES OF MAGNETIC HELICITY
Observations of jet dissipation. Robert Laing (ESO/Oxford)
 Observations of jet dissipation Robert Laing (ESO/Oxford) Overview X-ray radio connections in radio galaxies and quasars: High-energy emission from non-thermal electrons. The interaction of radio galaxies
Observations of jet dissipation Robert Laing (ESO/Oxford) Overview X-ray radio connections in radio galaxies and quasars: High-energy emission from non-thermal electrons. The interaction of radio galaxies
The Superbubble Power Problem: Overview and Recent Developments. S. Oey
 The Superbubble Power Problem: Overview and Recent Developments S. Oey It has been known for decades that superbubbles generated by massive star winds and supernovae are smaller than expected based on
The Superbubble Power Problem: Overview and Recent Developments S. Oey It has been known for decades that superbubbles generated by massive star winds and supernovae are smaller than expected based on
Radio emission in clusters of galaxies. An observational perspective
 Radio emission in clusters of galaxies An observational perspective Tiziana Venturi INAF, IRA, Bologna IV ESTRELA Workshop, Bologna, 19 January 2009 Overview - What are galaxy clusters - Radio emission
Radio emission in clusters of galaxies An observational perspective Tiziana Venturi INAF, IRA, Bologna IV ESTRELA Workshop, Bologna, 19 January 2009 Overview - What are galaxy clusters - Radio emission
Scope of this lecture ASTR 7500: Solar & Stellar Magnetism. Lecture 9 Tues 19 Feb Magnetic fields in the Universe. Geomagnetism.
 Scope of this lecture ASTR 7500: Solar & Stellar Magnetism Hale CGEG Solar & Space Physics Processes of magnetic field generation and destruction in turbulent plasma flows Introduction to general concepts
Scope of this lecture ASTR 7500: Solar & Stellar Magnetism Hale CGEG Solar & Space Physics Processes of magnetic field generation and destruction in turbulent plasma flows Introduction to general concepts
Uncovering magnetic field topology from synchrotron polarization
 Science at Low Frequencies III, Pasadena, 2016-12-06 Uncovering magnetic field topology from synchrotron polarization Niels Oppermann Multifrequency surveys Many existing / upcoming polarization surveys
Science at Low Frequencies III, Pasadena, 2016-12-06 Uncovering magnetic field topology from synchrotron polarization Niels Oppermann Multifrequency surveys Many existing / upcoming polarization surveys
Prediction of solar activity cycles by assimilating sunspot data into a dynamo model
 Solar and Stellar Variability: Impact on Earth and Planets Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 264, 2009 A. G. Kosovichev, A. H. Andrei & J.-P. Rozelot, eds. c International Astronomical Union 2010 doi:10.1017/s1743921309992638
Solar and Stellar Variability: Impact on Earth and Planets Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 264, 2009 A. G. Kosovichev, A. H. Andrei & J.-P. Rozelot, eds. c International Astronomical Union 2010 doi:10.1017/s1743921309992638
