Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters
|
|
|
- Stephen Stephens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) with Hyesung Kang (Pusan Nat. U, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (Chungnam Nat. U.), Sungwook E. Hong (KIAS, Korea), Kiwan Park (UNIST, Korea) T. W. Jones, David H.Porter (U of Minnesota, USA), and etc - Turbulence in clusters in simulations - Magnetohydrodynamic turbulence - Nature of magnetic fields in clusters
2 Physical quantities in clusters of galaxies size of clusters density of baryonic matter flow velocity gas temperature magnetic fields Energetics gas thermal energy gas kinetic energy cosmic-ray energy magnetic energy L ~ a n T ~ 10 8 ~ 10 2 cm 3 υ ~ several 10 K B ~ a few µ G E E E E thermal kinetic cosmic-ray magnetic few Mpc ~ 10 ~ ~ 10 ~ 10 2 km/s erg/cm erg/cm erg/cm erg/cm plasma beta β 100 dynamically not important! 3 3 β P P gas magnetic
3 Magnetic fields in galaxy clusters appears in observations CIZA J Sausage relic Hydra North (van Weeren et al 2010) (Shea Brown) Faraday rotation measure Vogt & Ensslin (2005) Coma cluster Relic halo
4 Origin of magnetic fields in galaxy clusters - turbulence generated at shocks in the LSS of the universe + turbulence dynamo with weak seed fields (Ryu et al 2008) probably energetically most important - AGN outflows operating all over clusters mostly in cluster core regions - microscopic instabilities such as mirror instab, fire-hose instab, macroscpic instabilities such cosmic-ray induced instab, cosmic-ray flux, and etc not yet clear!
5 Overview of a model for the origin of magnetic fields in galaxy clusters large-scale structure formation gravitational collapse & flow motions shocks in clusters & LSS shock shock dissipation the main channel to flow the gravitational energy to the intergalactic medium (gravity is the ultimate source of energy in astrophysics!) generation of heat fresh acc. & re-acc. of CRs genera. of magnetic fields generation of vorticity amp by stretching and comp turbulent amp. of mag. fields turbulent acceleration of CRs
6 Shocks around a simulated cluster in 3D Mach number distribution accretion shocks surrounding the cluster M s > ~10 internal shocks inside the cluster M s < ~ several Ryu et al (2003)
7 (6h -1 Mpc) 2 Shocks around a simulated cluster in 2D (in the plane through the center) Hong, Ryu et al (2014) gas density temperature shock Mach no. R200 accretion shock merger shock infall shock (accretion from Structures of shocks in galaxy clusters WHIM to hot IGM) are complex! 7
8 - Vorticity generated at cosmological shocks - directly at interacting and curved shocks at curved shocks at interacting shocks ϖ cs ~ Porter, Jones, Ryu (2015) 2 1 ( ρ2 ρ1) ρ ρ 2 U n R div(v) ω ρ 1 ρ 2 U n R preshock density postshock density preshock flow speed unit normal to shock surf. curvature radius of surf. - by the baroclinic term 1 ϖ bc = 2 ρ ρ p baroclinity constant ρ constant p due to entropy variation induced at shocks - Magnitude of vorticity enhance by compression and stretching during the development of turbulence
9 Turbulence in high resolution simulations of galaxy clusters vorticity in the plane through a cluster center Miniati (2013)
10 Turbulence energy estimated from simulation Ryu et al (2008) clusters E turb /E therm ~ 1 M turb ~ 1 (transonic turbulence) in filaments E turb /E therm ~ M turb < 1 (subsonic turbulence) inside and outskirts of clusters
11 Turbulence + magnetic field Magnetohydrodynamic turbulence Magnetic fields can be amplified by turbulence from weak seed fields Turbulence dynamo or small-scale dynamo
12 Seed magnetic fields in the large-scale structure (LSS) of the universe Suggestions include: - generation in the early universe(e.g., see Widrow, Ryu et al 2012 for review) e.g.) during the electroweak phase transition (t~10-12 sec) during the quark-hadron transition (t~10-5 sec) uncertain but maybe challenging (?) - generation before the formation of the LSS of the universe through plasma physical processes (e.g., see Ryu et al 2012 for review) e.g.) Biermann battery at shocks instabilities, thermal fluctuations, photo-ionization and etc weak (~ G) and some at small scales, yet most promising(?) - astrophysical processes e.g.) magnetic fields from the first stars maybe not the first magnetic field Origin of seeds for comic magnetic fields is uncertain!
13 Standard picture of MHD turbulence with weak initial field (small-scale dynamo) growth of magnetic energy E kin at saturation E mag /E kin ~ 2/3 exponential growth linear growth E mag saturation
14 Evolution of magnetic field power spectrum at early stages 1 inverse cascade linear growth exponential growth
15 Power spectrum at saturation E kin E mag
16 Effects of compressibility (Porter, Jones, Ryu, 2015) - simulations of compressible turbulence of M s ~ 0.45 at saturation - purely solenoidal forcing or driving purely compressive forcing or driving V 0, V = V = 0, V 0 0 E kin E kin,comp E mag E kin,sol E mag solenoidal forcing compressive forcing Magnetic field amplification is very inefficient in the case of compressive forcing.
17 Power spectrum at saturation P kin (k) for sol. mode P kin (k) for comp. mode P mag (k) P kin (k) for sol. mode P mag (k) P kin (k) for comp. mode purely solenoidal forcing purely compressible forcing Power spectrum is different in the two cases.
18 Turbulence in high resolution simulations of galaxy clusters total sol. mode comp. mode Miniati (2014) fraction of compressional mode ~ 20 30% turbulence with solenoidal forcing may be more relevant
19 Viscosity and resistivity in the ICM mean free-path for electron-electron & proton-proton collisions l p p Braginskii viscosity T (K) ~ le e ~ cm ~ a few kpc 3 ln Λ n (cm ) e ν ~ υ l therm p p p p ~ l t 2 p p p p T ~ n 5/2 e resistivity η ~ ( c / t ω p e p ) 2 ~ T 3/2 high temperature, low density high viscosity, low resistivity very high magnetic Prandtle number P m = ν η
20 Turbulence with large P m assuming that the plasma is described by a fluid with high viscosity and low resistivity (?) (Park, Ryu, et al 2015) E kin Growth of kinetic and magnetic energies E mag at saturation magnetic energy > kinetic energy
21 Power spectrum at saturation P(k) mag P(k) kin with E mag >> E kin, excitation of V by B B 2 B ~ ν V transfer of magnetic energy to smaller scale ε ~ B τ 2 decay ~ constant of k k P( k ) P( k ) kin mag ~ k 3 ~ k 1
22 A model for magnetic fields in galaxy clusters filaments - vorticity generated at shocks and also due to baroclinity - turbulence developed - standard picture of MHD turbulence applied - magnetic field produced by turbulence dynamo φ and E turb from simulation clusters E B 2 B = = φ( ω t) 8π (Ryu et al 2008) Ε turb conversion factor from separate MHD turbulence simulations no fine tuning to normalize B! ρ, v B
23 Magnetic fields in the large-scale structure averaged strength and integral scale of magnetic fields at z = 0 predicted from turbulence dynamo - in clusters <B> ~ a few µg, L int ~ a few x 10 kpc - in filaments (10 5 K < T < 10 7 K, or WHIM) <B> ~ 10 ng, L int ~ a few x 100 kpc the integral scale is a length scale of magnetic field, which would be relevant to Faraday rotation measure L int = 2π ( E / k) dk / B (Cho & Ryu 2009) E B dk
24 Schematic diagram for magnetic field power spectrum P mag (k) K +1 K -5/3 K -1 injection scale/2 ~100 kpc viscous scale ~ a few kpc k
25 Summary - Magnetic fields in galaxy clusters: ~ µg - Turbulence of E turb /E therm ~ 0.1 in galaxy clusters can amplify weak seed fields to magnetic field of ~ µg ( E mag /E therm ~ 0.01 or β ~ 100) L int ~ a few x 10 kpc through turbulence dynamo - Coulomb mean free path, l coul ~ a few kpc. - The nature of magnetic fields below l coul is not clear.
26 Thank you!
Turbulence and Magnetic Field in High-β Plasma of Intracluster Medium
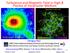 Turbulence and Magnetic Field in High-β Plasma of Intracluster Medium Coma cluster of galaxies Dongsu Ryu UNIST (Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) KASI (Korea Astronomy and Space
Turbulence and Magnetic Field in High-β Plasma of Intracluster Medium Coma cluster of galaxies Dongsu Ryu UNIST (Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) KASI (Korea Astronomy and Space
Intracluster Shock Waves
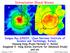 ρ Intracluster Shock Waves T R 200 Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) Hyesung Kang (Pusan National U, Korea) Sungwook E. Hong (Korea Institute for Advanced Study)
ρ Intracluster Shock Waves T R 200 Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) Hyesung Kang (Pusan National U, Korea) Sungwook E. Hong (Korea Institute for Advanced Study)
Cosmological Shocks and Their Signatures
 Cosmological Shocks and Their Signatures Dongsu Ryu (Chungnam National U, Korea) Hyesung Kang (PNU, Korea), Renyi Ma (CNU, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (CNU, Korea), David Porter (U of Minnesota), T. W. Jones
Cosmological Shocks and Their Signatures Dongsu Ryu (Chungnam National U, Korea) Hyesung Kang (PNU, Korea), Renyi Ma (CNU, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (CNU, Korea), David Porter (U of Minnesota), T. W. Jones
Growth of Magnetic Fields by Turbulent Motions and Characteristic Scales of MHD Turbulence
 Growth of Magnetic Fields by Turbulent Motions and Characteristic Scales of MHD Turbulence Jungyeon Cho Chungnam National University, Korea Cho, Vishniac, Beresnyak, Lazarian & Ryu 2009, ApJ Cho & Ryu,
Growth of Magnetic Fields by Turbulent Motions and Characteristic Scales of MHD Turbulence Jungyeon Cho Chungnam National University, Korea Cho, Vishniac, Beresnyak, Lazarian & Ryu 2009, ApJ Cho & Ryu,
Formation and properties of shock waves in galaxy clusters
 Formation and properties of shock waves in galaxy clusters Hyesung Kang (Pusan National University) Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Korea) T. W. Jones (Univ. of Minnesota) Sungwook E. Hong (KAIST, Korea) Ref: Kang,
Formation and properties of shock waves in galaxy clusters Hyesung Kang (Pusan National University) Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Korea) T. W. Jones (Univ. of Minnesota) Sungwook E. Hong (KAIST, Korea) Ref: Kang,
Turbulence and Magnetic Fields in the Large Scale Structure of the Universe
 arxiv:0805.2466v1 [astro-ph] 16 May 2008 Turbulence and Magnetic Fields in the Large Scale Structure of the Universe Dongsu Ryu, 1 Hyesung Kang, 2 Jungyeon Cho, 1 and Santabrata Das 3 1 Department of Astronomy
arxiv:0805.2466v1 [astro-ph] 16 May 2008 Turbulence and Magnetic Fields in the Large Scale Structure of the Universe Dongsu Ryu, 1 Hyesung Kang, 2 Jungyeon Cho, 1 and Santabrata Das 3 1 Department of Astronomy
Uri Keshet / CfA Impact of upcoming high-energy astrophysics experiments Workshop, KAVLI, October 2008
 Uri Keshet / CfA Impact of upcoming high-energy astrophysics experiments Workshop, KAVLI, October 008 Impact of upcoming high-energy astrophysics experiments Workshop, KAVLI, October 008 Relaxed, cool
Uri Keshet / CfA Impact of upcoming high-energy astrophysics experiments Workshop, KAVLI, October 008 Impact of upcoming high-energy astrophysics experiments Workshop, KAVLI, October 008 Relaxed, cool
PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS. ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP. NOTES: (references therein)
 PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP NOTES:http://www.astro.iag.usp.br/~dalpino (references therein) ICTP-SAIFR, October 7-18, 2013 Contents What is plasma? Why plasmas in astrophysics?
PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP NOTES:http://www.astro.iag.usp.br/~dalpino (references therein) ICTP-SAIFR, October 7-18, 2013 Contents What is plasma? Why plasmas in astrophysics?
Shocks in the ICM and the IPM
 Shocks in the ICM and the IPM Tom Jones (University of Minnesota) 1 Outline Setting the stage for following talks The Interplanetary and Intracluster Media as Collisionless Plasmas Basic Introduction to
Shocks in the ICM and the IPM Tom Jones (University of Minnesota) 1 Outline Setting the stage for following talks The Interplanetary and Intracluster Media as Collisionless Plasmas Basic Introduction to
PoS(ICRC2017)283. Acceleration of Cosmic Ray Electrons at Weak Shocks in Galaxy Clusters. Hyesung Kang. Dongsu Ryu
 Acceleration of Cosmic Ray Electrons at Weak Shocks in Galaxy Clusters Pusan National University E-mail: hskang@pusan.ac.kr Dongsu Ryu UNIST E-mail: ryu@sirius.unist.ac.kr T. W. Jones University of Minnesota
Acceleration of Cosmic Ray Electrons at Weak Shocks in Galaxy Clusters Pusan National University E-mail: hskang@pusan.ac.kr Dongsu Ryu UNIST E-mail: ryu@sirius.unist.ac.kr T. W. Jones University of Minnesota
ICMs and the IPM: Birds of a Feather?
 ICMs and the IPM: Birds of a Feather? Tom Jones University of Minnesota 11 November, 2014 KAW8: Astrophysics of High-Beta Plasma in the Universe 1 Outline: ICM plasma is the dominant baryon component in
ICMs and the IPM: Birds of a Feather? Tom Jones University of Minnesota 11 November, 2014 KAW8: Astrophysics of High-Beta Plasma in the Universe 1 Outline: ICM plasma is the dominant baryon component in
Intergalactic Magnetic Field and Arrival Direction of Ultra-High-Energy Protons
 Intergalactic Magnetic Field and Arrival Direction of Ultra-High-Energy Protons Dongsu Ryu (Chungnam National U, Korea) Hyesung Kang (Pusan National U, Korea) Santabrata Das (Indian Institute of Technology
Intergalactic Magnetic Field and Arrival Direction of Ultra-High-Energy Protons Dongsu Ryu (Chungnam National U, Korea) Hyesung Kang (Pusan National U, Korea) Santabrata Das (Indian Institute of Technology
Radio relics and magnetic field amplification in the Intra-cluster Medium
 Radio relics and magnetic field amplification in the Intra-cluster Medium Annalisa Annalisa Bonafede Bonafede Hamburger Hamburg Sternwarte University Hamburg University Jacobs University Bremen Collaborators:
Radio relics and magnetic field amplification in the Intra-cluster Medium Annalisa Annalisa Bonafede Bonafede Hamburger Hamburg Sternwarte University Hamburg University Jacobs University Bremen Collaborators:
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Sep 2010
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Sep 2010 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Sep 2010](/thumbs/88/115477948.jpg) Submitted to ApJ Faraday Rotation Measure due to the Intergalactic Magnetic Field arxiv:1009.0570v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Sep 2010 Takuya Akahori 1 and Dongsu Ryu 2,3 1 Research Institute of Basic Science, Chungnam
Submitted to ApJ Faraday Rotation Measure due to the Intergalactic Magnetic Field arxiv:1009.0570v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Sep 2010 Takuya Akahori 1 and Dongsu Ryu 2,3 1 Research Institute of Basic Science, Chungnam
Evolution and Impact of Cosmic Magnetic Fields
 Evolution and Impact of Cosmic Magnetic Fields Robi Banerjee University of Hamburg Collaborators: Dominik Schleicher (Göttingen), C. Federrath (Lyon, HD), Karsten Jedamzik (Montpellier), R. Klessen (Heidelberg),
Evolution and Impact of Cosmic Magnetic Fields Robi Banerjee University of Hamburg Collaborators: Dominik Schleicher (Göttingen), C. Federrath (Lyon, HD), Karsten Jedamzik (Montpellier), R. Klessen (Heidelberg),
Turbulence & particle acceleration in galaxy clusters. Gianfranco Brunetti
 Turbulence & particle acceleration in galaxy clusters Gianfranco Brunetti Mergers & CR-acceleration Cluster-cluster mergers are the most energetic events in the present Universe (10 64 erg/gyr). They can
Turbulence & particle acceleration in galaxy clusters Gianfranco Brunetti Mergers & CR-acceleration Cluster-cluster mergers are the most energetic events in the present Universe (10 64 erg/gyr). They can
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations. simulations of galaxy and structure formation
 Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 13 26 / Workshop Dark halos, UBC Vancouver Outline 1
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 13 26 / Workshop Dark halos, UBC Vancouver Outline 1
Intracluster Medium Plasmas
 arxiv:1903.08751v1 [astro-ph.he] 20 Mar 2019 PLASMA 2020 WHITE PAPER FOR THE DECADAL ASSESSMENT OF PLASMA SCIENCE Intracluster Medium Plasmas Damiano Caprioli 1, Gianfranco Brunetti 2, Thomas W. Jones
arxiv:1903.08751v1 [astro-ph.he] 20 Mar 2019 PLASMA 2020 WHITE PAPER FOR THE DECADAL ASSESSMENT OF PLASMA SCIENCE Intracluster Medium Plasmas Damiano Caprioli 1, Gianfranco Brunetti 2, Thomas W. Jones
AGN Outflows in Dynamic ICMs: Winds and Twists
 AGN Outflows in Dynamic ICMs: Winds and Twists Tom Jones University of Minnesota Pete Mendygral (UMN, Cray Computer) David Porter (UMN) Klaus Dolag (MPA, U Munich) 11/29/2012 Binary Black Holes & Dual
AGN Outflows in Dynamic ICMs: Winds and Twists Tom Jones University of Minnesota Pete Mendygral (UMN, Cray Computer) David Porter (UMN) Klaus Dolag (MPA, U Munich) 11/29/2012 Binary Black Holes & Dual
Cosmic Rays in Galaxy Clusters: Simulations and Perspectives
 Cosmic Rays in Galaxy Clusters: Simulations and Perspectives 1 in collaboration with Volker Springel 2, Torsten Enßlin 2 1 Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Canada 2 Max-Planck Institute
Cosmic Rays in Galaxy Clusters: Simulations and Perspectives 1 in collaboration with Volker Springel 2, Torsten Enßlin 2 1 Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Canada 2 Max-Planck Institute
Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA
 Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn & SKA Science Working Group Fundamental magnetic questions When and how were the first fields generated?
Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn & SKA Science Working Group Fundamental magnetic questions When and how were the first fields generated?
Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs
 Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs Klaus Dolag ( ) Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik ( ) Introduction Evolution of the structures in the Universe t =
Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs Klaus Dolag ( ) Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik ( ) Introduction Evolution of the structures in the Universe t =
The amplification of magnetic fields by the turbulent dynamo in the early Universe
 The amplification of magnetic fields by the turbulent dynamo in the early Universe Jacques M. Wagstaff Phys. Rev. D89:103001 arxiv:1304.4723 Hamburger Sternwarte, Hamburg University Robi Banerjee 1, Dominik
The amplification of magnetic fields by the turbulent dynamo in the early Universe Jacques M. Wagstaff Phys. Rev. D89:103001 arxiv:1304.4723 Hamburger Sternwarte, Hamburg University Robi Banerjee 1, Dominik
Numerical Study of Compressible Isothermal Magnetohydrodynamic Turbulence
 Numerical Study of Compressible Isothermal Magnetohydrodynamic Turbulence Junseong Park, Dongsu Ryu Dept. of Physics, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology. Ulsan, Korea 2016 KNAG meeting
Numerical Study of Compressible Isothermal Magnetohydrodynamic Turbulence Junseong Park, Dongsu Ryu Dept. of Physics, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology. Ulsan, Korea 2016 KNAG meeting
Magnetic fields generated by the Weibel Instability
 Magnetic fields generated by the Weibel Instability C. M. Ryu POSTECH, KOREA FFP14 Marseille 14.7.15-7.18 Outline I. Why Weibel instability? II. Simulations III. Conclusion Why Weibel instability? The
Magnetic fields generated by the Weibel Instability C. M. Ryu POSTECH, KOREA FFP14 Marseille 14.7.15-7.18 Outline I. Why Weibel instability? II. Simulations III. Conclusion Why Weibel instability? The
Suppressing the Cooling Flows in Massive Galaxies with Turbulent Stirring
 Snow Cluster 2018 Suppressing the Cooling Flows in Massive Galaxies with Turbulent Stirring Kung-Yi Su TAPIR, California Institute of Technology Collaborators Prof. Philip F. Hopkins Chris Hayward Prof.
Snow Cluster 2018 Suppressing the Cooling Flows in Massive Galaxies with Turbulent Stirring Kung-Yi Su TAPIR, California Institute of Technology Collaborators Prof. Philip F. Hopkins Chris Hayward Prof.
Enrico Fermi School Varenna Cool Cores and Mergers in Clusters Lecture 3
 Enrico Fermi School Varenna Cool Cores and Mergers in Clusters Lecture 3 Craig Sarazin Dept. of Astronomy University of Virginia A85 Chandra (X-ray) Cluster Merger Simulation Cool Cores in Clusters Central
Enrico Fermi School Varenna Cool Cores and Mergers in Clusters Lecture 3 Craig Sarazin Dept. of Astronomy University of Virginia A85 Chandra (X-ray) Cluster Merger Simulation Cool Cores in Clusters Central
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations. simulations of galaxy and structure formation
 Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 11 26 / Colloquium University of Victoria Outline 1 Cosmic
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 11 26 / Colloquium University of Victoria Outline 1 Cosmic
Magnetic Field in Galaxies and clusters
 Magnetic Field in Galaxies and clusters Kandaswamy Subramanian Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.0/27 Plan Observing
Magnetic Field in Galaxies and clusters Kandaswamy Subramanian Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.0/27 Plan Observing
Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies
 Lecture 4: Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies Rainer Beck, MPIfR Bonn Generation and amplification of cosmic magnetic fields Stage 1: Field seeding Stage 2: Field amplification Stage 3: Coherent field
Lecture 4: Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies Rainer Beck, MPIfR Bonn Generation and amplification of cosmic magnetic fields Stage 1: Field seeding Stage 2: Field amplification Stage 3: Coherent field
Amplification of magnetic fields from turbulence in the early Universe
 Amplification of magnetic fields from turbulence in the early Universe Jacques M. Wagstaff 1 arxiv:1304.4723 Robi Banerjee 1, Dominik Schleicher 2, Günter Sigl 3 1 Hamburg University 2 Institut für Astrophysik,
Amplification of magnetic fields from turbulence in the early Universe Jacques M. Wagstaff 1 arxiv:1304.4723 Robi Banerjee 1, Dominik Schleicher 2, Günter Sigl 3 1 Hamburg University 2 Institut für Astrophysik,
Amplification of magnetic fields in core collapse
 Amplification of magnetic fields in core collapse Miguel Àngel Aloy Torás, Pablo Cerdá-Durán, Thomas Janka, Ewald Müller, Martin Obergaulinger, Tomasz Rembiasz Universitat de València; Max-Planck-Institut
Amplification of magnetic fields in core collapse Miguel Àngel Aloy Torás, Pablo Cerdá-Durán, Thomas Janka, Ewald Müller, Martin Obergaulinger, Tomasz Rembiasz Universitat de València; Max-Planck-Institut
Turbulent Magnetic Helicity Transport and the Rapid Growth of Large Scale Magnetic Fields
 Turbulent Magnetic Helicity Transport and the Rapid Growth of Large Scale Magnetic Fields Jungyeon Cho Dmitry Shapovalov MWMF Madison, Wisconsin April 2012 The Large Scale Dynamo The accumulation of magnetic
Turbulent Magnetic Helicity Transport and the Rapid Growth of Large Scale Magnetic Fields Jungyeon Cho Dmitry Shapovalov MWMF Madison, Wisconsin April 2012 The Large Scale Dynamo The accumulation of magnetic
Feedback in Galaxy Clusters
 Feedback in Galaxy Clusters Brian Morsony University of Maryland 1 Not talking about Galaxy-scale feedback Local accretion disk feedback 2 Outline Galaxy cluster properties Cooling flows the need for feedback
Feedback in Galaxy Clusters Brian Morsony University of Maryland 1 Not talking about Galaxy-scale feedback Local accretion disk feedback 2 Outline Galaxy cluster properties Cooling flows the need for feedback
Gianluca Gregori 9 August 2017 TeVPA
 Cosmological magnetic fields and particle acceleration in the laboratory Gianluca Gregori 9 August 2017 TeVPA Magnetic fields are measured in ICM Magnetic Field Measu galaxies and cluster of galaxies Kronberg
Cosmological magnetic fields and particle acceleration in the laboratory Gianluca Gregori 9 August 2017 TeVPA Magnetic fields are measured in ICM Magnetic Field Measu galaxies and cluster of galaxies Kronberg
Cosmic Ray acceleration in clusters of galaxies. Gianfranco Brunetti. Istituto di Radioastronomia INAF, Bologna, ITALY
 Cosmic Ray acceleration in clusters of galaxies Gianfranco Brunetti Istituto di Radioastronomia INAF, Bologna, ITALY Outline NT components (CRe,CRp,B) in galaxy clusters : observations Physics and dynamics
Cosmic Ray acceleration in clusters of galaxies Gianfranco Brunetti Istituto di Radioastronomia INAF, Bologna, ITALY Outline NT components (CRe,CRp,B) in galaxy clusters : observations Physics and dynamics
Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields
 Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Ellen Zweibel zweibel@astro.wisc.edu Departments of Astronomy & Physics University of Wisconsin, Madison and Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical
Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Ellen Zweibel zweibel@astro.wisc.edu Departments of Astronomy & Physics University of Wisconsin, Madison and Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 19 Sep 2011
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 19 Sep 2011 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 19 Sep 2011](/thumbs/95/125570482.jpg) Space Science Reviews manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Magnetic fields in the Large-Scale Structure of the Universe D. Ryu D. R. G. Schleicher R. A. Treumann C. G. Tsagas L. M. Widrow arxiv:1109.4055v1
Space Science Reviews manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Magnetic fields in the Large-Scale Structure of the Universe D. Ryu D. R. G. Schleicher R. A. Treumann C. G. Tsagas L. M. Widrow arxiv:1109.4055v1
Radio relis (and halos) in galaxy clusters
 Radio relis (and halos) in galaxy clusters Matthias Hoeft Thüringer Landessternwarte Tautenburg - overall spectrum of relics - relic statistics - an unusual radio halo Radio relic: the textbook example
Radio relis (and halos) in galaxy clusters Matthias Hoeft Thüringer Landessternwarte Tautenburg - overall spectrum of relics - relic statistics - an unusual radio halo Radio relic: the textbook example
SKA AND THE COSMOLOGICAL EVOLUTION OF CLUSTER MAGNETIC FIELDS
 SKA AND THE COSMOLOGICAL EVOLUTION OF CLUSTER MAGNETIC FIELDS MARTIN KRAUSE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE, UNIVERSITÄTSSTERNWARTE MÜNCHEN & MAX-PLANCK-INSTITUT FÜR EXTRATERRESTRISCHE PHYSIK COLLABORATORS: PAUL
SKA AND THE COSMOLOGICAL EVOLUTION OF CLUSTER MAGNETIC FIELDS MARTIN KRAUSE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE, UNIVERSITÄTSSTERNWARTE MÜNCHEN & MAX-PLANCK-INSTITUT FÜR EXTRATERRESTRISCHE PHYSIK COLLABORATORS: PAUL
the ICM Power Spectrum:
 the ICM Power Spectrum: probing the gas physics of galaxy clusters Massimo Gaspari Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Collaborators: E. Churazov, D. Nagai, E. Lau, I. Zhuravleva, R. Sunyaev Power Spectrum
the ICM Power Spectrum: probing the gas physics of galaxy clusters Massimo Gaspari Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Collaborators: E. Churazov, D. Nagai, E. Lau, I. Zhuravleva, R. Sunyaev Power Spectrum
COSMOLOGICAL SHOCKS IN ADAPTIVE MESH REFINEMENT SIMULATIONS AND THE ACCELERATION OF COSMIC RAYS
 The Astrophysical Journal, 689:1063Y1077, 2008 December 20 # 2008. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. COSMOLOGICAL SHOCKS IN ADAPTIVE MESH REFINEMENT SIMULATIONS
The Astrophysical Journal, 689:1063Y1077, 2008 December 20 # 2008. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. COSMOLOGICAL SHOCKS IN ADAPTIVE MESH REFINEMENT SIMULATIONS
Fermi-LAT Analysis of the Coma Cluster
 Fermi-LAT Analysis of the Coma Cluster a Fabio Zandanel GRAPPA Institute University of Amsterdam f.zandanel@uva.nl In collaboration with S. Ando (GRAPPA) 18 th Symposium on Astroparticle Physics in the
Fermi-LAT Analysis of the Coma Cluster a Fabio Zandanel GRAPPA Institute University of Amsterdam f.zandanel@uva.nl In collaboration with S. Ando (GRAPPA) 18 th Symposium on Astroparticle Physics in the
Fluctuation dynamo amplified by intermittent shear bursts
 by intermittent Thanks to my collaborators: A. Busse (U. Glasgow), W.-C. Müller (TU Berlin) Dynamics Days Europe 8-12 September 2014 Mini-symposium on Nonlinear Problems in Plasma Astrophysics Introduction
by intermittent Thanks to my collaborators: A. Busse (U. Glasgow), W.-C. Müller (TU Berlin) Dynamics Days Europe 8-12 September 2014 Mini-symposium on Nonlinear Problems in Plasma Astrophysics Introduction
The Physics of Collisionless Accretion Flows. Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley)
 The Physics of Collisionless Accretion Flows Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Accretion Disks: Physical Picture Simple Consequences of Mass, Momentum, & Energy Conservation Matter Inspirals on Approximately
The Physics of Collisionless Accretion Flows Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Accretion Disks: Physical Picture Simple Consequences of Mass, Momentum, & Energy Conservation Matter Inspirals on Approximately
Probing RMs due to Magnetic Fields in the Cosmic Web
 Probing RMs due to Magnetic Fields in the Cosmic Web Takuya Akahori JSPS Postdoctoral Fellow for Research Abroad Sydney Institute for Astronomy, The University of Sydney Japan SKA Consortium Cosmic Magnetism
Probing RMs due to Magnetic Fields in the Cosmic Web Takuya Akahori JSPS Postdoctoral Fellow for Research Abroad Sydney Institute for Astronomy, The University of Sydney Japan SKA Consortium Cosmic Magnetism
CHAPTER 4. Basics of Fluid Dynamics
 CHAPTER 4 Basics of Fluid Dynamics What is a fluid? A fluid is a substance that can flow, has no fixed shape, and offers little resistance to an external stress In a fluid the constituent particles (atoms,
CHAPTER 4 Basics of Fluid Dynamics What is a fluid? A fluid is a substance that can flow, has no fixed shape, and offers little resistance to an external stress In a fluid the constituent particles (atoms,
Beyond Ideal MHD. Nick Murphy. Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics. February 8, 2016
 Beyond Ideal MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 8, 2016 These lecture notes are largely based on Plasma Physics for Astrophysics by
Beyond Ideal MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 8, 2016 These lecture notes are largely based on Plasma Physics for Astrophysics by
Plasma Physics for Astrophysics
 - ' ' * ' Plasma Physics for Astrophysics RUSSELL M. KULSRUD PRINCETON UNIVERSITY E;RESS '. ' PRINCETON AND OXFORD,, ', V. List of Figures Foreword by John N. Bahcall Preface Chapter 1. Introduction 1
- ' ' * ' Plasma Physics for Astrophysics RUSSELL M. KULSRUD PRINCETON UNIVERSITY E;RESS '. ' PRINCETON AND OXFORD,, ', V. List of Figures Foreword by John N. Bahcall Preface Chapter 1. Introduction 1
The Effects of Anisotropic Transport on Dilute Astrophysical Plasmas Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley)
 The Effects of Anisotropic Transport on Dilute Astrophysical Plasmas Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) in collaboration with Ian Parrish, Prateek Sharma, Jim Stone, Greg Hammett Hydra A w/ Chandra Galactic
The Effects of Anisotropic Transport on Dilute Astrophysical Plasmas Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) in collaboration with Ian Parrish, Prateek Sharma, Jim Stone, Greg Hammett Hydra A w/ Chandra Galactic
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 29 Jan 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 29 Jan 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 29 Jan 2014](/thumbs/72/66329558.jpg) International Journal of Modern Physics D c World Scientific Publishing Company arxiv:1401.7519v1 [astro-ph.co] 29 Jan 2014 COSMIC RAYS IN GALAXY CLUSTERS AND THEIR NON-THERMAL EMISSION GIANFRANCO BRUNETTI
International Journal of Modern Physics D c World Scientific Publishing Company arxiv:1401.7519v1 [astro-ph.co] 29 Jan 2014 COSMIC RAYS IN GALAXY CLUSTERS AND THEIR NON-THERMAL EMISSION GIANFRANCO BRUNETTI
Dynamo on the OMEGA laser and kinetic problems of proton radiography
 Dynamo on the OMEGA laser and kinetic problems of proton radiography Archie Bott, Alex Rigby, Tom White, Petros Tzeferacos, Don Lamb, Gianluca Gregori, Alex Schekochihin (and many others ) 2 th August
Dynamo on the OMEGA laser and kinetic problems of proton radiography Archie Bott, Alex Rigby, Tom White, Petros Tzeferacos, Don Lamb, Gianluca Gregori, Alex Schekochihin (and many others ) 2 th August
Production of helical magnetic fields during baryogenesis
 Production of helical magnetic fields during baryogenesis Francesc Ferrer Washington University in Saint Louis ferrer@wustl.edu NORDITA. June 23, 25 Outline Introduction: Observations of Magnetic Fields
Production of helical magnetic fields during baryogenesis Francesc Ferrer Washington University in Saint Louis ferrer@wustl.edu NORDITA. June 23, 25 Outline Introduction: Observations of Magnetic Fields
MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE UNIVERSE
 ARTICLE MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE UNIVERSE KANDASWAMY SUBRAMANIAN* The origin and maintenance of large scale magnetic fields in the Universe is discussed. A popular idea is that cosmic batteries generate
ARTICLE MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE UNIVERSE KANDASWAMY SUBRAMANIAN* The origin and maintenance of large scale magnetic fields in the Universe is discussed. A popular idea is that cosmic batteries generate
Hydra A (x-ray) Perseus ` (optical)
 The Biermann Lectures: Adventures in Theoretical Astrophysics I: The Physics of Galaxy Cluster Plasmas Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) w/ Mike McCourt, Ian Parrish, Prateek Sharma Perseus ` (optical) Hydra
The Biermann Lectures: Adventures in Theoretical Astrophysics I: The Physics of Galaxy Cluster Plasmas Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) w/ Mike McCourt, Ian Parrish, Prateek Sharma Perseus ` (optical) Hydra
Reduced MHD. Nick Murphy. Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics. February 19, 2014
 Reduced MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 19, 2014 These lecture notes are largely based on Lectures in Magnetohydrodynamics by Dalton
Reduced MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 19, 2014 These lecture notes are largely based on Lectures in Magnetohydrodynamics by Dalton
Non-Thermal Processes in Cosmological Simulations
 Space Sci Rev (2008) 134: 311 335 DOI 10.1007/s11214-008-9319-2 Non-Thermal Processes in Cosmological Simulations K. Dolag A.M. Bykov A. Diaferio Received: 17 September 2007 / Accepted: 7 November 2007
Space Sci Rev (2008) 134: 311 335 DOI 10.1007/s11214-008-9319-2 Non-Thermal Processes in Cosmological Simulations K. Dolag A.M. Bykov A. Diaferio Received: 17 September 2007 / Accepted: 7 November 2007
Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays I
 Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays I John Linsley (PRL 10 (1963) 146) reports on the detection in Vulcano Ranch of an air shower of energy above 1020 ev. Problem: the microwave background radiation is discovered
Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays I John Linsley (PRL 10 (1963) 146) reports on the detection in Vulcano Ranch of an air shower of energy above 1020 ev. Problem: the microwave background radiation is discovered
Basics of MHD. Kandaswamy Subramanian a. Pune , India. a Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics,
 Basics of MHD Kandaswamy Subramanian a a Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. The magnetic Universe, Feb 16, 2015 p.0/27 Plan Magnetic fields in Astrophysics MHD
Basics of MHD Kandaswamy Subramanian a a Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. The magnetic Universe, Feb 16, 2015 p.0/27 Plan Magnetic fields in Astrophysics MHD
Linear and non-linear evolution of the gyroresonance instability in Cosmic Rays
 Linear and non-linear evolution of the gyroresonance instability in Cosmic Rays DESY Summer Student Programme, 2016 Olga Lebiga Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv, Ukraine Supervisors Reinaldo
Linear and non-linear evolution of the gyroresonance instability in Cosmic Rays DESY Summer Student Programme, 2016 Olga Lebiga Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv, Ukraine Supervisors Reinaldo
Simulations of magnetic fields in core collapse on small and large scales
 Simulations of magnetic fields in core collapse on small and large scales Miguel Ángel Aloy Torás, Pablo Cerdá-Durán, Thomas Janka, Ewald Müller, Martin Obergaulinger, Tomasz Rembiasz CAMAP, Departament
Simulations of magnetic fields in core collapse on small and large scales Miguel Ángel Aloy Torás, Pablo Cerdá-Durán, Thomas Janka, Ewald Müller, Martin Obergaulinger, Tomasz Rembiasz CAMAP, Departament
origin of large scale magnetic fields: physics of the early Universe? plasma astrophysics in the late Universe?
 Magnetic fields at > Galactic scales Martin Lemoine Institut d Astrophysique de Paris CNRS, Université Pierre & Marie Curie Questions related to large scale magnetic fields origin of large scale magnetic
Magnetic fields at > Galactic scales Martin Lemoine Institut d Astrophysique de Paris CNRS, Université Pierre & Marie Curie Questions related to large scale magnetic fields origin of large scale magnetic
Dynamics of galaxy clusters A radio perspective
 Dynamics of galaxy clusters A radio perspective Tiziana Venturi, INAF, Istituto di Radioastronomia Collaborators S. Giacintucci, D. Dallacasa, R. Kale, G. Brunetti, R. Cassano, M. Rossetti GEE 3 Padova,
Dynamics of galaxy clusters A radio perspective Tiziana Venturi, INAF, Istituto di Radioastronomia Collaborators S. Giacintucci, D. Dallacasa, R. Kale, G. Brunetti, R. Cassano, M. Rossetti GEE 3 Padova,
COSMIC-RAY DRIVEN MAGNETIC FIELD DYNAMO IN GALAXIES
 COSMIC-RAY DRIVEN MAGNETIC FIELD DYNAMO IN GALAXIES Michał Hanasz, Centre for Astronomy Nicolaus Copernicus University, Toruń MAGNETIC FIELDS IN SPIRAL GALAXIES - RADIO OBSERVATIONS M51 NGC891 A. Fletcher
COSMIC-RAY DRIVEN MAGNETIC FIELD DYNAMO IN GALAXIES Michał Hanasz, Centre for Astronomy Nicolaus Copernicus University, Toruń MAGNETIC FIELDS IN SPIRAL GALAXIES - RADIO OBSERVATIONS M51 NGC891 A. Fletcher
Mixing in Highly Compressible Turbulence
 Mixing in Highly Compressible Turbulence Liubin Pan Evan Scannapieco School of Earth and Space Exploration Arizona State University Astrophysical motivation: Heavy elements from supernova and stellar winds
Mixing in Highly Compressible Turbulence Liubin Pan Evan Scannapieco School of Earth and Space Exploration Arizona State University Astrophysical motivation: Heavy elements from supernova and stellar winds
The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters
 IAU Joint Discussion # 10 Sydney, July, 2003 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al 2003 > 105
IAU Joint Discussion # 10 Sydney, July, 2003 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al 2003 > 105
X-ray and radio observations of the radio relic galaxy clusters 1RXS J and RXC J
 X-ray and radio observations of the radio relic galaxy clusters 1RXS J0603.3+4214 and RXC J1053.7+5453 Motokazu Takizawa (Yamagata University) Itahana, Takizawa, Akamatsu et al. (2015), PASJ, 67, 113 Itahana,
X-ray and radio observations of the radio relic galaxy clusters 1RXS J0603.3+4214 and RXC J1053.7+5453 Motokazu Takizawa (Yamagata University) Itahana, Takizawa, Akamatsu et al. (2015), PASJ, 67, 113 Itahana,
Cosmic-ray Acceleration and Current-Driven Instabilities
 Cosmic-ray Acceleration and Current-Driven Instabilities B. Reville Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg Sep 17 2009, KITP J.G. Kirk, P. Duffy, S.O Sullivan, Y. Ohira, F. Takahara Outline Analysis
Cosmic-ray Acceleration and Current-Driven Instabilities B. Reville Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg Sep 17 2009, KITP J.G. Kirk, P. Duffy, S.O Sullivan, Y. Ohira, F. Takahara Outline Analysis
Radio Continuum: Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields. Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn
 Radio Continuum: Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn Synchrotron emission Beam angle: Ψ/2=1/γ=E o /E Radio continuum tools to study GeV Cosmic ray electrons (CRE) Synchrotron spectrum:
Radio Continuum: Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn Synchrotron emission Beam angle: Ψ/2=1/γ=E o /E Radio continuum tools to study GeV Cosmic ray electrons (CRE) Synchrotron spectrum:
Simulating magnetic fields in structure formation
 Simulating magnetic fields in structure formation USM / MPE / MPA Harald Lesch & Klaus Dolag Annette Geng, Federico Stasyszyn & Marcus Beck July, 2012 (Mainz) Alexander Beck Magnetic fields in galaxies
Simulating magnetic fields in structure formation USM / MPE / MPA Harald Lesch & Klaus Dolag Annette Geng, Federico Stasyszyn & Marcus Beck July, 2012 (Mainz) Alexander Beck Magnetic fields in galaxies
PoS(EXTRA-RADSUR2015)063
 Constraining magnetic fields and particle acceleration processes in galaxy clusters: a joint VLA/LOFAR view on Coma and SKA perspectives Hamburger Sternwarte,Universität Hamburg, Gojenbergsweg 112,21029
Constraining magnetic fields and particle acceleration processes in galaxy clusters: a joint VLA/LOFAR view on Coma and SKA perspectives Hamburger Sternwarte,Universität Hamburg, Gojenbergsweg 112,21029
Mergers and Radio Sources in Abell 3667 and Abell 2061
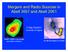 Mergers and Radio Sources in Abell 3667 and Abell 2061 Craig Sarazin University of Virginia A3667 XMM X-ray image and radio contours SLAM Simulation of A2061 Collaborators Alexis Finoguenov (MPE, UMBC)
Mergers and Radio Sources in Abell 3667 and Abell 2061 Craig Sarazin University of Virginia A3667 XMM X-ray image and radio contours SLAM Simulation of A2061 Collaborators Alexis Finoguenov (MPE, UMBC)
Killing Dwarfs with Hot Pancakes. Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) with Houjun Mo, Xiaohu Yang & Neal Katz
 Killing Dwarfs with Hot Pancakes Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) with Houjun Mo, Xiaohu Yang & Neal Katz The Paradigm... SN feedback AGN feedback The halo mass function is much steeper than luminosity function
Killing Dwarfs with Hot Pancakes Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) with Houjun Mo, Xiaohu Yang & Neal Katz The Paradigm... SN feedback AGN feedback The halo mass function is much steeper than luminosity function
Cosmic Rays in Galaxy Clusters Simulations and Reality
 Simulations and Reality 1,2 in collaboration with Torsten Enßlin 3, Volker Springel 3, Anders Pinzke 4, Nick Battaglia 1, Jon Sievers 1, Dick Bond 1 1 Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Canada
Simulations and Reality 1,2 in collaboration with Torsten Enßlin 3, Volker Springel 3, Anders Pinzke 4, Nick Battaglia 1, Jon Sievers 1, Dick Bond 1 1 Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Canada
Cosmic Rays, Photons and Neutrinos
 Cosmic Rays, Photons and Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline Plan of the lectures: Cosmic rays Galactic cosmic rays Basic observations Acceleration Supernova remnants Problems
Cosmic Rays, Photons and Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline Plan of the lectures: Cosmic rays Galactic cosmic rays Basic observations Acceleration Supernova remnants Problems
Lower bound on the extragalactic magnetic field
 Lower bound on the extragalactic magnetic field Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Dolag, MK, Ostapchenko, Tomàs 10 Neronov, Semikoz, MK, Ostapchenko, Elyiv 10 Introduction Mean free path of photons
Lower bound on the extragalactic magnetic field Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Dolag, MK, Ostapchenko, Tomàs 10 Neronov, Semikoz, MK, Ostapchenko, Elyiv 10 Introduction Mean free path of photons
Q: Why do the Sun and planets have magnetic fields?
 Q: Why do the Sun and planets have magnetic fields? Dana Longcope Montana State University w/ liberal borrowing from Bagenal, Stanley, Christensen, Schrijver, Charbonneau, Q: Why do the Sun and planets
Q: Why do the Sun and planets have magnetic fields? Dana Longcope Montana State University w/ liberal borrowing from Bagenal, Stanley, Christensen, Schrijver, Charbonneau, Q: Why do the Sun and planets
Feedback from growth of supermassive black holes
 Research Collection Other Conference Item Feedback from growth of supermassive black holes Author(s): Begelman, Mitchell C.; Ruszkowksi, Mateusz Publication Date: 2003 Permanent Link: https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-a-004585094
Research Collection Other Conference Item Feedback from growth of supermassive black holes Author(s): Begelman, Mitchell C.; Ruszkowksi, Mateusz Publication Date: 2003 Permanent Link: https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-a-004585094
Giant cosmic tsunamis: the impact of shocks and turbulence on galaxy evolution
 Giant cosmic tsunamis: the impact of shocks and turbulence on galaxy evolution Andra Stroe ESO Fellow astroe@eso.org Twitter: @Andra_Stroe www.eso.org/~astroe D. Sobral, M. J. Jee, W. Dawson, H. Hoekstra,
Giant cosmic tsunamis: the impact of shocks and turbulence on galaxy evolution Andra Stroe ESO Fellow astroe@eso.org Twitter: @Andra_Stroe www.eso.org/~astroe D. Sobral, M. J. Jee, W. Dawson, H. Hoekstra,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 10 Feb 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 10 Feb 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 10 Feb 2015](/thumbs/88/115586675.jpg) Journal of the Korean Astronomical Society http://dx.doi.org/10.5303/jkas.2015.48.2.1 48: 1 9, 2015 April pissn: 1225-4614 eissn: 2288-890X c 2015. The Korean Astronomical Society. All rights reserved.
Journal of the Korean Astronomical Society http://dx.doi.org/10.5303/jkas.2015.48.2.1 48: 1 9, 2015 April pissn: 1225-4614 eissn: 2288-890X c 2015. The Korean Astronomical Society. All rights reserved.
Title: Filaments of Galaxies as a Clue to the Origin of Ultra-High-Energy Cosmic Rays (Short Title: UHECRs and Filaments of Galaxies)
 Manuscript Template FRONT MATTER Title: Filaments of Galaxies as a Clue to the Origin of Ultra-High-Energy Cosmic Rays (Short Title: UHECRs and Filaments of Galaxies) Summary (or teaser): There are filaments
Manuscript Template FRONT MATTER Title: Filaments of Galaxies as a Clue to the Origin of Ultra-High-Energy Cosmic Rays (Short Title: UHECRs and Filaments of Galaxies) Summary (or teaser): There are filaments
Opportunities in Plasma Astrophysics with ngvla
 Opportunities in Plasma Astrophysics with ngvla Hui Li Los Alamos National Laboratory On behalf of ngvla Plasma Astrophysics Science Working Group Tim Bastian (NRAO), Arnold Benz (ETH), Paul Cassak (WVU),
Opportunities in Plasma Astrophysics with ngvla Hui Li Los Alamos National Laboratory On behalf of ngvla Plasma Astrophysics Science Working Group Tim Bastian (NRAO), Arnold Benz (ETH), Paul Cassak (WVU),
New Forms of Convection in Galaxy Cluster Plasmas (i.e., how do galaxy clusters boil?)
 New Forms of Convection in Galaxy Cluster Plasmas (i.e., how do galaxy clusters boil?) Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Hydra A w/ Chandra in collaboration with Ian Parrish Prateek Sharma Overview Hot Plasma
New Forms of Convection in Galaxy Cluster Plasmas (i.e., how do galaxy clusters boil?) Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Hydra A w/ Chandra in collaboration with Ian Parrish Prateek Sharma Overview Hot Plasma
The MRI in a Collisionless Plasma
 The MRI in a Collisionless Plasma Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Collaborators: Prateek Sharma, Greg Hammett, Jim Stone Modes of Accretion thin disk: energy radiated away (relevant to star & planet formation,
The MRI in a Collisionless Plasma Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Collaborators: Prateek Sharma, Greg Hammett, Jim Stone Modes of Accretion thin disk: energy radiated away (relevant to star & planet formation,
Fluid Dynamics. Massimo Ricotti. University of Maryland. Fluid Dynamics p.1/14
 Fluid Dynamics p.1/14 Fluid Dynamics Massimo Ricotti ricotti@astro.umd.edu University of Maryland Fluid Dynamics p.2/14 The equations of fluid dynamics are coupled PDEs that form an IVP (hyperbolic). Use
Fluid Dynamics p.1/14 Fluid Dynamics Massimo Ricotti ricotti@astro.umd.edu University of Maryland Fluid Dynamics p.2/14 The equations of fluid dynamics are coupled PDEs that form an IVP (hyperbolic). Use
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 18 Oct 2009
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 18 Oct 2009 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 18 Oct 2009](/thumbs/88/115478020.jpg) draft of October 19, 2009 arxiv:0910.3361v1 [astro-ph.he] 18 Oct 2009 Intergalactic Magnetic Field and Arrival Direction of Ultra-High-Energy Protons Dongsu Ryu 1,4, Santabrata Das 2, and Hyesung Kang
draft of October 19, 2009 arxiv:0910.3361v1 [astro-ph.he] 18 Oct 2009 Intergalactic Magnetic Field and Arrival Direction of Ultra-High-Energy Protons Dongsu Ryu 1,4, Santabrata Das 2, and Hyesung Kang
Gravitational Stability of Fluids in a Phase Transition. Andreas Füglistaler. July 17, 2017
 Gravitational Stability of Fluids in a Phase Transition July 17, 2017 Füglistaler & Pfenniger 2015, 2016 and 2017 (in preparation) Motivation Physics Simulations Conclusions Solid H2 in the ISM Gravitational
Gravitational Stability of Fluids in a Phase Transition July 17, 2017 Füglistaler & Pfenniger 2015, 2016 and 2017 (in preparation) Motivation Physics Simulations Conclusions Solid H2 in the ISM Gravitational
Gamma-ray Observations of Galaxy Clusters!
 Gamma-ray Observations of Galaxy Clusters! a! Fabio Zandanel! (GRAPPA Institute University of Amsterdam)! f.zandanel@uva.nl! SnowCluster 2015 The Physics Of Galaxy Clusters! Snowbird (Utah, US) March 15-20,
Gamma-ray Observations of Galaxy Clusters! a! Fabio Zandanel! (GRAPPA Institute University of Amsterdam)! f.zandanel@uva.nl! SnowCluster 2015 The Physics Of Galaxy Clusters! Snowbird (Utah, US) March 15-20,
Heat Transport and Buoyancy Instabilities in Astrophysical Plasmas. Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley)
 Heat Transport and Buoyancy Instabilities in Astrophysical Plasmas Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Galaxy Cluster Hydra A w/ Chandra Surface of the Sun ~ 1 Million light-years Overview Microscopic Energy
Heat Transport and Buoyancy Instabilities in Astrophysical Plasmas Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Galaxy Cluster Hydra A w/ Chandra Surface of the Sun ~ 1 Million light-years Overview Microscopic Energy
Prof. dr. A. Achterberg, Astronomical Dept., IMAPP, Radboud Universiteit
 Prof. dr. A. Achterberg, Astronomical Dept., IMAPP, Radboud Universiteit Rough breakdown of MHD shocks Jump conditions: flux in = flux out mass flux: ρv n magnetic flux: B n Normal momentum flux: ρv n
Prof. dr. A. Achterberg, Astronomical Dept., IMAPP, Radboud Universiteit Rough breakdown of MHD shocks Jump conditions: flux in = flux out mass flux: ρv n magnetic flux: B n Normal momentum flux: ρv n
Creation and destruction of magnetic fields
 HAO/NCAR July 30 2007 Magnetic fields in the Universe Earth Magnetic field present for 3.5 10 9 years, much longer than Ohmic decay time ( 10 4 years) Strong variability on shorter time scales (10 3 years)
HAO/NCAR July 30 2007 Magnetic fields in the Universe Earth Magnetic field present for 3.5 10 9 years, much longer than Ohmic decay time ( 10 4 years) Strong variability on shorter time scales (10 3 years)
the self-regulated agn feedback loop: chaotic cold accretion
 the self-regulated agn feedback loop: chaotic cold accretion Massimo Gaspari Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics the self-regulated agn feedback loop: raining onto black holes Massimo Gaspari Max Planck
the self-regulated agn feedback loop: chaotic cold accretion Massimo Gaspari Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics the self-regulated agn feedback loop: raining onto black holes Massimo Gaspari Max Planck
Gasdynamical and radiative processes, gaseous halos
 Gasdynamical and radiative processes, gaseous halos Houjun Mo March 19, 2004 Since luminous objects, such as galaxies, are believed to form through the collapse of baryonic gas, it is important to understand
Gasdynamical and radiative processes, gaseous halos Houjun Mo March 19, 2004 Since luminous objects, such as galaxies, are believed to form through the collapse of baryonic gas, it is important to understand
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 10 Jun 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 10 Jun 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 10 Jun 2017](/thumbs/75/72505050.jpg) Journal of the Korean Astronomical Society https://doi.org/10.5303/jkas.2017.50.3.1 50: 1 11, 2017 June pissn: 1225-4614 eissn: 2288-890X c 2017. The Korean Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. http://jkas.kas.org
Journal of the Korean Astronomical Society https://doi.org/10.5303/jkas.2017.50.3.1 50: 1 11, 2017 June pissn: 1225-4614 eissn: 2288-890X c 2017. The Korean Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. http://jkas.kas.org
Magnetisation of Interstellar and Intergalactic Media: The Prospects of Low-Frequency Radio Astronomy DFG Research Unit
 Mainz, 9 July, 2012 Galactic and Intergalactic Magnetic Fields 1 Magnetisation of Interstellar and Intergalactic Media: The Prospects of Low-Frequency Radio Astronomy DFG Research Unit Mainz, 9 July, 2012
Mainz, 9 July, 2012 Galactic and Intergalactic Magnetic Fields 1 Magnetisation of Interstellar and Intergalactic Media: The Prospects of Low-Frequency Radio Astronomy DFG Research Unit Mainz, 9 July, 2012
Selected Topics in Plasma Astrophysics
 Selected Topics in Plasma Astrophysics Range of Astrophysical Plasmas and Relevant Techniques Stellar Winds (Lecture I) Thermal, Radiation, and Magneto-Rotational Driven Winds Connections to Other Areas
Selected Topics in Plasma Astrophysics Range of Astrophysical Plasmas and Relevant Techniques Stellar Winds (Lecture I) Thermal, Radiation, and Magneto-Rotational Driven Winds Connections to Other Areas
Observational Evidence of AGN Feedback
 10 de maio de 2012 Sumário Introduction AGN winds Galaxy outflows From the peak to the late evolution of AGN and quasars Mergers or secular evolution? The AGN feedback The interaction process between the
10 de maio de 2012 Sumário Introduction AGN winds Galaxy outflows From the peak to the late evolution of AGN and quasars Mergers or secular evolution? The AGN feedback The interaction process between the
The Expanding Universe
 Cosmology Expanding Universe History of the Universe Cosmic Background Radiation The Cosmological Principle Cosmology and General Relativity Dark Matter and Dark Energy Primitive Cosmology If the universe
Cosmology Expanding Universe History of the Universe Cosmic Background Radiation The Cosmological Principle Cosmology and General Relativity Dark Matter and Dark Energy Primitive Cosmology If the universe
Fundamentals of Turbulence
 Fundamentals of Turbulence Stanislav Boldyrev (University of Wisconsin - Madison) Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical Plasmas What is turbulence? No exact definition.
Fundamentals of Turbulence Stanislav Boldyrev (University of Wisconsin - Madison) Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical Plasmas What is turbulence? No exact definition.
Dynamos on galactic scales, or Dynamos around us.
 Dynamos on galactic scales, or Dynamos around us. Part IV. Cluster dynamos Anvar Shukurov School of Mathematics and Statistics, Newcastle University, U.K. Outline 1. Evidence for intracluster magnetic
Dynamos on galactic scales, or Dynamos around us. Part IV. Cluster dynamos Anvar Shukurov School of Mathematics and Statistics, Newcastle University, U.K. Outline 1. Evidence for intracluster magnetic
