PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS. ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP. NOTES: (references therein)
|
|
|
- Johnathan Briggs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP NOTES: (references therein) ICTP-SAIFR, October 7-18, 2013
2 Contents What is plasma? Why plasmas in astrophysics? Quasi neutrality Fluid approximation: MHD Eqs. Magnetic Force Magnetic Flux Freezing Applications
3 What is PLASMA? Gas with sufficient number of free charged particles (positive + negative) so that its behaviour dominated by electromagnetic forces. Even low ionization degree (~1%) : sufficient for gas to show electromagnetic properties (electrical conductivity ~ fully ionized gas).
4 Why Plasmas?
5 Why Plasmas in Astrophysics?
6 Exs. Astrophysical Plasmas
7 Exs. Astrophysical Plasmas
8 Exs. Astrophysical Plasmas
9 Exs. Astrophysical Plasmas
10 Exs. Astrophysical Plasmas
11 Importance of Plasmas Magnetized plasmas are present in almost all astrophysical objects They are crucial in: - star formation; late stages - solar and stellar activity - formation of jets and accretion disks - formation and propagation of cosmic rays - galaxy structure
12 Importance of Plasmas They are also crucial in: - ISM - molecular clouds - supernova remnants - proto-planetary disks - planetary nebulae - GRBs
13 Importance of Plasmas Their importance not well understood yet in: - stellar evolution - galaxy evolution - structure formation in the early Universe
14 Exs. Plasmas in Earth
15 Plasmas in Laboratory Major goal: Thermonuclear fusion (as in the interior of stars) production of energy!
16 Plasmas in Laboratory: TOKAMAK Controlled thermonuclear fusion experiments: still in progress
17 PLASMA: simple definition
18 PLASMA: Microscopic Definition
19 PLASMA: Quasi Neutrality Assume local charge concentration (δn e) according to Coulomb law: generates the electric field: E // provokes on the thermal random motion of electrons: flow with velocity v // : Solution: simple harmonic motion with plasma electron frequency that in the average neutralizes E // :
20 Quasi Neutrality - Plasma Frequency ω pe defines natural plasma frequency (neutralizes E effect) ıons oscilate with much << frequency (practically at rest in relation to els.) Any external electric field E applied with freq. ω < ω pe is unable to penetrate the plasma Debye length: E does not penetrate plasma if: ω < ω pe ou λ > λ D
21 PLASMA: Debye length (λ D ) λ D scale within which separation between charges can be felt : λ D Within sphere of radius (λ D ) charge neutrality is not valid: electrostatic external oscillations with λ λ D penetrate the sphere and feel the collective effects of the charges strongly damped (Landau damping) Electric Potential Field of a charge within plasma: has its action screened (or partially blocked) by cloud of charges
22 PLASMA: collective behavior
23 PLASMA: Quasi Neutrality Tpypical dimension of astrophysical plasmas: L>> λ D quase neutrality is valid Internal E fields: little important (neutralized by strong oscillations ω pe ) External E fields typically do not penetrate (ω << ω pe, λ > λ D ) Below: macroscopic description of a plasma as a fluid
24 Plasma Physics
25 Plasma Physics
26 Motion of a single charge
27 Motion of a single charge
28 Motion of a single charge
29 Motion of a single charge
30 Plasma Physics
31 Plasma Physics (ω ω pe )
32 Plasma Physics
33 Fluid description: MHD Macroscopic definition Macroscopic model: size and time scales are large enough possible to apply AVERAGES over microscopic quantities: colective plasma oscillations and collective cyclotron motions of ions and electrons
34 Fluid description: MHD Maxwell eqs. + hidrodynamics eqs. = Eqs. MHD +
35 Fluid description: MHD One-fluid approximation: (combining eqs. of motion of els. and ions)
36 MHD Equations Electric Resistivity:
37 Magnetic Induction Equation Advection: gas and magnetic field coupling (freezing) Viscosity: dissipation of the magnetic field Biermann Battery: only important for generation of B (dynamos) -> non null differential rotation (in general neglected)
38 MHD Equations: ± usual (magnetic induction) (Ampere, divergencia) Where magnetic resistivity: (cm 2 /s) Eq. of state to close the system:
39 Magnetic Force Tension Force Magnetic Pressure Force Dipole magnetic field of a star magnetosphere (ex. pulsar): tension = pressure magnetic = 0
40 IDEAL MHD Ratio between these two terms: Magnetic Reynolds number In astrophysical plasmas in general: R em >>1 ideal MHD: Exceptions: R em 1:Ex. Magnetic Reconnection resistive MHD
41 Ideal MHD B Flux Freezing With η = 0: =0 and Integrating over an open surface A surrounded by a closed contour S and using Stokes' theorem: B A v e ds The magnetic flux through A with closed contour that moves with the electron gas is CONSTANT (if perfectly conductive fluid) Concept of flux freezing Where d/dt is comoving derivative:
42 B Flux Freezing: ideal MHD Magnetic flux freezing: It means we can see the lines of force of B as "frozen" in the electron gas and moving along with the gas Any motion transverse to the lines of force of the magnetic field, carries them along with the fluid A fluid element that moves along a flux tube remains moving with it.
43 Is B flux freezing always valid? In astrophysical plasmas: flux freezing valid in general because L,v >>1 >> 1 BUT there are exceptions: Ex. 1) magnetic reconnection sites Ex. 2) star formation Ex. 3) dynamos: magnetic field generation
44 Is B flux freezing always valid? NO Ex. 1) magnetic reconnection sites: B flux does not conserve because ~1
45 Is B flux freezing always valid? NO Ex. 2) collapse of an interstellar cloud to form a star: Cloud: ρ gcm 3 B 10 4 G Star: ρ * 1gcm 3 B * =?? If we use ideal MHD B flux conservation : + mass conservation eq., we obtain: B * 10 9 G! BUT, observations: B * 10 3 G Therefore: There was no flux conservation! There were flux removal. What resistive process did that?
46 Self-Gravitating collapsing clouds Self-gravitating gas + central spherical potential (~1/r²) Non-turbulent Turbulent Subcritical core b=3, n=100 cm -3 t~ 40Myr Supercritical core Leão et al. 2013
47 MHD turbulent diffusion: new scenario In presence of turbulence: field lines reconnect fast (Lazarian & Vishniac 1999) and magnetic flux transport becomes efficient t t Lazarian 2005, 2012 Santos-Lima et al. 2010, 2012, 2013 de Gouveia Dal Pino et al. 2012
48 Self-Gravitating collapsing clouds Turbulent Reconnection Diffusion (Lazarian 06; Santos-Lima, de Gouveia Dal Pino, Lazarian 2010, 2012, 2013) Leão, dgdp, Santos-Lima, Lazarian 2013
49 Is B flux freezing always valid? NO Ex. 3) dynamo: generates magnetic fields: obviously does not conserve magnetic flux NON IDEAL MHD...+ new terms
50 Solar Dynamo Example Guerrero & de Gouveia Dal Pino 2008
51 Turbulent Dynamo in ICM Hydra Magnetic field is turbulent (Ensslin & Vogt 2005) Turbulent dynamo operates (Brandenburg & Subramanian 05) Dynamo amplifies seed fields (AGNs, galactic winds, mergers)
52 ICM - COLLISIONLESS Low density of IGM & ICM: ion Larmor radius R i << mean free path λ mfp ~ L R i ~10 5 km << l mfp ~ km ~ L In absence of collisions: p // p MHD: INADEQUATE Kinetic-MHD description:
53 Kinetic-MHD Turbulence in the ICM Solve: MHD equations with p ij + Conservation of magnetic momentum + adiabatic law = CGL condition (Chew, Goldberger & Low 1956):
54 Turbulent Dynamo in the ICM: Amplification of Cosmic Magnetic Fields Santos-Lima et al. 2013; Kowal et al. 2011
55 (few more examples)
56 +Aplications: (Ideal) MHD: Waves
57 Normal compressible fluids: Acoustic waves (release of free energy associated with non-uniform density or velocities) In plasmas: - Besides these: new modes appear Waves: modes with real frequencies
58 Perturbing MHD equations Hypotesis: B o, o, v o, p o : constant and uniform at equilibrium state Consider perturbations in plasma: l << L (dimension of the system)
59 Perturbing the system Physical quantity at equilibrium (order 0) f1(x,t): 1 st order perturbation: f1(x,t) << fo Neglect: v= v o + v 1, take v o = 0, denote v 1 = v
60 1 st order equations Coeficients of eqs. are constants: solution: If n imaginary and k real WAVE If n real and n>0 growth rate of INSTABILITY: f ~ exp (nt) If n complex wave with growing (or non-growing) amplitude with time If k real wave with constant amplitude in space If k imaginary wave with growing or damping amplitude in space
61 Dispersion relation n(k) v 1 v 2 v 3 Since these eqs. are homogeneous: solutions only if determinant of coefficients = 0 -> result dispersion relation n(k)
62 Taking eq. for v 2 This mode: Alfven wave
63 Alfven wave First described bt Alfven (1953): Alfven wave. Velocity perturbation transverse to plan k and Bo Propagates // Bo Key role in transmiting forces, like acoustic waves in non-magnetized gas Since motion transverse to B: lines of force are bent by the motion of the wave and a restauring force due to magnetic tension is exerted by lines (similar tension in a rope):
64 Magneto-acoustic Waves If we consider motions in direction 1 (// k and B): Velocity // k implies compression of the gas (resistance of pressure) 2 Velocity normal to B means compression of B lines (resistance of magnetic pressure) magnetic-acoustic wave (longitudinal to motion): k B o
65 Other aplications Shock waves Particle Acceleration (next lectures) Instabilities Magnetic Reconnection (next lectures) Winds Dynamos Turbulence Etc.
Plasma Physics for Astrophysics
 - ' ' * ' Plasma Physics for Astrophysics RUSSELL M. KULSRUD PRINCETON UNIVERSITY E;RESS '. ' PRINCETON AND OXFORD,, ', V. List of Figures Foreword by John N. Bahcall Preface Chapter 1. Introduction 1
- ' ' * ' Plasma Physics for Astrophysics RUSSELL M. KULSRUD PRINCETON UNIVERSITY E;RESS '. ' PRINCETON AND OXFORD,, ', V. List of Figures Foreword by John N. Bahcall Preface Chapter 1. Introduction 1
The Physics of Fluids and Plasmas
 The Physics of Fluids and Plasmas An Introduction for Astrophysicists ARNAB RAI CHOUDHURI CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface Acknowledgements xiii xvii Introduction 1 1. 3 1.1 Fluids and plasmas in the
The Physics of Fluids and Plasmas An Introduction for Astrophysicists ARNAB RAI CHOUDHURI CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface Acknowledgements xiii xvii Introduction 1 1. 3 1.1 Fluids and plasmas in the
Space Plasma Physics Thomas Wiegelmann, 2012
 Space Plasma Physics Thomas Wiegelmann, 2012 1. Basic Plasma Physics concepts 2. Overview about solar system plasmas Plasma Models 3. Single particle motion, Test particle model 4. Statistic description
Space Plasma Physics Thomas Wiegelmann, 2012 1. Basic Plasma Physics concepts 2. Overview about solar system plasmas Plasma Models 3. Single particle motion, Test particle model 4. Statistic description
Waves in plasma. Denis Gialis
 Waves in plasma Denis Gialis This is a short introduction on waves in a non-relativistic plasma. We will consider a plasma of electrons and protons which is fully ionized, nonrelativistic and homogeneous.
Waves in plasma Denis Gialis This is a short introduction on waves in a non-relativistic plasma. We will consider a plasma of electrons and protons which is fully ionized, nonrelativistic and homogeneous.
Why study plasma astrophysics?
 Why study plasma astrophysics? Nick Murphy and Xuening Bai Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics January 25, 2016 Today s plan Definition of a plasma Plasma astrophysics:
Why study plasma astrophysics? Nick Murphy and Xuening Bai Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics January 25, 2016 Today s plan Definition of a plasma Plasma astrophysics:
Space Physics. An Introduction to Plasmas and Particles in the Heliosphere and Magnetospheres. May-Britt Kallenrode. Springer
 May-Britt Kallenrode Space Physics An Introduction to Plasmas and Particles in the Heliosphere and Magnetospheres With 170 Figures, 9 Tables, Numerous Exercises and Problems Springer Contents 1. Introduction
May-Britt Kallenrode Space Physics An Introduction to Plasmas and Particles in the Heliosphere and Magnetospheres With 170 Figures, 9 Tables, Numerous Exercises and Problems Springer Contents 1. Introduction
Beyond Ideal MHD. Nick Murphy. Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics. February 8, 2016
 Beyond Ideal MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 8, 2016 These lecture notes are largely based on Plasma Physics for Astrophysics by
Beyond Ideal MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 8, 2016 These lecture notes are largely based on Plasma Physics for Astrophysics by
Macroscopic plasma description
 Macroscopic plasma description Macroscopic plasma theories are fluid theories at different levels single fluid (magnetohydrodynamics MHD) two-fluid (multifluid, separate equations for electron and ion
Macroscopic plasma description Macroscopic plasma theories are fluid theories at different levels single fluid (magnetohydrodynamics MHD) two-fluid (multifluid, separate equations for electron and ion
Plasma Astrophysics Chapter 1: Basic Concepts of Plasma. Yosuke Mizuno Institute of Astronomy National Tsing-Hua University
 Plasma Astrophysics Chapter 1: Basic Concepts of Plasma Yosuke Mizuno Institute of Astronomy National Tsing-Hua University What is a Plasma? A plasma is a quasi-neutral gas consisting of positive and negative
Plasma Astrophysics Chapter 1: Basic Concepts of Plasma Yosuke Mizuno Institute of Astronomy National Tsing-Hua University What is a Plasma? A plasma is a quasi-neutral gas consisting of positive and negative
Ideal Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD)
 Ideal Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 1, 2016 These lecture notes are largely based on Lectures in Magnetohydrodynamics
Ideal Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 1, 2016 These lecture notes are largely based on Lectures in Magnetohydrodynamics
Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters
 Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) with Hyesung Kang (Pusan Nat. U, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (Chungnam Nat. U.),
Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) with Hyesung Kang (Pusan Nat. U, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (Chungnam Nat. U.),
Dispersive Media, Lecture 7 - Thomas Johnson 1. Waves in plasmas. T. Johnson
 2017-02-14 Dispersive Media, Lecture 7 - Thomas Johnson 1 Waves in plasmas T. Johnson Introduction to plasmas as a coupled system Magneto-Hydro Dynamics, MHD Plasmas without magnetic fields Cold plasmas
2017-02-14 Dispersive Media, Lecture 7 - Thomas Johnson 1 Waves in plasmas T. Johnson Introduction to plasmas as a coupled system Magneto-Hydro Dynamics, MHD Plasmas without magnetic fields Cold plasmas
Linear and non-linear evolution of the gyroresonance instability in Cosmic Rays
 Linear and non-linear evolution of the gyroresonance instability in Cosmic Rays DESY Summer Student Programme, 2016 Olga Lebiga Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv, Ukraine Supervisors Reinaldo
Linear and non-linear evolution of the gyroresonance instability in Cosmic Rays DESY Summer Student Programme, 2016 Olga Lebiga Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv, Ukraine Supervisors Reinaldo
Analysis of Jeans Instability of Partially-Ionized. Molecular Cloud under Influence of Radiative. Effect and Electron Inertia
 Adv. Studies Theor. Phys., Vol. 5, 2011, no. 16, 755-764 Analysis of Jeans Instability of Partially-Ionized Molecular Cloud under Influence of Radiative Effect and Electron Inertia B. K. Dangarh Department
Adv. Studies Theor. Phys., Vol. 5, 2011, no. 16, 755-764 Analysis of Jeans Instability of Partially-Ionized Molecular Cloud under Influence of Radiative Effect and Electron Inertia B. K. Dangarh Department
Introduction to Plasma Physics
 Introduction to Plasma Physics Hartmut Zohm Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik 85748 Garching DPG Advanced Physics School The Physics of ITER Bad Honnef, 22.09.2014 A simplistic view on a Fusion Power
Introduction to Plasma Physics Hartmut Zohm Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik 85748 Garching DPG Advanced Physics School The Physics of ITER Bad Honnef, 22.09.2014 A simplistic view on a Fusion Power
Magnetohydrodynamic Waves
 Magnetohydrodynamic Waves Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 17, 2016 These slides are largely based off of 4.5 and 4.8 of The Physics of
Magnetohydrodynamic Waves Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 17, 2016 These slides are largely based off of 4.5 and 4.8 of The Physics of
2/8/16 Dispersive Media, Lecture 5 - Thomas Johnson 1. Waves in plasmas. T. Johnson
 2/8/16 Dispersive Media, Lecture 5 - Thomas Johnson 1 Waves in plasmas T. Johnson Introduction to plasma physics Magneto-Hydro Dynamics, MHD Plasmas without magnetic fields Cold plasmas Transverse waves
2/8/16 Dispersive Media, Lecture 5 - Thomas Johnson 1 Waves in plasmas T. Johnson Introduction to plasma physics Magneto-Hydro Dynamics, MHD Plasmas without magnetic fields Cold plasmas Transverse waves
Magnetic Reconnection in Laboratory, Astrophysical, and Space Plasmas
 Magnetic Reconnection in Laboratory, Astrophysical, and Space Plasmas Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics namurphy@cfa.harvard.edu http://www.cfa.harvard.edu/ namurphy/ November 18,
Magnetic Reconnection in Laboratory, Astrophysical, and Space Plasmas Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics namurphy@cfa.harvard.edu http://www.cfa.harvard.edu/ namurphy/ November 18,
Amplification of magnetic fields in core collapse
 Amplification of magnetic fields in core collapse Miguel Àngel Aloy Torás, Pablo Cerdá-Durán, Thomas Janka, Ewald Müller, Martin Obergaulinger, Tomasz Rembiasz Universitat de València; Max-Planck-Institut
Amplification of magnetic fields in core collapse Miguel Àngel Aloy Torás, Pablo Cerdá-Durán, Thomas Janka, Ewald Müller, Martin Obergaulinger, Tomasz Rembiasz Universitat de València; Max-Planck-Institut
Magnetohydrodynamic waves in a plasma
 Department of Physics Seminar 1b Magnetohydrodynamic waves in a plasma Author: Janez Kokalj Advisor: prof. dr. Tomaž Gyergyek Petelinje, April 2016 Abstract Plasma can sustain different wave phenomena.
Department of Physics Seminar 1b Magnetohydrodynamic waves in a plasma Author: Janez Kokalj Advisor: prof. dr. Tomaž Gyergyek Petelinje, April 2016 Abstract Plasma can sustain different wave phenomena.
Prof. dr. A. Achterberg, Astronomical Dept., IMAPP, Radboud Universiteit
 Prof. dr. A. Achterberg, Astronomical Dept., IMAPP, Radboud Universiteit Rough breakdown of MHD shocks Jump conditions: flux in = flux out mass flux: ρv n magnetic flux: B n Normal momentum flux: ρv n
Prof. dr. A. Achterberg, Astronomical Dept., IMAPP, Radboud Universiteit Rough breakdown of MHD shocks Jump conditions: flux in = flux out mass flux: ρv n magnetic flux: B n Normal momentum flux: ρv n
High-Energy Plasma Astrophysics and Next Generation Gamma-Ray Observatory Cherenkov Telescope Array
 High-Energy Plasma Astrophysics and Next Generation Gamma-Ray Observatory Cherenkov Telescope Array FAPESP CUNY Week, New York, November 2018 M82 Star Formation- Clouds-SNRturbulence connection Sun & Stars
High-Energy Plasma Astrophysics and Next Generation Gamma-Ray Observatory Cherenkov Telescope Array FAPESP CUNY Week, New York, November 2018 M82 Star Formation- Clouds-SNRturbulence connection Sun & Stars
Introduction. Chapter Plasma: definitions
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Plasma: definitions A plasma is a quasi-neutral gas of charged and neutral particles which exhibits collective behaviour. An equivalent, alternative definition: A plasma is a
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Plasma: definitions A plasma is a quasi-neutral gas of charged and neutral particles which exhibits collective behaviour. An equivalent, alternative definition: A plasma is a
Particle Acceleration by Reconnection and VHE emission Around Black Holes and Relativistic Jets
 Particle Acceleration by Reconnection and VHE emission Around Black Holes and Relativistic Jets Deciphering the Violent Universe, Playa del Carmen, December 11-15, 2017 Accretion disk coronae Star Formation
Particle Acceleration by Reconnection and VHE emission Around Black Holes and Relativistic Jets Deciphering the Violent Universe, Playa del Carmen, December 11-15, 2017 Accretion disk coronae Star Formation
The Physics of Collisionless Accretion Flows. Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley)
 The Physics of Collisionless Accretion Flows Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Accretion Disks: Physical Picture Simple Consequences of Mass, Momentum, & Energy Conservation Matter Inspirals on Approximately
The Physics of Collisionless Accretion Flows Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Accretion Disks: Physical Picture Simple Consequences of Mass, Momentum, & Energy Conservation Matter Inspirals on Approximately
Magnetic Fields in Astrophysics: Origins and Evolution. Kinwah Wu Mullard Space Science Laboratory University College London
 Magnetic Fields in Astrophysics: Origins and Evolution Kinwah Wu Mullard Space Science Laboratory University College London Maxwell s equations covariant form in flat space time Lorentz force equation:
Magnetic Fields in Astrophysics: Origins and Evolution Kinwah Wu Mullard Space Science Laboratory University College London Maxwell s equations covariant form in flat space time Lorentz force equation:
Basic plasma physics
 Basic plasma physics SPAT PG Lectures Jonathan Eastwood 10-14 October 2016 Aims Provide new PhD students in SPAT and the SPC section with an overview of the most important principles in space plasma physics,
Basic plasma physics SPAT PG Lectures Jonathan Eastwood 10-14 October 2016 Aims Provide new PhD students in SPAT and the SPC section with an overview of the most important principles in space plasma physics,
Reduced MHD. Nick Murphy. Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics. February 19, 2014
 Reduced MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 19, 2014 These lecture notes are largely based on Lectures in Magnetohydrodynamics by Dalton
Reduced MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 19, 2014 These lecture notes are largely based on Lectures in Magnetohydrodynamics by Dalton
20. Alfven waves. ([3], p ; [1], p ; Chen, Sec.4.18, p ) We have considered two types of waves in plasma:
![20. Alfven waves. ([3], p ; [1], p ; Chen, Sec.4.18, p ) We have considered two types of waves in plasma: 20. Alfven waves. ([3], p ; [1], p ; Chen, Sec.4.18, p ) We have considered two types of waves in plasma:](/thumbs/79/79935500.jpg) Phys780: Plasma Physics Lecture 20. Alfven Waves. 1 20. Alfven waves ([3], p.233-239; [1], p.202-237; Chen, Sec.4.18, p.136-144) We have considered two types of waves in plasma: 1. electrostatic Langmuir
Phys780: Plasma Physics Lecture 20. Alfven Waves. 1 20. Alfven waves ([3], p.233-239; [1], p.202-237; Chen, Sec.4.18, p.136-144) We have considered two types of waves in plasma: 1. electrostatic Langmuir
CHAPTER 4. Basics of Fluid Dynamics
 CHAPTER 4 Basics of Fluid Dynamics What is a fluid? A fluid is a substance that can flow, has no fixed shape, and offers little resistance to an external stress In a fluid the constituent particles (atoms,
CHAPTER 4 Basics of Fluid Dynamics What is a fluid? A fluid is a substance that can flow, has no fixed shape, and offers little resistance to an external stress In a fluid the constituent particles (atoms,
3D Reconnection of Weakly Stochastic Magnetic Field and its Implications
 3D Reconnection of Weakly Stochastic Magnetic Field and its Implications Alex Lazarian Astronomy Department and Center for Magnetic Self- Organization in Astrophysical and Laboratory Plasmas Collaboration:
3D Reconnection of Weakly Stochastic Magnetic Field and its Implications Alex Lazarian Astronomy Department and Center for Magnetic Self- Organization in Astrophysical and Laboratory Plasmas Collaboration:
Introduction to Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD)
 Introduction to Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) Tony Arber University of Warwick 4th SOLARNET Summer School on Solar MHD and Reconnection Aim Derivation of MHD equations from conservation laws Quasi-neutrality
Introduction to Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) Tony Arber University of Warwick 4th SOLARNET Summer School on Solar MHD and Reconnection Aim Derivation of MHD equations from conservation laws Quasi-neutrality
Physical Processes in Astrophysics
 Physical Processes in Astrophysics Huirong Yan Uni Potsdam & Desy Email: hyan@mail.desy.de 1 Reference Books: Plasma Physics for Astrophysics, Russell M. Kulsrud (2005) The Physics of Astrophysics, Frank
Physical Processes in Astrophysics Huirong Yan Uni Potsdam & Desy Email: hyan@mail.desy.de 1 Reference Books: Plasma Physics for Astrophysics, Russell M. Kulsrud (2005) The Physics of Astrophysics, Frank
magnetic reconnection as the cause of cosmic ray excess from the heliospheric tail
 magnetic reconnection as the cause of cosmic ray excess from the heliospheric tail Paolo Desiati 1,2 & Alexander Lazarian 2 1 IceCube Research Center 2 Department of Astronomy University of Wisconsin -
magnetic reconnection as the cause of cosmic ray excess from the heliospheric tail Paolo Desiati 1,2 & Alexander Lazarian 2 1 IceCube Research Center 2 Department of Astronomy University of Wisconsin -
COSMIC-RAY DRIVEN MAGNETIC FIELD DYNAMO IN GALAXIES
 COSMIC-RAY DRIVEN MAGNETIC FIELD DYNAMO IN GALAXIES Michał Hanasz, Centre for Astronomy Nicolaus Copernicus University, Toruń MAGNETIC FIELDS IN SPIRAL GALAXIES - RADIO OBSERVATIONS M51 NGC891 A. Fletcher
COSMIC-RAY DRIVEN MAGNETIC FIELD DYNAMO IN GALAXIES Michał Hanasz, Centre for Astronomy Nicolaus Copernicus University, Toruń MAGNETIC FIELDS IN SPIRAL GALAXIES - RADIO OBSERVATIONS M51 NGC891 A. Fletcher
Turbulence & particle acceleration in galaxy clusters. Gianfranco Brunetti
 Turbulence & particle acceleration in galaxy clusters Gianfranco Brunetti Mergers & CR-acceleration Cluster-cluster mergers are the most energetic events in the present Universe (10 64 erg/gyr). They can
Turbulence & particle acceleration in galaxy clusters Gianfranco Brunetti Mergers & CR-acceleration Cluster-cluster mergers are the most energetic events in the present Universe (10 64 erg/gyr). They can
Cosmic Ray Acceleration by Magnetic Reconnection
 Cosmic Ray Acceleration by Magnetic Reconnection Black Hole sources are Cosmic Ray (CR) accelerators and Very High Energy (VHE) emitters AGNs (blazars, radio-galaxies, seyferts) Black Hole Binaries (Microquasars)
Cosmic Ray Acceleration by Magnetic Reconnection Black Hole sources are Cosmic Ray (CR) accelerators and Very High Energy (VHE) emitters AGNs (blazars, radio-galaxies, seyferts) Black Hole Binaries (Microquasars)
Recapitulation: Questions on Chaps. 1 and 2 #A
 Recapitulation: Questions on Chaps. 1 and 2 #A Chapter 1. Introduction What is the importance of plasma physics? How are plasmas confined in the laboratory and in nature? Why are plasmas important in astrophysics?
Recapitulation: Questions on Chaps. 1 and 2 #A Chapter 1. Introduction What is the importance of plasma physics? How are plasmas confined in the laboratory and in nature? Why are plasmas important in astrophysics?
Gravitational Collapse and Star Formation
 Astrophysical Dynamics, VT 010 Gravitational Collapse and Star Formation Susanne Höfner Susanne.Hoefner@fysast.uu.se The Cosmic Matter Cycle Dense Clouds in the ISM Black Cloud Dense Clouds in the ISM
Astrophysical Dynamics, VT 010 Gravitational Collapse and Star Formation Susanne Höfner Susanne.Hoefner@fysast.uu.se The Cosmic Matter Cycle Dense Clouds in the ISM Black Cloud Dense Clouds in the ISM
Basics of MHD. Kandaswamy Subramanian a. Pune , India. a Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics,
 Basics of MHD Kandaswamy Subramanian a a Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. The magnetic Universe, Feb 16, 2015 p.0/27 Plan Magnetic fields in Astrophysics MHD
Basics of MHD Kandaswamy Subramanian a a Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. The magnetic Universe, Feb 16, 2015 p.0/27 Plan Magnetic fields in Astrophysics MHD
Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields
 Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Ellen Zweibel zweibel@astro.wisc.edu Departments of Astronomy & Physics University of Wisconsin, Madison and Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical
Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Ellen Zweibel zweibel@astro.wisc.edu Departments of Astronomy & Physics University of Wisconsin, Madison and Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical
Typical anisotropies introduced by geometry (not everything is spherically symmetric) temperature gradients magnetic fields electrical fields
 Lecture 6: Polarimetry 1 Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Fundamentals of Polarized Light 3 Descriptions of Polarized Light Polarized Light in the Universe Polarization indicates anisotropy
Lecture 6: Polarimetry 1 Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Fundamentals of Polarized Light 3 Descriptions of Polarized Light Polarized Light in the Universe Polarization indicates anisotropy
AST 553. Plasma Waves and Instabilities. Course Outline. (Dated: December 4, 2018)
 AST 553. Plasma Waves and Instabilities Course Outline (Dated: December 4, 2018) I. INTRODUCTION Basic concepts Waves in plasmas as EM field oscillations Maxwell s equations, Gauss s laws as initial conditions
AST 553. Plasma Waves and Instabilities Course Outline (Dated: December 4, 2018) I. INTRODUCTION Basic concepts Waves in plasmas as EM field oscillations Maxwell s equations, Gauss s laws as initial conditions
Simulations of magnetic fields in core collapse on small and large scales
 Simulations of magnetic fields in core collapse on small and large scales Miguel Ángel Aloy Torás, Pablo Cerdá-Durán, Thomas Janka, Ewald Müller, Martin Obergaulinger, Tomasz Rembiasz CAMAP, Departament
Simulations of magnetic fields in core collapse on small and large scales Miguel Ángel Aloy Torás, Pablo Cerdá-Durán, Thomas Janka, Ewald Müller, Martin Obergaulinger, Tomasz Rembiasz CAMAP, Departament
Plasma waves in the fluid picture I
 Plasma waves in the fluid picture I Langmuir oscillations and waves Ion-acoustic waves Debye length Ordinary electromagnetic waves General wave equation General dispersion equation Dielectric response
Plasma waves in the fluid picture I Langmuir oscillations and waves Ion-acoustic waves Debye length Ordinary electromagnetic waves General wave equation General dispersion equation Dielectric response
Magnetic Reconnection: explosions in space and astrophysical plasma. J. F. Drake University of Maryland
 Magnetic Reconnection: explosions in space and astrophysical plasma J. F. Drake University of Maryland Magnetic Energy Dissipation in the Universe The conversion of magnetic energy to heat and high speed
Magnetic Reconnection: explosions in space and astrophysical plasma J. F. Drake University of Maryland Magnetic Energy Dissipation in the Universe The conversion of magnetic energy to heat and high speed
Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies
 Lecture 4: Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies Rainer Beck, MPIfR Bonn Generation and amplification of cosmic magnetic fields Stage 1: Field seeding Stage 2: Field amplification Stage 3: Coherent field
Lecture 4: Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies Rainer Beck, MPIfR Bonn Generation and amplification of cosmic magnetic fields Stage 1: Field seeding Stage 2: Field amplification Stage 3: Coherent field
Heating and current drive: Radio Frequency
 Heating and current drive: Radio Frequency Dr Ben Dudson Department of Physics, University of York Heslington, York YO10 5DD, UK 13 th February 2012 Dr Ben Dudson Magnetic Confinement Fusion (1 of 26)
Heating and current drive: Radio Frequency Dr Ben Dudson Department of Physics, University of York Heslington, York YO10 5DD, UK 13 th February 2012 Dr Ben Dudson Magnetic Confinement Fusion (1 of 26)
Electricity and magnetism
 Physics: Physics: Electricity and magnetism Fluid mechanics Magnetohydrodynamics he interaction of electrically conducting fluids with magnetic fields. The fluids can be ionized gases (commonly called
Physics: Physics: Electricity and magnetism Fluid mechanics Magnetohydrodynamics he interaction of electrically conducting fluids with magnetic fields. The fluids can be ionized gases (commonly called
Turbulence and Magnetic Field in High-β Plasma of Intracluster Medium
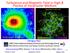 Turbulence and Magnetic Field in High-β Plasma of Intracluster Medium Coma cluster of galaxies Dongsu Ryu UNIST (Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) KASI (Korea Astronomy and Space
Turbulence and Magnetic Field in High-β Plasma of Intracluster Medium Coma cluster of galaxies Dongsu Ryu UNIST (Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) KASI (Korea Astronomy and Space
Introductory Review on Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) Simulations in Astrophysics
 Asian winter school on numerical astrophysics 13 March 2006 @Chiba Univ Introductory Review on Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) Simulations in Astrophysics Kazunari Shibata ( Kwasan and Hida Observatories, Kyoto
Asian winter school on numerical astrophysics 13 March 2006 @Chiba Univ Introductory Review on Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) Simulations in Astrophysics Kazunari Shibata ( Kwasan and Hida Observatories, Kyoto
Fluctuation dynamo amplified by intermittent shear bursts
 by intermittent Thanks to my collaborators: A. Busse (U. Glasgow), W.-C. Müller (TU Berlin) Dynamics Days Europe 8-12 September 2014 Mini-symposium on Nonlinear Problems in Plasma Astrophysics Introduction
by intermittent Thanks to my collaborators: A. Busse (U. Glasgow), W.-C. Müller (TU Berlin) Dynamics Days Europe 8-12 September 2014 Mini-symposium on Nonlinear Problems in Plasma Astrophysics Introduction
The MRI in a Collisionless Plasma
 The MRI in a Collisionless Plasma Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Collaborators: Prateek Sharma, Greg Hammett, Jim Stone Modes of Accretion thin disk: energy radiated away (relevant to star & planet formation,
The MRI in a Collisionless Plasma Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Collaborators: Prateek Sharma, Greg Hammett, Jim Stone Modes of Accretion thin disk: energy radiated away (relevant to star & planet formation,
SW103: Lecture 2. Magnetohydrodynamics and MHD models
 SW103: Lecture 2 Magnetohydrodynamics and MHD models Scale sizes in the Solar Terrestrial System: or why we use MagnetoHydroDynamics Sun-Earth distance = 1 Astronomical Unit (AU) 200 R Sun 20,000 R E 1
SW103: Lecture 2 Magnetohydrodynamics and MHD models Scale sizes in the Solar Terrestrial System: or why we use MagnetoHydroDynamics Sun-Earth distance = 1 Astronomical Unit (AU) 200 R Sun 20,000 R E 1
MHD Modes of Solar Plasma Structures
 PX420 Solar MHD 2013-2014 MHD Modes of Solar Plasma Structures Centre for Fusion, Space & Astrophysics Wave and oscillatory processes in the solar corona: Possible relevance to coronal heating and solar
PX420 Solar MHD 2013-2014 MHD Modes of Solar Plasma Structures Centre for Fusion, Space & Astrophysics Wave and oscillatory processes in the solar corona: Possible relevance to coronal heating and solar
Collisions and transport phenomena
 Collisions and transport phenomena Collisions in partly and fully ionized plasmas Typical collision parameters Conductivity and transport coefficients Conductivity tensor Formation of the ionosphere and
Collisions and transport phenomena Collisions in partly and fully ionized plasmas Typical collision parameters Conductivity and transport coefficients Conductivity tensor Formation of the ionosphere and
Course Syllabus for Spring 2016
 Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics Course Syllabus for Spring 2016 Instructors Xuening Bai (xbai@cfa.harvard.edu; P-216 at 60 Garden St; MS-51) Nick Murphy (namurphy@cfa.harvard.edu; P-140 at 60 Garden
Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics Course Syllabus for Spring 2016 Instructors Xuening Bai (xbai@cfa.harvard.edu; P-216 at 60 Garden St; MS-51) Nick Murphy (namurphy@cfa.harvard.edu; P-140 at 60 Garden
Lectures on A coherent dual vector field theory for gravitation.
 Lectures on coherent dual vector field theory for gravitation. The purpose of these lectures is to get more familiarized with gyrotation concepts and with its applications. Lecture : a word on the Maxwell
Lectures on coherent dual vector field theory for gravitation. The purpose of these lectures is to get more familiarized with gyrotation concepts and with its applications. Lecture : a word on the Maxwell
Cosmic Accelerators. 2. Pulsars, Black Holes and Shock Waves. Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford
 Cosmic Accelerators 2. Pulsars, Black Holes and Shock Waves Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford Particle Acceleration Unipolar Induction Stochastic Acceleration V ~ Ω Φ I ~ V / Z 0 Z 0 ~100Ω P ~ V I ~ V 2 /Z
Cosmic Accelerators 2. Pulsars, Black Holes and Shock Waves Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford Particle Acceleration Unipolar Induction Stochastic Acceleration V ~ Ω Φ I ~ V / Z 0 Z 0 ~100Ω P ~ V I ~ V 2 /Z
Alfvénic Turbulence in the Fast Solar Wind: from cradle to grave
 Alfvénic Turbulence in the Fast Solar Wind: from cradle to grave, A. A. van Ballegooijen, and the UVCS/SOHO Team Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Alfvénic Turbulence in the Fast Solar Wind:
Alfvénic Turbulence in the Fast Solar Wind: from cradle to grave, A. A. van Ballegooijen, and the UVCS/SOHO Team Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Alfvénic Turbulence in the Fast Solar Wind:
Evolution and Impact of Cosmic Magnetic Fields
 Evolution and Impact of Cosmic Magnetic Fields Robi Banerjee University of Hamburg Collaborators: Dominik Schleicher (Göttingen), C. Federrath (Lyon, HD), Karsten Jedamzik (Montpellier), R. Klessen (Heidelberg),
Evolution and Impact of Cosmic Magnetic Fields Robi Banerjee University of Hamburg Collaborators: Dominik Schleicher (Göttingen), C. Federrath (Lyon, HD), Karsten Jedamzik (Montpellier), R. Klessen (Heidelberg),
Shocks. Ellen Zweibel.
 Shocks Ellen Zweibel zweibel@astro.wisc.edu Departments of Astronomy & Physics University of Wisconsin, Madison and Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical Plasmas Shocks
Shocks Ellen Zweibel zweibel@astro.wisc.edu Departments of Astronomy & Physics University of Wisconsin, Madison and Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical Plasmas Shocks
Fundamentals of Plasma Physics
 Fundamentals of Plasma Physics Springer Science+Business Media, LLC J.A. Bittencourt Fundamentals of Plasma Physics Third Edition Springer J. A. Bittencourt National Institute for Space Research (INPE)
Fundamentals of Plasma Physics Springer Science+Business Media, LLC J.A. Bittencourt Fundamentals of Plasma Physics Third Edition Springer J. A. Bittencourt National Institute for Space Research (INPE)
Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs
 Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs Klaus Dolag ( ) Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik ( ) Introduction Evolution of the structures in the Universe t =
Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs Klaus Dolag ( ) Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik ( ) Introduction Evolution of the structures in the Universe t =
xkcd.com It IS about physics. It ALL is.
 xkcd.com It IS about physics. It ALL is. Introduction to Space Plasmas The Plasma State What is a plasma? Basic plasma properties: Qualitative & Quantitative Examples of plasmas Single particle motion
xkcd.com It IS about physics. It ALL is. Introduction to Space Plasmas The Plasma State What is a plasma? Basic plasma properties: Qualitative & Quantitative Examples of plasmas Single particle motion
Cosmic rays, astrophysical turbulence and magnetic reconnection
 Workshop, -, 09:15 am - 09:30 am 10:00 am - 10:10 am 10:10 am - 10:50 am 10:50 am - 11:30 am 11:30 am - 12:10 pm 01:10 pm - 01:50 pm 01:50 pm - 02:30 pm 02:30 pm - 03:00 pm 03:00 pm - 03:40 pm 03:40 pm
Workshop, -, 09:15 am - 09:30 am 10:00 am - 10:10 am 10:10 am - 10:50 am 10:50 am - 11:30 am 11:30 am - 12:10 pm 01:10 pm - 01:50 pm 01:50 pm - 02:30 pm 02:30 pm - 03:00 pm 03:00 pm - 03:40 pm 03:40 pm
ELECTROHYDRODYNAMICS IN DUSTY AND DIRTY PLASMAS
 ELECTROHYDRODYNAMICS IN DUSTY AND DIRTY PLASMAS Gravito-Electrodynamics and EHD by HIROSHI KIKUCHI Institute for Environmental Electromagnetics, Tokyo, Japan KLUWER ACADEMIC PUBLISHERS DORDRECHT / BOSTON
ELECTROHYDRODYNAMICS IN DUSTY AND DIRTY PLASMAS Gravito-Electrodynamics and EHD by HIROSHI KIKUCHI Institute for Environmental Electromagnetics, Tokyo, Japan KLUWER ACADEMIC PUBLISHERS DORDRECHT / BOSTON
The Weibel Instability in Collisionless Relativistic Shocks
 The Weibel Instability in Collisionless Relativistic Shocks Tanim Islam University of Virginia The Weibel instability[1], purely electromagnetic in nature, has been used to explain the strong magnetic
The Weibel Instability in Collisionless Relativistic Shocks Tanim Islam University of Virginia The Weibel instability[1], purely electromagnetic in nature, has been used to explain the strong magnetic
Scope of this lecture ASTR 7500: Solar & Stellar Magnetism. Lecture 9 Tues 19 Feb Magnetic fields in the Universe. Geomagnetism.
 Scope of this lecture ASTR 7500: Solar & Stellar Magnetism Hale CGEG Solar & Space Physics Processes of magnetic field generation and destruction in turbulent plasma flows Introduction to general concepts
Scope of this lecture ASTR 7500: Solar & Stellar Magnetism Hale CGEG Solar & Space Physics Processes of magnetic field generation and destruction in turbulent plasma flows Introduction to general concepts
Fluid Dynamics. Massimo Ricotti. University of Maryland. Fluid Dynamics p.1/14
 Fluid Dynamics p.1/14 Fluid Dynamics Massimo Ricotti ricotti@astro.umd.edu University of Maryland Fluid Dynamics p.2/14 The equations of fluid dynamics are coupled PDEs that form an IVP (hyperbolic). Use
Fluid Dynamics p.1/14 Fluid Dynamics Massimo Ricotti ricotti@astro.umd.edu University of Maryland Fluid Dynamics p.2/14 The equations of fluid dynamics are coupled PDEs that form an IVP (hyperbolic). Use
CIMPA/ICTP Geometric Structures and Theory of Control October Acceleration of Plasma Flows Theory and Simulation
 2369-11 CIMPA/ICTP Geometric Structures and Theory of Control 1-12 October 2012 Acceleration of Plasma Flows Theory and Simulation Nana L. Shatashvili Faculty of Exact & Natural Sciences and Andronikashvili
2369-11 CIMPA/ICTP Geometric Structures and Theory of Control 1-12 October 2012 Acceleration of Plasma Flows Theory and Simulation Nana L. Shatashvili Faculty of Exact & Natural Sciences and Andronikashvili
Selected Topics in Plasma Astrophysics
 Selected Topics in Plasma Astrophysics Range of Astrophysical Plasmas and Relevant Techniques Stellar Winds (Lecture I) Thermal, Radiation, and Magneto-Rotational Driven Winds Connections to Other Areas
Selected Topics in Plasma Astrophysics Range of Astrophysical Plasmas and Relevant Techniques Stellar Winds (Lecture I) Thermal, Radiation, and Magneto-Rotational Driven Winds Connections to Other Areas
Structure Formation and Particle Mixing in a Shear Flow Boundary Layer
 Structure Formation and Particle Mixing in a Shear Flow Boundary Layer Matthew Palotti palotti@astro.wisc.edu University of Wisconsin Center for Magnetic Self Organization Ellen Zweibel University of Wisconsin
Structure Formation and Particle Mixing in a Shear Flow Boundary Layer Matthew Palotti palotti@astro.wisc.edu University of Wisconsin Center for Magnetic Self Organization Ellen Zweibel University of Wisconsin
Solar Wind Turbulence
 Solar Wind Turbulence Presentation to the Solar and Heliospheric Survey Panel W H Matthaeus Bartol Research Institute, University of Delaware 2 June 2001 Overview Context and SH Themes Scientific status
Solar Wind Turbulence Presentation to the Solar and Heliospheric Survey Panel W H Matthaeus Bartol Research Institute, University of Delaware 2 June 2001 Overview Context and SH Themes Scientific status
Fundamentals of Turbulence
 Fundamentals of Turbulence Stanislav Boldyrev (University of Wisconsin - Madison) Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical Plasmas What is turbulence? No exact definition.
Fundamentals of Turbulence Stanislav Boldyrev (University of Wisconsin - Madison) Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical Plasmas What is turbulence? No exact definition.
Chapter 1. Introduction to Nonlinear Space Plasma Physics
 Chapter 1. Introduction to Nonlinear Space Plasma Physics The goal of this course, Nonlinear Space Plasma Physics, is to explore the formation, evolution, propagation, and characteristics of the large
Chapter 1. Introduction to Nonlinear Space Plasma Physics The goal of this course, Nonlinear Space Plasma Physics, is to explore the formation, evolution, propagation, and characteristics of the large
battery bond capacitance
 abrupt battery absolute temperature beats [heard when when two notes are slightly off pitch] absorption biochemical acceleration boil accelerator bond accuracy boundary acoustic wave brain algebraically
abrupt battery absolute temperature beats [heard when when two notes are slightly off pitch] absorption biochemical acceleration boil accelerator bond accuracy boundary acoustic wave brain algebraically
The ideal Maxwellian plasma
 The ideal Maxwellian plasma Dr. L. Conde Departamento de Física Aplicada. E.T.S. Ingenieros Aeronáuticos Universidad Politécnica de Madrid Plasmas are,... The plasma state of matter may be defined as a
The ideal Maxwellian plasma Dr. L. Conde Departamento de Física Aplicada. E.T.S. Ingenieros Aeronáuticos Universidad Politécnica de Madrid Plasmas are,... The plasma state of matter may be defined as a
Stellar Magnetohydrodynamics
 Stellar Magnetohydrodynamics 12 December 2006 by JJG Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) is the generalization of hydrodynamics to electrically conducting fluids. Major astrophysical applications include stellar
Stellar Magnetohydrodynamics 12 December 2006 by JJG Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) is the generalization of hydrodynamics to electrically conducting fluids. Major astrophysical applications include stellar
MULTI-FLUID PROBLEMS IN MAGNETOHYDRODYNAMICS WITH APPLICATIONS TO ASTROPHYSICAL PROCESSES
 MULTI-FLUID PROBLEMS IN MAGNETOHYDRODYNAMICS WITH APPLICATIONS TO ASTROPHYSICAL PROCESSES by Eric John Greenfield A Dissertation Submitted to the Faculty of the DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS In Partial Fulfillment
MULTI-FLUID PROBLEMS IN MAGNETOHYDRODYNAMICS WITH APPLICATIONS TO ASTROPHYSICAL PROCESSES by Eric John Greenfield A Dissertation Submitted to the Faculty of the DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS In Partial Fulfillment
Transition From Single Fluid To Pure Electron MHD Regime Of Tearing Instability
 Transition From Single Fluid To Pure Electron MHD Regime Of Tearing Instability V.V.Mirnov, C.C.Hegna, S.C.Prager APS DPP Meeting, October 27-31, 2003, Albuquerque NM Abstract In the most general case,
Transition From Single Fluid To Pure Electron MHD Regime Of Tearing Instability V.V.Mirnov, C.C.Hegna, S.C.Prager APS DPP Meeting, October 27-31, 2003, Albuquerque NM Abstract In the most general case,
Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD)
 Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) Robertus v F-S Robertus@sheffield.ac.uk SP RC, School of Mathematics & Statistics, The (UK) The Outline Introduction Magnetic Sun MHD equations Potential and force-free fields
Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) Robertus v F-S Robertus@sheffield.ac.uk SP RC, School of Mathematics & Statistics, The (UK) The Outline Introduction Magnetic Sun MHD equations Potential and force-free fields
TURBULENT TRANSPORT THEORY
 ASDEX Upgrade Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik TURBULENT TRANSPORT THEORY C. Angioni GYRO, J. Candy and R.E. Waltz, GA The problem of Transport Transport is the physics subject which studies the physical
ASDEX Upgrade Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik TURBULENT TRANSPORT THEORY C. Angioni GYRO, J. Candy and R.E. Waltz, GA The problem of Transport Transport is the physics subject which studies the physical
Astrofysikaliska Dynamiska Processer
 Astrofysikaliska Dynamiska Processer VT 2008 Susanne Höfner hoefner@astro.uu.se Aims of this Course - understanding the role and nature of dynamical processes in astrophysical contexts and how to study
Astrofysikaliska Dynamiska Processer VT 2008 Susanne Höfner hoefner@astro.uu.se Aims of this Course - understanding the role and nature of dynamical processes in astrophysical contexts and how to study
8.2.2 Rudiments of the acceleration of particles
 430 The solar wind in the Universe intergalactic magnetic fields that these fields should not perturb them. Their arrival directions should thus point back to their sources in the sky, which does not appear
430 The solar wind in the Universe intergalactic magnetic fields that these fields should not perturb them. Their arrival directions should thus point back to their sources in the sky, which does not appear
Sound. References: L.D. Landau & E.M. Lifshitz: Fluid Mechanics, Chapter VIII F. Shu: The Physics of Astrophysics, Vol. 2, Gas Dynamics, Chapter 8
 References: Sound L.D. Landau & E.M. Lifshitz: Fluid Mechanics, Chapter VIII F. Shu: The Physics of Astrophysics, Vol., Gas Dynamics, Chapter 8 1 Speed of sound The phenomenon of sound waves is one that
References: Sound L.D. Landau & E.M. Lifshitz: Fluid Mechanics, Chapter VIII F. Shu: The Physics of Astrophysics, Vol., Gas Dynamics, Chapter 8 1 Speed of sound The phenomenon of sound waves is one that
Lecture Note 1. 99% of the matter in the universe is in the plasma state. Solid -> liquid -> Gas -> Plasma (The fourth state of matter)
 Lecture Note 1 1.1 Plasma 99% of the matter in the universe is in the plasma state. Solid -> liquid -> Gas -> Plasma (The fourth state of matter) Recall: Concept of Temperature A gas in thermal equilibrium
Lecture Note 1 1.1 Plasma 99% of the matter in the universe is in the plasma state. Solid -> liquid -> Gas -> Plasma (The fourth state of matter) Recall: Concept of Temperature A gas in thermal equilibrium
Shocks in the ICM and the IPM
 Shocks in the ICM and the IPM Tom Jones (University of Minnesota) 1 Outline Setting the stage for following talks The Interplanetary and Intracluster Media as Collisionless Plasmas Basic Introduction to
Shocks in the ICM and the IPM Tom Jones (University of Minnesota) 1 Outline Setting the stage for following talks The Interplanetary and Intracluster Media as Collisionless Plasmas Basic Introduction to
Space Physics. ELEC-E4520 (5 cr) Teacher: Esa Kallio Assistant: Markku Alho and Riku Järvinen. Aalto University School of Electrical Engineering
 Space Physics ELEC-E4520 (5 cr) Teacher: Esa Kallio Assistant: Markku Alho and Riku Järvinen Aalto University School of Electrical Engineering The 6 th week: topics Last week: Examples of waves MHD: Examples
Space Physics ELEC-E4520 (5 cr) Teacher: Esa Kallio Assistant: Markku Alho and Riku Järvinen Aalto University School of Electrical Engineering The 6 th week: topics Last week: Examples of waves MHD: Examples
particle acceleration in reconnection regions and cosmic ray excess from the heliotail
 particle acceleration in reconnection regions and cosmic ray excess from the heliotail Paolo Desiati 1,2 & Alexander Lazarian 2 1 IceCube Research Center 2 Department of Astronomy University of Wisconsin
particle acceleration in reconnection regions and cosmic ray excess from the heliotail Paolo Desiati 1,2 & Alexander Lazarian 2 1 IceCube Research Center 2 Department of Astronomy University of Wisconsin
dt 2 = 0, we find that: K = 1 2 Ω (2)
 1 1. irial Theorem Last semester, we derived the irial theorem from essentially considering a series of particles which attract each other through gravitation. The result was that d = K + Ω (1) dt where
1 1. irial Theorem Last semester, we derived the irial theorem from essentially considering a series of particles which attract each other through gravitation. The result was that d = K + Ω (1) dt where
Dynamics of Astrophysical Discs
 Dynamics of Astrophysical Discs 16 lectures, 3 example classes http://www.damtp.cam.ac.uk/user/hl278/dad.html Henrik Latter e-mail: hl278@cam.ac.uk 16 lectures Tu. Th. 10 Course Outline Office: F1.19 hl278@cam.
Dynamics of Astrophysical Discs 16 lectures, 3 example classes http://www.damtp.cam.ac.uk/user/hl278/dad.html Henrik Latter e-mail: hl278@cam.ac.uk 16 lectures Tu. Th. 10 Course Outline Office: F1.19 hl278@cam.
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 23 Jul 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 23 Jul 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 23 Jul 2014](/thumbs/92/110757666.jpg) Magnetic Reconnection in Astrophysical Environments Alex Lazarian, Gregory L. Eyink, Ethan T. Vishniac and Grzegorz Kowal arxiv:1407.6356v1 [astro-ph.sr] 23 Jul 2014 Abstract Magnetic reconnection is a
Magnetic Reconnection in Astrophysical Environments Alex Lazarian, Gregory L. Eyink, Ethan T. Vishniac and Grzegorz Kowal arxiv:1407.6356v1 [astro-ph.sr] 23 Jul 2014 Abstract Magnetic reconnection is a
Fundamentals of wave kinetic theory
 Fundamentals of wave kinetic theory Introduction to the subject Perturbation theory of electrostatic fluctuations Landau damping - mathematics Physics of Landau damping Unmagnetized plasma waves The plasma
Fundamentals of wave kinetic theory Introduction to the subject Perturbation theory of electrostatic fluctuations Landau damping - mathematics Physics of Landau damping Unmagnetized plasma waves The plasma
Formation of Rotationally Supported Protostellar Disks: Some Theoretical Difficulties. Ruben Krasnopolsky Zhi-Yun Li Hsien Shang
 Formation of Rotationally Supported Protostellar Disks: Some Theoretical Difficulties Ruben Krasnopolsky Zhi-Yun Li Hsien Shang Protostars and disks Jet Envelope Jet Inside a protostellar core, a star
Formation of Rotationally Supported Protostellar Disks: Some Theoretical Difficulties Ruben Krasnopolsky Zhi-Yun Li Hsien Shang Protostars and disks Jet Envelope Jet Inside a protostellar core, a star
MAGNETIC NOZZLE PLASMA EXHAUST SIMULATION FOR THE VASIMR ADVANCED PROPULSION CONCEPT
 MAGNETIC NOZZLE PLASMA EXHAUST SIMULATION FOR THE VASIMR ADVANCED PROPULSION CONCEPT ABSTRACT A. G. Tarditi and J. V. Shebalin Advanced Space Propulsion Laboratory NASA Johnson Space Center Houston, TX
MAGNETIC NOZZLE PLASMA EXHAUST SIMULATION FOR THE VASIMR ADVANCED PROPULSION CONCEPT ABSTRACT A. G. Tarditi and J. V. Shebalin Advanced Space Propulsion Laboratory NASA Johnson Space Center Houston, TX
xkcd.com It IS about physics. It ALL is.
 xkcd.com It IS about physics. It ALL is. Introduction to Space Plasmas! The Plasma State What is a plasma? Basic plasma properties: Qualitative & Quantitative Examples of plasmas! Single particle motion
xkcd.com It IS about physics. It ALL is. Introduction to Space Plasmas! The Plasma State What is a plasma? Basic plasma properties: Qualitative & Quantitative Examples of plasmas! Single particle motion
Conservation Laws in Ideal MHD
 Conservation Laws in Ideal MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 3, 2016 These lecture notes are largely based on Plasma Physics for Astrophysics
Conservation Laws in Ideal MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 3, 2016 These lecture notes are largely based on Plasma Physics for Astrophysics
Physical modeling of coronal magnetic fields and currents
 Physical modeling of coronal magnetic fields and currents Participants: E. Elkina,, B. Nikutowski,, A. Otto, J. Santos (Moscow,Lindau,, Fairbanks, São José dos Campos) Goal: Forward modeling to understand
Physical modeling of coronal magnetic fields and currents Participants: E. Elkina,, B. Nikutowski,, A. Otto, J. Santos (Moscow,Lindau,, Fairbanks, São José dos Campos) Goal: Forward modeling to understand
MHD turbulence in the solar corona and solar wind
 MHD turbulence in the solar corona and solar wind Pablo Dmitruk Departamento de Física, FCEN, Universidad de Buenos Aires Motivations The role of MHD turbulence in several phenomena in space and solar
MHD turbulence in the solar corona and solar wind Pablo Dmitruk Departamento de Física, FCEN, Universidad de Buenos Aires Motivations The role of MHD turbulence in several phenomena in space and solar
