Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations. simulations of galaxy and structure formation
|
|
|
- Melvyn Ramsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, / Workshop Dark halos, UBC Vancouver
2 Outline 1 Motivation Cosmic rays in galaxies Violent structure formation Gravitational heating by shocks 2 Cosmic rays in GADGET Mach number finder Cosmological simulations 3 Cluster radio halos CR pressure influences Sunyaev-Zel dovic effect
3 Cosmic rays in galaxies Violent structure formation Gravitational heating by shocks M51: cosmic ray electron population Fletcher, Beck, Berkhuijsen und Horellou, in prep.
4 Cosmic rays in galaxies Violent structure formation Gravitational heating by shocks Observations of cluster shock waves 1E ( Bullet cluster ) (NASA/SAO/CXC/M.Markevitch et al.) Abell 3667 (Radio: Austr.TC Array. X-ray: ROSAT/PSPC.)
5 Gravitational heating by shocks Cosmic rays in galaxies Violent structure formation Gravitational heating by shocks The "cosmic web" today. Left: the projected gas density in a cosmological simulation. Right: gravitationally heated intracluster medium through cosmological shock waves.
6 Cosmic rays in GADGET Mach number finder Cosmological simulations Cosmic rays in GADGET collaboration The talk is based on the following papers: Detecting shock waves in cosmological smoothed particle hydrodynamics simulations, Pfrommer, Springel, Enßlin, & Jubelgas 26, MNRAS, 367, 113, astro-ph/63483 Cosmic ray physics in calculations of cosmological structure formation Enßlin, Pfrommer, Springel, & Jubelgas astro-ph/63484 of galaxy formation Jubelgas, Springel, Enßlin, & Pfrommer astro-ph/63485
7 Philosophy and description Cosmic rays in GADGET Mach number finder Cosmological simulations An accurate description of CRs should follow the evolution of the spectral energy distribution of CRs as a function of time and space, and keep track of their dynamical, non-linear coupling with the hydrodynamics. We seek a compromise between capturing as many physical properties as possible requiring as little computational resources as possible Assumptions: protons dominate the CR population a momentum power-law is a typical spectrum CR energy & particle number conservation
8 Philosophy and description Cosmic rays in GADGET Mach number finder Cosmological simulations An accurate description of CRs should follow the evolution of the spectral energy distribution of CRs as a function of time and space, and keep track of their dynamical, non-linear coupling with the hydrodynamics. We seek a compromise between capturing as many physical properties as possible requiring as little computational resources as possible Assumptions: protons dominate the CR population a momentum power-law is a typical spectrum CR energy & particle number conservation
9 Philosophy and description Cosmic rays in GADGET Mach number finder Cosmological simulations An accurate description of CRs should follow the evolution of the spectral energy distribution of CRs as a function of time and space, and keep track of their dynamical, non-linear coupling with the hydrodynamics. We seek a compromise between capturing as many physical properties as possible requiring as little computational resources as possible Assumptions: protons dominate the CR population a momentum power-law is a typical spectrum CR energy & particle number conservation
10 Philosophy and description Cosmic rays in GADGET Mach number finder Cosmological simulations CRs are coupled to the thermal gas by magnetic fields. We assume a single power-law CR spectrum: momentum cutoff q, normalization C, spectral index α (constant). determines CR energy density and pressure uniquely The CR spectrum can be expressed by three adiabatic invariants, which scale only with the gas density. Non-adiabatic processes are mapped into changes of the adiabatic constants using mass, energy and momentum conservation.
11 Cosmic rays in GADGET Mach number finder Cosmological simulations Cosmic rays in GADGET flowchart
12 Thermal & CR energy spectra Cosmic rays in GADGET Mach number finder Cosmological simulations Kinetic energy per logarithmic momentum interval: 1 ev 1 kev.1mev PSfrag replacements dtcr/d log p = p T p(p) f (p) in mp c α = 2.25 α = 2.5 α = MeV p
13 Radiative cooling Cosmic rays in GADGET Mach number finder Cosmological simulations Cooling of primordial gas: Cooling of cosmic rays: 1 1. ρ = 2.386*1-25 g/cm τ cool [ Gyr ] 1-3 τ cool [ Gyr ] ρ = 2.386*1-25 g/cm T [ K ] q
14 Cosmic rays in GADGET Mach number finder Cosmological simulations Cosmic rays in GADGET flowchart
15 Cosmic rays in GADGET Mach number finder Cosmological simulations Diffusive shock acceleration Fermi 1 mechanism Cosmic rays gain energy E/E υ 1 υ 2 through bouncing back and forth the shock front. Accounting for the loss probability υ 2 of particles leaving the shock downstream leads to power-law CR population. log f strong shock weak shock kev 1 GeV log p
16 Cosmic rays in GADGET Mach number finder Cosmological simulations Motivation for the Mach number finder cosmological shocks dissipate gravitational energy into thermal gas energy: where and when is the gas heated, and which shocks are mainly responsible for it? shock waves are tracers of the large scale structure and contain information about its dynamical history (warm-hot intergalactic medium) shocks accelerate cosmic rays through diffusive shock acceleration at structure formation shocks: what are the cosmological implications of such a CR component, and does this influence the cosmic thermal history? simulating realistic CR distributions within galaxy clusters provides detailed predictions for the expected radio synchrotron and γ-ray emission
17 Cosmic rays in GADGET Mach number finder Cosmological simulations Shock tube (CRs & gas, M = 1): thermodynamics Density Velocity Pressure Mach number
18 Cosmic rays in GADGET Mach number finder Cosmological simulations Shock tube (CRs & gas): Mach number statistics duth dt d log M log M replacements du th dt log M
19 Cosmic rays in GADGET Mach number finder Cosmological simulations Shock tube (th. gas): Mach number statistics duth dt d log M log M replacements du th dt log M
20 Motivation Cosmic rays in GADGET Mach number finder Cosmological simulations Cosmological Mach numbers: weighted by ε diss y [ h -1 Mpc ] 6 4 Mach number x [ h -1 Mpc ] 1
21 Motivation Cosmic rays in GADGET Mach number finder Cosmological simulations Cosmological Mach numbers: weighted by ε CR y [ h -1 Mpc ] 6 4 Mach number x [ h -1 Mpc ] 1
22 Cosmic rays in GADGET Mach number finder Cosmological simulations Cosmological Mach number statistics more energy is dissipated in weak shocks internal to collapsed structures than in external strong shocks more energy is dissipated at later times mean Mach number decreases with time
23 Cosmic rays in GADGET Mach number finder Cosmological simulations Cosmological statistics: influence of reionization reionization epoch at z reion = 1 suppresses efficiently strong shocks at z < z reion due to jump in sound velocity cosmological constant causes structure formation to cease
24 Cluster radio halos CR pressure influences SZ effect Radio halos as window for non-equilibrium processes Exploring complementary methods for studying cluster formation Each frequency window is sensitive to different processes and cluster properties: optical: gravitational lensing of background galaxies, galaxy velocity dispersion measure gravitational mass X-ray: thermal plasma emission, F X n 2 th Tth thermal gas with abundances, cluster potential, substructure Sunyaev-Zel dovich effect: IC upscattering of CMB photons by thermal electrons, F SZ p th cluster velocity, turbulence, high-z clusters radio synchrotron halos: F sy ε B ε CRe magnetic fields, CR electrons, shock waves diffuse γ-ray emission: F γ n th n CRp CR protons
25 Motivation Cluster radio halos CR pressure influences SZ effect Adiabatic cluster simulation: gas density y [ h -1 Mpc ] δ gas x [ h -1 Mpc ]
26 Motivation Mass weighted temperature 15 Cluster radio halos CR pressure influences SZ effect y [ h -1 Mpc ] <( 1 + δ gas ) T > [ K ] x [ h -1 Mpc ]
27 Cluster radio halos CR pressure influences SZ effect Mach number distribution weighted by ε diss y [ h -1 Mpc ] Mach number x [ h -1 Mpc ] 1
28 2 1-1 Cluster radio halos CR pressure influences SZ effect Relative CR pressure P CR /P total y [ h -1 Mpc ] P CR / ( P th + P CR ) x [ h -1 Mpc ] 1-3
29 Cluster radio halos CR pressure influences SZ effect Radio halos as window for non-equilibrium processes Coma radio halo, ν = 1.4 GHz, largest emission diameter 3 Mpc Coma thermal X-ray emission, ( , credit: ROSAT/MPE/Snowden) (2.5 2., credit: Deiss/Effelsberg)
30 Cluster radio halos CR pressure influences SZ effect Models for radio synchrotron halos in clusters Halo characteristics: smooth unpolarized radio emission at scales of 3 Mpc. Different CR electron populations: Primary accelerated CR electrons: synchrotron/ic cooling times too short to account for extended diffuse emission Re-accelerated CR electrons through resonant interaction with turbulent Alfvén waves: possibly too inefficient, no first principle calculations (Jaffe 1977, Schlickeiser 1987, Brunetti 21) Hadronically produced CR electrons in inelastic collisions of CR protons with the ambient gas (Dennison 198, Vestrad 1982, Miniati 21, Pfrommer 24)
31 Cluster radio halos CR pressure influences SZ effect Hadronic cosmic ray proton interaction
32 Cluster radio halos CR pressure influences SZ effect Energetically preferred CR pressure profiles.1 Coma cluster: hadronic minimum energy condition X CRpmin X Bmin XBmin (r), X CRp min (r).1 PSfrag replacements r [h 1 7 kpc] X CRp (r) = ε CRp ε th (r), X B (r) = ε B ε th (r) B Coma, min () = µg
33 Motivation Cluster radio halos CR pressure influences SZ effect Compton y parameter in radiative cluster simulation y [ h -1 Mpc ]. Compton y x [ h -1 Mpc ]
34 Cluster radio halos CR pressure influences SZ effect Compton y difference map: y CR y th y [ h -1 Mpc ] Compton-y difference map: y CR - y th x [ h -1 Mpc ] -1-5
35 Cluster radio halos CR pressure influences SZ effect Simulated CBI observation of y CR y th (with Sievers & Bond)
36 Cluster radio halos CR pressure influences SZ effect Pressure profiles with and without CRs P CR, P th [Code units] R [ h -1 kpc ]
37 Motivation Cluster radio halos CR pressure influences SZ effect Phase-space diagram of radiative cluster simulation log[ P CR / P th ] probability density [arbitrary units] log[ 1 + δ gas ] 1
38 Preliminary emerging picture Cluster radio halos CR pressure influences SZ effect Importance of central CR pressure relative to the gas pressure seems to depend on subtle interplay of the following effects: Presence of well developed cool core region Violent merger history of the cluster resulting flat effective spectral index of CRs Cluster mass: ratio of CR-to-thermal cooling times changes with the cluster s virial temperature
39 Cluster radio halos CR pressure influences SZ effect Non-radiative simulation: entropy profile 1 1 non-radiative simulation 1 9 A th [Code units] R [ h -1 kpc ]
40 Cluster radio halos CR pressure influences SZ effect Radiative simulation: entropy profile 1 1 radiative simulation 1 9 A th [Code units] R [ h -1 kpc ]
41 Cluster radio halos CR pressure influences SZ effect Radiative simulation: Schwazschild criterion 2 15 Schwarzschild criterion R [ h -1 kpc ] Cluster profile instable with respect to convection effective mixing?
42 Cluster radio halos CR pressure influences SZ effect 1. radiative simulation 1. P CR, P th [Code units] R [ h -1 kpc ]
43 Summary Motivation Cluster radio halos CR pressure influences SZ effect Understanding non-thermal processes is crucial for using clusters as cosmological probes (high-z scaling relations). Radio halos might be of hadronic origin as our simulations suggests tracer of structure formation Dynamical CR feedback influences Sunyaev-Zel dovic effect Outlook Galaxy evolution: CRs might influence energetic feedback, galactic winds, and disk galaxy formation Huge potential and predictive power of cosmological CR simulations/mach number finder provides detailed γ-ray/radio emission maps
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations. simulations of galaxy and structure formation
 Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 11 26 / Colloquium University of Victoria Outline 1 Cosmic
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 11 26 / Colloquium University of Victoria Outline 1 Cosmic
Cosmic Rays in Galaxy Clusters: Simulations and Perspectives
 Cosmic Rays in Galaxy Clusters: Simulations and Perspectives 1 in collaboration with Volker Springel 2, Torsten Enßlin 2 1 Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Canada 2 Max-Planck Institute
Cosmic Rays in Galaxy Clusters: Simulations and Perspectives 1 in collaboration with Volker Springel 2, Torsten Enßlin 2 1 Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Canada 2 Max-Planck Institute
Literature on which the following results are based:
 Cosmic rays in galaxy clusters Physical processes in galaxy clusters High-resolution simulations of galaxy clusters Literature on which the following results are based: Pfrommer, 28, MNRAS, in print, ArXiv:77.1693,
Cosmic rays in galaxy clusters Physical processes in galaxy clusters High-resolution simulations of galaxy clusters Literature on which the following results are based: Pfrommer, 28, MNRAS, in print, ArXiv:77.1693,
Cosmic Rays in Galaxy Clusters Simulations and Reality
 Simulations and Reality 1,2 in collaboration with Torsten Enßlin 3, Volker Springel 3, Anders Pinzke 4, Nick Battaglia 1, Jon Sievers 1, Dick Bond 1 1 Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Canada
Simulations and Reality 1,2 in collaboration with Torsten Enßlin 3, Volker Springel 3, Anders Pinzke 4, Nick Battaglia 1, Jon Sievers 1, Dick Bond 1 1 Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Canada
Particle Acceleration and Radiation from Galaxy Clusters
 Particle Acceleration and Radiation from Galaxy Clusters 1,2 in collaboration with Anders Pinzke 3, Torsten Enßlin 4, Volker Springel 4, Nick Battaglia 1, Jon Sievers 1, Dick Bond 1 1 Canadian Institute
Particle Acceleration and Radiation from Galaxy Clusters 1,2 in collaboration with Anders Pinzke 3, Torsten Enßlin 4, Volker Springel 4, Nick Battaglia 1, Jon Sievers 1, Dick Bond 1 1 Canadian Institute
Fermi-LAT Analysis of the Coma Cluster
 Fermi-LAT Analysis of the Coma Cluster a Fabio Zandanel GRAPPA Institute University of Amsterdam f.zandanel@uva.nl In collaboration with S. Ando (GRAPPA) 18 th Symposium on Astroparticle Physics in the
Fermi-LAT Analysis of the Coma Cluster a Fabio Zandanel GRAPPA Institute University of Amsterdam f.zandanel@uva.nl In collaboration with S. Ando (GRAPPA) 18 th Symposium on Astroparticle Physics in the
Uri Keshet / CfA Impact of upcoming high-energy astrophysics experiments Workshop, KAVLI, October 2008
 Uri Keshet / CfA Impact of upcoming high-energy astrophysics experiments Workshop, KAVLI, October 008 Impact of upcoming high-energy astrophysics experiments Workshop, KAVLI, October 008 Relaxed, cool
Uri Keshet / CfA Impact of upcoming high-energy astrophysics experiments Workshop, KAVLI, October 008 Impact of upcoming high-energy astrophysics experiments Workshop, KAVLI, October 008 Relaxed, cool
Intracluster Shock Waves
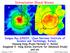 ρ Intracluster Shock Waves T R 200 Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) Hyesung Kang (Pusan National U, Korea) Sungwook E. Hong (Korea Institute for Advanced Study)
ρ Intracluster Shock Waves T R 200 Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) Hyesung Kang (Pusan National U, Korea) Sungwook E. Hong (Korea Institute for Advanced Study)
Radio Continuum: Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields. Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn
 Radio Continuum: Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn Synchrotron emission Beam angle: Ψ/2=1/γ=E o /E Radio continuum tools to study GeV Cosmic ray electrons (CRE) Synchrotron spectrum:
Radio Continuum: Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn Synchrotron emission Beam angle: Ψ/2=1/γ=E o /E Radio continuum tools to study GeV Cosmic ray electrons (CRE) Synchrotron spectrum:
MULTIWAVELENGTH OBSERVATIONS OF CLUSTERS OF GALAXIES AND THE ROLE OF CLUSTER MERGERS PASQUALE BLASI
 MULTIWAVELENGTH OBSERVATIONS OF CLUSTERS OF GALAXIES AND THE ROLE OF CLUSTER MERGERS PASQUALE BLASI NASA/Fermilab Astrophysics Center Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, Box 500, Batavia, IL 60510-0500,
MULTIWAVELENGTH OBSERVATIONS OF CLUSTERS OF GALAXIES AND THE ROLE OF CLUSTER MERGERS PASQUALE BLASI NASA/Fermilab Astrophysics Center Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, Box 500, Batavia, IL 60510-0500,
Dynamics of galaxy clusters A radio perspective
 Dynamics of galaxy clusters A radio perspective Tiziana Venturi, INAF, Istituto di Radioastronomia Collaborators S. Giacintucci, D. Dallacasa, R. Kale, G. Brunetti, R. Cassano, M. Rossetti GEE 3 Padova,
Dynamics of galaxy clusters A radio perspective Tiziana Venturi, INAF, Istituto di Radioastronomia Collaborators S. Giacintucci, D. Dallacasa, R. Kale, G. Brunetti, R. Cassano, M. Rossetti GEE 3 Padova,
Turbulence & particle acceleration in galaxy clusters. Gianfranco Brunetti
 Turbulence & particle acceleration in galaxy clusters Gianfranco Brunetti Mergers & CR-acceleration Cluster-cluster mergers are the most energetic events in the present Universe (10 64 erg/gyr). They can
Turbulence & particle acceleration in galaxy clusters Gianfranco Brunetti Mergers & CR-acceleration Cluster-cluster mergers are the most energetic events in the present Universe (10 64 erg/gyr). They can
The Plasma Physics and Cosmological Impact of TeV Blazars
 The Plasma Physics and Cosmological Impact of TeV Blazars Philip Chang (UW-Milwaukee) Avery Broderick (Waterloo/Perimeter) Astrid Lamberts (UW-Milwaukee) Christoph Pfrommer (HITS-Heidelberg) Ewald Puchwein
The Plasma Physics and Cosmological Impact of TeV Blazars Philip Chang (UW-Milwaukee) Avery Broderick (Waterloo/Perimeter) Astrid Lamberts (UW-Milwaukee) Christoph Pfrommer (HITS-Heidelberg) Ewald Puchwein
Radio emission in clusters of galaxies. An observational perspective
 Radio emission in clusters of galaxies An observational perspective Tiziana Venturi INAF, IRA, Bologna IV ESTRELA Workshop, Bologna, 19 January 2009 Overview - What are galaxy clusters - Radio emission
Radio emission in clusters of galaxies An observational perspective Tiziana Venturi INAF, IRA, Bologna IV ESTRELA Workshop, Bologna, 19 January 2009 Overview - What are galaxy clusters - Radio emission
The role of Planck in understanding galaxy cluster radio halos
 The role of Planck in understanding galaxy cluster radio halos Radio data Radio data Planck measurements Planck measurements 1 The role of Planck in understanding galaxy cluster radio halos Kaustuv Basu
The role of Planck in understanding galaxy cluster radio halos Radio data Radio data Planck measurements Planck measurements 1 The role of Planck in understanding galaxy cluster radio halos Kaustuv Basu
Structure of Dark Matter Halos
 Structure of Dark Matter Halos Dark matter halos profiles: DM only: NFW vs. Einasto Halo concentration: evolution with time Dark matter halos profiles: Effects of baryons Adiabatic contraction Cusps and
Structure of Dark Matter Halos Dark matter halos profiles: DM only: NFW vs. Einasto Halo concentration: evolution with time Dark matter halos profiles: Effects of baryons Adiabatic contraction Cusps and
Radiation processes and mechanisms in astrophysics I. R Subrahmanyan Notes on ATA lectures at UWA, Perth 18 May 2009
 Radiation processes and mechanisms in astrophysics I R Subrahmanyan Notes on ATA lectures at UWA, Perth 18 May 009 Light of the night sky We learn of the universe around us from EM radiation, neutrinos,
Radiation processes and mechanisms in astrophysics I R Subrahmanyan Notes on ATA lectures at UWA, Perth 18 May 009 Light of the night sky We learn of the universe around us from EM radiation, neutrinos,
Formation and properties of shock waves in galaxy clusters
 Formation and properties of shock waves in galaxy clusters Hyesung Kang (Pusan National University) Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Korea) T. W. Jones (Univ. of Minnesota) Sungwook E. Hong (KAIST, Korea) Ref: Kang,
Formation and properties of shock waves in galaxy clusters Hyesung Kang (Pusan National University) Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Korea) T. W. Jones (Univ. of Minnesota) Sungwook E. Hong (KAIST, Korea) Ref: Kang,
Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA
 Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn & SKA Science Working Group Fundamental magnetic questions When and how were the first fields generated?
Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn & SKA Science Working Group Fundamental magnetic questions When and how were the first fields generated?
Cosmic Ray acceleration in clusters of galaxies. Gianfranco Brunetti. Istituto di Radioastronomia INAF, Bologna, ITALY
 Cosmic Ray acceleration in clusters of galaxies Gianfranco Brunetti Istituto di Radioastronomia INAF, Bologna, ITALY Outline NT components (CRe,CRp,B) in galaxy clusters : observations Physics and dynamics
Cosmic Ray acceleration in clusters of galaxies Gianfranco Brunetti Istituto di Radioastronomia INAF, Bologna, ITALY Outline NT components (CRe,CRp,B) in galaxy clusters : observations Physics and dynamics
Nonthermal Emission in Starburst Galaxies
 Nonthermal Emission in Starburst Galaxies! Yoel Rephaeli!!! Tel Aviv University & UC San Diego Cosmic Ray Origin! San Vito, March 20, 2014 General Background * Stellar-related nonthermal phenomena * Particle
Nonthermal Emission in Starburst Galaxies! Yoel Rephaeli!!! Tel Aviv University & UC San Diego Cosmic Ray Origin! San Vito, March 20, 2014 General Background * Stellar-related nonthermal phenomena * Particle
The Physics and Cosmology of TeV Blazars
 1 in collaboration with Avery E. Broderick 2, Phil Chang 3, Ewald Puchwein 1, Volker Springel 1 1 Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies, Germany 2 Perimeter Institute/University of Waterloo, Canada
1 in collaboration with Avery E. Broderick 2, Phil Chang 3, Ewald Puchwein 1, Volker Springel 1 1 Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies, Germany 2 Perimeter Institute/University of Waterloo, Canada
Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters
 Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) with Hyesung Kang (Pusan Nat. U, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (Chungnam Nat. U.),
Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) with Hyesung Kang (Pusan Nat. U, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (Chungnam Nat. U.),
Constraints on physics of gas and dark matter from cluster mergers. Maxim Markevitch (SAO)
 Constraints on physics of gas and dark matter from cluster mergers Maxim Markevitch (SAO) November 2005 1E 0657 56 Chandra 0.5 Msec image 0.5 Mpc z=0.3 An overheated cluster From M T relation: T= 14 kev:
Constraints on physics of gas and dark matter from cluster mergers Maxim Markevitch (SAO) November 2005 1E 0657 56 Chandra 0.5 Msec image 0.5 Mpc z=0.3 An overheated cluster From M T relation: T= 14 kev:
New Forms of Convection in Galaxy Cluster Plasmas (i.e., how do galaxy clusters boil?)
 New Forms of Convection in Galaxy Cluster Plasmas (i.e., how do galaxy clusters boil?) Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Hydra A w/ Chandra in collaboration with Ian Parrish Prateek Sharma Overview Hot Plasma
New Forms of Convection in Galaxy Cluster Plasmas (i.e., how do galaxy clusters boil?) Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Hydra A w/ Chandra in collaboration with Ian Parrish Prateek Sharma Overview Hot Plasma
Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies
 Lecture 4: Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies Rainer Beck, MPIfR Bonn Generation and amplification of cosmic magnetic fields Stage 1: Field seeding Stage 2: Field amplification Stage 3: Coherent field
Lecture 4: Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies Rainer Beck, MPIfR Bonn Generation and amplification of cosmic magnetic fields Stage 1: Field seeding Stage 2: Field amplification Stage 3: Coherent field
The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters
 IAU Joint Discussion # 10 Sydney, July, 2003 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al 2003 > 105
IAU Joint Discussion # 10 Sydney, July, 2003 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al 2003 > 105
THE MAGIC TELESCOPES. Major Atmospheric Gamma Imaging Cherenkov Telescopes
 THE MAGIC TELESCOPES Observatorio del Roque de los Muchachos, La Palma (2200 m a.s.l.) System of two 17 m Cherenkov Telescopes for VHE γ-ray astronomy MAGIC-I operational since 2004, Stereo system since
THE MAGIC TELESCOPES Observatorio del Roque de los Muchachos, La Palma (2200 m a.s.l.) System of two 17 m Cherenkov Telescopes for VHE γ-ray astronomy MAGIC-I operational since 2004, Stereo system since
Particle Acceleration in the Universe
 Particle Acceleration in the Universe Hiroyasu Tajima Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology on behalf of SLAC GLAST team June 7, 2006 SLAC DOE HEP Program
Particle Acceleration in the Universe Hiroyasu Tajima Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology on behalf of SLAC GLAST team June 7, 2006 SLAC DOE HEP Program
Really, really, what universe do we live in?
 Really, really, what universe do we live in? Fluctuations in cosmic microwave background Origin Amplitude Spectrum Cosmic variance CMB observations and cosmological parameters COBE, balloons WMAP Parameters
Really, really, what universe do we live in? Fluctuations in cosmic microwave background Origin Amplitude Spectrum Cosmic variance CMB observations and cosmological parameters COBE, balloons WMAP Parameters
AST 541 Notes: Clusters of Galaxies Fall 2010
 Clusters 1 AST 541 Notes: Clusters of Galaxies Fall 2010 Galaxy clusters represent the largest bound and virialized structures in the Universe today. This extreme environment makes them interesting for
Clusters 1 AST 541 Notes: Clusters of Galaxies Fall 2010 Galaxy clusters represent the largest bound and virialized structures in the Universe today. This extreme environment makes them interesting for
Moving mesh cosmology: The hydrodynamics of galaxy formation
 Moving mesh cosmology: The hydrodynamics of galaxy formation arxiv:1109.3468 Debora Sijacki, Hubble Fellow, ITC together with: Mark Vogelsberger, Dusan Keres, Paul Torrey Shy Genel, Dylan Nelson Volker
Moving mesh cosmology: The hydrodynamics of galaxy formation arxiv:1109.3468 Debora Sijacki, Hubble Fellow, ITC together with: Mark Vogelsberger, Dusan Keres, Paul Torrey Shy Genel, Dylan Nelson Volker
Dark Matter. Homework 3 due. ASTR 433 Projects 4/17: distribute abstracts 4/19: 20 minute talks. 4/24: Homework 4 due 4/26: Exam ASTR 333/433.
 Dark Matter ASTR 333/433 Today Clusters of Galaxies Homework 3 due ASTR 433 Projects 4/17: distribute abstracts 4/19: 20 minute talks 4/24: Homework 4 due 4/26: Exam Galaxy Clusters 4 distinct measures:
Dark Matter ASTR 333/433 Today Clusters of Galaxies Homework 3 due ASTR 433 Projects 4/17: distribute abstracts 4/19: 20 minute talks 4/24: Homework 4 due 4/26: Exam Galaxy Clusters 4 distinct measures:
Where are the missing baryons?
 Where are the missing baryons? Qiang Wang (Brandon) B.Sc. Supervisor: Dr Scott Kay School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Manchester 27/29 June 2018 Image from Millennium Simulation 1 Content I.
Where are the missing baryons? Qiang Wang (Brandon) B.Sc. Supervisor: Dr Scott Kay School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Manchester 27/29 June 2018 Image from Millennium Simulation 1 Content I.
The Superbubble Power Problem: Overview and Recent Developments. S. Oey
 The Superbubble Power Problem: Overview and Recent Developments S. Oey It has been known for decades that superbubbles generated by massive star winds and supernovae are smaller than expected based on
The Superbubble Power Problem: Overview and Recent Developments S. Oey It has been known for decades that superbubbles generated by massive star winds and supernovae are smaller than expected based on
Detection of hot gas in multi-wavelength datasets. Loïc Verdier DDAYS 2015
 Detection of hot gas in multi-wavelength datasets Loïc Verdier SPP DDAYS 2015 Loïc Verdier (SPP) Detection of hot gas in multi-wavelength datasets DDAYS 2015 1 / 21 Cluster Abell 520; Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/UVic./A.Mahdavi
Detection of hot gas in multi-wavelength datasets Loïc Verdier SPP DDAYS 2015 Loïc Verdier (SPP) Detection of hot gas in multi-wavelength datasets DDAYS 2015 1 / 21 Cluster Abell 520; Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/UVic./A.Mahdavi
the ICM Power Spectrum:
 the ICM Power Spectrum: probing the gas physics of galaxy clusters Massimo Gaspari Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Collaborators: E. Churazov, D. Nagai, E. Lau, I. Zhuravleva, R. Sunyaev Power Spectrum
the ICM Power Spectrum: probing the gas physics of galaxy clusters Massimo Gaspari Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Collaborators: E. Churazov, D. Nagai, E. Lau, I. Zhuravleva, R. Sunyaev Power Spectrum
Observational Cosmology
 (C. Porciani / K. Basu) Lecture 7 Cosmology with galaxy clusters (Mass function, clusters surveys) Course website: http://www.astro.uni-bonn.de/~kbasu/astro845.html Outline of the two lecture Galaxy clusters
(C. Porciani / K. Basu) Lecture 7 Cosmology with galaxy clusters (Mass function, clusters surveys) Course website: http://www.astro.uni-bonn.de/~kbasu/astro845.html Outline of the two lecture Galaxy clusters
Enrico Fermi School Varenna Cool Cores and Mergers in Clusters Lecture 3
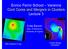 Enrico Fermi School Varenna Cool Cores and Mergers in Clusters Lecture 3 Craig Sarazin Dept. of Astronomy University of Virginia A85 Chandra (X-ray) Cluster Merger Simulation Cool Cores in Clusters Central
Enrico Fermi School Varenna Cool Cores and Mergers in Clusters Lecture 3 Craig Sarazin Dept. of Astronomy University of Virginia A85 Chandra (X-ray) Cluster Merger Simulation Cool Cores in Clusters Central
Radio relics and magnetic field amplification in the Intra-cluster Medium
 Radio relics and magnetic field amplification in the Intra-cluster Medium Annalisa Annalisa Bonafede Bonafede Hamburger Hamburg Sternwarte University Hamburg University Jacobs University Bremen Collaborators:
Radio relics and magnetic field amplification in the Intra-cluster Medium Annalisa Annalisa Bonafede Bonafede Hamburger Hamburg Sternwarte University Hamburg University Jacobs University Bremen Collaborators:
Hydra A (x-ray) Perseus ` (optical)
 The Biermann Lectures: Adventures in Theoretical Astrophysics I: The Physics of Galaxy Cluster Plasmas Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) w/ Mike McCourt, Ian Parrish, Prateek Sharma Perseus ` (optical) Hydra
The Biermann Lectures: Adventures in Theoretical Astrophysics I: The Physics of Galaxy Cluster Plasmas Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) w/ Mike McCourt, Ian Parrish, Prateek Sharma Perseus ` (optical) Hydra
Radio Halos From Simulations And Hadronic Models I: The Coma cluster
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 6 (2008) Printed 15 May 2009 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Radio Halos From Simulations And Hadronic Models I: The Coma cluster We use results from one of the constrained,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 6 (2008) Printed 15 May 2009 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Radio Halos From Simulations And Hadronic Models I: The Coma cluster We use results from one of the constrained,
AGN Outflows in Dynamic ICMs: Winds and Twists
 AGN Outflows in Dynamic ICMs: Winds and Twists Tom Jones University of Minnesota Pete Mendygral (UMN, Cray Computer) David Porter (UMN) Klaus Dolag (MPA, U Munich) 11/29/2012 Binary Black Holes & Dual
AGN Outflows in Dynamic ICMs: Winds and Twists Tom Jones University of Minnesota Pete Mendygral (UMN, Cray Computer) David Porter (UMN) Klaus Dolag (MPA, U Munich) 11/29/2012 Binary Black Holes & Dual
Energy Balance in Clusters of Galaxies. Patrick M. Motl & Jack O. Burns Center for Astrophysics and Space Astronomy University of Colorado at Boulder
 Energy Balance in Clusters of Galaxies Patrick M. Motl & Jack O. Burns Center for Astrophysics and Space Astronomy University of Colorado at Boulder X-ray and Radio Connections, February 6th, 2004 With
Energy Balance in Clusters of Galaxies Patrick M. Motl & Jack O. Burns Center for Astrophysics and Space Astronomy University of Colorado at Boulder X-ray and Radio Connections, February 6th, 2004 With
Tesla Jeltema. Assistant Professor, Department of Physics. Observational Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics
 Tesla Jeltema Assistant Professor, Department of Physics Observational Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics Research Program Research theme: using the evolution of large-scale structure to reveal the fundamental
Tesla Jeltema Assistant Professor, Department of Physics Observational Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics Research Program Research theme: using the evolution of large-scale structure to reveal the fundamental
Simulating magnetic fields in structure formation
 Simulating magnetic fields in structure formation USM / MPE / MPA Harald Lesch & Klaus Dolag Annette Geng, Federico Stasyszyn & Marcus Beck July, 2012 (Mainz) Alexander Beck Magnetic fields in galaxies
Simulating magnetic fields in structure formation USM / MPE / MPA Harald Lesch & Klaus Dolag Annette Geng, Federico Stasyszyn & Marcus Beck July, 2012 (Mainz) Alexander Beck Magnetic fields in galaxies
Feedback in Galaxy Clusters
 Feedback in Galaxy Clusters Brian Morsony University of Maryland 1 Not talking about Galaxy-scale feedback Local accretion disk feedback 2 Outline Galaxy cluster properties Cooling flows the need for feedback
Feedback in Galaxy Clusters Brian Morsony University of Maryland 1 Not talking about Galaxy-scale feedback Local accretion disk feedback 2 Outline Galaxy cluster properties Cooling flows the need for feedback
The High-Energy Interstellar Medium
 The High-Energy Interstellar Medium Andy Strong MPE Garching on behalf of Fermi-LAT collaboration Cosmic Ray Interactions: Bridging High and Low Energy Astrophysics Lorentz Centre Workshop March 14-18
The High-Energy Interstellar Medium Andy Strong MPE Garching on behalf of Fermi-LAT collaboration Cosmic Ray Interactions: Bridging High and Low Energy Astrophysics Lorentz Centre Workshop March 14-18
Hard X-ray emission from Novae
 Hard X-ray emission from Novae Indrek Vurm (Columbia University) in collaboration with: Brian D. Metzger, Andrei M. Beloborodov (Columbia) Koji Mukai (NASA) Shocks and Particle Acceleration in Novae and
Hard X-ray emission from Novae Indrek Vurm (Columbia University) in collaboration with: Brian D. Metzger, Andrei M. Beloborodov (Columbia) Koji Mukai (NASA) Shocks and Particle Acceleration in Novae and
Cosmological shock waves
 Highlights of Spanish Astrophysics VII, Proceedings of the X Scientific Meeting of the Spanish Astronomical Society held on July 9-13, 2012, in Valencia, Spain. J. C. Guirado, L. M. Lara, V. Quilis, and
Highlights of Spanish Astrophysics VII, Proceedings of the X Scientific Meeting of the Spanish Astronomical Society held on July 9-13, 2012, in Valencia, Spain. J. C. Guirado, L. M. Lara, V. Quilis, and
Cosmology and Astrophysics with Galaxy Clusters Recent Advances and Future Challenges
 Cosmology and Astrophysics with Galaxy Clusters Recent Advances and Future Challenges Daisuke Nagai Yale University IPMU, July 15 th, 2010 Large-scale structure in the Universe SDSS (optical) Today δρ/ρ>>1
Cosmology and Astrophysics with Galaxy Clusters Recent Advances and Future Challenges Daisuke Nagai Yale University IPMU, July 15 th, 2010 Large-scale structure in the Universe SDSS (optical) Today δρ/ρ>>1
Fundamental Physics with GeV Gamma Rays
 Stefano Profumo UC Santa Cruz Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics T.A.S.C. [Theoretical Astrophysics, Santa Cruz] Fundamental Physics with GeV Gamma Rays Based on: Kamionkowski & SP, 0810.3233 (subm.
Stefano Profumo UC Santa Cruz Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics T.A.S.C. [Theoretical Astrophysics, Santa Cruz] Fundamental Physics with GeV Gamma Rays Based on: Kamionkowski & SP, 0810.3233 (subm.
Cosmological Shocks and Their Signatures
 Cosmological Shocks and Their Signatures Dongsu Ryu (Chungnam National U, Korea) Hyesung Kang (PNU, Korea), Renyi Ma (CNU, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (CNU, Korea), David Porter (U of Minnesota), T. W. Jones
Cosmological Shocks and Their Signatures Dongsu Ryu (Chungnam National U, Korea) Hyesung Kang (PNU, Korea), Renyi Ma (CNU, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (CNU, Korea), David Porter (U of Minnesota), T. W. Jones
PoS(ICRC2017)283. Acceleration of Cosmic Ray Electrons at Weak Shocks in Galaxy Clusters. Hyesung Kang. Dongsu Ryu
 Acceleration of Cosmic Ray Electrons at Weak Shocks in Galaxy Clusters Pusan National University E-mail: hskang@pusan.ac.kr Dongsu Ryu UNIST E-mail: ryu@sirius.unist.ac.kr T. W. Jones University of Minnesota
Acceleration of Cosmic Ray Electrons at Weak Shocks in Galaxy Clusters Pusan National University E-mail: hskang@pusan.ac.kr Dongsu Ryu UNIST E-mail: ryu@sirius.unist.ac.kr T. W. Jones University of Minnesota
NUMERICAL STUDY OF NON-THERMAL EMISSION FROM LAGRANGIAN PARTICLES IN AGN ENVIRONMENTS.
 13th AGILE Workshop, ASI, Rome May 25, 2015 NUMERICAL STUDY OF NON-THERMAL EMISSION FROM LAGRANGIAN PARTICLES IN AGN ENVIRONMENTS. Dr. Bhargav Vaidya Università degli Studi di Torino, Torino. Collaborators:
13th AGILE Workshop, ASI, Rome May 25, 2015 NUMERICAL STUDY OF NON-THERMAL EMISSION FROM LAGRANGIAN PARTICLES IN AGN ENVIRONMENTS. Dr. Bhargav Vaidya Università degli Studi di Torino, Torino. Collaborators:
80 2 Observational Cosmology L and the mean energy
 80 2 Observational Cosmology fluctuations, short-wavelength modes have amplitudes that are suppressed because these modes oscillated as acoustic waves during the radiation epoch whereas the amplitude of
80 2 Observational Cosmology fluctuations, short-wavelength modes have amplitudes that are suppressed because these modes oscillated as acoustic waves during the radiation epoch whereas the amplitude of
Where are the missing baryons?
 Interview of BSc dissertation Where are the missing baryons? Brandon Qiang Wang 6 th February 2018 Image from Millennium Simulation Content I. Introduction II. Simulations III. Results IV. Conclusion 2
Interview of BSc dissertation Where are the missing baryons? Brandon Qiang Wang 6 th February 2018 Image from Millennium Simulation Content I. Introduction II. Simulations III. Results IV. Conclusion 2
Cosmic Accelerators. 2. Pulsars, Black Holes and Shock Waves. Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford
 Cosmic Accelerators 2. Pulsars, Black Holes and Shock Waves Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford Particle Acceleration Unipolar Induction Stochastic Acceleration V ~ Ω Φ I ~ V / Z 0 Z 0 ~100Ω P ~ V I ~ V 2 /Z
Cosmic Accelerators 2. Pulsars, Black Holes and Shock Waves Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford Particle Acceleration Unipolar Induction Stochastic Acceleration V ~ Ω Φ I ~ V / Z 0 Z 0 ~100Ω P ~ V I ~ V 2 /Z
Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields
 Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Ellen Zweibel zweibel@astro.wisc.edu Departments of Astronomy & Physics University of Wisconsin, Madison and Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical
Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Ellen Zweibel zweibel@astro.wisc.edu Departments of Astronomy & Physics University of Wisconsin, Madison and Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical
Title Sunyaev Zel dovich Signal & Cross Correlations
 Title Sunyaev Zel dovich Signal & Cross Correlations Relatore Pasquale Mazzotta Universita di Roma Tor Vergata on behalf of the Italian CMB community Overview Cosmic web and Clusters of Galaxies Observing
Title Sunyaev Zel dovich Signal & Cross Correlations Relatore Pasquale Mazzotta Universita di Roma Tor Vergata on behalf of the Italian CMB community Overview Cosmic web and Clusters of Galaxies Observing
The AGN Jet Model of the Fermi Bubbles
 The AGN Jet Model of the Fermi Bubbles Fulai Guo Shanghai Astronomical Observatory IAU 322 Symposium, Palm Cove, July 18-22, 2016 1 The All-sky Fermi View at E >10 GeV The Fermi bubbles! (NASA image based
The AGN Jet Model of the Fermi Bubbles Fulai Guo Shanghai Astronomical Observatory IAU 322 Symposium, Palm Cove, July 18-22, 2016 1 The All-sky Fermi View at E >10 GeV The Fermi bubbles! (NASA image based
The Physics of Collisionless Accretion Flows. Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley)
 The Physics of Collisionless Accretion Flows Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Accretion Disks: Physical Picture Simple Consequences of Mass, Momentum, & Energy Conservation Matter Inspirals on Approximately
The Physics of Collisionless Accretion Flows Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Accretion Disks: Physical Picture Simple Consequences of Mass, Momentum, & Energy Conservation Matter Inspirals on Approximately
Magnetisation of Interstellar and Intergalactic Media: The Prospects of Low-Frequency Radio Astronomy DFG Research Unit
 Mainz, 9 July, 2012 Galactic and Intergalactic Magnetic Fields 1 Magnetisation of Interstellar and Intergalactic Media: The Prospects of Low-Frequency Radio Astronomy DFG Research Unit Mainz, 9 July, 2012
Mainz, 9 July, 2012 Galactic and Intergalactic Magnetic Fields 1 Magnetisation of Interstellar and Intergalactic Media: The Prospects of Low-Frequency Radio Astronomy DFG Research Unit Mainz, 9 July, 2012
Radio Ghosts. T.A. Enßlin 1,2
 Radio Ghosts T.A. Enßlin 1,2 1 Department of Physics, University of Toronto, 60 St. George Street, Toronto, ON, M5S1A7, Canada 2 Max Planck Institut für Radioastronomie, Auf dem Hügel 69, 53121 Bonn, Germany
Radio Ghosts T.A. Enßlin 1,2 1 Department of Physics, University of Toronto, 60 St. George Street, Toronto, ON, M5S1A7, Canada 2 Max Planck Institut für Radioastronomie, Auf dem Hügel 69, 53121 Bonn, Germany
Exploring the Ends of the Rainbow: Cosmic Rays in Star-Forming Galaxies
 Exploring the Ends of the Rainbow: Cosmic Rays in Star-Forming Galaxies Brian Lacki With Todd Thompson, Eliot Quataert, Eli Waxman, Abraham Loeb 21 September 2010 The Cosmic SED Nonthermal Thermal Nonthermal
Exploring the Ends of the Rainbow: Cosmic Rays in Star-Forming Galaxies Brian Lacki With Todd Thompson, Eliot Quataert, Eli Waxman, Abraham Loeb 21 September 2010 The Cosmic SED Nonthermal Thermal Nonthermal
Where are the missing baryons? Craig Hogan SLAC Summer Institute 2007
 Where are the missing baryons? Craig Hogan SLAC Summer Institute 2007 Reasons to care Concordance of many measures of baryon number (BBN, CMB,.) Evolution of our personal baryons (galaxies, stars, planets,
Where are the missing baryons? Craig Hogan SLAC Summer Institute 2007 Reasons to care Concordance of many measures of baryon number (BBN, CMB,.) Evolution of our personal baryons (galaxies, stars, planets,
contents 1) Superbubbles a particular environment for acceleration 2) Multiple acceleration by shocks regular acceleration (Fermi 1)
 contents 1) Superbubbles a particular environment for acceleration 2) Multiple acceleration by shocks regular acceleration (Fermi 1) 3) Transport in the bubble stochastic acceleration (Fermi 2) and escape
contents 1) Superbubbles a particular environment for acceleration 2) Multiple acceleration by shocks regular acceleration (Fermi 1) 3) Transport in the bubble stochastic acceleration (Fermi 2) and escape
Course of Galaxies course organizer: Goeran Ostlin ESSAY. X-ray physics of Galaxy Clusters
 Course of Galaxies course organizer: Goeran Ostlin ESSAY X-ray physics of Galaxy Clusters Student: Angela Adamo angela@astro.su.se fall 2006 Front:-The double cluster A1750. The contours of the XMM-Newton
Course of Galaxies course organizer: Goeran Ostlin ESSAY X-ray physics of Galaxy Clusters Student: Angela Adamo angela@astro.su.se fall 2006 Front:-The double cluster A1750. The contours of the XMM-Newton
The cosmic background radiation II: The WMAP results. Alexander Schmah
 The cosmic background radiation II: The WMAP results Alexander Schmah 27.01.05 General Aspects - WMAP measures temperatue fluctuations of the CMB around 2.726 K - Reason for the temperature fluctuations
The cosmic background radiation II: The WMAP results Alexander Schmah 27.01.05 General Aspects - WMAP measures temperatue fluctuations of the CMB around 2.726 K - Reason for the temperature fluctuations
CMB constraints on dark matter annihilation
 CMB constraints on dark matter annihilation Tracy Slatyer, Harvard University NEPPSR 12 August 2009 arxiv:0906.1197 with Nikhil Padmanabhan & Douglas Finkbeiner Dark matter!standard cosmological model:
CMB constraints on dark matter annihilation Tracy Slatyer, Harvard University NEPPSR 12 August 2009 arxiv:0906.1197 with Nikhil Padmanabhan & Douglas Finkbeiner Dark matter!standard cosmological model:
Cosmic Ray Astronomy. Qingling Ni
 Cosmic Ray Astronomy Qingling Ni What is Cosmic Ray? Mainly charged particles: protons (hydrogen nuclei)+helium nuclei+heavier nuclei What s the origin of them? What happened during their propagation?
Cosmic Ray Astronomy Qingling Ni What is Cosmic Ray? Mainly charged particles: protons (hydrogen nuclei)+helium nuclei+heavier nuclei What s the origin of them? What happened during their propagation?
Galaxy Ecosystems Adam Leroy (OSU), Eric Murphy (NRAO/IPAC) on behalf of ngvla Working Group 2
 Next Generation Very Large Array Working Group 2 HI in M74: Walter+ 08 CO in M51: Schinnerer+ 13 Continuum in M82: Marvil & Owen Galaxy Ecosystems Adam Leroy (OSU), Eric Murphy (NRAO/IPAC) on behalf of
Next Generation Very Large Array Working Group 2 HI in M74: Walter+ 08 CO in M51: Schinnerer+ 13 Continuum in M82: Marvil & Owen Galaxy Ecosystems Adam Leroy (OSU), Eric Murphy (NRAO/IPAC) on behalf of
Simulating non-linear structure formation in dark energy cosmologies
 Simulating non-linear structure formation in dark energy cosmologies Volker Springel Distribution of WIMPS in the Galaxy Early Dark Energy Models (Margherita Grossi) Coupled Dark Energy (Marco Baldi) Fifth
Simulating non-linear structure formation in dark energy cosmologies Volker Springel Distribution of WIMPS in the Galaxy Early Dark Energy Models (Margherita Grossi) Coupled Dark Energy (Marco Baldi) Fifth
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 20 Sep 2006
 Formation of Neutrino Stars from Cosmological Background Neutrinos M. H. Chan, M.-C. Chu Department of Physics, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shatin, New Territories, Hong Kong, China arxiv:astro-ph/0609564v1
Formation of Neutrino Stars from Cosmological Background Neutrinos M. H. Chan, M.-C. Chu Department of Physics, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shatin, New Territories, Hong Kong, China arxiv:astro-ph/0609564v1
Analysis of differential observations of the cosmological radio background: studying the SZE-21cm
 Analysis of differential observations of the cosmological radio background: studying the SZE-21cm Charles Mpho Takalana Supervisor: Prof Sergio Colafrancesco University of the Witwatersrand November 28,
Analysis of differential observations of the cosmological radio background: studying the SZE-21cm Charles Mpho Takalana Supervisor: Prof Sergio Colafrancesco University of the Witwatersrand November 28,
X- ray surface brightness fluctuations and turbulence in galaxy clusters. Jeremy Sanders. Andy Fabian. Sanders & Fabian 2011, MNRAS, submitted
 X- ray surface brightness fluctuations and turbulence in galaxy clusters Jeremy Sanders Andy Fabian Sanders & Fabian 2011, MNRAS, submitted Simulations predict that in galaxy clusters turbulent energy
X- ray surface brightness fluctuations and turbulence in galaxy clusters Jeremy Sanders Andy Fabian Sanders & Fabian 2011, MNRAS, submitted Simulations predict that in galaxy clusters turbulent energy
Recent Progress in Modeling of Galaxy Formation. Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan)
 Recent Progress in Modeling of Galaxy Formation Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan) In current simulations, galaxies look like this: 10 kpc Disk galaxy at z=3: stars, molecular gas, atomic gas (Zemp,
Recent Progress in Modeling of Galaxy Formation Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan) In current simulations, galaxies look like this: 10 kpc Disk galaxy at z=3: stars, molecular gas, atomic gas (Zemp,
Mergers and Non-Thermal Processes in Clusters of Galaxies
 Mergers and Non-Thermal Processes in Clusters of Galaxies Craig Sarazin University of Virginia A85 Chandra A133 Chandra and VLA Collaborators Liz Blanton, Tracy Clarke, Scott Randall, Thomas Reiprich (UVa)
Mergers and Non-Thermal Processes in Clusters of Galaxies Craig Sarazin University of Virginia A85 Chandra A133 Chandra and VLA Collaborators Liz Blanton, Tracy Clarke, Scott Randall, Thomas Reiprich (UVa)
Diffusive shock acceleration: a first order Fermi process. jan.-fév NPAC, rayons cosmiques E. Parizot (APC)
 1 Diffusive shock acceleration: a first order Fermi process 2 Shock waves Discontinuity in physical parameters shock front n 2, p 2, T 2 n 1, p 1, T 1 v 2 v 1 downstream medium (immaterial surface) upstream
1 Diffusive shock acceleration: a first order Fermi process 2 Shock waves Discontinuity in physical parameters shock front n 2, p 2, T 2 n 1, p 1, T 1 v 2 v 1 downstream medium (immaterial surface) upstream
Accretion onto the Massive Black Hole in the Galactic Center. Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley)
 Accretion onto the Massive Black Hole in the Galactic Center Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Why focus on the Galactic Center? GR! Best evidence for a BH (stellar orbits) M 4x10 6 M Largest BH on the sky
Accretion onto the Massive Black Hole in the Galactic Center Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Why focus on the Galactic Center? GR! Best evidence for a BH (stellar orbits) M 4x10 6 M Largest BH on the sky
Astro-2: History of the Universe
 Astro-2: History of the Universe Lecture 13; May 30 2013 Previously on astro-2 Energy and mass are equivalent through Einstein s equation and can be converted into each other (pair production and annihilations)
Astro-2: History of the Universe Lecture 13; May 30 2013 Previously on astro-2 Energy and mass are equivalent through Einstein s equation and can be converted into each other (pair production and annihilations)
Gamma-ray Observations of Galaxy Clusters!
 Gamma-ray Observations of Galaxy Clusters! a! Fabio Zandanel! (GRAPPA Institute University of Amsterdam)! f.zandanel@uva.nl! SnowCluster 2015 The Physics Of Galaxy Clusters! Snowbird (Utah, US) March 15-20,
Gamma-ray Observations of Galaxy Clusters! a! Fabio Zandanel! (GRAPPA Institute University of Amsterdam)! f.zandanel@uva.nl! SnowCluster 2015 The Physics Of Galaxy Clusters! Snowbird (Utah, US) March 15-20,
The Physics and Cosmology of TeV Blazars
 1 in collaboration with Avery E. Broderick 2, Phil Chang 3, Ewald Puchwein 1, Volker Springel 1 1 Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies, Germany 2 Perimeter Institute/University of Waterloo, Canada
1 in collaboration with Avery E. Broderick 2, Phil Chang 3, Ewald Puchwein 1, Volker Springel 1 1 Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies, Germany 2 Perimeter Institute/University of Waterloo, Canada
Lecture 12 : Clusters of galaxies
 Lecture 12 : Clusters of galaxies All sky surveys in the later half of 20th century changed the earlier view that clusters of galaxies are rare and that only a small fraction of galaxies are grouped together
Lecture 12 : Clusters of galaxies All sky surveys in the later half of 20th century changed the earlier view that clusters of galaxies are rare and that only a small fraction of galaxies are grouped together
Galaxy Formation: Overview
 Galaxy Formation: Overview Houjun Mo March 30, 2004 The basic picture Formation of dark matter halos. Gas cooling in dark matter halos Star formation in cold gas Evolution of the stellar populaion Metal
Galaxy Formation: Overview Houjun Mo March 30, 2004 The basic picture Formation of dark matter halos. Gas cooling in dark matter halos Star formation in cold gas Evolution of the stellar populaion Metal
Feedback from growth of supermassive black holes
 Research Collection Other Conference Item Feedback from growth of supermassive black holes Author(s): Begelman, Mitchell C.; Ruszkowksi, Mateusz Publication Date: 2003 Permanent Link: https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-a-004585094
Research Collection Other Conference Item Feedback from growth of supermassive black holes Author(s): Begelman, Mitchell C.; Ruszkowksi, Mateusz Publication Date: 2003 Permanent Link: https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-a-004585094
(Toward) A Solution to the Hydrostatic Mass Bias Problem in Galaxy Clusters. Eiichiro Komatsu (MPA) UTAP Seminar, December 22, 2014
 (Toward) A Solution to the Hydrostatic Mass Bias Problem in Galaxy Clusters Eiichiro Komatsu (MPA) UTAP Seminar, December 22, 2014 References Shi & EK, MNRAS, 442, 512 (2014) Shi, EK, Nelson & Nagai, arxiv:1408.3832
(Toward) A Solution to the Hydrostatic Mass Bias Problem in Galaxy Clusters Eiichiro Komatsu (MPA) UTAP Seminar, December 22, 2014 References Shi & EK, MNRAS, 442, 512 (2014) Shi, EK, Nelson & Nagai, arxiv:1408.3832
LOFAR Observations of Galaxy Clusters
 LOFAR Observations of Galaxy Clusters The Toothbrush Radio Relic Reinout van Weeren Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics M. Brüggen, G. Brunetti, H. Röttgering F. de Gasperin, A. Bonafede, W. Forman,
LOFAR Observations of Galaxy Clusters The Toothbrush Radio Relic Reinout van Weeren Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics M. Brüggen, G. Brunetti, H. Röttgering F. de Gasperin, A. Bonafede, W. Forman,
High-Energy Astrophysics
 M.Phys. & M.Math.Phys. High-Energy Astrophysics Garret Cotter garret.cotter@physics.ox.ac.uk High-Energy Astrophysics MT 2016 Lecture 2 High-Energy Astrophysics: Synopsis 1) Supernova blast waves; shocks.
M.Phys. & M.Math.Phys. High-Energy Astrophysics Garret Cotter garret.cotter@physics.ox.ac.uk High-Energy Astrophysics MT 2016 Lecture 2 High-Energy Astrophysics: Synopsis 1) Supernova blast waves; shocks.
Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs
 Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs Klaus Dolag ( ) Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik ( ) Introduction Evolution of the structures in the Universe t =
Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs Klaus Dolag ( ) Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik ( ) Introduction Evolution of the structures in the Universe t =
Modelling the Sunyaev Zeldovich Scaling Relations
 Modelling the Sunyaev Zeldovich Scaling Relations (Implication for SZ Power Spectrum) Anya Chaudhuri (with Subha Majumdar) Tata Institute of Fundamental Research 31 Oct 2009 Outline Sunyaev Zeldovich effect
Modelling the Sunyaev Zeldovich Scaling Relations (Implication for SZ Power Spectrum) Anya Chaudhuri (with Subha Majumdar) Tata Institute of Fundamental Research 31 Oct 2009 Outline Sunyaev Zeldovich effect
Model Universe Including Pressure
 Model Universe Including Pressure The conservation of mass within the expanding shell was described by R 3 ( t ) ρ ( t ) = ρ 0 We now assume an Universe filled with a fluid (dust) of uniform density ρ,
Model Universe Including Pressure The conservation of mass within the expanding shell was described by R 3 ( t ) ρ ( t ) = ρ 0 We now assume an Universe filled with a fluid (dust) of uniform density ρ,
Constraining primordial magnetic fields with observations
 Constraining primordial magnetic fields with observations Kerstin Kunze (University of Salamanca and IUFFyM) KK PRD 83 (2011) 023006; PRD 85 (2012) 083004; PRD 87 (2013) 103005; PRD 89 (2014) 103016, arxiv:1703.03650
Constraining primordial magnetic fields with observations Kerstin Kunze (University of Salamanca and IUFFyM) KK PRD 83 (2011) 023006; PRD 85 (2012) 083004; PRD 87 (2013) 103005; PRD 89 (2014) 103016, arxiv:1703.03650
Astronomy. Astrophysics. Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy formation
 A&A 481, 33 63 (8) DOI: 1.151/4-6361:6595 c ESO 8 Astronomy & Astrophysics Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy formation M. Jubelgas 1, V. Springel 1, T. Enßlin 1, and C. Pfrommer
A&A 481, 33 63 (8) DOI: 1.151/4-6361:6595 c ESO 8 Astronomy & Astrophysics Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy formation M. Jubelgas 1, V. Springel 1, T. Enßlin 1, and C. Pfrommer
Galaxy formation and evolution II. The physics of galaxy formation
 Galaxy formation and evolution II. The physics of galaxy formation Gabriella De Lucia Astronomical Observatory of Trieste Outline: ü Observational properties of galaxies ü Galaxies and Cosmology ü Gas
Galaxy formation and evolution II. The physics of galaxy formation Gabriella De Lucia Astronomical Observatory of Trieste Outline: ü Observational properties of galaxies ü Galaxies and Cosmology ü Gas
> News < AMS-02 will be launched onboard the Shuttle Endeavour On May 2nd 2:33 P.M. from NASA Kennedy space center!
 > News < Anti-matter, dark matter measurement By measuring the cosmic rays (Mainly electron, positron, proton, anti-proton and light nuclei) AMS-02 will be launched onboard the Shuttle Endeavour On May
> News < Anti-matter, dark matter measurement By measuring the cosmic rays (Mainly electron, positron, proton, anti-proton and light nuclei) AMS-02 will be launched onboard the Shuttle Endeavour On May
Signatures of clumpy dark matter in the global 21 cm background signal D.T. Cumberland, M. Lattanzi, and J.Silk arxiv:
 Signatures of clumpy dark matter in the global 2 cm background signal D.T. Cumberland, M. Lattanzi, and J.Silk arxiv:0808.088 Daniel Grin Ay. Journal Club /23/2009 /8 Signatures of clumpy dark matter in
Signatures of clumpy dark matter in the global 2 cm background signal D.T. Cumberland, M. Lattanzi, and J.Silk arxiv:0808.088 Daniel Grin Ay. Journal Club /23/2009 /8 Signatures of clumpy dark matter in
Towards Understanding Simulations of Galaxy Formation. Nigel Mitchell. On the Origin of Cores in Simulated Galaxy Clusters
 Towards Understanding Simulations of Galaxy Formation Nigel Mitchell On the Origin of Cores in Simulated Galaxy Clusters Work published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomy Society Journal, 2009,
Towards Understanding Simulations of Galaxy Formation Nigel Mitchell On the Origin of Cores in Simulated Galaxy Clusters Work published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomy Society Journal, 2009,
Probing the Dark Ages with 21 cm Absorption
 May 13, 2008 Probing the Dark Ages with 21 cm Absorption Emil Polisensky (UMD/NRL) ABSTRACT A brief overview of detecting neutral hydrogen gas during the cosmic Dark Ages in absorption against the background
May 13, 2008 Probing the Dark Ages with 21 cm Absorption Emil Polisensky (UMD/NRL) ABSTRACT A brief overview of detecting neutral hydrogen gas during the cosmic Dark Ages in absorption against the background
A New View of the High-Energy γ-ray Sky with the Fermi Telescope
 A New View of the High-Energy γ-ray Sky with the Fermi Telescope Aurelien Bouvier KIPAC/SLAC, Stanford University On behalf of the Fermi collaboration SNOWPAC, 2010 The Fermi observatory Launch: June 11
A New View of the High-Energy γ-ray Sky with the Fermi Telescope Aurelien Bouvier KIPAC/SLAC, Stanford University On behalf of the Fermi collaboration SNOWPAC, 2010 The Fermi observatory Launch: June 11
