Constraining primordial magnetic fields with observations
|
|
|
- Felicity Fields
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Constraining primordial magnetic fields with observations Kerstin Kunze (University of Salamanca and IUFFyM) KK PRD 83 (2011) ; PRD 85 (2012) ; PRD 87 (2013) ; PRD 89 (2014) , arxiv: (PRD (2017) accepted for publication) KK, E. Komatsu, JCAP 1506 (2015) 06, 027 KK, E. Komatsu, JCAP 1401 (2014) 01, 009
2 Overview Observations of large scale magnetic fields Effects of primordial magnetic fields on the CMB and LSS
3 Observations: Methods Galactic and extra galactic magnetic fields Synchrotron radiation Diffuse Synchrotron radio emission NASA equipartition of energy between relativistic particles and magnetic fields allows estimate of magnetic field strength cosmic rays σ N 0 ν (γ 1)/2 B (γ+1)/2 γ 2.75 for galactic radio emission ρ CR B2 8π ρu2 2 kinetic energy Estimate of magnetic field component perpendicular to line of sight σ ν B N 0 emissivity frequency magnetic field perpendicular to line of sight n u m b e r o f re l a t i v i s t i c electrons per unit energy Faraday rotation Estimate of magnetic field component parallel to line of sight Faraday rotation measure RM = 812 L 0 n e B dl radians m 2 χ =RMλ 2 n e thermal electron density B magnetic field in μg wavelength Kronberg AIP 2002
4 M51 Observations Total synchrotron intensity around the galaxy cluster Abell 2255 (Neininger 1992) Total magnetic field strength B t =(13.7 ± 2)µG Galactic magnetic field Polarised emission from Milky Way dust ESA and the Planck Collaboration (2015) Magnetic field strength: near sun: 2 μg halo (north/south): 4 (2) μg Kronberg, Newton-McGee (2011) All-sky map of rotation measures in the Milky Way, using data of 2257 sources. (Govoni et al. 2006) Magnetic field strength at center ~2.5 μg.
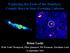
5 Observations: Methods Void magnetic fields / cosmological magnetic fields scattering of starlight with dust Extended emission due to deviation of electrons/ positrons in a magnetic field Interaction with EBL (Extragalactic background light) Energy of primary γ-ray: E γ m2 e ϵ Energy of EBL soft photon 250 ( ϵ ) 1 GeV 1 ev Interaction with CMB: inverse Compton scattering E IC = 4ϵ CMBE 2 e 3m 2 e Energy of CMB photon 3 ( ) 2 Ee GeV 1 TeV direct starlight emission EBL direct measurement σ NCMB 0 ν (γ 1)/2 B (γ+1)/2 Blazar Artist s impression. Image Credit: NASA/JPL B B limit Color code: Fraction of total energy emitted in this region Durrer, Neronov (2013)
6 Observations Spectral energy distribution of 1ES Fermi/lat HESS B(G) HESS Veritas Tavecchio et al. (2010) B G Assuming mean blazar TeV flux constant on large time scales Dermer et al. (2011) B G Assuming mean blazar TeV flux constant over 3-4 years of observations
7 Cosmological magnetic fields and the CMB Assumptions Origin of magnetic fields in the very early universe Stochastic magnetic field Bi ( k)b j ( q) = k,q P S (k) Most general form: helical magnetic field ij k i k j k 2 + kk 0P A (k)i ijmˆkm where P M (k, k m,k L )=A M k M = S, A k L nm W (k, k m ) pivot scale Example of helical magnetic field structure: Filament eruption in solar corona modelled by twisted flux rope window function W (k, k m )= 3 2 k 3 m e (k/k m) 2 damping scale upper cut-off Torok & Kliem (2005)
8 Cosmological magnetic fields and the CMB effects of magnetic field survival magnetic field effects of magnetic field decay contribution to perturbations of energy density, anisotropic stress and to baryon velocity via Lorentz force plasma interactions induce partly decay/damping energy injection CMB temperature anisotropies and polarisation CMB spectral distortions
9 Primary CMB anisotropies and polarisation induced by contribution of helical magnetic field ANGULAR POWER SPECTRA FOR SCALAR,VECTOR AND TENSOR MODES distinctive signature of helical magnetic field 2 TE 2 TT T 0 l(l+1)cl /(2π)[µK 2 T 0 l(l+1)cl /(2π)[µK 2 ] ] B=5 ng, n S =-2.9, β=0 Scalar n A =-2.9 Scalar n A =-1.9 Vector n A =-2.9 TT Vector n A =-1.9 Tensor n A =-1.9 Tensor n A = l B=5 ng, n S =-2.9, β=0 Scalar n A =-2.9 Scalar n A =-1.9 Vector n A =-2.9 TE Vector n A =-1.9 Tensor n A =-2.9 Tensor n A =-1.9 T 0 2 l(l+1)cl EE /(2π)[µK 2 ] T 0 2 l(l+1)cl BB /(2π)[µK 2 ] B=5 ng, n S =-2.9, β=0 Scalar n A =-2.9 Scalar n A =-1.9 Vector n A =-2.9 Vector n A =-1.9 Tensor n A =-2.9 Tensor n A =-1.9 EE l B=5 ng, n S =-2.9, β=0 Vector n A =-2.9 Vector n A =-1.9 Tensor n A =-2.9 Tensor n A =-1.9 BB T 0 2 l(l+1)cl EB /(2π)[µK 2 ] T 0 2 l(l+1)cl TB /(2π)[µK 2 ] B=5 ng, n S =-2.9, β=0 Vector n A =-2.9 Vector n A =-1.9 Tensor n A =-2.9 EB Tensor n A = B=5 ng, n S l =-2.9, β=0 Vector n A =-2.9 Vector n A =-1.9 Tensor n A =-2.9 TB Tensor n A = l MODIFIED VERSION OF CMBEASY l l KK 12
10 Bulk motions of electrons along the line of sight induce secondary temperature fluctuations in the postdecoupling, reionized universe. Fluctuations in baryon energy density along line-of-sight change number density of potential scatterers for CMB photons, thus change scattering probability and visibility function. Secondary CMB anisotropies In the presence of a magnetic field not only the scalar mode but also the vector mode source bulk motions.
11 Secondary CMB anisotropies Induced temperature anisotropies Future observations with ALMA might reach Credit: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO) KK 14 Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA): ALMA - the largest astronomical project in existence- is a single telescope of revolutionary design, composed of 66 high precision antennas located on the Chajnantor plateau, 5000 meters altitude in northern Chile.
12 Cosmological magnetic fields and the CMB Damping of magnetic fields There is also damping around neutrino decoupling at around z~ when a black body spectrum is always restored. (no spectral distortions) Before decoupling of photons viscous damping energy injection After decoupling of photons decaying MHD turbulence ambipolar diffusion change in thermal and ionisation history
13 Damping in the pre-decoupling era Subramanian, Barrow 1998 (nonlinear treatment) In a magnetized plasma: 3 additional modes Jedamzik, Katalinic, Olinto 1998 Fast magnetosonic modes: damp similarly to sonic waves (Silk damping) damping wave number k d = k γ Slow magnetosonic and Alfvén modes: overdamped limit damping wave number k d = k γ v A cos θ inverse of usual photon diffusion scale Alfvén velocity v A B 0 / ρ + p ( ) v A = B0 1nG a n g l e b e t w e e n background field direction and wave vector
14 Damping in the post-decoupling era Ambipolar diffusion After decoupling radiative viscosity dramatically drops. However magnetic fields can still be damped. Decaying MHD turbulence After decoupling turbulence no longer suppressed, nonlinear interactions transfer energy to smaller scales, dissipating magnetic field on large scale, inducing MHD turbulence to decay. non helical (open debate on inverse cascade for non helical fields: Kahniashvili et al. 13, 14, 15)
15 radiative viscosity decaying MHD turbulence ambipolar diffusion z>z dec z dec >z>100 z<100 Evolution of electron temperature T e = 2ȧ a T e + x e 1+x e 8ρ γ σ T 3m e c (T γ T e )+ x eγ 1.5k B n e KK, Komatsu 15
16 Effect of post-decoupling magnetic field damping on CMB anisotropies tot = reio + high z determined by (B 0,n B ) C EE ` at low l not affected magnetic field dissipation contributes C TT `! C TT ` e 2 tot KK, Komatsu 15
17 TT EE magnetic field parameters TE B =3nG n B = 1.5, 2.5, 2.9 Planck13+WP KK, Komatsu 15
18 The 95% CL upper bounds are B0 < 0.63, 0.39, and 0.18 ng for nb = 2.9, 2.5, and 1.5, respectively. y distortion y < 10 9, , and 10 9 for nb = 2.9, 2.5, and 1.5, respectively modified version of CLASS + montepython KK, Komatsu 15
19 Effect of pre-decoupling magnetic field damping on CMB anisotropies 6000 B=0.05 ng, n B = B=0.05 ng, n B = B=0.01 ng, n B =-2.5 B=0.005 ng, n B = B=0.01 ng, n B =-2.5 B=0.005 ng, n B =-1.5 T 0 2 l(l+1)cl TT /(2π)[µK 2 ] B=0 WMAP 9 T 0 2 l(l+1)cl EE /(2π)[µK 2 ] B= l l magnetic field parameters 200 B=0.05 ng, n B =-2.9 B =0.05 ng,n B = 2.9 B =0.01 ng,n B = 2.5 B =0.005 ng,n B = 1.5 T 0 2 l(l+1)cl TE /(2π)[µK 2 ] B=0.01 ng, n B =-2.5 B=0.005 ng, n B =-1.5 B= l KK 17
20 B=5 ng, n S =-2.9, β=0 Vector n A =-2.9 Vector n A EB =-1.9 Tensor n A =-2.9 Tensor n A =-1.9 Summary T 0 2 l(l+1)cl EB /(2π)[µK 2 ] CMB anisotropies Direct contribution of magnetic field l Linear matter power spectrum KK 11? primordial magnetic fields
21 Summary CMB anisotropies Indirect contribution: energy injection from decay of magnetic field? primordial magnetic fields CMB spectral distortions
EFFECTS OF HELICAL MAGNETIC FIELDS ON THE CMB
 EFFECTS OF HELICAL MAGNETIC FIELDS ON THE CMB KERSTIN KUNZE (UNIVERSITY OF SALAMANCA) KK, PRD 85 (2012) 083004 KK, PRD 83 (2011) 023006 OVERVIEW MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE UNIVERSE STOCHASTIC HELICAL MAGNETIC
EFFECTS OF HELICAL MAGNETIC FIELDS ON THE CMB KERSTIN KUNZE (UNIVERSITY OF SALAMANCA) KK, PRD 85 (2012) 083004 KK, PRD 83 (2011) 023006 OVERVIEW MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE UNIVERSE STOCHASTIC HELICAL MAGNETIC
Lower bound on the extragalactic magnetic field
 Lower bound on the extragalactic magnetic field Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Dolag, MK, Ostapchenko, Tomàs 10 Neronov, Semikoz, MK, Ostapchenko, Elyiv 10 Introduction Mean free path of photons
Lower bound on the extragalactic magnetic field Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Dolag, MK, Ostapchenko, Tomàs 10 Neronov, Semikoz, MK, Ostapchenko, Elyiv 10 Introduction Mean free path of photons
The amplification of magnetic fields by the turbulent dynamo in the early Universe
 The amplification of magnetic fields by the turbulent dynamo in the early Universe Jacques M. Wagstaff Phys. Rev. D89:103001 arxiv:1304.4723 Hamburger Sternwarte, Hamburg University Robi Banerjee 1, Dominik
The amplification of magnetic fields by the turbulent dynamo in the early Universe Jacques M. Wagstaff Phys. Rev. D89:103001 arxiv:1304.4723 Hamburger Sternwarte, Hamburg University Robi Banerjee 1, Dominik
Probing Primordial Magnetic Fields with Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
 Probing Primordial Magnetic Fields with Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation Department of Physics and Astrophysics University of Delhi IIT Madras, May 17, 2012 Collaborators: K. Subramanian, Pranjal
Probing Primordial Magnetic Fields with Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation Department of Physics and Astrophysics University of Delhi IIT Madras, May 17, 2012 Collaborators: K. Subramanian, Pranjal
Evolution and Signatures of Helical Magnetic Fields
 Evolution and Signatures of Helical Magnetic Fields Tina Kahniashvili McWilliams Center for Cosmology Carnegie Mellon University & Abastumani Astrophysical Observatory Ilia State University NORDITA June
Evolution and Signatures of Helical Magnetic Fields Tina Kahniashvili McWilliams Center for Cosmology Carnegie Mellon University & Abastumani Astrophysical Observatory Ilia State University NORDITA June
Effects of primordial kinetic and magnetic helicity
 Effects of primordial kinetic and magnetic helicity Tina Kahniashvili 1. T. Kahniashvili and B.Ratra, 2005, PRD, 71, 103006 2. T. Kahniashvili, G. Gogoberidze, and B. Ratra, astro-ph/0505628, Phys. Rev.
Effects of primordial kinetic and magnetic helicity Tina Kahniashvili 1. T. Kahniashvili and B.Ratra, 2005, PRD, 71, 103006 2. T. Kahniashvili, G. Gogoberidze, and B. Ratra, astro-ph/0505628, Phys. Rev.
The cosmic background radiation II: The WMAP results. Alexander Schmah
 The cosmic background radiation II: The WMAP results Alexander Schmah 27.01.05 General Aspects - WMAP measures temperatue fluctuations of the CMB around 2.726 K - Reason for the temperature fluctuations
The cosmic background radiation II: The WMAP results Alexander Schmah 27.01.05 General Aspects - WMAP measures temperatue fluctuations of the CMB around 2.726 K - Reason for the temperature fluctuations
The Secondary Universe
 Secondary photons and neutrinos from distant blazars and the intergalactic magnetic fields UC Berkeley September 11, 2011 The talk will be based on A new interpretation of the gamma-ray observations of
Secondary photons and neutrinos from distant blazars and the intergalactic magnetic fields UC Berkeley September 11, 2011 The talk will be based on A new interpretation of the gamma-ray observations of
Testing a DM explanation of the positron excess with the Inverse Compton scattering
 Testing a DM explanation of the positron excess with the Inverse Compton scattering Gabrijela Zaharijaš Oskar Klein Center, Stockholm University Work with A. Sellerholm, L. Bergstrom, J. Edsjo on behalf
Testing a DM explanation of the positron excess with the Inverse Compton scattering Gabrijela Zaharijaš Oskar Klein Center, Stockholm University Work with A. Sellerholm, L. Bergstrom, J. Edsjo on behalf
Hunting for Dark Matter in Anisotropies of Gamma-ray Sky: Theory and First Observational Results from Fermi-LAT
 Hunting for Dark Matter in Anisotropies of Gamma-ray Sky: Theory and First Observational Results from Fermi-LAT Eiichiro Komatsu (Texas Cosmology Center, Univ. of Texas at Austin) MPA Seminar, September
Hunting for Dark Matter in Anisotropies of Gamma-ray Sky: Theory and First Observational Results from Fermi-LAT Eiichiro Komatsu (Texas Cosmology Center, Univ. of Texas at Austin) MPA Seminar, September
Radio Continuum: Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields. Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn
 Radio Continuum: Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn Synchrotron emission Beam angle: Ψ/2=1/γ=E o /E Radio continuum tools to study GeV Cosmic ray electrons (CRE) Synchrotron spectrum:
Radio Continuum: Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn Synchrotron emission Beam angle: Ψ/2=1/γ=E o /E Radio continuum tools to study GeV Cosmic ray electrons (CRE) Synchrotron spectrum:
Fundamental Physics with GeV Gamma Rays
 Stefano Profumo UC Santa Cruz Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics T.A.S.C. [Theoretical Astrophysics, Santa Cruz] Fundamental Physics with GeV Gamma Rays Based on: Kamionkowski & SP, 0810.3233 (subm.
Stefano Profumo UC Santa Cruz Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics T.A.S.C. [Theoretical Astrophysics, Santa Cruz] Fundamental Physics with GeV Gamma Rays Based on: Kamionkowski & SP, 0810.3233 (subm.
Estimation of neutrino spectra from AGNs using measured VHE γ-ray spectra
 Estimation of neutrino spectra from AGNs using measured VHE -ray spectra Garabed HALLADJIAN December 9 th, 2008 -cr-ν workshop, PARIS 9 December 2008 G. Halladjian 1 Presentation plan Hypotheses & Aim
Estimation of neutrino spectra from AGNs using measured VHE -ray spectra Garabed HALLADJIAN December 9 th, 2008 -cr-ν workshop, PARIS 9 December 2008 G. Halladjian 1 Presentation plan Hypotheses & Aim
Amplification of magnetic fields from turbulence in the early Universe
 Amplification of magnetic fields from turbulence in the early Universe Jacques M. Wagstaff 1 arxiv:1304.4723 Robi Banerjee 1, Dominik Schleicher 2, Günter Sigl 3 1 Hamburg University 2 Institut für Astrophysik,
Amplification of magnetic fields from turbulence in the early Universe Jacques M. Wagstaff 1 arxiv:1304.4723 Robi Banerjee 1, Dominik Schleicher 2, Günter Sigl 3 1 Hamburg University 2 Institut für Astrophysik,
Indirect Dark Matter constraints with radio observations
 Indirect Dark Matter constraints with radio observations In collaboration with E.Borriello and G.Miele, University of Naples Federico II Alessandro Cuoco, Institute for Physics and Astronomy University
Indirect Dark Matter constraints with radio observations In collaboration with E.Borriello and G.Miele, University of Naples Federico II Alessandro Cuoco, Institute for Physics and Astronomy University
An Auger Observatory View of Centaurus A
 An Auger Observatory View of Centaurus A Roger Clay, University of Adelaide based on work particularly done with: Bruce Dawson, Adelaide Jose Bellido, Adelaide Ben Whelan, Adelaide and the Auger Collaboration
An Auger Observatory View of Centaurus A Roger Clay, University of Adelaide based on work particularly done with: Bruce Dawson, Adelaide Jose Bellido, Adelaide Ben Whelan, Adelaide and the Auger Collaboration
Cosmic Rays in Galaxy Clusters: Simulations and Perspectives
 Cosmic Rays in Galaxy Clusters: Simulations and Perspectives 1 in collaboration with Volker Springel 2, Torsten Enßlin 2 1 Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Canada 2 Max-Planck Institute
Cosmic Rays in Galaxy Clusters: Simulations and Perspectives 1 in collaboration with Volker Springel 2, Torsten Enßlin 2 1 Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Canada 2 Max-Planck Institute
Reduced MHD. Nick Murphy. Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics. February 19, 2014
 Reduced MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 19, 2014 These lecture notes are largely based on Lectures in Magnetohydrodynamics by Dalton
Reduced MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 19, 2014 These lecture notes are largely based on Lectures in Magnetohydrodynamics by Dalton
Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs
 Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs Klaus Dolag ( ) Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik ( ) Introduction Evolution of the structures in the Universe t =
Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs Klaus Dolag ( ) Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik ( ) Introduction Evolution of the structures in the Universe t =
Magnetic field structure from Planck polarization observations of the diffuse Galactic ISM
 Magnetic field structure from Planck polarization observations of the diffuse Galactic ISM François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale on behalf of the Planck Consortium Outline The Planck data
Magnetic field structure from Planck polarization observations of the diffuse Galactic ISM François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale on behalf of the Planck Consortium Outline The Planck data
Cosmology II: The thermal history of the Universe
 .. Cosmology II: The thermal history of the Universe Ruth Durrer Département de Physique Théorique et CAP Université de Genève Suisse August 6, 2014 Ruth Durrer (Université de Genève) Cosmology II August
.. Cosmology II: The thermal history of the Universe Ruth Durrer Département de Physique Théorique et CAP Université de Genève Suisse August 6, 2014 Ruth Durrer (Université de Genève) Cosmology II August
Jun. Prof. Dr. Alessandro MIRIZZI (Universität Hamburg)
 Bari Xmas Workshop Bari, 20th December 2012 AXION-LIKE PARTICLES AND THE TRANSPARENCY OF THE UNIVERSE Jun. Prof. Dr. Alessandro MIRIZZI (Universität Hamburg) AXION-LIKE PARTICLES L a 1 4 g a F ~ F a g
Bari Xmas Workshop Bari, 20th December 2012 AXION-LIKE PARTICLES AND THE TRANSPARENCY OF THE UNIVERSE Jun. Prof. Dr. Alessandro MIRIZZI (Universität Hamburg) AXION-LIKE PARTICLES L a 1 4 g a F ~ F a g
Imprint of Scalar Dark Energy on CMB polarization
 Imprint of Scalar Dark Energy on CMB polarization Kin-Wang Ng ( 吳建宏 ) Institute of Physics & Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Academia Sinica, Taiwan Cosmology and Gravity Pre-workshop NTHU, Apr
Imprint of Scalar Dark Energy on CMB polarization Kin-Wang Ng ( 吳建宏 ) Institute of Physics & Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Academia Sinica, Taiwan Cosmology and Gravity Pre-workshop NTHU, Apr
Second part of the talk
 Second part of the talk Homogeneous vs Inhomogeneous No matter where they come from, PMFs could have left an imprint on the CMB anisotropy pattern in temperature and polarization. In case of an homogeneous
Second part of the talk Homogeneous vs Inhomogeneous No matter where they come from, PMFs could have left an imprint on the CMB anisotropy pattern in temperature and polarization. In case of an homogeneous
Astro2020 Science White Paper Prospects for the detection of synchrotron halos around middle-age pulsars
 Astro2020 Science White Paper Prospects for the detection of synchrotron halos around middle-age pulsars Thematic Areas: Planetary Systems Star and Planet Formation Formation and Evolution of Compact Objects
Astro2020 Science White Paper Prospects for the detection of synchrotron halos around middle-age pulsars Thematic Areas: Planetary Systems Star and Planet Formation Formation and Evolution of Compact Objects
The Galactic diffuse gamma ray emission in the energy range 30 TeV 3 PeV
 The Galactic diffuse gamma ray emission in the energy range 30 TeV 3 PeV Mount Rainier by Will Christiansen Silvia Vernetto & Paolo Lipari 35th ICRC 12-20 July 2017 - Busan - South Korea Gamma ray astronomy
The Galactic diffuse gamma ray emission in the energy range 30 TeV 3 PeV Mount Rainier by Will Christiansen Silvia Vernetto & Paolo Lipari 35th ICRC 12-20 July 2017 - Busan - South Korea Gamma ray astronomy
The ultimate measurement of the CMB temperature anisotropy field UNVEILING THE CMB SKY
 The ultimate measurement of the CMB temperature anisotropy field UNVEILING THE CMB SKY PARAMETRIC MODEL 16 spectra in total C(θ) = CMB theoretical spectra plus physically motivated templates for the
The ultimate measurement of the CMB temperature anisotropy field UNVEILING THE CMB SKY PARAMETRIC MODEL 16 spectra in total C(θ) = CMB theoretical spectra plus physically motivated templates for the
CMB constraints on dark matter annihilation
 CMB constraints on dark matter annihilation Tracy Slatyer, Harvard University NEPPSR 12 August 2009 arxiv:0906.1197 with Nikhil Padmanabhan & Douglas Finkbeiner Dark matter!standard cosmological model:
CMB constraints on dark matter annihilation Tracy Slatyer, Harvard University NEPPSR 12 August 2009 arxiv:0906.1197 with Nikhil Padmanabhan & Douglas Finkbeiner Dark matter!standard cosmological model:
Magnetic Fields in Astrophysics: Origins and Evolution. Kinwah Wu Mullard Space Science Laboratory University College London
 Magnetic Fields in Astrophysics: Origins and Evolution Kinwah Wu Mullard Space Science Laboratory University College London Maxwell s equations covariant form in flat space time Lorentz force equation:
Magnetic Fields in Astrophysics: Origins and Evolution Kinwah Wu Mullard Space Science Laboratory University College London Maxwell s equations covariant form in flat space time Lorentz force equation:
Really, really, what universe do we live in?
 Really, really, what universe do we live in? Fluctuations in cosmic microwave background Origin Amplitude Spectrum Cosmic variance CMB observations and cosmological parameters COBE, balloons WMAP Parameters
Really, really, what universe do we live in? Fluctuations in cosmic microwave background Origin Amplitude Spectrum Cosmic variance CMB observations and cosmological parameters COBE, balloons WMAP Parameters
Cosmology and fundamental physics with extragalactic TeV γ-rays?
 Cosmology and fundamental physics with extragalactic TeV γ-rays? Matthias Lorentz PhD with Pierre Brun at Irfu/SPP DDays 7-8 July 2016 Introduction : my PhD topic What we can learn from TeV photons propagating
Cosmology and fundamental physics with extragalactic TeV γ-rays? Matthias Lorentz PhD with Pierre Brun at Irfu/SPP DDays 7-8 July 2016 Introduction : my PhD topic What we can learn from TeV photons propagating
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 28 May 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 28 May 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 28 May 2018](/thumbs/93/113357000.jpg) 21 cm line signal from magnetic modes arxiv:1805.10943v1 [astro-ph.co] 28 May 2018 Kerstin E. Kunze Departamento de Física Fundamental, Universidad de Salamanca, Plaza de la Merced s/n, 37008 Salamanca,
21 cm line signal from magnetic modes arxiv:1805.10943v1 [astro-ph.co] 28 May 2018 Kerstin E. Kunze Departamento de Física Fundamental, Universidad de Salamanca, Plaza de la Merced s/n, 37008 Salamanca,
SKA AND THE COSMOLOGICAL EVOLUTION OF CLUSTER MAGNETIC FIELDS
 SKA AND THE COSMOLOGICAL EVOLUTION OF CLUSTER MAGNETIC FIELDS MARTIN KRAUSE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE, UNIVERSITÄTSSTERNWARTE MÜNCHEN & MAX-PLANCK-INSTITUT FÜR EXTRATERRESTRISCHE PHYSIK COLLABORATORS: PAUL
SKA AND THE COSMOLOGICAL EVOLUTION OF CLUSTER MAGNETIC FIELDS MARTIN KRAUSE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE, UNIVERSITÄTSSTERNWARTE MÜNCHEN & MAX-PLANCK-INSTITUT FÜR EXTRATERRESTRISCHE PHYSIK COLLABORATORS: PAUL
Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies
 Lecture 4: Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies Rainer Beck, MPIfR Bonn Generation and amplification of cosmic magnetic fields Stage 1: Field seeding Stage 2: Field amplification Stage 3: Coherent field
Lecture 4: Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies Rainer Beck, MPIfR Bonn Generation and amplification of cosmic magnetic fields Stage 1: Field seeding Stage 2: Field amplification Stage 3: Coherent field
Evolution and Impact of Cosmic Magnetic Fields
 Evolution and Impact of Cosmic Magnetic Fields Robi Banerjee University of Hamburg Collaborators: Dominik Schleicher (Göttingen), C. Federrath (Lyon, HD), Karsten Jedamzik (Montpellier), R. Klessen (Heidelberg),
Evolution and Impact of Cosmic Magnetic Fields Robi Banerjee University of Hamburg Collaborators: Dominik Schleicher (Göttingen), C. Federrath (Lyon, HD), Karsten Jedamzik (Montpellier), R. Klessen (Heidelberg),
A New View of the High-Energy γ-ray Sky with the Fermi Telescope
 A New View of the High-Energy γ-ray Sky with the Fermi Telescope Aurelien Bouvier KIPAC/SLAC, Stanford University On behalf of the Fermi collaboration SNOWPAC, 2010 The Fermi observatory Launch: June 11
A New View of the High-Energy γ-ray Sky with the Fermi Telescope Aurelien Bouvier KIPAC/SLAC, Stanford University On behalf of the Fermi collaboration SNOWPAC, 2010 The Fermi observatory Launch: June 11
Primordial gravitational waves detected? Atsushi Taruya
 21 May 2014 Lunch seminar @YITP Primordial gravitational waves detected? Atsushi Taruya Contents Searching for primordial gravitational waves from cosmic microwave background polarizations Gravitational-wave
21 May 2014 Lunch seminar @YITP Primordial gravitational waves detected? Atsushi Taruya Contents Searching for primordial gravitational waves from cosmic microwave background polarizations Gravitational-wave
EBL Studies with the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope
 EBL Studies with the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Luis C. Reyes KICP The Extragalactic Background Light (EBL) What is it? Accumulation of all energy releases in the form of electromagnetic radiation.
EBL Studies with the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Luis C. Reyes KICP The Extragalactic Background Light (EBL) What is it? Accumulation of all energy releases in the form of electromagnetic radiation.
Structures in the early Universe. Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4
 Structures in the early Universe Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4 overview Part 1: problems in Standard Model of Cosmology: horizon and flatness problems presence of structures Part : Need for
Structures in the early Universe Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4 overview Part 1: problems in Standard Model of Cosmology: horizon and flatness problems presence of structures Part : Need for
Primordial Magnetic Field Effects on CMB polarization
 Primordial Magnetic Field Effects on CMB polarization Tina Kahniashvili McWilliams Center for Cosmology Carnegie Mellon University, USA & Abastumani Astrophysical Observatory, Ilia Chavchavadze State University,
Primordial Magnetic Field Effects on CMB polarization Tina Kahniashvili McWilliams Center for Cosmology Carnegie Mellon University, USA & Abastumani Astrophysical Observatory, Ilia Chavchavadze State University,
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations. simulations of galaxy and structure formation
 Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 13 26 / Workshop Dark halos, UBC Vancouver Outline 1
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 13 26 / Workshop Dark halos, UBC Vancouver Outline 1
Exploring the Ends of the Rainbow: Cosmic Rays in Star-Forming Galaxies
 Exploring the Ends of the Rainbow: Cosmic Rays in Star-Forming Galaxies Brian Lacki With Todd Thompson, Eliot Quataert, Eli Waxman, Abraham Loeb 21 September 2010 The Cosmic SED Nonthermal Thermal Nonthermal
Exploring the Ends of the Rainbow: Cosmic Rays in Star-Forming Galaxies Brian Lacki With Todd Thompson, Eliot Quataert, Eli Waxman, Abraham Loeb 21 September 2010 The Cosmic SED Nonthermal Thermal Nonthermal
99 Years from Discovery : What is our current picture on Cosmic Rays? #6 How cosmic rays travel to Earth? Presented by Nahee Park
 99 Years from Discovery : What is our current picture on Cosmic Rays? #6 How cosmic rays travel to Earth? Presented by Nahee Park #5 How do Cosmic Rays gain their energy? I. Acceleration mechanism of CR
99 Years from Discovery : What is our current picture on Cosmic Rays? #6 How cosmic rays travel to Earth? Presented by Nahee Park #5 How do Cosmic Rays gain their energy? I. Acceleration mechanism of CR
M. Lattanzi. 12 th Marcel Grossmann Meeting Paris, 17 July 2009
 M. Lattanzi ICRA and Dip. di Fisica - Università di Roma La Sapienza In collaboration with L. Pieri (IAP, Paris) and J. Silk (Oxford) Based on ML, Silk, PRD 79, 083523 (2009) and Pieri, ML, Silk, MNRAS
M. Lattanzi ICRA and Dip. di Fisica - Università di Roma La Sapienza In collaboration with L. Pieri (IAP, Paris) and J. Silk (Oxford) Based on ML, Silk, PRD 79, 083523 (2009) and Pieri, ML, Silk, MNRAS
Cosmic Microwave Background
 Cosmic Microwave Background Carlo Baccigalupi,, SISSA CMB lectures at TRR33, see the complete program at darkuniverse.uni-hd.de/view/main/winterschoollecture5 These lectures are available in pdf format
Cosmic Microwave Background Carlo Baccigalupi,, SISSA CMB lectures at TRR33, see the complete program at darkuniverse.uni-hd.de/view/main/winterschoollecture5 These lectures are available in pdf format
Indirect dark matter detection and the Galactic Center GeV Excess
 Image Credit: Springel et al. 2008 Indirect dark matter detection and the Galactic Center GeV Excess Jennifer Siegal-Gaskins Caltech Image Credit: Springel et al. 2008 Jennifer Siegal-Gaskins Caltech Image
Image Credit: Springel et al. 2008 Indirect dark matter detection and the Galactic Center GeV Excess Jennifer Siegal-Gaskins Caltech Image Credit: Springel et al. 2008 Jennifer Siegal-Gaskins Caltech Image
Magnetic fields in the early universe
 Magnetic fields in the early universe KandaswamySubramanian a a Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. Heidelberg Joint Astronomical Colloquium, 1st December, 2009
Magnetic fields in the early universe KandaswamySubramanian a a Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. Heidelberg Joint Astronomical Colloquium, 1st December, 2009
Search for exotic process with space experiments
 Search for exotic process with space experiments Aldo Morselli INFN, Sezione di Roma 2 & Università di Roma Tor Vergata Rencontres de Moriond, Very High Energy Phenomena in the Universe Les Arc, 20-27
Search for exotic process with space experiments Aldo Morselli INFN, Sezione di Roma 2 & Università di Roma Tor Vergata Rencontres de Moriond, Very High Energy Phenomena in the Universe Les Arc, 20-27
Soma De Post-doctoral Fellow, Arizona State University presentation at 27th Texas Symposium, Dec 11,2013
 Linear Polarization of CMB and 21cm & Circular Polarization of CMB Soma De Post-doctoral Fellow, Arizona State University presentation at 27th Texas Symposium, Dec 11,2013 Collaboration: Levon Pogosian
Linear Polarization of CMB and 21cm & Circular Polarization of CMB Soma De Post-doctoral Fellow, Arizona State University presentation at 27th Texas Symposium, Dec 11,2013 Collaboration: Levon Pogosian
Galactic radio loops. Philipp Mertsch with Subir Sarkar. The Radio Synchrotron Background Workshop, University of Richmond 21 July 2017
 Galactic radio loops Philipp Mertsch with Subir Sarkar The Radio Synchrotron Background Workshop, University of Richmond 21 July 2017 Foregrounds in B-modes Adam et al., arxiv:1502.01588 1409.5738 (Planck
Galactic radio loops Philipp Mertsch with Subir Sarkar The Radio Synchrotron Background Workshop, University of Richmond 21 July 2017 Foregrounds in B-modes Adam et al., arxiv:1502.01588 1409.5738 (Planck
The ALMA contribution to the
 The ALMA contribution to the study of the blazar jets M. Orienti (Bologna University, INAF-IRA) Outline The extragalactic γ-ray sky and relativistic jets The Atacama Large Millimeter Array Relativistic
The ALMA contribution to the study of the blazar jets M. Orienti (Bologna University, INAF-IRA) Outline The extragalactic γ-ray sky and relativistic jets The Atacama Large Millimeter Array Relativistic
Gamma-ray echo (pair echo) from TeV sources and extragalactic magnetic fields
 Gamma-ray echo (pair echo) from TeV sources and extragalactic magnetic fields Keitaro Takahashi Nagoya University, Japan Dec./15/2010 @APC with K. Ichiki, S. Inoue, M. Mori K. Murase, S. Nagataki, T. Nakamura,
Gamma-ray echo (pair echo) from TeV sources and extragalactic magnetic fields Keitaro Takahashi Nagoya University, Japan Dec./15/2010 @APC with K. Ichiki, S. Inoue, M. Mori K. Murase, S. Nagataki, T. Nakamura,
WMAP 9-Year Results and Cosmological Implications: The Final Results
 WMAP 9-Year Results and Cosmological Implications: The Final Results Eiichiro Komatsu (Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik) 17th Paris Cosmology Colloquium 2013 Observatoire de Paris, July 24, 2013 1 used
WMAP 9-Year Results and Cosmological Implications: The Final Results Eiichiro Komatsu (Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik) 17th Paris Cosmology Colloquium 2013 Observatoire de Paris, July 24, 2013 1 used
Emmanuel Moulin! on behalf of the CTA Consortium!!! Rencontres de Moriond 2013! Very High Energy Phenomena in the Universe! March 9-16, La Thuile,
 Emmanuel Moulin! on behalf of the CTA Consortium!!! Rencontres de Moriond 2013! Very High Energy Phenomena in the Universe! March 9-16, La Thuile, Italy Emmanuel Moulin CTA meeting, Zürich 2009 1 Core-energy
Emmanuel Moulin! on behalf of the CTA Consortium!!! Rencontres de Moriond 2013! Very High Energy Phenomena in the Universe! March 9-16, La Thuile, Italy Emmanuel Moulin CTA meeting, Zürich 2009 1 Core-energy
Tesla Jeltema. Assistant Professor, Department of Physics. Observational Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics
 Tesla Jeltema Assistant Professor, Department of Physics Observational Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics Research Program Research theme: using the evolution of large-scale structure to reveal the fundamental
Tesla Jeltema Assistant Professor, Department of Physics Observational Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics Research Program Research theme: using the evolution of large-scale structure to reveal the fundamental
Concordance Cosmology and Particle Physics. Richard Easther (Yale University)
 Concordance Cosmology and Particle Physics Richard Easther (Yale University) Concordance Cosmology The standard model for cosmology Simplest model that fits the data Smallest number of free parameters
Concordance Cosmology and Particle Physics Richard Easther (Yale University) Concordance Cosmology The standard model for cosmology Simplest model that fits the data Smallest number of free parameters
Lecture 3. - Cosmological parameter dependence of the temperature power spectrum. - Polarisation of the CMB
 Lecture 3 - Cosmological parameter dependence of the temperature power spectrum - Polarisation of the CMB Planck Collaboration (2016) Let s understand the peak heights Silk+Landau Damping Sachs-Wolfe Sound
Lecture 3 - Cosmological parameter dependence of the temperature power spectrum - Polarisation of the CMB Planck Collaboration (2016) Let s understand the peak heights Silk+Landau Damping Sachs-Wolfe Sound
Rayleigh scattering:
 Rayleigh scattering: blue sky thinking for future CMB observations arxiv:1307.8148; previous work: Takahara et al. 91, Yu, et al. astro-ph/0103149 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/rayleigh_scattering Antony
Rayleigh scattering: blue sky thinking for future CMB observations arxiv:1307.8148; previous work: Takahara et al. 91, Yu, et al. astro-ph/0103149 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/rayleigh_scattering Antony
Dark matter annihilations and decays after the AMS-02 positron measurements
 Dark matter annihilations and decays after the AMS-02 positron measurements Anna S. Lamperstorfer Technische Universität München SISSA - International School for Advanced Studies of Trieste Workshop The
Dark matter annihilations and decays after the AMS-02 positron measurements Anna S. Lamperstorfer Technische Universität München SISSA - International School for Advanced Studies of Trieste Workshop The
Lecture 13 Interstellar Magnetic Fields
 Lecture 13 Interstellar Magnetic Fields 1. Introduction. Synchrotron radiation 3. Faraday rotation 4. Zeeman effect 5. Polarization of starlight 6. Summary of results References Zweibel & Heiles, Nature
Lecture 13 Interstellar Magnetic Fields 1. Introduction. Synchrotron radiation 3. Faraday rotation 4. Zeeman effect 5. Polarization of starlight 6. Summary of results References Zweibel & Heiles, Nature
The 2006 Giant Flare in PKS and Unidentified TeV Sources. Justin Finke Naval Research Laboratory 5 June 2008
 The 2006 Giant Flare in PKS 2155-304 and Unidentified TeV Sources Justin Finke Naval Research Laboratory 5 June 2008 Outline Part I: The SSC Model Part II: The giant flare in PKS 2155-304 Part III: Blazars
The 2006 Giant Flare in PKS 2155-304 and Unidentified TeV Sources Justin Finke Naval Research Laboratory 5 June 2008 Outline Part I: The SSC Model Part II: The giant flare in PKS 2155-304 Part III: Blazars
Spectra of Cosmic Rays
 Spectra of Cosmic Rays Flux of relativistic charged particles [nearly exactly isotropic] Particle density Power-Law Energy spectra Exponent (p, Nuclei) : Why power laws? (constraint on the dynamics of
Spectra of Cosmic Rays Flux of relativistic charged particles [nearly exactly isotropic] Particle density Power-Law Energy spectra Exponent (p, Nuclei) : Why power laws? (constraint on the dynamics of
Cosmological Constraints on Dark Energy via Bulk Viscosity from Decaying Dark Matter
 Cosmological Constraints on Dark Energy via Bulk Viscosity from Decaying Dark Matter Nguyen Quynh Lan Hanoi National University of Education, Vietnam (University of Notre Dame, USA) Rencontres du Vietnam:
Cosmological Constraints on Dark Energy via Bulk Viscosity from Decaying Dark Matter Nguyen Quynh Lan Hanoi National University of Education, Vietnam (University of Notre Dame, USA) Rencontres du Vietnam:
Probing the Dark Ages with 21 cm Absorption
 May 13, 2008 Probing the Dark Ages with 21 cm Absorption Emil Polisensky (UMD/NRL) ABSTRACT A brief overview of detecting neutral hydrogen gas during the cosmic Dark Ages in absorption against the background
May 13, 2008 Probing the Dark Ages with 21 cm Absorption Emil Polisensky (UMD/NRL) ABSTRACT A brief overview of detecting neutral hydrogen gas during the cosmic Dark Ages in absorption against the background
Diagnostics of Leptonic vs. Hadronic Emission Models for Blazars Prospects for H.E.S.S.-II and CTA Markus Böttcher North-West University
 Diagnostics of Leptonic vs. Hadronic Emission Models for Blazars Prospects for H.E.S.S.-II and CTA Markus Böttcher North-West University Potchefstroom South Africa Q e (g,t) Injection, acceleration of
Diagnostics of Leptonic vs. Hadronic Emission Models for Blazars Prospects for H.E.S.S.-II and CTA Markus Böttcher North-West University Potchefstroom South Africa Q e (g,t) Injection, acceleration of
Lecture 4. - Cosmological parameter dependence of the temperature power spectrum (continued) - Polarisation
 Lecture 4 - Cosmological parameter dependence of the temperature power spectrum (continued) - Polarisation Planck Collaboration (2016) Let s understand the peak heights Silk+Landau Damping Sachs-Wolfe
Lecture 4 - Cosmological parameter dependence of the temperature power spectrum (continued) - Polarisation Planck Collaboration (2016) Let s understand the peak heights Silk+Landau Damping Sachs-Wolfe
Solutions for Assignment of Week 06 Introduction to Astroparticle Physics
 s for Assignment of Week 06 Introduction to Astroparticle Physics Georg G. Raffelt Max-Planck-Institut für Physik (Werner-Heisenberg-Institut) Föhringer Ring 6, 80805 München Email: raffelt(at)mppmu.mpg.de
s for Assignment of Week 06 Introduction to Astroparticle Physics Georg G. Raffelt Max-Planck-Institut für Physik (Werner-Heisenberg-Institut) Föhringer Ring 6, 80805 München Email: raffelt(at)mppmu.mpg.de
Cosmic Inflation and Neutrino Masses at POLARBEAR CMB Polarization Experiment
 KEK Inter-University Research Institute Corporation High Energy Accelerator Research Organization Institute of Particle and Nuclear Studies Cosmic Inflation and Neutrino Masses at POLARBEAR CMB Polarization
KEK Inter-University Research Institute Corporation High Energy Accelerator Research Organization Institute of Particle and Nuclear Studies Cosmic Inflation and Neutrino Masses at POLARBEAR CMB Polarization
Particle Acceleration in the Universe
 Particle Acceleration in the Universe Hiroyasu Tajima Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology on behalf of SLAC GLAST team June 7, 2006 SLAC DOE HEP Program
Particle Acceleration in the Universe Hiroyasu Tajima Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology on behalf of SLAC GLAST team June 7, 2006 SLAC DOE HEP Program
Power spectrum exercise
 Power spectrum exercise In this exercise, we will consider different power spectra and how they relate to observations. The intention is to give you some intuition so that when you look at a microwave
Power spectrum exercise In this exercise, we will consider different power spectra and how they relate to observations. The intention is to give you some intuition so that when you look at a microwave
Cosmic Ray Astronomy. Qingling Ni
 Cosmic Ray Astronomy Qingling Ni What is Cosmic Ray? Mainly charged particles: protons (hydrogen nuclei)+helium nuclei+heavier nuclei What s the origin of them? What happened during their propagation?
Cosmic Ray Astronomy Qingling Ni What is Cosmic Ray? Mainly charged particles: protons (hydrogen nuclei)+helium nuclei+heavier nuclei What s the origin of them? What happened during their propagation?
Structure in the CMB
 Cosmic Microwave Background Anisotropies = structure in the CMB Structure in the CMB Boomerang balloon flight. Mapped Cosmic Background Radiation with far higher angular resolution than previously available.
Cosmic Microwave Background Anisotropies = structure in the CMB Structure in the CMB Boomerang balloon flight. Mapped Cosmic Background Radiation with far higher angular resolution than previously available.
Cosmic Magnetism. Abstract. 1 Introduction. Battaner et al. 141
 Spanish SKA White Book, 2015 Battaner et al. 141 Cosmic Magnetism Eduardo Battaner, 1,2, Iván Agudo, 3, Antxon Alberdi, 3, Estrella Florido, 1,2, Ana Guijarro, 4, Beatriz Ruiz-Granados, 5, and José Alberto
Spanish SKA White Book, 2015 Battaner et al. 141 Cosmic Magnetism Eduardo Battaner, 1,2, Iván Agudo, 3, Antxon Alberdi, 3, Estrella Florido, 1,2, Ana Guijarro, 4, Beatriz Ruiz-Granados, 5, and José Alberto
Cosmic ray electrons from here and there (the Galactic scale)
 Cosmic ray electrons from here and there (the Galactic scale) Julien Lavalle Department of Theoretical Physics Torino University and INFN Outline: (i) local electrons (ii) comments on synchrotron [based
Cosmic ray electrons from here and there (the Galactic scale) Julien Lavalle Department of Theoretical Physics Torino University and INFN Outline: (i) local electrons (ii) comments on synchrotron [based
Making Light from the Dark Universe
 Oxford University Physics Society, 1st May 2014 Talk Structure 1. Prelude: What is Dark Radiation? 2. Experimental motivation for dark radiation: CMB and BBN 3. Theoretical motivation for dark radiation:
Oxford University Physics Society, 1st May 2014 Talk Structure 1. Prelude: What is Dark Radiation? 2. Experimental motivation for dark radiation: CMB and BBN 3. Theoretical motivation for dark radiation:
Inferring source polarisation properties from SKA observations. Joern Geisbuesch
 Inferring source polarisation properties from SKA observations In collaboration with Paul Alexander, Rosie Bolton, Martin Krause April 2008 University of Cambridge Department of Physics Motivation and
Inferring source polarisation properties from SKA observations In collaboration with Paul Alexander, Rosie Bolton, Martin Krause April 2008 University of Cambridge Department of Physics Motivation and
Structures in the early Universe. Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4
 Structures in the early Universe Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4 overview problems in Standard Model of Cosmology: horizon and flatness problems presence of structures Need for an exponential
Structures in the early Universe Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4 overview problems in Standard Model of Cosmology: horizon and flatness problems presence of structures Need for an exponential
Polarized Relic Gravitational Waves
 Polarized Relic Gravitational Waves Tina Kahniashvili CCPP, New York University, USA & Abastumani Astrophysical Observatory, Georgia based on: T.K., G. Gogoberidze, and B.Ratra, PRL 2005, 2007 (in preparation),
Polarized Relic Gravitational Waves Tina Kahniashvili CCPP, New York University, USA & Abastumani Astrophysical Observatory, Georgia based on: T.K., G. Gogoberidze, and B.Ratra, PRL 2005, 2007 (in preparation),
PERSPECTIVES of HIGH ENERGY NEUTRINO ASTRONOMY. Paolo Lipari Vulcano 27 may 2006
 PERSPECTIVES of HIGH ENERGY NEUTRINO ASTRONOMY Paolo Lipari Vulcano 27 may 2006 High Energy Neutrino Astrophysics will CERTAINLY become an essential field in a New Multi-Messenger Astrophysics What is
PERSPECTIVES of HIGH ENERGY NEUTRINO ASTRONOMY Paolo Lipari Vulcano 27 may 2006 High Energy Neutrino Astrophysics will CERTAINLY become an essential field in a New Multi-Messenger Astrophysics What is
II. The Universe Around Us. ASTR378 Cosmology : II. The Universe Around Us 23
 II. The Universe Around Us ASTR378 Cosmology : II. The Universe Around Us 23 Some Units Used in Astronomy 1 parsec distance at which parallax angle is 1 ; 1 pc = 3.086 10 16 m ( 3.26 light years; 1 kpc
II. The Universe Around Us ASTR378 Cosmology : II. The Universe Around Us 23 Some Units Used in Astronomy 1 parsec distance at which parallax angle is 1 ; 1 pc = 3.086 10 16 m ( 3.26 light years; 1 kpc
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 8 Sep 2006
 Cosmic Magnetic Fields and the CMB Ruth Durrer arxiv:astro-ph/0609216v1 8 Sep 2006 Abstract Université de Genève, Ecole de Physique 24 Quai E. Ansermet, CH-1211 Genève Switzerland I describe the imprint
Cosmic Magnetic Fields and the CMB Ruth Durrer arxiv:astro-ph/0609216v1 8 Sep 2006 Abstract Université de Genève, Ecole de Physique 24 Quai E. Ansermet, CH-1211 Genève Switzerland I describe the imprint
Polarization from Rayleigh scattering
 Polarization from Rayleigh scattering Blue sky thinking for future CMB observations Previous work: Takahara et al. 91, Yu, et al. astro-ph/0103149 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/rayleigh_scattering Antony
Polarization from Rayleigh scattering Blue sky thinking for future CMB observations Previous work: Takahara et al. 91, Yu, et al. astro-ph/0103149 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/rayleigh_scattering Antony
The Once and Future CMB
 The Once and Future CMB DOE, Jan. 2002 Wayne Hu The On(c)e Ring Original Power Spectra of Maps 64º Band Filtered Ringing in the New Cosmology Gravitational Ringing Potential wells = inflationary seeds
The Once and Future CMB DOE, Jan. 2002 Wayne Hu The On(c)e Ring Original Power Spectra of Maps 64º Band Filtered Ringing in the New Cosmology Gravitational Ringing Potential wells = inflationary seeds
Cosmological observables and the nature of dark matter
 Cosmological observables and the nature of dark matter Shiv Sethi Raman Research Institute March 18, 2018 SDSS results: power... SDSS results: BAO at... Planck results:... Planck-SDSS comparison Summary
Cosmological observables and the nature of dark matter Shiv Sethi Raman Research Institute March 18, 2018 SDSS results: power... SDSS results: BAO at... Planck results:... Planck-SDSS comparison Summary
Cosmic Accelerators. 2. Pulsars, Black Holes and Shock Waves. Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford
 Cosmic Accelerators 2. Pulsars, Black Holes and Shock Waves Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford Particle Acceleration Unipolar Induction Stochastic Acceleration V ~ Ω Φ I ~ V / Z 0 Z 0 ~100Ω P ~ V I ~ V 2 /Z
Cosmic Accelerators 2. Pulsars, Black Holes and Shock Waves Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford Particle Acceleration Unipolar Induction Stochastic Acceleration V ~ Ω Φ I ~ V / Z 0 Z 0 ~100Ω P ~ V I ~ V 2 /Z
PICO - Probe of Inflation and Cosmic Origins
 PICO - Probe of Inflation and Cosmic Origins Shaul Hanany University of Minnesota Executive Committee Bock, Borrill, Crill, Devlin, Flauger, Hanany, Jones, Knox, Kogut, Lawrence, McMahon, Pryke, Trangsrud
PICO - Probe of Inflation and Cosmic Origins Shaul Hanany University of Minnesota Executive Committee Bock, Borrill, Crill, Devlin, Flauger, Hanany, Jones, Knox, Kogut, Lawrence, McMahon, Pryke, Trangsrud
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations. simulations of galaxy and structure formation
 Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 11 26 / Colloquium University of Victoria Outline 1 Cosmic
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 11 26 / Colloquium University of Victoria Outline 1 Cosmic
- Synchrotron emission: A brief history. - Examples. - Cyclotron radiation. - Synchrotron radiation. - Synchrotron power from a single electron
 - Synchrotron emission: A brief history - Examples - Cyclotron radiation - Synchrotron radiation - Synchrotron power from a single electron - Relativistic beaming - Relativistic Doppler effect - Spectrum
- Synchrotron emission: A brief history - Examples - Cyclotron radiation - Synchrotron radiation - Synchrotron power from a single electron - Relativistic beaming - Relativistic Doppler effect - Spectrum
Diffuse Gamma-Ray Emission
 Diffuse Gamma-Ray Emission Debbijoy Bhattacharya Manipal Centre for Natural Sciences (MCNS) Manipal University 5 Sept 2014 Observational Gamma-Ray Astronomy Atmospheric Window 00 11 00 11 Figure: Atmospheric
Diffuse Gamma-Ray Emission Debbijoy Bhattacharya Manipal Centre for Natural Sciences (MCNS) Manipal University 5 Sept 2014 Observational Gamma-Ray Astronomy Atmospheric Window 00 11 00 11 Figure: Atmospheric
Interstellar gamma rays. New insights from Fermi. Andy Strong. on behalf of Fermi-LAT collaboration. COSPAR Scientific Assembly, Bremen, July 2010
 Interstellar gamma rays New insights from Fermi Andy Strong on behalf of Fermi-LAT collaboration COSPAR Scientific Assembly, Bremen, July 2010 Session E110: ' The next generation of ground-based Cerenkov
Interstellar gamma rays New insights from Fermi Andy Strong on behalf of Fermi-LAT collaboration COSPAR Scientific Assembly, Bremen, July 2010 Session E110: ' The next generation of ground-based Cerenkov
Constraints on Extragalactic Background Light from Cherenkov telescopes: status and perspectives for the next 5 years
 Constraints on Extragalactic Background Light from Cherenkov telescopes: status and perspectives for the next 5 years Daniel Mazin 1 and Martin Raue 2 1: IFAE, Barcelona 2: MPIK, Heidelberg This research
Constraints on Extragalactic Background Light from Cherenkov telescopes: status and perspectives for the next 5 years Daniel Mazin 1 and Martin Raue 2 1: IFAE, Barcelona 2: MPIK, Heidelberg This research
DARK MATTER INTERACTIONS
 DARK MATTER INTERACTIONS Jonathan H. Davis Institut d Astrophysique de Paris jonathan.h.m.davis@gmail.com LDMA 2015 Based on J.H.Davis & J.Silk, Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 051303 and J.H.Davis, JCAP 03(2015)012
DARK MATTER INTERACTIONS Jonathan H. Davis Institut d Astrophysique de Paris jonathan.h.m.davis@gmail.com LDMA 2015 Based on J.H.Davis & J.Silk, Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 051303 and J.H.Davis, JCAP 03(2015)012
COSMIC MICROWAVE BACKGROUND ANISOTROPIES
 COSMIC MICROWAVE BACKGROUND ANISOTROPIES Anthony Challinor Institute of Astronomy & Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge, U.K. a.d.challinor@ast.cam.ac.uk 26
COSMIC MICROWAVE BACKGROUND ANISOTROPIES Anthony Challinor Institute of Astronomy & Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge, U.K. a.d.challinor@ast.cam.ac.uk 26
The cosmic microwave background radiation
 The cosmic microwave background radiation László Dobos Dept. of Physics of Complex Systems dobos@complex.elte.hu É 5.60 May 18, 2018. Origin of the cosmic microwave radiation Photons in the plasma are
The cosmic microwave background radiation László Dobos Dept. of Physics of Complex Systems dobos@complex.elte.hu É 5.60 May 18, 2018. Origin of the cosmic microwave radiation Photons in the plasma are
Recent Observations of Supernova Remnants
 1 Recent Observations of Supernova Remnants with VERITAS Tülün Ergin (U. of Massachusetts Amherst, MA) on behalf of the VERITAS Collaboration (http://veritas.sao.arizona.edu) 2 Contents Supernova Remnants
1 Recent Observations of Supernova Remnants with VERITAS Tülün Ergin (U. of Massachusetts Amherst, MA) on behalf of the VERITAS Collaboration (http://veritas.sao.arizona.edu) 2 Contents Supernova Remnants
Miguel A. Sánchez Conde (Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias)
 Miguel A. Sánchez Conde (Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias) In collaboration with: F. Prada, A. Cuesta, A. Domínguez, M. Fornasa, F. Zandanel (IAA/CSIC) E. Bloom, D. Paneque (KIPAC/SLAC) M. Gómez, M.
Miguel A. Sánchez Conde (Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias) In collaboration with: F. Prada, A. Cuesta, A. Domínguez, M. Fornasa, F. Zandanel (IAA/CSIC) E. Bloom, D. Paneque (KIPAC/SLAC) M. Gómez, M.
² The universe observed ² Relativistic world models ² Reconstructing the thermal history ² Big bang nucleosynthesis ² Dark matter: astrophysical
 ² The universe observed ² Relativistic world models ² Reconstructing the thermal history ² Big bang nucleosynthesis ² Dark matter: astrophysical observations ² Dark matter: relic particles ² Dark matter:
² The universe observed ² Relativistic world models ² Reconstructing the thermal history ² Big bang nucleosynthesis ² Dark matter: astrophysical observations ² Dark matter: relic particles ² Dark matter:
CMB polarization and cosmology
 Fundamental physics and cosmology CMB polarization and cosmology Institut d'astrophysique Spatiale Orsay Standard cosmology : reverse the expansion... 10 16 GeV GUT 10-42 s 10 15 GeV 10-32 s 300 GeV 0.1
Fundamental physics and cosmology CMB polarization and cosmology Institut d'astrophysique Spatiale Orsay Standard cosmology : reverse the expansion... 10 16 GeV GUT 10-42 s 10 15 GeV 10-32 s 300 GeV 0.1
Cosmic Rays, Photons and Neutrinos
 Cosmic Rays, Photons and Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline Plan of the lectures: Cosmic rays Galactic cosmic rays Basic observations Acceleration Supernova remnants Problems
Cosmic Rays, Photons and Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline Plan of the lectures: Cosmic rays Galactic cosmic rays Basic observations Acceleration Supernova remnants Problems
The High-Energy Interstellar Medium
 The High-Energy Interstellar Medium Andy Strong MPE Garching on behalf of Fermi-LAT collaboration Cosmic Ray Interactions: Bridging High and Low Energy Astrophysics Lorentz Centre Workshop March 14-18
The High-Energy Interstellar Medium Andy Strong MPE Garching on behalf of Fermi-LAT collaboration Cosmic Ray Interactions: Bridging High and Low Energy Astrophysics Lorentz Centre Workshop March 14-18
