Turbulence and Magnetic Field in High-β Plasma of Intracluster Medium
|
|
|
- Roland Bradford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Turbulence and Magnetic Field in High-β Plasma of Intracluster Medium Coma cluster of galaxies Dongsu Ryu UNIST (Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) KASI (Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute, Korea) Hyesung Kang (PNU, Korea), T. W. Jones (Minnesota, USA), others 1/48
2 Magnetic field (and plasma) is everywhere! Earth s magnetic field reversal of magnetic field computer simulation strength ~ G (1 G = 10-4 T) interval ~ 0.1 to 50 million years the last event the Brunhes-Matuyama reversal of ~0.78 million years ago magnetosphere - shields harmful radiations from space history of reversal 2/48
3 Solar and Galactic magnetic field Sun s photosphere ~ 1 G sunspots ~ 1 kg interstellar medium ~ several μg molecular clouds ~ mg 3/48
4 The large-scale structure of the universe observation of galaxies clusters of galaxies filaments void regions the cosmic web simulation of matter distribution 4/48
5 100 h -1 Mpc Cosmic magnetic fields Mpc = 3.26 x 10 6 light-years h = Hubble constant / 100 km/s = ~0.7 void regions: B > ~10-16 G filaments of galaxies: B ~ 10 ng distribution of cosmological shocks clusters of galaxies: B ~ a few μg 5/48
6 Magnetic field is ubiquitous in the Universe. Star Magnetar ~ G Neutron star ~ G White dwarf ~ 10 6 G Ap/Bp star ~ 10 3 G Normal star ~ 1 G Molecular cloud ~ 10-3 G Interstellar medium ~ several x10-6 G Cluster of galaxies ~ a few x 10-6 G Filament of galaxies ~ G (?) Void ~ G (?) stronger field larger scale Early universe ~ G (?) Planck mass monopole ~ G 6/48
7 Clusters of galaxies MACSJ0717 aggregates of galaxies, which are the largest known gravitationally bound objects to have arisen thus far in the process of cosmic structure formation MACSJ0717 Hubble space telescope image mostly star light The intracluster medium (ICM) optical (Hubble, white) X-ray (Chandra, blue) hot gas radio (VLA, red) cosmic rays the superheated plasma with T ~ a few to several kev, presented in clusters of galaxies 7/48
8 ICMs are dynamical: - large-scale flow motion - shocks - turbulence - magnetic fields - cosmic-rays Perseus cluster: X-ray Coma cluster: X-ray Radio relic in CIZA J /48
9 Some Evidence for turbulence in clusters - pressure fluctuations in Coma (Schuecker et al 2004) P/P ~ 0.1 n ~ 1/3 7/3 (P k ~ k -n ) -> consistent to Kolmogorov - X-ray surface brightness fluctuations in Coma (Churazov et al 2011) r/r ~ 0.1 n ~ 2 -> steeper than Kolmorogov (shock-dominated?) - line broadening limit in A1835 (Sanders et al 2010) v < 274 km/sec -> E turb / E tot <~ patchy Faraday rotation distributions in clusters (Murgia et al 2004) n ~ 0 for B -> broken power-law? - and etc 9/48
10 Turbulence in Coma cluster 250 kpc P ρ ~ k -5/3 (power spectrum of density) (XMM X-ray) Mach number of turbulence in ICMs, M turb, less than 1, ~ 0.5 if incompressible mode dominates 10/48
11 Magnetic fields in galaxy clusters appears in observations CIZA J Sausage relic Hydra North (van Weeren et al 2010) (Shea Brown) Faraday rotation measure (Vogt & Ensslin 2005) Coma cluster Relic halo 11/48
12 (Govoni & Feretti 2004) 12/48
13 Fluid quantities in the ICM size of clusters density of baryonic matter flow velocity gas temperature magnetic fields gas thermal energy gas kinetic energy cosmic-ray energy magnetic energy L size 2 n ~ 10 cm 3 υ ~ several 10 T 8 3 ~ 10 K c s ~ 10 km/s B µ E E E E 2 km/s 2 ~ a few G c A ~ 10 km/s thermal kinetic 20 ~ a few Mpc ~ 10 km flows are subsonic (M s ~ 0.5) and super-alfvenic (M A > 1) plasma beta is high β ~ 100 cosmic-ray magnetic β ~ 10 ~ erg/cm erg/cm 3 ~ a few 10 ~ a few 10 P P gas magnetic erg/cm erg/cm 13/48 3 3
14 A model for turbulence and magnetic fields in clusters of galaxies large-scale structure formation (Ryu et al 2008) gravitational collapse, mergers, & flow motions shocks in the LSS of the Univ shock dissipation generation of vorticity stretching and compression development into turbulence seed fields small-scale or turbulent dynamo amplification of magnetic fields 14/48
15 Origin of turbulence and magnetic fields in clusters - generation of turbulence structure formation? AGN outflows? wakes of galaxies? instabilities? etc - generation of seed fields primordial? or astrophysical? - amplification of seed fields by turbulent flow motions 15/48
16 Observation of shocks in clusters: X-ray The Bullet Cluster M X 3.0 (no associated radio relic) (Markevitch 2006) M X 2.5 (Shimwell et al. 2015) Cluster A665 shock cold front cold front M X = 3± 0.6 (no associated radio relic) (Dasadia et al. 2016) 16/48
17 Observation of shocks in clusters: radio relics Giant Gischt Relic Sausage relic Abell PLCKG (van Weeren et al. + Ryu 2016) 17/48
18 Shock waves induced during the formation of the large-scale structure of the universe Shock waves in a simulated clusters of galaxies strong accretion shocks with M>10 (green) weak inreacluster shocks with M<4 (orange) Simulation credits: Vazza, Jones, Gheller, Bruggen, Brunetti & Ryu, on ITASCA at Minnesota Supercomputing Institute (MSI). Visualization credits: 3D renderings (Jones) with Hierarchical Volume Rendering, 'HVR, developed in the LCSE at the University of Minnesota. Critical support from MSI (D. Porter) and LCSE (M. Knox). 18/48
19 Shocks around a simulated cluster in a 2D slice (in the plane through the center) (6h -1 Mpc) 2 (Hong, Ryu, Kang, & Cen 2014) gas density temperature shock Mach no. R200 accretion shock from voids to clusters Structures of shocks in galaxy clusters are complex! shocks due to mergers of sub-clusters 20 infall shock (accretion from WHIM to hot IGM) 20/48
20 Vorticity generated at cosmological shocks - directly at interacting and curved shocks interacting shocks div(v) - by the baroclinic term 1 ϖ bc = 2 ρ ρ p ω ϖ ρ 1 ρ 2 U n R cs ~ at shocks 2 1 ( ρ2 ρ1) ρ ρ U n R preshock density postshock density preshock flow speed unit normal to shock surf. curvature radius of surf. baroclinity constant ρ constant p due to entropy variation induced at shocks Magnitude of vorticity or enstropy (e) enhanced by stretching and compression increases during the development of turbulence (Porter, Jones, Ryu 2015) 21/48 2
21 X-ray Vorticity in a cluster complex shocks (Ryu, Kang, Cho, & Das 2008) velocity field ω x ω (25 h -1 Mpc) 2 2D slice 22/48
22 Theory of turbulence Kolmogorov's theory for incompressible hydrodynamic turbulence: it is based on the notion that that large eddies can feed energy to the smaller eddies and these in turn feed still smaller eddies, resulting in a cascade of energy from the largest eddies to the smallest ones. a schematic representation of the turbulent energy cascade from large to small scales on dimensional grounds, the only way of writing ε (energy transfer rate) in terms of V (velocity) and l (scale) is ε ~ V 2 ~ t V P k ~ l ~ V 1/3 k 5/3 power spectrum of velocity! l 3 ~ constant the spectrum of Kolmogorov turbulence 23/48
23 Turbulence in high resolution simulations of galaxy clusters vorticity in the plane through the cluster center (Miniati 2013) 24/48
24 Solenoidal & compressional components of turbulence fraction of turbulent kinetic energy flux in compressive component mostly in solenoidal (incompressible) component the fraction of compressional component <~ 10 % (Vazza et al + Ryu 2016) distance from cluster center 25/48
25 Turbulence energy of in the ICM assuming that turbulence is contained in vortical motions M turb ~ 1 (transonic turbulence) in filaments clusters M turb < ~1 (subsonic turbulence) E turb /E therm ~ inside and outskirts of clusters (Ryu et al 2008) 26/48
26 Origin of turbulence and magnetic fields in clusters - generation of turbulence structure formation? AGN outflows? wakes of galaxies? instabilities? etc - generation of seed fields primordial? or astrophysical? - amplification of seed fields by turbulent flow motions 27/48
27 Seed magnetic fields in the large-scale structure (LSS) of the universe Suggestions include: - generation in the early universe (e.g., see Widrow, Ryu et al 2012 for review) e.g.) during the electroweak phase transition (t~10-12 sec) during the quark-hadron transition (t~10-5 sec) uncertain but maybe challenging (?) - generation before the formation of the LSS of the universe through plasma physical processes (e.g., see Ryu et al 2012 for review) e.g.) Biermann battery or Weibel Instability at shocks (Kulsrud, Cen, Ostriker, & Ryu 1997) (Medvedev & Loeb 1999) instabilities, thermal fluctuations, photo-ionization and etc weak (~ G) and some at small scales, yet most promising(?) - astrophysical processes e.g.) magnetic fields from the first stars maybe not the first magnetic field Origin of seeds for comic magnetic fields is uncertain! 28/48
28 Laboratory reproduction of magnetic field generation through the Biermann battery mechanism at shock waves (Kulsrud, Cen, Ostriker, Ryu 1997) theory: predicted the generation of seeds of cosmic magnetic fields at curved intergalactic shock waves ~ G by t ~ 10 9 years or t~ 1/10 t univ-age experiment: after scaling, confirmed the generation of G magnetic field in the cosmic scale (Gregori et al 2012) 29/48
29 Toward magnetic field generation by the Weibel instability at collisionless shocks theory: requires magnetic fields at astrophysical collisionless shocks what if a shock forms in collisionless plasma with no or weak magnetic field? (Huntington et al 2015) simulation: predicts magnetic field generation by the Weibel instability experiments: confirms the prediction 30/48
30 Origin of turbulence and magnetic fields in clusters - generation of turbulence structure formation? AGN outflows? wakes of galaxies? instabilities? etc - generation of seed fields primordial? or astrophysical? - amplification of seed fields by turbulent flow motions 31/48
31 Turbulence with magnetic fields Magnetic fields play an important or crucial role with magnetic field fluid drags magnetic field magnetic field exerts tension and pressure fluid and magnetic field moves together ( frozen ) with large magnetic Reynolds number υ + t B t ( ) 1 1 ( ) υ υ + p = B B = ρ ( ) B υ 4πρ B o Turbulence + magnetic field Magnetohydrodynamic turbulence 32/48
32 Turbulence in astrophysical environments - Turbulence in the interstellar medium (ISM) with β ~ 1 (strong regular or background field field) Goldreich & Sridhar model - Turbulence in the intracluster medium (ICM) with β >> 1 (no regular or background field field) super-alfvenic turbulence magnetic fields are amplified by turbulence from weak seed fields turbulence dynamo or small-scale dynamo - Two turbulences should have different properties! 33/48
33 Small-scale dynamo of MHD turbulence with weak initial field (Jo, Ryu, et al, in preparation) growth of magnetic energy E kin at saturation E mag /E kin ~ 2/3 exponential growth linear growth E mag saturation 34/48
34 Evolution of magnetic field power spectrum at early stages (From Cho) 1 inverse cascade linear growth exponential growth 35/48
35 Power spectrum at saturation E kin E mag 37/48
36 A model for magnetic fields in galaxy clusters - vorticity generated at shocks and also due to baroclinity - turbulence developed - standard picture of MHD turbulence applied - magnetic field produced by turbulence dynamo In galaxy clusters - B ~ a few μg - L int ~ a few x 10 kpc ω B (Ryu et al 2008) 38/48
37 Magnetic fields in clusters (Cho & Ryu 2009) energy injection scale: turbulent flow speed: L inj ~ a few x 100 kpc v turb ~ several x 10 2 km/s eddy turn-over time: t eddy ~ several x 10 8 yrs - magnetic fields in clusters <B> ~ a few μg, L int ~ several x 10 kpc the integral scale is a length scale of magnetic field, which would be relevant to Faraday rotation measure L int = 2π ( E / k) dk / B E B dk 39/48
38 Large-scale magnetic fields? CIZA J (sausage radio relic) (van Weeren et al 2010) magnetic field geometry: large-scale field of ~ 2 Mpc? 40/48
39 Laboratory reproduction of magnetic field amplification through turbulence (turbulence or small-scale dynamo): TDYNO (Tzeferacos et al + Ryu 2016) ~ 4.5x10 8 light-years several x100 kg In lab experimental exploration for the turbulence dynamo origin of magnetic fields in clusters of galaxies ~ a few µg In clusters 41/48
40 Plasma properties in of high β plasma in the ICM size of clusters Coulomb mean free path gyro-radius of thermal protons gyro-radius of thermal electrons ion inertial length electron skin depth Debye length plasma parameter Λ 4π n λ e 3 Debye = 4π k e 4π 2 3/ 2 n l 1 / 2 e ~ a few kpc ~ L /10 Coul 6 r gp ~ 10 km r ge λ i λ e λ D 3 ~ 10 km 4 ~ 10 km 2 ~ 10 km ~ 10 km 17 Λ ~ 10 T 3 / 2 e 20 ~ a few Mpc ~ 10 km ~ thermal K.E. Coulomb P.E. plasma is collisionless (l Coul >> r gp ) and weakly coupled (Λ >>1) 42/48 L size size 3/2 3
41 Intracluster media (ICMs) of galaxy clusters - may be treated as fluids on the cluster scale, L size > ~ Mpc - host turbulence, which would be hydrodynamic (HD) on largest scales but MHD on smaller scales - contain shock waves with M s ~ a few - below Coulomb collision scale l Coul ~ a few kpc, plasma effects may enter - gyro and inertial scales of thermal particles are much smaller than l Coul - with Λ >> 1, they are good plasmas, e.g., carry plasma waves We need to study fluid phenomena as well plasma phenomena to understand ICMs! 43/48
42 Viscosity and resistivity the ICM kinetic viscosity p p p p p p p p t l l 2 therm ~ ~ υ ν resistivity p e p t c 2 ) / ( ~ ω η = 2 1/ 2 4 e e p m e n π ω high magnetic Prandtle number? or larger? ~ η ν = P m or substantially smaller? much smaller than viscosity? 44/48
43 Turbulence with B 0 << δb and large P m - Time evolution of kinetic and magnetic energies P m >>1 E kin at saturation magnetic energy >> kinetic energy P m =1 E mag 45/48
44 - Power spectrum at saturation with ν >> η, V k << B k E mag E M ~ constant, E ~ in the inertial range K k 3 E kin P m >>1 P m =1 46/48
45 Summary - Magnetic field is ubiquitous, even in the large-scale structure of the universe. - Magnetic field of ~ a few μg of coherence length of ~ several 10 kpc in clusters of galaxies could be explained by turbulence (small-scale) dynamo. - But there are a number of issues to be further resolved e.g., mean-free-path ~ a few kpc (size of clusters ~ a few Mpc) plasma effects in collisionless regime? Mpc-scale magnetic field? 47/48
46 Thank you! 48/48
Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters
 Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) with Hyesung Kang (Pusan Nat. U, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (Chungnam Nat. U.),
Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) with Hyesung Kang (Pusan Nat. U, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (Chungnam Nat. U.),
Intracluster Shock Waves
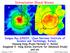 ρ Intracluster Shock Waves T R 200 Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) Hyesung Kang (Pusan National U, Korea) Sungwook E. Hong (Korea Institute for Advanced Study)
ρ Intracluster Shock Waves T R 200 Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) Hyesung Kang (Pusan National U, Korea) Sungwook E. Hong (Korea Institute for Advanced Study)
Cosmological Shocks and Their Signatures
 Cosmological Shocks and Their Signatures Dongsu Ryu (Chungnam National U, Korea) Hyesung Kang (PNU, Korea), Renyi Ma (CNU, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (CNU, Korea), David Porter (U of Minnesota), T. W. Jones
Cosmological Shocks and Their Signatures Dongsu Ryu (Chungnam National U, Korea) Hyesung Kang (PNU, Korea), Renyi Ma (CNU, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (CNU, Korea), David Porter (U of Minnesota), T. W. Jones
Shocks in the ICM and the IPM
 Shocks in the ICM and the IPM Tom Jones (University of Minnesota) 1 Outline Setting the stage for following talks The Interplanetary and Intracluster Media as Collisionless Plasmas Basic Introduction to
Shocks in the ICM and the IPM Tom Jones (University of Minnesota) 1 Outline Setting the stage for following talks The Interplanetary and Intracluster Media as Collisionless Plasmas Basic Introduction to
ICMs and the IPM: Birds of a Feather?
 ICMs and the IPM: Birds of a Feather? Tom Jones University of Minnesota 11 November, 2014 KAW8: Astrophysics of High-Beta Plasma in the Universe 1 Outline: ICM plasma is the dominant baryon component in
ICMs and the IPM: Birds of a Feather? Tom Jones University of Minnesota 11 November, 2014 KAW8: Astrophysics of High-Beta Plasma in the Universe 1 Outline: ICM plasma is the dominant baryon component in
Growth of Magnetic Fields by Turbulent Motions and Characteristic Scales of MHD Turbulence
 Growth of Magnetic Fields by Turbulent Motions and Characteristic Scales of MHD Turbulence Jungyeon Cho Chungnam National University, Korea Cho, Vishniac, Beresnyak, Lazarian & Ryu 2009, ApJ Cho & Ryu,
Growth of Magnetic Fields by Turbulent Motions and Characteristic Scales of MHD Turbulence Jungyeon Cho Chungnam National University, Korea Cho, Vishniac, Beresnyak, Lazarian & Ryu 2009, ApJ Cho & Ryu,
Formation and properties of shock waves in galaxy clusters
 Formation and properties of shock waves in galaxy clusters Hyesung Kang (Pusan National University) Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Korea) T. W. Jones (Univ. of Minnesota) Sungwook E. Hong (KAIST, Korea) Ref: Kang,
Formation and properties of shock waves in galaxy clusters Hyesung Kang (Pusan National University) Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Korea) T. W. Jones (Univ. of Minnesota) Sungwook E. Hong (KAIST, Korea) Ref: Kang,
Turbulence and Magnetic Fields in the Large Scale Structure of the Universe
 arxiv:0805.2466v1 [astro-ph] 16 May 2008 Turbulence and Magnetic Fields in the Large Scale Structure of the Universe Dongsu Ryu, 1 Hyesung Kang, 2 Jungyeon Cho, 1 and Santabrata Das 3 1 Department of Astronomy
arxiv:0805.2466v1 [astro-ph] 16 May 2008 Turbulence and Magnetic Fields in the Large Scale Structure of the Universe Dongsu Ryu, 1 Hyesung Kang, 2 Jungyeon Cho, 1 and Santabrata Das 3 1 Department of Astronomy
Radio relics and magnetic field amplification in the Intra-cluster Medium
 Radio relics and magnetic field amplification in the Intra-cluster Medium Annalisa Annalisa Bonafede Bonafede Hamburger Hamburg Sternwarte University Hamburg University Jacobs University Bremen Collaborators:
Radio relics and magnetic field amplification in the Intra-cluster Medium Annalisa Annalisa Bonafede Bonafede Hamburger Hamburg Sternwarte University Hamburg University Jacobs University Bremen Collaborators:
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Sep 2010
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Sep 2010 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Sep 2010](/thumbs/88/115477948.jpg) Submitted to ApJ Faraday Rotation Measure due to the Intergalactic Magnetic Field arxiv:1009.0570v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Sep 2010 Takuya Akahori 1 and Dongsu Ryu 2,3 1 Research Institute of Basic Science, Chungnam
Submitted to ApJ Faraday Rotation Measure due to the Intergalactic Magnetic Field arxiv:1009.0570v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Sep 2010 Takuya Akahori 1 and Dongsu Ryu 2,3 1 Research Institute of Basic Science, Chungnam
PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS. ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP. NOTES: (references therein)
 PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP NOTES:http://www.astro.iag.usp.br/~dalpino (references therein) ICTP-SAIFR, October 7-18, 2013 Contents What is plasma? Why plasmas in astrophysics?
PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP NOTES:http://www.astro.iag.usp.br/~dalpino (references therein) ICTP-SAIFR, October 7-18, 2013 Contents What is plasma? Why plasmas in astrophysics?
PoS(ICRC2017)283. Acceleration of Cosmic Ray Electrons at Weak Shocks in Galaxy Clusters. Hyesung Kang. Dongsu Ryu
 Acceleration of Cosmic Ray Electrons at Weak Shocks in Galaxy Clusters Pusan National University E-mail: hskang@pusan.ac.kr Dongsu Ryu UNIST E-mail: ryu@sirius.unist.ac.kr T. W. Jones University of Minnesota
Acceleration of Cosmic Ray Electrons at Weak Shocks in Galaxy Clusters Pusan National University E-mail: hskang@pusan.ac.kr Dongsu Ryu UNIST E-mail: ryu@sirius.unist.ac.kr T. W. Jones University of Minnesota
Uri Keshet / CfA Impact of upcoming high-energy astrophysics experiments Workshop, KAVLI, October 2008
 Uri Keshet / CfA Impact of upcoming high-energy astrophysics experiments Workshop, KAVLI, October 008 Impact of upcoming high-energy astrophysics experiments Workshop, KAVLI, October 008 Relaxed, cool
Uri Keshet / CfA Impact of upcoming high-energy astrophysics experiments Workshop, KAVLI, October 008 Impact of upcoming high-energy astrophysics experiments Workshop, KAVLI, October 008 Relaxed, cool
Gianluca Gregori 9 August 2017 TeVPA
 Cosmological magnetic fields and particle acceleration in the laboratory Gianluca Gregori 9 August 2017 TeVPA Magnetic fields are measured in ICM Magnetic Field Measu galaxies and cluster of galaxies Kronberg
Cosmological magnetic fields and particle acceleration in the laboratory Gianluca Gregori 9 August 2017 TeVPA Magnetic fields are measured in ICM Magnetic Field Measu galaxies and cluster of galaxies Kronberg
Enrico Fermi School Varenna Cool Cores and Mergers in Clusters Lecture 3
 Enrico Fermi School Varenna Cool Cores and Mergers in Clusters Lecture 3 Craig Sarazin Dept. of Astronomy University of Virginia A85 Chandra (X-ray) Cluster Merger Simulation Cool Cores in Clusters Central
Enrico Fermi School Varenna Cool Cores and Mergers in Clusters Lecture 3 Craig Sarazin Dept. of Astronomy University of Virginia A85 Chandra (X-ray) Cluster Merger Simulation Cool Cores in Clusters Central
Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA
 Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn & SKA Science Working Group Fundamental magnetic questions When and how were the first fields generated?
Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn & SKA Science Working Group Fundamental magnetic questions When and how were the first fields generated?
Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies
 Lecture 4: Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies Rainer Beck, MPIfR Bonn Generation and amplification of cosmic magnetic fields Stage 1: Field seeding Stage 2: Field amplification Stage 3: Coherent field
Lecture 4: Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies Rainer Beck, MPIfR Bonn Generation and amplification of cosmic magnetic fields Stage 1: Field seeding Stage 2: Field amplification Stage 3: Coherent field
Intracluster Medium Plasmas
 arxiv:1903.08751v1 [astro-ph.he] 20 Mar 2019 PLASMA 2020 WHITE PAPER FOR THE DECADAL ASSESSMENT OF PLASMA SCIENCE Intracluster Medium Plasmas Damiano Caprioli 1, Gianfranco Brunetti 2, Thomas W. Jones
arxiv:1903.08751v1 [astro-ph.he] 20 Mar 2019 PLASMA 2020 WHITE PAPER FOR THE DECADAL ASSESSMENT OF PLASMA SCIENCE Intracluster Medium Plasmas Damiano Caprioli 1, Gianfranco Brunetti 2, Thomas W. Jones
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations. simulations of galaxy and structure formation
 Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 11 26 / Colloquium University of Victoria Outline 1 Cosmic
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 11 26 / Colloquium University of Victoria Outline 1 Cosmic
Evolution and Impact of Cosmic Magnetic Fields
 Evolution and Impact of Cosmic Magnetic Fields Robi Banerjee University of Hamburg Collaborators: Dominik Schleicher (Göttingen), C. Federrath (Lyon, HD), Karsten Jedamzik (Montpellier), R. Klessen (Heidelberg),
Evolution and Impact of Cosmic Magnetic Fields Robi Banerjee University of Hamburg Collaborators: Dominik Schleicher (Göttingen), C. Federrath (Lyon, HD), Karsten Jedamzik (Montpellier), R. Klessen (Heidelberg),
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations. simulations of galaxy and structure formation
 Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 13 26 / Workshop Dark halos, UBC Vancouver Outline 1
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 13 26 / Workshop Dark halos, UBC Vancouver Outline 1
Cosmic Rays in Galaxy Clusters: Simulations and Perspectives
 Cosmic Rays in Galaxy Clusters: Simulations and Perspectives 1 in collaboration with Volker Springel 2, Torsten Enßlin 2 1 Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Canada 2 Max-Planck Institute
Cosmic Rays in Galaxy Clusters: Simulations and Perspectives 1 in collaboration with Volker Springel 2, Torsten Enßlin 2 1 Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Canada 2 Max-Planck Institute
Beyond Ideal MHD. Nick Murphy. Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics. February 8, 2016
 Beyond Ideal MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 8, 2016 These lecture notes are largely based on Plasma Physics for Astrophysics by
Beyond Ideal MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 8, 2016 These lecture notes are largely based on Plasma Physics for Astrophysics by
Intergalactic Magnetic Field and Arrival Direction of Ultra-High-Energy Protons
 Intergalactic Magnetic Field and Arrival Direction of Ultra-High-Energy Protons Dongsu Ryu (Chungnam National U, Korea) Hyesung Kang (Pusan National U, Korea) Santabrata Das (Indian Institute of Technology
Intergalactic Magnetic Field and Arrival Direction of Ultra-High-Energy Protons Dongsu Ryu (Chungnam National U, Korea) Hyesung Kang (Pusan National U, Korea) Santabrata Das (Indian Institute of Technology
the ICM Power Spectrum:
 the ICM Power Spectrum: probing the gas physics of galaxy clusters Massimo Gaspari Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Collaborators: E. Churazov, D. Nagai, E. Lau, I. Zhuravleva, R. Sunyaev Power Spectrum
the ICM Power Spectrum: probing the gas physics of galaxy clusters Massimo Gaspari Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Collaborators: E. Churazov, D. Nagai, E. Lau, I. Zhuravleva, R. Sunyaev Power Spectrum
SKA AND THE COSMOLOGICAL EVOLUTION OF CLUSTER MAGNETIC FIELDS
 SKA AND THE COSMOLOGICAL EVOLUTION OF CLUSTER MAGNETIC FIELDS MARTIN KRAUSE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE, UNIVERSITÄTSSTERNWARTE MÜNCHEN & MAX-PLANCK-INSTITUT FÜR EXTRATERRESTRISCHE PHYSIK COLLABORATORS: PAUL
SKA AND THE COSMOLOGICAL EVOLUTION OF CLUSTER MAGNETIC FIELDS MARTIN KRAUSE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE, UNIVERSITÄTSSTERNWARTE MÜNCHEN & MAX-PLANCK-INSTITUT FÜR EXTRATERRESTRISCHE PHYSIK COLLABORATORS: PAUL
Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs
 Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs Klaus Dolag ( ) Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik ( ) Introduction Evolution of the structures in the Universe t =
Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs Klaus Dolag ( ) Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik ( ) Introduction Evolution of the structures in the Universe t =
MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE UNIVERSE
 ARTICLE MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE UNIVERSE KANDASWAMY SUBRAMANIAN* The origin and maintenance of large scale magnetic fields in the Universe is discussed. A popular idea is that cosmic batteries generate
ARTICLE MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE UNIVERSE KANDASWAMY SUBRAMANIAN* The origin and maintenance of large scale magnetic fields in the Universe is discussed. A popular idea is that cosmic batteries generate
LOFAR Observations of Galaxy Clusters
 LOFAR Observations of Galaxy Clusters The Toothbrush Radio Relic Reinout van Weeren Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics M. Brüggen, G. Brunetti, H. Röttgering F. de Gasperin, A. Bonafede, W. Forman,
LOFAR Observations of Galaxy Clusters The Toothbrush Radio Relic Reinout van Weeren Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics M. Brüggen, G. Brunetti, H. Röttgering F. de Gasperin, A. Bonafede, W. Forman,
Radio relis (and halos) in galaxy clusters
 Radio relis (and halos) in galaxy clusters Matthias Hoeft Thüringer Landessternwarte Tautenburg - overall spectrum of relics - relic statistics - an unusual radio halo Radio relic: the textbook example
Radio relis (and halos) in galaxy clusters Matthias Hoeft Thüringer Landessternwarte Tautenburg - overall spectrum of relics - relic statistics - an unusual radio halo Radio relic: the textbook example
AGN Outflows in Dynamic ICMs: Winds and Twists
 AGN Outflows in Dynamic ICMs: Winds and Twists Tom Jones University of Minnesota Pete Mendygral (UMN, Cray Computer) David Porter (UMN) Klaus Dolag (MPA, U Munich) 11/29/2012 Binary Black Holes & Dual
AGN Outflows in Dynamic ICMs: Winds and Twists Tom Jones University of Minnesota Pete Mendygral (UMN, Cray Computer) David Porter (UMN) Klaus Dolag (MPA, U Munich) 11/29/2012 Binary Black Holes & Dual
Cosmic Ray acceleration in clusters of galaxies. Gianfranco Brunetti. Istituto di Radioastronomia INAF, Bologna, ITALY
 Cosmic Ray acceleration in clusters of galaxies Gianfranco Brunetti Istituto di Radioastronomia INAF, Bologna, ITALY Outline NT components (CRe,CRp,B) in galaxy clusters : observations Physics and dynamics
Cosmic Ray acceleration in clusters of galaxies Gianfranco Brunetti Istituto di Radioastronomia INAF, Bologna, ITALY Outline NT components (CRe,CRp,B) in galaxy clusters : observations Physics and dynamics
Observations of diffuse radio emission in cool-core clusters
 Observations of diffuse radio emission in cool-core clusters Simona Giacintucci U.S. Naval Research Laboratory Maxim Markevitch (GSFC), Tracy Clarke (NRL), Tiziana Venturi (INAF-IRA), Rossella Cassano
Observations of diffuse radio emission in cool-core clusters Simona Giacintucci U.S. Naval Research Laboratory Maxim Markevitch (GSFC), Tracy Clarke (NRL), Tiziana Venturi (INAF-IRA), Rossella Cassano
Magnetic fields generated by the Weibel Instability
 Magnetic fields generated by the Weibel Instability C. M. Ryu POSTECH, KOREA FFP14 Marseille 14.7.15-7.18 Outline I. Why Weibel instability? II. Simulations III. Conclusion Why Weibel instability? The
Magnetic fields generated by the Weibel Instability C. M. Ryu POSTECH, KOREA FFP14 Marseille 14.7.15-7.18 Outline I. Why Weibel instability? II. Simulations III. Conclusion Why Weibel instability? The
The amplification of magnetic fields by the turbulent dynamo in the early Universe
 The amplification of magnetic fields by the turbulent dynamo in the early Universe Jacques M. Wagstaff Phys. Rev. D89:103001 arxiv:1304.4723 Hamburger Sternwarte, Hamburg University Robi Banerjee 1, Dominik
The amplification of magnetic fields by the turbulent dynamo in the early Universe Jacques M. Wagstaff Phys. Rev. D89:103001 arxiv:1304.4723 Hamburger Sternwarte, Hamburg University Robi Banerjee 1, Dominik
Dark Matter ASTR 2120 Sarazin. Bullet Cluster of Galaxies - Dark Matter Lab
 Dark Matter ASTR 2120 Sarazin Bullet Cluster of Galaxies - Dark Matter Lab Mergers: Test of Dark Matter vs. Modified Gravity Gas behind DM Galaxies DM = location of gravity Gas = location of most baryons
Dark Matter ASTR 2120 Sarazin Bullet Cluster of Galaxies - Dark Matter Lab Mergers: Test of Dark Matter vs. Modified Gravity Gas behind DM Galaxies DM = location of gravity Gas = location of most baryons
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 19 Sep 2011
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 19 Sep 2011 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 19 Sep 2011](/thumbs/95/125570482.jpg) Space Science Reviews manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Magnetic fields in the Large-Scale Structure of the Universe D. Ryu D. R. G. Schleicher R. A. Treumann C. G. Tsagas L. M. Widrow arxiv:1109.4055v1
Space Science Reviews manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Magnetic fields in the Large-Scale Structure of the Universe D. Ryu D. R. G. Schleicher R. A. Treumann C. G. Tsagas L. M. Widrow arxiv:1109.4055v1
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 10 Feb 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 10 Feb 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 10 Feb 2015](/thumbs/88/115586675.jpg) Journal of the Korean Astronomical Society http://dx.doi.org/10.5303/jkas.2015.48.2.1 48: 1 9, 2015 April pissn: 1225-4614 eissn: 2288-890X c 2015. The Korean Astronomical Society. All rights reserved.
Journal of the Korean Astronomical Society http://dx.doi.org/10.5303/jkas.2015.48.2.1 48: 1 9, 2015 April pissn: 1225-4614 eissn: 2288-890X c 2015. The Korean Astronomical Society. All rights reserved.
Plasma Physics for Astrophysics
 - ' ' * ' Plasma Physics for Astrophysics RUSSELL M. KULSRUD PRINCETON UNIVERSITY E;RESS '. ' PRINCETON AND OXFORD,, ', V. List of Figures Foreword by John N. Bahcall Preface Chapter 1. Introduction 1
- ' ' * ' Plasma Physics for Astrophysics RUSSELL M. KULSRUD PRINCETON UNIVERSITY E;RESS '. ' PRINCETON AND OXFORD,, ', V. List of Figures Foreword by John N. Bahcall Preface Chapter 1. Introduction 1
The Physics of Fluids and Plasmas
 The Physics of Fluids and Plasmas An Introduction for Astrophysicists ARNAB RAI CHOUDHURI CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface Acknowledgements xiii xvii Introduction 1 1. 3 1.1 Fluids and plasmas in the
The Physics of Fluids and Plasmas An Introduction for Astrophysicists ARNAB RAI CHOUDHURI CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface Acknowledgements xiii xvii Introduction 1 1. 3 1.1 Fluids and plasmas in the
Reduced MHD. Nick Murphy. Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics. February 19, 2014
 Reduced MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 19, 2014 These lecture notes are largely based on Lectures in Magnetohydrodynamics by Dalton
Reduced MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 19, 2014 These lecture notes are largely based on Lectures in Magnetohydrodynamics by Dalton
Turbulence & particle acceleration in galaxy clusters. Gianfranco Brunetti
 Turbulence & particle acceleration in galaxy clusters Gianfranco Brunetti Mergers & CR-acceleration Cluster-cluster mergers are the most energetic events in the present Universe (10 64 erg/gyr). They can
Turbulence & particle acceleration in galaxy clusters Gianfranco Brunetti Mergers & CR-acceleration Cluster-cluster mergers are the most energetic events in the present Universe (10 64 erg/gyr). They can
Fundamentals of Turbulence
 Fundamentals of Turbulence Stanislav Boldyrev (University of Wisconsin - Madison) Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical Plasmas What is turbulence? No exact definition.
Fundamentals of Turbulence Stanislav Boldyrev (University of Wisconsin - Madison) Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical Plasmas What is turbulence? No exact definition.
X-ray and radio observations of the radio relic galaxy clusters 1RXS J and RXC J
 X-ray and radio observations of the radio relic galaxy clusters 1RXS J0603.3+4214 and RXC J1053.7+5453 Motokazu Takizawa (Yamagata University) Itahana, Takizawa, Akamatsu et al. (2015), PASJ, 67, 113 Itahana,
X-ray and radio observations of the radio relic galaxy clusters 1RXS J0603.3+4214 and RXC J1053.7+5453 Motokazu Takizawa (Yamagata University) Itahana, Takizawa, Akamatsu et al. (2015), PASJ, 67, 113 Itahana,
The Origin and Evolution of Cosmic Magnetism: Perspective from SKA. Luigina Feretti IRA - Bologna MCCT-SKADS School, Medicina,
 The Origin and Evolution of Cosmic Magnetism: Perspective from SKA Luigina Feretti IRA - Bologna MCCT-SKADS School, Medicina, 25 9-07 This topic is one of the 5 Key Science Projects of SKA, selected by
The Origin and Evolution of Cosmic Magnetism: Perspective from SKA Luigina Feretti IRA - Bologna MCCT-SKADS School, Medicina, 25 9-07 This topic is one of the 5 Key Science Projects of SKA, selected by
PoS(EXTRA-RADSUR2015)063
 Constraining magnetic fields and particle acceleration processes in galaxy clusters: a joint VLA/LOFAR view on Coma and SKA perspectives Hamburger Sternwarte,Universität Hamburg, Gojenbergsweg 112,21029
Constraining magnetic fields and particle acceleration processes in galaxy clusters: a joint VLA/LOFAR view on Coma and SKA perspectives Hamburger Sternwarte,Universität Hamburg, Gojenbergsweg 112,21029
Amplification of magnetic fields from turbulence in the early Universe
 Amplification of magnetic fields from turbulence in the early Universe Jacques M. Wagstaff 1 arxiv:1304.4723 Robi Banerjee 1, Dominik Schleicher 2, Günter Sigl 3 1 Hamburg University 2 Institut für Astrophysik,
Amplification of magnetic fields from turbulence in the early Universe Jacques M. Wagstaff 1 arxiv:1304.4723 Robi Banerjee 1, Dominik Schleicher 2, Günter Sigl 3 1 Hamburg University 2 Institut für Astrophysik,
Dynamics of galaxy clusters A radio perspective
 Dynamics of galaxy clusters A radio perspective Tiziana Venturi, INAF, Istituto di Radioastronomia Collaborators S. Giacintucci, D. Dallacasa, R. Kale, G. Brunetti, R. Cassano, M. Rossetti GEE 3 Padova,
Dynamics of galaxy clusters A radio perspective Tiziana Venturi, INAF, Istituto di Radioastronomia Collaborators S. Giacintucci, D. Dallacasa, R. Kale, G. Brunetti, R. Cassano, M. Rossetti GEE 3 Padova,
Numerical Study of Compressible Isothermal Magnetohydrodynamic Turbulence
 Numerical Study of Compressible Isothermal Magnetohydrodynamic Turbulence Junseong Park, Dongsu Ryu Dept. of Physics, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology. Ulsan, Korea 2016 KNAG meeting
Numerical Study of Compressible Isothermal Magnetohydrodynamic Turbulence Junseong Park, Dongsu Ryu Dept. of Physics, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology. Ulsan, Korea 2016 KNAG meeting
Title: Filaments of Galaxies as a Clue to the Origin of Ultra-High-Energy Cosmic Rays (Short Title: UHECRs and Filaments of Galaxies)
 Manuscript Template FRONT MATTER Title: Filaments of Galaxies as a Clue to the Origin of Ultra-High-Energy Cosmic Rays (Short Title: UHECRs and Filaments of Galaxies) Summary (or teaser): There are filaments
Manuscript Template FRONT MATTER Title: Filaments of Galaxies as a Clue to the Origin of Ultra-High-Energy Cosmic Rays (Short Title: UHECRs and Filaments of Galaxies) Summary (or teaser): There are filaments
Introduction to Plasma Physics
 Introduction to Plasma Physics Hartmut Zohm Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik 85748 Garching DPG Advanced Physics School The Physics of ITER Bad Honnef, 22.09.2014 A simplistic view on a Fusion Power
Introduction to Plasma Physics Hartmut Zohm Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik 85748 Garching DPG Advanced Physics School The Physics of ITER Bad Honnef, 22.09.2014 A simplistic view on a Fusion Power
Magnetic Field in Galaxies and clusters
 Magnetic Field in Galaxies and clusters Kandaswamy Subramanian Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.0/27 Plan Observing
Magnetic Field in Galaxies and clusters Kandaswamy Subramanian Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.0/27 Plan Observing
Feedback in Galaxy Clusters
 Feedback in Galaxy Clusters Brian Morsony University of Maryland 1 Not talking about Galaxy-scale feedback Local accretion disk feedback 2 Outline Galaxy cluster properties Cooling flows the need for feedback
Feedback in Galaxy Clusters Brian Morsony University of Maryland 1 Not talking about Galaxy-scale feedback Local accretion disk feedback 2 Outline Galaxy cluster properties Cooling flows the need for feedback
X- ray surface brightness fluctuations and turbulence in galaxy clusters. Jeremy Sanders. Andy Fabian. Sanders & Fabian 2011, MNRAS, submitted
 X- ray surface brightness fluctuations and turbulence in galaxy clusters Jeremy Sanders Andy Fabian Sanders & Fabian 2011, MNRAS, submitted Simulations predict that in galaxy clusters turbulent energy
X- ray surface brightness fluctuations and turbulence in galaxy clusters Jeremy Sanders Andy Fabian Sanders & Fabian 2011, MNRAS, submitted Simulations predict that in galaxy clusters turbulent energy
Basics of MHD. Kandaswamy Subramanian a. Pune , India. a Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics,
 Basics of MHD Kandaswamy Subramanian a a Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. The magnetic Universe, Feb 16, 2015 p.0/27 Plan Magnetic fields in Astrophysics MHD
Basics of MHD Kandaswamy Subramanian a a Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. The magnetic Universe, Feb 16, 2015 p.0/27 Plan Magnetic fields in Astrophysics MHD
Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields
 Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Ellen Zweibel zweibel@astro.wisc.edu Departments of Astronomy & Physics University of Wisconsin, Madison and Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical
Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Ellen Zweibel zweibel@astro.wisc.edu Departments of Astronomy & Physics University of Wisconsin, Madison and Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical
Feedback from growth of supermassive black holes
 Research Collection Other Conference Item Feedback from growth of supermassive black holes Author(s): Begelman, Mitchell C.; Ruszkowksi, Mateusz Publication Date: 2003 Permanent Link: https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-a-004585094
Research Collection Other Conference Item Feedback from growth of supermassive black holes Author(s): Begelman, Mitchell C.; Ruszkowksi, Mateusz Publication Date: 2003 Permanent Link: https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-a-004585094
Chapter 25: Galaxy Clusters and the Structure of the Universe
 Chapter 25: Galaxy Clusters and the Structure of the Universe Distribution of galaxies Evolution of galaxies Study of distant galaxies Distance derived from redshift Hubble s constant age of the Universe:
Chapter 25: Galaxy Clusters and the Structure of the Universe Distribution of galaxies Evolution of galaxies Study of distant galaxies Distance derived from redshift Hubble s constant age of the Universe:
Mergers and Radio Sources in Abell 3667 and Abell 2061
 Mergers and Radio Sources in Abell 3667 and Abell 2061 Craig Sarazin University of Virginia A3667 XMM X-ray image and radio contours SLAM Simulation of A2061 Collaborators Alexis Finoguenov (MPE, UMBC)
Mergers and Radio Sources in Abell 3667 and Abell 2061 Craig Sarazin University of Virginia A3667 XMM X-ray image and radio contours SLAM Simulation of A2061 Collaborators Alexis Finoguenov (MPE, UMBC)
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 7 Nov 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 7 Nov 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 7 Nov 2017](/thumbs/82/84973887.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 27 May 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Resolved magnetic dynamo action in the simulated intracluster medium arxiv:1711.02673v1 [astro-ph.co] 7 Nov
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 27 May 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Resolved magnetic dynamo action in the simulated intracluster medium arxiv:1711.02673v1 [astro-ph.co] 7 Nov
Amplification of magnetic fields in core collapse
 Amplification of magnetic fields in core collapse Miguel Àngel Aloy Torás, Pablo Cerdá-Durán, Thomas Janka, Ewald Müller, Martin Obergaulinger, Tomasz Rembiasz Universitat de València; Max-Planck-Institut
Amplification of magnetic fields in core collapse Miguel Àngel Aloy Torás, Pablo Cerdá-Durán, Thomas Janka, Ewald Müller, Martin Obergaulinger, Tomasz Rembiasz Universitat de València; Max-Planck-Institut
Energy Balance in Clusters of Galaxies. Patrick M. Motl & Jack O. Burns Center for Astrophysics and Space Astronomy University of Colorado at Boulder
 Energy Balance in Clusters of Galaxies Patrick M. Motl & Jack O. Burns Center for Astrophysics and Space Astronomy University of Colorado at Boulder X-ray and Radio Connections, February 6th, 2004 With
Energy Balance in Clusters of Galaxies Patrick M. Motl & Jack O. Burns Center for Astrophysics and Space Astronomy University of Colorado at Boulder X-ray and Radio Connections, February 6th, 2004 With
Observational Evidence of AGN Feedback
 10 de maio de 2012 Sumário Introduction AGN winds Galaxy outflows From the peak to the late evolution of AGN and quasars Mergers or secular evolution? The AGN feedback The interaction process between the
10 de maio de 2012 Sumário Introduction AGN winds Galaxy outflows From the peak to the late evolution of AGN and quasars Mergers or secular evolution? The AGN feedback The interaction process between the
Hydra A (x-ray) Perseus ` (optical)
 The Biermann Lectures: Adventures in Theoretical Astrophysics I: The Physics of Galaxy Cluster Plasmas Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) w/ Mike McCourt, Ian Parrish, Prateek Sharma Perseus ` (optical) Hydra
The Biermann Lectures: Adventures in Theoretical Astrophysics I: The Physics of Galaxy Cluster Plasmas Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) w/ Mike McCourt, Ian Parrish, Prateek Sharma Perseus ` (optical) Hydra
Radio emission in clusters of galaxies. An observational perspective
 Radio emission in clusters of galaxies An observational perspective Tiziana Venturi INAF, IRA, Bologna IV ESTRELA Workshop, Bologna, 19 January 2009 Overview - What are galaxy clusters - Radio emission
Radio emission in clusters of galaxies An observational perspective Tiziana Venturi INAF, IRA, Bologna IV ESTRELA Workshop, Bologna, 19 January 2009 Overview - What are galaxy clusters - Radio emission
Cosmic Accelerators. 2. Pulsars, Black Holes and Shock Waves. Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford
 Cosmic Accelerators 2. Pulsars, Black Holes and Shock Waves Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford Particle Acceleration Unipolar Induction Stochastic Acceleration V ~ Ω Φ I ~ V / Z 0 Z 0 ~100Ω P ~ V I ~ V 2 /Z
Cosmic Accelerators 2. Pulsars, Black Holes and Shock Waves Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford Particle Acceleration Unipolar Induction Stochastic Acceleration V ~ Ω Φ I ~ V / Z 0 Z 0 ~100Ω P ~ V I ~ V 2 /Z
Simulating magnetic fields in structure formation
 Simulating magnetic fields in structure formation USM / MPE / MPA Harald Lesch & Klaus Dolag Annette Geng, Federico Stasyszyn & Marcus Beck July, 2012 (Mainz) Alexander Beck Magnetic fields in galaxies
Simulating magnetic fields in structure formation USM / MPE / MPA Harald Lesch & Klaus Dolag Annette Geng, Federico Stasyszyn & Marcus Beck July, 2012 (Mainz) Alexander Beck Magnetic fields in galaxies
Magnetisation of Interstellar and Intergalactic Media: The Prospects of Low-Frequency Radio Astronomy DFG Research Unit
 Mainz, 9 July, 2012 Galactic and Intergalactic Magnetic Fields 1 Magnetisation of Interstellar and Intergalactic Media: The Prospects of Low-Frequency Radio Astronomy DFG Research Unit Mainz, 9 July, 2012
Mainz, 9 July, 2012 Galactic and Intergalactic Magnetic Fields 1 Magnetisation of Interstellar and Intergalactic Media: The Prospects of Low-Frequency Radio Astronomy DFG Research Unit Mainz, 9 July, 2012
NONLINEAR MHD WAVES THE INTERESTING INFLUENCE OF FIREHOSE AND MIRROR IN ASTROPHYSICAL PLASMAS. Jono Squire (Caltech) UCLA April 2017
 NONLINEAR MHD WAVES THE INTERESTING INFLUENCE OF FIREHOSE AND MIRROR IN ASTROPHYSICAL PLASMAS Jono Squire (Caltech) UCLA April 2017 Along with: E. Quataert, A. Schekochihin, M. Kunz, S. Bale, C. Chen,
NONLINEAR MHD WAVES THE INTERESTING INFLUENCE OF FIREHOSE AND MIRROR IN ASTROPHYSICAL PLASMAS Jono Squire (Caltech) UCLA April 2017 Along with: E. Quataert, A. Schekochihin, M. Kunz, S. Bale, C. Chen,
Heat Transport and Buoyancy Instabilities in Astrophysical Plasmas. Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley)
 Heat Transport and Buoyancy Instabilities in Astrophysical Plasmas Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Galaxy Cluster Hydra A w/ Chandra Surface of the Sun ~ 1 Million light-years Overview Microscopic Energy
Heat Transport and Buoyancy Instabilities in Astrophysical Plasmas Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Galaxy Cluster Hydra A w/ Chandra Surface of the Sun ~ 1 Million light-years Overview Microscopic Energy
Campus Observatory. 7pm. you are here
 Announcements Homework #9 is due today Course Evaluations available on line now Post-test Survey for At Play in the Cosmos now ready For extra credit: - must complete all 8 missions by Dec 10 - must complete
Announcements Homework #9 is due today Course Evaluations available on line now Post-test Survey for At Play in the Cosmos now ready For extra credit: - must complete all 8 missions by Dec 10 - must complete
Constraints on physics of gas and dark matter from cluster mergers. Maxim Markevitch (SAO)
 Constraints on physics of gas and dark matter from cluster mergers Maxim Markevitch (SAO) November 2005 1E 0657 56 Chandra 0.5 Msec image 0.5 Mpc z=0.3 An overheated cluster From M T relation: T= 14 kev:
Constraints on physics of gas and dark matter from cluster mergers Maxim Markevitch (SAO) November 2005 1E 0657 56 Chandra 0.5 Msec image 0.5 Mpc z=0.3 An overheated cluster From M T relation: T= 14 kev:
The Effects of Anisotropic Transport on Dilute Astrophysical Plasmas Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley)
 The Effects of Anisotropic Transport on Dilute Astrophysical Plasmas Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) in collaboration with Ian Parrish, Prateek Sharma, Jim Stone, Greg Hammett Hydra A w/ Chandra Galactic
The Effects of Anisotropic Transport on Dilute Astrophysical Plasmas Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) in collaboration with Ian Parrish, Prateek Sharma, Jim Stone, Greg Hammett Hydra A w/ Chandra Galactic
Probing RMs due to Magnetic Fields in the Cosmic Web
 Probing RMs due to Magnetic Fields in the Cosmic Web Takuya Akahori JSPS Postdoctoral Fellow for Research Abroad Sydney Institute for Astronomy, The University of Sydney Japan SKA Consortium Cosmic Magnetism
Probing RMs due to Magnetic Fields in the Cosmic Web Takuya Akahori JSPS Postdoctoral Fellow for Research Abroad Sydney Institute for Astronomy, The University of Sydney Japan SKA Consortium Cosmic Magnetism
Course of Galaxies course organizer: Goeran Ostlin ESSAY. X-ray physics of Galaxy Clusters
 Course of Galaxies course organizer: Goeran Ostlin ESSAY X-ray physics of Galaxy Clusters Student: Angela Adamo angela@astro.su.se fall 2006 Front:-The double cluster A1750. The contours of the XMM-Newton
Course of Galaxies course organizer: Goeran Ostlin ESSAY X-ray physics of Galaxy Clusters Student: Angela Adamo angela@astro.su.se fall 2006 Front:-The double cluster A1750. The contours of the XMM-Newton
Snowballs in hell! X-ray galactic coronae in galaxy! clusters and the need for sub-arcsecond resolution! Simona Giacintucci (NRL)!
 Snowballs in hell X-ray galactic coronae in galaxy clusters and the need for sub-arcsecond resolution Simona Giacintucci (NRL) M. Markevitch (GSFC), T. Clarke (NRL), E. Richards (NRC-NRL) X-ray Skies with
Snowballs in hell X-ray galactic coronae in galaxy clusters and the need for sub-arcsecond resolution Simona Giacintucci (NRL) M. Markevitch (GSFC), T. Clarke (NRL), E. Richards (NRC-NRL) X-ray Skies with
Cosmic Rays in Galaxy Clusters Simulations and Reality
 Simulations and Reality 1,2 in collaboration with Torsten Enßlin 3, Volker Springel 3, Anders Pinzke 4, Nick Battaglia 1, Jon Sievers 1, Dick Bond 1 1 Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Canada
Simulations and Reality 1,2 in collaboration with Torsten Enßlin 3, Volker Springel 3, Anders Pinzke 4, Nick Battaglia 1, Jon Sievers 1, Dick Bond 1 1 Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Canada
Why are central radio relics so rare?
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 421, 1868 1873 (2012) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.20160.x Why are central radio relics so rare? F. Vazza, 1,2 M. Brüggen, 1 R. van Weeren, 3 A. Bonafede, 1 K. Dolag 4 and G.
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 421, 1868 1873 (2012) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.20160.x Why are central radio relics so rare? F. Vazza, 1,2 M. Brüggen, 1 R. van Weeren, 3 A. Bonafede, 1 K. Dolag 4 and G.
Observations of Magnetic Fields in Intracluster Medium. Govoni Federica INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Cagliari
 Observations of Magnetic Fields in Intracluster Medium Govoni Federica INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Cagliari Collaborators: M. Murgia, L. Feretti, G. Giovannini, V. Vacca, A. Bonafede IAU 2012 China
Observations of Magnetic Fields in Intracluster Medium Govoni Federica INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Cagliari Collaborators: M. Murgia, L. Feretti, G. Giovannini, V. Vacca, A. Bonafede IAU 2012 China
What are the Contents of the Universe? Taking an Inventory of the Baryonic and Dark Matter Content of the Universe
 What are the Contents of the Universe? Taking an Inventory of the Baryonic and Dark Matter Content of the Universe Layout of the Course Sept 4: Introduction / Overview / General Concepts Sept 11: No Class
What are the Contents of the Universe? Taking an Inventory of the Baryonic and Dark Matter Content of the Universe Layout of the Course Sept 4: Introduction / Overview / General Concepts Sept 11: No Class
Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays I
 Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays I John Linsley (PRL 10 (1963) 146) reports on the detection in Vulcano Ranch of an air shower of energy above 1020 ev. Problem: the microwave background radiation is discovered
Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays I John Linsley (PRL 10 (1963) 146) reports on the detection in Vulcano Ranch of an air shower of energy above 1020 ev. Problem: the microwave background radiation is discovered
Gravitational Stability of Fluids in a Phase Transition. Andreas Füglistaler. July 17, 2017
 Gravitational Stability of Fluids in a Phase Transition July 17, 2017 Füglistaler & Pfenniger 2015, 2016 and 2017 (in preparation) Motivation Physics Simulations Conclusions Solid H2 in the ISM Gravitational
Gravitational Stability of Fluids in a Phase Transition July 17, 2017 Füglistaler & Pfenniger 2015, 2016 and 2017 (in preparation) Motivation Physics Simulations Conclusions Solid H2 in the ISM Gravitational
Why study plasma astrophysics?
 Why study plasma astrophysics? Nick Murphy and Xuening Bai Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics January 25, 2016 Today s plan Definition of a plasma Plasma astrophysics:
Why study plasma astrophysics? Nick Murphy and Xuening Bai Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics January 25, 2016 Today s plan Definition of a plasma Plasma astrophysics:
Ideal Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD)
 Ideal Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 1, 2016 These lecture notes are largely based on Lectures in Magnetohydrodynamics
Ideal Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 1, 2016 These lecture notes are largely based on Lectures in Magnetohydrodynamics
The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters
 IAU Joint Discussion # 10 Sydney, July, 2003 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al 2003 > 105
IAU Joint Discussion # 10 Sydney, July, 2003 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al 2003 > 105
New Forms of Convection in Galaxy Cluster Plasmas (i.e., how do galaxy clusters boil?)
 New Forms of Convection in Galaxy Cluster Plasmas (i.e., how do galaxy clusters boil?) Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Hydra A w/ Chandra in collaboration with Ian Parrish Prateek Sharma Overview Hot Plasma
New Forms of Convection in Galaxy Cluster Plasmas (i.e., how do galaxy clusters boil?) Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Hydra A w/ Chandra in collaboration with Ian Parrish Prateek Sharma Overview Hot Plasma
3/1/18 LETTER. Instructors: Jim Cordes & Shami Chatterjee. Reading: as indicated in Syllabus on web
 Astro 2299 The Search for Life in the Universe Lecture 9 Last time: Star formation Formation of protostars and planetary systems This time A few things about the epoch of reionization and free fall times
Astro 2299 The Search for Life in the Universe Lecture 9 Last time: Star formation Formation of protostars and planetary systems This time A few things about the epoch of reionization and free fall times
Cosmologists dedicate a great deal of effort to determine the density of matter in the universe. Type Ia supernovae observations are consistent with
 Notes for Cosmology course, fall 2005 Dark Matter Prelude Cosmologists dedicate a great deal of effort to determine the density of matter in the universe Type Ia supernovae observations are consistent
Notes for Cosmology course, fall 2005 Dark Matter Prelude Cosmologists dedicate a great deal of effort to determine the density of matter in the universe Type Ia supernovae observations are consistent
Large-Scale Structure
 Large-Scale Structure Evidence for Dark Matter Dark Halos in Ellipticals Hot Gas in Ellipticals Clusters Hot Gas in Clusters Cluster Galaxy Velocities and Masses Large-Scale Distribution of Galaxies 1
Large-Scale Structure Evidence for Dark Matter Dark Halos in Ellipticals Hot Gas in Ellipticals Clusters Hot Gas in Clusters Cluster Galaxy Velocities and Masses Large-Scale Distribution of Galaxies 1
Gamma-ray Observations of Galaxy Clusters!
 Gamma-ray Observations of Galaxy Clusters! a! Fabio Zandanel! (GRAPPA Institute University of Amsterdam)! f.zandanel@uva.nl! SnowCluster 2015 The Physics Of Galaxy Clusters! Snowbird (Utah, US) March 15-20,
Gamma-ray Observations of Galaxy Clusters! a! Fabio Zandanel! (GRAPPA Institute University of Amsterdam)! f.zandanel@uva.nl! SnowCluster 2015 The Physics Of Galaxy Clusters! Snowbird (Utah, US) March 15-20,
Fluctuation dynamo amplified by intermittent shear bursts
 by intermittent Thanks to my collaborators: A. Busse (U. Glasgow), W.-C. Müller (TU Berlin) Dynamics Days Europe 8-12 September 2014 Mini-symposium on Nonlinear Problems in Plasma Astrophysics Introduction
by intermittent Thanks to my collaborators: A. Busse (U. Glasgow), W.-C. Müller (TU Berlin) Dynamics Days Europe 8-12 September 2014 Mini-symposium on Nonlinear Problems in Plasma Astrophysics Introduction
Cosmological shock waves
 Highlights of Spanish Astrophysics VII, Proceedings of the X Scientific Meeting of the Spanish Astronomical Society held on July 9-13, 2012, in Valencia, Spain. J. C. Guirado, L. M. Lara, V. Quilis, and
Highlights of Spanish Astrophysics VII, Proceedings of the X Scientific Meeting of the Spanish Astronomical Society held on July 9-13, 2012, in Valencia, Spain. J. C. Guirado, L. M. Lara, V. Quilis, and
Where are the missing baryons?
 Interview of BSc dissertation Where are the missing baryons? Brandon Qiang Wang 6 th February 2018 Image from Millennium Simulation Content I. Introduction II. Simulations III. Results IV. Conclusion 2
Interview of BSc dissertation Where are the missing baryons? Brandon Qiang Wang 6 th February 2018 Image from Millennium Simulation Content I. Introduction II. Simulations III. Results IV. Conclusion 2
Killing Dwarfs with Hot Pancakes. Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) with Houjun Mo, Xiaohu Yang & Neal Katz
 Killing Dwarfs with Hot Pancakes Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) with Houjun Mo, Xiaohu Yang & Neal Katz The Paradigm... SN feedback AGN feedback The halo mass function is much steeper than luminosity function
Killing Dwarfs with Hot Pancakes Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) with Houjun Mo, Xiaohu Yang & Neal Katz The Paradigm... SN feedback AGN feedback The halo mass function is much steeper than luminosity function
Physical Processes in Astrophysics
 Physical Processes in Astrophysics Huirong Yan Uni Potsdam & Desy Email: hyan@mail.desy.de 1 Reference Books: Plasma Physics for Astrophysics, Russell M. Kulsrud (2005) The Physics of Astrophysics, Frank
Physical Processes in Astrophysics Huirong Yan Uni Potsdam & Desy Email: hyan@mail.desy.de 1 Reference Books: Plasma Physics for Astrophysics, Russell M. Kulsrud (2005) The Physics of Astrophysics, Frank
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 24 Jul 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 24 Jul 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 24 Jul 2017](/thumbs/87/97235705.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 14 (2014) Printed 26 July 2017 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) arxiv:1707.07677v1 [astro-ph.he] 24 Jul 2017 The correlation between radio power and Mach number for radio relics
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 14 (2014) Printed 26 July 2017 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) arxiv:1707.07677v1 [astro-ph.he] 24 Jul 2017 The correlation between radio power and Mach number for radio relics
CHAPTER 4. Basics of Fluid Dynamics
 CHAPTER 4 Basics of Fluid Dynamics What is a fluid? A fluid is a substance that can flow, has no fixed shape, and offers little resistance to an external stress In a fluid the constituent particles (atoms,
CHAPTER 4 Basics of Fluid Dynamics What is a fluid? A fluid is a substance that can flow, has no fixed shape, and offers little resistance to an external stress In a fluid the constituent particles (atoms,
DARC - DYNAMICAL ANALYSIS OF RADIO CLUSTERS
 DARC - DYNAMICAL ANALYSIS OF RADIO CLUSTERS Marisa Girardi, Rafael Barrena, and Walter Boschin (1) Dip. di Fisica, Univ. di Trieste Trieste Italy; (2) I.A.C.; (3) INAF-TNG Abstract Extended, diffuse radio
DARC - DYNAMICAL ANALYSIS OF RADIO CLUSTERS Marisa Girardi, Rafael Barrena, and Walter Boschin (1) Dip. di Fisica, Univ. di Trieste Trieste Italy; (2) I.A.C.; (3) INAF-TNG Abstract Extended, diffuse radio
Non-Thermal Processes in Cosmological Simulations
 Space Sci Rev (2008) 134: 311 335 DOI 10.1007/s11214-008-9319-2 Non-Thermal Processes in Cosmological Simulations K. Dolag A.M. Bykov A. Diaferio Received: 17 September 2007 / Accepted: 7 November 2007
Space Sci Rev (2008) 134: 311 335 DOI 10.1007/s11214-008-9319-2 Non-Thermal Processes in Cosmological Simulations K. Dolag A.M. Bykov A. Diaferio Received: 17 September 2007 / Accepted: 7 November 2007
Astronomy 422! Lecture 7: The Milky Way Galaxy III!
 Astronomy 422 Lecture 7: The Milky Way Galaxy III Key concepts: The supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way Radio and X-ray sources Announcements: Test next Tuesday, February 16 Chapters
Astronomy 422 Lecture 7: The Milky Way Galaxy III Key concepts: The supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way Radio and X-ray sources Announcements: Test next Tuesday, February 16 Chapters
