Gianluca Gregori 9 August 2017 TeVPA
|
|
|
- Audrey Fleming
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cosmological magnetic fields and particle acceleration in the laboratory Gianluca Gregori 9 August 2017 TeVPA
2 Magnetic fields are measured in ICM Magnetic Field Measu galaxies and cluster of galaxies Kronberg (2002) Faraday Rotation B-field vectors and optical image (Hubble) of M51 Faraday rotation and synchrotron emission are used to measure ICM magnetic fields very challenging. The emerging picture, based on F magnetic fields in galaxies and clusters. is essentially that (Clarke+ 2001, Guidetti 2008, Govoni+2010, Bonafede+ The Universe is ubiquitously magnetized: Clusters 1. B~few-several and galaxies (a µg few μg) filaments (a few ng) voids 2. ( 0.1 plasma fg) beta within 1 Mpc ~ Primordial processes produce a magnetic seed ~10 21 G (much smaller 3. than magnetic observed field values) coherence length ~ tens of kpc
3 A large fraction of the luminous matter in the Universe is in a turbulent state Gas density Shocks filaments clusters voids Courtesy of F Miniati (ETH) Structure formation results in a hierarchical web made of clusters, filaments and voids Shocks inject vorticity into the intra-cluster medium The overall state of the Universe is that of a turbulent fluid
4 n intracluster medium is rather tricky, s there is not well understood. The standard model of cosmic generation of magnetic fields invokes MHD turbulence help understand turbulence as well as ena in intracluster media Courtesy D. Ryu 0.1 ng 10 µg 100 Mpc Assume there are tiny magnetic fields generated before structure formation Magnetic field are then amplified to dynamical strength and coherence length by turbulent motions It follows directly from the induction equation: db dt = u B B~B 0 exp( utτl)
5 The dynamo mechanism: stretch, twist and fold In the kinematic regime the magnetic energy grows exponentially (at a rate set by the eddy-turnover time τ L = L/u) However: cosmological numerical models of MHD dynamo in the ICM typically achieve only modest magnetic field amplification, by factors of order 10 3 (e.g., Xu et al. 2012) We need experiments!
6 Laboratory experiments to study field amplification
7 Laboratory experiments are a viable tool to study complex processes such as dynamo Equations of ideal MHD have no intrinsic scale, hence a similarity relation exists This requires that particle localization, Reynolds number, Peclet number, magnetic Reynolds number are all large in both the astrophysical and laboratory systems Can be complementary to astrophysical observations and numerical simulations: o Compared to observations, experiments allow detailed measurements of the plasma properties o Experiments can achieve conditions unattainable in simulations (beyond linear regimes, larger scales, etc.) o The difficulty, so far, remained in achieving Reynolds numbers large enough for dynamo to be operative o The full range of parameters (highest energies, temperatures, etc.) are not accessible in experiments
8 Experiments are done on laser facilities Nanosecond pulses (10-9 s) Mega-joules energy Petawatt peak powers (10 15 W = 2 million nuclear power plants) NIF Omega LMJ We use these lasers to create finite volumes (cm 3 ) of high energy density plasma (T=1 kev, N=10 20 ) Gekko
9 Experiment uses colliding flows and grids to create strong turbulence
10 Experiment uses colliding flows and grids to create strong turbulence
11 Multiple diagnostics are used to monitor the plasma properties and magnetic fields X-ray imaging Proton radiography Thomson scattering X-ray camera view Foil Foil Stalk Stalk 63 o Foil Shields Foil Probe beam Time resolved x-ray images provides will be used to infer density fluctuation spectrum Use similar analysis approach as the one to analyze x-ray maps from galaxy cluster Proton radiography images map the magnetic field topology Provides estimate of the magnetic field produced by turbulence Local, time-resolved, temperature measurement at the center of the interaction region Modified to include Faraday Rotation capabilities
12 Experimental results show colliding plasma creating turbulence
13 Experimental results show colliding plasma creating turbulence
14 X-ray emission is used to determine power spectrum of density fluctuations Assume an optically thin plasma with Planck opacity κ P ~κ 0 ρ α T β Fluctuation of X-ray emission depends on density variations δi ~a I α,β න δn dz + b 0 n α,β න δn 0 n 0 2 dz + If δn n 0 < l n L 1/2 1 then the quadratic term can be neglected The 2D Fourier transform of the intensity fluctuations can thus be related to the 3D spectrum of the density fluctuations
15 X-ray emission is used to determine power spectrum of density fluctuations Density fluctuations exhibit a Kolmogorov power law There is strong indication density and velocity fluctuations have the same spectrum (Zhuravleva et al. 2015) Assuming Kolmogorov spectrum for the motions, velocities at different scales in the inertial range are related by u L ~ Lu 3 l Τl 1/3
16 Optical Thomson scattering gives detailed information of the plasma velocities Bulk velocity of the flows from global shift of the scattering features Before the collision, U km/s After the collision, U km/s Sound velocity from separation of ion-acoustic waves Before the collision, T e 250 ev After the collision, T e ev Additional broadening due to turbulent velocity At the scale of the Thomson scattering probe (50 μm), u l ~50 km/s This gives a velocity of 100 km/s at the outer scale
17 Omega conditions are in the regime where turbulent dynamo can be excited Experiment v T e 100 km/s 450 ev n e ~10 20 cm -3 M 1 Re 600 Rm 700 Pm 1 We have achieved magnetic Reynolds number much larger that the threshold value for turbulent dynamo action Expect to reach dynamical equipartition between fluid motions and magnetic field
18 Proton deflections track magnetic fields in turbulent plasma (caustics) No structures appear in the images before the collision, but filaments are seen after the collision Proton deflections are a measurement of the path-integrated magnetic field
19 Proton deflections track magnetic fields in turbulent plasma (caustics) Non-linear reconstruction of the magnetic field from the proton deflections is possible (Bott et al. arxiv )
20 Magnetic field reconstruction from 15 MeV proton deflections No structures appear in the images before the collision, but filaments are seen after the collision Our analysis suggests 25x amplification of the RMS field and peaks of 450 kg (near saturation)
21 Validation of magnetic field reconstruction algorithm Our analysis suggests 25x amplification of the RMS field and peaks of 450 kg (near saturation) 15 MeV reconstructed B field Predicted and actual 3.3 MeV proton deflections are very similar But lines in data are more diffuse 3.3 MeV predicted deflections 3.3 MeV data
22 Magnetic fields and particle acceleration
23 Very high energy particles (Cosmic Rays) observed on Earth CRs are in apparent defiance of thermodynamics Wagner (2004)
24 Fermi acceleration is a universal process for particle energization Fast particles collide with moving magnetized clouds (Fermi, 1949). Particles can gain or lose energy, but head-on collisions (gain) are slightly more probable Protheroe (2004) The evolution of CRs as they are accelerated in the plasma is governed by a diffusion equation (Kaplan, 1955; Cowsik & Sarkar, 1984; Blandford & Eichler, 1987) In addition to astrophysical sources, laboratory plasmas can also potentially accelerate particle
25 We use the dynamo platform to study proton diffusion through plasma High energy protons produced by capsule implosion are collimated with a pinhole As they pass through the turbulent plasma they acquire transverse deflections (diffusion)
26 We use the dynamo platform to study proton diffusion through plasma
27 We use the dynamo platform to study proton diffusion through plasma
28 We use the dynamo platform to study proton diffusion through plasma δ Δv = e L න E z dz ~ eel n m p V p 0 m p V p L l n 1/2 Δθ = Δv /v The proton deflection at later times is determined by the electric fields in the plasma The electric field is given by the generalized Ohm s law: E = V p B η μ 0 B E te
29 Preliminary analysis shows deflections are due to baroclinic electric fields E = V p B η μ 0 B E te This term gives a smaller velocity deflection independent on the proton energy (does not agree with data at later times) The second term is always small since the magnetic Reynolds number is large. That is, resistive diffusion is negligible The thermoelectric (baroclinic) field is largest at the resistive scale: E te = P e ~ 1 T en e (1 δ) λ μ This gives for the 3.3 MeV protons Δv ~ cm/s, in agreement with data The predicted acceleration is ΔW~E te Ll n 1/2 ~100 kev
30 Thanks to all collaborators A Rigby, A Bott, TG White, L Chen, M Oliver, J Meinecke, AR Bell, A Schekochihin, S Sakar, G Gregori (U Oxford) P Tzeferacos, C Graziani, S. Feister, F Cattaneo, DQ Lamb (U Chicago) D Froula, J Katz (LLE) B Albertazzi, M Koenig (LULI) F Cruz, L Silva (IST Lisbon) S Ross, J Emig, D Ryutov, B Remington, H-S Park (LLNL) C-K Li, R Petrasso (MIT) D Ryu (Unist) S Lebedev (Imperial College) F Miniati (ETH) B Reville (QUB) C Forest (U Wisconsin) J Foster (AWE) A Casner (CEA) F Fiuza (SLAC) E Churazov (MPI for Astrophysics) B Bingham, R Bamford (Rutherford Appleton Laboratory)
31 Summary Magnetic fields are ubiquitous in the Universe. Their strength suggest turbulent dynamo is operative Laser-plasma experiments have reached the conditions were turbulent dynamo could be initiated, and we have seen large amplification Turbulent magnetic fields are associated to particle acceleration and CR s We have measured the diffusion of protons through the turbulent plasma Laboratory laser-based platforms offer the ability to directly test theory of particle acceleration
Dynamo on the OMEGA laser and kinetic problems of proton radiography
 Dynamo on the OMEGA laser and kinetic problems of proton radiography Archie Bott, Alex Rigby, Tom White, Petros Tzeferacos, Don Lamb, Gianluca Gregori, Alex Schekochihin (and many others ) 2 th August
Dynamo on the OMEGA laser and kinetic problems of proton radiography Archie Bott, Alex Rigby, Tom White, Petros Tzeferacos, Don Lamb, Gianluca Gregori, Alex Schekochihin (and many others ) 2 th August
Laboratory evidence of dynamo amplification of magnetic fields in a turbulent plasma
 Laboratory evidence of dynamo amplification of magnetic fields in a turbulent plasma P. Tzeferacos a,b, A. Rigby a, A. Bott a, A. R. Bell a, R. Bingham c,d, A. Casner e, F. Cattaneo b, E. M. Churazov f,g,
Laboratory evidence of dynamo amplification of magnetic fields in a turbulent plasma P. Tzeferacos a,b, A. Rigby a, A. Bott a, A. R. Bell a, R. Bingham c,d, A. Casner e, F. Cattaneo b, E. M. Churazov f,g,
Growth of Magnetic Fields by Turbulent Motions and Characteristic Scales of MHD Turbulence
 Growth of Magnetic Fields by Turbulent Motions and Characteristic Scales of MHD Turbulence Jungyeon Cho Chungnam National University, Korea Cho, Vishniac, Beresnyak, Lazarian & Ryu 2009, ApJ Cho & Ryu,
Growth of Magnetic Fields by Turbulent Motions and Characteristic Scales of MHD Turbulence Jungyeon Cho Chungnam National University, Korea Cho, Vishniac, Beresnyak, Lazarian & Ryu 2009, ApJ Cho & Ryu,
Laboratory evidence of dynamo amplification of magnetic fields in a turbulent plasma
 PSFC/JA-17-14 Laboratory evidence of dynamo amplification of magnetic fields in a turbulent plasma P. Tzeferacos a,b, A. Rigby a, A. Bott a, A. R. Bell a, R. Bingham c,d, A. Casner e, F. Cattaneo b, E.
PSFC/JA-17-14 Laboratory evidence of dynamo amplification of magnetic fields in a turbulent plasma P. Tzeferacos a,b, A. Rigby a, A. Bott a, A. R. Bell a, R. Bingham c,d, A. Casner e, F. Cattaneo b, E.
Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters
 Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) with Hyesung Kang (Pusan Nat. U, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (Chungnam Nat. U.),
Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) with Hyesung Kang (Pusan Nat. U, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (Chungnam Nat. U.),
FLASH SIMULATIONS OF EXPERIMENTS TO EXPLORE THE GENERATION OF COSMOLOGICAL MAGNETIC FIELDS AT LABORATOIRE d'utilisation DES LASERS INTENSES (LULI)
 FLASH SIMULATIONS OF EXPERIMENTS TO EXPLORE THE GENERATION OF COSMOLOGICAL MAGNETIC FIELDS AT LABORATOIRE d'utilisation DES LASERS INTENSES (LULI) Anthony Scopatz RAL Tutorial May 2012 1 Collaborators
FLASH SIMULATIONS OF EXPERIMENTS TO EXPLORE THE GENERATION OF COSMOLOGICAL MAGNETIC FIELDS AT LABORATOIRE d'utilisation DES LASERS INTENSES (LULI) Anthony Scopatz RAL Tutorial May 2012 1 Collaborators
The amplification of magnetic fields by the turbulent dynamo in the early Universe
 The amplification of magnetic fields by the turbulent dynamo in the early Universe Jacques M. Wagstaff Phys. Rev. D89:103001 arxiv:1304.4723 Hamburger Sternwarte, Hamburg University Robi Banerjee 1, Dominik
The amplification of magnetic fields by the turbulent dynamo in the early Universe Jacques M. Wagstaff Phys. Rev. D89:103001 arxiv:1304.4723 Hamburger Sternwarte, Hamburg University Robi Banerjee 1, Dominik
Amplification of magnetic fields from turbulence in the early Universe
 Amplification of magnetic fields from turbulence in the early Universe Jacques M. Wagstaff 1 arxiv:1304.4723 Robi Banerjee 1, Dominik Schleicher 2, Günter Sigl 3 1 Hamburg University 2 Institut für Astrophysik,
Amplification of magnetic fields from turbulence in the early Universe Jacques M. Wagstaff 1 arxiv:1304.4723 Robi Banerjee 1, Dominik Schleicher 2, Günter Sigl 3 1 Hamburg University 2 Institut für Astrophysik,
Turbulence and Magnetic Field in High-β Plasma of Intracluster Medium
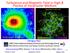 Turbulence and Magnetic Field in High-β Plasma of Intracluster Medium Coma cluster of galaxies Dongsu Ryu UNIST (Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) KASI (Korea Astronomy and Space
Turbulence and Magnetic Field in High-β Plasma of Intracluster Medium Coma cluster of galaxies Dongsu Ryu UNIST (Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) KASI (Korea Astronomy and Space
SKA AND THE COSMOLOGICAL EVOLUTION OF CLUSTER MAGNETIC FIELDS
 SKA AND THE COSMOLOGICAL EVOLUTION OF CLUSTER MAGNETIC FIELDS MARTIN KRAUSE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE, UNIVERSITÄTSSTERNWARTE MÜNCHEN & MAX-PLANCK-INSTITUT FÜR EXTRATERRESTRISCHE PHYSIK COLLABORATORS: PAUL
SKA AND THE COSMOLOGICAL EVOLUTION OF CLUSTER MAGNETIC FIELDS MARTIN KRAUSE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE, UNIVERSITÄTSSTERNWARTE MÜNCHEN & MAX-PLANCK-INSTITUT FÜR EXTRATERRESTRISCHE PHYSIK COLLABORATORS: PAUL
Implementation of a Faraday rotation diagnostic at the OMEGA laser facility
 High Power Laser Science and Engineering, (2018), Vol. 6, e49, 10 pages. The Author(s) 2018. This is an Open Access article, distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution licence (http://creativecommons.org/
High Power Laser Science and Engineering, (2018), Vol. 6, e49, 10 pages. The Author(s) 2018. This is an Open Access article, distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution licence (http://creativecommons.org/
Radio relics and magnetic field amplification in the Intra-cluster Medium
 Radio relics and magnetic field amplification in the Intra-cluster Medium Annalisa Annalisa Bonafede Bonafede Hamburger Hamburg Sternwarte University Hamburg University Jacobs University Bremen Collaborators:
Radio relics and magnetic field amplification in the Intra-cluster Medium Annalisa Annalisa Bonafede Bonafede Hamburger Hamburg Sternwarte University Hamburg University Jacobs University Bremen Collaborators:
Cosmic Rays in Galaxy Clusters: Simulations and Perspectives
 Cosmic Rays in Galaxy Clusters: Simulations and Perspectives 1 in collaboration with Volker Springel 2, Torsten Enßlin 2 1 Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Canada 2 Max-Planck Institute
Cosmic Rays in Galaxy Clusters: Simulations and Perspectives 1 in collaboration with Volker Springel 2, Torsten Enßlin 2 1 Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Canada 2 Max-Planck Institute
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations. simulations of galaxy and structure formation
 Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 13 26 / Workshop Dark halos, UBC Vancouver Outline 1
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 13 26 / Workshop Dark halos, UBC Vancouver Outline 1
Collisionless Shock and Particle Acceleration Computation and Experiment
 Collisionless Shock and Particle Acceleration Computation and Experiment H. Takabe (Aki) ILE, Osaka University, Japan Meudon Observatory, Paris December 3, 2011 1 Challenging Basic Science in Laboratory
Collisionless Shock and Particle Acceleration Computation and Experiment H. Takabe (Aki) ILE, Osaka University, Japan Meudon Observatory, Paris December 3, 2011 1 Challenging Basic Science in Laboratory
Magnetic fields generated by the Weibel Instability
 Magnetic fields generated by the Weibel Instability C. M. Ryu POSTECH, KOREA FFP14 Marseille 14.7.15-7.18 Outline I. Why Weibel instability? II. Simulations III. Conclusion Why Weibel instability? The
Magnetic fields generated by the Weibel Instability C. M. Ryu POSTECH, KOREA FFP14 Marseille 14.7.15-7.18 Outline I. Why Weibel instability? II. Simulations III. Conclusion Why Weibel instability? The
Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs
 Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs Klaus Dolag ( ) Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik ( ) Introduction Evolution of the structures in the Universe t =
Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs Klaus Dolag ( ) Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik ( ) Introduction Evolution of the structures in the Universe t =
Progress in Vlasov-Fokker- Planck simulations of laserplasma
 Progress in Vlasov-Fokker- Planck simulations of laserplasma interactions C. P. Ridgers, M. W. Sherlock, R. J. Kingham, A.Thomas, R. Evans Imperial College London Outline Part 1 simulations of long-pulse
Progress in Vlasov-Fokker- Planck simulations of laserplasma interactions C. P. Ridgers, M. W. Sherlock, R. J. Kingham, A.Thomas, R. Evans Imperial College London Outline Part 1 simulations of long-pulse
The PETAL+ project X-ray and particle diagnostics for plasma experiments at LMJ - PETAL
 PETAL+ plasma diagnostics The PETAL+ project X-ray and particle diagnostics for plasma experiments at LMJ - PETAL Jean-Éric Ducret CEA-Saclay/IRFU/Service d Astrophysique & CELIA UMR5107, U. Bordeaux CEA
PETAL+ plasma diagnostics The PETAL+ project X-ray and particle diagnostics for plasma experiments at LMJ - PETAL Jean-Éric Ducret CEA-Saclay/IRFU/Service d Astrophysique & CELIA UMR5107, U. Bordeaux CEA
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations. simulations of galaxy and structure formation
 Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 11 26 / Colloquium University of Victoria Outline 1 Cosmic
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 11 26 / Colloquium University of Victoria Outline 1 Cosmic
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Sep 2010
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Sep 2010 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Sep 2010](/thumbs/88/115477948.jpg) Submitted to ApJ Faraday Rotation Measure due to the Intergalactic Magnetic Field arxiv:1009.0570v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Sep 2010 Takuya Akahori 1 and Dongsu Ryu 2,3 1 Research Institute of Basic Science, Chungnam
Submitted to ApJ Faraday Rotation Measure due to the Intergalactic Magnetic Field arxiv:1009.0570v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Sep 2010 Takuya Akahori 1 and Dongsu Ryu 2,3 1 Research Institute of Basic Science, Chungnam
Intracluster Shock Waves
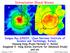 ρ Intracluster Shock Waves T R 200 Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) Hyesung Kang (Pusan National U, Korea) Sungwook E. Hong (Korea Institute for Advanced Study)
ρ Intracluster Shock Waves T R 200 Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) Hyesung Kang (Pusan National U, Korea) Sungwook E. Hong (Korea Institute for Advanced Study)
NONLINEAR MHD WAVES THE INTERESTING INFLUENCE OF FIREHOSE AND MIRROR IN ASTROPHYSICAL PLASMAS. Jono Squire (Caltech) UCLA April 2017
 NONLINEAR MHD WAVES THE INTERESTING INFLUENCE OF FIREHOSE AND MIRROR IN ASTROPHYSICAL PLASMAS Jono Squire (Caltech) UCLA April 2017 Along with: E. Quataert, A. Schekochihin, M. Kunz, S. Bale, C. Chen,
NONLINEAR MHD WAVES THE INTERESTING INFLUENCE OF FIREHOSE AND MIRROR IN ASTROPHYSICAL PLASMAS Jono Squire (Caltech) UCLA April 2017 Along with: E. Quataert, A. Schekochihin, M. Kunz, S. Bale, C. Chen,
Radio Continuum: Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields. Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn
 Radio Continuum: Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn Synchrotron emission Beam angle: Ψ/2=1/γ=E o /E Radio continuum tools to study GeV Cosmic ray electrons (CRE) Synchrotron spectrum:
Radio Continuum: Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn Synchrotron emission Beam angle: Ψ/2=1/γ=E o /E Radio continuum tools to study GeV Cosmic ray electrons (CRE) Synchrotron spectrum:
Fundamentals of Turbulence
 Fundamentals of Turbulence Stanislav Boldyrev (University of Wisconsin - Madison) Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical Plasmas What is turbulence? No exact definition.
Fundamentals of Turbulence Stanislav Boldyrev (University of Wisconsin - Madison) Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical Plasmas What is turbulence? No exact definition.
Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA
 Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn & SKA Science Working Group Fundamental magnetic questions When and how were the first fields generated?
Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn & SKA Science Working Group Fundamental magnetic questions When and how were the first fields generated?
Magnetic Field in Galaxies and clusters
 Magnetic Field in Galaxies and clusters Kandaswamy Subramanian Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.0/27 Plan Observing
Magnetic Field in Galaxies and clusters Kandaswamy Subramanian Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.0/27 Plan Observing
Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies
 Lecture 4: Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies Rainer Beck, MPIfR Bonn Generation and amplification of cosmic magnetic fields Stage 1: Field seeding Stage 2: Field amplification Stage 3: Coherent field
Lecture 4: Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies Rainer Beck, MPIfR Bonn Generation and amplification of cosmic magnetic fields Stage 1: Field seeding Stage 2: Field amplification Stage 3: Coherent field
Small-Scale Dynamo and the Magnetic Prandtl Number
 MRI Turbulence Workshop, IAS, Princeton, 17.06.08 Small-Scale Dynamo and the Magnetic Prandtl Number Alexander Schekochihin (Imperial College) with Steve Cowley (Culham & Imperial) Greg Hammett (Princeton)
MRI Turbulence Workshop, IAS, Princeton, 17.06.08 Small-Scale Dynamo and the Magnetic Prandtl Number Alexander Schekochihin (Imperial College) with Steve Cowley (Culham & Imperial) Greg Hammett (Princeton)
Cosmological Shocks and Their Signatures
 Cosmological Shocks and Their Signatures Dongsu Ryu (Chungnam National U, Korea) Hyesung Kang (PNU, Korea), Renyi Ma (CNU, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (CNU, Korea), David Porter (U of Minnesota), T. W. Jones
Cosmological Shocks and Their Signatures Dongsu Ryu (Chungnam National U, Korea) Hyesung Kang (PNU, Korea), Renyi Ma (CNU, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (CNU, Korea), David Porter (U of Minnesota), T. W. Jones
Laser-driven proton acceleration from cryogenic hydrogen jets
 Laser-driven proton acceleration from cryogenic hydrogen jets new prospects in tumor therapy and laboratory astroparticle physics C. Roedel SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory & Friedrich-Schiller-University
Laser-driven proton acceleration from cryogenic hydrogen jets new prospects in tumor therapy and laboratory astroparticle physics C. Roedel SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory & Friedrich-Schiller-University
A Tunable (1100-nm to 1500-nm) 50-mJ Laser Enables a Pump-Depleting Plasma-Wave Amplifier
 A Tunable (1100-nm to 1500-nm) 50-mJ Laser Enables a Pump-Depleting Plasma-Wave Amplifier Focused intensity (W/cm 2 ) 10 30 10 25 10 20 10 15 10 10 Nonlinear quantum electrodynamics (QED) Ultrarelativistic
A Tunable (1100-nm to 1500-nm) 50-mJ Laser Enables a Pump-Depleting Plasma-Wave Amplifier Focused intensity (W/cm 2 ) 10 30 10 25 10 20 10 15 10 10 Nonlinear quantum electrodynamics (QED) Ultrarelativistic
Integrated simulations of fast ignition of inertial fusion targets
 Integrated simulations of fast ignition of inertial fusion targets Javier Honrubia School of Aerospace Engineering Technical University of Madrid, Spain 11 th RES Users Meeting, Santiago de Compostela,
Integrated simulations of fast ignition of inertial fusion targets Javier Honrubia School of Aerospace Engineering Technical University of Madrid, Spain 11 th RES Users Meeting, Santiago de Compostela,
the ICM Power Spectrum:
 the ICM Power Spectrum: probing the gas physics of galaxy clusters Massimo Gaspari Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Collaborators: E. Churazov, D. Nagai, E. Lau, I. Zhuravleva, R. Sunyaev Power Spectrum
the ICM Power Spectrum: probing the gas physics of galaxy clusters Massimo Gaspari Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Collaborators: E. Churazov, D. Nagai, E. Lau, I. Zhuravleva, R. Sunyaev Power Spectrum
The MIT Accelerator for development of ICF diagnostics at OMEGA / OMEGA-EP and the NIF
 Introduction The MIT Accelerator for development of ICF diagnostics at OMEGA / OMEGA-EP and the NIF SBDs d + or 3 He +(2+) D or 3 He target Present MIT Graduate Students and the MIT Accelerator OLUG 21
Introduction The MIT Accelerator for development of ICF diagnostics at OMEGA / OMEGA-EP and the NIF SBDs d + or 3 He +(2+) D or 3 He target Present MIT Graduate Students and the MIT Accelerator OLUG 21
Fluctuation dynamo amplified by intermittent shear bursts
 by intermittent Thanks to my collaborators: A. Busse (U. Glasgow), W.-C. Müller (TU Berlin) Dynamics Days Europe 8-12 September 2014 Mini-symposium on Nonlinear Problems in Plasma Astrophysics Introduction
by intermittent Thanks to my collaborators: A. Busse (U. Glasgow), W.-C. Müller (TU Berlin) Dynamics Days Europe 8-12 September 2014 Mini-symposium on Nonlinear Problems in Plasma Astrophysics Introduction
Beyond Ideal MHD. Nick Murphy. Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics. February 8, 2016
 Beyond Ideal MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 8, 2016 These lecture notes are largely based on Plasma Physics for Astrophysics by
Beyond Ideal MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 8, 2016 These lecture notes are largely based on Plasma Physics for Astrophysics by
Simulating magnetic fields in structure formation
 Simulating magnetic fields in structure formation USM / MPE / MPA Harald Lesch & Klaus Dolag Annette Geng, Federico Stasyszyn & Marcus Beck July, 2012 (Mainz) Alexander Beck Magnetic fields in galaxies
Simulating magnetic fields in structure formation USM / MPE / MPA Harald Lesch & Klaus Dolag Annette Geng, Federico Stasyszyn & Marcus Beck July, 2012 (Mainz) Alexander Beck Magnetic fields in galaxies
HED Physics. 1) By means of laser-driven shock waves (LMJ as driver, PETAL as a backlighter)
 HED Physics High-energy lasers allow reaching HED states: 1) By means of laser-driven shock waves (LMJ as driver, PETAL as a backlighter) 2) By using short laser pulses to heat matter using lasergenerated
HED Physics High-energy lasers allow reaching HED states: 1) By means of laser-driven shock waves (LMJ as driver, PETAL as a backlighter) 2) By using short laser pulses to heat matter using lasergenerated
Lower bound on the extragalactic magnetic field
 Lower bound on the extragalactic magnetic field Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Dolag, MK, Ostapchenko, Tomàs 10 Neronov, Semikoz, MK, Ostapchenko, Elyiv 10 Introduction Mean free path of photons
Lower bound on the extragalactic magnetic field Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Dolag, MK, Ostapchenko, Tomàs 10 Neronov, Semikoz, MK, Ostapchenko, Elyiv 10 Introduction Mean free path of photons
Probing RMs due to Magnetic Fields in the Cosmic Web
 Probing RMs due to Magnetic Fields in the Cosmic Web Takuya Akahori JSPS Postdoctoral Fellow for Research Abroad Sydney Institute for Astronomy, The University of Sydney Japan SKA Consortium Cosmic Magnetism
Probing RMs due to Magnetic Fields in the Cosmic Web Takuya Akahori JSPS Postdoctoral Fellow for Research Abroad Sydney Institute for Astronomy, The University of Sydney Japan SKA Consortium Cosmic Magnetism
Betatron radiation from a hybrid self-modulated wakefield and direct laser accelerator
 Betatron radiation from a hybrid self-modulated wakefield and direct laser accelerator 1, N. Lemos 2, J.L. Shaw 2, B.B. Pollock 1, G. Goyon 1, W. Schumaker 3, F. Fiuza 3, A. Saunders 4, K. A. Marsh 2,
Betatron radiation from a hybrid self-modulated wakefield and direct laser accelerator 1, N. Lemos 2, J.L. Shaw 2, B.B. Pollock 1, G. Goyon 1, W. Schumaker 3, F. Fiuza 3, A. Saunders 4, K. A. Marsh 2,
AGN Outflows in Dynamic ICMs: Winds and Twists
 AGN Outflows in Dynamic ICMs: Winds and Twists Tom Jones University of Minnesota Pete Mendygral (UMN, Cray Computer) David Porter (UMN) Klaus Dolag (MPA, U Munich) 11/29/2012 Binary Black Holes & Dual
AGN Outflows in Dynamic ICMs: Winds and Twists Tom Jones University of Minnesota Pete Mendygral (UMN, Cray Computer) David Porter (UMN) Klaus Dolag (MPA, U Munich) 11/29/2012 Binary Black Holes & Dual
Cosmic-ray Acceleration and Current-Driven Instabilities
 Cosmic-ray Acceleration and Current-Driven Instabilities B. Reville Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg Sep 17 2009, KITP J.G. Kirk, P. Duffy, S.O Sullivan, Y. Ohira, F. Takahara Outline Analysis
Cosmic-ray Acceleration and Current-Driven Instabilities B. Reville Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg Sep 17 2009, KITP J.G. Kirk, P. Duffy, S.O Sullivan, Y. Ohira, F. Takahara Outline Analysis
Constraining primordial magnetic fields with observations
 Constraining primordial magnetic fields with observations Kerstin Kunze (University of Salamanca and IUFFyM) KK PRD 83 (2011) 023006; PRD 85 (2012) 083004; PRD 87 (2013) 103005; PRD 89 (2014) 103016, arxiv:1703.03650
Constraining primordial magnetic fields with observations Kerstin Kunze (University of Salamanca and IUFFyM) KK PRD 83 (2011) 023006; PRD 85 (2012) 083004; PRD 87 (2013) 103005; PRD 89 (2014) 103016, arxiv:1703.03650
Reduced MHD. Nick Murphy. Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics. February 19, 2014
 Reduced MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 19, 2014 These lecture notes are largely based on Lectures in Magnetohydrodynamics by Dalton
Reduced MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 19, 2014 These lecture notes are largely based on Lectures in Magnetohydrodynamics by Dalton
The Madison Dynamo Experiment: magnetic instabilities driven by sheared flow in a sphere. Cary Forest Department of Physics University of Wisconsin
 The Madison Dynamo Experiment: magnetic instabilities driven by sheared flow in a sphere Cary Forest Department of Physics University of Wisconsin February 28, 2001 Planets, stars and perhaps the galaxy
The Madison Dynamo Experiment: magnetic instabilities driven by sheared flow in a sphere Cary Forest Department of Physics University of Wisconsin February 28, 2001 Planets, stars and perhaps the galaxy
Intracluster Medium Plasmas
 arxiv:1903.08751v1 [astro-ph.he] 20 Mar 2019 PLASMA 2020 WHITE PAPER FOR THE DECADAL ASSESSMENT OF PLASMA SCIENCE Intracluster Medium Plasmas Damiano Caprioli 1, Gianfranco Brunetti 2, Thomas W. Jones
arxiv:1903.08751v1 [astro-ph.he] 20 Mar 2019 PLASMA 2020 WHITE PAPER FOR THE DECADAL ASSESSMENT OF PLASMA SCIENCE Intracluster Medium Plasmas Damiano Caprioli 1, Gianfranco Brunetti 2, Thomas W. Jones
Turbulent Magnetic Helicity Transport and the Rapid Growth of Large Scale Magnetic Fields
 Turbulent Magnetic Helicity Transport and the Rapid Growth of Large Scale Magnetic Fields Jungyeon Cho Dmitry Shapovalov MWMF Madison, Wisconsin April 2012 The Large Scale Dynamo The accumulation of magnetic
Turbulent Magnetic Helicity Transport and the Rapid Growth of Large Scale Magnetic Fields Jungyeon Cho Dmitry Shapovalov MWMF Madison, Wisconsin April 2012 The Large Scale Dynamo The accumulation of magnetic
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 11 Dec 2015
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 11 Dec 2015 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 11 Dec 2015](/thumbs/82/85900018.jpg) Creation of Magnetized Jet Using a Ring of Laser Beams arxiv:1409.4273v2 [astro-ph.he] 11 Dec 2015 Wen Fu a, Edison P. Liang a, Petros Tzeferacos b, Donald Q. Lamb b a Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Creation of Magnetized Jet Using a Ring of Laser Beams arxiv:1409.4273v2 [astro-ph.he] 11 Dec 2015 Wen Fu a, Edison P. Liang a, Petros Tzeferacos b, Donald Q. Lamb b a Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Thomson Scattering from Nonlinear Electron Plasma Waves
 Thomson Scattering from Nonlinear Electron Plasma Waves A. DAVIES, 1 J. KATZ, 1 S. BUCHT, 1 D. HABERBERGER, 1 J. BROMAGE, 1 J. D. ZUEGEL, 1 J. D. SADLER, 2 P. A. NORREYS, 3 R. BINGHAM, 4 R. TRINES, 5 L.O.
Thomson Scattering from Nonlinear Electron Plasma Waves A. DAVIES, 1 J. KATZ, 1 S. BUCHT, 1 D. HABERBERGER, 1 J. BROMAGE, 1 J. D. ZUEGEL, 1 J. D. SADLER, 2 P. A. NORREYS, 3 R. BINGHAM, 4 R. TRINES, 5 L.O.
ICMs and the IPM: Birds of a Feather?
 ICMs and the IPM: Birds of a Feather? Tom Jones University of Minnesota 11 November, 2014 KAW8: Astrophysics of High-Beta Plasma in the Universe 1 Outline: ICM plasma is the dominant baryon component in
ICMs and the IPM: Birds of a Feather? Tom Jones University of Minnesota 11 November, 2014 KAW8: Astrophysics of High-Beta Plasma in the Universe 1 Outline: ICM plasma is the dominant baryon component in
Ion-Acoustic-Wave Instability from Laser-Driven Return Currents
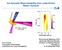 Ion-Acoustic-Wave Instability from Laser-Driven Return Currents 3.0 3~ beam 2.5 4~ TS beam 60 100 100-nm TS volume Thomsonscattered light 5 0 5 Wavelength shift (Å) 0.5 0.0 D. H. Froula University of Rochester
Ion-Acoustic-Wave Instability from Laser-Driven Return Currents 3.0 3~ beam 2.5 4~ TS beam 60 100 100-nm TS volume Thomsonscattered light 5 0 5 Wavelength shift (Å) 0.5 0.0 D. H. Froula University of Rochester
Turbulence & particle acceleration in galaxy clusters. Gianfranco Brunetti
 Turbulence & particle acceleration in galaxy clusters Gianfranco Brunetti Mergers & CR-acceleration Cluster-cluster mergers are the most energetic events in the present Universe (10 64 erg/gyr). They can
Turbulence & particle acceleration in galaxy clusters Gianfranco Brunetti Mergers & CR-acceleration Cluster-cluster mergers are the most energetic events in the present Universe (10 64 erg/gyr). They can
Laboratory Astrophysics: magnetically driven plasma jets on pulsed power facilities
 Laboratory Astrophysics: magnetically driven plasma jets on pulsed power facilities S.V. Lebedev, F. Suzuki-Vidal, S.N. Bland, A. Harvey-Thompson, G. Hall, A. Marocchino, J.P. Chittenden Imperial College
Laboratory Astrophysics: magnetically driven plasma jets on pulsed power facilities S.V. Lebedev, F. Suzuki-Vidal, S.N. Bland, A. Harvey-Thompson, G. Hall, A. Marocchino, J.P. Chittenden Imperial College
HiPER: a laser fusion facility for Europe
 HiPER: a laser fusion facility for Europe Prof Mike Dunne Director, Central Laser Facility, Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, UK m.dunne@rl.ac.uk www.hiper-laser.eu We are entering a new era Demonstration
HiPER: a laser fusion facility for Europe Prof Mike Dunne Director, Central Laser Facility, Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, UK m.dunne@rl.ac.uk www.hiper-laser.eu We are entering a new era Demonstration
Constraints on physics of gas and dark matter from cluster mergers. Maxim Markevitch (SAO)
 Constraints on physics of gas and dark matter from cluster mergers Maxim Markevitch (SAO) November 2005 1E 0657 56 Chandra 0.5 Msec image 0.5 Mpc z=0.3 An overheated cluster From M T relation: T= 14 kev:
Constraints on physics of gas and dark matter from cluster mergers Maxim Markevitch (SAO) November 2005 1E 0657 56 Chandra 0.5 Msec image 0.5 Mpc z=0.3 An overheated cluster From M T relation: T= 14 kev:
Magnetized High-Energy-Density Plasma
 LLNL PRES 446057 Magnetized High-Energy-Density Plasma D.D. Ryutov Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA 94551, USA Presented at the 2010 Science with High-Power Lasers and Pulsed Power
LLNL PRES 446057 Magnetized High-Energy-Density Plasma D.D. Ryutov Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA 94551, USA Presented at the 2010 Science with High-Power Lasers and Pulsed Power
The cosmic background radiation II: The WMAP results. Alexander Schmah
 The cosmic background radiation II: The WMAP results Alexander Schmah 27.01.05 General Aspects - WMAP measures temperatue fluctuations of the CMB around 2.726 K - Reason for the temperature fluctuations
The cosmic background radiation II: The WMAP results Alexander Schmah 27.01.05 General Aspects - WMAP measures temperatue fluctuations of the CMB around 2.726 K - Reason for the temperature fluctuations
SPARCLAB. Source For Plasma Accelerators and Radiation Compton. On behalf of SPARCLAB collaboration
 SPARCLAB Source For Plasma Accelerators and Radiation Compton with Laser And Beam On behalf of SPARCLAB collaboration EMITTANCE X X X X X X X X 2 BRIGHTNESS (electrons) B n 2I nx ny A m 2 rad 2 The current
SPARCLAB Source For Plasma Accelerators and Radiation Compton with Laser And Beam On behalf of SPARCLAB collaboration EMITTANCE X X X X X X X X 2 BRIGHTNESS (electrons) B n 2I nx ny A m 2 rad 2 The current
Radiation processes and mechanisms in astrophysics I. R Subrahmanyan Notes on ATA lectures at UWA, Perth 18 May 2009
 Radiation processes and mechanisms in astrophysics I R Subrahmanyan Notes on ATA lectures at UWA, Perth 18 May 009 Light of the night sky We learn of the universe around us from EM radiation, neutrinos,
Radiation processes and mechanisms in astrophysics I R Subrahmanyan Notes on ATA lectures at UWA, Perth 18 May 009 Light of the night sky We learn of the universe around us from EM radiation, neutrinos,
Exploring Astrophysical Magnetohydrodynamics Using High-power Laser Facilities
 Exploring Astrophysical Magnetohydrodynamics Using High-power Laser Facilities Mario Manuel Einstein Fellows Symposium Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics October 28 th, 2014 Ø Collimation and
Exploring Astrophysical Magnetohydrodynamics Using High-power Laser Facilities Mario Manuel Einstein Fellows Symposium Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics October 28 th, 2014 Ø Collimation and
Magnetic Reconnection and Plasma Dynamics in Two-Beam Laser Solid Interactions
 Magnetic Reconnection and Plasma Dynamics in Two-Beam Laser Solid Interactions P. M. Nilson University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 48th Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society
Magnetic Reconnection and Plasma Dynamics in Two-Beam Laser Solid Interactions P. M. Nilson University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 48th Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society
Diagnosing OMEGA and NIF Implosions Using the D 3 He Spectrum Line Width
 Introduction Diagnosing OMEGA and NIF Implosions Using the D 3 He Spectrum Line Width A. B. Zylstra, M. Rosenberg, N. Sinenian, C. Li, F. Seguin, J. Frenje, R. Petrasso (MIT) R. Rygg, D. Hicks, S. Friedrich,
Introduction Diagnosing OMEGA and NIF Implosions Using the D 3 He Spectrum Line Width A. B. Zylstra, M. Rosenberg, N. Sinenian, C. Li, F. Seguin, J. Frenje, R. Petrasso (MIT) R. Rygg, D. Hicks, S. Friedrich,
Fukuoka, Japan. 23 August National Ignition Facility (NIF) Laboratory for Laser Energetics (OPERA)
 Fukuoka, Japan 23 August 2012 National Ignition Facility (NIF) LLNL-PRES-562760 This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under
Fukuoka, Japan 23 August 2012 National Ignition Facility (NIF) LLNL-PRES-562760 This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under
MULTIWAVELENGTH OBSERVATIONS OF CLUSTERS OF GALAXIES AND THE ROLE OF CLUSTER MERGERS PASQUALE BLASI
 MULTIWAVELENGTH OBSERVATIONS OF CLUSTERS OF GALAXIES AND THE ROLE OF CLUSTER MERGERS PASQUALE BLASI NASA/Fermilab Astrophysics Center Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, Box 500, Batavia, IL 60510-0500,
MULTIWAVELENGTH OBSERVATIONS OF CLUSTERS OF GALAXIES AND THE ROLE OF CLUSTER MERGERS PASQUALE BLASI NASA/Fermilab Astrophysics Center Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, Box 500, Batavia, IL 60510-0500,
Observations of Magnetic Fields in Intracluster Medium. Govoni Federica INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Cagliari
 Observations of Magnetic Fields in Intracluster Medium Govoni Federica INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Cagliari Collaborators: M. Murgia, L. Feretti, G. Giovannini, V. Vacca, A. Bonafede IAU 2012 China
Observations of Magnetic Fields in Intracluster Medium Govoni Federica INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Cagliari Collaborators: M. Murgia, L. Feretti, G. Giovannini, V. Vacca, A. Bonafede IAU 2012 China
What is. Inertial Confinement Fusion?
 What is Inertial Confinement Fusion? Inertial Confinement Fusion: dense & short-lived plasma Fusing D and T requires temperature to overcome Coulomb repulsion density & confinement time to maximize number
What is Inertial Confinement Fusion? Inertial Confinement Fusion: dense & short-lived plasma Fusing D and T requires temperature to overcome Coulomb repulsion density & confinement time to maximize number
The Large Area Telescope on-board of the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope Mission
 The Large Area Telescope on-board of the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope Mission 1 Outline Mainly from 2009 ApJ 697 1071 The Pair Conversion Telescope The Large Area Telescope Charged Background and Events
The Large Area Telescope on-board of the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope Mission 1 Outline Mainly from 2009 ApJ 697 1071 The Pair Conversion Telescope The Large Area Telescope Charged Background and Events
Ion Induced Beam disruption Mechanism
 Ion Induced Beam disruption Mechanism C. Vermare CEA, Polygone d Expérimentation de Moronvilliers, France H. Davis, D.C. Moir, R. Olson Los Alamos National Laboratory, NM, USA T. Hughes Mission Research
Ion Induced Beam disruption Mechanism C. Vermare CEA, Polygone d Expérimentation de Moronvilliers, France H. Davis, D.C. Moir, R. Olson Los Alamos National Laboratory, NM, USA T. Hughes Mission Research
PoS(EXTRA-RADSUR2015)063
 Constraining magnetic fields and particle acceleration processes in galaxy clusters: a joint VLA/LOFAR view on Coma and SKA perspectives Hamburger Sternwarte,Universität Hamburg, Gojenbergsweg 112,21029
Constraining magnetic fields and particle acceleration processes in galaxy clusters: a joint VLA/LOFAR view on Coma and SKA perspectives Hamburger Sternwarte,Universität Hamburg, Gojenbergsweg 112,21029
Target Simulations. Roman Samulyak in collaboration with Y. Prykarpatskyy, T. Lu
 Muon Collider/Neutrino Factory Collaboration Meeting May 26 28, CERN, Geneva U.S. Department of Energy Target Simulations Roman Samulyak in collaboration with Y. Prykarpatskyy, T. Lu Center for Data Intensive
Muon Collider/Neutrino Factory Collaboration Meeting May 26 28, CERN, Geneva U.S. Department of Energy Target Simulations Roman Samulyak in collaboration with Y. Prykarpatskyy, T. Lu Center for Data Intensive
80 2 Observational Cosmology L and the mean energy
 80 2 Observational Cosmology fluctuations, short-wavelength modes have amplitudes that are suppressed because these modes oscillated as acoustic waves during the radiation epoch whereas the amplitude of
80 2 Observational Cosmology fluctuations, short-wavelength modes have amplitudes that are suppressed because these modes oscillated as acoustic waves during the radiation epoch whereas the amplitude of
Using Pulsars to study the Magnetic Field in The Milky way
 Using Pulsars to study the Magnetic Field in The Milky way Dipanjan Mitra ( MPIFR Bonn) R. Wielebinski ( MPIFR Bonn) M. Kramer ( Jodrell Bank) A. Jessner ( MPIFR Bonn) MPIFR, Bonn (24 th April 2003) To
Using Pulsars to study the Magnetic Field in The Milky way Dipanjan Mitra ( MPIFR Bonn) R. Wielebinski ( MPIFR Bonn) M. Kramer ( Jodrell Bank) A. Jessner ( MPIFR Bonn) MPIFR, Bonn (24 th April 2003) To
Evolution and Impact of Cosmic Magnetic Fields
 Evolution and Impact of Cosmic Magnetic Fields Robi Banerjee University of Hamburg Collaborators: Dominik Schleicher (Göttingen), C. Federrath (Lyon, HD), Karsten Jedamzik (Montpellier), R. Klessen (Heidelberg),
Evolution and Impact of Cosmic Magnetic Fields Robi Banerjee University of Hamburg Collaborators: Dominik Schleicher (Göttingen), C. Federrath (Lyon, HD), Karsten Jedamzik (Montpellier), R. Klessen (Heidelberg),
Fermi-LAT Analysis of the Coma Cluster
 Fermi-LAT Analysis of the Coma Cluster a Fabio Zandanel GRAPPA Institute University of Amsterdam f.zandanel@uva.nl In collaboration with S. Ando (GRAPPA) 18 th Symposium on Astroparticle Physics in the
Fermi-LAT Analysis of the Coma Cluster a Fabio Zandanel GRAPPA Institute University of Amsterdam f.zandanel@uva.nl In collaboration with S. Ando (GRAPPA) 18 th Symposium on Astroparticle Physics in the
PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS. ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP. NOTES: (references therein)
 PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP NOTES:http://www.astro.iag.usp.br/~dalpino (references therein) ICTP-SAIFR, October 7-18, 2013 Contents What is plasma? Why plasmas in astrophysics?
PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP NOTES:http://www.astro.iag.usp.br/~dalpino (references therein) ICTP-SAIFR, October 7-18, 2013 Contents What is plasma? Why plasmas in astrophysics?
Amplification of magnetic fields in core collapse
 Amplification of magnetic fields in core collapse Miguel Àngel Aloy Torás, Pablo Cerdá-Durán, Thomas Janka, Ewald Müller, Martin Obergaulinger, Tomasz Rembiasz Universitat de València; Max-Planck-Institut
Amplification of magnetic fields in core collapse Miguel Àngel Aloy Torás, Pablo Cerdá-Durán, Thomas Janka, Ewald Müller, Martin Obergaulinger, Tomasz Rembiasz Universitat de València; Max-Planck-Institut
Cosmic Rays, Photons and Neutrinos
 Cosmic Rays, Photons and Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline Plan of the lectures: Cosmic rays Galactic cosmic rays Basic observations Acceleration Supernova remnants Problems
Cosmic Rays, Photons and Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline Plan of the lectures: Cosmic rays Galactic cosmic rays Basic observations Acceleration Supernova remnants Problems
MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE UNIVERSE
 ARTICLE MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE UNIVERSE KANDASWAMY SUBRAMANIAN* The origin and maintenance of large scale magnetic fields in the Universe is discussed. A popular idea is that cosmic batteries generate
ARTICLE MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE UNIVERSE KANDASWAMY SUBRAMANIAN* The origin and maintenance of large scale magnetic fields in the Universe is discussed. A popular idea is that cosmic batteries generate
Compressible MHD Turbulence in Strongly Radiating Molecular Clouds in Astrophysics*
 Poster T25 Compressible MHD Turbulence in Strongly Radiating Molecular Clouds in Astrophysics* D.D. Ryutov LLNL, Livermore, CA 94551, USA Presented at 8 th International Workshop on the Physics of Compressible
Poster T25 Compressible MHD Turbulence in Strongly Radiating Molecular Clouds in Astrophysics* D.D. Ryutov LLNL, Livermore, CA 94551, USA Presented at 8 th International Workshop on the Physics of Compressible
MHD turbulence in the solar corona and solar wind
 MHD turbulence in the solar corona and solar wind Pablo Dmitruk Departamento de Física, FCEN, Universidad de Buenos Aires Turbulence, magnetic reconnection, particle acceleration Understand the mechanisms
MHD turbulence in the solar corona and solar wind Pablo Dmitruk Departamento de Física, FCEN, Universidad de Buenos Aires Turbulence, magnetic reconnection, particle acceleration Understand the mechanisms
Shocks in the ICM and the IPM
 Shocks in the ICM and the IPM Tom Jones (University of Minnesota) 1 Outline Setting the stage for following talks The Interplanetary and Intracluster Media as Collisionless Plasmas Basic Introduction to
Shocks in the ICM and the IPM Tom Jones (University of Minnesota) 1 Outline Setting the stage for following talks The Interplanetary and Intracluster Media as Collisionless Plasmas Basic Introduction to
COSMOLOGY AND GRAVITATIONAL WAVES. Chiara Caprini (APC)
 COSMOLOGY AND GRAVITATIONAL WAVES Chiara Caprini (APC) the direct detection of GW by the LIGO interferometers has opened a new era in Astronomy - we now have a new messenger bringing complementary informations
COSMOLOGY AND GRAVITATIONAL WAVES Chiara Caprini (APC) the direct detection of GW by the LIGO interferometers has opened a new era in Astronomy - we now have a new messenger bringing complementary informations
GA A25842 STUDY OF NON-LTE SPECTRA DEPENDENCE ON TARGET MASS IN SHORT PULSE LASER EXPERIMENTS
 GA A25842 STUDY OF NON-LTE SPECTRA DEPENDENCE ON TARGET MASS IN SHORT PULSE LASER EXPERIMENTS by C.A. BACK, P. AUDBERT, S.D. BATON, S.BASTIANI-CECCOTTI, P. GUILLOU, L. LECHERBOURG, B. BARBREL, E. GAUCI,
GA A25842 STUDY OF NON-LTE SPECTRA DEPENDENCE ON TARGET MASS IN SHORT PULSE LASER EXPERIMENTS by C.A. BACK, P. AUDBERT, S.D. BATON, S.BASTIANI-CECCOTTI, P. GUILLOU, L. LECHERBOURG, B. BARBREL, E. GAUCI,
Scope of this lecture ASTR 7500: Solar & Stellar Magnetism. Lecture 9 Tues 19 Feb Magnetic fields in the Universe. Geomagnetism.
 Scope of this lecture ASTR 7500: Solar & Stellar Magnetism Hale CGEG Solar & Space Physics Processes of magnetic field generation and destruction in turbulent plasma flows Introduction to general concepts
Scope of this lecture ASTR 7500: Solar & Stellar Magnetism Hale CGEG Solar & Space Physics Processes of magnetic field generation and destruction in turbulent plasma flows Introduction to general concepts
Linear and non-linear evolution of the gyroresonance instability in Cosmic Rays
 Linear and non-linear evolution of the gyroresonance instability in Cosmic Rays DESY Summer Student Programme, 2016 Olga Lebiga Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv, Ukraine Supervisors Reinaldo
Linear and non-linear evolution of the gyroresonance instability in Cosmic Rays DESY Summer Student Programme, 2016 Olga Lebiga Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv, Ukraine Supervisors Reinaldo
Intrinsic beam emittance of laser-accelerated electrons measured by x-ray spectroscopic imaging
 Intrinsic beam emittance of laser-accelerated electrons measured by x-ray spectroscopic imaging G. Golovin 1, S. Banerjee 1, C. Liu 1, S. Chen 1, J. Zhang 1, B. Zhao 1, P. Zhang 1, M. Veale 2, M. Wilson
Intrinsic beam emittance of laser-accelerated electrons measured by x-ray spectroscopic imaging G. Golovin 1, S. Banerjee 1, C. Liu 1, S. Chen 1, J. Zhang 1, B. Zhao 1, P. Zhang 1, M. Veale 2, M. Wilson
Scaling Hot-Electron Generation to High-Power, Kilojoule-Class Lasers
 Scaling Hot-Electron Generation to High-Power, Kilojoule-Class Lasers 75 nm 75 75 5 nm 3 copper target Normalized K b /K a 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 Cold material 1 ps 10 ps 0.2 10 3 10 4 Heating 2.1 kj, 10
Scaling Hot-Electron Generation to High-Power, Kilojoule-Class Lasers 75 nm 75 75 5 nm 3 copper target Normalized K b /K a 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 Cold material 1 ps 10 ps 0.2 10 3 10 4 Heating 2.1 kj, 10
Production of helical magnetic fields during baryogenesis
 Production of helical magnetic fields during baryogenesis Francesc Ferrer Washington University in Saint Louis ferrer@wustl.edu NORDITA. June 23, 25 Outline Introduction: Observations of Magnetic Fields
Production of helical magnetic fields during baryogenesis Francesc Ferrer Washington University in Saint Louis ferrer@wustl.edu NORDITA. June 23, 25 Outline Introduction: Observations of Magnetic Fields
> News < AMS-02 will be launched onboard the Shuttle Endeavour On May 2nd 2:33 P.M. from NASA Kennedy space center!
 > News < Anti-matter, dark matter measurement By measuring the cosmic rays (Mainly electron, positron, proton, anti-proton and light nuclei) AMS-02 will be launched onboard the Shuttle Endeavour On May
> News < Anti-matter, dark matter measurement By measuring the cosmic rays (Mainly electron, positron, proton, anti-proton and light nuclei) AMS-02 will be launched onboard the Shuttle Endeavour On May
Making Light from the Dark Universe
 Oxford University Physics Society, 1st May 2014 Talk Structure 1. Prelude: What is Dark Radiation? 2. Experimental motivation for dark radiation: CMB and BBN 3. Theoretical motivation for dark radiation:
Oxford University Physics Society, 1st May 2014 Talk Structure 1. Prelude: What is Dark Radiation? 2. Experimental motivation for dark radiation: CMB and BBN 3. Theoretical motivation for dark radiation:
Mikhail V. Medvedev (KU)
 Students (at KU): Sarah Reynolds, Sriharsha Pothapragada Mikhail V. Medvedev (KU) Collaborators: Anatoly Spitkovsky (Princeton) Luis Silva and the Plasma Simulation Group (Portugal) Ken-Ichi Nishikawa
Students (at KU): Sarah Reynolds, Sriharsha Pothapragada Mikhail V. Medvedev (KU) Collaborators: Anatoly Spitkovsky (Princeton) Luis Silva and the Plasma Simulation Group (Portugal) Ken-Ichi Nishikawa
The MEC endstation at LCLS New opportunities for high energy density science
 The MEC endstation at LCLS New opportunities for high energy density science Singapore, fttp-5, April 20th, 2011 Bob Nagler BNagler@slac.stanford.edu SLAC national accelerator laboratory 1 Overview Motivation
The MEC endstation at LCLS New opportunities for high energy density science Singapore, fttp-5, April 20th, 2011 Bob Nagler BNagler@slac.stanford.edu SLAC national accelerator laboratory 1 Overview Motivation
Down-to-earth searches for cosmological dark matter
 Down-to-earth searches for cosmological dark matter Carter Hall, University of Maryland October 19, 2016 Astrophysical evidence for dark matter Galaxy cluster collisions Rotation curves Ω 380,000 years
Down-to-earth searches for cosmological dark matter Carter Hall, University of Maryland October 19, 2016 Astrophysical evidence for dark matter Galaxy cluster collisions Rotation curves Ω 380,000 years
Magnetic Disruption of Inertially Collimated Flows on the Titan Laser Facility
 Magnetic Disruption of Inertially Collimated Flows on the Titan Laser Facility B = 1 mm n e [1 18 cm -3 ] 1 Mario Manuel Magnetic Meeting University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics April 23
Magnetic Disruption of Inertially Collimated Flows on the Titan Laser Facility B = 1 mm n e [1 18 cm -3 ] 1 Mario Manuel Magnetic Meeting University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics April 23
Waves in plasma. Denis Gialis
 Waves in plasma Denis Gialis This is a short introduction on waves in a non-relativistic plasma. We will consider a plasma of electrons and protons which is fully ionized, nonrelativistic and homogeneous.
Waves in plasma Denis Gialis This is a short introduction on waves in a non-relativistic plasma. We will consider a plasma of electrons and protons which is fully ionized, nonrelativistic and homogeneous.
Turbulence and Magnetic Fields in the Large Scale Structure of the Universe
 arxiv:0805.2466v1 [astro-ph] 16 May 2008 Turbulence and Magnetic Fields in the Large Scale Structure of the Universe Dongsu Ryu, 1 Hyesung Kang, 2 Jungyeon Cho, 1 and Santabrata Das 3 1 Department of Astronomy
arxiv:0805.2466v1 [astro-ph] 16 May 2008 Turbulence and Magnetic Fields in the Large Scale Structure of the Universe Dongsu Ryu, 1 Hyesung Kang, 2 Jungyeon Cho, 1 and Santabrata Das 3 1 Department of Astronomy
Mergers and Non-Thermal Processes in Clusters of Galaxies
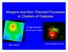 Mergers and Non-Thermal Processes in Clusters of Galaxies Craig Sarazin University of Virginia A85 Chandra A133 Chandra and VLA Collaborators Liz Blanton, Tracy Clarke, Scott Randall, Thomas Reiprich (UVa)
Mergers and Non-Thermal Processes in Clusters of Galaxies Craig Sarazin University of Virginia A85 Chandra A133 Chandra and VLA Collaborators Liz Blanton, Tracy Clarke, Scott Randall, Thomas Reiprich (UVa)
Magnetic Fields in Astrophysics: Origins and Evolution. Kinwah Wu Mullard Space Science Laboratory University College London
 Magnetic Fields in Astrophysics: Origins and Evolution Kinwah Wu Mullard Space Science Laboratory University College London Maxwell s equations covariant form in flat space time Lorentz force equation:
Magnetic Fields in Astrophysics: Origins and Evolution Kinwah Wu Mullard Space Science Laboratory University College London Maxwell s equations covariant form in flat space time Lorentz force equation:
