Fluctuating governing parameters in galaxy dynamo
|
|
|
- Kelly Baldwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fluctuating governing parameters in galaxy dynamo E.A.Mikhailov, V.V.Pushkarev M.V.Lomonosov Moscow State University Russian Federation X Serbian-Bulgarian Astronomical Conference Belgrade, Serbia
2 Introduction Some galaxies have magnetic fields of several μg. Their evolution is described by the so-called dynamo theory (Beck et al., 1996). It is important to describe the magnetic field in galaxies with such processes as star formation, supernova explosions, outflows from stars etc.
3 Dynamo mechanism The dynamo mechanism is based on joint action of alpha-effect and differential rotation. Alpha-effect transforms the angular component of the field to the radial one: B B r Differential rotation transforms the radial field to angular: B B r
4 Basic equation The field is described by Steenbeck Krause Rädler equation: B t curl v, B curl B B.
5 no-z approximation The galaxy disc is very thin. We can neglect the z-component of the field. The z-derivatives of the magnetic field can be replaced by algebraic expressions (Moss, 1995; Phillips, 2001): B 2 2 r, B 2 2 r,. z 4h
6 System of equations The equations will be rewritten as: Br B B B t h 4h 2 ; 2 r r r B r Br B B t r 4h 2. 2 r h is the half-thickness of the disc, α is the alpha-effect coefficient, η=lv/3 is the turbulent diffusivity coefficient.
7 Galaxies with active processes Usually averaged values of the coefficients are used. This approach is useful for calm galaxies, where the kinematical characteristics are nearly the same in different parts of galaxies. If there are active star formation, supernova explosions etc, the kinematical characteristics can differ very much.
8 Random coefficients The HII regions usually exist for quite small times (about 10 7 years). Their location can be described by random laws. Some works described the dynamo model with random alpha-effect (Mikhailov & Modyaev, 2015) and with random injections of the magnetic fields (Moss et al., 2015).
9 Diffusivity We describe the equations with random diffusivity coefficient. For calm regions v 0 =10 km/s, for HII regions v 1 =30 km/s. So for the diffusivity coefficient η=lv/3 we have: η 1 =3η 0
10 Dimensionless form We can rewrite the equations, measuring time in h 2 /η 0, and neglect the diffusion in disc plane: db dt r db dt R B kb R α characterizes alpha-effect, R ω characterizes differential rotation, k characterizes turbulent diffusion. R B r kb r ;.
11 k coefficient The k coefficient takes random values: k 7.5 with probability p; 2.5 with probability (1 p). The coefficient is constant for Δt=0.01 and after that renews. p characterizes the intensity of active processes.
12 Theoretical approximations The field grows exponentially with velocity: k R R. The main features are described by the highest value. If we take R α =1, R ω =10, the values of velocities for k 0 and k 1 will be: γ 0 =0.66, γ 1 =-4.33
13 Magnetic field for large time The magnetic field will be: B(nΔt)=B(0)exp(γ(0)Δt) exp(γ((n-1)δt)δt) m p p n m nm With probability 1 the field is: B(nΔt)=B(0)exp(mγ 1 Δt)exp((n-m)γ 0 Δt) Using these values, we can average the field and its square.
14 Different momentums Mean value: <B(nΔt)>=B(0)exp(γ 0 nδt)(1-p+pexp((γ 1 -γ 0 )Δt)) n Mean-square field: <B 2 (nδt )>1/2= B(0)exp(γ 0 nδt)(1-p+pexp(2(γ 1 -γ 0 )Δt)) n/2
15 Estimeates for velocities of different momentums Typical realization: Mean field: Mean-square field: λ 0 =0.66-5p λ 1 =0.66-5p+12.5p(1-p)Δt λ 2 = p+25p(1-p)Δt Higher momentums grow faster than lower ones intermittency effect.
16 Critical value (theoretical estimates) Assuming λ 0 =0, we will obtain p cr =0.13. λ 0 >0 if p>0.13 (the field grows). λ 0 <0 if p>0.13 (the field decays).
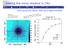
17 Numerical results (p=0.1)
18 Various probabilities
19 Growth rates Numerical values Theoretical estimates p λ 0 λ 1 λ 2 λ 0 λ 1 λ
20 Critical value (numerical) If p<0.16, the field grows. If p>0.16, it decays. The critical value (p cr =0.16) is higher than for rough estimates.
21 Star formation and our model The probability p can be associated with the fraction κ of the HII regions in the galaxy. For rough approximation κ p. If we study the star formation, it can be shown (e.g. Mikhailov, 2014), that κ 12Σ SFR (star formation density measured in M /yr kpc 2 )
22 Growth rates in dimensional form Numerical values Theoretical estimates Σ SFR, M /yr kpc 2 λ 0, Gyr -1 λ 1, Gyr -1 λ 2, Gyr -1 λ 0, Gyr -1 λ 1, Gyr -1 λ 2, Gyr
23 Critical value for star formation For star formation we can obtain Σ cr 0.013M /yr kpc 2. If Σ SFR >Σ cr, the field decays. This value is few times more than in the Milky Way.
24 Summary The dynamo model with random diffusivity coefficients has been studied. It can be useful to describe the influence of active processes on the magnetic field. According to this approach, intensive active processes make the field decay. As for the star formation rate, the field decays if Σ SFR >Σ cr 0.013M /yr kpc 2. It is quite similar to the results obtained in deterministic dynamo model with star formation (Mikhailov et al., 2012; Mikhailov, 2014). It is interesting to study a model where both alpha-effect coefficient and the diffusion coefficient are random. It can make our results more precise.
25 References Beck R., Brandenburg A., Moss D., Shukurov A., Sokoloff D. 1996, ARAA, 34, 155. Mikhailov E.A., Sokoloff D.D., Efremov Yu.N. 2012, Astron.Lett., 38, 543. Mikhailov E.A. 2014, Astron. Lett., 40, 398. Mikhailov E.A., Modyaev I.I. 2015, Magnetohydrodynamics, 51,2, 285. Moss D. 1995, MNRAS, 275, 1, 191 Moss D., Stepanov R., Krause M., Beck R., Sokoloff D. 2015, AA, 578, A94. Phillips A. 2001, GAFD, 94, 135.
26 THANK YOU FOR ATTENTION!
University, Bld. 1, GSP-2, Leninskie Gory, Moscow, Russia;
 Baltic Astronomy, vol. 24, 194 200, 2015 STAR FORMATION AND GALAXY DYNAMO EQUATIONS WITH RANDOM COEFFICIENTS E. A. Mikhailov 1 and I. I. Modyaev 2 1 Faculty of Physics, M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University,
Baltic Astronomy, vol. 24, 194 200, 2015 STAR FORMATION AND GALAXY DYNAMO EQUATIONS WITH RANDOM COEFFICIENTS E. A. Mikhailov 1 and I. I. Modyaev 2 1 Faculty of Physics, M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University,
Magnetic Field in Galaxies and clusters
 Magnetic Field in Galaxies and clusters Kandaswamy Subramanian Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.0/27 Plan Observing
Magnetic Field in Galaxies and clusters Kandaswamy Subramanian Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.0/27 Plan Observing
Magnetic waves in a two-component model of galactic dynamo: metastability and stochastic generation
 Center for Turbulence Research Annual Research Briefs 006 363 Magnetic waves in a two-component model of galactic dynamo: metastability and stochastic generation By S. Fedotov AND S. Abarzhi 1. Motivation
Center for Turbulence Research Annual Research Briefs 006 363 Magnetic waves in a two-component model of galactic dynamo: metastability and stochastic generation By S. Fedotov AND S. Abarzhi 1. Motivation
A New Mechanism of Nonlinearity in the Disc Dynamo
 A New Mechanism of Nonlinearity in the Disc Dynamo W. Dobler Astrophysics Institute, Göttingen University, Germany A.D. Poezd Physics Department, Moscow University, Moscow 119899, Russia and A. Shukurov
A New Mechanism of Nonlinearity in the Disc Dynamo W. Dobler Astrophysics Institute, Göttingen University, Germany A.D. Poezd Physics Department, Moscow University, Moscow 119899, Russia and A. Shukurov
Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies
 Lecture 4: Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies Rainer Beck, MPIfR Bonn Generation and amplification of cosmic magnetic fields Stage 1: Field seeding Stage 2: Field amplification Stage 3: Coherent field
Lecture 4: Origin of Magnetic Fields in Galaxies Rainer Beck, MPIfR Bonn Generation and amplification of cosmic magnetic fields Stage 1: Field seeding Stage 2: Field amplification Stage 3: Coherent field
Nonlinear galactic dynamo models with magnetic-supported interstellar gas-density stratification
 Astron. Astrophys. 319, 781 787 1997) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Nonlinear galactic dynamo models magnetic-supported interstellar gas-density stratification G. Rüdiger and M. Schultz Astrophysikalisches
Astron. Astrophys. 319, 781 787 1997) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Nonlinear galactic dynamo models magnetic-supported interstellar gas-density stratification G. Rüdiger and M. Schultz Astrophysikalisches
COSMIC-RAY DRIVEN MAGNETIC FIELD DYNAMO IN GALAXIES
 COSMIC-RAY DRIVEN MAGNETIC FIELD DYNAMO IN GALAXIES Michał Hanasz, Centre for Astronomy Nicolaus Copernicus University, Toruń MAGNETIC FIELDS IN SPIRAL GALAXIES - RADIO OBSERVATIONS M51 NGC891 A. Fletcher
COSMIC-RAY DRIVEN MAGNETIC FIELD DYNAMO IN GALAXIES Michał Hanasz, Centre for Astronomy Nicolaus Copernicus University, Toruń MAGNETIC FIELDS IN SPIRAL GALAXIES - RADIO OBSERVATIONS M51 NGC891 A. Fletcher
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 12 Jun 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 12 Jun 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 12 Jun 2008](/thumbs/93/112965100.jpg) To appear in Magnetic Fields in the Universe II (2008) RevMexAA(SC) MAGNETIC FIELDS AND STAR FORMATION IN SPIRAL GALAXIES Marita Krause, 1 RESUMEN arxiv:0806.2060v1 [astro-ph] 12 Jun 2008 ABSTRACT The
To appear in Magnetic Fields in the Universe II (2008) RevMexAA(SC) MAGNETIC FIELDS AND STAR FORMATION IN SPIRAL GALAXIES Marita Krause, 1 RESUMEN arxiv:0806.2060v1 [astro-ph] 12 Jun 2008 ABSTRACT The
The Magnetic Field of the Large Magellanic Cloud Revealed Through Faraday Rotation
 The Magnetic Field of the Large Magellanic Cloud Revealed Through Faraday Rotation arxiv:astro-ph/0503226v1 9 Mar 2005 B. M. Gaensler, 1,2, M. Haverkorn, 1 L. Staveley-Smith, 3 J. M. Dickey, 4 N. M. McClure-Griffiths,
The Magnetic Field of the Large Magellanic Cloud Revealed Through Faraday Rotation arxiv:astro-ph/0503226v1 9 Mar 2005 B. M. Gaensler, 1,2, M. Haverkorn, 1 L. Staveley-Smith, 3 J. M. Dickey, 4 N. M. McClure-Griffiths,
Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA
 Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn & SKA Science Working Group Fundamental magnetic questions When and how were the first fields generated?
Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn & SKA Science Working Group Fundamental magnetic questions When and how were the first fields generated?
Dynamic simulations of the Galactic Dynamo based on supernova-driven ISM turbulence
 Dynamic simulations of the Galactic Dynamo based on supernova-driven ISM turbulence Oliver Gressel, Axel Brandenburg Astrophysics group, NORDITA, Stockholm Abhijit Bendre, Detlef Elstner, Udo Ziegler &
Dynamic simulations of the Galactic Dynamo based on supernova-driven ISM turbulence Oliver Gressel, Axel Brandenburg Astrophysics group, NORDITA, Stockholm Abhijit Bendre, Detlef Elstner, Udo Ziegler &
DYNAMO THEORY: THE PROBLEM OF THE GEODYNAMO PRESENTED BY: RAMANDEEP GILL
 DYNAMO THEORY: THE PROBLEM OF THE GEODYNAMO PRESENTED BY: RAMANDEEP GILL MAGNETIC FIELD OF THE EARTH DIPOLE Field Structure Permanent magnetization of Core? 80% of field is dipole 20 % is non dipole 2)
DYNAMO THEORY: THE PROBLEM OF THE GEODYNAMO PRESENTED BY: RAMANDEEP GILL MAGNETIC FIELD OF THE EARTH DIPOLE Field Structure Permanent magnetization of Core? 80% of field is dipole 20 % is non dipole 2)
Radio Continuum: Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields. Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn
 Radio Continuum: Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn Synchrotron emission Beam angle: Ψ/2=1/γ=E o /E Radio continuum tools to study GeV Cosmic ray electrons (CRE) Synchrotron spectrum:
Radio Continuum: Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn Synchrotron emission Beam angle: Ψ/2=1/γ=E o /E Radio continuum tools to study GeV Cosmic ray electrons (CRE) Synchrotron spectrum:
The coexistence of odd and even parity magnetic fields in disc galaxies
 June 4, 28 The coexistence of odd and even parity magnetic fields in disc galaxies D. Moss and D. Sokoloff 2 School of Mathematics, University of Manchester, Oxford Road, Manchester, M3 9PL, UK 2 Department
June 4, 28 The coexistence of odd and even parity magnetic fields in disc galaxies D. Moss and D. Sokoloff 2 School of Mathematics, University of Manchester, Oxford Road, Manchester, M3 9PL, UK 2 Department
Fluctuation dynamo amplified by intermittent shear bursts
 by intermittent Thanks to my collaborators: A. Busse (U. Glasgow), W.-C. Müller (TU Berlin) Dynamics Days Europe 8-12 September 2014 Mini-symposium on Nonlinear Problems in Plasma Astrophysics Introduction
by intermittent Thanks to my collaborators: A. Busse (U. Glasgow), W.-C. Müller (TU Berlin) Dynamics Days Europe 8-12 September 2014 Mini-symposium on Nonlinear Problems in Plasma Astrophysics Introduction
Circulation-dominated solar shell dynamo models with positive alpha-effect
 A&A 374, 301 308 (2001) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20010686 c ESO 2001 Astronomy & Astrophysics Circulation-dominated solar shell dynamo models with positive alpha-effect M. Küker,G.Rüdiger, and M. Schultz
A&A 374, 301 308 (2001) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20010686 c ESO 2001 Astronomy & Astrophysics Circulation-dominated solar shell dynamo models with positive alpha-effect M. Küker,G.Rüdiger, and M. Schultz
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 12 Nov 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 12 Nov 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 12 Nov 2014](/thumbs/80/81946401.jpg) A Vector Potential implementation for Smoothed Particle Magnetohydrodynamics Federico A. Stasyszyn, Detlef Elstner Leibniz-Institut für Astrophysik Potsdam (AIP), An der Sternwarte 16, 14482, Postdam,
A Vector Potential implementation for Smoothed Particle Magnetohydrodynamics Federico A. Stasyszyn, Detlef Elstner Leibniz-Institut für Astrophysik Potsdam (AIP), An der Sternwarte 16, 14482, Postdam,
THE DYNAMO EFFECT IN STARS
 THE DYNAMO EFFECT IN STARS Axel Brandenburg NORDITA, Blegdamsvej 17, DK-2100 Copenhagen 0, Denmark; and Department of Mathematics, University of Newcastle upon Tyne, NEl 7RU, UK brandenb@nordita.dk Abstract
THE DYNAMO EFFECT IN STARS Axel Brandenburg NORDITA, Blegdamsvej 17, DK-2100 Copenhagen 0, Denmark; and Department of Mathematics, University of Newcastle upon Tyne, NEl 7RU, UK brandenb@nordita.dk Abstract
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 13 Jul 2012
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 13 Jul 2012 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 13 Jul 2012](/thumbs/74/70127793.jpg) Magnetic field transport from disk to halo via the galactic chimney process in NGC 6946 George H. Heald 1 ASTRON, Postbus 2, 7990 AA Dwingeloo, The Netherlands arxiv:1206.6569v2 [astro-ph.co] 13 Jul 2012
Magnetic field transport from disk to halo via the galactic chimney process in NGC 6946 George H. Heald 1 ASTRON, Postbus 2, 7990 AA Dwingeloo, The Netherlands arxiv:1206.6569v2 [astro-ph.co] 13 Jul 2012
Large-scale field and small scale dynamo
 Large-scale field and small scale dynamo Franck Plunian & Yannick Ponty Université de Grenoble, LGIT Observatoire de la Côte d'azur Large scale magnetic fields are ubiquitous in planetary and stellar objects
Large-scale field and small scale dynamo Franck Plunian & Yannick Ponty Université de Grenoble, LGIT Observatoire de la Côte d'azur Large scale magnetic fields are ubiquitous in planetary and stellar objects
MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE UNIVERSE
 ARTICLE MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE UNIVERSE KANDASWAMY SUBRAMANIAN* The origin and maintenance of large scale magnetic fields in the Universe is discussed. A popular idea is that cosmic batteries generate
ARTICLE MAGNETIC FIELDS IN THE UNIVERSE KANDASWAMY SUBRAMANIAN* The origin and maintenance of large scale magnetic fields in the Universe is discussed. A popular idea is that cosmic batteries generate
Dynamos on galactic scales, or Dynamos around us.
 Dynamos on galactic scales, or Dynamos around us. Part IV. Cluster dynamos Anvar Shukurov School of Mathematics and Statistics, Newcastle University, U.K. Outline 1. Evidence for intracluster magnetic
Dynamos on galactic scales, or Dynamos around us. Part IV. Cluster dynamos Anvar Shukurov School of Mathematics and Statistics, Newcastle University, U.K. Outline 1. Evidence for intracluster magnetic
Spiral Structure. m ( Ω Ω gp ) = n κ. Closed orbits in non-inertial frames can explain the spiral pattern
 Spiral Structure In the mid-1960s Lin and Shu proposed that the spiral structure is caused by long-lived quasistatic density waves The density would be higher by about 10% to 20% Stars, dust and gas clouds
Spiral Structure In the mid-1960s Lin and Shu proposed that the spiral structure is caused by long-lived quasistatic density waves The density would be higher by about 10% to 20% Stars, dust and gas clouds
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 13 Mar 2000
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, L1 L6 (0000) Printed 15 April 2008 (MN LATEX style file v1.4) Pressure-driven outflow from a dynamo active disc A. Brandenburg, W. Dobler, A. Shukurov and B. von Rekowski
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, L1 L6 (0000) Printed 15 April 2008 (MN LATEX style file v1.4) Pressure-driven outflow from a dynamo active disc A. Brandenburg, W. Dobler, A. Shukurov and B. von Rekowski
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 24 Oct 2011
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 24 Oct 2011 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 24 Oct 2011](/thumbs/75/72583506.jpg) Astrophysics and Space Science DOI 10.1007/s - - - The role of Hall diffusion in the magnetically threaded thin accretion discs Mohsen Shadmehri 1 arxiv:1110.5142v1 [astro-ph.sr] 24 Oct 2011 c Springer-Verlag
Astrophysics and Space Science DOI 10.1007/s - - - The role of Hall diffusion in the magnetically threaded thin accretion discs Mohsen Shadmehri 1 arxiv:1110.5142v1 [astro-ph.sr] 24 Oct 2011 c Springer-Verlag
Dynamo theory and its experimental validation
 Dynamo theory and its experimental validation Karl-Heinz Rädler Astrophysical Institute Potsdam Stockholm February 2009 Outline The idea of the self-exciting dynamo and elements of dynamo theory The Riga
Dynamo theory and its experimental validation Karl-Heinz Rädler Astrophysical Institute Potsdam Stockholm February 2009 Outline The idea of the self-exciting dynamo and elements of dynamo theory The Riga
Numerical simulation of the Gailitis dynamo David Moss 1 School of Mathematics University of Manchester Oxford Rd Manchester M13 9PL UK
 Abstract Numerical simulation of the Gailitis dynamo David Moss 1 School of Mathematics University of Manchester Oxford Rd Manchester M13 9PL UK The linear magnetohydrodynamic equations are solved with
Abstract Numerical simulation of the Gailitis dynamo David Moss 1 School of Mathematics University of Manchester Oxford Rd Manchester M13 9PL UK The linear magnetohydrodynamic equations are solved with
A wide-field view of the Phoenix transition type dwarf galaxy (Battaglia et al., MNRAS accepted, airxv/ )
 A wide-field view of the Phoenix transition type dwarf galaxy (Battaglia et al., MNRAS accepted, airxv/1205.2704) Giuseppina Battaglia INAF Astronomical Observatory of Bologna With thanks to M.Rejkuba,
A wide-field view of the Phoenix transition type dwarf galaxy (Battaglia et al., MNRAS accepted, airxv/1205.2704) Giuseppina Battaglia INAF Astronomical Observatory of Bologna With thanks to M.Rejkuba,
arxiv:physics/ v1 8 Sep 2005
 On the inverse cascade of magnetic helicity Alexandros Alexakis, Pablo Mininni, and Annick Pouquet National Center for Atmospheric Research (Dated: September 12, 2005) arxiv:physics/0509069 v1 8 Sep 2005
On the inverse cascade of magnetic helicity Alexandros Alexakis, Pablo Mininni, and Annick Pouquet National Center for Atmospheric Research (Dated: September 12, 2005) arxiv:physics/0509069 v1 8 Sep 2005
Simulating magnetic fields in structure formation
 Simulating magnetic fields in structure formation USM / MPE / MPA Harald Lesch & Klaus Dolag Annette Geng, Federico Stasyszyn & Marcus Beck July, 2012 (Mainz) Alexander Beck Magnetic fields in galaxies
Simulating magnetic fields in structure formation USM / MPE / MPA Harald Lesch & Klaus Dolag Annette Geng, Federico Stasyszyn & Marcus Beck July, 2012 (Mainz) Alexander Beck Magnetic fields in galaxies
Prediction of solar activity cycles by assimilating sunspot data into a dynamo model
 Solar and Stellar Variability: Impact on Earth and Planets Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 264, 2009 A. G. Kosovichev, A. H. Andrei & J.-P. Rozelot, eds. c International Astronomical Union 2010 doi:10.1017/s1743921309992638
Solar and Stellar Variability: Impact on Earth and Planets Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 264, 2009 A. G. Kosovichev, A. H. Andrei & J.-P. Rozelot, eds. c International Astronomical Union 2010 doi:10.1017/s1743921309992638
Chapter 7. Basic Turbulence
 Chapter 7 Basic Turbulence The universe is a highly turbulent place, and we must understand turbulence if we want to understand a lot of what s going on. Interstellar turbulence causes the twinkling of
Chapter 7 Basic Turbulence The universe is a highly turbulent place, and we must understand turbulence if we want to understand a lot of what s going on. Interstellar turbulence causes the twinkling of
Magnetic fields and radio polarization of barred galaxies
 A&A 384, 48 55 (2002) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20020027 c ESO 2002 Astronomy & Astrophysics Magnetic fields and radio polarization of barred galaxies 3D dynamo simulations K. Otmianowska-Mazur 1,D.Elstner
A&A 384, 48 55 (2002) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20020027 c ESO 2002 Astronomy & Astrophysics Magnetic fields and radio polarization of barred galaxies 3D dynamo simulations K. Otmianowska-Mazur 1,D.Elstner
Primordial Origin of Magnetic Fields in Spiral Galaxies
 PASJ: Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan, 1??, c 2009. Astronomical Society of Japan. Primordial Origin of Magnetic Fields in Spiral Galaxies Yoshiaki Sofue 1,2, Mami Machida 3,4, and Takahiro Kudoh 3 1. Department
PASJ: Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan, 1??, c 2009. Astronomical Society of Japan. Primordial Origin of Magnetic Fields in Spiral Galaxies Yoshiaki Sofue 1,2, Mami Machida 3,4, and Takahiro Kudoh 3 1. Department
Small-scale magnetic helicity losses from a mean-field dynamo
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 398, 1414 1422 (2009) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.15188.x Small-scale magnetic helicity losses from a mean-field dynamo Axel Brandenburg, 1,2 Simon Candelaresi 1,2 and Piyali
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 398, 1414 1422 (2009) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.15188.x Small-scale magnetic helicity losses from a mean-field dynamo Axel Brandenburg, 1,2 Simon Candelaresi 1,2 and Piyali
Short-lived 244 Pu points to compact binary mergers as sites for heavy r-process nucleosynthesis
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NPHYS3574 Short-lived 244 Pu points to compact binary mergers as sites for heavy r-process nucleosynthesis 1 Interpretation of the deep sea measurement Wallner et
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NPHYS3574 Short-lived 244 Pu points to compact binary mergers as sites for heavy r-process nucleosynthesis 1 Interpretation of the deep sea measurement Wallner et
Anisotropic turbulence in rotating magnetoconvection
 Anisotropic turbulence in rotating magnetoconvection André Giesecke Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam An der Sternwarte 16 14482 Potsdam MHD-Group seminar, 2006 André Giesecke (AIP) Anisotropic turbulence
Anisotropic turbulence in rotating magnetoconvection André Giesecke Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam An der Sternwarte 16 14482 Potsdam MHD-Group seminar, 2006 André Giesecke (AIP) Anisotropic turbulence
Why does the magnetic field of the Earth reverse?
 IMPRS Solar System Seminar June 2002 Why does the magnetic field of the Earth reverse? Dieter Schmitt (Katlenburg-Lindau) 1. Geomagnetic field >99% of matter in universe is plasma: gas of electrons, ions
IMPRS Solar System Seminar June 2002 Why does the magnetic field of the Earth reverse? Dieter Schmitt (Katlenburg-Lindau) 1. Geomagnetic field >99% of matter in universe is plasma: gas of electrons, ions
Beyond Ideal MHD. Nick Murphy. Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics. February 8, 2016
 Beyond Ideal MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 8, 2016 These lecture notes are largely based on Plasma Physics for Astrophysics by
Beyond Ideal MHD Nick Murphy Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Astronomy 253: Plasma Astrophysics February 8, 2016 These lecture notes are largely based on Plasma Physics for Astrophysics by
Formation of Inhomogeneous Magnetic Structures in MHD Turbulence and Turbulent Convection
 Formation of Inhomogeneous Magnetic Structures in MHD Turbulence and Turbulent Convection Igor ROGACHEVSKII and Nathan KLEEORIN Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Beer-Sheva, Israel Axel BRANDENBURG and
Formation of Inhomogeneous Magnetic Structures in MHD Turbulence and Turbulent Convection Igor ROGACHEVSKII and Nathan KLEEORIN Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Beer-Sheva, Israel Axel BRANDENBURG and
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Sep 2010
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Sep 2010 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Sep 2010](/thumbs/88/115477948.jpg) Submitted to ApJ Faraday Rotation Measure due to the Intergalactic Magnetic Field arxiv:1009.0570v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Sep 2010 Takuya Akahori 1 and Dongsu Ryu 2,3 1 Research Institute of Basic Science, Chungnam
Submitted to ApJ Faraday Rotation Measure due to the Intergalactic Magnetic Field arxiv:1009.0570v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Sep 2010 Takuya Akahori 1 and Dongsu Ryu 2,3 1 Research Institute of Basic Science, Chungnam
SPACE- AND TIME-CORRELATIONS IN THE SUPERNOVA DRIVEN INTERSTELLAR MEDIUM
 DRAFT VERSION MARCH 5, 2017 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 05/12/14 SPACE- AND TIME-CORRELATIONS IN THE SUPERNOVA DRIVEN INTERSTELLAR MEDIUM J. F. HOLLINS, 1 G. R. SARSON, 1 A. SHUKUROV,
DRAFT VERSION MARCH 5, 2017 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 05/12/14 SPACE- AND TIME-CORRELATIONS IN THE SUPERNOVA DRIVEN INTERSTELLAR MEDIUM J. F. HOLLINS, 1 G. R. SARSON, 1 A. SHUKUROV,
Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs
 Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs Klaus Dolag ( ) Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik ( ) Introduction Evolution of the structures in the Universe t =
Simulating magnetic fields within large scale structure an the propagation of UHECRs Klaus Dolag ( ) Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik ( ) Introduction Evolution of the structures in the Universe t =
Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters
 Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) with Hyesung Kang (Pusan Nat. U, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (Chungnam Nat. U.),
Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) with Hyesung Kang (Pusan Nat. U, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (Chungnam Nat. U.),
The Primordial Origin Model of Magnetic Fields in Spiral Galaxies
 PASJ: Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 62, 1191 1201, 2010 October 25 c 2010. Astronomical Society of Japan. The Primordial Origin Model of Magnetic Fields in Spiral Galaxies Yoshiaki S OFUE, 1,2 Mami MACHIDA,
PASJ: Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 62, 1191 1201, 2010 October 25 c 2010. Astronomical Society of Japan. The Primordial Origin Model of Magnetic Fields in Spiral Galaxies Yoshiaki S OFUE, 1,2 Mami MACHIDA,
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 24 Apr 2008
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 24 Apr 2008 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 24 Apr 2008](/thumbs/90/103028861.jpg) Astrophysics and Space Science DOI 10.1007/sXXXXX-XXX-XXXX-X Galactic Dynamos and Galactic Winds Rainer Beck arxiv:0711.4700v2 [astro-ph] 24 Apr 2008 c Springer-Verlag Abstract Spiral galaxies host dynamically
Astrophysics and Space Science DOI 10.1007/sXXXXX-XXX-XXXX-X Galactic Dynamos and Galactic Winds Rainer Beck arxiv:0711.4700v2 [astro-ph] 24 Apr 2008 c Springer-Verlag Abstract Spiral galaxies host dynamically
Astronomy 330 Lecture 7 24 Sep 2010
 Astronomy 330 Lecture 7 24 Sep 2010 Outline Review Counts: A(m), Euclidean slope, Olbers paradox Stellar Luminosity Function: Φ(M,S) Structure of the Milky Way: disk, bulge, halo Milky Way kinematics Rotation
Astronomy 330 Lecture 7 24 Sep 2010 Outline Review Counts: A(m), Euclidean slope, Olbers paradox Stellar Luminosity Function: Φ(M,S) Structure of the Milky Way: disk, bulge, halo Milky Way kinematics Rotation
Large scale magnetic fields and Dynamo theory. Roman Shcherbakov, Turbulence Discussion Group 14 Apr 2008
 Large scale magnetic fields and Dynamo theory Roman Shcherbakov, Turbulence Discussion Group 14 Apr 2008 The Earth Mainly dipolar magnetic field Would decay in 20kyr if not regenerated Declination of the
Large scale magnetic fields and Dynamo theory Roman Shcherbakov, Turbulence Discussion Group 14 Apr 2008 The Earth Mainly dipolar magnetic field Would decay in 20kyr if not regenerated Declination of the
Week 8: Stellar winds So far, we have been discussing stars as though they have constant masses throughout their lifetimes. On the other hand, toward
 Week 8: Stellar winds So far, we have been discussing stars as though they have constant masses throughout their lifetimes. On the other hand, toward the end of the discussion of what happens for post-main
Week 8: Stellar winds So far, we have been discussing stars as though they have constant masses throughout their lifetimes. On the other hand, toward the end of the discussion of what happens for post-main
Small-Scale Dynamo and the Magnetic Prandtl Number
 MRI Turbulence Workshop, IAS, Princeton, 17.06.08 Small-Scale Dynamo and the Magnetic Prandtl Number Alexander Schekochihin (Imperial College) with Steve Cowley (Culham & Imperial) Greg Hammett (Princeton)
MRI Turbulence Workshop, IAS, Princeton, 17.06.08 Small-Scale Dynamo and the Magnetic Prandtl Number Alexander Schekochihin (Imperial College) with Steve Cowley (Culham & Imperial) Greg Hammett (Princeton)
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Magnetic field generation in weak-line T Tauri stars: an α 2 -dynamo
 Astron. Astrophys. 346, 922 928 (1999) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Magnetic field generation in weak-line T Tauri stars: an α 2 -dynamo M. Küker and G. Rüdiger Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam, An der
Astron. Astrophys. 346, 922 928 (1999) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Magnetic field generation in weak-line T Tauri stars: an α 2 -dynamo M. Küker and G. Rüdiger Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam, An der
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 27 Dec 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 27 Dec 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 27 Dec 2018](/thumbs/92/110910405.jpg) MAGNETOHYDRODYNAMICS Vol. 0 (2019), No. 0, pp. 1 8 arxiv:1812.10634v1 [astro-ph.sr] 27 Dec 2018 Influence of Ohmic and ambipolar heating on thermal structure of accretion discs S.A. Khaibrakhmanov 1,2,
MAGNETOHYDRODYNAMICS Vol. 0 (2019), No. 0, pp. 1 8 arxiv:1812.10634v1 [astro-ph.sr] 27 Dec 2018 Influence of Ohmic and ambipolar heating on thermal structure of accretion discs S.A. Khaibrakhmanov 1,2,
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 6 Aug 2015
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 6 Aug 2015 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 6 Aug 2015](/thumbs/82/86411124.jpg) Generation of large-scale magnetic fields by small-scale dynamo in shear flows J. Squire and A. Bhattacharjee Max Planck/Princeton Center for Plasma Physics, Department of Astrophysical Sciences and Princeton
Generation of large-scale magnetic fields by small-scale dynamo in shear flows J. Squire and A. Bhattacharjee Max Planck/Princeton Center for Plasma Physics, Department of Astrophysical Sciences and Princeton
Creation and destruction of magnetic fields
 HAO/NCAR July 30 2007 Magnetic fields in the Universe Earth Magnetic field present for 3.5 10 9 years, much longer than Ohmic decay time ( 10 4 years) Strong variability on shorter time scales (10 3 years)
HAO/NCAR July 30 2007 Magnetic fields in the Universe Earth Magnetic field present for 3.5 10 9 years, much longer than Ohmic decay time ( 10 4 years) Strong variability on shorter time scales (10 3 years)
Accretion disc dynamos
 Accretion disc dynamos (i) Relative field orientation (ii) Ambient field vs dynamo (iii) Spin-up vs spin-down B. von Rekowski, A. Brandenburg, 2004, A&A 420, 17-32. von Rekowski, A. Brandenburg, W. Dobler,
Accretion disc dynamos (i) Relative field orientation (ii) Ambient field vs dynamo (iii) Spin-up vs spin-down B. von Rekowski, A. Brandenburg, 2004, A&A 420, 17-32. von Rekowski, A. Brandenburg, W. Dobler,
Simulation of the Accretion of Matter onto a White Dwarf Star
 Simulation of the Accretion of Matter onto a White Dwarf Star Evan Figg 2010 NSF/REU Program Physics Department, University of Notre Dame Advisor: Dr. Dinshaw Balsara Abstract White dwarf stars in binary
Simulation of the Accretion of Matter onto a White Dwarf Star Evan Figg 2010 NSF/REU Program Physics Department, University of Notre Dame Advisor: Dr. Dinshaw Balsara Abstract White dwarf stars in binary
Evolving Magnetic Fields and the Conservation of Magnetic Moment
 Evolving Magnetic Fields and the Conservation of Magnetic Moment Wolfgang Dobler Max-Planck-Institut für Aeronomie, Max-Planck-Straße 2, 37191 Katlenburg/Lindau, Germany (dobler@uni-sw.gwdg.de) 3 November
Evolving Magnetic Fields and the Conservation of Magnetic Moment Wolfgang Dobler Max-Planck-Institut für Aeronomie, Max-Planck-Straße 2, 37191 Katlenburg/Lindau, Germany (dobler@uni-sw.gwdg.de) 3 November
Using Pulsars to study the Magnetic Field in The Milky way
 Using Pulsars to study the Magnetic Field in The Milky way Dipanjan Mitra ( MPIFR Bonn) R. Wielebinski ( MPIFR Bonn) M. Kramer ( Jodrell Bank) A. Jessner ( MPIFR Bonn) MPIFR, Bonn (24 th April 2003) To
Using Pulsars to study the Magnetic Field in The Milky way Dipanjan Mitra ( MPIFR Bonn) R. Wielebinski ( MPIFR Bonn) M. Kramer ( Jodrell Bank) A. Jessner ( MPIFR Bonn) MPIFR, Bonn (24 th April 2003) To
Geometrically Thick Dust Layer in Edge-on Galaxies
 Geometrically Thick Dust Layer in Edge-on Galaxies A Case Study of NGC 891! Kwang-Il Seon 1, Adolf N. Witt 2, Jong-Ho Shinn 1, & Il-Joong Kim 1!! 1 Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute! 2 University
Geometrically Thick Dust Layer in Edge-on Galaxies A Case Study of NGC 891! Kwang-Il Seon 1, Adolf N. Witt 2, Jong-Ho Shinn 1, & Il-Joong Kim 1!! 1 Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute! 2 University
Testing the magnetic field models of disk galaxies with the SKA
 Testing the magnetic field models of disk galaxies with the SKA, a R. Stepanov b, R. Beck a, P. Frick b and M. Krause a a Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie, Auf dem Hügel 69, 3121 Bonn, Germany b
Testing the magnetic field models of disk galaxies with the SKA, a R. Stepanov b, R. Beck a, P. Frick b and M. Krause a a Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie, Auf dem Hügel 69, 3121 Bonn, Germany b
Distance Measurement of Spiral Arms in the Galactic-Center Direction Using Radial-Velocity Gradients
 PASJ: Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 58, 335 341, 2006 April 25 c 2006. Astronomical Society of Japan. Distance Measurement of Spiral Arms in the Galactic-Center Direction Using Radial-Velocity Gradients Yoshiaki
PASJ: Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 58, 335 341, 2006 April 25 c 2006. Astronomical Society of Japan. Distance Measurement of Spiral Arms in the Galactic-Center Direction Using Radial-Velocity Gradients Yoshiaki
Seeing the moon shadow in CRs
 Seeing the moon shadow in CRs and using the Earth field as a spectrometer Tibet III Amenomori et al. arxiv:0810.3757 see also ARGO-YBJ results Bartoli et. al, arxiv:1107.4887 Milargo: 100% coverage r owe
Seeing the moon shadow in CRs and using the Earth field as a spectrometer Tibet III Amenomori et al. arxiv:0810.3757 see also ARGO-YBJ results Bartoli et. al, arxiv:1107.4887 Milargo: 100% coverage r owe
The Madison Dynamo Experiment: magnetic instabilities driven by sheared flow in a sphere. Cary Forest Department of Physics University of Wisconsin
 The Madison Dynamo Experiment: magnetic instabilities driven by sheared flow in a sphere Cary Forest Department of Physics University of Wisconsin February 28, 2001 Planets, stars and perhaps the galaxy
The Madison Dynamo Experiment: magnetic instabilities driven by sheared flow in a sphere Cary Forest Department of Physics University of Wisconsin February 28, 2001 Planets, stars and perhaps the galaxy
Magnetic field escape from a stellar convection zone and the dynamo-cycle period
 Astron. Astrophys. 359, 531 538 2000 Magnetic field escape from a stellar convection zone and the dynamo-cycle period ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS L.L. Kitchatinov 1,2, M.V. Mazur 2, and M. Jardine 1 1 School
Astron. Astrophys. 359, 531 538 2000 Magnetic field escape from a stellar convection zone and the dynamo-cycle period ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS L.L. Kitchatinov 1,2, M.V. Mazur 2, and M. Jardine 1 1 School
On Cosmic-Ray Production Efficiency at Realistic Supernova Remnant Shocks
 On Cosmic-Ray Production Efficiency at Realistic Supernova Remnant Shocks, 1 T. Inoue 2, Y. Ohira 1, R. Yamazaki 1, A. Bamba 1 and J. Vink 3 1 Department of Physics and Mathematics, Aoyama-Gakuin University,
On Cosmic-Ray Production Efficiency at Realistic Supernova Remnant Shocks, 1 T. Inoue 2, Y. Ohira 1, R. Yamazaki 1, A. Bamba 1 and J. Vink 3 1 Department of Physics and Mathematics, Aoyama-Gakuin University,
Understanding Helical Magnetic Dynamo Spectra with a Nonlinear Four-Scale Theory
 Understanding Helical Magnetic Dynamo Spectra with a Nonlinear Four-Scale Theory Eric G. Blackman Department of Physics &Astronomy and Laboratory for Laser Energetics, University of Rochester, Rochester
Understanding Helical Magnetic Dynamo Spectra with a Nonlinear Four-Scale Theory Eric G. Blackman Department of Physics &Astronomy and Laboratory for Laser Energetics, University of Rochester, Rochester
Marita Krause. Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie, Bonn
 Galactic winds, magnetic fields,, and dynamo action in spiral galaxies Marita Krause Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie, Bonn based on total and polarized radio emission of spiral galaxies of different
Galactic winds, magnetic fields,, and dynamo action in spiral galaxies Marita Krause Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie, Bonn based on total and polarized radio emission of spiral galaxies of different
Global three-dimensional simulations of magnetic field evolution in a galactic disk
 Astron. Astrophys. 323, 56 70 (1997) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Global three-dimensional simulations of magnetic field evolution in a galactic disk I. Barred galaxies K. Otmianowska-Mazur 1,4, S. von Linden
Astron. Astrophys. 323, 56 70 (1997) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Global three-dimensional simulations of magnetic field evolution in a galactic disk I. Barred galaxies K. Otmianowska-Mazur 1,4, S. von Linden
where G is Newton s gravitational constant, M is the mass internal to radius r, and Ω 0 is the
 Homework Exercise Solar Convection and the Solar Dynamo Mark Miesch (HAO/NCAR) NASA Heliophysics Summer School Boulder, Colorado, July 27 - August 3, 2011 PROBLEM 1: THERMAL WIND BALANCE We begin with
Homework Exercise Solar Convection and the Solar Dynamo Mark Miesch (HAO/NCAR) NASA Heliophysics Summer School Boulder, Colorado, July 27 - August 3, 2011 PROBLEM 1: THERMAL WIND BALANCE We begin with
Predicting a solar cycle before its onset using a flux transport dynamo model
 *** TITLE *** Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 335, 2017 ***NAME OF EDITORS*** c 2017 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X Predicting a solar cycle before its onset using a flux
*** TITLE *** Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 335, 2017 ***NAME OF EDITORS*** c 2017 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X Predicting a solar cycle before its onset using a flux
Cosmic-ray Acceleration and Current-Driven Instabilities
 Cosmic-ray Acceleration and Current-Driven Instabilities B. Reville Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg Sep 17 2009, KITP J.G. Kirk, P. Duffy, S.O Sullivan, Y. Ohira, F. Takahara Outline Analysis
Cosmic-ray Acceleration and Current-Driven Instabilities B. Reville Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg Sep 17 2009, KITP J.G. Kirk, P. Duffy, S.O Sullivan, Y. Ohira, F. Takahara Outline Analysis
Lecture 8. Observational Cosmology. Parameters of Our Universe. The Concordance Model
 Lecture 8 Observational Cosmology Parameters of Our Universe The Concordance Model Time and Distance vs Redshift d dt x =1+ z = R 0 R dt = dx x H(x) Friedmann : H(x) = x 3 + Ω Λ + (1 Ω 0 ) x 2 look - back
Lecture 8 Observational Cosmology Parameters of Our Universe The Concordance Model Time and Distance vs Redshift d dt x =1+ z = R 0 R dt = dx x H(x) Friedmann : H(x) = x 3 + Ω Λ + (1 Ω 0 ) x 2 look - back
Lecture 13 Interstellar Magnetic Fields
 Lecture 13 Interstellar Magnetic Fields 1. Introduction. Synchrotron radiation 3. Faraday rotation 4. Zeeman effect 5. Polarization of starlight 6. Summary of results References Zweibel & Heiles, Nature
Lecture 13 Interstellar Magnetic Fields 1. Introduction. Synchrotron radiation 3. Faraday rotation 4. Zeeman effect 5. Polarization of starlight 6. Summary of results References Zweibel & Heiles, Nature
Astronomy 330 Lecture Nov 2010
 Astronomy 330 Lecture 19 12 Nov 2010 Outline Ellipticals: Formation Quenching of star-formation Mergers and heating Stellar populations Fuel consumption theorem Dominant phases with time M3 Direct approach
Astronomy 330 Lecture 19 12 Nov 2010 Outline Ellipticals: Formation Quenching of star-formation Mergers and heating Stellar populations Fuel consumption theorem Dominant phases with time M3 Direct approach
Superbubble Feedback in Galaxy Formation
 Superbubble Feedback in Galaxy Formation Ben Keller (McMaster University) James Wadsley, Samantha Benincasa, Hugh Couchman Paper: astro-ph/1405.2625 (Accepted MNRAS) Keller, Wadsley, Benincasa & Couchman
Superbubble Feedback in Galaxy Formation Ben Keller (McMaster University) James Wadsley, Samantha Benincasa, Hugh Couchman Paper: astro-ph/1405.2625 (Accepted MNRAS) Keller, Wadsley, Benincasa & Couchman
EXCESS OF VHE COSMIC RAYS IN THE CENTRAL 100 PC OF THE MILKY WAY. Léa Jouvin, A. Lemière and R. Terrier
 1 EXCESS OF VHE COSMIC RAYS IN THE CENTRAL 100 PC OF THE MILKY WAY Léa Jouvin, A. Lemière and R. Terrier 2 Excess of VHE cosmic rays (CRs) γ-ray count map Matter traced by CS 150 pc After subtracting the
1 EXCESS OF VHE COSMIC RAYS IN THE CENTRAL 100 PC OF THE MILKY WAY Léa Jouvin, A. Lemière and R. Terrier 2 Excess of VHE cosmic rays (CRs) γ-ray count map Matter traced by CS 150 pc After subtracting the
galaxies: individual: NGC 6946 galaxies: spiral galaxies:
 Baltic Astronomy, vol. 25, 369 376, 2016 UNUSUAL OBJECTS IN THE SPIRAL GALAXY NGC 6946 Yu. N. Efremov Sternberg Astronomical Institute, M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Universitetskij pr. 13,
Baltic Astronomy, vol. 25, 369 376, 2016 UNUSUAL OBJECTS IN THE SPIRAL GALAXY NGC 6946 Yu. N. Efremov Sternberg Astronomical Institute, M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Universitetskij pr. 13,
Inter University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Post Bag 4, Ganeshkhind, Pune , India.
 Inter University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Post Bag 4, Ganeshkhind, Pune-411007, India. E-mail: kandu@iucaa.ernet.in The origin of cosmic magnetism is an issue of fundamental importance in
Inter University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Post Bag 4, Ganeshkhind, Pune-411007, India. E-mail: kandu@iucaa.ernet.in The origin of cosmic magnetism is an issue of fundamental importance in
Creation and destruction of magnetic fields
 HAO/NCAR July 20 2011 Magnetic fields in the Universe Earth Magnetic field present for 3.5 10 9 years, much longer than Ohmic decay time ( 10 4 years) Strong variability on shorter time scales (10 3 years)
HAO/NCAR July 20 2011 Magnetic fields in the Universe Earth Magnetic field present for 3.5 10 9 years, much longer than Ohmic decay time ( 10 4 years) Strong variability on shorter time scales (10 3 years)
Cosmic Rays, Photons and Neutrinos
 Cosmic Rays, Photons and Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline Plan of the lectures: Cosmic rays Galactic cosmic rays Basic observations Acceleration Supernova remnants Problems
Cosmic Rays, Photons and Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline Plan of the lectures: Cosmic rays Galactic cosmic rays Basic observations Acceleration Supernova remnants Problems
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations. simulations of galaxy and structure formation
 Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 11 26 / Colloquium University of Victoria Outline 1 Cosmic
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 11 26 / Colloquium University of Victoria Outline 1 Cosmic
Systematic bias in interstellar magnetic field estimates
 A&A 411, 99 107 (2003) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20031101 c ESO 2003 Astronomy & Astrophysics Systematic bias in interstellar magnetic field estimates R. Beck 1, A. Shukurov 1,2, D. Sokoloff 3, and R. Wielebinski
A&A 411, 99 107 (2003) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20031101 c ESO 2003 Astronomy & Astrophysics Systematic bias in interstellar magnetic field estimates R. Beck 1, A. Shukurov 1,2, D. Sokoloff 3, and R. Wielebinski
Scale Length of the Galactic Thin Disk
 J. Astrophys. Astr. (2000) 21, 53-59 Scale Length of the Galactic Thin Disk D. Κ. Ojha, Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Dr. Homi Bhabha Road, Mumbai 400 005, India Received 1999 September 14; accepted
J. Astrophys. Astr. (2000) 21, 53-59 Scale Length of the Galactic Thin Disk D. Κ. Ojha, Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Dr. Homi Bhabha Road, Mumbai 400 005, India Received 1999 September 14; accepted
Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009
 Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009 Galactic Winds: Mathews, W. et al. 1971 Effects of Supernovae on the Early Evolution of Galaxies: Larson, R. 1974 The origin
Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009 Galactic Winds: Mathews, W. et al. 1971 Effects of Supernovae on the Early Evolution of Galaxies: Larson, R. 1974 The origin
PROPERTIES OF MAGNETIC HELICITY FLUX IN TURBULENT DYNAMOS
 The Astrophysical Journal, 780:144 (10pp), 014 January 10 C 014. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in the U.S.A. doi:10.1088/0004-637x/780//144 PROPERTIES OF MAGNETIC HELICITY
The Astrophysical Journal, 780:144 (10pp), 014 January 10 C 014. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in the U.S.A. doi:10.1088/0004-637x/780//144 PROPERTIES OF MAGNETIC HELICITY
Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields
 Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Ellen Zweibel zweibel@astro.wisc.edu Departments of Astronomy & Physics University of Wisconsin, Madison and Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical
Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Ellen Zweibel zweibel@astro.wisc.edu Departments of Astronomy & Physics University of Wisconsin, Madison and Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical
Disk Formation and the Angular Momentum Problem. Presented by: Michael Solway
 Disk Formation and the Angular Momentum Problem Presented by: Michael Solway Papers 1. Vitvitska, M. et al. 2002, The origin of angular momentum in dark matter halos, ApJ 581: 799-809 2. D Onghia, E. 2008,
Disk Formation and the Angular Momentum Problem Presented by: Michael Solway Papers 1. Vitvitska, M. et al. 2002, The origin of angular momentum in dark matter halos, ApJ 581: 799-809 2. D Onghia, E. 2008,
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 9 Mar 2006
 Astron. Nachr./AN xxx (xxxx) x, xxx xxx The distribution of current helicity at the solar surface at the beginning of the solar cycle arxiv:astro-ph/63242v1 9 Mar 6 D. SOKOLOFF 1,2, S.D. BAO 1, N. KLEEORIN
Astron. Nachr./AN xxx (xxxx) x, xxx xxx The distribution of current helicity at the solar surface at the beginning of the solar cycle arxiv:astro-ph/63242v1 9 Mar 6 D. SOKOLOFF 1,2, S.D. BAO 1, N. KLEEORIN
The Milky Way Part 2 Stellar kinematics. Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 7
 The Milky Way Part 2 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 7 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s look at the rotation of the Galactic disk First, we need to introduce the concept of the Local
The Milky Way Part 2 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 7 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s look at the rotation of the Galactic disk First, we need to introduce the concept of the Local
The Sun s Internal Magnetic Field
 The Sun s Internal Magnetic Field... and Rotation and Stratification Toby Wood & Michael McIntyre DAMTP, University of Cambridge Toby Wood & Michael McIntyre (DAMTP) The Sun s Internal Magnetic Field 1
The Sun s Internal Magnetic Field... and Rotation and Stratification Toby Wood & Michael McIntyre DAMTP, University of Cambridge Toby Wood & Michael McIntyre (DAMTP) The Sun s Internal Magnetic Field 1
Our Milky Way (MW) Galaxy L*, M* but not SFR*
 Our Milky Way (MW) Galaxy L*, M* but not SFR* (Our galaxy is revered as Galaxy and others are merely galaxy ;-).) (SFR is less than 5 solar mass per year) MW Structure Diagram Midplane molecular layer
Our Milky Way (MW) Galaxy L*, M* but not SFR* (Our galaxy is revered as Galaxy and others are merely galaxy ;-).) (SFR is less than 5 solar mass per year) MW Structure Diagram Midplane molecular layer
Propagation of TeV PeV Cosmic Rays in the Galactic Magnetic Field
 Propagation of TeV PeV Cosmic Rays in the Galactic Magnetic Field Gwenael Giacinti Clarendon Laboratory, University of Oxford In collaboration with : GG & G.Sigl / Based on : Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 071101(2012)
Propagation of TeV PeV Cosmic Rays in the Galactic Magnetic Field Gwenael Giacinti Clarendon Laboratory, University of Oxford In collaboration with : GG & G.Sigl / Based on : Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 071101(2012)
Meridional Flow, Differential Rotation, and the Solar Dynamo
 Meridional Flow, Differential Rotation, and the Solar Dynamo Manfred Küker 1 1 Leibniz Institut für Astrophysik Potsdam, An der Sternwarte 16, 14482 Potsdam, Germany Abstract. Mean field models of rotating
Meridional Flow, Differential Rotation, and the Solar Dynamo Manfred Küker 1 1 Leibniz Institut für Astrophysik Potsdam, An der Sternwarte 16, 14482 Potsdam, Germany Abstract. Mean field models of rotating
Turbulent Magnetic Helicity Transport and the Rapid Growth of Large Scale Magnetic Fields
 Turbulent Magnetic Helicity Transport and the Rapid Growth of Large Scale Magnetic Fields Jungyeon Cho Dmitry Shapovalov MWMF Madison, Wisconsin April 2012 The Large Scale Dynamo The accumulation of magnetic
Turbulent Magnetic Helicity Transport and the Rapid Growth of Large Scale Magnetic Fields Jungyeon Cho Dmitry Shapovalov MWMF Madison, Wisconsin April 2012 The Large Scale Dynamo The accumulation of magnetic
Modeling the magnetized accretion and outflows in young stellar objects
 Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 48, 40 47, (2018) Modeling the magnetized accretion and outflows in young stellar objects Ch. Fendt Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Heidelberg, Germany (E-mail:
Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 48, 40 47, (2018) Modeling the magnetized accretion and outflows in young stellar objects Ch. Fendt Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Heidelberg, Germany (E-mail:
GALAXIES 626. The Milky Way II. Chemical evolution:
 GALAXIES 626 The Milky Way II. Chemical evolution: Chemical evolution Observation of spiral and irregular galaxies show that the fraction of heavy elements varies with the fraction of the total mass which
GALAXIES 626 The Milky Way II. Chemical evolution: Chemical evolution Observation of spiral and irregular galaxies show that the fraction of heavy elements varies with the fraction of the total mass which
Chapter 4. Galactic Chemical Evolution. 4.1 Introduction. 4.2 Chemical Abundances
 Chapter 4 Galactic Chemical Evolution 4.1 Introduction Chemical evolution is the term used for the changes in the abundances of the chemical elements in the Universe over time, since the earliest times
Chapter 4 Galactic Chemical Evolution 4.1 Introduction Chemical evolution is the term used for the changes in the abundances of the chemical elements in the Universe over time, since the earliest times
Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Ṁ M gas / dyn. Log SFR. Kennicutt Log. gas / dyn
 Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Ṁ 0.017 M gas / dyn Log SFR Kennicutt 1998 Log gas / dyn Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Moster 2009 No Feedback 10% of baryons Log(
Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Ṁ 0.017 M gas / dyn Log SFR Kennicutt 1998 Log gas / dyn Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Moster 2009 No Feedback 10% of baryons Log(
THE GAS MASS AND STAR FORMATION RATE
 THE GAS MASS AND STAR FORMATION RATE OF STAR-FORMING GALAXIES AT z ~ 1.3 Nissim Kanekar National Centre for Radio Astrophysics, Pune Apurba Bera Shiv Sethi Ben Weiner K. Dwarakanath Image: B. Premkumar
THE GAS MASS AND STAR FORMATION RATE OF STAR-FORMING GALAXIES AT z ~ 1.3 Nissim Kanekar National Centre for Radio Astrophysics, Pune Apurba Bera Shiv Sethi Ben Weiner K. Dwarakanath Image: B. Premkumar
Production of helical magnetic fields during baryogenesis
 Production of helical magnetic fields during baryogenesis Francesc Ferrer Washington University in Saint Louis ferrer@wustl.edu NORDITA. June 23, 25 Outline Introduction: Observations of Magnetic Fields
Production of helical magnetic fields during baryogenesis Francesc Ferrer Washington University in Saint Louis ferrer@wustl.edu NORDITA. June 23, 25 Outline Introduction: Observations of Magnetic Fields
