Unifying Principle for Active Devices: Charge Control Principle
|
|
|
- Shanon Willis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ES 330 Electncs II Supplemental Tpc #1 (August 2015) Unfyng Pncple f Actve Devces: hage ntl Pncple Dnald Estech An actve devce s an electn devce, such as a tansst, capable f delveng pwe amplfcatn by cnvetng dc bas pwe nt tme vayng sgnal pwe. It delves a geate enegy t ts lad than f the devce wee absent. The chage cntl famewk [13] pesents a unfed undestandng f the peatn f all electn devces and smplfes the cmpasn f the seveal actve devces used n cmpund semcnduct analg and dgtal ntegated ccuts. hage Q c ntllng Electde Emttng Electde (electns) llectng Electde hage Q Tanspt Regn Fgue 1. Genec chage cntl devce cnsstng f thee electdes embedded aund a chage tanspt egn. nsde the genec electn devce shwn n Fg. 1. It cnssts f thee electdes encmpassng a chage tanspt egn. The tanspt egn s capable f supptng chage flw (the electns shwn n the fgue) between an emttng electde and a cllectng electde. A thd electde, called the cntl electde, s used t
2 establsh the electn cncentatn wthn the tanspt egn. Placng a cntl chage, Q, n the cntl electde establshes a cntlled chage, dented as Q, n the tanspt egn. The peatn f actve devces depends upn the chage cntl pncple [1]: Each chage placed upn the cntl electde can at mst ntduce an equal and ppste chage n the tanspt egn between the emttng and cllectng electde. At mst we have the elatnshp, Q = Q. Any paastc cuplng f the cntl chage t chage n the the electdes, emte pats f the devce, wll decease the cntlled chage n the tanspt egn, that s, Q < Q me geneally. F example, chage cuplng between the cntl electde and the cllectng electde fms a feedback utput capactance, say. Tme vaatn f Q leads t the mdulatn f the cuent flw between emttng and cllectng electdes. The genec stuctue n Fg. 1 culd epesent any ne f a numbe f actve devces (e.g., vacuum tubes, unpla tanssts, bpla tanssts, phtcnducts, etc.). Hence, chage cntl analyss s vey bad n scpe and t apples t all electnc tanssts. Statng wth the chage cntl pncple, we asscate tw chaactestc tme cnstants wth an actve devce, theeby, leadng t a fstde descptn f ts behav. Applcatn f a ptental dffeence between the emttng and cllectng electdes, say V, establshes an electc feld n the tanspt egn, althugh ths appled feld s nt always needed when dffusn ntenal felds fm dpng pfles ae effectve. Electns n the tanspt egn espnd t the electc feld and mve 2
3 acss ths egn wth a tanst tme. The tanst tme 1 s the fst f the tw mptant chaactestc tmes used n chage cntl mdellng. Wth chage Q n the tanst egn, the statc (dc) cuent I between emttng and cllectng electdes s I = Q/ = Q c / (1) A smple ntepetatn f s as fllws: s equal t the length l f the tanspt egn dvded by the aveage velcty f tanst (.e., = l/v). Fm ths pespectve a chage f Q (culmbs) s swept ut the cllectng electde evey secnds. v n R n ntllng Electde Emttng Electde Tanspt Regn V R L llectng Electde v ut Fgue 2. Genec chage cntl devce f Fg cnnected t nput and utput essts, R n and R L, espectvely, wth bas vltage and nput sgnal appled. nsde Fg. 2 shwng the cmmnemttng electde cnnectn f the actve devce f Fg cnnected t nput and utput (.e., lad) esstances, say R n and R L, 1 The tanst tme s best ntepeted as an aveage tanst tme pe cae (n u case the electn). We nte that 1/ s cmmn t all devces t s elated t a devce s ultmate capablty t pcess nfmatn. 3
4 espectvely. The secnd chaactestc tme f mptance can nw be defned t s the lfetme tme cnstant and we dente t by the symbl. It s a measue f hw lng a chage placed n the cntl electde wll eman n the cntl temnal. The lfetme tme cnstant s establshed n ne f seveal ways dependng upn the physcs f the actve devce and ts cnnectn envnment. The cntllng chage may leak away by (1) dschagng thugh the extenal esst R n as typcally happens wth FET devces, (2) ecmbnng wth ntemxed ppstely chaged caes wthn the devce (e.g., base ecmbnatn n a bpla tansst), (3) dschagng thugh an ntenal shunt leakage path wthn the devce. The dc cuent flwng t eplensh the lst cntl chage s I n = Q/ = Q c / (2) The statc (dc) cuent gan G I f a devce s defned as the cuent delveed t the utput dvded by the cuent eplenshng the cntl chage dung the same tme ped. Whee n secnds chage Q s bth lst and eplenshed, chage Q c tmes the at / has been suppled t the utput esst R L. In symbls, the statc cuent gan s G I = I /I n = / (3) pvded Q = Q hlds. In the dynamc case the pcess f smallsgnal amplfcatn cnssts f an ncemental vaatn f the cntl chage Q c dectly esultng n an ncemental change n the cntlled chage, Q. The esultng vaatn n utput cuent flwng n the lad esst tanslates nt a tme vayng vltage v. The chage cntl fmalsm hlds just as well f lagesgnal stuatns. In the lagesgnal case the changes n cntl chage 4
5 ae n lnge small ncemental changes. hage cntl analyss unde lage chage vaatns s less accuate due t the smplcty f the mdel, but stll vey useful f appxmate swtchng calculatns n dgtal ccuts. An mptant dynamc paamete s the nput capactance f the actve devce. apactance s a measue f the wk equed t ntduce a chage cae n the tanspt egn. apactance s gven by the change n chage Q fm a cespndng change n nput vltage v n. It s desable t maxmze n an actve devce. The tanscnductance g m s calculated fm g m I v n I Q Q v v n (4) The fst patal devatve n the ghthandsde f Eq. (2.2.4) s smply (1/ ) and the secnd patal devatve s. Hence, the tanscnductance g m s the at g m (5) A physcal ntepetatn f g m s the at f the wk equed t ntduce a chage cae t the aveage tanst tme f a chage cae n the tanspt egn. The tanscnductance s ne f the mst cmmnly used devce paametes n ccut desgn and analyss. In addtn t anthe capactance, say, s ntduced and asscated wth the cllectng electde. apactance accunts f chage n the cllectng electde cupled t ethe statc chage n the tanspt egn chage n the cntl electde. A nnze ndcates that the cuplng between the cntllng electde and the chage n tanst s less than unty (.e.,q < Q ). 5
6 F smallsgnal analyss the capactance paametes ae usually taken a fxed numbes evaluated abut the devce s bas state. When usng chage cntl n the lagesgnal case, the capactance paametes must nclude the vltage dependences. F example, the nput capactance can be stngly dependent upn the cntl electde t emttng electde and cllectng electde ptentals. Hence, dung the change n bas state wthn a devce the magntude f the capactance s tme vayng. Ths vaatn can damatcally affect the swtchng speed f the actve devce. Paametc dependences upn the nstantaneus bas state f the devce ae at the heat f accuate mdellng f lagesgnal swtchng behav f actve devces. ntllng Electde llectng Electde v y y v y f v y v Emttng Electde y = y f g m = y = y = Fgue 3. A twpt smallsgnal admttance paamete mdel f an actve devce. Ntce the fwad admttance y f s the tanscnductance f the devce. We ntduce the smallsgnal admttance chage cntl mdel shwn n Fg. 3. Ths mdel uses the emttng electde as the cmmn temnal n a twpt cnnectn. 6
7 The tanscnductance g m s the magntude f the eal pat f the fwad admttance y f and s epesented as a vltagecntlled cuent suce pstned fm cllectngtemttng electde. The nput admttance, dented by y, s equvalent t ( /), whee s the cntl chage lfetme tme cnstant. Paamete y can be expessed n the fm (g s ) whee s = j. An utput admttance, smlaly dented by y, s gven by ( / ) whee s the tanst tme and, n geneal y = (g s ) n geneal. Fnally, the utputtnput feedback admttance y s ncluded usng a vltagecntlled cuent suce at the nput. Often y s small enugh t appxmate as ze (the mdel s then sad t be unlateal). nsde the fequency dependence f the dynamc (ac) cuent gan G. The lwfequency cuent gan s ntepeted as fllws: An ncemental chage q c s ntduced n the cntl electde wth lfetme. Ths pduces a cespndng ncemental chage q n the tanspt egn. hage q s swept acss the tanspt egn evey tanst tme secnds. In tme chage q csses the tanst egn 7
8 tmes, whch s dentcally equal t the lwfequency cuent gan. v g g m v y (a) Shtccut lg G / 20 db/decade T 0 db B lg Fgue 4. cut used t calculate the smallsgnal cuent gan G f u actve devce. The lfetme asscated wth the cntl electde ases fm chage leakng ff the cntllng electde. Ths s mdeled as an R tme cnstant at the nput f the equvalent ccut shwn n Fg. 4(a) wth equal t R n. The beak fequency B asscated wth the cntl electde s (t s 3dB belw the lw fequency value) B 1 1 R n (6) When the chage n the cntl electde vaes at a ate less than B, G s equal t / because chage leaks ff the cntllng electde faste than 1/. Altenatvely, when 8
9 s geate than B, G deceases wth nceasng because the appled sgnal chage vaes me apdly than 1/. Hence, G s nvesely pptnal t G 1 T (7) whee T s the cmmnemtte unty cuent gan fequency. At T (= 2f T ) the ac cuent gan equals unty as llustated n Fg. 4(b). Nw cnsde the cuent ganbandwdth pduct G f. Puely capactve nput mpedance can t defne a bandwdth. Hweve, a fnte, eal mpedance always appeas at the nput temnal n any pactcal applcatn. Let R be the effectve nput esstance f the devce (.e., R wll be equal t (1/g ) n paallel wth the extenal nput esstance R n ). Snce the nput cuent s equal t q c / and the utput cuent s equal t q/, the cuent ganbandwdth pduct s G q / f q / 2 c (8) F B, at =1/, and assumng q c = q, G 1 T f 2 2 f T (9) f T T ) s a wdely quted paamete used t cmpae benchmak actve devces. Smetmes f T T ) s ntepeted as a measue f the maxmum speed a devce can dve a eplca f tself. It s easy t cmpute and hstcally has been easy t measue wth bdges and late usng Spaamete test equpment. Hweve, f T des have ntepetatve lmtatns because t s defned as cuent nt a shtccut utput. 9
10 Theefe, t gnes the effect f bth nput esstance and utput capactance upn actual ccut pefmance. Lkewse, vltage and pwe gan expessns can be deved. It s necessay t defne the utput mpedance befe ethe can be quantfed hweve. Let R be the effectve utput esstance at the utput temnal f the actve devce. We shall make the assumptn that nput and utput R tme cnstants ae dentcal, that s, R = R. That may nt be tue n geneal, but we must assume smethng t defne these utput paametes and t nt t fa fm ealty n many applcatns. The vltage gan G v can be expessed n tems f G, R G G G v R, (10) whee R s the paallel equvalent utput esstance fm all esstances at the utput nde. The pwe gan G p s cmputed fm the pduct f G G v alng wth the pwe ganbandwdth pduct. These esults ae lsted n Table 1 as summazed fm Jhnsn and Rse [1]. These smple expessns ae vald f all devces as ntepeted fm the chage cntl pespectve. They pvde f a fstde cmpasn, n tems f a few smple paametes, amng the actve devces cmmnly avalable. Fm an examnatn f Table 1 t s evdent that maxmzng and mnmzng leads t hghe tanscnductance, hghe paametc gans and geate fequency espnse. Ths s an mptant bsevatn n undestandng hw t mpve upn the pefmance f any actve devce. 10
11 Wheeas f T has lmtatns, the fequency at whch the maxmum pwe gan extaplates t unty, dented by max, s a me useful ndcat f the fequency lmt f the devce s actve egn. The pmay lmtatn f max s that t s vey dffcult t measue dectly and s theefe usually extaplated fm Spaamete measuements n whch the extaplatn s an appxmatn. The smple chage cntl mdel s useful because f the physcal nsght t gves n undestandng actve devces. Fst, all actve devces have ntenal capactance fm the pesence f chage n the cntllng electde and n the tanst egn. Evey actve devce expeences a 20 db/decade gan fallff because f the exstence f capactance. In a feldeffect tansst, s establshed by the cuplng f the chage n the gate electde t the chage n the channel. In cntast, n a bpla junctn tansst cnssts f bth the cntllng chage and the cntlled chage (.e., the mnty cae chage n tanst) cexstng smultaneusly n the base egn. F ths easn s geneally much geate n a bpla tansst than n a feldeffect tansst ths s the pncple easn bpla tanssts aea capable f achevng much geate tanscnductance g m than feldeffect devces. Tansst desgnes ty t maxmze as much as pssble whle stll achevng the values needed f the tansst paametes. 11
12 Refeences [1] E. O. Jhnsn and A. Rse, Smple geneal analyss f amplfe devces wth emtte, cntl, and cllect functns, Pceedngs f the IRE, 47, 407, [2] E. M. hey, and D. E. Hpe, Amplfyng Devces and LwPass Amplfe Desgn, Wley, New Yk, 1968, haptes 2 and 5. [3] R. Beaufy, and J. J. Spakes, The junctn tansst as a chagecntlled devce, ATE Junal, 13, 310, Table 1. Afte Jhnsn & Rse [1] Paamete Symbl Expessn Tanscnductance g m T uent Amplfcatn G 1 T Vltage Amplfcatn G v 1 T Pwe Amplfcatn G p = G G v uent GanBandwdth Pduct G f 1 Vltage GanBandwdth Pduct G v f 1 Pwe GanBandwdth Pduct G p f 2 1 Nte: Table assumes R = R. 2 These ntes wee taken fm D. B. Estech, mpund Semcnduct Devces f Analg and Dgtal cuts, hapte 72, n The VLSI Handbk, 2 nd edtn, edted by WaKa hen, R Pess (Tayl & Fancs Gup), Bca Ratn, FL, 2007; pages 724 t 729. ISBN T 2 T 2 T 2 T 12
T-model: - + v o. v i. i o. v e. R i
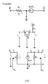 T-mdel: e gm - V Rc e e e gme R R R 23 e e e gme R R The s/c tanscnductance: G m e m g gm e 0 The nput esstance: R e e e e The utput esstance: R R 0 /c unladed ltage gan, R a g R m e gmr e 0 m e g me e/e
T-mdel: e gm - V Rc e e e gme R R R 23 e e e gme R R The s/c tanscnductance: G m e m g gm e 0 The nput esstance: R e e e e The utput esstance: R R 0 /c unladed ltage gan, R a g R m e gmr e 0 m e g me e/e
Introduction of Two Port Network Negative Feedback (Uni lateral Case) Feedback Topology Analysis of feedback applications
 Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w Pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83h 3 Feedback w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w Pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83h 3 Feedback w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
Lecture 2 Feedback Amplifier
 Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w-pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un-lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse-Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83hkn 3 Feedback mples w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w-pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un-lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse-Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83hkn 3 Feedback mples w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
ANALOG ELECTRONICS DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH
 24 ANALOG LTRONIS lass 5&6&7&8&9 DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH 3.3.3 n-ase cnfguatn V V Rc I π π g g R V /p sgnal appled t. O/p taken f. ted t ac gnd. The hybd-π del pdes an accuate epesentatn f the sall-sgnal
24 ANALOG LTRONIS lass 5&6&7&8&9 DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH 3.3.3 n-ase cnfguatn V V Rc I π π g g R V /p sgnal appled t. O/p taken f. ted t ac gnd. The hybd-π del pdes an accuate epesentatn f the sall-sgnal
LEAP FROG TECHNIQUE. Operational Simulation of LC Ladder Filters ECEN 622 (ESS) TAMU-AMSC
 LEAP FOG TEHNQUE Opeatnal Smulatn f L Ladde Fltes L pttype lw senstvty One fm f ths technque s called Leapf Technque Fundamental Buldn Blcks ae - nteats - Secnd-de ealzatns Fltes cnsdeed - LP - BP - HP
LEAP FOG TEHNQUE Opeatnal Smulatn f L Ladde Fltes L pttype lw senstvty One fm f ths technque s called Leapf Technque Fundamental Buldn Blcks ae - nteats - Secnd-de ealzatns Fltes cnsdeed - LP - BP - HP
Transistors. Lesson #10 Chapter 4. BME 372 Electronics I J.Schesser
 Tanssts essn #10 Chapte 4 BM 372 lectncs 154 Hmewk Ps. 4.40, 4.42, 4.43, 4.45, 4.46, 4.51, 4.53, 4.54, 4.56 BM 372 lectncs 155 Hmewk Answes #20 Ps. 4.40 See fgue 4.33 BM 372 lectncs 156 Ps. 4.42 Hmewk
Tanssts essn #10 Chapte 4 BM 372 lectncs 154 Hmewk Ps. 4.40, 4.42, 4.43, 4.45, 4.46, 4.51, 4.53, 4.54, 4.56 BM 372 lectncs 155 Hmewk Answes #20 Ps. 4.40 See fgue 4.33 BM 372 lectncs 156 Ps. 4.42 Hmewk
Exercises for Frequency Response. ECE 102, Fall 2012, F. Najmabadi
 Eecses Fequency espnse EE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabad Eecse : Fnd the d-band an and the lwe cut- equency the aple belw. µ n (W/ 4 A/, t 0.5, λ 0, 0 µf, and µf Bth capacts ae lw- capacts. F. Najabad, EE0, Fall
Eecses Fequency espnse EE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabad Eecse : Fnd the d-band an and the lwe cut- equency the aple belw. µ n (W/ 4 A/, t 0.5, λ 0, 0 µf, and µf Bth capacts ae lw- capacts. F. Najabad, EE0, Fall
Design of Analog Integrated Circuits
 Desgn f Analg Integrated Crcuts I. Amplfers Desgn f Analg Integrated Crcuts Fall 2012, Dr. Guxng Wang 1 Oerew Basc MOS amplfer structures Cmmn-Surce Amplfer Surce Fllwer Cmmn-Gate Amplfer Desgn f Analg
Desgn f Analg Integrated Crcuts I. Amplfers Desgn f Analg Integrated Crcuts Fall 2012, Dr. Guxng Wang 1 Oerew Basc MOS amplfer structures Cmmn-Surce Amplfer Surce Fllwer Cmmn-Gate Amplfer Desgn f Analg
Active Load. Reading S&S (5ed): Sec. 7.2 S&S (6ed): Sec. 8.2
 cte La ean S&S (5e: Sec. 7. S&S (6e: Sec. 8. In nteate ccuts, t s ffcult t fabcate essts. Instea, aplfe cnfuatns typcally use acte las (.e. las ae w acte eces. Ths can be ne usn a cuent suce cnfuatn,.e.
cte La ean S&S (5e: Sec. 7. S&S (6e: Sec. 8. In nteate ccuts, t s ffcult t fabcate essts. Instea, aplfe cnfuatns typcally use acte las (.e. las ae w acte eces. Ths can be ne usn a cuent suce cnfuatn,.e.
hitt Phy2049: Magnetism 6/10/2011 Magnetic Field Units Force Between Two Parallel Currents Force Between Two Anti-Parallel Currents
 6/0/0 Phy049: Magsm Last lectue: t-avat s and Ampee s law: Magc eld due t a staght we Cuent lps (whle bts)and slends Tday: emnde and aaday s law. htt Tw lng staght wes pece the plane f the pape at vetces
6/0/0 Phy049: Magsm Last lectue: t-avat s and Ampee s law: Magc eld due t a staght we Cuent lps (whle bts)and slends Tday: emnde and aaday s law. htt Tw lng staght wes pece the plane f the pape at vetces
OBJECTIVE To investigate the parallel connection of R, L, and C. 1 Electricity & Electronics Constructor EEC470
 Assignment 7 Paallel Resnance OBJECTIVE T investigate the paallel cnnectin f R,, and C. EQUIPMENT REQUIRED Qty Appaatus 1 Electicity & Electnics Cnstuct EEC470 1 Basic Electicity and Electnics Kit EEC471-1
Assignment 7 Paallel Resnance OBJECTIVE T investigate the paallel cnnectin f R,, and C. EQUIPMENT REQUIRED Qty Appaatus 1 Electicity & Electnics Cnstuct EEC470 1 Basic Electicity and Electnics Kit EEC471-1
EEE2146 Microelectronics Circuit Analysis and Design. MIC2: Investigation of Amplifier Parameters of a Common-Collector Amplifier
 EEE2146 Mcelectncs Ccut Analyss and Desgn Expement MIC2 MIC2: Inestgatn f Amplfe Paametes f a Cmmn-Cllect Amplfe Ttal Pecentage: 5% (Fm 40% Cusewk Mak) 1. Objecte T nestgate the ltage and cuent gans and
EEE2146 Mcelectncs Ccut Analyss and Desgn Expement MIC2 MIC2: Inestgatn f Amplfe Paametes f a Cmmn-Cllect Amplfe Ttal Pecentage: 5% (Fm 40% Cusewk Mak) 1. Objecte T nestgate the ltage and cuent gans and
Introduction to Electronic circuits.
 Intrductn t Electrnc crcuts. Passve and Actve crcut elements. Capactrs, esstrs and Inductrs n AC crcuts. Vltage and current dvders. Vltage and current surces. Amplfers, and ther transfer characterstc.
Intrductn t Electrnc crcuts. Passve and Actve crcut elements. Capactrs, esstrs and Inductrs n AC crcuts. Vltage and current dvders. Vltage and current surces. Amplfers, and ther transfer characterstc.
FEEDBACK AMPLIFIERS. β f
 FEEDBC MPLFES X - X X X * What negatve eedback? ddng the eedback gnal t the nput a t patally cancel the nput gnal t the ample. * What eedback? Takng a ptn the gnal avng at the lad and eedng t back t the
FEEDBC MPLFES X - X X X * What negatve eedback? ddng the eedback gnal t the nput a t patally cancel the nput gnal t the ample. * What eedback? Takng a ptn the gnal avng at the lad and eedng t back t the
(8) Gain Stage and Simple Output Stage
 EEEB23 Electoncs Analyss & Desgn (8) Gan Stage and Smple Output Stage Leanng Outcome Able to: Analyze an example of a gan stage and output stage of a multstage amplfe. efeence: Neamen, Chapte 11 8.0) ntoducton
EEEB23 Electoncs Analyss & Desgn (8) Gan Stage and Smple Output Stage Leanng Outcome Able to: Analyze an example of a gan stage and output stage of a multstage amplfe. efeence: Neamen, Chapte 11 8.0) ntoducton
Electric potential energy Electrostatic force does work on a particle : Potential energy (: i initial state f : final state):
 Electc ptental enegy Electstatc fce des wk n a patcle : v v v v W = F s = E s. Ptental enegy (: ntal state f : fnal state): Δ U = U U = W. f ΔU Electc ptental : Δ : ptental enegy pe unt chag e. J ( Jule)
Electc ptental enegy Electstatc fce des wk n a patcle : v v v v W = F s = E s. Ptental enegy (: ntal state f : fnal state): Δ U = U U = W. f ΔU Electc ptental : Δ : ptental enegy pe unt chag e. J ( Jule)
9/12/2013. Microelectronics Circuit Analysis and Design. Modes of Operation. Cross Section of Integrated Circuit npn Transistor
 Mcoelectoncs Ccut Analyss and Desgn Donald A. Neamen Chapte 5 The pola Juncton Tanssto In ths chapte, we wll: Dscuss the physcal stuctue and opeaton of the bpola juncton tanssto. Undestand the dc analyss
Mcoelectoncs Ccut Analyss and Desgn Donald A. Neamen Chapte 5 The pola Juncton Tanssto In ths chapte, we wll: Dscuss the physcal stuctue and opeaton of the bpola juncton tanssto. Undestand the dc analyss
6. Cascode Amplifiers and Cascode Current Mirrors
 6. Cascde plfes and Cascde Cuent Ms Seda & Sth Sec. 7 (MOS ptn (S&S 5 th Ed: Sec. 6 MOS ptn & ne fequency espnse ECE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabad Cascde aplfe s a ppula buldn blck f ICs Cascde Cnfuatn CG stae
6. Cascde plfes and Cascde Cuent Ms Seda & Sth Sec. 7 (MOS ptn (S&S 5 th Ed: Sec. 6 MOS ptn & ne fequency espnse ECE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabad Cascde aplfe s a ppula buldn blck f ICs Cascde Cnfuatn CG stae
Feedback Principle :-
 Feedback Prncple : Feedback amplfer s that n whch a part f the utput f the basc amplfer s returned back t the nput termnal and mxed up wth the nternal nput sgnal. The sub netwrks f feedback amplfer are:
Feedback Prncple : Feedback amplfer s that n whch a part f the utput f the basc amplfer s returned back t the nput termnal and mxed up wth the nternal nput sgnal. The sub netwrks f feedback amplfer are:
ME 3600 Control Systems Frequency Domain Analysis
 ME 3600 Cntl Systems Fequency Dmain Analysis The fequency espnse f a system is defined as the steady-state espnse f the system t a sinusidal (hamnic) input. F linea systems, the esulting utput is itself
ME 3600 Cntl Systems Fequency Dmain Analysis The fequency espnse f a system is defined as the steady-state espnse f the system t a sinusidal (hamnic) input. F linea systems, the esulting utput is itself
is needed and this can be established by multiplying A, obtained in step 3, by, resulting V = A x y =. = x, located in 1 st quadrant rotated about 2
 Ct Cllege f New Yk MATH (Calculus Ntes) Page 1 f 1 Essental Calculus, nd edtn (Stewat) Chapte 7 Sectn, and 6 auth: M. Pak Chapte 7 sectn : Vlume Suface f evlutn (Dsc methd) 1) Estalsh the tatn as and the
Ct Cllege f New Yk MATH (Calculus Ntes) Page 1 f 1 Essental Calculus, nd edtn (Stewat) Chapte 7 Sectn, and 6 auth: M. Pak Chapte 7 sectn : Vlume Suface f evlutn (Dsc methd) 1) Estalsh the tatn as and the
Wp/Lmin. Wn/Lmin 2.5V
 UNIVERITY OF CALIFORNIA Cllege f Engneerng Department f Electrcal Engneerng and Cmputer cences Andre Vladmrescu Hmewrk #7 EEC Due Frday, Aprl 8 th, pm @ 0 Cry Prblem #.5V Wp/Lmn 0.0V Wp/Lmn n ut Wn/Lmn.5V
UNIVERITY OF CALIFORNIA Cllege f Engneerng Department f Electrcal Engneerng and Cmputer cences Andre Vladmrescu Hmewrk #7 EEC Due Frday, Aprl 8 th, pm @ 0 Cry Prblem #.5V Wp/Lmn 0.0V Wp/Lmn n ut Wn/Lmn.5V
Announcements Candidates Visiting Next Monday 11 12:20 Class 4pm Research Talk Opportunity to learn a little about what physicists do
 Wed., /11 Thus., /1 Fi., /13 Mn., /16 Tues., /17 Wed., /18 Thus., /19 Fi., / 17.7-9 Magnetic Field F Distibutins Lab 5: Bit-Savat B fields f mving chages (n quiz) 17.1-11 Pemanent Magnets 18.1-3 Mic. View
Wed., /11 Thus., /1 Fi., /13 Mn., /16 Tues., /17 Wed., /18 Thus., /19 Fi., / 17.7-9 Magnetic Field F Distibutins Lab 5: Bit-Savat B fields f mving chages (n quiz) 17.1-11 Pemanent Magnets 18.1-3 Mic. View
Amplifier Constant Gain and Noise
 Amplfe Constant Gan and ose by Manfed Thumm and Wene Wesbeck Foschungszentum Kalsuhe n de Helmholtz - Gemenschaft Unvestät Kalsuhe (TH) Reseach Unvesty founded 85 Ccles of Constant Gan (I) If s taken to
Amplfe Constant Gan and ose by Manfed Thumm and Wene Wesbeck Foschungszentum Kalsuhe n de Helmholtz - Gemenschaft Unvestät Kalsuhe (TH) Reseach Unvesty founded 85 Ccles of Constant Gan (I) If s taken to
PHYSICS 536 Experiment 12: Applications of the Golden Rules for Negative Feedback
 PHYSICS 536 Experment : Applcatns f the Glden Rules fr Negatve Feedback The purpse f ths experment s t llustrate the glden rules f negatve feedback fr a varety f crcuts. These cncepts permt yu t create
PHYSICS 536 Experment : Applcatns f the Glden Rules fr Negatve Feedback The purpse f ths experment s t llustrate the glden rules f negatve feedback fr a varety f crcuts. These cncepts permt yu t create
Physics Exam II Chapters 25-29
 Physcs 114 1 Exam II Chaptes 5-9 Answe 8 of the followng 9 questons o poblems. Each one s weghted equally. Clealy mak on you blue book whch numbe you do not want gaded. If you ae not sue whch one you do
Physcs 114 1 Exam II Chaptes 5-9 Answe 8 of the followng 9 questons o poblems. Each one s weghted equally. Clealy mak on you blue book whch numbe you do not want gaded. If you ae not sue whch one you do
Consider the simple circuit of Figure 1 in which a load impedance of r is connected to a voltage source. The no load voltage of r
 1 Intductin t Pe Unit Calculatins Cnside the simple cicuit f Figue 1 in which a lad impedance f L 60 + j70 Ω 9. 49 Ω is cnnected t a vltage suce. The n lad vltage f the suce is E 1000 0. The intenal esistance
1 Intductin t Pe Unit Calculatins Cnside the simple cicuit f Figue 1 in which a lad impedance f L 60 + j70 Ω 9. 49 Ω is cnnected t a vltage suce. The n lad vltage f the suce is E 1000 0. The intenal esistance
CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF KY BOOST CONVERTER
 70 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF KY BOOST CONERTER 3.1 Intrductn The KY Bst Cnverter s a recent nventn made by K.I.Hwu et. al., (2007), (2009a), (2009b), (2009c), (2010) n the nn-slated DC DC cnverter segment,
70 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF KY BOOST CONERTER 3.1 Intrductn The KY Bst Cnverter s a recent nventn made by K.I.Hwu et. al., (2007), (2009a), (2009b), (2009c), (2010) n the nn-slated DC DC cnverter segment,
Chapter 7. Systems 7.1 INTRODUCTION 7.2 MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF LIQUID LEVEL SYSTEMS. Steady State Flow. A. Bazoune
 Chapter 7 Flud Systems and Thermal Systems 7.1 INTODUCTION A. Bazune A flud system uses ne r mre fluds t acheve ts purpse. Dampers and shck absrbers are eamples f flud systems because they depend n the
Chapter 7 Flud Systems and Thermal Systems 7.1 INTODUCTION A. Bazune A flud system uses ne r mre fluds t acheve ts purpse. Dampers and shck absrbers are eamples f flud systems because they depend n the
Work, Energy, and Power. AP Physics C
 k, Eneg, and Pwe AP Phsics C Thee ae man diffeent TYPES f Eneg. Eneg is expessed in JOULES (J) 4.19 J = 1 calie Eneg can be expessed me specificall b using the tem ORK() k = The Scala Dt Pduct between
k, Eneg, and Pwe AP Phsics C Thee ae man diffeent TYPES f Eneg. Eneg is expessed in JOULES (J) 4.19 J = 1 calie Eneg can be expessed me specificall b using the tem ORK() k = The Scala Dt Pduct between
Unit 3: Transistor at Low Frequencies
 Unt 3: Tansst at Lw Fquncs JT Tansst Mdlng mdl s an qualnt ccut that psnts th chaactstcs f th tansst. mdl uss ccut lmnts that appxmat th ha f th tansst. Th a tw mdls cmmnly usd n small sgnal analyss f
Unt 3: Tansst at Lw Fquncs JT Tansst Mdlng mdl s an qualnt ccut that psnts th chaactstcs f th tansst. mdl uss ccut lmnts that appxmat th ha f th tansst. Th a tw mdls cmmnly usd n small sgnal analyss f
Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapte 3 lectmagnetic Waves 3.1 Maxwell s quatins and ectmagnetic Waves A. Gauss s Law: # clsed suface aea " da Q enc lectic fields may be geneated by electic chages. lectic field lines stat at psitive
Chapte 3 lectmagnetic Waves 3.1 Maxwell s quatins and ectmagnetic Waves A. Gauss s Law: # clsed suface aea " da Q enc lectic fields may be geneated by electic chages. lectic field lines stat at psitive
Optimization Frequency Design of Eddy Current Testing
 5th WSEAS Int. Cnfeence n Appled Electagnetcs, Weless and Optcal Cuncatns, Tenefe, Span, Decebe 14-16, 2007 127 Optzatn Fequency Desgn f Eddy Cuent Testng NAONG MUNGKUNG 1, KOMKIT CHOMSUWAN 1, NAONG PIMPU
5th WSEAS Int. Cnfeence n Appled Electagnetcs, Weless and Optcal Cuncatns, Tenefe, Span, Decebe 14-16, 2007 127 Optzatn Fequency Desgn f Eddy Cuent Testng NAONG MUNGKUNG 1, KOMKIT CHOMSUWAN 1, NAONG PIMPU
5/20/2011. HITT An electron moves from point i to point f, in the direction of a uniform electric field. During this displacement:
 5/0/011 Chapte 5 In the last lectue: CapacitanceII we calculated the capacitance C f a system f tw islated cnducts. We als calculated the capacitance f sme simple gemeties. In this chapte we will cve the
5/0/011 Chapte 5 In the last lectue: CapacitanceII we calculated the capacitance C f a system f tw islated cnducts. We als calculated the capacitance f sme simple gemeties. In this chapte we will cve the
Circuits Op-Amp. Interaction of Circuit Elements. Quick Check How does closing the switch affect V o and I o?
 Crcuts Op-Amp ENGG1015 1 st Semester, 01 Interactn f Crcut Elements Crcut desgn s cmplcated by nteractns amng the elements. Addng an element changes vltages & currents thrughut crcut. Example: clsng a
Crcuts Op-Amp ENGG1015 1 st Semester, 01 Interactn f Crcut Elements Crcut desgn s cmplcated by nteractns amng the elements. Addng an element changes vltages & currents thrughut crcut. Example: clsng a
Electric Fields and Electric Forces
 Cpyight, iley 006 (Cutnell & Jhnsn 9. Ptential Enegy Chapte 9 mgh mgh GPE GPE Electic Fields and Electic Fces 9. Ptential Enegy 9. Ptential Enegy 9. The Electic Ptential Diffeence 9. The Electic Ptential
Cpyight, iley 006 (Cutnell & Jhnsn 9. Ptential Enegy Chapte 9 mgh mgh GPE GPE Electic Fields and Electic Fces 9. Ptential Enegy 9. Ptential Enegy 9. The Electic Ptential Diffeence 9. The Electic Ptential
A NEW FAMILY OF TRANSFORMERLESS MODULAR DC-DC CONVERTERS FOR HIGH POWER APPLICATIONS
 A NEW FAMIY OF TRANSFORMERESS MODUAR D-D ONVERTERS FOR HIGH POWER APPIATIONS by Abdelahman Haga A thess submtted n cnfmty wth the equements f the degee f Dct f Phlsphy Gaduate Depatment f Electcal and
A NEW FAMIY OF TRANSFORMERESS MODUAR D-D ONVERTERS FOR HIGH POWER APPIATIONS by Abdelahman Haga A thess submtted n cnfmty wth the equements f the degee f Dct f Phlsphy Gaduate Depatment f Electcal and
Example
 hapte Exaple.6-3. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5 A single hllw fibe is placed within a vey lage glass tube. he hllw fibe is 0 c in length and has a
hapte Exaple.6-3. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5 A single hllw fibe is placed within a vey lage glass tube. he hllw fibe is 0 c in length and has a
Integral Vector Operations and Related Theorems Applications in Mechanics and E&M
 Dola Bagayoko (0) Integal Vecto Opeatons and elated Theoems Applcatons n Mechancs and E&M Ι Basc Defnton Please efe to you calculus evewed below. Ι, ΙΙ, andιιι notes and textbooks fo detals on the concepts
Dola Bagayoko (0) Integal Vecto Opeatons and elated Theoems Applcatons n Mechancs and E&M Ι Basc Defnton Please efe to you calculus evewed below. Ι, ΙΙ, andιιι notes and textbooks fo detals on the concepts
Optimization of the Electron Gun with a Permanent Ion Trap
 4.3.-178 Optmzatn f the Electn Gun wth a Pemanent In Tap We Le Xabng Zhang Jn Dng Fe Dpla Technlg R&D CenteSutheat Unvet Nangjng Chna Danel den Engelen Pduct and Pce Develpment(PPD)LG.Phlp Dpla 5600 MD
4.3.-178 Optmzatn f the Electn Gun wth a Pemanent In Tap We Le Xabng Zhang Jn Dng Fe Dpla Technlg R&D CenteSutheat Unvet Nangjng Chna Danel den Engelen Pduct and Pce Develpment(PPD)LG.Phlp Dpla 5600 MD
A) (0.46 î ) N B) (0.17 î ) N
 Phys10 Secnd Maj-14 Ze Vesin Cdinat: xyz Thusday, Apil 3, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Thee chages, 1 = =.0 μc and Q = 4.0 μc, ae fixed in thei places as shwn in Figue 1. Find the net electstatic fce n Q due t 1 and.
Phys10 Secnd Maj-14 Ze Vesin Cdinat: xyz Thusday, Apil 3, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Thee chages, 1 = =.0 μc and Q = 4.0 μc, ae fixed in thei places as shwn in Figue 1. Find the net electstatic fce n Q due t 1 and.
WYSE Academic Challenge Sectional Mathematics 2006 Solution Set
 WYSE Academic Challenge Sectinal 006 Slutin Set. Cect answe: e. mph is 76 feet pe minute, and 4 mph is 35 feet pe minute. The tip up the hill takes 600/76, 3.4 minutes, and the tip dwn takes 600/35,.70
WYSE Academic Challenge Sectinal 006 Slutin Set. Cect answe: e. mph is 76 feet pe minute, and 4 mph is 35 feet pe minute. The tip up the hill takes 600/76, 3.4 minutes, and the tip dwn takes 600/35,.70
Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors
 Senss and Actuats Intductin t senss Sande Stuij (s.stuij@tue.nl) Depatment f Electical Engineeing Electnic Systems AMPLIFIES (Chapte 5.) Infmatin pcessing system nncntact sens cntact sens abslute sens
Senss and Actuats Intductin t senss Sande Stuij (s.stuij@tue.nl) Depatment f Electical Engineeing Electnic Systems AMPLIFIES (Chapte 5.) Infmatin pcessing system nncntact sens cntact sens abslute sens
Solution: (a) C 4 1 AI IC 4. (b) IBC 4
 C A C C R A C R C R C sin 9 sin. A cuent f is maintaine in a single cicula lp f cicumfeence C. A magnetic fiel f is iecte paallel t the plane f the lp. (a) Calculate the magnetic mment f the lp. (b) What
C A C C R A C R C R C sin 9 sin. A cuent f is maintaine in a single cicula lp f cicumfeence C. A magnetic fiel f is iecte paallel t the plane f the lp. (a) Calculate the magnetic mment f the lp. (b) What
Summary chapter 4. Electric field s can distort charge distributions in atoms and molecules by stretching and rotating:
 Summa chapte 4. In chapte 4 dielectics ae discussed. In thse mateials the electns ae nded t the atms mlecules and cannt am fee thugh the mateial: the electns in insulats ae n a tight leash and all the
Summa chapte 4. In chapte 4 dielectics ae discussed. In thse mateials the electns ae nded t the atms mlecules and cannt am fee thugh the mateial: the electns in insulats ae n a tight leash and all the
5.1 Moment of a Force Scalar Formation
 Outline ment f a Cuple Equivalent System Resultants f a Fce and Cuple System ment f a fce abut a pint axis a measue f the tendency f the fce t cause a bdy t tate abut the pint axis Case 1 Cnside hizntal
Outline ment f a Cuple Equivalent System Resultants f a Fce and Cuple System ment f a fce abut a pint axis a measue f the tendency f the fce t cause a bdy t tate abut the pint axis Case 1 Cnside hizntal
Summary 7. ELECTROMAGNETIC JOINT. ROTATING MAGNETIC FIELD. SPACE-PHASOR THEORY... 2
 uay 7. ELECTROMAGETIC JOIT. ROTATIG MAGETIC FIELD. PACE-PHAOR THEORY... 7.1 ELECTROMAGETIC JOIT... 7. UMER OF POLE... 4 7. DITRIUTED WIDIG... 5 7.4 TORQUE EXPREIO... 6 7.5 PACE PHAOR... 7 7.6 THREE-PHAE
uay 7. ELECTROMAGETIC JOIT. ROTATIG MAGETIC FIELD. PACE-PHAOR THEORY... 7.1 ELECTROMAGETIC JOIT... 7. UMER OF POLE... 4 7. DITRIUTED WIDIG... 5 7.4 TORQUE EXPREIO... 6 7.5 PACE PHAOR... 7 7.6 THREE-PHAE
ME2142/ME2142E Feedback Control Systems. Modelling of Physical Systems The Transfer Function
 Mdellng Physcal Systems The Transer Functn Derental Equatns U Plant Y In the plant shwn, the nput u aects the respnse the utput y. In general, the dynamcs ths respnse can be descrbed by a derental equatn
Mdellng Physcal Systems The Transer Functn Derental Equatns U Plant Y In the plant shwn, the nput u aects the respnse the utput y. In general, the dynamcs ths respnse can be descrbed by a derental equatn
Microelectronics Circuit Analysis and Design. ac Equivalent Circuit for Common Emitter. Common Emitter with Time-Varying Input
 Micelectnics Cicuit Analysis and Design Dnald A. Neamen Chapte 6 Basic BJT Amplifies In this chapte, we will: Undestand the pinciple f a linea amplifie. Discuss and cmpae the thee basic tansist amplifie
Micelectnics Cicuit Analysis and Design Dnald A. Neamen Chapte 6 Basic BJT Amplifies In this chapte, we will: Undestand the pinciple f a linea amplifie. Discuss and cmpae the thee basic tansist amplifie
COMPLEMENTARY ENERGY METHOD FOR CURVED COMPOSITE BEAMS
 ultscence - XXX. mcocd Intenatonal ultdscplnay Scentfc Confeence Unvesty of skolc Hungay - pl 06 ISBN 978-963-358-3- COPLEENTRY ENERGY ETHOD FOR CURVED COPOSITE BES Ákos József Lengyel István Ecsed ssstant
ultscence - XXX. mcocd Intenatonal ultdscplnay Scentfc Confeence Unvesty of skolc Hungay - pl 06 ISBN 978-963-358-3- COPLEENTRY ENERGY ETHOD FOR CURVED COPOSITE BES Ákos József Lengyel István Ecsed ssstant
Prof. Paolo Colantonio a.a
 Pro. Paolo olantono a.a. 3 4 Let s consder a two ports network o Two ports Network o L For passve network (.e. wthout nternal sources or actve devces), a general representaton can be made by a sutable
Pro. Paolo olantono a.a. 3 4 Let s consder a two ports network o Two ports Network o L For passve network (.e. wthout nternal sources or actve devces), a general representaton can be made by a sutable
24-2: Electric Potential Energy. 24-1: What is physics
 D. Iyad SAADEDDIN Chapte 4: Electc Potental Electc potental Enegy and Electc potental Calculatng the E-potental fom E-feld fo dffeent chage dstbutons Calculatng the E-feld fom E-potental Potental of a
D. Iyad SAADEDDIN Chapte 4: Electc Potental Electc potental Enegy and Electc potental Calculatng the E-potental fom E-feld fo dffeent chage dstbutons Calculatng the E-feld fom E-potental Potental of a
1.4 Small-signal models of BJT
 1.4 Small-sgnal models of J Analog crcuts often operate wth sgnal levels that are small compared to the bas currents and voltages n the crcut. Under ths condton, ncremental or small-sgnal models can be
1.4 Small-sgnal models of J Analog crcuts often operate wth sgnal levels that are small compared to the bas currents and voltages n the crcut. Under ths condton, ncremental or small-sgnal models can be
Energy in Closed Systems
 Enegy n Closed Systems Anamta Palt palt.anamta@gmal.com Abstact The wtng ndcates a beakdown of the classcal laws. We consde consevaton of enegy wth a many body system n elaton to the nvese squae law and
Enegy n Closed Systems Anamta Palt palt.anamta@gmal.com Abstact The wtng ndcates a beakdown of the classcal laws. We consde consevaton of enegy wth a many body system n elaton to the nvese squae law and
March 15. Induction and Inductance Chapter 31
 Mach 15 Inductin and Inductance Chapte 31 > Fces due t B fields Lentz fce τ On a mving chage F B On a cuent F il B Cuent caying cil feels a tque = µ B Review > Cuents geneate B field Bit-Savat law = qv
Mach 15 Inductin and Inductance Chapte 31 > Fces due t B fields Lentz fce τ On a mving chage F B On a cuent F il B Cuent caying cil feels a tque = µ B Review > Cuents geneate B field Bit-Savat law = qv
(5) Furthermore, the third constraint implies the following equation: (6)
 T-Element Refactng System f Gaussan and Annula-Gaussan Beams Tansfmatn Abdallah K. Che *, Nabl I. Khachab, Mahmud K. Habb Electcal Engneeng Depatment, Cllege f Engneeng and Petleum, Kuat Unvesty, P. O.
T-Element Refactng System f Gaussan and Annula-Gaussan Beams Tansfmatn Abdallah K. Che *, Nabl I. Khachab, Mahmud K. Habb Electcal Engneeng Depatment, Cllege f Engneeng and Petleum, Kuat Unvesty, P. O.
IGEE 401 Power Electronic Systems. Solution to Midterm Examination Fall 2004
 Jós, G GEE 401 wer Electrnc Systems Slutn t Mdterm Examnatn Fall 2004 Specal nstructns: - Duratn: 75 mnutes. - Materal allwed: a crb sheet (duble sded 8.5 x 11), calculatr. - Attempt all questns. Make
Jós, G GEE 401 wer Electrnc Systems Slutn t Mdterm Examnatn Fall 2004 Specal nstructns: - Duratn: 75 mnutes. - Materal allwed: a crb sheet (duble sded 8.5 x 11), calculatr. - Attempt all questns. Make
Physics 2A Chapter 11 - Universal Gravitation Fall 2017
 Physcs A Chapte - Unvesal Gavtaton Fall 07 hese notes ae ve pages. A quck summay: he text boxes n the notes contan the esults that wll compse the toolbox o Chapte. hee ae thee sectons: the law o gavtaton,
Physcs A Chapte - Unvesal Gavtaton Fall 07 hese notes ae ve pages. A quck summay: he text boxes n the notes contan the esults that wll compse the toolbox o Chapte. hee ae thee sectons: the law o gavtaton,
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION PREVIOUS EAMCET BITS
 P P Methd EECTOMAGNETIC INDUCTION PEVIOUS EAMCET BITS [ENGINEEING PAPE]. A cnduct d f length tates with angula speed ω in a unifm magnetic field f inductin B which is pependicula t its mtin. The induced
P P Methd EECTOMAGNETIC INDUCTION PEVIOUS EAMCET BITS [ENGINEEING PAPE]. A cnduct d f length tates with angula speed ω in a unifm magnetic field f inductin B which is pependicula t its mtin. The induced
Surface and Interface Science Physics 627; Chemistry 542. Lecture 10 March 1, 2013
 Suface and Inteface Science Physics 67; Chemisty 54 Lectue 0 Mach, 03 Int t Electnic Ppeties: Wk Functin,Theminic Electn Emissin, Field Emissin Refeences: ) Wduff & Delcha, Pp. 40-4; 46-484 ) Zangwill
Suface and Inteface Science Physics 67; Chemisty 54 Lectue 0 Mach, 03 Int t Electnic Ppeties: Wk Functin,Theminic Electn Emissin, Field Emissin Refeences: ) Wduff & Delcha, Pp. 40-4; 46-484 ) Zangwill
55:041 Electronic Circuits
 55:04 Electrnc Crcuts Feedback & Stablty Sectns f Chapter 2. Kruger Feedback & Stablty Cnfguratn f Feedback mplfer S S S S fb Negate feedback S S S fb S S S S S β s the feedback transfer functn Implct
55:04 Electrnc Crcuts Feedback & Stablty Sectns f Chapter 2. Kruger Feedback & Stablty Cnfguratn f Feedback mplfer S S S S fb Negate feedback S S S fb S S S S S β s the feedback transfer functn Implct
Multistage Median Ranked Set Sampling for Estimating the Population Median
 Jounal of Mathematcs and Statstcs 3 (: 58-64 007 ISSN 549-3644 007 Scence Publcatons Multstage Medan Ranked Set Samplng fo Estmatng the Populaton Medan Abdul Azz Jeman Ame Al-Oma and Kamaulzaman Ibahm
Jounal of Mathematcs and Statstcs 3 (: 58-64 007 ISSN 549-3644 007 Scence Publcatons Multstage Medan Ranked Set Samplng fo Estmatng the Populaton Medan Abdul Azz Jeman Ame Al-Oma and Kamaulzaman Ibahm
P 365. r r r )...(1 365
 SCIENCE WORLD JOURNAL VOL (NO4) 008 www.scecncewoldounal.og ISSN 597-64 SHORT COMMUNICATION ANALYSING THE APPROXIMATION MODEL TO BIRTHDAY PROBLEM *CHOJI, D.N. & DEME, A.C. Depatment of Mathematcs Unvesty
SCIENCE WORLD JOURNAL VOL (NO4) 008 www.scecncewoldounal.og ISSN 597-64 SHORT COMMUNICATION ANALYSING THE APPROXIMATION MODEL TO BIRTHDAY PROBLEM *CHOJI, D.N. & DEME, A.C. Depatment of Mathematcs Unvesty
Chapter 23: Electric Potential
 Chapte 23: Electc Potental Electc Potental Enegy It tuns out (won t show ths) that the tostatc foce, qq 1 2 F ˆ = k, s consevatve. 2 Recall, fo any consevatve foce, t s always possble to wte the wok done
Chapte 23: Electc Potental Electc Potental Enegy It tuns out (won t show ths) that the tostatc foce, qq 1 2 F ˆ = k, s consevatve. 2 Recall, fo any consevatve foce, t s always possble to wte the wok done
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Kbe Unvesty Repsty : Kenel タイトル Ttle 著者 Auth(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Ctatn 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resuce Type 版区分 Resuce Vesn 権利 Rghts DOI JaLCDOI URL Tansent ctcal heat fluxes f subcled wate flw blng n a SUS304-ccula
Kbe Unvesty Repsty : Kenel タイトル Ttle 著者 Auth(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Ctatn 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resuce Type 版区分 Resuce Vesn 権利 Rghts DOI JaLCDOI URL Tansent ctcal heat fluxes f subcled wate flw blng n a SUS304-ccula
PHYS 705: Classical Mechanics. Derivation of Lagrange Equations from D Alembert s Principle
 1 PHYS 705: Classcal Mechancs Devaton of Lagange Equatons fom D Alembet s Pncple 2 D Alembet s Pncple Followng a smla agument fo the vtual dsplacement to be consstent wth constants,.e, (no vtual wok fo
1 PHYS 705: Classcal Mechancs Devaton of Lagange Equatons fom D Alembet s Pncple 2 D Alembet s Pncple Followng a smla agument fo the vtual dsplacement to be consstent wth constants,.e, (no vtual wok fo
Electric Charge. Electric charge is quantized. Electric charge is conserved
 lectstatics lectic Chage lectic chage is uantized Chage cmes in incements f the elementay chage e = ne, whee n is an intege, and e =.6 x 0-9 C lectic chage is cnseved Chage (electns) can be mved fm ne
lectstatics lectic Chage lectic chage is uantized Chage cmes in incements f the elementay chage e = ne, whee n is an intege, and e =.6 x 0-9 C lectic chage is cnseved Chage (electns) can be mved fm ne
Exercises for Differential Amplifiers. ECE 102, Fall 2012, F. Najmabadi
 Execises f iffeential mplifies ECE 0, Fall 0, F. Najmabai Execise : Cmpute,, an G if m, 00 Ω, O, an ientical Q &Q with µ n C x 8 m, t, λ 0. F G 0 an B F G. epeat the execise f λ 0. -. This execise shws
Execises f iffeential mplifies ECE 0, Fall 0, F. Najmabai Execise : Cmpute,, an G if m, 00 Ω, O, an ientical Q &Q with µ n C x 8 m, t, λ 0. F G 0 an B F G. epeat the execise f λ 0. -. This execise shws
Contact, information, consultations
 ontact, nfomaton, consultatons hemsty A Bldg; oom 07 phone: 058-347-769 cellula: 664 66 97 E-mal: wojtek_c@pg.gda.pl Offce hous: Fday, 9-0 a.m. A quote of the week (o camel of the week): hee s no expedence
ontact, nfomaton, consultatons hemsty A Bldg; oom 07 phone: 058-347-769 cellula: 664 66 97 E-mal: wojtek_c@pg.gda.pl Offce hous: Fday, 9-0 a.m. A quote of the week (o camel of the week): hee s no expedence
Scalars and Vectors Scalar
 Scalas and ectos Scala A phscal quantt that s completel chaacteed b a eal numbe (o b ts numecal value) s called a scala. In othe wods a scala possesses onl a magntude. Mass denst volume tempeatue tme eneg
Scalas and ectos Scala A phscal quantt that s completel chaacteed b a eal numbe (o b ts numecal value) s called a scala. In othe wods a scala possesses onl a magntude. Mass denst volume tempeatue tme eneg
Lecture 12. Heat Exchangers. Heat Exchangers Chee 318 1
 Lecture 2 Heat Exchangers Heat Exchangers Chee 38 Heat Exchangers A heat exchanger s used t exchange heat between tw fluds f dfferent temperatures whch are separated by a sld wall. Heat exchangers are
Lecture 2 Heat Exchangers Heat Exchangers Chee 38 Heat Exchangers A heat exchanger s used t exchange heat between tw fluds f dfferent temperatures whch are separated by a sld wall. Heat exchangers are
A) 100 K B) 150 K C) 200 K D) 250 K E) 350 K
 Phys10 Secnd Maj-09 Ze Vesin Cdinat: k Wednesday, May 05, 010 Page: 1 Q1. A ht bject and a cld bject ae placed in themal cntact and the cmbinatin is islated. They tansfe enegy until they each a final equilibium
Phys10 Secnd Maj-09 Ze Vesin Cdinat: k Wednesday, May 05, 010 Page: 1 Q1. A ht bject and a cld bject ae placed in themal cntact and the cmbinatin is islated. They tansfe enegy until they each a final equilibium
CHAPTER 24 GAUSS LAW
 CHAPTR 4 GAUSS LAW LCTRIC FLUX lectic flux is a measue f the numbe f electic filed lines penetating sme suface in a diectin pependicula t that suface. Φ = A = A csθ with θ is the angle between the and
CHAPTR 4 GAUSS LAW LCTRIC FLUX lectic flux is a measue f the numbe f electic filed lines penetating sme suface in a diectin pependicula t that suface. Φ = A = A csθ with θ is the angle between the and
Analysis and Simulation of a 42V Power System for Automotive Applications
 Analyss and Smulatn f a 42V Pwe System f Autmtve Applcatns Mhamed A Shud Hgh nsttute f Electnc Pfessns TplLbya mshud@htmalcm D Ama Busbane Unvesty f Deby Deby UK Abusbane@debyacuk Abdulghena Elazag Lughbugh
Analyss and Smulatn f a 42V Pwe System f Autmtve Applcatns Mhamed A Shud Hgh nsttute f Electnc Pfessns TplLbya mshud@htmalcm D Ama Busbane Unvesty f Deby Deby UK Abusbane@debyacuk Abdulghena Elazag Lughbugh
ECEN474/704: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Spring 2018
 EEN474/704: (Anal) LSI cut De S 08 Lectue 8: Fequency ene Sa Pale Anal & Mxed-Sal ente Texa A&M Unety Annunceent & Aenda HW Due Ma 6 ead aza hate 3 & 6 Annunceent & Aenda n-suce A Fequency ene Oen-cut
EEN474/704: (Anal) LSI cut De S 08 Lectue 8: Fequency ene Sa Pale Anal & Mxed-Sal ente Texa A&M Unety Annunceent & Aenda HW Due Ma 6 ead aza hate 3 & 6 Annunceent & Aenda n-suce A Fequency ene Oen-cut
V. Principles of Irreversible Thermodynamics. s = S - S 0 (7.3) s = = - g i, k. "Flux": = da i. "Force": = -Â g a ik k = X i. Â J i X i (7.
 Themodynamcs and Knetcs of Solds 71 V. Pncples of Ievesble Themodynamcs 5. Onsage s Teatment s = S - S 0 = s( a 1, a 2,...) a n = A g - A n (7.6) Equlbum themodynamcs detemnes the paametes of an equlbum
Themodynamcs and Knetcs of Solds 71 V. Pncples of Ievesble Themodynamcs 5. Onsage s Teatment s = S - S 0 = s( a 1, a 2,...) a n = A g - A n (7.6) Equlbum themodynamcs detemnes the paametes of an equlbum
Multipole Radiation. March 17, 2014
 Multpole Radaton Mach 7, 04 Zones We wll see that the poblem of hamonc adaton dvdes nto thee appoxmate egons, dependng on the elatve magntudes of the dstance of the obsevaton pont,, and the wavelength,
Multpole Radaton Mach 7, 04 Zones We wll see that the poblem of hamonc adaton dvdes nto thee appoxmate egons, dependng on the elatve magntudes of the dstance of the obsevaton pont,, and the wavelength,
Celso José Faria de Araújo, M.Sc.
 Celso José Faa de Aaújo, M.c. he deal dode: (a) dode ccut symbol; (b) - chaactestc; (c) equalent ccut n the eese decton; (d) equalent ccut n the fowad decton. odes (a) Rectfe ccut. (b) nput waefom. (c)
Celso José Faa de Aaújo, M.c. he deal dode: (a) dode ccut symbol; (b) - chaactestc; (c) equalent ccut n the eese decton; (d) equalent ccut n the fowad decton. odes (a) Rectfe ccut. (b) nput waefom. (c)
Lecture 13. Wireless Communications. Agenda: Simplified Transceiver Architecture. A 3-Band MEMS Wireless System. RF MEMS: Introduction
 EE6935 Advanced MEMS (Spng 25) Instucto: D. Huka Xe Weless Communcatons Agenda: ectue 3 RF MEMS: Intoducton G Analog (sngle-band) 9 MHz Voce Maco cell 2G Dgtal (dual-mode, dual-band) GSM (Global System
EE6935 Advanced MEMS (Spng 25) Instucto: D. Huka Xe Weless Communcatons Agenda: ectue 3 RF MEMS: Intoducton G Analog (sngle-band) 9 MHz Voce Maco cell 2G Dgtal (dual-mode, dual-band) GSM (Global System
A) N B) 0.0 N C) N D) N E) N
 Cdinat: H Bahluli Sunday, Nvembe, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Five identical pint chages each with chage =10 nc ae lcated at the cnes f a egula hexagn, as shwn in Figue 1. Find the magnitude f the net electic fce
Cdinat: H Bahluli Sunday, Nvembe, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Five identical pint chages each with chage =10 nc ae lcated at the cnes f a egula hexagn, as shwn in Figue 1. Find the magnitude f the net electic fce
CHAPTER 17. Solutions for Exercises. Using the expressions given in the Exercise statement for the currents, we have
 CHATER 7 Slutin f Execie E7. F Equatin 7.5, we have B gap Ki ( t ) c( θ) + Ki ( t ) c( θ 0 ) + Ki ( t ) c( θ 40 a b c ) Uing the expein given in the Execie tateent f the cuent, we have B gap K c( ωt )c(
CHATER 7 Slutin f Execie E7. F Equatin 7.5, we have B gap Ki ( t ) c( θ) + Ki ( t ) c( θ 0 ) + Ki ( t ) c( θ 40 a b c ) Uing the expein given in the Execie tateent f the cuent, we have B gap K c( ωt )c(
Physics 11b Lecture #2. Electric Field Electric Flux Gauss s Law
 Physcs 11b Lectue # Electc Feld Electc Flux Gauss s Law What We Dd Last Tme Electc chage = How object esponds to electc foce Comes n postve and negatve flavos Conseved Electc foce Coulomb s Law F Same
Physcs 11b Lectue # Electc Feld Electc Flux Gauss s Law What We Dd Last Tme Electc chage = How object esponds to electc foce Comes n postve and negatve flavos Conseved Electc foce Coulomb s Law F Same
Hotelling s Rule. Therefore arbitrage forces P(t) = P o e rt.
 Htelling s Rule In what fllws I will use the tem pice t dente unit pfit. hat is, the nminal mney pice minus the aveage cst f pductin. We begin with cmpetitin. Suppse that a fim wns a small pa, a, f the
Htelling s Rule In what fllws I will use the tem pice t dente unit pfit. hat is, the nminal mney pice minus the aveage cst f pductin. We begin with cmpetitin. Suppse that a fim wns a small pa, a, f the
CSJM University Class: B.Sc.-II Sub:Physics Paper-II Title: Electromagnetics Unit-1: Electrostatics Lecture: 1 to 4
 CSJM Unvesty Class: B.Sc.-II Sub:Physcs Pape-II Ttle: Electomagnetcs Unt-: Electostatcs Lectue: to 4 Electostatcs: It deals the study of behavo of statc o statonay Chages. Electc Chage: It s popety by
CSJM Unvesty Class: B.Sc.-II Sub:Physcs Pape-II Ttle: Electomagnetcs Unt-: Electostatcs Lectue: to 4 Electostatcs: It deals the study of behavo of statc o statonay Chages. Electc Chage: It s popety by
Remember: When an object falls due to gravity its potential energy decreases.
 Chapte 5: lectc Potental As mentoned seveal tmes dung the uate Newton s law o gavty and Coulomb s law ae dentcal n the mathematcal om. So, most thngs that ae tue o gavty ae also tue o electostatcs! Hee
Chapte 5: lectc Potental As mentoned seveal tmes dung the uate Newton s law o gavty and Coulomb s law ae dentcal n the mathematcal om. So, most thngs that ae tue o gavty ae also tue o electostatcs! Hee
UNIT10 PLANE OF REGRESSION
 UIT0 PLAE OF REGRESSIO Plane of Regesson Stuctue 0. Intoducton Ojectves 0. Yule s otaton 0. Plane of Regesson fo thee Vaales 0.4 Popetes of Resduals 0.5 Vaance of the Resduals 0.6 Summay 0.7 Solutons /
UIT0 PLAE OF REGRESSIO Plane of Regesson Stuctue 0. Intoducton Ojectves 0. Yule s otaton 0. Plane of Regesson fo thee Vaales 0.4 Popetes of Resduals 0.5 Vaance of the Resduals 0.6 Summay 0.7 Solutons /
Magnetism. Chapter 21
 1.1 Magnetic Fields Chapte 1 Magnetism The needle f a cmpass is pemanent magnet that has a nth magnetic ple (N) at ne end and a suth magnetic ple (S) at the the. 1.1 Magnetic Fields 1.1 Magnetic Fields
1.1 Magnetic Fields Chapte 1 Magnetism The needle f a cmpass is pemanent magnet that has a nth magnetic ple (N) at ne end and a suth magnetic ple (S) at the the. 1.1 Magnetic Fields 1.1 Magnetic Fields
element k Using FEM to Solve Truss Problems
 sng EM t Slve Truss Prblems A truss s an engneerng structure cmpsed straght members, a certan materal, that are tpcall pn-ned at ther ends. Such members are als called tw-rce members snce the can nl transmt
sng EM t Slve Truss Prblems A truss s an engneerng structure cmpsed straght members, a certan materal, that are tpcall pn-ned at ther ends. Such members are als called tw-rce members snce the can nl transmt
Section 4.2 Radians, Arc Length, and Area of a Sector
 Sectin 4.2 Radian, Ac Length, and Aea f a Sect An angle i fmed by tw ay that have a cmmn endpint (vetex). One ay i the initial ide and the the i the teminal ide. We typically will daw angle in the cdinate
Sectin 4.2 Radian, Ac Length, and Aea f a Sect An angle i fmed by tw ay that have a cmmn endpint (vetex). One ay i the initial ide and the the i the teminal ide. We typically will daw angle in the cdinate
3. A Review of Some Existing AW (BT, CT) Algorithms
 3. A Revew of Some Exstng AW (BT, CT) Algothms In ths secton, some typcal ant-wndp algothms wll be descbed. As the soltons fo bmpless and condtoned tansfe ae smla to those fo ant-wndp, the pesented algothms
3. A Revew of Some Exstng AW (BT, CT) Algothms In ths secton, some typcal ant-wndp algothms wll be descbed. As the soltons fo bmpless and condtoned tansfe ae smla to those fo ant-wndp, the pesented algothms
Stellar Astrophysics. dt dr. GM r. The current model for treating convection in stellar interiors is called mixing length theory:
 Stella Astophyscs Ovevew of last lectue: We connected the mean molecula weght to the mass factons X, Y and Z: 1 1 1 = X + Y + μ 1 4 n 1 (1 + 1) = X μ 1 1 A n Z (1 + ) + Y + 4 1+ z A Z We ntoduced the pessue
Stella Astophyscs Ovevew of last lectue: We connected the mean molecula weght to the mass factons X, Y and Z: 1 1 1 = X + Y + μ 1 4 n 1 (1 + 1) = X μ 1 1 A n Z (1 + ) + Y + 4 1+ z A Z We ntoduced the pessue
PT326 PROCESS TRAINER
 PT326 PROCESS TRAINER 1. Descrptn f the Apparatus PT 326 Prcess Traner The PT 326 Prcess Traner mdels cmmn ndustral stuatns n whch temperature cntrl s requred n the presence f transprt delays and transfer
PT326 PROCESS TRAINER 1. Descrptn f the Apparatus PT 326 Prcess Traner The PT 326 Prcess Traner mdels cmmn ndustral stuatns n whch temperature cntrl s requred n the presence f transprt delays and transfer
Solutions: Solution. d = 3.0g/cm we can calculate the number of Xe atoms per unit volume, Given m and the given values from Table 7.
 Tutial-09 Tutial - 09 Sectin6: Dielectic Mateials ECE:09 (Electnic and Electical Ppeties f Mateials) Electical and Cmpute Engineeing Depatment Univesity f Watel Tut: Hamid Slutins: 7.3 Electnic plaizatin
Tutial-09 Tutial - 09 Sectin6: Dielectic Mateials ECE:09 (Electnic and Electical Ppeties f Mateials) Electical and Cmpute Engineeing Depatment Univesity f Watel Tut: Hamid Slutins: 7.3 Electnic plaizatin
The three major operations done on biological signals using Op-Amp:
 The three majr peratns dne n blgcal sgnals usng Op-Amp: ) Amplcatns and Attenuatns 2) DC settng: add r subtract a DC 3) Shape ts requency cntent: Flterng Ideal Op-Amp Mst belectrc sgnals are small and
The three majr peratns dne n blgcal sgnals usng Op-Amp: ) Amplcatns and Attenuatns 2) DC settng: add r subtract a DC 3) Shape ts requency cntent: Flterng Ideal Op-Amp Mst belectrc sgnals are small and
Notes on Inductance and Circuit Transients Joe Wolfe, Physics UNSW. Circuits with R and C. τ = RC = time constant
 Nes n Inducance and cu Tansens Je Wlfe, Physcs UNSW cus wh and - Wha happens when yu clse he swch? (clse swch a 0) - uen flws ff capac, s d Acss capac: Acss ess: c d s d d ln + cns. 0, ln cns. ln ln ln
Nes n Inducance and cu Tansens Je Wlfe, Physcs UNSW cus wh and - Wha happens when yu clse he swch? (clse swch a 0) - uen flws ff capac, s d Acss capac: Acss ess: c d s d d ln + cns. 0, ln cns. ln ln ln
Example 11: The man shown in Figure (a) pulls on the cord with a force of 70
 Chapte Tw ce System 35.4 α α 100 Rx cs 0.354 R 69.3 35.4 β β 100 Ry cs 0.354 R 111 Example 11: The man shwn in igue (a) pulls n the cd with a fce f 70 lb. Repesent this fce actin n the suppt A as Catesian
Chapte Tw ce System 35.4 α α 100 Rx cs 0.354 R 69.3 35.4 β β 100 Ry cs 0.354 R 111 Example 11: The man shwn in igue (a) pulls n the cd with a fce f 70 lb. Repesent this fce actin n the suppt A as Catesian
If there are k binding constraints at x then re-label these constraints so that they are the first k constraints.
 Mathematcal Foundatons -1- Constaned Optmzaton Constaned Optmzaton Ma{ f ( ) X} whee X {, h ( ), 1,, m} Necessay condtons fo to be a soluton to ths mamzaton poblem Mathematcally, f ag Ma{ f ( ) X}, then
Mathematcal Foundatons -1- Constaned Optmzaton Constaned Optmzaton Ma{ f ( ) X} whee X {, h ( ), 1,, m} Necessay condtons fo to be a soluton to ths mamzaton poblem Mathematcally, f ag Ma{ f ( ) X}, then
Design of Analog Integrated Circuits
 Design f Analg Integated Cicuits Opeatinal Aplifies Design f Analg Integated Cicuits Fall 01, D. Guxing Wang 1 Outline Mdel f Opeatinal Aplifies Tw Stage CMOS Op Ap Telescpic Op Ap Flded-Cascde Op Ap Refeence
Design f Analg Integated Cicuits Opeatinal Aplifies Design f Analg Integated Cicuits Fall 01, D. Guxing Wang 1 Outline Mdel f Opeatinal Aplifies Tw Stage CMOS Op Ap Telescpic Op Ap Flded-Cascde Op Ap Refeence
ANALOG ELECTRONICS 1 DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH
 24 ANALOG LTRONIS TUTORIAL DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH . 0 8kΩ Gen, Y β β 00 T F 26, 00 0.7 (a)deterne the dc ltages at the 3 X ternals f the JT (,, ). 0kΩ Z (b) Deterne g,r π and r? (c) Deterne the ltage gan
24 ANALOG LTRONIS TUTORIAL DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH . 0 8kΩ Gen, Y β β 00 T F 26, 00 0.7 (a)deterne the dc ltages at the 3 X ternals f the JT (,, ). 0kΩ Z (b) Deterne g,r π and r? (c) Deterne the ltage gan
Lecture #2 : Impedance matching for narrowband block
 Lectue # : Ipedance atching f nawband blck ichad Chi-Hsi Li Telephne : 817-788-848 (UA) Cellula phne: 13917441363 (C) Eail : chihsili@yah.c.cn 1. Ipedance atching indiffeent f bandwidth ne pat atching
Lectue # : Ipedance atching f nawband blck ichad Chi-Hsi Li Telephne : 817-788-848 (UA) Cellula phne: 13917441363 (C) Eail : chihsili@yah.c.cn 1. Ipedance atching indiffeent f bandwidth ne pat atching
