(5) Furthermore, the third constraint implies the following equation: (6)
|
|
|
- Elwin Chambers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 T-Element Refactng System f Gaussan and Annula-Gaussan Beams Tansfmatn Abdallah K. Che *, Nabl I. Khachab, Mahmud K. Habb Electcal Engneeng Depatment, Cllege f Engneeng and Petleum, Kuat Unvesty, P. O. Bx 99, Safat, Kuat abdallah.che@ku.edu.k (Receved th Octbe, 7; Revsed th Decembe 7; Accepted th Decembe, 7; Publshed: 9 th Januay, ) Abstact- In ths pape, a efactng system cmpsed f t sepaate lenses s desgned t btan specfc lase adance dstbutns. Namely, the lens sufaces (nput and utput) ae deved f thee types f lase beam tansfmatn: () Gaussan t Annula-unfm; () Annula-Gaussan t Annula-unfm; and () Annula-Gaussan t Gaussan, takng nt cnsdeatn the system length, the sufaces ad f cuvatue and the ntal efactng angle f annula beams. Key Wds: Gaussan beam, Refactng system, Lens desgn.. INTRODUCTION The TEM (Gaussan) lase beam s ne f the mst lase types n cuent use f many applcatns hee a small fcusng spt s needed. Heve, thee ae many the applcatns hee unfm ntensty dstbutn s equed such as n cheent mage pcessng, patten ecgntn, and mateals pcessng tasks [-7]. Thus, t fulfl ths need, the cnvesn f Gaussan and nn-gaussan lase beams t unfm beam pfles appeas t be vey benefcal. Refactve ptcal system methd, hch eles n gemetc ptcs, s amng the methds that can make ths cnvesn [-]. Ove the yeas, seveal publcatns, descbng snglelens and t-lens efactng system, ee ppsed t acheve beam shapng such as Gaussan and annula-gaussan beam tansfmatn t unfm beams, as ell as t Bessel beam pfles [-]. In ths k, e ae ppsng a t-element efactng beam shapng systems t cnvet thee types f beams that ee nt cnsdeed befe: () Gaussan t Annula-unfm; () Annula-Gaussan t Annula-unfm; and () Annula- Gaussan t Gaussan. The mathematcal expessns that epesent the cuvatue and the asphecty f the nput and utput lenses ae deved. In addtn, dscussns f the vaus paametes that ae affectng the ppsed desgns ae pesented such as the veall length f the system, the ad f cuvatue f the sufaces, and the ntal efactng angle f annula beams.. DESIGN PROCEDURE The gemetcal ptcs methd f beam shapng mpses thee man cnstants hen desgnng the efactng ptcal system. These ae: () Optcal path length: all the ays that ente the fst lens and leave the secnd lens must have the same ptcal path length. () Ray Paallelsm: the utput ays that exst fm the system must be paallel t the nput ays. () Enegy cnsevatn: the at f the nput beam pe t the utput beam pe must be a cnstant. Fg. llustates the gemetcal cnfguatn f the tlens efactng system f Gaussan t annula-unfm beam tansfmatn. The same set-up can als be used f the beam shapes by makng sme apppate mdfcatns. The t lenses ae made fm glass (ndex f efactn n = 7) and ae sepaated (by a hee ndex f efactn n = ) by a dstance D. A ay entes nput lens th an angle θ and then s efacted by an angle θ. Ths ay tavels n a and eaches the secnd lens th an angle θ and then t s efacted by an angle θ and exts paallel t the fst ncdent ay. In the fgue, the nput and utput lenses ae epesented by the mathematcal sufaces functns y ( ) and y ( ), espectvely. Fm the gemety f the set-up n Fg., ne can deduce that: tan( ) tan( ) () D y y N, the abve fst cnstant s tanslated nt the fllng equatn: ny ( ) ( Dy y ) n( dy ) f () hee f s a cnstant. Addng (-nd) tem t bth sdes f Eq. (), yelds: ndny ny ( ) ( Dy y ) f ndnd Let f = f-nd-ndand use Eq. (), e btan: ' n sec( ) f () tan( ) tan( ) Next, the ay s paallelsm cnstant dctates that bth the nput and the utput sufaces slpes must be equal t each the, namely: dy dy tan tan () d Futhe, by applyng Snell s la at the nput lens (nsnθ = snθ ) and usng tgnmetc denttes, ne can btan fm Eq. () and Eq. () the fllng mptant elatnshp: dy dy () f' n Futheme, the thd cnstant mples the fllng equatn: Enegy k cnstant () Enegy Eq. () and Eq. () ll be usedt btan the mathematcal expessns y ( ) and y ( ) f the nput and the utput Page
2 sufaces f the lenses. The desgn pcedue stats th the selectn f the system length and the pe at k fm hch ne btans the elatnshp beteen the adal dstances and. Next, the sufaces slpes dy / and dy / n Eq. () ae numecally btaned fm hch e get the numecal values f the sufaces y ( ) and y ( ) by numecal ntegatn. A plynmal cuve-fttng utne s used t btan the mathematcal expessns f these sufaces. Nte that e need t apply apppate ntal values n the sufaces t btan the cnstants f ntegatns. It s th mentnng that f pactcal ssues, bth the veall system length and the statng suface slpe ae pefeed t be as small as pssble. Futhe, a lage adus f cuvatue ρ() f the sufaces s pefeable t help manage the fabcatn pcess. ρ() f any suface s gven by: / [( dy ) ] ( ) (7) d y Eventually, the secnd devatve f the statng suface slpe d y needs t be small. Glass A Glass R y y D d Ie k () I( R ) Whee s the adus f the nput Gaussan beam; R and ae the nne and the ute ad f the utput annula beam. Eq. () ll be slved t btan: (e ) k R (9a) ln( k ( R ) ) (9b) These equatns alng th Eq. () ae used t desgn the t-lens efactng system. T demnstate the desgn pcedue, let us cnsde the tansfmatn f a Gaussan beam ( = cm) t an annulaunfm beam (R = cm) hee the pe at f the t beams s k =. An apppate system length D needs t be chsen. In ths egad, e have pvded a plt (Fg. a) that llustates the system length, the statng suface slpe, and the stang adus f cuvatue vesus the statng dffactn angle θ. Fm the fgue, bth the system length and the adus f cuvatue decease hen the efactng angle θ nceases. Cnsequently, e have selected a mdeate value f θ =.77 hch cespnds t D =.9 cm and f =. Usng these values n equatns (), (), and (), e can btan the numecal values f the suface slpes dy and d dy. The mathematcal expessns f these slpes ae acheved usng a plynmal cuve-fttng utne t yeld: dy (.) (.) (.) (a) (.) dy (9) (.77) (.99) (.7). Integatng the abve expessns t btan appxmate equatns f lenses sufaces as: - - y ( ) (.x ) (.) (.7x ) (a) (.) ().7 (b) Fg. : The gemetc set-up f the t-element efactn system beam tansfmatn.. LASER BEAM TRANSFORMATIONS In ths sectn, the mathematcal expessns y ( ) and y ( ) f the nput and the utput sufaces f the lenses ae deved f thee dffeent types f beam tansfmatns.. GAUSSIAN TO ANNULAR-UNIFORM BEAM TRANSFORMATION As shn n Fg., a Gaussan nput beam pfle ll be edstbuted by the t-lens set-up t fm an annulaunfm utput beam pfle. The cnsevatn f enegy cnstant mples that ntenstes must be cnseved ve the css-sectnal aeas f the t beams: y ( ) (.7) (9) (.99) (b) (9) -(.).99 Equatn () s pltted n Fg. b. The ad f cuvatue f the sufaces f ths desgn ae shn n Fgs. c and d. The adus f cuvatue f the nput lens stats th a value f. cm t each a maxmum value f 7 cm and then deceases t a value f 7.9 cm; hle f the utput suface, t stats th a value f.9 cm t each a maxmum value f cm and then deceases t a value f. cm. In geneal f annula beam, f a fxed pe at k, the statng efactng angle θ = sn - (nsnθ ) fm the nne adus s ctcal n decdng the length f the t-element lens desgn, n addtn t the facts such as the ntal suface slpe and the ntal adus f cuvatue f the suface. Fg. shs the lenses sufaces f anthe desgn hee the nne adus f the annula beam s set t R = cm nstead f cm. Page
3 . f' = ; R = ; k = f' = ; R = ; k = D: System length (cm) dy/: Intal suface slpe Intal adus f cuvatue.. X:.77 Y:.9 Radal dstance (cm) (a) - efactng angle n degee (b) f' = ; R = ; k = 7 x f' = ; R = ; k = suface adus f cuvatue (cm) X:. Y:.7e+ suface adus f cuvatue (cm) X:. Y:.e+ Radal dstance Radal dstance (c) (d) Fg. : Gaussan t annula-unfm desgn: (a) effect f the efactng angle n the system length; (b) the nput and the utput sufacesy ( ) and y ( );(c) and (d) the ad f cuvatue. Fm Fg. a, ne ecgnzes that f a efactng angle θ =.77, the system length s almst dubled (D = 7.7 cm). T btan a system length f D =.9 cm, θ must ncease t 7. as ndcated by the a shn n Fg. a.. ANNULAR-GAUSSIAN TO ANNULAR-UNIFORM BEAM TRANSFORMATION The efactng t-lens beam tansfmatn desgn f annula-gaussan t annula-unfm pfle s demnstated n ths subsectn. Statng th the enegy balance equatn beteen the t dffeent beams: I [ Re ] e R g k () I( Ra) Whee R a and ae the nne and the ute ad f the utput annula-unfm beam and I s the peak nput beam ntensty. F the annula-gaussan beam, R g and ae the nne and the ute ad; s the annula-gaussan beam adus; ( M ) s the beam spt sze n the lage Fesnel numbe lmt; M s the magnfcatn; R s the eflectvty f the cental m. Page 7
4 R = ; k = D: System length (cm) dy/: Intal suface slpe Intal adus f cuvatue f' = ; R = ; k = X:.77 Y: Refactn angle (degee) Radal dstance (a) (b) Fg. : Gaussan t annula-unfm desgn: (a) effect f nne adus R f the annula beam n the efactng angle and n the system length; (b) the nput and the utput sufaces f R = cm. Ra = ; Rg = ; k = D: System length (cm) dy/: Intal suface slpe Intal adus f cuvatue. X:.77 Y:.9 Radus f cuvatue. - Refactng angle (degee) Radal dstance Radal dstance (a) (b) (c) Fg. : Annula-Gaussan t annula-unfm desgn: (a) chsng the system length f a specfc efactng angle; (b) the nput and the utput ad f cuvatue; (c) the nput and the utput sufaces. The ntegal n Eq. () can be slved t btan the utput adus: R/ ( [ ) R ( g ) ] e e ( ) {( ) } R a k R g () ( e e )/ Nte that hen M.Cnsequently, Eq. () s smplfed t: ( Rg )/ {( ) R e e R } a k R g () ( e e )/ The desgn shn n Fg. s f tansfmng beams th R a =, R g =, =, k =, R =.9, hee e have selected a mdeate value f θ =.77 hch cespnds t D =.9 cm and f =. Usng these values n equatns (), (), and (), e can btan the numecal values f the suface slpes dy and d dy. The mathematcal expessns f these Page
5 a = ; g = ; Rg = ; k = D: System length dy/: Intal suface slpe Intal adus f cuvatue Radus f cuvatue. x a = ; g = ; Rg = ; k =.... a = ; g = ; Rg =; k = - Refactng angle (degee) Radal dstance Radal dstance (a) (b) (c) Fg. : Annula-Gaussan t Gaussan desgn: (a) chsng the system length f a specfc efactng angle; (b) the nput and the utput ad f cuvatue; (c) the nput and the utput sufaces. slpes ae acheved usng a plynmal cuve-fttng utne t yeld: dy (.) (.9) (.979) (a) (.) dy (.) (.9) (.77) (.99).7 N, ntegate the abve equatns t btan the appxmate expessns f lens sufaces as: - (b) y ( ) (7.7x ) (.7 (9) (a) (.) (). y ( ) (.) (.) () (b) (9) -(.7) 9 Nte that the adus f cuvatue f nput suface changes fm a mnmum value f. cm t maxmum value f 9.7 cm. And the adus f cuvatue f utput suface changes fm a mnmum value f. cm and eaches a maxmum value f 9 cm.. ANNULAR-GAUSSIAN TO GAUSSIAN BEAM TRANSFORMATION The pe at f the annula-gaussan beam t the Gaussan beam s: k I [ R e R g a ] e (7) g I ( e ) g Whee g s the adus f the utput Gaussan beam; a s the annula Gaussan beam adus; and R g ae the ute and the nne ad f the nput annula-gaussan beam; I s the ( M ) peak nput beam ntensty; s the beam spt sze n the lage Fesnel numbe lmt; M s the magnfcatn; R s the eflectvty f the cental m. Nte that a hen M. The ntegal n Eq. (7) s slved t btan the utput adus f the Gaussan beam: a a R ( e e a) k g () g { ln } R R a a ( ) e e a k g In ths subsectn, e pvde a desgn f tansfmng beams th R g =, a =, g =, k =, R =.9. In de t btan a system length smla t the pevus t desgns,.e. D =.9 cm and f =, e have selected θ = 7. (see Fg. ). Agan, usng these values n equatns (),(), and (), e can btan the numecal values f the sufaces slpes dy dy and, fm hch the mathematcal expessns f d these slpes ae: dy (.) (.) (.7) (9a) (9) 9 dy (.7) (.7). () (7) (9b) Accdngly, the appxmate equatns f the lens sufaces ae: y( ) (.x (.9) ) (9) - (.).9 (.7) (a) y ( ) (.9x ) (.) (.7) (b) (.) -(.) Page 9
6 The adus f cuvatue f the nput suface changes fm a value f 9. cm t a value f.x cm; hle the adus f cuvatue f utput suface changes fm a mnmum f 9.7 cm eachng.x cm.. CONCLUSION A desgn pcedue f tansfmng lase beam pfles s dscussed n ths k usng t-element ptcal efactng system. The pcedue s appled t thee types f beam tansfmatns, hch ee nt adessed pevusly: () Gaussan t annula-unfm; () annula-gaussan t annulaunfm; and () annula-gaussan t Gaussan. The mathematcal expessns f the t plan-asphec sufaces ae deved f the thee types f lase beams. In addtn, fe mptant paametes such as the length f the set-up, the ad f cuvatue f the sufaces, and the ntal efactng angle f annula beam ee dscussed. REFERENCES [] J. Wlsn, and J. F. B. Hakes, Lase Pncples and Applcatns, Pentce Hall Intenatnal, Hetfdshe, UK, 97. [] J. C. In, Lase Pcessng f Engneeng Mateals: Pncples, Pcedue, and Industal Applcatn, Elseve Butteth-Henemann, Bulngtn, MA,. [] Naena B. Dahte, Sandp Hamka, Lase Fabcatn and Machnng f Mateals, Spnge, Ne Yk, NY,. [] C. Bschff, E. Jäge, and U. Umhfe, Beam Shapng Optcs f Pcess Acceleatn: Inceasng the pductvty f lase mcmachnng, Lase Technk Junal, vl., n., pp. -7,. [] M. Ducastella, and C. B. Anld, Bessel and annula beams f mateals pcessng, Lase Phtncs Rev., vl., n., pp. 7,. [] M. Allmen, and A. Blatte, Lase-Beam Inteactns th Mateals, Spnge-Velag, Beln, pp., 99. [7] F. M. Dckey, Lase Beam Shapng: They and Technques, Secnd Edtn, CRC Pess Publshng, 7. [] F. M. Dckey, and T. E. Lztte, Lase Beam Shapng Applcatns, Secnd Edtn, CRC Pess, publshng, 7. [9] D. L. Shealy, and S. Cha, Gemetc Optcs-based desgn f lase beam shapes, Opt. Eng., vl., n., pp. -,. [] A. J. Cx, and D. C. Dbble, Hlgaphc epductn f a dffactn-fee beam, Appl. Opt., vl., n., pp. -, 99. [] M. L, Y. Meuet, M. Vevaeke, H. Thenpnt, and F. Due, Desgn f fcal beam shapng system thugh adance and phase cntl, SPIE Pc. In Optcal Mdellng and Desgn IV (Vl. 99),. [] F. Due, and H. Thenpnt, Refactve lase beam shapng by means f a functnal dffeental equatn based desgn appach, Opt. Exp., vl., n. 7, pp. -,. [] G. Ede, G. Szavas, E. Lncz, and S. Vakny, Sngle-element efactve ptcal devce f lase beam pflng, Pc. SPIE Senss, Sens System, and Sens Data Pcessng, vl., pp., 997. [] J. A. Hffnagle, and C. M. Jeffesn, Beam shapng th a plan-asphec lens pa, Opt. Eng., vl., n., pp. 9-99,. [] M. Af, N. M. Hssan, A. A. S. Aal, and M. N. Islam, T-element efactng system f annula Gaussan-t-Bessel beam tansfmatn, Appl. Opt., vl. 7, n. 9, pp. -9, 99. [] H. K. Iftekhauddn, A. A. S.Aal, and M. A. Kam, Gaussan-t-Bessel beam tansfmatn usng a splt efactng system, Appl. Opt., vl., n., pp. -, 99. [7] M. A. Kam, A. K. Che, A. A. S.Aal, A. Bast, Refactng system f annula lase beam tansfmatn, Appl. Opt., vl., n., pp. - 9, 97. [] S. R. Jahan, and M. A. Kam, Refactng systems f Gaussan-t-unfm beam tansfmatns, Opt. Lase Technl., vl., n., pp. 7-, 99. [9] K. Thees, M. A. Kam, and A. A. S. Aal, Dffactn-fee beam geneatn usng efactng systems, Opt. Lase Technl., vl., n., pp., 99. [] M. Af, M. N. Hssan, A. A. S. Aal, and M. N. Islam, Refactng system f annula Gaussan-t- Bessel beam tansfmatn, Appl. Opt., vl. 7, n., pp. 9-, 99. Page
is needed and this can be established by multiplying A, obtained in step 3, by, resulting V = A x y =. = x, located in 1 st quadrant rotated about 2
 Ct Cllege f New Yk MATH (Calculus Ntes) Page 1 f 1 Essental Calculus, nd edtn (Stewat) Chapte 7 Sectn, and 6 auth: M. Pak Chapte 7 sectn : Vlume Suface f evlutn (Dsc methd) 1) Estalsh the tatn as and the
Ct Cllege f New Yk MATH (Calculus Ntes) Page 1 f 1 Essental Calculus, nd edtn (Stewat) Chapte 7 Sectn, and 6 auth: M. Pak Chapte 7 sectn : Vlume Suface f evlutn (Dsc methd) 1) Estalsh the tatn as and the
A criterion of warpage about center-anchored deformable focusing micromirrors
 A cten f wapage abut cente-anched defmable fcusng mcms MENG-JU LIN Depatment f Mechancal and Cmpute Aded Engneeng Feng Cha Unvesty N., Wen-Hwa Rd., achung, awan 7, R. O. C. AIWAN, R.O.C. Abstact: - A cten
A cten f wapage abut cente-anched defmable fcusng mcms MENG-JU LIN Depatment f Mechancal and Cmpute Aded Engneeng Feng Cha Unvesty N., Wen-Hwa Rd., achung, awan 7, R. O. C. AIWAN, R.O.C. Abstact: - A cten
Electric potential energy Electrostatic force does work on a particle : Potential energy (: i initial state f : final state):
 Electc ptental enegy Electstatc fce des wk n a patcle : v v v v W = F s = E s. Ptental enegy (: ntal state f : fnal state): Δ U = U U = W. f ΔU Electc ptental : Δ : ptental enegy pe unt chag e. J ( Jule)
Electc ptental enegy Electstatc fce des wk n a patcle : v v v v W = F s = E s. Ptental enegy (: ntal state f : fnal state): Δ U = U U = W. f ΔU Electc ptental : Δ : ptental enegy pe unt chag e. J ( Jule)
LEAP FROG TECHNIQUE. Operational Simulation of LC Ladder Filters ECEN 622 (ESS) TAMU-AMSC
 LEAP FOG TEHNQUE Opeatnal Smulatn f L Ladde Fltes L pttype lw senstvty One fm f ths technque s called Leapf Technque Fundamental Buldn Blcks ae - nteats - Secnd-de ealzatns Fltes cnsdeed - LP - BP - HP
LEAP FOG TEHNQUE Opeatnal Smulatn f L Ladde Fltes L pttype lw senstvty One fm f ths technque s called Leapf Technque Fundamental Buldn Blcks ae - nteats - Secnd-de ealzatns Fltes cnsdeed - LP - BP - HP
Drawing of Hollow Multilayered All-Polymer Fibers
 Mate. Res. Sc. Symp. Pc. Vl. 90 006 Mateals Reseach Scety 090-S01-05 Dawng f Hllw Multlayeed All-Plyme Fbes El Pne, Chales Dubs, Nng Gu, Yan Ga, Alexande Dupus, Suanne Lacx, and Maksm Skbgaty Écle Plytechnque
Mate. Res. Sc. Symp. Pc. Vl. 90 006 Mateals Reseach Scety 090-S01-05 Dawng f Hllw Multlayeed All-Plyme Fbes El Pne, Chales Dubs, Nng Gu, Yan Ga, Alexande Dupus, Suanne Lacx, and Maksm Skbgaty Écle Plytechnque
Cork Institute of Technology. Spring 2005 DCE 3.5 Thermodynamics & Heat Transfer (Time: 3 Hours) Section A
 Ck Insttute f echnlgy Bachel f Engneeng (Hnus) n Chemcal and Pcess Engneeng Stage 3 Bachel f Engneeng n Chemcal and Pcess Engneeng Stage 3 (NFQ Level 8) Spng 005 DCE 3.5 hemdynamcs & Heat ansfe (me: 3
Ck Insttute f echnlgy Bachel f Engneeng (Hnus) n Chemcal and Pcess Engneeng Stage 3 Bachel f Engneeng n Chemcal and Pcess Engneeng Stage 3 (NFQ Level 8) Spng 005 DCE 3.5 hemdynamcs & Heat ansfe (me: 3
Designs of One-Element Refracting System for Gaussian and Annular-Gaussian Beams Transformations
 International Journal of Optics and Applications 9, 8(): - DOI:.9/j.optics.98. Designs of One-Element Refracting System for Gaussian and Annular-Gaussian Beams Transformations Abdallah K. Cherri *, Nabil
International Journal of Optics and Applications 9, 8(): - DOI:.9/j.optics.98. Designs of One-Element Refracting System for Gaussian and Annular-Gaussian Beams Transformations Abdallah K. Cherri *, Nabil
Module 9 Thin and thick cylinders
 Mdule 9 Thn and thck cylndes Vesn 2 ME, IIT Khaagu Lessn 3 Desgn ncles f thck cylndes Vesn 2 ME, IIT Khaagu Instuctnal Objectves: At the end f ths lessn, the students shuld have the knwledge f: Falue thees
Mdule 9 Thn and thck cylndes Vesn 2 ME, IIT Khaagu Lessn 3 Desgn ncles f thck cylndes Vesn 2 ME, IIT Khaagu Instuctnal Objectves: At the end f ths lessn, the students shuld have the knwledge f: Falue thees
CSJM University Class: B.Sc.-II Sub:Physics Paper-II Title: Electromagnetics Unit-1: Electrostatics Lecture: 1 to 4
 CSJM Unvesty Class: B.Sc.-II Sub:Physcs Pape-II Ttle: Electomagnetcs Unt-: Electostatcs Lectue: to 4 Electostatcs: It deals the study of behavo of statc o statonay Chages. Electc Chage: It s popety by
CSJM Unvesty Class: B.Sc.-II Sub:Physcs Pape-II Ttle: Electomagnetcs Unt-: Electostatcs Lectue: to 4 Electostatcs: It deals the study of behavo of statc o statonay Chages. Electc Chage: It s popety by
Optimization of the Electron Gun with a Permanent Ion Trap
 4.3.-178 Optmzatn f the Electn Gun wth a Pemanent In Tap We Le Xabng Zhang Jn Dng Fe Dpla Technlg R&D CenteSutheat Unvet Nangjng Chna Danel den Engelen Pduct and Pce Develpment(PPD)LG.Phlp Dpla 5600 MD
4.3.-178 Optmzatn f the Electn Gun wth a Pemanent In Tap We Le Xabng Zhang Jn Dng Fe Dpla Technlg R&D CenteSutheat Unvet Nangjng Chna Danel den Engelen Pduct and Pce Develpment(PPD)LG.Phlp Dpla 5600 MD
COMPLEMENTARY ENERGY METHOD FOR CURVED COMPOSITE BEAMS
 ultscence - XXX. mcocd Intenatonal ultdscplnay Scentfc Confeence Unvesty of skolc Hungay - pl 06 ISBN 978-963-358-3- COPLEENTRY ENERGY ETHOD FOR CURVED COPOSITE BES Ákos József Lengyel István Ecsed ssstant
ultscence - XXX. mcocd Intenatonal ultdscplnay Scentfc Confeence Unvesty of skolc Hungay - pl 06 ISBN 978-963-358-3- COPLEENTRY ENERGY ETHOD FOR CURVED COPOSITE BES Ákos József Lengyel István Ecsed ssstant
P 365. r r r )...(1 365
 SCIENCE WORLD JOURNAL VOL (NO4) 008 www.scecncewoldounal.og ISSN 597-64 SHORT COMMUNICATION ANALYSING THE APPROXIMATION MODEL TO BIRTHDAY PROBLEM *CHOJI, D.N. & DEME, A.C. Depatment of Mathematcs Unvesty
SCIENCE WORLD JOURNAL VOL (NO4) 008 www.scecncewoldounal.og ISSN 597-64 SHORT COMMUNICATION ANALYSING THE APPROXIMATION MODEL TO BIRTHDAY PROBLEM *CHOJI, D.N. & DEME, A.C. Depatment of Mathematcs Unvesty
ME311 Machine Design
 ME311 Machne Desgn Lectue 8: Cylnes W Dnfel Nv017 Fafel Unvesty Schl f Engneeng Thn-Walle Cylnes (Yu aleay cvee ths n Bee & Jhnstn.) A essuze cylne s cnsee t be Thn-Walle f ts wall thckness s less than.5%
ME311 Machne Desgn Lectue 8: Cylnes W Dnfel Nv017 Fafel Unvesty Schl f Engneeng Thn-Walle Cylnes (Yu aleay cvee ths n Bee & Jhnstn.) A essuze cylne s cnsee t be Thn-Walle f ts wall thckness s less than.5%
Selective Convexity in Extended GDEA Model
 Appled Mathematcal Scences, Vl. 5, 20, n. 78, 386-3873 Selectve nvet n Etended GDEA Mdel Sevan Shaee a and Fahad Hssenadeh Ltf b a. Depatment f Mathematcs, ehan Nth Banch, Islamc Aad Unvest, ehan, Ian
Appled Mathematcal Scences, Vl. 5, 20, n. 78, 386-3873 Selectve nvet n Etended GDEA Mdel Sevan Shaee a and Fahad Hssenadeh Ltf b a. Depatment f Mathematcs, ehan Nth Banch, Islamc Aad Unvest, ehan, Ian
ME 3600 Control Systems Frequency Domain Analysis
 ME 3600 Cntl Systems Fequency Dmain Analysis The fequency espnse f a system is defined as the steady-state espnse f the system t a sinusidal (hamnic) input. F linea systems, the esulting utput is itself
ME 3600 Cntl Systems Fequency Dmain Analysis The fequency espnse f a system is defined as the steady-state espnse f the system t a sinusidal (hamnic) input. F linea systems, the esulting utput is itself
Physics 11b Lecture #2. Electric Field Electric Flux Gauss s Law
 Physcs 11b Lectue # Electc Feld Electc Flux Gauss s Law What We Dd Last Tme Electc chage = How object esponds to electc foce Comes n postve and negatve flavos Conseved Electc foce Coulomb s Law F Same
Physcs 11b Lectue # Electc Feld Electc Flux Gauss s Law What We Dd Last Tme Electc chage = How object esponds to electc foce Comes n postve and negatve flavos Conseved Electc foce Coulomb s Law F Same
More Effective Optimum Synthesis of Path Generating Four-Bar Mechanisms
 Junal f Multdscplnay Engneeng Scence and Technlgy (JMEST) ISSN: 59- Vl. Issue 5, May - 5 Me Effectve Optmum Synthess f Path Geneatng Fu-Ba Mechansms Wen-Y Ln Depatment f Mechancal Engneeng De Ln Insttute
Junal f Multdscplnay Engneeng Scence and Technlgy (JMEST) ISSN: 59- Vl. Issue 5, May - 5 Me Effectve Optmum Synthess f Path Geneatng Fu-Ba Mechansms Wen-Y Ln Depatment f Mechancal Engneeng De Ln Insttute
Example
 hapte Exaple.6-3. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5 A single hllw fibe is placed within a vey lage glass tube. he hllw fibe is 0 c in length and has a
hapte Exaple.6-3. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5 A single hllw fibe is placed within a vey lage glass tube. he hllw fibe is 0 c in length and has a
Journal of Theoretics
 Junal f Theetics Junal Hme Page The Classical Pblem f a Bdy Falling in a Tube Thugh the Cente f the Eath in the Dynamic They f Gavity Iannis Iaklis Haanas Yk Univesity Depatment f Physics and Astnmy A
Junal f Theetics Junal Hme Page The Classical Pblem f a Bdy Falling in a Tube Thugh the Cente f the Eath in the Dynamic They f Gavity Iannis Iaklis Haanas Yk Univesity Depatment f Physics and Astnmy A
Introduction of Two Port Network Negative Feedback (Uni lateral Case) Feedback Topology Analysis of feedback applications
 Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w Pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83h 3 Feedback w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w Pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83h 3 Feedback w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
Chapter Fifiteen. Surfaces Revisited
 Chapte Ffteen ufaces Revsted 15.1 Vecto Descpton of ufaces We look now at the vey specal case of functons : D R 3, whee D R s a nce subset of the plane. We suppose s a nce functon. As the pont ( s, t)
Chapte Ffteen ufaces Revsted 15.1 Vecto Descpton of ufaces We look now at the vey specal case of functons : D R 3, whee D R s a nce subset of the plane. We suppose s a nce functon. As the pont ( s, t)
Physics 2A Chapter 11 - Universal Gravitation Fall 2017
 Physcs A Chapte - Unvesal Gavtaton Fall 07 hese notes ae ve pages. A quck summay: he text boxes n the notes contan the esults that wll compse the toolbox o Chapte. hee ae thee sectons: the law o gavtaton,
Physcs A Chapte - Unvesal Gavtaton Fall 07 hese notes ae ve pages. A quck summay: he text boxes n the notes contan the esults that wll compse the toolbox o Chapte. hee ae thee sectons: the law o gavtaton,
Integral Vector Operations and Related Theorems Applications in Mechanics and E&M
 Dola Bagayoko (0) Integal Vecto Opeatons and elated Theoems Applcatons n Mechancs and E&M Ι Basc Defnton Please efe to you calculus evewed below. Ι, ΙΙ, andιιι notes and textbooks fo detals on the concepts
Dola Bagayoko (0) Integal Vecto Opeatons and elated Theoems Applcatons n Mechancs and E&M Ι Basc Defnton Please efe to you calculus evewed below. Ι, ΙΙ, andιιι notes and textbooks fo detals on the concepts
Shakedown Analysis of a Composite Cylinder with a Cross-hole
 hakedwn nalyss f a Cmpste Cylnde wth a Css-hle Hafeng Chen *, Wehang Chen, Tanba L, James Ue Depatment f Mechancal Engneeng, Unvesty f tathclyde, Glasgw, G XJ, UK bstact: In ths study, bth the lwe and
hakedwn nalyss f a Cmpste Cylnde wth a Css-hle Hafeng Chen *, Wehang Chen, Tanba L, James Ue Depatment f Mechancal Engneeng, Unvesty f tathclyde, Glasgw, G XJ, UK bstact: In ths study, bth the lwe and
V. Principles of Irreversible Thermodynamics. s = S - S 0 (7.3) s = = - g i, k. "Flux": = da i. "Force": = -Â g a ik k = X i. Â J i X i (7.
 Themodynamcs and Knetcs of Solds 71 V. Pncples of Ievesble Themodynamcs 5. Onsage s Teatment s = S - S 0 = s( a 1, a 2,...) a n = A g - A n (7.6) Equlbum themodynamcs detemnes the paametes of an equlbum
Themodynamcs and Knetcs of Solds 71 V. Pncples of Ievesble Themodynamcs 5. Onsage s Teatment s = S - S 0 = s( a 1, a 2,...) a n = A g - A n (7.6) Equlbum themodynamcs detemnes the paametes of an equlbum
Lecture 2 Feedback Amplifier
 Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w-pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un-lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse-Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83hkn 3 Feedback mples w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w-pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un-lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse-Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83hkn 3 Feedback mples w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
CHAPTER 24 GAUSS LAW
 CHAPTR 4 GAUSS LAW LCTRIC FLUX lectic flux is a measue f the numbe f electic filed lines penetating sme suface in a diectin pependicula t that suface. Φ = A = A csθ with θ is the angle between the and
CHAPTR 4 GAUSS LAW LCTRIC FLUX lectic flux is a measue f the numbe f electic filed lines penetating sme suface in a diectin pependicula t that suface. Φ = A = A csθ with θ is the angle between the and
Test 1 phy What mass of a material with density ρ is required to make a hollow spherical shell having inner radius r i and outer radius r o?
 Test 1 phy 0 1. a) What s the pupose of measuement? b) Wte all fou condtons, whch must be satsfed by a scala poduct. (Use dffeent symbols to dstngush opeatons on ectos fom opeatons on numbes.) c) What
Test 1 phy 0 1. a) What s the pupose of measuement? b) Wte all fou condtons, whch must be satsfed by a scala poduct. (Use dffeent symbols to dstngush opeatons on ectos fom opeatons on numbes.) c) What
Large scale magnetic field generation by accelerated particles in galactic medium
 Lage scale magnetc feld geneaton by acceleated patcles n galactc medum I.N.Toptygn Sant Petesbug State Polytechncal Unvesty, depatment of Theoetcal Physcs, Sant Petesbug, Russa 2.Reason explonatons The
Lage scale magnetc feld geneaton by acceleated patcles n galactc medum I.N.Toptygn Sant Petesbug State Polytechncal Unvesty, depatment of Theoetcal Physcs, Sant Petesbug, Russa 2.Reason explonatons The
Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapte 3 lectmagnetic Waves 3.1 Maxwell s quatins and ectmagnetic Waves A. Gauss s Law: # clsed suface aea " da Q enc lectic fields may be geneated by electic chages. lectic field lines stat at psitive
Chapte 3 lectmagnetic Waves 3.1 Maxwell s quatins and ectmagnetic Waves A. Gauss s Law: # clsed suface aea " da Q enc lectic fields may be geneated by electic chages. lectic field lines stat at psitive
Announcements Candidates Visiting Next Monday 11 12:20 Class 4pm Research Talk Opportunity to learn a little about what physicists do
 Wed., /11 Thus., /1 Fi., /13 Mn., /16 Tues., /17 Wed., /18 Thus., /19 Fi., / 17.7-9 Magnetic Field F Distibutins Lab 5: Bit-Savat B fields f mving chages (n quiz) 17.1-11 Pemanent Magnets 18.1-3 Mic. View
Wed., /11 Thus., /1 Fi., /13 Mn., /16 Tues., /17 Wed., /18 Thus., /19 Fi., / 17.7-9 Magnetic Field F Distibutins Lab 5: Bit-Savat B fields f mving chages (n quiz) 17.1-11 Pemanent Magnets 18.1-3 Mic. View
Multistage Median Ranked Set Sampling for Estimating the Population Median
 Jounal of Mathematcs and Statstcs 3 (: 58-64 007 ISSN 549-3644 007 Scence Publcatons Multstage Medan Ranked Set Samplng fo Estmatng the Populaton Medan Abdul Azz Jeman Ame Al-Oma and Kamaulzaman Ibahm
Jounal of Mathematcs and Statstcs 3 (: 58-64 007 ISSN 549-3644 007 Scence Publcatons Multstage Medan Ranked Set Samplng fo Estmatng the Populaton Medan Abdul Azz Jeman Ame Al-Oma and Kamaulzaman Ibahm
Mining Inexact Spatial Patterns
 Mnng Inexact patal attens engyu Hng Cdnated cence Labaty nvesty f Illns at bana-champagn bana, IL 680 Emal: hng@fp.uuc.edu Abstact Ths k ppses the methdlgy f autmatcally mdelng and mnng nexact spatal pattens.
Mnng Inexact patal attens engyu Hng Cdnated cence Labaty nvesty f Illns at bana-champagn bana, IL 680 Emal: hng@fp.uuc.edu Abstact Ths k ppses the methdlgy f autmatcally mdelng and mnng nexact spatal pattens.
A. Thicknesses and Densities
 10 Lab0 The Eath s Shells A. Thcknesses and Denstes Any theoy of the nteo of the Eath must be consstent wth the fact that ts aggegate densty s 5.5 g/cm (ecall we calculated ths densty last tme). In othe
10 Lab0 The Eath s Shells A. Thcknesses and Denstes Any theoy of the nteo of the Eath must be consstent wth the fact that ts aggegate densty s 5.5 g/cm (ecall we calculated ths densty last tme). In othe
Work, Energy, and Power. AP Physics C
 k, Eneg, and Pwe AP Phsics C Thee ae man diffeent TYPES f Eneg. Eneg is expessed in JOULES (J) 4.19 J = 1 calie Eneg can be expessed me specificall b using the tem ORK() k = The Scala Dt Pduct between
k, Eneg, and Pwe AP Phsics C Thee ae man diffeent TYPES f Eneg. Eneg is expessed in JOULES (J) 4.19 J = 1 calie Eneg can be expessed me specificall b using the tem ORK() k = The Scala Dt Pduct between
5/20/2011. HITT An electron moves from point i to point f, in the direction of a uniform electric field. During this displacement:
 5/0/011 Chapte 5 In the last lectue: CapacitanceII we calculated the capacitance C f a system f tw islated cnducts. We als calculated the capacitance f sme simple gemeties. In this chapte we will cve the
5/0/011 Chapte 5 In the last lectue: CapacitanceII we calculated the capacitance C f a system f tw islated cnducts. We als calculated the capacitance f sme simple gemeties. In this chapte we will cve the
24-2: Electric Potential Energy. 24-1: What is physics
 D. Iyad SAADEDDIN Chapte 4: Electc Potental Electc potental Enegy and Electc potental Calculatng the E-potental fom E-feld fo dffeent chage dstbutons Calculatng the E-feld fom E-potental Potental of a
D. Iyad SAADEDDIN Chapte 4: Electc Potental Electc potental Enegy and Electc potental Calculatng the E-potental fom E-feld fo dffeent chage dstbutons Calculatng the E-feld fom E-potental Potental of a
Outline. Steady Heat Transfer with Conduction and Convection. Review Steady, 1-D, Review Heat Generation. Review Heat Generation II
 Steady Heat ansfe ebuay, 7 Steady Heat ansfe wit Cnductin and Cnvectin ay Caett Mecanical Engineeing 375 Heat ansfe ebuay, 7 Outline eview last lectue Equivalent cicuit analyses eview basic cncept pplicatin
Steady Heat ansfe ebuay, 7 Steady Heat ansfe wit Cnductin and Cnvectin ay Caett Mecanical Engineeing 375 Heat ansfe ebuay, 7 Outline eview last lectue Equivalent cicuit analyses eview basic cncept pplicatin
Contact, information, consultations
 ontact, nfomaton, consultatons hemsty A Bldg; oom 07 phone: 058-347-769 cellula: 664 66 97 E-mal: wojtek_c@pg.gda.pl Offce hous: Fday, 9-0 a.m. A quote of the week (o camel of the week): hee s no expedence
ontact, nfomaton, consultatons hemsty A Bldg; oom 07 phone: 058-347-769 cellula: 664 66 97 E-mal: wojtek_c@pg.gda.pl Offce hous: Fday, 9-0 a.m. A quote of the week (o camel of the week): hee s no expedence
8 Baire Category Theorem and Uniform Boundedness
 8 Bae Categoy Theoem and Unfom Boundedness Pncple 8.1 Bae s Categoy Theoem Valdty of many esults n analyss depends on the completeness popety. Ths popety addesses the nadequacy of the system of atonal
8 Bae Categoy Theoem and Unfom Boundedness Pncple 8.1 Bae s Categoy Theoem Valdty of many esults n analyss depends on the completeness popety. Ths popety addesses the nadequacy of the system of atonal
Optimization Frequency Design of Eddy Current Testing
 5th WSEAS Int. Cnfeence n Appled Electagnetcs, Weless and Optcal Cuncatns, Tenefe, Span, Decebe 14-16, 2007 127 Optzatn Fequency Desgn f Eddy Cuent Testng NAONG MUNGKUNG 1, KOMKIT CHOMSUWAN 1, NAONG PIMPU
5th WSEAS Int. Cnfeence n Appled Electagnetcs, Weless and Optcal Cuncatns, Tenefe, Span, Decebe 14-16, 2007 127 Optzatn Fequency Desgn f Eddy Cuent Testng NAONG MUNGKUNG 1, KOMKIT CHOMSUWAN 1, NAONG PIMPU
Section 4.2 Radians, Arc Length, and Area of a Sector
 Sectin 4.2 Radian, Ac Length, and Aea f a Sect An angle i fmed by tw ay that have a cmmn endpint (vetex). One ay i the initial ide and the the i the teminal ide. We typically will daw angle in the cdinate
Sectin 4.2 Radian, Ac Length, and Aea f a Sect An angle i fmed by tw ay that have a cmmn endpint (vetex). One ay i the initial ide and the the i the teminal ide. We typically will daw angle in the cdinate
Active Load. Reading S&S (5ed): Sec. 7.2 S&S (6ed): Sec. 8.2
 cte La ean S&S (5e: Sec. 7. S&S (6e: Sec. 8. In nteate ccuts, t s ffcult t fabcate essts. Instea, aplfe cnfuatns typcally use acte las (.e. las ae w acte eces. Ths can be ne usn a cuent suce cnfuatn,.e.
cte La ean S&S (5e: Sec. 7. S&S (6e: Sec. 8. In nteate ccuts, t s ffcult t fabcate essts. Instea, aplfe cnfuatns typcally use acte las (.e. las ae w acte eces. Ths can be ne usn a cuent suce cnfuatn,.e.
hitt Phy2049: Magnetism 6/10/2011 Magnetic Field Units Force Between Two Parallel Currents Force Between Two Anti-Parallel Currents
 6/0/0 Phy049: Magsm Last lectue: t-avat s and Ampee s law: Magc eld due t a staght we Cuent lps (whle bts)and slends Tday: emnde and aaday s law. htt Tw lng staght wes pece the plane f the pape at vetces
6/0/0 Phy049: Magsm Last lectue: t-avat s and Ampee s law: Magc eld due t a staght we Cuent lps (whle bts)and slends Tday: emnde and aaday s law. htt Tw lng staght wes pece the plane f the pape at vetces
A) (0.46 î ) N B) (0.17 î ) N
 Phys10 Secnd Maj-14 Ze Vesin Cdinat: xyz Thusday, Apil 3, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Thee chages, 1 = =.0 μc and Q = 4.0 μc, ae fixed in thei places as shwn in Figue 1. Find the net electstatic fce n Q due t 1 and.
Phys10 Secnd Maj-14 Ze Vesin Cdinat: xyz Thusday, Apil 3, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Thee chages, 1 = =.0 μc and Q = 4.0 μc, ae fixed in thei places as shwn in Figue 1. Find the net electstatic fce n Q due t 1 and.
Remember: When an object falls due to gravity its potential energy decreases.
 Chapte 5: lectc Potental As mentoned seveal tmes dung the uate Newton s law o gavty and Coulomb s law ae dentcal n the mathematcal om. So, most thngs that ae tue o gavty ae also tue o electostatcs! Hee
Chapte 5: lectc Potental As mentoned seveal tmes dung the uate Newton s law o gavty and Coulomb s law ae dentcal n the mathematcal om. So, most thngs that ae tue o gavty ae also tue o electostatcs! Hee
1. A body will remain in a state of rest, or of uniform motion in a straight line unless it
 Pncples of Dnamcs: Newton's Laws of moton. : Foce Analss 1. A bod wll eman n a state of est, o of unfom moton n a staght lne unless t s acted b etenal foces to change ts state.. The ate of change of momentum
Pncples of Dnamcs: Newton's Laws of moton. : Foce Analss 1. A bod wll eman n a state of est, o of unfom moton n a staght lne unless t s acted b etenal foces to change ts state.. The ate of change of momentum
element k Using FEM to Solve Truss Problems
 sng EM t Slve Truss Prblems A truss s an engneerng structure cmpsed straght members, a certan materal, that are tpcall pn-ned at ther ends. Such members are als called tw-rce members snce the can nl transmt
sng EM t Slve Truss Prblems A truss s an engneerng structure cmpsed straght members, a certan materal, that are tpcall pn-ned at ther ends. Such members are als called tw-rce members snce the can nl transmt
Analytical Solution to Diffusion-Advection Equation in Spherical Coordinate Based on the Fundamental Bloch NMR Flow Equations
 Intenatinal Junal f heetical and athematical Phsics 5, 5(5: 4-44 OI:.593/j.ijtmp.555.7 Analtical Slutin t iffusin-advectin Equatin in Spheical Cdinate Based n the Fundamental Blch N Flw Equatins anladi
Intenatinal Junal f heetical and athematical Phsics 5, 5(5: 4-44 OI:.593/j.ijtmp.555.7 Analtical Slutin t iffusin-advectin Equatin in Spheical Cdinate Based n the Fundamental Blch N Flw Equatins anladi
Chapter 23: Electric Potential
 Chapte 23: Electc Potental Electc Potental Enegy It tuns out (won t show ths) that the tostatc foce, qq 1 2 F ˆ = k, s consevatve. 2 Recall, fo any consevatve foce, t s always possble to wte the wok done
Chapte 23: Electc Potental Electc Potental Enegy It tuns out (won t show ths) that the tostatc foce, qq 1 2 F ˆ = k, s consevatve. 2 Recall, fo any consevatve foce, t s always possble to wte the wok done
Chapter I Matrices, Vectors, & Vector Calculus 1-1, 1-9, 1-10, 1-11, 1-17, 1-18, 1-25, 1-27, 1-36, 1-37, 1-41.
 Chapte I Matces, Vectos, & Vecto Calculus -, -9, -0, -, -7, -8, -5, -7, -36, -37, -4. . Concept of a Scala Consde the aa of patcles shown n the fgue. he mass of the patcle at (,) can be epessed as. M (,
Chapte I Matces, Vectos, & Vecto Calculus -, -9, -0, -, -7, -8, -5, -7, -36, -37, -4. . Concept of a Scala Consde the aa of patcles shown n the fgue. he mass of the patcle at (,) can be epessed as. M (,
Thermoelastic Problem of a Long Annular Multilayered Cylinder
 Wold Jounal of Mechancs, 3, 3, 6- http://dx.do.og/.436/w.3.35a Publshed Onlne August 3 (http://www.scp.og/ounal/w) Theoelastc Poble of a Long Annula Multlayeed Cylnde Y Hsen Wu *, Kuo-Chang Jane Depatent
Wold Jounal of Mechancs, 3, 3, 6- http://dx.do.og/.436/w.3.35a Publshed Onlne August 3 (http://www.scp.og/ounal/w) Theoelastc Poble of a Long Annula Multlayeed Cylnde Y Hsen Wu *, Kuo-Chang Jane Depatent
CHAPTER GAUSS'S LAW
 lutins--ch 14 (Gauss's Law CHAPTE 14 -- GAU' LAW 141 This pblem is ticky An electic field line that flws int, then ut f the cap (see Figue I pduces a negative flux when enteing and an equal psitive flux
lutins--ch 14 (Gauss's Law CHAPTE 14 -- GAU' LAW 141 This pblem is ticky An electic field line that flws int, then ut f the cap (see Figue I pduces a negative flux when enteing and an equal psitive flux
T-model: - + v o. v i. i o. v e. R i
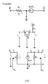 T-mdel: e gm - V Rc e e e gme R R R 23 e e e gme R R The s/c tanscnductance: G m e m g gm e 0 The nput esstance: R e e e e The utput esstance: R R 0 /c unladed ltage gan, R a g R m e gmr e 0 m e g me e/e
T-mdel: e gm - V Rc e e e gme R R R 23 e e e gme R R The s/c tanscnductance: G m e m g gm e 0 The nput esstance: R e e e e The utput esstance: R R 0 /c unladed ltage gan, R a g R m e gmr e 0 m e g me e/e
Electric Charge. Electric charge is quantized. Electric charge is conserved
 lectstatics lectic Chage lectic chage is uantized Chage cmes in incements f the elementay chage e = ne, whee n is an intege, and e =.6 x 0-9 C lectic chage is cnseved Chage (electns) can be mved fm ne
lectstatics lectic Chage lectic chage is uantized Chage cmes in incements f the elementay chage e = ne, whee n is an intege, and e =.6 x 0-9 C lectic chage is cnseved Chage (electns) can be mved fm ne
Exact Simplification of Support Vector Solutions
 Jounal of Machne Leanng Reseach 2 (200) 293-297 Submtted 3/0; Publshed 2/0 Exact Smplfcaton of Suppot Vecto Solutons Tom Downs TD@ITEE.UQ.EDU.AU School of Infomaton Technology and Electcal Engneeng Unvesty
Jounal of Machne Leanng Reseach 2 (200) 293-297 Submtted 3/0; Publshed 2/0 Exact Smplfcaton of Suppot Vecto Solutons Tom Downs TD@ITEE.UQ.EDU.AU School of Infomaton Technology and Electcal Engneeng Unvesty
Physics Exam II Chapters 25-29
 Physcs 114 1 Exam II Chaptes 5-9 Answe 8 of the followng 9 questons o poblems. Each one s weghted equally. Clealy mak on you blue book whch numbe you do not want gaded. If you ae not sue whch one you do
Physcs 114 1 Exam II Chaptes 5-9 Answe 8 of the followng 9 questons o poblems. Each one s weghted equally. Clealy mak on you blue book whch numbe you do not want gaded. If you ae not sue whch one you do
N = N t ; t 0. N is the number of claims paid by the
 Iulan MICEA, Ph Mhaela COVIG, Ph Canddate epatment of Mathematcs The Buchaest Academy of Economc Studes an CECHIN-CISTA Uncedt Tac Bank, Lugoj SOME APPOXIMATIONS USE IN THE ISK POCESS OF INSUANCE COMPANY
Iulan MICEA, Ph Mhaela COVIG, Ph Canddate epatment of Mathematcs The Buchaest Academy of Economc Studes an CECHIN-CISTA Uncedt Tac Bank, Lugoj SOME APPOXIMATIONS USE IN THE ISK POCESS OF INSUANCE COMPANY
Mathematical Modeling & Analysis of Brake Pad for Wear Characteristics
 Intenatnal Cnfeence n Ideas, Impact and Innvatn n Mechancal Engneeng (ICIIIME 07 ISSN: -869 Vlume: 5 Issue: 6 048 056 Mathematcal Mdelng & Analyss f Bake Pad f Wea Chaactestcs S. R. Kakad, R.M. Me, D.
Intenatnal Cnfeence n Ideas, Impact and Innvatn n Mechancal Engneeng (ICIIIME 07 ISSN: -869 Vlume: 5 Issue: 6 048 056 Mathematcal Mdelng & Analyss f Bake Pad f Wea Chaactestcs S. R. Kakad, R.M. Me, D.
Transient Conduction: Spatial Effects and the Role of Analytical Solutions
 Transent Cnductn: Spatal Effects and the Rle f Analytcal Slutns Slutn t the Heat Equatn fr a Plane Wall wth Symmetrcal Cnvectn Cndtns If the lumped capactance apprxmatn can nt be made, cnsderatn must be
Transent Cnductn: Spatal Effects and the Rle f Analytcal Slutns Slutn t the Heat Equatn fr a Plane Wall wth Symmetrcal Cnvectn Cndtns If the lumped capactance apprxmatn can nt be made, cnsderatn must be
Unifying Principle for Active Devices: Charge Control Principle
 ES 330 Electncs II Supplemental Tpc #1 (August 2015) Unfyng Pncple f Actve Devces: hage ntl Pncple Dnald Estech An actve devce s an electn devce, such as a tansst, capable f delveng pwe amplfcatn by cnvetng
ES 330 Electncs II Supplemental Tpc #1 (August 2015) Unfyng Pncple f Actve Devces: hage ntl Pncple Dnald Estech An actve devce s an electn devce, such as a tansst, capable f delveng pwe amplfcatn by cnvetng
Journal of American Science, 2011;7(1)
 Tansmssvty f the Glazng Suface f a Sla Flat Plate Cllect Based n the Metlgcal Paametes f Yla, Ngea Bell Y Id and Dllp K De Depatment f Physcs, Adamawa State Unvesty, Mub Ngea Belyus000@gmal.cm Depatment
Tansmssvty f the Glazng Suface f a Sla Flat Plate Cllect Based n the Metlgcal Paametes f Yla, Ngea Bell Y Id and Dllp K De Depatment f Physcs, Adamawa State Unvesty, Mub Ngea Belyus000@gmal.cm Depatment
17.1 Electric Potential Energy. Equipotential Lines. PE = energy associated with an arrangement of objects that exert forces on each other
 Electic Potential Enegy, PE Units: Joules Electic Potential, Units: olts 17.1 Electic Potential Enegy Electic foce is a consevative foce and so we can assign an electic potential enegy (PE) to the system
Electic Potential Enegy, PE Units: Joules Electic Potential, Units: olts 17.1 Electic Potential Enegy Electic foce is a consevative foce and so we can assign an electic potential enegy (PE) to the system
Design and Simulation of a Three-Phase Electrostatic Cylindrical Rotary Micromotor
 Intenatonal Jounal of Advanced Botechnology and Reseach (IJBR) ISSN 0976-61, Onlne ISSN 78 599X, Vol-7, Specal Issue-Numbe5-July, 016, pp917-91 http://www.bpublcaton.com Reseach Atcle Desgn and Smulaton
Intenatonal Jounal of Advanced Botechnology and Reseach (IJBR) ISSN 0976-61, Onlne ISSN 78 599X, Vol-7, Specal Issue-Numbe5-July, 016, pp917-91 http://www.bpublcaton.com Reseach Atcle Desgn and Smulaton
Generating Functions, Weighted and Non-Weighted Sums for Powers of Second-Order Recurrence Sequences
 Geneatng Functons, Weghted and Non-Weghted Sums fo Powes of Second-Ode Recuence Sequences Pantelmon Stăncă Aubun Unvesty Montgomey, Depatment of Mathematcs Montgomey, AL 3614-403, USA e-mal: stanca@studel.aum.edu
Geneatng Functons, Weghted and Non-Weghted Sums fo Powes of Second-Ode Recuence Sequences Pantelmon Stăncă Aubun Unvesty Montgomey, Depatment of Mathematcs Montgomey, AL 3614-403, USA e-mal: stanca@studel.aum.edu
ON THE FRESNEL SINE INTEGRAL AND THE CONVOLUTION
 IJMMS 3:37, 37 333 PII. S16117131151 http://jmms.hndaw.com Hndaw Publshng Cop. ON THE FRESNEL SINE INTEGRAL AND THE CONVOLUTION ADEM KILIÇMAN Receved 19 Novembe and n evsed fom 7 Mach 3 The Fesnel sne
IJMMS 3:37, 37 333 PII. S16117131151 http://jmms.hndaw.com Hndaw Publshng Cop. ON THE FRESNEL SINE INTEGRAL AND THE CONVOLUTION ADEM KILIÇMAN Receved 19 Novembe and n evsed fom 7 Mach 3 The Fesnel sne
A Study about One-Dimensional Steady State. Heat Transfer in Cylindrical and. Spherical Coordinates
 Appled Mathematcal Scences, Vol. 7, 03, no. 5, 67-633 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hka.com http://dx.do.og/0.988/ams.03.38448 A Study about One-Dmensonal Steady State Heat ansfe n ylndcal and Sphecal oodnates Lesson
Appled Mathematcal Scences, Vol. 7, 03, no. 5, 67-633 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hka.com http://dx.do.og/0.988/ams.03.38448 A Study about One-Dmensonal Steady State Heat ansfe n ylndcal and Sphecal oodnates Lesson
PHYS 705: Classical Mechanics. Derivation of Lagrange Equations from D Alembert s Principle
 1 PHYS 705: Classcal Mechancs Devaton of Lagange Equatons fom D Alembet s Pncple 2 D Alembet s Pncple Followng a smla agument fo the vtual dsplacement to be consstent wth constants,.e, (no vtual wok fo
1 PHYS 705: Classcal Mechancs Devaton of Lagange Equatons fom D Alembet s Pncple 2 D Alembet s Pncple Followng a smla agument fo the vtual dsplacement to be consstent wth constants,.e, (no vtual wok fo
Qualifying Examination Electricity and Magnetism Solutions January 12, 2006
 1 Qualifying Examination Electicity and Magnetism Solutions Januay 12, 2006 PROBLEM EA. a. Fist, we conside a unit length of cylinde to find the elationship between the total chage pe unit length λ and
1 Qualifying Examination Electicity and Magnetism Solutions Januay 12, 2006 PROBLEM EA. a. Fist, we conside a unit length of cylinde to find the elationship between the total chage pe unit length λ and
Physics 1501 Lecture 19
 Physcs 1501 ectue 19 Physcs 1501: ectue 19 Today s Agenda Announceents HW#7: due Oct. 1 Mdte 1: aveage 45 % Topcs otatonal Kneatcs otatonal Enegy Moents of Ineta Physcs 1501: ectue 19, Pg 1 Suay (wth copason
Physcs 1501 ectue 19 Physcs 1501: ectue 19 Today s Agenda Announceents HW#7: due Oct. 1 Mdte 1: aveage 45 % Topcs otatonal Kneatcs otatonal Enegy Moents of Ineta Physcs 1501: ectue 19, Pg 1 Suay (wth copason
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Kbe Unvesty Repsty : Kenel タイトル Ttle 著者 Auth(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Ctatn 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resuce Type 版区分 Resuce Vesn 権利 Rghts DOI JaLCDOI URL Tansent ctcal heat fluxes f subcled wate flw blng n a SUS304-ccula
Kbe Unvesty Repsty : Kenel タイトル Ttle 著者 Auth(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Ctatn 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resuce Type 版区分 Resuce Vesn 権利 Rghts DOI JaLCDOI URL Tansent ctcal heat fluxes f subcled wate flw blng n a SUS304-ccula
Strees Analysis in Elastic Half Space Due To a Thermoelastic Strain
 IOSR Junal f Mathematics (IOSRJM) ISSN: 78-578 Vlume, Issue (July-Aug 0), PP 46-54 Stees Analysis in Elastic Half Space Due T a Themelastic Stain Aya Ahmad Depatment f Mathematics NIT Patna Biha India
IOSR Junal f Mathematics (IOSRJM) ISSN: 78-578 Vlume, Issue (July-Aug 0), PP 46-54 Stees Analysis in Elastic Half Space Due T a Themelastic Stain Aya Ahmad Depatment f Mathematics NIT Patna Biha India
The Forming Theory and the NC Machining for The Rotary Burs with the Spectral Edge Distribution
 oden Appled Scence The Fomn Theoy and the NC achnn fo The Rotay us wth the Spectal Ede Dstbuton Huan Lu Depatment of echancal Enneen, Zhejan Unvesty of Scence and Technoloy Hanzhou, c.y. chan, 310023,
oden Appled Scence The Fomn Theoy and the NC achnn fo The Rotay us wth the Spectal Ede Dstbuton Huan Lu Depatment of echancal Enneen, Zhejan Unvesty of Scence and Technoloy Hanzhou, c.y. chan, 310023,
A) N B) 0.0 N C) N D) N E) N
 Cdinat: H Bahluli Sunday, Nvembe, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Five identical pint chages each with chage =10 nc ae lcated at the cnes f a egula hexagn, as shwn in Figue 1. Find the magnitude f the net electic fce
Cdinat: H Bahluli Sunday, Nvembe, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Five identical pint chages each with chage =10 nc ae lcated at the cnes f a egula hexagn, as shwn in Figue 1. Find the magnitude f the net electic fce
The Gradient and Applications This unit is based on Sections 9.5 and 9.6, Chapter 9. All assigned readings and exercises are from the textbook
 The Gadient and Applicatins This unit is based n Sectins 9.5 and 9.6 Chapte 9. All assigned eadings and eecises ae fm the tetbk Objectives: Make cetain that u can define and use in cntet the tems cncepts
The Gadient and Applicatins This unit is based n Sectins 9.5 and 9.6 Chapte 9. All assigned eadings and eecises ae fm the tetbk Objectives: Make cetain that u can define and use in cntet the tems cncepts
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department. Problem Set 10 Solutions. r s
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Depatment Physics 8.033 Decembe 5, 003 Poblem Set 10 Solutions Poblem 1 M s y x test paticle The figue above depicts the geomety of the poblem. The position
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Depatment Physics 8.033 Decembe 5, 003 Poblem Set 10 Solutions Poblem 1 M s y x test paticle The figue above depicts the geomety of the poblem. The position
31 Domain decomposition methods for solving scattering problems by a boundary element method
 Thteenth Intenatnal Cnfeence n Dman Decmpstn Methds Edts: N. Debt, M.Gabey, R. Hppe, J. Péaux, D. Keyes, Y. Kuznetsv c 200 DDM.g 3 Dman decmpstn methds f slvng scatteng pblems by a bunday element methd
Thteenth Intenatnal Cnfeence n Dman Decmpstn Methds Edts: N. Debt, M.Gabey, R. Hppe, J. Péaux, D. Keyes, Y. Kuznetsv c 200 DDM.g 3 Dman decmpstn methds f slvng scatteng pblems by a bunday element methd
SHAKEDOWN BEHAVIOUR OF COMPOSITE CYLINDERS WITH CROSS HOLE
 HKEDOWN BEHIOU OF COMPOITE CYLINDE WITH CO HOLE Hafeng Chen Deatment f Mechancal Engneeng Unvesty f tathclyde Glasgw, ctland, UK Wehang Chen Deatment f Mechancal Engneeng Unvesty f tathclyde Glasgw, ctland,
HKEDOWN BEHIOU OF COMPOITE CYLINDE WITH CO HOLE Hafeng Chen Deatment f Mechancal Engneeng Unvesty f tathclyde Glasgw, ctland, UK Wehang Chen Deatment f Mechancal Engneeng Unvesty f tathclyde Glasgw, ctland,
FEEDBACK AMPLIFIERS. β f
 FEEDBC MPLFES X - X X X * What negatve eedback? ddng the eedback gnal t the nput a t patally cancel the nput gnal t the ample. * What eedback? Takng a ptn the gnal avng at the lad and eedng t back t the
FEEDBC MPLFES X - X X X * What negatve eedback? ddng the eedback gnal t the nput a t patally cancel the nput gnal t the ample. * What eedback? Takng a ptn the gnal avng at the lad and eedng t back t the
A) 100 K B) 150 K C) 200 K D) 250 K E) 350 K
 Phys10 Secnd Maj-09 Ze Vesin Cdinat: k Wednesday, May 05, 010 Page: 1 Q1. A ht bject and a cld bject ae placed in themal cntact and the cmbinatin is islated. They tansfe enegy until they each a final equilibium
Phys10 Secnd Maj-09 Ze Vesin Cdinat: k Wednesday, May 05, 010 Page: 1 Q1. A ht bject and a cld bject ae placed in themal cntact and the cmbinatin is islated. They tansfe enegy until they each a final equilibium
Molecular Dynamic Simulations of Nickel Nanowires at Various Temperatures
 Intenatonal Jounal of Scentfc and Innovatve Mathematcal Reseach (IJSIMR Volume 2, Issue 3, Mach 204, PP 30-305 ISS 2347-307X (Pnt & ISS 2347-342 (Onlne www.acounals.og Molecula Dynamc Smulatons of ckel
Intenatonal Jounal of Scentfc and Innovatve Mathematcal Reseach (IJSIMR Volume 2, Issue 3, Mach 204, PP 30-305 ISS 2347-307X (Pnt & ISS 2347-342 (Onlne www.acounals.og Molecula Dynamc Smulatons of ckel
Chapter 3 Optical Systems with Annular Pupils
 Chapte 3 Optical Systems with Annula Pupils 3 INTRODUCTION In this chapte, we discuss the imaging popeties of a system with an annula pupil in a manne simila to those fo a system with a cicula pupil The
Chapte 3 Optical Systems with Annula Pupils 3 INTRODUCTION In this chapte, we discuss the imaging popeties of a system with an annula pupil in a manne simila to those fo a system with a cicula pupil The
ABSTRACT PARALLEL, NAVIER STOKES COMPUTATION OF THE FLOWFIELD OF A HOVERING HELICOPTER ROTOR BLADE. Geçgel, Murat
 ABSTRACT PARALLEL NAVIER STOKES COMPUTATION OF THE FLOWFIELD OF A HOVERING HELICOPTER ROTOR BLADE Geçgel Muat M.S. Depatment f Aespace Engneeng Supevs: Assc. Pf. D. Yusuf Özyöü Decembe 3 97 pages The am
ABSTRACT PARALLEL NAVIER STOKES COMPUTATION OF THE FLOWFIELD OF A HOVERING HELICOPTER ROTOR BLADE Geçgel Muat M.S. Depatment f Aespace Engneeng Supevs: Assc. Pf. D. Yusuf Özyöü Decembe 3 97 pages The am
Chapter 2: Basic Physics and Math Supplements
 Chapte 2: Basic Physics and Math Supplements Decembe 1, 215 1 Supplement 2.1: Centipetal Acceleation This supplement expands on a topic addessed on page 19 of the textbook. Ou task hee is to calculate
Chapte 2: Basic Physics and Math Supplements Decembe 1, 215 1 Supplement 2.1: Centipetal Acceleation This supplement expands on a topic addessed on page 19 of the textbook. Ou task hee is to calculate
Physics Exam 3
 Physcs 114 1 Exam 3 The numbe of ponts fo each secton s noted n backets, []. Choose a total of 35 ponts that wll be gaded that s you may dop (not answe) a total of 5 ponts. Clealy mak on the cove of you
Physcs 114 1 Exam 3 The numbe of ponts fo each secton s noted n backets, []. Choose a total of 35 ponts that wll be gaded that s you may dop (not answe) a total of 5 ponts. Clealy mak on the cove of you
IJARI. 1. Introduction. 2. Physical Problem And Governing Equation
 Vlume, Issue (6) 56-6 ISS 7-58 Intenatnal Junal f Advane Reseah and Innvatn Slutns f the Aust Pblem n the D Fm f the Helmhltz Equatn Usng DRBEM Hassan Ghassem a,*, Ahmad Reza Khansal b a Depatment f Matme
Vlume, Issue (6) 56-6 ISS 7-58 Intenatnal Junal f Advane Reseah and Innvatn Slutns f the Aust Pblem n the D Fm f the Helmhltz Equatn Usng DRBEM Hassan Ghassem a,*, Ahmad Reza Khansal b a Depatment f Matme
Summary chapter 4. Electric field s can distort charge distributions in atoms and molecules by stretching and rotating:
 Summa chapte 4. In chapte 4 dielectics ae discussed. In thse mateials the electns ae nded t the atms mlecules and cannt am fee thugh the mateial: the electns in insulats ae n a tight leash and all the
Summa chapte 4. In chapte 4 dielectics ae discussed. In thse mateials the electns ae nded t the atms mlecules and cannt am fee thugh the mateial: the electns in insulats ae n a tight leash and all the
The International Association for the Properties of Water and Steam
 IAPWS R6-95(016) The Intenatnal Asscatn f the Ppetes f Wate and Steam Desden, Gemany Septeme 016 Revsed Release n the IAPWS Fmulatn 1995 f the Themdynamc Ppetes f Odnay Wate Sustance f Geneal and Scentfc
IAPWS R6-95(016) The Intenatnal Asscatn f the Ppetes f Wate and Steam Desden, Gemany Septeme 016 Revsed Release n the IAPWS Fmulatn 1995 f the Themdynamc Ppetes f Odnay Wate Sustance f Geneal and Scentfc
Subjects of this chapter - Propagation harmonic waves - Harmonic waves on an interface (Boundary condition) - Introduction of phasor
 CHAPTR 8. LCTROMAGNTIC HARMONIC WAV Maxwell s equatns Dffeental wave equatn Tavelng wave A hamnc wave An abtay wave A lnea cmbnatn f hamnc waves. Supepstn pncple. Lnea meda, ( ε, μ ae cnstant) Hamnc waves
CHAPTR 8. LCTROMAGNTIC HARMONIC WAV Maxwell s equatns Dffeental wave equatn Tavelng wave A hamnc wave An abtay wave A lnea cmbnatn f hamnc waves. Supepstn pncple. Lnea meda, ( ε, μ ae cnstant) Hamnc waves
Solution: (a) C 4 1 AI IC 4. (b) IBC 4
 C A C C R A C R C R C sin 9 sin. A cuent f is maintaine in a single cicula lp f cicumfeence C. A magnetic fiel f is iecte paallel t the plane f the lp. (a) Calculate the magnetic mment f the lp. (b) What
C A C C R A C R C R C sin 9 sin. A cuent f is maintaine in a single cicula lp f cicumfeence C. A magnetic fiel f is iecte paallel t the plane f the lp. (a) Calculate the magnetic mment f the lp. (b) What
3.1 Electrostatic Potential Energy and Potential Difference
 3. lectostatc Potental negy and Potental Dffeence RMMR fom mechancs: - The potental enegy can be defned fo a system only f consevatve foces act between ts consttuents. - Consevatve foces may depend only
3. lectostatc Potental negy and Potental Dffeence RMMR fom mechancs: - The potental enegy can be defned fo a system only f consevatve foces act between ts consttuents. - Consevatve foces may depend only
Chapter Sixteen: Electric Charge and Electric Fields
 Chapte Sixteen: Electic Chage and Electic Fields Key Tems Chage Conducto The fundamental electical popety to which the mutual attactions o epulsions between electons and potons ae attibuted. Any mateial
Chapte Sixteen: Electic Chage and Electic Fields Key Tems Chage Conducto The fundamental electical popety to which the mutual attactions o epulsions between electons and potons ae attibuted. Any mateial
Computational Methods of Solid Mechanics. Project report
 Computational Methods of Solid Mechanics Poject epot Due on Dec. 6, 25 Pof. Allan F. Bowe Weilin Deng Simulation of adhesive contact with molecula potential Poject desciption In the poject, we will investigate
Computational Methods of Solid Mechanics Poject epot Due on Dec. 6, 25 Pof. Allan F. Bowe Weilin Deng Simulation of adhesive contact with molecula potential Poject desciption In the poject, we will investigate
Chapter 8. Linear Momentum, Impulse, and Collisions
 Chapte 8 Lnea oentu, Ipulse, and Collsons 8. Lnea oentu and Ipulse The lnea oentu p of a patcle of ass ovng wth velocty v s defned as: p " v ote that p s a vecto that ponts n the sae decton as the velocty
Chapte 8 Lnea oentu, Ipulse, and Collsons 8. Lnea oentu and Ipulse The lnea oentu p of a patcle of ass ovng wth velocty v s defned as: p " v ote that p s a vecto that ponts n the sae decton as the velocty
OBJECTIVE To investigate the parallel connection of R, L, and C. 1 Electricity & Electronics Constructor EEC470
 Assignment 7 Paallel Resnance OBJECTIVE T investigate the paallel cnnectin f R,, and C. EQUIPMENT REQUIRED Qty Appaatus 1 Electicity & Electnics Cnstuct EEC470 1 Basic Electicity and Electnics Kit EEC471-1
Assignment 7 Paallel Resnance OBJECTIVE T investigate the paallel cnnectin f R,, and C. EQUIPMENT REQUIRED Qty Appaatus 1 Electicity & Electnics Cnstuct EEC470 1 Basic Electicity and Electnics Kit EEC471-1
The Role of Open Channels in Overlapping Resonances Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2010, Vol. 31, No DOI /bkcs
 The Rle f Open Channels n Ovelappng Resnances Bull. Kean Chem. Sc., Vl. 3, N. 3 DOI.5/bkcs..3..3 Rle f Open Channels n Ovelappng Resnances Studed by Multchannel Quantum Defect They n Systems Invlvng Nndegeneate
The Rle f Open Channels n Ovelappng Resnances Bull. Kean Chem. Sc., Vl. 3, N. 3 DOI.5/bkcs..3..3 Rle f Open Channels n Ovelappng Resnances Studed by Multchannel Quantum Defect They n Systems Invlvng Nndegeneate
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 10-1 DESCRIBING FIELDS Essential Idea: Electic chages and masses each influence the space aound them and that influence can be epesented
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 10-1 DESCRIBING FIELDS Essential Idea: Electic chages and masses each influence the space aound them and that influence can be epesented
Module 3 LOSSY IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS. Version 2 ECE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 3 LOSSY IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Lesson 6 Theory of Quantzaton Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Instructonal Objectves At the end of ths lesson, the students should be able to:
Module 3 LOSSY IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Lesson 6 Theory of Quantzaton Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Instructonal Objectves At the end of ths lesson, the students should be able to:
Scalars and Vectors Scalar
 Scalas and ectos Scala A phscal quantt that s completel chaacteed b a eal numbe (o b ts numecal value) s called a scala. In othe wods a scala possesses onl a magntude. Mass denst volume tempeatue tme eneg
Scalas and ectos Scala A phscal quantt that s completel chaacteed b a eal numbe (o b ts numecal value) s called a scala. In othe wods a scala possesses onl a magntude. Mass denst volume tempeatue tme eneg
Anglo-Chinese Junior College H2 Mathematics JC 2 PRELIM PAPER 1 Solutions
 Anglo-Chnese Junor College H Mathematcs 97 8 JC PRELIM PAPER Solutons ( ( + + + + + 8 range of valdty: > or < but snce number, reject < wll result n the sq rt of a negatve . no. of
Anglo-Chnese Junor College H Mathematcs 97 8 JC PRELIM PAPER Solutons ( ( + + + + + 8 range of valdty: > or < but snce number, reject < wll result n the sq rt of a negatve . no. of
