hitt Phy2049: Magnetism 6/10/2011 Magnetic Field Units Force Between Two Parallel Currents Force Between Two Anti-Parallel Currents
|
|
|
- Roger Golden
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 6/0/0 Phy049: Magsm Last lectue: t-avat s and Ampee s law: Magc eld due t a staght we Cuent lps (whle bts)and slends Tday: emnde and aaday s law. htt Tw lng staght wes pece the plane f the pape at vetces f an equlateal tangle as shwn. They each cay A but n the ppste ectn. The we n the left has the cuent cmng ut f the pape whle the we n the ght caes the cuent gng nt the pape. The c feld at the thd vetex (P) has the magntude and ectn (th s up): () 0 T, east () 7 T, west () 5T, nth (4) 6 T, suth (5) nne f these 4 cm X Magc eld Unts m the expessn f fce n a cuent-cayng we: max / I L Unts: ewtns/a m Tesla (I unt) Anthe unt: gauss 0-4 Tesla me sample c feld stengths: Eath: 0.5 gauss 0.5 x 0-4 T 5 x 0-5 T Galaxy: 0-6 gauss 0-0 T a : gauss tng elect: T upecnductng : 0 40 T Pulse : 00 T eutn sta: T Maga: 0 T ce etween Tw Paallel Cuents ce n I fm I 0I 0II IL I π π H ce twads I ce n I fm I 0I 0II I L I π π H ce twads I I I I Magc fces cause attactn between tw paallel cuents I ce etween Tw Ant-Paallel Cuents ce n I fm I 0I 0II I L I π π H ce away fm I ce n I fm I 0I 0II I L I π π H ce away fm I I I Magc fces epel tw antpaallel cuents I I Paallel Cuents (cnt.) Lk at them edge n t see felds me clealy Antpaallel: epel Paallel: attact
2 6/0/0 Cente f Ccula Cuent Lp aus and cuent : fnd feld at cente f lp 0 Dectn: H # (see pctue) If tuns clse tgethe Cuent Lp Example 500 A, 5 cm, 0 7 ( )( ) π.6t Challenge: Hw much heat s pduced? eld f lend mula fund fm Ampee s law cuent n tuns / mete 0n ~ cnstant nsde slend ~ ze utsde slend Mst accuate when L>> Example: 00A, n 0 tuns/cm n 000 tuns / m 7 ( π )( )( ) T eld at Cente f Patal Lp uppse lp cves angle φ 0 φ π Use example whee φ π (half ccle) Defne ectn nt page as pstve 0 π 0 π π π 0 4 Patal Lps (cnt.) te n pblems when yu have t evaluate a feld at a pnt fm seveal patal lps Only lp pats cntbute, pptnal t angle (pevus slde) taght sectns amed at pnt cntbute nthng e caeful abut sgns, e.g.n (b) felds patally cancel, wheeas n (a) and (c) they add ( z) π z The c feld f a c ple. Cnsde the c feld geneated by a we cl f aus whch caes a cuent. The c feld at a pnt P n the z-axs s gven by: ( + z ) / Hee z s the stance between P and the cl cente. pnts fa fm the lp ( z ) we can use the appxmatn: z π A Hee s the c pz π z π z ple mment f the lp. In vect fm: ( z) π z The lp geneates a c feld that has the same fm as the feld geneated by a ba. (9 4)
3 6/0/0 Chapte 0 Inductn and Inductance In ths chapte we wll study the fllwng tpcs: -aaday s law f nductn -Lenz s ule -Electc feld nduced by a changng c feld Electc cuent wthut a battey -Inductance and mutual nductance - L ccuts -Enegy sted n a c feld (0 ) (0 ) aaday's expements In a sees f expements Mchael aaday n England and Jseph Heny n the U wee able t geneate electc cuents wthut the use f battees elw we descbe sme f these expements that helped fmulate whats s knwn as "aaday's law f nductn" The ccut shwn n the fgue cnssts f a we lp cnnected t a senstve ammete (knwn as a "galvanmete"). If we appach the lp wth a pemanent we see a cuent beng egsteed by the galvanmete. The esults can be summazed as fllws:. A cuent appeas nly f thee s elatve mtn between the and the lp. aste mtn esults n a lage cuent. If we evese the ectn f mtn the platy f the, the cuent eveses sgn and flws n the ppste ectn. The cuent geneated s knwn as " nduced cuent "; the emf that appeas s knwn as " nduced emf"; the whle effect s called " nductn" (0 ) lp lp In the fgue we shw a secnd type f expement n whch cuent s nduced n lp when the swtch n lp s ethe clsed pened. When the cuent n lp s cnstant n nduced cuent s bseved n lp. The cnclusn s that the c feld n an nductn expement can be geneated ethe by a pemanent by an electc cuent n a cl. aaday summazed the esults f hs expements n what s knwn as " aaday's law f nductn" An emf s nduced n a lp when the numbe f c feld lnes that pass thugh the lp s changng aaday's law s nt an explanatn f nductn but meely a descptn f f what nductn s. It s ne f the fu " Maxwell's equatns f electsm" all f whch ae statements f expemental esults. We have aleady encunteed Gauss' law f the electc feld, and Ampee's law (n ts ncmplete fm) da da ˆn φ Magc lux The c flux thugh a suface that bdes a lp s detemned as fllws:. we vde the suface that has the lp as ts bde nt aea elements f aea da.. each element we calculate the c flux thugh t: dacsφ Hee φ s the angle between the nmal nˆ and the c feld vects at the pstn f the element.. We ntegate all the tems. csφ da da I c flux unt : T m knwn as the Webe (symbl Wb) We can expess aaday's law f nductn n the flwng fm: The magntude f the emf E nduced n a cnductve lp s equal t ate at whch the c flux thugh the lp changes wth tme E (0 4) dacsφ da da ˆn φ Methds f changng thugh a lp. Change the magntude f wthn the lp. Change ethe the ttal aea f the cl the ptn f the aea wthn the c feld. Change the angle φ between and nˆ E Lenz's ule We nw cncentate n the negatve sgn n the equatn that expesses aaday's law. The ectn f the flw f nduced cuent n a lp s acuately pected by what s knwn as Lenz's ule. lp φ ˆn An Example. Pblem 0- A csφ ab cs ( ωt) E ωab sn ( ωt) ω π f E π fab sn ( π t) (0 5) An nduced cuent has a ectn such that the c feld due t the nduced cuent ppses the change n the c flux that nduces the cuent Lenz's ule can be mplemented usng ne f tw methds:. Oppstn t ple mvement In the fgue we shw a ba appachng a lp. The nduced cuent flws n the ectn ncated because ths cuent geneates an nduced c feld that has the feld lnes pntng fm left t ght. The lp s equvalent t a whse nth ple haces the cespnng nth ple f the ba appachng the lp. The lp epels the appachng and thus ppses the change n whch geneated the nduced cuent. (0 6)
4 6/0/0 mtn. Oppstn t flux change Example a : a appaches the lp wth the nth ple facng the lp. As the ba appaches the lp the feld pnts twads the left and ts magntude nceases wth tme at the lcatn f the lp. Thus the magntude f the lp c flux als nceases. The nduced cuent flws n the cunteclckwse (CCW) ectn s that the nduced c feld ppses the feld. The feld. The nduced cuent s thus tyng t pevent fm nceasng. emembe t was the ncease n that geneated the nduced cuent n the fst place. mtn. Oppstn t flux change Example b : a mves away fm the lp wth nth ple facng the lp. As the ba mves away fm the lp the feld pnts twads the left and ts magntude deceases wth tme at the lcatn f the lp. Thus the magntude f the lp c flux als deceases. The nduced cuent flws n the clckwse (CW) ectn s that the nduced c feld adds t the feld. The feld +. The nduced cuent s thus tyng t pevent fm deceasng. emembe t was the decease n that geneated the nduced cuent n the fst place. (0 7) (0 8). Oppstn t flux change Example c : a appaches the lp wth suth ple facng the lp. mtn As the ba appaches the lp the feld pnts twads the ght and ts magntude nceases wth tme at the lcatn f the lp. Thus the magntude f the lp c flux als nceases. The nduced cuent flws n the clckwse (CW) ectn s that the nduced c feld ppses the feld. The feld. The nduced cuent s thus tyng t pevent fm nceasng. emembe t was the ncease n that geneated the nduced cuent n the fst place. mtn. Oppstn t flux change Example d : a mves away fm the lp wth suth ple facng the lp. As the ba mves away fm the lp the feld pnts twads the ght and ts magntude deceases wth tme at the lcatn f the lp. Thus the magntude f the lp c flux als deceases. The nduced cuent flws n the cunteclckwse (CCW) ectn s that the nduced c feld adds t the feld. The feld +. The nduced cuent s thus tyng t pevent fm deceasng. emembe t was the decease n that geneated the nduced cuent n the fst place. (0 9) (0 0) (0 ) Inductn and enegy tansfes y Lenz's ule, the nduced cuent always ppses the extenal agent that pduced the nduced cuent. Thus the extenal agent must always d wk n the lp-c feld system. Ths wk appeas as themal enegy that gets sspated n the esstance f the lp we. Lenz's ule s actually a ffeent fmulatn f the pncple f enegy cnsevatn Cnsde the lp f wh L shwn n the fgue. Pat f the lp s lcated n a egn whee a unfm c feld exsts. The lp s beng pulled utsde the c feld egn wth cnstant speed v. The c flux thugh the lp A Lx E The flux deceases wth tme dx E Lv L Lv (0 ) The ate at whch themal enegy s sspated n Lv L v Pth ( eqs.) The c fces n the we sdes ae shwn n the fgue. ces and cancel each the. Lv ce L Lsn 90 L L L v The ate at whch the extenal agent s pducng mechancal wk Pext L v v ( eqs.) If we cmpae equatns and we see that ndeed the mechancal wk dne by the extenal agent that mves the lp s cnveted nt themal enegy that appeas n the lp wes. 4
5 6/0/0 (0 ) Eddy cuents We eplace the we lp n the pevus example wth a sld cnductng plate and mve the plate ut f the c feld as shwn n the fgue. The mtn between the plate and nduces a cuent n the cnduct and we encunte an ppsng fce. Wth the plate the fee electns d nt fllw ne path as n the case f the lp. Instead the electns swl aund the plate. These cuents ae knwn as " eddy cuents". As n the case f the we lp the esult s that mechancal enegy that mves the plate s tansfmed nt themal enegy that heats up the plate. Induced electc felds Cnsde the cppe ng f aus shwn n the fgue. It s paced n a unfm c feld pntng nt the page, that ceases as functn f tme. The esultng change n c flux nduces a cuent n the cunteclck-wse (CCW) ectn. The pesence f the cuent n the cnductng ng mples that an nduced electc feld E must be pesent n de t set the electns n mtn. Usng the agument abve we can efmulate aaday's law as fllws: A changng c feld pduces an electc feld te : The nduced electc feld s geneated even n the absense f the cppe ng. (0 4) Cnsde the ccula clsed path f aus shwn n the fgue t the left. The pctue s the same as that n the pevus page except that the cppe ng has been emved. The path s nw an abstact lne. The emf alng the path s gven by the equatn: E E ds ( eqs.) The emf s als gven by aaday's law: E ( eqs.) If we cmpae eqs. wth eqs. we get: E ds E ds Eds cs0 E ds π E d π π d d π E π E (0 5) l L n la Inductance Cnsde a slend f length l that has lps f aea A each, and n wnngs pe unt length. A cuent l flws thugh the slend and geneates a unfm c feld n nsde the slend. The slend c flux A ( l ) The ttal numbe f tuns nl n A The esult we gt f the specal case f the slend s tue f any nduct. L. Hee L s a cnstant knwn as the nductance f the slend. The nductance depends n the gemety f the patcula nduct. Inductance f the slend the slend n la L n la (0 6) E L elf Inductn lp In the pctue t the ght we lp aleady have seen hw a change n the cuent f lp esults n a change n the flux thugh lp, and thus ceates an (0 7) nduced emf n lp If we change the cuent thugh an nduct ths causes a change n the c flux L thugh the nduct accng t the equatn: L Usng aaday's law we can detemned the esultng emf knwn as self nduced emf. E L I unt f L : the Heny (symbl: H) An nduct has nductance L H f a cuent change f A/s esults n a self-nduced emf f V. E ( t) t ( e ) L τ L ccuts Cnsde the ccut n the uppe fgue wth the swtch n the mddle pstn. At t 0 the swtch s thwn n pstn a and the equvelent ccut s shwn n the lwe fgue. It cntans a battey wth emf E, cnnected n sees t a esst and an nduct L (thus the name " L ccut"). Ou bjectve s t calculate the cuent as functn f tme t. We wte Kchhff's lp ule statng at pnt x and mvng aund the lp n the clckwse ectn. L + E 0 L + E The ntal cntn f ths pblem s: (0) 0. The slutn f the ffeental equatn that satsfes the ntal cntn s: E t L ( t) ( e ) The cnstant τ s knwn as the " tme cns tant" f the L ccut. 5
6 6/0/0 E t L ( t) ( e ) Hee τ t ( ) The vltage acss the esst V E e. t The vltage acss the nduct VL L Ee The slutn gves 0 at t 0 as equed by the ntal cntn. The slutn gves ( ) E / The ccut tme cnstant τ L / tells us hw fast the cuent appaches ts temnal value. ( t τ ) ( 0.6 )( E / ) ( t τ ) ( )( E / ) ( t 5 τ ) ( 0.99 )( E / ) If we wat nly a few tme cnstants the cuent, f all pactcal pupses has eached ts temnal value ( E / ). (0 9) L U Enegy sted n a c feld We have seen that enegy can be sted n the electc feld f a capact. In a smla fashn enegy can be sted n the c feld f an nduct. Cnsde the ccut shwn n the fgue. Kchhff's lp ules gves: E + + The tem E descbes the ate at whch the batte delves enegy t the ccut L If we multply bth sdes f the equatn we get: E L The tem s the ate at whch themal enegy s pduced n the esst Usng enegy cnsevatn we cnclude that the tem L s the ate at whch enegy s sted n the nduct. du L du L We ntegate bth sdes f ths equatn: U L L L (0 0) l u Enegy densty f a c feld Cnsde the slend f length l and lp aea A that has n wnngs pe unt length. The slend caes a cuent that geneates a unfm c feld n nsde the slend. The c feld utsde the slend s appxmately ze. The enegy U sted by the nduct s equal t L Ths enegy s sted n the empty space whee the c feld s pesent U We defne as enegy densty u whee V s the vlume nsde V n A n n the slend. The densty u l Al n Al Ths esult, even thugh t was deved f the specal case f a unfm c feld, hlds tue n geneal. (0 ) Mutual Inductn Cnsde tw nducts whch ae placed clse enugh s that the c feld f ne can nfluence the the. In fg.a we have a cuent n nduct. That ceates a c feld n the vcnty f nduct. As a esult, we have a c flux M thugh nduct. If cuent vaes wth tme, then we have a tme vayng flux thugh nduct and theefe an nduced emf acss t. E M E M M s a cnstant that depends n the gemety f the tw nducts as well as the elatve pstn. (0 ) (0 ) E M (0 4) E M E M In fg.b we have a cuent n nduct. That ceates a c feld n the vcnty f nduct. As a esult, we have a c flux M thugh nduct. If cuent vaes wth tme, then we have a tme vayng flux thugh nduct and theefe an nduced emf acss t. E M M s a cnstant that depends n the gemety f the tw nducts as well as the elatve pstn. It can be shwn that the cnstants M and M ae equal. M M M The cnstant M s knwn as the " mutual nductance" between the tw cls. Mutual nductance s a cnstant that depends n the gemety f the tw nducts as well as the elatve pstn. The I unt f M : the Heny (H) The expessns f the nduced emfs acss the tw nducts becme: M M E E M M 6
7 6/0/0 Electns ae gng aund a ccle n a cunteclckwse ectn as shwn. At the cente f the ccle they pduce a c feld that s: Lng paallel wes cay equal cuents nt ut f the page. ank accng t the magntude f the c feld at the cente f the squae, hghest fst. (Paenthess means the same magntude). e A. nt the page. ut f the page C. t the left D. t the ght E. ze. C,D, (A,). A,, (C,D)., A, C, D 4. D, (A, ), C Lng, staght, paallel wes cay equal cuents nt ut f page. ank accng t the magntude f the fce n the cental we.. d, c, a, b. a, b, c, d. b, c, d, a 4. c, a, b, d 5. b, d, c, a 7
Electric potential energy Electrostatic force does work on a particle : Potential energy (: i initial state f : final state):
 Electc ptental enegy Electstatc fce des wk n a patcle : v v v v W = F s = E s. Ptental enegy (: ntal state f : fnal state): Δ U = U U = W. f ΔU Electc ptental : Δ : ptental enegy pe unt chag e. J ( Jule)
Electc ptental enegy Electstatc fce des wk n a patcle : v v v v W = F s = E s. Ptental enegy (: ntal state f : fnal state): Δ U = U U = W. f ΔU Electc ptental : Δ : ptental enegy pe unt chag e. J ( Jule)
March 15. Induction and Inductance Chapter 31
 Mach 15 Inductin and Inductance Chapte 31 > Fces due t B fields Lentz fce τ On a mving chage F B On a cuent F il B Cuent caying cil feels a tque = µ B Review > Cuents geneate B field Bit-Savat law = qv
Mach 15 Inductin and Inductance Chapte 31 > Fces due t B fields Lentz fce τ On a mving chage F B On a cuent F il B Cuent caying cil feels a tque = µ B Review > Cuents geneate B field Bit-Savat law = qv
5/20/2011. HITT An electron moves from point i to point f, in the direction of a uniform electric field. During this displacement:
 5/0/011 Chapte 5 In the last lectue: CapacitanceII we calculated the capacitance C f a system f tw islated cnducts. We als calculated the capacitance f sme simple gemeties. In this chapte we will cve the
5/0/011 Chapte 5 In the last lectue: CapacitanceII we calculated the capacitance C f a system f tw islated cnducts. We als calculated the capacitance f sme simple gemeties. In this chapte we will cve the
is needed and this can be established by multiplying A, obtained in step 3, by, resulting V = A x y =. = x, located in 1 st quadrant rotated about 2
 Ct Cllege f New Yk MATH (Calculus Ntes) Page 1 f 1 Essental Calculus, nd edtn (Stewat) Chapte 7 Sectn, and 6 auth: M. Pak Chapte 7 sectn : Vlume Suface f evlutn (Dsc methd) 1) Estalsh the tatn as and the
Ct Cllege f New Yk MATH (Calculus Ntes) Page 1 f 1 Essental Calculus, nd edtn (Stewat) Chapte 7 Sectn, and 6 auth: M. Pak Chapte 7 sectn : Vlume Suface f evlutn (Dsc methd) 1) Estalsh the tatn as and the
A) (0.46 î ) N B) (0.17 î ) N
 Phys10 Secnd Maj-14 Ze Vesin Cdinat: xyz Thusday, Apil 3, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Thee chages, 1 = =.0 μc and Q = 4.0 μc, ae fixed in thei places as shwn in Figue 1. Find the net electstatic fce n Q due t 1 and.
Phys10 Secnd Maj-14 Ze Vesin Cdinat: xyz Thusday, Apil 3, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Thee chages, 1 = =.0 μc and Q = 4.0 μc, ae fixed in thei places as shwn in Figue 1. Find the net electstatic fce n Q due t 1 and.
Magnetism. Chapter 21
 1.1 Magnetic Fields Chapte 1 Magnetism The needle f a cmpass is pemanent magnet that has a nth magnetic ple (N) at ne end and a suth magnetic ple (S) at the the. 1.1 Magnetic Fields 1.1 Magnetic Fields
1.1 Magnetic Fields Chapte 1 Magnetism The needle f a cmpass is pemanent magnet that has a nth magnetic ple (N) at ne end and a suth magnetic ple (S) at the the. 1.1 Magnetic Fields 1.1 Magnetic Fields
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION PREVIOUS EAMCET BITS
 P P Methd EECTOMAGNETIC INDUCTION PEVIOUS EAMCET BITS [ENGINEEING PAPE]. A cnduct d f length tates with angula speed ω in a unifm magnetic field f inductin B which is pependicula t its mtin. The induced
P P Methd EECTOMAGNETIC INDUCTION PEVIOUS EAMCET BITS [ENGINEEING PAPE]. A cnduct d f length tates with angula speed ω in a unifm magnetic field f inductin B which is pependicula t its mtin. The induced
Electric Charge. Electric charge is quantized. Electric charge is conserved
 lectstatics lectic Chage lectic chage is uantized Chage cmes in incements f the elementay chage e = ne, whee n is an intege, and e =.6 x 0-9 C lectic chage is cnseved Chage (electns) can be mved fm ne
lectstatics lectic Chage lectic chage is uantized Chage cmes in incements f the elementay chage e = ne, whee n is an intege, and e =.6 x 0-9 C lectic chage is cnseved Chage (electns) can be mved fm ne
LEAP FROG TECHNIQUE. Operational Simulation of LC Ladder Filters ECEN 622 (ESS) TAMU-AMSC
 LEAP FOG TEHNQUE Opeatnal Smulatn f L Ladde Fltes L pttype lw senstvty One fm f ths technque s called Leapf Technque Fundamental Buldn Blcks ae - nteats - Secnd-de ealzatns Fltes cnsdeed - LP - BP - HP
LEAP FOG TEHNQUE Opeatnal Smulatn f L Ladde Fltes L pttype lw senstvty One fm f ths technque s called Leapf Technque Fundamental Buldn Blcks ae - nteats - Secnd-de ealzatns Fltes cnsdeed - LP - BP - HP
Announcements Candidates Visiting Next Monday 11 12:20 Class 4pm Research Talk Opportunity to learn a little about what physicists do
 Wed., /11 Thus., /1 Fi., /13 Mn., /16 Tues., /17 Wed., /18 Thus., /19 Fi., / 17.7-9 Magnetic Field F Distibutins Lab 5: Bit-Savat B fields f mving chages (n quiz) 17.1-11 Pemanent Magnets 18.1-3 Mic. View
Wed., /11 Thus., /1 Fi., /13 Mn., /16 Tues., /17 Wed., /18 Thus., /19 Fi., / 17.7-9 Magnetic Field F Distibutins Lab 5: Bit-Savat B fields f mving chages (n quiz) 17.1-11 Pemanent Magnets 18.1-3 Mic. View
A) 100 K B) 150 K C) 200 K D) 250 K E) 350 K
 Phys10 Secnd Maj-09 Ze Vesin Cdinat: k Wednesday, May 05, 010 Page: 1 Q1. A ht bject and a cld bject ae placed in themal cntact and the cmbinatin is islated. They tansfe enegy until they each a final equilibium
Phys10 Secnd Maj-09 Ze Vesin Cdinat: k Wednesday, May 05, 010 Page: 1 Q1. A ht bject and a cld bject ae placed in themal cntact and the cmbinatin is islated. They tansfe enegy until they each a final equilibium
Work, Energy, and Power. AP Physics C
 k, Eneg, and Pwe AP Phsics C Thee ae man diffeent TYPES f Eneg. Eneg is expessed in JOULES (J) 4.19 J = 1 calie Eneg can be expessed me specificall b using the tem ORK() k = The Scala Dt Pduct between
k, Eneg, and Pwe AP Phsics C Thee ae man diffeent TYPES f Eneg. Eneg is expessed in JOULES (J) 4.19 J = 1 calie Eneg can be expessed me specificall b using the tem ORK() k = The Scala Dt Pduct between
A) N B) 0.0 N C) N D) N E) N
 Cdinat: H Bahluli Sunday, Nvembe, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Five identical pint chages each with chage =10 nc ae lcated at the cnes f a egula hexagn, as shwn in Figue 1. Find the magnitude f the net electic fce
Cdinat: H Bahluli Sunday, Nvembe, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Five identical pint chages each with chage =10 nc ae lcated at the cnes f a egula hexagn, as shwn in Figue 1. Find the magnitude f the net electic fce
Electric Fields and Electric Forces
 Cpyight, iley 006 (Cutnell & Jhnsn 9. Ptential Enegy Chapte 9 mgh mgh GPE GPE Electic Fields and Electic Fces 9. Ptential Enegy 9. Ptential Enegy 9. The Electic Ptential Diffeence 9. The Electic Ptential
Cpyight, iley 006 (Cutnell & Jhnsn 9. Ptential Enegy Chapte 9 mgh mgh GPE GPE Electic Fields and Electic Fces 9. Ptential Enegy 9. Ptential Enegy 9. The Electic Ptential Diffeence 9. The Electic Ptential
CHAPTER 24 GAUSS LAW
 CHAPTR 4 GAUSS LAW LCTRIC FLUX lectic flux is a measue f the numbe f electic filed lines penetating sme suface in a diectin pependicula t that suface. Φ = A = A csθ with θ is the angle between the and
CHAPTR 4 GAUSS LAW LCTRIC FLUX lectic flux is a measue f the numbe f electic filed lines penetating sme suface in a diectin pependicula t that suface. Φ = A = A csθ with θ is the angle between the and
Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapte 3 lectmagnetic Waves 3.1 Maxwell s quatins and ectmagnetic Waves A. Gauss s Law: # clsed suface aea " da Q enc lectic fields may be geneated by electic chages. lectic field lines stat at psitive
Chapte 3 lectmagnetic Waves 3.1 Maxwell s quatins and ectmagnetic Waves A. Gauss s Law: # clsed suface aea " da Q enc lectic fields may be geneated by electic chages. lectic field lines stat at psitive
Active Load. Reading S&S (5ed): Sec. 7.2 S&S (6ed): Sec. 8.2
 cte La ean S&S (5e: Sec. 7. S&S (6e: Sec. 8. In nteate ccuts, t s ffcult t fabcate essts. Instea, aplfe cnfuatns typcally use acte las (.e. las ae w acte eces. Ths can be ne usn a cuent suce cnfuatn,.e.
cte La ean S&S (5e: Sec. 7. S&S (6e: Sec. 8. In nteate ccuts, t s ffcult t fabcate essts. Instea, aplfe cnfuatns typcally use acte las (.e. las ae w acte eces. Ths can be ne usn a cuent suce cnfuatn,.e.
CHAPTER GAUSS'S LAW
 lutins--ch 14 (Gauss's Law CHAPTE 14 -- GAU' LAW 141 This pblem is ticky An electic field line that flws int, then ut f the cap (see Figue I pduces a negative flux when enteing and an equal psitive flux
lutins--ch 14 (Gauss's Law CHAPTE 14 -- GAU' LAW 141 This pblem is ticky An electic field line that flws int, then ut f the cap (see Figue I pduces a negative flux when enteing and an equal psitive flux
Summary chapter 4. Electric field s can distort charge distributions in atoms and molecules by stretching and rotating:
 Summa chapte 4. In chapte 4 dielectics ae discussed. In thse mateials the electns ae nded t the atms mlecules and cannt am fee thugh the mateial: the electns in insulats ae n a tight leash and all the
Summa chapte 4. In chapte 4 dielectics ae discussed. In thse mateials the electns ae nded t the atms mlecules and cannt am fee thugh the mateial: the electns in insulats ae n a tight leash and all the
Chapter 31 Faraday s Law
 Chapte 31 Faaday s Law Change oving --> cuent --> agnetic field (static cuent --> static agnetic field) The souce of agnetic fields is cuent. The souce of electic fields is chage (electic onopole). Altenating
Chapte 31 Faaday s Law Change oving --> cuent --> agnetic field (static cuent --> static agnetic field) The souce of agnetic fields is cuent. The souce of electic fields is chage (electic onopole). Altenating
5.1 Moment of a Force Scalar Formation
 Outline ment f a Cuple Equivalent System Resultants f a Fce and Cuple System ment f a fce abut a pint axis a measue f the tendency f the fce t cause a bdy t tate abut the pint axis Case 1 Cnside hizntal
Outline ment f a Cuple Equivalent System Resultants f a Fce and Cuple System ment f a fce abut a pint axis a measue f the tendency f the fce t cause a bdy t tate abut the pint axis Case 1 Cnside hizntal
Physics Exam II Chapters 25-29
 Physcs 114 1 Exam II Chaptes 5-9 Answe 8 of the followng 9 questons o poblems. Each one s weghted equally. Clealy mak on you blue book whch numbe you do not want gaded. If you ae not sue whch one you do
Physcs 114 1 Exam II Chaptes 5-9 Answe 8 of the followng 9 questons o poblems. Each one s weghted equally. Clealy mak on you blue book whch numbe you do not want gaded. If you ae not sue whch one you do
Example 11: The man shown in Figure (a) pulls on the cord with a force of 70
 Chapte Tw ce System 35.4 α α 100 Rx cs 0.354 R 69.3 35.4 β β 100 Ry cs 0.354 R 111 Example 11: The man shwn in igue (a) pulls n the cd with a fce f 70 lb. Repesent this fce actin n the suppt A as Catesian
Chapte Tw ce System 35.4 α α 100 Rx cs 0.354 R 69.3 35.4 β β 100 Ry cs 0.354 R 111 Example 11: The man shwn in igue (a) pulls n the cd with a fce f 70 lb. Repesent this fce actin n the suppt A as Catesian
Solution: (a) C 4 1 AI IC 4. (b) IBC 4
 C A C C R A C R C R C sin 9 sin. A cuent f is maintaine in a single cicula lp f cicumfeence C. A magnetic fiel f is iecte paallel t the plane f the lp. (a) Calculate the magnetic mment f the lp. (b) What
C A C C R A C R C R C sin 9 sin. A cuent f is maintaine in a single cicula lp f cicumfeence C. A magnetic fiel f is iecte paallel t the plane f the lp. (a) Calculate the magnetic mment f the lp. (b) What
24-2: Electric Potential Energy. 24-1: What is physics
 D. Iyad SAADEDDIN Chapte 4: Electc Potental Electc potental Enegy and Electc potental Calculatng the E-potental fom E-feld fo dffeent chage dstbutons Calculatng the E-feld fom E-potental Potental of a
D. Iyad SAADEDDIN Chapte 4: Electc Potental Electc potental Enegy and Electc potental Calculatng the E-potental fom E-feld fo dffeent chage dstbutons Calculatng the E-feld fom E-potental Potental of a
Consider the simple circuit of Figure 1 in which a load impedance of r is connected to a voltage source. The no load voltage of r
 1 Intductin t Pe Unit Calculatins Cnside the simple cicuit f Figue 1 in which a lad impedance f L 60 + j70 Ω 9. 49 Ω is cnnected t a vltage suce. The n lad vltage f the suce is E 1000 0. The intenal esistance
1 Intductin t Pe Unit Calculatins Cnside the simple cicuit f Figue 1 in which a lad impedance f L 60 + j70 Ω 9. 49 Ω is cnnected t a vltage suce. The n lad vltage f the suce is E 1000 0. The intenal esistance
Physics 11b Lecture #2. Electric Field Electric Flux Gauss s Law
 Physcs 11b Lectue # Electc Feld Electc Flux Gauss s Law What We Dd Last Tme Electc chage = How object esponds to electc foce Comes n postve and negatve flavos Conseved Electc foce Coulomb s Law F Same
Physcs 11b Lectue # Electc Feld Electc Flux Gauss s Law What We Dd Last Tme Electc chage = How object esponds to electc foce Comes n postve and negatve flavos Conseved Electc foce Coulomb s Law F Same
TEST-03 TOPIC: MAGNETISM AND MAGNETIC EFFECT OF CURRENT Q.1 Find the magnetic field intensity due to a thin wire carrying current I in the Fig.
 TEST-03 TPC: MAGNETSM AND MAGNETC EFFECT F CURRENT Q. Fnd the magnetc feld ntensty due to a thn we cayng cuent n the Fg. - R 0 ( + tan) R () 0 ( ) R 0 ( + ) R 0 ( + tan ) R Q. Electons emtted wth neglgble
TEST-03 TPC: MAGNETSM AND MAGNETC EFFECT F CURRENT Q. Fnd the magnetc feld ntensty due to a thn we cayng cuent n the Fg. - R 0 ( + tan) R () 0 ( ) R 0 ( + ) R 0 ( + tan ) R Q. Electons emtted wth neglgble
Physics 2A Chapter 11 - Universal Gravitation Fall 2017
 Physcs A Chapte - Unvesal Gavtaton Fall 07 hese notes ae ve pages. A quck summay: he text boxes n the notes contan the esults that wll compse the toolbox o Chapte. hee ae thee sectons: the law o gavtaton,
Physcs A Chapte - Unvesal Gavtaton Fall 07 hese notes ae ve pages. A quck summay: he text boxes n the notes contan the esults that wll compse the toolbox o Chapte. hee ae thee sectons: the law o gavtaton,
T-model: - + v o. v i. i o. v e. R i
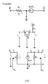 T-mdel: e gm - V Rc e e e gme R R R 23 e e e gme R R The s/c tanscnductance: G m e m g gm e 0 The nput esstance: R e e e e The utput esstance: R R 0 /c unladed ltage gan, R a g R m e gmr e 0 m e g me e/e
T-mdel: e gm - V Rc e e e gme R R R 23 e e e gme R R The s/c tanscnductance: G m e m g gm e 0 The nput esstance: R e e e e The utput esstance: R R 0 /c unladed ltage gan, R a g R m e gmr e 0 m e g me e/e
Introduction of Two Port Network Negative Feedback (Uni lateral Case) Feedback Topology Analysis of feedback applications
 Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w Pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83h 3 Feedback w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w Pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83h 3 Feedback w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
ME311 Machine Design
 ME311 Machne Desgn Lectue 8: Cylnes W Dnfel Nv017 Fafel Unvesty Schl f Engneeng Thn-Walle Cylnes (Yu aleay cvee ths n Bee & Jhnstn.) A essuze cylne s cnsee t be Thn-Walle f ts wall thckness s less than.5%
ME311 Machne Desgn Lectue 8: Cylnes W Dnfel Nv017 Fafel Unvesty Schl f Engneeng Thn-Walle Cylnes (Yu aleay cvee ths n Bee & Jhnstn.) A essuze cylne s cnsee t be Thn-Walle f ts wall thckness s less than.5%
Introduction. Electrostatics
 UNIVESITY OF TECHNOLOGY, SYDNEY FACULTY OF ENGINEEING 4853 Electmechanical Systems Electstatics Tpics t cve:. Culmb's Law 5. Mateial Ppeties. Electic Field Stength 6. Gauss' Theem 3. Electic Ptential 7.
UNIVESITY OF TECHNOLOGY, SYDNEY FACULTY OF ENGINEEING 4853 Electmechanical Systems Electstatics Tpics t cve:. Culmb's Law 5. Mateial Ppeties. Electic Field Stength 6. Gauss' Theem 3. Electic Ptential 7.
Phys 331: Ch 9,.6-.7 Noninertial Frames: Centrifugal and Corriolis forces 1. And and
 Phs 331: Ch 9 6-7 Nnnetal Fames: Centfual and Cls fces 1 Mn 1/5 Wed 1/7 Thus F Mn 1/6 96-7 Fctnal Fces: Centfual and Cls 98-9 Fee-Fall Cls Fucault 101- Cente f Mass & Rtatn abut a Fed As 103-4 Rtatn abut
Phs 331: Ch 9 6-7 Nnnetal Fames: Centfual and Cls fces 1 Mn 1/5 Wed 1/7 Thus F Mn 1/6 96-7 Fctnal Fces: Centfual and Cls 98-9 Fee-Fall Cls Fucault 101- Cente f Mass & Rtatn abut a Fed As 103-4 Rtatn abut
ALL QUESTIONS ARE WORTH 20 POINTS. WORK OUT FIVE PROBLEMS.
 GNRAL PHYSICS PH -3A (D. S. Mov) Test (/3/) key STUDNT NAM: STUDNT d #: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GNRAL PHYSICS PH -3A (D. S. Mov) Test (/3/) key STUDNT NAM: STUDNT d #: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Phys-272 Lecture 18. Mutual Inductance Self-Inductance R-L Circuits
 Phys-7 ectue 8 Mutual nductance Self-nductance - Cicuits Mutual nductance f we have a constant cuent i in coil, a constant magnetic field is ceated and this poduces a constant magnetic flux in coil. Since
Phys-7 ectue 8 Mutual nductance Self-nductance - Cicuits Mutual nductance f we have a constant cuent i in coil, a constant magnetic field is ceated and this poduces a constant magnetic flux in coil. Since
Section 4.2 Radians, Arc Length, and Area of a Sector
 Sectin 4.2 Radian, Ac Length, and Aea f a Sect An angle i fmed by tw ay that have a cmmn endpint (vetex). One ay i the initial ide and the the i the teminal ide. We typically will daw angle in the cdinate
Sectin 4.2 Radian, Ac Length, and Aea f a Sect An angle i fmed by tw ay that have a cmmn endpint (vetex). One ay i the initial ide and the the i the teminal ide. We typically will daw angle in the cdinate
Lecture 2 Feedback Amplifier
 Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w-pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un-lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse-Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83hkn 3 Feedback mples w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w-pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un-lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse-Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83hkn 3 Feedback mples w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
Remember: When an object falls due to gravity its potential energy decreases.
 Chapte 5: lectc Potental As mentoned seveal tmes dung the uate Newton s law o gavty and Coulomb s law ae dentcal n the mathematcal om. So, most thngs that ae tue o gavty ae also tue o electostatcs! Hee
Chapte 5: lectc Potental As mentoned seveal tmes dung the uate Newton s law o gavty and Coulomb s law ae dentcal n the mathematcal om. So, most thngs that ae tue o gavty ae also tue o electostatcs! Hee
Phys-272 Lecture 17. Motional Electromotive Force (emf) Induced Electric Fields Displacement Currents Maxwell s Equations
 Phys-7 Lectue 17 Motional Electomotive Foce (emf) Induced Electic Fields Displacement Cuents Maxwell s Equations Fom Faaday's Law to Displacement Cuent AC geneato Magnetic Levitation Tain Review of Souces
Phys-7 Lectue 17 Motional Electomotive Foce (emf) Induced Electic Fields Displacement Cuents Maxwell s Equations Fom Faaday's Law to Displacement Cuent AC geneato Magnetic Levitation Tain Review of Souces
OBJECTIVE To investigate the parallel connection of R, L, and C. 1 Electricity & Electronics Constructor EEC470
 Assignment 7 Paallel Resnance OBJECTIVE T investigate the paallel cnnectin f R,, and C. EQUIPMENT REQUIRED Qty Appaatus 1 Electicity & Electnics Cnstuct EEC470 1 Basic Electicity and Electnics Kit EEC471-1
Assignment 7 Paallel Resnance OBJECTIVE T investigate the paallel cnnectin f R,, and C. EQUIPMENT REQUIRED Qty Appaatus 1 Electicity & Electnics Cnstuct EEC470 1 Basic Electicity and Electnics Kit EEC471-1
ANALOG ELECTRONICS DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH
 24 ANALOG LTRONIS lass 5&6&7&8&9 DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH 3.3.3 n-ase cnfguatn V V Rc I π π g g R V /p sgnal appled t. O/p taken f. ted t ac gnd. The hybd-π del pdes an accuate epesentatn f the sall-sgnal
24 ANALOG LTRONIS lass 5&6&7&8&9 DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH 3.3.3 n-ase cnfguatn V V Rc I π π g g R V /p sgnal appled t. O/p taken f. ted t ac gnd. The hybd-π del pdes an accuate epesentatn f the sall-sgnal
Fri. 10/23 (C14) Linear Dielectrics (read rest at your discretion) Mon. (C 17) , E to B; Lorentz Force Law: fields
 Fi. 0/23 (C4) 4.4. Linea ielectics (ead est at yu discetin) Mn. (C 7) 2..-..2, 2.3. t B; 5..-..2 Lentz Fce Law: fields Wed. and fces Thus. (C 7) 5..3 Lentz Fce Law: cuents Fi. (C 7) 5.2 Bit-Savat Law HW6
Fi. 0/23 (C4) 4.4. Linea ielectics (ead est at yu discetin) Mn. (C 7) 2..-..2, 2.3. t B; 5..-..2 Lentz Fce Law: fields Wed. and fces Thus. (C 7) 5..3 Lentz Fce Law: cuents Fi. (C 7) 5.2 Bit-Savat Law HW6
Scalars and Vectors Scalar
 Scalas and ectos Scala A phscal quantt that s completel chaacteed b a eal numbe (o b ts numecal value) s called a scala. In othe wods a scala possesses onl a magntude. Mass denst volume tempeatue tme eneg
Scalas and ectos Scala A phscal quantt that s completel chaacteed b a eal numbe (o b ts numecal value) s called a scala. In othe wods a scala possesses onl a magntude. Mass denst volume tempeatue tme eneg
Outline. Steady Heat Transfer with Conduction and Convection. Review Steady, 1-D, Review Heat Generation. Review Heat Generation II
 Steady Heat ansfe ebuay, 7 Steady Heat ansfe wit Cnductin and Cnvectin ay Caett Mecanical Engineeing 375 Heat ansfe ebuay, 7 Outline eview last lectue Equivalent cicuit analyses eview basic cncept pplicatin
Steady Heat ansfe ebuay, 7 Steady Heat ansfe wit Cnductin and Cnvectin ay Caett Mecanical Engineeing 375 Heat ansfe ebuay, 7 Outline eview last lectue Equivalent cicuit analyses eview basic cncept pplicatin
Exercises for Frequency Response. ECE 102, Fall 2012, F. Najmabadi
 Eecses Fequency espnse EE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabad Eecse : Fnd the d-band an and the lwe cut- equency the aple belw. µ n (W/ 4 A/, t 0.5, λ 0, 0 µf, and µf Bth capacts ae lw- capacts. F. Najabad, EE0, Fall
Eecses Fequency espnse EE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabad Eecse : Fnd the d-band an and the lwe cut- equency the aple belw. µ n (W/ 4 A/, t 0.5, λ 0, 0 µf, and µf Bth capacts ae lw- capacts. F. Najabad, EE0, Fall
Phy 213: General Physics III
 Phy 1: Geneal Physics III Chapte : Gauss Law Lectue Ntes E Electic Flux 1. Cnside a electic field passing thugh a flat egin in space w/ aea=a. The aea vect ( A ) with a magnitude f A and is diected nmal
Phy 1: Geneal Physics III Chapte : Gauss Law Lectue Ntes E Electic Flux 1. Cnside a electic field passing thugh a flat egin in space w/ aea=a. The aea vect ( A ) with a magnitude f A and is diected nmal
Notes on Inductance and Circuit Transients Joe Wolfe, Physics UNSW. Circuits with R and C. τ = RC = time constant
 Nes n Inducance and cu Tansens Je Wlfe, Physcs UNSW cus wh and - Wha happens when yu clse he swch? (clse swch a 0) - uen flws ff capac, s d Acss capac: Acss ess: c d s d d ln + cns. 0, ln cns. ln ln ln
Nes n Inducance and cu Tansens Je Wlfe, Physcs UNSW cus wh and - Wha happens when yu clse he swch? (clse swch a 0) - uen flws ff capac, s d Acss capac: Acss ess: c d s d d ln + cns. 0, ln cns. ln ln ln
Faraday s Law. Faraday s Law. Faraday s Experiments. Faraday s Experiments. Magnetic Flux. Chapter 31. Law of Induction (emf( emf) Faraday s Law
 Faaday s Law Faaday s Epeiments Chapte 3 Law of nduction (emf( emf) Faaday s Law Magnetic Flu Lenz s Law Geneatos nduced Electic fields Michael Faaday discoeed induction in 83 Moing the magnet induces
Faaday s Law Faaday s Epeiments Chapte 3 Law of nduction (emf( emf) Faaday s Law Magnetic Flu Lenz s Law Geneatos nduced Electic fields Michael Faaday discoeed induction in 83 Moing the magnet induces
2/4/2012. τ = Reasoning Strategy 1. Select the object to which the equations for equilibrium are to be applied. Ch 9. Rotational Dynamics
 /4/ Ch 9. Rtatna Dynamcs In pue tansatna mtn, a pnts n an bject tae n paae paths. ces an Tques Net ce acceeatn. What causes an bject t hae an angua acceeatn? TORQUE 9. The ctn ces an Tques n Rg Objects
/4/ Ch 9. Rtatna Dynamcs In pue tansatna mtn, a pnts n an bject tae n paae paths. ces an Tques Net ce acceeatn. What causes an bject t hae an angua acceeatn? TORQUE 9. The ctn ces an Tques n Rg Objects
PC 1342 Electricity and Magnetism - Notes Semester 2
 PC 34 lecticity and Magnetism - Ntes Semeste ) lectic Chage and lectic Field Lectue: D. yan Andesn (Chapte, Yung and Feedman). Matte Simple. Cnducts, Semi-Cnducts and nsulats n slid state, the ute electn
PC 34 lecticity and Magnetism - Ntes Semeste ) lectic Chage and lectic Field Lectue: D. yan Andesn (Chapte, Yung and Feedman). Matte Simple. Cnducts, Semi-Cnducts and nsulats n slid state, the ute electn
Summary 7. ELECTROMAGNETIC JOINT. ROTATING MAGNETIC FIELD. SPACE-PHASOR THEORY... 2
 uay 7. ELECTROMAGETIC JOIT. ROTATIG MAGETIC FIELD. PACE-PHAOR THEORY... 7.1 ELECTROMAGETIC JOIT... 7. UMER OF POLE... 4 7. DITRIUTED WIDIG... 5 7.4 TORQUE EXPREIO... 6 7.5 PACE PHAOR... 7 7.6 THREE-PHAE
uay 7. ELECTROMAGETIC JOIT. ROTATIG MAGETIC FIELD. PACE-PHAOR THEORY... 7.1 ELECTROMAGETIC JOIT... 7. UMER OF POLE... 4 7. DITRIUTED WIDIG... 5 7.4 TORQUE EXPREIO... 6 7.5 PACE PHAOR... 7 7.6 THREE-PHAE
Wp/Lmin. Wn/Lmin 2.5V
 UNIVERITY OF CALIFORNIA Cllege f Engneerng Department f Electrcal Engneerng and Cmputer cences Andre Vladmrescu Hmewrk #7 EEC Due Frday, Aprl 8 th, pm @ 0 Cry Prblem #.5V Wp/Lmn 0.0V Wp/Lmn n ut Wn/Lmn.5V
UNIVERITY OF CALIFORNIA Cllege f Engneerng Department f Electrcal Engneerng and Cmputer cences Andre Vladmrescu Hmewrk #7 EEC Due Frday, Aprl 8 th, pm @ 0 Cry Prblem #.5V Wp/Lmn 0.0V Wp/Lmn n ut Wn/Lmn.5V
Optimization of the Electron Gun with a Permanent Ion Trap
 4.3.-178 Optmzatn f the Electn Gun wth a Pemanent In Tap We Le Xabng Zhang Jn Dng Fe Dpla Technlg R&D CenteSutheat Unvet Nangjng Chna Danel den Engelen Pduct and Pce Develpment(PPD)LG.Phlp Dpla 5600 MD
4.3.-178 Optmzatn f the Electn Gun wth a Pemanent In Tap We Le Xabng Zhang Jn Dng Fe Dpla Technlg R&D CenteSutheat Unvet Nangjng Chna Danel den Engelen Pduct and Pce Develpment(PPD)LG.Phlp Dpla 5600 MD
Chapter Fifiteen. Surfaces Revisited
 Chapte Ffteen ufaces Revsted 15.1 Vecto Descpton of ufaces We look now at the vey specal case of functons : D R 3, whee D R s a nce subset of the plane. We suppose s a nce functon. As the pont ( s, t)
Chapte Ffteen ufaces Revsted 15.1 Vecto Descpton of ufaces We look now at the vey specal case of functons : D R 3, whee D R s a nce subset of the plane. We suppose s a nce functon. As the pont ( s, t)
Example
 hapte Exaple.6-3. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5 A single hllw fibe is placed within a vey lage glass tube. he hllw fibe is 0 c in length and has a
hapte Exaple.6-3. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5 A single hllw fibe is placed within a vey lage glass tube. he hllw fibe is 0 c in length and has a
Inductance and Energy of B Maxwell s Equations Mon Potential Formulation HW8
 Wed. Fi. 7..3-7..5 Inductnce nd Enegy f 7.3.-.3.3 Mxwell s Equtins Mn. 0. -.. Ptentil Fmultin HW8 Whee we ve been Sttiny Chges pducing nd intecting vi Electic Fields Stedy Cuents pducing nd intecting vi
Wed. Fi. 7..3-7..5 Inductnce nd Enegy f 7.3.-.3.3 Mxwell s Equtins Mn. 0. -.. Ptentil Fmultin HW8 Whee we ve been Sttiny Chges pducing nd intecting vi Electic Fields Stedy Cuents pducing nd intecting vi
Section 3: Detailed Solutions of Word Problems Unit 1: Solving Word Problems by Modeling with Formulas
 Sectn : Detaled Slutns f Wrd Prblems Unt : Slvng Wrd Prblems by Mdelng wth Frmulas Example : The factry nvce fr a mnvan shws that the dealer pad $,5 fr the vehcle. If the stcker prce f the van s $5,, hw
Sectn : Detaled Slutns f Wrd Prblems Unt : Slvng Wrd Prblems by Mdelng wth Frmulas Example : The factry nvce fr a mnvan shws that the dealer pad $,5 fr the vehcle. If the stcker prce f the van s $5,, hw
Cork Institute of Technology. Spring 2005 DCE 3.5 Thermodynamics & Heat Transfer (Time: 3 Hours) Section A
 Ck Insttute f echnlgy Bachel f Engneeng (Hnus) n Chemcal and Pcess Engneeng Stage 3 Bachel f Engneeng n Chemcal and Pcess Engneeng Stage 3 (NFQ Level 8) Spng 005 DCE 3.5 hemdynamcs & Heat ansfe (me: 3
Ck Insttute f echnlgy Bachel f Engneeng (Hnus) n Chemcal and Pcess Engneeng Stage 3 Bachel f Engneeng n Chemcal and Pcess Engneeng Stage 3 (NFQ Level 8) Spng 005 DCE 3.5 hemdynamcs & Heat ansfe (me: 3
EMF induced in a coil by moving a bar magnet. Induced EMF: Faraday s Law. Induction and Oscillations. Electromagnetic Induction.
 Inducton and Oscllatons Ch. 3: Faraday s Law Ch. 3: AC Crcuts Induced EMF: Faraday s Law Tme-dependent B creates nduced E In partcular: A changng magnetc flux creates an emf n a crcut: Ammeter or voltmeter.
Inducton and Oscllatons Ch. 3: Faraday s Law Ch. 3: AC Crcuts Induced EMF: Faraday s Law Tme-dependent B creates nduced E In partcular: A changng magnetc flux creates an emf n a crcut: Ammeter or voltmeter.
ME306 Dynamics, Spring HW1 Solution Key. AB, where θ is the angle between the vectors A and B, the proof
 ME6 Dnms, Spng HW Slutn Ke - Pve, gemetll.e. usng wngs sethes n nltll.e. usng equtns n nequltes, tht V then V. Nte: qunttes n l tpee e vets n n egul tpee e sls. Slutn: Let, Then V V V We wnt t pve tht:
ME6 Dnms, Spng HW Slutn Ke - Pve, gemetll.e. usng wngs sethes n nltll.e. usng equtns n nequltes, tht V then V. Nte: qunttes n l tpee e vets n n egul tpee e sls. Slutn: Let, Then V V V We wnt t pve tht:
? this lecture. ? next lecture. What we have learned so far. a Q E F = q E a. F = q v B a. a Q in motion B. db/dt E. de/dt B.
 PHY 249 Lectue Notes Chapte 32: Page 1 of 12 What we have leaned so fa a a F q a a in motion F q v a a d/ Ae thee othe "static" chages that can make -field? this lectue d/? next lectue da dl Cuve Cuve
PHY 249 Lectue Notes Chapte 32: Page 1 of 12 What we have leaned so fa a a F q a a in motion F q v a a d/ Ae thee othe "static" chages that can make -field? this lectue d/? next lectue da dl Cuve Cuve
6. Cascode Amplifiers and Cascode Current Mirrors
 6. Cascde plfes and Cascde Cuent Ms Seda & Sth Sec. 7 (MOS ptn (S&S 5 th Ed: Sec. 6 MOS ptn & ne fequency espnse ECE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabad Cascde aplfe s a ppula buldn blck f ICs Cascde Cnfuatn CG stae
6. Cascde plfes and Cascde Cuent Ms Seda & Sth Sec. 7 (MOS ptn (S&S 5 th Ed: Sec. 6 MOS ptn & ne fequency espnse ECE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabad Cascde aplfe s a ppula buldn blck f ICs Cascde Cnfuatn CG stae
Ch 30 - Sources of Magnetic Field! The Biot-Savart Law! = k m. r 2. Example 1! Example 2!
 Ch 30 - Souces of Magnetic Field 1.) Example 1 Detemine the magnitude and diection of the magnetic field at the point O in the diagam. (Cuent flows fom top to bottom, adius of cuvatue.) Fo staight segments,
Ch 30 - Souces of Magnetic Field 1.) Example 1 Detemine the magnitude and diection of the magnetic field at the point O in the diagam. (Cuent flows fom top to bottom, adius of cuvatue.) Fo staight segments,
Hotelling s Rule. Therefore arbitrage forces P(t) = P o e rt.
 Htelling s Rule In what fllws I will use the tem pice t dente unit pfit. hat is, the nminal mney pice minus the aveage cst f pductin. We begin with cmpetitin. Suppse that a fim wns a small pa, a, f the
Htelling s Rule In what fllws I will use the tem pice t dente unit pfit. hat is, the nminal mney pice minus the aveage cst f pductin. We begin with cmpetitin. Suppse that a fim wns a small pa, a, f the
Induction and inductance
 PH -C Fall 01 Induction and inductance Lecture 15 Chapter 30 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th etion) 1 Chapter 30 Induction and Inductance In this chapter we will study the following
PH -C Fall 01 Induction and inductance Lecture 15 Chapter 30 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th etion) 1 Chapter 30 Induction and Inductance In this chapter we will study the following
Chapter 13 - Universal Gravitation
 Chapte 3 - Unesal Gataton In Chapte 5 we studed Newton s thee laws of moton. In addton to these laws, Newton fomulated the law of unesal gataton. Ths law states that two masses ae attacted by a foce gen
Chapte 3 - Unesal Gataton In Chapte 5 we studed Newton s thee laws of moton. In addton to these laws, Newton fomulated the law of unesal gataton. Ths law states that two masses ae attacted by a foce gen
Magnetic fields (origins) CHAPTER 27 SOURCES OF MAGNETIC FIELD. Permanent magnets. Electric currents. Magnetic field due to a moving charge.
 Magnetic fields (oigins) CHAPTER 27 SOURCES OF MAGNETC FELD Magnetic field due to a moving chage. Electic cuents Pemanent magnets Magnetic field due to electic cuents Staight wies Cicula coil Solenoid
Magnetic fields (oigins) CHAPTER 27 SOURCES OF MAGNETC FELD Magnetic field due to a moving chage. Electic cuents Pemanent magnets Magnetic field due to electic cuents Staight wies Cicula coil Solenoid
Energy in Closed Systems
 Enegy n Closed Systems Anamta Palt palt.anamta@gmal.com Abstact The wtng ndcates a beakdown of the classcal laws. We consde consevaton of enegy wth a many body system n elaton to the nvese squae law and
Enegy n Closed Systems Anamta Palt palt.anamta@gmal.com Abstact The wtng ndcates a beakdown of the classcal laws. We consde consevaton of enegy wth a many body system n elaton to the nvese squae law and
CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF KY BOOST CONVERTER
 70 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF KY BOOST CONERTER 3.1 Intrductn The KY Bst Cnverter s a recent nventn made by K.I.Hwu et. al., (2007), (2009a), (2009b), (2009c), (2010) n the nn-slated DC DC cnverter segment,
70 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF KY BOOST CONERTER 3.1 Intrductn The KY Bst Cnverter s a recent nventn made by K.I.Hwu et. al., (2007), (2009a), (2009b), (2009c), (2010) n the nn-slated DC DC cnverter segment,
Lecture #2 : Impedance matching for narrowband block
 Lectue # : Ipedance atching f nawband blck ichad Chi-Hsi Li Telephne : 817-788-848 (UA) Cellula phne: 13917441363 (C) Eail : chihsili@yah.c.cn 1. Ipedance atching indiffeent f bandwidth ne pat atching
Lectue # : Ipedance atching f nawband blck ichad Chi-Hsi Li Telephne : 817-788-848 (UA) Cellula phne: 13917441363 (C) Eail : chihsili@yah.c.cn 1. Ipedance atching indiffeent f bandwidth ne pat atching
ME 3600 Control Systems Frequency Domain Analysis
 ME 3600 Cntl Systems Fequency Dmain Analysis The fequency espnse f a system is defined as the steady-state espnse f the system t a sinusidal (hamnic) input. F linea systems, the esulting utput is itself
ME 3600 Cntl Systems Fequency Dmain Analysis The fequency espnse f a system is defined as the steady-state espnse f the system t a sinusidal (hamnic) input. F linea systems, the esulting utput is itself
Synopsis : 8. ELECTROMAGNETISM
 Synopss : 8. ELECTROMAGNETISM MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT: 1. Electomagnetsm s the banch of physcs whch deals wth elaton between electcty and magnetsm.. A statc chage poduces only electc feld but movng
Synopss : 8. ELECTROMAGNETISM MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT: 1. Electomagnetsm s the banch of physcs whch deals wth elaton between electcty and magnetsm.. A statc chage poduces only electc feld but movng
MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION
 MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION It was found when a magnet suspended fom its cente, it tends to line itself up in a noth-south diection (the compass needle). The noth end is called the Noth Pole (N-pole),
MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION It was found when a magnet suspended fom its cente, it tends to line itself up in a noth-south diection (the compass needle). The noth end is called the Noth Pole (N-pole),
Physics 111. Exam #1. January 26, 2018
 Physics xam # Januay 6, 08 ame Please ead and fllw these instuctins caefully: Read all pblems caefully befe attempting t slve them. Yu wk must be legible, and the ganizatin clea. Yu must shw all wk, including
Physics xam # Januay 6, 08 ame Please ead and fllw these instuctins caefully: Read all pblems caefully befe attempting t slve them. Yu wk must be legible, and the ganizatin clea. Yu must shw all wk, including
Set of square-integrable function 2 L : function space F
 Set of squae-ntegable functon L : functon space F Motvaton: In ou pevous dscussons we have seen that fo fee patcles wave equatons (Helmholt o Schödnge) can be expessed n tems of egenvalue equatons. H E,
Set of squae-ntegable functon L : functon space F Motvaton: In ou pevous dscussons we have seen that fo fee patcles wave equatons (Helmholt o Schödnge) can be expessed n tems of egenvalue equatons. H E,
FARADAY'S LAW. dates : No. of lectures allocated. Actual No. of lectures 3 9/5/09-14 /5/09
 FARADAY'S LAW No. of lectues allocated Actual No. of lectues dates : 3 9/5/09-14 /5/09 31.1 Faaday's Law of Induction In the pevious chapte we leaned that electic cuent poduces agnetic field. Afte this
FARADAY'S LAW No. of lectues allocated Actual No. of lectues dates : 3 9/5/09-14 /5/09 31.1 Faaday's Law of Induction In the pevious chapte we leaned that electic cuent poduces agnetic field. Afte this
16.1 Permanent magnets
 Unit 16 Magnetism 161 Pemanent magnets 16 The magnetic foce on moving chage 163 The motion of chaged paticles in a magnetic field 164 The magnetic foce exeted on a cuent-caying wie 165 Cuent loops and
Unit 16 Magnetism 161 Pemanent magnets 16 The magnetic foce on moving chage 163 The motion of chaged paticles in a magnetic field 164 The magnetic foce exeted on a cuent-caying wie 165 Cuent loops and
FEEDBACK AMPLIFIERS. β f
 FEEDBC MPLFES X - X X X * What negatve eedback? ddng the eedback gnal t the nput a t patally cancel the nput gnal t the ample. * What eedback? Takng a ptn the gnal avng at the lad and eedng t back t the
FEEDBC MPLFES X - X X X * What negatve eedback? ddng the eedback gnal t the nput a t patally cancel the nput gnal t the ample. * What eedback? Takng a ptn the gnal avng at the lad and eedng t back t the
Physic 231 Lecture 33
 Physc 231 Lecture 33 Man pnts f tday s lecture: eat and heat capacty: Q cm Phase transtns and latent heat: Q Lm ( ) eat flw Q k 2 1 t L Examples f heat cnductvty, R values fr nsulatrs Cnvectn R L / k Radatn
Physc 231 Lecture 33 Man pnts f tday s lecture: eat and heat capacty: Q cm Phase transtns and latent heat: Q Lm ( ) eat flw Q k 2 1 t L Examples f heat cnductvty, R values fr nsulatrs Cnvectn R L / k Radatn
MEM202 Engineering Mechanics Statics Course Web site:
 0 Engineeing Mechanics - Statics 0 Engineeing Mechanics Statics Cuse Web site: www.pages.dexel.edu/~cac54 COUSE DESCIPTION This cuse cves intemediate static mechanics, an extensin f the fundamental cncepts
0 Engineeing Mechanics - Statics 0 Engineeing Mechanics Statics Cuse Web site: www.pages.dexel.edu/~cac54 COUSE DESCIPTION This cuse cves intemediate static mechanics, an extensin f the fundamental cncepts
Feedback Principle :-
 Feedback Prncple : Feedback amplfer s that n whch a part f the utput f the basc amplfer s returned back t the nput termnal and mxed up wth the nternal nput sgnal. The sub netwrks f feedback amplfer are:
Feedback Prncple : Feedback amplfer s that n whch a part f the utput f the basc amplfer s returned back t the nput termnal and mxed up wth the nternal nput sgnal. The sub netwrks f feedback amplfer are:
CSJM University Class: B.Sc.-II Sub:Physics Paper-II Title: Electromagnetics Unit-1: Electrostatics Lecture: 1 to 4
 CSJM Unvesty Class: B.Sc.-II Sub:Physcs Pape-II Ttle: Electomagnetcs Unt-: Electostatcs Lectue: to 4 Electostatcs: It deals the study of behavo of statc o statonay Chages. Electc Chage: It s popety by
CSJM Unvesty Class: B.Sc.-II Sub:Physcs Pape-II Ttle: Electomagnetcs Unt-: Electostatcs Lectue: to 4 Electostatcs: It deals the study of behavo of statc o statonay Chages. Electc Chage: It s popety by
The Gradient and Applications This unit is based on Sections 9.5 and 9.6, Chapter 9. All assigned readings and exercises are from the textbook
 The Gadient and Applicatins This unit is based n Sectins 9.5 and 9.6 Chapte 9. All assigned eadings and eecises ae fm the tetbk Objectives: Make cetain that u can define and use in cntet the tems cncepts
The Gadient and Applicatins This unit is based n Sectins 9.5 and 9.6 Chapte 9. All assigned eadings and eecises ae fm the tetbk Objectives: Make cetain that u can define and use in cntet the tems cncepts
Physics Exam 3
 Physcs 114 1 Exam 3 The numbe of ponts fo each secton s noted n backets, []. Choose a total of 35 ponts that wll be gaded that s you may dop (not answe) a total of 5 ponts. Clealy mak on the cove of you
Physcs 114 1 Exam 3 The numbe of ponts fo each secton s noted n backets, []. Choose a total of 35 ponts that wll be gaded that s you may dop (not answe) a total of 5 ponts. Clealy mak on the cove of you
Subjects of this chapter - Propagation harmonic waves - Harmonic waves on an interface (Boundary condition) - Introduction of phasor
 CHAPTR 8. LCTROMAGNTIC HARMONIC WAV Maxwell s equatns Dffeental wave equatn Tavelng wave A hamnc wave An abtay wave A lnea cmbnatn f hamnc waves. Supepstn pncple. Lnea meda, ( ε, μ ae cnstant) Hamnc waves
CHAPTR 8. LCTROMAGNTIC HARMONIC WAV Maxwell s equatns Dffeental wave equatn Tavelng wave A hamnc wave An abtay wave A lnea cmbnatn f hamnc waves. Supepstn pncple. Lnea meda, ( ε, μ ae cnstant) Hamnc waves
WYSE Academic Challenge Sectional Mathematics 2006 Solution Set
 WYSE Academic Challenge Sectinal 006 Slutin Set. Cect answe: e. mph is 76 feet pe minute, and 4 mph is 35 feet pe minute. The tip up the hill takes 600/76, 3.4 minutes, and the tip dwn takes 600/35,.70
WYSE Academic Challenge Sectinal 006 Slutin Set. Cect answe: e. mph is 76 feet pe minute, and 4 mph is 35 feet pe minute. The tip up the hill takes 600/76, 3.4 minutes, and the tip dwn takes 600/35,.70
Chapter 7. Systems 7.1 INTRODUCTION 7.2 MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF LIQUID LEVEL SYSTEMS. Steady State Flow. A. Bazoune
 Chapter 7 Flud Systems and Thermal Systems 7.1 INTODUCTION A. Bazune A flud system uses ne r mre fluds t acheve ts purpse. Dampers and shck absrbers are eamples f flud systems because they depend n the
Chapter 7 Flud Systems and Thermal Systems 7.1 INTODUCTION A. Bazune A flud system uses ne r mre fluds t acheve ts purpse. Dampers and shck absrbers are eamples f flud systems because they depend n the
FARADAY'S LAW dt
 FAADAY'S LAW 31.1 Faaday's Law of Induction In the peious chapte we leaned that electic cuent poduces agnetic field. Afte this ipotant discoey, scientists wondeed: if electic cuent poduces agnetic field,
FAADAY'S LAW 31.1 Faaday's Law of Induction In the peious chapte we leaned that electic cuent poduces agnetic field. Afte this ipotant discoey, scientists wondeed: if electic cuent poduces agnetic field,
Chapter I Matrices, Vectors, & Vector Calculus 1-1, 1-9, 1-10, 1-11, 1-17, 1-18, 1-25, 1-27, 1-36, 1-37, 1-41.
 Chapte I Matces, Vectos, & Vecto Calculus -, -9, -0, -, -7, -8, -5, -7, -36, -37, -4. . Concept of a Scala Consde the aa of patcles shown n the fgue. he mass of the patcle at (,) can be epessed as. M (,
Chapte I Matces, Vectos, & Vecto Calculus -, -9, -0, -, -7, -8, -5, -7, -36, -37, -4. . Concept of a Scala Consde the aa of patcles shown n the fgue. he mass of the patcle at (,) can be epessed as. M (,
Transistors. Lesson #10 Chapter 4. BME 372 Electronics I J.Schesser
 Tanssts essn #10 Chapte 4 BM 372 lectncs 154 Hmewk Ps. 4.40, 4.42, 4.43, 4.45, 4.46, 4.51, 4.53, 4.54, 4.56 BM 372 lectncs 155 Hmewk Answes #20 Ps. 4.40 See fgue 4.33 BM 372 lectncs 156 Ps. 4.42 Hmewk
Tanssts essn #10 Chapte 4 BM 372 lectncs 154 Hmewk Ps. 4.40, 4.42, 4.43, 4.45, 4.46, 4.51, 4.53, 4.54, 4.56 BM 372 lectncs 155 Hmewk Answes #20 Ps. 4.40 See fgue 4.33 BM 372 lectncs 156 Ps. 4.42 Hmewk
gravity r2,1 r2 r1 by m 2,1
 Gavtaton Many of the foundatons of classcal echancs wee fst dscoveed when phlosophes (ealy scentsts and atheatcans) ted to explan the oton of planets and stas. Newton s ost faous fo unfyng the oton of
Gavtaton Many of the foundatons of classcal echancs wee fst dscoveed when phlosophes (ealy scentsts and atheatcans) ted to explan the oton of planets and stas. Newton s ost faous fo unfyng the oton of
Optimization Frequency Design of Eddy Current Testing
 5th WSEAS Int. Cnfeence n Appled Electagnetcs, Weless and Optcal Cuncatns, Tenefe, Span, Decebe 14-16, 2007 127 Optzatn Fequency Desgn f Eddy Cuent Testng NAONG MUNGKUNG 1, KOMKIT CHOMSUWAN 1, NAONG PIMPU
5th WSEAS Int. Cnfeence n Appled Electagnetcs, Weless and Optcal Cuncatns, Tenefe, Span, Decebe 14-16, 2007 127 Optzatn Fequency Desgn f Eddy Cuent Testng NAONG MUNGKUNG 1, KOMKIT CHOMSUWAN 1, NAONG PIMPU
PHYS Week 5. Reading Journals today from tables. WebAssign due Wed nite
 PHYS 015 -- Week 5 Readng Jounals today fom tables WebAssgn due Wed nte Fo exclusve use n PHYS 015. Not fo e-dstbuton. Some mateals Copyght Unvesty of Coloado, Cengage,, Peason J. Maps. Fundamental Tools
PHYS 015 -- Week 5 Readng Jounals today fom tables WebAssgn due Wed nte Fo exclusve use n PHYS 015. Not fo e-dstbuton. Some mateals Copyght Unvesty of Coloado, Cengage,, Peason J. Maps. Fundamental Tools
Module 18: Outline. Magnetic Dipoles Magnetic Torques
 Module 18: Magnetic Dipoles 1 Module 18: Outline Magnetic Dipoles Magnetic Toques 2 IA nˆ I A Magnetic Dipole Moment μ 3 Toque on a Cuent Loop in a Unifom Magnetic Field 4 Poblem: Cuent Loop Place ectangula
Module 18: Magnetic Dipoles 1 Module 18: Outline Magnetic Dipoles Magnetic Toques 2 IA nˆ I A Magnetic Dipole Moment μ 3 Toque on a Cuent Loop in a Unifom Magnetic Field 4 Poblem: Cuent Loop Place ectangula
iclicker Quiz a) True b) False Theoretical physics: the eternal quest for a missing minus sign and/or a factor of two. Which will be an issue today?
 Clce Quz I egsteed my quz tansmtte va the couse webste (not on the clce.com webste. I ealze that untl I do so, my quz scoes wll not be ecoded. a Tue b False Theoetcal hyscs: the etenal quest fo a mssng
Clce Quz I egsteed my quz tansmtte va the couse webste (not on the clce.com webste. I ealze that untl I do so, my quz scoes wll not be ecoded. a Tue b False Theoetcal hyscs: the etenal quest fo a mssng
The Law of Biot-Savart & RHR P θ
 The Law of iot-savat & RHR P R dx x Jean-aptiste iot élix Savat Phys 122 Lectue 19 G. Rybka Recall: Potential Enegy of Dipole Wok equied to otate a cuentcaying loop in a magnetic field Potential enegy
The Law of iot-savat & RHR P R dx x Jean-aptiste iot élix Savat Phys 122 Lectue 19 G. Rybka Recall: Potential Enegy of Dipole Wok equied to otate a cuentcaying loop in a magnetic field Potential enegy
Rigid Bodies: Equivalent Systems of Forces
 Engneeng Statcs, ENGR 2301 Chapte 3 Rgd Bodes: Equvalent Sstems of oces Intoducton Teatment of a bod as a sngle patcle s not alwas possble. In geneal, the se of the bod and the specfc ponts of applcaton
Engneeng Statcs, ENGR 2301 Chapte 3 Rgd Bodes: Equvalent Sstems of oces Intoducton Teatment of a bod as a sngle patcle s not alwas possble. In geneal, the se of the bod and the specfc ponts of applcaton
Unifying Principle for Active Devices: Charge Control Principle
 ES 330 Electncs II Supplemental Tpc #1 (August 2015) Unfyng Pncple f Actve Devces: hage ntl Pncple Dnald Estech An actve devce s an electn devce, such as a tansst, capable f delveng pwe amplfcatn by cnvetng
ES 330 Electncs II Supplemental Tpc #1 (August 2015) Unfyng Pncple f Actve Devces: hage ntl Pncple Dnald Estech An actve devce s an electn devce, such as a tansst, capable f delveng pwe amplfcatn by cnvetng
V. Principles of Irreversible Thermodynamics. s = S - S 0 (7.3) s = = - g i, k. "Flux": = da i. "Force": = -Â g a ik k = X i. Â J i X i (7.
 Themodynamcs and Knetcs of Solds 71 V. Pncples of Ievesble Themodynamcs 5. Onsage s Teatment s = S - S 0 = s( a 1, a 2,...) a n = A g - A n (7.6) Equlbum themodynamcs detemnes the paametes of an equlbum
Themodynamcs and Knetcs of Solds 71 V. Pncples of Ievesble Themodynamcs 5. Onsage s Teatment s = S - S 0 = s( a 1, a 2,...) a n = A g - A n (7.6) Equlbum themodynamcs detemnes the paametes of an equlbum
